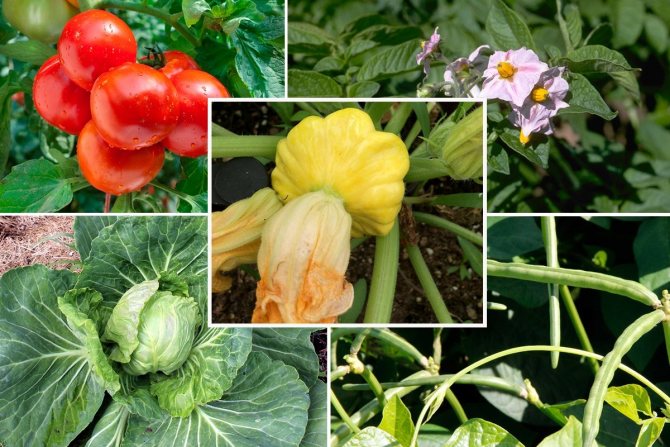
Patisson is a type of pumpkin, but to someone it tastes like mushrooms, and to someone - zucchini. Its varieties have a variety of colors and ripening periods. However, the technology of planting and further cultivation on the site, in the open field, the rules of care and breeding methods for them are practically the same.
Vegetable squash - description
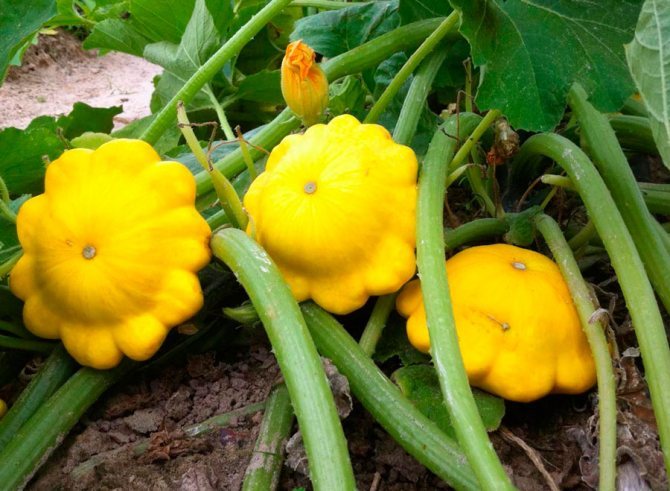
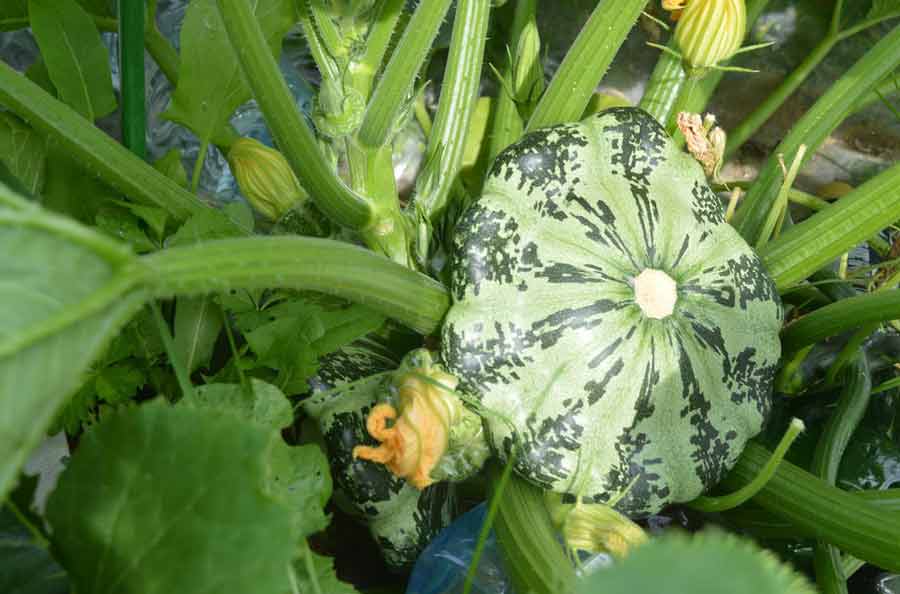
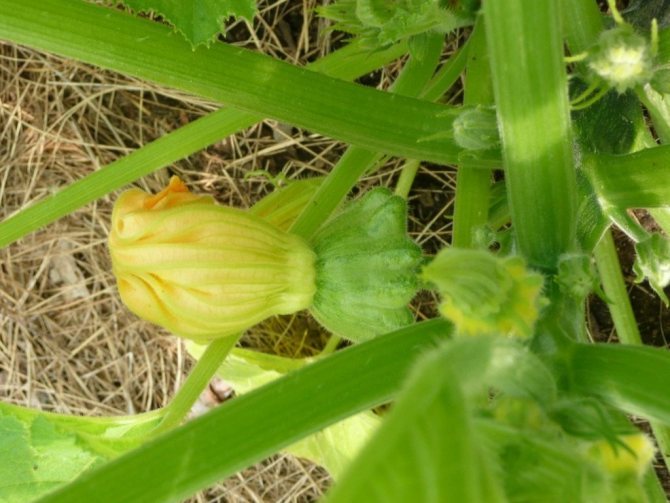
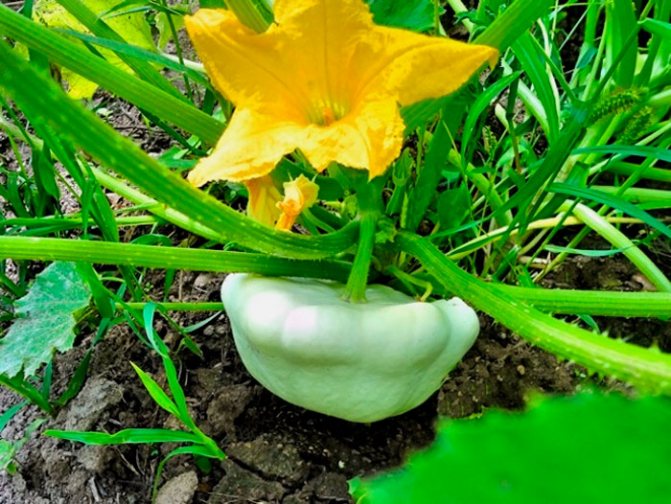
Patisson is a moisture-loving annual culture of a bushy form with hard, wide leaves and yellow single flowers. The appearance of the fruit depends on the variety and can resemble a disc, an umbrella, a bell flower, or a plate with a jagged or even edge. The color palette ranges from white, light yellow and cream to bright orange, dark green and lilac.
Squash - useful properties
Ripe fruits are rich in fiber, lecithin, vitamins A, C and some B vitamins. Patissons are low in calories and nutritious, they are recommended for people suffering from diseases of the stomach, liver, cardiovascular system.
It is customary to eat very young fruits, the pulp of which is the most saturated and easy to prepare.
Varieties popular with gardeners
Patisson is a crop popular with breeders. They bred quite a few varieties and hybrids, differing mainly in the color of the skin and the shape of the fruit.
Most often, the following varieties of squash are grown:
- White 13. Variety of medium ripening, was bred in the mid-60s of the last century. It is still considered one of the best for growing without shelter. Differs in unpretentious care (even against the background of "relatives") and frost resistance. Productivity - 3-5 kg per bush. Fully ripe squash weighs 400-500 g, young fruits - 90-100 g. In shape, they resemble a plate, "teeth" along the edge are weakly expressed. The skin is white or pale green, glossy. Fruits ripen 65–70 days after germination.
- Umbrella. Early variety. The crop ripens in 45-50 days. You can count on 4–5 kg / m². The plant is quite powerful, semi-bushy. The fruit looks like a bell, the surface is slightly bumpy. The skin is whitish or greenish. It is thin, so the fruits do not differ in keeping quality and transportability. The average weight of the squash is 300-400 g, the diameter is 10-12 cm.
- Disk. The fruits are harvested 40-50 days after germination. Squash disc-shaped, with a pronounced division into segments, "teeth" along the edge are almost invisible. The average weight is 350–400 g. The skin is white. The pulp is of medium density, not particularly juicy. The fruits are well stored, they can last until the middle of winter. A significant drawback is the tendency to defeat powdery mildew.
- Cheburashka. One of the earliest varieties, it takes 39 days from the emergence of seedlings to the fruits of technical maturity. The plant is powerful, forms up to eight lashes. Fruit weight - 200-400 g, diameter - 9-10 cm, white skin, thin. The pulp is snow-white, tender in consistency, juicy. It is appreciated for its increased frost resistance, taste, mass ripening of fruits.
- Fouetté. Medium early variety, fruits ripen in 50–55 days. Fruits are one-dimensional, symmetrical, in the form of a plate with a "wavy" edge. Weight - 280-300 g. The skin is golden-orange, thin, but strong. The pulp is snow-white, dense. The variety stands out for its good keeping quality.
- Sun.The growing season is 58–70 days, depending on the weather. The bush is very compact, weakly branching. The fruit is disc-shaped, with a "scalloped" edge. Weight - 250-300 g. As it ripens, the skin color changes from pale yellow to bright orange. The pulp is dense, creamy beige, very tasty. Plants rarely suffer from true and downy mildew.
- UFO orange. Early variety. The plant is compact, bushy. Fruit weight varies from 280-300 g to 500 g. The skin is pale yellow, shiny. The taste is excellent. Average yield - 3–5.5 kg / m². There is also a white UFO variety, which practically does not differ in anything, except for the color of the skin.
- Chunga-Changa. An early variety that is frost-resistant. The plant is compact. The fruits ripen in 42–45 days. The peel is a deep dark green color, the pulp is creamy beige, juicy. Average weight - 400-450 g. Patissons are disc-shaped, with a "scalloped" edge. The variety has good immunity.
- Gosh. The fruits ripen in 45-50 days. The bush is compact, the leaves are small. Fruits are dark malachite, almost black. The division into segments is clearly expressed. The pulp is snow-white, dense, not particularly juicy. The average weight of the squash is 150–250 g. The yield is 1.3–4.2 kg / m². It depends on agricultural technology, the variety is quite demanding in care.
- Bingo Bongo. An early variety with unusual blue-violet fruit. They are disc-shaped in shape, almost without "teeth". The bush is distinguished by its growth rate, but at the same time it is quite compact. The crop ripens in an average of 40 days.
- Polo. Early ripe squash. The average fruit weight is 300–400 g. The plant is compact. The fruit is in the form of a plate, the color of the skin varies from milky green to salad. The pulp is snow-white, not too dense. The variety is valued for its consistently high yield (8.8 kg / m²) and resistance to downy mildew.
- Sunny Bunny. An early variety, it takes 42–46 days to ripen the crop. The fruit is disc-shaped, the skin is dark yellow, the flesh is creamy orange. The average weight of the squash is 150–250 g. The variety is valued for the presentability and taste of the fruit, good yield (4.5 kg / m²), and resistance to powdery mildew.
- Watermelon F1. Mid-season hybrid, distinguished by the original variegated color of the fruit. Wide light and dark green longitudinal stripes alternate on the skin. As they ripen, the disc-shaped squash is slightly "rounded", becoming even more like watermelons. The average fruit weight is 300-450 g. The plant is powerful, intensively branching.
- Chartreuse F1. A hybrid of early ripening, distinguished by the taste of the fruit. The skin is dark green, sometimes with yellowish-white or salad stripes and spots, the pulp is salad. As it ripens, it gradually turns white. Fruit diameter - no more than 3 cm, weight - 50-70 g.
- Piglet. Early ripe squash, ripen on average in 50 days. The skin is milky green, smooth. Average weight - 225 g. Taste is not bad, but the yield is only 1.5 kg / m². However, the variety tolerates drought very well.
- Sunny Delight. An early variety of squash from the Netherlands. Fruits are of a typical culture shape, the skin is yellow, glossy, the flesh is white. Average weight - 80–100 g. It is appreciated for its excellent taste, high yield (up to 16.5 kg / m²) and good keeping quality. Fruiting lasts almost until the first frost, the plants tolerate drought well.
- Mini crumb. The plant is compact, the leaves are small. Fruit diameter - 3-5 cm. The harvest ripens in 50 days. You can count on 3-5 kg per bush. The skin of the disc-shaped fruit is pale green, the flesh is almost white.
Photo gallery: varieties of squash popular among Russian gardeners

Squash White 13 - one of the old time-tested varieties


Patisson Umbrella is not suitable for transportation and long-term storage
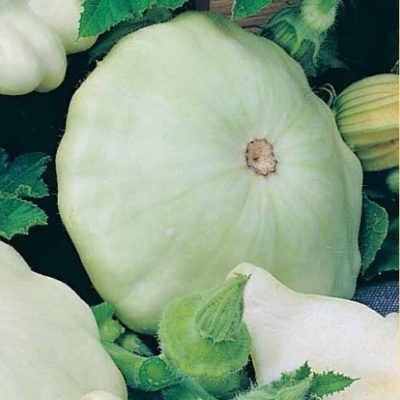


Patisson Disc is often infected with powdery mildew Patisson Cheburashka belongs to the category of ultra-early varieties Patisson Fuete is distinguished by the presentability of the type of fruit


Squash Sun is a very compact plant, it can be grown even at home


Squash UFO orange is valued for the taste of the fruit
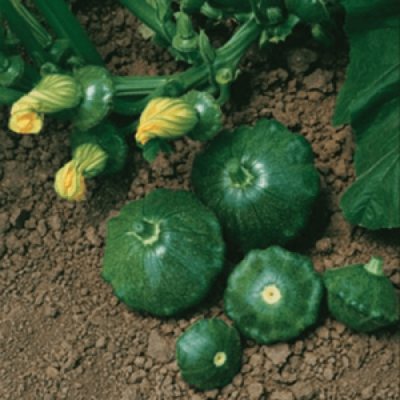


Chung-Chang patisson stands out for its frost resistance and good immunity
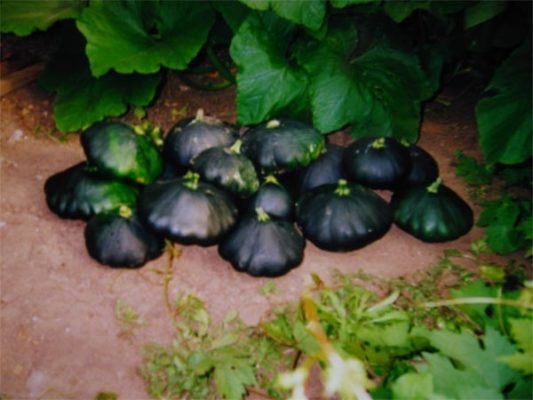


Patisson Gosha, unlike other varieties, is quite demanding in care
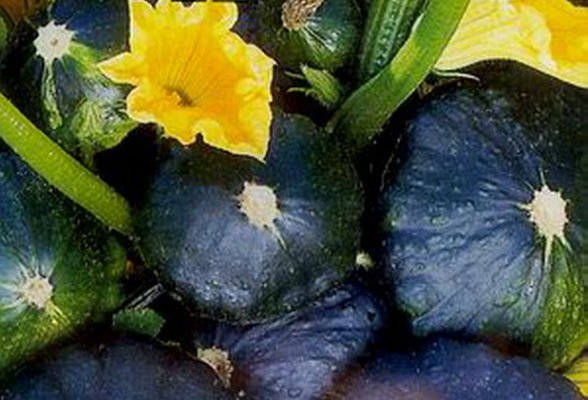


Patisson Bingo-Bongo stands out for its unusual fruit color
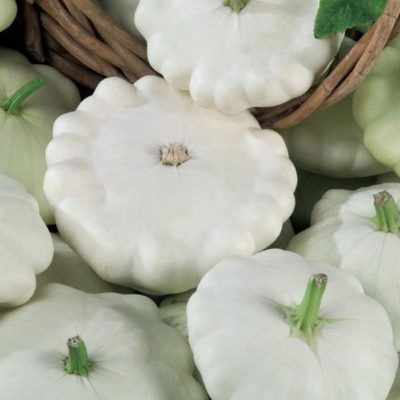


Patisson Polo consistently brings crops, even if the weather in summer is not very good


Patisson Solnechny Bunny is one of the popular early varieties


Patisson Watermelon F1 looks very unusual
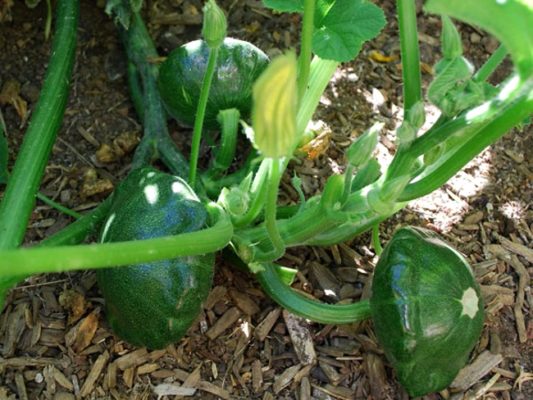


Patisson Chartreuse F1 is highly regarded by professional culinary professionals.
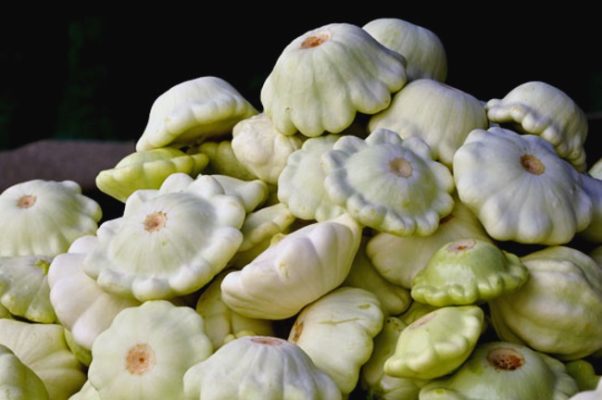


Patisson Piglet tolerates drought well, but does not differ in high yield
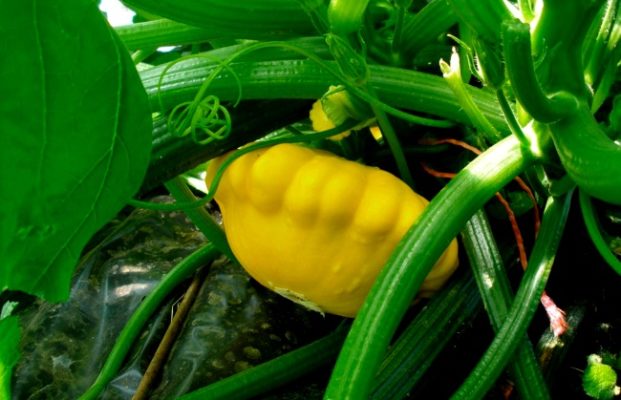


Squash Sunny Delight is a worldwide popular Dutch variety
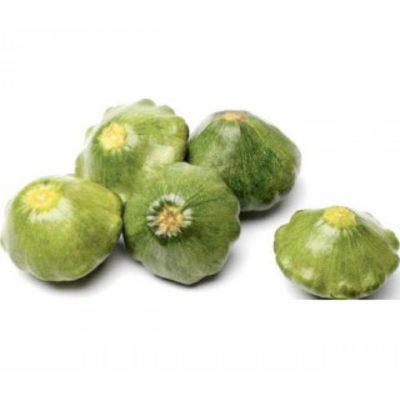


Patissons Mini crumb can be salted and pickled whole
Seed preparation and planting
Productivity largely depends on properly selected and prepared seeds. There are several stages of their processing before disembarkation:
- Selection of seeds ready for sowing. The seed does not lose its germination for about 8 years, but the best sowing characteristics are those of 2-3-year ripening. The most ripe seeds can be selected by placing them in a weak solution of sodium chloride for 10-15 minutes. Those that sink to the bottom are washed, dried and used for further work.
- Mandatory warming up. You can put the seeds in an oven preheated to 50 ° C for 4-5 hours, or leave them in the sun for a couple of days.
- Soaking in stimulating solutions. Dried seeds are left for a day in gauze bags moistened with water or 002% boric acid solution. Judging by the reviews of experienced summer residents, aloe juice diluted with water is an effective stimulant. After soaking, the seeds are washed and dried at room temperature.
- Hardening. A bag of seeds is put into the refrigerator for a day, setting the temperature from 0 to 1 degrees. This technique guarantees fast seed germination.
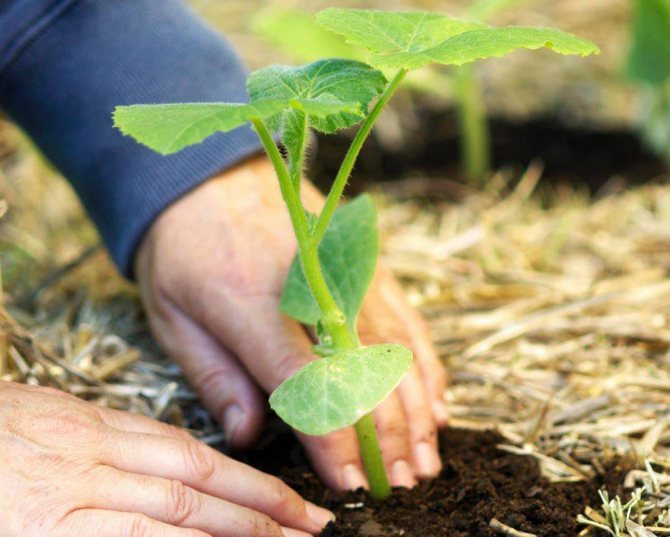


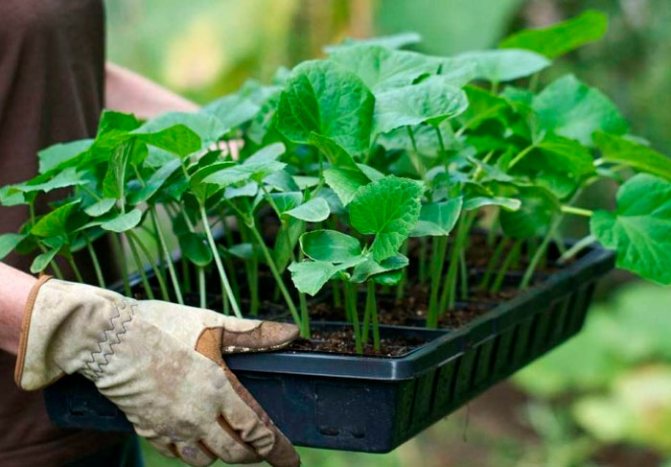
Selected seeds are sown in advance in 2-3 pieces in peat pots, later the strongest of several shoots is left, the rest are carefully cut off so as not to damage the root system.
Sowing in the beds
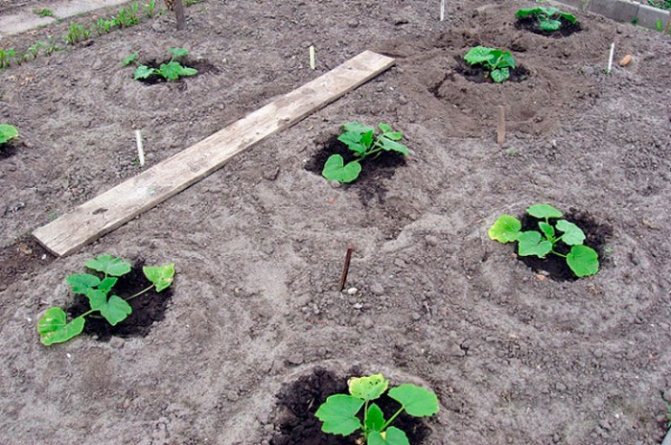
With the seedless method of growing crops, swollen seeds are sown in the ground in the last days of May or at the beginning of June. Here you need to focus on the temperature of the soil. For germination in the beds, the squash needs warmth, otherwise they can rot without sprouting. Mature plants are sprawling shrubs, so it is important to leave enough space between the seeds when sowing.
They can be planted in a ribbon or square-nesting way. In the first case, the holes are placed according to the scheme 50x90x70 cm. In the second, 60 cm or 70 cm recede from each nest with seeds. Observance of this distance will avoid plant decay.
Having outlined the holes, they put several seeds in them. The depth of their incorporation is determined by the type of soil. If it is heavy, 3-4 cm will be enough. In light soil, the holes are made deeper - 5-7 cm. It is better to plant seeds in the nest with an interval of 5-6 cm. They are covered with a thin layer of soil on top.
Sowing is completed with drip irrigation. It is carried out carefully so as not to expose the seeds. The surface of the hole is mulched with peat, after which the plantings are covered with a film. The emerging seedlings are allowed to grow a little stronger, and then they are thinned out, leaving the strongest plant. You can spread the seedlings to adjacent beds.
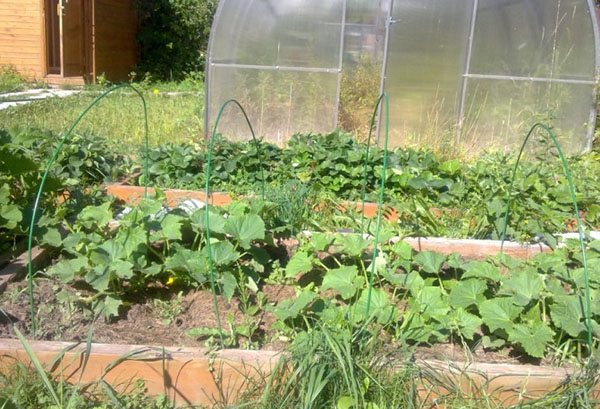


Outdoor squash care
Growing squash is possible even for a novice gardener, and subject to agricultural technology, proper planting and timely care, the yield can be up to 10-12 kilograms per bush. When choosing a planting site, it must be remembered that squash is a thermophilic culture that actively bears fruit in areas open to the sun.Growing squash in open ground is possible in two ways: in the southern regions it is customary to sow from seeds directly into the ground, and in temperate latitudes, planting by seedling is more popular.
Preparation and planting of seedlings in open ground
Cultivation of squash by the method of potted seedlings accelerates the ripening of vegetables by 1-2 weeks, and the yield increases 1.5-2 times compared to planting from seeds in open ground. A favorable time for planting is the second half of April. Until the first shoots, the pots are kept warm, covered with foil. As soon as shoots appear, the seedlings are transferred to the brightest, well-ventilated place and watered with water at room temperature.
Seedlings can be planted in the soil for 20-25 days, when there are already 2-3 leaves on each stem, and the root densely occupies the entire volume of the pot.
Planting seeds in open ground
When growing squash in open ground from seeds, special attention is paid to the preparation and care of the land. The soil should be nourished in autumn by sowing siderates: mustard or legumes. In the spring, the garden bed is dug up, watered abundantly with warm water, and loosened. Squash can be planted not earlier than June, when there is no threat of night frosts, and the topsoil warms up to 13-15 degrees. Seeds are placed in holes of 2-3 pieces to a depth of 5-7 centimeters and sprinkled with earth. The wells are located at a distance of at least 60-70 centimeters from each other. To preserve heat, a covering material is used, which is removed only after the first shoots appear.
Squash - care and feeding
Caring for established squash in the open field is simple. It includes:
- Regular watering. The moisture content of the beds must be at least 70%. The plant should be watered at the root so as not to provoke rotting of the flowers.
- Weeding and hilling.
- Fertilizing and feeding. It is necessary to feed the plant twice a season: before budding and after removing the first fruits. A solution of mineral and organic fertilizers is suitable for this.
- Removing excess leaves. It is recommended to pinch off the lower, and sometimes lateral, leaves for better air circulation and access to sunlight and insects to the flowers.
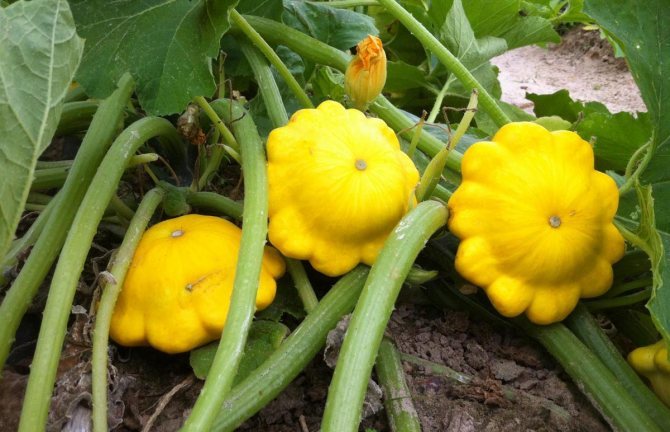


Fertilizing and feeding. What and when to use
If you want to harvest a good harvest, you cannot do without fertilizers. They need to be added 2-3 times per season. This is one of the foundations of proper squash care. Apply a mineral fertilizer before flowering. During the period of fruit formation, use potassium salt as a fertilizer (50 g per bucket of water). You can take organics diluted with water: mullein (in a ratio of 1:10) or chicken droppings (ratio - 1:20).
No less important is the pre-fertilization of the soil. If the soil is acidic, in the fall you need to add lime to it (up to 0.6 kg per 1 sq. M). If it is slightly acidic, the ash introduced before sowing is suitable (30-40 g per 1 well). Clay and peat soil before planting squash should be fed with organic matter or minerals.
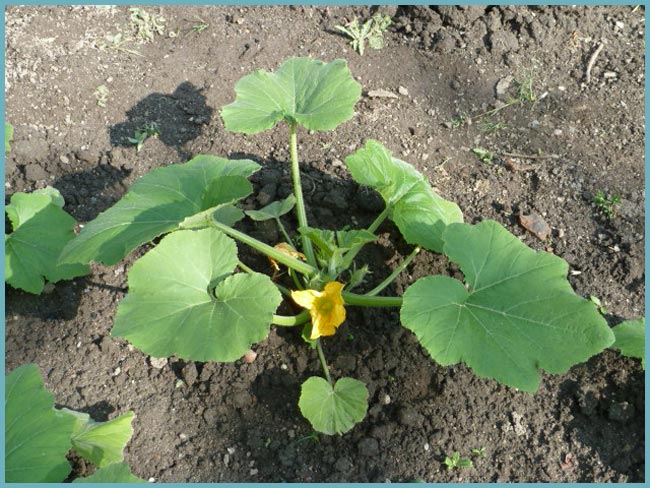


Squash bush
Beneficial features
The health benefits of regular use of squash are obvious to doctors, therefore they often prescribe this vegetable to people suffering from a variety of diseases. The possible positive effects of a diet high in this vegetable can have different vectors and influence a variety of ailments, we will highlight only the most visible results.
- Those who do not want to get cancer should use squash together with the skin. This part of the vegetable contains carotene, zeaxanthin and lutein - antioxidants that are actively involved in the elimination of free radicals from the human body, which are the main cause of oncology. In addition, such an action affects the appearance of a person - he looks younger, and he feels accordingly.
- Pectin, which is present in sufficient quantities in squash, also "works" against cancer, but acts more narrowly, protecting the large intestine from potential problems.
- The vegetable contains a relatively rare substance - folate, which takes an active part in the process of synthesizing new cells and is necessary for the production of DNA. These processes are vital for the proper development of the fetus, because patisson in moderation will be very useful for pregnant women.
- Potassium, present in squash, has a positive effect on the condition of hypertensive patients, helping to reduce blood pressure and reduce heart rate. Thanks to the same mineral, the myocardium is strengthened.

- Any child knows about the benefits of vitamin C, and after all, only 100 grams of squash provide a third of the daily intake of this substance. It turns out that such a vegetable is an excellent remedy for any infection.
- The same vitamin C, combined with a significant percentage of magnesium, also found in the vegetable, helps reduce the risk of stroke.
- Patisson refers to active choleretic products, therefore it usually has a positive effect on digestion, even if the food is mainly heavy.
- Vitamins of group B help to establish the production of all the necessary hormones in the body, first of all - serotonin, which, according to external sensations, is expressed as a consistently good mood and vigor, as well as regular sound sleep. For this reason, squash is recommended both for those whose endocrine system does not work properly, and for patients recovering from nervous diseases.
- Oil squeezed from squash seeds is used to eliminate harmful microorganisms from the digestive tract. True, here it should be clarified that there is no official recognition for this method yet, it should rather be attributed to traditional medicine.


- The vegetable is very useful for men as it increases potency and libido. Here again, the ability of the composition of the squash to prevent cancer affects - in this case, the effect is directed to the prostate gland.
- For vegetarians who do not accept meat and other animal products for themselves, squash is one of the best sources of B vitamins available.
- Patisson has a pronounced diuretic effect, therefore it is indicated for those who suffer from edema. In this case, the components of the product remove from the body not only excess water, but also sodium salts, which are often the catalyst for the accumulation of fluid in the body.
- Riboflavin in squash can help people suffering from migraines or persistent headaches of any other nature. However, it should be noted here that the vegetable is still not so rich in useful components to solve the problem completely, because vitamin supplements will have to be taken too, just in smaller quantities.
Finally, it is worth saying that the squash has no "extra" parts - not only the pulp, but also the peel and seeds of this vegetable can benefit a person.


"Solar squash" (another popular name for squash), like most other products on our planet, for all its benefits, has certain contraindications, which somewhat limit or even completely prohibit its use for certain groups of people. You should be interested in such moments in advance, otherwise the product, considered by many as almost a panacea, can aggravate an already imperfect state of the body.
- Like many fiber-rich vegetables, squash helps to mildly weaken the digestive system, and this is generally considered a beneficial effect in helping to relieve constipation. However, if the problem is completely opposite, that is, regular diarrhea or chronic dyspepsia is observed, the consumption of the vegetable in question will only exacerbate the described symptoms.
- Patisson helps hypertensive patients to lower blood pressure, but it has a similar effect on healthy people, and even on hypotensive patients. For the latter, such an effect can be very dangerous, therefore, it is undesirable to use a vegetable.


- Like many diuretic products, dish pumpkin contains substances that contribute to the formation of kidney and gallstones. For a healthy person, moderate consumption of the product is most likely not dangerous, but if such a disease has already been diagnosed, then the risk turns out to be double: here the stones can also increase, and their movement will become more active.
- Separately, it should be said about canned squash, which are contraindicated for even more groups of people than fresh vegetables. In addition to all the categories described, such a product is also undesirable for diabetics, since dish pumpkin is usually canned with sugar. For the kidneys and pancreas, canned squash is more dangerous than fresh vegetables. This product is also not recommended for children under 10 years old.
- Patisson is a rather rare product in our country, therefore even an adult may not even suspect that he may be allergic to such a product. Therefore, if a person tries the product for the first time, the portion must be limited, taking time to observe the reaction of the body.
Crop care tips
Caring for squash is no more difficult than for squash. But in addition to watering and fertilizing, they need the "help" of the gardener for pollination. Insects also carry pollen, but you should not rely on them too much, especially if the weather is cool, damp during flowering. To attract bees and bumblebees to the site, the buds are sprayed with honey or sugar syrup diluted with water (20-30 ml per liter).
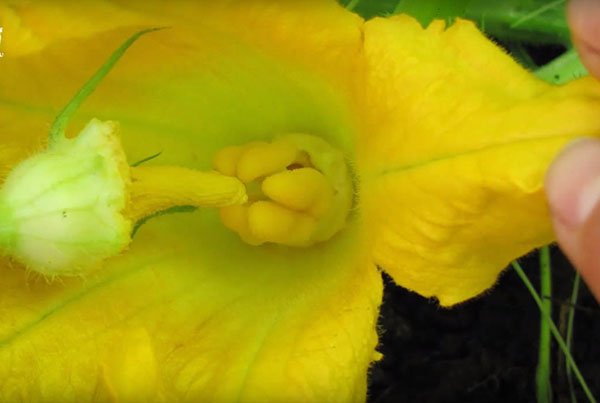


Gardeners carry out pollination of squash manually
Female flowers can be easily distinguished from male flowers by the presence of a fruit ovary at the base of the bud. To pollinate a male flower, you need to cut off the petals and run the pistil over the stamens several times. The pollen is also transferred with a soft brush or cotton pad. Pollination is carried out exclusively in dry weather.
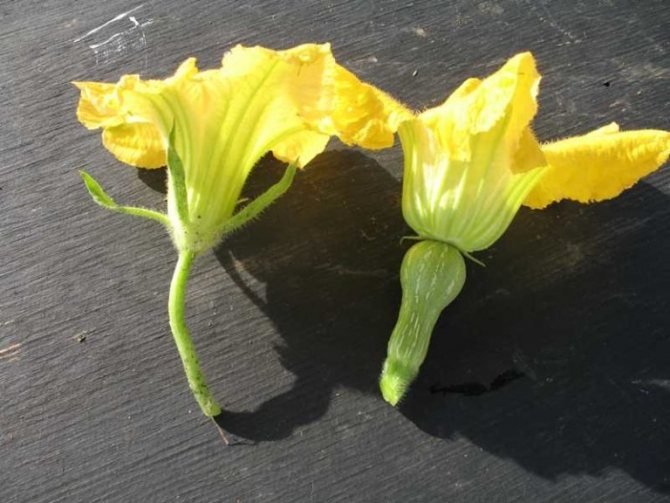


The female squash flower can be distinguished by the presence of a fruit ovary
The bed should be weeded and loosened regularly, but very carefully. The root system of plants is superficial. It is advisable to mulch the soil. This will help to retain moisture in the soil, prevent weeds from breaking through, and protect the roots from drying out.
If the flowering of the squash is delayed, experienced gardeners recommend cutting 1-2 of the oldest leaves from the bush. After 4–5 days, the procedure will need to be repeated. They spend it in the early morning.
Like all Pumpkin squash, squash loves moisture. Before flowering, they are watered with water at room temperature every 5-6 days, consuming about 10 liters of water per 1 m². After the formation of ovaries, the interval between watering is reduced to 3-4 days, the rate is increased to 10-12 liters. Water is poured under the root or into the furrows between the bushes. It is undesirable for drops to fall on leaves, flowers and fruits.
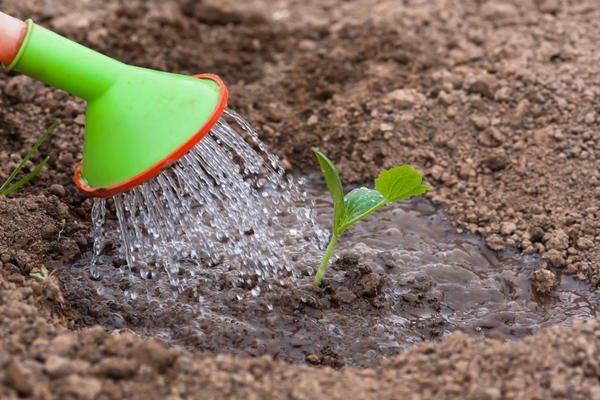


Squash, like all Pumpkin, need frequent and abundant watering.
A piece of plywood, glass, roofing material and so on is placed under the formed fruits lying on the ground to protect them from contact with wet soil. Otherwise, the development of rot is almost inevitable. For the same purpose, remove old wilted leaves and the remnants of flower petals from the fruit ovary.
The vegetative period in squash is quite short, so two additional fertilizing is enough for the plant. Before flowering, 40-50 g of potassium and phosphorus fertilizer and half of nitrogen fertilizer are distributed in a dry state over the garden bed. You can also use complex preparations - Azofosk, Ammofosk and so on.
Ripening fruits need phosphorus and potassium. Nitrogen stimulates the bushes to intensively build up the green mass, they have no strength left for the squash themselves.5-7 days after the formation of fruit ovaries, squash is watered with infusion of fresh manure, bird droppings, nettle or dandelion leaves. It is being prepared within 3-4 days. Before use, the product is filtered and diluted with water 1:10 or 1:15, if it is droppings. Any fertilizer based on vermicompost, infusion of wood ash is also suitable. Each plant consumes about 0.5 liters.


Nettle infusion - a natural source of phosphorus and potassium
Video: recommendations for caring for squash
Patissons - protection against diseases and pests
Prevention and timely treatment of diseases of squash and squash helps to maintain a high yield throughout the summer. The greatest danger to plants is represented by:
- Insects. The most common danger to all pumpkin species is aphids. You can rid the plant of the parasite with the help of pepper or onion infusion.
- Fungal diseases (powdery mildew). The fungus primarily damages the leaves, forming white spots on them, and easily passes from one plant to another. You can save the plant from the disease using a solution of colloidal sulfur (20 grams per 5 liters of water).
- Bacterial fruit rot. Rot can be caused by over-watering the plant or by thick leaves. At the first signs of the disease, it is necessary to reduce the amount of moisture, remove damaged leaves and fruits, water the bush with a weak solution of copper sulfate (1 spoon per bucket of water).
Preventive measures help to avoid diseases of seeds and fruits: timely fertilization, weeding, soil preparation in autumn, crop rotation.
Pests and diseases of squash with photos and names
Diseases
Most often, squash is sick with ascochitis, powdery mildew, anthracnose, white rot and black mold. These diseases are fungal, and in order to cure the plant affected by them, it is necessary to process it in a timely manner, and for this you should know the signs of damage to the bush by this or that disease.
Anthracnose


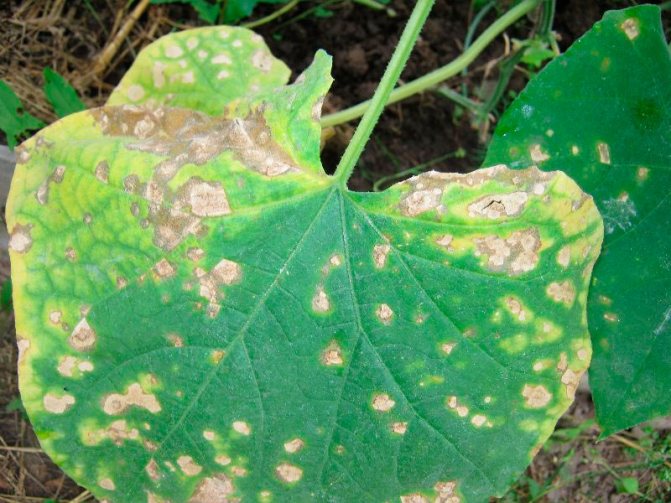
In a plant that is affected by anthracnose, large watery specks of a pale yellow color form on the foliage, a coating of pink spores of the fungus appears on the surface of the veins. After that, pink sores are formed on the fruits, shoots and petioles, which turn black by the onset of the autumn period. Such a fungal disease is most active in rainy weather.
Ascochitosis


When squash is affected by ascochitosis, black spots are formed on the stems, in the nodes of the shoots and on the leaf plates. As the disease progresses, the affected parts of the bush dry up, which can lead to the death of the entire plant.
White rot


If the plant is affected by white rot, then pale brown specks form on the foliage and shoots, in their place after a while deep ulcers form, which are filled with pink mucus. Such spots can also form on fruits. This disease develops most actively in conditions of high humidity.
Powdery mildew
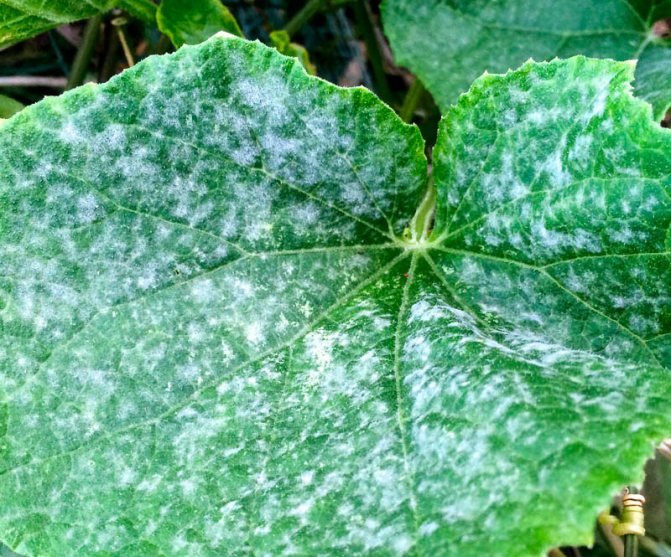


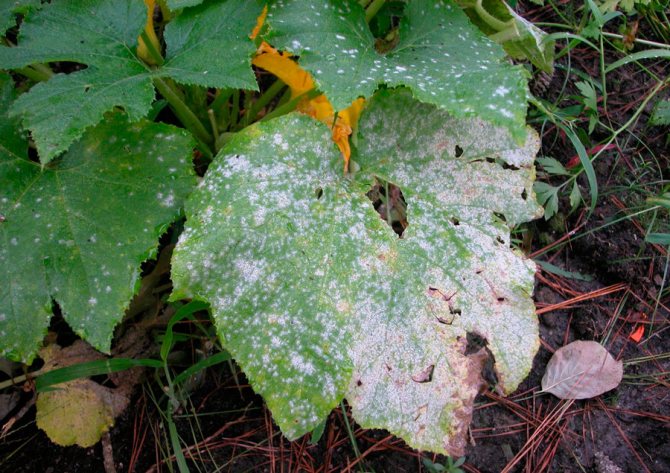
When the patisson is affected by powdery mildew, a powdery loose bloom of white color is formed on the front surface of the leaf plates, over time, the affected leaves begin to dry. Another such plaque can appear on the fruits and shoots of the bush. Increased humidity contributes to a more active development of the disease.
Black mold
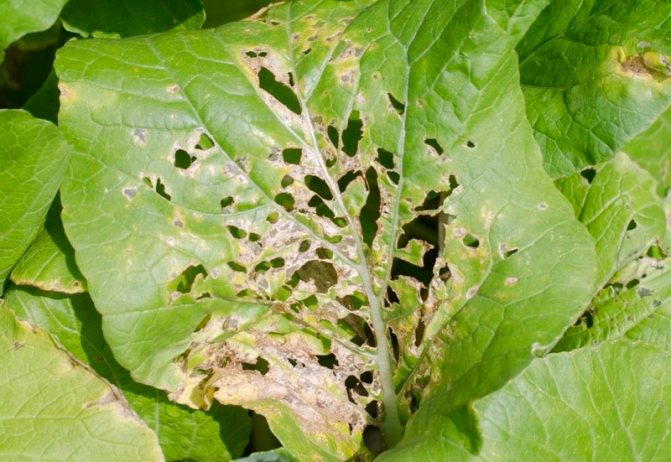
On the bushes affected by black mold, specks of a brownish-yellow color appear between the veins of the leaf plates, after a while a dark bloom forms in their place, which contains spores of the fungus. Then such spots dry out, and holes appear on the plates. In those fruits that are affected by black mold, there is a cessation of development and their shrinkage.
Pests
The most dangerous for such a culture of all pests are: winter and garden scoops, as well as melon aphids. Slugs can also harm the bushes.
Scoops
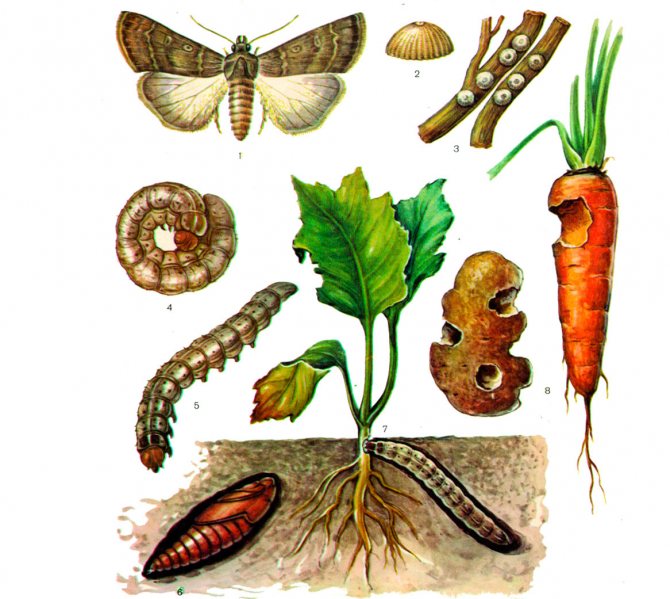


The scoops arrange egg-laying on the bushes, from which caterpillars appear after a while. They gnaw off parts of the bush located above the ground, and also gnaw at the roots.
Melon aphid
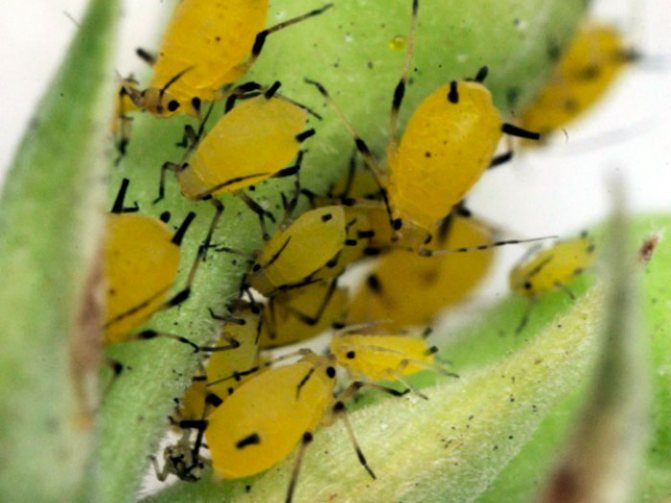


The melon aphid settles on the flowers, stems and ovaries of such a plant, and also on the seamy surface of the leaf plates, due to which their folding and wrinkling is observed. Such a pest is most active in warm weather with high humidity.
Slugs


Slugs are most dangerous for young bushes, since they are able to eat all their foliage or make very large holes in it.
Treatment


Squash bushes are recommended to be systematically processed in order to prevent the development of various diseases or the appearance of harmful insects. If you make such treatments systematically and correctly, then all diseases and pests will bypass the squash. Another treatment is simply necessary for the affected plant.
You should also remember about preventive measures:
- Crop rotation rules... Plant squash only in areas where good predecessors have grown (see above).
- Agrotechnical rules... Adhere to all agronomic rules of this crop. For example, before sowing, do not forget to prepare the seed in accordance with all the rules, and also make sure that the bushes do not grow thickly on the garden bed, otherwise the humidity in the area will be excessively high.
- Preventive treatment... It is carried out before the bushes bloom.
The most effective in the fight against fungal diseases was shown by the Bordeaux mixture solution (1%), and also fungicidal preparations such as Topsin or Fitosporin. To get rid of slugs, baits are made on the site; for this, pieces of melon, pumpkin or watermelon crust are placed on its surface in several places. After the slugs crawl over to eat, they are collected by hand and destroyed. To get rid of aphids, the bushes must be treated with soapy water (300 grams of soap for 1 bucket of water). To get rid of scoop caterpillars, plants need to be treated with a solution of Gomelin (0.5%) or Bitoxibacillin (1%).
There are other chemicals that can help get rid of both harmful insects and diseases. But experienced gardeners prefer not to neglect preventive measures, and this helps to keep the squash healthy.
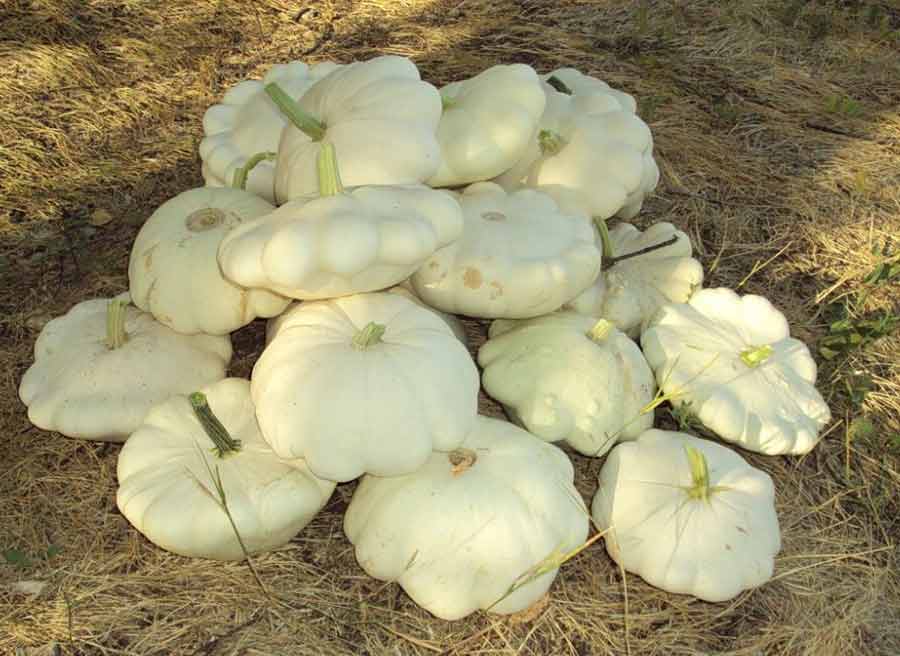
Collection and storage
It is better to collect squash for fresh consumption when their peel and pulp are still soft. Overripe vegetables with dense skin are suitable for harvesting seeds.
To maintain high yields, vegetables are cut along with the stalk every few days. This will keep fruiting until autumn. The last harvest is carried out before frosts, and the tops and stems are laid in compost (but provided that the plant was healthy).


Figure 7. Harvesting and storage of crops
Young squash can be stored in a cool room for no more than two weeks. Ripe vegetables with coarse skins can be stored in the basement, along with pumpkins and zucchini (Figure 7). The room must be dry, cool and well ventilated. It is desirable that the fruits are not in contact with each other. In addition, they are periodically examined and spoiled vegetables are removed.
Squash at home
Patisson is a bushy plant and, moreover, quite compact. It can be planted in a container or large pot and grown at home.
Its root system is shallow, so the capacity should not be too deep. Diameter - about 60–70 cm. Drainage holes are required. A layer of expanded clay, pebbles, brick chips 3-5 cm thick is poured onto the bottom.
As for the soil, any universal seedling substrate is suitable if it is mixed with humus or fertile turf soil in equal proportions.For the prevention of fungal diseases, a tablespoon of crushed chalk or powdered activated carbon is added to each liter of the finished mixture.
The container is placed near a window facing southeast or southwest. In order to avoid burns of the leaves, it is advisable to protect the squash from direct sunlight. In the summer, the pot is taken out to the loggia, balcony, veranda.
Water the "home" squash as the topsoil dries out, every 3-4 days. They are fed every 15–20 days with any biohumus-based fertilizers. This culture prefers natural organic matter.
Features of growing squash in a greenhouse
The optimal time for planting squash in a greenhouse or greenhouse is mid-spring. The technology of planting seedlings is exactly the same as in open ground, but it must be taken into account that the squash does not tolerate excessive air humidity. Growing squash in a greenhouse requires regular ventilation.
Modern varieties rarely form long lashes. In case of excessive overgrowth of the bush, it is better to pinch, removing excess shoots and leaves. This trick allows you to prevent the growth of vegetative mass in the plant to the detriment of the fetus. Vegetables ripen faster and there is more pulp.
Description of landing technique
When planting squash, two methods are used:
- Direct sowing with seeds in the ground;
- Growing through seedlings.
Direct sowing is carried out in the southern regions of the country. In the middle lane, film shelters are used, but the unstable temperature and the likelihood of late frosts make growing seedlings the most acceptable method of planting. The method will reduce the risks of plant death and allow you to get an early harvest. In the northern regions, it is even safer to plant seedlings under a film or in a greenhouse.
Selection and preparation of seeds
One gram contains 7 to 10 seeds. For planting, choose the largest, full-bodied. 2 seeds are planted in each well, leaving one of the healthiest plants after germination. When growing seedlings, the germination of seeds is taken into account and they are purchased with a margin of 15–20%.
There is no need to prepare seeds painted in different colors for planting - they are processed by the manufacturer, and there is a special warning about this on the package.
Before planting, the seeds of squash are subjected to the following procedures: Heating increases the energy of growth and partially disinfects the seeds. Etching in a solution of potassium permanganate (2%) or special purchased preparations (phytolavin, phytoplasmin) will prevent viral and bacterial diseases of seedlings, protect the sprouts when planting seeds in the ground. Treatment with microelements increases germination, accelerates plant growth and development.
For processing, use funds from the store ("Kemira", "Nutrisol"), or prepare the mixture yourself, adding 0.5 g of copper sulfate, boric acid, potassium permanganate per liter of water. Soaking lasts 10-12 hours, after which the seeds are washed in cold water and dried. Germination before sprouting occurs at a temperature of 24-28 ° C. The procedure will speed up the cultivation when planting in the ground and will save on the purchase of planting material - the germinated seeds are embedded in the holes one by one.
It is important not to overgrow the sprouts - this will damage them during planting. Hardening of seeds is carried out at the stage of swelling, lowering the temperature to 0 ° C for one day. This treatment helps plants to cope with the cold when planting in the ground.
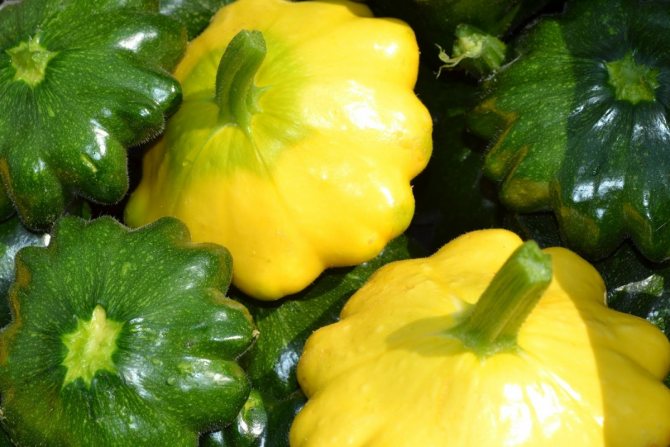


Photo: <1.bp.
Direct sowing by seeds
The time of planting and preparation of seeds was mentioned above. To accelerate the heating of the soil and retain moisture, the prepared bed is covered with a film that is not removed before sowing. The work algorithm is as follows:
- On a leveled surface, markings are made using a cord.
- Grooves with a depth of 5-8 cm are formed along the indicated line.
- Superphosphate is added to the bottom at the rate of 1 tbsp. l.per linear meter of the furrow, peat is also laid out there with a layer of 2-3 cm and the surface is lightly powdered with ash.
- The grooves are shed with warm water, and preferably hot for pest control, water.
- Seeds are laid out at the bottom with a step of 70 cm. Dry seeds are placed in pairs, germinated - one at a time.
- The furrows are covered with loose soil (peat), slightly compacted and again spilled with warm water from a watering can.
- The beds are covered with a film at night, removing it during the day.
- Seedlings are examined by removing damaged plants. Distances from 60 to 70 cm are left between future bushes.
When choosing an interval, they are guided by the manufacturer's recommendations - the bushes can be different in size.
Growing through seedlings
Dry or sprouted seeds are planted in prepared soil, bought in a store (any suitable for seedlings) or prepared on their own.


Photo: collage <>
As a substrate, mixtures are suitable:
- Sod and leafy land, peat, humus in equal proportions. A full glass of ash and 1 tbsp. l. urea.
- On two parts of the sod land add one part of weathered peat, rotted sawdust treated with boiling water, humus. For 5 kg of the resulting mixture, 1 tbsp. l. universal complex fertilizer.
The prepared mixtures are steamed to destroy pathogenic microorganisms.
The roots of the squash are fragile and easily damaged when planted in the ground. For growing seedlings, peat pots or cups rolled from old newspapers are used. After planting, the walls of the containers dissolve with water and decompose in the ground.
Cups are filled with prepared earth, leaving 1.5 - 2 cm to the upper cut. Dry seeds are laid out in 2 pieces, germinated by 1 piece. into prepared holes 3-4 cm deep. Sprinkled with soil on top, watered with warm, settled water and placed for germination in a warm (24-28 ° C) dark room. After the appearance of the cotyledons, the temperature regime is changed, maintaining 20-22 ° C during the day and 16-18 ° C at night, and the seedlings are placed in a well-lit place.
This mode will not allow the seedlings to stretch out. A week later, strong shoots are left, removing damaged and lagging behind in development. Water the seedlings with warm water. The need for top dressing is determined by the appearance of the leaves - if they are painted bright green, fertilizers are not needed.


Fertilizers must be applied 4-5 days before planting in open ground, using complex compounds or dissolving a teaspoon of granular superphosphate in 5 liters of water. During the last week of growing, the seedlings are hardened by taking them out to the balcony or garden during the day. It is not worth delaying the landing at the onset of warm weather - the stretched planting material takes root worse in a permanent place. They are planted in the same way as the seeds according to the scheme 70x70 cm. For better access to sunlight and air, it is recommended to arrange the plants in a checkerboard pattern.
What is it and what does a vegetable look like?
Patisson has another name - dish-shaped pumpkin, which gives answers to many questions of those who have little idea of what it is. The plant really belongs to the Pumpkin family, but it is not worth calling it a pumpkin, because cucumbers, for example, belong to the same family. The vegetable is famous for its pulp, which surpasses even cucumbers in tenderness, as for the taste, this fruit is often compared to artichokes.
As for the shape, it, as the official name suggests, is flat and vaguely resembling a plate, and the size is usually relatively small - somewhere in the palm of your hand. Even the word "squash" is a kind of attempt to describe the appearance of a vegetable: it comes from the French word "pie", because it reminded the French of this particular dish.


The fact that in our area the vegetable is relatively unpopular is not so surprising.For a long time, it remained a huge wonder for the whole of Europe, because, along with potatoes and tomatoes, it was originally an American culture, which the first Europeans saw only at the end of the 15th century. However, the squash moved to Western Europe from its homeland, which is modern Mexico and Guatemala, rather quickly, not far behind the two popular aforementioned cultures, this happened in the 17th century.
At the same time, the expansion did not continue further: unlike the same potato, the vegetable turned out to be quite demanding on climatic conditions, and therefore, until recently, did not claim the gastronomic conquest of our country.
What do squash look like and how are they useful?
Squash is an annual bushy plant or shrub belonging to the Pumpkin family. Its closest "relatives", pumpkin and vegetable marrow have long been well known to gardeners. Most botanists consider South America to be the homeland of the squash, although there is evidence that this plant was cultivated in Ancient Egypt. Wild squash in nature has not yet been found, so the question remains open.
Europe got to know them during the era of great geographical discoveries. The plant was brought home by Spanish sailors. The Mediterranean climate suited the culture very well, and it quickly gained popularity. Now squash is almost an integral part of French cuisine. Even the common name comes from the French pâté (pie), which describes the unusual shape of the fruit. And squash is often called "dish pumpkins".
An exotic vegetable came to Russia in the 17th century. It cannot be said that the culture fell in love immediately and forever, nevertheless, two hundred years later, squash could be found even in Siberia. They have adapted well to the harsh climate. Although their frost resistance is such that most varieties will not tolerate even a short-term drop in temperature to negative values.
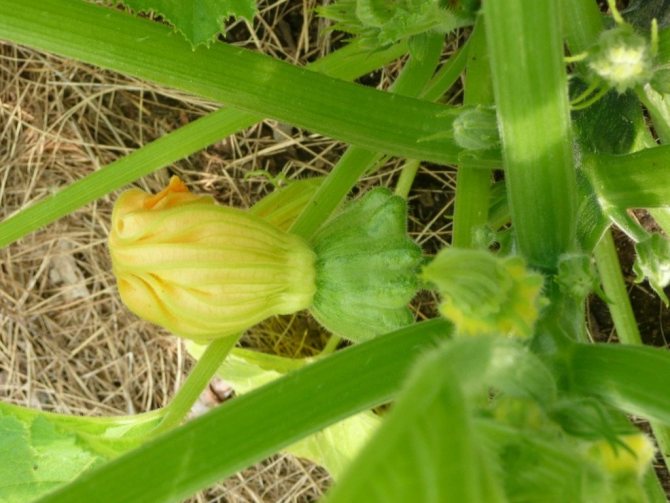
The plant is quite compact, the whips are short. The leaves are large, harsh to the touch, covered with sparse "villi". The flowers are solitary, golden yellow, bell-shaped in shape. They are unisexual, so in order for the fruit to set, the plant needs the "help" of insects or a gardener.


Squash bushes, as a rule, are quite compact
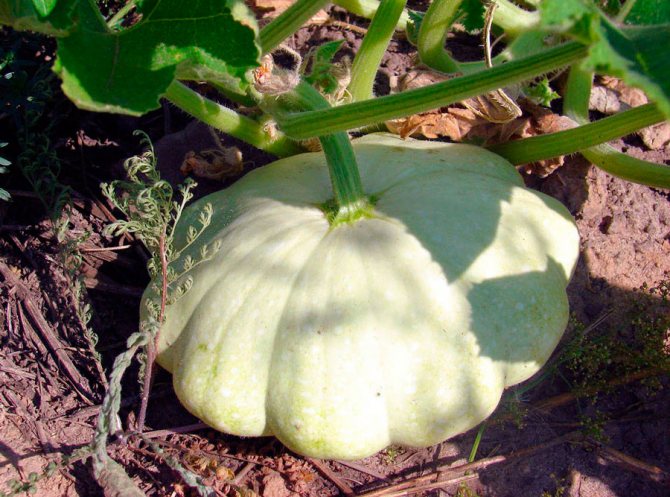
The fruit of the squash is pumpkin. Weight varies from 250-300 g to 800-1000 g, diameter - from 7-10 cm to 25-30 cm. You should not hesitate with harvesting. The larger the squash becomes, the more its skin coarsens. The pulp becomes cottony, almost tasteless. Such specimens can only be used for harvesting seeds if the variety being grown is not a hybrid.
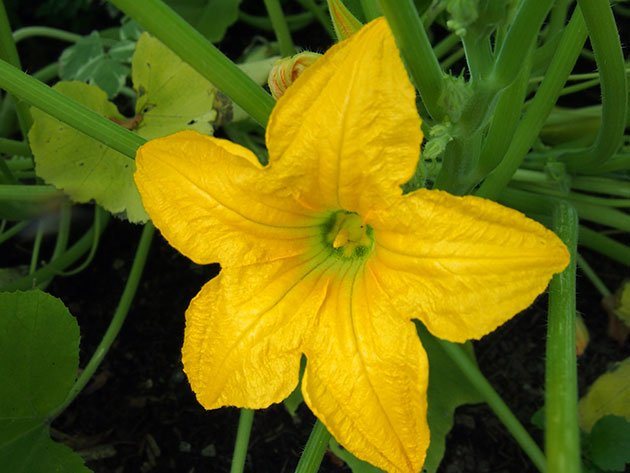


The flowers of the squash are unisexual, pollination is impossible without assistance
Most often, the skin is colored white, salad or dark green. But breeders have bred yellow, orange, purple, variegated squash. The fruit resembles a plate or bowl in shape. The pulp is tender, with a light nutty flavor. Although some gourmets note that the taste of the squash reminds them of asparagus or artichokes.
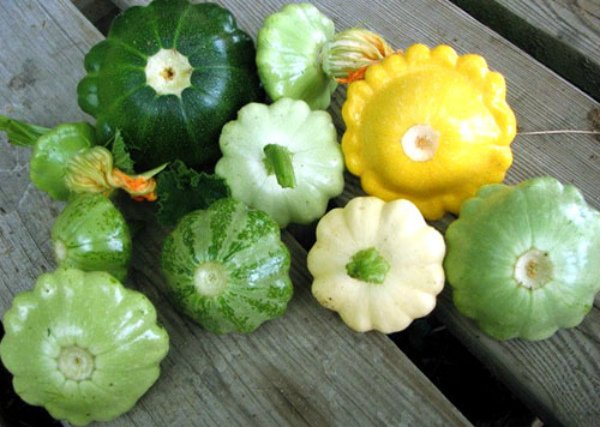


Breeding varieties of squash differ mainly in the color of the skin and the shape of the fruit
Squash are widely used in cooking. They can replace zucchini in any recipe. The unusual shape of the fruit makes it ideal for stuffing. Both mature and young squash are eaten. The latter can generally be eaten raw. It is the fruits at the age of 7–10 days, which have reached a diameter of 5–7 cm, that are most highly valued by professional culinary specialists. They are also stewed, fried, pickled, salted.
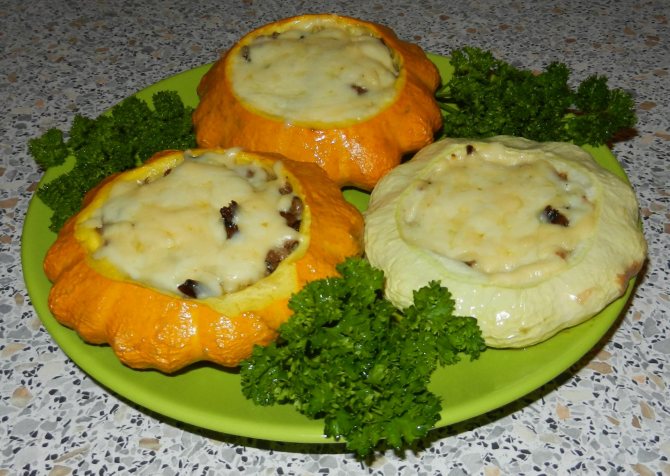


Patissons are stuffed with meat, vegetables, rice, the shape of the fruit is very convenient for this
Patissons are not only tasty, but also healthy. The pulp is rich in pectin, fiber, protein, unsaturated fatty acids, glucose and fructose. It is absorbed quickly and helps to digest heavier foods.Of the trace elements, the presence of potassium, phosphorus, magnesium, calcium, copper, iron, zinc, cobalt, sodium can be noted. In terms of the content of vitamins of group B, C, E, PP squash surpasses pumpkins and squash. Yellow-skinned varieties are rich in carotenoids and lutein. This natural antioxidant helps to improve blood composition (especially in case of hemoglobin deficiency), lower cholesterol levels, and has a beneficial effect on vision.
The squash diet has long been known and proven to be effective. Its main product can be easily replaced with squash. They are also low in calories. Nutritionists recommend using the fruit to prevent diseases of the cardiovascular system, normalize bowel function, with kidney and liver problems. Squash are hypoallergenic, mashed potatoes are suitable even for small children. The only contraindication is individual intolerance.
Squash seeds can be compared to eggs in terms of lecithin content. It is a valuable source of protein for vegetarians. The powder from them helps to normalize the activity of the endocrine and nervous systems. The juice effectively removes excess salts and fluids from the body. Its regular use is an effective prevention of kidney disease. A good diuretic and mild laxative is pulp puree.


The pulp of the squash is very useful for health, and its seeds are also used in folk medicine.
It is quite simple to distinguish squash from zucchini. Just look at the fruits. If we talk about less noticeable differences, the squash bushes are more compact, the leaves are smaller. The pulp of the fruit is denser, it has its own pronounced, rich taste. But squash is much superior to squash in yield and early maturity.
Video: squash and their health benefits
Squash - growing on the balcony
It is quite easy to grow squash on the balcony even for a novice agronomist. There are no daily temperature fluctuations, the plants are protected from pests and infections. Squash can be planted in a regular large-capacity clay pot, barrel or deep box.
The only feature of growing vegetables on the balcony is the absence of pollinating insects for full fruit setting. Such squash must be pollinated artificially: insert the corolla from a male flower into a female-type flower.
How to prepare for boarding
The first step is to choose a suitable place on the site. Culture loves light and warmth. A shaded place has a bad effect on the development of the plant, so it is better to plant the vegetable in a sunny place.
It is good if the site is protected from strong gusts of wind, and the sun's rays are diffused.
This place will be the best for growing squash in the open field.
Sowing dates


To get a high-quality tasty harvest, you need to seriously approach the question of the timing of planting a vegetable.
The wrong sowing time can affect the fact that the vegetable does not have time to ripen before the onset of cold weather.
The climatic conditions of the country are very different in different regions, so the sowing time is different.
The table shows the approximate time that is suitable for a particular region of the country.
Table 1. Dates of sowing squash in open ground by regions of Russia:
| Sowing dates | Country region |
| May 15-20 (with cover), May 20-30, June 5-10 | Moscow region and middle lane |
| May 10-June 15 | Central |
| April 20 - May 10 | Yuzhny |
| From June 15 | Far East |
| Greenhouse | Northwestern |
| Greenhouse | Siberia and the Urals |
Features of soil preparation
The recommended soil for the vegetable is black soil, light loam. The best choice is a neutral soil, so mistakes can be avoided.
If the soil is acidic, wood ash is added to it.
The preparation of the soil for the squash is carried out in the fall or spring. At the same time, an important place is occupied by the question of applying fertilizers, which affect the quality and quantity of the crop.
Autumn preparation
To properly prepare a bed for a crop, you need to follow the instructions:
- First, the preceding culture is removed.
- They dig up the soil with a rake, remove the rhizomes of plants, weeds.
- Fertilizers are also applied since autumn. Humus or compost is used for digging. At the same time, light soils require less organic fertilizers, heavy soils more.
Spring preparation
In early spring, after the snow melts, when the soil warms up, they begin to prepare it.
To do this, loosen it 2 times, harrow. The first time, loosening is carried out to a depth of 5 cm.
Just before sowing, you need to loosen the soil again. Here, the depth is already shallower - 10 cm. At this stage, all weeds are also removed.
Fertilizing the soil and preparing seeds before planting
Before planting the squash, 5 kg of humus, 40 g of superphosphate, 25 g of potassium salt are added per 1 square meter.
All fertilizers are distributed in such a way that they are evenly distributed throughout the entire area.


Regardless of the method of growing the vegetable, the planting material must be prepared for sowing:
disinfect, warm up, harden, treat with growth stimulants.
The first stage is warming up. To do this, you need to place the planting material in an oven heated to 50 ° C.
The seeds are heated for 5 hours. You can also warm them up on the battery for 7 days. The heated seeds need to be cooled.
Next, they proceed to etching. You can disinfect the planting material in a 1% solution of potassium permanganate.
For dressing, simply dip the seeds in a hot pink solution and hold for 20-30 minutes. Then rinse with clean water, dry.
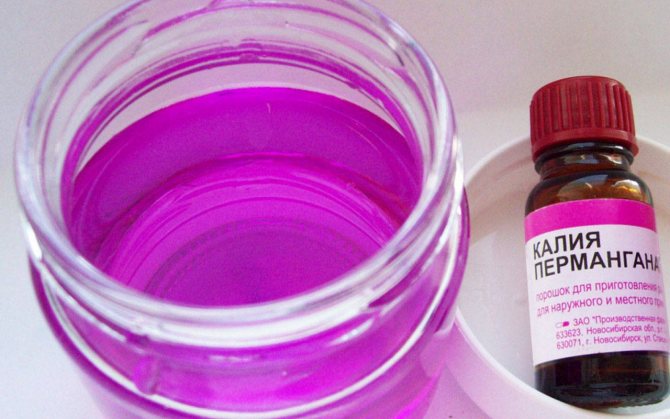


You can harden the planting material in the refrigerator. It is enough to put it on the lower shelf for 6 hours.
The last stage will be treatment with growth stimulants. They are purchased in the store, these are the preparations Epin, Buton, Energen.
You can also use folk remedies. Experienced gardeners use aloe juice diluted with water to accelerate seed germination.
After all the procedures, the seeds are washed with clean water and placed on wet gauze for 2 days.
During this time, you need to ensure that they are constantly wet.
The air temperature in the room at this stage should be + 23 ° С.
Squash in the garden: combination with other plants
To increase the yield and prevent the occurrence of many diseases, it is important to choose the right neighborhood for the crop.
It is best if they grow along with radishes, onions, garlic, corn.
It is also good to grow squash together with cucumber, thyme or nasturtium. Marigolds planted next to the vegetable will help scare off aphids.
Facilitates care, planting a combination of squash with pumpkin, beans or cabbage. In this case, you can harvest one crop and plant another.
Planting greenery is also successful. For example, dill or salad.
Potatoes will be a bad neighbor for squash. However, if you plant a vegetable in the place where the potato tubers used to be, it will delight the gardener with a good harvest.
It is also not recommended to grow side-by-side squash and zucchini. They are related plants.
In order to prevent cross-pollination, you cannot plant a vegetable next to cucumbers. Beets are unfavorable neighbors for squash.
Harvesting squash
Squash fruits can be harvested up to 3 times a week. During this time, they can grow from 7 to 12 centimeters in diameter. For canning, smaller fruits from 3 to 5 centimeters are often removed. It is important not to let the fruit overgrow in order to maintain its softness and taste.


If the harvest is delayed, there is a delay in flowering, the ovaries crumble, and the formation of fruits is delayed. If the skin of the fruit has hardened, it is better to leave it for seeds and remove it closer to autumn, when the plant dries up.
Seedling preparation rules
A gardener who wants to grow squash for the first time should know that these vegetables grow faster if they were planted in open ground from seedlings.
Growing plants in greenhouse conditions or under a special film that covers young seedlings allows you to get bountiful harvests.
If containers for pre-growing seedlings are not enough, seeds can be germinated in plastic bags or in flowerpots.


Seeds are sown when the weather is already warm outside. This period usually begins by early May. For this, glasses with a diameter of ten centimeters are suitable.
For soil, you can use soil purchased from a specialist gardening store. Forest soil mixed with sand as well as humus will also be appropriate.
And in what way do you grow squash?
Seedling
Planting seedlings:
- Seeds, prepared in advance, are placed in cups at a distance of 4 centimeters, then poured over them with water. The glass is covered with foil until the first shoots and removed to a warm balcony or windowsill.
- After pecking the first shoots, the glasses are removed from a warm place and placed in a room where the temperature is no more than 18 degrees.
- After one week, the seedlings are put back in their former warm place. Watering is carried out rarely and in moderation.
- After the seeds germinate, you need to fertilize. To do this, a mullein is bred with clean water in a ratio of 1:10. The same feeding method is used before planting in open ground.


Planting is recommended three, and sometimes four weeks after sowing. By this time, three true leaves will already appear on the seedlings.- Planting is carried out in the early hours before sunrise in order to reduce the shock situation for young plants. Planting is carried out together with a lump of earth from a cup.
- After planting, you need to water the seedlings with clean water.
- Patissons are large vegetables, so planting is carried out at a distance of 76-80 centimeters. If planting is carried out in spring, then it is recommended to cover young plants with a film. This will allow you to transfer possible frost.
- If the weather continues without rain, then the first flowers will appear in two weeks. In this case, the protection from the cold is no longer needed; it can be eliminated.
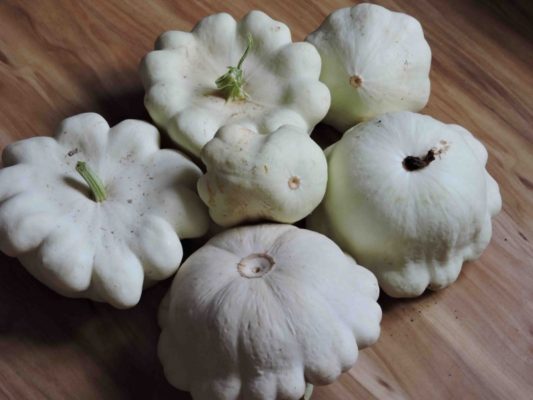
Small-fruited varieties for canning
In canning, pumpkins of any varieties harvested unripe are used. Having plucked fruits up to 7 cm for pickling, the vegetable grower stimulates the appearance of new pumpkins.
It is useful and beautiful to use fruits of small-fruited varieties for pickling. Small squash looks more impressive among pickled vegetables.
Vegetable growers recommend using mini squash seeds for planting:
- "umbrella";
- "disk";
- "Cheburashka";
- "Marrov" - a high-yielding mid-season variety;
- "Patch";
- "Marinka" - an early ripening variety;
- "Cheburashka".


Photo:
Let's consider some small-fruited varieties: Fruits of the “mini-crumb” variety are used for canning as a whole, their diameter is up to 5 cm, weight is up to 70 g. They taste no worse than large-fruited squash. The crop ripens after 50 days; in a few weeks of fruiting, up to 5 kg are harvested from one bush. Growing does not require any special technology. The bushes themselves with small fruits and leaves look decorative. Mini-squash "solar explosion" recently appeared on the sites of Russian vegetable growers. Not much different from the "mini-crumb" variety. "Chartreuse" differs not only in small fruits, but also in early ripening, a little more than a month. On dark green glossy fruits, stripes of white or yellow appear over time. Both delicious and beautiful! The fruits of the early ripe hybrid "sunny bunny" grow up to 200 g, have a dense, light orange, tasty pulp. Up to 20 squash can ripen on one bush, the harvest can reach 15 kg per season. The plant does not suffer from powdery mildew or other diseases.


Photo: <>
Care
Caring for squash consists in timely watering, dressing, weeding.
Watering
When watering, follow the rules:
- Watering is carried out with water heated in the sun - cold water will cause stress and slow down development for several days.
- Watered in a garden bed at the root, avoiding moistening of the stem, leaves, flowers and ovaries.
- Watering is carried out rarely, but abundantly - the soil should be soaked 20-25 cm deep.
The frequency of watering is influenced by the weather and the composition of the soil on the site. On cool days, dry watering is recommended - loosening the soil around the plant. After the soil has dried, loosening is carried out to a depth of no more than 5 cm, trying not to damage the roots of the plant.
Top dressing
In a dry summer, 3 dressings are enough for development and fruiting. In the rainy season, when the nutrients are washed out of the soil by rains, 4-5 dressings are carried out with intervals of 10-15 days. The first time it is necessary to support the plant is two weeks after planting, when 3-4 true leaves appear. Apply a complex fertilizer according to the instructions.


Photo: <>
The second introduction of nutrients coincides with the beginning of fruiting. Use the infusion of mullein (1:10), bird droppings (1:15), add superphosphate or potassium sulfate at the rate of 15-20 g / 10 l of water. Liquid consumption 1 liter per bush. The third time is "fed" after the first harvest. Apply the composition as for the first feeding or ash solution (glass per liter) with the addition of urea (1 tbsp. L.). Consumption - 1.5-2 liters per plant.
Bush formation and pinching
It is important when growing to respect the manufacturer's recommended distances between plants. Insufficient air movement worsens the ventilation of the bush, provokes rot, and reduces productivity. During flowering and fruiting, some of the leaves are cut out, improving the illumination.


Photo: collage <>
Modern varieties do not form long lashes, therefore, they do not need pinching - it is necessary to stop the growth of new shoots only in case of excessive thickening of the bush, removing unnecessary large moldings.
Squash - popular varieties
according to the rate of ripening, the varieties of squash are divided into early, mid and late ripening.
- Early maturing varieties: Umbrella, Cheburashka, Disk, Sunny Bunny, Gosha, Bingo-Bongo, UFO orange, Kopeyka;
- Early ripening varieties: Chunga-Changa, Solnyshko, UFO White, Malachite;
- Late-ripening varieties: White 13;
There are classifications of squash according to shape, size, color, suitability for canning, etc.
For blanks, Kopeyka and Mini crumb are suitable, the fruits of which are no more than 4-5 centimeters, and for decorating the table and stuffing - the Sun. Squash Snow White are resistant to diseases, and Loaf is valued as the highest-yielding. Gardeners who want to harvest all summer long plant several different varieties at once.
Post Views: 310
Types and varieties of squash
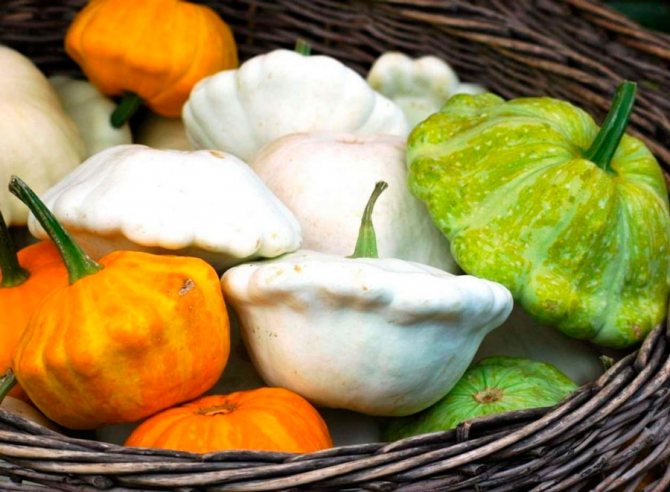


Squash are intended for growing in open soil, and in a greenhouse, as a rule, only their seedlings are grown. If desired, the bushes can also be grown in a greenhouse until ripe, but this is a pointless exercise. Varieties intended for open ground are divided into semi-bush and bush, as well as medium-ripening and early-maturing. The varieties are also divided according to the shape of the fruit and the color of the bark. In their shape, squash are similar to a bowl, plate, disc or bell, while their edges are jagged, wavy and even. As a rule, the fruit bark is greenish or white, but to date, in the course of breeding work, varieties with purple, orange-yellow or dark green bark have appeared.
Varieties of white squash
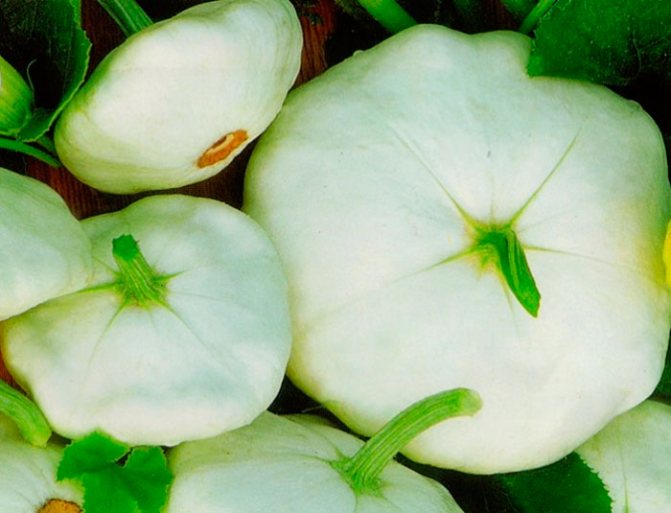


- White 13... This semi-shrub or bush variety of medium ripening has medium size or small, white or greenish fruits with a slightly toothed edge. Rough seeds are yellowish.
- Disk... This early maturing variety is thin-barked. Fruit weight is about 0.35 kg, their flesh is unsweetened and not juicy.
- Loaf... This early maturing variety is fruitful, it needs special growing conditions. Fruit weight is about 270 grams.
- Umbrella... The early ripening variety has a high yield, the weight of the fruits is about 1.5 kg, they are bell-shaped or bowl-shaped.
- Rodeo... This early variety is fruitful. Small fruits have a not too juicy dense pulp with a piquant taste.
- Cheburashka... This early ripening variety is frost-resistant. The mass of thin-barked fruits is about 0.4 kg, their flesh is juicy, they ripen in 35-40 days.
Squash varieties with orange-yellow crust
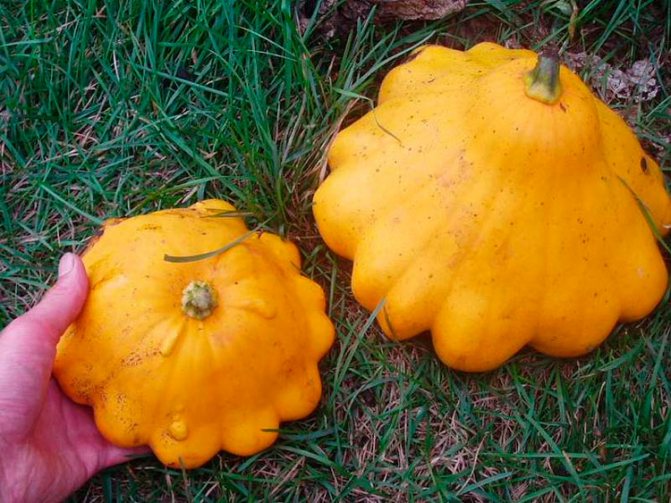


- Tobolinsky... Such a medium-ripening bush variety is disease-resistant. Smooth orange fruits have a plate-like shape and weigh 220-300 grams.
- Sun... The average ripening variety differs in yield, fruit weight is about 0.3 kg. The pulp is cream colored. In young fruits, the bark is colored deep yellow, while at the stage of biological maturity it turns orange.
- Fouette... This early variety keeps very well. The white pulp has a pleasant taste. Fruit weight varies from 0.25 to 0.3 kg.
- UFO... This early-ripening variety, even under unfavorable conditions, has a high germination capacity. The fruits are not too juicy, they weigh about 0.28 kg. The bark and flesh are colored orange. The pulp contains magnesium, iron, and vitamin C in a fairly large amount.
The most popular of all varieties of squash with a purple bark is Bingo-bongo: the ripening period of such an early-ripening variety is about 40 days, the weight of the fruits is about 0.45 kg, their pulp is juicy.
Squash varieties with dark green fruits
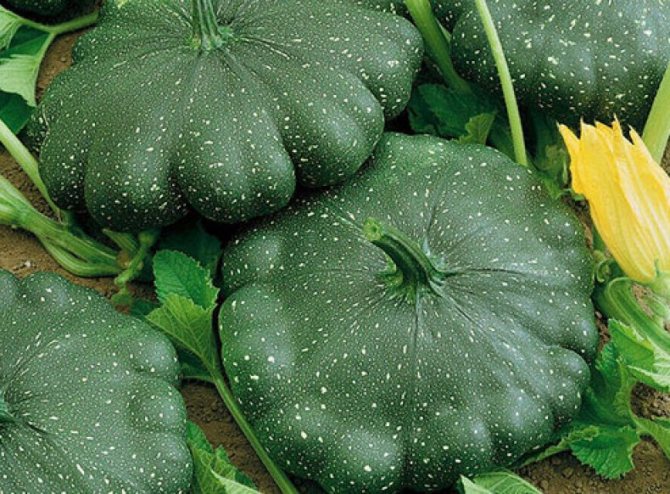


- Gosh... Such an early variety, has a milky pulp and a crust of a dark, almost black color.
- Chunga-Changa... The medium ripening variety is distinguished by its yield. Delicate and juicy fruits have a dark color, their weight is about 0.7 kg.
Patisson penny. Patisson and everything connected with it
Patisson is the closest relative of squash and pumpkin, a delicious, beautiful and rather unpretentious vegetable for growing in gardens and vegetable gardens in Russia, Ukraine and Belarus. But many gardeners have a lot of questions about the cultivation of this crop, the correct selection of varieties and care.
Is the patisson a species or a variety?
The Internet contains a lot of information about the squash plant, but what is true and what is not is difficult to determine. This is a type of common pumpkin. It was from her that the plants inherited the ability to change the color, shape and hardness of the vegetable when fully ripe. The fruit of a bizarre plant that has been lying for too long is extremely difficult to eat, because it is woody.
Since the squash itself is already a variety, it is impossible to talk about the types of vegetables. But you can classify these plants according to their characteristic features. Breeders have provided an opportunity to group varieties in a way that is convenient for a person:
The choice of varieties of squash for the Moscow region
The mild climate of the Moscow region by no means contributes to the rapid growth of thermophilic crops. Taking this fact into account, it is better to grow early maturing varieties and hybrids with indicators of increased cold resistance in the region. The richness of the assortment gives the gardener the opportunity to choose a variety both by color and by ripening time. The best representatives of the species for the Moscow region:
- White: Disc,
- Cheburashka,
- Umbrella,
- UFO white,
- White-13.
- Piglet,
The place of the squash in the culture rotation
Like other pumpkin crops, squash in the culture rotation can return to their old place after five years. The most suitable antecedent vegetables are various types of cabbage, nightshades, including potatoes. You should not engage in planting seedlings and sowing squash on plots of land where related cultures previously grew.
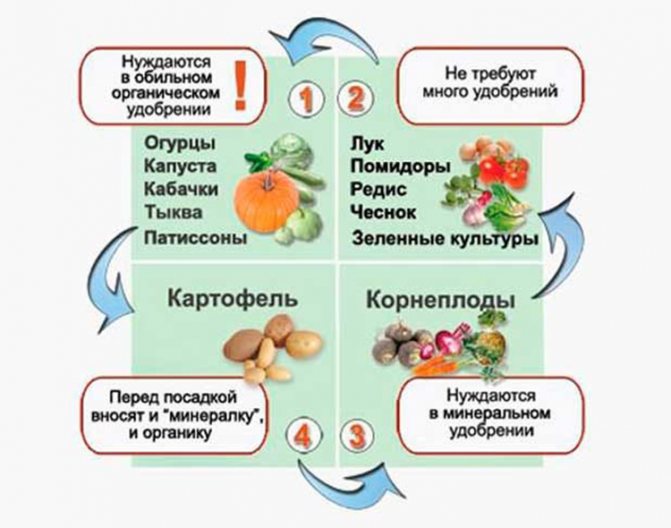

Types of soils and fertilizers for squash
Peat soils... For 1 m², 2 kg of manure humus or compost, 1 bucket of sod land (loamy or clay soil) are applied; scatter 1 teaspoon of superphosphate, potassium sulfate and 2 tbsp.spoons of wood ash. After adding all the components, the bed is dug to a depth of 20-25 cm, 60-70 cm wide, the surface is leveled and watered with a warm (35-40 ° C) solution (2 tablespoons of the Agricola-5 liquid fertilizer are diluted in 10 liters of water), 3 liters per 1 m². Cover the bed with foil to prevent moisture evaporation and to preserve heat.
Clay and light loamy soils... 2-3 kg of peat, humus and sawdust are applied per 1 m². From mineral fertilizers add 1 tablespoon of superphosphate and 2 tbsp. spoons of wood ash.
Sandy soils... For 1 m², 1 bucket of sod land, peat and 3 kg of humus and sawdust are applied. From fertilizers, the same components are applied as on clay soils.
Fertile chernozem soils... For 1 m², add 2 kg of sawdust, 1 tablespoon of powdered superphosphate and 2 tablespoons of wood ash.
Newly developed lands (virgin lands). All roots, wireworm and May beetle larvae must be carefully selected from the soil. In the first year of planting, 2-3 kg of humus or compost are introduced into these soils, and from mineral fertilizers - 1 tablespoon of nitrophoska and 2 tablespoons of wood ash. After the introduction of nutrients, the site is dug up and, as mentioned above for peat soils, it is watered with a nutrient solution "Agricola-5".
After adding nutrients, digging, leveling and compaction, the bed is covered with foil. After 3-5 days, the film is lifted and sowing of squash is started.


A bed of squash. <>
Preparation of squash seeds
To get friendly shoots of squash, it is better to buy seed material in a store or trading companies licensed to sell seeds.
When self-harvesting squash seeds, they must be prepared for sowing:
- Disinfect for 15-20 minutes in a solution of potassium permanganate. Rinse and dry.
- After 2-3 days, to increase germination, treat the seeds in a solution of boric acid (20 mg / 1 l of oxen). Withstand - 24 hours, rinse, dry.
- Before sowing, soak in water so that the seeds of the squash swell or hatch. Dry seeds can also be sown.
Remember! For sowing, only the seeds of squash 2 - 3 years ago are used. The seeds should be well dried. Underdried, raw seeds form male flowers.


Squash, or dish pumpkin.








































