In order to grow a healthy crop, it is imperative to know as much information as possible about the selected crop. Only under such conditions will you be able to identify the problems that have appeared and eliminate them in a timely manner.
Honeysuckle is susceptible to various diseases and pest attacks, therefore it needs protection. To prevent them, it is necessary to carry out preventive measures. A well-groomed plant is more resistant to negative factors. But it is not always possible to prevent diseases of honeysuckle, and the fight against them is one of the tasks of the gardener. Shrubs can be susceptible to fungal and viral diseases, they are attacked by various pests: caterpillars, aphids, bugs, scale insects and others.
The topic of this article is honeysuckle diseases and their treatment.
Mottling of leaves
Caring for honeysuckle in case of illness consists in removing all affected parts and processing with chemicals. The most common diseases of ornamental honeysuckle are spotting, which completely deprive the shrub of its visual appeal.
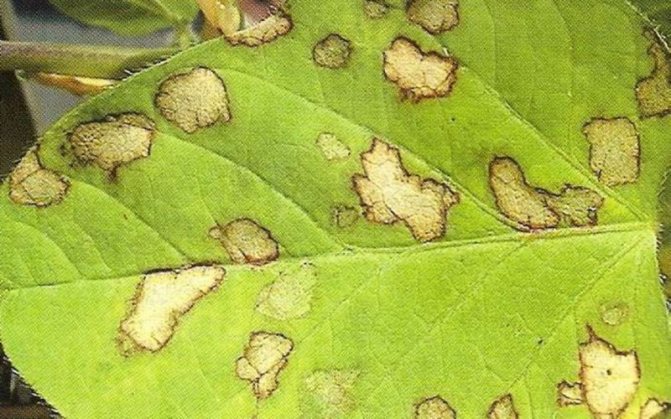

Ascochitous spot of honeysuckle.
The causative agent of this disease of honeysuckle leaves is the Ascochyta tenerrima Sacc mushroom. et Roum. Blackish-gray, irregularly shaped spots appear on the leaves, often located on the edge of the leaf blade. In the center, the spots gradually brighten and numerous dotted black fruit bodies - pycnidia - are formed in the necrotic tissue.
Control measures. Collection and removal of plant residues. Preventive spraying of bushes in the spring, immediately after flowering, with 1% Bordeaux mixture or its substitutes (HOM, Abiga-Peak). With a strong spread of spotting, spraying is repeated in the summer, after picking berries, with the same preparations.
If spots of black plaque appear on the shoots and leaves of honeysuckle, which, without proper attention from the gardener, quickly expand and merge, then in this case it is mono to talk about the activity of mushrooms. As a result, at first the foliage looks "dirty", then it begins to dry out and fall off, and the activity of the causative agent of the disease, edible honeysuckle, can also affect the berries.
You can cope with the problem:
- timely cutting off dry and damaged shoots;
- collecting and destroying affected foliage;
- in early spring, annually spraying the plants with an aga-peak or Bordeaux mixture and repeating the treatment after flowering.
Some types of soil nematodes can spread mottling of honeysuckle leaves, which is expressed in a change in the natural color of the foliage, the appearance of whitish streaks and spots on the leaf plates.
As a rule, treatment with chemicals before this disease of honeysuckle is powerless, so the affected shoots and individual plants are simply removed.
With mottling, very light streaks and spots appear on the leaves, which are immediately visible. One of the reasons is soil nematodes. They cannot be destroyed with chemicals; it is better to remove the most affected parts of the shoots. Sometimes Epin and similar remedies help. Once I stopped the beginning mottling of the leaves by fertilizing with potash fertilizers. The goal is to strengthen honeysuckle. After all, any sore affects, first of all, weakened plants.
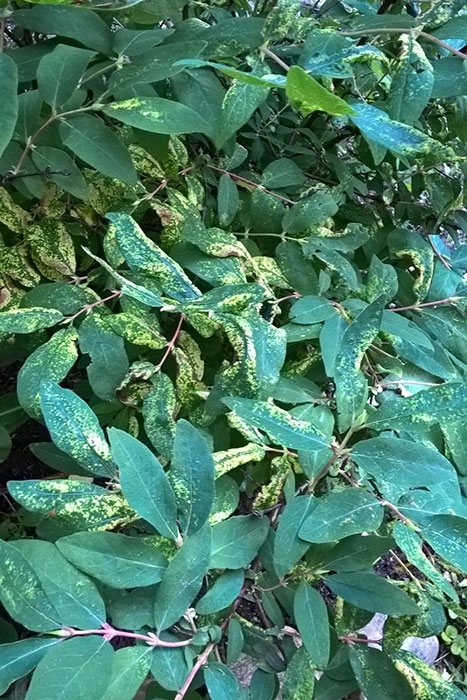


Mottling of honeysuckle leaves
Several years ago I planted a new honeysuckle bush that turned out to be sick. I removed it, because no treatment helped. And the berries were tasteless.A sapling was transplanted from the school next to the vacant place. Unfortunately, now he also suffers from mottled leaves. Don't repeat my mistake. Plant honeysuckle only in a completely clean area.
There are several reasons for the appearance of such leaves on the honeysuckle bush.
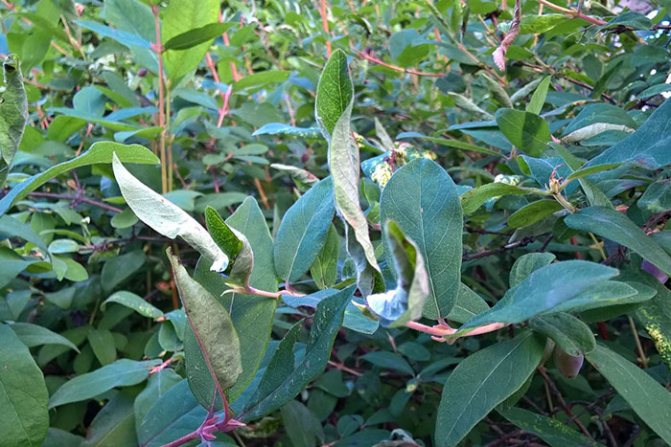


Rolled and rolled honeysuckle leaves
The honeysuckle mite more often affects those honeysuckle bushes that are thickened or in the shade. If you arm yourself with a strong magnifying glass and unfold the twisted leaf, then spots with tick eggs and a cobweb can be visible on the underside. The honeysuckle mite weakens the plant. In case of mass damage after harvest, they are treated with Confidor, Aktellik, Rogor-S or, at your own peril and risk, try the contact action acaricide Omite (white powder or emulsion) or Mavrik (water-oil emulsion). These are more expensive strong drugs. They are effective at high air temperatures.
The rose leafworm also twists the leaf along the central vein to stay and eat in a comfortable environment. Honeysuckle does not suffer from a small brown butterfly, but from its larvae. They spoil young foliage and growth points. The pest is usually noticed when they see twisted leaves with lumps of cobwebs on a branch. Rose leafworm gets on honeysuckle bushes from other garden plants.


Currant currant leafworm twists a leaf and wraps it in cobwebs.
To destroy a mass pest, it is better to use the systemic insectoacaricide of contact-intestinal action Rogor-S. Processing is carried out in early spring.
Fingerwing honeysuckle can also cause leaves to curl. If we look at a golden brown moth under a magnifying glass, then we will see an incredibly beautiful butterfly with wings made of miniature "feathers". Its caterpillars are real gourmets. They feed on the seeds of the ovary, resulting in unripe shriveled fruits. Like the larvae of the honeysuckle fingerwing and the pulp of berries. The result is deformation and shedding of fruits, i.e. decrease in yield.
How to treat scales on honeysuckle branches
Despite the fact that honeysuckle is a plant that is resistant to diseases and pests, some insects can still settle on shrubs and weaken them.
Often, small brown scales can be seen on branches and leaves, which are almost impossible to separate by hand. This is not a disease, but a special type of pest - the scabbard, which attaches to the shoots and feeds on plant juices.
The reasons
There are several types of scale insects that can attach to both young leaves and shoots, and to adult branches. As a rule, the larvae of the pest spread through the soil or through infected garden tools.
In order to prevent damage to the plant by scabbards, you need to disinfect all tools, remove weeds in the garden in time, and also prevent the spread of pests by watering garden shrubs with boiling water in early spring or spraying with special chemicals.
Symptoms
It's easy to spot scale insects on honeysuckle. On the leaves and branches, characteristic scales appear, which are almost impossible to separate mechanically. These are adult pests, the body of which is covered with a dense shell.
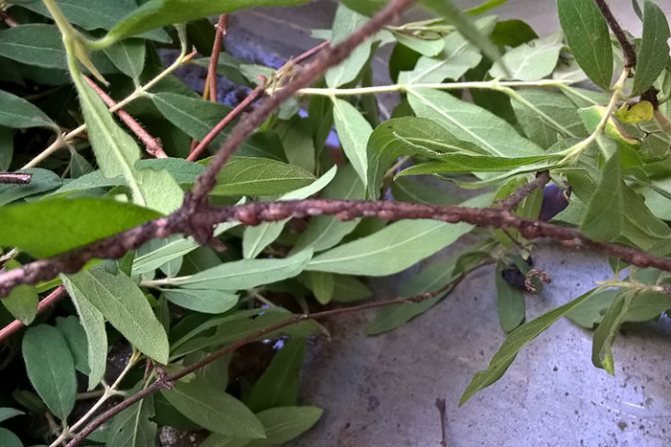
With a minor lesion, the symptoms of scabbard infection will be as follows (picture 1):
- Plants begin to stunted;
- Leaves wither, become covered with a sticky substance and lose their natural shine;
- Leaf plates gradually turn yellow and fall off prematurely;
- If the scale insects have reached the fruit, the berries are covered with yellow or brown spots.


Figure 1. Shoots affected by the scabbard
With a minor lesion, you can treat the affected parts with a water-soap solution with alcohol (30 ml of liquid soap and 20 ml of denatured alcohol are diluted in 2-4 liters of warm water).
Note: It should be borne in mind that some varieties of crops are sensitive to alcohol, therefore, the solution should be tested in a small area before processing. If a burn appears, the solution cannot be used.
In case of mass defeat, spraying with the preparations "Admiral", "Aktara", "Aktellik", "Bankol" or "Confidor" is used. Treatment should be carried out several times at regular intervals in order to destroy not only adult pests, but also their larvae.
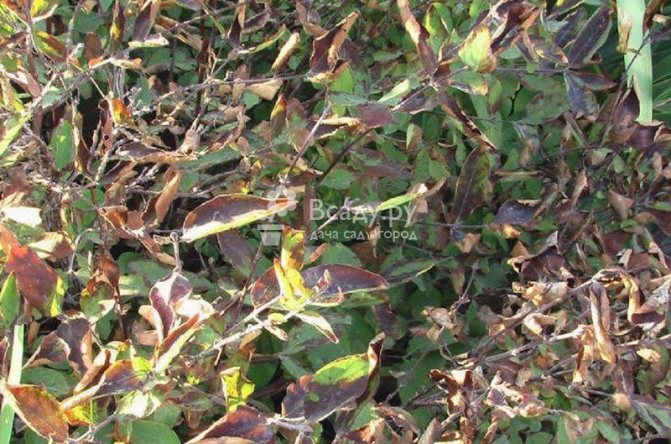
Why does honeysuckle dry out with ramulariasis?
Sometimes the drying out of individual sections of the leaves, and then of the entire foliage, is a consequence of the activity of fungi belonging to the Ramularia family. Visually, such marks on the foliage of the affected plant look like spots of yellow-brown or brown color with a dark rim.
The shape of the spots can be either round or irregular. Moreover, over time, they grow, and the area affected by the disease of honeysuckle, like ramulariasis or spotting, expands. Ripe spores in the form of a white powder are crumbled several times during the growing season from the places where the fungus accumulates and are scattered on the root litter and healthy leaves. See honeysuckle honeysuckle photo.
The danger of the disease is not only that the crown of the honeysuckle dries up, and the plant weakens, but also in the ability of the spores to winter in the middle lane and settle again in the spring. Therefore, as a security measure:
- the affected shoots are carefully removed;
- collect fallen old foliage;
- all parts of plants infected with the fungus are burned.
Diseases of the variety honeysuckle
Honeysuckle, honeysuckle, like other plants, is most susceptible to infection during the winter season and damp weather. The most common are fungal diseases.
A sign of infection is the appearance of brown-olive spots with a dark border on both sides of the leaves. After a while, the foliage darkens and dries up. As a struggle, the affected parts are collected and burned, treated with 1% Bordeaux liquid before or after flowering. In advanced cases, spraying is repeated after harvest.
Cercosporosis - a dangerous disease of honeysuckle
The answer to the question: "Why does honeysuckle dry?" often it becomes the detection of spots on the leaves, first having a dirty green tint, and then acquiring a brown or light gray color and a dark border around the edge. This is an obvious sign of the presence on the plant of the fungi Cercospora libicola, which cause the edible disease of cercospora, which is dangerous for honeysuckle.
Measures to combat cercosporosis are:
- in the collection and burning of fallen and already infected with fungus foliage;
- pruning shrubs in order to prevent their excessive density and better ventilation of the crown;
- regular fertilizing of plants with mineral fertilizers;
- spraying before opening the buds and after picking the berries of plantings and row spacings with Bordeaux liquid, cuprozan and fungicides.
The first method of propagation of honeysuckle by seeds
I collect the ripe, delicious and sweet berries from the bush. I cultivate the soil in a sunny place, add humus or compost, level the soil, water it well. When the water is absorbed, I make dimples in one row with my finger, the distance between them is 10 cm. I crush one berry and put it in the hole with my fingers, lightly sprinkling it with earth.
Nearby I stick a stick as long as a pencil: how many berries, so many sticks.
WHAKAMAHI I TE WHAKAMAHI KAUPAPA MO TANGOU KAUPAPA - TE WHAKAMAHI MAI. HE KAUPAPA KAUPAPA. He arotake

I water it carefully, I can cover it with a piece of film and fix it with something so that it doesn't blow away. It is important to keep the ground moist. Shoots appear in 10-14 days, then I remove the shelter, water, weed the weeds.
Shoots in heaps, and remain until winter. I close the planting with leaves, which I remove in the spring. In the spring I feed it with infusion of manure or herbs.
During the summer, I weed and water, and closer to autumn it is necessary to open it or leave it until spring.
Shrinking branches


The honeysuckle root system can be easily damaged by loosening the soil under the bush, which often leads to drying out of the branches. Moles and shrews help. Another reason is damage to the shoots in the winter.
The reason for the rapid drying of branches with leaves can be a fungal disease, similar to moniliosis (monilial burn) of stone fruit crops. The fungus penetrates any damage, then spreads quickly. Branches with instantly dried leaves and berries can be seen. In my huge bush, for several years now, a couple of large branches have dried up on the southern side of the crown. The bush itself does not suffer.
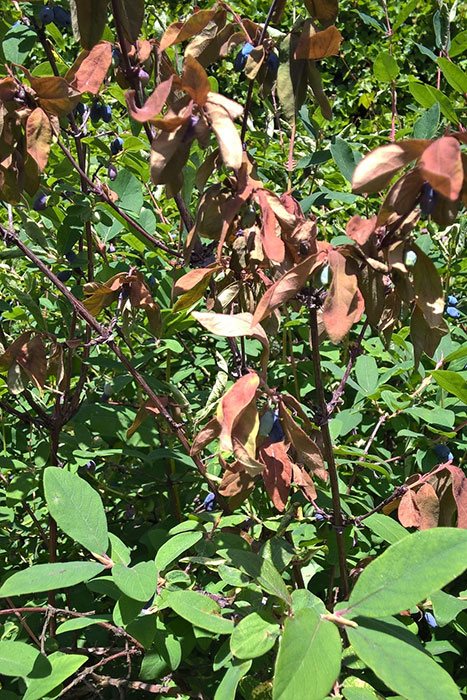


Honeysuckle branches with unexpectedly dried leaves and fruits
So far, I manage to cope with this nuisance by removing (pruning shears) dead branches, capturing part of the living wood. It is recommended to process honeysuckle with medicinal preparations (after complete harvesting), using Bordeaux mixture, "Oxyhom" or "Hom". If brown spots are noticeable on drying leaves, then Fundazol (0.2%) is used.
We suggest that you familiarize yourself with: Measures for pest and disease control of apricot
Treatment of damaged bushes is carried out in early spring before the buds begin to bloom. Along the way, mulch the soil under the bush with loose compost or fresh soil. They are fed with phosphorus-potassium fertilizers.
Already in June, darkening becomes noticeable, and then wilting and drying of foliage and individual shoots. Why does honeysuckle dry out in this case? The mushrooms that have settled on the fruiting bush are guilty - the causative agents of tuberculariosis. Shoots affected by this disease of honeysuckle can be recognized by the characteristic red-brown tubercles, inside which spores mature, spreading to healthy branches and hibernating inside the shoots and on fallen diseased leaves.
To prevent disease:
- cut off and necessarily burn the stems affected by the mushrooms;
- in early spring and after flowering, the shrubs are treated with Bordeaux liquid.
Features of spring processing of honeysuckle
Preventive treatment is carried out in early spring, when the frost has already passed, but the buds have not yet blossomed. The procedures are carried out to strengthen the immunity of the plant, to combat overwintered insects. How to process honeysuckle in spring:
- Top dressing of the soil with various fertilizers. In April - nitrogen (nitrate 50 g per 1 m2 or urea 20 g 1 m2), in May or early June - phosphorus and potassium (100 g nitrophoska per 1 m2).
- Chemical treatment is carried out before flowering. To remove weeds, herbicides are used (Tornado, Roundup). Chemical preparations Actellik and Confidor are used to eliminate overwintered insects.
- Proceed with pruning honeysuckle if the work was not completed in the fall.
- If a dry summer is expected, the roots should be sprinkled with mulch. A protective layer will protect the plant's root system from drying out.
Work should be started at temperatures above +5 ºС.


Shields and false shields


Scabbards (acacia scabbard, apple scabbard, willow scabbard, etc.) have also chosen honeysuckle. Several years ago, my huge bush, about three meters high, was attacked by a massive pest. At first, I diligently cleaned the branches. It took a long time, but there was no result. The leaves of the bush, sweet from the secretions of the scale insect, began to turn black. A bloom of a sooty fungus was visible on them.
I had to remove and burn many affected branches, especially in the lower part of the bush.


The lower branches of the honeysuckle bush are a great place for a pest
After that, I began to spray the honeysuckle with complex systemic preparations. I wiped the branches and leaves with a sponge dipped in an aqueous solution of green soap. Finally, I managed to destroy both the scabbard and the traces of the sooty fungus.Now I try to prevent their spread. Later I was told that spraying with water with kerosene helps from the scabbard.
Recently, I began to use a cleaning agent (con Loc, which I dilute strongly with water. This saved my houseplants from the scabbard. It dries up and falls off soon after spraying. The dosage is "by eye", about a teaspoon in a glass of water. I think that some other household chemicals have a similar effect.It is worth trying their aqueous solutions of weak concentration to destroy pests.
I could not completely get rid of the scabbard on the old bush. But it is possible to restrain the reproduction of the pest and "keep it under control" by cutting the lower and thickened branches, plus spraying with a diluted concentrate of a cleaning agent.
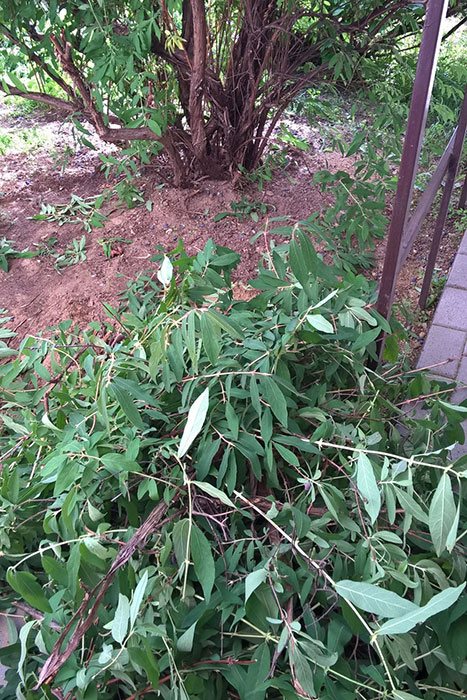


We remove the lower branches from the honeysuckle bush. It will be easier to care for such a bush.
The scale insects suck the juice out of the honeysuckle. It is easier for them to eat on shoots with thin bark, but the accumulations of the pest are not on them, but on old branches. Shields are often visible in the depressions. You need to pay attention to these places of honeysuckle bushes.
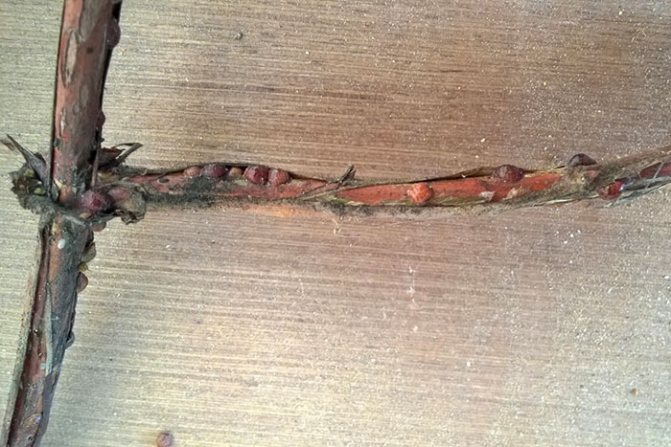


The shield reliably protects the pest, so it is difficult to deal with it
Standard control measures: Actellik, Confidor, Rogor-S and Aktara.
Remember
- Start treatment immediately. As soon as you find any signs of illness on honeysuckle, take action. It is difficult, and sometimes impossible, to cure a plant in the late stages of disease development.
- Treat seedlings before planting... For example, viral diseases can be introduced into the soil along with the seedlings when planting. Disinfect the planting material.
- Monitor soil moisture... From excess or lack of moisture, dangerous fungal diseases develop.
- Burn fallen leaves, branches, plucked weeds. Spores of fungi can persist in the dying leaves, which, under favorable conditions, begin to develop.
Powdery mildew of honeysuckle
The mushrooms, which are the cause of this disease of edible honeysuckle, form a white, cobweb-like bloom on the shoots, the upper and lower surfaces of the leaves. Young branches are the first to suffer, but over time the disease spreads to the entire plant. The leaves turn brown, dry up and fall off ahead of schedule, similar processes take place on the shoots, where the bark first dries up, and then the branches themselves are deformed, the plant withers and noticeably weakens.
It is possible to cope with the fungus wintering on the bark and thicker plant debris by destroying fallen leaves and diseased branches, as well as treating shrubs with sulfur-containing preparations at the first signs of honeysuckle disease.
A whitish coating of powdery mildew on the leaves often appears in wet summers. Spraying with a soda solution helps to get rid of it. Soda ash is stronger. I was told that the simplest washing powders diluted in water and dusting with wood ash are effective. Studies have been conducted that have proven that powdery mildew is destroyed by calcium chloride and salicylic acid.
Topaz is recommended as a strong remedy. All spraying can be carried out only after complete harvest.
Pest attack
Unfortunately, honeysuckle can not only be infected with dangerous diseases, but also be attacked by insects. What exactly are the pests of honeysuckle, we will find out further.
Shield
The foliage and branches of the bush are covered with unusual "scales". It is almost impossible to separate them. In fact, these are adult scale insects. The plant stops growing, and the foliage is covered with a sticky substance, as a result of which they wither and fall off. Honeysuckle fruit can also be affected. In this case, yellow spots appear on them. If the scabbard has spread only slightly, spraying with a solution of soap and alcohol may help. In case of large volumes of damage, "Admiral", "Aktarm", "Confidorm" are repeatedly used.
Aphid
It sucks out the sap of the plant, which leads to its strong weakening.Aphids spread quickly, therefore, measures to eliminate it need to be carried out immediately. To do this, use a soap or tobacco solution. When processing, make sure that the liquid gets on all sides of the plant.
Fungal diseases of honeysuckle and their treatment (with photo)
Improper care of honeysuckle and violation of planting rules are the main causes of plant damage by fungal diseases. Heavy acidic soils, not enough or too much light, lack of cross-pollinator - significantly weaken the honeysuckle, and make it vulnerable to infection.


Fungal diseases of honeysuckle and their treatment - photo of the affected bush
The common popular name for the disease is white spot. In the early stages of infection, gray-brown spots with a white core are formed on the leaves and stems. In high humidity conditions, they rapidly increase to form a powder-like coating.
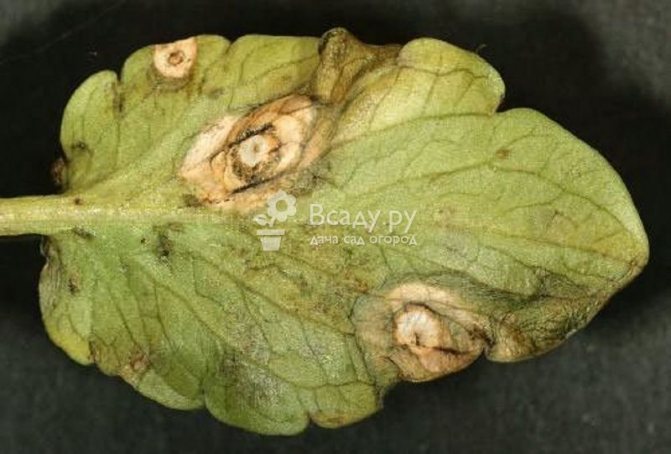


Honeysuckle, diseases - photos of ramulariasis
The main cause of ramularia infection is wet and rainy weather. The fungus easily tolerates winter in the soil and on plant debris.


You can fight the disease with the help of copper-containing substances. It is worth refraining from spraying during the flowering period. An effective remedy is the fungicide Fundazol.
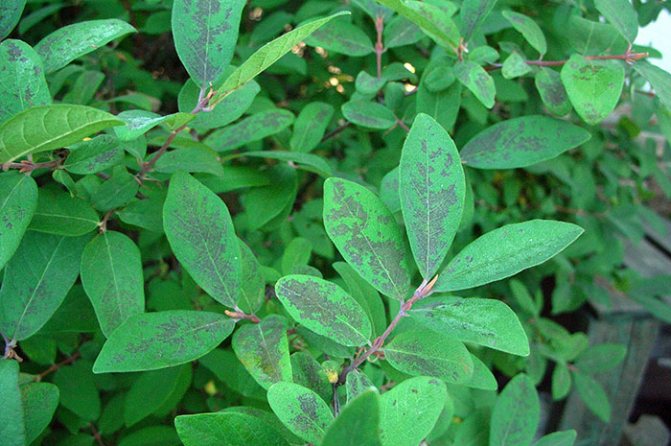
Considering the fungal diseases of honeysuckle in pictures, it is important to pay attention to one of the most dangerous - cercosporosis. Spots of dirty green appear on the leaves, which gradually grow, acquiring a gray tint with a brown frame. Gradually, the affected parts of the plant dry up, and a "black rash" (fungal spores) forms under them.
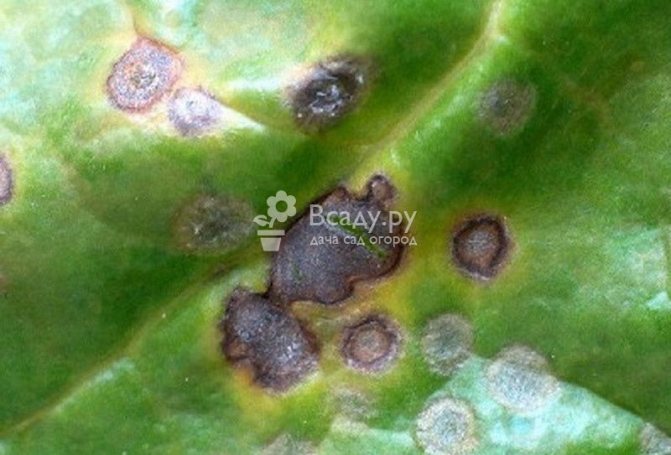


Honeysuckle diseases - cercospora
Infected leaves must be removed and burned. Starting in early spring, the shrubs are treated with a Bordeaux mixture, a solution of copper and soap (0.1 kg of copper sulfate and soap shavings per 10 liters of liquid), or Kuprozan according to the instructions.
The main reason for the onset of the disease is a lack of water. White and gray dust-like spots appear on the leaves. The whole plant is gradually affected, and new shoots are deformed. Most often, those bushes that are in the shade are affected.
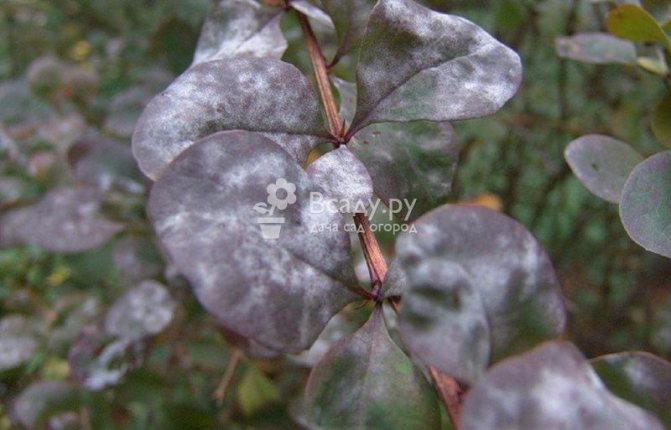


Diseases of honeysuckle - photo of powdery mildew
Affected shoots should be removed. If the correct watering regime and sunlight does not help to overcome the disease, it is recommended to resort to the use of fungicides: Vectra, Cumulus, Speed.
Honeysuckle has poor resistance to cold weather. In the spring, during the period of return frosts, the bark on the shoots often bursts, and a saprotrophic fungus settles in the cracks formed. A dark bloom forms on the wounds, and the shoots gradually dry out.
We suggest you familiarize yourself with: Strawberry varieties - the sweetest and largest berries


Frostbones on the trunk of honeysuckle lead to fungal infection
Damaged shoots must be removed and destroyed. Immediately after flowering honeysuckle, the bushes are treated with Bordeaux mixture.
Lack of moisture and a dry climate weaken the honeysuckle, and make it vulnerable to European cancer. The leaves turn yellow and wither, the shoots become covered with gray spots and dry out.


European cancer is a dangerous disease of honeysuckle that cannot be cured
The affected parts of the plant are a source of infection, therefore, must be removed (be sure to use disposable gloves or napkins). Sections should be treated with linseed oil paint.
If signs of infection are found, water the honeysuckle regularly in the morning. Also, it is worth reducing the amount of mulch for faster drying of the soil around the bush. As a preventive measure, it is recommended to spray with Bordeaux liquid in early spring, and after flowering.
Fungal diseases of honeysuckle lead to the death of the shrub within 1-2 seasons. Therefore, it is important to know all the necessary information about the diseases of honeysuckle and their treatment, which will allow you to start acting without delay.


Brown spot of honeysuckle.
The causative agent is the mushroom Ramularia lonicerae Vogl. The spots on the leaves are brownish-brown, irregular in shape, often merging, sometimes limited by leaf veins. A weak whitish bloom of sporulation develops on the necrotic tissue on the underside of the leaf blade at high humidity. Leaves turn brown and fall off prematurely. The infection persists in the affected plant debris.
Control measures. The same as against the ascochitous spot.


Light gray spot of honeysuckle.
The causative agent is the mushroom Septoria xylostei Sacc. et Wint. The spots on the leaves are numerous, rounded, on both sides of the leaf blade, gray in color and surrounded by a black border. Over time, on the upper side of the necrotic tissue, numerous dotted black fruiting bodies - pycnidia - are formed. Affected leaves turn brown and fall off prematurely. The infection persists in the affected plant debris.
Sooty mushrooms appear on weakened bushes. Often on sticky pest secretions. The leaves of the bush are covered with dark "dust" or bloom. A heavily affected plant quickly withers and loses strength.


Plaque of sooty mushroom on the leaves
Spraying with the systemic fungicide Fundazol and the use of Tsineb help.
Diseases of the Tatar honeysuckle
Tatar honeysuckle is one of the most widespread in parks and squares due to its high decorativeness and unpretentiousness. Its fruits are inedible, moreover, they are poisonous. The plant is susceptible to fungal disease in damp and warm weather. Powdery mildew is considered especially dangerous, the signs of which are white bloom and brown spots on branches and leaves. The damaged parts of the shrub must be cut off and burned, then the plant must be treated with Ordan and Topaz. It is recommended to spray them several times per season, with different preparations in turn.
When affected by different types of aphids, the leaves and tops of the shoots are twisted in Tatar honeysuckle. Means of aphid control - spraying with Aktara during the season and Aktellik before bud break.
Another disease - cercosporosis - is characterized by the appearance of gray spots with a burgundy border. It is treated by treatment with Bordeaux liquid, Fundazol, a solution of copper sulfate with soap.
Now you know all about the diseases of honeysuckle and how to deal with them, which means that you are armed and able to achieve a good harvest. The main thing is to remember that plants, like people, need care, attention and love. We wish you a good harvest.
Viral diseases of edible honeysuckle and their treatment
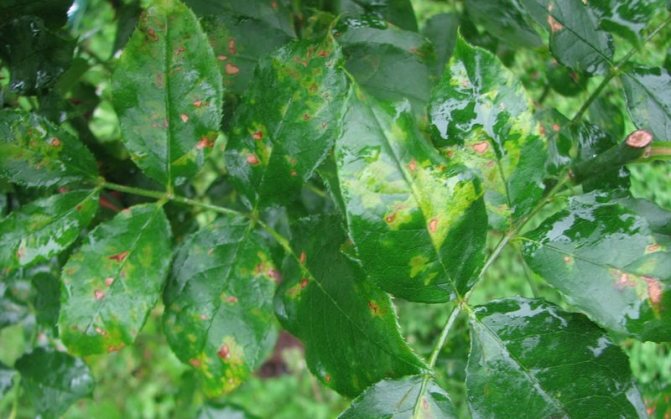


Reddish-olive blotch of honeysuckle.
The Arabis mosaic virus (AMV) (syn. Raspberry yellow dwarf virus) is a disease common on many berry and ornamental plants. Symptoms of this disease of edible honeysuckle are very diverse - from yellow mottling, wrinkling to yellowing of veins and bushiness of young plants.
Control measures. Compliance with all requirements of agricultural cultivation, the use of high-quality planting material, timely removal and burning of individual shoots and affected bushes.
There are other viral diseases of edible honeysuckle, but their treatment is generally carried out in the same way.
Plants affected by viruses have to be destroyed. There is no cure for them. Other plants are also infected.
You can try to save the honeysuckle bush by spraying the crown with phytohormones such as Epin, Silk, El and Ambiol. They even increase resistance to viruses. These are artificially obtained phytohormones that stimulate the protective capabilities of plants.
Inexpensive Epin is used not only by indoor plant lovers, but also by gardeners. It is believed to be an environmentally friendly product that can be sprayed near apiaries. Not everyone knows that it is recommended to store an ampoule with epin in a cool place, preferably in the refrigerator. Shake it for at least a few minutes before use.
Mosaic rash virus is spread by nematodes. With it, internodes are shortened, the nature of shoot growth changes.
Cucumber Mosaic Virus is easily confused with leaf mottling.
The disease caused by a virus and spread by nematodes is manifested in the fact that in newly rooted honeysuckle seedlings, internodes are sharply shortened, and uncontrolled growth of lateral shoots from axillary buds begins. The foliage does not develop, the plants wither and die.
Control measures for this disease of honeysuckle include careful selection of planting material, as well as the mandatory destruction of shrubs with signs of the disease.
Viral diseases of honeysuckle are much less common fungal, and their treatment is reduced to limiting the spread (preventive treatment of healthy and removal of affected ones), and protection of unaffected plants.
The best way to protect honeysuckle, as well as other shrubs from the spread of viruses, is to choose resistant varieties. Some of them have natural resistance, and do not require additional protection measures: common honeysuckle, Tatarskaya, Maak, Korolkova.
The main reason for the defeat is poor-quality planting material. The virus leads to excessive bushiness of the plant. The internodes are shortened and a large number of lateral shoots appear. The leaves remain underdeveloped, and the bush gradually dies.
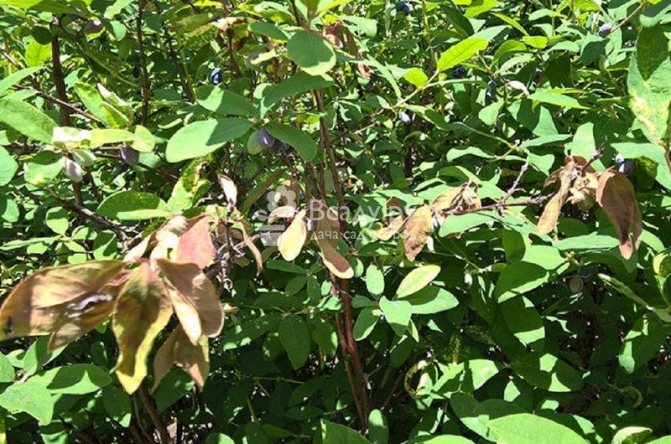


Mosaic rash virus leads to excessive bushiness of honeysuckle and disrupts development
Affected shoots should be regularly removed and destroyed. The fact that you need to know when growing honeysuckle is that viral diseases do not have drug treatment.
The virus is carried by various types of nematodes (roundworms). The main symptom: speckled or streaky brown spots form on the leaves, the whole plant gradually turns yellow.
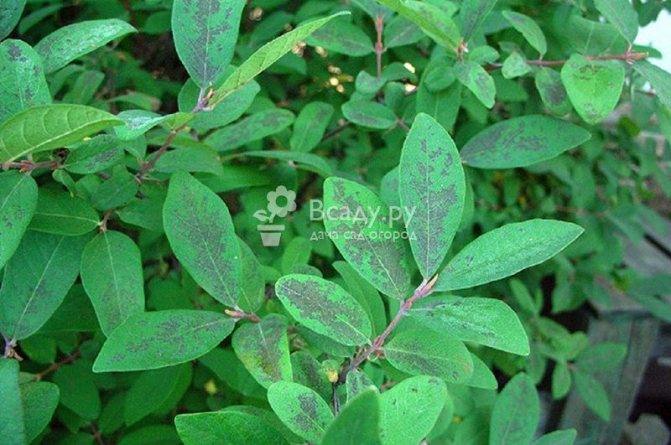


Honeysuckle leaf mottling is carried by nematodes
Sick bushes are dug up and destroyed. In autumn, the standard pruning of dried shoots and branches of the surviving plants is carried out.
Viral diseases
In addition to fungal diseases, you can face viral diseases. Let's consider the most common ones.
Advertisement 2
Foliage mottling
Visible signs include a change in the color of foliage and the appearance of white spots and stripes on them. The disease is incurable, and the only method of salvation is to get rid of infected shoots or the entire plant.


Symptoms of mottled leaves
Mosaic rash virus
The infection is caused by nematodes. In young plants, the distance between the nodes and the growth of lateral processes change. The plant dries up and dies. Treatment is not possible. For prevention, it is recommended to choose planting material with special responsibility.


Signs of a mosaic of cessation
Protection from pests and prevention of damage
A hot topic for any gardener is honeysuckle pests and how to control them using effective, but safe for the garden tools. We will talk about this later in the article.
Common spider mite Tetranychus urticae Koch. - very small pests of honeysuckle, feeding on the sap of young plant tissues. They have 4 pairs of legs. The body is 0.25-0.43 mm long, oval, greenish-yellow or orange-red. Females hibernate under plant debris and under the bark of trees and shrubs.
In spring, young leaves are populated, feed, weave a thin web and lay eggs. Larvae of each generation, depending on weather conditions, develop from 8 to 20 days. During the growing season in the open field, more than 10 generations of the pest develop. Damaged leaves turn yellow, deform, turn brown and dry out.
Control measures. Spraying plants when a pest appears with one of the drugs: fitoverm, fufanon, kemifos, actellik, lightning.
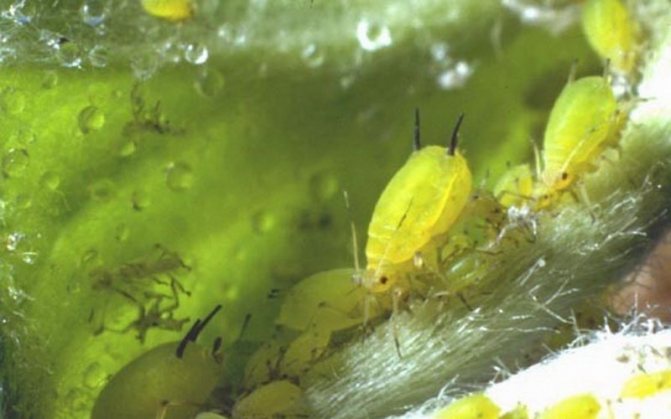


Apical honeysuckle aphid.
Apical honeysuckle aphid Hayhurstia tataricum Aizenb. - a small sucking insect of olive green color. It feeds on the juice of young leaves at the ends of the shoots.Damaged leaves are deformed, folded up, turn yellow and dry out.
Control measures. Pruning and burning single tops of shoots with aphid colonies. Spraying bushes immediately after flowering and with a large number in summer, after picking berries, with one of the drugs: fitoverm, fufanon, kemifos, kinmix, actellik, spark, Inta-Vir.
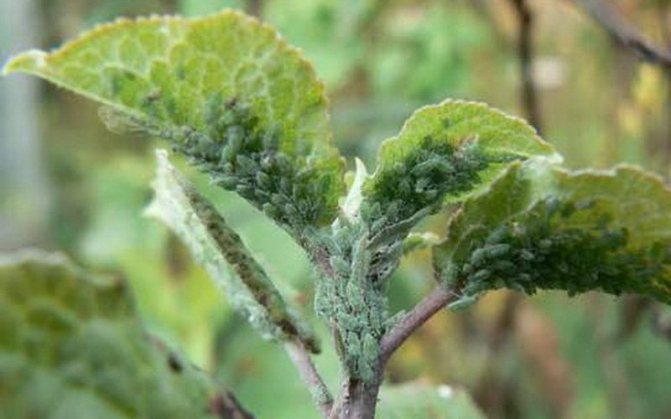


Aphid cereal-honeysuckle.
Grass-honeysuckle aphid Rhopalosiphoninus lonicerae Sieb. - a small insect of light yellow color, it feeds on tissue sap. Aphids suck the sap from the underside of the leaves, the edges of which are curled down. On the upper side of the leaf, yellow necrotic spots appear, which turn brown and dry, but a yellow halo always remains. With a large number of pests, the leaves dry out prematurely.
We suggest you familiarize yourself with: Sprinkling apple trees with copper sulfate in spring
Measures, fight. The same as against the apical honeysuckle aphid.
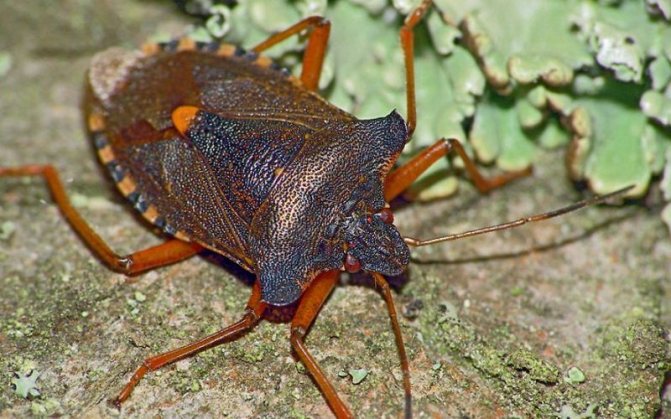


Red-footed shtitnik.
Red-footed duckweed Pentatoma rufipes L. is a large bug with a body length of 13-17 mm. The coloration above is brown with a bronze sheen in frequent black dots, below it is rusty-red in black dots. Antennae, middle part of incision of anterior margin of pronotum, tip of scutellum and legs orange, 2 last antennal segments blackish, ventral rim black dorsally with reddish-yellow stripes. Adult bugs and their larvae feed on the sap of deciduous trees and shrubs.
Control measures. Preventive spraying of shrubs in the spring, before flowering or immediately after it, with one of the drugs: fufanon, kemifos, kinmix, actellik, caviar, Inta-Vir. With a large number of pests, repeated spraying in the summer with the same preparations is carried out.
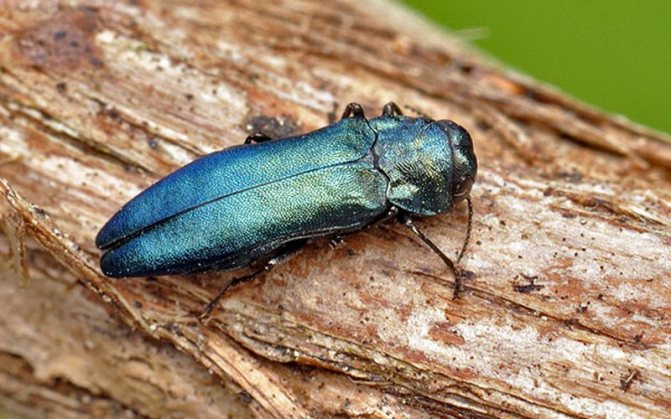


Narrow-bodied honeysuckle.


Narrow-bodied goldfish Agrilus coeruleus Rossi. - a beetle of shiny green color with a body length of 7-8 mm. The larvae are white, legless, almost cylindrical in shape, have 2 corneous processes at the posterior end of the body. Beetles fly in late May - June, feed on honeysuckle bushes, gnawing leaves from the edges. After fertilization, the females lay eggs on the shoots and leaf petioles.
The hatched larvae bite into the shoots and eat out the ringing and longitudinally sinuous passages under the bark, filling them with dark brown excrement. Until autumn, the larvae finish feeding, overwinter in damaged shoots and pupate there in the spring. The shoots damaged by the goldfish gradually dry out.
Control measures. Annual preventive spraying of bushes in spring, before flowering and immediately after it, with fufanon or its analogues.
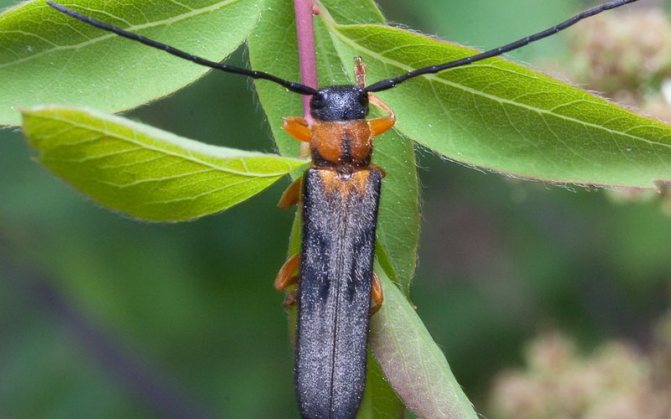


Honeysuckle barbel.
Longhorn beetle Oberea pupillata Gyllh. -large beetle with a body 20 mm long and long antennae. The beetle is brown-yellow, elytra are gray-black. The larva is white-yellow, lives and feeds inside the honeysuckle shoots, eating away the middle. The damaged shoots gradually dry out, and on the lignified ones, holes are visible left after the beetles emerge. During additional feeding, adult beetles damage the leaves by roughly nibbling the leaf blades.
Control measures. Timely pruning and burning of drying branches with larvae. Annual preventive spraying of bushes in spring, before or after flowering, with fufanon or its analogues. On lignified shoots, injections are additionally carried out into the holes with a solution of the drug fufanon. Single beetles are collected and destroyed.
Pests of edible honeysuckle damage all parts of the shrub. But they cause the main harm to inflorescences, buds and ripening fruits.
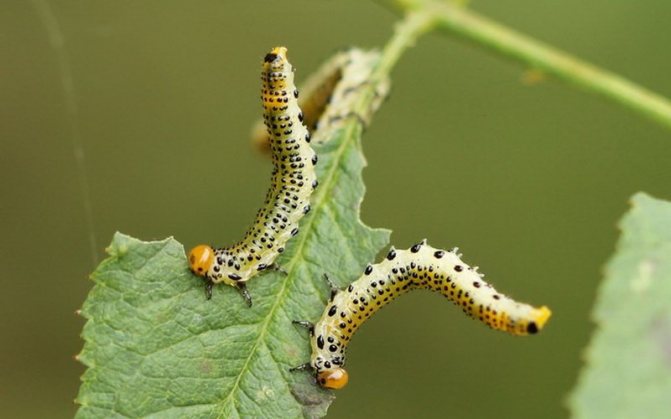


Sawfly honeysuckle striped.
The striped honeysuckle sawfly Zaraea fasciata L. is an insect with complete transformation. It has two pairs of membranous wings with clearly visible venation and a wide dark brown band.
The adult insect is 9-11 mm long, the body is bronze-black, the thorax is black, the first segment of the abdomen is yellow-white, the legs are black with a faint bronze sheen. The caterpillar is 20-22 mm long, cylindrical, gray-green, has 3 pairs of thoracic and 8 pairs of abdominal legs.There are 5 rows of black dots on the body, a black line above the spiracles, and a row of small yellowish spots below it. The head is brown-black. Damages ripening fruits.
False caterpillars of younger (I-II) instars are grayish-green, small, covered with a waxy bloom and have no black dots on their bodies. One generation develops a year. Adult larvae hibernate in cocoons in the soil, pupate there in the spring. In June, adult insects emerge, their flight continues until mid-July.
The females lay eggs one at a time in the leaf tissue under the epidermis. False caterpillars feed alone, roughly eating leaves, leaving only petioles. With a large number of false caterpillars on individual bushes, the leaves are completely eaten. The feeding of the caterpillars continues until the end of August, after which they leave the plants and make cocoons for wintering.
Control measures. Preventive spraying of shrubs in the spring before flowering or immediately after it with one of the drugs: fufanon, kemifos, kinmix, actellik, caviar, Inta-Vir. Single false caterpillars are collected and destroyed, with a large number of pests, repeated spraying in the summer with the same preparations is carried out.
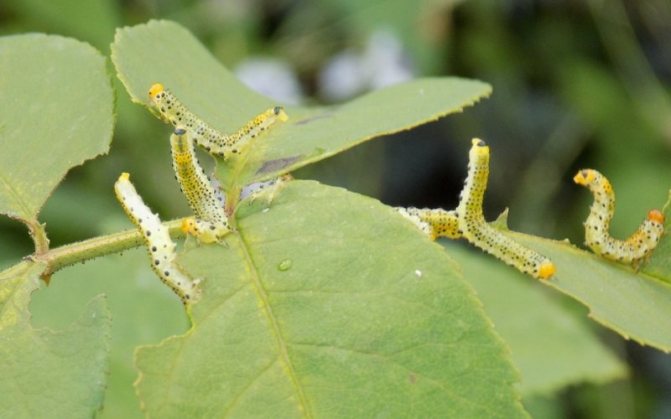


Sawfly honeysuckle changeable.
Sawfly honeysuckle changeable Zaraeae mutica Thoms. - insect 9-10 mm long. Wings without dark band, body bronze-green, antennae black, tibiae and tarsus yellow-white. The flight of adult insects is observed in May-June. False caterpillars are gray-white in color with 5 longitudinal rows of black and two rows of yellow spots, but above the spiracles there are only black stripes, not a stripe. False caterpillars roughly eat leaves and flower buds, leaving only stalks. Meals continue from July to the end of August.
Control measures. Same as against striped honeysuckle sawfly.
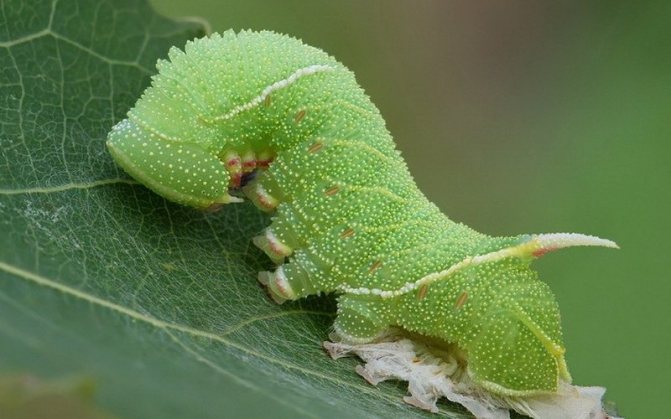


Sawfly honeysuckle.
The honeysuckle sawfly Abia lonicerae L. is an insect 10-12 mm long. The body is dark bronze, the tibiae and tarsi are yellow-white, the antennae are black. False caterpillars are bluish-gray with a lighter bottom and sides, the head is black. Along the back there is a row of black spots with wide yellow (orange) edging, bordered on the sides by large black spots, and in front and behind by a black transverse stripe. The sides of the segments are with black spots, specks and dots. False caterpillars roughly eat the leaves of the honeysuckle and destroy the set berries.
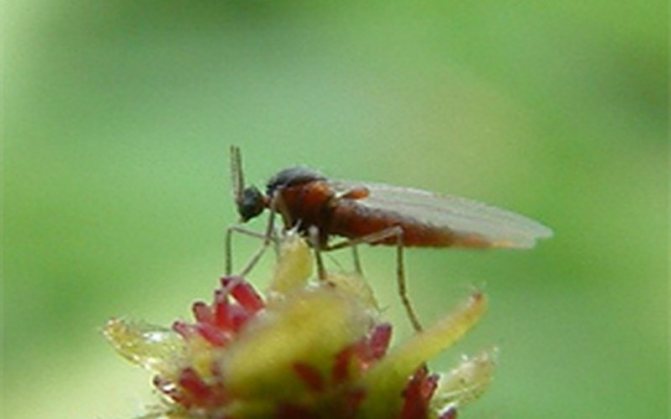


Gall midge is honeysuckle, leaf.
Gall midge, leaf honeysuckle Dasyneura periclymeni Rubs. - a small dipteran insect 2-2.5 mm long, with delicate transparent wings, long legs and antennae. It flies in May, after fertilization, the females lay eggs on young blossoming leaves. White legless, worm-like larvae hatch from the eggs, which subsequently become yellowish-red in color.
The larvae suck the juice, as a result of which the edges of the leaves curl upward, thicken, forming dense yellowish and reddish ridges, inside which there are several dozen larvae. The development of the insect lasts 30-40 days, and 3-4 generations develop during the year. With a large number of pests, damaged leaves at the ends of the shoots are underdeveloped and curl along the central vein.
Control measures. Preventive spraying in the spring before flowering and immediately after it with one of the drugs: fufanon, kemifos, kinmix, actellik, spark, Inta-Vir.
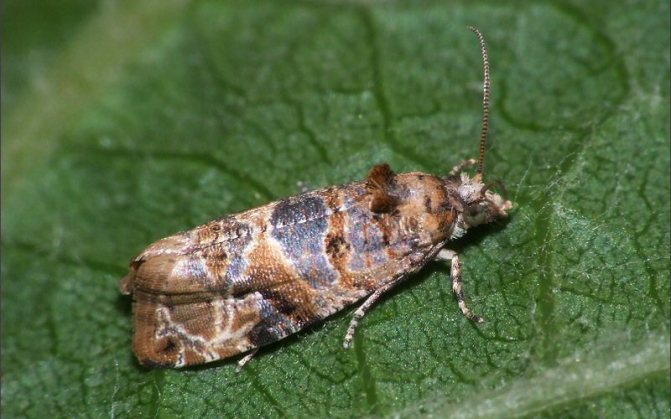


Biennial leafworm.
Biennial leafworm Eupoecilia atbiguella Hb. - a small butterfly, the caterpillars of which often damage privet, honeysuckle and buckthorn. Caterpillar 12-14 mm long, fleshy red, with a shiny black head, prothoracic scutellum and thoracic legs. The anal plate is brown. Each segment of the body has transverse rows of small hairy warts.
Control measures. Preventive spraying of trees and shrubs in spring, before flowering or immediately after it, with one of the drugs: fufanon, kemifos, kinmix, actellik, caviar, Inta-Vir.
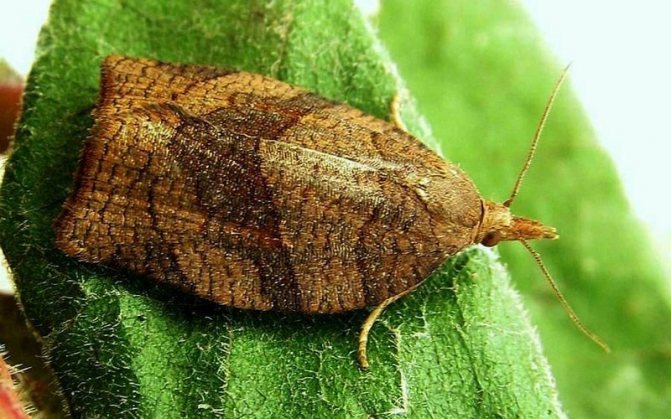


Willow curved leafworm.
Willow curved leafworm Pandemis he-parana Den. et Schiff. - a butterfly with a wingspan of 24 mm in females and 16 mm in males. The forewings are reddish-brown, the bases of the wings and the middle band are darker, the hindwings are light gray in color. The caterpillar is green, with a yellow or pale green head. Pupa light brown, 12-14 mm long.
Ovipositions are bright green. Caterpillars of the second instar hibernate in cobweb cocoons under dry bud scales. In spring, at an average daily temperature of 15-17 ° C, caterpillars emerge from cocoons and begin to feed on buds and young leaves. Having finished feeding, they pupate. Mass flight of butterflies is observed in June.
Tags: disease, spring, pest, honeysuckle, treatment
About
«Previous post
Leaf-eating harmful insects
Leaf-eating insects affect edible and wild-growing honeysuckle less than other species. In this case, only the decorative attractiveness of the bushes suffers, but the plant itself does not die.
The rose leafworm is attracted by the vegetative organs of the honeysuckle: buds, leaves, fruits and young shoots. Females of butterflies make their way into the bark of plants, where they leave their offspring, which winter without problems until the next season. Caterpillars of currant currant leafworms damage the fruits and leaves of the plant. They roll the leaves along the central vein and wrap spider webs around them. Caterpillars of honeysuckle striped sawflies, when touching them, produce a yellow liquid. The larva has a gray-green color and 5 rows of black dots on the back. She gnaws holes in the leaves of various shapes and sizes.
The narrow-bodied honeysuckle goldfish and the honeysuckle miner, in the form of larvae, make a long and narrow mine passage on a leaf. The speckled honeysuckle moth leaves behind a white passage on the leaf plate. The larvae of the honeysuckle barbel feed on the cores of the shoots, and the beetles gnaw the tissue of the leaves of the plant.
Ways to fight.
During massive attacks of these pests, honeysuckle is processed: "Decis", "Intra-Vir", "Eleksar".
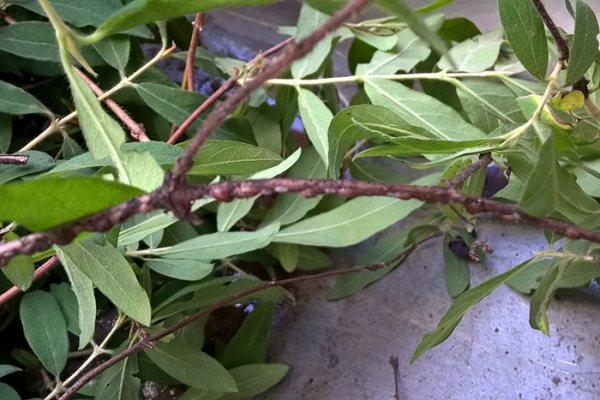


Honeysuckle fingerfly
Honeysuckle fingerfly, in the form of a caterpillar, penetrates the fruits of honeysuckle, consuming their juice and seeds. This leads to the fact that still unripe fruits begin to darken, wrinkle and fall off. As a result, the yield and the appearance of the fruits are reduced. Fingerwing butterfly is gray, small in size.
Ways to fight.
You can fight the honeysuckle fingerwing with chlorophos. Plants spray it with a 0.2% solution at the moment when many insects are seen on it. An intra-plant insecticide will help to destroy the larvae: Rogor 0.2%, as well as Intra-Vir. You can also use the folk method, using infusions from the tops of tomatoes or potatoes. It is necessary to spray shrubs only on dry and not hot days. It is important to dilute chemicals in accordance with the instructions, without exceeding the specified rates.