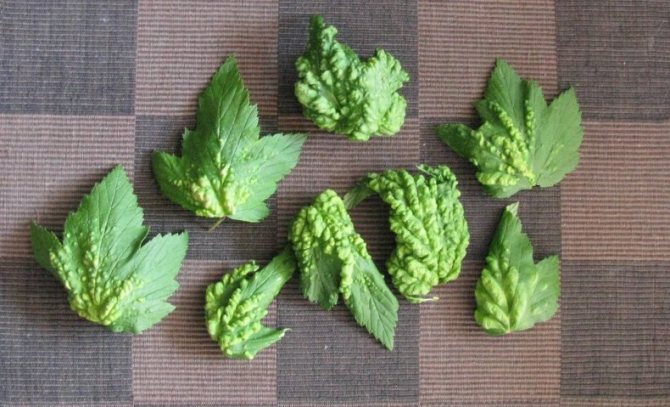
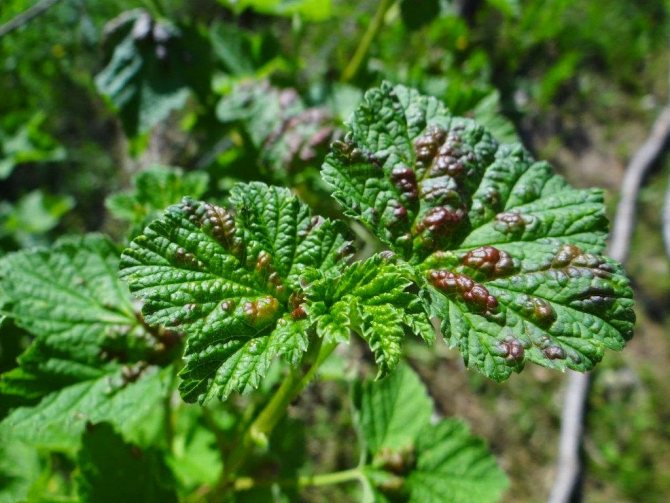
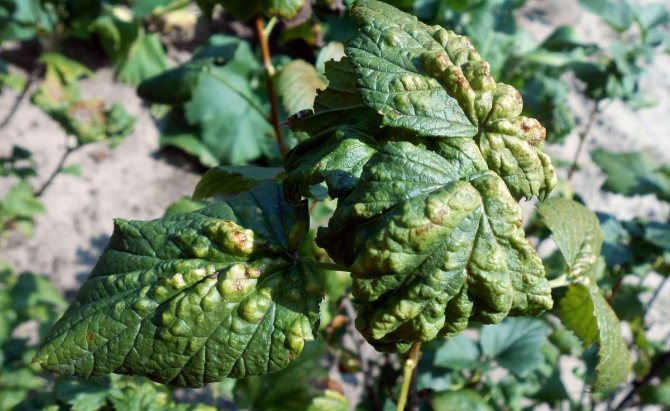
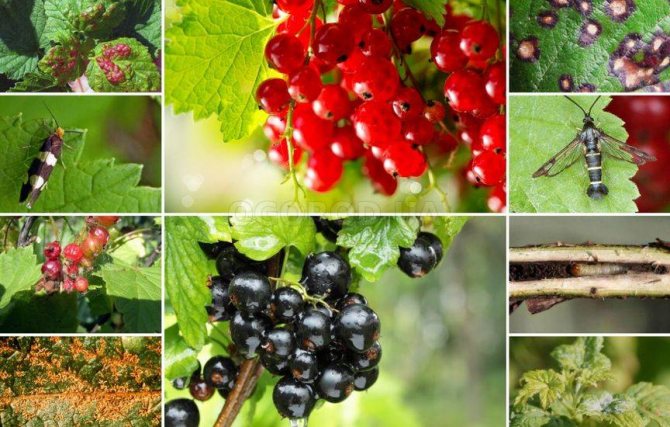
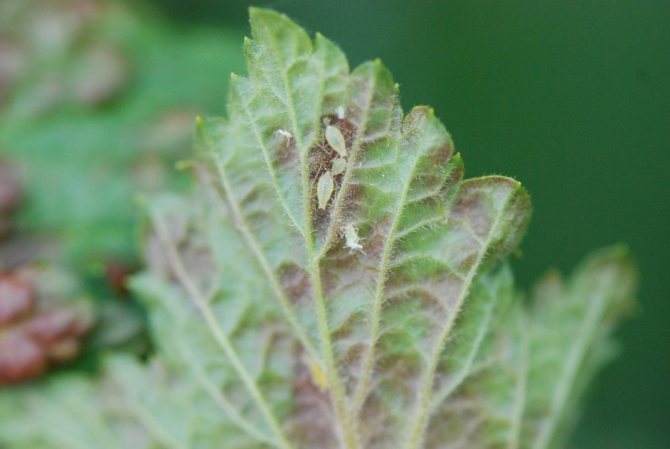
Redcurrant gall aphid
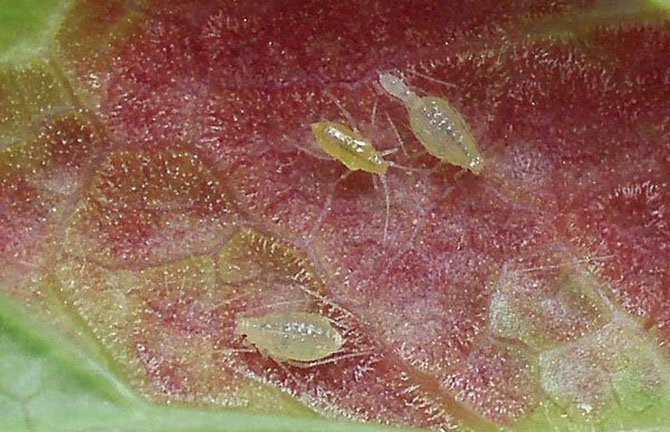

- The insect is yellow with red eyes.
- The larvae hatch from the eggs overwintering on the branches during the opening of the leaves.
- Until mid-summer, aphids feed on the underside of the leaf. When the leaves become coarse, some of the winged females migrate to herbaceous plants and continue to reproduce.
- In autumn, females return back to the bush and lay eggs for the winter.
- When aphids feed on the upper side of the leaves, swellings are formed in the form of dark red or yellow tumors.
Goblet Rust of Red Currant Description with Photos and Treatment Methods
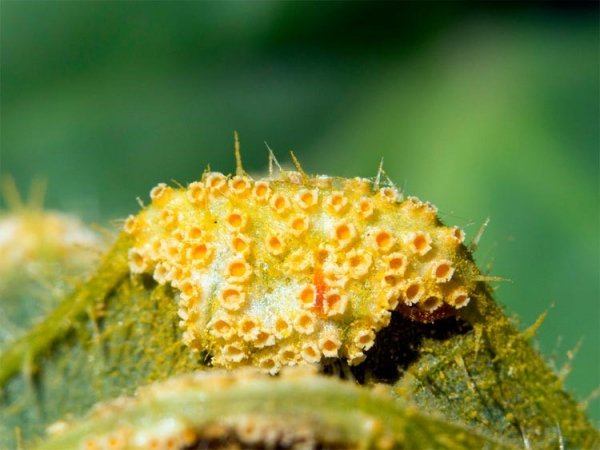


The symptoms of this disease are not immediately noticed, since everything happens on the lower part of the red currant leaves. It is not possible to detect the problem during a routine inspection.
The main manifestation of the disease is the appearance on the underside of the leaves of small (0.5-1.5 mm in diameter) growths of orange or red-yellow color with small depressions. This is the culprit of the problem - a rust fungus, one of the most common Pucciniomycetes, an extensive class of fungi that parasitize various types of living organisms.
As the disease spreads, the lower surface of the leaf is completely covered with the parasite, from where they move to neighboring leaves.
An interesting fact is that red currant is only a temporary host of the fungus. To continue its development, the fungus needs to spray the spores. This happens at the moment when the dying leaf falls from the bush. Further development of the rust fungus occurs on another host.
Goblet rust is a very unpleasant disease. It can lead to a loss of 50% to 70% of the crop. Most often, plants growing near natural reservoirs and in conditions of high humidity are susceptible to it.
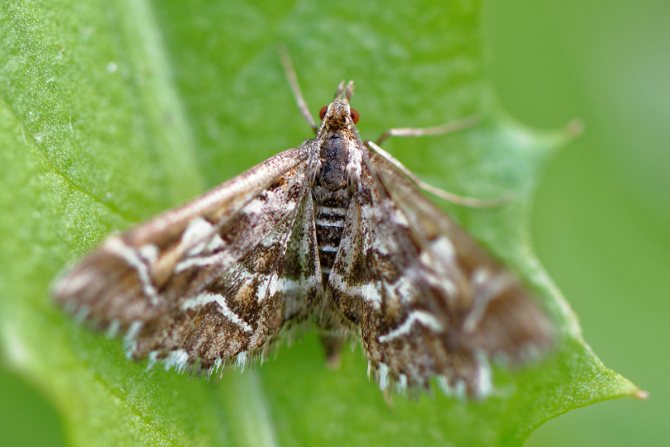
Currant glass
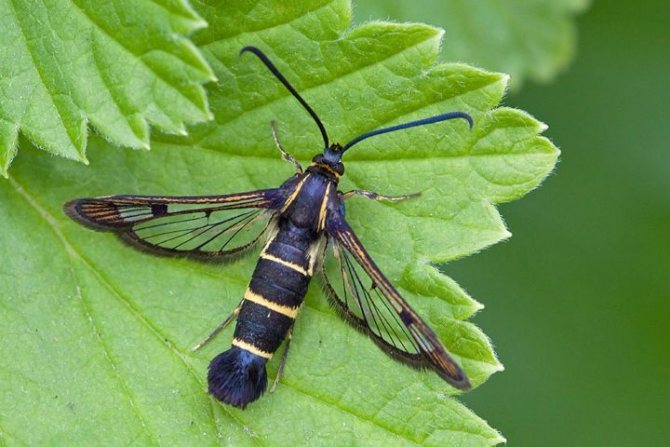


- A butterfly with a wingspan of up to 28 mm. The wings are glassy-transparent, narrow.
- The caterpillar is white, 16-legged; the head and thoracic plate are dark brown.
- Hibernates inside shoots. In the spring it pupates there.
- At the end of flowering, butterflies fly out and lay eggs near the buds. After 10-15 days, the hatched caterpillars penetrate into the shoots and make up and down passages in the wood. Damaged branches and shoots wither and dry out.
- In places of damage, branches break off.
Some bushes have up to 20% of damaged shoots. Caterpillars live inside shoots for 2 years.
To combat, systematic cutting and burning of affected shoots is used. Treatment with 10% karbofos at the rate of 75 g per 10 l of water 10-12 days after flowering or at the time of hatching of caterpillars.
Reverse red currant description with photos and treatment methods
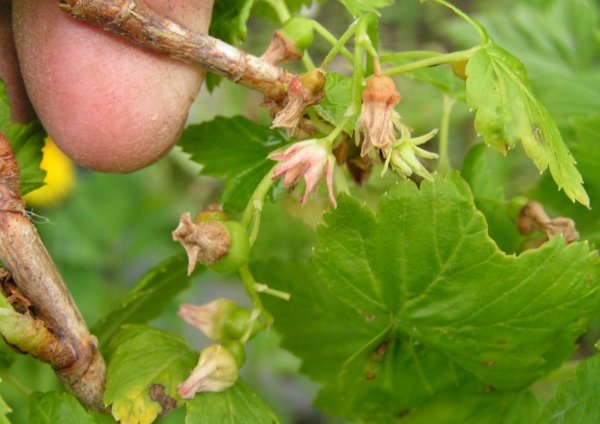


Black currants are more susceptible to this disease, but recently red currants have also been suffering. The causative agent of the virus is a kidney mite that enters the garden along with infected seedlings.
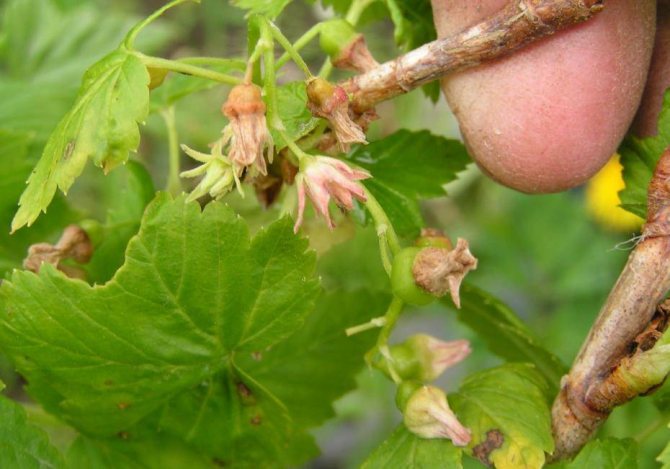
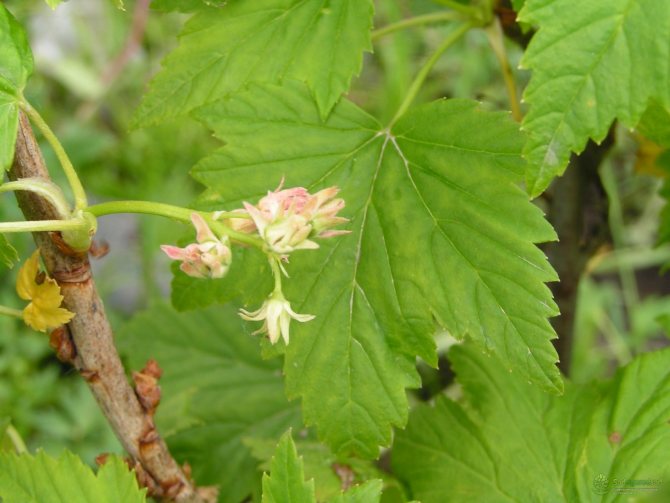
The disease passes from bush to bush, roaming around the site for several years. Flowers are a signal that the plant is ill with reversion. They become acicular-terry (almost curly) and take on a purple hue.
The disease also manifests itself on the leaves. They become smaller, acquire an irregular shape, and lose their specific smell.Instead of 5, 3 lobes grow with coarse sparse veins. The sheets are framed with large teeth.
There is a great thickening of the bush. The currant stops producing and gradually loses its grade. The problem is that it is not immediately detected. Therefore, careful monitoring of new bushes (and those adjacent to them) is required for 4 years in order to detect infection in time.
The main therapy includes the following points:
- preventive treatment of bushes by spraying with colloidal sulfur, acaricidal preparations (Vertimek, Nitrafen, Neoron), biological agents (Aktofit, Fitoverm); procedures are carried out at the time of bud break and during budding;
- finding damaged branches, they are cut off and burned away from the site;
- if the lesion is significant, then a more radical method is used - they uproot the entire bush in order to save the rest of the plants from terry.
To prevent an "epidemic", it is recommended to keep the seedlings for 2-3 days in Fitoverm solution before planting. From folk remedies, tea leaves are used for this purpose (0.25 kg per bucket of water). It is worth planting rows of garlic around the young shrub - its specific smell will scare away the tick.
Currant goldfish
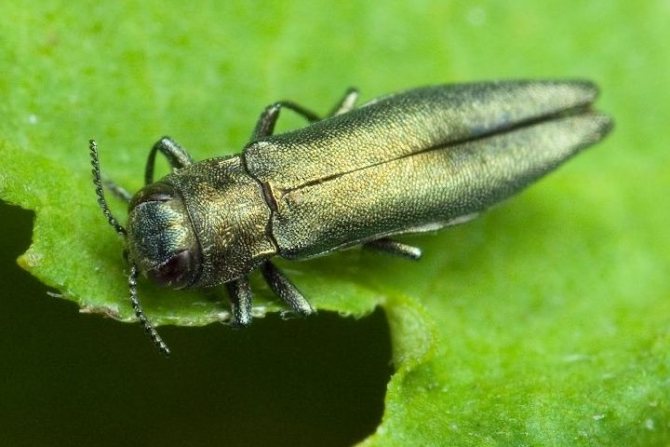


- A small bug with a shiny greenish-golden color.
- The larva of the goldfish makes moves in the core of the shoots. Affected stems dry out and die.
- Adult bugs fly out in June and feed on leaves.
- They lay eggs on the bark of young shoots, and the released larvae gnaw through the passages in them and remain for the winter.
- In summer, in warm weather, the flight of the goldfish begins, and the cycle repeats.
To combat goldfish, regular sanitary pruning of shoots to healthy tissue is carried out not only in spring and autumn, but also throughout the summer. During the mass emergence of beetles, spraying with a 0.3% solution of karbofos is effective.
Non-communicable diseases
The manifestation of such pathologies is associated with improper care, deficiency of nutrients, excess content of any element in the soil.
Marginal necrosis
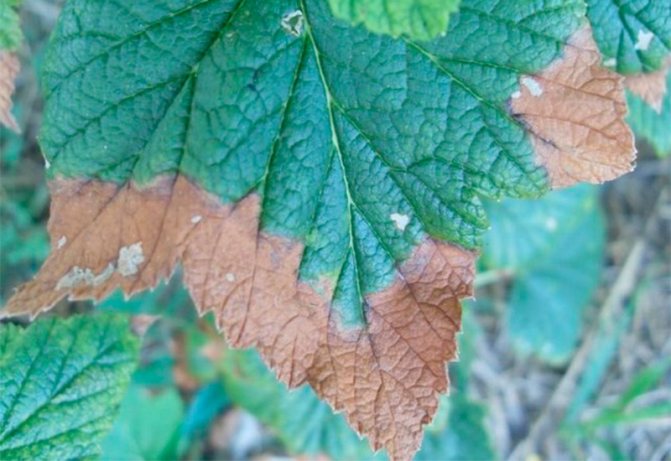


The cause of this pathology is the excessive content of chlorine in the soil. A gray border appears at the leaf plates of the culture, which gradually dries out and falls off. The boundary between healthy and diseased tissue is sharp, which distinguishes necrosis from similar signs of potassium deficiency.
Usually the disease manifests itself in August, although the appearance of a border is possible in the middle of summer. For treatment, top dressing is carried out with a solution of ammonium nitrate. Affected shoots with leaves are cut off, burned.
Withering
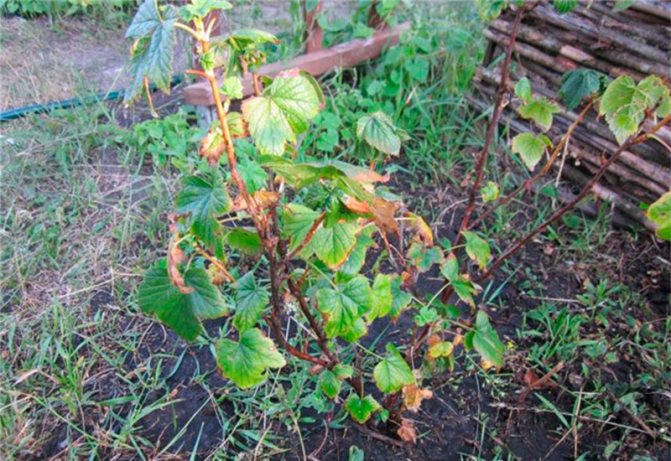


In dry and hot summers, wilting of currant leaves is observed. If there are no visible signs of damage, the presence of pests, then, most likely, the bushes suffer from a lack of moisture.
The problem is solved simply: provide the culture with timely watering, while avoiding waterlogging of the soil. It is recommended to mulch the soil around the berry fields with grass, compost.
Change in leaf color
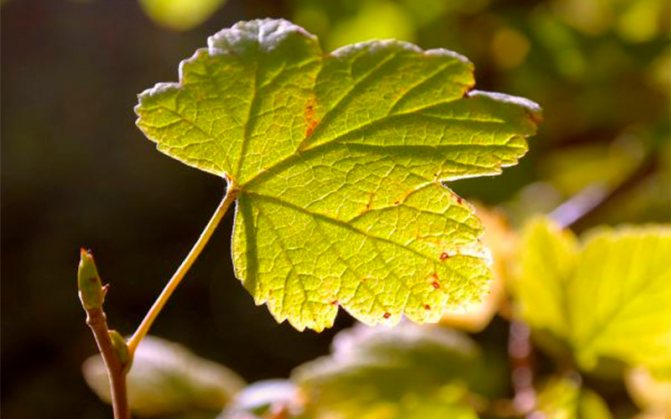


Lack of iron, magnesium - the reasons for the change in the color of the leaf plates.
Signs:
- with a deficiency of magnesium, the leaf plate turns yellow, while the veins remain bright green;
- lack of iron is manifested by complete yellowing of the leaves.


To replenish the deficiency of trace elements in the first case, the currants are fed with solutions of potassium sulfate (30 grams per bucket of water), or potassium magnesium.


The composition of chelated iron will help to eliminate the lack of iron. Proportions: 5 grams of the product are diluted in a bucket of water, sprayed over the leaves.
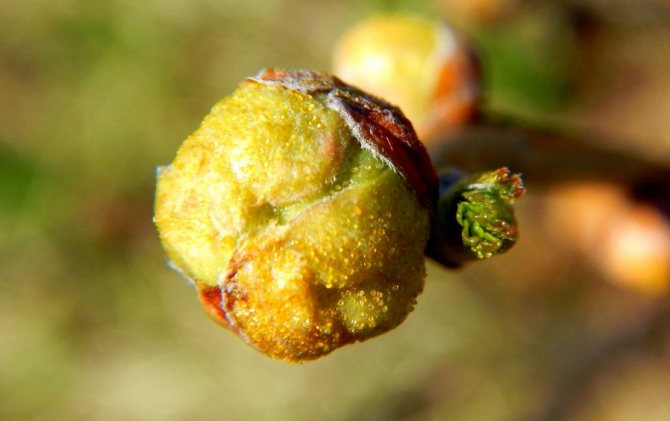
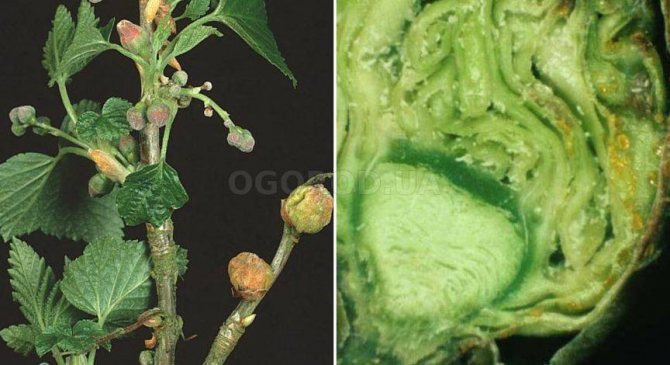
Kidney mite
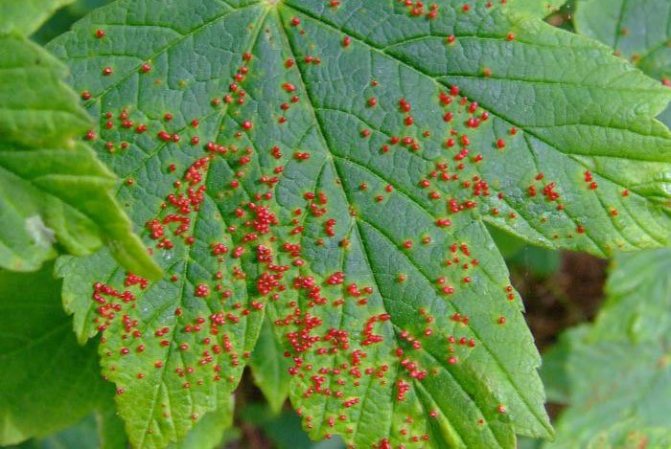


Threatens members of the entire gooseberry family. Unnaturally enlarged, rounded buds indicate the damage to the plant. Normal shoots and leaves will not develop from them, the crop will not form.Instead, many mites spread, which weaken the plant and can kill the bush. They are carriers of reversion pathogens.
Methods of struggle: Revealing and destruction of deformed kidneys. The use of acaricides, since insecticides such as Nissoran or Envidor do not act on ticks. Carry out two treatments with an interval of 10 days, starting before flowering currants, when the mite leaves the bud. After harvesting, use more toxic drugs: Accent, BI-58 or Phosphamide.
Viral diseases
The causative agents of this group of diseases are non-cellular organisms that can live and reproduce only in living cells. The fight against them is ineffective, infections are considered incurable, often lead to complete sterility of plants.
Striped mosaic
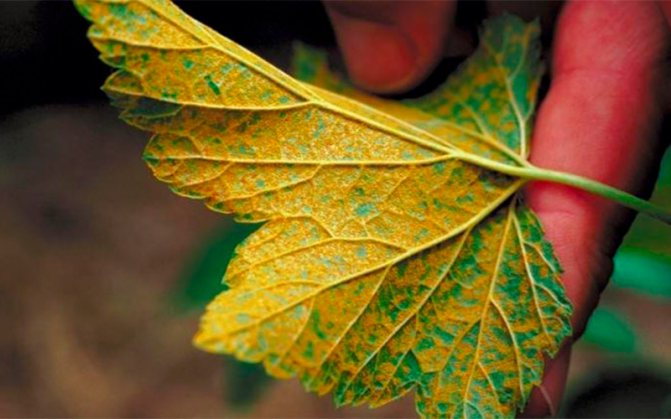


As with many viral lesions, in this case, the changes are associated with the color of the leaves. Patterned grayish-yellow spots appear on the leaf plates of the culture. They appear first in the area near the veins, gradually covering the entire leaf area.
A patterned ornament is a sign that a virus has infected the currants, and it is useless to fight it. It remains only to carefully dig up and burn the bush.
Attention! When uprooting bushes, do not leave pieces of infected currant roots in the ground. The viral pathogen can pass from them to healthy bushes.
After digging, the soil is spilled with a solution of Fitosporin or a saturated solution of potassium permanganate.
Terry


All types of currants are susceptible to the terry virus. The causative agent is Ribes virus 1, moving through the vessels of branches, shoots of culture. Mycoplasma infection is typical for all climatic zones, it affects the bush partially or completely, while it can subside for a certain period and then return again.
Signs:
- deformation of sheet plates - the formation of instead of five or three blades;
- coarsening of leaves;
- a sharp darkening of the color of the foliage;
- unnatural elongation of the plates, the absence of small veins;
- the disappearance of the pleasant aroma characteristic of black currant;
- stretching flower brushes that resemble tentacles;
- color change (instead of pink-white flowers, lilac-lilac, violet are formed);
- the appearance of short shoots;
- deformation of flowers (doubleness, separate petals).
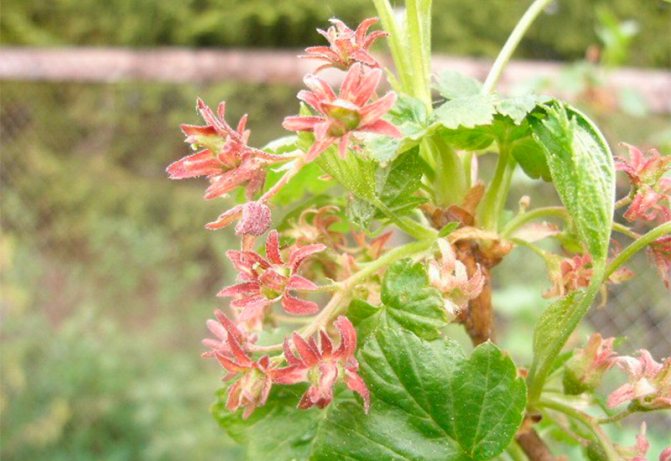


With partial infection, the deformation affects only the apical part of the bushes (small three-lobed leaves, underdevelopment of the shoots). The formation of buds, flowering, the formation of berries is possible, but their number and size are very small.
The virus mainly spreads a dangerous pest - a kidney mite, although there are frequent cases of infection of plantings with bugs, aphids, spider mites. Also, infection occurs from diseased bushes when pruning through garden tools, when grafting cuttings (from sick to healthy plants).
The disease develops gradually, the yield indicators decrease with each season, which ultimately leads to the complete sterility of the bushes and their death. There is no effective treatment for terry.
Affected bushes are uprooted and burned. Healthy bushes are treated with immunostimulants, fed on a leaf with formulations containing boron, molybdenum, manganese.


To exterminate the carriers of the virus, biological products are used:
- Bitoxibacillin;
- Lepidocyte.
Biological agents are allowed at all stages of the growing season of the crop, since they do not accumulate in the fruits and leaves of plants, and are moderately toxic.


With a large number of pests, you will have to use chemical insecticides:
- Akarin;
- Fufanon;
- Fitoverm.
For propagation by cuttings, only bushes are taken that have not been sick with terry over the past 4-5 years. When feeding, preference is given to potassium and phosphorus supplements, which increase the immunity of plants. At the same time, an excess of nitrogen fertilization is avoided.
Virus-resistant varieties are planted:
- Nara;
- Desirable, Memory Michurin;
- Binar;
- Dubrovskaya.
Currant fire
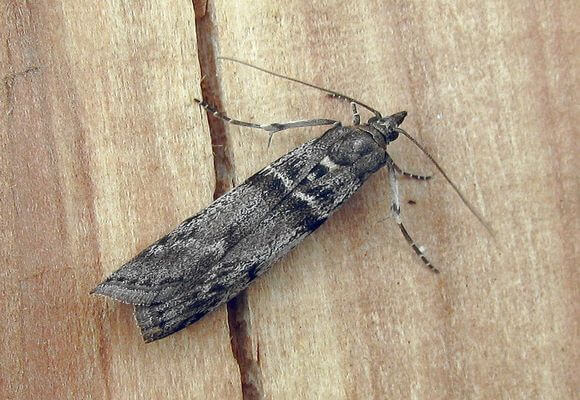


- It starts flying at a time when buds are forming on the currants. She lays eggs in them.
- The hatched larvae eat the flowers, then crawl to the neighboring ovaries.
- So they, voracious and numerous, are able to destroy the entire crop.
In case of significant fire damage, the bushes are sprayed with insecticides such as Actellik or Iskra. A good result is given by Fitoverm treatments against larvae.
Septoria red currant description with photos and treatment methods
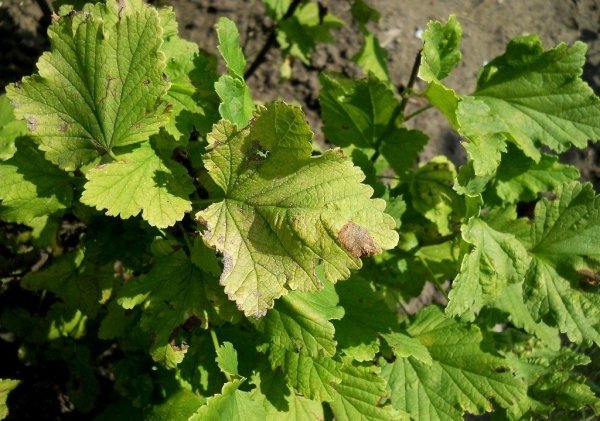


This disease is from a number of fungal, spreads on the plant with lightning speed. The first signs are found on currants in June - gray rounded spots with a dark brown edging appear on the leaves. A little later, black blotches begin to appear in the foci, which are mature spores of the fungus. If you do not stop their further growth, the leaves dry and fall off. The synthesis of chloroform is disrupted, and the plant dies
Treatment of currants for white spot includes the following points:
- treatment of bushes with copper-containing Kuprozan in a concentration of 0.4% or colloidal sulfur (1%);
- spraying with fungicides - Pervikur, Acrobat, Ridomil, Fitosporin;
- removal of part of the shoots on which infected leaves are found.
The success of therapeutic measures depends on the timely detection of septoria. Therefore, with the beginning of the summer period, the berry should be regularly inspected.
Spider mite
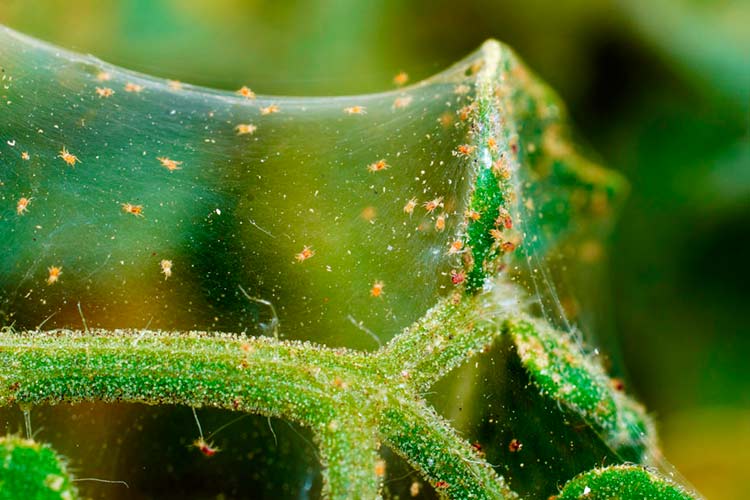


- It mainly affects red currant bushes.
- It feeds on young leaves and berries.
- It is usually located on the underside of the leaf blade. Yellow and red spots appear on its surface.
- Small mites gradually entangle leaves and bunches of currants with their cobwebs.
- Berries lose their presentation, their taste deteriorates.
To combat spider mites, toxic acaricides are used: BI-58 or Fufanon. Use only in sunny weather, observing protective measures. Also, watering the bushes with a stream of water has a beneficial effect on plants. Some of the ticks are washed off and, having lost access to food, dies. It is recommended to pick the affected leaves and bunches by hand.
Currant bacterial diseases
Bacteriosis is caused by non-spore-bearing bacteria that penetrate into plants either through various injuries, or naturally (through the stomata of leaves). Black currant is affected by bacterial spotting, some other species have not been recorded.
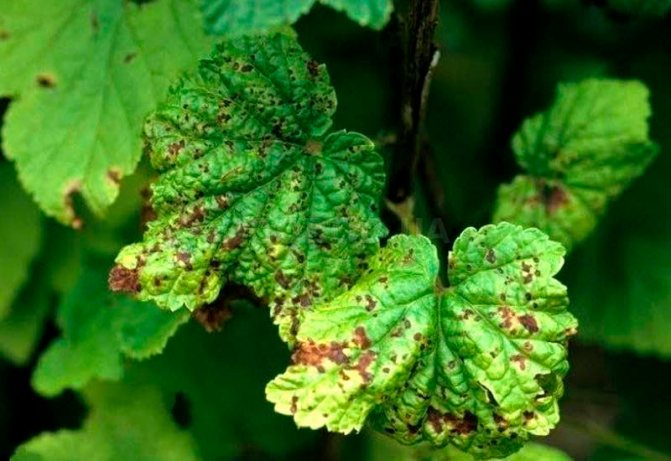


The pathogen is activated in hot weather and high humidity. On the leaves of the culture, watery spots appear between the veins, which eventually turn black. The plates change color, die off and fall off.


The infection is stopped with treatments using:
- drug Maxim;
- Bordeaux mixture;
- copper sulfate;
- HOM drug.
Severely affected bushes are removed and burned.
Gallica
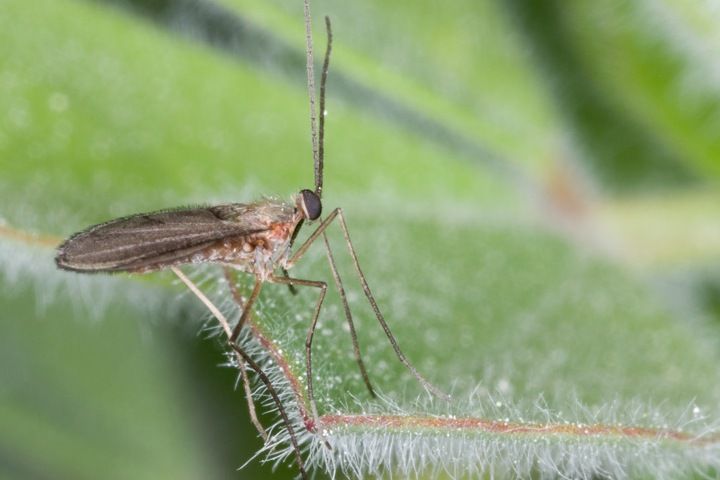


The larvae damage young currant tissues. After the invasion, ugly leaves remain, the stems are covered with ulcers and cracks, the damaged buds are deformed, the flowers fall off.
To combat gall midge, the condition of the bushes is systematically checked. If signs of damage are found, the affected buds, buds, leaves are immediately removed, shoots are cut off and all collected plant residues are burned. In order to complicate the flight of adults, the root zone is dug up, mulched with peat or humus. Spraying of bushes with 0.3% karbofos is used before flowering, if necessary, after picking berries, the treatment is repeated.
Gray rot of red currant description with photos and methods of treatment
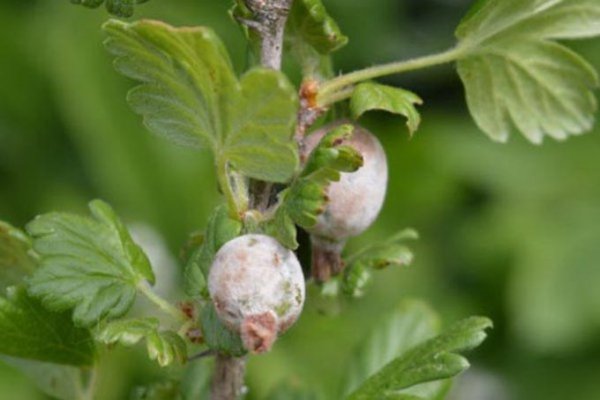


Fungal spores are carried by the wind. Sources of infection can be any fruit and berry crops. Mycelium hibernates well on fallen fruits and foliage. After waking up, he is looking for a new owner.
Symptomatic signs include:
- moldy pimples on the shoots;
- spots of a brown tint on the leaves.
Perfectly works against this mycotic ailment "Zircon", which is sprayed with currants in the early - spring period. In the fall, after dropping the foliage, the shoots are treated with a solution of urea. To do this, dissolve 350 g of urea in half a bucket of liquid.
Sawfly currant
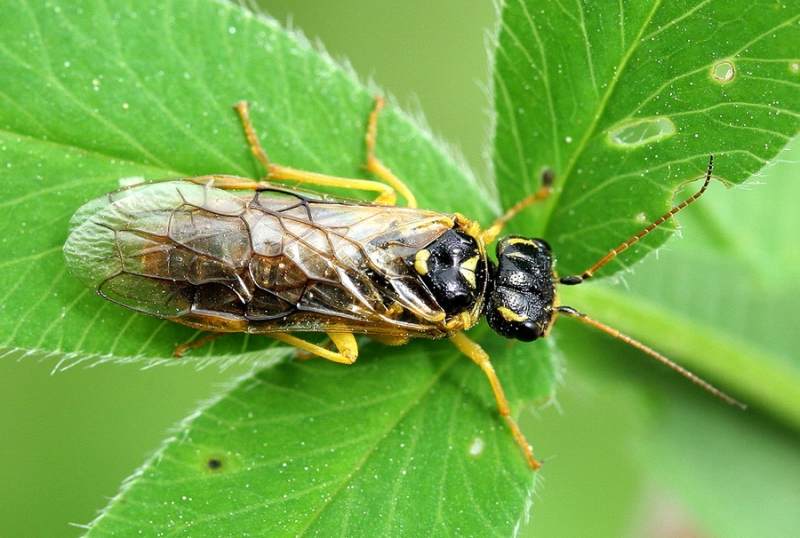


Sawfly larvae can eat up the entire leaf blade to the veins, this leads to a weakening of the bush and crushing of the berries.
Control measures are reduced to checking the condition of the leaves. When holes are found on them, and in the later stages of leaves eaten to the veins, all diseased parts of the plants are removed and destroyed. Take Actellic from chemicals.
Spheroteka (American Powdery Mildew)


The causative agent is fungi of the genus Sphaerotheca. The first signs of infection of currants with spheroteka are noticeable already in May: the leaves, stems of the bush, and subsequently the fruits are covered with a white bloom (later the color turns brown). Then the berries become smaller and lose their sweetness, diseased bushes do not have time to grow and die. The development of the disease is facilitated by high air humidity, dry, nitrogen-saturated soil.
Control measures
The affected parts of the plant must be immediately cut out and burned, and the bushes themselves must be treated with a fungicide (
Fundazol
,
Topaz
and etc.). For the prevention of spheroteka in the fall, it is necessary to remove fallen leaves, thin out the bushes. Dusting is also effective
wood ash
.
The causative agent is fungi of the genus Sphaerotheca. The first signs of infection of currants and gooseberries with spheroteka are noticeable already in May: the leaves, stems of the bush, and subsequently the fruits are covered with a white bloom (later the color turns brown). Then the berries become smaller and lose their sweetness, diseased bushes do not have time to grow and die. The development of the disease is facilitated by high air humidity, dry, nitrogen-saturated soil.
Control measures
The affected parts of the plant must be immediately cut out and burned, and the bushes themselves must be treated with a fungicide (Fundazol, Topaz, etc.). For the prevention of spheroteka in the fall, it is necessary to remove fallen leaves, thin out the bushes. Dusting with wood ash and the use of modern biofungicide Ampelomycin are also effective. Spraying is carried out with a 0.5% suspension 3-5 times per season with an interval of 7-10 days.
What do experienced gardeners advise
Experienced gardeners believe that currant health begins from the moment of planting. More precisely, from the moment of purchasing the planting material. It is recommended to abandon the dead-end practice - the propagation of currants by cuttings from old bushes.
Using such planting material, the number of pests and diseases in the garden is increased. It is necessary to acquire new varieties that are resistant to diseases and pests. When planting, treat it with insecticides or infusions of wormwood, tansy.
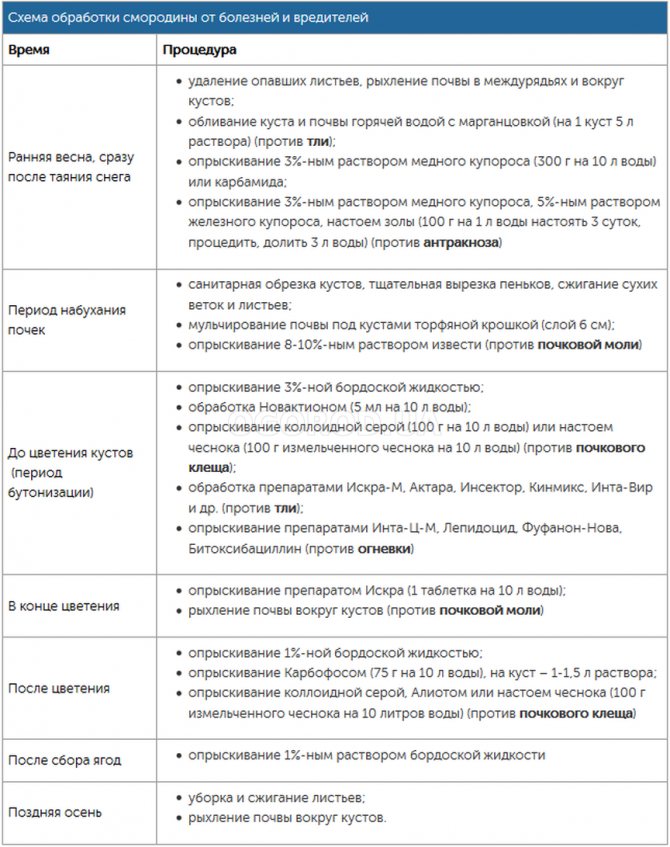
Taking care of the bushes:
- Autumn, spring - sanitary pruning.
- Autumn, spring - we dig up the aisles and the ground around the bushes.
- Spring - pour mulch around the bush.
- Autumn, spring - preventive treatments with herbal infusions or chemicals.
- Remove infected plants and burn them.
- Autumn, spring - fertilizers containing nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium.
Growing a healthy, fruiting currant bush is not that difficult. A systematic approach and careful attention to currants is important. Regular inspections of the bushes allow you to identify the disease, the pest at an early stage and start the fight in time.
Preparations for septoria disease (fungicides)
The following drugs are effective in the fight against white spot:
- Hom is a copper-containing fungicide of systemic-local action to combat fungal diseases - scab, septoria, late blight, peronosporosis and others;
- Oxyhom is a systemic contact copper-containing fungicide of a wide spectrum of action, used to combat fungal diseases;
- Copper sulfate is a broad-spectrum contact fungicide designed to combat fungal diseases of fruit, berry, ornamental crops;
- Iron vitriol - a remedy used for the prevention and treatment of fungal diseases;
- Bordeaux mixture - a copper-containing fungicide of a wide spectrum of action to protect vegetable, fruit, berry, citrus, melon, ornamental and flower crops from a complex of diseases;
- Profit is a contact fungicide to combat Alternaria, Septoria, late blight and other fungal diseases;
- Nitrofen - a drug for the destruction of fungal, mold and parasitic infections, inhibiting the growth of weeds and disinfecting the soil;
- Homecin is a protective contact fungicide recommended for treatment of plants during the growing season;
- Captan is a fungicide of therapeutic and prophylactic action, a substitute for Bordeaux liquid;
- Phthalan is a fungicide of a wider spectrum of action than Captan.
To combat septoria, Acrobat MC, Previkur, Ridomil Gold MC, Fundazol, Skor, Ordan are also used, and Rovral, Trichodermin and Glyokladin are used for preventive treatments, preparing solutions in accordance with the manufacturer's instructions.
Nectric drying of shoots
If the rules of care are violated, currant bushes may be susceptible to necrotic drying of shoots. The disease is caused by the marsupial fungus. The main features include the appearance of orange dots on the branches, the size of which is gradually increasing... Over time, brown tubercles appear in place of the points. If untreated, young shoots dry out.
This disease is most often found on white and red currants. If the leaves turn yellow on the currant, pruning of the bushes is required to remove all damaged parts. Bordeaux mixture is used to treat red currant disease. It is recommended to follow the rules of caring for the bushes, which include regular feeding, removing weeds and dangerous leaves, and standardized watering. This will increase the immunity of the bushes and prevent them from becoming infected with a fungal disease.
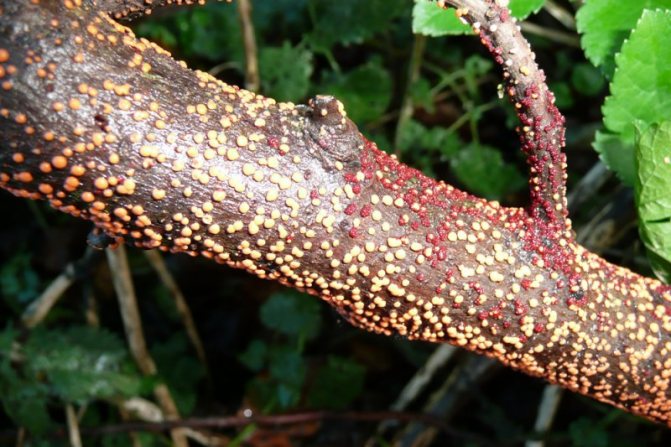


Nectric drying of shoots
Care rules and preventive measures
In order for the planting of currants to be healthy and invariably pleasing with the harvest, it is necessary to adhere to a number of simple rules for caring for plants:
- Mandatory agrotechnical methods are:
- planting seedlings with a 3-5 cm deepening of the root collar and cutting off the shoots, so that 2-3 buds remain above the ground;
- timely watering and mulching of the soil with peat, compost or humus;
- replacing bushes older than 7 years with young plants;
- correct annual pruning, in which 2-3 best basal shoots are left every year, and the rest are cut out.
- Fresh manure should not be applied for planting currants; nitrogen fertilizers should be used carefully. The best fertilizing for berry growers is the introduction of humus-powder and wood ash for digging.
- In autumn, foliage is collected, remove the berries dried on the bushes, dig up the aisles.
- Before the start of frost, you should inspect and peel off the loose bark on the branches and burn it.
- In the spring, before the juice begins to move, old and sick shoots affected by powdery mildew, mites or insect larvae are cut out. Places of cuts are disinfected with a 1% solution of copper sulfate and covered with garden varnish.
Advice. The introduction of wood ash under the currant bushes as a combined phosphorus-potassium fertilizer will increase the resistance of plants to powdery mildew. - During the growing season, the bushes are regularly examined, branches affected by larvae and buds inhabited by ticks are destroyed.
Advice. A valuable variety of currants can be saved even with a strong kidney mite infestation. To do this, cut off all the old infected branches, leaving several annual shoots, which are bent down and sprinkled with earth. In covered buds, the mite cannot develop and transfer to new buds.Healthy young stems grow from the covered areas, thus, uninfected layers are formed. - An obligatory measure for the prevention of diseases is the purchase of healthy planting material from certified growers., as well as the selection of the most resistant varieties for the region.
- Regular chemical or herbal treatments, carried out in the required time frame, will create a healthy phytosanitary background on the site and will contribute to the guaranteed obtaining of a high-quality harvest.
Rust
Currants and gooseberries are attacked by 2 types of this disease: goblet (yellow-orange "warts" are formed on the underside of the leaf) and columnar (reddish small spots on the leaves are characteristic) rust. After some time, the berries and foliage of the diseased bush fall off.
Control measures
When the leaves are just beginning to bloom, the bushes are treated with a 1% solution of Bordeaux liquid (or other fungicides), then the treatment is repeated during the formation of buds. The final spraying is carried out after flowering. You can also use Alirin-B (2 tablets per 1 liter of water) with the addition of liquid soap (1 ml per 1 liter of water).


Currants are attacked by 2 types of this disease: goblet (yellow-orange "warts" are formed on the underside of the leaf) and columnar (reddish small spots on the leaves are characteristic). After some time, the berries and foliage of the diseased bush fall off.
Control measures
When the leaves are just beginning to bloom, the bushes are treated with a 1% solution
bordeaux liquid
(or others
fungicides
), then repeat the treatment during the formation of buds. The final spraying is carried out after flowering.
Anthracnose
It is a serious disease caused by the Colletotrichum fungus. The first sign is the appearance of red spots on the leaves. Later, they enlarge and form obstacles to the movement of nutrients. Also, the disease can be recognized by rolling the leaves. Treatment should be started immediately.
The methods of fighting the fungus are as follows:
- Copper sulfate. The plant is treated with a 1% solution, consuming, on average, 1.5 liters per adult bush.
- Fitosporin. Usually 5 grams of the drug is diluted in one bucket of water.
- Previkur.
- Fundazol.
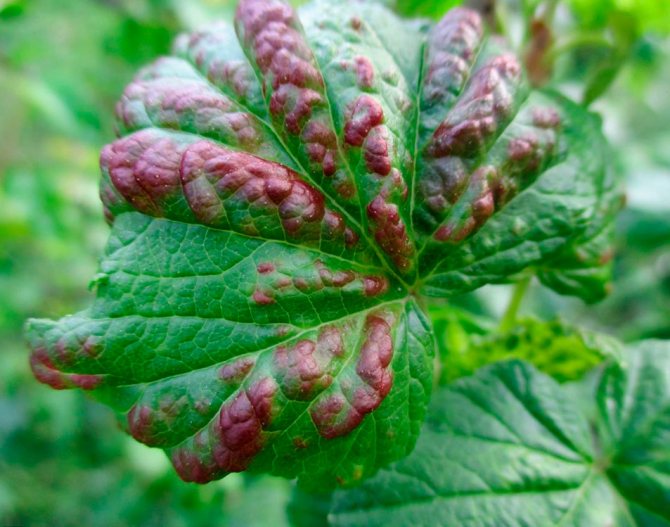


The disease is caused by ascomycete fungi


Tomatoes, cucumbers, melons, grapes, cherries and other crops are also susceptible to this disease.
Causes of occurrence
Septoria on currants is caused by the Septoria fungus. The fungus infects both garden and indoor plants, spreads very actively. A favorable environment for its development is high humidity and air temperature in the range of 15-20 degrees. Wet soils and winters with little snow also increase the risks of plant diseases. Read about the characteristics of the Dubovsky grape variety here.
Septoria's best friend is high humidity. So if it's damp in your area, take a look at this point.
Infection with septoria in the spring months occurs through ascospores that develop in the fruit bodies, on the shoots of bushes. Soon after the first signs of the disease appear, small pycnidia of the fungus appear in the affected areas, in which conidiospores mature. Through conidiespores, septoria spreads already in the summer. This is additionally facilitated by high humidity and significant air temperatures.
Resistant varieties
It will not be possible to choose a variety of currants that has absolute immunity against diseases. Simply because there are none yet. If there is a resistance to one disease, then another without preventive measures can destroy not only the crop, but also the bush. Therefore, you need to know which diseases are most common in a particular region and buy seedlings that are less susceptible to this pathology. In Russia, varieties with high resistance to powdery mildew and rust have appeared.Among the best are Temptation and Kipiana. The choice of a variety for a site is not at all easy. Indeed, not only the yield of shrubs depends on this, but also their longevity. Below are examples of disease resistant currant varieties:
Red
Red currants can be affected by viral and fungal diseases. Such as terry, anthracnose, rust, etc. The most resistant varieties from these pathologies:
- Roland. The result of the work of Dutch breeders. Resistant to almost all diseases caused by the fungus;
- Cherry Viksne. Has immunity against anthracnose;
- Alpha. Not affected by powdery mildew;
- Victoria. Resists anthracnose and goblet rust well;
- Faya is fertile. Has a relative resistance to goblet rust, white bloom, anthracnose;
- Chulkovskaya. It has immunity against fungal diseases, but is susceptible to currant terry.
Black
There are some varieties of black currant, strong and medium resistant against certain diseases:
- Binar (In memory of Pavlov). Resistant to powdery mildew and anthracnose;
- Kipiana. Immune to powdery mildew, but moderately resistant to anthracnose;
- Katyusha. Not affected by anthracnose and powdery mildew;
- Klussonovskaya, Kupalinka, In memory of Vavilov. Varieties of the Belarusian selection. Resistant to powdery mildew, and the latter also to anthracnose;
- Titania. The variety is highly resistant to fungal diseases, especially anthracnose and powdery mildew.
Reverse (terry)
A viral disease from which the plant cannot be cured. Basically, they are more black currant. Signs of double currant: the appearance of the leaves changes - they lengthen and become pointed, later sterile flowers of irregular shape grow. The disease is carried by sucking pests - ticks and aphids.
Control measures
Sick bushes will have to be removed from the site; partial pruning of heavily affected shoots is unlikely to help. To prevent the emergence of this virus, carefully consider the choice of planting material. Since the terry virus is carried by insects, treat the garden with pesticides in a timely manner.


A viral disease from which the plant cannot be cured. Signs of double currant: the appearance of the leaves changes - they lengthen and become pointed, later sterile flowers of irregular shape grow.
Control measures


Sick bushes will have to be removed from the site, partial pruning of heavily affected shoots will not help. To prevent the emergence of this virus, carefully consider the choice of planting material. Since the terry virus is carried by insects (kidney mites, aphids), treat the garden with pesticides in a timely manner.
Outcome
Many gardeners like to grow such useful berries as currants in their summer cottages. Unfortunately, she is often exposed to diseases caused by various fungi and parasitic insects. To save the bushes and preserve the harvest, it is necessary to determine the disease in time and begin treatment with the recommended drugs.
If the plant cannot be cured, it must be urgently removed and burned. Observing all the rules of agricultural technology for growing currants, and regularly carrying out preventive treatment, damage to the bushes can be easily avoided.