Dill is an annual herb of the Umbrella family, found in the wild in the southwest and in central Asia, as a garden crop is widespread everywhere. Before planting dill at home, you should consider a number of features:
- the plant loves warmth and moisture;
- needs abundant lighting, which requires the installation of energy-consuming equipment in winter;
- develops poorly on acidic soils;
- fresh seeds grow slowly due to their high content of essential oils.
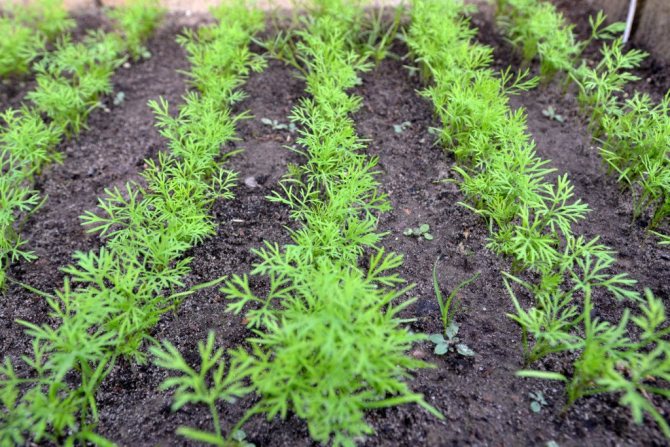
Greens sprouted at home
Important! Fresh spices on the table will be all year round, if you do not forget to sow new seeds every month.
Dill planting in spring

Dill seeds are sown from early spring to late autumn. Prepare the site for sowing in advance. Dig up the soil in the fall with organic fertilizers (3-4 kg of rotted manure or compost per 1 m2) to a depth of 20-25 cm. In the spring, add 100-200 g of wood ash per 1 m2.
For growing dill
enough fertile soil, timely watering and sunlight. Necessarily open sunny area, in the shade dill grows poorly
Good predecessors of dill are cucumbers, peas, early cabbage, tomatoes; it is unacceptable to plant dill after carrots and dill itself.


Dill
grows very well together with other crops, it is often sown with cucumbers, cabbage, tomatoes, zucchini and others. When planted in this way, dill should not grow in close proximity to the stems of vegetable plants, so as not to take away moisture and nutrients from the plants.
How to plant correctly?
The yield of the selected variety of dill depends on compliance with the requirements for planting and further care, so whichever one you like best, you should consider the following information.
Timing
Often dill is sown on the territory of the garden in spring or early summer, although the option of planting in winter is not excluded. With the arrival of the first stable heat, the culture is placed on the site only after the air temperature has not dropped below + 2 ... + 5 ° C for a week, and the soil in the chosen place has thawed.


On average, the calendar dates for planting a plant fall in mid-March or early (mid) May, and more accurate numbers will have to be determined based on the geographic location of the region of your residence.
In summer, planting of greenery is carried out at any time, re-sowing dill every 15–20 days. In some cases, a winter sowing of the plant is carried out on fresh spring greenery. In this case, the best time to complete the procedure is October or November.
Choosing a place on the site
Regardless of the variety of dill, the selected area for planting it should be well lit by the sun's rays or slightly hidden from them in partial shade. It is not worth planting a plant in full shade, since a lack of light will negatively affect its external characteristics: the bushes will grow weak, and their color will become paler.


The soil in the selected area should be loose, nutritious and moderately moist, without the possibility of excess moisture accumulation. For this reason, you should not plant a crop where groundwater is close to the surface of the site, and if there is no other option, then you cannot do without organizing a drainage layer.
The acidity of the substrate should be neutral or close to this, since at increased rates, the culture will quickly acquire a reddish tint, and in alkaline it will become yellowish. It is impossible to achieve maximum yield indicators in such growth conditions.
Of the predecessor plants, the best for dill will be tomatoes, cucumbers, tomatoes and cabbage, under which a large amount of organic fertilizers and mineral nutrients were once applied. You can also plant the crop next to other vegetables, avoiding joint placement with celery or carrots. In addition, when choosing a site, it is worth making sure that they are not grown on it in the past year.
Important! At first, immature dill sprouts are sensitive to drowning by weeds, so it is advisable to choose such a place for sowing seeds so that no plant residues remain on it after previous crops.
Preparatory work
Preparation for the process of sowing dill in the selected area begins with pre-planting seed treatment and soil treatment, providing for its loosening and fertilization. Each of these processes has specific features.
Seed preparation
Peduncles of bush forms of dill are finally formed towards the end of the warm season, therefore, in regions with a short summer, it is not possible to achieve full maturation of seeds. In order for the future planting material to mature before the onset of cold weather, it is necessary to plant the plant on seedlings and only after its strengthening, transplant the shoots to a permanent place of growth.
The seed collected in autumn is dried and stored in fabric bags until the next planting season, and 5-6 days before the intended sowing, it is taken out and soaked in warm water (+ 50 ° C). The liquid is changed at least once a day, each time filling the planting material with only warm liquid. It is she who helps to get rid of the oil film that covers the surface of the dill seeds and hinders their germination.


After soaking for three days, the wet seed should be spread out on damp gauze and covered with a cloth or sawdust. The seeds must be in this state for at least 3 days, and during this time they must be regularly moistened, preventing the gauze from drying out. An hour before sowing, the planting material must be dried and only then placed in the substrate. The first young shoots usually appear not earlier than 2 weeks after sowing the seeds.
Garden bed preparation
Dill bush varieties prefer loose and fertile soil that absorbs moisture well. Given the long root system of this plant, it is worth paying attention to the thickness of the nutrient layer, which can be fertilized with mineral and organic fertilizers.
It is advisable to add 15–20 g of urea, 20–30 g of superphosphate and up to 3 kg of humus per 1 m² of territory to the soil dug up since autumn, a few weeks before the planned planting of dill. You can replace humus with rotted mature manure, in the same proportions.
Important! It is better not to add dolomite flour and lime for dill, because because of these substances, it is able to change its natural green color and will begin to lag behind in development.
Planting scheme and depth
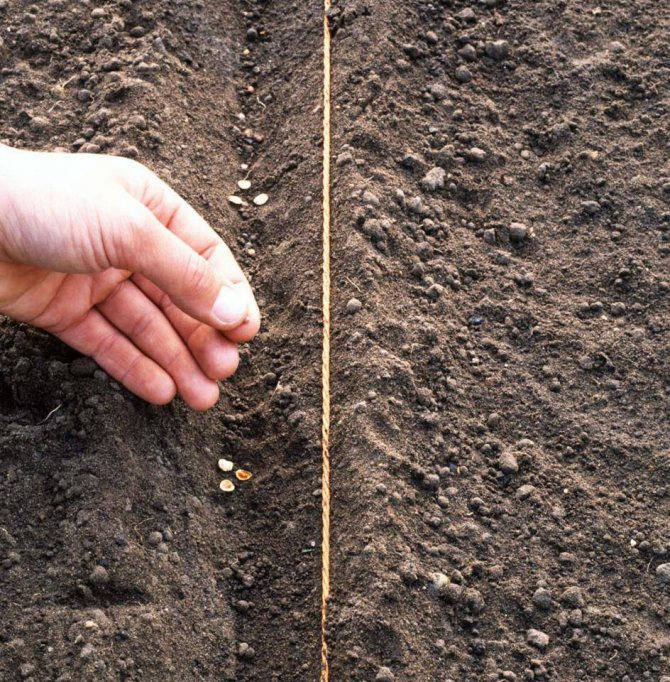
For the convenience of organizing the furrows for the seeds, you can use a small wooden plank, the indentation marks of which will serve as planting holes. The distance between adjacent furrows should be at least 15–20 cm, which will allow the formation of a sufficient number of lateral shoots. Having prepared two-centimeter holes, gently spill the soil with water and place the seeds inside, leaving 2 cm of free space between them.
At the end of planting, it remains to fill the grooves with a layer of soil and compact a little.With a high probability of recurrent frosts, it is better to cover the dill planting sites with plastic wrap, periodically airing the young plants. After sprouting, it is useful to thin them out, especially if you did not care about adhering to a suitable planting scheme.


To accelerate the germination of dill, you can sow it first on seedlings and only after strengthening it, transplant the seedlings to a permanent place of growth. This option is suitable for regions with a harsh climate, in which frequent frosts can be observed even in April. Sowing dill seeds for seedlings is performed about a month before the intended transplantation to a permanent place of growth.
On average, the planting of grown seedlings on the site is carried out not earlier than May, and by that time 5–7 true leaves should have already formed on the plant. Seedling planting scheme: 30 cm between adjacent seedlings and 20 cm between rows.
It will be interesting for you to read about the peculiarities of planting dill in open ground in the summer.
Sowing dates


For quick germination, dill seeds can be pre-prepared. Place gauze bags with seeds in hot water (50 degrees) for 15-20 minutes, preferably in a thermos, then cool sharply in cold. After that, dry the seeds so that it is convenient to sow.
Attention - the germination of dill seeds is 2-3 years.
As soon as the snow melts, you can sow dill seeds in moist soil, they are able to germinate at a temperature of +3 degrees (April-May, depending on the climate in your region). Since dill is a cold-resistant culture, it tolerates frosts down to -6 degrees.
The optimum temperature for sprouting and growing dill is + 12-18 degrees.
By sowing dill on a plot with an interval of 2 weeks, you will be with young, fragrant greens throughout the summer period.As the main crop, dill can be sown twice, the second sowing is done in the first decade of July.
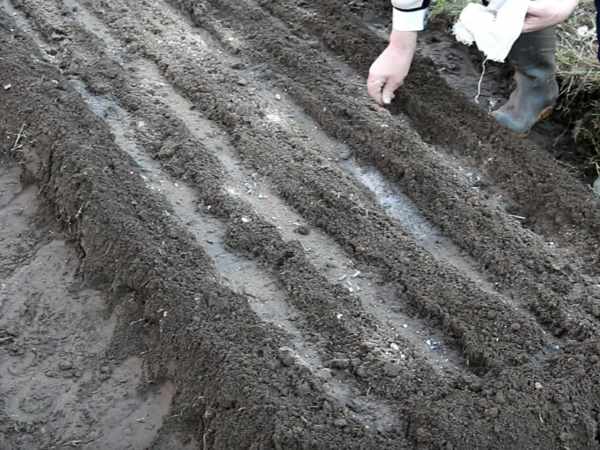


On the plot, make furrows 2 cm deep, sow seeds evenly and sprinkle with moist soil. If there is a threat of severe frost, cover with covering material at night. The sowing distance between plants is 5-7 cm, between rows 15-20 cm.
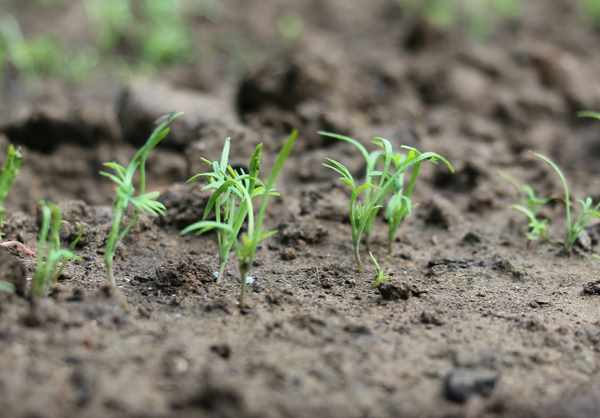


Dill seedlings will appear at the optimum temperature in 2 weeks.


On top of the sown area with dill, you can throw snow, in a layer of up to 20 cm, it will create a short-term wintering, stratify the seeds, then awaken the seeds to grow in the soil saturated with melt water.
Modern use of dill
Today, dill is an important garden crop in almost all agricultural regions of the world. Since it is very unpretentious to growing conditions, it is eagerly bred by both large-scale agricultural enterprises and ordinary residents of rural areas for their own needs.
It is a cheap and widely available spice that is added to many dishes. Dill is used both fresh and dried or salted. Fresh dill leaves and stems are commonly added to hot and cold dishes and salads. Blooming buds or even ripe buds are often used when canning vegetables and making aromatic sauces or seasonings. The phytoncides contained in dill not only give canned vegetables a specific flavor, but also prevent mold.


Dried shredded dill is a standard flavoring for many convenience and packaged foods, such as chips and croutons. The essential oil obtained from dill is also used in the food industry. In particular, it is used in the manufacture of food additives, including canned food, as well as in the production of alcoholic beverages.
The medicinal properties of dill have been proven by science, so this plant has found application in medicine. For example, dill tincture is recommended as an adjuvant for hypertension, as well as a diuretic.Essential oil and seeds are a natural and safe sedative and antispasmodic agent. Seed tincture is recommended as an anti-hemorrhoidal agent (for internal use) and as a wound healing agent, including against allergic rashes (for external use).
Dill is used to create pharmaceuticals used in clinical medicine.
As for the perfumery and cosmetic industry, it uses both aromatic and medicinal properties of dill. Creams, soaps, colognes, toothpaste - these and other products are often made with the addition of certain substances derived from dill.
Dill planting in autumn


Before winter, dill is sown in open ground at temperatures below +3 degrees so that the seeds do not germinate in the fall. Mulch the autumn plantings of dill, this will prevent the formation of a crust in the winter, it interferes with the germination of seeds in the spring.
Many gardeners believe that planting dill in the fall yields much better than planting in spring. Dill is less susceptible to disease, as the seeds are stratified in the soil.
Video - We sow UKROP in open ground
Dill care outdoors
Dill will not require significant effort and time, but if agrotechnical recommendations are followed, this culture will certainly delight the gardener with a juicy and abundant harvest.
Watering
Watering the dill bushes is recommended often and abundantly, because without moisture, the leaves will slow down development and the plants will throw out the arrow. Pouring the beds so that there is water in them is also not worth it - in this case, the greens will be less fragrant.
The recommended volume of liquid is 20-30 liters per 1 sq. m.
Watering is recommended in the evening or in cool cloudy weather.
Top dressing
No fertilization is applied during the growing season. All dressings are laid in the soil even before planting seeds or dill seedlings.
Top dressing during the growing season will only be needed if the plant is developing slowly. Under such conditions, you need to apply a little fertilizer. If the bush turns yellow, it means that it lacks nitrogen.
Weeding and loosening
The first weeding should be done after the bush is well rooted. While it is still weak, weeds should be removed regularly. In the future, this event can be performed once every 2 weeks.
Loosening is performed to a depth of 5 cm after the rooting of the plant. If the soil is loose on its own, no additional processing is required.
Shelter in the heat
On very hot days, dill can wilt. To avoid this, you can arrange a semblance of a canopy over the beds of greenery.
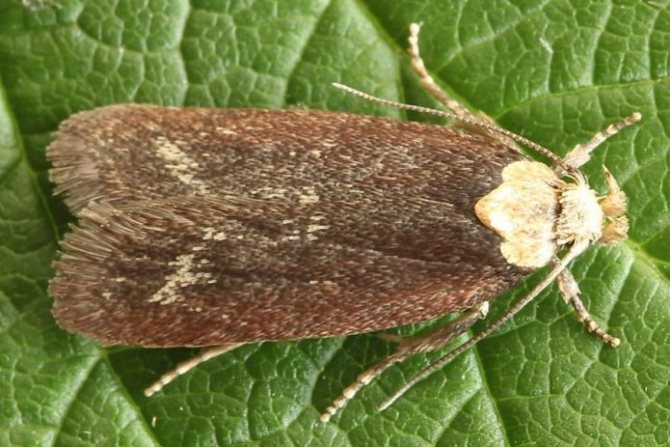
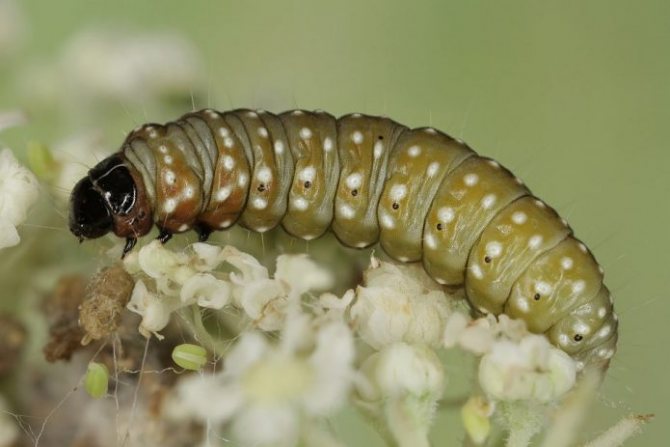
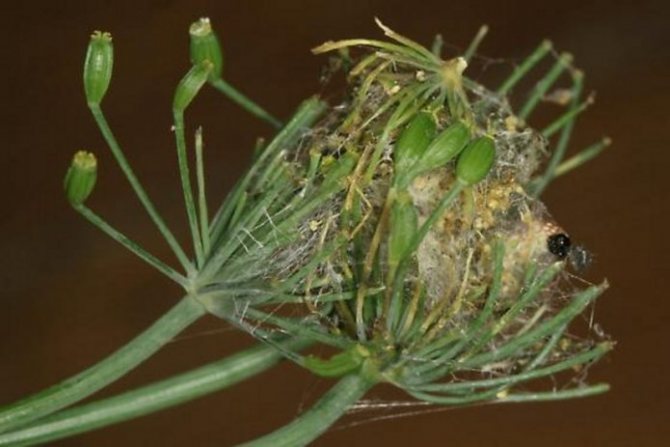
Pest and disease control
Most often, the culture is affected by fungal diseases:
- powdery mildew;
- cercosporosis;
- blackleg.
Their development is associated with a poor soil composition, excessive moisture, violation of the rules of crop rotation. For decay processes, it is recommended to use Fundazol solution.
To prevent the occurrence of diseases and pests, the soil must be treated with biofungicidal preparations before planting.
There are no pests that specifically target dill bushes. It is attacked by insects that parasitize nearby crops. That is why it is necessary to distribute sowing areas in advance.
Harvesting and storage
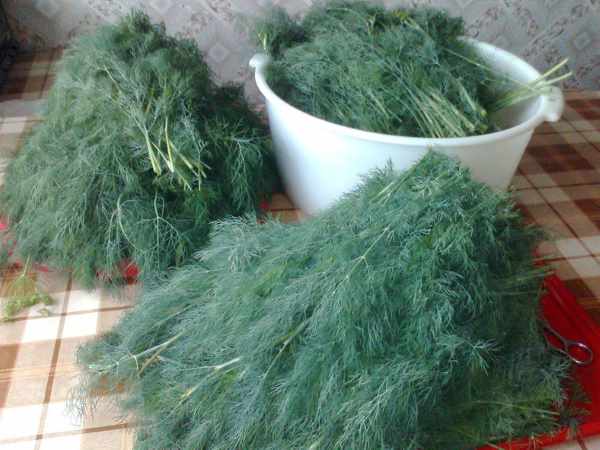


Young dill
can be eaten immediately. For harvesting for the winter and storage, collect the dill after the inflorescences have formed. The height of the plants is at least 30 cm. It is better to harvest dill early in the morning, as the dew disappears. Plants may wilt a little during the day.
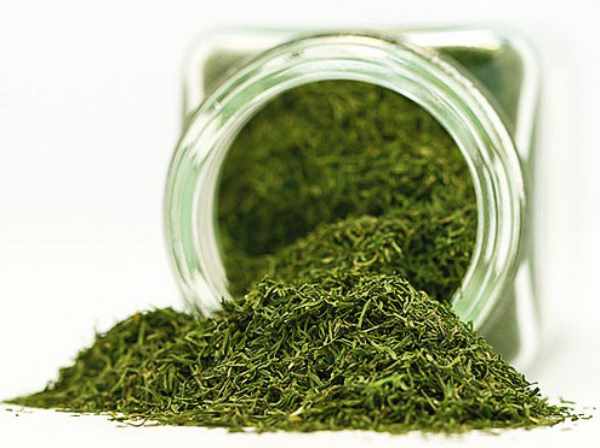


You can store dill in different forms. For dry storage, wash the harvested pieces of dill and dry in the shade, turning the dill periodically. Then we put it in fabric bags and store in a dark place.
If you store plants with umbrellas, they are tied in bunches and kept hanging in the winter.
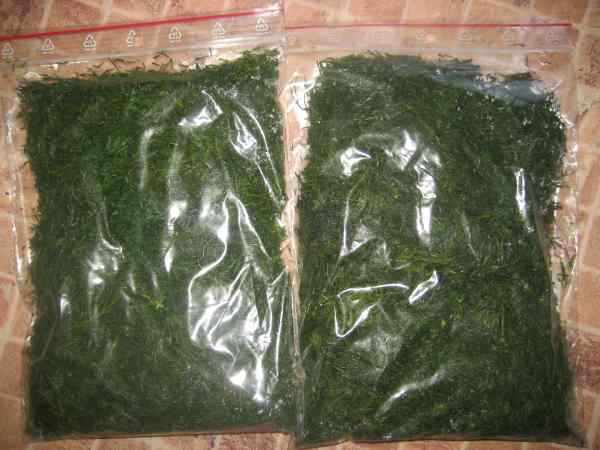


Young, juicy greens can be frozen for the winter.To do this, rinse the cut pieces, dry, chop finely and store in zip-lock plastic bags in the freezer. This is great for adding dill to your meals in winter.
Video - How and when to sow dill
Commercial cultivation of dill
Dill is such a demanded and popular seasoning for the most common home dishes that a rare housewife does not use it in the family menu at least once a week. Many people even add a little dill for beauty and flavor to almost any dish, from soups to milk porridge.
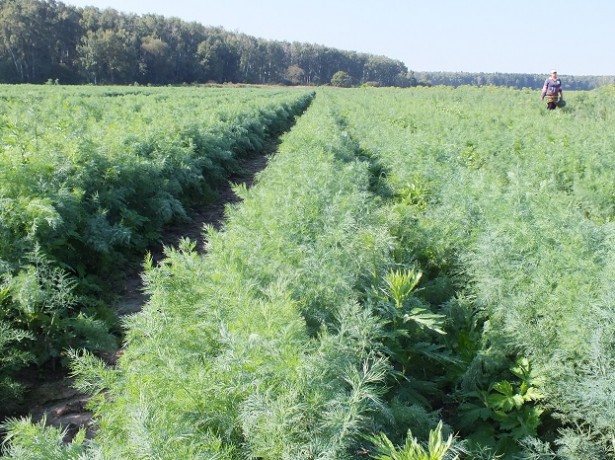


Given the consistently high demand for dill throughout the year, it is worth considering commercial cultivation. Although today many private traders specialize in it and it is not a problem to buy fresh herbs even in January, the prices for dill make it possible to consider it as a very promising option for business.
The advantages of dill as a commercial crop include the following features:
- Unpretentiousness. In the southern regions, dill often grows self-seeding like weeds, which in itself is a good indicator of the endurance of this culture. Even if you have never been involved in gardening, you can master the technology of growing dill without any problems. At the same time, it is also not necessary to spend energy on creating any special conditions for it. Almost any conditions are suitable for dill.
- Demand. As already mentioned, dill is in high demand all year round. This means that you will never have problems with the sale of products, no matter what volume you have.
- Low costs. If you have at least a small plot of your own land, you can establish commercial cultivation of dill with minimal investment. You will have to spend only on tillage, fertilization and purchase of seeds. True, if you intend to grow dill all year round, you will have to build a greenhouse for the winter. This will require higher costs, but one should not forget that dill prices also rise several times in winter.


- Minimal risks. Unlike other agricultural crops, dill is slightly susceptible to diseases and pests. He also endures unfavorable weather conditions quite persistently. So, in order to lose a crop, something completely out of the ordinary must happen.
If we talk about the cons, then the main problem is the extremely short shelf life. There are not so many garden crops that could compete with dill in terms of the rate of arrival in a non-marketable form. It is necessary to sell the harvested crop within a few days (usually no more than 3-4), or it will become unsuitable for sale. However, in this case, it is possible to reduce the risks by establishing a clear and, what is important, a multi-channel system of product sales.
Popular varieties of dill
As they ripen, dill varieties are divided into early, mid and late ripening
.
Grenadier
- unpretentious variety, with juicy, fragrant greens. An early ripe variety, a month after germination, the first crop can be harvested. After 1.5 months, dill releases arrows, after 2 months you can collect stems and seeds.


Dill Lesnogorodskoy
- the variety is mid-season, stably producing greens, even after the formation of inflorescences and ripening of the seeds.
Kibray
- late-ripening variety with wide, beautiful and aromatic leaves.


By following the tips for growing dill outdoors, you will get a harvest of fragrant and healthy greens.
How to feed dill
Fragrant dill loves nitrogen-containing fertilizers, but it is important to understand that such feeding is capable of accumulating nitrates in itself, therefore, it is better to use nettle tincture as a fertilizer, which has fermented for five days. Such a remedy will not only enrich the plant with nitrogen, but will also help kill aphids. It is not recommended to use insecticidal agents, especially later than 15 days before harvest.Also, if circumstances require it, potassium-phosphate fertilizer is introduced into the plot during cultivation, at the rate of 10-15 g per 1 sq. M.


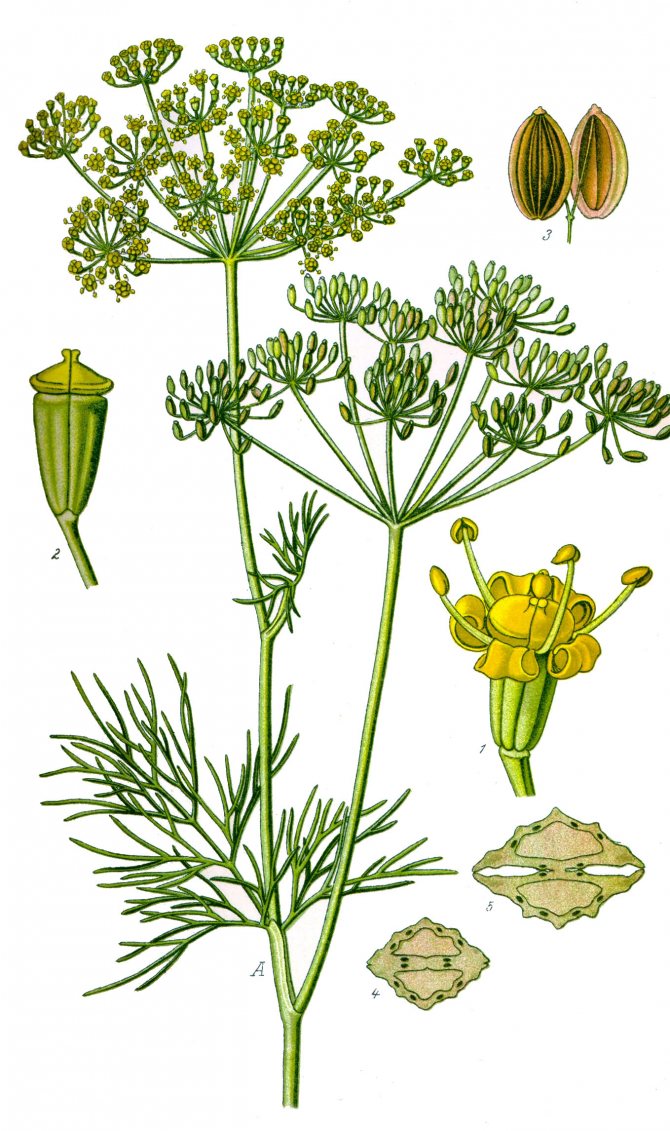
Description and botanical characteristics of the plant
To begin with, let's find out what dill is - is it an annual plant or a perennial one? Dill is an annual herb that belongs to the monotypic genus... It exists in a single form, which is called Fragrant Dill or Garden Dill. Belongs to the Umbrella family, it is considered to be short-lived.


Appearance
A plant with a strong characteristic odor, reaching a height of 1.5 m with a straight or weakly branching single non-pubescent stem... The stem is furrowed, gray-green, branches in the upper part, curved between the branches.
Leaves on petioles are located below, the upper sessile leaves are without petioles. The shape of the leaves is ovoid, they are pinnately dissected, the lobules of the last order are filiform.
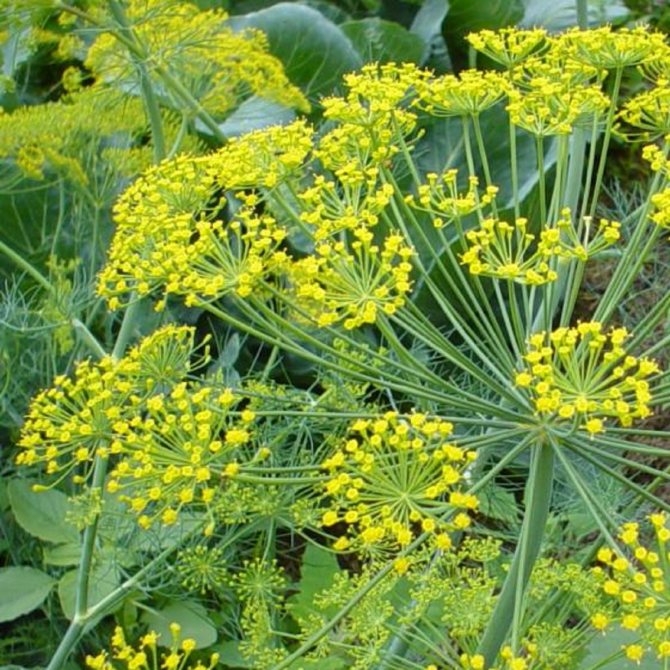
Blooms from June. Small flowers with yellow petals are collected in umbrellas with a diameter of 2-4 cm, which in turn form double ray umbrellas with a diameter of up to 20 cm.
The seeds ripen in late summer. They have an oblong flattened shape, up to 5 mm in length and about 2 mm in thickness. Ripe fruits are brown in color and have a bright spicy aroma. Many are interested in how dill seeds are otherwise called, by analogy with cilantro and coriander. However, there is no particular name for them - they are just dill seeds.
Views
There are several varieties of dill:
- Normal - with one stem on which the leaves are attached. It quickly fades into color, developing an umbrella with seeds.
- Bushy - forms several internodes from the base, from which additional shoots appear. The main stem grows slowly and produces more greenery.
- Leafy - there are many leaves on the main stem, it looks like a small spruce.


Where grows
Dill has spread throughout the world. It is grown in vegetable gardens, often growing in plots on its own like a weed. In the wild, it is found in Central and Southwest Asia, North Africa, the Himalayas and Iran, which are traditionally considered the birthplace of dill.
Edible parts of Dill
Leaves are raw or cooked. Used as a flavoring agent in salads, etc. the leaves lose their flavor if they are cooked for a long time and are therefore best used raw or added to cooked dishes only a few minutes before cooking is complete. Leaves can be harvested at any time of plant growth, but preferably just before flowering. Per 100 grams, the plant contains 253 calories, 7.2 grams. water, 20 gr. proteins, 4.4 gr. fat, carbohydrates 55.8 g., 11.9 g. fiber, 12.6 gr. ash, 1784 mg. calcium, phosphorus 543 mg., 48.8 mg. iron, magnesium 451 mg., 208 mg. sodium, 3308 mg potassium, zinc 3.3 mg., 0.42 mg. thiamine, riboflavin 0.28 mg, 2.8 mg. niacin and 1.5 mg. vitamin B6. The essential oil from the seeds is used as a flavoring agent in the food industry.
Dill stimulates appetite and can be beneficial for people who, due to illness or injury, need appetite support. Dill is also considered a mild diuretic, able to strengthen nails, for this you need to make baths from dill seeds or as an ointment for wounds.
The first mention of dill was in Egyptian medical writings dating back to 3000 BC. It was also mentioned in the Bible (Matthew 23:23) and it is believed that dill was one of nine sacred herbs found in Mary's tomb (other sage, lovage, yarrow, calendula, arnica, wormwood, valerian, tansy).
Long before Viagra, dill was also considered a cure for impotence.
In Ethiopia, dill and fennel leaves are chewed together to treat headaches.
This plant contains high amounts of monoterpenes (naturally occurring hydrocarbons), a substance known to promote the activity of an enzyme that helps counteract the effects of cancer-causing cells.
In addition, polyacetylene, also found in dill, is known to have antibacterial, anti-inflammatory, and antifungal effects.
Nutritional value Dill is a good source of iron, manganese, calcium and dietary fiber.One tablespoon of dill seeds contains calcium equivalent to one third of a glass of milk.
Methods of preparation and use
- Dill water is a decoction of dill seeds and crushed dill seeds in water, cook together 2 tablespoons of a mixture of whole and crushed seeds in a glass of water for 10 minutes, let it brew, and refrigerate. One half teaspoon of this mixture at room temperature, given to a child with an abdominal upset, should help relieve discomfort.
- This mixture should not be used after twenty four hours, and should not be mixed with milk as the milk will curdle.
Dill oil. About the benefits of dill oil, as well as about what diseases it is used for, how to prepare it and how to take it, read here.
Dill tea can be beneficial for people suffering from indigestion and / or diarrhea, menstrual cramps, bad breath and cough, and flu symptoms. Traditional medicine recommends boiling two teaspoons of chopped dill seeds in one glass of boiling water for ten minutes. Strain.
Dill leaves contain small amounts of estrogen and may be beneficial for postmenopausal women. Because of its antifungal and antibacterial properties, juice from fresh dill leaves can be beneficial for the urinary system, and is consumed several times a day for two weeks.
Dill in aromatherapy
Aroma, when contacted through the olfactory system, can have a direct effect on a person's mood and well-being. In the case of dill, it is mainly seed-derived essential oils used in aromatherapy and is believed to be beneficial in times of stress.
A few drops of dill essential oil in a vaporizer can help relieve tension. Adding oil to a hot bath can not only benefit an individual through its fragrance, but also through contact with the user's skin.
An herbal alternative to commercial chemical air fresheners can be to create a mixture of uropic oil and water in a plastic spray bottle. A few bubbles in the air (but away from the furniture) will refresh the room. Dill essential oils can also be blended with other herbal essential oils to create a blend of scents.
Harm
Dill oil should be avoided during pregnancy. It is believed that dill can cause miscarriage, so it is best to limit its use during this time.
Traditional medicine recipes
From high blood pressure
Grind the seeds into powder and take ½ teaspoon with a meal. Prepare an infusion of 1 tsp. raw materials and 300 ml of boiling water. Drink 3 times 100 ml.
Normalization of bowel function
The recipe will relieve gas, colic, constipation. It will take 2 tsp. fruits that are poured into 1 liter of boiling water. Insist until cooling, filter.
To increase potency
Men's health will be supported by the collection of dill (200 g) and valerian root (35 g). The composition is poured into a thermos and 1.5 liters of boiling water are poured. Add honey. The infusion is being prepared for a day.
Advice. A warm bath with a decoction of spicy herbs will help to calm the nervous system (1 glass of seeds brew 1 liter of water, soak for 30 minutes).
Useful properties and benefits of dill
Dill, giving food a peculiar aroma and flavor, increases gastric juice production, improves appetite and digestibility of food, which, of course, speaks of the benefits of dill. This spice not only improves the high quality of cooked dishes, but also enriches them with vitamins and minerals.
In addition, the essential oils contained in dill and forming its aroma stimulate appetite, and, thanks to the monoterpenes contained in them, contribute to the suppression of carcinogens.
If we take into account the high content of beta-carotene (4.5mg / 100g), vitamin A (750mkg / 100g) and vitamin E (1.7mg / 100g), which are powerful antioxidants, then the anti-cancer property of dill is evident, and therefore its benefit as a cancer protector
The benefits of dill essential oils are not limited to this.They have bactericidal (used for intestinal imbalance), analgesic properties, and normalize the secretion of the gastrointestinal tract. Dill as a pain reliever for pain in the intestines is used in the form of a warm decoction in a tablespoon 30 minutes before meals.
Flavanoids support the function of hormones that affect the menstrual cycle in women, and some of them have antihistamine properties, which also confirms the beneficial properties of dill. Vitamin E, folic acid, zinc, manganese cause the benefits of dill for men, significantly increasing their reproductive function, reducing the risk of prostate adenoma.
Nicotinic acid affects metabolic processes, and B vitamins: B1 (0.03mg / 100g); B2 (0.1mg / 100g); B5 (0.3mg / 100g); B6 (0.2mg / 100g) promotes the growth of hair, nails, and, along with magnesium (70mg / 100g), prevents the onset of diseases of the nervous system. Vitamin C (100mg / 100g!) Counteracts colds, so dill is useful in the cold season as a prophylactic agent that strengthens the immune system.
The presence of calcium, copper and phosphorus promotes bone growth. At the same time, sodium, along with potassium, maintains the acid-base balance in the body and is actively involved in the life of cells. The presence of iron (1.6mg / 100g) counteracts anemia.
The main organic substances are distributed as follows: proteins (2.5g / 100g); fats (0.5g / 100g); carbohydrates (6.3g / 100g). The calorie content of the green part of dill is 40 kcal per 100g. Proteins account for 1 kcal / 100g, carbohydrates 2.52 kcal / 100g. Thanks to its composition, this low-calorie product makes a good addition to any nutritious vegetable meal such as potatoes or beans.
In medicine, dill seeds are commonly used. In the form of powders, infusions, broths, they are good as an expectorant and laxative. They are used to achieve a bactericidal effect, as well as to normalize the state of the gastrointestinal tract, in particular, to restore the normal level of acidity.
Dill water is made from seeds - a remedy that prevents flatulence in babies. You can also make a compress for the eyes from them by placing them in gauze bags and dipping them into boiling water. Apply warm to the eyelids. Dill infusion is recommended for lactating women to increase lactation. Dill greens are used as a choleretic and digestive aid.
Dill is unique in that, for all its usefulness, there is no need to force it to be prescribed for diets. He is already constantly and imperceptibly, he himself is present in the human diet, thereby maintaining his health.


Dill harm
The beneficial properties of dill are undeniable, but it is not recommended to use it in very large quantities for people with low blood pressure, as well as for those who are allergic to its components. For everyone else who does not have this kind of problems, dill will only benefit, saturating the body with many useful vitamins and minerals.
How to choose the right dill?
When choosing dill, you need to pay attention to the color. Stems and leaves should be green without yellow tints, without sluggishness and signs of moldiness.
It is fresh dill that retains a maximum of vitamins and fully reveals all its beneficial properties.
How to store dill?
Dill can be stored finely chopped and dried for no more than 2 years. It can be frozen and stored at low temperatures for a maximum of 1 year. At the same time, after defrosting the dill, it must be consumed with a rhinestone while its useful properties are still preserved.