Preparation of grapes for wintering begins in the summer.
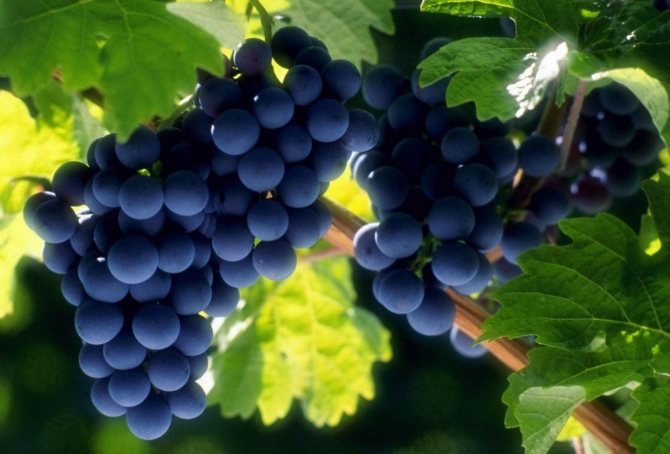
The cultivation of grapes as a horticultural crop in personal plots is widespread, regardless of the region. The grapes grows and bears fruit with success in the middle lane, in the Urals, in Western and Eastern Siberia. Modern covering materials and technologies make it possible to create sufficiently reliable protection of bushes from frost, ice on vines and freezing of the root system. However, the success of overwintering largely depends on the condition of the bushes and how the grapes are prepared for wintering.
Grape varieties by their nature are subdivided into winter-hardy and covering. Many modern winter-hardy varieties and interspecific hybrids can withstand temperatures down to -37.40 degrees. This is quite enough to successfully grow grapes in all climatic zones of our country. Covering varieties also withstand frosts at - 18.24 degrees, which ensures their growth without shelter in the Crimea and Krasnodar Territory, but to the north and in central Russia there are more significant frosts and therefore the vineyard needs protection from the effects of low negative temperatures.
Covering bushes tolerate winter conditions in different ways. So, young grapes need a stronger shelter, they should literally be buried under a layer of earth 30-40 cm. Grapes heavily overloaded with harvest, as well as weakened by the influence of fungal diseases, endure the winter much worse than healthy plants with an optimal load of bunches.
Important! Ailing grapes and bearing too large a crop, they endure the winter worse!

Experienced growers can easily determine the number of bunches that will pick up a sufficient amount of sugar. If there are too many bunches, they will all remain sour and may also be sluggish, unmarketable, and not transportable. The vines will remain unripe, and such bushes will not be able to winter. On a young bush, four sleeves should be left, on each sleeve there are 2-3 vines, each carrying one bunch, no more. On mature bushes, you can leave 5-6 fruiting vines, but also observing the rule: on one vine - one bunch. Extra brushes should be removed without regret.
Preventing diseases of the vines is very important to ensure the normal development of the bark tissues. Only healthy vegetation can withstand frost. Treatments against fungal diseases of grapes (mildew and oidium) are carried out several times over the summer. The minimum number of treatments is three. Spraying preparations - Abiga Peak, Topaz, Cabrio Top, Tiovit Jet.
In addition to spraying, bushes need green operations:
- fragment of excess shoots;
- pinching;
- chasing.
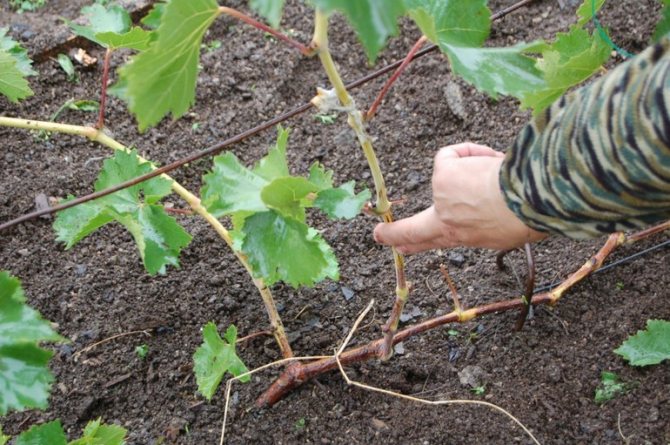
At the beginning of summer, all thin and sterile shoots are removed from perennial vines. They can be easily broken off from the attachment point when they have not yet reached a large size. They can be removed later with a secateurs. If the shoot comes out of the ground, it can be left to rejuvenate the bush in the near future.
From vines that are tied horizontally, remove all shoots on which no bunches are left. This measure will help to avoid thickening of the bush, the remaining clusters will be large and sweet.
During the summer, the main concern of the grower is pinching. In the axils of the leaves, shoots of the following order are formed, they must be removed with a pruner. This measure will help to achieve good maturation of the vines, which will be left for wintering.
Attention! Ripe vines are easy to recognize: they are warm, damp to the touch and covered with light brown bark.
The stepchildren should be removed in the phase of two or three leaves. At a later removal, the bush will already spend a lot of nutrients on their growth.
This technique allows you to largely prepare grape bushes for wintering. It consists in removing all growth over the top wire of the trellis. At the same time, nutrients are stored in the vines, and they will be able to withstand the unfavorable factors of winter, preserving the fruit buds.


Regardless of the region where the grapes are grown, no watering of the vines is carried out in August and September. The roots of the grapes penetrate deep enough that they are able to extract enough moisture. Excess water with irrigation will prevent the wood on the shoots from ripening and accumulating nutrients for overwintering. In late September - early October, autumn water-charging irrigation is given at a very high rate.
Watering of grapes is not carried out in August and September!
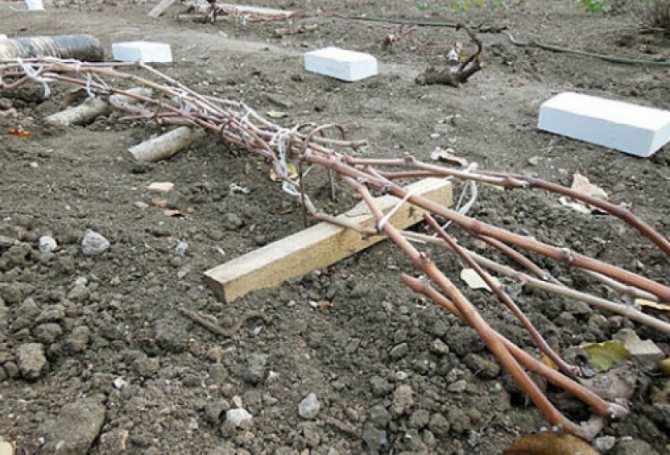
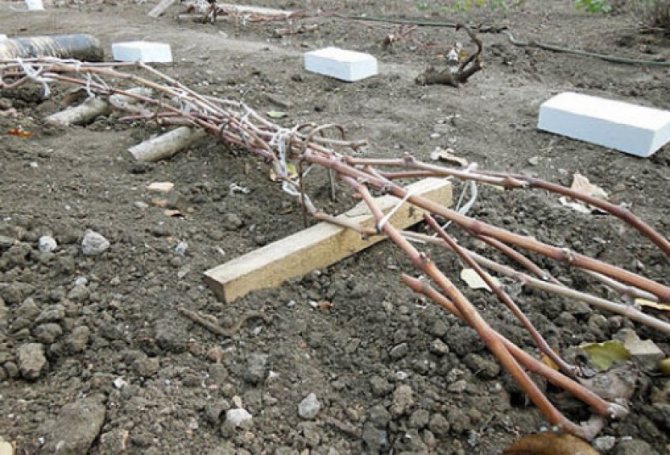
In the fall, careful preparation of the grapes for wintering is necessary. Harvesting crop residues must be timely, so as not to spread the spores of pathogenic fungi on the remaining berries. With the onset of light frost -2. 3 degrees, the leaves from the vines are cut off, and the branches themselves are removed from the support. Pruning in the fall involves pruning vines and removing immature shoots with green bark. The rest of this technique is done in the spring.
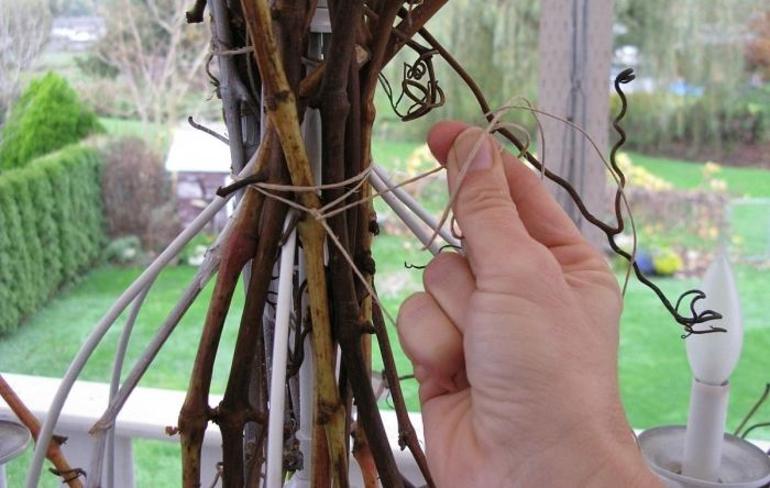
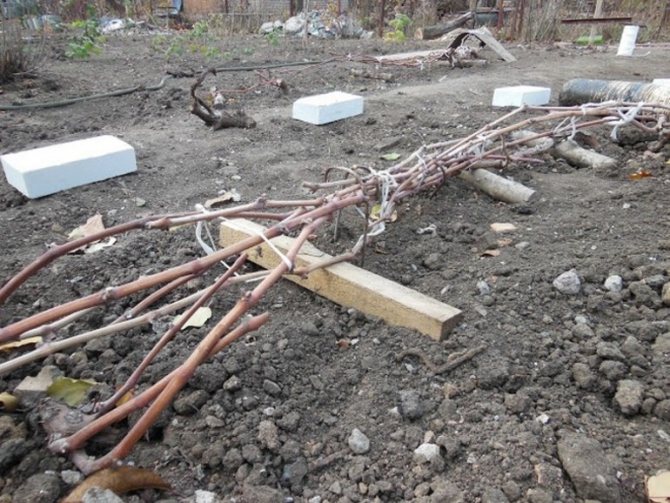
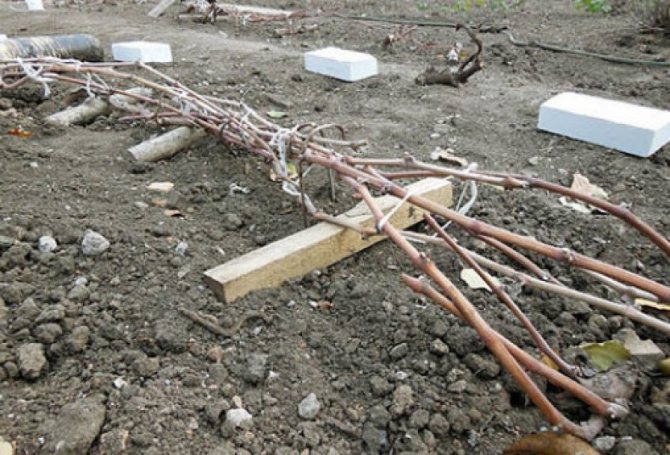
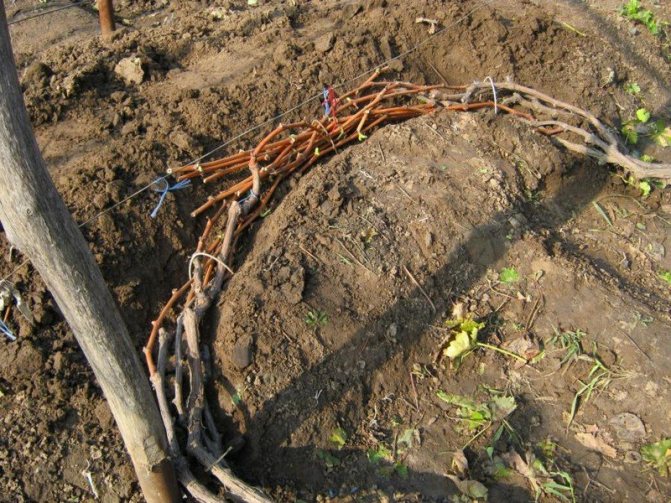
After pruning, carefully remove all plant residues from the row of the vineyard, cleaning the soil with a rake. The branches removed from the trellis are lowered to the ground, twisted compactly and pinned to the ground with wire brackets. Before the final covering, spraying with 4% iron sulfate is carried out to eradicate wintering forms of diseases and pests.
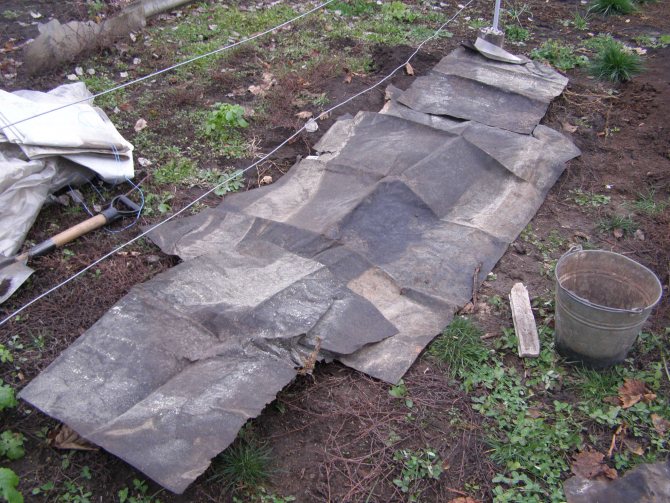
The sprinkled grapes are covered completely after a few days. Modern covering materials in black provide reliable protection against frost. On top of the material, you can pour an earthen slide, cover the bushes with wooden boxes, shields or spruce branches.
In order for the grape bush to winter well, it is important to carefully carry out all the care operations and prepare it for covering in advance: to carry out rationing and fragmenting the bushes, spraying, pinching and chasing in time, and to finish watering in early August. The main thing is to take care of your grapes throughout the summer, and then it will give a high yield every year and successfully endure wintering.
What includes
Preparation for the winter period begins, depending on the region, from mid-September to the last days of November. Farmers say that healthy and full-fledged bushes retain their ability to bud up to 80%, and frost-resistant varieties up to 100%. Ideally, the thickness of the vines should be in this case from 6 to 14 mm, and the veneer should be one third of the total section. Find out about the benefits and harms of grape seeds here.
Read also How to cook black eye beans
Top dressing
It is recommended to spray vineyards with fertilizers only after complete harvesting.
Top dressing for bushes is introduced in several stages and in various ways:
- The first and safest means of plant nutrition is humus. To do this, you can collect rotten leaves mixed with turf in the area of the root system, potassium components are added on top.
- Adding lime. Vineyards love calcareous soils, but, unfortunately, this component is quickly washed out, so regular autumn and spring feeding of the bushes is necessary.
- If it is necessary to plant new seedlings in the fall, then the planting pit is first filled with humus, then sod, and after strengthening the trunk, sprinkle with potassium-molybdenum fertilizers.Usually they are dissolved in 100 ml per 10 liters of liquid.
Watering
Before covering a fruit-bearing garden, there is an opinion that it is necessary to water the bushes abundantly, but this is far from the case. The grapes will rot for several months from the abundance of moisture, respectively, rot and deteriorate. Therefore, experienced farmers say that the moisture in the autumn soil is sufficient for the farm to endure the cold. Read about planting grapes in the Moscow region here.
Small numbers of young animals are watered, which were planted this season.
Autumn pruning
Pruning of vines is carried out 2, and in some cases 3 times per year. Each season has its own characteristics:
- In the fall, all elements are examined for diseases, dense branching.
- Usually, the crown is being formed, excess shoots are removed, leaving 5-7 eyes on the vine. In the case of technical varieties, there should be no more than 1-2 bunches on one shoot. This is done to lighten the weight of the branches, increase yields in the future, harvest and subsequent propagation by cuttings in the spring.
The pruning rules are pretty simple:
- the branch is taken carefully, without breaking;
- inspect and, if necessary, cut;
- it is necessary to cut immediately, without breaking or breaking the vine, thereby injuring it.
For pruning, special pruners are used that eliminate shoots with one touch.
Sometimes farmers process the cut with soda solution, charcoal or brilliant green. This is done for better corking.
Treatment
Preparation for the winter season cannot be complete without treatment against insects, fungal infections, gray mold and other diseases that plants are prone to. Such solutions are called fungicides. They can be purchased in concentrated or ready-to-use form, and can also be prepared from available products. Learn about Malbec grapes at this link.
It is best for them to process them in the autumn, due to the fact that insects usually hibernate under shelters with the vines, which can significantly harm the fragile branches in the spring.
The following subspecies are distinguished from folk substances that are harmless to fruits:
- Potassium permanganate solution. Dissolve 5 g of potassium permanganate in 10 l of water, this solution and spray the surface, including the root part of the trunk.
- Soda solution. 100 g of soda is diluted in a bucket of liquid and the entire bush is sprayed.
Processing can be combined with simultaneous feeding, so the perception of nutrients will be more effective.
Shelter
Pinot Noir and Augustine grapes, like any others, are covered with several options:
- reed shields;
- spruce branches;
- humus;
- dry improvised material;
- film.
There is no one-size-fits-all advice on which of the above methods is better. Each is suitable for a specific locality and a specific grape variety. But most farmers do not lean towards any one species. As a rule, a mixed version is used: combining dry material with film and spruce branches or humus with reeds. This material will tell you about the Krasnotop grape variety.
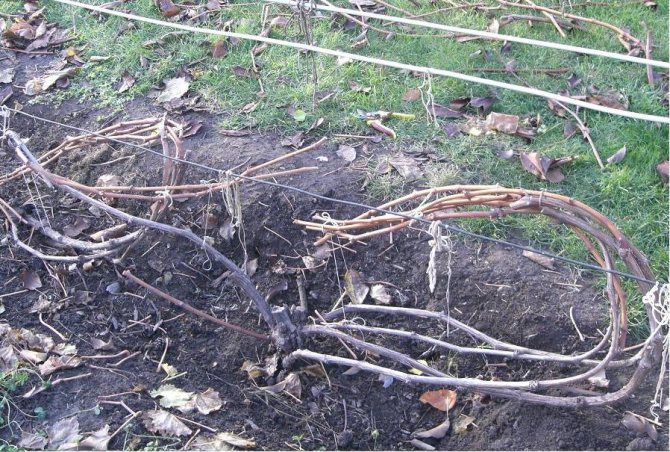
With the exception of the method of dropping, in the rest, slats are placed under the inclined vine, so that the plant does not come into contact with the ground, and the branches themselves are attracted with wire or metal arcs.
It is very good if the winter is snowy, then the snowdrift plays an additional role as a heat curtain. And for additional ventilation, holes are left in the shelter, which are closed when the temperature drops below -20 ° C.
Features of care in the fall
Taking care of the grapes in the fall should take into account the characteristics of its ripening. If the fruits ripen before the end of August, the autumn maintenance of the vineyard will not be difficult.
Watering grapes in autumn
After harvesting, the grapes are watered if it is hot outside.At a moderate temperature, watering is carried out at the end of October, so the plant receives the required amount of moisture.
Top dressing
Fertilizer is applied in early September. At the same time, they mix:
- potassium magnesium - up to 70 g;
- superphosphate - up to 100 g.
The resulting mixture is poured under 1 grape bush. Half the dose is enough for a young plant. The bushes are fertilized for the second time after 2-3 weeks.
Pruning
In vineyards, pruning work is carried out in the fall, this allows the bushes to form better and give larger yields in the future. Timely pruning affects the number of berries set in the next year and their taste.
Late October-early November is a good time for the formation of a bush that needs shelter in winter. On the fallen leaves in the fall, set a period for pruning the grapes. After the colored foliage has fallen, they wait 14-21 days and start pruning. During this time, the branches are saturated with useful substances.
Late pruning will damage the twigs of the plants. At low temperatures, shoots become brittle and break easily.
Pruning rules
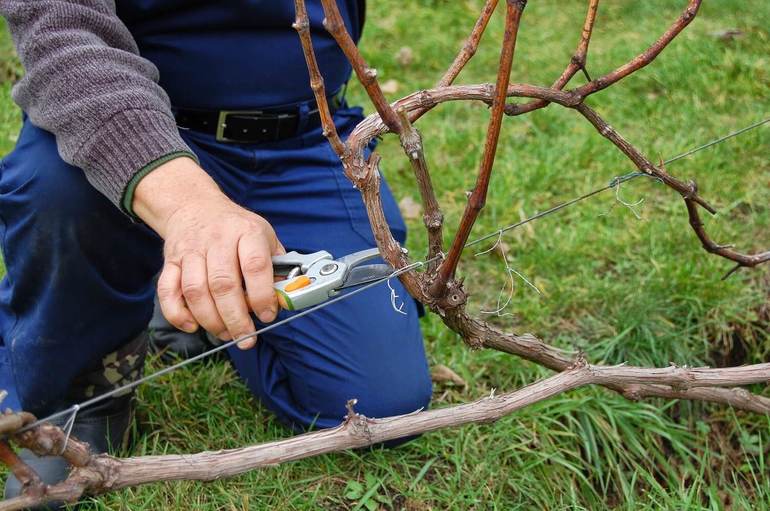
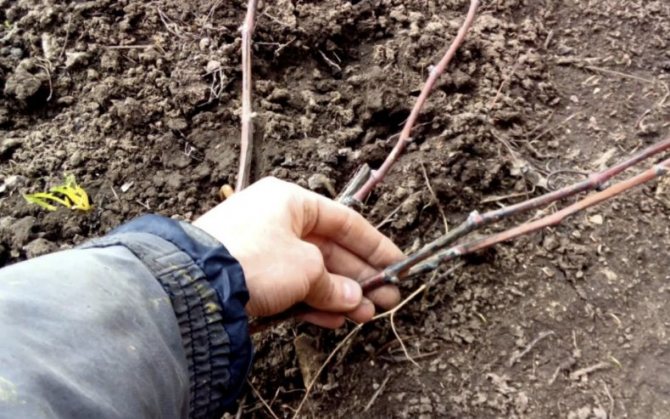
Pruning grapes begins with the removal of diseased parts and branches with damage. A burning pit is being prepared for them. This helps prevent disease and pests from spreading to healthy bushes.
All shoots are not pruned: they can be useful for replacement. If all or part of the crown dies, the replacement shoots will be able to replace the entire bush.
Pruning methods
Grapes are pruned in autumn in different ways:
- Short pruning involves the elimination of a large part of the shoots; only 2-4 eyes are left on the twig. Pruning is suitable for sprouts needed to replace a dead bush.
- Medium pruning involves leaving up to 8 healthy eyes on each shoot. The arrowhead consists of 50 kidneys. The type of pruning allows you to get a frost-resistant variety with healthy vines.
- Long pruning assumes that up to 15 eyes will be located on the shoot, the total number of buds - up to 60. The stem consists of 4 side shoots.
- Mixed trim is a combination of short and long. Shoots are pruned for replacement, branches are left to ripen the future harvest. Using the method, a loop is formed, the vine is removed after fruiting, a replacement sprout appears instead.
A mixed method for growing a plant at home is considered the best. With it, the bush is renewed, the fruits increase in size, their taste improves.
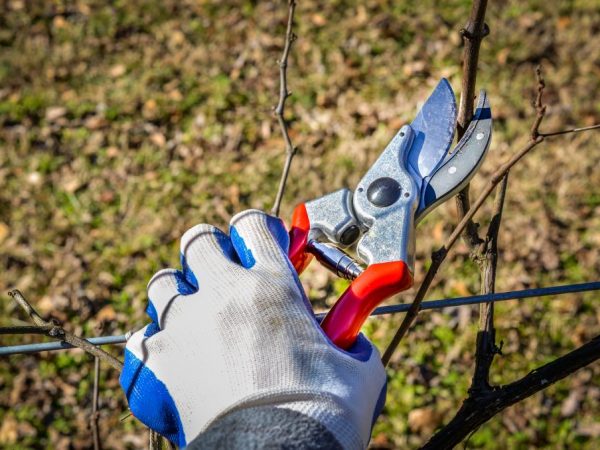


Pruning the vine for a better harvest
Grape pruning 1st year
In the first year, the grape bushes are not pruned in the fall. If the bush has curvatures or damage, the haircut is carried out in the first year, leaving 2 healthy eyes.
Pruning a 2nd year plant
In the second year, a vine of 2 buds is formed on the bush, in the spring it is reduced by 4 eyes. In the fall, each eye on the branches is added by a branch, as a result, a bush of 8 sprouts is obtained. There are 4 branches on each side of the trunk. At the end of autumn, 2 large shoots are chosen each, others are cut, and the stumps are left, since when the trunk dries, it can burst.
By the age of 2, 4 strong sprouts grow. In the fall, pruning is carried out in a long way, in the spring they are shortened by 4 eyes.
Pruning grapes of the 3rd and following years
In the fall of the 3rd year, the grape bush has 4 large stems, 4 branches on each of them. For pruning in the fall of a bush of the 3rd year, the largest shoots on each side are chosen, 2 weak branches are subject to pruning.
After pruning, they try to graft the branches. Of the large remaining sprouts, 1 must be shortened by 3 eyes (it will become a replacement sprout), the other remains with 12-15 buds.
In the third year, the bush is rejuvenated, which bears fruit in the future. In the fourth year, pruning is carried out, as a result of which the yield will increase, the vineyard grows stronger.
In the autumn, in the 4th year of the growth of the bush and in all subsequent periods, when pruning, the vine is removed after fruiting, new growth buds are formed on the replacement shoots.
Top dressing after pruning
After the end of pruning for the winter, grape shrubs are fed with fertilizers. The following fertilizers help accelerate the maturation of young shoots:
- wood ash - 500-650 g;
- potassium sulfate - 20-25 g per bucket of water.
Use additional feeding:
- superphosphate - up to 80 g;
- phosphorus-potassium fertilizers - 60-75 g;
- potassium chloride - up to 30 g;
- manure - 10 parts are mixed with 1 part of superphosphate.
Top dressing is applied on 1 m² around the base of the bush.
Preparing for winter
Pruning is the initial stage of preparation for winter, after it is carried out, shoots are removed from the trellises, the shoots are tied. When the temperature changes to -3 ° C-5 ° C, the plant is covered for the winter.
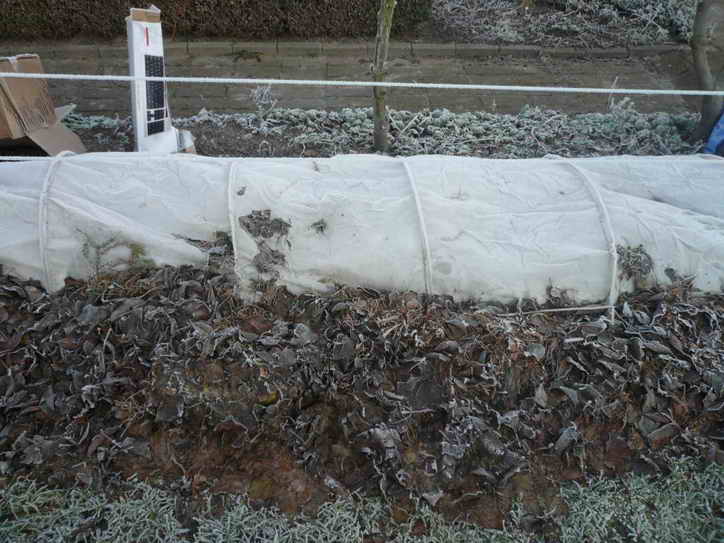
There are the following methods of sheltering vineyards in late autumn:
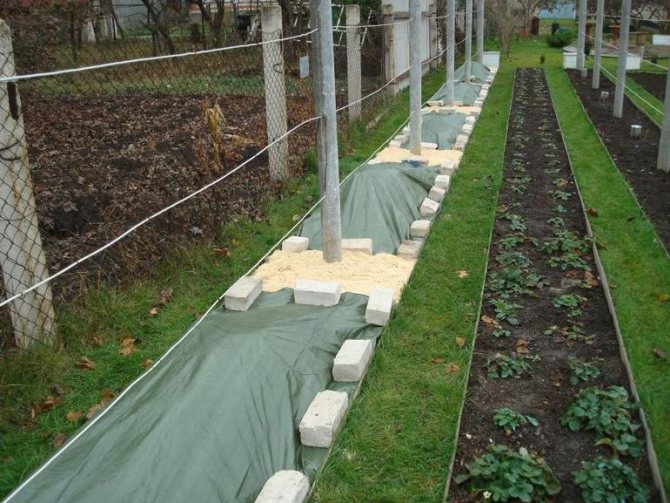
- The ground. A pit-trench with a depth of 25 cm is prepared near the base of the vineyard. The previously removed vine is sprayed with insecticides against pests and placed in the pit, and the top is dripped with a soil layer of 20-30 cm. For spring detection, pegs are placed. The method is not suitable for cities in the northern regions due to heavy rainfall: this leads to wetting of the earth and wetting of the vine. The bush rots and freezes.
- Dry. Grape sprouts are placed on the ground, hay, sawdust or mulch, and they are covered with material on top that does not allow moisture and precipitation to pass through. Suitable plastic bags, tarpaulin, roofing felt, nylon films. From above they are fixed with clamps or staples. During the wintering period, a microenvironment is formed under the shelter. Untimely removal of the shelter provokes the development of fungal diseases.
The constructions protect against rodent penetration. Poison is placed in the center. The penetration of dangerous inhabitants harms the grape bushes, they destroy the buds and vines.
Types of covering material for vines
How to cover grapes for the winter in the suburbs? The technique depends on the choice of covering material. And the main ways of sheltering grapes are divided into three types:
- Hilling. It is carried out for young seedlings using a mound up to 25 cm high.
- Semi-shelter. Only the part of the grapes that is above the ground is covered. Agrofibre or straw are considered optimal materials.
- Shelter is complete. It is with this method that shoots are removed from the supports, cut, processed, bent to the ground and covered.
The third method is considered the most reliable for the Moscow region climate. What materials are used for this?
Natural - soil and snow. If you plan to cover the vine with earth, then you need to dig a groove, insulate it with spruce branches and lay the vine.


Then sprinkle gently with earth. The layer of the embankment depends on the type and relief of the site. As the plants mature, they will need more reliable protection. It is easier to cover with snow, but for this you need to be sure that the thickness of the snow cover will provide protection to the grapes throughout the winter. Otherwise, summer residents have to put up shields for snow retention or manually add snow.
Read also: "Valek" grape variety
What other material is used to cover grapes in the Moscow region? There are several possible options, you just have to choose the most acceptable one:
Autumn watering
Regardless of whether it is old or young grapes, care in the fall, preparation for winter, first of all, requires water-charging irrigation. While berries are still hanging on the vine, it is impossible to flood the culture with water strongly. The berries will begin to crack from excess moisture. Wasps, bees, small flies will flock to the sweet juice and the crop will be spoiled.
Watering the grapes begins in the fall after harvesting the berries. Often it is not necessary to fill the bushes, but the soil should be kept moist. After the return of the crop, the roots require recharge. The quantity and intensity of watering are determined by growers intuitively, being guided by the weather, the state of the soil, the depth of the underground water layers. Despite all the nuances, in October the vineyard is necessarily poured abundantly with water once.In order for moisture to penetrate exactly to the roots, grooves are dug in the ground around the bush or holes are drilled with a drill.
You need to take care of the grapes wisely, that is, do not pour water under the bush just like that. First, the composition of the soil is taken into account. Loose soil, sandstones absorb a lot of moisture and do not retain it. On such soil, a bush of grapes is poured into 60 liters of water. Heavy soil with admixtures of clay or chernozem poorly permeates moisture, retains it. Vineyard care in such a plot is reduced to minimal watering. It is enough to pour 25 liters of water under the bush.
In the video, grapes, care in the fall, methods of water-charging irrigation:
Winter work
In most cases, winter care is reduced to regular inspection of the ridges for damage:
- ventilation control;
- is there too much moisture or dry soil
- whether mice are wound up in the covering material.
Pruning
It is very rare, but some gardeners practice winter pruning. This way of leaving is typical for southern latitudes, where winters are mild and with little snow.... In this case, pruning of incapacitated branches that can be seen through the film is possible.
Pruning in the cold period is carried out only at a temperature not lower than -5 ° C, while also focusing on the vegetative ability of the variety. If the grapes are not frost-hardy and do not tolerate interventions well, then the removal of branches is left until spring.
Watering
In winter, watering is done in extremely rare cases, only with snowless and dry winters. Signs that the plant needs hydration are immediately visible:
- the ground under the bushes cracks;
- spots appear on the branches, a lot of dry, dying branches.
In this case, it is watered not only with clean water, but fertilizers with minerals are added there. Watering is carried out by the method of dispersive irrigation.
Pruning for the winter
One of the important stages of caring for grapes in the fall is pruning the vines for the winter. The procedure has the following positive aspects:
- After pruning in the fall, the bush is rejuvenated in the spring. The yield increases. The berries grow larger than uncut grapes.
- After pruning in the fall in the grown young stems, metabolism and the movement of sap occur more intensively. The berries ripen faster.
- Pruned vines withstand severe frosts better.
- A neatly shaped crown of grapes is easier to care for.
- Pruning diseased and diseased branches reduces the likelihood of spreading the disease throughout the bush.
Leaving associated with pruning grapes begins after leaf fall. The vine goes into dormancy in the fall, and the removal of branches is painless. Before the leaves fall off, the branches cannot be cut off. Such withdrawal will only harm the culture. Until the bush has thrown off the foliage, the process of photosynthesis continues in the grapes. Early removal of leafy branches in the fall will weaken the vine. The grapes will not have time to accumulate nutrients that help to endure the winter easier.
It is also impossible to delay with leaving. Pruning too late with the first frost in the fall will cause unexpected damage to the vineyard. The vine becomes fragile in the cold. During pruning, the branch may crack in an unnecessary place.
Vine care begins with the removal of diseased, dry and damaged shoots. The branches are burned immediately after pruning, as they are infected with pest larvae and fungal spores. The next stage of care is the formation of the bush in the fall. In the vineyard, excess branches are cut. The scheme for pruning a vineyard in the fall may differ for each variety, but in general terms, caring for a bush takes place according to the following principle:
- The load of the bush is regulated by shortening the annual branches. Two buds at the base of the shoot are not counted. They are not considered mature. For example, if a feature of a variety requires shortening the shoot by 4 buds, then taking into account two unripe buds, six of them are obtained.
- They start leaving in early autumn at the beginning of September. All young growth is removed on the old vine, the tops of which rise 60 cm from the ground level.Branches, the tops of which rise 30 cm from ground level, are shortened by 15%.
- Further maintenance of the grapes, associated with pruning, continues in October. The process is directed to the formation of a bush in the fall. Fruit branches and replacement knots are left on the vine. First, the lower strong, but short shoots with three eyes are cut off. The knots of replacement are obtained from them. The upper long branches on the bush are shortened by six eyes, forming fruit arrows. The eyes may be less or more, depending on the varietal characteristics of the grapes.
The cut sites are treated with garden varnish, which protects the wood from infection.
The video shows the care of the vine in the fall:
Top dressing and tillage
Taking care of the vineyard is not complete without top dressing. In the fall, after harvesting, the crop is in a depleted state. In order for the vine to overwinter and give a good growth in the spring, it needs to restore the lost strength.
Leaving in the fall means feeding the crop only with phosphorus and potassium. From mineral fertilizers, 40 g of superphosphate are applied under an adult bush. The substance enriches grapes with phosphorus. From potash fertilizers, 30 g of potassium sulfate or potassium magnesium are added. Many gardeners give preference to potassium monophosphate, contributing 40 g of the substance under the bush. Dry mineral fertilizers are diluted in a bucket of water, poured under the root, combining top dressing with watering.
Instead of mineral fertilizers, fertilizing in the fall can be done with organic matter. Under an adult vineyard, 300 g of ash or 15 kg of compost are introduced. The organic matter is dug up with the soil to a depth of 30 cm, departing from the trunk 50 cm.
Protection against diseases and pests
An important process of caring for grapes in the fall and preparing for winter is the preventive protection of the vines. The choice of a spray product depends on the condition of the vineyard:
- If, during the inspection, traces of mildew are revealed, the affected shoots with leaves are cut off and burned. The vineyard is sprayed with "Folpan", "Ridomil" or another similar preparation.
- If signs of oidium are detected, the vine is sprayed with any preparation containing sulfur even before dropping the foliage in early autumn.
- Against anthracnose, drugs used to treat oidium and mildew are used.
- When, when examining the grapes in the fall, traces of a leaf roll are found, the bush is treated with a decoction of tobacco or medicinal chamomile.
- The raining of berries and bunches in early autumn may be associated with cercospora. The disease still manifests itself in brown spots on the leaf plates. For the care of a sick vineyard, use "Fundazol". Polihoma helps a lot.
- In the fall, ticks like to get along on the vine. Most often, they sit on the tops of young branches. A measure of getting rid of the pest is pruning the tops of the shoots.
- In the case of the development of gray rot in autumn, the processing of the culture is carried out with "Euparen" or with the preparation "Skala".
Healthy bushes also need preventive care. The vineyard is sprayed in late autumn after leaf fall with a 3% solution of copper sulfate.
conclusions
For successful wintering of grapes, several simple rules are followed:
- Autumn preparation, which includes not only pruning, but also watering, fertilizing, as well as processing against possible fungal infections.
- Shelter in the winter in the Urals, Siberia and other regions. The more thoroughly and better the work is done, the easier the vineyard will endure the cold. Do not forget about ventilation, air exchange in the ridges.
- In the winter period itself, care is reduced to monitoring the condition vineyards and making any adjustments to improve the condition.
- After winter, the vine is opened, but give her a few days or weeks to breathe, get stronger and adapt. After that, the film is finally removed.
Shelter for the winter
Caring for grapes in cold regions is not complete without another important measure - the shelter of the vine. Most cultivated varieties can withstand frosts from 17 to 24 o C. It is impossible to rush with early shelter.On a sunny day, fruit buds can push against. The procedure begins in late autumn, when frosts of about -5 o C. were established on the street. However, before that time the vine should be tied with a tourniquet and laid on the ground. If you try to bend branches during frost, they can break.
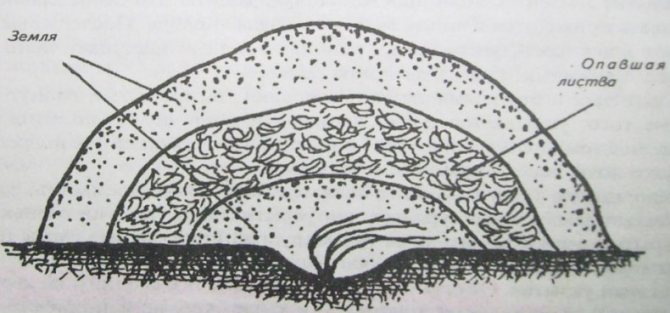
For shelter, a warm, lightweight and breathable material is used. Straw, reeds will do; sometimes gardeners use old clothes. Burying the vine in the ground is practiced. First, a ditch is dug, a vineyard tied with a rope is laid, a layer of straw or foliage 30 cm thick is poured on top, and this whole cake is covered with loose earth.
From above, the shelter can be reinforced with foil. The waterproof material will prevent organic matter from rotting and saturating it with water. The film itself cannot be used without insulation. A greenhouse effect is formed under the shelter during the thaw. The buds will begin to wake up, and with the return of frost they will freeze.
Helpful hints
Do not take cover next to a bush. This leads to the exposure of the roots, their freezing and death of the plant. It is optimal to retreat from the head of the bush by half a meter.
Use a three-layer shelter in the suburbs. For the first layer, take garden soil (from 5 to 15 cm), for the second - organic matter of the same thickness, for the third - loose soil 25 cm thick.
Provide additional protection to the roots, especially in winters with little snow.
Be sure to dig the soil twice a year - in spring and autumn. So, you will ensure good moisture absorption and reduce the risk of freezing grapes.
In a snowy winter, do not rush to make a powerful shelter. The snow will perfectly protect the plants, just take it from the paths and place it on the bushes.