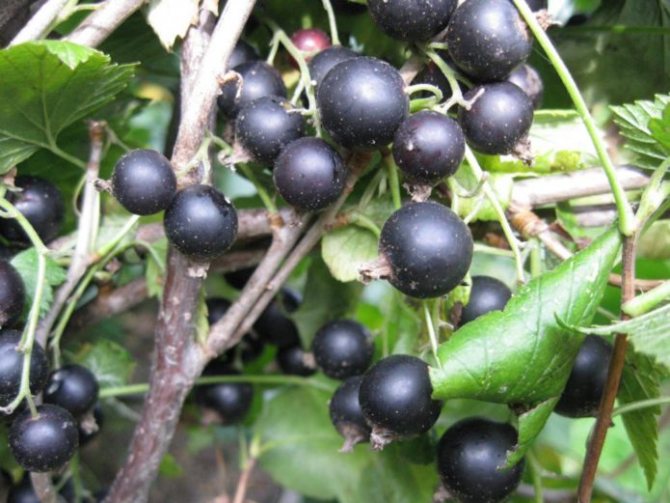
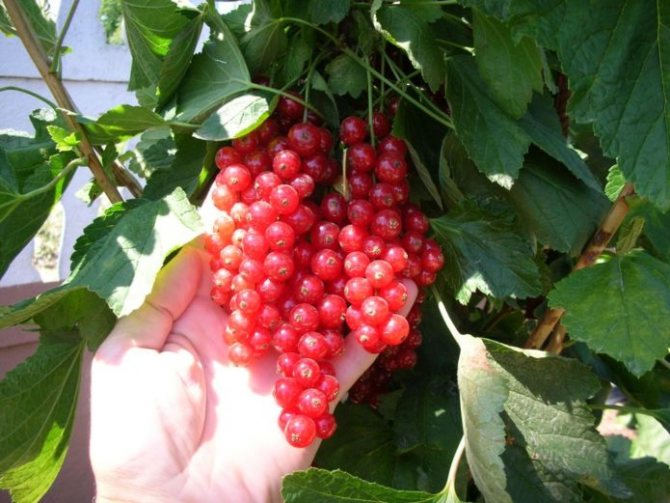
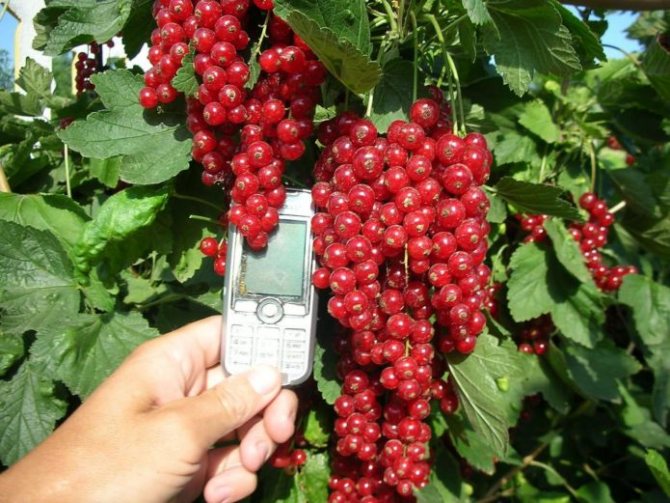
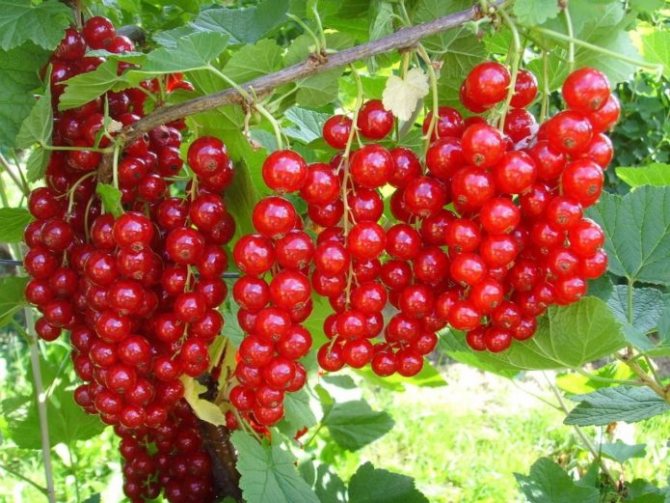
These plants have an increased resistance to pathogens and pests, in addition, they have amazing longevity - in the wild, shrubs do not need to frequently renew themselves, because they are able to maintain their vegetative qualities for up to half a century.
In Russia, black currant bushes began to be cultivated in the 11th century. The spread of the currant culture in Russia has long been hampered by the richness of wild thickets, which are not inferior in the quality of fruits to cultivated varieties.
In the wild, it lives for 40-50 years, but after 20-25 years, the harvest drops, the berries become smaller. In amateur gardens, with good care, it grows and bears fruit in one place for up to 15 years. This berry culture is relatively shade-tolerant, but it is one of the most moisture-loving. It grows on almost all types of soils, and the most productive - on well-fertilized, nutritious.
When growing and caring for black currants, it is necessary to take into account the distinctive feature of this culture: the fruiting of these shrubs is concentrated mainly on one-, two- and three-year shoots. Every year, fruiting moves to the periphery of the bush, branches of 3-4 years old gradually lose the ability to form a new young growth. Root shoots grow to replace them.
Currant - description, characteristics, photo
The height of the currant, depending on the species, is 1-5 meters. The root system of the shrub is powerful, in some species it goes into the depth of the soil by 1.5 meters. The shoots of the plant are straight, elongated, red, brown or gray, slightly pubescent at a young age.
Currant leaves are alternate, consisting of 3-5 lobes, serrated, elongated or rounded. The color of currant leaves depends on the type of plant and can be dark green, bright or dull, with the top of the leaf in most species being darker than the bottom. The leaves can be smooth or pubescent; in most currant species, hairiness is observed on the underside of the leaf or along the veins.


Ornamental types of currants are distinguished by an unusual color of foliage: from carmine-red to orange and crimson, which changes during the season.
Most currant species are deciduous shrubs, but evergreen forms are found in tropical areas.


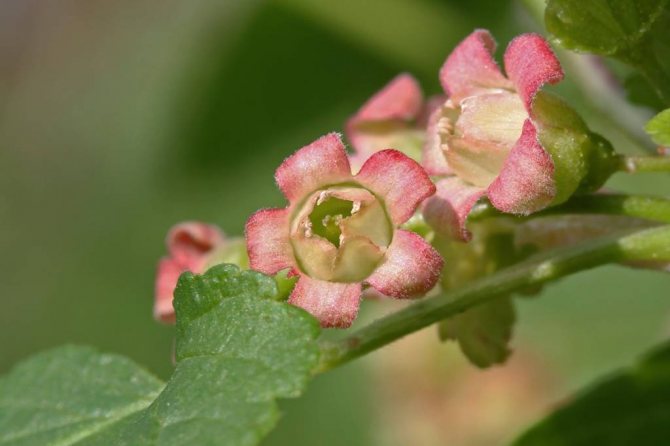
The currant inflorescence is a drooping or erect racemes with smooth or fluffy pedicels. Most of the species are monoecious plants, but there are dioecious species in which female and male flowers are collected in separate brushes.
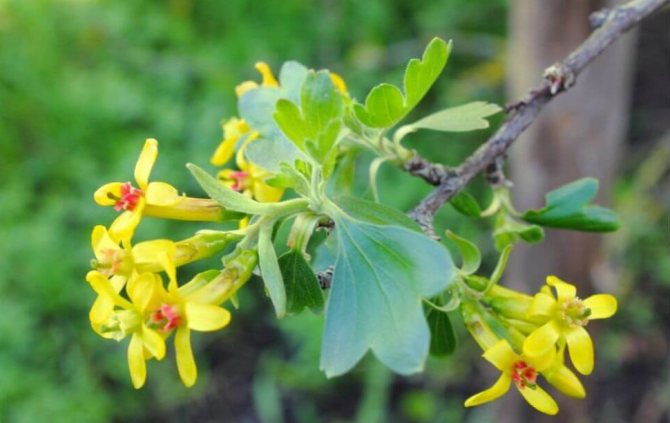
Currant flowers up to 1 cm long can be white, yellow, yellow-green, pink, red or purple. One flower cluster can contain from 5 to several dozen flowers. Currant flowering depends on the area, begins in April-May and can last until the end of June.


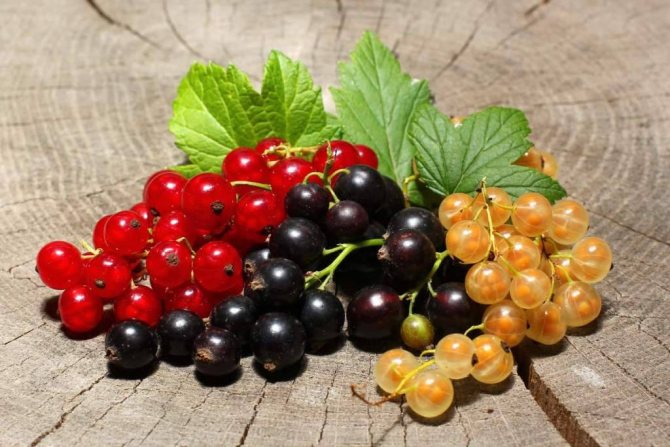
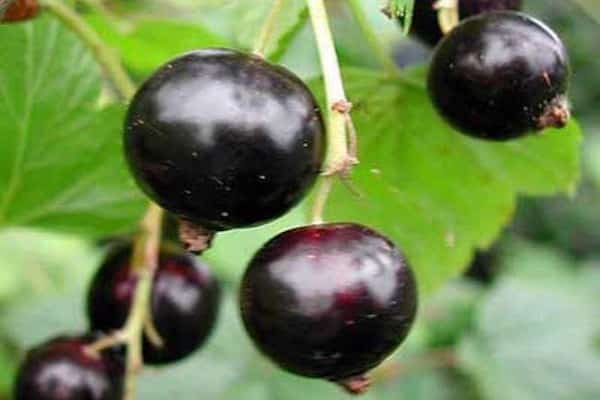
The fruit of the currant is a berry that is round or oval-elongated. Currant berries have a sweet-sour, sour, sweet taste or can be bland, completely tasteless.
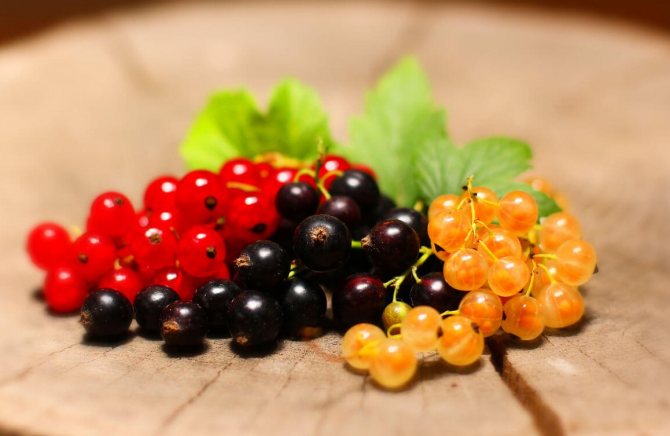
The color of the berries can be black, red, white, yellowish, inky, glossy, matte or with a waxy bloom.


Testimonials
I chased this form of decorative currant for a long time, and in the spring I finally found it and planted it in my garden. they say it is not very winter-hardy, but I do not think that it is more tender than kerria, weigel and action. The gain for the season was quite impressive without any dancing.While she bent down and pinned the branches to the ground, so that in winter she would not stick out from under the snow. In the absence of snow, I'll cover it with lutrasil just in case. The value of this form is in the incredibly beautiful bloom. Unusually red flowers are collected in beautiful clusters. Photos from the Internet, for general presentation. Hopefully in the spring there will be photos of my own bush.
Svetlana
Types of currants - names, descriptions, photos
The modern classification includes about 190 types of currants, each of which has certain characteristics. The following varieties are considered the most interesting:
- Black currant (Ribes nigrum)
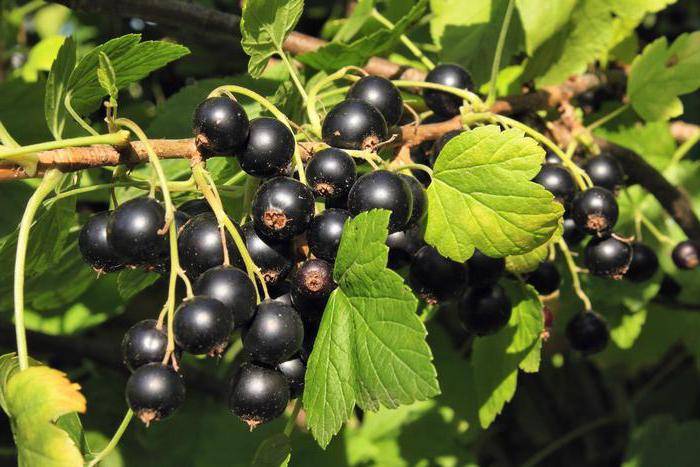
grows throughout Europe, in the European part of Russia, in Siberia, Kazakhstan, Mongolia, and also introduced to North America. In the wild, currants grow in wet swampy places, deciduous and mixed forests, pine forests and conifers, in meadows and along the banks of water bodies. It is found both as single plants and thickets. It is one of the favorite crops of gardeners. The height of the black currant reaches 1-2 meters. Old shoots are brown, while young ones are green and fluffy. Currant leaves are elongated, up to 12 cm wide. The top is smooth, dark green in color, the bottom is pubescent and lighter. Brushes consist of 5-10 flowers. The flowering period of currants falls on May-early June. Fruiting of the currant bush, depending on the variety, begins in July-August. Black currant berries grow up to 1 cm in diameter, have a tart, sweet and sour taste and pronounced aroma.


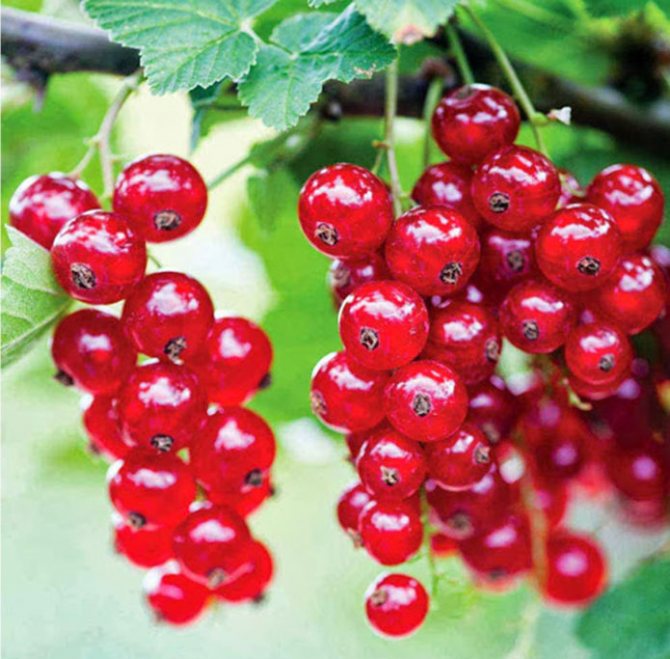
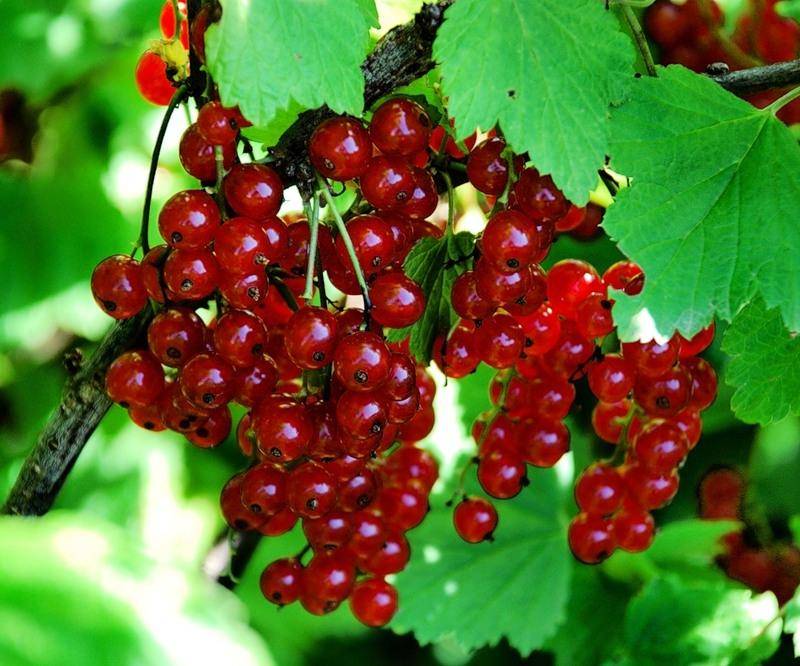
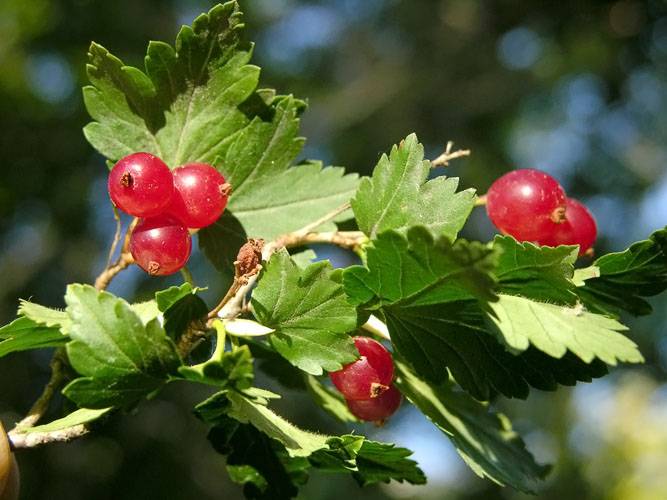
- Red currant (ordinary, garden currant) (Ribes rubrum)
grows throughout the forest zone of Europe, Russia, Asia, where it is often found along the banks of reservoirs in the form of dense thickets. Shrub 1-2 m high is distinguished by shoots of gray or sandy color. The jagged leaves of the currant are darker on top, and the bottom may be with fleecy veins. Red currant blooms in mid-May, begins to bear fruit in mid-June. Juicy bright red berries with a diameter of 0.8-1.2 cm grow in long clusters and have a sour taste.


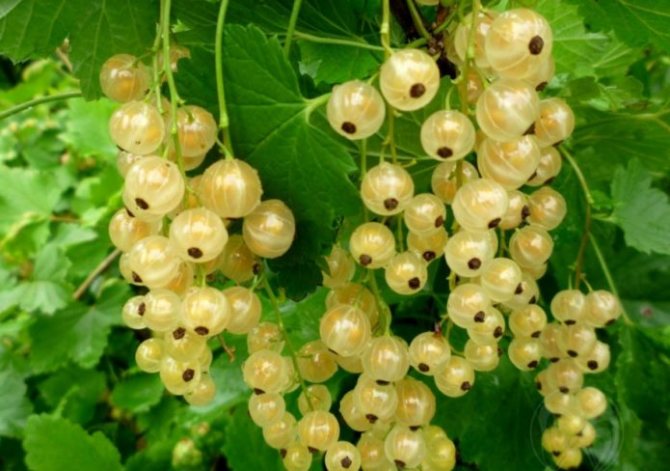
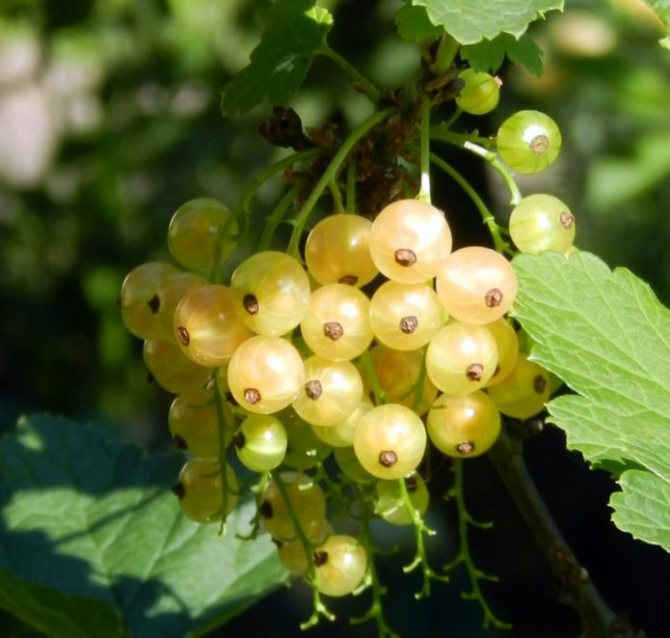
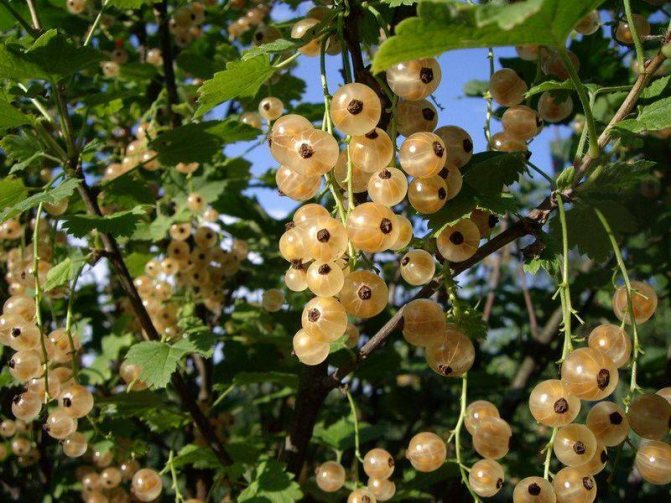
- White currant (Ribes niveum)
grows in humid forests throughout Europe and Asia. The structure resembles a red currant, on average it has a bush height of up to 1-1.5 m, sometimes it grows up to 2.5 m. The period of flowering and fruiting also coincides with red currants (May and June, respectively). Currant berries with a diameter of 0.6-1 cm are collected in a long bunch and are white or yellowish in color. The taste of ripe berries is sweet, with a slight sourness.


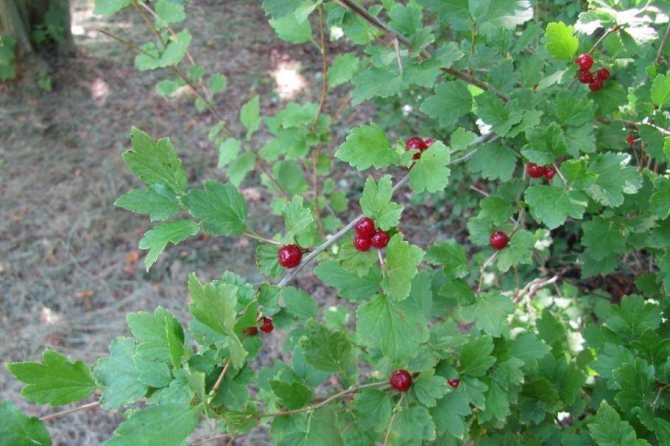
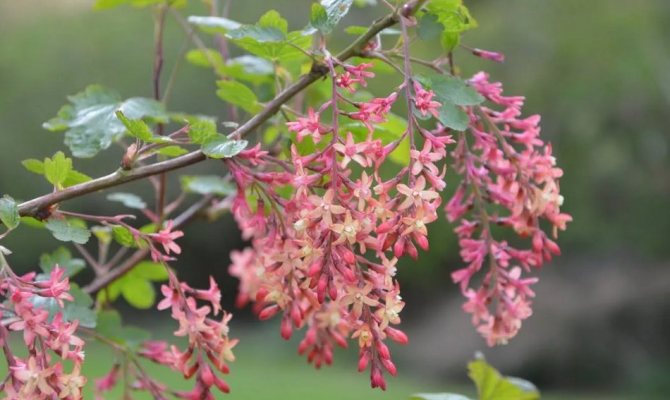
- Blood red currant (Ribes sanguineum)
grows in the western part of the North American continent, from Canada to California. It is grown as an ornamental shrub all over the world. A currant bush up to 4 m high has straight, dense branches of a red-brown color. The leaves are long, up to 8 cm, dark green above, white, tomentose below, very fragrant at the beginning of growth. The currant begins to bloom in May, the inflorescence contains about 20 flowers up to 1 cm in diameter. The brushes look very decorative and have a rich red or pink color. Currant berries are elongated up to 1 cm, blue-black, with a bluish bloom. Suitable for consumption at the beginning of August, but practically tasteless.
- Ice currant (Ribes glaciale)
grows in China, India, Pakistan and the Himalayas. Prefers rocky terrain and mountain valleys. The currant bush grows up to 5 m and is distinguished by bare or slightly fleecy reddish shoots. The leaves are serrated, round or oval, up to 6 cm wide. Ice currant is a dioecious plant, moreover, male brushes are longer than female ones and grow up to 5 cm. Flowering occurs from April to June, cupped flowers are red-brown in color. Currant berries are red, round or elongated, sour taste, ripening period lasts from July to September.


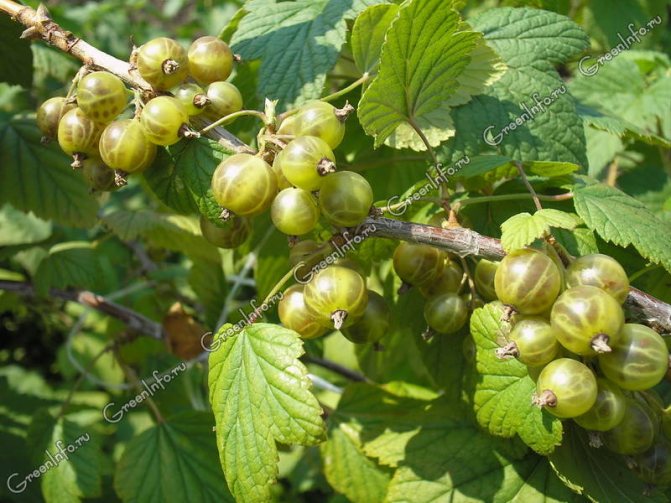
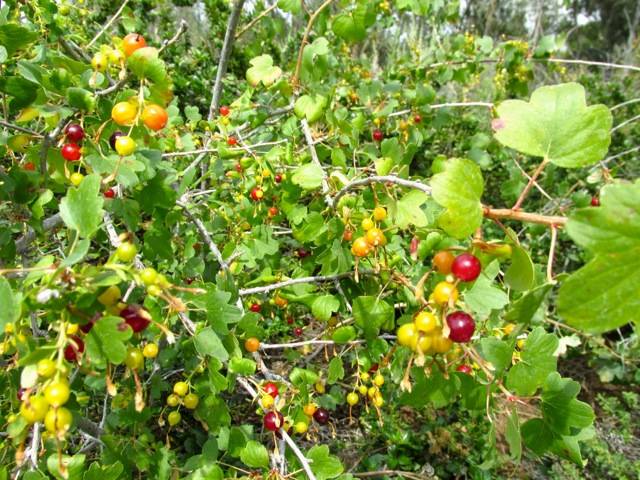
- Golden currant (golden currant) (Ribes aureum)
only grows in the wild in Canada, Central America and Mexico. Introduced and successfully grown in the European part of Russia, in Altai, the Caucasus, in the Far East region, in Europe, Central Asia and North America. The currant shrub grows up to 2-2.5 m in height, low-branched, with red branches, bare or slightly pubescent. Leaf length is 5 cm, width is up to 6 cm, no pubescence. By the end of summer, the leaves of the currant acquire a bright orange-red color, turn purple in September and remain a rich carmine color until the beginning of winter. Currant flowering begins in late spring and lasts 3 weeks. Flowers are collected in clusters from 5 to 15 pieces, yellow or green-yellow in color, with a pleasant aroma. Begins fruiting in early July. Round berries of golden currant up to 6-8 mm in diameter are distinguished by red-brown or black color, pleasant to the taste.


- Grouse currant (okhta, aldan grapes) (Ribes dikuscha)
grows in the forests of Siberia and the Far East. The shrub reaches a height of 1.5 m and has large bare leaves up to 10 cm long. Inflorescences, up to 5 cm in length, consist of white flowers, collected in 8-12 pieces. Fruiting is abundant, the berries of the wild grouse currant are very large, up to 1.3 cm in diameter, ink-colored with a waxy bloom, slightly aromatic, sweet and sour. Due to its increased winter hardiness and resistance to fungal diseases, Siberian grouse is widely used in breeding.
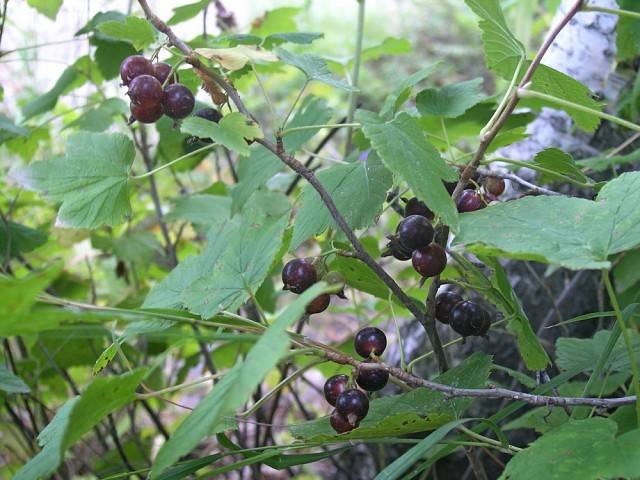


- Alpine currant (Ribes alpinum)
compact and not too sprawling bush that reaches a height of about one and a half meters. The branches are densely covered with dark green shiny leaves, which have rather stiff bristles on top. On the reverse side, the leaf plate is much lighter, absolutely smooth. Alpine currant flowers are yellow-green in color, cluster-like inflorescences rarely droop, pedicels are also covered with glandular bristles. The berries of the plant are pink in color, 6 to 8 mm in diameter, slightly starchy in taste. This type of currant blooms in May-June, bears fruit in July-August. Alpine currant is widespread in Europe, in the west of Turkey, grows in the Caucasus, in the north of Africa. Most often grows along the shores of lakes and rivers, prefers bright forest glades.


The best black currant varieties with large berries
Here you can find photos and descriptions of black currant varieties, which have the largest berries.
Selechinskaya 2. This variety does not quite resemble the usual black currant - it has collected the best hereditary characteristics of wild currant and gooseberry species. The bushes can withstand extreme heat. Early variety, universal, high-yielding (4-5 kg per bush). The berries of this variety of black currant are large, round, shiny, weighing 3-6 g, with an excellent taste. Suitable for growing in all regions of Russia. Bushes with strong, erect branches, do not require a garter.
"Exotics". One of the largest-fruited varieties for early ripening. The taste is sweet and sour. The berries of this variety are large black currants with a dry separation, they can be picked quickly and pleasantly, they can be stored in the refrigerator for several days. The bush is fast-growing, productive, medium-sized, erect. The variety is resistant to powdery mildew, can be affected by anthracnose. Winter-hardy.
"Dubrovskaya" - the variety is winter-hardy, relatively resistant to kidney mites, moderately resistant to anthracnose, immune to terry. Productivity is 3 kg per bush. The bush is undersized, compact. Medium to medium-sized berries.
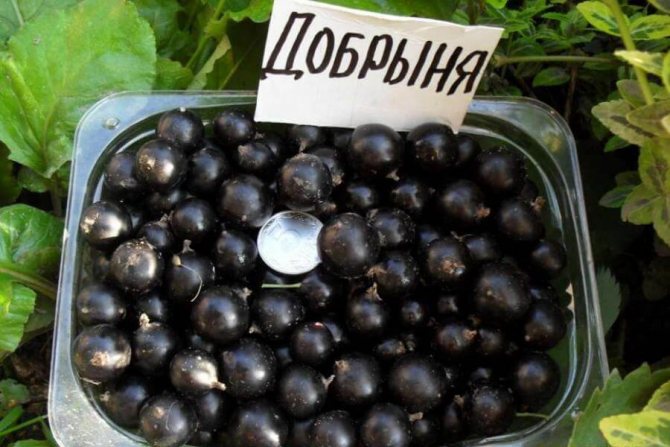
"Dobrynya" - resistant to drought and spring frosts. It is immune to powdery mildew, moderately resistant to anthracnose and kidney mites. The bush is weak, erect. The berries are very large.
"Raisin". Dessert variety of medium ripening.Berries are large and medium, weighing up to 3 g, with a refreshing aroma, high yield. Resistant to powdery mildew, drought and spring frost. The description of this variety of black currant is similar to the variety "Dubravskaya", with the only difference that the berries of this form are much sweeter and never crumble, on the contrary, sometimes wither on the bush.
"Perun" - resistant to drought, frost; moderately resistant to powdery mildew, anthracnose, kidney mite, weakly affected by aphids. The yield of this one of the best black currant varieties is 3-4 kg per bush. The bush is medium-sized, semi-spreading. The berries are large, with a strong aroma.
"Vologda" - winter-hardy, resistant to powdery mildew, relatively resistant to kidney mites, susceptible to rust. Productivity 3-4 kg per bush. The bush is vigorous, the berries are large, they do not ripen simultaneously.
"Katyusha" - winter-hardy, resistant to anthracnose, relatively resistant to powdery mildew, susceptible to kidney mites. The bush is vigorous, slightly spreading. The berries are large, with a very dense skin.
"Mermaid" - begins to bear fruit early. Winter-hardy. Resistant to powdery mildew and kidney mites, moderately resistant to septoria, weakly affected by anthracnose. Productivity up to 3.5 kg per bush. The bush is vigorous, medium spreading. The berries are very large.
"Vigorous". A variety for lovers of very large berries (with proper agricultural technology, they reach 8 g), in a cluster up to 8 berries. The pulp of large berries of this variety of black currant is dense, with a refreshing taste, and sour. Late ripening, fast-growing, highly winter-resistant. Relatively resistant to powdery mildew, rust, kidney mites, moderately resistant to anthracnose. Productivity 3-4 kg per bush. The bush is medium-sized, semi-spreading.
Look at the photo of the varieties of black currant, most often cultivated in amateur gardens:
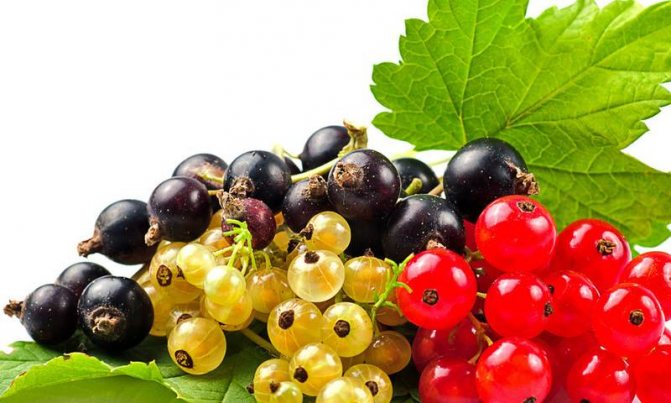
What is the difference between black, red and white currants?
The most popular and demanded are black and red currants, less often - white. What is the difference between different types of currants besides the color of the berries?
- In black currant, all aboveground parts of the plant are extremely fragrant and aromatic, thanks to the essential oils contained in special glands, densely located on the lower surface of the leaves. Unlike black, red and white currants practically do not smell, their berries taste more sour and watery. Therefore, you can get 10% more juice from red and white berries than from black currant berries.
- Black currant is the record holder for the content of ascorbic acid; red currant contains 4 times less vitamin C. The chemical composition of red and white currants is almost identical, and yet the difference between red and white currants is that white loses red in vitamin C.
- It is customary to propagate red and white currants by dividing the bush, black currants, in contrast to them, are more often propagated by cuttings.
- Black currant differs from red and white in that it does not tolerate drought. Red and white currants are less demanding on moisture and tolerate a lack of water more easily.
- Black currants are much more vulnerable to diseases and pests. Red and white currants get sick much less often.
- Red and white currants are relatively durable and can grow for 15-20 years without transplanting. Black currant begins to degenerate noticeably after 6-7 years. In addition, black currant needs regular competent formation of the bush, otherwise excessive thickening has a detrimental effect on the yield and health of the plant itself.


Use in landscape design
Red currant Natalie
Ornamental currant bushes are widely used to decorate lawns, parks and gardens. They are used in the role:
- tapeworms on lawns with ground cover and flowering plants;
- original hedge;
- in groups with other trees and shrubs, the flowering time of which coincides with the flowering of currants.
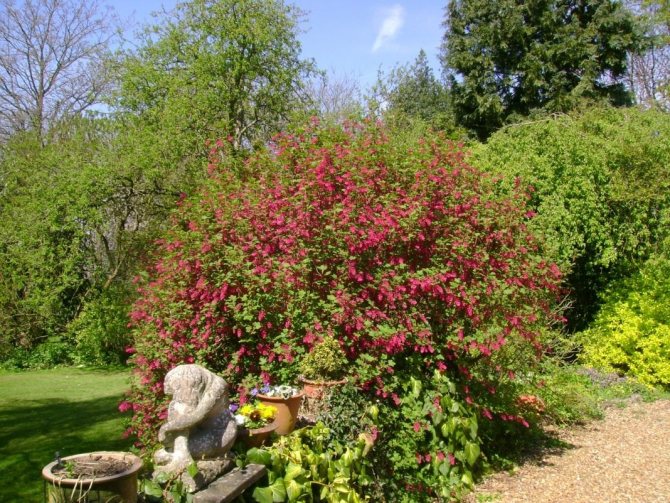


Ornamental currant
The plant is often grown in the form of a stem grafted onto a golden currant bush. The reddish currant bush looks great next to the yellow-blooming forsythia. Bulbous plants, perennials blooming in spring, as well as irga and viburnum will be good neighbors for him. The composition will be decorated with daffodils, forget-me-nots and tulips.
Currants - useful properties, vitamins and minerals. Why is currant useful?
Currants are rightfully considered a storehouse of vitamins, and a high concentration of vitamin C was found not only in fruits, but also in currant leaves (after harvest), as well as in buds, buds and flowers. In addition to vitamin C, currant berries contain B vitamins, and in terms of vitamin A content, currants are much superior to fruits such as pineapple, peach, orange or apple.
The mineral composition of currants is represented by the following components: sodium, calcium, magnesium, copper, sulfur, lead, silver, iron, phosphorus. Also, a high content of coumarins, pectin and iodine is found in currant fruits.
Currant berries have a number of components that are irreplaceable for the human body:
- malic, phosphoric and citric acids;
- essential oils;
- tannins;
- phytoncides;
- anthocyanins.
Due to its beneficial properties, currants are often used to alleviate a number of pathological conditions:
- improvement of hematopoiesis in diseases of the lymphatic and circulatory system;
- normalization of blood pressure in hypertension;
- lowering blood glucose levels in diabetes mellitus;
- restoration of immunity in case of vitamin deficiency and after serious illnesses;
- laxative, diuretic and diaphoretic effect;
- treatment of dermatitis and diathesis;
- rheumatism, gout and polyarthritis;
- gastritis and stomach ulcers;
- bleeding gums;
- increased nervous irritability and sleep disturbances.
The useful properties of currants also manifest themselves in decoctions and infusions: decoctions and infusions of currant berries, its leaves, buds and shoots are used to treat skin diseases. The beneficial properties of red currant are mainly concentrated in the fruits, therefore, its juices and fresh berries are used for treatment.


Harm to the plant and its fruits
Despite its low calorie content (63 kilocalories per 100 grams) and positive qualities, the plant also has negative properties and contraindications. It is not recommended to eat a lot of berries for people who are prone to overweight, since the fruits contain a large amount of sugar.
Currants are contraindicated in diseases of the stomach and intestines (ulcers), chronic gastritis, increased acidity in the stomach, thrombophlebitis. Juice and berries have a positive effect on the liver, but with hepatitis, the use of black currants is prohibited.
Scientists have proven that if you eat currants every day in unlimited quantities, there is a possibility that the blood will clot faster, and this can lead to negative consequences.
The plant can harm a person if he has an individual intolerance to berries, as a result of which the following symptoms will appear: a rash and an allergic reaction. In this case, you should contact the doctor to prescribe anti-allergy drugs, but only after a detailed examination and the test results obtained.
Planting currants
For the correct planting of currants, you need to know:
- How to choose a place for a seedling,
- What are the terms (time) of planting currants,
- What should be the ideal soil for a plant,
- What should be the distance between currant bushes when planting,
- How to dig a planting hole
- What fertilizers are needed.
The best place to plant currants is in open areas with maximum light throughout the day. Currant grows well on any permeable, optimally moist soils, but prefers black earth loam.
Planting currant seedlings can be done in early spring, before bud break, or in autumn, in September, the main thing is to plant bushes in prepared soil. 1-2 weeks before planting, it is necessary to dig planting holes or ditches 35-40 cm deep and apply 5-6 kg of fertilizers under each currant bush: rotted manure or compost, 20-25 g of superphosphate and potassium sulfate, and then mix them well with earth.
The distance between the bushes when planting currants should be at least 2-3 meters. On heavy loams, the pits are deepened to 50-60 cm and drainage from a layer of sand is equipped at the bottom, and the fertilizer rate is increased by one and a half times. On the eve of planting, the fertilized pits are spilled with water, and the currant seedlings are shortened, leaving 3-5 buds on each shoot. The seedling is planted vertically, the roots are straightened, covered with earth and watered. The settled soil is trampled down and mulched with peat or straw. It is better not to use sawdust as mulch, because they acidify the soil and take nitrogen from it.
For subsequent breeding, the seedling is planted obliquely, deepening the root collar by 10 cm, then additional roots and shoots will grow.


Reproduction methods of decorative culture
Ornamental currants are propagated by cuttings, seeds or layering.
- Experienced gardeners recommend using the first technique. Shoots cut in the summer with a length of 25 cm are planted in containers with moistened soil. A transparent mini-greenhouse is installed on top. 90% of the petioles are rooted, they are planted in the fall.
- The technique of propagation by layering is also in demand. Shoots located close to the soil are placed in prepared grooves, covered with soil. So that they do not rise, they are fixed with wire clips. When the ground is constantly wet, the cuttings take root. The bushes grown according to this technique, after separation and planting in a permanent place, quickly grow.
- Ornamental currants are rarely propagated by seeds. This is a laborious method, it is used when it is not possible to buy petioles or ready-made seedlings. Before planting in the soil, stratification is carried out for 2-3 months. 1/3 of the planted seeds germinate. Seeds can be sown before winter in containers or directly into the garden. Then, in the spring, close care will be required for young sprouts.


With full compliance with the rules, even inexperienced gardeners will be able to propagate decorative currants.
Currant care: pruning, feeding
Currant care does not cause much trouble. During the season, it is necessary to remove weeds and loosen the soil in the root zone. Currants need regular, but not plentiful watering, otherwise the plant will immediately shed its leaves in a drought.
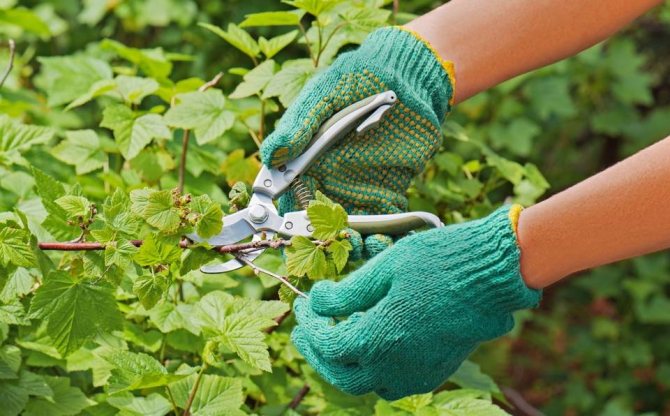
Currant pruning
In early spring or late autumn, black currant bushes need to be rejuvenated by cutting out old branches at the root, removing diseased and little fruit-bearing shoots. Red currant branches are shortened by 5-6 eyes. The main thing is that no more than 10-15 shoots of various ages remain on one bush.


Fertilizing currants
Caring for currants involves the timely feeding of the bushes with fertilizers. If the planting of currants was carried out in well-fertilized soil, the first 2-3 years you can do without top dressing. An autumn planting of mulching material in the soil will be enough for the bushes, which is placed in the root zone every spring.
After 2-3 years, under the autumn digging, they begin to apply dry forfor-potash mineral fertilizers, at the rate of 30 g per currant bush. Urea and ammonium nitrate are washed out by melt water, so they are applied in early spring - directly in the snow or in dissolved form (20-25 g per bush). During flowering, fertilizing is carried out with organic fertilizers (mullein 1:10 or bird droppings 1:15). To improve fruit setting and improve the quality and size of berries, after flowering, currant bushes are sprayed with the preparation "Ovary" or a solution of zinc sulfate.
Errors when growing ornamental currants
When cultivating ornamental currants, gardeners often make the following mistakes:
- Abundant watering, which leads to decay of the rhizome.
- The use of dressings immediately after planting, which leads to an excess of nutrients and provokes yellowing of the leaves.
- Planting in an area with poor lighting. May lead to poor shrub growth.


Blood red currants are used to decorate the site. Gardeners choose this type of shrub for its unpretentious care and beautiful appearance.
Propagation of currants by cuttings, layering, dividing the bush
There are 3 ways to breed currants:
- By dividing the bush,
- Cuttings,
- Layers.
Let's take a closer look at each of these methods.
Reproduction of currants by dividing the bush
The method of propagation of currants by dividing the bush is not used very often. This method is great when there is a shortage of planting material or in case of forced transplantation of very valuable varieties from the site to another place. Another advantage of this method of transplanting currants is the rapid rooting of a new bush without special techniques and manipulations.
The technique is quite simple: in the fall, in late September - early October, or in early spring, the desired currant bush is carefully dug out of the ground, trying not to damage the root system. Absolutely all old branches should be cut out with a pruner or a sharp garden saw, and young branches should be shortened to a height of 25-30 cm. With a sharp ax, the bush should be divided into 3-4 parts (depending on its size). The main thing is that each part of the plant, which you will plant in the future, has well-formed buds and sufficiently branched and healthy roots. In a prepared hole, 60-80 cm deep and fertilized with rotted manure, planting material is set in the center, covered with earth, which is neatly but tightly tamped and carefully watered (1-1.5 buckets for each bush).


Propagation of currants by cuttings
This method of propagation of currants is considered the most productive when preserving varieties or breeding hybrids, especially when there is not very much initial planting material. Cuttings are carried out in an already prepared substrate, consisting of a mixture of soil, compost and organic fertilizer - rotted manure. Surprisingly, cuttings can be carried out both in spring and autumn (woody shoots are used for this), and in summer, using green currant cuttings. Therefore, there are no specific dates for cuttings.
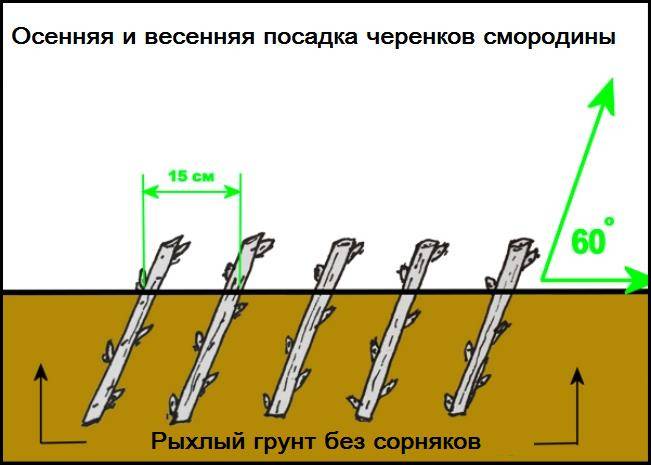
- Cutting currants in spring or autumn
One-year shoots are taken as lignified cuttings. Cutting currant cuttings for reproduction is necessary only from healthy bushes. It is very convenient to do this, combining with the next pruning of the currant bush. The length of the currant shank should be within 16-25 cm, the diameter of the shank should be at least 6 mm. When harvesting the cuttings, a cut in their upper part is made directly above the kidney, retreating upward 1-1.5 cm. In the lower part of the cutting, an oblique cut is made under the kidney.
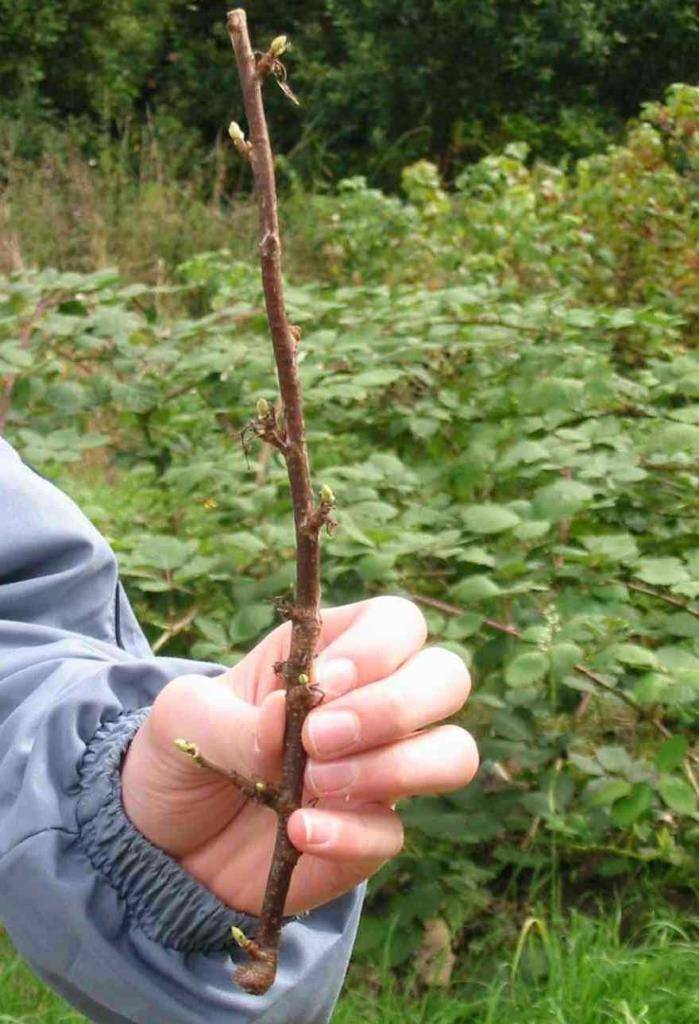


The cuttings are buried obliquely, 2-3 buds are left above the soil surface. The planting site of the currant cuttings should be watered abundantly and mulched with a layer of humus or peat. If the cuttings were planted in the spring, then by the fall, rather powerful roots are formed on them, and the plant can be transplanted to a permanent place. When planting currants in the autumn with the onset of cold weather, cuttings should be covered with spruce branches, fallen leaves or straw, in order to prevent them from freezing. Please note that it is necessary to plant currant cuttings before winter, taking into account the entry of the bush into a dormant phase. In black currants, it begins in September-early October, but in red currants - already at the end of August. It is during these months that it is necessary to start breeding currants.

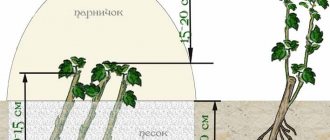
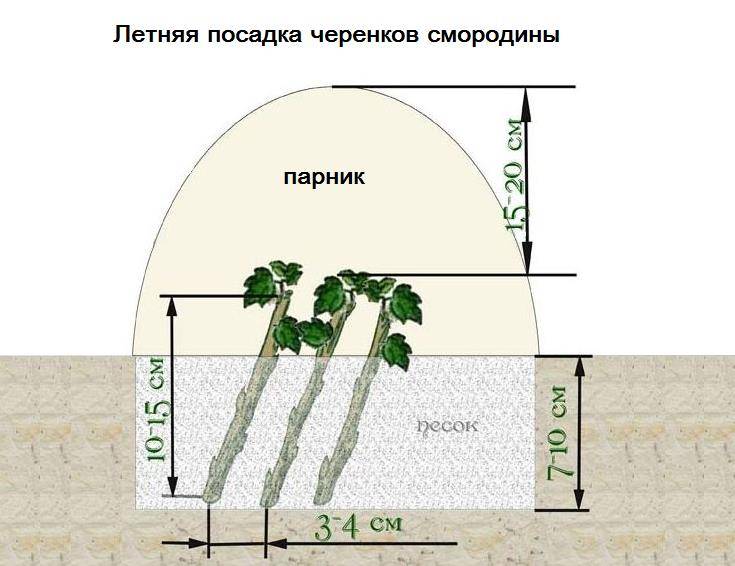
- Cutting currants in summer
You need to cut green currant cuttings for reproduction in the summer, it is better to do this on a cool day.Branches that are just beginning to turn to lignification are suitable for cutting: they should be flexible enough, but break with a sharp bend. 3-5 leaf plates are left on a 10-12 cm long stalk, but for a pair of lower leaves, the plate is shortened by half or removed completely, leaving only the petioles. The prepared material is immersed with the lower ends in a solution of any growth substance for a day, after which green currant cuttings are planted in prepared greenhouses or greenhouses, buried in the ground by 2-3 cm.The main condition for excellent survival is high humidity in the greenhouse in the first 3 weeks. Plants should be watered regularly and sprayed additionally in hot weather. After about a month, currant cuttings will give strong roots, then they can be fed with nitrogen fertilizer and watering reduced. The next spring, young bushes are planted from the greenhouse into the soil, and by autumn they will turn into powerful currant bushes.

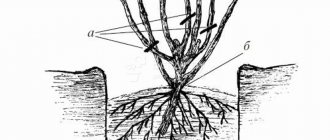
Reproduction of currants by layering
The method of propagating currants by layering is quite simple and effective. In the spring, always before the flowering phase, grooves are dug around the bushes selected for varietal and taste qualities to a depth of 5-7 cm.The strong lower shoots of the plant are shortened by a third of the length, carefully bent to the soil, laid horizontally in the grooves and securely pinned to the ground. This can be done with ordinary wire hooks. From one adult currant bush, no more than 6-8 shoots are allowed for layering. The bent branches are not initially sprinkled with earth, but as soon as vertical shoots appear on them and reach a height of 12-15 cm, the grooves are carefully covered with moist soil mixed with peat. Only green tops should be left above the surface. As they grow back, they are huddled two or three times per season. By the fall, the cuttings of the currants are already perfectly rooted, they are buried in, separated from the mother branch with a sharp pruner or knife and transplanted to a permanent place.
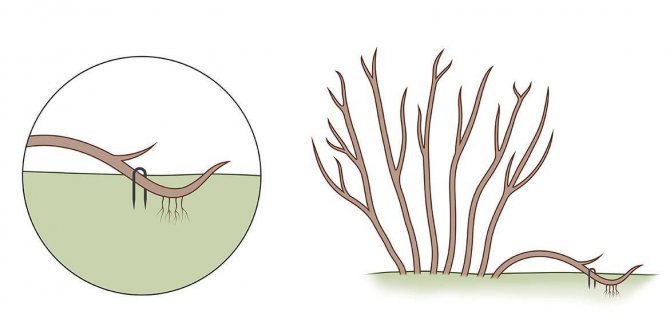

Breeding methods
For this, the following methods are used:
- For propagation by cuttings, twigs 25 centimeters long are cut. They are rooted using a moist substrate, warm. To create suitable conditions, this is done under a transparent cover.
- To obtain cuttings, suitable branches in the middle are sprinkled with earth, then they must be watered intensively until roots are formed. After that, the branches are cut off and planted in a suitable place.
- You can use seeds. The bush will begin to give them from the third year of its existence. They are sown in boxes or pots and germinated. After that, they can be planted in the ground.
Currant diseases and pests - description, photo, treatment
Like all members of the gooseberry family, currants are susceptible to a number of major diseases:
- Currant anthracnose
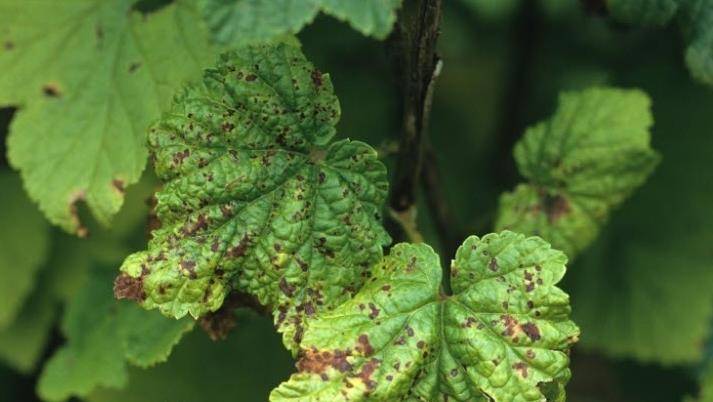
a fungal disease that affects the leaves. Diseased foliage becomes covered with red or dark brown spots, currant leaves turn brown, curl and dry out. To combat anthracnose, spraying with a solution of copper sulfate (40 g per 10 l of water) or Bordeaux liquid (100 g per 10 l) is used. The affected leaves are cut off and burned.


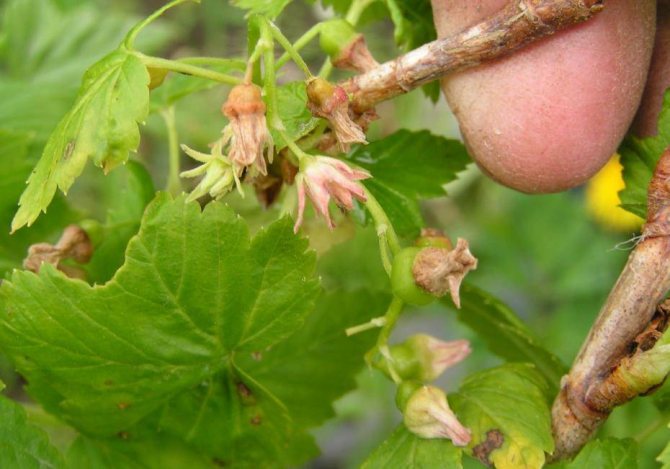
- Terry currant (reversion)
manifested by the following symptoms: the flowers become small and double, acquire a purple color and gradually dry out, the leaves of the plant are deformed and lengthened, become three-lobed (instead of five-lobed), the number of cloves on them decreases, the characteristic aroma of currant disappears, small veins on the leaves become thicker and coarser , the berries are not formed, and the bush itself becomes sterile. Black currants are susceptible to this disease much more often than red and white ones. Aphids, ticks and bugs can carry this disease, these pests are especially active in the spring during the formation of flower brushes.As a prophylaxis and treatment of currants, currant bushes should be treated with insecticides and fungicides that destroy pests. Processing is carried out in spring and early summer. Disease-affected currant branches must be cut off, deformed and swollen buds should be cut off immediately. To destroy pests, the bushes can be treated with biological preparations (0.3% lepidocid or 1% bitoxidacillin) or chemical preparations (0.2% acarin, 0.1% fufanon, 0.04% phytoverm). Sometimes the only way to combat terry is the complete removal of the diseased bush so that it does not infect the currant bushes growing nearby.


- Striped mosaic
a viral disease of currants, which is transmitted by ticks or aphids. The disease can also be caused by grafting the affected cuttings onto a healthy plant. A sign of this disease is the appearance of a bright yellow pattern on currant leaves in the form of large veins. As a preventive measure, only healthy planting material should be used, it is imperative to treat the bushes with anti-pest agents, and carefully examine the plants for the presence of this disease. There is no cure for striped mosaic. The currant bush will have to be uprooted and burned. A new plant should not be planted in its place for 5 years so that it is not affected by the same disease.


- Powdery mildew on currants
affects all parts of the plant. At first, the buds, leaves and berries are covered with a whitish bloom, which is easily erased, but over time it becomes dense and brown. Affected currant leaves are deformed and dry up, fruits are tied in very small quantities. As a fight, all affected parts of the plant should be cut out and burned. Then treat the plant and soil with a solution of copper sulfate (300 g per 10 l of water) or Topaz and Fitosporin.
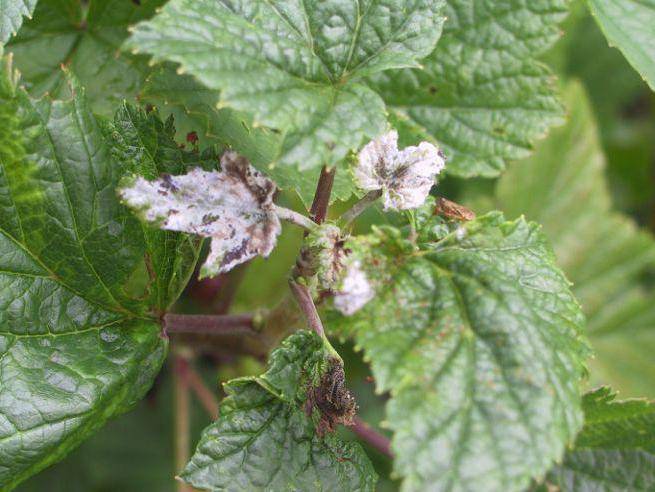


- Aphids on currants
densely occupies leaves and young shoots, and ants actively crawling along the branches will help to notice the appearance of pests. To avoid depletion of the plant, at the very beginning of the appearance of aphids, currant bushes are sprayed with a strong solution of laundry soap. Also, as a treatment, you can treat the currant bush with an infusion of garlic, tobacco or spraying the leaves with a solution of karbofos.
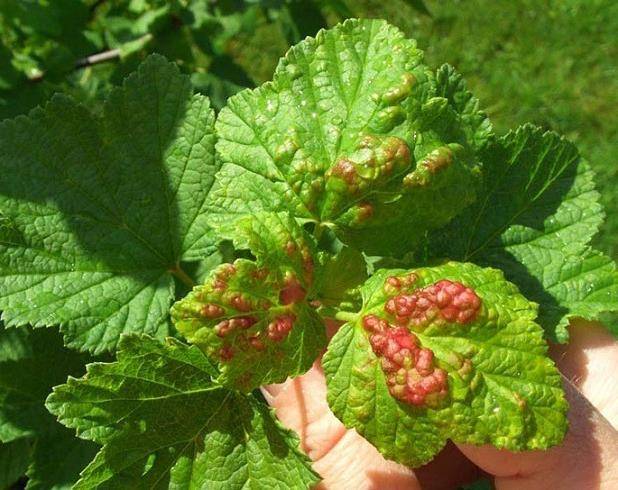


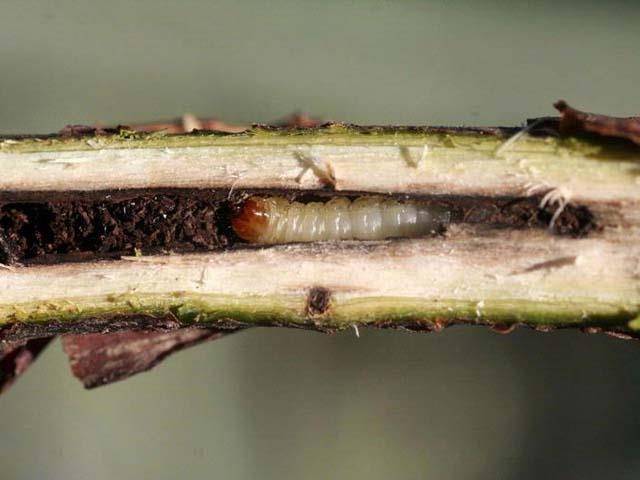
- Currant glass
or rather, the caterpillar of this butterfly, gnaws through the branches of the currant from the inside, making moves in the direction from the ground to the tops of the shoots. As a result, whole branches of currants dry up and die off. As a preventive measure, the loosened soil under the bushes is covered with a mixture of ash, tobacco, mustard and hot pepper, at the rate of half a glass per 1 bush. Spraying with Intavir, Iskra or Fitoferm preparations is also effective.


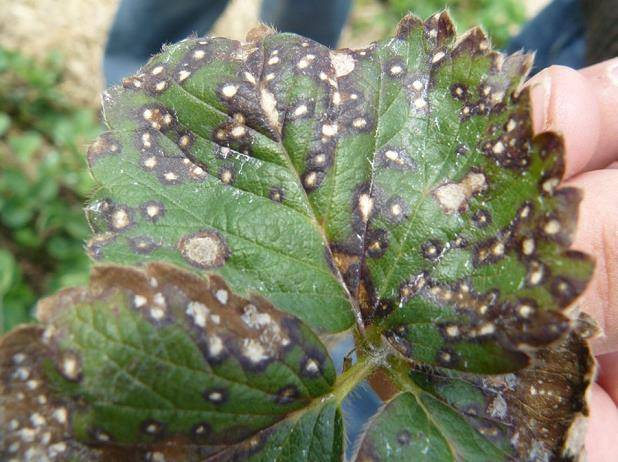
- White spot on currants
or septoria is characterized by round brown spots on the leaves, which subsequently turn white. The plant can become infected through the spores that are in the fallen leaves. It is necessary to treat currants in the same way as with anthrocnosis: by spraying with a solution of copper sulfate or Bordeaux liquid.


- Columnar rust on currants
manifests itself as spots on the leaves of a rusty yellow color. On the back of the leaves, orange-yellow bubbles also appear. The culprit of this disease is a fungus introduced from conifers (Siberian cedar or Weymouth pine). Measures to combat this disease: spray currant bushes with 1% Bordeaux liquid 3 times: when the first leaves appear, when buds appear on the bush and after currant blossoms. As a preventive measure, you need to remove fallen leaves and loosen the soil under the currant bushes.
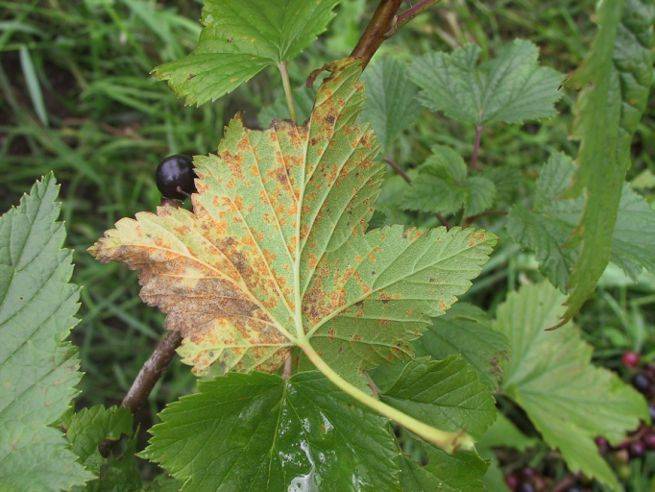


- Goblet currant rust
manifests itself as yellow-orange swellings on the leaves of the plant. It is a fungal disease that can be caused by frequent rains and high humidity. Also, the fungus multiplies on sedge, so if the currant grows near this plant, then fungal spores may well get on it.For the treatment of currants, you can spray the foliage and soil around the bush with a 3% nitrafen solution (in spring or autumn). If the treatment is carried out in the summer, then you can take a 0.4% suspension of 80% cuprozan + 1% colloidal sulfur. You need to spray the currants several times: before flowering, immediately after flowering, 2 weeks after the 2nd time, and also after picking berries. It is important to treat the underside of the leaves well. As a preventive measure, it is necessary to collect and destroy fallen leaves, weed the ground from weeds and dig up the soil under the currant bushes.
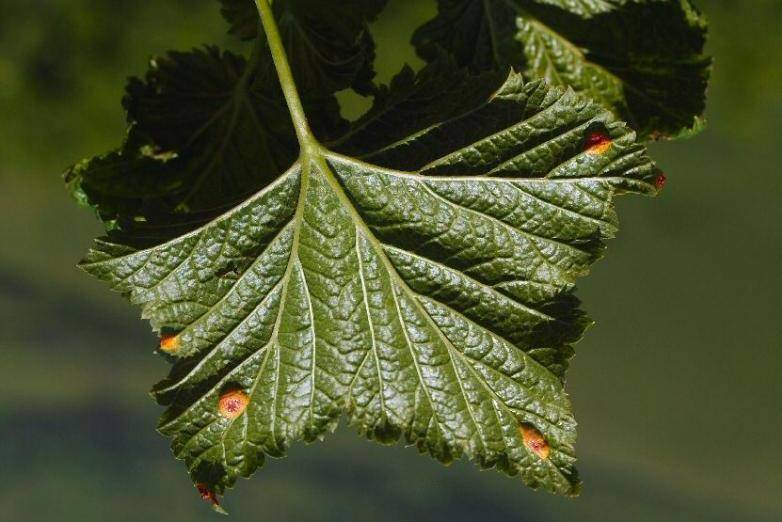


- Currant gall midge
manifests itself in May, as a result of which the currant leaves turn brown, curl and dry out. This pest eats the young leaves of the plant and can lead to its death. As a method of dealing with this pest, damaged currant branches should be cut off, and the rest of the bush should be sprayed with a solution of chlorophos with karbofos (20g + 30g per 10 liters of water). For prevention, the land under the currant bushes must be dug up in the fall.
Advantages and disadvantages of the variety
Blood-red currant King Edward 7 is an undemanding plant. It has the following advantages:
- grows well in sunny areas, but can grow in partial shade;
- drought resistant;
- it is easy to look after her.
The disadvantages include the low frost resistance of the shrub. Without protection, parts of the bushes that are above the snow level freeze out. In harsh winters, flower buds can also freeze.
Blood-red currant bushes are unpretentious and disease-resistant. They bloom in May and delight the eye with lush bloom for a month. In June, beautiful berries of an unusual appearance appear on them. These plants retain their decorative appearance until late autumn and remain a wonderful decoration of the garden.
Interesting facts about currants
- In ancient times, currants grew in abundance on the banks of the Moskva River, so the famous waterway of our country was then called "Smorodinovka".
- Unripe currant berries contain 4 times more nutrients than when fully ripe. Therefore, you should not drive the kids away from the bush when they are picking green berries.
- Blackcurrant leaves, placed in cans with home preservation, not only improve the taste of vegetables and mushrooms, but also enrich them with their useful substances.
- Currant is an excellent melliferous plant, and its honey has medicinal and prophylactic properties.


Did you like the article?
New varieties


New varieties have better characteristics, but their maintenance is more time consuming.
Modern varieties of black-fruited shrubs obtained during selection are included in the national register of achievements. This document indicates in which area it is best to grow the variety.
Variety trials in Russia are undergoing the following new types:
- Oasis
- Monisto
- Blakeston
- Sight for sore eyes
- Beauty of Lviv
- Dessert Ogoltsova
- Creole
Also, new hybrids have been bred in breeding farms:
- Talisman, Cardinal, Swan (mix of Black Pearl and Poltava 800).
- Kupava, Magician, Fairy of the Night, Geisha (combines the characteristics of Ojebin and Black Pearl).
- Sensei, Divo Zvyagina (mix of varieties Dikovinka and Lyubava).
back to menu ↑
See also: Peas: a description of the 43 most popular varieties, undersized, medium-sized and grain-fodder varieties + Reviews
Cooking applications
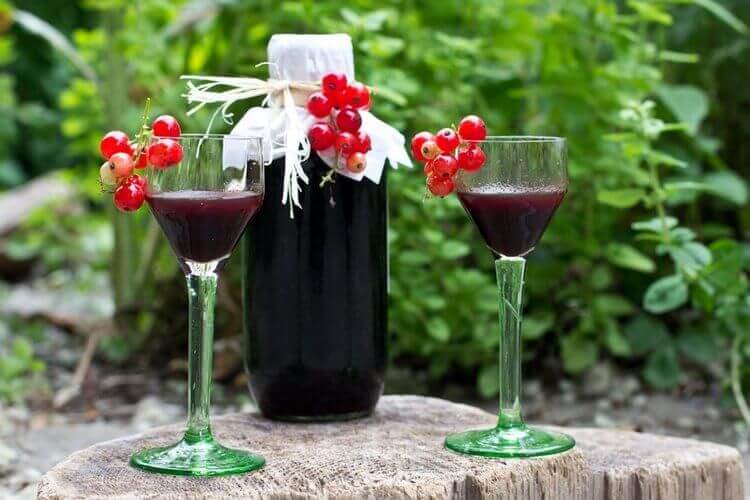
The berries are delicious fresh and are widely used in cooking in the preparation of appetizers, hot dishes, desserts, ice cream and marinades. The currants are ground with sugar, marmalade, jams, preserves, compotes, jelly, creams, jellies, syrups, kvass, sbitni are prepared from it, canned, alcoholic drinks, liqueurs, and wine are made. Fragrant fillings for pies and pastries are made from the fruits. A special sauce of white and red currants is prepared for steaks and chops. Berries are also added to the first courses: okroshka, borscht and soups to add a sour and fresh note.
Currants go well with various foods:
- fruits, berries and vegetables
- spices
- honey and nuts
- dairy products
- poultry
- lightly salted fish
- homemade noodles
Finns use currants in traditional cuisine for fish and bushmeat dishes. In Burgundy, the famous Dijon liqueur is made from black currant fruits. In the Caucasus, large leaves of the plant are used to make dolma; sour berries are added to the sauce for lamb dishes. The Mongols ennoble the taste of pies, dairy-flour dishes and lamb meat with fruits. The Slavs use fresh spicy currant leaves when salting vegetables and mushrooms; dried ones are brewed and drunk in the form of tea.


For Moscow region
Most of the well-known and beloved black currant varieties bear fruit well in the Moscow region and neighboring regions, including Nizhny Novgorod.
Popular varieties are successfully cultivated here: Dachnitsa, Selechenskaya-2, Dobrynya, Lazy, and many others.


Moscow
On a long brush, large currants are located - 1.3-2.2 grams. The sugar content is 9.8%. The description of the variety allows for a pear-shaped currant.
The best harvest is obtained with careful care - top dressing, regular pruning. Collection from a bush - 4 kilograms.
Litvinovskaya
The currant grows in a tall bush, reaching 2 meters. Due to the weak branching, it does not take up much space.
The taste of the berries is sour, since the sugar content is 7%. It spins amicably, the harvest is large - up to 8 kilograms per plant.
Loves not very heavy soils, does not have drought resistance, and requires regular watering. It tolerates frost well.


Scientific classification
From a botanical point of view, currant belongs to the kingdom of herbaceous plants. A detailed scientific classification of culture is presented in the table below.
| Domain | Eukaryotes |
| Kingdom | Plants |
| The Department | Flowering |
| Class | Dicotyledons |
| Order | Stonefragmented |
| Family | Gooseberry |
| Genus | Currant |
| View | Black currant |
How to grow blueberry-flavored currants
Golden currant is a plant that does not seem to have any flaws, but for some reason is not particularly popular with amateur gardeners. A lecture by a senior researcher at the Scientific Research Institute of Horticulture of Siberia named after V.I. MA Lisavenko, breeder, cytologist of berry crops Valentina Salykova.


Late ripening
They bloom along with other types of black currants, ripen for a long time, gradually gaining taste and smell, therefore they are the sweetest and most fragrant. Most varieties are fruitful, with a dense skin. Stored for a long time. They ripen in turn - they also need to be harvested so that the finished fruits do not crack and fall to the ground.
Daughter
This variety has a medium-sized shrub with indistinct branching. Daughter's berries - from 1.2 to 2.3 grams, on a brush 5-7 centimeters long.
Currants come off easily, without damage, well stored. From a plant get up to 4 kilograms per year. Powdery mildew is dangerous for Daughter.
Vologda
Has large lush bushes. The skin is dense, ribbed. There is sourness in the taste, sugar - 8.1%. Berries of Vologda adhere well to the hand, but crack if not picked in time. The harvest can be up to 4 kilograms.
It is considered frost-resistant, but with a strong drop in temperature, the kidneys can freeze.


Lazy person
Ripe berries are blackish-brown in color, grow on a powerful bush with a lot of shoots. Currant weight - 2.5-3.1 grams.
A distinctive feature of the Lazy Man is the instability of the crop, which fluctuates within significant limits - 1-8 kilograms. The harvest depends on care and the vagaries of the weather. Resistant to diseases and cold weather.
Arcadia
Excellent view with a sugar content of 8.4% and a yield of about 2.5 kilograms. Arcadia has fruits - 2.7-5.2 grams.
Not afraid of frost, protected from powdery mildew and mites. Light thin branches often fall to the ground due to the large number of berries.
Recipes
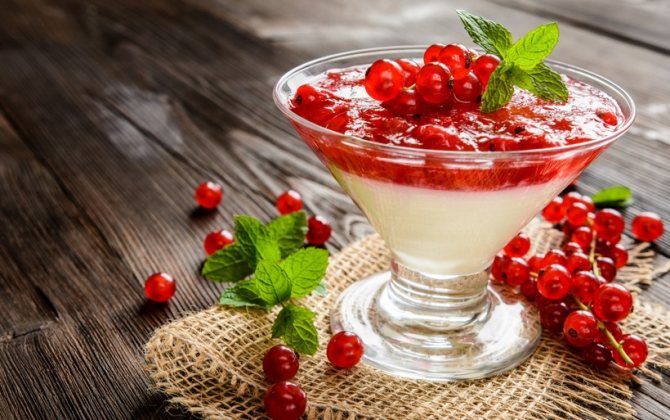
Currant dessert
Ingredients:
- orange;
- 250 g of black and red currants;
- 2 tbsp. l.honey;
- 2 tbsp. l. liqueur "Cointreau";
- whipped cream.
Preparation:
- Separate the berries from the twigs, rinse gently in a colander.
- Place the currants on a paper towel and let dry.
- Wash the orange thoroughly, dry and remove the zest, squeeze the juice.
- In a bowl, combine the zest with juice, add honey and liqueur.
- Transfer the berries to a deep dish, pour over the syrup.
- Leave the currants in the refrigerator overnight.
- Arrange the finished dessert in bowls and garnish with whipped cream.


Application in medicine
Currants have long been used in folk medicine to treat a number of ailments:
- dermatitis
- diabetes
- hypertension
- diathesis
- rheumatism and gout
- polyarthritis
- bleeding gums
- demodicosis
- heart rhythm disturbances
- low acid gastritis
- urolithiasis disease
- respiratory diseases
- cataract
- kidney disease
- urethritis
- Addison's disease
- lymph node tuberculosis
- inflammation of the genitourinary system
- eye diseases
- trachoma


Storage
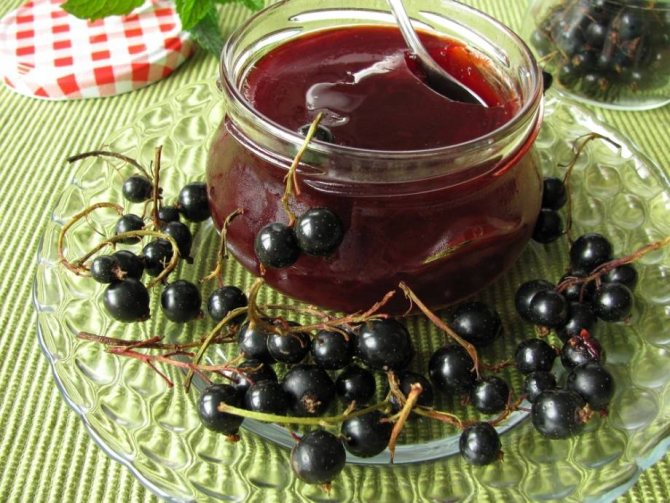
Currants can be beneficial all year round and can be easily prepared for the winter, either dried or frozen. At the same time, the fruits perfectly retain their beneficial properties. If you don't have the opportunity to stock up on fruits in the freezer, you can prepare them with sugar.
Raw jam
- mash the berries thoroughly with a wooden pestle;
- weigh the finished puree, add 900 g of sugar for each kilogram;
- stir the mixture with a wooden spoon until the sugar is completely dissolved;
- place the jam in sterilized jars and cover with parchment paper or plastic lids. Store the treat in the refrigerator.
Dried currant
- sort the berries, rinse in a colander and dry;
- cover the baking sheet with thin paper and sprinkle the berries in one layer;
- heat the oven to 50 degrees and place the berries in it, leave the door ajar;
- when the berries have dried up a little, increase the temperature to 65 degrees and keep in the oven for another 3-4 hours.


Tincture recipe
Tincture to strengthen the immune system
Ingredients:
- 200 ml of water;
- 250 g sugar;
- 2 cups of currants;
- 500 ml of vodka.
Preparation:
- Boil the syrup from the water and sugar, add the currants and boil for 3 minutes.
- Mash the berries in the syrup, when the mass cools down, pour in the vodka.
- Pour into a tinted glass container and close tightly.
- Leave the drink for 20 days in a dark place, shake the bottle every 3 days.
- Filter the finished tincture and store in the basement or refrigerator for up to 2 years.
The drink strengthens the immune system well, it should be consumed in moderation, 1-2 tbsp. l. per day, before meals.


Growing
Before planting bushes, you need to decide on a place. It should not be shaded, open to the sun. Currant grows well on chernozems, dark chestnut, chestnut soils, gray soils. But it can bear fruit well on any reclaimed ones. That is, enriched with humus, moist. You can read more about the specifics of growing currants here.
Landing features


The currant bush is installed in a pit at an angle when planting.
Preparation for planting and the process itself is somewhat different from the breakdown of a garden of pome or stone fruit crops:
- Since black currants love moisture, it is better to plant seedlings in grooves to make it easier to water.
- In the fall, it is necessary to feed the soil well with organic fertilizers and dig up to the depth of a shovel bayonet, placed vertically to the ground.
- It is constantly necessary to carry out loosening in order to prevent the appearance of weeds.
- Features of the planting itself: before planting, the bushes are cut so that no more than 15 cm remains of the ground.In early spring, this is done even lower, leaving hemp with 4 buds.
In spring, currants begin to develop very early, so planting is best done in autumn.
Distance between bushes
The distance depends on the variety. Because the bushes are tall, medium-sized and low-growing.Black currants are placed according to the scheme 2 x 1, 5 meters, and red and white - 1, 5 x 1, 25 m. If you plant thicker, then the berries will be small, and the care of the bushes is somewhat complicated.
Tips for choosing a variety


When choosing a variety of shrubs for planting, you need to focus on the agrotechnical characteristics of the plant
In order not to regret choosing a variety, it is useful to know the tips and recommendations of experienced gardeners before buying:
1 When choosing a large-fruited variety, there is no need to chase novelty - there are no rules of care for newly bred varieties.
2 Adapted varieties in the second and third generations will be better accepted and yield higher yields.
3 Abundant fruiting will not give the most fertile plants, if you do not take proper care of them in compliance with the rules of agricultural technology.
4 Large-fruited varieties need increased watering and feeding.
5 It is necessary to choose healthy and high quality planting material.
6 It is better to buy a dessert variety of currant, it is more aromatic and much more delicious than the universal one.
7 Industrial varieties (Dana, Osipovskaya, Dar Orla, Ural beauty, Marmaladnitsa) are less demanding for care, but their taste is inferior to dessert and sweet-fruited ones.
8 When buying foreign varieties, you need to be prepared for the fact that the planting material will not be accepted. Domestic selection for planting is best suited.
9 In terms of the degree of resistance against pests, infections and diseases, old varieties (Belarusian sweet, Green haze, Golubka) are inferior to modern ones, which means that the fruits will have to be processed more with chemicals.
Despite such an abundance of varieties, the selection of black currant continues. The ideal view does not yet exist. New varieties of the plant are constantly appearing, and its positive characteristics only increase.
To understand which variety to give an advantage, you need to plant 5-6 types of shrubs on the site with different fruiting periods and agrotechnical characteristics. Having tasted the fruits of each, you can choose one species, the most delicious, which you can then propagate in the garden.
back to menu ↑
See also: What vegetables can be planted before winter? TOP-8 of the most suitable plants and their best varieties | + Reviews
VIDEO: 7 secrets of currant harvest. Why does a gardener need currants
Read also: 15 Recipes for cranberries (tinctures, vodka, alcohol, fruit drink, etc.) cooked at home, as well as how to properly freeze and save it
conclusions
Currant is a berry shrub, about the medicinal and beneficial properties of which the ancient Slavs knew. Now the gardener has plenty to choose from, since there are several types of this plant, and each species has a certain number of varieties. Here are the gardeners' favorites:
- Decorative. King Edward VII, Blood-red (Ribes sanguineum Pursh), Alpine currant (Ribes alpinum).
- Black. Junnat, Goliath, Slavuta, Pygmy, Exotic.
- Red. Rosetta, Natalie, Dutch red.
- Gold. Shafak, Laysan, Venus.
- Green-fruited. Inca Gold, Emerald Necklace, Vertti.
- White. Diamond white, Dutch white, Diamond.
- Pink. Lyubava, Dutch pink, Pink pearls.
- Yellow. Ermak, Muscat, Isabella.
You can propagate currants by dividing the bush, cuttings, layering. Standard care: watering, loosening, treating bushes from pests and diseases, feeding.
Care
Care consists in the simplest agrotechnical measures. Currant bushes need to be watered. And since the black one feels a great need for this, then it must be done more often. It is advisable to pour 3-4 buckets of water under one bush. It is imperative after watering, as soon as the earth dries up a little, it is necessary to loosen it, and then mulch it. In addition, in the spring, the bushes must be properly trimmed and periodically treated against pests and diseases during the growing season.
Trimming
In early spring, you need to shorten the young shoots by 6-7 buds, and remove the old branches.It should be remembered that large berries grow only on young branches, so if you do not remove old ones, leaving only skeletal ones, then the yield will be low.
The correct formation of the bush is the presence of 15–20 branches of different ages.
Top dressing
For the growth and development of currants, top dressing is necessary:
- Nitrogen fertilizers are applied at the beginning of spring in the phase of active plant growth;
- After two weeks, you can feed the currants with a mullein solution;
- In the middle of summer, for better ripening of fruits and laying of new buds for the next season, phosphorus and potash fertilizers are applied.
Processing
All types of currants require regular treatments against pests and diseases. Indeed, due to the carelessness of the gardener, pests can settle on the plants, and then you will have to spend energy and money to prevent their spread. After all, pests and diseases can destroy not only the entire crop, but also shrubs. Therefore, it is necessary to know their main features to select effective methods of control.


Diseases of the currant:
- Powdery mildew - fungal disease. The berries become smaller, and the young shoots do not have time to ripen. In May, all vegetative parts of the plant are covered with a whitish bloom, which then darkens. The causative agent is fungi of the genus Sphaerotheca. Treatment of bushes with fungicides such as Fundazol, Topaz, etc.
- Currant anthracnose. Black spots appear on the leaves. They grow and the plastic sheet dries up. Treatment of bushes with Bordeaux liquid.
- White spot of black currant leaves. Fungal disease. At first, small spots appear on the leaves, which spread and this leads to the drying of the leaf blades. And as a result - a decrease in yield. The bushes are treated with Bordeaux liquid.
Read more about currant anthracnose in this article.
Currant pests:
- Aphid. A sign of pest activity is twisted leaves on the top of the shoots. If you look at the bottom plate, you can see these tiny pests. They are treated with insecticides.
- Mite. In early spring, unnaturally large buds are found on the bushes. Apparently, a tick has wound up in them. The larvae, destroying the kidney, go to the second. It is this insect that can also carry the terry virus.
- Glass-maker. A butterfly that starts flying in May and lays eggs on the shoots. The caterpillars emerging from them make wormholes in the plants, and the bushes begin to dry out.
How to process currants in the spring from diseases and pests will tell this material.