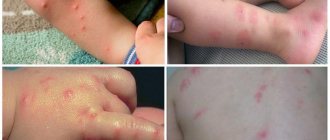
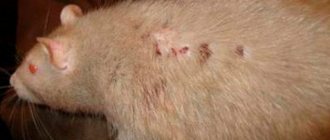
These insects are some of our most unpleasant neighbors, inevitable companions of wars and social disasters. Fortunately, nowadays such terrible epidemics as typhus or plague are rare. However, due to the large overcrowding of the population and the arrival of migrants from disadvantaged areas, our infectious diseases hospitals are not empty. The ability to quickly determine who is in front of you: fleas or lice can save a lot of nerves and time, because further actions depend on this knowledge.
Unfortunately, careful observance of hygiene standards in everyday life does not at all guarantee that you will not meet a person infected with these parasites. You, at least occasionally, ride public transport, go shopping, your children attend schools and kindergartens, your pets walk on the street - all these are risk factors that are almost impossible to avoid.
Let's try to figure out what these parasites are, why they are dangerous and what is the difference between lice and fleas.
Appearance
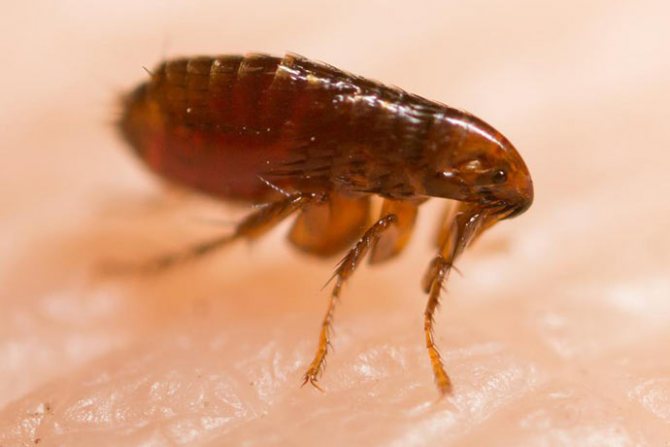
Fleas
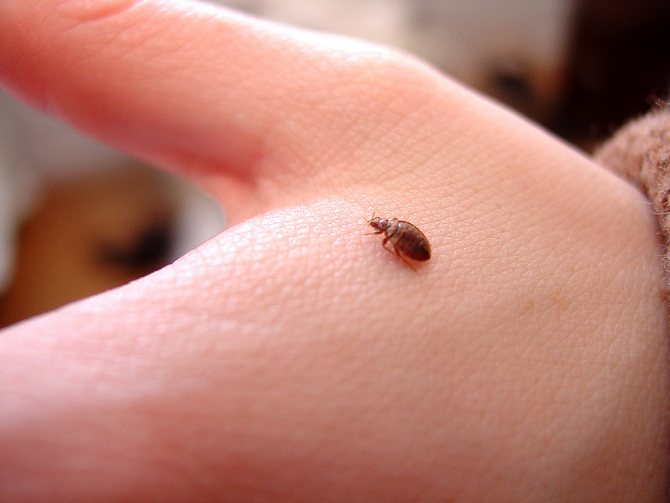
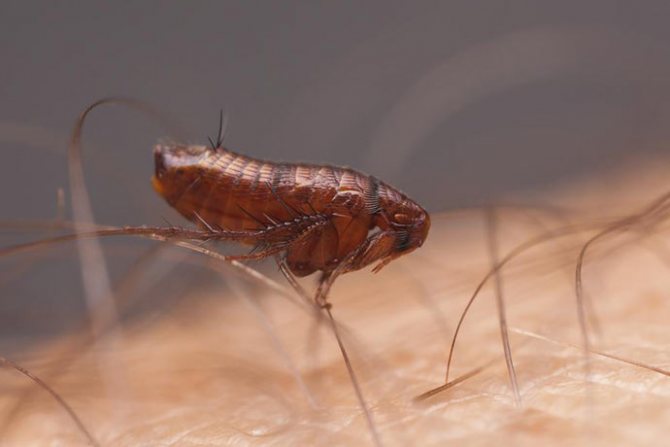
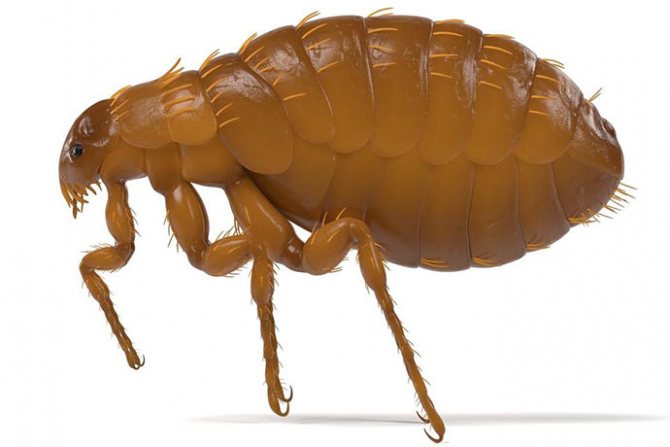
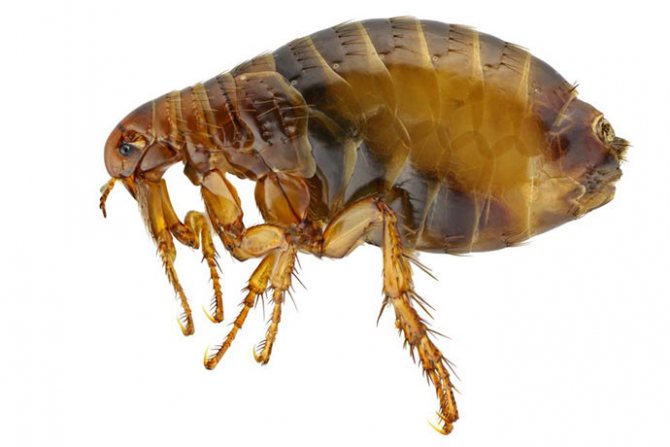
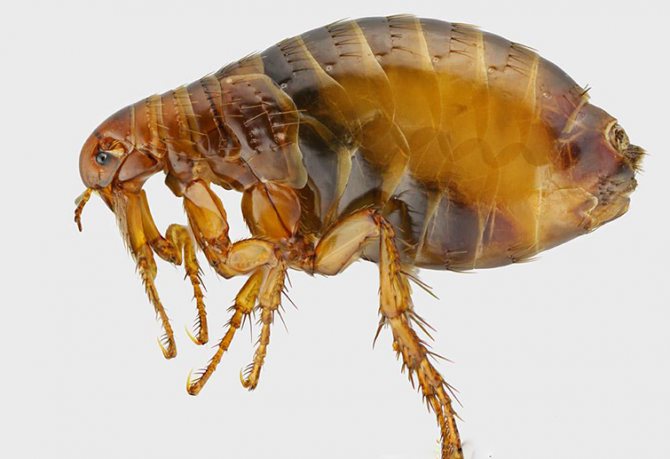
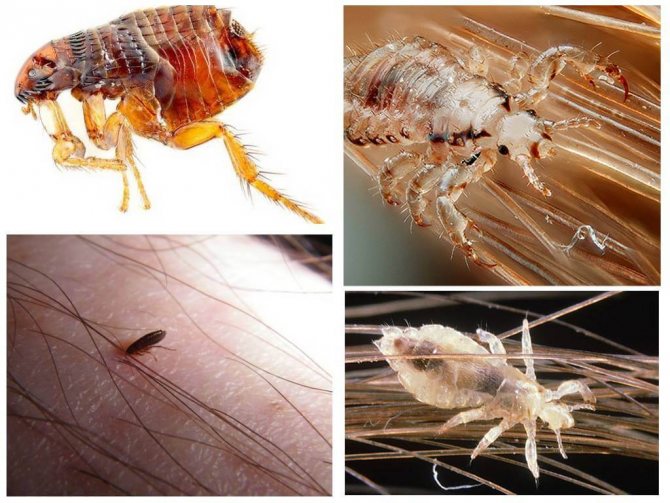
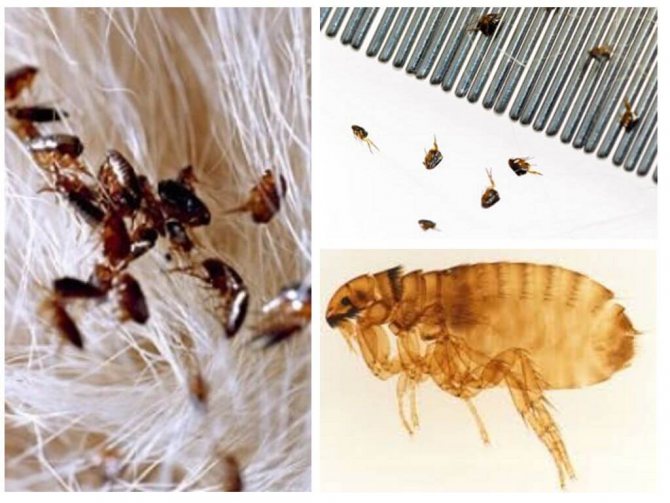
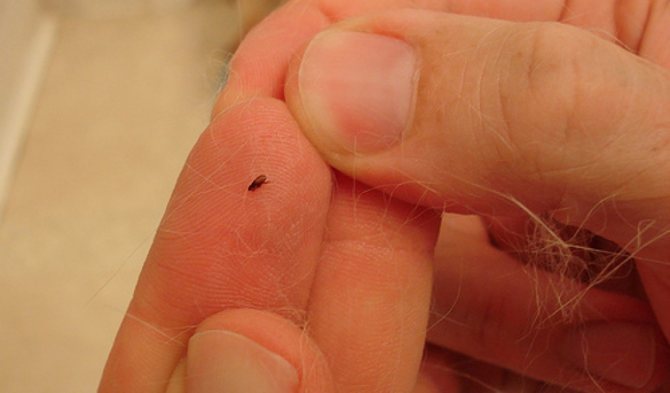
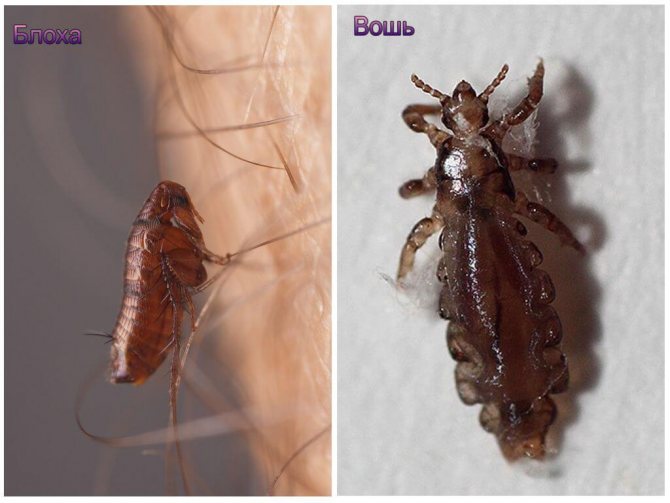
A small nimble insect of black-brown color, which is difficult to see in the fur of our smaller brothers. The size of a human flea does not exceed 0.5 mm, and insects that parasitize pets are two times smaller. In some species of fleas, females up to 10 mm come across, but this does not apply to human fleas.
The entire body of the insect is covered with ugly thorns for better attachment to the wool. The flea's back and chest have serrated ridges for the same purpose. Very strong chest legs and long hind legs enable this insect to jump at distances hundreds of times longer than the body length. The flea jump is indistinguishable to the human eye. That is, you can catch a glimpse of the movement, but the flea itself and where it jumped cannot be seen with the human eye.
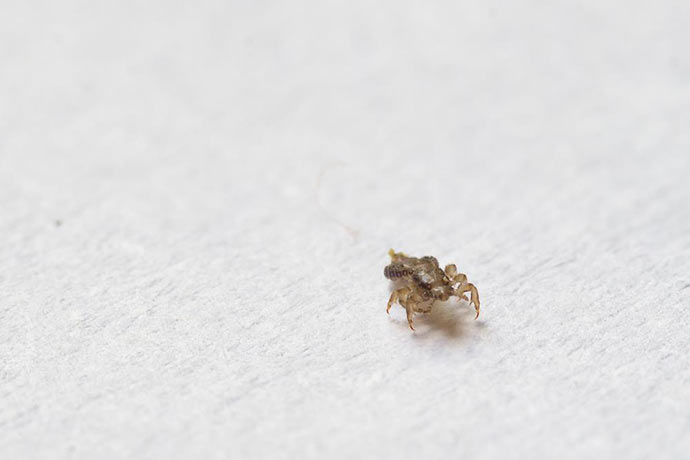
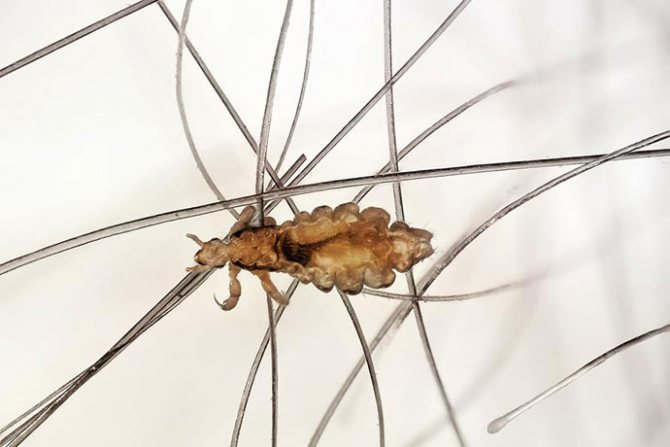
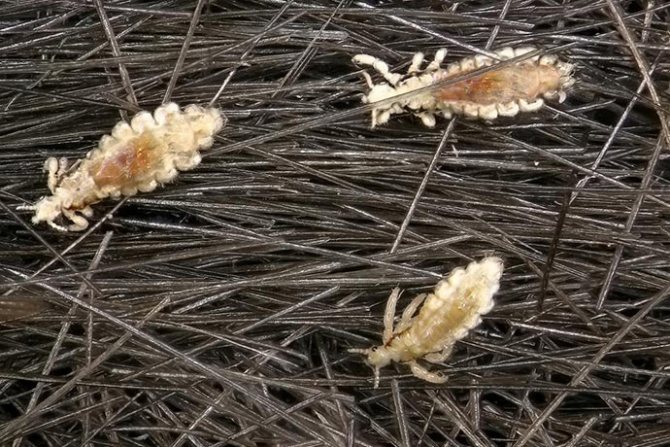
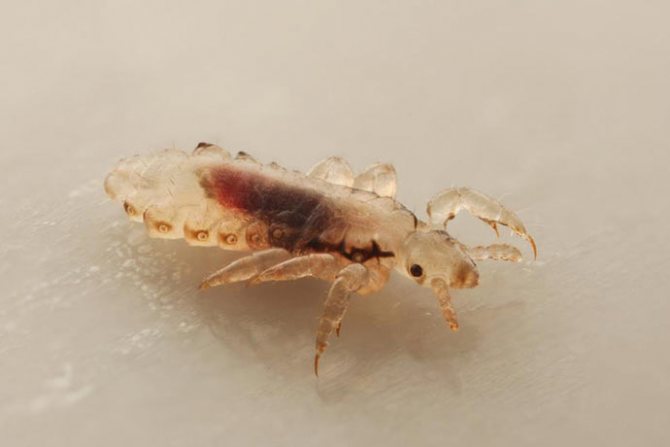
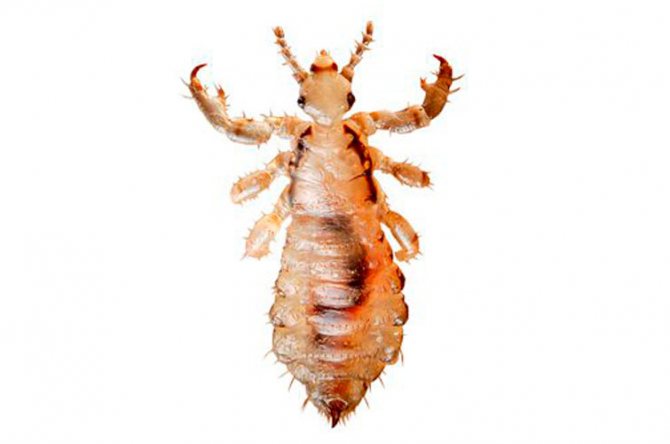
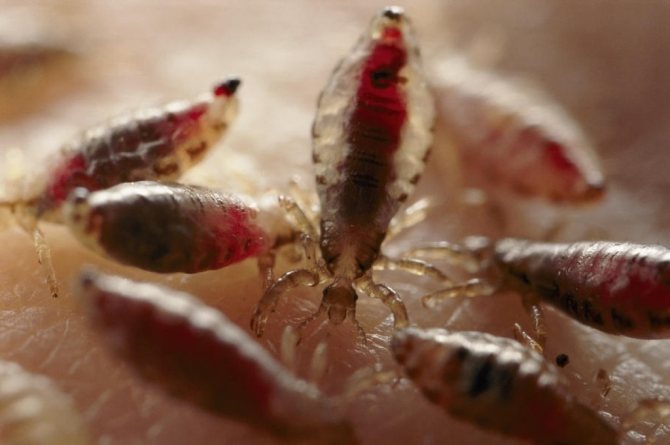
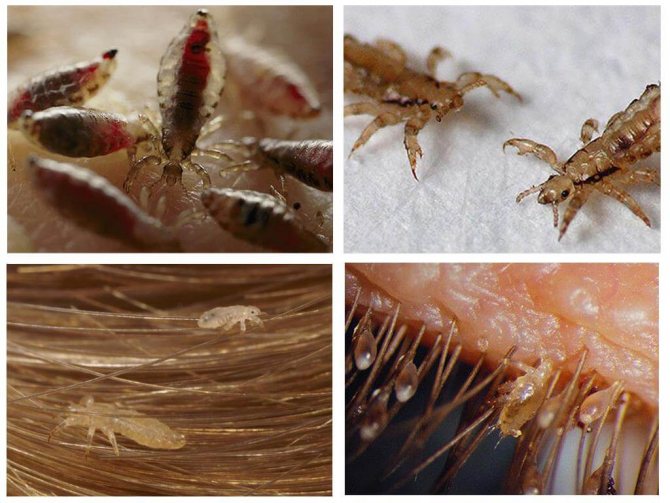
Lice
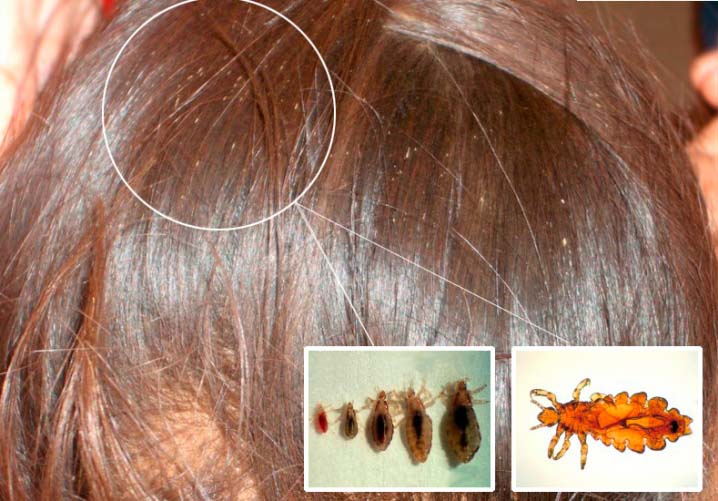
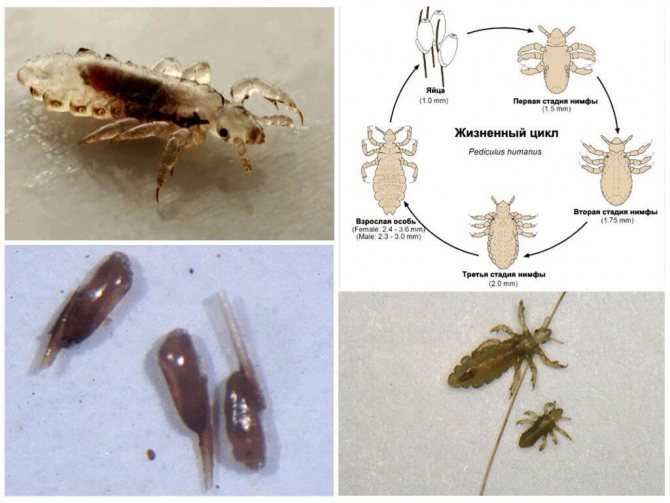
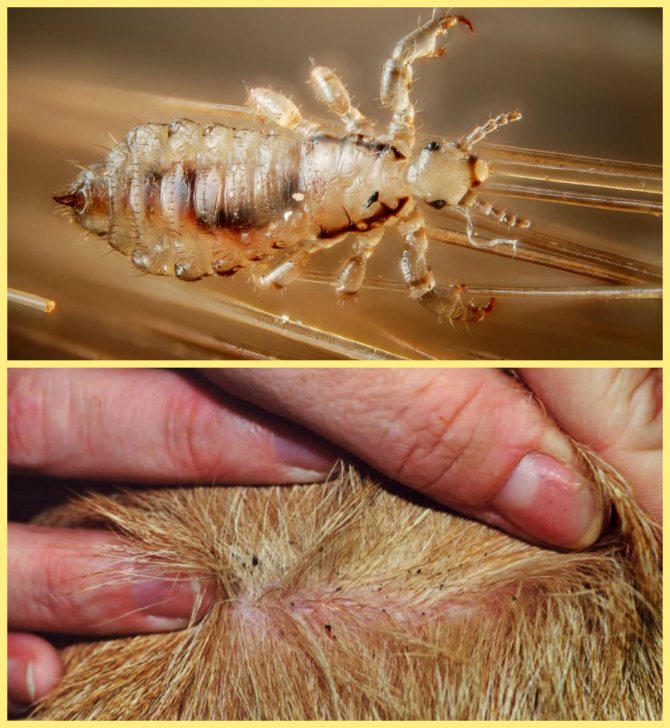
Small, grayish insects belonging to the order of chewing lice. According to the habitat of lice, it is customary to divide into two types: hair and clothes. These two species split quite recently, no more than 70 thousand years ago. Therefore, with a long stay in one place, they easily switch to another form. So, for example, a head louse can become a body louse and vice versa. You can visually distinguish one species from another if you have good eyesight. The body louse is almost white in color and is more stretched in size. Head lice are considered safer because they do not carry dangerous infectious diseases.
Body structure
How do you recognize fleas and lice? Paying attention to their appearance.
- The flea has a body flattened on the sides; in a louse it is flat.
- The first will be slightly larger than the second.
- Lice have short walking limbs with small hooks at the ends. With their help, individuals are attached to the hair. Fleas have long legs, especially a race pair.
- Flea covers are brown: light to dark in color. While lice are colored gray, and their chitin is translucent.
The color of the lice will be different depending on whether they are full or hungry - when filled with blood, their body becomes much darker: from burgundy to black
Habitat
Fleas
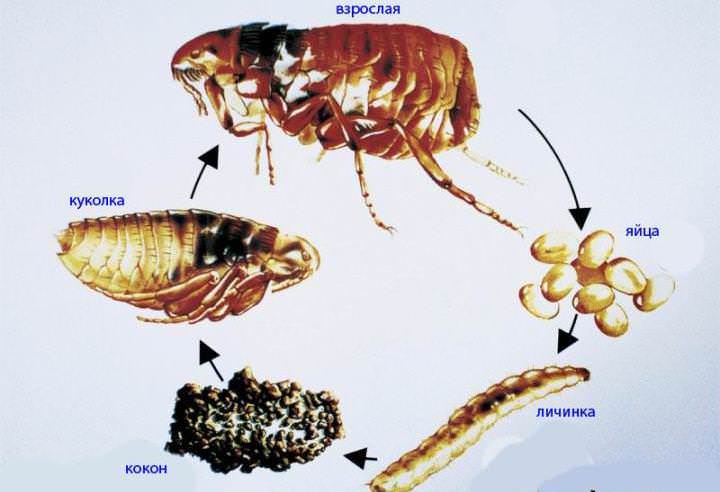
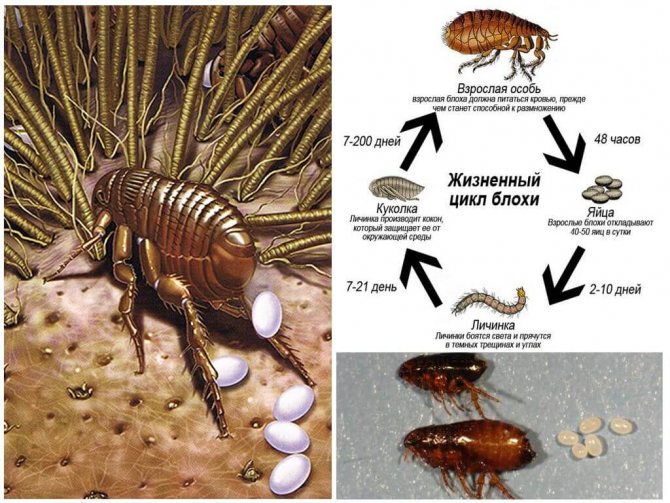
Flea classification is extremely confusing. The so-called human fleas (Pulex irritans) are cosmopolitan, they bite not only people, but also animals and birds.Obviously, we owe its appearance on our continent to the first sailors to South America. The main donors of these fleas were baker's pigs. Human fleas do not live permanently on the human body, but hide in clothes, upholstered furniture, or simply on the floor.
Other types of fleas are distinguished by the preferred types of donors: feline, canine, rat, etc.
Fleas belong to the order of bloodsucking, they are not found on humans. They can bite a person in the absence of the main donor, but this is rather a forced measure in order to survive. Their presence is of great concern to animals. In addition to the debilitating itching, flea bites cause allergic dermatitis.
Of course, people do not care which flea bites it: a starving species or a human.
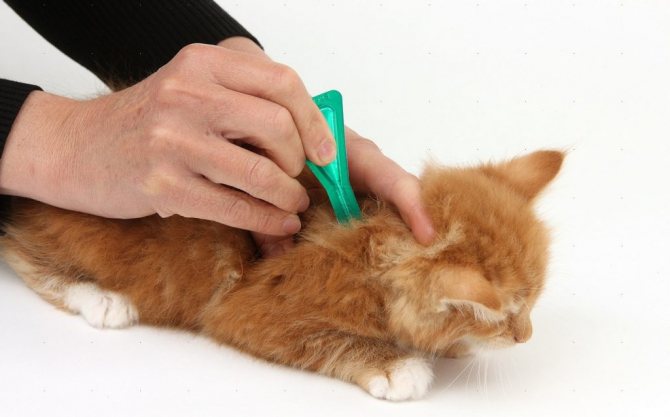
To detect the presence of fleas, place a white sheet of paper next to the animal and start combing the fur with a fine comb. The presence of small dark lumps on white paper indicates the presence of parasites in the animal's fur. In addition to treating the animal (collar, drops, spray, tablets), you will have to disinfect bedding and houses, upholstered furniture and rugs. Take the household with the animals out for a 2-hour walk and spray any of the above items with any flea spray. Open windows and join the family. Perhaps this processing will have to be carried out more than once.
Although all flea medications are considered safe for warm-blooded animals, they can cause allergic reactions in both humans and animals. Be very careful when using antiparasitic drugs on pregnant bitches and puppies, consult your veterinarian or your breeder.
Lice
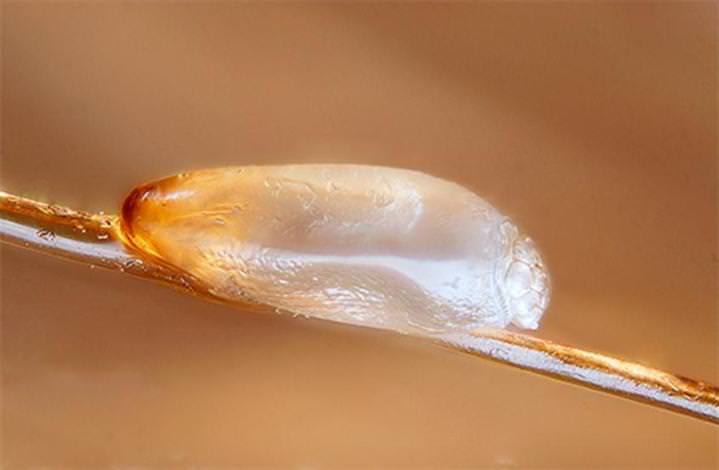
The head louse lives constantly in the hair of a person, here its life cycle passes. The female lays eggs (nits) and attaches them with sticky saliva to the base of the hair. Under suitable temperature conditions, about 28 degrees, young lice hatch from the eggs. And this process can go on indefinitely. Infestation with head lice is called head lice. The body louse lives in the folds and seams of clothing, from where it temporarily gets out to drink the blood of a donor, that is, a person. It is to this small parasite that we owe the massive epidemics of typhus.
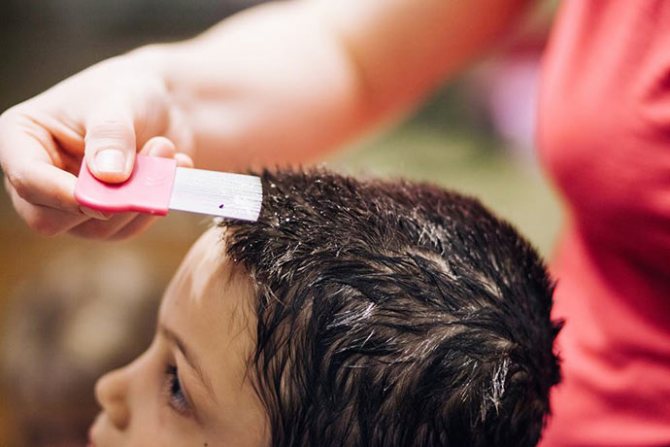

How is head lice and flea infestation diagnosed?
Each insect bite is accompanied by itching, burning. Because of this, inflammation can occur. This is called symptomatology. It includes:
- Dandruff.
- Severe rash in the affected area.
- The presence of live or dead insects in the hair.
- The appearance of dermatitis or other skin lesions.
These are the reasons why citizens turn to doctors for help. To confirm the diagnosis, a diagnosis is needed, which is carried out as follows. First, the doctor checks the areas behind the ears and neck for lesions. Gently probes and examines the scalp. The main tool here is the comb. This process is the same for adults, children and animals. If there are sufficient grounds, the doctor prescribes complex treatment (it is this that is most effective).
Infection routes
The spread of parasites such as fleas and lice is always a sign of social crises. Large crowding and lack of basic hygiene skills lead to a wide spread of these parasites among the population.
Another factor contributing to the infection with these parasites is migration processes, especially from areas that are unfavorable for epizootics.
Lice
Head lice are transmitted by contact with hair, by using hair care items of an infected person (comb, hairpins, etc.) and by wearing other people's hats.
Clothing fleas are spread by contact with clothing, by wearing a sick person's belongings, and even by close bodily contact.This disease can be picked up in public transport, crowded places and child care facilities.
Fleas
You can get infected with this parasite almost everywhere. Due to its jumping ability, a flea can jump on you in public transport, from the ground, or arrive on your pet after a walk. In urban environments, residents of the lower and upper floors are at particular risk. Fleas often take a fancy to attics and basements; they have their own bloody donors: birds and rats.
Taste preferences
Fleas and lice are similar in that they feed exclusively on blood. They are not interested in the garbage accumulated in the bucket, or the plants on the windowsills, or the crumbs on the table. However, there are also differences here. For example, if fleas can parasitize both pets and humans, then lice bite only people.
This fact suggests that it is necessary to choose a remedy for combating fleas and lice correctly - this will help you quickly forget about painful bites. However, the processing should be thorough and repeated, since only one female who managed to survive, regardless of the species, is able to resume the population of the colony in a short time.
The danger
They say that we owe the terrible plague epidemics to the rats, namely the fleas that lived on them. To this day, rat fleas are considered the most dangerous. They are the carriers of plague vibrios, pathogens of tularemia, pseudotuberculosis, salmonella, brucella and other no less dangerous diseases. And as if this were not enough, fleas carry hepatitis B and C and are the transmitting link of parasitic worms.
Both head and body lice can transmit such a terrible disease as typhus and infect a person with bacterial diseases.
Control methods
Fleas and lice behave differently, and therefore the methods of dealing with representatives of each type of pest will be different.
If we talk about fleas, then they give in to destruction rather poorly. Fighting them involves carrying out several stages, moreover, simultaneous ones. The following should be processed:
- pets;
- their rugs and houses;
- rooms of your apartment.
In order to get rid of lice, the premises are not treated - the fight in this case is based on the destruction of adults and nits that live in the hair, as well as in boiling of wearable items and bed linen.
Worms are destroyed by the same preparations as adult insects. The tool works 100% upon detection of congestion spots. In this case, powders, solutions, aerosols are used. Folk remedies give a good result.
Frequently used concentrates with a high degree of efficiency - Executioner, Tetrix, Cucaracha. They generally prefer aerosols. The most popular brands are Raptor, Reid, Clean House, Combat, Dichlorvos, Karbofos.
Vinegar, turpentine, kerosene are used as folk remedies. There is no point in fighting worms with herbs and deterrent substances - they are insensitive to this matter. Powders and dusts also give poor results because they act when ingested.
The struggle is carried out in a complex manner. Since it is necessary to destroy both adult parasites and their offspring. You should pay attention to the pet, otherwise re-infection of the room or animal will follow, you will have to do everything all over again.
How do lice differ from fleas?
Although lice and fleas are blood-sucking parasites, both males and females of both species participate in the bloody orgy. They have many differences from each other.
- These parasites belong to completely different species. Although both suck blood, lice belong to the species of chewing lice and always nest on the hairline of a person and never change their donor to another species. A louse will not drink the blood of your pets, while a flea will happily feast on your blood when there is no breadwinner.
- You can also distinguish them in appearance, although this can only be seen under a microscope. A louse is larger than a flea, its shell is grayish, and fleas wear a black-brown outfit. It is impossible to see it, but fleas have eyes and lice are blind.
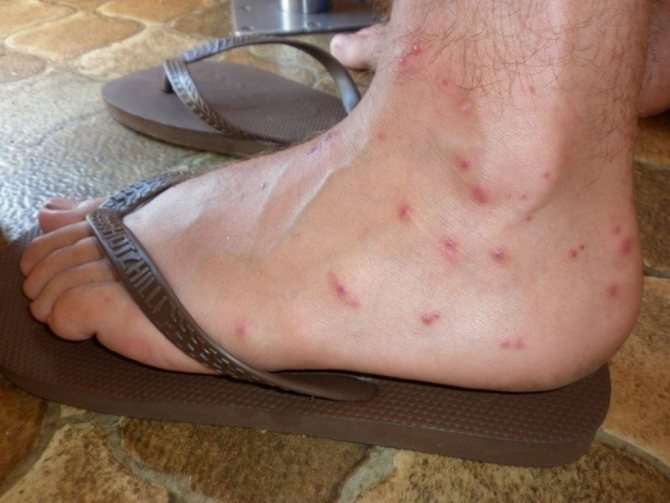
- The appearance of bites also varies:
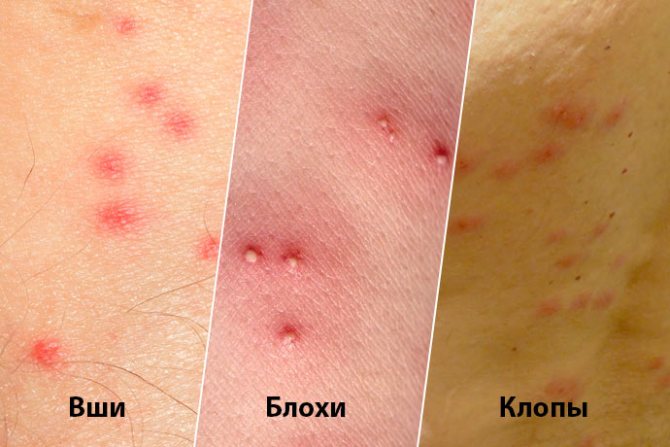

The difference in lice, flea and bed bug bites - Lice differ from fleas and in terms of life span. If the lifespan of an adult louse is a little more than a month, then a flea can slip for a year and a half. Both males and females feed on blood.
- Even these insects reproduce in different ways. The flea throws eggs from the belly, as they say, to whom God sends, and the louse leaves its offspring next to it in the hair of a person.
- And most importantly, lice live only on the hairline of a person or in his clothes, fleas are taken on a person or animal only for a bite. They prefer to hide in more secluded places.
In conclusion, I would like to note that, subject to simple hygiene skills, the chances of meeting these parasites are small. The main danger factors: children's groups and nearby dwellings filled with migrants. As for pets, be sure to carry out anti-mite treatment for pets that go outside. The substances included in the composition of acaricidal preparations kill not only ticks, but also fleas of different species.
If you find an error or inaccuracy, please select a piece of text and press Ctrl + Enter.
What harm do these parasites do
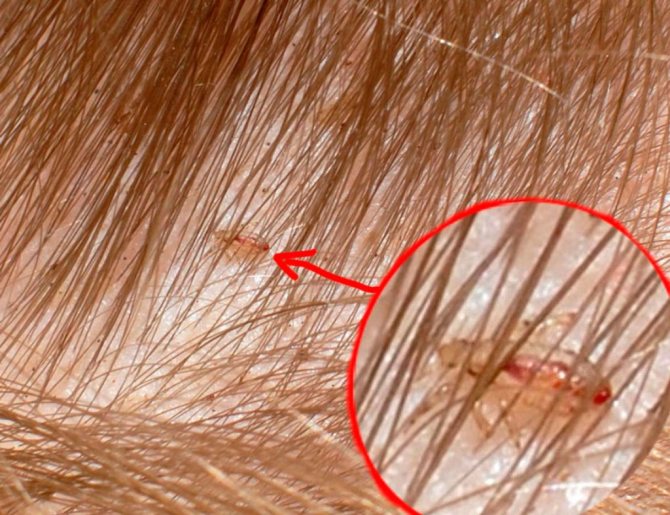

The main danger posed by both types of parasites is infection with serious diseases.
Several centuries ago, during the plague and typhus epidemics, lice were considered deadly because they carried these diseases. Today they do not pose such a threat, and they can be easily dealt with with the help of medicines.
Fleas are indiscriminate in their diet, so they can carry a wide range of diseases. from worms to severe infections. In addition, insect bites themselves cause serious discomfort. Having bitten the victim, the parasite secretes a special secret. That, getting into the circulatory system, provokes a strong allergic reaction, and because of this, unbearable itching occurs.
A person or an animal combs the bite site before the appearance of wounds, as a result of which pathogenic microorganisms can enter the affected area and cause infection, suppuration and a number of dangerous complications.
Treatment of bites
At the initial stage of infection with head lice, you can use folk remedies, pharmaceutical preparations with antipruritic, anti-inflammatory properties. With the development of an allergic reaction, antihistamine ointments, lotions are used. If an infection has got into the wounds, abscesses have formed, local antibiotics are used.
Folk remedies for linen lice bites:
Pharmacy first aid products:
Antihistamines, antiallergic drugs:
Local antibiotics:
If the condition does not return to normal within 3 days, you should seek help from specialists.
Prophylaxis
It is recommended to use the following as preventive procedures:
- Treat the premises with the use of appropriate means against parasites (once a month after removing adult nits, larvae).
- Perform water procedures at least 2-3 times a week (wash the body, head, genitals).
- Regularly wash clothes, clean shoes, change bedding.
- Place 1-2 dried wormwood bushes indoors, if possible. They scare away harmful insects. Thus, people and animals will be protected.
- Regularly perform dry and wet cleaning in the house so that dirt and dust do not accumulate. The child is especially sensitive to them.
These are the main actions that should become a habit to get rid of parasites and prevent them in the future.