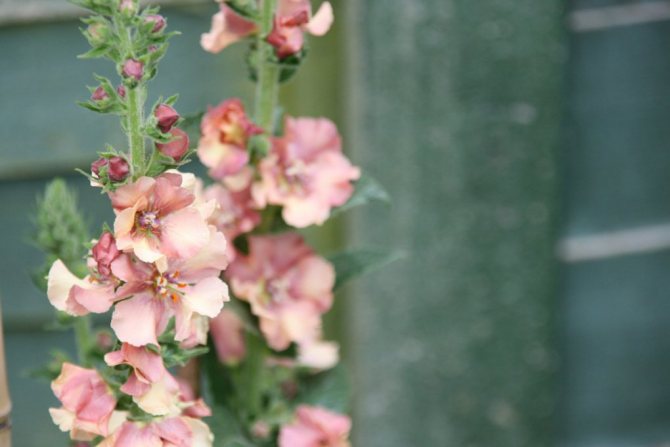
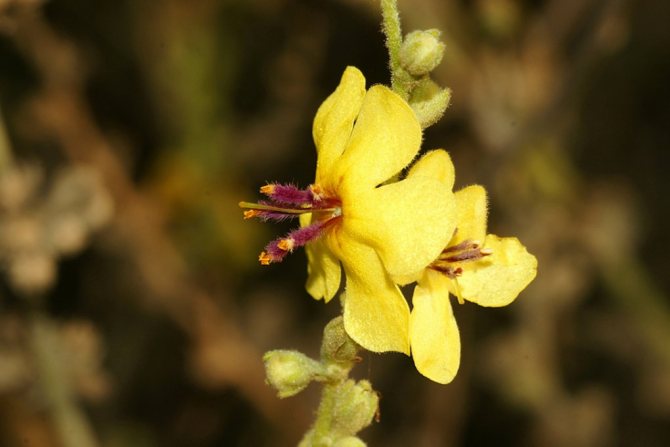
The royal scepter mullein, the cultivation of which is not difficult, has a lot of useful properties. In addition to the healing effect, the composition of verbascum in combination with salvia will become a real decoration of the flower bed.
Compliance with the rules for caring for a mullein will allow you to grow healthy plants that will delight you with lush flowering all summer.

How to recognize a mullein in the wild: a brief description
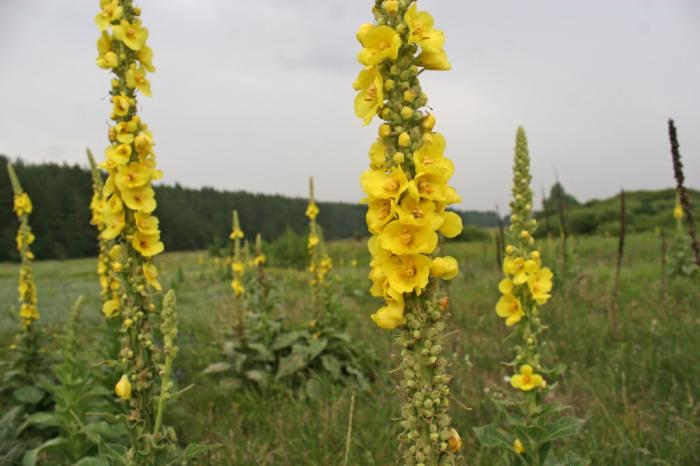
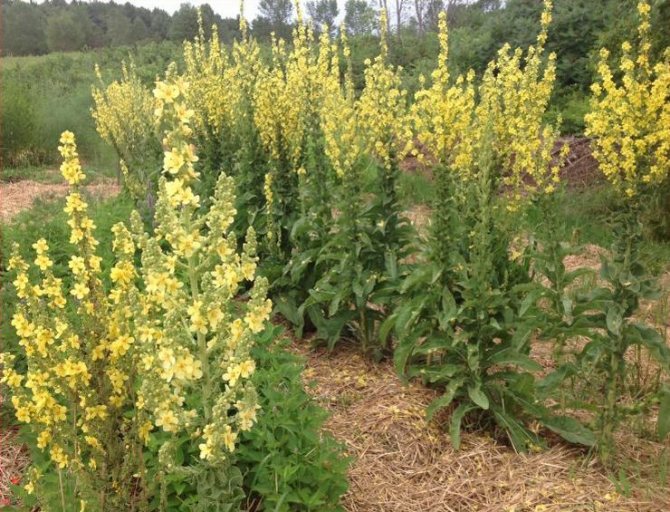
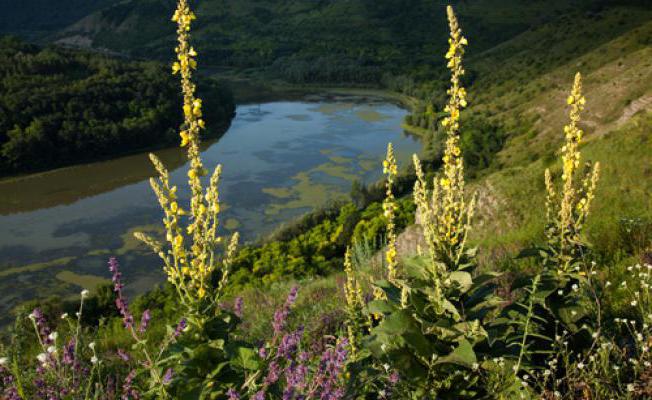
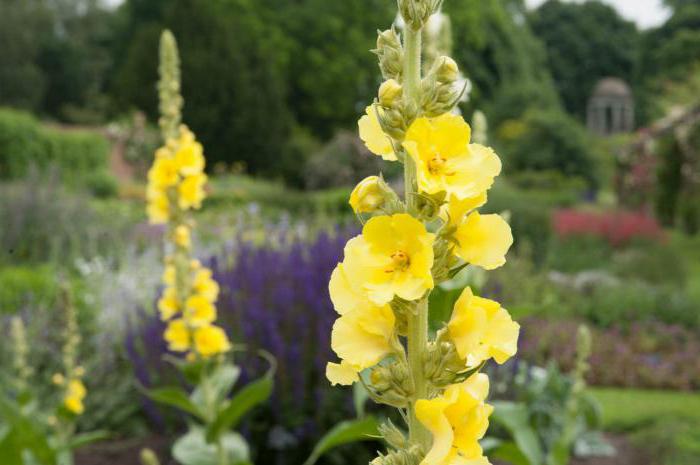
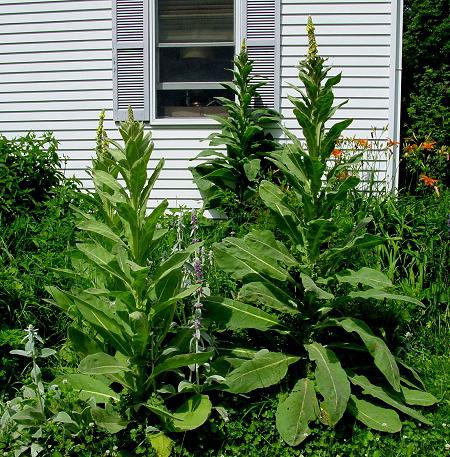
All varieties of this herb belong to the Norichnik family. The scepter-like mullein is a wild plant that has other unofficial names (bear's ear, Mary's candle, royal scepter). The grass can be up to two meters high. Mullein grows mainly in sandy soil. It is most often found on forest slopes that are bathed in sun for most of the day.
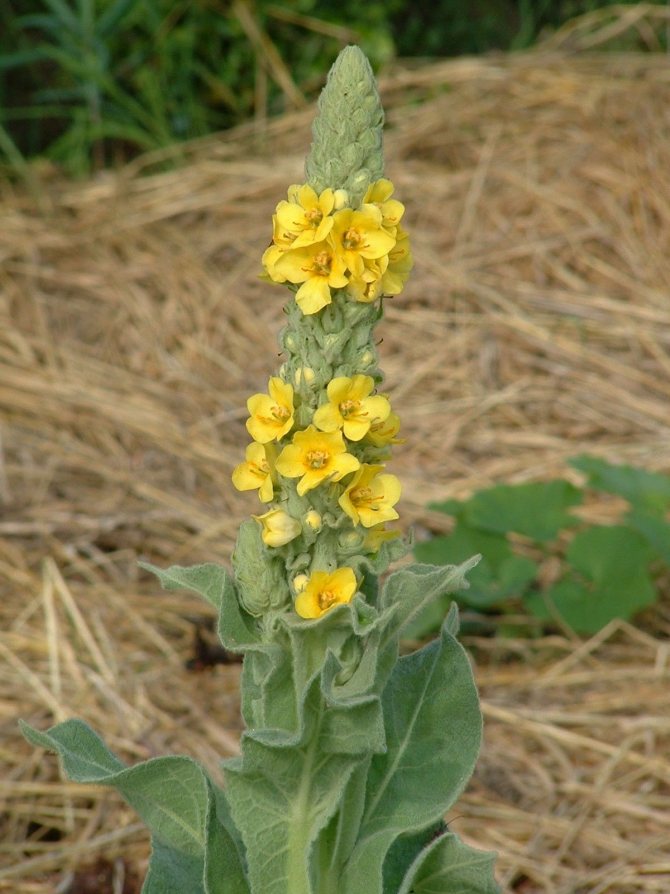
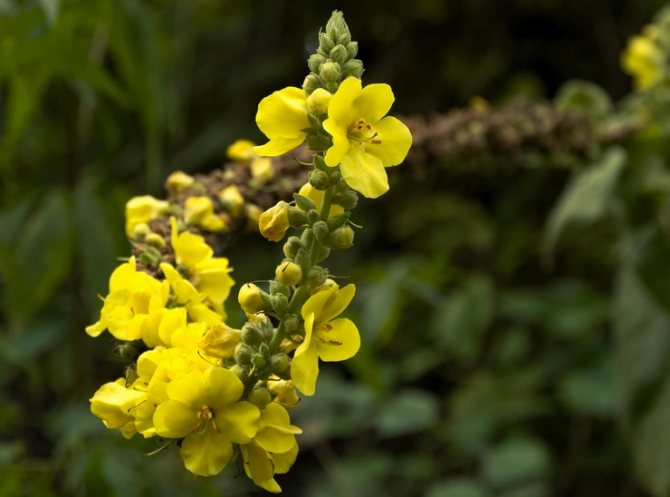
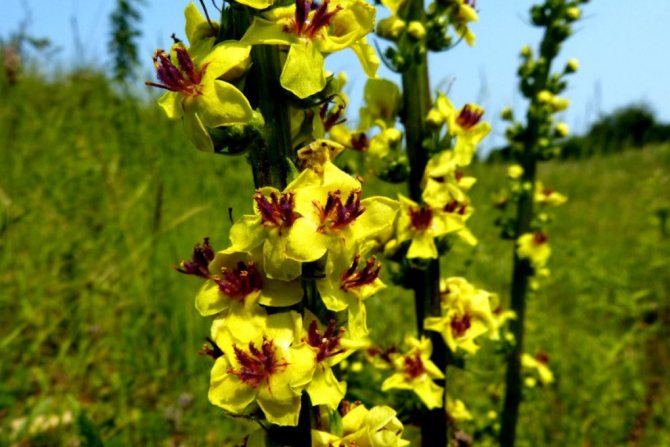
If you look closely at the photo of the scepter mullein, it is easy to see that it blooms with yellow one-day flowers.


They are collected in inflorescences and resemble spikelets. During the flowering period, which falls in early June - early September, traditional healers try to collect the maximum number of flowers. Nevertheless, other parts of the plant (foliage, root, trunk) are considered valuable for medicinal purposes. They are used in traditional medicine. In official pharmacology, only flower corollas are used for the production of drugs.
Views
There are more than 240 varieties of mullein, but in our country you can find only 6-8 varieties of the plant. These species can adapt perfectly to our climate. Below are the species of verbascum found in our latitudes.
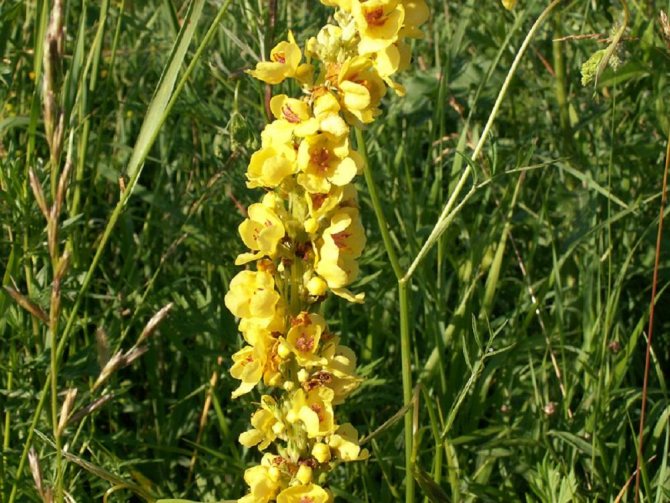
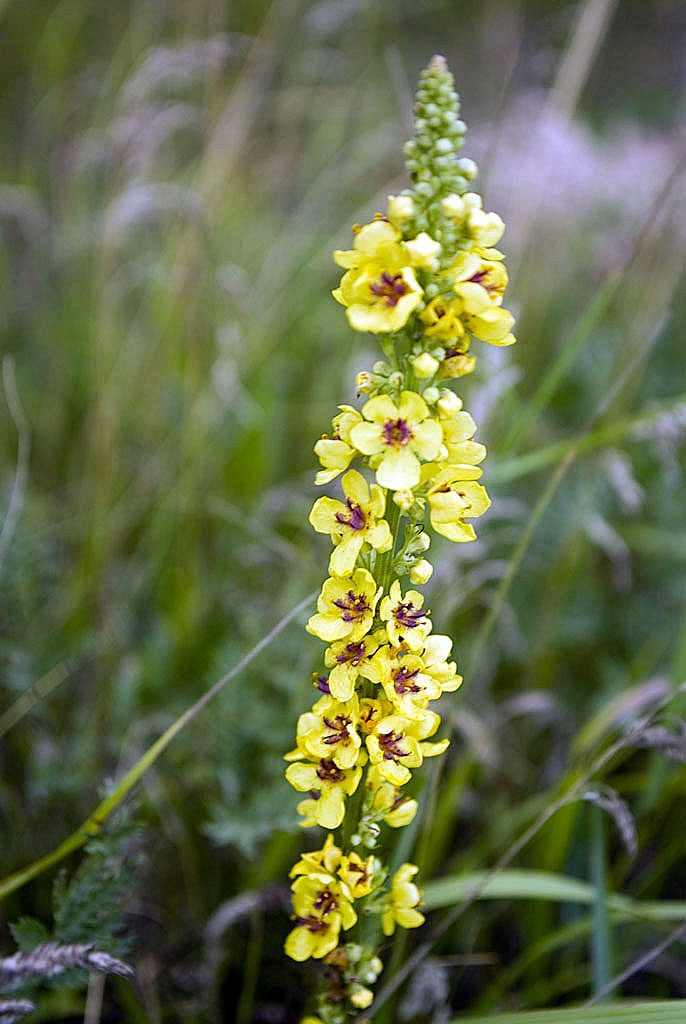
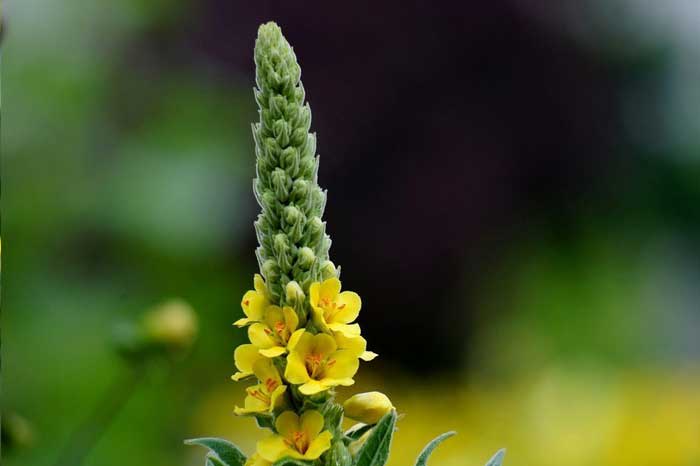
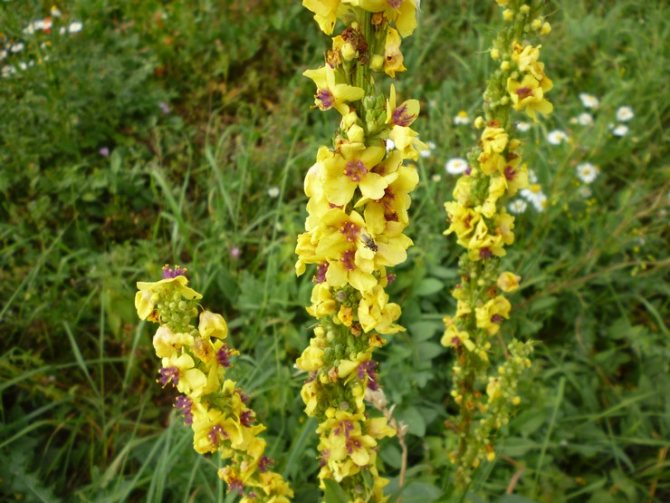
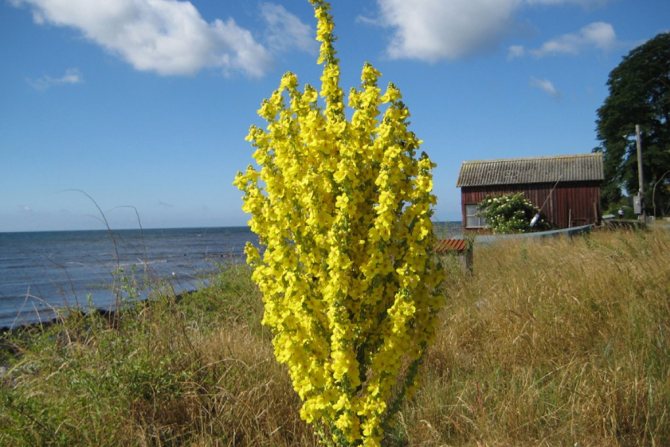
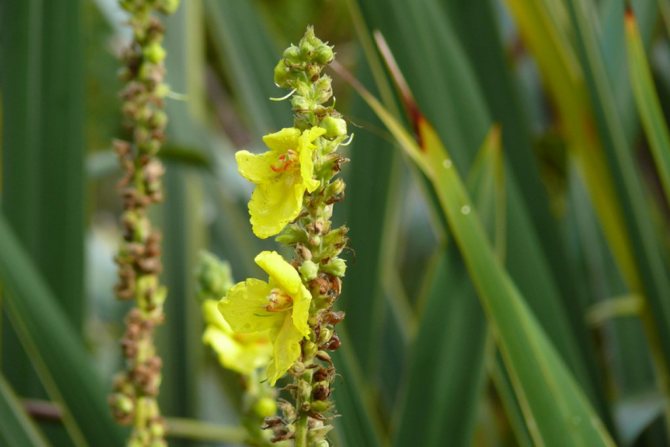
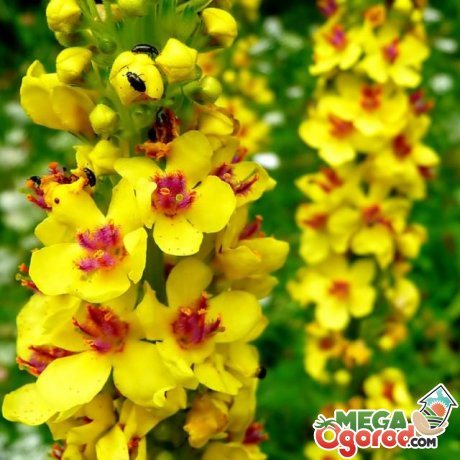
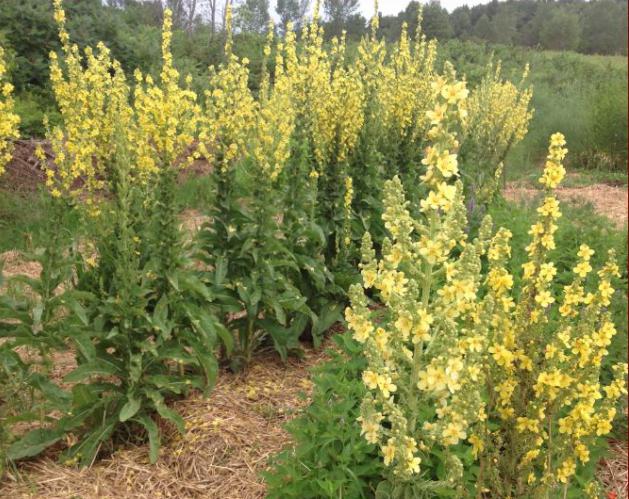
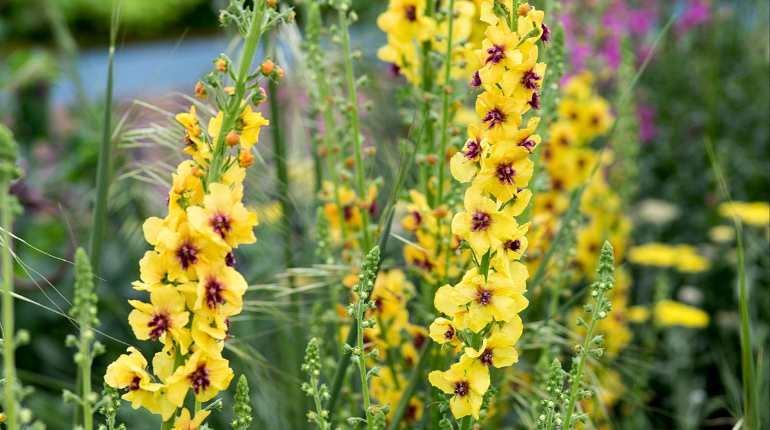
- The scepter (densely flowered) mullein. The height of the ornamental culture reaches 20-110 cm. Thick erect stems are densely covered with leaf plates. The lower foliage is oval in shape, reaching 15-35 cm in length. The upper leaf plates are much smaller. Their length does not exceed 10 cm. Long spike-shaped inflorescences are dotted with bunches of flowers, painted in a yellow palette. The inflorescences resemble a golden royal scepter. Each of the corollas is 5 cm wide. Fresh flowers have an amazing delicate aroma. Dried inflorescences are endowed with a pronounced honey smell.
- Common mullein (bear ear). Any part of the culture is densely pubescent with long silvery hairs. The foliage is colored dark green. Leaf plates are concentrated along the entire length of the shoots. At the very top of the shoot, there is a short inflorescence that has the shape of a spikelet. The length of the lower petiole foliage reaches 16-30 cm. The size of the green mass in the upper part of the stem is much smaller. Foliage shrinking upward resembles the outline of a cone from afar. A large number of small flowers form an inflorescence. The diameter of small flowers barely reaches 1.5-2 cm.
- The black mullein, whose height reaches 55-115 cm, is distinguished by erect stems. Large leaves are concentrated from below in the area of the third part of the shoot. The lower petiole foliage has an ovoid or heart-shaped shape. The length of the leaf plates reaches 20 cm. Long inflorescences are covered with bunches of small yellow flowers. The presence of brown spots can be noted near the base of the petals.Purple villi adorn the stamen columns.
- Medicinal mullein. Each of the stems, the height of which can exceed 120-140 cm, is densely covered with leaf blades. Long inflorescences, located in the upper region of the stems, branch out into several shoots. Each part of the perennial is dotted with thick felt fibers. The length of the oval leaves exceeds 15-20 cm. The flower petals are long and soft to the touch. Flowers are collected in groups along the entire length of the inflorescences. The anthers are colored bright red.
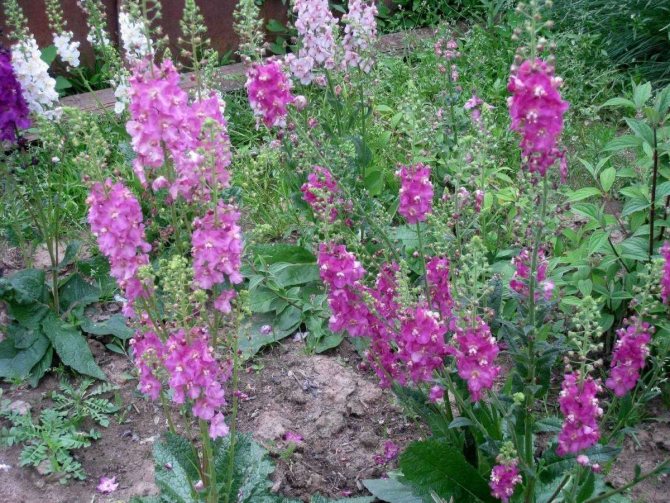
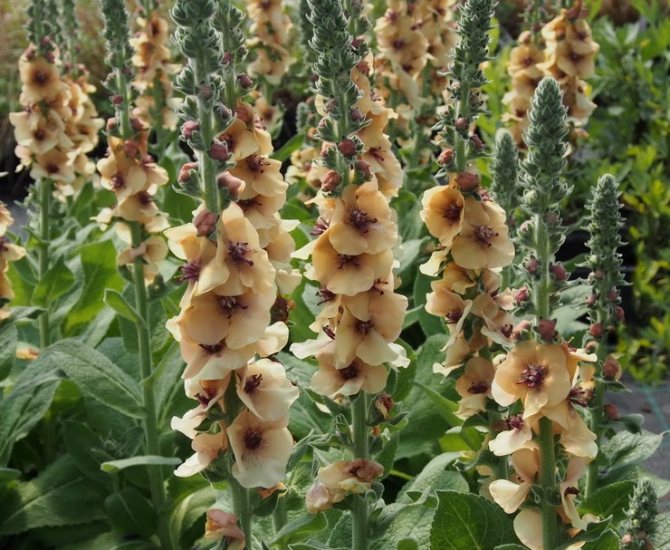
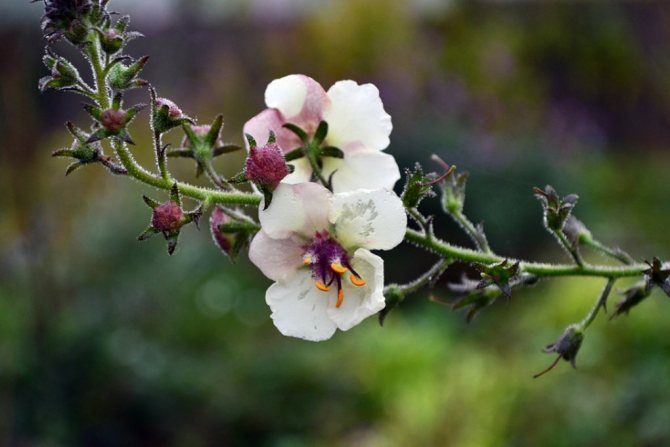
- The hybrid mullein is a decorative species that breeders have obtained through interspecific crossing. Large flowers are colored in various shades. The height of the shoots, depending on the variety, can reach 50-170 cm. Among the best hybrid species of verbascum, it is worth highlighting Mont Blanc, Pink Domino, Jackie and Herry Helen.
Why is this herb used in medicine?
It is not difficult to argue for the need to include the scepter mullein in the manufacturing process of medicines. The chemical composition of herbal fibers contains many valuable and useful substances for the human body:
- Sahara;
- flavonoids;
- gum;
- saponin;
- carotene;
- ascorbic acid;
- coumarin;
- essential oils.
In addition, mullein fibers contain a lot of mucus and mineral salts. This complex of chemicals is involved in most of the natural physical and biological processes of the human body.


It has been proven that mullein has a number of healing properties, affecting various organs and systems. The plant has the following types of therapeutic effects:
- hemostatic;
- antispasmodic;
- astringent;
- expectorant;
- anti-inflammatory;
- anticonvulsant;
- pain relievers;
- diuretic;
- antiseptic;
- sedative.
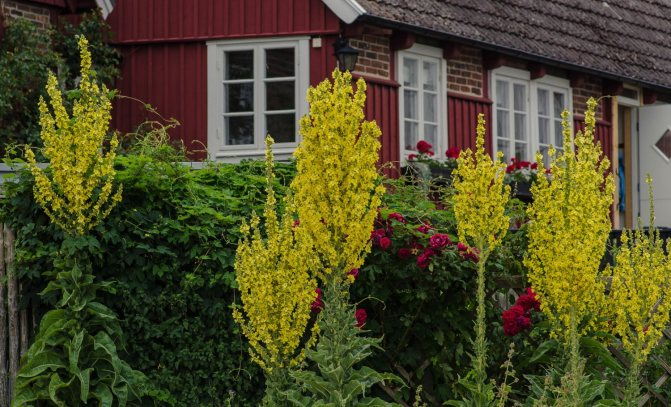
Application in landscape design
Blooming spikelets of decorative culture attract the attention of even the most sophisticated grower. Landscape designers use the mullein for planting in small groups on the lawn. Verbascum is also actively used in decorating flower beds on which bulbous perennials are planted. Mullein is ideally combined with salvia, anaphalis, stachis, catnip, orchis.
Luchinnik is an effective medicinal plant that not only benefits the human body, but also decorates the design of the local area. An unpretentious culture can decorate any flower bed.
Watch a video about these beautiful flowers:
The beneficial effects of mullein decoction on the body
Internal use of the scepter mullein in the form of a tincture or decoction can have a strong diuretic effect. This plant is also used for infectious diseases of a fungal nature of origin, since its components adversely affect the microbial microflora. The version of the vasoconstrictor properties of the mullein has not yet found one hundred percent confirmation by researchers. However, this does not in the least interfere with the use of the plant for the treatment of ulcerative diseases of the gastrointestinal tract. Mullein has an enveloping effect on the mucous membrane of the organ and has a wound-healing effect. Of course, it is hardly possible to heal an ulcer with the help of a herbal composition alone, but in combination with conservative methods of traditional treatment, it is possible to accelerate the dynamics of recovery.
Mullein as an ornamental plant
Mullein has the ability to hybridize when cross-pollinated. In nature, mullein species rarely intersect, but in floriculture in an area with more than one type of plant, this cannot be avoided. With seed reproduction, non-standard shoots appear, species differences are blurred. If you want to preserve varietal traits, use the vegetative method by harvesting root cuttings.
Gardeners prefer to call the mullein - verbascum. Garden forms have lost their medicinal properties, but they continue to possess many excellent qualities.Verbaskum is a perennial that is not demanding on soil and watering. On fertile soil, it goes into greenery, the flowers are not so spectacular, it may not emerge already in the second year of life. Flowers can be exotic shades, bloom during the summer months, when the primroses have departed, and the autumn bulbous flowers are still far from blooming. The size of the plant allows the use of verbascum, creating the desired architectural forms, combining with other plants. The honey smell attracts insects, creating a pleasant revitalization.
Using the plant for colds
The medicinal properties and contraindications of the scepter mullein often become a subject for discussion in narrow circles of homeopaths and representatives of official medicine. Some are sure that this herb is absolutely safe and can be used at any age. Others insist on the presence of toxic elements in the stamen and calyx of the plant.
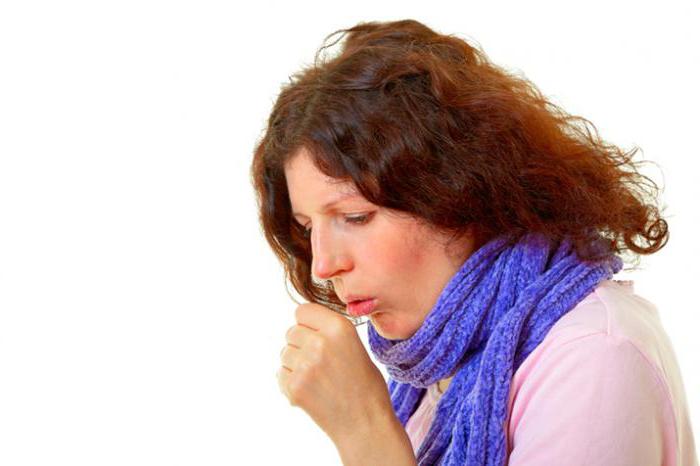


The only thing that no one has any doubts about today is the content of flavonoids in the fibers of the herb. These trace elements are used to treat diseases of the respiratory tract, oral cavity, esophagus, nasal mucosa. With a dry cough, flavonoids are indispensable - they help to thin out phlegm and contribute to its early elimination from the body. In turn, due to the thinning and discharge of sputum, it is possible to remove the swelling of the throat, eliminate painful spasms in the bronchi.
In most cases, mullein is used for colds accompanied by:
- runny nose;
- cough;
- hoarseness of the vocal cords;
- laryngitis;
- pleurisy.
The essential oils contained in mullein have a beneficial effect on the tissues and mucous membranes of the respiratory organs, improving the flow of mucus and relieving inflammation. Decoctions are used for tuberculosis and pulmonary emphysema, whooping cough and shortness of breath caused by an allergic reaction, bronchial asthma. Exacerbation of chronic sinusitis is an indication for the use of herbs: with its help, the sinuses and nasal passages are washed several times a day. To gargle with laryngitis, sore throat and pharyngitis, use a tincture of flowers and leaves of the scepter mullein. The plant eliminates perspiration, sore throat, swelling.
Collection and storage
In the preparation of folk remedies used:
Flowers
Corollas together with stamens are harvested in dry, clear weather. Each flower lives only one day, so even one plant can be harvested with small, but daily, harvests. We do not take the withered, unopened and fallen to the ground. We dry in a dark dry place, 1 cm layer. Ultraviolet light, like moisture, negatively affects the raw material during drying, the corollas become dirty brown and lose their medicinal properties. Flowers are ready in about 5 days. They become brittle, sweet, with a honey aroma. We store them in tightly closed glass or tin cans.
Leaves
We harvest before flowering, or at the same time as the corollas. Dry in the shade or outdoors. The leaves are felted, gray-green, bitter in taste, slimy. Storage is possible both in jars and in fabric bags.
Root
Dug out in the fall, after the death of the aerial part, or in early spring, before the first shoots. Then the maximum amount of active substances is concentrated in it. We clean it from the ground, rot, wash it in cold water, cut it, dry it.
The shelf life of raw materials is up to 2 years with proper storage.
The use of mullein is recommended in the following cases:
- inflammatory processes in the oral cavity, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, intestines;
- tuberculosis;
- flu;
- cold;
- whooping cough;
- bronchitis;
- cough;
- dyspnea;
- bronchial asthma;
- atherosclerosis;
- hemorrhoids;
- purulent acne;
- lichen;
- eczema;
- burns;
- cracks on the lips, hands, feet;
- urolithiasis disease;
- kidney disease.
Traditional medicine recipes
Important: it is necessary to thoroughly filter the herbal infusions before use, the villi can irritate the stomach and intestines.
Powder
Dry mullein flowers are ground into powder. Effective for bedsores, wounds and ulcers.
Infusion of flowers for diseases of the upper respiratory tract, bronchitis, whooping cough
2 tbsp. spoon mullein flowers pour a glass of boiling water for 5 hours, drink, be sure to filter. It has anti-inflammatory, expectorant and analgesic properties. Drink 1/3 cup 4 times a day.
Tincture for rheumatism, sciatica, arthritis
2 tbsp. spoon flowers of the scepter mullein pour 200 grams of vodka. Insist in a dark place for 3 days. It is recommended to rub the sore spots. Can be used for neuralgia.
Ear pain oil
2 tbsp. pour spoons of whisk with 100 grams of oil, preferably olive oil. We keep the container in a sunny place for 30 days, shaking regularly. Then we filter, put it in the refrigerator. The resulting oil has disinfecting properties, cures eczema, stomatitis.
Sedative at night
1 tbsp. We keep a spoonful of mullein flowers and a glass of boiling water in a water bath for 10 minutes, cool, filter with squeezing out the raw materials. We use the infusion warm at night, adding a spoonful of honey.
The use of mullein in the treatment of hemorrhoids
- Bath infusion for hemorrhoids:
Bring 0.5 cups of corollas and 0.5 cups of root in 5 liters of water to a boil, cool to an acceptable temperature. We filter the solution, pour it into a basin, convenient for a sitz bath. We take a bath for 10 minutes. 7 such procedures are recommended, with pauses of 3 days.
- Infusion for hemorrhoids:
1 tbsp. pour a spoonful of corollas of the scepter mullein with 300 grams of boiling water, insist in a thermos for an hour. Strain. 3 times a day, after meals, 1/3 cup. Duration of admission - according to health, maximum - two weeks.
- Suppositories for hemorrhoids, cracks and bleeding:
- We soften 100 grams of butter in a water bath.
- Add: 1 tbsp. spoon of mullein flowers, 1 tbsp. a spoonful of chamomile pharmacy, 1 tbsp. spoon of toadflax ordinary. We keep an hour in a water bath, stirring occasionally.
- Leave to cool, covering with something warm.
- We heat in a water bath, filter, squeezing out the grass.
- Heat again in a water bath, adding 10 grams of beeswax.
- Pour into a shallow container, form candles as it cools and put them in the cold.
Candles are placed at night, after a bowel movement.
General recommendations for use
- the root of the scepter mullein is used as a diuretic for urolithiasis, gout, chronic cystitis;
- leaves scalded with boiling water are applied to the affected skin - burn, frostbite, wound. In addition, leaves boiled in milk can be used as applications;
- with a decoction of mullein leaves, you can rinse your head - with dandruff, alopecia;
- baths with the addition of mullein infusion are useful for diathesis;
- apply a compress from a decoction of a mullein to a place covered with purulent acne;
- ointment from ground mullein flower and water heals cracks on the heels and lips.
When treating with the help of medical fees, it must be remembered that even if it is not a drug, almost any herb can be harmful under certain conditions and in case of an overdose.
Decoctions, infusions, ointments prepared on the basis of medicinal herbs must be made from high-quality collected and stored raw materials in compliance with the recipe. Self-medication is unacceptable. If you feel unwell, competent diagnosis and consultation with a doctor are necessary.
Traditional medicine recipes are an additional or preventive treatment. The compatibility of herbal medicines with mainstream medicines should be discussed with your doctor or herbalist.
Treatment of blood vessels with grass bear's ear
Folk healers are sure that the skeleton mullein can be used to treat hypertension, atherosclerosis. Allegedly, the grass helps to expand blood vessels, make their walls more elastic and stronger.


There is no official confirmation of this property of the mullein yet, but the followers of this version are sure that it is possible to lower blood pressure using the tops of the plant brewed in boiling water. The course of treatment for hypertension and atherosclerosis is 30 days. For prophylaxis, the broth is taken every 3 months for two weeks.
Gallery: mullein plant (25 photos)
Treatment of skin diseases
In fact, it is impossible to list all the diseases in the treatment of which the scepter mullein can be used. For example, in France, the plant has received the greatest prevalence in the treatment of chronic skin diseases. A decoction of mullein is drunk and applied externally in the form of compresses and lotions for psoriasis, dermatitis, eczema. To prepare such a potion, you will need 1 tbsp. l. dry flowers and a glass of water. The raw materials are poured with water and sent to the fire, bringing to a boil, after which the contents are infused for an hour. Strain before use. Take an infusion of 3 tbsp. l. morning, afternoon and evening after meals.

If you systematically use the tincture as a compress, it can be used to cure fungus, lichen, mycoses, candidiasis of the skin and mucous membranes. Mullein also has cosmetic properties: it is regularly rinsed with a decoction of the head, which allows you to get rid of seborrhea and dandruff.
External use of the medicinal herb will benefit patients with purulent wounds, ulcerations, boils. Mullein is an excellent alternative to the simplest pharmacy antiseptics for any other skin problems:
- bedsores;
- burns;
- bruises;
- abrasions.
Growing from seeds at home
The plant does not belong to the category of capricious. Abundant flowering throughout the summer is a definite advantage. The presence of a tap root system allows the mullein to extract moisture from the depth. The presence of pubescence on the leaf plates reduces moisture evaporation. The plant can grow both in a sunny area and in a shaded area.
When choosing a place for planting, it should be borne in mind that verbascum will not please with lush flowering on loamy soil. In order to propagate a culture, you need to use seeds. Small seeds are sown in open ground at the end of spring, when the threat of night frosts has passed. The seeds are spread over the bed and lightly sprinkled with a small layer of soil. After the emergence of seedlings, it is necessary to thin them out, leaving only strong and healthy specimens. The distance between plants should be up to 20-25 cm.
Saplings need abundant systematic soil moisture. A year after planting, the plants will begin to bloom. When transplanting a biennial, it is important not to separate the clod of soil from the root system, which will allow the plant to quickly adapt to a new place. Perennial reproduces well by self-seeding.
Note! From the seed collected from one plant, descendants with different colors of flowers grow.
When watering, it should be borne in mind that verbascum does not like swampy soil. Therefore, water is added under the mullein gradually as it is absorbed into the soil. To extend the life of a two-year-old, cut the stems as soon as the flowers begin to dry out. You should not wait for the fruit to ripen. Frequent fertilizing of fertile soil will shorten the life of flowers.


Care features
In order for the plant to bloom for a long time, it is necessary to follow the recommendations of experienced agronomists regarding the care of a two-year-old. Below are the main features of care.
- Top dressing.Before sowing verbascum seeds, it is necessary to add a small percentage of mineral dressing to the soil. After applying the fertilizer, it is recommended to loosen the soil. Organic and mineral fertilizers are suitable for an adult mullein as a top dressing. Top dressing is applied to the root zone.
- Weeding is a necessary item of mullein care. The medicinal plant needs systematic loosening of the soil. Weed grass picks up useful elements and soil and creates additional shading, which negatively affects the development of young seedlings.
- Mulching will have a positive effect on the appearance of the mullein. By sprinkling the soil with sawdust, you can get rid of weeds, saturate the soil with useful elements, and keep the moisture of the earth for a long time. Verbascum is fragrant under similar conditions.
- The removal of flowers is carried out in stages as they wilt. This process slows down the flowering process of the remaining buds and prevents the pulling of forces from the plant. After the culture has flowered, the stems are also cut, dried and used as mulch.
- Cooking mullein for winter. It is necessary to prepare plants for cold weather in October. The root system of the biennial is covered with a layer of sawdust, peat, ash and fallen leaves. The bedding layer should be up to 7-10 cm.
Reproduction
For the purpose of reproduction, the seed method or the method of dividing the bush can be used. Seed material retains germination for a long time. The seeds can be sown directly into the open ground, as the mullein is frost-resistant. In the fields, biennials reproduce by self-seeding. The first shoots appear after 10 days. In the first months, seedlings grow slowly. With proper care, the growth rate increases from 9-10 weeks.
To preserve varietal characteristics, you must use the method of dividing the bush. The process is carried out in September, when the flowering has come to an end. The plant, together with the root, is dug up and shaken off from the earthen coma. The root is cut into 2-3 parts, so that buds remain on each of them. The indicator of the length of each root should be within 5-6 cm. Each division is placed in separate holes. A small layer of sand is poured over the root with the presence of a kidney. Only then can the depression be filled with soil. The distance between the holes should not be less than 35 cm.
Diseases and pests
Mullein is most commonly harmed by aphids and fungal infections. In order to cope with the pest, you should use drugs of the type:
- Actars;
- Anti-mite Max;
- Decis;
- Inta-Vira;
- Golden spark;
- Calypso Spray;
- Fitoverma;
- Tanreca;
- Tsvetolyuksa.
It is very important to accurately observe the dosage of the drugs. As soon as signs of aphids are found on the plant, processing should be started as soon as possible.
Note! When spraying flowers, it is unacceptable to get the solution on edible plants growing nearby, since the harvest in this case will need to be postponed for a month.
If a fungal infection is found on the flowers, the plantings should be sprayed with Fitosporin-M or Topaz as soon as possible. Fungicidal agents will help to quickly cope with the disease.
Mullein ointment for cracked nipples
Breastfeeding mothers use the plant to treat cracked nipples at the beginning of lactation. I only use it in the form of an ointment, which can be made according to the following recipe:
- Grind fresh flowers of the scepter mullein to a powdery state.
- Add pork fat to the resulting mass.
- For the correct proportion of plant materials, take half as much.
- Heat everything together in a steam bath, strain, then send the mass to freeze in the refrigerator.
- Lubricate small wounds several times throughout the day, and store the ointment itself at temperatures up to +6 degrees for no more than six months.
Growing on the site
The common mullein loves the sun and well-permeable soil, so if you decide to "settle" this doctor on your site by nature, then choose an appropriate sunny place for him.


You can sow seeds in three terms: in early spring, summer and late August. In any of the three options, the mullein will have time to form a rosette before the onset of cold weather. If you plant a plant at the end of summer, then the rosette will be small, but this is not an obstacle to normal further development.
Mullein seeds are small, so they need to be sown with a minimum embedment in the ground, the recommended depth is 1 cm. There is no need to prepare the seed for planting. In order for the seedlings to sprout sooner, the garden bed must be watered, especially in the summer and in the absence of rain.
The first thirty days, seedlings develop very slowly. Caring for them consists in the timely removal of weeds and loosening the soil. Care must be taken not to form a crust on the surface of the ground. If the seedlings are too thick, then they should be broken through, leaving 14-18 plants per row per meter.
It is best to determine the place for the mullein near the fence, where it will be protected from gusts of wind.
Gastrointestinal disorders and mullein use
The scepter mullein is also considered an effective adjuvant for the treatment of gastrointestinal disorders. With dyspepsia caused by infection (dysentery, enterocolitis, enterobiasis) or functional disorders, the tincture of the plant is also taken orally. Mullein is especially useful for diarrhea (has a fastening effect). With the help of the tincture, they wash the eyes with conjunctivitis, wipe the diathetic rashes on the cheeks of babies. Due to the diuretic properties of the plant, its use in the treatment of kidney and bladder diseases is considered very effective. Its trace elements help relieve swelling and pain, eliminate cramps during urination.


The healing properties of the scepter mullein, according to traditional healers, increase if the plant is infused or brewed with milk. Alcoholic tinctures from this plant serve as local chondroprotectors, warming joints, relieving pain in arthritis and arthrosis. To combat external hemorrhoids, it is also recommended to apply mullein lotions, which reduce inflammation and help reduce knots.
Composition and healing properties
Mullein is beneficial due to its chemical composition. It contains many components, including amino acids, macronutrients, essential oils and vitamins. It is used for medicinal and prophylactic purposes. The plant strengthens the immune system and prevents the development of diseases.
The common mullein is popularly called the bear's ear. It includes the following components:
- Mucus. They envelop the sites of inflammation and promote the discharge of phlegm.
- Saponins. They thin phlegm, have a diuretic effect, and prevent the proliferation of cancer cells.
- Glucose. It is a source of energy and vivacity. It strengthens the immune system and normalizes metabolism.
- Carotene. It protects against the negative effects of free radicals, strengthens the immune system.
- Organic acids. They have antifungal, expectorant and astringent properties.
- Ash. It is a natural antiseptic that heals wounds. Ash dissolves blood clots and slows down blood clotting.
- Flavonoids have a beneficial effect on the circulatory and nervous systems.
- Coumarins. They thin the blood and prevent blood clots. Verbaxum is useful for people prone to thrombosis and strokes.
- Tannins. They have bactericidal and astringent properties.
- Essential oils. These components have a beneficial effect on the work of the digestive tract, cardiovascular and nervous systems.
- Alkaloids. It is a natural pain reliever. Alkaloids lower blood pressure.
- Gum. This component is indispensable for losing weight. It normalizes metabolism, digestive tract function and reduces appetite.
- Vitamin C.It has a beneficial effect on the nervous and endocrine systems. Participates in the process of hematopoiesis.
- Iridoids. These substances are useful for people whose body has a predisposition to the formation of cancerous tumors. Iridoids have analgesic, choleretic and immunomodulatory properties.
- Macronutrients - iron, calcium, potassium and magnesium.
- Tannin. It is effective for stomatitis, sore throat.
How to properly collect and store medicinal raw materials?
Taking advantage of the healing properties of the scepter mullein on your own is not as difficult as it might seem. Of course, its preparation is associated with certain difficulties, but the final result in the form of universal medicinal raw materials will compensate for any costs. Knowledge of the rules for collecting a plant and its drying will allow you to preserve the maximum of valuable trace elements and properties. So, what matters in the course of harvesting the scepter mullein:
- It is necessary to collect flowers carefully and carefully, as they quickly lose their natural color.
- Raw materials, which have acquired a gray-brown hue during the drying process, are unusable in the future.
- The optimal period for collecting mullein is June-July. It is advisable to harvest flowers in the first half of the day, after the dew has dried.
- It is advisable to dry it on paper or absorbent fabric, protecting the raw material from the sun and wind, but providing it with high-quality air circulation.
- Dry flowers are saved in a tightly closed jar - the mullein is very hygroscopic, therefore it is able to absorb moisture from the air.
Common mullein
The most common is the common mullein. It is also popularly called the bear's ear. And this is just the beginning of a long list of different names for the same plant. In the nineteenth century, more than forty names of mullein were known. The most memorable ones are the beard of a hare, an Adam's twig, an ice sheet. Due to the hairiness, it was also awarded with such names as velvet, obscure, flannel and many others.


This species, unlike the others, has small flowers. This is why the common mullein is called small-flowered. In European reference books, it is listed as a large mullein, in North America - as an ordinary mullein. This plant is very useful and, one might say, famous. Perhaps this is precisely the reason for such a variety of names.
Are there any contraindications for mullein?
Despite the fact that the herb itself is not dangerous, there are still some precautions for its use. In particular, before preparing medicines from the mullein, it is important to remove all parts of the plant: stamens, petals, leaves, villi, etc.


Strain the drink before drinking - this will prevent the accumulation of toxic substances and irritation of the mucous membrane of the internal organs. Store mullein products, prepared according to folk recipes, should be away from food. Pregnant women should also use the scepter mullein flower with caution. A contraindication to its use can be called individual intolerance.
Restrictions, contraindications
There are no serious contraindications for mullein treatment. Traditional healers claim that this plant is completely harmless. However, it is important to follow the dosage. If you exceed the permissible amount of decoction or oil per day, side reactions may occur.
Professional doctors categorically prohibit pregnant women from using folk remedies based on verbaxum. It is not recommended to use decoctions and ointments from it during lactation. A contraindication to treatment with this folk remedy is an individual intolerance to the components.


If a person is allergic to this plant, then it cannot be used as a medicine.
Some people complain of constipation after consuming verbaxum decoctions.This is due to the fact that it has a bonding property. The feces are getting harder. Therefore, during the period of therapy, it is necessary to drink at least 2 liters of clean water per day. Tea, coffee and other drinks do not count. If constipation persists, see your doctor.
The use of verbaxum is generally safe for health. If you use folk remedies correctly, they will become a worthy alternative to traditional treatment. But in case of severe pathologies, it is worth listening to the opinion of the doctor and not giving up professional medical care. Mullein is used as a complementary treatment. The main therapy should be traditional.
Treatment of hemorrhoids with infusion of mullein flowers


Bear's ear is considered to be one of the most effective plants for hemorrhoids. The herb contains elements that activate the functions of the digestive tract, quickly stop bleeding, relieve inflammation on the hemorrhoids.
Traditional medicine recommends increasing the effectiveness of home medicine with a special laxative diet - introducing light meals based on vegetables into the diet. Step by step recipe:
- Grind the flowers of the bear ear (20 g.).
- Combine boiling water (200-210 ml), flower mass.
- Cover the container tightly with a lid, wrap with a terry towel.
- Insist for 10 minutes, after straining, add bee honey (20 gr.).
Consume 25 ml of the product every three hours. A prerequisite for successful treatment is to warm up the healing liquid before each dose, drink only hot infusion.
Alternative medicine recommends treatment in courses - a month of regular intake of the composition, a week of a break. In case of complications, it is allowed to extend the course of using the infusion - drink continuously for two months, then make an interval.
Mullein bear ear - application
Mullein bear's ear was known as a medicinal plant in the Middle Ages. Flowers, leaves and roots of mullein are widely used in folk medicine in various countries.
Flowers and leaves have an expectorant, emollient, enveloping, anti-inflammatory, analgesic and wound healing effect. Flowers also have the ability to stop seizures.
Infusion of flowers, less often leaves, is used for coughing, hemoptysis, whooping cough, pneumonia and bronchial inflammation, severe rhinitis with lacrimation, shortness of breath, asthma, hoarseness of the voice. Infusion of flowers is also used for diseases of the liver, spleen and inflammation of the stomach and intestines.
The flowers of the mullein bear ear are part of the pectoral expectorants, collections.
Flowers, leaves and roots are used externally. Alcoholic tincture of flowers is used for rubbing as an anesthetic for rheumatic, arthric and especially nervous pains. Powder of flowers is sprinkled with cracks on breast nipples, cuts and wounds, after having lubricated them with carrot juice. The scalded flowers and leaves of the mullein bear's ear are crushed and applied to burns, inflammatory foci and wounds as an anti-inflammatory, analgesic, wound healing agent. An aqueous infusion of flowers or leaves is used to rinse the throat and mouth in case of inflammatory processes. The decoction of the roots is used for sitz baths and washings for hemorrhoids.
The flowers of the mullein, along with the grass of the string, thyme, sage, black currant leaves, pine needles, oak bark and burdock roots, are used for baths against scrofula.
Mode of application.
1) Insist 1 tablespoon of dried mullein flowers for 4 hours in 2 cups of boiling water in a closed vessel, strain, add sugar. Take 1/2 cup 2-3 times a day 1/2 hour before meals warm.
2) Boil 3-4 teaspoons of flowers for 5 minutes in 2.5 cups of hot water or hot milk in a closed vessel, leave for 1/2 hour, strain, add sugar to taste. Take 1 glass warm at night.
3) Boil 7.5 g of mullein flowers and 7.5 g of marshmallow roots in 1.5 cups of water, strain, add 200 g of sugar and boil again until the syrup is thick. Take 1 teaspoon 3 - 5 times a day for coughing in children (E. Yu. Shass).
4) Boil the leaves or flowers of the mullein, chop, wrap in gauze. Use the pads as an analgesic poultice.
5) Insist 50 g of flowers for 2 weeks in 1/2 liter of alcohol or vodka. Use for rubbing into sore spots.
See also:
- Tall mullein - Paniculata mullein - Cockroach mullein
Contraindications to taking mullein
- Pregnancy and feeding (except for cracked nipples and topical application locally).
- Menses (complete prohibition).
- Blood clotting disorders, hemophilia (complete ban).
- Mullein allergy (complete ban).
- Age up to 1.5 years is a complete ban, later the generally accepted doses by age should be taken into account: 1/8 to 3 years; 1/6 to 4 years old; 1/3 to 7 years old; ½ to 14 years old; 2/3 to 25 years old and the full dose over 25 years old, and children should be given only when indicated and as directed by a doctor. Dose coefficients for overweight adults: 80-100 kg - 1.25; more than 100 kg - 1.5 normal dose.
The appointment of a phytotherapist is also desirable when using herbs in the treatment of older ages.
Mullein in pharmacy - dry herb, herb extract
In pharmacies, dry herbal raw materials are sold, which are recommended to be used for the preparation of home medicines. The cost of packaging is from 150 rubles. The herb is sold without a doctor's prescription, but it is better to first undergo a medical examination, consult with a specialist about the advisability of using decoctions, infusions.
The pharmacy also sells an extract of mullein for alcohol (price from 120 rubles), recommended for heart disease, high blood pressure, colds, tuberculous coughs.
It is recommended to take the extract twice a day, the recommended dosage is 20 drops. In case of difficulties with the use of alcohol-containing preparations, an aqueous solution should be used - mix the product with a small amount of water.
The duration of treatment is prescribed by a specialist individually. The duration of the course depends on the general state of health, the degree of development of the disease, the presence of complications.
Treatment of diseases of the gastrointestinal tract (diseases of the liver, stomach, spleen) with infusion of leaves of bear's ear


In case of inflammatory processes developing on the mucous membranes of the stomach, liver, spleen, unofficial medicine is recommended to undergo a course of treatment using an infusion of fresh mullein leaves.
A prerequisite is to first agree on home treatment with a doctor; in case of complications, you will have to use a herbal remedy as an auxiliary therapy. Preparation:
- Cut the leaves of the plant with a sharp knife (20 gr.).
- Steam the green mass with boiled water (300 ml), stir.
- Leave to infuse, to increase the concentration of useful elements, tightly cover the container, wrap with a handkerchief.
- Strain through half an hour, squeeze out the cake using a gauze cloth folded in several layers.
Drink infusion three times a day, 50 ml. If, after the first doses, mild nausea worries, reduce the dosage to 20-25 ml, increase gradually to the required amount.
The duration of alternative treatment is three weeks. If it was not possible to completely cope with the disease, continue using the infusion after a break (after 5-10 days).
Contraindications and side effects of mullein
The use of folk remedies made from mullein are useful for:
- gastrointestinal ailments: gastritis, hepatitis, ulcers.
- atherosclerosis and hypertension;
- respiratory diseases;
- hemorrhoids;
- dermatological diseases (primarily eczema);
- dental diseases associated with a violation of the integrity of the oral mucosa (gingivitis, stomatitis, etc.).
Mullein does not contain hazardous substances, therefore, the use of traditional medicines with its content has practically no contraindications. The exceptions are:
- pregnant and lactating women;
- Small children;
- people with individual intolerance;
- bleeding tendency.
The question of starting treatment with bear ear is strongly recommended to be addressed in conjunction with the attending physician. With any worsening of the condition, the use of the herb should be discontinued.


Use in the garden
Tall plants with such large and beautiful flowers will not go unnoticed in the garden. Especially when it comes to decorative varieties with different colors of petals. Throughout the summer, the mullein will attract insects and birds. It begins to bloom when the primroses have already withered, and later perennials have not yet formed buds. Thus, the mullein fills the pause in flowering. It is important to choose the right neighbors so that the flower garden looks harmonious. They can be orchis, catnip, salvia, anaphalis, sage.
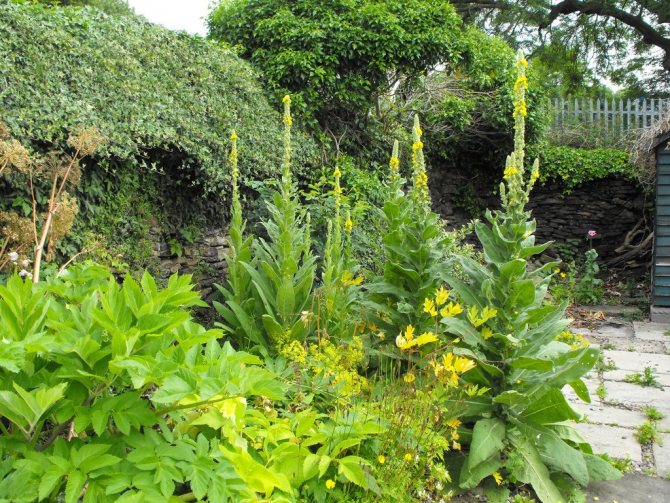


Mullein thickets are also used as a background in the background of the flower bed. It can be planted in small groups in the middle of the lawn, in rockeries or along paths.
Brief description of mullein, growth


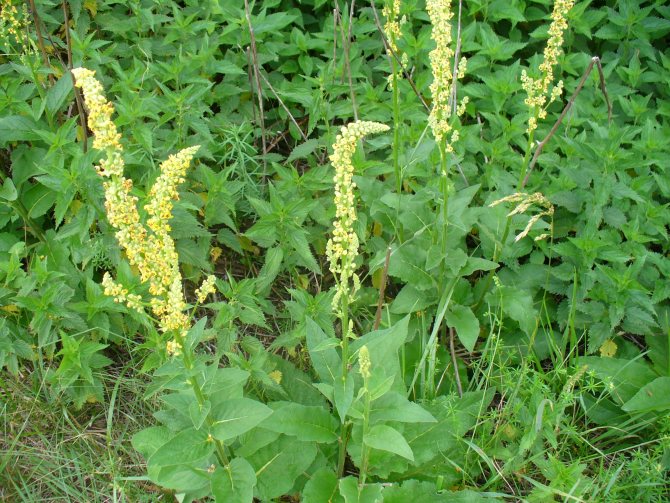
Mullein is a herbaceous biennial, the height of which usually ranges from 50-80 cm. Under favorable conditions, the plant can reach one and a half meters. The stem is straight, the leaves are ovoid, forming a regular rosette at the bottom of the grass. The peculiarity of the bear's ear is a short, hard pile that covers the entire plant (stem, leaves).
Flowers of irregular shape, bright yellow, form a dense inflorescence - a spike-shaped raceme. Flowering begins in the first month of summer and lasts until autumn. At the beginning of September, elliptical capsules-fruits, filled with small brown or black seeds, begin to ripen.
Mullein is widespread in Australia, America, found in New Zealand. The plant grows throughout the territory of the Russian Federation, especially in the European part.
Prefers open places - sandstones, roadsides, river banks. Often the plant is used for decorative purposes for landscaping parks, flower gardens, squares.
Flowering time
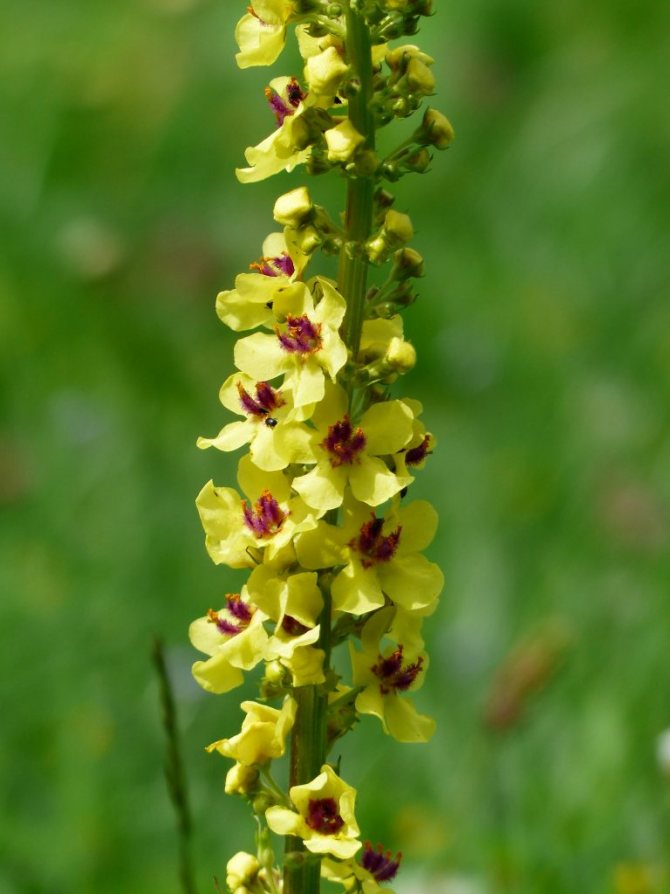
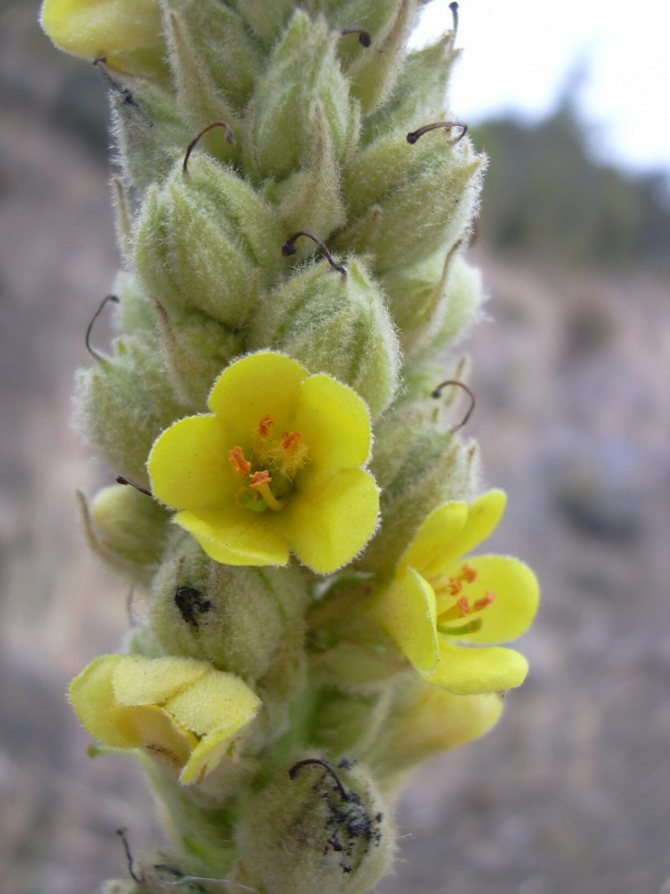
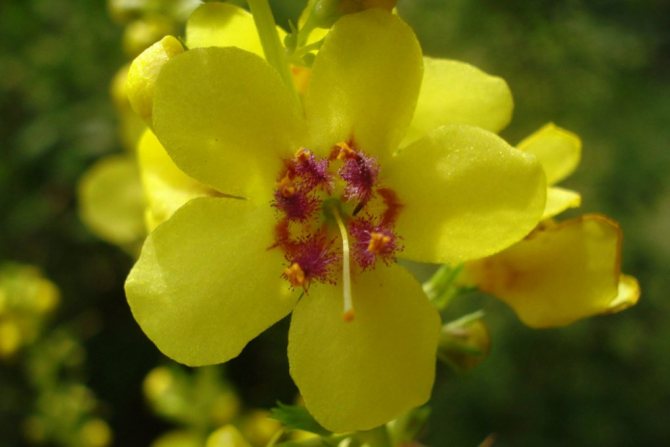
The flower of the common mullein has a bright yellow color. It is very small and delicate in appearance. Here is its structure:
- bract (has a pointed shape in the form of a lancet);
- pedicel (thick and short, adherent to the solid axis of the inflorescence);
- calyx (has pointed lobes converging at the base);
- corolla (fifteen to twenty millimeters in diameter, yellow);
- stamen (there are only five of them, the front two are slightly thicker and longer than the rest);
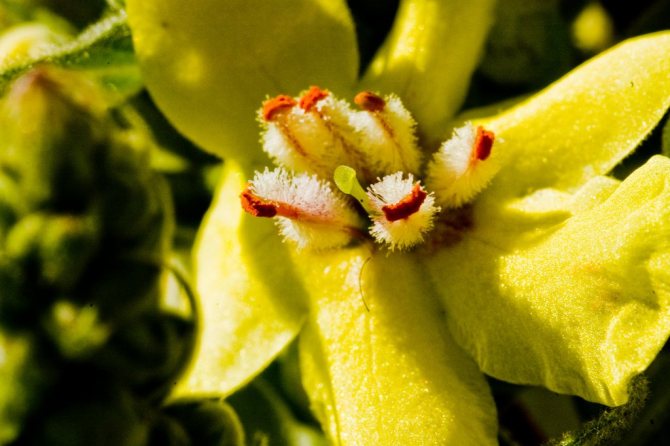
- pistil (in the form of short thin threads).
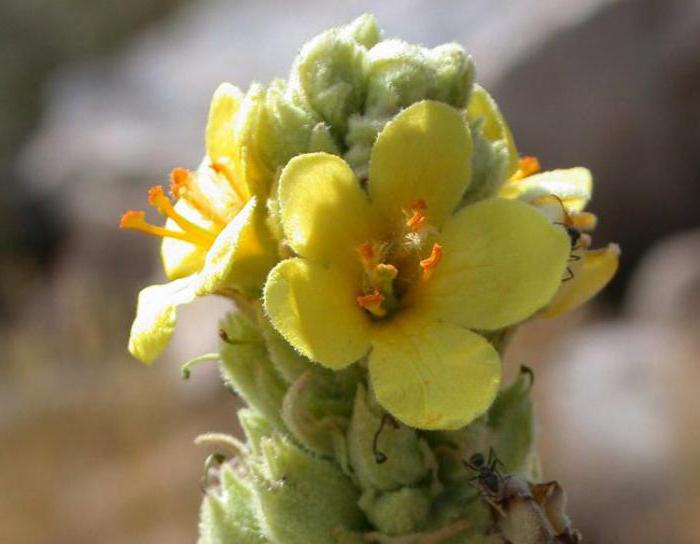


The royal scepter begins to bloom from the second year of life.
Reproduction methods
Mullein propagation can be carried out by sowing seeds or rooting cuttings. The seeds remain viable for a long time and are resistant to frost, so they can be sown directly into open ground. The plant also often self-seeds. Due to the core rhizome, which goes deep into the soil, it is not worth replanting the mullein. Therefore, sowing for seedlings is impractical. In open ground, seeds are sown immediately to a permanent place. This is done in mid-May or later, when the average daily temperature is set at + 13 ... + 18 ° C. Seedlings appear in 1-2 weeks. In the first month, seedlings grow very slowly. Later, they develop rather quickly and do not require much maintenance. Flowering is expected in the second year of life. It should be remembered that the mullein is easily cross-pollinated, so the seedlings can be very different from the mother plants.


Cutting helps to preserve varietal characteristics. Cuttings should be cut after the end of the flowering period (August-September), then the likelihood of successful rooting will be much greater. The main plant with basal shoots is dug up and freed from the ground. The root is cut into several pieces with buds or small shoots.The length of each rhizome should be at least 5-7 cm. The strips are laid horizontally in prepared holes. First, they are covered with a layer of sand 5 mm thick, and on top - with earth to a height of 15-20 mm. A distance of 40 cm must be maintained between seedlings.
Interesting Facts
- Westerners in the United States call the mullein because of its hairiness "cowboy toilet paper."
- Mullein has been considered a magical plant since ancient times.
- According to legends, witches used mullein to prepare witchcraft potions.


- Some peoples believe that the medicinal mullein removes curses and drives away evil spirits.
- Our distant ancestors, having dipped the stem of a mullein in resin, made a torch out of it, which burned for a long time. Translated from German, Koenigskerze is a "royal candle".
- The mullein was used to dye fabrics, and sometimes even to dye hair. Bear ear flowers produced a bright yellow or green color.
Mullein care
Caring for a mullein is not a hassle, even a beginner in horticulture can handle it. In order for the plant to develop normally, an illuminated area, heated by the sun's rays, is selected for growing the mullein. A small shade will not affect the development of the bushes. However, the constant lack of light negatively affects the growth of culture.
The substrate is chosen with a loose structure. Clay soil types must be diluted with coarse sand, gravel and peat. As for the fertility indicator, planting mullein needs moderately fertile soil. Without a transplant, the plant is actively developing for a couple of years. Too nutritious substrate or excess moisture near the rhizome inhibits it and can cause death.
Watering is provided during periods of drought. Water is added in a small amount. Before the next watering, the top layer of the earth should dry out. If the groundwater is deep, the roots will lack moisture. In case of violation of the irrigation regime, rotting of the underground part occurs. The death of the mullein is ultimately inevitable.
The plot with crops of mullein is fed if necessary. A one-time feeding with mineral fertilizers at the budding stage is enough. Fertile substrate does not need to be fed.
A mullein will live much longer if the buds are trimmed before the seeds ripen. Hybrids will re-bloom during the season with early pruning.
What do you need to remember?
To extract the maximum benefit from the mullein, careful observance of the basic rules of alternative treatment, which are recommended to be remembered in advance, will help. The main requirements for a successful impact on diseases:
- do not start taking decoctions, infusions without a preliminary medical examination, the permission of a specialist;
- do not deviate from the requirements set out in the recipe, carefully measure the required amount of the active ingredient;
- follow the rules for taking, do not exceed the required amount of home medicine;
- store independently collected or purchased raw materials out of the reach of children;
- adhere to the rules for storing grass - avoid direct sunlight, proximity to heat sources.


You should also not self-medicate - combine different herbal ingredients or supplement the effect on the disease with pharmaceutical preparations without consulting your doctor. The consequences of such actions threaten with serious disruptions in the work of systems, organs, and severe side effects.
Mullein is a herb that is abundant in useful substances; with the correct use of plant raw materials, it will be easy to cope with even serious ailments.
The main rule of effective impact on the problems of the body is a careful study of the requirements of alternative and official medicine, preliminary medical consultation, compliance with the rules of preparation, use of home medicines.
Botanical description
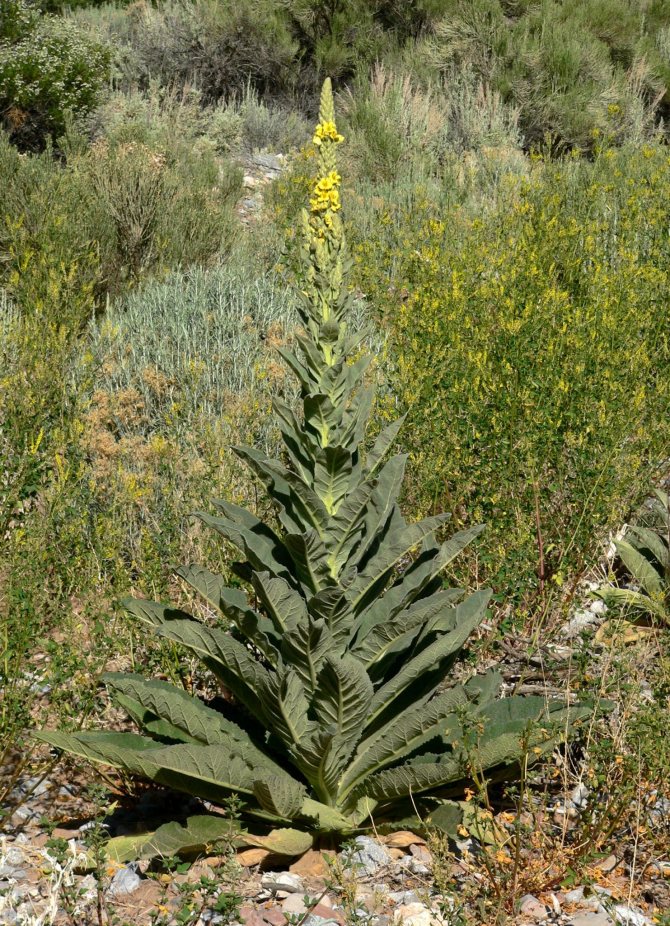
Mullein is a biennial or perennial plant, although annuals are also found in nature.It has a strong tap root and an erect, almost unbranched stem 0.5-3 m high. At the base there is a rather dense basal leaf rosette. The lower leaves have petioles half the length of the leaf plate. Sessile foliage is located higher along the stem. It is attached opposite or in a spiral. The leaves have a solid oval or heart-shaped leaf blade. Their entire surface, as well as shoots and flowers, is densely covered with felt pile. Shoots and foliage are dark green or gray-green.
From the second year of life, a long stem, which is crowned with an inflorescence, develops above the leaf rosette. A flowering ear consists of several tiers of buds. At the bottom there are bunches of 4-7 corollas, and at the top there is a bunch of 1-4 smaller flowers. Corolla diameter is about 2 cm. It consists of yellow drooping petals and is tubular or funnel-shaped. Under the fluffy, wide-open petals, 5 stamens, different in size and shape, are hidden. Flowering continues throughout the summer.
After pollination, a small oblong seed capsule ripens. It is also densely pubescent. Inside are small oblong seeds. Their rough surface is colored yellow-brown.
Useful qualities of mullein, the composition of the grass
Mullein is a herb containing a number of elements, which, with the necessary knowledge, can be easily directed to get rid of serious illnesses. The composition of plant materials contains vitamins, saponins, mucus, glucose, flavonoids, essential oils. The main medicinal properties of bear ear:
- anti-inflammatory;
- cardiotonic;
- diuretic;
- pain reliever;
- astringent;
- calming;
- anticonvulsant;
- vasoconstrictor;
- enveloping;
- regenerating.
Herbal remedies are also used for bleeding, non-healing wounds, and diseases of the digestive tract.


The elements contained in the grass stabilize metabolic processes, inhibit the growth and spread of cancer cells, have a positive effect on the vascular system - strengthen, stimulate blood formation, and increase the elasticity of the walls.
Preparation of medicinal raw materials
Collect, dry and store the flowers of the bear's ear should be, observing all the rules. It is very important that the flowers during harvesting can change their yellow color with a golden tint and become gray-brown. At the same time, most of the healing properties are also lost. So what's the right way to harvest and dry a mullein?
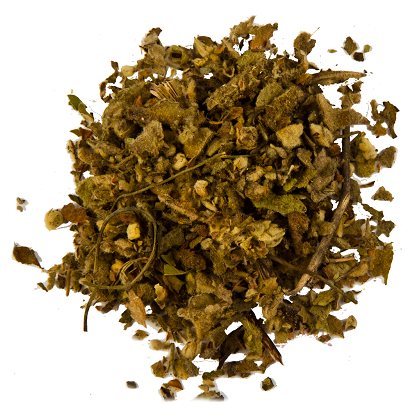


Medicinal fee
Usually, bear ear flowers are harvested in the morning, after 8-9 am, when the sun's rays have dried the morning dew. Accordingly, medicinal raw materials are not collected in rainy or cloudy weather, because the collected wet raw materials will not dry well and may start to rot. Usually corollas and stamens are collected, but it is better not to collect the flower cups themselves.
Flowers should be dried in a well-ventilated room, the air temperature should be 45 - 50⸰С.
After the raw material is dry, it is placed in a glass container with a lid. This is a prerequisite - dry raw materials can very quickly pick up moisture from the environment and begin to deteriorate.
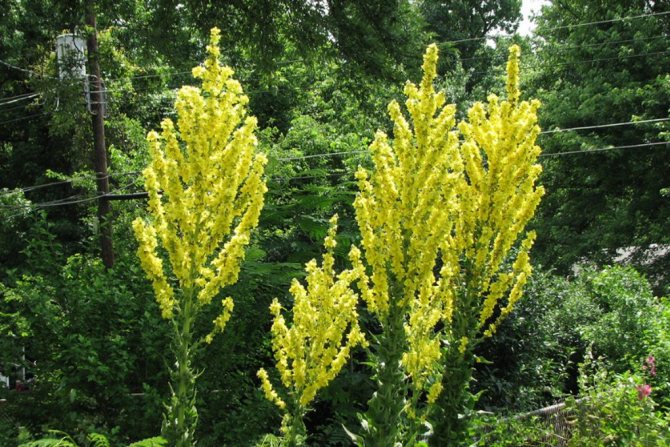
Growing a plant mullein royal scepter
The royal scepter mullein is a biennial plant that grows up to 2 m in height and has a shape similar to a scepter. Small yellow flowers with a diameter of about 1.5 cm are densely placed on the upper half of the stem. They bloom alternately, starting from about the middle of the stem. Thus, the flowering of the mullein occurs throughout almost the entire warm period.
Verbascum leaves are located horizontally above the ground, they are quite wide and pubescent. It has a powerful root system, especially for perennial species.
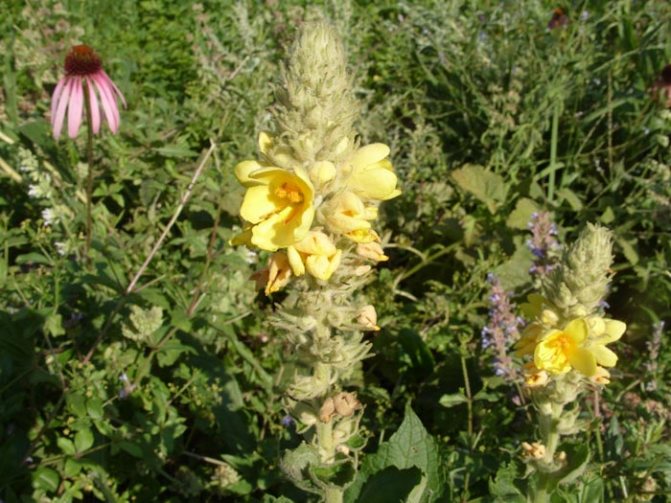


Flowering variety of the Royal scepter
Most often, this plant can be seen on roadsides, in yards, gardens and parks, in fields and forest areas.It also grows in household plots, where it receives proper care, and is subsequently used as a medicine.
Attention! Mullein grows best on sandy soil, although black soil is also suitable for it. You cannot sow the royal scepter mullein into clay soil.
Mullein reproduces in several ways:
- Separation of rhizomes. Since the royal scepter mullein is a two-year-old plant, by the end of the first year of flowering in the last days of September - early October, gardeners dig out the rhizomes and separate the shoots. They are treated with disinfectants and planted in the soil. Thus, the multiplication of the mullein occurs, and a person can control the place where flowers grow, so that they are not placed too close to each other. Even before the onset of frost, the divided rhizomes will give small sprouts.
- Self seeding. At the end of flowering, seeds are formed in place of the flower, which, after drying under the influence of wind or rain, leave the mother plant and fall into the ground. This type of reproduction does not require effort, but it has a number of disadvantages: the impossibility of growing in rows, in the presence of several species in the same territory, self-seeding will lead to the degeneration of some of them.
- Growing the royal scepter from the seeds of the mullein plant. This is the most suitable option. It is less energy intensive than separating rhizomes and more controlled by humans than self-seeding. Seeds are collected from the largest inflorescences and dried. In May, they are sown in prepared soil and watered. After a few weeks, seedlings appear that need to be thinned out, leaving only the strongest plants at a distance of at least 30-40 cm from one another. Mullein flowers grown from seeds will bloom in the second year. After which it will be necessary to collect and sow the seeds again.
Attention! Don't bury the seeds too much. It is best to scatter them over the soil, and then sprinkle with a little earth. As it grows, the root system itself will be located at the required depth.
Chemical composition
In its composition mullein (other names - "curiosity", "bear's ear", "royal scepter", "divina", "royal candle") contains biologically active substances iridoids (catalpol, aucubin, harpagid acetate, harpagid).
The flowers of the plant contain polysaccharides, ascorbic acid, phenol carboxylic acids, flavonoids, tannins and mucous substances. The latter consist of gum, essential oils, saponins, ash, glucose, sugars, carotene, coumarin.
The composition of flowers and seeds includes the following minerals: calcium, potassium, magnesium, iron, manganese, copper, zinc, molybdenum, chromium, selenium, nickel, strontium, lead, boron, lithium. Mullein seeds also contain 11 fatty acids, among which linolenic and linoleic unsaturated fatty acids predominate.
Active ingredients
Corolla of mullein flowers contain up to 2.5% mucus (and in the leaves up to 8%), which include D-galactose, arabinose, D-glucose, D-xylose, L-rhamnose, D-mannose, uronic acid; 0.5-4% flavonoids (hesperidin, verbascoside, luteolin, apigenin, kaempferol, quercetin, rutin, chrysoeriol), polyphenol carboxylic acids (vanillic, ferulic, caffeic, hydroxybenzoic), triterpene saponins (verbascosaponine) , β-carotene), iridoid glycosides (aucubin, catalpol, isocatalpol), sugars (about 11%), up to 2.4% fatty acids (palmitic, linolenic, myristicic), essential oil, gum, malic and phosphoric acids, and others substances. In addition, the raw material contains macro and microelements: potassium (17.3 mg / g, magnesium (1.9 mg / g), iron (0.22 mg / g, manganese (49.2 μg / g), zinc (23 , 6 μg / g), selenium (0.05 μg / g), etc.
Mullein - useful properties
For medical purposes, two types of mullein are used - the scepter and the royal scepter. Until the flowering period, they do not differ from each other. But with the beginning of flowering, these plants cannot be confused with each other.
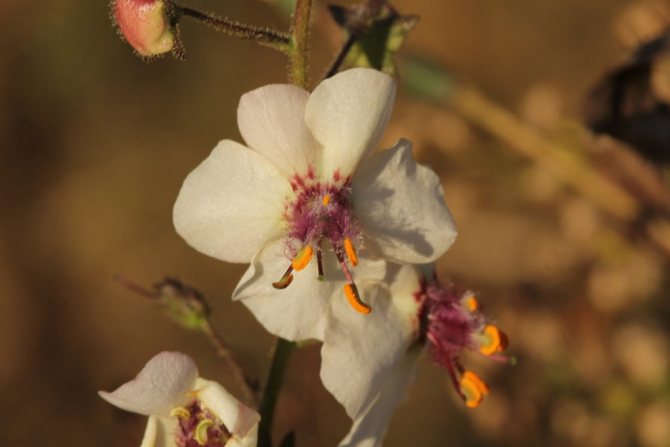
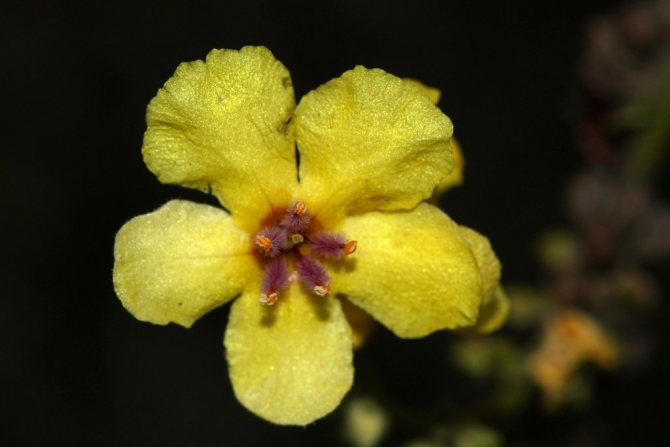
The scepter has large five-petal flowers, they are similar in shape to violets, but have a bright yellow color. The stamens of the scepter-like mullein have long legs, which are covered with bright orange hairs.
The royal scepter has small flowers, and its buds completely cover the stem. The flowers are so dense that they form a solid cylinder by their number. The royal scepter is slightly lower and reaches only one and a half meters. Not all flowers bloom at once. Therefore, it turns out that in one pile there can be boxes with green seeds, as well as flowers and buds. Mullein bloom lasts about 3 months.
Growing
Agrotechnics
It is undemanding to soils. Grows best in open areas. Regular loosening and weeding should be carried out.


Tall mullein
Reproduction
Propagated by seeds that have a high germination rate. Sowing is done with surface spread in April-May. Then the soil is rolled up and watered well. Seedlings appear on the 3rd -11th day. In the first year, the plant forms a large rosette with a diameter of 45-60 cm. Mass flowering begins in the second year of life.
Varieties
Species of the genus Verbascum, used in medicine as medicinal plants, belong to the section Fasciculate Murb., Whose representatives are characterized by the presence of 2 - 7 flowers in bunches. At the top of the inflorescence, the flowers are sometimes single; seeds with a number of transverse fossae. The mullein (Verbascum densiflorum), the common mullein (V. thapsus L.) and the mullein (V. phlomoides L.) belong to the subsection Heterandra Franch. ex Murb., whose representatives are characterized by descending anthers in the two front, longer stamens. Great mullein - Verbascum speciosum Schrad. belongs to the isandra Franch subsection. ex Murb., whose representatives are characterized by the median attachment of the anthers of all stamens to their filaments. Common mullein - Verbascum thapsus L. - biennial densely pubescent plant. The stem bears strongly descending leaves. Flowers adherent to the inflorescence axis, corolla 15 - 25 mm in diameter, with pronounced transparent dots. Inflorescence in the form of a dense, spike-shaped apical brush.
The type of area is Euro-Asian. Of all the medicinal species of the genus Verbascum, the common mullein has the most extensive range. It grows on the territory of almost the entire European part of Russia, in the Transcaucasus, Central Asia and Western Siberia. Occurs in the southern part of the forest zone, in the forest-steppe and the adjacent part of the steppe zone. Usually grows in open places: on dry meadows, on meadow-steppe and rocky slopes, forest edges, in sparse pine forests.
Mullein - Verbascum phlomoides L. - a plant with tomentose pubescence; its stem leaves are not descending or slightly descending, sessile, stalk-enveloping, with a heart-shaped base. The inflorescence is a dense spike-shaped raceme. Pedicels are free, not adherent to the inflorescence axis. Corolla 35 - 55 mm in diameter, without transparent dots.
The type of area is Central European. Grows in the southern regions of the European part of Russia, in the Crimea and the Caucasus. It is confined to pine forests, hills and slopes. In the Caucasus, it is found from low-lying areas to the middle mountain belt. It grows on grassy slopes, along forest edges, in bushes, river valleys and streams, on pebbles, and also as a weed in fields and fallow lands. Fla Ukraine is found mainly in the southern regions. Sometimes it forms sparse thickets with an area of several tens of hectares.
The magnificent mullein - Verbascum speciosum Schrad. Is a grayish or yellowish tomentose, densely leaved plant. All leaves are whole-edge. Inflorescence-apical, branched, ovoid panicle in outline. Flowers in dense multi-flowered bunches; corollas are yellow, 20 - 30 mm in diameter, stellate-hairy outside. The anthers of all stamens are reniform.
The range of the magnificent mullein is small, consisting of two parts. A large, Caucasian part of the range covers the Transcaucasia (Lesser Caucasus, Talysh). A smaller part of the range is located in Moldova. To the north, isolated localities of the magnificent mullein are noted, where it is an invasive plant. It grows on dry slopes, gravelly soils, along coastal gravels of rivers. In the Caucasus, it is found in the upper and middle mountain belts, sometimes it enters the subalpine belt.



















































