Due to its surprisingly fresh aroma, mint is considered one of the most famous plants used not only in cooking and cosmetology, but also in medicine. For the use of the plant to bring real benefits, it is necessary to take into account both the medicinal properties and contraindications of mint.
Different types of mint differ in the level of content of biologically active substances, and accordingly their pharmacological value also differs. Peppermint has the richest healing potential.
Botanical description
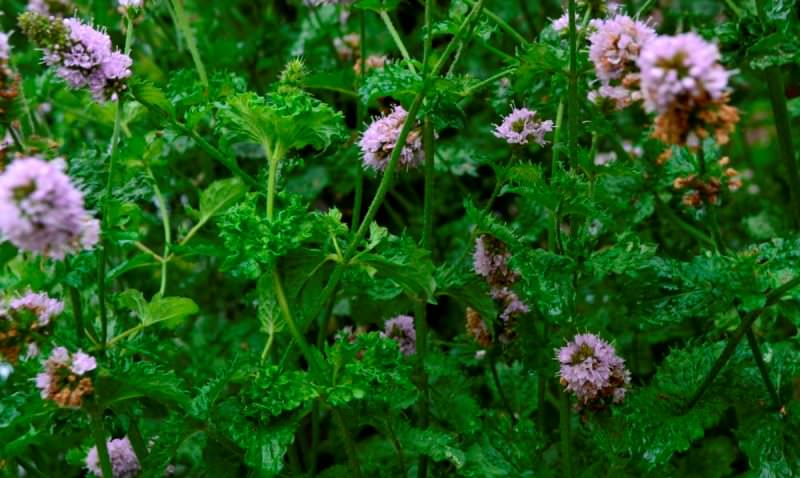
Mint is a perennial crop with a creeping rhizome and erect, branchy stems. The average height of the plant varies between 50-70 cm. Leaves of mint are short-petiolized, elongated with serrated edges. Moreover, the outer surface of their plates is painted in a dark green color, and the bottom - in a light salad shade. The corollas of the grass are small, light purple, collected at the tops of the shoots in spike-shaped inflorescences.
The most common varieties of mint: peppermint, aromatic, cat, water, field, Japanese. For medicinal and culinary purposes, the aerial part of the grass is used, which is plucked in dry weather during the flowering period. To dry the plant, it is better to choose a shaded, ventilated place where direct sunlight does not fall. After sublimation, the mint is placed in cardboard boxes or cotton bags. The shelf life of the blank does not exceed 2 years.
Peppermint for pregnancy and breastfeeding

The use of mint while waiting for a child is not prohibited, since the plant has a beneficial effect on the woman's body:
- calms nerves, reduces excitability and irritability;
- improves sleep;
- relieves dizziness;
- eliminates puffiness;
- helps to cope with toxicosis;
- during a cold - reduces the temperature, fights coughing.
However, pregnant women should not abuse the use of mint drinks, as the plant can provoke an allergy attack, a decrease in pressure and impaired kidney function.
Before introducing mint tea into the diet of a pregnant woman, it is better to consult a doctor.
Beneficial features
Mint is one of the oldest plants used in both Western and Eastern medicine. In ancient times, culture was considered an integral "symbol" of women's health, and was used primarily as an aphrodisiac. Several centuries later, the Assyrians discovered that the herb improved mental performance, sleep, and digestion. Interestingly, in Ancient Greece, mint was rubbed on the body, using it as a deodorant, and in the Roman Empire, tables were decorated with it and the air was scented (before important receptions). It was believed that the menthol smell increases the clarity of thought, and therefore, tune in to the conversation. The plant owes this "effect" to the volatile ethers present in its aboveground part.

Mint properties:
- Stimulates blood circulation, relieves pain in angina pectoris, dilates coronary vessels, increases the tone of the vascular wall.
- Eliminates stomach cramps, stimulates bile secretion, reduces the intensity of nausea attacks, relieves migraines, reduces pain in spastic colitis and enterocolitis.
- Normalizes cardiac R myocardium.
- Suppresses putrefactive flora, reduces the risk of gastrointestinal infections.
- Stimulates the secretion of the digestive glands, increases appetite, improves metabolism.
- Relieves emotional stress, speeds up the process of falling asleep, eliminates anxiety.
- Reduces inflammation in the oral cavity, freshens breath.
- Increases the protective functions of the dermis, potentiates hair growth.
The pharmaceutical industry uses mint as a raw material for the manufacture of various medicines: tablets, aerosols, balms, drops, ointments, soothing teas and alcoholic infusions.
Indications for the use of the aromatic herb:
- infectious diseases: colds, tonsillitis, pharyngitis, rhinitis, bronchitis;
- pathologies of the cardiovascular system: spasm of the coronary vessels, angina pectoris, tachycardia, hypertension, circulatory failure;
- nervous dysfunctions: depression, insomnia, stress, nervous agitation, migraine, decreased memory and attention;
- disorders of the digestive system: colic, "poor" appetite, gastritis, helminthic invasions, spasms, vomiting, flatulence, cholecystitis, constipation;
- lesions of mucous membranes and skin: urticaria, herpes, dermatitis, burns, acne, insect bites, bruises, sprains;
- reproductive disorders: profuse menstruation, painful menopause.
- Along with this, mint-based preparations are used to prevent skin cancer, improve the functioning of the immune system, and stimulate bile secretion.


Contraindications for use:
- decreased secretion of gastric juice (including achlorhydria);
- heartburn;
- arterial hypotension;
- thrombophlebitis;
- allergic reactions;
- pregnancy, lactation.
In addition, mint should be used with caution by men, as the herb lowers the concentration of testosterone in the blood, which is fraught with a weakening of libido.
Remember, in case of abuse of medicinal herb, the victim has dizziness, nausea, "split" in the eyes, drowsiness, muscle weakness, gag reflex, pain in the sternum, decreased venous tone.
Contraindications and possible harm
Despite the huge list of indications for the use of mint, there are restrictions, non-observance of which can lead to the development of side effects.
First of all, mint is contraindicated for people with low stomach acidity - the herb has the property of reducing the production of gastric juice and can lead to gastrointestinal dysfunction.


Chemical composition
100 g of mint contains 70 kcal and a wide range of biologically active substances. The most important component of the plant is essential oil, which makes up 2.4-2.75% of the mass of leaves and 4-6% of inflorescences. In addition, it contains tannins, bitterness, aromatic resins, vitamins, phytosterols, minerals, organic acids and flavonoid structures.
Table number 1 "Nutritional value of mint"
| Name | Concentration in 100 grams of grass, grams |
| Water | 78,65 |
| Alimentary fiber | 8,00 |
| Carbohydrates | 6,89 |
| Protein | 3,75 |
| Ash | 1,76 |
| Fats | 0,94 |
Table number 2 "Chemical composition of mint"
| Name | Concentration of nutrients in 100 grams of grass, milligrams |
| Vitamins | |
| Ascorbic acid (C) | 31,82 |
| Niacin (B3) | 1,71 |
| Pantothenic Acid (B5) | 0,34 |
| Riboflavin (B2) | 0,27 |
| Beta carotene (A) | 0,21 |
| Pyridoxine (B6) | 0,13 |
| Folic acid (B9) | 0,11 |
| Thiamin (B1) | 0,08 |
| Macronutrients | |
| Potassium | 569 |
| Calcium | 243 |
| Magnesium | 80 |
| Phosphorus | 73 |
| Sodium | 31 |
| Trace elements | |
| Iron | 5,08 |
| Manganese | 1,18 |
| Zinc | 1,11 |
| Copper | 0,33 |
Table No. 3 "Amino acid composition of mint"
| Name | Concentration in 100 grams of grass, grams |
| Aspartic acid | 0,44 |
| Glutamic acid | 0,41 |
| Leucine | 0,28 |
| Valine | 0,19 |
| Phenylalanine | 0,19 |
| Glycine | 0,18 |
| Arginine | 0,17 |
| Lysine | 0,16 |
| Serine | 0,15 |
| Proline | 0,15 |
| Isoleucine | 0,15 |
| Threonine | 0,15 |
| Tyrosine | 0,11 |
| Histidine | 0,08 |
| Tryptophan | 0,06 |
| Methionine | 0,05 |
Due to the high concentration of menthol, mint is used both for therapeutic purposes and for culinary and cosmetic purposes.
The main thing about mint


Mint
Peppermint is a herb that has synonymous names: chill, peppermint, motherboard. The genus of mint includes forty-two plant species.Chilly is a hybrid product of two popular mint varieties. The plant grows in gardens, on private estates. Mint is even grown on an industrial scale. It is unpretentious, grows on poor soils and in the shade. If desired, the grass can even be grown as an indoor culture in an apartment environment. The plant grows best in moist and light soil. To propagate mint, you can use cuttings, cuttings or rhizome fragments. The grass blooms from early summer to early autumn. The fruits are extremely rare.
The chemical composition of the medicinal herb is very rich:
- menthol;
- saponin;
- vegetable resins;
- tannins;
- fatty oil;
- various acids;
- phytosterols.
The main advantage of a herbal product is essential oil. There is a lot of this product in the leaves. On average - from three to six percent. The menthol flavor of the essential oil provides a distinctive cooling flavor.
Due to its rich chemical composition, the plant has a wide range of useful abilities.
Essential oil
Menthol ether is obtained from peppermint leaves by steam distillation. Moreover, from 1 kg of collected raw materials it is possible to extract only 1.5 g of pure volatile oil. Depending on the region of growth, the concentration of menthol in the ether varies between 40-70%.
Peppermint oil is a light yellow (sometimes greenish) liquid with a sharp refreshing scent with subtle notes of camphor. The main actions of the ether: tonic, antiseptic, expectorant, anthelmintic, antispasmodic.
In addition, peppermint oil is used on the farm to repel ants, cockroaches, rats and mice (as a repellent).
Table number 4 "Ways of using essential oil"
| Application method | Dosage | Indications for the use of menthol ether |
| Aromolamp | 1-2 drops per 5 sq. m. area | Respiratory diseases, nervous excitement, stress, insomnia |
| Aroma medallion | 2 drops | Motion sickness in transport, nausea, rhinitis, colds |
| Internal use | 1 drop (together with honey or jam) 2-3 times a day. Wash down with kefir, yogurt, green tea, juice | Flatulence, heartburn, nausea, lack of appetite, stomach and intestinal cramps |
| Bath | 2-6 drops (previously dissolved in an emulsifier) | Headache, nasal congestion, muscle cramps |
| Massage | 6 drops of ether per 15 g base oil | Insomnia, rhinitis, convulsions, hyperexcitability |
| Enrichment of cosmetics | 3-5 drops of ether per 10 g base | Acne, rosacea, pruritus, dandruff |
| Aromatization of alcoholic beverages (vodka, wine, liquor) | 6-8 drops per 200 ml of alcohol | Aromatization |
| Sauna | 2-4 drops per 10 sq. m area | Respiratory disease, acne |
| Douching | 1 drop in 1 liter of water (dissolved in 10 ml of chlorophyllipt aqueous solution) | Genitourinary tract infections |
| Cold compress | 8-10 drops of essential oil per 200 ml of water | Muscle pains, trauma, burns, headache, migraines |
Read the list of contraindications carefully before using volatile menthol.


Peppermint essential oil should not be used for:
- pregnancy, lactation;
- allergic rhinitis;
- childhood (up to 7 years old);
- individual intolerance to mint;
- atopic dermatitis.
In addition, menthol oil should not be used for more than 20 days, and should also be combined with homeopathic treatment.
Remember, ether overdose threatens general weakness, dizziness, low blood pressure, sleep dysfunctions, irritation of the gastric mucosa.
Applications


Due to its unique aroma and medicinal properties, mint has found application not only in medicine, but also in cosmetology and cooking.
In cooking
Adding mint to food and drinks allows you to emphasize and improve the taste of dishes, add spice and sophistication to them.


Dried mint is an indispensable component of the set of spices of Provencal herbs used for preparing meat and vegetable dishes, soups, sauces and preservation. Fresh mint leaves are used to decorate meat dishes and desserts. And peppermint oil and menthol are considered the best flavors for alcohol-based drinks.
In cosmetology
For cosmetology, the antiseptic, anti-inflammatory and disinfecting and soothing properties of mint are of particular interest. Extracts from the plant are recognized as an effective remedy for combating skin imperfections caused by irritations, rashes, and acne.


If you wipe your face with ice cubes made from mint water, you can not only easily eliminate skin inflammations, but also increase tone and elasticity, improve blood circulation and complexion, and eliminate fine wrinkles and age spots.
Brushing with a massage brush with applied drops of peppermint oil strengthens and grows hair. After the massage, the hair must be rinsed.
And if you add a few drops of essential oil to toothpaste, you can quickly and safely whiten your teeth, and at the same time refresh your mouth.
Mint in cosmetology
Over the past 5 centuries, mint has been widely used in cosmetology to care for oily problematic dermis. Funds based on it successfully fight skin problems: rashes, boils, purulent abscesses, acne, increased sebum secretion. In addition, mint is used as an astringent to reduce skin irritation.
The effect of the plant on the dermis (when used externally):
- normalizes the work of the sebaceous glands;
- has a local anesthetic effect, eliminates itching;
- accelerates the healing of microdamages in the dermis;
- stimulates blood circulation, strengthens the capillary wall, tones the stratum corneum;
- reduces the intensity of acne;
- evens out skin tone;
- prevents the appearance of dandruff, reduces the intensity of hair loss;
- eliminates "tiredness" in the legs.
For cosmetic purposes, mint can be used both as a mono-agent (fresh) and as an ingredient in multicomponent products (in the form of an extract, dried wood or essential oil).


Homemade beauty recipes:
- Lotion for oily skin. Ingredients: 45 g dry mint leaves, 40 ml cucumber juice, 10 ml lemon nectar. Pour boiling water over the grass (200 ml), and after 30 minutes add the rest of the ingredients. The lotion is used twice a day after a thorough make-up removal procedure.
With regular use of the composition, the complexion improves, fine wrinkles are smoothed, the tone of the dermis is evened out.
- Mask for problematic acne prone skin. Combine 15 ml of mint broth with chicken protein and aloe juice (3 ml). Apply the mask to thoroughly cleansed skin in several layers. The frequency of the procedure is 2 times a week.
- Conditioner to strengthen hair. Mix in equal proportions (15 g each) mint leaves, oak bark and horsetail. Pour 500 ml of boiling water over dried flowers, and after 30 minutes strain the drug.
With regular use of the composition (2-3 times a week), the hair becomes thicker, stronger and silky.
- Anti-inflammatory acne mask. Ingredients: 15 g of natural cocoa powder, 7 drops of peppermint ether, 1 tablet of ascorutin (crushed). Combine the indicated components, and then carefully move the mixture. Apply the mask in a circular motion to cleansed skin, avoiding the area around the eyelids. After 15 minutes, rinse off the product with mineral water with the addition of mint broth (15 ml) and lemon juice (1 ml).
The composition reduces irritation of the dermis, accelerates the healing of pustules, and reduces the severity of acne.
- Purifying mask for combined dermis. Ingredients: 30 g of cucumbers, 8 g of "pharmacy" bodyagi, 6 drops of mint essential oil. Method of preparation: bring the pressed seaweed to a powdery consistency, combine with a peeled vegetable. Puree the mask ingredients in a blender or food processor.
The composition is used to normalize the secretion of the sebaceous glands, restore the hydrolipid balance of the skin, deeply cleanse the pores, heal microcracks, and strengthen the superficial vessels.
- Rejuvenating mask for aging dermis. To create a composition, you will need: mint broth (20 ml), chopped kelp (15 g), peach fatty oil (5 ml). To prepare the mask, it is enough to mix all the components. The composition is applied to a cleansed, steamed face for 15 minutes, then washed off with water.


The mask perfectly nourishes, cleanses and soothes irritated skin.
- Purifying mask for mature skin. Active ingredients: 15 g of avocado pulp, 5 g of pink clay, 7 drops of peppermint ether, 2 drops of jojoba oil. The principle of preparation and application of the mask is the same as in the previous case.
With regular use of the product, the "severity" of age-related wrinkles decreases, the microrelief of the skin is leveled, and the turgor of the face increases.
- Mint ice cubes. Cooking scheme: combine mint broth (30 g of herbs per 150 ml of boiling water) with 0.5 ml of mint ether and 0.3 ml of almond oil. Pour the mixture into molds, place in the refrigerator. Herbal ice is used to refresh the dermis, correct the oval of the face, slow down the aging process, and improve muscle tone. To obtain a therapeutic effect, the aroma composition is applied once a day (in the morning after cleansing the skin).
Remember, wipe your face with a "healing" cube with quick sliding movements strictly along the lines of the lymph flow.
In addition to homemade "menthol" beauty masks, it is recommended to additionally use purchased cosmetics containing mint extract or essential oil. Remember, maintaining youthful skin is not an easy task that requires a competent, comprehensive approach.
What does mint look like?
The medicinal herb mint from the wild labiate family is not found. There are two forms of peppermint — black mint and white mint.
Black mint has stems of a dark reddish-purple hue. Several valuable varieties with a high menthol content have been developed.
White mint has light green stems and leaves. The essential oil of this herb has a more delicate scent than black peppermint oil. Especially valuable for the manufacture of perfumery products, used for the food industry, where aroma is important.
Russia cultivates both forms of this plant. Peppermint is a good honey plant. The plant honey is transparent, with a pleasant refreshing taste and, of course, a large number of useful substances.
The grass has a powerful horizontal rhizome with bundles of adventitious roots extending from it. Stem up to one meter tall, tetrahedral, reddish glabrous. Leaves are dark green, opposite, petiolate, oblong, with a solid blade. Pink or pale purple flowers in whorls, collected in a spike-shaped inflorescence. Flowering begins in June and lasts until September. The fruit is four smooth, red-brown nuts.


Mint in folk medicine
Means prepared from representatives of the family of lamines are used both orally (in the form of infusions, decoctions, extracts) and externally (in the form of baths, lotions, rinses, poultices).
Traditional medicine recipes:
- Syrup to improve appetite. Ingredients: 100 g fresh mint, 200 g honey. Cooking scheme: pour 400 ml of boiling water over the chopped grass, combine with bee nectar. Insist the composition in a thermos for at least 15 minutes. To stimulate the work of the digestive glands, take the mixture three times a day before meals (150 ml each).
- Decoction for stomach colic, colds, bronchitis. Pour mint dried flowers (200 g) and dill seeds (15 g) with cold purified water (500 ml). Bring the mixture to a boil, and then leave for 40 minutes in a water bath. Take the broth four times a day, 150 ml (preferably between meals). With pathologies of the digestive tract, the drug is consumed without the addition of honey, sugar.
- Phytocomposition for tachycardia. To create a therapeutic "cocktail" you will need 250 ml of milk, 15 g of fresh mint, 5 g of cloves. Combine the indicated components, and then roast in a water bath (20 minutes). Natural honey or maple syrup can be added to the warm mixture. To normalize the heartbeat, the composition is taken on an empty stomach in a warm form, 200 ml.
- Ointment for muscle pain relief. Combine 400 ml of interior fat with 200 ml of mint juice (or strong broth). Apply to local areas. This composition will help reduce pain in stretched ligaments, accelerate the healing of superficial microcracks, and eliminate muscle spasm.
- Soothing baths. Pour 100 g of mint with 2 liters of cold liquid, boil the raw material for 15 minutes. Add the resulting mixture to a hot bath (37-39 degrees). The optimal duration of the procedure is 15 minutes.
Mint bath perfectly copes with nervous overexcitation, muscle cramps, fatigue. To enhance the therapeutic effect, geranium or grapefruit essential oil is added to the broth.
- Antihemorrhoidal compress. You will need fresh peppermint leaves to make the poultice. Medicinal raw materials are thoroughly washed and then crushed until juice appears. After that, the chopped raw materials are laid out on a cotton sponge and applied to the hemorrhoidal lump for 15 minutes.
- Throat rinse. Irrigation solution is prepared from fresh mint (15 g) and garlic (10 g). The specified raw materials are crushed, and then 200 ml of hot water (90 degrees) is poured, cooled. Gargle with the obtained bactericidal agent 2-3 times a day. The composition is indicated for pain in the larynx, enlarged tonsils, inflammation of the oral mucosa.
Despite the wide range of pharmacological properties, tea + with mint is most often prepared from menthol herb. The medicinal drink perfectly quenches thirst, eliminates gastric spasm, relaxes the heart muscle, and stimulates the secretion of bile.
Photos and drawings
You can see what the mint herb looks like from the photographs. In the images presented, you can see the names and descriptions of all varieties of this plant.
Output
The best materials of the month
- Why you can't go on a diet on your own
- 21 tips on how not to buy a stale product
- How to keep vegetables and fruits fresh: simple tricks
- How to beat your sugar cravings: 7 unexpected foods
- Scientists say youth can be prolonged
Mint is a perennial medicinal plant with a pleasant menthol scent. The herb contains aromatic ethers, bitterness, tannins, flavanoids, vitamins, micro- and macroelements. Due to the high concentration of phytonutrients, the plant has pronounced antispasmodic, anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, choleretic and bactericidal properties.
Peppermint is used to reduce nervous tension, eliminate stomach colic, stimulate bile secretion, relieve headaches, and increase the protective functions of the dermis. In addition to its pharmacological properties, perennial has excellent taste characteristics. Mint is used in almost all countries of the world to add a spicy "chill" to the dish. So, in England it is added to sauces for meat and fish side dishes, and in America it is mixed with tomato drinks, fruit and vegetable salads. Interestingly, in Spanish, Arabic and Italian cuisines, mint is used as an aromatic spice. Along with this, the plant is used to flavor alcoholic beverages and improve the taste of confectionery products.
More fresh and relevant health information on our Telegram channel. Subscribe: https://t.me/
Benefits of Peppermint and Peppermint
Unlike other species, peppermint and meadow mint (Japanese) contain record amounts of menthol. The characteristic refreshing taste and its cooling properties can be found in toothpaste, cosmetic products or various confectionery products.
In addition, menthol is used in the production of pharmaceuticals because it has antiseptic and bactericidal properties, promotes vasodilation, and also provides a sedative effect.


For medicinal purposes, use:
- as an antispasmodic for the relief of convulsive conditions and stomach cramps;
- to eliminate nausea. Menthol substances effectively affect intestinal motility, irritating the mucous membrane and increasing contractions;
- to stop coughing attacks;
- to relieve muscle pain;
- externally - for inflammatory processes and fungal skin lesions.
On contact with the skin, menthol irritates the nerve endings and promotes their activation, causing a tingling sensation and slight coldness. As a result of excitation of cold receptors, capillaries and small vessels located in the upper layers of the epidermis narrow, which contributes to the expansion of blood vessels in deep tissues.
Also, the substance has a slight anesthetic effect.
Typically, essential oils derived from other types of mint are low in menthol.
What heals and can you drink mint
Due to the huge amount of nutrients in the composition, mint tea is used in the treatment of many diseases. Consider what mint cures for and how to properly take these healing drinks.
Did you know? The mint family also includes rosemary, basil, valerian and oregano.
With a cold
Mint tea is an excellent remedy for strengthening natural immunity during colds. When coughing, a fragrant drink, to which you can add honey, is able to relieve inflammation of the mucous membranes and make breathing easier.


With menstruation
A mint-based drink not only has a pleasant aroma, but it will also help reduce pain and other problems that arise during this time. Getting rid of pain is due to the presence of menthol in peppermint - one of the main components that has good antispasmodic properties. To obtain the desired effect, it is enough to drink 1 cup of mint tea 2 times a day.
Under pressure
People who suffer from high blood pressure also need peppermint tea. This is especially true in hot weather. Popularity is due to the vasodilating effect, due to which the pressure decreases. It is important to understand that such a drink is prohibited for hypotensive patients; it can be consumed exclusively at high blood pressure.

The drink is prepared from 10 g of leaves (dry or fresh), which are poured over 250 ml of boiling water. After 15 minutes of infusion, it is ready to use. At high pressure, it is allowed to drink up to 3 cups of this drink per day.
For stomach problems
For the treatment of gastrointestinal ailments, formulations based on peppermint are most often used. In addition to essential oil, its leaves contain a large amount of vitamins, trace elements and amino acids, which are useful for high stomach acidity. With the help of these substances, cramps are relieved and colic is reduced, as well as appetite increases and an anti-inflammatory effect is provided. Most often, peppermint is used to treat:
- gastritis;
- duodenitis;
- gastroenterocolitis;
- ulcers.
The drink is prepared in the same way as for other problems with the gastrointestinal tract (this will be discussed below). The reception that doctors recommend is 3 glasses a day.


For constipation
Thanks to its relaxing qualities, this tea, drunk before bedtime, will help relax the intestines and, as a result, solve the problem the next morning, without the use of medications.
With heartburn
Doctors do not recommend consuming mint for heartburn, despite the fact that it helps with stomach cramps, as well as nausea and vomiting. This plant stimulates appetite and, consequently, the production of gastric juice.All this leads to an increase in the work of the glands of the stomach, which means that it will further provoke the manifestation of heartburn.
Read about popular heartburn medications.
With diarrhea
Thanks to its composition, mint-based tea allows you to cope with gastrointestinal diseases, which are accompanied by flatulence, cramps and stools with an unpleasant odor. Most often, after drinking 1 glass of tea, most of the unpleasant symptoms get rid of.


The drink is prepared from 20 g of plant leaves, which are poured over 250 ml of boiling water. Insist in a closed container for 10 minutes, and then consume. Within 1 day, it is allowed to drink up to 3 glasses.
For insomnia
The benefits of mint tea have been known for a long time, and people have been taking this drink before bed for centuries. This tea will make the rest calm and long-lasting due to the sedative effect, thanks to which the body relaxes and calms down, the tension accumulated during the day goes away.
Read about how to fall asleep if you have insomnia.
To prepare a drink, 20 g of leaves are poured with 500 ml of boiling water. Insist for 5 hours, and after straining, consume half a glass before bedtime.
Flea


Perennial herb
family Yasnotkovye. The stem is erect, branched, 20-60 centimeters high. The leaves are oblong in the form of an ellipse at the base, wedge-shaped, serrate along the edge.
Small flowers collected in dense spherical rings, the corolla is pink-lilac with a white tube. Blooms in July-August. Grows in floodplain meadows, along the banks of rivers in the western regions of Ukraine, in the south of the Caucasus, in Central Asia.
How to dry and store medicinal herbs
It is better to collect a spicy plant outside the city, where it is environmentally friendly. Many people planted it on their personal plots, so that later it could be harvested. Any species of mint must be harvested during active flowering. During this period, it is filled with essential oils and useful ingredients. Cut the stems and lay them out in the open air, under a canopy, so that they dry. Dry raw materials are crushed and placed in a glass jar, tightly closed with a lid. It is necessary to store medicinal herb in a dark place.
Important! It is forbidden to pick mint early in the morning when there is dew on it or after rain. The plant must be dry, so it retains all its beneficial properties.
The medicinal plant can be frozen. Instant decrease in temperature, will preserve all essential substances and useful components of mint.


Diseases and pests
Like any plant, black mint is susceptible to certain types of diseases. The plant may show symptoms of rust or powdery mildew. At the first signs of damage, it is necessary to remove the damaged leaves, and treat the entire bush with antifungal drugs. Bordeaux mixture works well against powdery mildew; Topaz or Trichophyte should be used against rust. The frequency of processing is once a week. Final - 1.5 months before the start of the collection of raw materials.
Among the pests, the danger is represented by ticks, aphids, mint leaf beetle and flea beetles. They more often infect plants in the absence of care and gross violation of the rules of agricultural technology. The fight will have to be carried out by spraying with folk remedies or insecticide solutions.
Food


Since mint normalizes metabolism, removes toxins from the body and regulates gastric juice, it is often used in diets. It also helps with constipation, in eliminating putrefactive processes in the intestines and lowering acidity.
Mint leaves are added to:
- first and second courses;
- baking pastries, pies, cakes and cookies;
- fruit and berry desserts;
- sauces and marinades;
- milkshakes.
Peppermint is a spice, an enhancer of the taste of dishes, a natural flavoring agent, an element that improves appetite.
The tonic properties are used in various drinks, the most widespread of which is the non-alcoholic "Mojito". Teas and infusions will wonderfully quench your thirst and at the same time drown out the feeling of hunger.
Mint works well with foods such as:
- meat;
- bird;
- a fish;
- vegetables;
- fruits;
- berries;
- greens;
- cottage cheese;
- spices;
- spice.
Menthol


Perennial herbaceous plant with a pronounced taste and smell of menthol. The stem is ordinary erect tetrahedral, slightly pubescent, 60-120 centimeters high. Leaves in the form of an ellipse of medium length. The flowers are collected in false whorls of white-pink color. Blooms in June-August. It grows everywhere.
Content
- Listen to the article
- Description
- Growing mint on a windowsill Sowing seeds
- Home mint care
- When to plant
- How to grow
- Diseases
- Healing properties
Melissa


Perennial herb, medicinal, melliferous plant. The stem is erect, tetrahedral, branched, pubescent with a height of 30-120 centimeters. The leaves are opposite, pubescent, the lower ones are cordate, long-petiolate, serrate at the edges, the upper ones are oblong, toothed. The flowers are usually small, white or pink.
Growing


The plant is unpretentious and does not require special care. Reproduces vegetatively. Prefers lighted areas, but does not tolerate the scorching sun.
Fertile, well-drained soil with moderate moisture is suitable for planting. This plant is creepingtherefore it is necessary to constantly monitor its distribution
Long-leaved
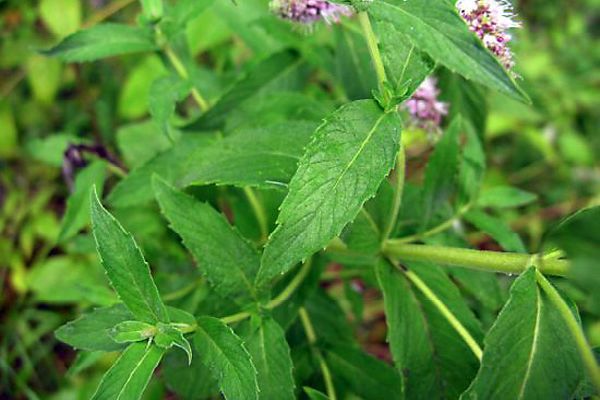


Perennial tall, soft-fluffy herb. The whole plant has a grayish tint. The stem is branched, erect, weakly pubescent, reaching a height of 120 centimeters. Leaves are sessile, lanceolate, ovoid, up to 20 centimeters long. Contains vitamin C, succinic, citric and malic acids. Whorls of small, light purple flowers are collected in dense cylindrical spikes. Blooms in June-August. Grows in Africa, Asia, throughout Europe, in the North Caucasus.
Japanese
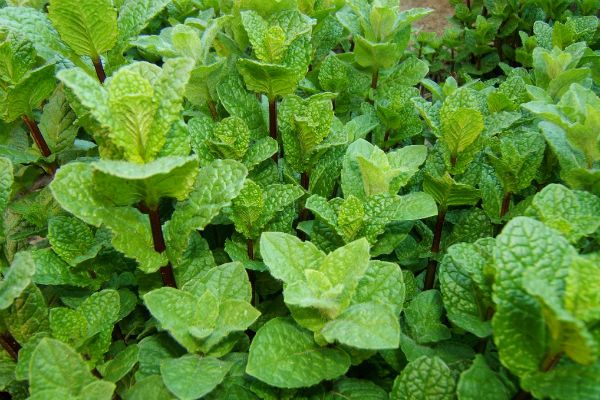


Perennial herbaceous plant. The stem is erect, less often creeping, 40 centimeters high. The leaves are small in length, barely reaching 2 centimeters. Small white or lavender flowers are collected in rare inflorescences. Blooms in August. It grows only on the two islands of Honshu and Hokkaido.
Where does mint grow?
Mint grows mainly in wetlands, along river banks, along streams and ravines. And also in the steppes, forest-steppes, practically in the entire European part of Russia. You can grow mint in your garden. Each species grows in different countries... For example: meadow is more common in Russia, in the Far East. Garden mint is more common in the southwest. Curly mint grows in Asia and Africa. Fragrant mint is widespread in the Mediterranean, Europe, Asia Minor.
Contraindications to the use of mint
Mint tea has some contraindications. Peppermint and its preparations should not be used uncontrollably. The pungent odor of drugs, when the dose is increased, can cause heartburn, provoke bronchospasm, and respiratory distress. In large quantities, mint will impair sleep. With inept consumption of mint, pain in the heart may occur. Treatment with mint should be minimized for those with low blood pressure. With varicose veins, it is generally advised to exclude these drugs.
A contraindication to the use of mint preparations is infertility, especially if a course of treatment is being carried out. It is better not to use mint tea for those who are expecting a baby. In any case, pregnant women need to be careful and listen carefully to their bodies.Mint preparations are not prescribed for children under 6 years of age.
Water
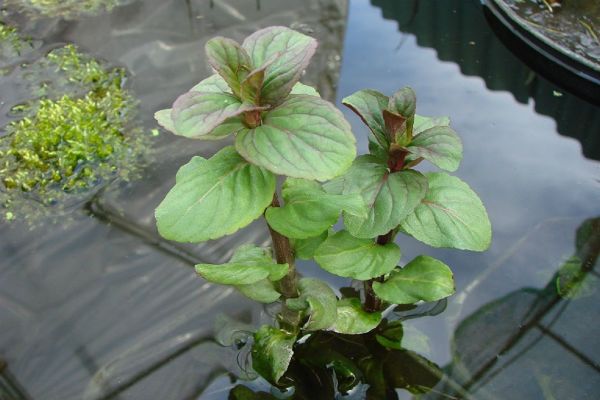


Perennial herb. Stems are hairy, tetrahedral, often creeping. Leaves are oval on the edge serrated up to 6 centimeters in length, sometimes reddish, more often green, with a pungent aroma of bergamot. The flowers are very small, light lilac, collected in small fluffy inflorescences. It usually blooms in July.
Sadovaya
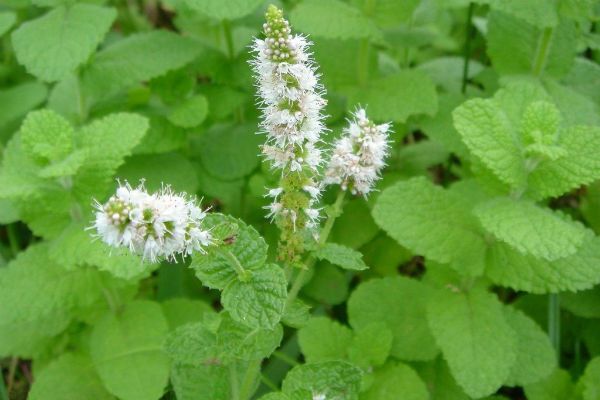


Perennial herb. The stem is an annual tetrahedral with a height of 30 to 100 centimeters. Leaves are oblong, ovate with pointed tips, smooth above, pubescent below. The flowers are small, lilac in color. Flowering period from July to the end of summer. Grows in the south and southwest of Russia.