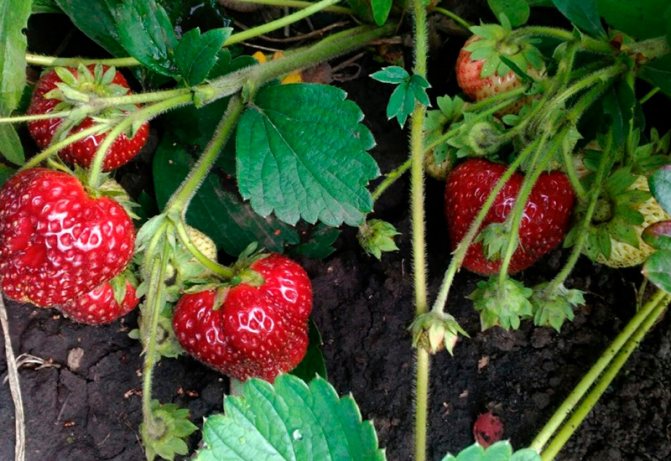
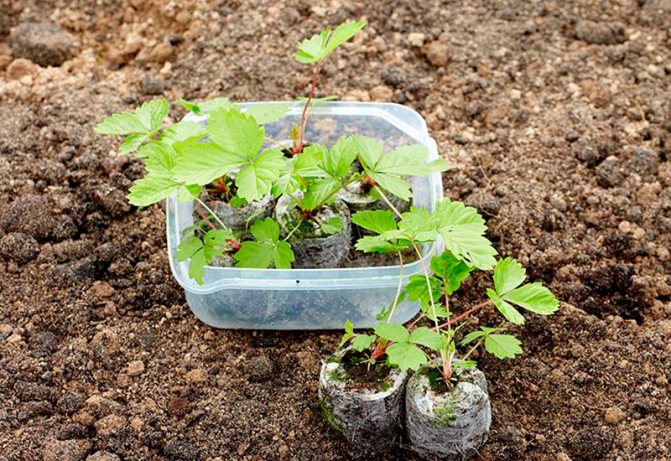
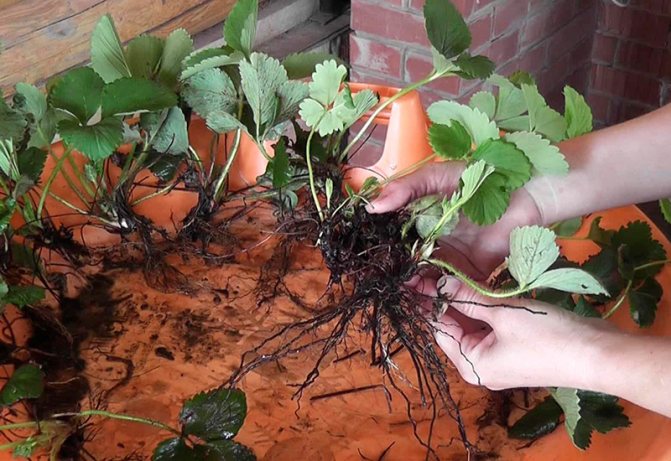
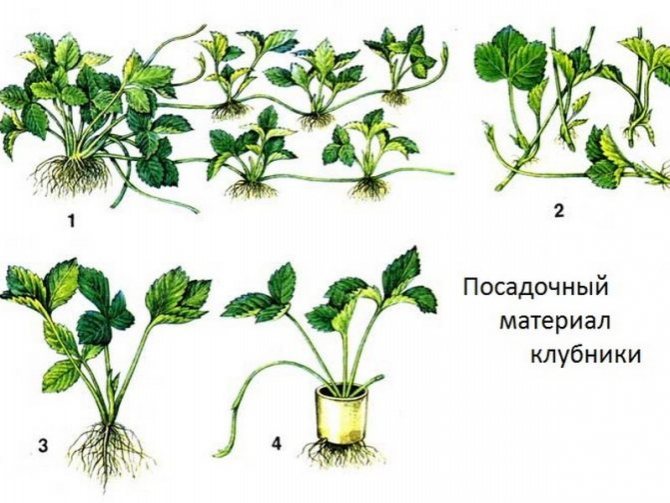
What are the benefits?
The main advantage of propagating strawberries by dividing an adult bush, as opposed to breeding with a mustache and seed, is the simplicity and accessibility of the process for novice gardeners. The method is great for increasing the plantings of severely deficient mustacheless varieties that can be taken from neighbors. In addition to this, the method has other attractive aspects:
- The renewal of berry beds can be done over an extended period (from mid-spring to mid-autumn);
- High survival rate of seedlings - up to 90%;
- Since the horn (bush with a root) is part of an adult plant, it can bear fruit already in the next season;
- Choosing to divide only powerful, healthy rosettes that yielded a rich harvest of large berries, you are working to increase yields year after year.
Unlike propagation of strawberries with a mustache, you can first get a crop, and then only divide the bush;
The only case when it is impossible to propagate strawberries from your garden by dividing a bush is an infection of berry rosettes. If they are sick, then the disease will persist on the horns. Propagation of strawberries with a mustache in this case is also undesirable. It is better to allocate a new area for strawberries and plant healthy material taken from neighbors.
Features of planting remontant varieties
Breeders have bred a strawberry that bears fruit twice a season or pleases with berries all summer, but does not form young shoots. Many remontant varieties are bred only by dividing the bush. It is better to plant such strawberries in the fall 3 weeks before the onset of frost. During this time, the strawberries will give roots and get stronger, at the beginning of June the first berries will ripen.
In the spring, remontant strawberry bushes are transplanted less often and do the work until the peduncles appear.
If the plant has time to release them, everyone breaks off, otherwise the strawberry will waste energy on setting the ovary and may not take root.
Ordinary strawberry varieties do not bear fruit during spring planting; in remontant species, the first berries ripen by the end of summer, provided that the procedure is performed correctly:
- Dig up healthy and strong strawberries and shake them off from the soil.
- The bush is divided into parts, each of which must have a root not shorter than 5 cm.
- The shoots are soaked in a turbulence, cutting off the peduncles. To prevent the defeat of the socket by a fungal infection, the roots are treated with the drug "Fitosporin - M".
- The seedling is lowered into a hole at least 10 cm deep, watered abundantly. When the water sucks in the roots, the hole is covered with soil, leaving the neck at surface level.
Transplanting strawberries in the fall is just as important as watering or feeding. And if the gardener wants to get stable, rich yields, then he must carry out this procedure correctly. However, it should be remembered that strawberries are a crop that is not desirable to grow in one place for more than 4 years, since after this time it begins to bear fruit worse.
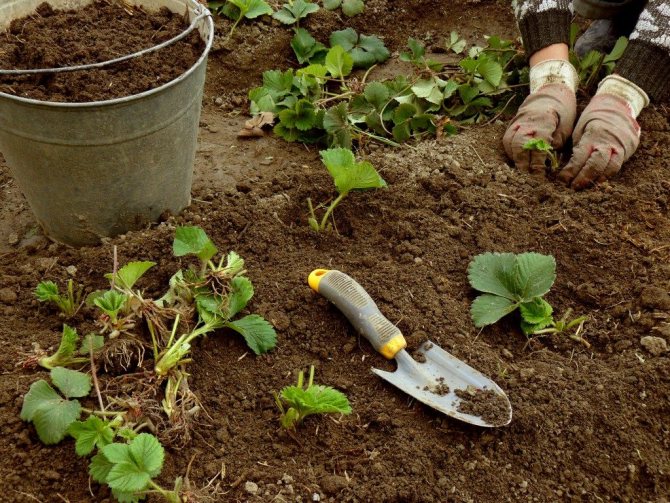


The main thing is to choose the right site and prepare the soil.
When is the best time to divide the bushes?
It is better to plan the propagation of strawberries by dividing the bush in the spring. The sooner young horns take root, the better they will endure the winter and will bear fruit well next year. But then the "growing generation" of fruit crops will have to cut off all the flower stalks.This will allow all forces and nutrients to be directed to the development of the root system and the growth of green mass.
In addition to spring, strawberry bushes can be divided for reproduction throughout the summer and in autumn, until the end of September. You cannot do this procedure in October and later. Young plants will not have time to get stronger due to the poorly developed root system. As a result, in winter, most of the seedlings may die even from a slight frost. The advantage of late breeding by dividing the bush into horns is the ability to harvest. However, you need to understand that immature seedlings in the next year may not produce berries at all.
Why strawberries do not take root well
The main reason why strawberries do not take root well is unprepared soil. Substances remain in it after the growth of other crops. This makes it difficult for strawberries to feed, develop and bear fruit. It is best not to plant young plants after tomatoes and potatoes. Strawberries cannot tolerate their root secretions, the bushes will be strongly oppressed. The longer the nightshades grew in a given place, the more secretions they left, and the more the strawberry seedlings would be inhibited.


Crop rotation
If the predecessor, for example early potatoes, was in the ground for a very short time, then it left less root exudates. Young strawberry bushes will not react strongly to them. If there is no other piece of land, and you have to plant strawberry seedlings after the nightshade, then you should take into account the fact that the plants will gradually straighten out, just the first harvest will be very meager.
Another undesirable precursor is pumpkin crops. During growth, they remove from the soil all the nitrogen that is needed after breeding, for development and preparation for winter. When planting seedlings after pumpkin crops, increased doses of organic fertilizers are introduced into the soil. On sandy soils and heavy loams - 5 buckets per m², on medium and light - 3 buckets per m².
Selection of mother bushes
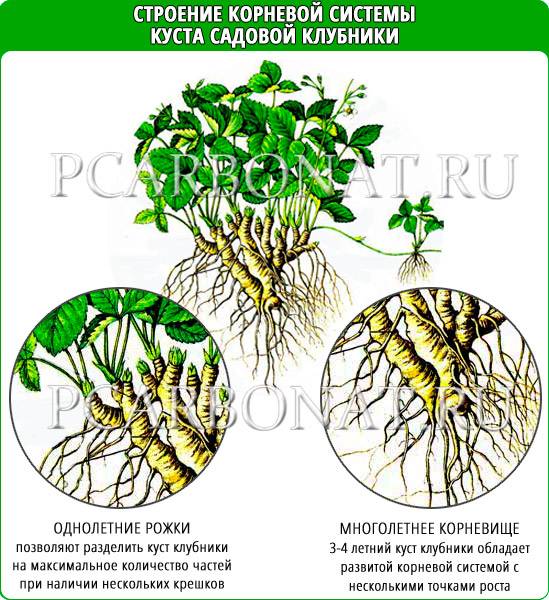
Experienced summer residents use the method of dividing bushes during reproduction every year to maintain a stable strawberry harvest. As a result, there are four beds, each of which grows berries of the 1st, 2nd, 3rd and 4th years. It makes no sense to keep the garden berry longer, since the yield of the bushes decreases. In addition, the bushes of the 4th year are most suitable for reproduction. From one such plant, 15 to 18 horns can be separated.
Before propagating strawberries by dividing the bush, follow the plantation throughout the year and mark for yourself the healthiest, most powerful and abundantly fruiting rosettes. To do this, you can stick in pegs or put a stone (gravel, a piece of brick) next to it. Then next year you will surely find a bush that you have planned for dividing.


How to divide correctly?
To propagate strawberry bushes by dividing, follow the following step-by-step algorithm:
- Dig a four-year-old socket by alternately stuck in a shovel on each side of the bush;
- Remove dry and dying leaves;
- Shake the outlet and help a little with your hands so that only the roots remain, and the earth crumbles;
- Lower the rosette by the roots into a basin of water;
- Gently begin to divide the bush into horns - in the water they diverge on their own. Do not pull too hard, otherwise the plant may be damaged;
- If the horn is double (2 small rosettes on one thick root), you can cut them in half. Then you get two seedlings;
- Examine the roots. Cut off old, dark and shrunken roots, and leave strong, light and young ones;
- Remove stalks if present.
After dividing the strawberry bushes for subsequent reproduction, horns are obtained with small roots that are not able to fully power the outlet. To prevent excessive moisture evaporation and stimulation, each leaf blade of the plant should be cut in half.


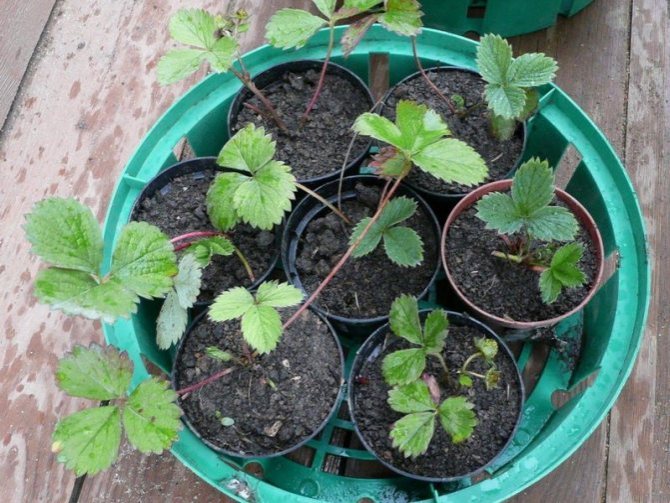
Planting horns for growing
After dividing the strawberry bush, summer residents often plant the horns immediately in a permanent place. This is not to say that nothing impressive will come of this, but there are ways that allow seedlings to take root faster and form an adult outlet. This is possible if young bushes are grown as follows:
- Prepare pots for each horn (diameter 8-10 cm);
- Fill two-thirds of the height with garden soil mixed with peat 1: 1;
- Place the horn in the center;
- Gently cover it with soil on all sides so that the socket remains open;
- Water the pots liberally;
- Transfer them to a greenhouse for 1.5 months.
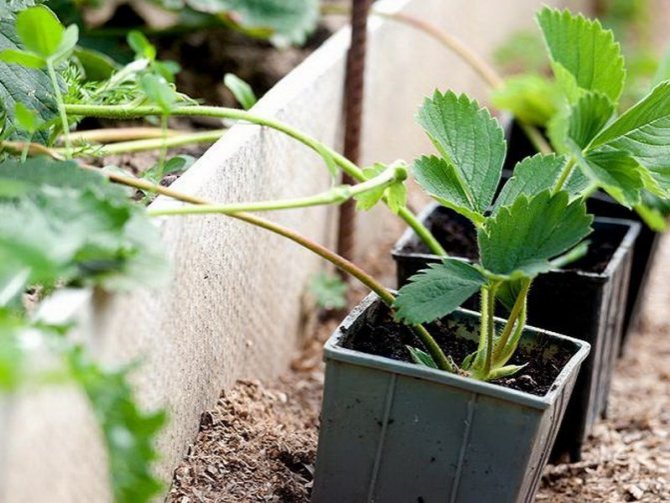
By propagating strawberries by division, you can grow young growth in a small spunbond greenhouse. You can often plant bushes: 1 horn per 10x20 cm plot. The only disadvantage of a greenhouse is that when planted in a permanent place, the root system will again suffer, which remains when the earthen coma is removed from the pot.
How to properly care for a plant
When caring for remontant strawberries, it should be borne in mind that in order to obtain a good harvest, you will need to sacrifice some peduncles. Removal of the first bloom occurs in the spring in order to obtain larger berries from the second bloom. But not only for the abundance of the future harvest, this work is being done, but also in order to get it much earlier.
Garden strawberries
After the completion of the entire fruiting period, all bushes must be removed from the plantations. It is best to do this work before the first snowfall.
To insulate the beds, it is worth using hay or straw. You can also insulate with sawdust. This is necessary so that severe frosts do not destroy the root system of plants.
During the fruiting period, this strawberry needs abundant regular watering and feeding.
In order for moisture to remain in the soil as long as possible, soil mulching will be required. In addition, for free air circulation, you need to loosen the ground.
For plant feeding, it is necessary to use organic and mineral fertilizers.
Caring for beardless strawberries consists in watering, feeding, removing peduncles and preparing for the winter period.
Care features
To prevent the strawberries multiplied by dividing the bush from drooping, pay special attention to caring for the seedlings. Maintain high humidity in pots or greenhouses. Do not allow the earthy coma to dry out. Otherwise, fragile roots will suffer from a lack of moisture, which will slow down their development. Use mulch (peat, sawdust, chopped straw) to retain moisture.
If it is very sunny in a greenhouse or split-propagated greenhouse, provide partial shade for the split horns. This will eliminate a lot of water evaporation from the leaves. For better formation of the root system and the aerial part of the plant, apply a complex fertilizer. Strawberry especially loves potash dressings. Hilling will help to improve root formation.
Landing in the ground
Various techniques are used for planting remontant strawberries in the ground, but the two-line bush method is considered the best. It prevents thickening of plantings and contributes to additional protection of shrubs from fungal infections.
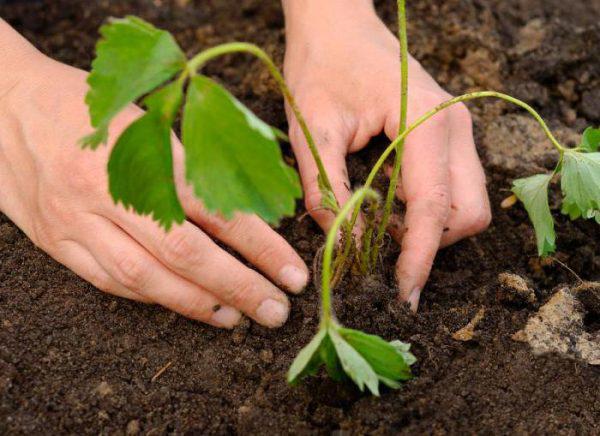


Strawberries can optionally be planted in narrow beds with a width of 90 cm-110 cm at a distance of 40-50 cm from each other. Sometimes more thickened plantings are made, but this is not the best option for plants. Before planting, loosen the soil well, make holes in them about 25 by 25 cm and spill with water. Add organic fertilizers to the wells immediately - for example, ash or compost with vermicompost.
In the process of planting, make sure that the roots of the plants do not burrow vertically and do not bend.The apical bud should be above the soil surface, but not too high.
After planting, the plants need to be watered and mulched. Ideal mulch - needles, grass, compost, sawdust. Coarse straw, however, is not the best choice in this case.
Proper care of remontant strawberries without fail includes mulching. You can use hay, straw, sawdust as mulch. Mulch will improve the composition of the soil, will help to retain moisture in it and prevent the growth of weeds.


In hot weather, soils dry out quickly, and a lack of moisture leads to a decrease in yield, so do not forget to water the plantings. It is especially important to ensure sufficient watering of the plants in the phases of their development and growth. To preserve moisture in the soils, the row spacings are loosened. During the period of active fruiting, loosening is not done.
As for weeding, it must be done. Weeds, of course, will not "eat" strawberries, but they will negatively affect the quality of the crop. When weeding, remove not only weeds, but also reddening old leaves - this is necessary to rejuvenate the bushes. Remove mustache rudiments from time to time.
Be sure to prepare the bushes for winter by reducing watering in advance, as well as trimming mustache and diseased leaves from them.
You need to fertilize the planting, but carefully. Most often, a small amount of rotted organic matter (that is, compost) is introduced into the soil. In order to protect against pests, the sheets are sprinkled with ash.
How to properly grow strawberries with a mustache
Mostly strawberries are grown with the help of a mustache. Therefore, the method is more in demand and popular.
After the strawberry has bloomed and bore a crop, it begins to actively grow mustache. At this time, it is advisable to clean the soil from weeds, loosen and water.


The rosette mustache should be straightened out. It is advisable to deepen the rosettes themselves a little into the soil.
In early autumn, roots appear at the outlets. They should be dug up and transplanted to a new location. You can also propagate a strawberry using a mustache in other ways.
After the bushes have yielded a crop and a mustache with rosettes has formed, it is recommended to carefully remove them. The sockets should be planted on a separate bed. A distance of at least 13-14 centimeters should be made between the bushes.
It is recommended to water such beds constantly and regularly, loosen the soil on them and protect them from direct sunlight.


After they take root well, it is recommended to transplant to other permanent beds.
Why transplant strawberries?
To begin with, you should talk about why a strawberry transplant is carried out. This process is carried out in order to rejuvenate the plantings. This culture is not recommended to be grown in one place for more than 3-4 years, since during this time a fairly large number of pathogenic bacteria and fungi accumulate in the soil, which pose a serious threat to strawberry bushes. And if the transplant is not carried out in a timely manner, then the yield of the plants will begin to fall, and the berry will noticeably shrink.
Important! It makes no sense to simply transplant whole bushes to a new place, since three- or four-year-old plants are considered old - they begin to throw out few inflorescences, bear poor fruit and over time their yield dwindles. Therefore, it is imperative to plant strawberries: either by dividing the bushes, or with the help of a mustache!
Transplant timing
When to transplant strawberries to a new location? This can be done in spring, late summer, or fall. But most gardeners carry out this procedure in the fall. And that's why.
In the spring - the culture transplanted at this time of the year takes root well and begins to develop very quickly, especially if the work was planned and carried out in early spring. But there is also a significant disadvantage - this year, the transplanted plants will not please with the harvest, since the first flowering will begin only next season.
How to propagate strawberries with seeds
This method is the most difficult. In order to get a beardless bush, this method is used.
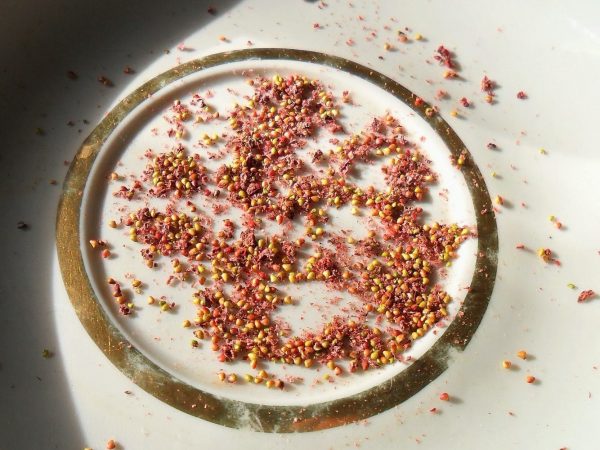
Seeds of a certain variety are recommended to be purchased at a specialty store or prepared by yourself. To do this, choose large, unripe berries. The top layer with seeds is removed from them and dried in the sun. Further, it is recommended to grind the mass thoroughly, place the seeds in small bags and store until sowing.


Strawberry seeds are grown in several ways:
- At the end of winter, seeds should be planted in special containers to a depth of no more than half a centimeter. The pots should be covered with plastic wrap for several weeks. Put them in a room where the temperature is in the range of 15-25 degrees. It is advisable to air it once a day. Also, the soil should not be allowed to dry out. After the soil has dried, it should be sprayed with a special spray bottle. As the seedlings appeared, the pots should be placed in places where there is a lot of light. After a few weeks, the bushes should be dived.
- Strawberry seeds should be washed well and soaked in warm water and dried on leaves. The leaves must be kept wet. Then you should wait only for the seeds to hatch. Then they are planted in pots with fertile soil to a depth of no more than half a centimeter. After several leaves have appeared, it is better to dive the plants. Seedlings require a lot of sunlight. Watering should be moderate, as the plant can become infected with a fungal infection and die. Before planting seedlings in the soil, it is advisable to put the pots in the shade on the street. This will temper her so that she does not die.


Choosing a place
Before replanting strawberries in a new place in the fall, you must select a site. Strawberries are a fairly unpretentious crop and will grow well in almost any soil. But in order for it to give really decent harvests, the gardener needs to take care of top dressing - to fertilize the soil with nutrients and enrich it with minerals important for culture.
On a note! The ideal strawberry bed is an area where the soil contains 2% humus!
Crop rotation
Good precursors for strawberries are:
Advice! For an autumn transplant, it is best to fill the selected bed in front of the strawberries with onions or garlic, or siderates - lupines, cereals.
But we should not forget about those crops after which it is highly discouraged to plant strawberries. These include:
- nightshades, in particular potatoes;
- cabbage;
- cucumbers.
Seedless strawberry
Strawberries produced using this method are believed to grow healthier.
Seed preparation. Ripe berries are selected, the pulp is removed with a blade in a thin layer, the mass is laid out on a paper sheet to dry, after which it is rubbed.
Stratification... Wet sand is poured into the seeds obtained, everything is transferred to a glass jar, which is kept in a refrigerator (temperature about 5 ° C) for about 30 days. Or they simply expose planting containers with seeds spread out on the soil under the snow (for example, on an open balcony) and leave there until planting.
Landing time. Seeds beardless strawberry usually planted in the second half of February (the period is indicated for the middle lane).
Soil mix... It should be fertile and loose, for example, you can take in equal amounts and thoroughly mix the compost and leafy soil. The soil for disinfection must first be sieved and spilled with boiling water or a solution of potassium permanganate.
Landing... The soil mixture is poured into planting containers and moistened. Seeds, spread out on a flat surface, are slightly pressed down, but they are not covered with soil.Advanced gardeners recommend covering the crops first with an ordinary paper napkin (when watering it should be moistened without removing it), and put glass on top of it or stretch plastic wrap.
Care... At first, it is advisable to keep the crops at a temperature of about 22-25 ° C, periodically ventilating and sprinkling with a spray bottle with water before the first shoots germinate on the surface.
After that, the glass can be removed, and the containers with the seedlings can be rearranged on a light window sill and the temperature can be maintained at no more than 22 ° C. It is best to water tiny plants with a pipette to prevent them from sticking to the ground. We must not forget to regularly air them so that they do not appear blackleg... When the second real leaf appears, the sprouts dive into separate cups.
Fertilize begin after the appearance of the third true leaflet. You can use fertilizers such as Kemira Lux, Solution (no more than 1 g per 1 liter of water, once every 10 days). To street conditions seedlings accustom gradually. They are transplanted to a permanent place after real warmth comes, and the plants acquire 4-5 leaves.
Types and varieties
Consider the most popular remontant small-fruited strawberry varieties:
- Alexandria - the variety was bred in 1964 and is characterized by a small adult plant height (up to 20 cm). The berries are sweet, the fruiting period is record-breaking - from May to October inclusive. The mass of one berry is about 8 g, one bush gives about 50 pieces of fruit per season. The variety is highly resistant to frost, diseases and pests;


- Baron Solemacher - the oldest variety of remontant strawberries. The berries are small, with a pronounced sourness in taste, covered with foliage. Sugar content - from 7%;
- Solemacher - bushes with compact and strong peduncles. They bloom in the first year after sowing and begin to bear fruit almost immediately. Over the summer, about 0.5 kg of berries are harvested from one bush. The variety loves phosphate soil, which must be taken into account when applying top dressing, it can withstand temperature changes and droughts normally. Solemacher's strawberries love shade, they can also be planted on balconies and window sills. After three years of active fruiting, the plant ceases to produce a sufficient number of fruits and needs to be transplanted;
- Gross Fraser - early strawberries, berries are bright red conical elongated, shiny. Average yield, sweet and sour taste. The variety loves the sun;
- White Swan - an interesting variety, but not very popular among Russian gardeners. It is represented by relatively small plants with colorless medium berries. The taste of the fruit is melting, with notes of lime. The variety tolerates frosts well, is resistant to diseases, but is picky about watering and dies quickly during droughts;


- Yellow miracle - berries are elongated, cone-shaped and yellow in color, taste similar to pineapple. The plant loves the sun, it is not demanding for watering and retains excellent yields in drought;
- Rugen Island Is an old variety with a history of over 100 years. The bushes are compact, bloom until November, bear fruit well. The culture is excellent against various pathogens;
- Ruyana - Czech remontant strawberries, which can be grown in moist soils (the main condition is high-quality drainage). Has a strong immunity from gray rot, grows well in shady places, can be planted under crowns. The berries are elastic, fragrant, located above the leaves, therefore they do not get dirty on the ground. Provide Ruyan with high-quality regular irrigation - and she will delight you with high yields;
- Holiday - 30-centimeter bushes with 12-tigram fruits, bred in the USA. They vaguely resemble garden strawberries, but with achenes compacted into the pulp. The variety belongs to dessert varieties, ripens in July and August. Yield indicators are high;
- Bolero - English breeding variety.The bushes are small, easy to cultivate, the berries are very sweet and large. The plant is not afraid of temperature extremes and other changing weather conditions. Drought does not affect the quality and size of berries;
- Lyubasha - Russian variety, the bushes are low, the flowers are white, the berries are large and sweet. The beginning of fruiting is June. The plant perfectly tolerates both cold and drought, is not afraid of pests;
- Merlan F1 - hybrid of the remontant Swiss selection. The most hardy large-fruited variety that is not afraid of viruses, frost, insects. The flowers are large pink, the berries are small and very sweet;
- Selva - a classic variety of Czech selection, which, by the way, is most often found in our greenhouses and on the shelves of Russian stores. The fruits are large, uneven in shape and sour taste. The variety needs constant abundant watering;
Read also: When to plant cucumbers for seedlings in 2020 according to the lunar calendar - the best days for sowing cucumbers with seeds in January, February, March, April and May


As you can see, there are a huge variety of varieties and each of them has its own characteristics and care rules. Remember that the yield of the crop depends on compliance with the rules of care.
Plants are grown mainly by seedlings, seedlings are obtained from seeds. Seeds should be sown in containers filled with fertile soil. Disembarkation is carried out in the spring - from February to May. The containers are covered with glass or foil and kept until the seeds are fully germinated. The room temperature should be 18-20 degrees. If the soil is not enriched with organic matter, then bone or fish meal can be added to it.
In order for the seeds to germinate better, it is recommended to sprinkle them with compost or humus, although not all gardeners do this.
The picking of seedlings is carried out as usual. When 5-6 leaves appear on the plant, you will need to transplant it into open ground. Reproduction is possible both by seeds and by a vegetative method.
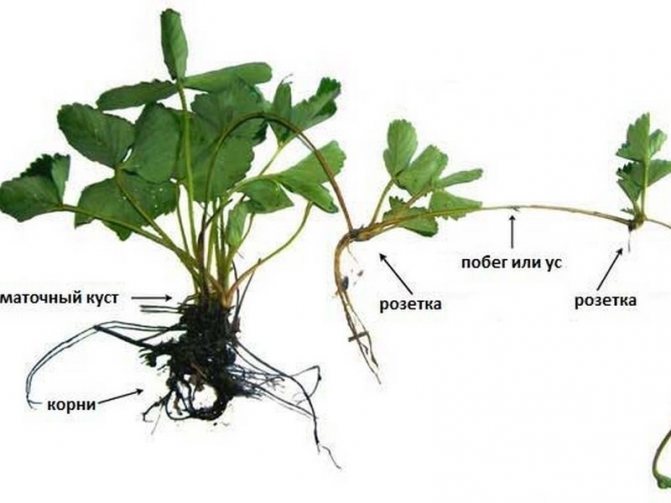
Propagation of strawberries by dividing the bush
Timing... Bushes can be planted from spring (preferred) to September. It is impossible to delay the transplant - the delenki will not have time to get comfortable in a new place and build up a decent root system in order to survive the winter frosts.
Ridge preparation... Everything is as usual: they dig up the soil, remove weeds, add compost (or rotted manure), potash and phosphorus fertilizers for digging. Wells are prepared (40x40 cm).
Transfer... This method is used for strawberries that have reached 3-4 years of age. Part of the leaves is usually removed, divided into seedlings (obtained from 1 bush up to 20 divisions). For each seedling, when planting, the root system is straightened, 2-3 divisions are installed in the prepared hole, watered and covered with soil to the hearts.
Caring for newly planted plants. Planted strawberries it is necessary to water and sprinkle periodically without falling asleep in the heart. After a week, planting is mulched with peat.
Self seeding. Sometimes it happens. An overripe berry fell somewhere, and a plant grew in this place. It can also be transplanted to a new location. Just keep in mind that Strawberrygrown from self-seeding may not have the qualities of a mother plant.
Wild strawberries can be propagated in 2 ways: by seeds and by dividing the bush. In the first case, uterine bushes should grow relatively far from other varieties of strawberries in order to exclude over-pollination (with over-pollination, the maternal signs are washed out and the planted bushes will not meet your expectations).
The seeds should be taken exclusively from the finally ripe berries. Since their size is extremely small, the seeds are cut with a thin layer of pulp using a sharp knife or blade. After that, the pulp is laid out on paper and wait until it dries. As soon as this happens, it is rubbed, while extracting seeds from it.
Sow the prepared seeds as soon as they dry out.Seedlings will have time to appear in the year of planting. They will germinate unevenly (some earlier, some later). Also, seeds of beardless strawberries can be planted in late autumn or early spring.
With the spring planting popular with summer residents, the seeds should first be stratified. To do this, they are mixed with wet clean sand and the resulting mixture is placed in a glass jar. You need to store the container in the refrigerator at a temperature of + 3 ... + 5 C for a month. Prepared seeds at the end of January - February are planted in boxes with soil (gently press them to damp ground and cover with glass or plastic wrap; the optimum temperature for germination is + 18 C). The soil must be periodically sprayed with a spray bottle to keep it constantly slightly moist (but not waterlogged!).
If done correctly, the first shoots will begin to emerge from the ground about 3-5 weeks after planting. As soon as this has happened, the seedlings should be rearranged in a bright place (for example, on a windowsill). After the appearance of 2-3 true leaves, the seedlings are picked into peat-distilled pots. When 4-5 true leaves appear (May), seedlings are transplanted into open ground at a distance of 40 cm from each other (the planting depth remains the same as in the pots).
It is very important, especially the first time after transplanting, to periodically loosen the soil around the strawberries and do regular, moderate watering. When new leaves appear, it is advisable to carry out not strong feeding with complex mineral fertilizers (while avoiding an overdose, especially nitrogen: it increases foliage growth, but at the same time significantly reduces the yield).
The second method of breeding mustacheless strawberries is by dividing the mother bushes. Each split part must have both roots and horns at the same time. Delenki should be planted in the chosen place and watered well. In this way, it is advisable to plant the beardless strawberries before September 15, so that all the bushes have time to adapt to the coming winter.
Remember that remontant strawberry varieties bear fruit most productively only in the first few years, so it is advisable to renew the planting of these plants on your plots from time to time.
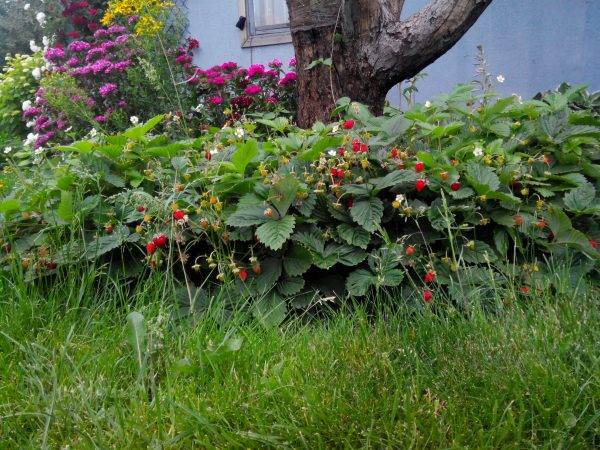


There are many varieties and varieties of this beloved berry. But it is worth paying attention to the beardless remontant large-fruited strawberries, which are capable of producing crops from June to September.
For busy city dwellers, this is a godsend. It is very important that strawberries (unlike their large-fruited counterparts - strawberry bushes) prefer light partial shade.
This means that it can be planted in the aisles of the garden, along a row of currant bushes, its neat bushes look original just along the garden path.
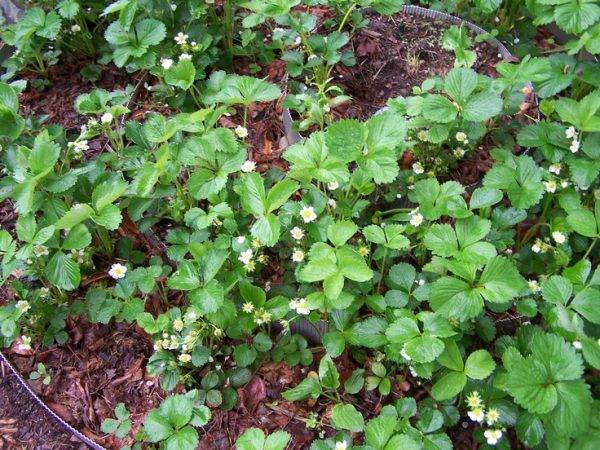


This type of strawberry is less susceptible to pest infestation and is less afraid of fungal diseases., which means that you can do without the notorious "chemistry".
Compact bushes with stable peduncles do not allow the berries to sink to the ground, which of course does not eliminate the desired mulching of the plantings, but you can do it.
And most importantly (whoever did this - remembered for a long time!) - your strawberry garden will not grow a couple of seasons before the boundaries of the site.
This struggle (it cannot be called otherwise) with the aggressive behavior of the "mustachioed" berry may end not in your compassionate owner, who is sorry to ruthlessly suppress the spread of the mustache.
However, the lack of a mustache is a double-edged sword. There may be problems with the reproduction of a favorite berry. The first thing you come across is a seed propagation option.
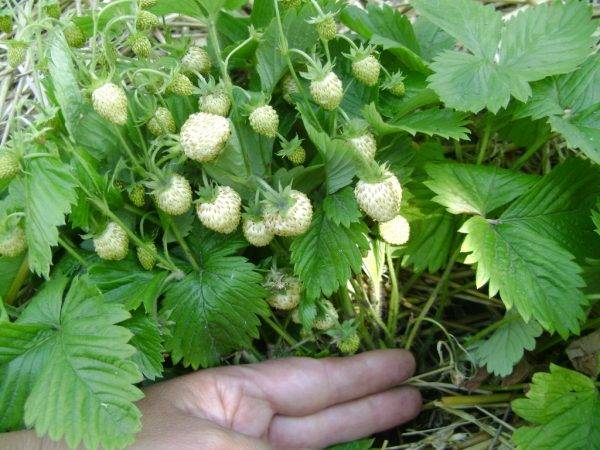


This business seems dreary and hopeless. Although there is nothing complicated about it.
To do this, it is enough to stock up on seeds from a trusted source and the required amount of peat tablets.
It makes no sense to start growing seedlings too early, in conditions of a short daylight hours, young shoots will stretch out strongly. Nothing good will come of it without equipped additional lighting.
Therefore, if start germinating seeds in March - by April they will germinate, and already in May a cute miniature bush with 3-4 real leaves will grow in a peat tablet.
Therefore, we are not in a hurry, and after March 8, on a damp napkin of dark color (this is to immediately see the germinated seeds), we put it in a bowl, for example, Cover it with glass or film and put it in a well-lit place.
The fact is that strawberry seeds need light for germination. And if someone sows directly into the ground - this must be taken into account and not to bury the seeds, leave them on the surface.
They will germinate in about a week, most likely not at the same time. And even then it is carefully transferred into a soaked peat tablet with a toothpick or a match, as it is more convenient for anyone.
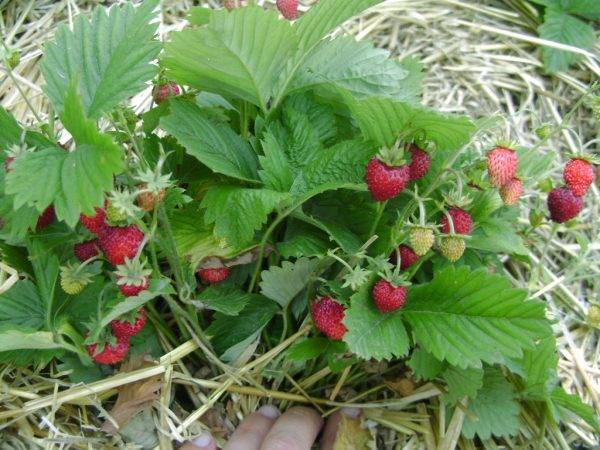


Further, there is no more trouble with the seedlings - wait until a developed root system is formed (this usually occurs in the phase of 4-5 true leaves and immediately noticeable - the roots begin to break through the peat tablet shell).
During this time, it is necessary to find a place for planting strawberries - after all, it will grow there for more than one year.
Although it is difficult to find such a stress-resistant plant among fruit crops, she "will not even notice" a transplant with a lump of earth.
By autumn, the bushes will bloom and give several berries. But this is only the first year of their life.
Those who do not want to mess with seeds and seedlings can use the vegetative method - dividing the bush. The fact is that for 3-4 years of life, the bush by itself, as it were, "breaks up" into several.
And it is enough to mark the bushes during the berry season, which are noted for their yield, or the taste of berries - which is really there who likes it.
After fruiting, we dig out the marked bushes, divide them into a reasonable number of divisions and equip a new bed. After a week, it is advisable to feed with complex fertilizers. Everything, we are leaving for the winter.
The nuances of growing beardless strawberries
Having listed all the benefits of remontant, mustache-free strawberries, we can notice that they lack the usual way of propagation. Therefore, such varieties are grown by sowing seeds. The method is quite laborious at home. The seeds are small and require careful maintenance when grown.
Typically, gardeners propagate beardless strawberries by dividing the bush.
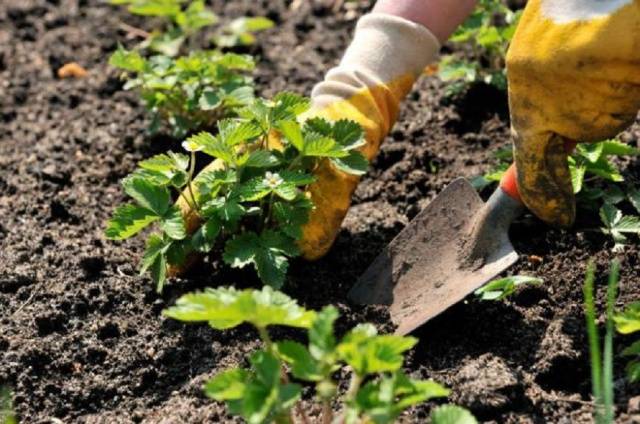


This method is proven and reliable. But for varietal breeding, sowing of seeds is also needed. Experienced gardeners take on this difficult but worthy job.
How to grow barnyard strawberry varieties from seeds
First, about the soil. The beardless beauty-strawberry loves sandy loam and loam, but the seeds will still gratefully respond to the presence of humus. You can take ready-made soil for seedlings. Important! Be sure to read the composition of the soil and its acidity.
There are special mixtures for growing strawberries, they contain sand.
To distribute small seeds evenly in the ground, they are also mixed with dry sand.
Then the planting container is filled with soil and watered.
The seeds are sown on the surface, trying to distribute them evenly.
The container is covered with a film, as if creating a mini-greenhouse. This is necessary to create optimal conditions for seeds to germinate. These treatments are best done in late March or early April.
As soon as shoots appear, the greenhouse is periodically opened for ventilation.
At the age of three true leaves, small seedlings dive.
Caring for dived seedlings consists of moderate watering, hardening, loosening, and removing weeds. Beerless strawberry seedlings are mulched to retain moisture. The hardening time is increased gradually so that the seedlings "get used" to the temperature of the open beds.
As soon as six leaves grow on the seedlings, it's time to go to the garden.


Preparing the ground, marking the rows and planting new residents in the open space.
Mustacheless strawberries do not like soil after eggplant, potato and tomato. Grows well after carrots or onions.
Plants are placed on the site according to the rules. We maintain the width of the ridges 1.2 m, and leave 30 cm between the bushes.
When planting, we enrich the soil with ash, superphosphate (1 tbsp. L) or ready-made mineral fertilizer (according to the instructions). We try to keep the roots from touching the fertilizer.
The procedure is carried out at a time when the active sun does not affect the plants - in the evening or in the morning. When the bushes are planted, it is time to care for the mustacheless strawberries.
Now you need to ensure that:
- the soil did not dry out - we water and mulch on time;
- feeding was carried out on time - we draw up a schedule, but we monitor the condition of the plants;
- we carry out prophylaxis against the invasion of pests and the usual diseases of mustache strawberries.
After a week, which we give the bushes for adaptation, young leaves appear. In autumn, a young bush of beardless strawberries will give the first fruits, so that you can judge the quality of the selected variety.
During this period of life, remontant strawberries require removal of the leaves two months after their appearance.
We monitor the condition of the soil, apply the required types of fertilizers, water, introduce modern technologies for growing strawberries without a mustache and get a good high-quality harvest.
What are the best varieties of beanless remontant strawberries that experienced gardeners recommend growing? What are the main criteria for choosing a culture?
Characteristics of Barless Strawberries
In terms of its characteristics, the plant is in many ways superior to its relatives:
- fruiting occurs from mid-June to the onset of autumn frosts
- berries in taste and aroma are not inferior to wild strawberries
- the size of the berries is large
- the number of berries from a bush can reach 1000 pieces
The fact that a mustache-less strawberry is not capable of sprouting and forming new rosettes is undoubtedly a positive quality. This greatly simplifies the maintenance of the beds, and also contributes to a more stable harvest.
Choosing the best types of remontant, beardless strawberries
What are the best varieties? What varieties of mustache-free garden strawberries should you focus on? The main criteria are:
- high varietal qualities;
- long-term fruiting;
- taste and aroma of berries;
- ability to transport;
- the ability to resist parasites and diseases;
- endurance and undemandingness to growing conditions;
- the ability to grow on soils with different compositions.
Consider the most popular types of garden strawberries.


Large-fruited and, of course, remontant beardless. Refers to early ripening varieties. The bushes are lush, beautiful, spreading with long peduncles. This makes it possible to grow the variety in high ridges and get clean berries. One mustardless berry weighs about 23 grams, has a cone shape and has a sweet and sour taste. It is considered a berry with stable yields. Suitable for fresh treats, in the form of blanks and freezing. The only drawback is that it weakly resists the strawberry mite. But drought tolerance and ability to withstand diseases are decent. Recommended for regions with different climatic characteristics. A popular type of beardless strawberry in summer cottages.
"Queen Elizabeth"


Among lovers of beardless garden strawberries, this variety is called imperial. Varietal quality of strawberries at the highest level. Begins to bear fruit early, at the end of spring it is already possible to pick beautiful large berries with a pleasant taste. During the season, the taste changes. By September, it is not so thin, the strawberries are preparing for the winter vacation. The same bushes have not been grown for more than three years. Since the variety does not reproduce with a mustache, you need to take care of the planting material in advance.Either you buy seedlings, or you plant the best bushes, or you collect and sow the seeds yourself. Grows well in any soil. It attracts many gardeners by the fact that it is possible to observe crop rotation in areas with different types of soil.


A variety of beardless garden strawberries with luxurious bushes. The dark green foliage with a slight sheen makes it very attractive. Straight peduncles are considered an advantage of the variety without a mustache. The harvest is always removed clean, because the berries do not reach the ground. It is drought-resistant, which is convenient with a tight work schedule, but it is afraid of frost. If in your region a cool climate and frosts are the usual manifestations of the weather, then you will have to cover the plantings. In the south, you can safely do without additional shelter. Strawberries "Albion" are large-fruited, musty-free varieties with bright red berries. It is convenient to transport them due to their high density.
Read also: Apple tree ligol: description of the variety with photo and video
It is considered a high-yielding species.


Gardeners know firsthand about the Bolero beardless strawberry. A variety with excellent characteristics bred by English breeders. Among the advantages of "Bolero" are:
- compactness of the bush, its small size;
- high resistance to unstable climate manifestations;
- stability of taste characteristics in hot weather;
- perfectly resists fungal diseases and the development of mold;
- stable fruiting for 5 years.
The large-fruited variety and the taste of the berries made it a favorite in many summer cottages.


The Dutch mustacheless variety is in great demand. Refers to neutral day types. Flower buds "Vima Rina" lays regardless of the length of daylight hours, and even the break between fruiting is only three weeks.
The bushes of this strawberry are large, the buds are located at the level of the leaves.
In case of prolonged heat, this does not threaten gardeners, but the Vima Rina strawberry is distinguished by good drought resistance. She will perfectly survive even the lack of watering (temporary!).


Renovated strawberries donated to gardeners by Czech breeders. Attractive in many qualities:
- withstands heavy rainfall (drained soil is required);
- almost not affected by gray rot (observe planting density);
- perfectly tolerates shade, so summer residents plant the variety in an orchard under the crowns of trees;
- elevation of berries above the ground;
- aroma and wonderful taste of fruits;
- undemanding to watering.
Of course, if you do not water "Ruyana", then next year the yield of the beardless beauty will decrease.
"Yellow miracle"


Strawberry without a mustache got its name for a reason. Many summer residents consider it a miracle of nature. Very beautiful cone-shaped berries of light yellow color give the strawberries originality and decorativeness. Landings perfectly decorate the site.
The taste does not lag behind - the berry resembles a pineapple. Besides the attractive look, the mustacheless strawberry:
- does not react sharply to the hot sun;
- does not reduce productivity when irrigation is disturbed, tolerates moderate drought.
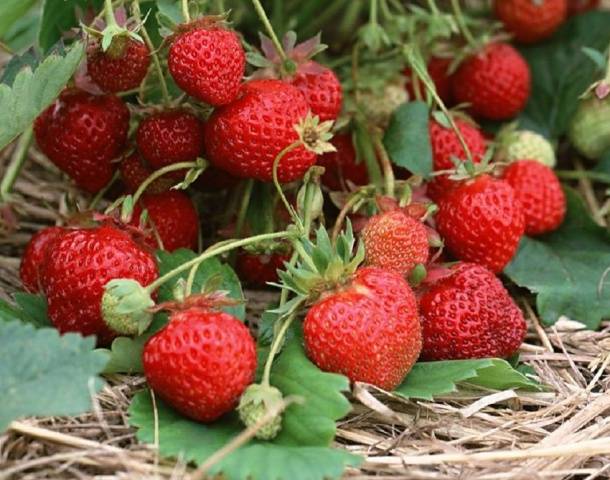


A large-fruited species of remontant garden strawberry without a mustache. Genetically has the ability to flowering and fruiting continuously. This process does not depend on the length of daylight hours, so the yield of the variety is very high. The plant is very hardy and productive. A small number of bushes on the site are enough to feast on delicious berries all summer long. Strawberry "Garland" has a pleasant smell, excellent taste and dense texture of berries. This makes it possible to transport the crop without fear of injuring the musty strawberry. Large-fruited remains until the end of fruiting, the berries do not become smaller and do not lose their taste. Another advantage is long peduncles. Harvesting is easy, there is no need to protect the fruit from dirt.Feels great on ridges and trellises, so you can grow this variety of strawberries in a container and hanging pots.
Propagation of beardless strawberries
There is only one way to propagate mustardless strawberries - by growing new plants from seeds. This is not to say that this occupation is too difficult, but it will require certain knowledge.
- First, you need to properly prepare the soil, loose and nutritious, clearing it of coarse fractions.
- Seeds should be sown in a small box with soil, the distance between the seeds should be at least 1 cm. The box should be covered with a glass frame or foil to ensure a constant level of soil moisture.
- You do not need to bury the seeds in the ground, they should germinate in the light.
- The grown crops are hardened, constantly accustoming them to room temperature and drier air.
The recommended time for sowing seeds is spring-early summer. Planting seeds earlier will require additional lighting of the plants with fluorescent lamps. Depending on the quality of the seeds, mustacheless strawberries can sprout in two to three weeks.
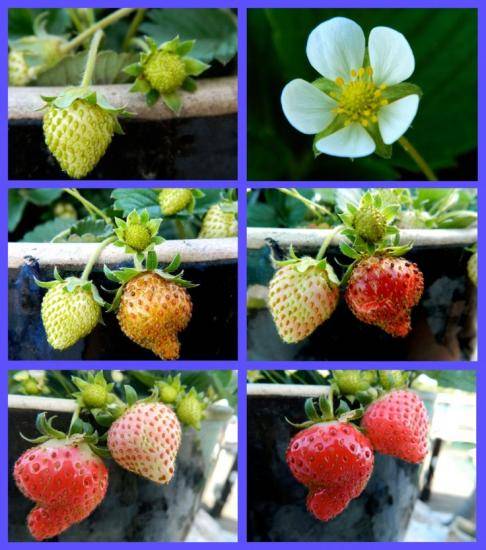
Strawberry photos


Due to the particularization of strawberry plants, division of the mother bush is also possible. In the third or fourth year of life, old rhizomes naturally die off in the bushes, the rosettes disintegrate into separate particles (parts). Particulation is a simple and natural way to propagate remontant mustacheless varieties.
Care for barny strawberries
For some reason, some gardeners in the fall radically cut off strawberry bushes. Perhaps this is due to the desire to protect plants from fungal diseases. But after all, nature is so laid down that a perennial plant so protects itself from frost, preserves snow for itself, and feeds itself. In the wild, gradually dying leaves form a layer of mulch.
Therefore, if you have a desire to prune dead leaves, then do it in the spring. But instead of the strawberry you need to add a layer of organic mulch. Since the mustacheless varieties are not aggressive, lawn grass mulch, as well as pine mulch, are perfect for prepared beds.
In addition to organic mulch, a film coating will help fight weeds. The British, Americans and Europeans grow it this way. Their berries never touch the ground.


And it used to be like this with us, and why they refused it is not clear. It is best to take roofing material and roll it out over the prepared bed. Press the edges tightly with boards. Walking on the covered garden is strictly prohibited. Try to walk only on planks during both planting and operation.
For planting strawberries, small cross-shaped cuts are made (preferably only with a knife, not torn). Then young plants are crammed into them quite tightly. With growth, these cuts-crosses themselves will expand to meet the needs of the bush.
Two or three rows are made on the bed with a row spacing of 30 cm, the planting density in a row is 20-25 cm. The beds covered with mulch do without watering the whole season. And you can feed your pet with microelements. Strawberries also respond well to the following top dressing: a drop of iodine, a thin potassium permanganate, a pinch of copper and iron sulfate on a bucket of water. You can water directly over the foliage from a watering can with a splitter.
How to keep moisture in the soil
Since the roots of strawberries do not go deep into the depths, the protection from the mulch saves moisture, preserves the looseness of the soil, and also protects the berries from rot. It is estimated that with such a simple agricultural technique, they get a third increase in yield, and even more in rainy times.
Re-laying the beds is done after four years. It is excellent if the crop rotation is followed and you plant remontant strawberries after legumes. So less pests will accumulate in the soil, such as nematodes. If this is not possible, remove the covering material and apply a generous layer of mature organic matter (8-10 cm).Then spread a layer of new roofing material, since the old one will no longer have the necessary tightness.
Today on sale you can find different varieties of beardless strawberries and strawberries, the technology of their cultivation is almost the same, and the timing and activity of fruiting are determined by the varieties.
nashsad.su
How to propagate mustardless strawberries
Diseases and pests
Modern strawberry varieties are quite resistant to most pests and diseases, but they require some care. The most common plant ailments:
- black and gray rotwhich infects berries, leaves, flowers, peduncles and most often appears in rainy weather. Visually, rot looks like a gray or black bloom. The main control measure is correct agricultural technology, do not thicken the plantings;
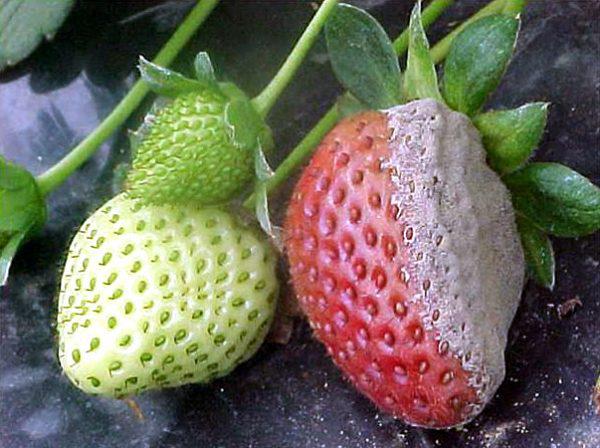


- white and brown spotting - affects all plant organs. At first, the spots are red-brown, then they begin to darken. The affected organs may die. The main control measure is fungicide treatment;
- strawberry mite - occurs often, carried by the wind. Damaged leaves wrinkle, become yellow-oily and die off, and the bushes become smaller (decrease in size). To destroy the tick, they are treated with colloidal sulfur, Aktofit and Actellik preparations.
Other types of diseases (verticillary wilting, powdery mildew, late blight rot, etc.) are less common. Control measures are the same as for the diseases described above.