Icer Grows a cucumber variety Siberian garland
Cucumber Siberian garland F1 caught my attention in a photo on the net. There were so many fruits on the plants that at first I didn't believe it was true. I found out what kind of variety, bought seeds and planted it last season.
I figured out all the nuances of leaving and got so many cucumbers that I did not know what to do with it. In the review I will tell you about all the features and analyze all the nuances of agricultural technology.
Description of the variety
The variety is early maturing, parthenocarpic (does not require insects for pollination), high-yielding. The stem of an adult bush during the fruiting period resembles a New Year's garland, densely covered with greens. All this, plus tolerance for cold weather, gave rise to the name of the cucumber.
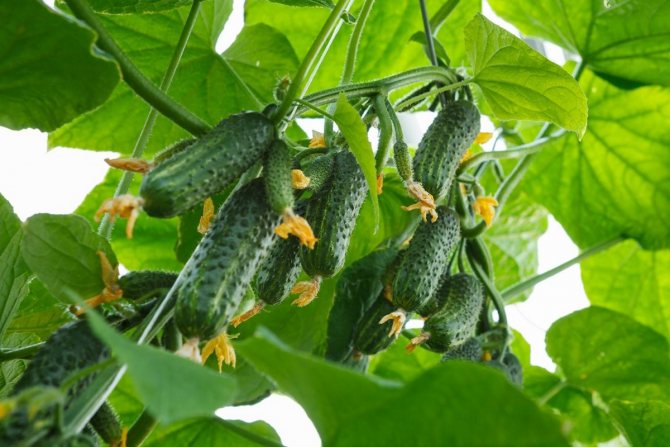
The bush is powerful, the internode is shortened, the leaves are of medium size. Zelentsy are small, from 5–8 cm, small tuberous, covered with thornless thorns and white fluff. Skin color is dark green at the base, gradually brightens towards the top of the fruit. It has a pleasant taste, without bitterness, the pulp is crispy and juicy, with a small seed chamber. The fruits do not outgrow.
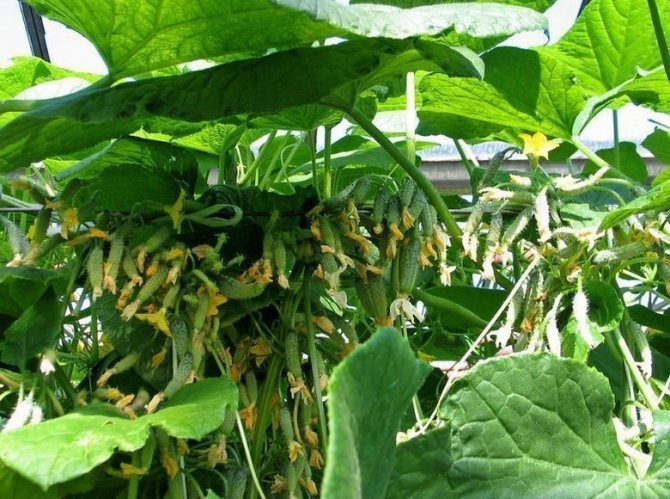
In a knot in place of one flower, three or more ovaries are formed. The yield of the variety, with the correct shaping of the bush, reaches up to 400 fruits from one bush or up to 40 kg from 1 sq. m.
The first greens appear 40–45 days after germination. When planted in late April or early May, the cucumbers are harvested in mid-June.
The variety is excellent for growing throughout Russia, Ukraine, Moldova and Belarus. The main condition: not too cold weather, temperate climate, short drought, abundant watering and top dressing.
Table: advantages and disadvantages of the variety Siberian garland F1
| Dignity | disadvantages |
| High yield | High price |
| Early maturity and self-pollination | When pollinated by insects, the fruits are disfigured. |
| Long-term fruiting | Correct molding of the bush into one stem |
| Does not outgrow | It is necessary to remove cucumbers once a day, otherwise fruiting is inhibited |
| High yield | |
| Excellent taste and versatility | |
| Well assimilated to weather conditions | |
| Disease resistance |
Photo gallery: cucumber Siberian garland F1

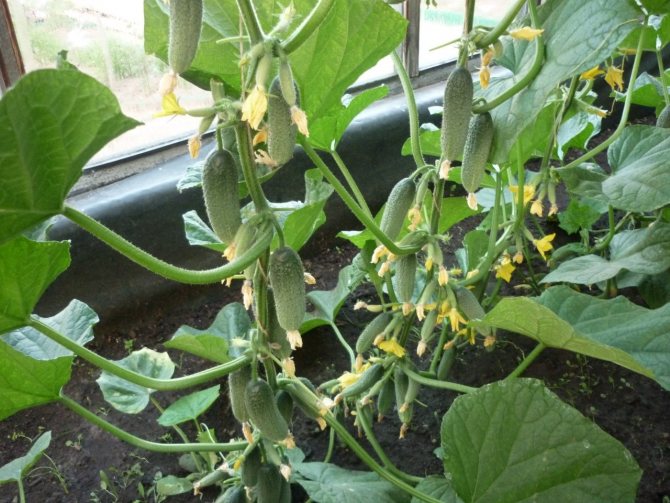
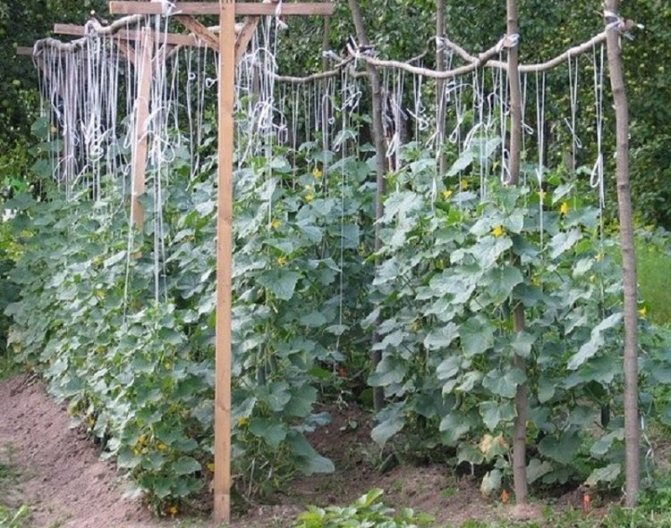
Cucumber Siberian garland F1 on a trellis


Cucumber Siberian garland F1 in a greenhouse


The first cucumber ovaries Siberian Garland


Seed packaging Siberian garland F1
Video: Growing cucumbers of the Siberian garland F1
Planting cucumbers
Siberian Garland cucumbers can be grown in two ways: by planting seeds for seedlings or by direct sowing into the soil.
Both methods bring a bountiful harvest, but their choice depends on the climatic characteristics of the region.
The northern climate requires pre-growing seedlings and planting them in a heated greenhouse. This is due to the high probability of the return of night frosts.
In open ground, the culture is planted at a stable rate of 15 °.
Selection and preparation of seeds
To obtain healthy adult cucumber bushes, always carry out pre-sowing seed germination: at the initial stage, you will be able to reject weak plants, lay a good foundation for the future harvest.
The preparation is carried out by soaking the seeds in a solution of a bioactivator and a disinfectant. This stimulates seed germination by obtaining trace elements, which, in turn, will make it possible to protect seedlings from a number of fungal diseases affecting the root system and young shoots.
Table: preparing seeds for germination
| Bioactvator | Breeding rate | Soaking time |
| Vermisol | Dilute with warm water in a ratio of 1: 5 | 12 hours |
| Epin | In 2 liters of water, dilute 1 ml of the drug | 24 hours |
| Azotofit | Dissolve 1 teaspoon in 500 ml of water, add 2 tablespoons of sugar, leave for 2 hours | 1.5-2 hours, dry from 4 to 8 hours |
| Zircon | Dilute 1-2 drops of the drug in 300 ml of water | 8-18 hours |
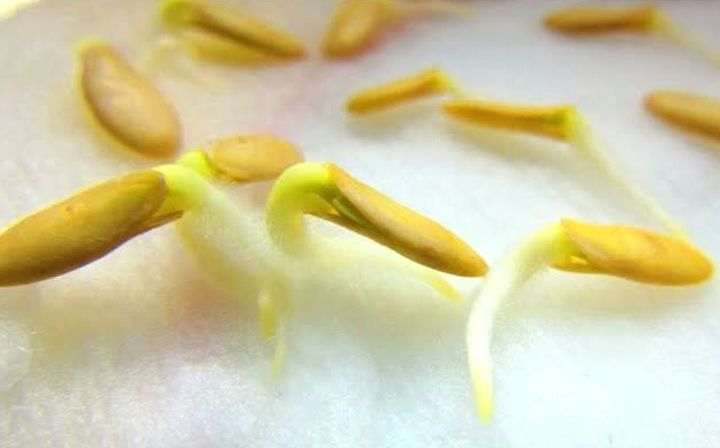
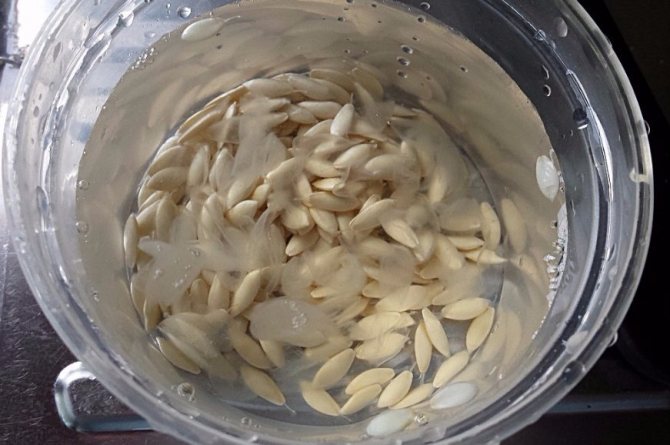
The soaked seeds are transferred to half of a well-moistened napkin, covered and left in a warm place until the first shoots appear. They appear in 1-2 days.
Another way of germinating seeds is planting in sawdust. Prepared seeds are lined with moistened sawdust. From above they cover another layer of sawdust 1–2 cm thick and spill well with water. They put the dishes in a warm place until the cotyledon leaves appear, after which the seeds are transplanted into pots.
Transplanting cucumber seedlings must be done very carefully, along with sawdust, so as not to damage the root system and stem. If you do not have the proper experience, it is better not to experiment.


Sprouted cucumber seeds
Planting seeds for seedlings
Regardless of the method chosen, the quality of the planting material affects the yield.
Seeds of cucumbers Siberian Garland cannot be prepared on their own, because the variety is classified as hybrid. It is recommended to buy them in a specialized store, which can provide all quality certificates.
Pay particular attention to the condition of the packaging and the characteristics of the variety indicated on the reverse side.
The technology of planting seeds for seedlings
First, the purchased material must be prepared: it is immersed in salted water (30-50 g per 1 liter of water) for 120 minutes. Seeds that have sunk to the bottom are suitable for planting.
Selected seeds are dipped in a 1% solution of potassium permanganate and kept for 24 hours to exclude infection with pathogenic microorganisms.
The disinfected material is heated for 3 hours at a temperature of 55-60 °. Hardening is also practiced: the seeds are laid out on a damp cloth and sent to the refrigerator for 48 hours.
Process features


Plants need to be properly cared for
Planting seeds for seedlings takes place in late March and early April, depending on the regional climate.
It is recommended to prepare individual containers for each sprout so as not to injure the root system during transplantation.
Seeds are placed in containers filled with universal soil to a depth of 2-2.5 cm, moistened and covered with foil.
Future cucumbers are sent to a well-lit and warm (25-28 °) place. Watering is carried out every 3-4 days, and the first shoots should be expected in 7 days.
Growing seedlings requires the introduction of nutrients that stimulate the growth of the green mass of the plant. Use a solution of urea in a proportion of 2 g per 1 liter of water and add no more than 100 ml per bush.
At the first shoots, the film is gradually removed for 10 minutes a day. When the first full-fledged sheet is formed, it is removed completely.
A week before transplanting into open ground conditions, the seedlings are hardened by taking them to fresh air or to a greenhouse.
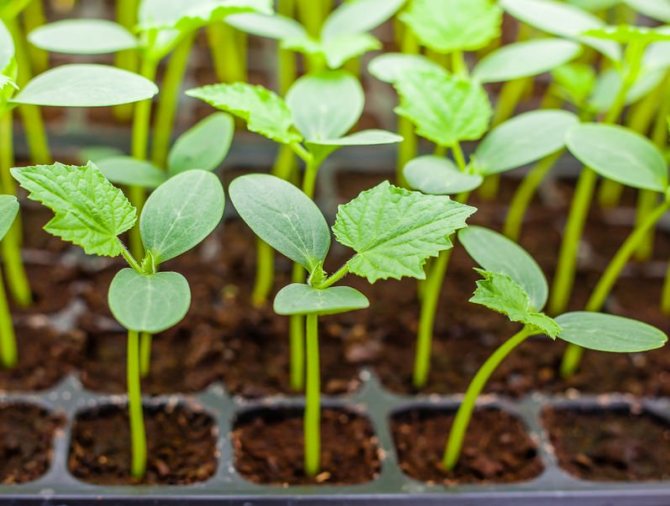
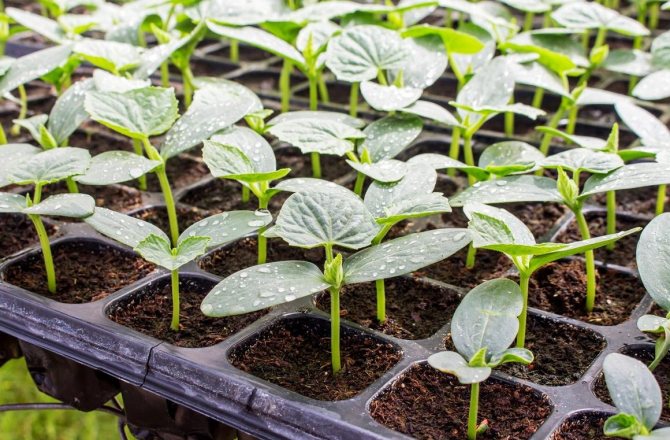
Growing seedlings
The best period for planting cucumber seeds for seedlings is late March or early April. Thanks to this, you will save the bushes from the "tricks" of spring weather, get an early harvest.
Sprouted seeds are placed in plastic cups filled with a soil mixture consisting of sod or forest land, to which an equal amount of peat is added.To get a bucket of planting soil, add 1 tbsp. a spoonful of nitroamofoska and 3 tablespoons of earth. Remember - young roots need an active supply of oxygen, so the soil should be soft and fluffy. If your soil is lumpy and does not divide into granules, add 1 scoop of sifted sand to a bucket of soil. Planting depth - 3-4 cm, after planting, the pits are covered with soil and carefully watered the ground, trying not to get to the seed planting site.
Approximately on the 5-6th day, the first cotyledonous leaves will appear in the glass. After the appearance of 3-4 true leaves, the plant begins to feed. They are transplanted into the ground in mid - late May, when the danger of severe spring frosts disappears. If you want to get an early harvest, seedlings are planted in greenhouses or hotbeds.
We recommend using tunnel greenhouses for owners of small household plots. Structurally simple and easy to operate, they allow you to create a reliable shelter for seedlings.
It is very important not to outgrow the cucumber and transplant it into the ground in time. If the seedlings stretch out, the plant will weaken and begin to hurt.


Cucumber seedlings at 1 and 2 weeks
Features of growing cucumber varieties Garland
Cucumbers can be called a capricious vegetable, because caring for them requires attention from the gardener. However, don't be intimidated. Agrotechnics of the Garland hybrid is not so difficult. Observing some of the nuances, you will be able to appreciate the capabilities of the variety.
Do I need to prepare seeds for planting
The seeds from the manufacturer have already passed the necessary processing and are covered with a special shell. Therefore, they do not need soaking or other preparation before planting. All you have to do with the seeds is plant them in the ground.


Cucumber seeds Garland from producers have already been processed and are awaiting sowing
Growing methods
The garland is preferable to grow in seedlings. To do this, you will need seeds and separate planting containers. It is best to use peat tablets. This is a great help for those who grow a large number of seedlings. The tablets are neutralized, and the shell is impregnated with fungicides, which will protect the plant from diseases. The only drawback, and even then controversial, can be called the quick drying of the filler.
- Place tablets in a container, add water.
- After the tablets have increased 5-6 times, plant the seeds in the indentations.
- Cover the container with plastic wrap and keep it moist.
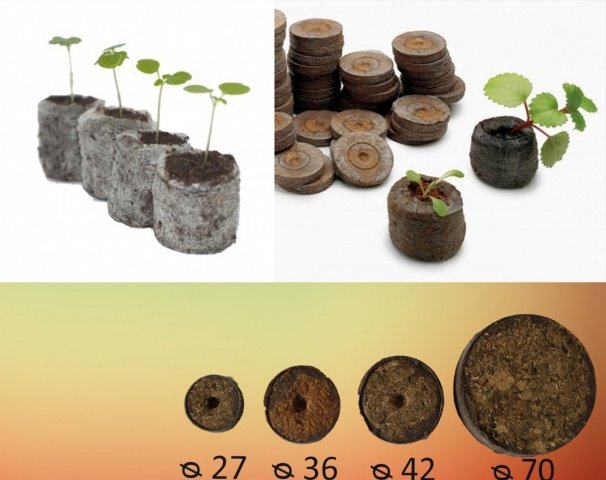


Peat tablets make the work of the gardener easier
You can use disposable cups, cassettes or small pots (plastic or peat) for seedlings. In this case, you will need a primer. It is advisable to purchase a universal soil for seedlings, it has the necessary water and air permeability.
- Each seed must be sown in a separate container. A suitable temperature for germination should be within 27 ° C.
- With the appearance of the first leaves, the temperature can be lowered to 21-23 ° C. Maintain humidity at least 75%. If the seedlings are in greenhouses, but they need to be regularly ventilated so that the soil does not mold.
- When 3-5 true leaves appear on the plants, you can plant it in open ground.


Cucumbers do not tolerate picking well, so peat pots are a good option for growing seedlings: they are lightweight, and it is convenient to transport plants in them.
Seeds are planted on seedlings from mid-April to the end of the month. They are transplanted into the ground no earlier than 25 days after planting.
First of all, the Garland is intended for growing in indoor conditions, where ideal temperature conditions are created for the growth and development of the hybrid. But greenhouse and greenhouse cucumbers must be protected from drafts and temperature changes during the day and at night. Also, during growth, you should not get carried away with nitrogen-containing dressings.They stimulate the development of the tops, while the root does not keep pace with the growth of the stem. This can cause deformation of the greenhouses and even their shedding.
In addition to the seedling method, you can sow seeds in open ground. But this is possible only after the soil has warmed up to 13–15 ° C and provided that the threat of frost has passed. As a rule, such an opportunity appears in the last ten days of May, and in some areas at the beginning of June.
Soil preparation and crop rotation
Regardless of where the Garland cucumbers will be grown, in a greenhouse or in the open field, it is necessary to prepare the land before planting. The culture is very responsive to the introduction of organic matter. Therefore, 2-3 buckets of well-rotted manure should be added for digging for 1 m2. Do not forget about mineral fertilizers. 2 tbsp. l. superphosphate and 1 tbsp. l. ureas will be quite useful.
Cucumbers grow well on loose loam and sandy loam. But you should determine the acidity of the soil and, if necessary, bring it to a neutral indicator.
Compliance with crop rotation also plays a role in increasing yields. Planting cucumbers after cabbage, onions, potatoes, celery and tomatoes will be the right move. Unwanted predecessors are members of the pumpkin family:
- zucchini;
- squash;
- pumpkin;
- watermelons;
- melons.
It is better not to grow herbs next to cucumbers. They are believed to slow down the growth of the whips. The only exception is dill, which has a positive effect on the fruiting of borage. Great neighbors are:
- peas;
- cabbage;
- salad;
- beet;
- beans;
- beans (enrich the soil with nitrogen);
- corn (tall plants protect the cucumber plantings from the wind);
- radish (scares off spider mites and leaf beetles);
- onions (phytoncides kill spider mites).
He really does not like cucumber growing nearby nightshades:
- eggplant;
- potatoes;
- tomatoes.
This is especially noticeable in the greenhouse, because cucumbers and, for example, tomatoes need different temperatures and humidity. Fertilizers for these crops are also different. In the open field, tomatoes and potatoes will oppress cucumbers even in neighboring beds.
It is impossible to grow cucumbers in one place for more than 3-4 years. By swapping crops, you help save the soil from depletion, which inevitably occurs when growing plants of the same type in one place for a long time.
Watering, weeding and mulching
About cucumbers, we can definitely say that this culture loves plentiful drinking. The period from the moment of planting to the appearance of the first flowers can be called moderate in terms of moisture. Watering occurs every 3-5 days (depending on the ambient temperature), the norm is up to 4 liters of water under a bush. As soon as fruiting begins, the frequency of watering and the amount of moisture should be increased. You will have to water every 2-3 days, pouring up to 8 liters of liquid under the bush. On hot days, you need to monitor the condition of the soil. It should be of medium humidity, but in no case dry out.
Watering rules are as follows:
- The delicate root system of cucumbers accepts only warm water well.
- Watering is carried out exclusively at the root. Moisture on the leaves can cause burns.
- The best periods for hydration are early morning or evening.
The most correct method of moistening the Garland will be drip irrigation. It allows you to carefully use up precious moisture and brings it to the root of the plant. Dripping water is quickly absorbed into the soil rather than spreading over the surface.
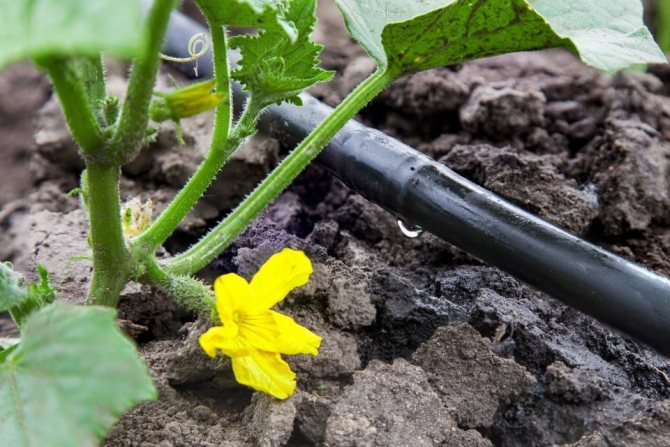


Drip irrigation system allows water to feed directly the plant root
Weeding is an integral part of cucumber care. But since it takes too long, experienced gardeners have found a great way to save themselves from unnecessary work. It consists in mulching plantings. The beds, previously cleared of weeds and watered, are covered with a layer of dry grass of 10-15 cm. This method not only inhibits the growth of weeds, but also helps to retain moisture in the soil for a long time. Reducing evaporation, in turn, prevents the development of many fungal diseases.
Top dressing
For cucumbers, the Garland will be enough to make 4 dressings per season.
Table: root fertilization
| Period | Fertilizer type and dose | Method of application |
| 2 weeks after planting in the ground | For a bucket of water:
| Water only at the root, after moistening the soil. For one plant, 0.5 l of the mixture is enough. |
| At the beginning of flowering | Chicken droppings or horse manure. The working solution is prepared taking into account the peculiarities of organic matter. Since the composition of chicken manure is considered richer in trace elements, it can more aggressively affect the roots due to the concentration of nutrients. Therefore, the dung infusion is diluted in more water - 1:15. Cow dung can be used 1: 6. | |
| Twice during fruiting | To avoid recessions in the fruiting process, during the growth of the ovary, use the following solution - thoroughly stir in a bucket of water:
|
Root feeding is carried out in warm weather. Fertilizers can be applied in the morning or evening after watering or rain. But if summers are cold and damp, the root system of the cucumber is not very active in absorbing nutrients. During such a period, it is more advisable to carry out foliar feeding using nitrogen-containing fertilizers, for example, urea.
Video: feeding cucumbers with potassium humate
Planting scheme and plant formation
Thickening of cucumber plantings will certainly lead to competition between plants for moisture and nutrition. In crowded conditions, diseases can arise and harmful insects can quickly spread. But you should not plant cucumbers at long distances from each other. Irrational use of the land will result in the loss of potential crops.
If you are planting a Garland in a greenhouse, then it is permissible to place 4–5 plants per 1 m2. In open ground, the planting density is somewhat different and allows from 3 to 4 bushes per 1 m2.
In order for the Garland to show yielding opportunities, the plant is formed into one stem, while the side stepsons are removed. In addition, all flowers and ovaries that appear in the axils of the first 4 leaves must also be torn off. This procedure is called blinding. Its main task is to form a strong plant.
Video: forming a cucumber into one stem
Parthenocarpics need tying up. To do this, young plants are directed up the trellis, fixing the free end of the rope over 2 or 3 leaves. A good alternative to a trellis is a cucumber net stretched between the stakes. Cucumbers grown on a trellis or net have many advantages. They are better lit, it is very convenient to take care of the plants, and the fruiting period increases.
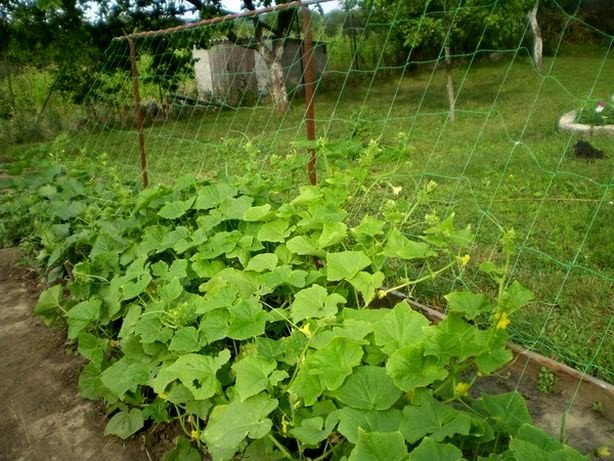


Cucumber whips with the help of antennae will stretch up the mesh, will dry out faster after rain, and slugs will not get to tasty fruits
Seedless method
Cucumber seeds are sown in the soil warmed up to 18–20 degrees, it is at this temperature that friendly shoots appear. If the soil temperature is below 16 degrees, then the seeds die.... Therefore, carefully monitor the weather conditions, even if the air warms up to 20 - 25 degrees during the day, but at night the temperature on the surface drops to 15 degrees - the cucumber will not grow.
The best period for sowing cucumber in the soil is considered the end of May - beginning of June. At this time, the soil is well warmed up, there is no frost at night, and there is sufficient precipitation.


Non-seedling cucumber. Be sure to hilling on the top sheet
Preventive measures
Every experienced gardener, before planting a Siberian garland on the site, should think about preventive measures that will help not only grow a good harvest, but also prevent the occurrence of diseases and the appearance of pests. The requirements to be met are quite simple:
- Use only high-quality, prepared seeds for planting.
- Sow seeds in warm and fertile soil.
- Look for varieties that are most resistant to disease.
- Weeding regularly.
- In autumn, completely clear the beds from all plant residues.
- Observe the correct care regimen, norms and amount of dressings.
- Disinfect the soil before sowing.
Planting scheme for the seedless and seedling method, trellis formation
An important feature of the variety Siberian garland F1 is the formation of a trellis in one stem. This saves space on the garden bed, while providing good lighting and fruiting. Seeds are planted at a distance of 5–7 cm from each other, between rows should be 12–15 cm. After the first shoots appear, they break through, leaving 10–15 cm between the plants. Seedlings are planted after 10–15 cm, the row spacing is 12– 15 cm.
The first 3-4 knots of the Siberian garland are completely blinded (buds and ovaries are cut off), in addition, lateral shoots (stepsons) are pinched until the very end of the trellis. Only the ovaries are left. When the cucumber reaches the top of the trellis, the lateral shoots stop pinching, pinching at 5-6 leaves. The central stem, several times wrapped around the top of the trellis, is also pinched.
By dazzling a cucumber up to 5-6 leaves, you contribute to increased nutrition of the central stem. This promotes rapid growth, the plant develops organically, does not waste energy on fruiting. In addition, the survival instinct is spurred, which contributes to a good harvest in the later stages of development, and the cucumber forms more ovaries.
It is worth planting a cucumber in shaded areas where there is a shelter from the midday heat. It is advisable to choose a site so that in the morning the cucumber is well lit, and in the afternoon it is covered by tall plants (sunflower, corn, trees).
A shading grid provides a good shelter from the sun. The size of its cell allows you to reduce the intensity of sunlight, while at the same time not interfering with its passage. The only drawback is the limited use over large plantations.
Video: how to properly form cucumbers for large yields
Photo gallery: ways to organize a cucumber trellis


Trellis net installed in the form of a hut


Conical cucumber trellis


Cucumber trellis on a metal mesh


Hut cucumber trellis


Cucumber trellis on shingles


Cucumber trellis on a wire


Cucumber trellis on a grid


Garter "Tsar's loop" of cucumber
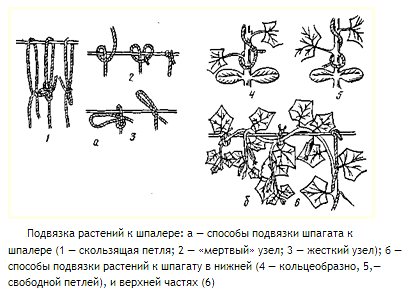

Ways to tie a cucumber trellis
Caring for cucumbers after planting
Despite the uniquely high yield rates, the Siberian garland F1 bunched cucumbers are not distinguished by high whimsical care. The main thing is to adhere to the basic rules: moistening, feeding, loosening the soil and preventive treatment for ailments.
Watering and fertilizing
Since cucumbers are almost 98% water, then when they are grown, it is necessary to organize frequent and abundant watering, which will also be determined by climatic conditions. Irrigation activities for the vegetable should be carried out early in the morning or late in the evening. Watering at lunchtime can burn foliage if water spills on it. Before flowering, the plant should be moistened every 3-4 days. It is recommended to reduce watering to once every 2 days during the period when the first ovaries form on the cucumbers.
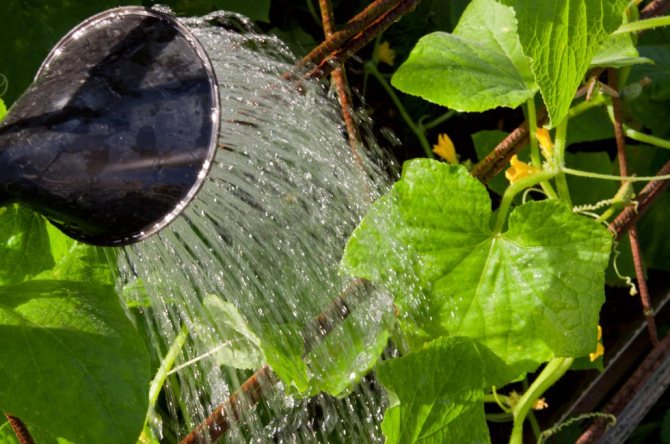


To moisten the beds, watering cans are used, in which the soil is irrigated with a watering can or the ditch irrigation method is used. To do this, small ditches are dug between the rows, into which water is poured. In this case, the water should be quite warm - + 23 ... + 25 ° С, standing for about a day. Dense fruiting quickly depletes the plant, so it requires good, high-quality feeding. It is recommended to apply fertilizers about four times per season.
The first feeding is carried out two weeks after planting seedlings in open soil or after the appearance of the first full leaves.As a rule, during the first application of fertilizers, nitrogen complexes are used, which make it possible to activate the growth and development of bushes. The use of superphosphates, humus, bird droppings is also allowed.
Important! At high temperatures and extreme heat, the crop needs to be watered daily, and sometimes even twice a day - in the morning and evening hours.
The second time the cucumbers are fertilized 2 weeks after the first, in this case they use an integrated approach:
- foliage is sprayed with a superphosphate solution;
- the bushes are watered with a composition of superphosphate, ammonium and potassium sulfates;
- chalk and charcoal are scattered over the soil.
The third time fertilization is applied one week after the formation of the first fruits. Ripening cucumbers are in dire need of potassium products, which can speed up the ripening process. But the percentage of nitrogen fertilizers, on the contrary, is reduced. The fourth feeding is carried out 10 days after the third. It is recommended to use organic products for her, for example, cow dung or bird droppings. Fertilizers are stirred in water, in a ratio of 1: 2, let it brew a little. The slightly fermented infusion is diluted with 10 liters of water and poured over the garden with it.


Garter and shrub formation
The cucumber variety Siberian Garland belongs to vigorous plants and in order to get a good harvest, it requires shaping into one stem and the obligatory presence of support. A homemade trellis is perfect as a support, which can be made from several vertical posts and horizontal slats installed between them. For shaping it is necessary to remove all stepchildren to the “dew point” at 3-4 points of the bush branching, leaving only fruit ovaries.
When the cucumbers grow another 3-5 leaves, all side shoots and flowers should be removed. Further pruning is carried out in the same way until the stem reaches the top of the greenhouse or trellis. Then it should be wrapped 2-3 times around the support, carefully fixed and cut. Stems that reach a length of 20-25 cm should be immediately wrapped around the vertical support, and the top should be left free.
Find out in more detail how and why you need to cut cucumbers.
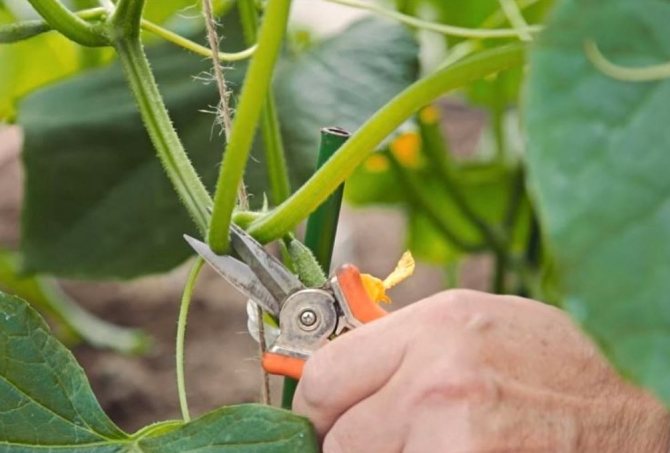
In order for the pruning of shoots to take place with minimal injury to the plant, it should be carried out subject to a few simple rules:
- carry out pruning activities in the morning, ideally before sunrise;
- all places of cuts, in order to prevent diseases, should be treated with crushed wood or activated carbon;
- at a time it is allowed to remove up to 7 cm of shoots;
- while placing the stem on the trellis, you should maintain the most natural position, you can not twist it or forcefully bend it;
- on the plant, it is imperative to remove dried, rotten leaves, weak stems.


Soil care
Cucumbers of this variety categorically do not accept the presence of weeds in the garden. That is why it is recommended to regularly weed the soil. In order not to waste extra time on weed control, experts advise mulching. To do this, a layer of mulch should be laid on the surface of the soil, which can be sawdust, straw, hay, mowed grass, etc.
The mulching procedure will also preserve moisture in the soil, saturate it with oxygen and nutrients, thereby activating the process of fruit development and ripening. For bushes that are grown not in a greenhouse, but in open ground, it is especially important to loosen the ground. Digging the upper hardened soil layer will enrich the soil with valuable components and provide the root system with high-quality oxygen nutrition.
Organization of watering
When growing a cucumber, do not forget: it is a moisture-loving plant. The correct irrigation regime, especially in varieties such as the Siberian garland F1, which do not like extreme heat, provides not only the flow of moisture, but also becomes the key to a full supply of microelements.
In hot weather, an adult plant consumes up to 3 liters of water. In less intense heat up to 2 liters. By correctly regulating watering, you will not only save the cucumber from drying out, but also from various diseases affecting the root system.
The organization of drip irrigation helps to distribute moisture well. In small areas, plastic bottles with a cut-off bottom, suspended over a cucumber bush, are used for this purpose. By making holes in the walls or lids, they provide a continuous flow of moisture under the root. Another way to adjust the water flow is to open the lid slightly so that the water can drain freely. And although it is rather difficult to get drops, the water flows down gradually and, evenly wetting the soil, does not spread over the surface.
In large household farms where a lot of bushes are grown, a pipe-belt system helps to automate irrigation. It consists of:
- water tank;
- drip tape or pipes for supplying moisture to the roots;
- fittings for branching organization;
- taps and mini-taps for adjusting the flow of water through a tape or pipes.
The advantage of such a drip system is the ability to control the flow of water and its heating; the disadvantage is that plants located closer to the water reservoir receive more moisture.
Photo gallery: organization of drip irrigation
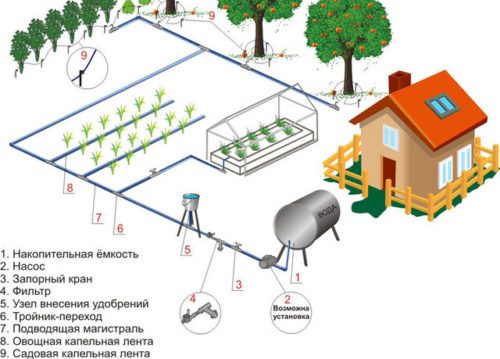

Drip irrigation scheme for a summer cottage


Tubular drip irrigation system
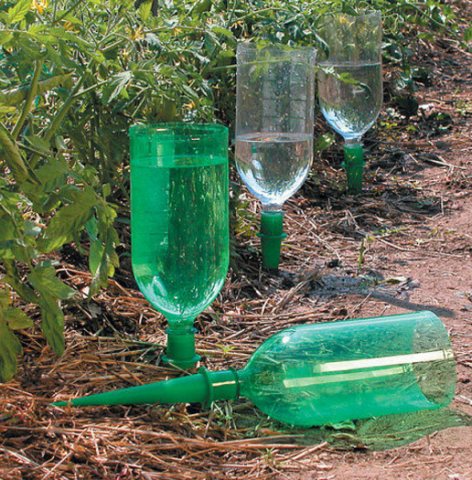


Automatic watering with plastic bottles
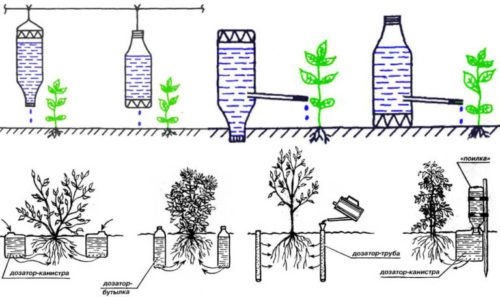

Diagram of homemade drip irrigation from plastic bottles
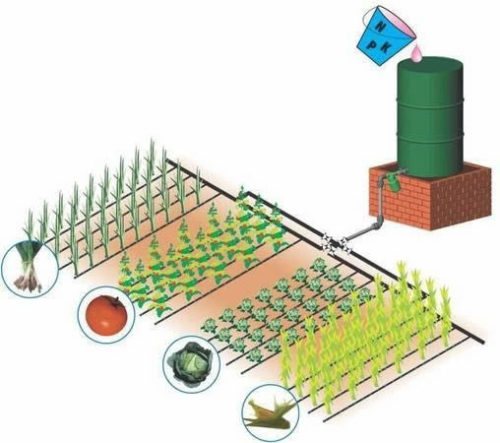

Drip irrigation of a small garden
Breeding history


Cucumbers Siberian garland F1 - a unique hybrid resistant to aggressive growing conditions
Siberian garland F1 is a hybrid type of cucumber, bred on the basis of the seeds of "Uralsky Dachnik". The variety was developed by breeders of the Chelyabinsk station. Cucumbers got their name due to their appearance: long branchy shoots are literally dotted with fruits, which resembles a New Year's garland. In addition to the subarctic and arctic regions, the variety grows successfully in all regions of the country.
Top dressing
When starting to feed a cucumber, remember that a special "diet" is needed at different stages of its development. As it grows, it needs a complex supply of chelates, metals and mineral salts. At the beginning of the formation of the green mass, potassium is needed more, starting to bear fruit, the plant needs more nitrogen. The latter is especially relevant in view of the high productivity of the Siberian garland, so, having received the first fruits, feed the cucumber with a fertilizer containing a large amount of nitrogen and phosphorus: this will spur the formation of new ovaries in the sinuses. But for their successful growth, potassium is needed.
Table: fertilizer for cucumber
| Fertilizer | Preparation of top dressing | Application method |
| Chicken droppings | 50 grams of chicken manure is diluted in 10 liters of water. After mixing well, leave to ferment for 10 days. | Root dressing |
| Manure | 1 kg of rotted manure (2-3 years old) is diluted in 10 liters of water | Root dressing |
| Wood ash | Throw a scoop of ash under the root before watering, once a season. Or prepare a chatterbox: 1 tablespoon of ash per 10 liters of water | Root dressing |
| Humate fertilizers | 200 grams of concentrate is diluted in 10 liters of water | Root and foliar feeding |
| Chelated fertilizers | 25 g of powder is diluted in 10 liters of water | Foliar dressing |
Cucumber is fed at intervals of 10-14 days from the day of the previous feeding. In the case of an excess of trace elements, "fat" begins... Its first signs: the cessation of the formation of ovaries, increased growth of green mass, the leaves acquire a rich dark color, bulge.In this case, watering is stopped, a small amount of sawdust is introduced under the root and added dropwise.
Table: signs of lack and overabundance of micronutrients in cucumbers
| Trace element | a lack of | Elimination | Fat | Elimination |
| Iron and copper | Chlorosis - the plant turns yellow, the leaves become smaller, growth slows down, buds crumble. | Chicken droppings are added, sprinkled with chelated fertilizers | The leaves are covered with brown spots, on young leaves there is a mezzanine chlorosis. | Stop processing with copper and iron sulfate. |
| Manganese | The leaves are deeply dark green in color, curl, covered with tubercles. | Spraying with chelated fertilizers | On old leaves, mezzhilkovy chlorosis is formed, covered with brown spots. | The soil is too acidic. Lime, dolomite flour, chalk powder are introduced, mulching is carried out. |
| Potassium | Yellow border along the edge of the leaf, pear-shaped greens | Humate fertilizers are introduced, compost infusion with ash, sprayed with chelates | The leaves are covered with white spots, elongated internodes, the foliage withers, the plant dies. | Stop feeding the plant and watering. |
| Nitrogen | The leaves of the cucumber turn pale, the upper ones turn yellow, the lower ones fade, the stem becomes thinner, gradually drying out, the tips of the greens are sharpened | Chicken droppings, mullein solution are introduced. Sprayed with chelated fertilizers and humates. | The plant stops bearing fruit. Leaves and stem are dark green. | Stop feeding and watering. Wood sawdust is introduced under the root, mixed with the soil. |
| Magnesium | The leaves burn out, become thinner, the lower ones are covered with yellow spots, the green color remains only on the veins. | Sprayed with chelated fertilizers | Twisted leaves darken. The roots die off, the cucumber dies. | Stop watering. Add chalk, lime, dolomite flour |
| Boron | Ovaries and lateral lashes die off, flowers crumble. | Foliar top dressing with chelated fertilizers. | The edge of the leaf dies off, the leaves acquire a domed shape. | Stop feeding |
| Phosphorus | The ovaries and buds fall off. The lower leaves turn yellow and die off. | Sprayed with chelates. When watering, phosphorus-potassium fertilizers are added to the water. | Leaves die off. | They are fed with potash fertilizers, which do not include phosphorus. |
| Sulfur | Rugged sheet plate. Leaves change color. | Spraying with chelated fertilizers. | Coarse. The leaves become grayish brown. Covered with outgrowths of "scales". | Stop feeding. |
| Zinc | Leaves are uneven, yellowed. | Sprayed with chelated fertilizers, zinc sulfate is added under the root. | The leaf near the veins becomes discolored. | Stop feeding. |


Signs of micronutrient starvation in cucumber
Diseases and pests of the variety Siberian garland F1
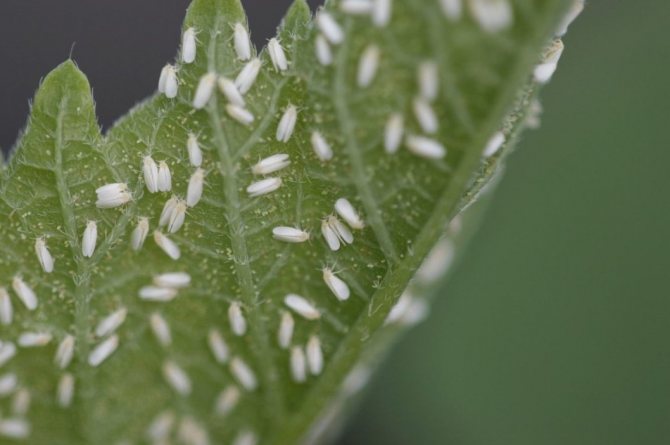
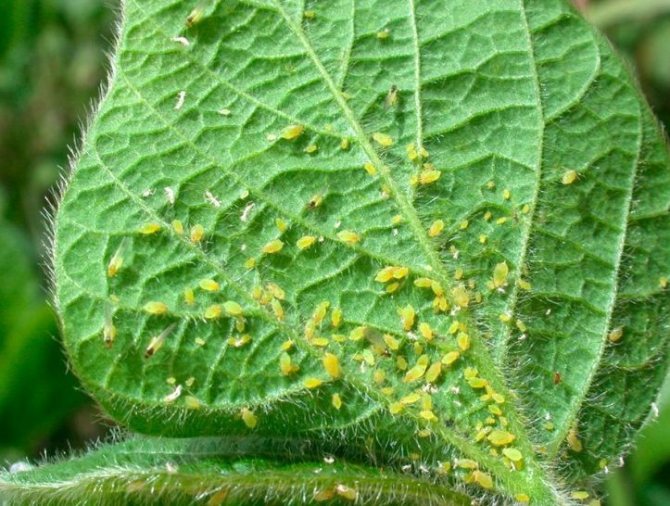
The variety is resistant to cladosporium disease, mosaic virus, powdery mildew, poorly tolerates peronosporosis, anthracnose. It is attacked by typical cucumber pests: spider mites, aphids, thrips. The best way to protect a plant from pests and diseases is through preventive treatment. For this, folk and chemical plant protection products are used.
Table: signs of damage to cucumber, prevention and treatment with folk remedies
| Disease pest | Signs | Method of treatment and prevention |
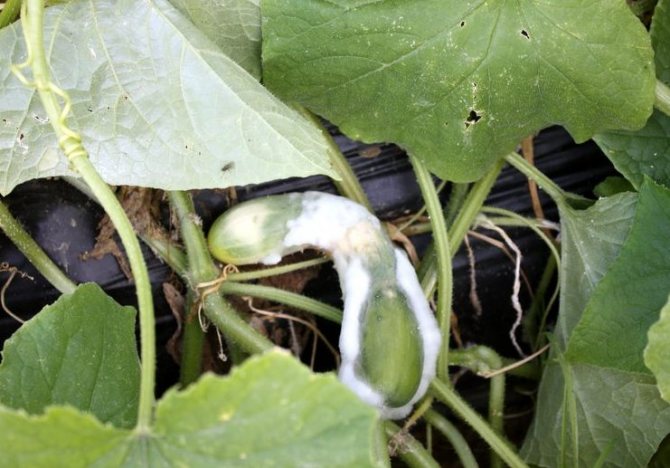
| Peronosporosis | The leaves are covered with yellow spots, a gray coating with black dots of fungal spores appears below, the plant dries up. | Spraying solutions: dilute urea with water in a ratio of 1:10; 3 liters of sour milk per 10 liters of water: Bordeaux mixture - 10 liters of water are mixed with 100 g of copper sulphate and 100 g of lime |
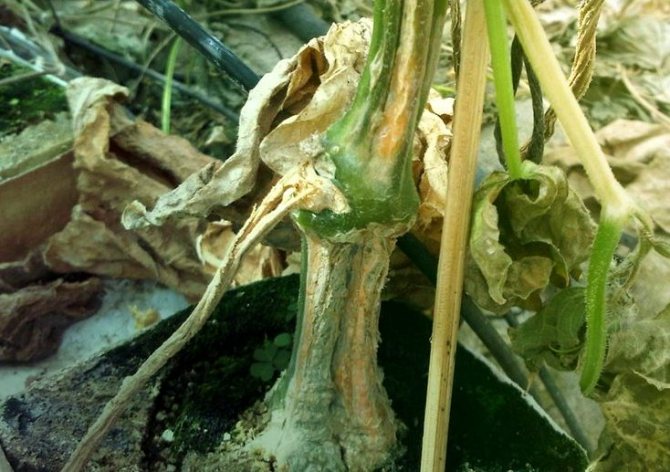
| Anthracnose | The stem, leaves and fruits are covered with brown, depressed spots. | Spray with Bordeaux mixture. Dust the affected areas with charcoal, lime or chalk powder |
| Aphid | The inside is covered with a colony of black or green insects. The leaves of the plant are curled. | Spray with solutions: Add 1 kg of grass to 10 liters of water and insist; 200 g of ash are diluted in 10 liters of water, 50 g of planed laundry soap is added |
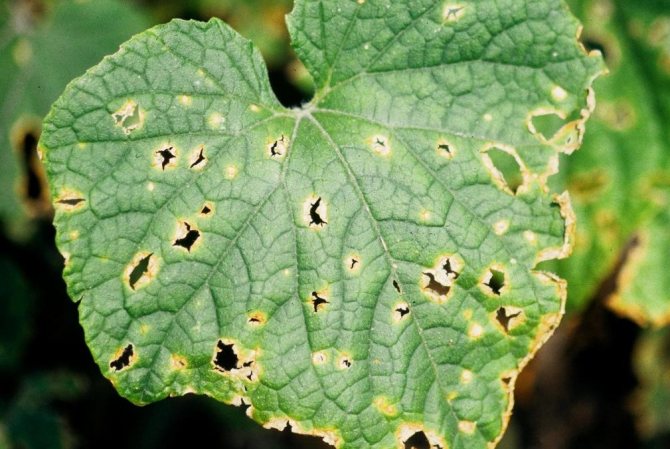
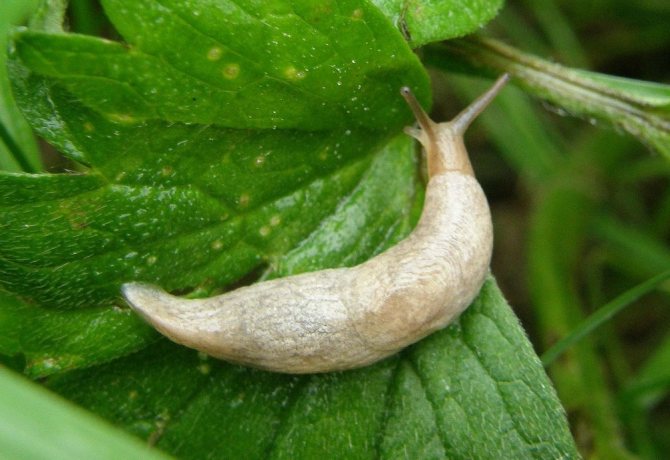
| Slugs | Silvery marks on leaves, stems and soil. The surface of the leaf is covered with holes, the stems eat up and fall. | Sprinkle the soil with lime, ash or salt |
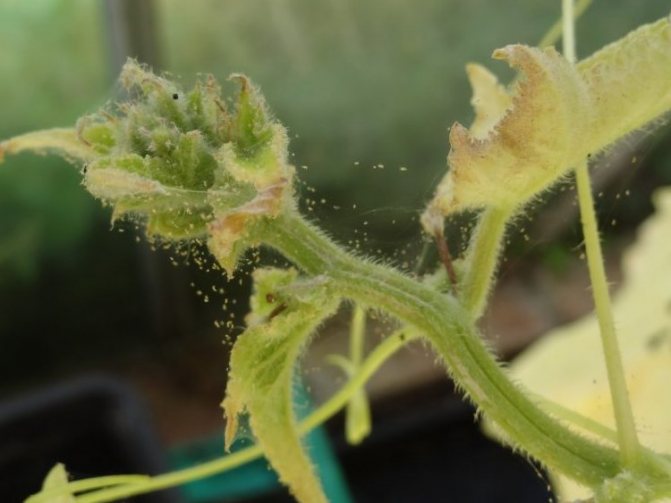
| Spider mite | The leaves are entangled with a cobweb, under which there is a colony of small insects - mites. | Treated with a solution of ash and laundry soap |
| Thrips | They gnaw the leaves, suck out the juices. | Not |
Photo gallery: diseases and pests of the Siberian garland F1 variety


Cucumber leaf affected by peronosporosis Cucumber cluster affected by aphids Thrips and their larvae


Cucumber leaf with spider mite colony


The slug eats the leaves


Slug eggs
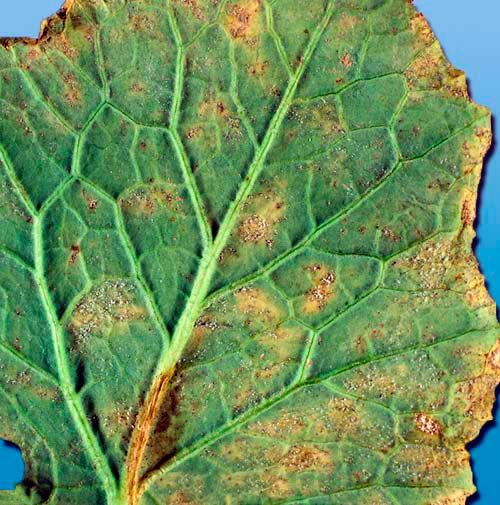


Gray spore bloom on the back of the leaf
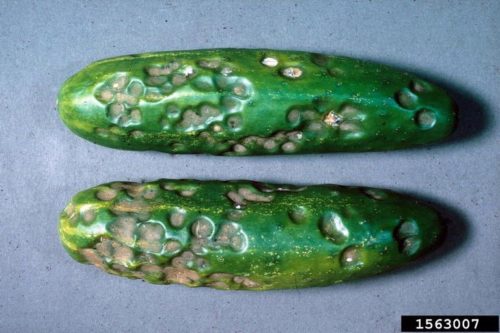

Anthracnose-infested cucumber
Applying chemical methods of protection as prophylactic agents, do not forget that these are contact-intestinal poisons, therefore, fresh they pose a danger to all living organisms. Their use should be strictly regulated and carried out according to the schemes proposed by the manufacturer.
Table: chemical treatment
| Cucumber development stages | Disease, pest | A drug |
| 3-4 sheet | Peronosporosis | Quadris 6 g is diluted in 5 liters of water or Previkur Energy 1.5 ml per 1 liter of water |
| 6-8 sheet | Peronosporosis, aphids, spider mites | 6 g Topaz, 25 g Ridomil Golda, package Vertimek 018 EC are added to 5 liters of water; or Allet 25 g per 10 l of water and Confidor 1 g per 10 l of water |
| 10-12 sheet | Peronosporosis | Ridomil Gold 25 g per 10 l of water or Previkur Energy |
| Budding and flowering | Peronosporosis | Quadris or Infinito 12 ml per 10 liters of water |
| The beginning of fruiting | Aphids, peronosproz, anthracnose | Infinito + Confidor or Quadris Actellic 12 ml per 5 l |
| Fruiting | Peronosporosis, anthracnose | Infinito or Quadris |
The waiting times between processing and the beginning of fruit collection must be respected. Failure to observe them can lead to fatal consequences.
Harvesting and storage
The high ability of the variety to bear fruit requires a careful approach to harvesting from the gardener, which is removed once a day, and with a very large harvest - 2 times. Fruits that have reached 8-9 cm are considered ripe. Leaving the cucumbers for a long period, you do not risk getting overgrown fruits, but there is a threat of continued fruiting. Greens not collected in time dull the formation of new cucumbers.
The fruits of the Siberian garland can be stored for up to 10 days, in basements at a temperature of 7 to 10 degrees and a humidity of 75–90% - up to two weeks. Well transported, perfect for preservation and fresh consumption.
Advantages and disadvantages
- The cucumber variety Siberian garland has a whole range of advantages, among which gardeners note:
- early ripening;
- self-pollination (there is no need to artificially pollinate the plant);
- resistance to low temperature indicators;
- high resistance to many ailments and parasites;
- excellent product performance;
- high yield rates;
- good taste;
- versatility in application: fresh, for canning and salting;
- suitable for growing in regions with different climatic conditions.
- Since the variety was artificially bred by breeders, it is practically devoid of disadvantages. Those who are engaged in its cultivation note the following disadvantages:
- high cost of planting material;
- the need to comply with the basic rules of agricultural technology to obtain a stable, high yield;
- inhibition of the development of new ovaries in case of untimely harvesting.
Testimonials
I planted a Siberian garland in 2014, and also bought into super-yields. My yield was no higher than that of the rest of my cucumbers. In the Siberian garland, 3-4 pieces grow from the bosoms at the same time. ovary. In the picture, the cucumbers are pimply, but in fact they are smooth. I don't like those like that.I liked the taste: the skin is thin, not "oak". As a salad variety - not bad. But for the salad I plant Mamen's favorite from Gavrish, I like the taste and the PRICE is much cheaper than that of SG. I don’t want to try the rest of their super-yielding varieties.
Natalia X
Pluses: A very productive variety of cucumbers. Disadvantages: price. All oh-very good afternoon. I would like to introduce you to very good seeds of cucumbers "Siberian Garland". Last year, I accidentally saw these seeds on the counter of the Sadovod store. I must say right away that they are quite expensive, 85 rubles per bag, which contains only 5 pieces. I am a rather economical person, and I already have varieties that I completely trust, but my hand itself reached for a bag of seeds. Summer in the Urals is pretty lousy, and the past was so very bad. My tested seeds, which were also planted by me, did not produce the harvest that I expected. But the new seeds just made me happy. If not for them, I would have been left without cucumbers for harvesting for the winter.
The variety is very early ripening, self-pollinated. The cucumbers are small, do not taste bitter. There is no emptiness in them, at first I cut off the ends to check, then I stopped. These are gherkin cucumbers, they do not outgrow, for those who like to make preparations of just small cucumbers. All 5 seeds have sprung up, 4 I led in one stem, but I decided to start 5 in two. Better still grow in one stem. These seeds are hybrid, so this year I had to buy them again. If you see such seeds on the counter of the store, take them, do not hesitate. You will not confuse this bag with anything.
Curious Barabara
I also bought a Siberian garland, however, twice cheaper, at 75 rubles. Last year, my bunches grew (I don’t know the varieties, I bought seedlings, because I bought a house late, I didn’t have my own), they proved to be excellent. 30 not 30, but 10–15 cucumbers are always on the bush :) No more than 3 grew in one bosom. I only grew 6 bushes, of which 3 were bunches, enough for both “eating” and pickling.
Lyubov Nikolaevna
The huge popularity of the variety due to its high yield is also confirmed by its wonderful taste. And the ability to breed in latitudes with a cold climate makes it simply indispensable for harvesting for the winter and even for additional income.
Harvesting, storage and use
The collection of cucumbers of the Siberian garland, as a rule, is carried out one and a half months after disembarkation, at the end of July. The fruits are harvested every day or every other day, without allowing longer intervals between harvests. It is better to carry out this event in the morning or in the evening, when the cucumbers contain the maximum amount of moisture. The fruits must be carefully cut with a sharp knife, leaving a small tail of a few centimeters. You cannot pull, pull and twist the cucumbers so as not to damage the plant.
You will be interested to learn about ways to increase the yield of cucumbers.
It is recommended to put the plucked fruits in wooden or plastic boxes and store them in a dry, cool place, at constant temperature values of + 7 ... + 10 ° С. The maximum storage period is 14 days. It is also allowed to store the crop in the refrigerator, in open bags. In this form, the fruits are able to maintain their presentable appearance and taste for 7-10 days.


The hybrid is great for fresh consumption or for preparing preparations for the winter: pickling, pickling, sourdough. Siberian garland F1 is one of the most popular cucumber hybrids today, with practically no flaws. If you follow the simple basic rules of agricultural technology, even a novice gardener will be able to get a large harvest of tasty, juicy and extremely useful fruits from a small plot.





































