Perilla - bushy annual from 30 to 60 cm in height and up to 25 cm in diameter. Growing a perilla has its own characteristics, which you will learn about now.
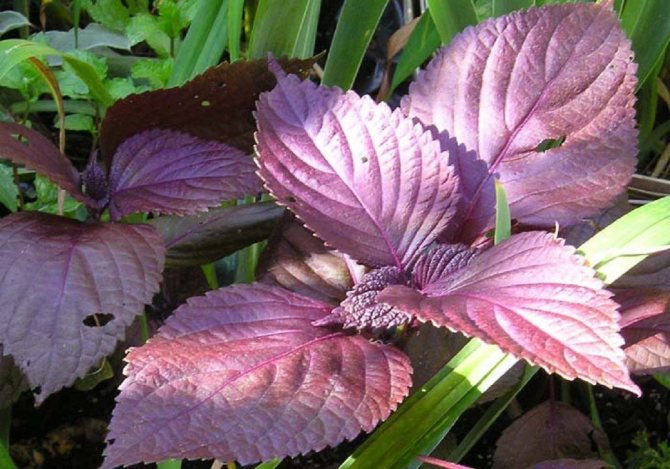
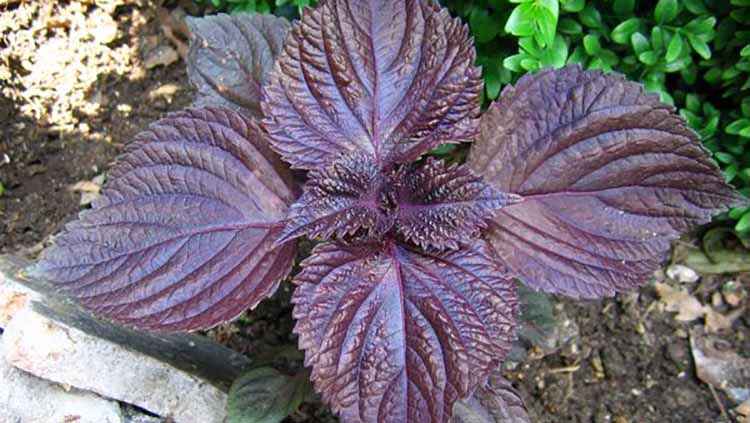
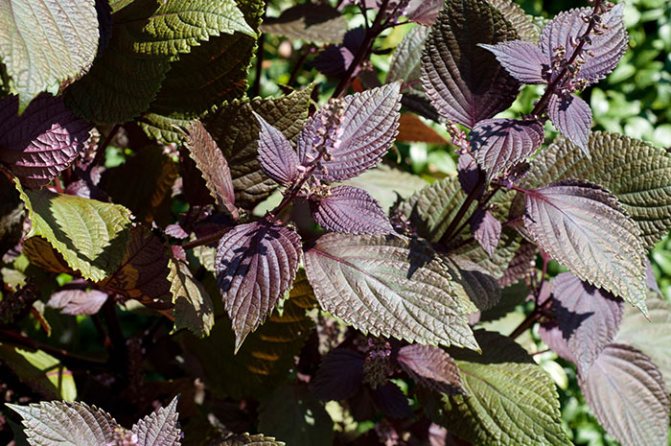
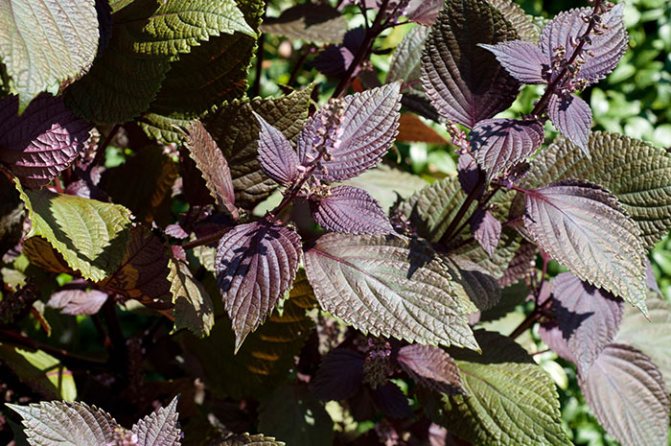
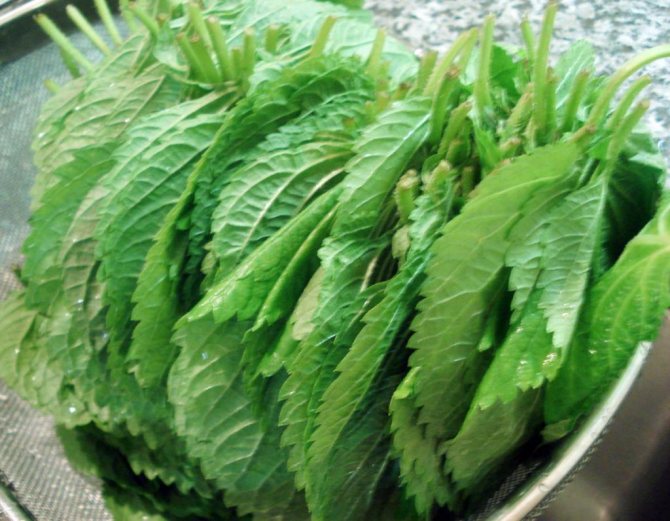
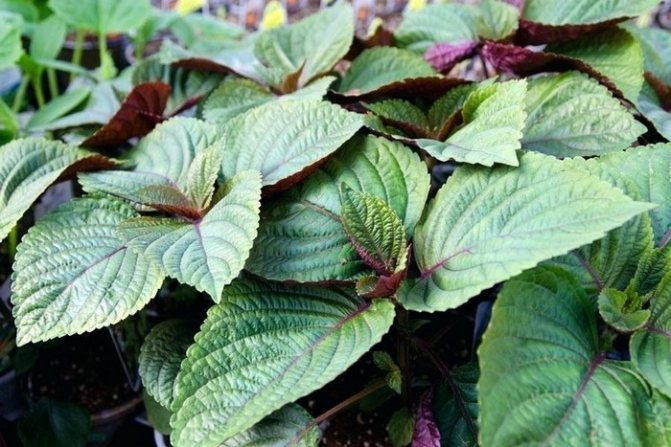
Perilla leaves have different colors depending on the variety. SinsoRed has a purple to bronze leaf color, while the new Shiso Green has pale green leaves.
Both varieties smell of cinnamon and have a pungent flavor similar to curge. It is grown to obtain young tender greens.
Perilla blooms during the period from August-September to October. Her flowers are small white or lavender spikelets. For its successful growth and development, perilla prefers to be in partial shade.
Location
Perilla grows best on moist, well-drained soils rich in humus.
Reproduction
Spring sowing of seeds in the soil warmed by the sun.
Care
Pinching the first flower shoots makes the bush thicker and more spreading.
Pests and diseases
Almost not amazed.
Procurement and storage
Leaves are harvested in summer (for fresh use or for drying). The inflorescences are cut at the height of flowering. The seeds are harvested in the fall.
Care requirements
Perilla (see photo) is unpretentious. The plant must be periodically watered, loosened, removed weeds and fertilized.
Young seedlings need weeding every 3 weeks. Plants feel comfortable at a temperature of + 18-27 ° and watering 2-3 times a week. Water more frequently on hot days. Stagnant water should be avoided so that rot does not appear, and the plant does not kill the fungus, fusarium or spotting.
Potted perilla
Organic fertilizing is applied every month during the season. Compost or bird manure that has been aged for several years will do. After fertilization, the color of the leaves becomes more saturated, growth is enhanced.
With the onset of the autumn cold, the plants are transferred to the greenhouse or to the house, because wilting begins. To form a bush and the appearance of lateral processes, the tops of the stems are pinched.
For decorative cultivation, the perilla is not cut off. Long shoots are supported.
The plant is susceptible to damage by caterpillars, ticks, scoops. To combat them, insecticides are used. In the case of eating the culture, only natural remedies are suitable.
During the season, the procurement of raw materials is done twice. Young shoots are cut off as soon as the flowers open, leaving 10-15 cm above the ground. Fresh leaves are dried or stored in the cold for about 7 days.
Basic properties
Many gardeners grow it on their backyards, as they are highly valued for its decorative and useful qualities. The perilla plant has such qualities as:
- decorativeness;
- the presence of antioxidants;
- many useful substances.
This plant has decorative properties, as the different color of the leaves attracts many gardeners. This color is due to the presence of the pigment substance perillamine. When planting a plant, you can be sure that it will delight you with its beauty. It can look very good in flowerpots, as well as borders, next to tall plants. Will be a very good backdrop for flowering plants.The leaves can be used in a variety of floral arrangements.

The beneficial properties of the perilla plant are due to the content of many vitamins, minerals, and essential oils. In terms of the amount of carotene, it is many times greater than even carrots.
It is a very good antioxidant, so it can be a good substitute for pain relievers, diaphoretic and anti-inflammatory drugs.
Perilla application
Perilla has many useful properties, thanks to which medicines and cosmetic products for skin and hair care are prepared on its basis. Often, fresh leaves of a plant or essential oil obtained from seeds are used for these purposes.
The plant's flavoring properties are to the taste of many gourmets. Perilla is used in cooking, to give them a special spicy aroma, piquant taste.
The unusual morphological characteristics of the plant make it possible to use it for aesthetic and decorative purposes. They decorate the landscape with a railing, sow along the garden plots, and grow houses to create comfort.
In folk medicine and cosmetology
In Ayurveda, perilla is used in the treatment of infectious diseases, disorders of the digestive tract, poisoning, allergies, and skin diseases.
Some folk recipes based on perilla:
- A remedy from a tablespoon of crushed dried leaves, a glass of boiling water will have a healing effect for colds. Cover the broth with a lid and let it brew for half an hour. Take in portions 3 times daily.
- The same broth with the addition of a tablespoon of wormwood will help with disorders of the gastrointestinal tract.
- With bronchitis, a strong cough, a decoction of a tablespoon of seeds, 6 tablespoons of dried foliage will help. For cooking, pour hot water, boil in a water bath for 15 minutes, leave to infuse for several hours. Take in portions 4-5 times daily.
- To cure diarrhea, nausea, a decoction of 1 cup boiling water, 1 tablespoon of crushed dry shoots, leaves will help. Boil for 10 minutes, let it brew for several hours. Take in portions 3 times daily.
- When applied externally, perilla essential oil helps relieve inflammation, itching, and cure acne and allergic rashes. The ether, when taken internally, will help relieve the symptoms of diabetes, leprosy.
Perilla essential oil is considered a useful addition to cosmetic products. In homemade recipes for masks and ready-made perilla creams:
- Smoothes wrinkles, rejuvenates the skin.
- It will have a mild anti-inflammatory and antiseptic effect, which will help get rid of acne, acne and comedones.
- Saturates the epidermis with vitamins and microelements, gives the skin a healthy and well-groomed look.
The easiest way to use an essential oil is to add 1-2 drops to a serving of cream or mask according to your skin type. Homemade masks and a couple of drops of essential oil in the balm will have a positive effect on the hair:
- the extract will restore the oil and water balance of the scalp, help to retain moisture;
- relieve seborrhea and dandruff, relieve itching and redness;
- will give the curls volume, visually make them thicker.
View this post on Instagram
Posted by LIFE IN AMERICAN VILLAGE (@olga_country_life) 2 Sep 2019 at 6:40 PDT
In cooking
The peppery taste of perilla and the subtle aroma with aniseed, cinnamon notes are present in many culinary dishes. The plant is often used in Asian, Vietnamese cuisine. Colorful leaves are added to salads, used as a decoration when serving. They are often used:
- in marinades, sauces;
- soups;
- fish, meat dishes;
- vegetable stews;
- lemonades, carbonated drinks.
Most often, varieties of green shades are used as a spice. Ground dried leaves are added to the dish 10-15 minutes before cooking.
Red leaves in cooking are used in marinades in the preparation of pickles, for coloring food red.
In the absence of perilla in the recipe, the spice can be replaced with basil, anise, or cinnamon with lemon juice.
A video will complement the topic:
Here's a simple way to use leaves in cooking:
What varieties exist
Having studied the description of the perilla plant, one can be sure that, despite the fact that it is called shrub, it is herbaceous. It also has many other names. The list of plant species of the genus Perilla is very wide, they differ in the color of the leaves. Among the more popular varieties are Green Cumin, which has lush green foliage with a caraway and cinnamon aroma.
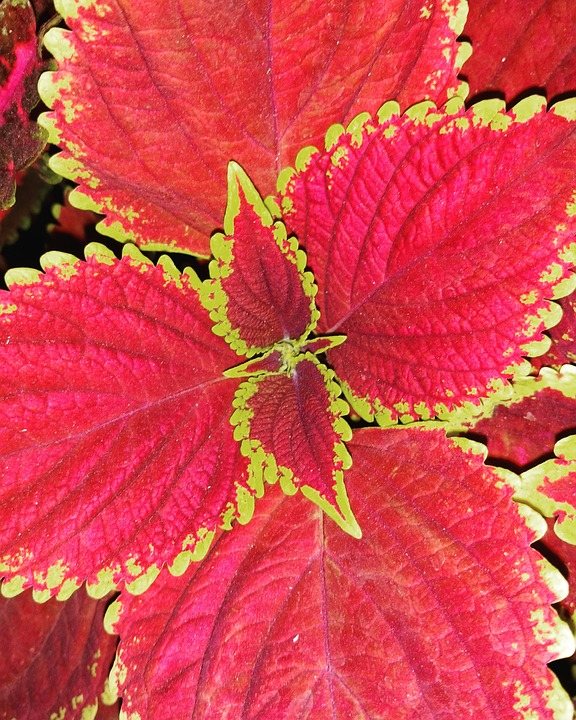


The green Aojiso has a delicate ginger flavor and is often used as a sashimi flavoring. Large leaves of Korean perilla are used as a wrapper for food products and are also added to salads. Alternatively, you can use the seeds as a seasoning.
Perilla - description, cultivation, photo. Perilla from seeds, as well as its beauty and benefits.


Railings are a genus of annual herbaceous plants of the Labiate family (L a m Iaseae), which has been known since ancient times in Korea, Japan, India, China, but India (Himalayas) is considered its historical homeland. Several types of railings are grown in East and Southeast Asia. In China and Japan, it is in demand as an oilseed, essential oil and salad culture, in Western Europe and the USA - as an ornamental one. In Russia, it is grown as a technical crop in the Far East. Recently, handrails can be found in Ukraine on city lawns. It came to us more than 300 years ago, but until recently it was grown exclusively by Koreans as a ridge garden crop. For a long time, it could be seen in the form of narrow protective strips that were sown in rice fields, because its strong smell can scare away domestic animals. But already in the 19th century, the cultivation of this crop for seeds began. The locals processed it in an artisanal way into oil, which was used for food and medicinal purposes. During the Soviet era, cultural studies were carried out by many agricultural institutes with varying success. Despite the fact that in Ukraine there were amateur crops at the end of the 19th century, the study of it at a serious level began only in the 20-30s of the last century. Before the Great Patriotic War, the collective farms of Ukraine collected railing seeds at 8-10 c / ha, and individual links at 13.5 c / ha. Even higher yields are harvested at variety plots - from 10 to 17 c / ha. Further development of agricultural technology, the breeding of new and early ripening varieties made it possible to dramatically increase the yield of this crop and draw attention to it. The most common are two cultivated types of railings - Perilla ocymoides or Perilla frutescens and Perilla nankinensis. In the Far East, there are many varieties of railings: with raspberry or green leaves. The railing leaves, which are dark green on top and purple on the bottom, have an aniseed flavor with a hint of licorice. The green banister tastes like lemongrass and has a rich lemon scent. The purple varieties sometimes resemble cinnamon-tinged basil.
Botanical characteristics and bioecological features


Railing oil basil, cornflower-like, or sudza (su-tsza) - an annual herb with a large vegetative mass. The stem, leaves and seeds have a pungent aromatic odor characteristic of the railings, due to the essential oil content. The growing season of the railing lasts 100-130 days. During the growing season, it goes through phases: shoots, four pairs of leaves, the formation of inflorescences (budding), flowering, seed ripening. The state of fruit ripening is also distinguished.Unlike other plants, railing seeds very soon lose their germination, so sowing with seeds of 2-3 years of age is unacceptable. Seedlings appear 8-10 days after sowing. In the first phases, to the formation of 4-5 pairs of leaves, plant growth occurs very slowly, and starting from the branching phase (30-35 days after germination), the growth of the stem is more intensive. The period from germination to the beginning of flowering is 65-75% of the time of the entire growing season of the crop. Flowering occurs 75-80 days after germination, spreading through the plant from the bottom up. The duration of flowering within the inflorescence at a temperature of 30-35 ° C reaches an average of 8-12 days, and at low temperatures, the duration of flowering increases by 2-2.5 times. Railings are basically a self-sucking plant, this is facilitated by both the location of the stamens and pistils in the flower, and the cracking of the anthers before the bud opens. But with excessive moisture and low air temperatures, pollen maturation is delayed, and cracking of the anthers can occur after the opening of the buds. In these cases, cross-pollination by bees, wasps and other insects, which are attracted by the smell of essential oil and the presence of nectaries in flowers, is not excluded. It takes 25-30 days from flowering to seed ripening. Railings are a thermophilic plant, but less demanding for heat than peanuts, sesame seeds, castor oil plants and other thermophilic crops. Seeds begin to germinate at 6-8 ° C, but friendly shoots appear at 13-14 ° C. Seedlings can withstand frosts up to -2 ° C, adult plants die at -1-2 ° C. Temperatures above 28 ° C and drought during the period the formation of reproductive organs cause a decrease in seed yield. In the first growing season, when the vegetative mass grows, drought is less harmful for the rail. Railings are demanding on soil moisture, especially in the first period of development, before flowering. In a later period, it is less demanding in this regard, but it does not tolerate droughts, especially dry winds, reducing the seed yield under these conditions. Railing is a plant demanding soil fertility. With a yield of air-dry biomass of 40 c / ha, the railing carries out from the soil: 22.5 kg of phosphorus, 19.6 kg of potassium, 60 kg of nitrogen. Therefore, fertilization contributes to a sharp increase in yields. Railings bear fruit well on soils with sufficient water permeability and rich in nutrients. The high yields of the railings provide for sowing it on ordinary and leached chernozems, on sandy loam and alluvial river soils, after spring rains they do not form a crust. The soils are saline and waterlogged, sandy and structureless, easily floated, unsuitable for this crop, since it does not tolerate even partial stagnation of water on the soil surface, especially during germination. Railings are a short-day plant, promotes faster formation of reproductive organs and accelerates its budding phase, a decrease in the length of the day sharply shortens the growing season as a whole. With late spring and summer crops, it sharply reduces the passage of phases, with the exception of flowering and ripening; with the advancement of crops to the northern regions, the growing season increases. Based on the bioecology of the railings, its requirements for living conditions correspond to the soil and climatic conditions of Ukraine in the regions of the northern Steppe, southeastern and northwestern Forest-steppe, southern regions of Polesie. The most areas for growing it in Ukraine are Poltava, Cherkasy, Vinnitsa, Kiev, Khmelnitsky and the south of Zhytomyr regions. There are not many types of railings. The best of them is the Ukrainian variety 30, bred at the Ukrainian station of oilseeds (now the Institute of Oilseeds of the National Academy of Sciences of Ukraine). These are plants 62 cm tall. The bush is compact, rather branched. The stem and branches are green, before ripening with an anthocyanin coloration. Leaves are medium in size. The flowers are white.Seeds are dark brown, small. The mass of 1000 seeds is 2-3 g. The oil content in the seeds is from 42.8 to 48.1%. The variety is mid-season. Drought resistance is average. Withstands early spring frosts relatively well. The technological process of growing the railings consists of the same operational methods of growing as for other row-crop small-seeded crops in the corresponding soil and climatic zone, for example, oil poppy. But when drawing up a diagram of a zonal minimalized agricultural complex, a technological project and a railing cultivation map, one should take into account the peculiarities of the technology of its cultivation. For example, railing-tilled small-seeded crops, for uniform sowing of seeds during sowing, the field before sowing should be rolled with a smooth roller, against the background of a high supply of the railing with phosphorus and potassium on gray podzolized soils and on ordinary chernozems of the northern Steppe, it is necessary to apply nitrogen fertilizers and uneven ripening, dusting seeds determine certain characteristics of collection and the like. If a technological map for the cultivation of railings is being developed, then it is necessary to make an energy analysis of its effectiveness according to the established method.
Features of agricultural technology. The best predecessors of the railings are winter cereals, perennial grasses, grain legumes and row crops. It is sensitive to the introduction of manure (30 t / ha) and mineral fertilizers (N 45 P 60 K 45) for fall plowing. The main cultivation of the soil under the railings is carried out in the same way as under other row-crop spring crops. In the spring, before sowing, the fall is harrowed, one or two cultivation is carried out (by 8-10 and 5-6 cm) with harrowing and pre-sowing rolling with smooth rollers. The railings are sown early, when the soil warms up at a depth of 5 cm to 10-12 ° C. Experiments carried out in Ukraine have shown that the best time for sowing railings in the northern Steppe and the southeastern part of the Forest-Steppe is early - simultaneously with the sowing of early ear crops and not later than the first decade from the beginning of spring field work. At late sowing dates, the seeds fall into the upper dried layer of soil, which leads to a thinning of the stairs and a decrease in yield. In the areas of the northwestern forest-steppe and in Polesie, with a wet and cool spring, the best sowing time for the fixed ropes is later, at the end of the second decade from the beginning of spring field work. The railing is sown in a wide-row way with a row spacing of 45-60 cm. High yields are harvested when one plant has from 600 cm 2 (North Step) to 250 cm 2 (Polesie) of the feeding area. This is achieved by setting the appropriate seeding rate: 6 kg / ha for the Steppe regions, 7 kg / ha for the Forest-steppe and 8 kg / ha for Polesie. The seeding depth: on structural and light soils with sufficient moisture content is 3-4 cm, and on heavy loams - no more than 2 cm. Before the emergence of seedlings when the soil crust is formed, rotary hoes or light tooth harrows are used. In order to destroy weed seedlings of stairs, the railings in the phase of 2-3 pairs of leaves can be harrowed with light harrows. The row spacings are cultivated 3-4 times to a depth of 4-5 and 6-8 cm. During the first treatments, protective devices are used against the railing of the staircase with soil.
Handrail pests and diseases and control of them. The greatest losses in the yield of the railings are caused by pests: sandy midliak, caterpillars of peril and cotton scoop, spider mite. Sandy midlask damages seeds during germination or gnaws at the stem. An effective means of control is the decomposition of poisonous baits. Scoops: caterpillar eats seeds in clusters, adult caterpillar damages leaves and stems. An effective means of control is biological - the release of trichogramma during the period when the scoop lays its testicles. The spider mite sucks the juice out of the leaves, settling on its lower part. Damaged leaves dry up and die off. Means of control - pollination of plants with the necessary preparations.The handrail is also damaged by the spinning top. Among the diseases of the railing, wilting and spotting are the most dangerous. Withering (fusarium and verticillosis) affects the entire plant. Affected plants turn brown, the leaves curl, as a result of which it dies. Most often, the disease manifests itself in hot, dry weather. Spotting is observed mainly before flowering. The disease affects the edges of the leaf blade, turns brown and dries up. Affected plants are stunted and yield less. Compliance with a high level of agricultural technology is the main prophylactic means of combating diseases.
Harvesting. The railing ripens unevenly, the seeds fall off easily, so it is harvested in a separate way. The berry is harvested when 20% of the seeds are of normal color. The seeds are quite light, the average weight is 1000 pcs. is 2-4 g. Harvesting is started at the beginning of seed ripening, when about 20% of it becomes brown or gray in color and a mesh pattern, and the total mass of seeds has a yellowish color with a somewhat noticeable mesh pattern. Threshing of rolls is carried out by combines equipped with devices for harvesting small-seeded crops. Threshed seeds are cleaned and dried to 8-9% moisture. The seed yield ranges from 8-10 centners to 15 centners per hectare.
Economic value. Railings (or suza) are a very valuable oilseed crop. It is grown for the sake of seeds (small round nuts), which contains, depending on the variety and soil and climatic conditions, 44-58% of technical fast-drying oil (iodine number 181-206). The fatty acid composition of railing oil is almost identical to linseed oil and is: myristic acid <0.1%, palmitic acid - 4-8%, palmitoleic <1%, margaric <0.3%, margaroleic <0.3%, stearic - 1.0 -3.0%, oleic - 11-18%, linoleic - 12-20%, alpha-linolenic 44-68%, arachidic <0.5%, aicosenic <0.8%, behenic acid <0.5%. The high iodine value is due to the significant content of unsaturated fatty acids in perilova oil, which indicates its valuable technical qualities. The drying capacity of perilovy oil is higher than that of lionovy and lalemantia and is close to the best technical oil - tung oil. Perilova oil is of particular value in the paint and varnish industry. The varnishes and paints made from it, when dried, provide the best film in terms of thinness and plasticity, do not crack during deformation, therefore it is widely used in aviation, shipbuilding, automobile, automotive, electrical, printing, carriage-building, rubber techno-woven, medical and other industries. The oil has excellent insulating properties, and the impregnated cloth and paper are the raw materials for making raincoats, do not get wet, and insulating materials. In the countries of East Asia, handrail oil after processing is also used in the food industry. Used for flavoring sweets, as well as an additive to dental preparations. In Japan, oil is used for the preparation of sweeteners, since one of the two isomeric forms of perilaldehyde oxime is 2000 times sweeter than sugar, and 4-8 times sweeter than saccharin.
Railings are a good honey plant. Fresh railing leaves contain from 5 to 33 mg of vitamin C, the amount of carotene, iron, niacin, riboflavin, thiamine and about 0.2% of essential oils, which have a wide composition, is not large. The leaves also contain 0.3% protein. From the leaves of the railing, essential oil is produced, which is used in the confectionery industry (in Japan), fresh leaves are used in the preparation of salads. The essential oil is obtained by steam stripping the low temperature dried leaves for the next two weeks. The composition of the oil, as with many related spices, depends on the growing conditions. The main components are a-pinene, limonene (9%), perilovic aldehyde (up to 50%).The cake after pressing the oil is a valuable feed for animals, it has the following chemical composition: 11.7% fat, 37.6% protein, 19.4% nitrogen-free extractives, 16.3% fiber, 7.9% ash, and 7 , 1% water. The cake before use]]> should be steamed well in hot water for feed, which evaporates the essential oil and almost completely disappears the unpleasant odor. Railing and oriental cooking are widely used. The railing leaves are rich in essential oils and give off a strong lemon scent when ripe. Therefore, handrails are more often used for preparing and serving fish dishes and vegetable salads. Vietnamese chefs use banister leaves in spicy concoctions to soups, rice, noodles, grilled meats, and seafood. Koreans ferment and wrap them in gimbap (Korean version of Japanese rolls) - rice rolls with vegetables. In Japanese cuisine, the red version of the handrail is called akajiso, and the green one is aojiso. Plants are also used in pharmaceutical production in the manufacture of various medicines for the treatment of diseases of the liver, gallbladder, nircocamian disease, and enuresis. So, if the stem is cut off during the flowering of the plant, then in the crushed and dry form it acquires medicinal properties. Railing leaves have long been used in medicine: in the east, they are prescribed as an antitoxic, sedative, analgesic agent, in the west, as a homeopathic, antiallergenic, stimulating or regulating the digestive system, and as diaphoretic drugs. In addition, railing seeds contain a sugar acid neutralizer, slows down caries, plaque formation and has antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory effects, protecting the oral mucosa. In cosmetology, the raw material of the sudza is used in anti-cellulite gels. When growing a railing in personal plots, seeds to accelerate germination can be soaked for 2-3 days and sown in boxes with a peat mixture, and in April-May in film greenhouses. Seedlings dive and plant in a permanent place at a distance of 20-30 cm from each other. Plant care includes periodic weeding, soil loosening and watering.
How to choose the right seeds
When growing a perilla plant, it is worth remembering that there are only 2 varieties of it. One of them is required to obtain oil from seeds, but it is of little interest to gardeners, since the seeds do not always fully ripen, and it is very difficult to make oil on their own. Most of these varieties are grown on an industrial scale.
Therefore, a vegetable variety of perilla is more often grown, presented in a wide variety. It is worth purchasing seeds from reliable, proven companies, while paying attention to the name and characteristics.
Handrail cleaning and storage
The cleaning of the perilla is started simultaneously with the beginning of its flowering. Its shoots are cut 10 cm from the ground or, if desired, you can selectively cut off the branches you like. Usually there are 2 cuts per season. From 1m2 you can get about 5kg of greenery and less - it all depends on the conditions in which it is grown.
The greens are harvested before the plant blooms. It can be kept moist for a week in the refrigerator, preferably in a glass container with a lid.
It is better to refuse plastic bags, because greens rot in them. For long-term storage, there are old proven methods of harvesting. Perilla leaves are pickled, salted, sauces and drinks are prepared from them, they can be finely chopped and frozen.
Planting seedlings
In the southern regions, the seeds of the perilla plant can be planted directly in the beds, and it is quite possible to do this even for the winter. In this case, it can also be done by self-seeding. In cooler regions, seeds often do not ripen, and it is best to plant with seedlings.
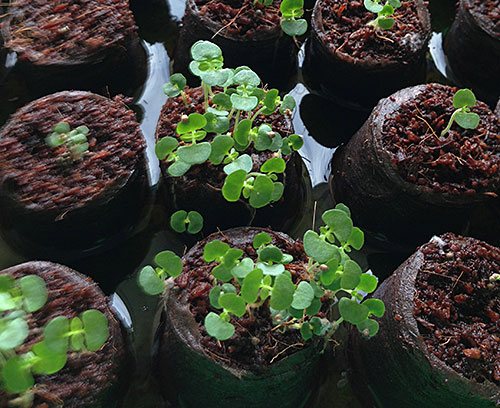


If conditions permit, then seedlings can be started to grow from February, but it is best to wait until early April. Seeds will germinate much better if they are soaked in water for several days before sowing, which must be changed daily. In this case, wet seeds should periodically receive air access. After that, it is advisable to dig them a little in slightly damp sand or keep them in the refrigerator for a week. However, perilla often grows well even without presoaking.
For sowing, it is best to take light soil, and the boxes should have holes so that excess moisture goes away quickly and easily. You need to sow the perilla thickly, so that later you can easily remove weak plants. After planting, it is advisable to sprinkle perilla seeds a little with soil on top and put in a warm place. You can also leave them open for better light access. On the windowsill, the air temperature should be approximately 20-25 degrees. The first shoots appear literally in 1-2 weeks. The sprouts are very much like basil.
When the first shoots appear, you need to sprinkle them with sand a little and moisten them. This procedure can be repeated several more times. After the appearance of the first 2-3 leaves, the seedlings can be transplanted into separate cups. Do not plant the railing in a common box, as when planting in the soil, you can damage the root system. It can be planted in the ground at the beginning of June.
How to plant correctly and by what methods to propagate
Railings are planted according to the following points:
- In the fall, a garden bed is prepared in a sunny area. The soil is carefully shovel and compost is applied.
Advice. It is advisable that the planting of the perilla be carried out in an area where legumes grew last season.
- In the spring, holes are dug and fertilizer containing a complex of minerals is applied to each of them.
- Planting seedlings on a garden bed is carried out at temperatures not lower than + 12 ° C.
- A distance of about 30 cm is maintained between the seedlings. In the future, such an interval will facilitate maintenance.
- Make abundant watering.
- It is advisable to sprinkle the landing with sand on top. This will prevent the soil from drying out and the development of fungal diseases.
Perilla propagation is practiced using seeds. In the southern regions, they can be sown directly in the open field in spring or autumn. Growing through seedlings is desirable in cooler areas.
- Prepare a substrate from peat and sand (1: 1).
- Seeds are pre-disinfected in water with manganese.
- They are sown into grooves 5 mm deep.
- Watering is done carefully.
- Cover the container with plastic wrap and place in a warm place.
Seedlings break through in 2 weeks. They are provided with appropriate care, including regular watering and thinning. Fertilization of seedlings is not required.


Grow a crop from seeds
Some amateurs propagate perilla by cuttings. To do this, you need to cut off the stems, put them in water, wait for the roots to appear and plant them in the ground. This method of reproduction is used when planting a plant for the winter from a garden to a pot.
Transplanting seedlings into soil
The soil for growing the plant must be waterproof and loose. It is best if beans or peas have previously grown on the site. In the fall, rotted compost must be added to the site, and in the spring - complex mineral fertilizer.
In early June, perilla can be planted in open soil. The planting density is 25 bushes per m2. The plant normally tolerates a transplant, since it is completely unpretentious to care for. It is important to provide proper care for the perilla plant, which means:
- watering;
- loosening;
- top dressing;
- weeding;
- pinching.
A small amount of chicken manure is good for feeding. It needs to be scattered under the bushes of the plant.Perilla normally tolerates summer heat and drought, but it is advisable to carry out periodic watering, not allowing the soil to dry out too much. The optimum temperature is 22-28 degrees. An adult plant does not tolerate a drop in temperature very well. However, it is worth remembering that in extreme heat, petals and not yet ripe seeds can also fall off.
How perilla reproduces
Reproduction most often occurs by seeds. They are sown directly into the ground or for seedlings. In warm climates, sowing in open ground is performed in March or sown for the winter. In mid-latitudes, cultivation begins with seedlings. Seed material is pre-soaked in manganese solution or growth stimulator for 2 days.
The containers are filled with a sand-peat mixture and seeds are placed in it. The depth of the deepening is 0.5 cm. The soil mixture is moistened with a spray bottle. Cover with foil and place in a warm place.
The shoots that appear after 2-3 weeks are thinned out several times. A small layer of sand is poured into the glass from above. The appearance of 2 full-fledged leaves serves as a signal for landing in open ground. Disembarkation time falls in the middle of May.
Perilla seeds
At the end of September, the stems are cut off at the perilla and rooted in water or a nutrient mixture. Under indoor conditions, the plant continues to grow and re-flowering occurs.
Preparing for landing
Site preparation begins in the fall. An open, illuminated area is allocated for the railing. High illumination is especially important for variegated and red-leaved varieties. Drafts must be avoided, otherwise the plants will grow frail.
The earth is dug up with compost to get loose soil. Planting after peas and legumes favorably affects the growth of perilla. Spring planting of seedlings is started at an average temperature of + 12 ° per day. Mineral fertilizer is added to the prepared hole and a bush is placed. The seedlings are placed at intervals of 20-30 cm. Sand is poured around the plants to protect against fungal infections.
Railing description
Perilla is a perennial with beautiful foliage, which is used not only for decorative purposes, but also as a medicinal and cosmetic agent. This plant is also used in cooking as a spice. The culture is thermophilic, so in mid-latitudes in the open air it can grow only from spring to autumn. Dies in winter.
The shrub perilla looks like this:
- Despite the name, perilla is not a shrub at all. It is just a very branched plant, the height of which in different species can be from 50 to 150 cm.
- The stems grow, have 4 edges.
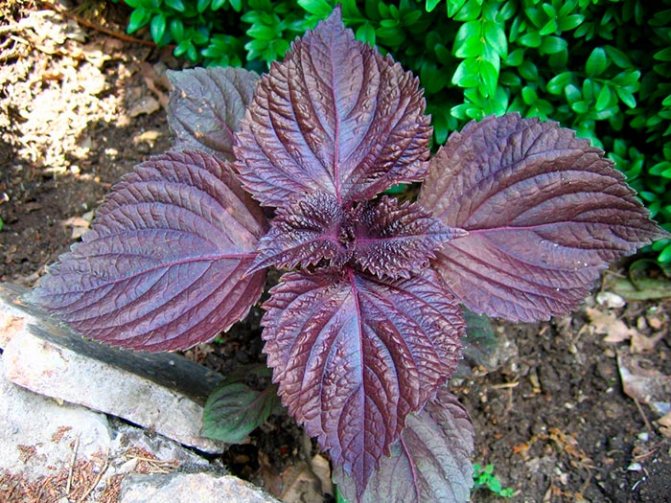
- The leaves are large enough (up to 12 cm), ovoid, serrated along the edge, often wavy. Their color depends on the variety and can be green, purple, dark purple, almost black.
- The flowers are plain white or pale pink bells. Inflorescences are located at the tops of the shoots in the form of elongated brushes.
- Flowering begins in mid-summer and ends in early fall.
- Fruits containing four nuts do not ripen in the open ground of a temperate climate.


In Asian countries, perilla shrub is a very popular crop added to salads and used as a spice. Moreover, under appropriate conditions, it was revealed that there is much more carotene in its leaves than in the roots of the well-known carrot. Oil obtained from seeds is also used for food.
The content of the substance perillamine makes it possible to use perilla shrub as a medicine. It is used for disorders of the heart, poor eyesight, a decrease in the body's immune activity.
Beneficial features
Perilla belongs to natural antioxidants. It has an antiseptic, anti-inflammatory effect, due to which it has a healing, strengthening effect on the body in certain areas:
- Perilla relieves allergy symptoms. Relieves nasal congestion, relieves seasonal rhinitis and other discomfort.
- Increases immunity, fights viral, infectious diseases. Strengthens the protective function of the body during the season of colds, flu epidemics.
- Strengthens the walls of blood vessels, improves blood circulation and heart function. Strengthens blood flow to internal organs.
- The flowers of the plant, when taken internally, have a positive effect on the nervous system, bringing the state of mind into balance. Regular consumption of the plant will reduce the level of anxiety, relieve symptoms of chronic stress.
- Accelerates the restoration of bone, cartilage tissue, which is why decoctions based on perilla are especially useful for fractures and joint diseases.
- The use of spicy herbs also has a positive effect on the condition of the skin and hair.
To view a review about the plant and its properties:
Known plant varieties and varieties
For growing in the open field of a temperate strip, the following varieties are most often used:
- The mulatto is a very decorative, low plant. The leaves are purple, corrugated, serrated along the edge. The crown is pyramidal.
Advice. So that the plant does not lose its decorative effect longer, flower growers recommend cutting off the peduncles.
- Aoshisa is a Japanese variety with green leaves that exude anise and caramel aromas.
- Akoshisa is also a representative of Japanese varieties. The red leaves are endowed with a peppery scent.
- Dewdrop - This variety is eaten. The leaves are red. In the open field, its planting is not damaged by the first frost.
- Mint Red - Purple fringed leaves with mint, lemon and cinnamon scent.


All varieties are very easy to distinguish by photo. The care and reproduction of the varieties is the same.
What to combine perilla with. Diseases and pests
In the garden, the shrub perilla looks very decorative. A wonderful combination of varieties with different colors of leaves, planted in the same flower bed. The railing is also good in the monotypic design of the borders. Planting a plant as a vegetable crop is also possible in a flower bed. The overall look will only benefit from the combination of bright foliage with flowers.
Groups of shrub railings look great against the background of conifers, ferns, deciduous shrubs.


The culture is affected mainly by fungi. These organisms, in stagnant water, damp and cold weather, can cause diseases such as fusarium, verticellosis and spotting. Prevention is compliance with the rules of care.
Of the pests that can damage any part of the plant, spider mites, scoops and various caterpillars can be noted. If they are found, the perilla must be treated with suitable insecticides.
Attention! If the plant is planned to be eaten, then the chemical preparations for processing should be selected with great care.
Perilla shrub is a wonderful culture that can decorate the garden, diversify the diet and improve health. With all its advantages, it is absolutely unpretentious, does not require a lot of time and attention from the gardener.
Perilla (Perílla) stands out for its beautiful foliage and serves as a decoration for the garden.


Perilla
Perilla is actively used in landscape design, cooking, folk medicine and cosmetology. In terms of carotene content, perilla is not inferior to carrots, and the amount of omega acids in plant oil is 2 times higher than fish oil.
How to care. Fertilizers and feeding
Handrail maintenance is not difficult. It is enough to provide watering, loosen the soil and sometimes remove weeds.
Advice. In autumn, during the first frosts, almost all plant varieties wither quickly, therefore, for further use, it is better to transplant the perilla into a container in advance and bring it into the room.
The plant is fed monthly. For this, compost and manure are used as mulch and fertilizer. When growing perilla for food, cutting of the stems is included in the grooming. It begins when the plant reaches 10 cm. After complete regrowth, the procedure is repeated.
If the perilla is grown for decorative purposes, then pruning is not needed.In this case, taller varieties should be supported to prevent them from lodging.
Contraindications for use
Perilla is a medicinal plant used in food preparation and medicinal products. You should know the diseases and features in which its use can harm the body. These include:
- individual intolerance, allergies;
- pregnancy, breastfeeding period;
- hemophilia;
- time of preparation of the body for surgery;
- peptic ulcer in the acute stage.
It is important to use the herb correctly, observing the dosage. Excessive use of the spice can lead to unwanted side effects - stomach problems, kidney problems, and an allergic reaction.
Reproduction methods
Perilla is propagated mainly by seeds. They can be sown directly into open ground or pre-grown seedlings. In open ground, seeds are sown before winter or in March. This method is suitable for southern regions, as the seedlings will take a long time to germinate and develop slowly. In temperate climates, it is advisable to grow seedlings. The seeds are soaked in warm water with the addition of potassium permanganate for 2 days, and then sown in sandy-peat soil to a depth of 5 mm. The soil surface is sprayed with a spray bottle and covered with foil. Store containers in a warm place.
Seedlings appear in 2-3 weeks. They should be thinned out periodically. The surface of the earth is sprinkled with a thin layer of sand. When 2 true leaves appear on the seedlings, it can be planted in open ground. This usually happens in mid-May.
In September, perilla stems are cut and rooted in light, fertile soil or water. The plant pots are moved indoors. As a houseplant, perilla continues to grow and bloom again. In temperate climates, this is the only way to wait for the seeds to ripen.


[collapse]
Description
The herbaceous perennial belongs to the family of the lacustrine plants. Plant height reaches 40-60 cm. The tetrahedral stem has few branches.
The color of the leaves is varied: bright green, with purple blotches, variegated, wine-red. Beautiful rounded leaves have short petioles and opposite arrangement. A structured leaf surface with a sharp end and jagged edges. The lower leaves are larger, up to 10 cm long.
In the garden, perilla is prized for its decorative effect. Therefore, varieties with a long growing season are more often planted.
Perilla throws out flower stalks in autumn, when the day becomes shorter. At the top of the plant, tiny axillary flowers bloom, white, purple or lavender, as in the photo. Bells are located on a short pedicel and are collected in racemose or paniculate inflorescences. The pollinated flower gives dry fruit with small nuts. The plant itself is sown when the fruit reaches maturity and opens.
Perilla is a thermophilic plant (pictured), does not have resistance to frost, therefore, it is sown annually in the regions of the middle lane.


Perilla shrub
Names, varieties and varieties of perilla kutarnikova
Although the Nanking Perilla is called a shrub plant, it is clearly herbaceous. The specific name "shrub" is not quite a correct translation from the Latin name (frutescens). It would be more correct to call it "bushy" or "bushy", that is, lush, branchy. Sometimes they also mistakenly translate "fruit", confusing the Latin "fruit" (frut) and "fruit".
Perilla of Nanking has many other names. Probably, no plant has so many names (it's not even about varieties). For example: - perilla basilic, wrinkled, fringed, vegetable; - Japanese parsley; - red mint, Chinese lemon balm, Chinese basil; - Chinese shiso (jiso), Japanese suza; - Vietnamese coriander, wild sesame.And these names do not exhaust the list of perilla names.
But we will not drown in this bottomless sea of names. In fact, all this is a variety of names of one type of plant, the birthplace of which is the Himalayan mountains. It is important for us to know that there are two types of Nanking shrub perilla. One of them is used to extract oil from seeds (it is usually called Japanese suza). But our gardeners are not interested in it: after all, perilla seeds do not ripen everywhere. And it is too difficult to squeeze oil from perilla seeds on your own, this is for an industrial scale. We need another variety, the seeds of which (hopefully) are sold in our stores - vegetable perilla
... She is also very many-sided: bushes of different heights; leaves are small or large, monochromatic or spotted; the leaf blade is even or curly, dissected; the edges of the leaves are jagged or fringed. The color of the leaves of perilla is green, dark red, purple-violet or almost black.
Russian seed companies offer perilla varieties: Mulatka, Purple, Ornamental, Florist's Dream, Absinta, etc. At the same time, only four perilla varieties are listed in the official Russian seed register: - Novinka - very old variety, back in 1946 it was proposed by the Far Eastern Experimental Station for obtaining oil from the seeds of this plant; - "Rosinka" is a vegetable variety (green-leaved), although we often pack different red-leaved forms of perilla in bags with this variety; - "Aozhiso" (green-leaved) and "Akazhiso" (red-leaved) - two Japanese varieties of perilla, which can be found in variants of partial translation from Japanese into English: "Giso Green" and "Giso Red" or "Aozhiso Green" and "Akazhiso Ed. "
In order to enjoy communication with the vegetable perilla in our garden, we try to purchase seeds from the most reliable companies, while paying attention not so much to the name of the perilla variety, but to its characteristics.
Growing from seeds
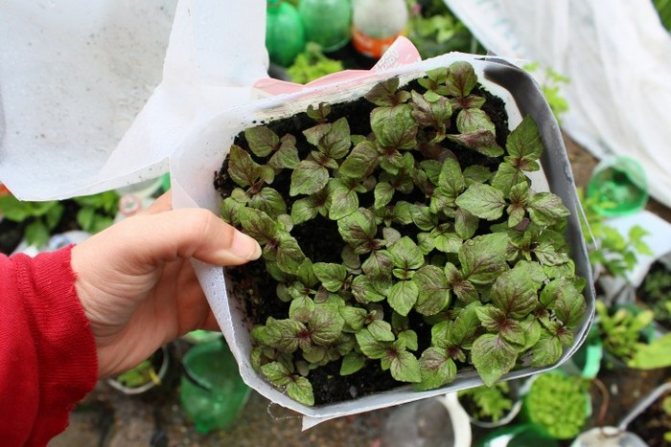


When growing vegetable perilla from seeds, two aspects are important. For germination, the seeds require light, the seeds are slightly pressed into the substrate, the pot is placed in a foil bag. The second aspect is the temperature of the moist soil. Temperature is about 20 ° C, lower, germination will be long and uneven, making the subsequent pick difficult.
The surface temperature of the substrate is important when propagating by cuttings. A pot of seeds can be placed on a radiator, then problems may arise with cuttings. Be sure to use a root former for herbaceous plants to speed up the process.
Perilla in the kitchen
Perilla greens are delicate and juicy, its light peppery taste is diluted with notes of anise and lemon. Salads are prepared from the aromatic leaves of the plant. Green species with a fresh lemon scent are more suitable for this. They are used to season fish and seafood dishes. Colored leaves have a spicy, sweet scent.
They are eaten in salads or pickled. Foods and pickles with red leaves turn out tinted in a beautiful pink color. Dried and crushed leaves are used in marinades for meat and fish, seasoned in soups and vegetable dishes.
After special processing, butter is used by confectioners, it is added to baked goods, fillings, candies.
Bright, colorful greens are used to decorate various dishes before serving.
Watch also the video
Perilla (Perilla frutescens) is an oilseed crop from the labiate family. It is an annual plant reaching a height of 60 cm to 1 meter. At the bottom of the plant, the leaves are large, with long petioles, resembling an egg in shape, the petioles of the upper leaves are short. At first glance, perilla can be confused with basil. But these plants have differences:
Perilla leaves are not as smooth and cool as those of basil. The surface layer of perilla leaves is warm and rough to the touch.
The edges of the perilla leaves are larger and jagged.
Perilla seeds, in contrast to the seeds of basil plants, do not stick together, do not become slippery after being exposed to moisture.
The leaves are located at the perilla opposite each other. The color of the leaves can be different - from green to reddish, there are plants with purple hues. Such a multicolor leaf color allows using perilla not only as a useful plant, but also as an ornamental plant.
Perilla flowers (pink, purple, white) are similar to racemes or panicles and are located on short pedicels with fine hairs. The flower's calyx, which resembles a glass or a bell, is also covered with thick fine "pile". The fluffy, bell-shaped corolla is equal in length to four stamens.
The dry, rounded fruit splits into 4 nuts.
Origin
The origin of the perilla is Japan and China. The plant is cultivated all over the world and in each country they give their name. For example, wild sesame, Chinese basil, shiso, tylkke, Vietnamese coriander. In Russia, perilla is not deservedly forgotten, although in the middle of the 20th century it was popular among gardeners.

The birthplace of perilla
Where is the best place to grow
This thermophilic plant loves a bright place, and also does not tolerate cold winds. Perilla tolerates partial shade well, although most of all it prefers sunny places with constant moisture near the rhizome, however, you should not allow stagnation of water.
Low-growing shrubs look good in the foreground of flower beds and borders. Against the background of lush shrubs with an abundance of luxurious foliage, absolutely any garden plants are in harmony, especially those with a contrasting color of foliage and bright flowering.
Medicinal properties
The seeds and beautiful large leaves of perilla contain a large percentage of essential oils used to treat and prevent many diseases. From these parts of the plant, decoctions are cooked with an analgesic, antiseptic and sedative effect. Perilla decoction is effective for bronchitis, coughs of any origin, colds, it can be used as a diuretic or diaphoretic.
But the most beneficial for health is perilla oil, obtained by cold pressing from the seeds of the plant. The oil contains 64%, which is among the top most beneficial for the functioning of the human body. In addition, this oil contains alfalinoleic and, and it contains twice as much as in. Perilla leaves and seeds contain protein, and, and, as well as the already mentioned carotene in a huge concentration (about 9%).
The use of oil for the prevention and treatment of many diseases leads to a decrease in blood levels, heals skin diseases, lowers blood pressure in hypertension, relieves inflammation in the joints and has a calming effect. Tannins, glycosides, terpenes, flavonoids and phenolic compounds in the composition of the product have antioxidant, anti-inflammatory and antiviral properties. Western European homeopathy widely uses the plant as an excellent regulator of digestive processes. The rosmarinic acid present in the oil has sunscreen properties, prevents the penetration of free radicals into the skin, stabilizes cell membranes, and has protective properties against cancer.
Perilla oil is widely popular in Asian cosmetology and perfumery. It is able to nourish and deeply moisturize the skin, eliminate irritation and itching. Thanks to these properties, creams, scrubs and masks for the skin, as well as shampoos and hair balms are made on the basis of this ingredient.
Perilla shrub plant is a unique storehouse of vitamins, minerals, for beauty and human health. The use of this plant makes it easy to avoid many diseases, and in the presence of chronic pathologies - to do without pharmaceuticals.The effectiveness of perilla oil and infusions has been confirmed by many medical studies, and the taste of vegetable and meat dishes prepared with its use is noticeably improved and acquires multifaceted shades. That is why, if there is an opportunity to buy and use this plant, it is better not to give it up.
Perilla is a useful and beautiful plant, which is still quite rare in our gardens, although it deserves it.
Of the several existing species of perilla, which include annual and perennial grasses and semi-shrubs native to temperate, subtropical or tropical regions of Asia, only one species is used in horticulture and ornamental floriculture - perilla shrub Nanking
(Perilla frutescens var. Nankinensis).
In the perilla of the Nanking shrubbery, gardeners are attracted by the fact that it belongs to a small group of universal plants - "multi-plant". Indeed, perilla is a green culture, a dye, and a beauty!
Perilla shrub Nanking by its nature is a herbaceous perennial. But in regions with cold winters, this plant is grown as an annual. Its height depends on the specific variety and cultivation conditions (from 40 cm to 100 cm, and sometimes even up to 150 cm in the tropics and subtropics). However, in our climatic conditions, too high perilla is a rarity; more often in our gardens there are undersized (40-45 cm) and medium-sized (60-80 cm) varieties.
Perilla belongs to the vast family of the caramel, consisting of the most aromatic and medicinal herbs, summer cottages and meadows. We are well aware of the popular representatives of this family:, (oregano), motherwort, (salvia), lamb, etc. All these plants are rich in essential oils and complexes of active organic compounds - terpenoids, saponins, flavonoids, alkaloids. But even the alkaloids in lamines have such a mild effect that they are not poisonous and dangerous. They are not comparable to such strong alkaloids as poppy morphine, dopey atropine, aconitine from, solanine (found in immature and green tubers), digitaline from - they all deserve to be compared in terms of toxicity with nicotine, cocaine, strychnine and tubocurarine (poison). On the contrary, in comparison with many of our other garden pets, plants from the lamb family are quite harmless and very useful; it is time to include the Nanking shrub perilla in this circle.
Growing perilla outdoors
Growing from seeds is possible in two ways: through seedlings or immediately in the open field.
As for the choice of the Perilla variety, usually Russian gardeners choose the Rosinka variety, whose yield is 0.5-5 kg per square meter, and the mass of the bush reaches 500 grams.
Vegetable perilla "Rosinka": how to grow from seeds
To grow perilla directly from seed, follow these instructions.
Preparing the ridge in which it will grow
We choose for sowing a sunny, fertile plot of land, not blown by strong winds.
We feed the soil with compost at the rate of 3 kg per square meter. We apply half of the compost immediately, the other half when the plants begin to grow green mass.
Ideally, perilla is best sown in areas where beans, peas or beans grew last year.
Sowing seeds
We sow perilla seeds when the ground warms up to 10-12 degrees: sprouts appear in warm ground after 10-14 days.
Seeds are sown in groups of three at a distance of 40 cm from each other and to a depth of no more than 0.5 cm.
Thinning the plants
As soon as the perilla grows up, in each group we leave one of the strongest plants, the rest are pulled out and used as greens.
In order for the plants to grow rich green mass, no more than 25 railings should remain per square meter. By the way, in the southern part of Russia, perilla can be sown before winter.
Perilla "Rosinka": growing by seedlings
If you live in the middle lane, we grow perilla in a seedling way so that it has time to give a couple of decent harvests of greenery:
- Preparing the soil
... Best of all, perilla seeds sprout in the soil from peat and humus: we put it in a box for seedlings. - Preparing the seeds
... So that the achenes germinate sooner, we put them in wet sand and put them in a cool place for a week. The second option: we soak them in water for three days, regularly changing the water. - Sowing seeds
... You can sow perilla seedlings at the end of March or in early April. We sow achenes in moist, shallow rows, without covering them with earth. Cover with plastic and put in a warm, bright place. When the roots appear from the achenes, sprinkle them with sand a little and moisten them so that they take root well.
We plant seedlings in the garden at the beginning of June, when there is no longer any frost.
Growing perilla in the garden
Perilla seedlings are relocated to open ground at the onset of stable heat, when there is no longer a risk of frost return.
The heat-loving perilla loves a bright place, does not tolerate cold winds. She will also endure partial shade, although she prefers sunny places with constant moisture at the roots (without stagnant water).
Perilla seedlings can withstand transplanting quite easily, they are not capricious. Perilla seedlings are placed in a group at a distance of 20-25 cm or 30 cm from each other, depending on the future size of adult plants.
For greater bushiness, young plants are pinched. In tall forms of the perilla, you can make a decorative haircut of the bush.
Low-growing elegant perilla bushes are good in the foreground of flower beds and in borders. Against the background of lush perilla bushes with an abundance of spectacular foliage, any garden plants look great, especially with contrasting leaves and bright flowers.
On site site on site site on site site
Weekly Free Site Digest Site
Every week, for 10 years, for our 100,000 subscribers, an excellent selection of relevant materials about flowers and garden, as well as other useful information.
Subscribe and receive!
It has a very strong resemblance to basil, but they have certain differences. The surface of the leaves near the perilla is warm and somewhat rough to the touch. Their color can be completely different - from green to purple.
The variety of color shades allows using perilla not only as a useful plant, but also as an ornamental plant. The flowers are very similar to tassels and are located on short pedicels.
The perilla plant, the photo of which demonstrates its peculiarity, belongs to aromatic and medicinal herbs. It is very rich in essential oils and organic acid complexes. It is worth noting that the alkaloids that make up the plant have a very mild effect, so they are not dangerous or poisonous.
Varieties


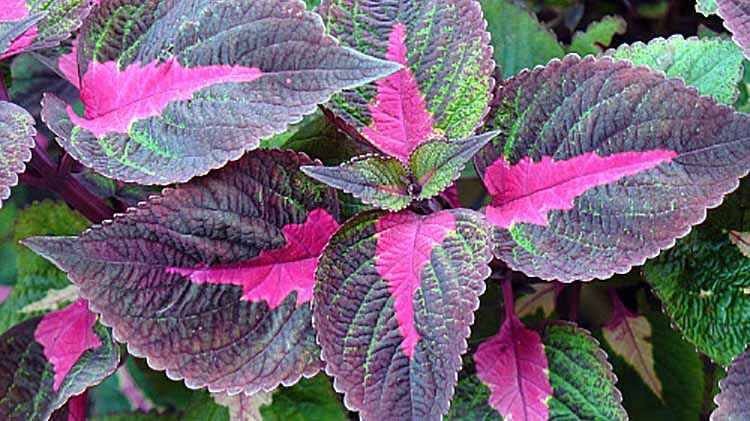
- Mulatto - leaves are purple, curly.
- Dewdrop is a precocious, frost-resistant variety, the growing season is 135-150 days. Height - 120-140 cm, stem erect, branching, tetrahedral.
- Oriental doctor is a spicy plant, 40-60 cm, strongly branched. The leaves are large, double-toothed. Contains minerals calcium, iron, potassium and essential oils. Contains more carotene than carrots. Teas and decoctions are prepared from the leaves.
- Akazhiso Red is a 60-100 cm high variety, highly branched. Leaves are red-burgundy, broadly ovate, with a jagged edge. The taste is delicate, with a mild lemon-aniseed aroma and a light peppery flavor. The variety is used for pickles and pickles, "Japanese parsley" will give a beautiful pink color and pleasant aroma.
- Akashiso is a perilla variety with purple leaves.
Heterosis varieties are hybrids of two types obtained by repeated crossing. Hybrids cannot be propagated from their own seeds.
Growing perilla
In Japan, it is customary to decorate many gardens with a rail.The plant is strongly branched, it has large wrinkled and dryish leaves. Japanese crop selection is widespread in Europe. The most productive varieties are akashiso and aoshioso. Of the Russian varieties of perilla, the most used is dewdrop, which perfectly adapts to cold climates and gives high-quality fruits very quickly. Breeders are constantly developing new varieties of this wonderful plant.
Growing perilla requires good soil cultivation. The plant loves loose and fertilized soils. The seeds of the culture do not germinate quickly, therefore, it is bred on an industrial scale using seedlings. To do this, the seeds are soaked for several days before planting in pots, and after that they are already rooted. This process can be carried out not earlier than April-May, otherwise the perilla will not germinate. After 2 full leaves of the plant grow in the pot, it can be safely transferred to the ground. All bushes are planted at a distance of about 25 centimeters from each other so that the seedlings can develop freely.
As soon as a crop begins to bloom, it must be harvested. At a height of 10 centimeters from the soil surface, the perilla is cut off, after which the rest of the plant is able to give another crop. The average crop yield is up to 5 kilograms per 1 square meter.
Fresh perilla is kept in the refrigerator for about a week. It is not recommended to use polyethylene for these purposes, since such storage will promote leaf rot. Fresh herbs are best preserved in glass, tightly covered with a lid.
Plant application
The scope of application of the perilla plant is very different, and it is associated with its qualities. Its decorative properties help to apply it in landscape design, namely:
- flower arrangements are made with the addition of leaves;
- rockeries are created at their summer cottage;
- can be grown in flowerpots that decorate country houses.
Essential oils, contained in large quantities in the leaves and seeds of the plant, make it widely used in alternative medicine. Perilla decoction has a calming effect on respiratory tract diseases. In addition, it can be an excellent diuretic, helps with abdominal pain, food poisoning.
The varieties with green leaves are the most delicate. Red-leaved species have tougher leaves, but they are very beautiful and adorn flower beds throughout the summer. Suitable as a natural color for drinks and marinades.
In all varieties, the leaves can be used as a spice. Aromas differ in their types, so lemon, cinnamon, pepper and anise notes are present in the taste and aroma.
Leaves can be put in tea and other drinks, added to main courses, salads and pickles. Young greens can be pickled and fermented to fully preserve the beneficial qualities and vitamins. In Japan, the plant is used as a sweetener. It is worth remembering that prolonged contact with the perilla can provoke dermatitis.
What are the varieties of perilla
There are not many popular plant varieties:
- A fragrant plant with a bouquet of lemon, cinnamon, mint aromas. Leaves with a fringed edge are colored purple.
- Russian selection of frost-resistant species. The early ripening variety is decorated with red foliage.


- The plant has a peppery aroma and a red color.


- Aoshiso
Green perilla with a pleasant smell of pepper, caramel and anise. - Nanjing or vegetable perilla (pictured)
It is most popular for its taste. Nanjing perilla is very similar in appearance to basil, only the leaves are larger. It is found in several varieties, each with its own pleasant aroma of varying intensity. The aroma includes a combination of anise, mint, cinnamon, basil and lemon balm. - Shrub or basil
A tall plant reaches 80-140 cm.The wavy leaves are shaped like an egg. The contour of the leaf is jagged. Flowering begins in July, when a long spike appears at the top, strewn with small bell-shaped flowers.
Leaves with a pungent, rich aroma are edible. The variety is more interesting in its seeds. Essential oil is extracted from them.
Perilla harm
One should be very careful when using perilla, as well as other plants containing essential oils. In addition, it is worth remembering that it has a contraceptive effect. That is why it should be taken with extreme caution by women wishing to become pregnant.
More exotic plants, both decorative and spicy, appear on the personal plots of Russian summer residents and gardeners.
These plants include the spicy herb perilla, which can be grown in garden conditions and even on a windowsill. We will learn how to grow this tasty and aromatic herb with beautiful serrated leaves at home and outdoors.
Culinary uses of the plant
The juicy and delicate greens of this plant have many shades of tastes and aromas. A light peppery note in the taste is combined with aromas and. Perilla can be used in dishes, both fresh and pickled, salted or dried.
For sauces and all kinds of drinks, it is better to use pickled greens, but as a spice for meat or stewed vegetables, powder from dry leaves is better. The spice is made from green-leaved perilla varieties. Red-leaved varieties are used in all kinds of blanks and marinades. The plant gives not only an unforgettable taste to pickles, but also a rich color. For example, when salting stachis, you can use a red perilla, as is often done in Japan. The tubers of the plant, due to the red-leaved culture, become pinkish and acquire an unusual taste and aroma.
The healing properties of perilla
Perilla essential and fatty oils, which are found in large quantities in the seeds and leaves of the plant, have the main healing effect. Various infusions and decoctions are made from seeds and leaves, which have an antiseptic, sedative and analgesic effect. They are used for coughs, colds, bronchitis, and are also used as a diaphoretic and diuretic.
Perilla oil has great medicinal properties. It is obtained from plant seeds by cold pressing.
Perilla oil contains a large amount of alfalinoleic acid - about 64%. This acid is the most important unsaturated acid necessary for the full functioning of the human body. Oleic and linoleic acids are present in perilla oil in the amount of 15% and 17%, respectively. It should also be noted that perilla oil is the only vegetable oil that contains twice as much omega-3 acids as fish oil.
The use of oil helps with various skin diseases, lowers blood cholesterol and blood pressure, has a positive effect on the state of the nervous system, and reduces inflammation of the joints.
Perilla oil contains tannins and phenolic compounds (luteolin, catechin, rosmarinic acid, apigenin), as well as glycosides, flavonoids, terpenes, which have powerful anti-inflammatory, antibacterial, antiviral and antioxidant properties.
Rosemary acid protects the skin from the harmful effects of ultraviolet radiation, stabilizes cell membranes, fights free radicals, which is also associated with the anti-cancer properties of perilla oil.
In addition, perilla oil is widely used in Southeast and Japanese cosmetology and perfumery. It moisturizes and nourishes the skin well, relieves itching and irritation. Various creams, scrubs and face masks, as well as hair conditioners and shampoos are prepared on the basis of the oil.
YouTube video related to the article:
Found a mistake in the text? Select it and press Ctrl + Enter.
Do you know that:
The liver is the heaviest organ in our body. Its average weight is 1.5 kg.
74-year-old Australian resident James Harrison has donated blood about 1000 times. He has a rare blood group whose antibodies help newborns with severe anemia survive. Thus, the Australian saved about two million children.
Dentists have appeared relatively recently. Back in the 19th century, pulling out bad teeth was part of the duties of an ordinary hairdresser.
Millions of bacteria are born, live and die in our gut. They can only be seen at high magnification, but if they were gathered together, they would fit in a regular coffee cup.
Even if a person's heart does not beat, he can still live for a long period of time, which was demonstrated to us by the Norwegian fisherman Jan Revsdal. His "motor" stopped for 4 hours after the fisherman got lost and fell asleep in the snow.
Smiling just twice a day can lower blood pressure and reduce the risk of heart attacks and strokes.
More than $ 500 million a year is spent on allergy drugs in the United States alone. Do you still believe that a way to finally defeat allergies will be found?
The cough medicine "Terpinkod" is one of the best sellers, not at all because of its medicinal properties.
Four slices of dark chocolate contain about two hundred calories. So if you do not want to get better, it is better not to eat more than two slices a day.
Most women are able to get more pleasure from the contemplation of their beautiful body in the mirror than from sex. So, women, strive for harmony.
According to many scientists, vitamin complexes are practically useless for humans.
In an effort to get the patient out, doctors often go too far. So, for example, a certain Charles Jensen in the period from 1954 to 1994. survived over 900 surgeries to remove neoplasms.
The person taking antidepressants will, in most cases, be depressed again. If a person coped with depression on his own, he has every chance to forget about this state forever.
In addition to people, only one living creature on planet Earth suffers from prostatitis - dogs. These are really our most loyal friends.
It used to be thought that yawning enriches the body with oxygen. However, this opinion has been refuted. Scientists have proven that yawning can cool the brain and improve its performance.
What to do after tooth extraction?
Everyone can face the situation when he loses a tooth. This could be a routine dental procedure or a trauma. In each and ...
Perilla is a thermophilic herbaceous perennial of the Yasnotkovye family, whose homeland is considered to be Asia. The plant was first cultivated in Japan and China. Later they began to grow in the Far East and the Caucasus. Now gardeners can easily find the seeds of this plant and grow it.


They use perilla in cooking, in folk medicine and cosmetology, decorate flower beds with it, make industrial and edible oil.