Origin story
Photo:
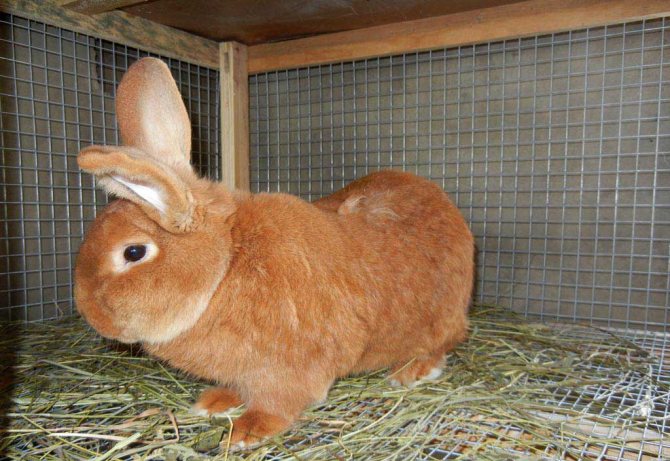

For the first time rabbits of this breed were presented at an exhibition in 1910. They were bred in the United States, in the state of California, as a result of crossing three breeds at once: the Belgian Hare, Flanders and the Silver Rabbit.
Due to their early maturity and high meat productivity, New Zealanders quickly gained great popularity and commercial demand, including in the world market.
Later, albinos were artificially selected from the litter of the red New Zealand rabbit (NZB), which became the genetic basis for breeding the white variety of the breed (NZB).
There are also black New Zealand rabbits, but they are usually raised as an ornamental animal. New Zealand rabbits became widespread only in the 90s; today they are bred in many European countries for meat and fur.
Description of the red breed
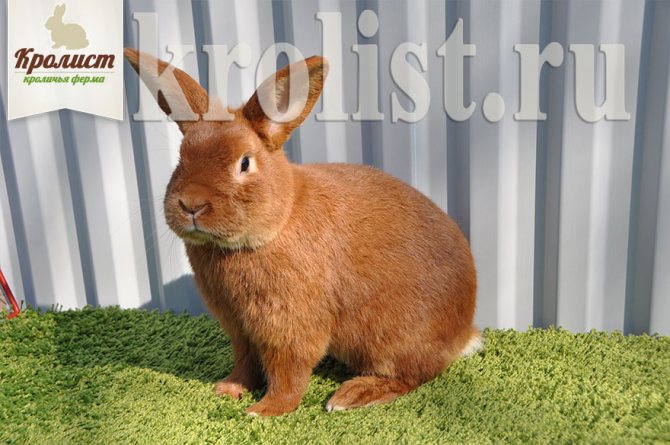
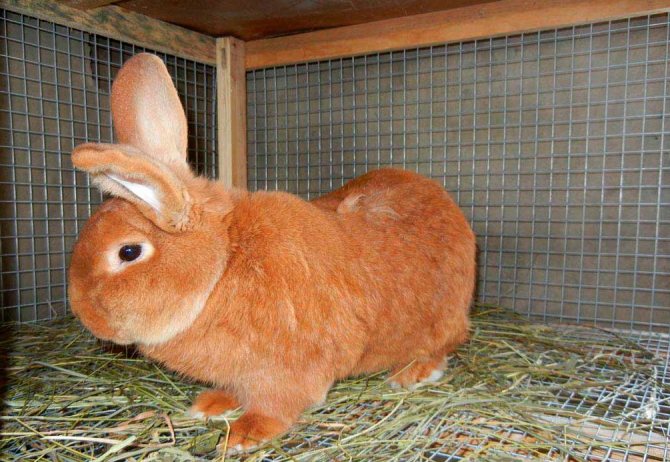
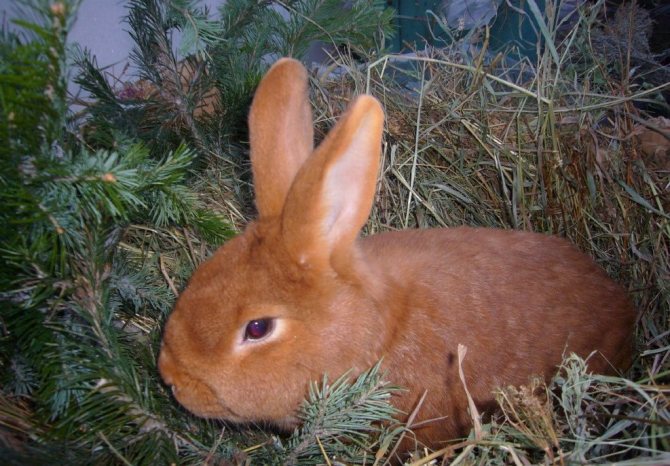
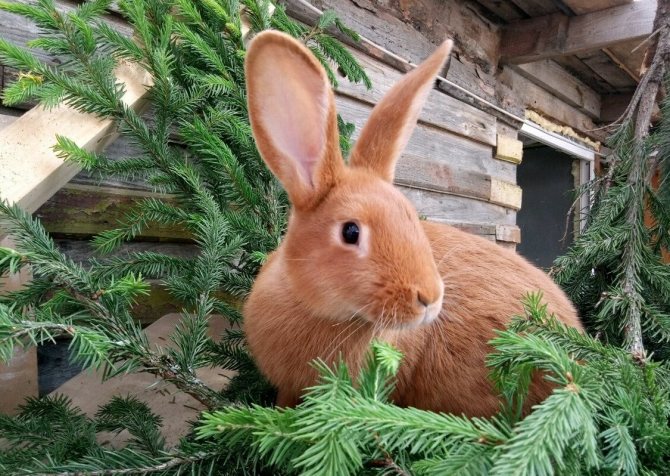
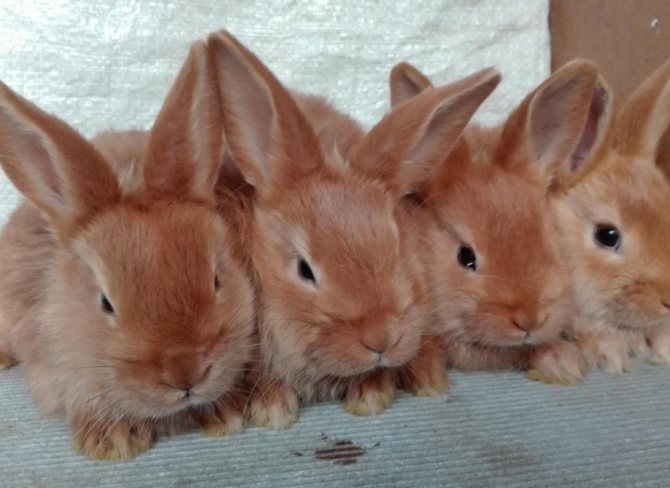
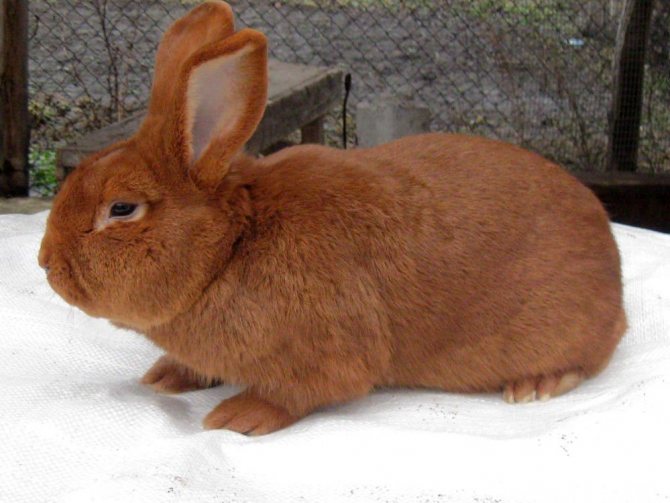
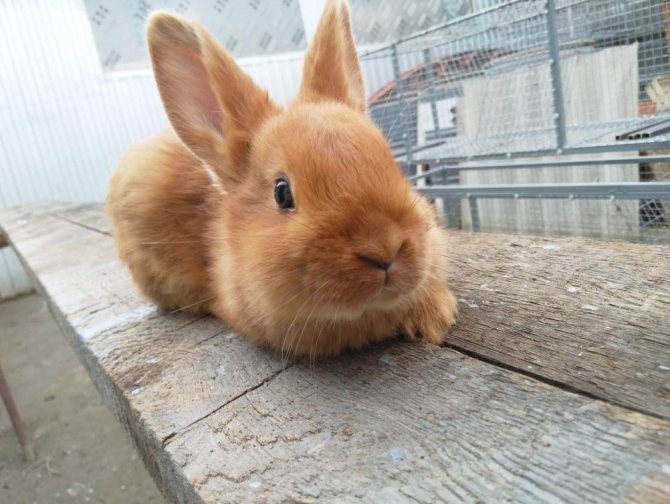
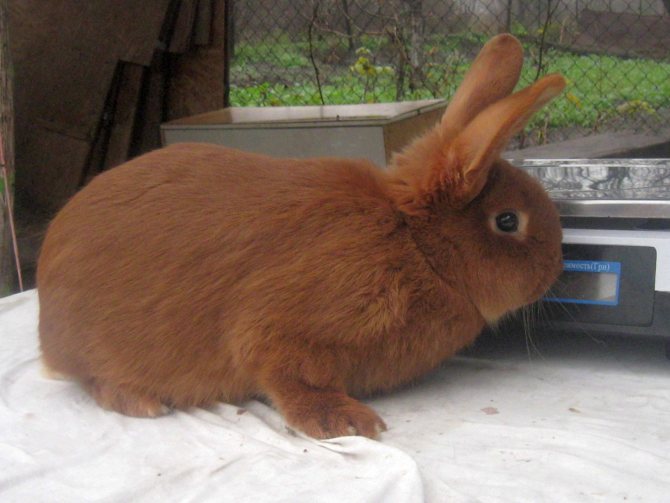
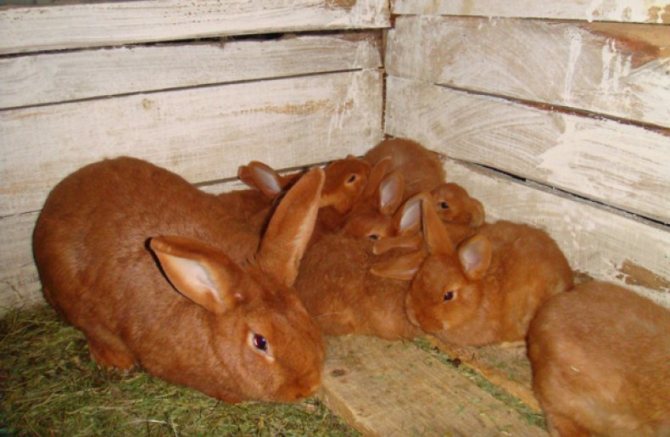
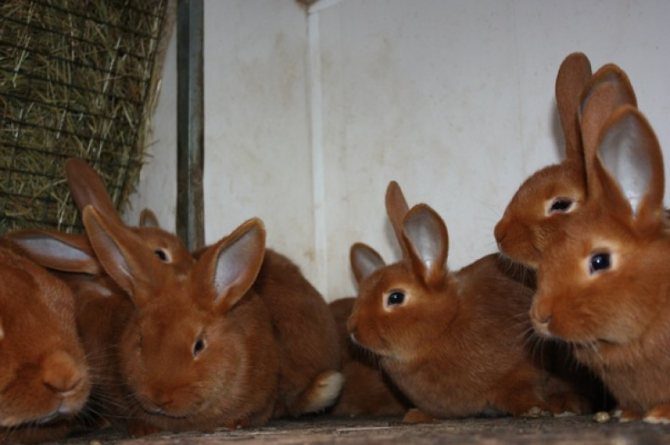
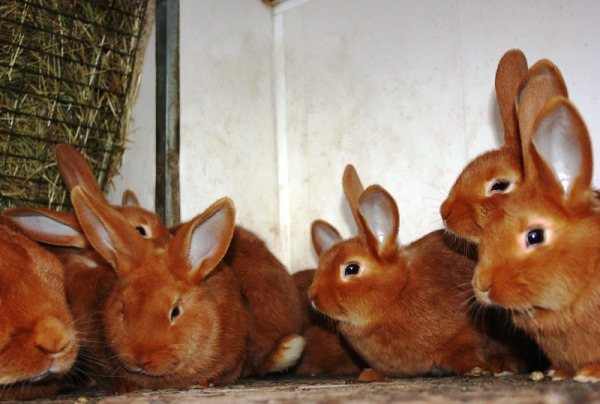
They are the classic version of the breed. Rabbits have a powerful constitution, well-developed muscles and beautiful red-brown fur.
Animal skins are actively used to create clothing due to the thick and wear-resistant fur. The head is large, with straight, erect ears.
The red color on the face, especially near the eyes of the mouth, and also on the belly is slightly lighter. The eyes are expressive, dark brown in color. The body can reach a length of up to 50 cm, females always grow larger than males.
The animals are extremely fertile, have a calm and accommodating character, but rather shy.
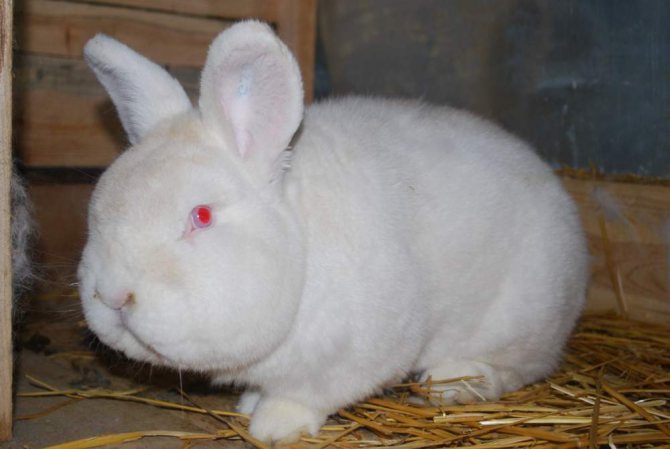
Description of the white breed
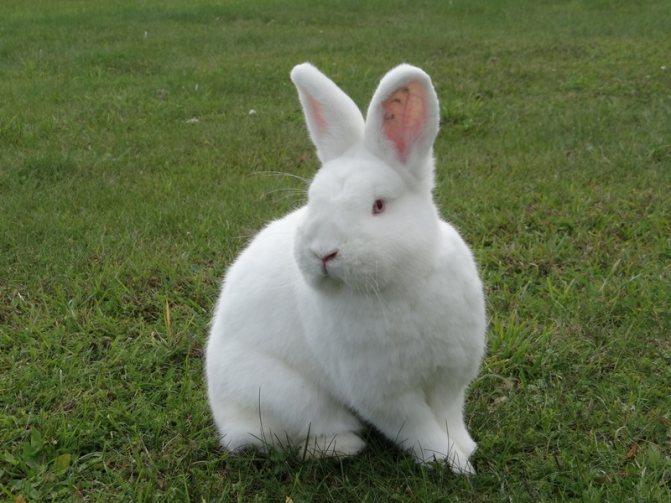


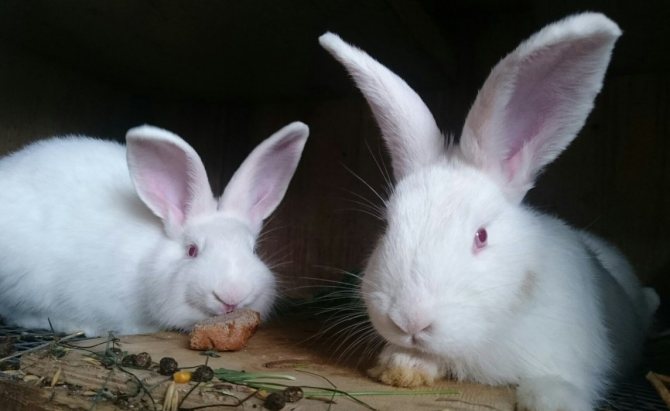
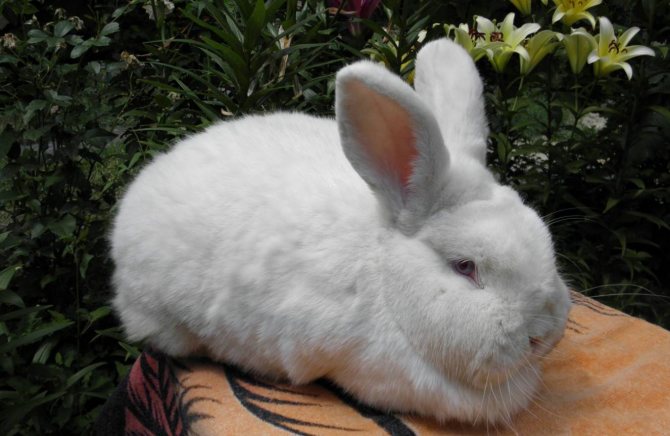
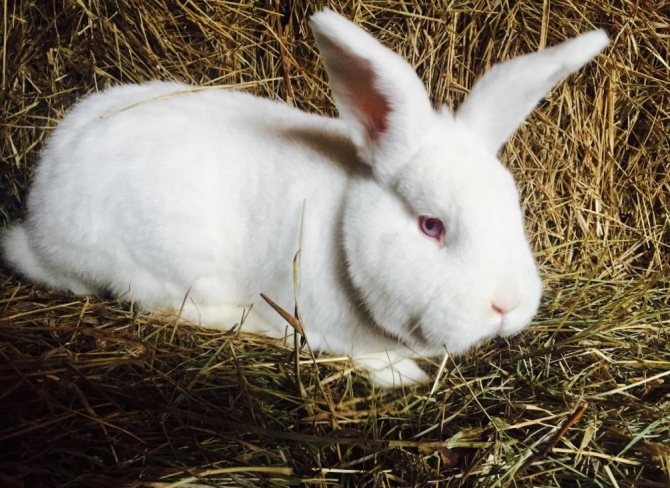
White rabbits (WBRs) are commonly raised on commercial farms. They are larger than NZK, have a powerful and sturdy physique. The skeleton is well developed, the legs are powerful and long.
The neck is short, the head is set low with thick and short ears up to 10 cm long. Females may have a slight dewlap, in males this is a marriage.
Outwardly they differ from red New Zealand rabbits in snow-white fur color and red eyes. The presence of other colors on the skin is a breed defect.
Fur is used to create premium class clothing, is in great demand, since any paint fits well on it. They are calm and docile animals.
Rabbits are able to show friendliness to the owner. They develop rapidly, the body length of adults can reach 47-50 cm.
Varieties of New Zealand rabbits
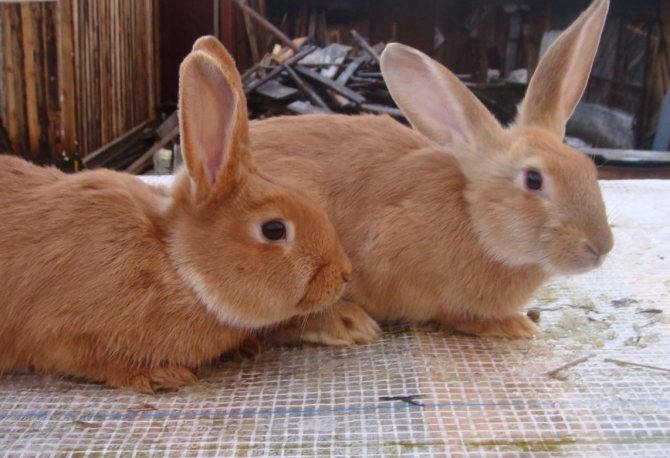
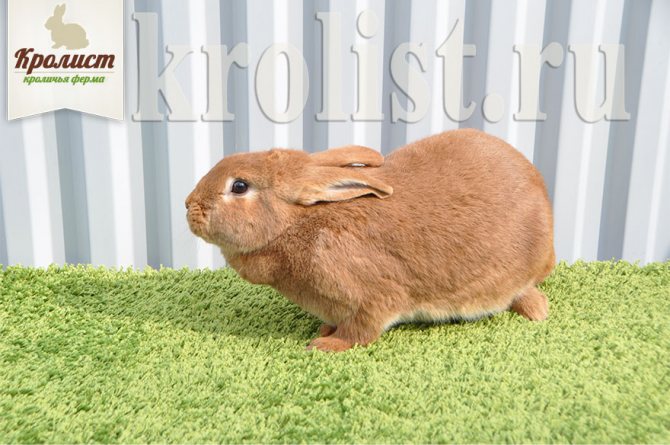
New Zealand Red
Feature Description
| Direction for breeding | Meat skin |
| Color | Red to dark red |
| Growth rate | Gains weight quickly up to 4 months |
New Zealand Red was the very first
Muscular cylindrical body, well-developed strong limbs. The length of the ears is up to 12 cm, the ears are well pubescent. The fur over the entire surface of the body is shiny, dense. Pile length from 3 to 5 cm.
New Zealand White
Feature Description
| Direction for breeding | Meat |
| Color | Snow white |
| Growth rate | Gains weight quickly up to 3 months |
New Zealand White was bred from albino New Zealand Reds
Muscular cylindrical body, well-developed strong limbs. Developed round head. The length of the ears is up to 12 cm, the ears are well pubescent.The fur over the entire surface of the body is shiny, dense. Pile length from 3 to 5 cm.
Video - White New Zealand rabbit
Rarely, but there are New Zealand Black and Blue representatives of the breed, however, they have not received wide distribution, although all parameters are similar to the popular Red and White breeds.
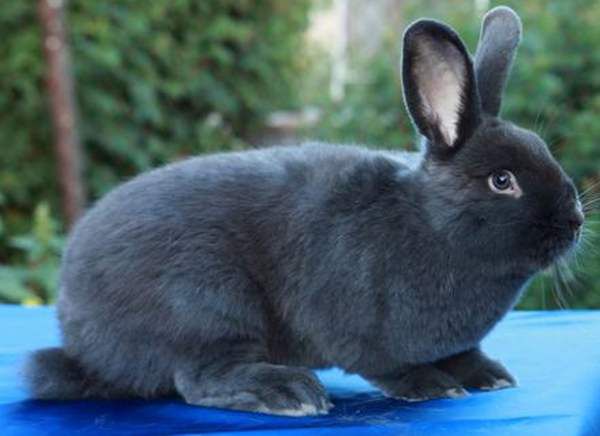


New Zealand Blue
Additional care
Caring for rabbits will not cause much trouble, but will allow you to maintain their health, which means preserving all the advantages that make their breeding profitable (reproduction rate and presentation).
- Veterinary examination should be systematic (about once every six months in the absence of an urgent need).
- Preventive vaccinations can significantly increase life expectancy and prevent possible diseases.
- Combing the fur and clipping the mats will keep the pelt in good condition. The main place of localization of matted wool is the belly, the wool on it should be combed out regularly. A special comb is used for the procedure.
- After washing, let the rabbit dry properly in a warm room to avoid colds and subsequent illness. When bathing, the main task is to prevent water from entering the ears. The otitis media provoked in this way in rabbits is practically not treated. Do not abuse the bathing procedure, since frequent wetting is harmful both for the fur and for the mood of the animal. If you cannot do without washing, you should use a special veterinary shampoo.
Productivity
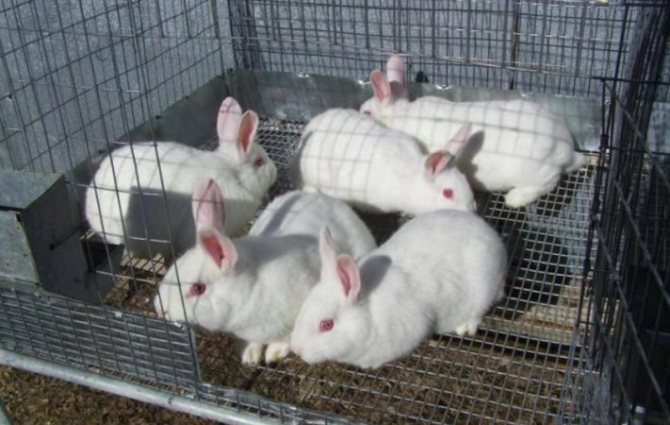
Rabbits of the New Zealand breed are raised for meat and skins. Young animals are actively gaining slaughter weight, by 3 months they can reach 2.3 kg. The average weight of adults is 4.7-5 kg, females are usually slightly larger. The meat contains a minimum amount of fat, the taste is delicate and pleasant.
The skins are in high demand in the market. White rabbit fur is more expensive because it is used for subsequent dyeing.
Wool grows 3-3.5 cm, has an elastic and silky texture. It should not be soft, but also not very hard. This characteristic is regulated by nutrition and conditions of detention.
In addition, New Zealand rabbits are often used in laboratory research. They are tested on various medications, as well as cosmetics after they have been tested on rats.
Keeping track of your health: vaccinations
Vaccination is the only prevention of some serious infectious diseases among rabbits. New Zealand rabbits are vaccinated according to the approved schedule.
| Rabbit vaccination calendar | |
| 28 days | Myxomatosis |
| 45 days | Viral hemorrhagic disease |
| 90 days | Coccidiosis |
| 120 days (repeat every six months) | Myxomatosis (revaccination) |
| 135 days (repeat every six months) | Viral hemorrhagic disease (revaccination) |
Price


New Zealand white rabbits can be purchased starting at 500 rubles per one month old. NZKs are slightly more expensive, the price of good breeders starts from 1000 rubles.
The black variety of New Zealanders is quite rare on sale, usually they are sold as decorative animals. The cost starts from 3000 rubles.
You need to purchase rabbits only from trusted breeders or farmers who have all the necessary veterinary and sanitary quality certificates.
For commercial cultivation and subsequent breeding, you need to buy only healthy and robust individuals that do not show signs of disease. Particular attention should be paid to the condition of the ears, eyes and to check the genitals. A young rabbit should be active and curious.
What to look for when buying
If, after reading the description of the breed, you decide that you want to breed New Zealanders, then there is only one thing left: to acquire them.To choose the right healthy individual, follow the recommendations of experienced farmers:
- the optimal age for purchase is 2-3 months;
- take the rabbit in your arms - it must be plump and active;
- there should be no discharge from the nose and eyes;
- the skin is shiny, soft and without bald spots;
- be sure to check the external genitals - the skin should be free of rashes.
Testimonials
New Zealanders are considered one of the most promising breeds of meat and skin direction. They grow quickly, and when properly fed, the meat tastes good and is low in fat.
Beautiful red, white skins are also in demand. Animals are conveniently kept, suitable for cage breeding They rarely get sick, pododermatitis and other diseases typical for rabbits are rare.
The main disadvantage of the breed is its tendency to obesity if feeding norms are not followed. In addition, rabbits of this breed are quite shy and susceptible to external factors, which reduces productivity indicators.
Feeding


A competent and moderate diet is important for this breed, as they are prone to obesity, and when using poor quality feed, the quality of the fur decreases. Feeding is carried out twice a day.
The daily diet should include:
- quality hay;
- concentrated feed;
- root vegetables (carrots or beets);
- aspen twigs;
- grains of oats, wheat or corn.
The recommended feeding rate for adults is 160-200 g per day, for females and lactating females, as well as before preparing for mating, the rate is raised to 330-400 g.
Rabbits should not be fed with lettuce, mushrooms, cabbage, tomato leaves. It is not recommended to offer nuts, sugar, bread and turnips. Greens should be given to New Zealanders with care to avoid digestive problems.
The cage should have free access to clean and fresh water, which should not be boiled, as this washes out all minerals and oxygen. It is recommended to use nipple drinkers to provide water, and if there are a large number of animals in the herd, bunker troughs are considered optimal for feeding.
What to feed rabbits
The condition of the coat and skin directly depends on what you will feed the animals. The diet should be varied - daily rabbits are fed with green food, hay, root crops, mixed fodder, and fresh twigs are also allowed to gnaw.
Eared eared should be fed only high quality feed. There should be a drinking bowl in the cage all the time - the main thing is to remember to regularly change the water and monitor its availability. Having decided to give grass - make sure that no poisonous herbs get into the feeder.
Did you know? If you want to pamper your pets with green food, add the following herbs to the feeder - alfalfa, dandelion or clover. Rabbits love them very much. From vegetables, animals are not averse to crunching apples, potatoes and carrots.
Care and maintenance
Rabbits of this breed are distinguished by their unpretentiousness and quickly adapt to the conditions of detention. New Zealanders are recommended to be housed indoors, kept in a cage manner.
Thanks to the feathering on the feet, you can use a mesh floor. When kept outdoors, productive qualities deteriorate, animals can lose weight.
No more than 2-3 individuals can be placed on 1 m2, males and females are kept separately, bringing them together only for covering. Animals do not tolerate heat, noise and bright light. The optimal temperature regime is considered to be in the range of 18-20 ° C in summer and winter. The room should be well ventilated and the light should be dim.
Caring for the NZK is the same as for other varieties of rabbits. They need to regularly clean the cage, feeders and drinkers, and change the bedding.
It is recommended to comb out animals of this breed as often as possible in order to avoid the appearance of tangles on the fur. Veterinary care is also required.
The first vaccination against myxomatosis is carried out at 28 days, at 45 days from birth, vaccination against HBV is given.
Re-vaccination of this dangerous disease should be administered after 3 months, again after 6 months. Rabbits are active animals that often injure themselves, so you need to check your veterinarian regularly.
What you need to start a business
Number of rabbits
The number of rabbits in the first step is an important point. In order to understand how successfully the project will develop, it takes some time. You shouldn't start your first experience with buying a real “herd”. To acquire the necessary skills for caring for animals, you can have one male and two or three females.
If you are just starting a breeding business, start with a small number of heads
Such a small farm will not require large financial investments and time expenditures from the owner, but it guarantees a return in the case of a competent approach to business. Given that the breeding rate of rabbits is high, the primary herd will grow in a few months to a full-fledged livestock that can bring real income.
Breeding


To enhance the breed qualities, it is recommended to carry out homogeneous or purebred mating. To prevent inbreeding, some breeders practice crossing New Zealanders with other meat breeds, for example, the gray giant, Vienna blue or California rabbit.
The animals reach sexual maturity by 3-4 months, it is recommended to let females into the first mating not earlier than 5 months with a weight of 3-3.5 kg, and males not earlier than 6-8 months.
Hunting in rabbits lasts up to 5 days, in summer it is repeated with an interval of 5-7 days. The animal becomes restless, refuses to feed and pluck out its fur, and the genitals swell and turn red.
It is at this point that she can be launched into a cage with a male for cover. The rabbit must be fertilized between 10 and 20 days from the beginning of the birth, otherwise the animal will quickly gain weight. The fruit is formed within 28-32 days.
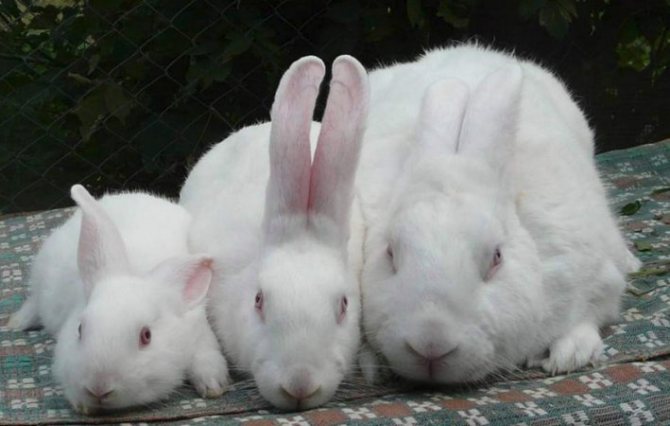
New Zealanders' rabbits are fertile, in one round they bring 8-10 rabbits weighing up to 45 g. Females are distinguished by good milkiness and pronounced maternal qualities.
Information in pictures
In the first days, the offspring is hidden in the fluff that the female rips off of herself. Rabbits are only 3-4 days old


Baby size at 4 days Baby size at 14 days




Female


Male