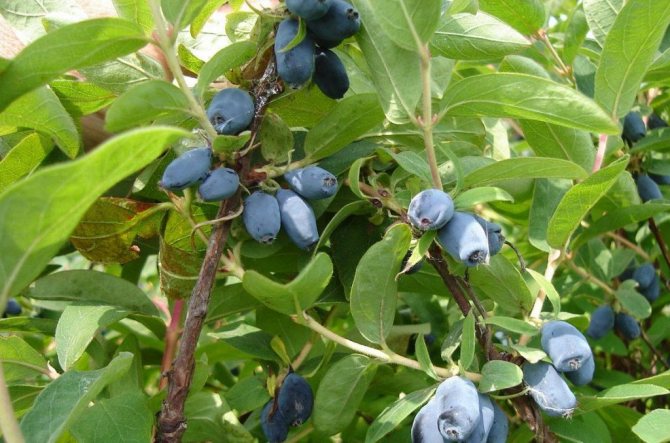
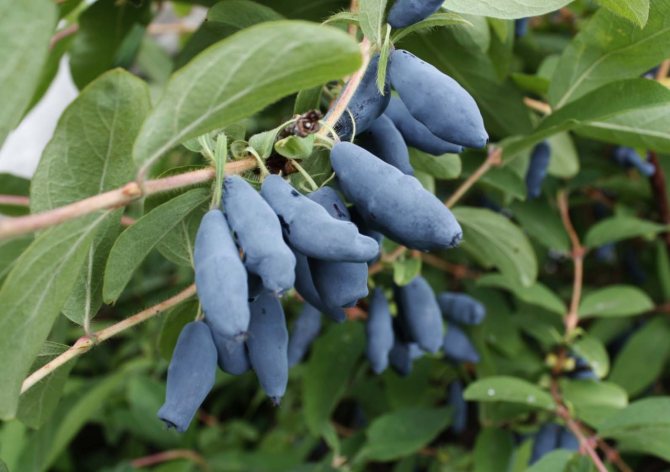
To enjoy the harvest of these wonderful berries, honeysuckle planting and subsequent care must be carried out against a high agricultural background. Those authors are surprised who first say that it is very easy to grow this crop, and then add: only you take seedlings of three varieties, only plant in a damp place, just watch the acidity of the soil, and so on.
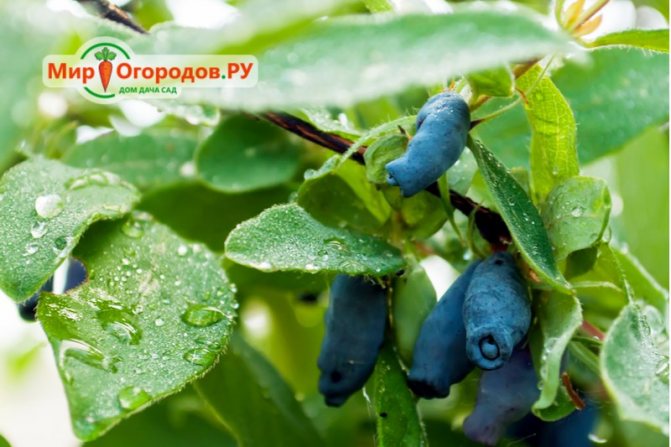

Berries just ask to be in your mouth
Therefore, we decided to tell you how to plant honeysuckle correctly, and how then to take care of it, so that every year in June we have these wonderful fruits rich in vitamins and nutrients.
Autumn or spring planting: which to choose?


In the wild, honeysuckle grows in Siberia and the Far East. It was from such samples that the edible varieties of this shrub were bred by breeders. The plant is not afraid of even the most severe frosts, but reacts poorly to heat and drought. A sudden thaw in winter can destroy the shrub, since immediately after the snow melts, the buds of the plant awaken and the growing season begins. Therefore, it is important to let the honeysuckle grow stronger after planting in order to survive the winter safely.
Pros of spring planting:
- the ability to monitor the development of the plant;
- fast foliage growth;
- a large number of fruit buds.
In the spring, the seedling is placed in the open field from mid-March to the end of April. It is important not to miss the moment when planting is allowed, because if you do this too sooner or later (during the period of swelling of the kidneys), then it will not take root. This is the main disadvantage of spring planting. It is very difficult to calculate the exact timing, so the young plant will hurt and may die.
Benefits of autumn planting:
- high survival rate;
- fast and comfortable rooting;
- hardening (stratification) of the seedling.
There are no drawbacks to this method, so honeysuckle is best planted in the fall. This will allow the young plant to get stronger, and in the spring it will quickly begin to build up the green mass.
Gardeners reviews
Honeysuckle, a low bush with berries, has been growing in my dacha for four years now. When I was buying it, they explained to me that I needed to buy in a pair, and I did that. Honeysuckle berries appeared in the second year. The harvest is getting bigger every year.
Tamrico
In general, earlier in childhood we collected honeysuckle in the forest. Forest - they are strongly sour. And as a child, I didn't really like them, although the jam even then turned out to be delicious. We currently have honeysuckle bushes in our garden. They begin to bloom in early spring. And honeysuckle is the very first shrub, which already at the end of May or at the beginning of June pleases us with its berries. You can read about the benefits and dangers of honeysuckle on the Internet. It is necessary, of course, to take care of the bushes a little. It has never been before that there were no berries on the bushes. The size, flavor and shape of the berries are very dependent on the variety of these bushes. We have 4 species growing. First grade - Amphora, 2 - Blue Spindle, 3 - Pavlovsky and 4 unknown grade. They just didn't remember. We bought sprouts at the market in the spring. And they were all bought and planted at different times. Some bushes are already 8-9 years old, some 2-3 years old. The bushes are mainly located next to the pines. And the pines protect them well from the wind. Although, they probably lack the sun. But, despite this, they bear fruit well.
Ilkasimov
Many years ago, we bought two bushes of a berry that we had never seen before, planted it and waited impatiently for the harvest, but ... The berry tasted bitter, it was impossible to eat it. In general, we got disappointed. The bushes from the garden were transplanted into the front garden. And surprisingly, the birds liked the taste, they eagerly pecked the berries. Well, well, at least someone will benefit from it. In the front garden, it grows and pleases the birds to this day.
IrinS
Honeysuckle is rightfully considered one of the most useful berries, you can make wonderful jams, jams, compotes from it. Berries are eaten fresh, frozen for the winter, ground with sugar. When planting, be sure to take into account the peculiarity of honeysuckle to bear fruit only when cross-pollinated with other varieties of this plant and plant at least three bushes.
Planting dates for honeysuckle in autumn


The timing of planting honeysuckle in the fall can vary from mid-September to mid-October, but it is worth considering the peculiarities of the climate in certain regions of the Russian Federation.
| Region | Timing |
| The middle band of the Russian Federation | Until September 15 |
| Moscow and Moscow region | First decade of September |
| Leningrad region. | September 15-18 |
| South of Russia | Until October 15 |
| Siberia and the Urals | Planting in autumn is undesirable, it is better to plant in spring |
In the southern regions, it is not easy to get a good harvest of honeysuckle due to the inappropriate climate. The plant bears fruit only after 2 years, and there are very few berries on it.
The best days for planting in the fall of 2019:
- 1, 5-6, 18-19 and 27-29 September,
- October 1, 3, 5, 10.
Recommended dates depending on the region
- In the middle lane, Moscow region, the period of planting honeysuckle falls in mid-September.
- You can plant in the south until the end of October - mid-November.
- Gardeners of the Leningrad Region carry out planting work from early to mid-September.
- In the most severe climate in the Urals and Siberia, the planting period lasts from the first days of September to the first ten days of October. In the northern regions they are planted a little earlier, and in the southern parts a couple of weeks later.
Good to know. Having missed the moment and planting the berry bush too late, he will not have time to take root in a new place and may die in a harsh winter.
How to choose quality seedlings and a place for a plant
The key to the health and fertility of a plant is a properly selected seedling and a good place. Check out our tips for choosing a cutting and planting site.
The choice of planting material
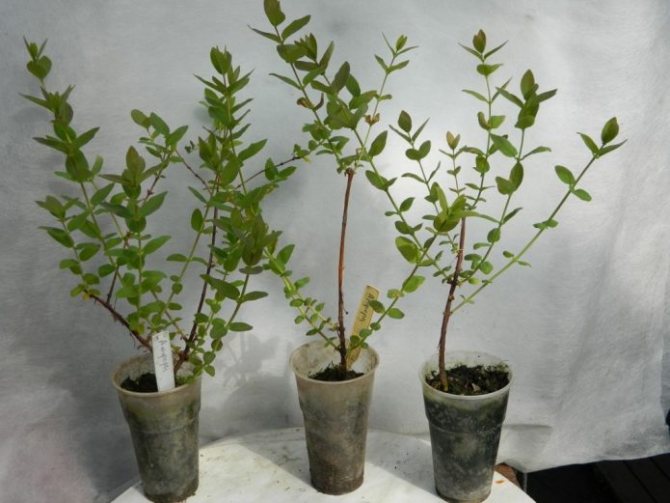


It is necessary to purchase edible honeysuckle seedlings only in specialized stores with a good reputation. You should not buy planting material from hands, from unknown sellers. When choosing a seedling, it is imperative to clarify that only edible varieties are needed, not decorative ones. It is better to purchase a biennial plant, with several trunks, about 40 cm high, with a well-developed root system. Too high or low seedlings, weakened, with traces of damage are not suitable for purchase.
Choosing a place for planting
Honeysuckle is an unpretentious culture, but the right choice of a site for planting is of great importance. It will grow best in fertile soil with a neutral pH. It is necessary to place the bush so that its top is always in the sun, and the root part is in the shade. This can be achieved by planting low-growing plants and flowers next to the seedling.
Do not plant honeysuckle on hills and hills, in shady places and areas with poor sandy soil. Lowlands with surface groundwater are also not suitable. The ideal planting site should be well lit, protected from winds and drafts.
Neighbors for honeysuckle
Honeysuckle is rarely damaged by various pests, so it can be planted next to other shrubs, but it especially likes the neighborhood with black currants.In the near-stem circle, you should also not plant any plants, since the root system of honeysuckle is superficial.
Recent Entries
Rose Petal Jam and Its 7 Health Benefits You Likely Didn't Know About What Fruit Are You According to the Zodiac Sign 11 Best Grape Varieties That Will Help You Create Unique Homemade Wine
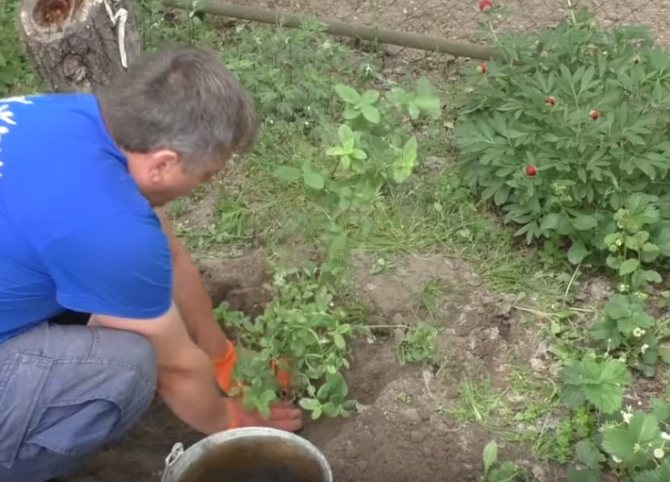
Step-by-step planting instructions
In order for the plant to overwinter painlessly, you need to responsibly approach the planting process, which consists of several stages.
Well and soil preparation
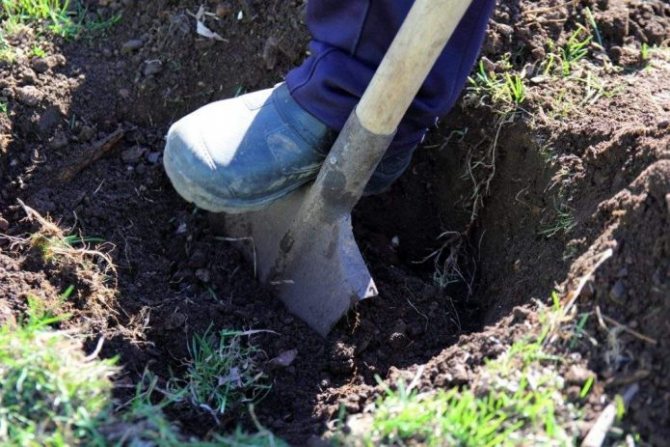


To get started, carefully prepare a place for planting a honeysuckle cutting:
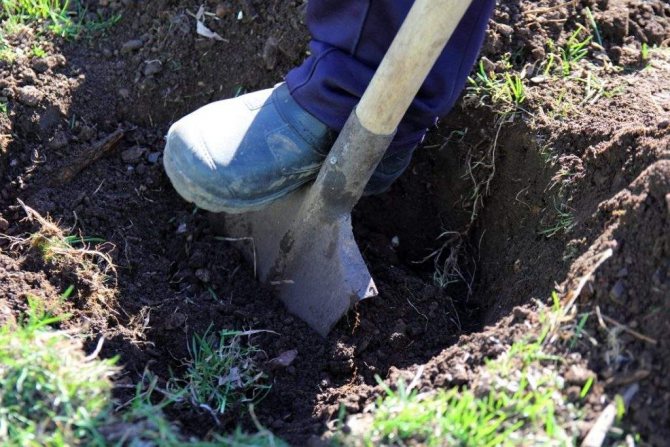
- Dig the planting holes in 7-10 days. Clear the area of weeds and debris.
- For each seedling, prepare a hole 40 cm deep and about half a meter wide. The distance between them should be at least 2 m, and between the rows - 2.5–3 m.
- Lay the top fertile soil layer separately, and put 10-15 cm of drainage on the bottom of the hole.
- Mix the removed upper part of the soil with humus (10 kg), superphosphate (150 g) and potassium salt (150 g). Fill the hole with the resulting mixture by 2/3 of the volume, and place a little black soil on top.
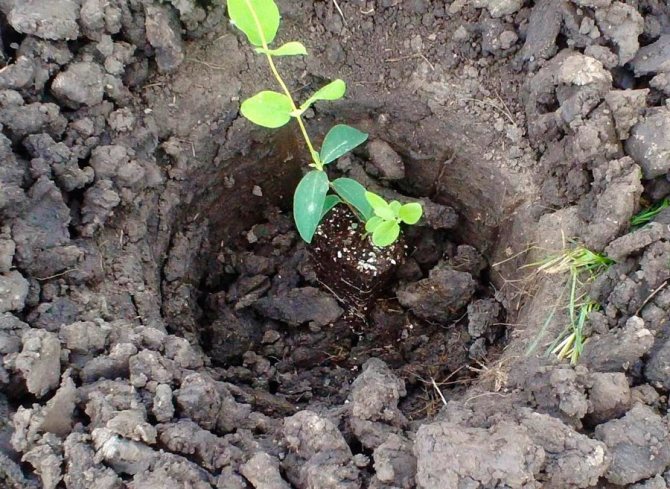
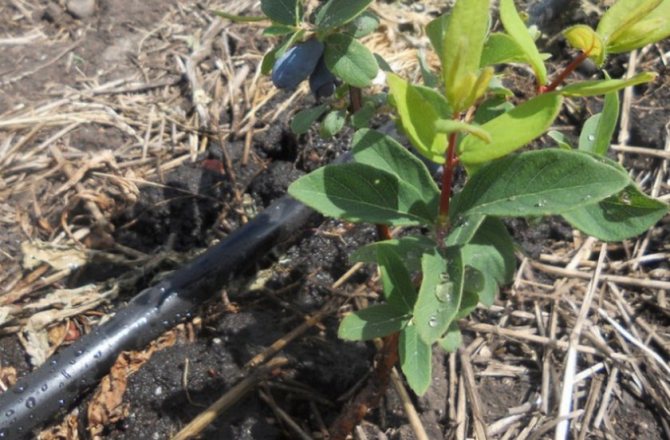
Planting guide with photo and diagram
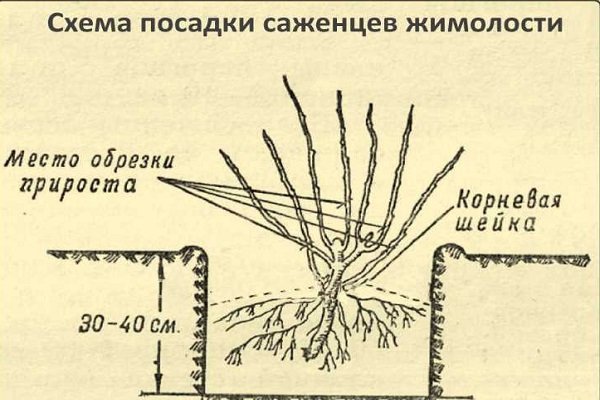

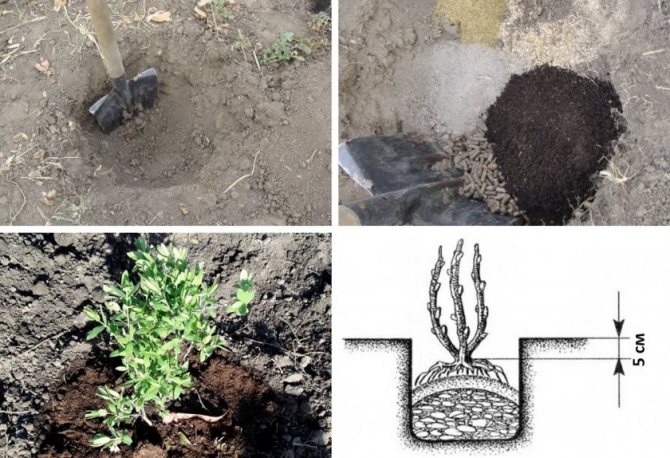
After the preparation of the site has been carried out, and the soil has settled, you can start planting:
Honeysuckle transplant in July. Transplant process
A summer honeysuckle transplant is a simple exercise. But, despite this, it is worth preparing for it. The first thing to do is to find the optimal place for planting the bush. The location of the lower branches in partial shade is considered ideal, and the upper ones under the open sun. On such a site, it is possible to collect the maximum possible yield.


You should also take into account the structure of the soil. Honeysuckle, undemanding to the composition of the soil, the transplant of an adult bush of which is performed, nevertheless prefers light and nutritious loam without stagnant water at the root system. Laying a drainage layer: sand, expanded clay, broken brick or ceramics will help prevent the adverse effects of groundwater.


The neighborhood with other plants is also taken into account. Mature trees should be at least 1 meter away from the seedling.
The process of transplanting adult honeysuckle is as follows:
- Prune mature shrubs. Remove dry and damaged branches. Young specimens should not be shortened.
- Dig a hole 45 cm deep.If the soil is too heavy, dig a hole no more than 30 cm deep.
- Lay drainage.
- Add nutrients. It is best to use wood ash, as manure can burn the root system.
- Dig out the planting material, keeping an earthen lump near the roots, being careful not to injure them.
- Place the bush in the hole by straightening the roots.
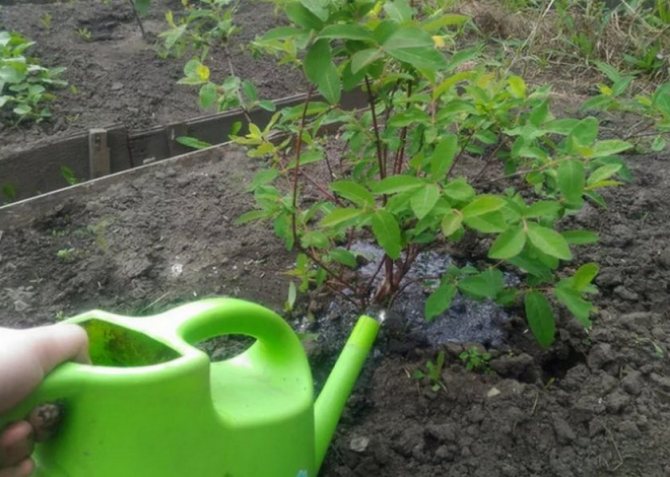
- Cover with soil, lightly tamp, make a side in diameter and water abundantly.


It is very important to mulch the soil surface using sawdust, dry grass or hay.
Advice! The root collar of the “new” specimen should be flush with the soil.
Secrets of a generous harvest of honeysuckle: video
Planting and caring for honeysuckle will not be difficult for a novice gardener. With proper planting, the culture will bear fruit the next year. The main thing is to choose a good place and time for planting, buy a good healthy seedling and properly care for the plant.


Planting honeysuckle in the fall carried out in all regions of Russia, if the desire is ripe to acquire a fruiting bush. In addition to honeysuckle, which bears fruit, there are ornamental shrubs. Experts advise planting seedlings in the first month of autumn and until mid-October.
Honeysuckle belongs to the genus of shrubs, among which there are climbing species. The plant is able to survive in severe frosts and at the same time produce a large harvest of berries. In addition, in one place it can grow for many years.
The use of honeysuckle in medicine and garden design
This option of sowing honeysuckle seeds is also possible. Spread the thinnest toilet paper over the soil and evenly pour the seed mixture on it. Seeds are easier to spot on paper and easier to spread more evenly over light colored paper (with a dry stick or finger).
In many varieties of honeysuckle, the berries are slightly bitter, which is a feature of this plant. But children, oddly enough, love these bitter berries ...
Curly Tatar honeysuckle and its other varieties are considered quite susceptible to diseases and pests. Nevertheless, even if proper care was carried out, it is impossible to be completely sure that such an attack will not touch them. This garden shrub in spring, autumn and other times of the year can strike:
Valuable properties of honeysuckle
The main advantage of this plant is that it begins to bear fruit in early summer. In June, you can already enjoy delicious berries and replenish your body with vitamins and microelements. Honeysuckle in its composition contains a lot of useful substances, thanks to which it is used for the preparation of medicines.
The medicinal properties of the fruit are used for cardiovascular diseases, vitamin deficiency, to normalize blood pressure. Honeysuckle is recommended for people who live in areas with radiation contamination. There is a huge list of characteristics of medicinal berries.
- This plant is able to survive at an air temperature of around -50 ° C.
- The root and flower buds can withstand frosts down to -40 ° C.
- When the plant releases its first shoots, the air temperature of -8 ° C will not interfere with their development. Therefore, honeysuckle began to be boldly grown not only in outskirts of Moscow and in middle lane Russia, but also in gardens Siberia.
Important! Climbing bushes prefer a warmer climate.
If a plant is properly cared for, it can bear fruit for nearly 20 years. Moreover, honeysuckle is resistant to various harmful insects.
Honeysuckle transplant in spring. When and how you can transplant honeysuckle: rules and terms


Honeysuckle is a fruit shrub with excellent taste of berries, endowed with medicinal properties. But a certain disadvantage of some varieties of this culture is its strong growth. Because of this, the plant has to be transplanted to another place, but this must be done correctly, otherwise you can lose a good harvest.
Transplant timing
The main mistakes inexperienced gardeners make is placing honeysuckle in swampy or shaded areas, where it does not have enough sunlight, and humidity can cause diseases. This can greatly slow down the growth of the culture, the development of its root system, which will lead to inhibition of the appearance of the aboveground green mass and the subsequent flowering. All these factors affect the fruiting of the plant, that is, the quality and quantity of the crop. And then it is necessary to transplant the bush to a new place.
Another problem is planting bushes too close next to each other or other adjacent garden trees. At the same time, honeysuckle bushes can grow up to one and a half meters in width, which is also unacceptable and requires a transplant. In this regard, the question of when to transplant becomes especially important.
It is known that honeysuckle buds wake up very quickly in spring - any short-term thaw can wake up this process. Even if it freezes during night frosts, the buds begin to bloom again after a while, this happens several times without harm to the culture.
Bearing in mind that the first fruits appear already at the end of May, it is clear why it is better not to touch the plants at this moment - there is always a threat of damage to the roots and branches.
In addition, it is inconvenient to carry out transplanting work before the awakening and sap flow of honeysuckle, because at this time there is still snow in the garden.In summer, in August, the annual life cycle of the plant slows down until it hibernates. It turns out that in the fall, in the middle or at the end of September, the most favorable moment for transplantation and circumcision comes.
Transplanting is possible only for young plants up to five years of age; later, it is not recommended to transfer old bushes to another place, this will destroy them.
The plant can instantly shed foliage and get sick. In the most extreme cases, a summer transplant of young shoots is possible - in June after the harvest has already been harvested. But this will be associated with additional watering, mulching of the trunk circle and mandatory shading.
How to choose seedlings
Experienced gardeners recommend choosing seedlings in the fall. Various varieties of honeysuckle can be picked up in the markets at this time of year. It is important that there are still leaves on the branches, thanks to which one can judge the state of the bush. In addition, the root of the dug plant practically does not waste energy on rooting.
Sapling purchase rules:
- To plant quality in the garden edible a type of honeysuckle, it is best to buy seedlings from garden organizations or from reputable suppliers. This eliminates the risk of acquiring re-grading or decorative culture.
- It is worth choosing seedlings 2-3 years old, and preferably 3 years old.
- For pollination to be successful, you should choose 3 varieties of honeysuckle for planting, which will bloom at the same time.
- The trunk and 2-4 branches should be healthy and free from defects, the buds are whole and dense, the leaves are clean and well developed.
- The roots must be strong, free from rot and signs of disease.
- In the fall, open-rooted seedlings can be planted without soil, which is not allowed in the spring. But it is better to buy a bush with closed root system.
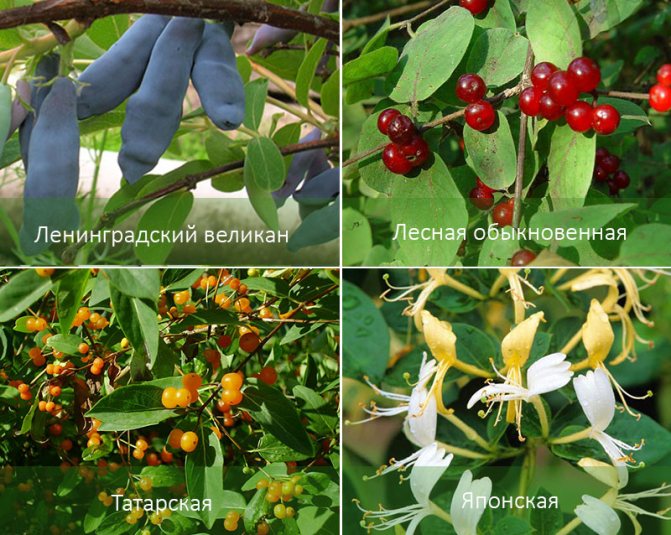
In the regions of Russia, you can grow the following varieties of honeysuckle:
- Altair;
- Cinderella;
- Moraine;
- Blue bird;
- Bakchar giant.
- Leningrad giant;
- Blue spindle;
- Long-fruited;
- Nymph;
- Tomichka.
Popular types and varieties of garden honeysuckle
More than a hundred species of honeysuckle and even more varieties are known. In most species, the fruits are inedible and sometimes poisonous. One of the most famous representatives of the latter is the wolfberry, which is found in abundance in the forests of the middle zone.
In our country, about 20 species of honeysuckle grow, in cultural plantings - no more than a dozen.
Distinguish between curly honeysuckle and shrub. Curly (honeysuckle, Brown's honeysuckle, etc.) is used to decorate walls, gazebos, buildings, etc. So, in honeysuckle, branches can grow up to 5-6 meters, braid any support. Shrub honeysuckle can be edible or inedible. Edible is the so-called blue honeysuckle (or blue), which has many subspecies and varieties.


Ornamental honeysuckle is grown for its beautiful flowers and leaves
There are a lot of varieties of edible honeysuckle: even in the State Register of the Russian Federation there are more than a hundred of them. The most popular are the following.
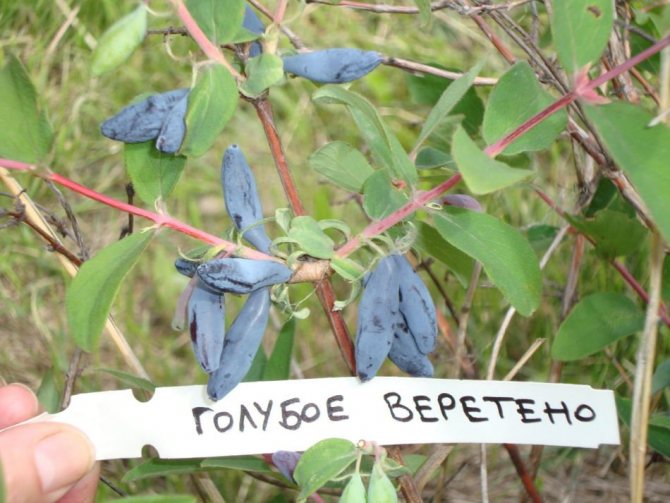
- The blue spindle is an early ripening variety, considered by many gardeners to be one of the best. True, it is noted that with a lack of watering, the berries are very bitter, and this variety is considered one of the most moisture-loving. Blue Spindle berries, like many other varieties, are rather weak on the bushes.


The blue spindle is one of the most popular varieties
- Cinderella is a variety characterized by high disease resistance and resistance to spring frosts, its berries have a strawberry aroma. Fast-growing. The bushes of this honeysuckle are lower than the gooseberry or currant bushes, which is convenient for harvesting.
- The Leningrad giant is a large-fruited variety, but its berries ripen unevenly. However, some gardeners consider this one of the advantages of the variety. Fruiting is extended, the harvest lasts for a month.The flowers of the Leningrad giant can withstand frosts down to -7 ° C, it can be grown in harsh climatic regions.
- Morena is a medium early variety, with large berries of a dessert taste. This honeysuckle almost does not get sick, the berries do not crumble for a long time. Frost resistance is very high, which allows you to grow Morena everywhere.


Morena has delicious berries
- Nymph is a variety for very difficult climatic conditions. Berries do not crumble from young bushes for a long time, but they do not hold well on old ones. The fruits are sweet-sour, aromatic.
- The blue bird is an unpretentious variety, the bushes are quite tall, the berries taste like blueberries. The bluebird never freezes and is rarely infested with pests.
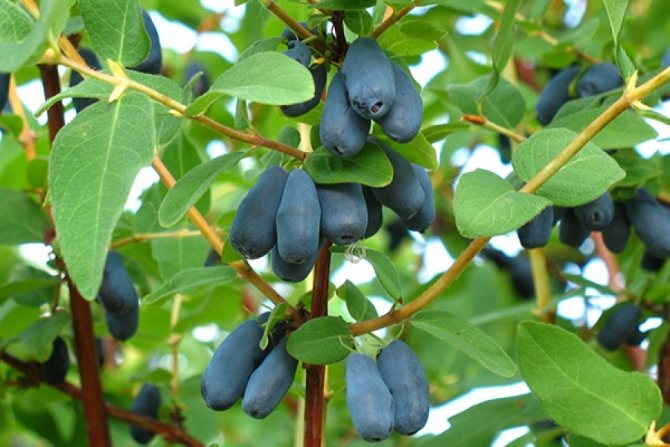


Honeysuckle Bluebird is one of the most hassle-free
- Malvina is a very high-yielding variety, which is due, among other things, to the size of the berries. They have a dessert taste, do not crumble for a long time. There are almost no berries without pollinators, but an additional bush of the same variety sharply increases productivity.
Soil preparation
Before planting seedlings, the soil should be properly prepared, since the plant will grow in this place for more than 25 years:
- Previously, 5 days before landing, a hole is prepared. Its dimensions will be as follows: diameter - 40 cm, depth 25 - 40 cm.
- Compost or humus is poured into the hole - about 12 kg, double superphosphate and potassium salt - 150-200 g each. Instead of the last two minerals, you can add the following fertilizers: nitrophoska about 400 g or Ammophos - 350 g.
Advice! If top dressing is introduced, which does not contain potassium, then wood ash can be added: 0.5 kg per bush.
- Mix all fertilizers introduced into the pit with the ground and water well.
- Cover the well with the mixture and let it brew for 4 days.
Dividing the honeysuckle bush. Dividing the bush
It is very easy to propagate honeysuckle by dividing the bush. You can use this method if there are young honeysuckle bushes in the garden. To do this, you need to dig up a healthy bush not older than 5 years in early spring or in September, using a pruner, divide it into several parts along with the roots and plant the formed bushes in a new place. A disinfectant solution must be used to treat the cut sites.
The early bird - edible honeysuckle - begins the berry season and delights gardeners with the first blue berries at the very end of spring or early summer. Its berries are rich in vitamins and minerals, they strengthen the walls of blood vessels, stabilize blood pressure and help to strengthen the immune system.
If honeysuckle bushes have been growing on your site for a long time, isn't it time to think about changing? Still, over time, even the most "prolific" bushes grow decrepit and the number of berries from year to year gives less and less. And if you are not yet growing this wonderful berry, maybe it's time to start? Honeysuckle is planted with seeds, cuttings, and layering. It is unprofitable to propagate by seeds - honeysuckle loses all varietal properties. Therefore, most often gardeners resort to vegetative reproduction.
This method of breeding honeysuckle is the easiest. It is similar to the propagation of gooseberry bushes. To get layering, in June, the soil around the bushes is dug up and slightly "raised". Then they select several strong annual branches from the lower tier of the bush, pin them to the ground using a U-shaped wire and sprinkle them with soil 3-5 centimeters.
In this form, the child branches remain until next spring. During this time, they should take root, and then you can use a pruner to separate them from the mother plant and transplant them to the right place. After two years, each “daughter” will turn into a full-fledged honeysuckle bush.
There is only one drawback to the reproduction of honeysuckle by layering: it is not suitable for all varieties. Some bushes simply do not have lower annual branches. You have to use green or woody cuttings or propagate the honeysuckle by dividing the bush.
Landing
It's important to know, when and how to plant honeysuckle, since the correct development of the plant depends on it.Before planting, the bush should be checked so that there are no bad twigs on it. They need to be cut, and long root shoots are cut to 30 cm.
- The best age for seedlings is 3 years. During this period, their root system develops well.
- You need to plant up to 4 types of honeysuckle at the same time to achieve full pollination.
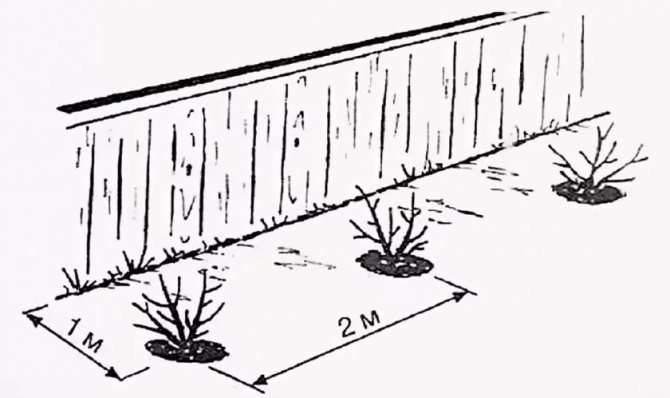
- We distribute the seedlings at a distance of 1.5 m from each other.
- We put the root of the plant in the hole so that its root collar is level with the site. Also, you can lower it 2 cm below the ground.
- We fill the pit with the seedling with soil and pour in a bucket of water.
- The upper part of the soil must be mulched. For this, humus or peat is used.
Important! When planting a large number of seedlings, it is necessary to maintain a distance of approximately 1 m between them, and 2.5 m between rows.
Transplanting honeysuckle to a new location
If for some reason it is necessary to transplant a honeysuckle bush to a new place, it is easy to do this only in the case of young bushes: after the age of five, failure is very possible. If the young plant is transplanted correctly, avoiding serious damage, then it will not hurt for long and will again continue active growth and fruiting.
When to transplant honeysuckle
Honeysuckle is transplanted exclusively in autumn: best of all - in the first half of September, but no later than mid-October. Spring transplantation is possible, but very difficult and can even lead to the death of the bush. By the time it is possible to work in the garden, when the ground thaws, the honeysuckle has already begun a period of active sap flow, and without disrupting some of the branches and roots, it will still not be possible to transplant. This means that in the spring, when transplanting, the plant will lose a lot of strength, which should not be allowed.
Video: timing of honeysuckle transplant
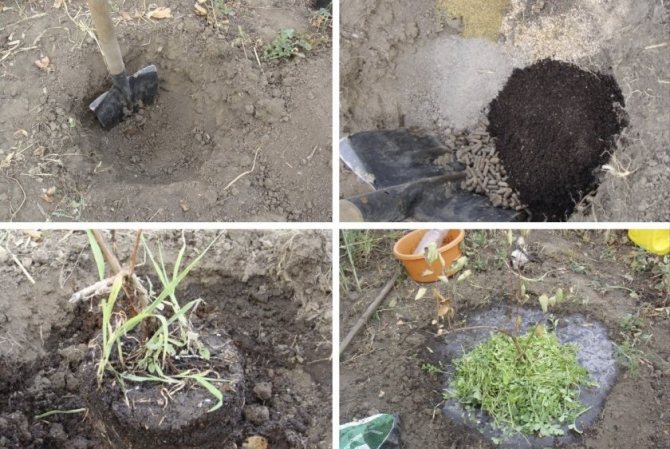
Planting pit preparation
A new hole should be dug larger than when planting young plants. The minimum dimensions are 70 cm both in depth and in diameter. The pit should contain drainage and nutrient soil with an increased amount of both organic and mineral fertilizers. Humus, superphosphate, and ash are needed, about twice as much as with a normal planting.
Preparing a bush for transplanting
Before digging the bush, it is necessary to cut off all dry, broken and obviously unnecessary branches, and shorten the ones left by about a third. It is desirable that in the end the height of the bush was no more than 50 cm. The bush is dug out very carefully, starting to dig a circular trench about half a meter from the base of the bush. The task is to remove the bush along with the earthy clod without damaging the roots. This means that the bush must first be watered well. After digging in, carefully remove the bush onto a tarp. Roots protruding beyond the soil clod can be trimmed.
When planting a bush in a new place, you must try so that the roots are not broken or strongly bent, but take the same position that they had in the old place. The root collar is also left at the same level as in the old pit. The voids are covered with fertile soil and the bush is watered very well. Be sure to mulch.
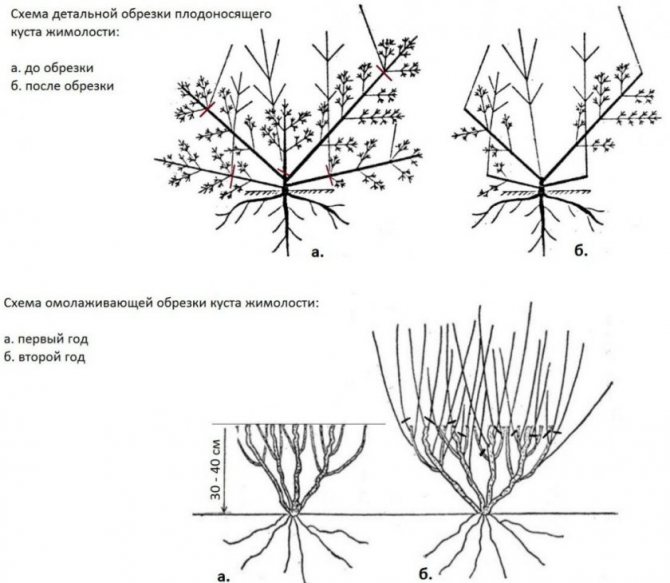
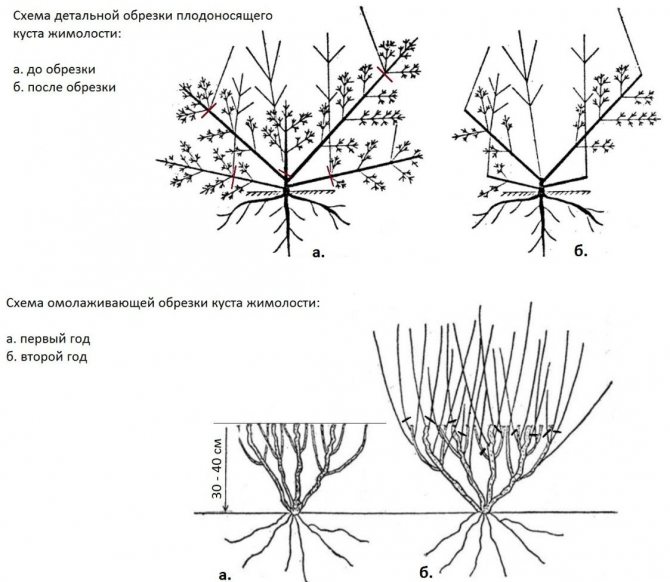
Pruning in the fall
After planting, the honeysuckle branches do not need to be pruned for 2 years. Next, you need to act according to the circumstances. There are cases when a plant undergoes cultivation at the 8th year of life. The best time for pruning is autumn.
All dry and damaged branches are removed from the bush. For better air circulation, pruning inside the bush is recommended. It is important to remember that berries mainly grow on annual branches. They should not be cut off, but the tips of new shoots should be cut off.
Important! The old bush must be cleaned of perennial branches, and it is better to leave young shoots.
Any variety of honeysuckle develops slowly for the first 3-4 years. In the 4th year of life, many shrubs can reach about 70-80 cm in height with a crown span of 1 meter. If the planting of honeysuckle was carried out according to all the rules, then from 4-5 years old it begins to bear fruit in full force.
Watch the video! Pruning honeysuckle
Honeysuckle is an attractive, fast-growing perennial plant, usually propagating by cuttings or cuttings. Planting is an important step in growing it, since the growth and flowering of the plant will depend on the right place. Honeysuckle is best planted in the fall, although it can also be planted in the spring.
Honeysuckle harvesting
With green cuttings of honeysuckle, cuttings should be taken immediately after the first collection of berries. The soil is made from sand and peat. A prerequisite is high soil and air humidity and a temperature of about + 25C. Honeysuckle cuttings can first be put in water for rooting, but there is a trick: there should be no more than 3-4 cuttings in 200 ml of water, otherwise they will not take root.
Early varieties of honeysuckle - June 12-18: Morena, Viola, Long-fruited.
Preparing a landing site
Honeysuckle grows in most climatic conditions, but especially appreciates sunny, slightly shaded, not too hot places... Shady areas should be avoided, as the lower part of the vine can become significantly bald, and flowering can be weak or even stop altogether.


Saplings are planted quite far apart for good growth and ventilation. If you plant the bushes close, they will not get enough air circulation. This can lead to mold and mildew growth.
Calculating the distance between plants
For shrubs or climbing varieties, the correct distance is 1.5 to 4.5 m. There is no need to be afraid of such a long distance, because in one place the plant can perfectly live and please the owners up to 25 years. In addition, one must proceed from the extent to which this or that variety grows. There are varieties that, when ideal conditions are created, can reach, over time, up to 8 m in height, with growth in width up to 3 m.

Soil and pit preparation
Land for planting may not be very fertile, as honeysuckle refers to plants that do not draw nutrients from the soil too much. However, if the soil on the site is clay, then it must be mixed with sand and small pebbles.
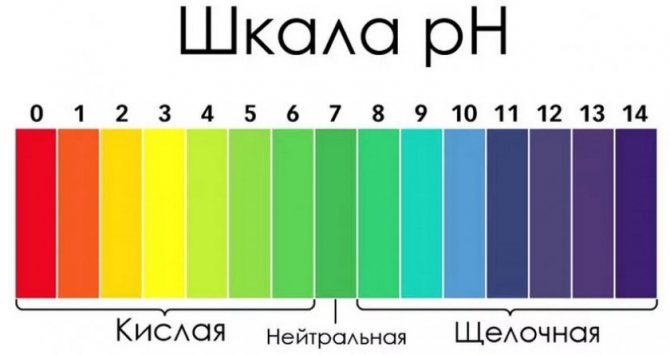

Honeysuckle loves a fairly neutral pH; the soil should not be acidic or too alkaline. The pH should be kept between 6.1 and 7.8.
Reproduction of honeysuckle
The basic breeding methods are similar to those for other shrubs.
Sowing with seeds
Seed propagation is difficult and the result is often unpredictable. Seeds are extracted from ripe berries, washed, sown in a garden bed, some of them will sprout. More often, sowing is carried out in boxes and honeysuckle is grown like seedlings of vegetable crops. Seedlings grow very slowly in boxes. Sowing is carried out in the summer, and for the winter the boxes are taken out into the street, covered with spruce branches. After the seedlings grow up to 7–8 cm, they are transplanted into a garden bed. They are planted in a permanent place at least a year later.
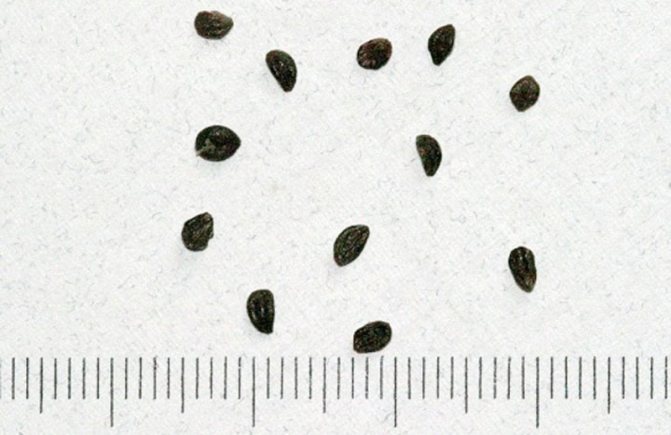


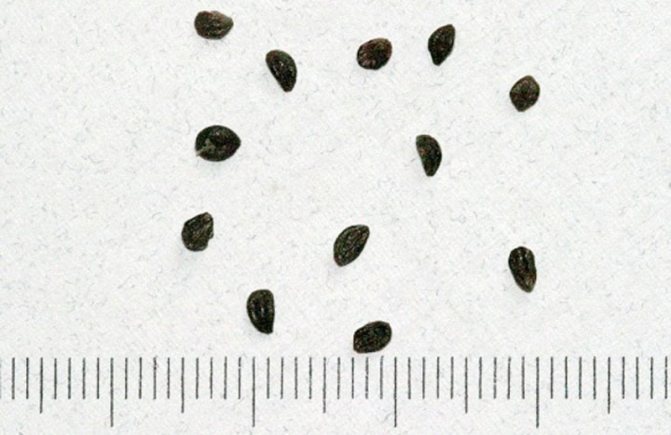
Honeysuckle seeds are quite small
Planting by cuttings
Propagation by cuttings is a common method of propagation for many shrubs, including honeysuckle. It is propagated by green or lignified cuttings. The easiest way is to use lignified ones.
- In early spring, cuttings about 20 cm long and 6–8 mm thick are cut from strong shoots.


Cuttings are cut from strong shoots
- Cuttings are inserted into the soil obliquely at half the height: one bud should be at the soil surface, one above it.
- Cover the cuttings with plastic bags or glass jars, sometimes removing them for airing.
- They keep the soil moist: after about a month, the cuttings give roots.
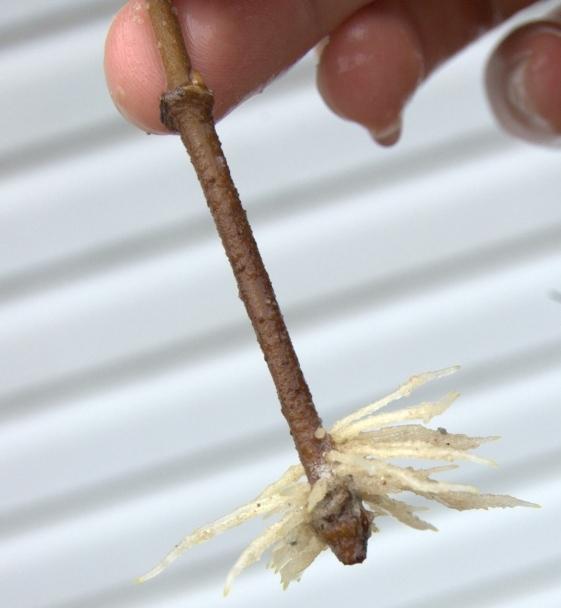


The roots grow pretty strong
- Already in the fall, young seedlings can be planted.
From green cuttings, it is guaranteed to get seedlings only in greenhouses, creating high air humidity there.
Reproduction by layering
Reproduction by layering is quite simple.In early June, powerful shoots that grow from the edge of the bush should be bent to the ground and pinned into a groove (3-4 cm below the soil surface). The crown of the shoot is taken out. They water the shoots well and mulch the soil. The cuttings are watered all summer long. A new bush may appear from each buried bud, and next spring they are ready for transplantation. The cuttings are cut into pieces, after digging them up, and small seedlings are immediately planted.
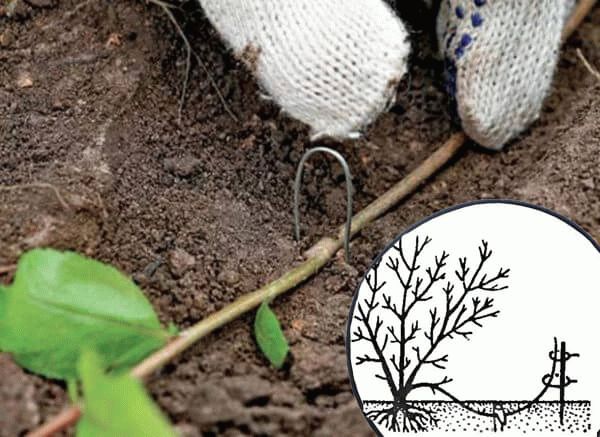


Layers are made in the same way as for currants.
Sapling selection
Honeysuckle bushes can grow from 2.5 to 8 m in height. If there is a desire to ennoble a fence or a wall of a house with a hedge, then you need to buy tall varieties of seedlings. If there is a need to steal a flower bed, then you can purchase undersized varieties.
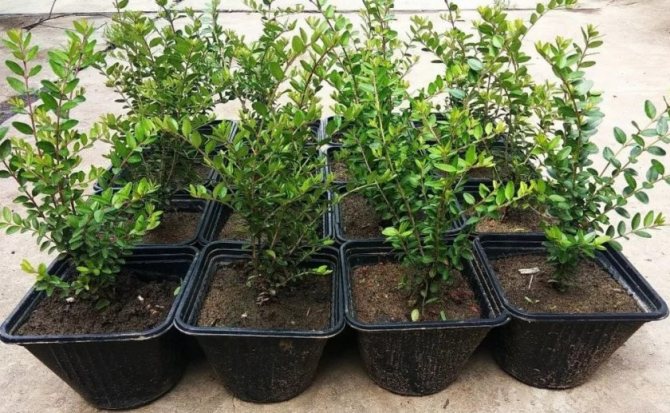
In container
Seedlings with a closed root system are sold in containers. They can be planted both in spring and autumn. Plants thrive better with a protected root system. During the first year, honeysuckle should be watered regularly.


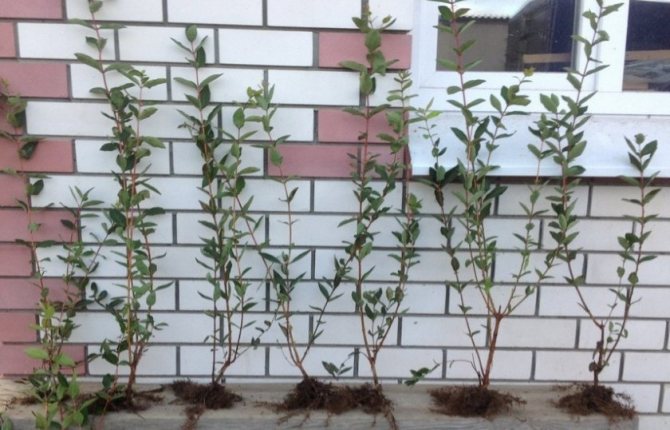
With an open root system
Open-root seedlings are often sold at themed garden exhibitions and nurseries.
When choosing such a seedling, you should pay attention to the following:
- age - it is better that these are seedlings of 2-3 years old with 2-3 increments;
- the height of the shoots - they should be from 30 to 65 cm;
- the appearance of the shoots - they should not be dry, of a healthy color, without cracking and damage, flexible, peeling on the bark is allowed;
- the state of the root system - it must be developed, with a certain number of buds.


Honeysuckle is cross-pollinated, so you can safely purchase several different varieties at once.
The maximum amount of information about the acquired variety will create a complete picture of the plant and its further care:
- the exact name of the variety to determine the edibility or inedibility of the fruit, the possibilities of cultivation (bush or liana);
- flower color;
- taste of edible fruit;
- yield from the 1st bush and the period of onset of fruiting.
How to care for honeysuckle to bear fruit?
Rodionov Sergey
For rooting cuttings, prepare a soil mixture: peat and sand (in a ratio of 1: 3). Plant the cuttings at an angle of 45 °, placing them according to a 7 × 5 cm pattern. A prerequisite for rooting is a high humidity of the substrate and air (up to 85%) at a temperature of 20-25 ° С.
Gulnaz Aglieva
Every spring, you can feed the honeysuckle bushes with nitrogen fertilizers, but in the fall - only with phosphorus and potash. The harvest from seedlings takes up to 5. Honeysuckle reproduces in several ways: by seeds and vegetatively. I will give advice on seed reproduction of honeysuckle.scale - the bush affected by it looks lifeless and dries quickly; At the end of fruiting of its edible variety, it is recommended to cut the faded shoot in half and process it with a Bordeaux mixture. Such care will prevent the appearance of fungal infection on the bushes in the fall.As an autumn feeding for honeysuckle, it is better to use organic fertilizer - humus or mature compost. At the same time, you only need to make such dressings once every three or four years.Since honeysuckle develops very slowly, it is better not to show excessive zeal. It is correct not to cut the plant for three or four years at all. If the bush has an irregular shape, then it is better to prune branches from the ground.If you are going to transplant honeysuckle in the fall, work should be done as follows: If you decide to buy bushes, then when buying edible honeysuckle "off hand" be careful , since in nature there is also decorative honeysuckle, the fruits of which are poisonous! Medium early varieties of honeysuckle - June 15-22: "Gerda", "Cinderella", "Blue Bird." Blue honeysuckle is easy to propagate by seeds. It is best to sow seeds in March - April in wooden boxes or flower pots.To do this, prepare light fertile soil, consisting of equal parts of humus, peat and river sand. Sow seeds superficially, sprinkle with sand on top (1 cm) and cover with glass or transparent film. For successful germination, maintain a temperature of 20-24 ° C, and moisten the soil regularly. Water should be done carefully, adjusting the pressure of the jet so that it does not wash out the seeds. Seedlings appear in 30-35 days.
***
It is desirable to form honeysuckle bushes, then they will be beautiful and more productive. I carry out the first pruning of young bushes immediately after planting honeysuckle seedlings in a permanent place. It is necessary to cut out all weak shoots, leaving 3-5 strong shoots on the bush and shortening them by a third of the length. In the future, during the first 5-6 years of growing honeysuckle, it is enough only to cut dry and broken branches. At the age of 7 years and older, honeysuckle bushes reduce fruiting - you need to thin out the crown every 2-3 years, cutting out aging 5-6-year-old branches from the plant. When propagated by seeds, honeysuckle, like most fruit and ornamental crops, does not retain varietal properties.If you received dry honeysuckle seeds at the end of summer, then leave them until autumn. In October, pour a layer of sand into a low, wide vessel (18-20 cm in diameter and 5-6 cm in height). Sprinkle the sand with water, place the honeysuckle seeds on it. Sprinkle the seeds with wet sand. Cover the seed bowl with the cake lid and place it on the bottom shelf of the refrigerator.
Brown's honeysuckle, Tatar, brilliant, honeysuckle and its other varieties are cross-pollinated, so it would be correct to have several of its bushes of different types. Thus, you can achieve not only an increase in the yield, but also the decoration of your garden plot, if, of course, you take proper care of them both in spring and summer and even in autumn. In general, there is nothing difficult in caring for honeysuckle, but If a gardener wants to grow a well-bearing crop, then he needs to focus on the autumn procedures. Proper pruning of honeysuckle in autumn, combined with normal care, allows the plant not only to exist in excellent shape for several decades, but also to give good yields. As for the edible varieties - Nymphs, Titmouses, etc. - their first seven or even nine years do not need to be cut at all. This allows the plant to grow calmly and form its flower buds.The root collar should be located at the level of the soil;
I have one shrub and I do not particularly care for it, it grows and bears fruit well Average varieties of honeysuckle - June 23-25: “Nymph”, “Amphora”, “Lenita.” Honeysuckle is affected by a microscopic mite, which causes the leaves to dry out and curl up. With increased air humidity, fungal diseases appear: spotting and powdery mildew. Occasionally the honeysuckle aphid, a carrier of viruses, settles. When I want to rejuvenate a very old bush, I just cut it out to the bottom. Then I water the cut plant, feed it with herbal infusion, infusion of manure and nettle. Watering again. Pruned honeysuckle bushes grow quickly, flowering and fruiting on them is restored. Therefore, in horticultural practice they mainly use vegetative methods of propagation of honeysuckle by cuttings and layering. Every 10-15 days, take out a container with honeysuckle seeds. If the sand is dry on top, moisten it with a spray bottle (for this purpose, you can adapt an empty, washed "sprinkler" of cleaning agents). And this should be done until spring. powdery mildew - forms a whitish bloom on the underside of the leaves, you can get rid of the damage by treating the plant with wood ash; This plant, like many other ornamental shrubs, multiplies in three ways: Honeysuckle - it is a magnificent garden shrub that can be used both as an element of landscape design and for harvesting sweet and sour fruits with a slight bitterness. Some of its varieties, for example, honeysuckle, are great for vertical gardening. It is used to decorate garden pavilions, fences and walls of country houses.Brown's honeysuckle is distinguished by its dense greenery and beautiful flowers with a delicious delicate aroma. Tatarskaya will be ideal for lazy gardeners, caring for it is impossibly simple. And curly will be an excellent option for a hedge. How and when to plant this garden shrub and how to properly care for it is the topic of our article.
Tatyana
At the same time, light sanitary pruning is periodically done to five-year-old bushes, which consists in cutting out, first of all, the shoots lying on the soil, as well as removing old and diseased branches.
Liang
The distance between seedlings should be at least one meter;
Why is your honeysuckle not bearing fruit? The only possible reason .. A very old bush !!. If the young growth on the branches is not more than 10 cm, then a simple pruning is required. Cut off the entire bush at a height of 20-30 cm from the ground. The harvest will be only next year. More and more every year.
- How to properly plant aster seedlings


How to properly plant cucumbers in open ground- Where to plant honeysuckle on the site
- Plant honeysuckle
- How to properly plant asters for seedlings
- How to plant honeysuckle
- Plant the gladiolus correctly
- Plant honeysuckle in spring
- How to plant irises correctly
- How to plant a greenhouse in it correctly
- Planting honeysuckle in the fall video
- Correct planting of peonies in the fall
Planting seedlings
To grow any plant, it is important to follow all planting steps. This is the only way to get a healthy culture that bears fruit and beautiful flowering.
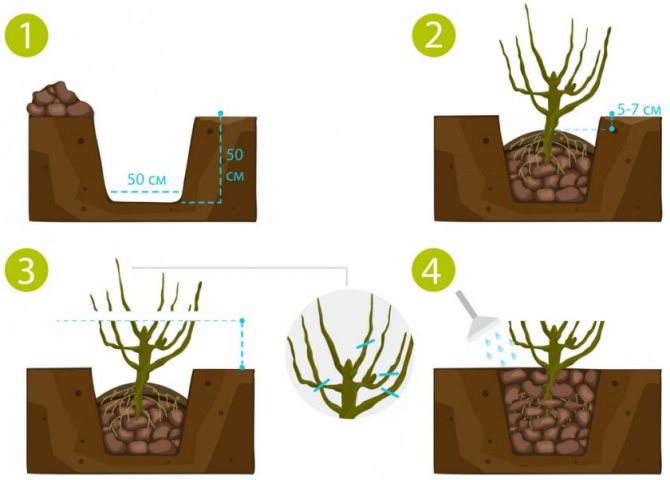
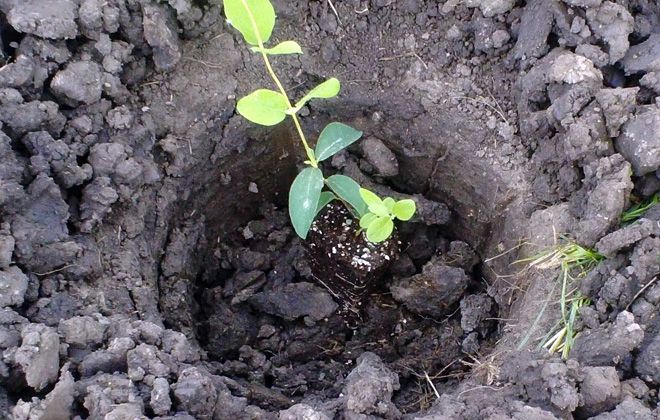
Algorithm for planting a seedling with an open root system:
- Prepare a seedling hole 2 weeks before planting.
- Lay drainage at the bottom of the pit and prepare the soil for planting.
- Install the plant in the middle of the hole, and the root collar does not need to be deepened, it should be flush with the ground surface.
- Water the plant properly. Watering should be phased. The water should completely fill the soil.
- Mulch the soil (humus or compost). Mulch layer - about 5 cm.

Algorithm for planting a plant purchased in a container:
- Dig a hole 3 times larger than the lump of soil around the root system of the seedling. Lay a small layer of drainage (broken brick, pebbles) at the bottom.
- Lift the plant out of the container and lightly run your fingers through the lump of soil to ventilate the roots that have stuck together in the pot.
- Place the plant in the planting hole so that the root collar is 2 cm above ground level.
- Fill the entire space with a mixture of garden soil.
- Water liberally and then lightly tamp the soil.


Transplant a large honeysuckle bush. 1 Practical value of honeysuckle
The honeysuckle bush is a popular resident of the backyards of many gardeners. It is known not only for its taste, but also for its medicinal properties. Berries carry a supply of useful trace elements that every person needs. For people suffering from vascular diseases, honeysuckle is very valuable.


Honeysuckle is also characterized by the fact that fruiting begins even in bushes at the age of two years. These berries are probably the very first to ripen. How to properly care for such a valuable plant so that the yield always meets the needs of the owners.
The number of fruits always depends on the care. For a valuable shrub, care is as follows:
- Watering. Honeysuckle likes the soil not to be dry, but at the same time not very wet. Watering is especially important during the ripening period of the berries. The volume of water is approximately 1-1.5 buckets. In dry weather, the number of buckets can be increased. Loosening after watering increases the supply of oxygen to the roots, which has a beneficial effect on green creation. And weeding is very necessary for him.
- For best fruiting, pruning is necessary. This rejuvenates the twigs and many new buds appear. But the bush grows very slowly, so the first abundant pruning is best done only for 5-6 years of growth.And pruning of adult bushes (over 8 years old) must be done very carefully, cutting off only skeletal and broken off branches at the very root.
- Top dressing with organic fertilizers has not prevented anyone yet. If you feed the plantings with manure, humus or compost every 2-3 years, then this will only benefit them.
- With a strongly growing plant, it is necessary to transplant the honeysuckle bush to a new place. This is necessary if the correct position under the sun has not been chosen, which can affect fruiting.
Caring for planted plants
The honeysuckle culture takes root very quickly. By 10-12 days after planting, the honeysuckle should completely take root. Usually planted fruit seedlings are pruned. In the case of honeysuckle, pruning should be avoided altogether for the first 2 years. Pruning too early will inhibit growth and limit the number of flowers that will emerge.

Pruning too early can even kill the plant. Shoots are significantly pruned at the end of the next growing season to form the crown and prepare the honeysuckle for winter. Shoots of delicate varieties are cut by 1/3 before wintering.
Watering
It is imperative to keep the soil evenly moist until the plant is fully rooted. When the honeysuckle begins to show signs of constant growth, you can reduce the watering a little. After the honeysuckle is completely rooted, it needs very little water, enough normal rainfall. If less than 2.5 cm of precipitation falls weekly in the region of residence, it is recommended to carry out deep watering a couple of times a month.


Top dressing
Honeysuckle is a garden crop that does not draw much nutrients from the soil. By regularly mulching the soil and enriching it with compost, the need to add artificial fertilizers disappears.


In the fall, before the first frost, applying fresh compost will help to retain moisture in the soil, protect the roots from frost, remove weeds and naturally feed the honeysuckle. Composting the soil during planting and adding a layer of compost to the soil annually are all the fertilizers that honeysuckle needs.
Preparing for winter and hibernation
The honeysuckle plant is frost-resistant, therefore it does not need shelter. A good layer of mulch will protect the root system of the bush from frost.


You need to understand that a honeysuckle seedling is in ideal conditions, being in a nursery, therefore, when planting it on your site, it is very important to create favorable conditions for the plant for growth and development. Gardeners have noticed that the honeysuckle that was planted in the fall, and not in the spring, develops better.
How to divide an adult honeysuckle bush. Reproduction from a bush: 4 proven methods
For different varieties of berry bushes, several methods of vegetative propagation are actively used:
- Cuttings - the method is convenient for all types of honeysuckle, cuttings can be harvested both in spring and autumn.
- Layering is one method suitable for shrubs with strong annual shoots.
- Dividing a bush is a method of obtaining new seedlings by dividing the rhizome in shrubs aged 3-5 years.
- Root offspring are rarely used, only when the root accessory bud awakens.


Variety with large berries
Honeysuckle cuttings
Cuttings can be harvested throughout the growing season. For reproduction, both young green growth of the current year and lignified annual shoots are used. The latter have a lower percentage of rooting, so gardeners recommend that novice summer residents use green cuttings in the summer.
Blanks are collected from the end of May after the first flowers bloom and until mid-June, when the first fruits begin to form.
To propagate the honeysuckle bush in the fall, it is necessary to cut off the lignified brown shoots. They are harvested in October after leaf fall or in early spring before bud break.
Growing new seedlings by cuttings
Sequence for collecting green shoots:
- Actively growing branches are suitable for propagation by cuttings. When bent, a suitable shoot should break with a crunch.
- The collection is carried out in cool weather in the morning or in the evening.
- The branches are separated from the shrub with an oblique cut. Shoots are divided into several cuttings, each of which should have 3-4 internodes. The length of green cuttings is from 7 to 12 cm.
- The lower leaves are removed from the blanks, the upper ones are cut in half. This will retain more moisture in the trunk, which is necessary for building up the root system.
- Before rooting, the lower cut of the cutting is treated with a drug that stimulates the formation of roots (Kornevin, Zircon, Epin).
- Cuttings are rooted in a substrate of peat and sand, taken in equal quantities. The first 2-3 weeks the planting material is kept in greenhouse conditions - under a transparent film or lid. For rooting, it is necessary to maintain moisture, warmth and protect the planting from direct sunlight.


Growing in containers
Collecting lignified cuttings:
- With such cuttings, honeysuckle bushes reproduce worse than green ones, so it is recommended to collect them in large quantities.
- Shoots cut in the fall are wrapped in a dense cloth and stored in a cool place until spring. It is advisable to bury them with sand or place them in wet sawdust. You can start rooting cuttings taken in early spring right away.
- Before planting, the shoots are divided, leaving 2 to 5 internodes on each part. Further cultivation is carried out in the same way as for green cuttings.
Reproduction by layering
This method is considered the simplest, but not suitable for all varieties. Layers can produce varieties with strong annual shoots.
Rooting agrotechnics:
- Around the mother bush in the spring they dig and loosen the soil, all weeds are removed.
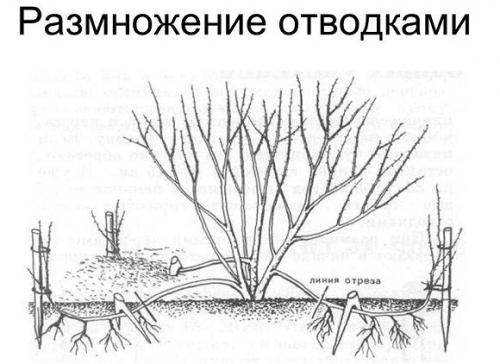

Using layering
- In the lower part of the bush, strong annual shoots are chosen, 3-4 pieces are enough. They are bent to the ground and secured with wire in several places. You need to act carefully so as not to accidentally break the branches. In fruit honeysuckle, they are fragile.
- Sprinkle shoots with soil, layer thickness 3-5 cm.During the season, maintain proper soil moisture and additionally spud the branches. Over the season, they must grow the root system.
- Full rooting occurs during the season. By the next spring, the cuttings build up a strong root system in order to exist on their own. You can separate them from the mother bush using a pruner, then plant the daughter plants in a new place.
Dividing the bush
Reproduction by dividing the bush is carried out on the condition that the mother plant is at least 3-5 years old. In older perennials, shoots develop in the upper part. Delenkas can be received both in early spring and in autumn. 5, maximum 12 divisions are usually selected from one plant.
It is convenient to divide the shrub in the following sequence:
- The mother plant is completely dug up. Using a pruner, the root system is divided into several parts. Each fragment should have at least 3 shoots and a strong rhizome.
- Sections are treated with a disinfectant solution (ash, weak manganese solution).
- Delenki are seated in a new place. Planting pits are prepared in advance, providing for a drainage layer and nutrient soil consisting of peat, humus or compost. Planting is added dropwise and watered abundantly.


Vitamin harvest
Description of honeysuckle and its types
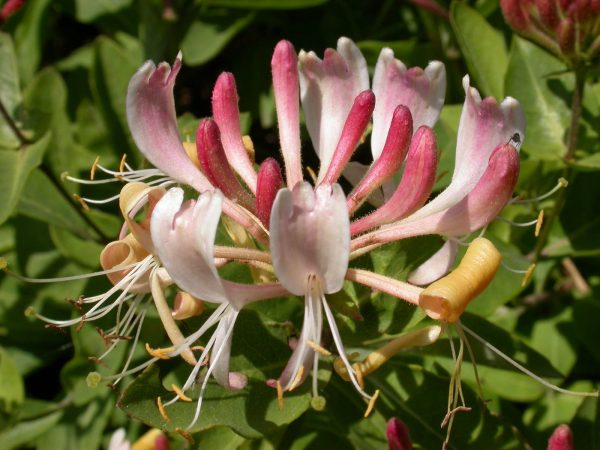
About 100 species of this plant grow in their natural environment, mainly in Asia. Honeysuckle is a durable shrub no higher than 3 m, curly, creeping or with an erect stem. The flowers are large white, yellowish, pinkish, form a capitate inflorescence at the ends of the branches, or are arranged in pairs together with the leaves. The berries are also arranged in pairs and are colored red, yellow, orange or blue, depending on the species.


With its beauty, honeysuckle disguises the most unsightly corners of the garden
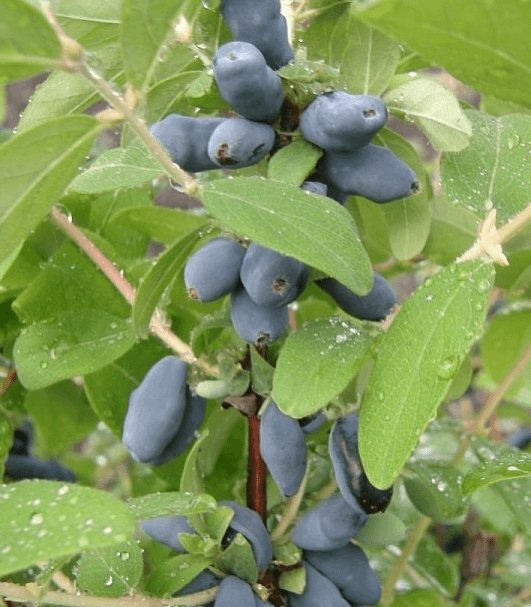
Attention! Only blue and purple berries with a whitish bloom are considered edible! In terms of chemical composition, they surpass the berries of other crops.
In Russian horticulture, no more than 10 plant species are cultivated, which are conventionally divided into shrubby and climbing.


They are mainly decorative, and only two species produce edible fruits. All cultivars are bred from them.
Table 1. Types of honeysuckle with edible fruits.
| View | Description |
| Kamchatka Honeysuckle (Lonicera caerulea) | Tall (about 2-2.5 m) fast-growing, highly branched shrub with a compact crown. Outwardly, it is similar to Edible Honeysuckle, but differs in larger berries, which can be considered dessert. The taste of the berries is reminiscent of blueberries, but without the bitterness characteristic of other varieties of the crop. |
| Honeysuckle Edible (Lonicera edulis) | It is an upright shrub up to 1.5 m high. Its crown is dense, spherical. Young shoots and leaves have pubescence, old branches are covered with yellow-brown, easily peeling bark. Paired flowers are pale yellow, tubular, located in the axils of the leaves and bloom by early summer. The berries are dark blue with purple pulp, elongated in length up to one and a half centimeters. |
Honeysuckle prices
honeysuckle
Features of working with soil and pruning
Throughout the growth of the shrub, it needs regular weeding and loosening.
The porous soil facilitates the penetration of oxygen to the roots of the plant. It begins to actively develop.
Weeds take useful trace elements from the soil, so it is important to remove them in time.
When is it better to prune in spring or autumn pruning dates
The honeysuckle plant must be pruned. You can increase productivity or decorativeness by timely pruning.


New branches grow faster when old or damaged shoots are removed.
It is best to prune honeysuckle in the fall or early spring. It is recommended to be in time before the onset of cold weather and to do it in November.
For decorative species, pruning is necessary to form stems. Edible varieties are pruned when the plant is 8-10 years old.
Features of pruning young and old honeysuckle
This item also has some features. Pruning edible honeysuckle under 5 years of age is the removal of empty branches.
These are branches where there are no shoots. They must be cut off immediately at the base. It is also necessary to get rid of damaged and frozen branches.
Also, if they are too thickened, it is recommended to thin out the bush. The treated areas are poured with garden pitch.

You can see the correct anti-aging pruning of honeysuckle in the spring in the diagram.
An adult plant needs anti-aging pruning. Remove old branches, stem growth.
Pruning is also necessary to form the edible honeysuckle bush.
Top dressing and care after pruning
Proper care of the shrub promotes rapid development. Young branches develop, the next year fruits appear.
After trimming, all places need to be treated with oil paint or garden varnish. This measure will prevent bacteria from entering the exposed areas.
Compost or manure is used as top dressing.
The main thing is not to overdo it with the introduction of fertilizing. It is recommended to fertilize the shrub once every 3 years.
Another important point: you cannot use fertilizers containing nitrogen in the fall.
It helps to build up green mass. Thus, before the onset of cold weather, the leaves will bloom.
Shelter for the winter
Unpretentious honeysuckle is not afraid of frost, but if you do not take care of preparing for winter, the bushes can freeze during the thaw.
Most edible crops do not need shelter. The culture easily tolerates temperatures below minus 50ºC, flower buds and roots do not suffer. The danger is posed by sudden thaws in winter, when frost sets in after warm days.
Curly varieties of decorative honeysuckle protect from cold weather, removing from supports and covering with spruce branches or agrofibre. In this form, the bushes are not afraid of even the most severe frosts.
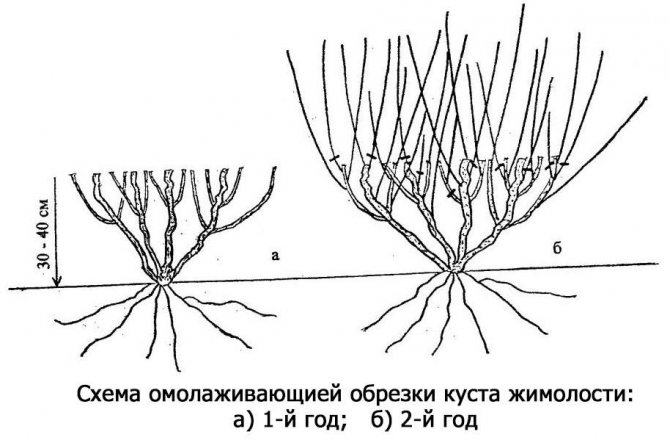
Pruning honeysuckle
For good fruiting and decorative appearance, the honeysuckle bush must be formed by pruning.
- The first time, the honeysuckle is pruned immediately after placement in a permanent location. Leave 3-5 strong branches, each of which is shortened by one third.
- Every spring, dried and broken shoots are removed for sanitary purposes.
- Until the age of seven, if honeysuckle gives many young shoots, some of them must be cut out so that the plant spends less energy and does not suffer fruiting.
- After 7 years after planting, you need to carry out anti-aging pruning, since by this age the yield of the bushes decreases. Old (5-6 year old) branches are removed.
- For honeysuckle, radical rejuvenating pruning is also permissible, very old bushes are completely cut out at the root. Plants then quickly recover and begin to bear fruit.
Storage of seedlings before planting in the ground
How to preserve seedlings if it is impossible to immediately plant them in a permanent place? Consider:
- the condition of the bushes;
- season (spring or autumn);
- own capabilities.
In early spring, if the buds are still sleeping, and the weather does not allow planting, the plants are removed to the refrigerator. If the plant comes to life, then first it is planted in a prepared container at home, and only then, when favorable days come, it is planted outside.
In the fall, seedlings must be planted, and if there is no possibility, then dig in the garden. It is not worth planting such honeysuckle in a pot for growing at home in winter, since there is a high risk of losing the plant.
What honeysuckle is better to plant in the suburbs
Honeysuckle varieties, like any other crop, come in early, middle and late ripeness. The berries of edible honeysuckle varieties vary in shape and color (from dark purple to black). They also vary greatly in taste. There are sweet, less sweet, sweet and sour, with or without bitterness.
The selection of new varieties of honeysuckle with dessert indicators of taste for cultivation in the Moscow region and in the Moscow region began in the Main Moscow Botanical Garden in the middle of the twentieth century. Breeders A. Kuklina, L. Kuminov, A. Skvortsov studied specimens of the culture brought from Siberia and the Far East. They were faced with the task of removing bitterness from the berries, preserving the maximum of useful substances and natural vitamins in the fruits. As a result of their labor, the now well-known Moscow varieties appeared, which today are respected by gardeners. They are conventionally classified into several groups.
Dessert varieties for home use
They have large berries with a sweet taste and thin skin, easily detached from the stalk. Each bush of the variety gives a crop of 2–4 kg. These are varieties such as:
- Gzhel early,
- Wiliga,
- Gourmet,
- Kuminovka,
- Fast-growing,
- Nizhny Novgorod early,
- Korchaga,
- Nipple.


The honeysuckle variety Kuminovka was created by Russian breeders for the Moscow region
Varieties of universal use
In addition to nutritional value, these varieties also have a decorative function. Resistance to frost and early ripening of berries - these are the distinctive features of these shrubs. The height of the plants is decent - up to 2-3 meters, they have decorative leaves and fragrant fruits. More than 4 kg of berries are harvested from one bush. The following varieties are suitable for cross-pollination:
- Shahinya,
- Moscow 23,
- Gzhelka,
- Titmouse,
- Kingfisher,
- Fortune.


Honeysuckle variety Kingfisher is hardy, sweet taste and lack of bitterness
Here are some more recommended varieties of honeysuckle suitable for planting in the Moscow region.
- The chosen one. Late grade. Bushes are weak, semicircular in shape. The fruits are large, oblong-oval, sweet, with a pleasant taste, weighing 1.2 g. The bushes of the Chosen One have a strong crumbling of fruits.
- Nymph.A mid-season variety, considered the best for breeding in the climate of the Moscow region. Winter hardy. The sweet berries of the Nymph have a pronounced sourness and a dessert taste. Berries weigh 1.1–1.3 g, length 26–30 mm. Productivity - 1.5 kg per bush. The surface of the berries is wavy, the skin is thin, the flesh is tender.
- Moraine. It is characterized by early ripening of berries, shows good resistance to diseases and harmful insects. Bushes are oval. The berries are large - up to 2 g in weight, up to 25 mm long, have an elongated-cylindrical shape, thin peel, blue-blue color with a touch of wax. Dessert taste with a pronounced aroma. Productivity - 1.5 kg per bush.
- Silginka. The variety has vigorous, spreading bushes with an oval crown. In the conditions of the climate near Moscow, it develops and bears fruit perfectly. It tolerates periods of drought well. The berries are elongated, large, with a pointed tip, weighing 1.4 g, 3.5 cm long. Silginka is the best honeysuckle among sweet varieties, has sweet and aromatic fruits with delicate pulp.
- Bakchar giant. Large-fruited and abundant harvest distinguish the variety of this honeysuckle. Semi-sprawling bushes, up to 1.9 m high, shoots have an anthocyanin coloration. Berries are pear-shaped, weighing up to 1.8–2.0 g, up to 4 cm long. Their flesh is juicy, sweet and sour, with a good taste.
Photo gallery: popular varieties of honeysuckle suitable for the Moscow region


Honeysuckle Chosen One has sweet berries, which, having ripened, quickly crumble from the bushes


Honeysuckle Nymph is considered the best cultivar for breeding in the Moscow region.


Silginka - the best sweet variety of honeysuckle with large berries


Bakchar giant is a large-fruited and abundantly fruiting variety of honeysuckle
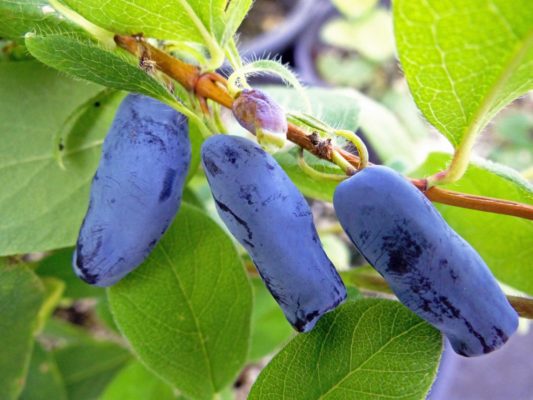


Morena honeysuckle berries have a dessert flavor
Since honeysuckle is self-fertile, it needs cross-pollination to set fruit. For this, up to three different varieties of this shrub should be planted on the site. At the same time, the choice of a variety for the Moscow region climate should be done by familiarizing yourself with the peculiarities of growing crops in a particular region, as well as reading reviews of gardeners with experience.
Recent Entries
Rose Petal Jam and Its 7 Health Benefits You Likely Didn't Know About What Fruit Are You According to the Zodiac Sign 11 Best Grape Varieties That Will Help You Create Unique Homemade Wine
Care after landing
Those who have summer cottages know how important it is to organize proper crop care. Honeysuckle is unpretentious, but the basic conditions of agricultural technology should be observed.
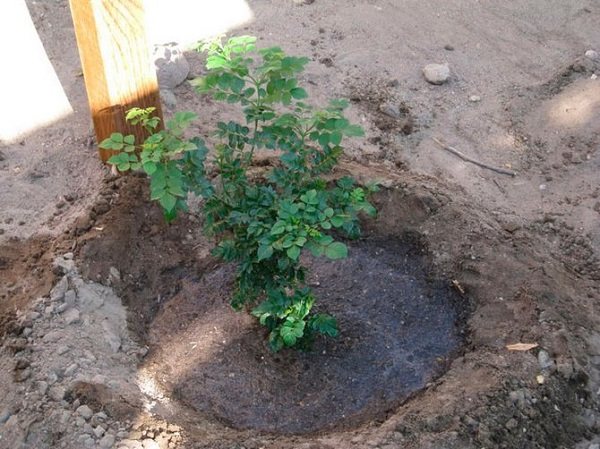


Seedling after planting
The first 3 years after planting, when the plants are not yet bearing fruit, all care comes down to regular watering, weed removal and mulching. All other events fall on the following years.
If the shrubs are watered moderately before the beginning of summer, then from June under each bush 4-5 times a season they pour in a bucket of water. In a hot summer without rain, the number of irrigations should be increased, otherwise the berry will lose its juiciness and become tasteless.
Food
The fertilizer that was applied during planting is enough for the plant for 3 years. Then they are fed with rotted manure or compost, adding a bucket of organic matter under each bush in the spring. But first, even on the melting snow, diluted urea is poured under the plants (1 tablespoon per bucket of water).


Before the honeysuckle begins to bloom, apply foliar dressing, spraying the plants with "Aquarium", "Solution", "Master". In autumn, it is enough to pour wood ash under the bushes (150 g each).
Trimming
For the first 6 years, the berry growers do without pruning. Then, in the spring, sanitary pruning is carried out: damaged, diseased and dry branches are removed. But the tops of the shoots should not be touched - the main flower buds are concentrated here, from which the fruits will then appear.
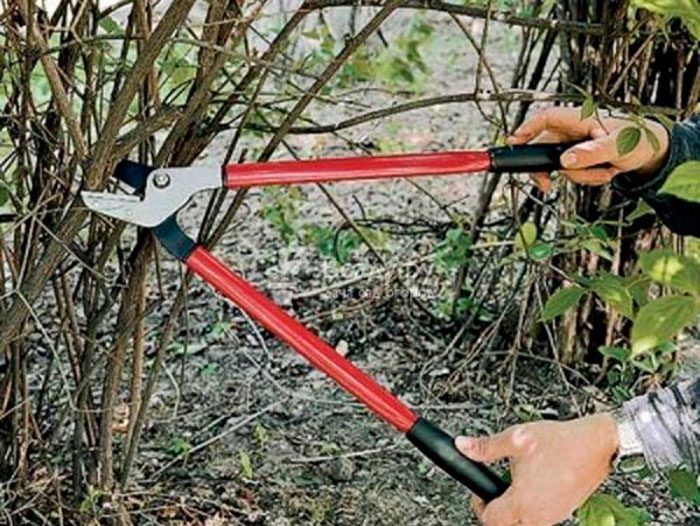


Formation of a honeysuckle bush
Formative pruning is carried out in March or autumn, after leaf fall. Once every 2 years, a couple of unproductive shoots are removed.If the bush is more than 15 years old, a complete rejuvenating pruning is needed - only 0.5 m stumps are left. A new bush will form in a couple of years from young growth.
Diseases and pests
Honeysuckle is quite resistant to disease, except that powdery mildew can develop if the season turns out to be too rainy. Here "Fitosporin" will come to the rescue. The main control should be aimed at harmful insects:
- when aphids appear, it is recommended to treat the bushes 2-3 times with vodka solution - dilute ½ glass of alcohol in a liter of water;
- if there is a hidden or sucking pest on the bush, use systemic chemistry ("Confidor", "Aktelilik", etc.).
On a note! Chemicals can be used before the berries are set. But if there is a need for them during the ripening period, then, saving the plant, you will have to abandon the harvest - the fruit will be inedible.
If a plant is planted and looked after, observing all the rules, the next year fruits may appear. After planting honeysuckle, it is necessary to collect weeds in a timely manner, which deprive weak seedlings of moisture and nutrition. Also, care must be taken to ensure that the ground does not dry out.
In order for the plant to take root, you need to know the timing of planting honeysuckle in the fall. Saplings should be planted before frost, then they will take root and will well endure the winter. You can add mulch or coniferous needles under the tree with a layer of 10-15 cm. If the winter is snowy, then it is good to warm up more snow under the bush. In the spring, when the sun dries up the earth, it is necessary to loosen it around the seedling.
We suggest that you familiarize yourself with: How to process eggplants from pests in a greenhouse. How eggplants are processed: protection against diseases and pests
If mulch was not used, for 3 years in a row with the arrival of spring, the plant must be hilled high. In hot summers, the bush requires abundant watering. If watering is not sufficient, the berries will be bitter.
Watch the video! Honeysuckle. Planting and leaving


If the summer is not hot, honeysuckle can be watered about 4 times per season. It will be enough to pour 10 liters of water under each bush.
At the same time, do not forget to remove weeds and loosen the ground around the flower. Due to the shallow location of the root system, the soil can be loosened only 8 cm deep.
Honeysuckle, according to the rules of outdoor care, is not fed for two years. In the third year, organic fertilizers are introduced and this procedure is repeated annually. Every autumn, the soil is fertilized per 1 square meter with the following composition:
- compost - 5 kg;
- ash - 0.1 kg;
- double superphosphate - 40 g.
With the arrival of spring, the plant is fed with saltpeter: 15 g per 1 sq. m.
In a container with a volume of 10 liters, urea (1 tbsp. L) is diluted and the soil under the bush is impregnated with this solution.
After harvesting the fruits, the plant should be fertilized again with a manure solution. To prepare it, you need to take water - 4 parts and manure - 1 part.
The choice of planting material
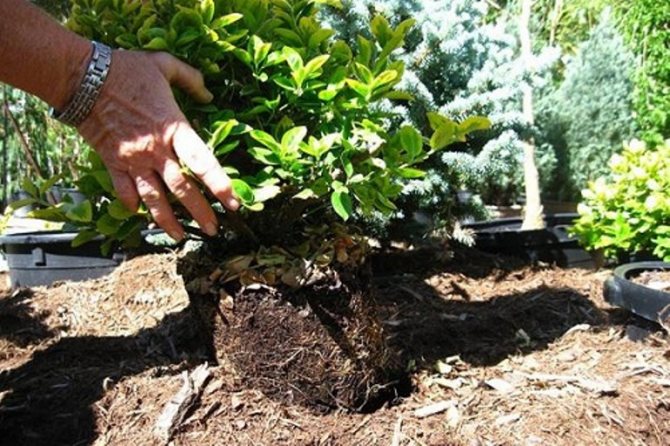


In autumn, nurseries offer a large selection of honeysuckle seedlings. How to choose planting material:
- Buy plants that are no more than 150 and at least 25 centimeters high. "Giants", like "babies" take a long time, bear fruit poorly, so it is better not to take them.
- Honeysuckle should be 2-3 years old.
- For one site, at least three different varieties are selected. The culture is self-fertile, pollination is required. In this case, it is desirable to find varieties that bloom at the same time.
- They buy healthy, strong plants, without defects on the bark, with whole and dense buds.
- When buying honeysuckle varieties for planting in the fall, plants in containers or pots with closed roots are preferable.
Seedlings from containers take root faster, actively grow.
Where to plant honeysuckle?
You need to choose a place consciously, because culture has lived for about 30 years. In addition, you will not need to carry out a transplant in the future. For full growth and fruiting, the place for honeysuckle should be sunny, in the shade all indicators are much lower.Unlike most other crops, the plant does not react in any way to the wind, so it can even be placed on the north side. It is better to choose a place where green manure grew before or it was empty, the land on it is the most fertile.


Soil for honeysuckle
With unpretentiousness, the culture still has some preferences. The soil for the honeysuckle should meet the following preferences:
- high level of fertility;
- acidity at pH 5.5-6.5;
- grows poorly on sandy soils;
- it is not recommended to choose wetlands.
Best neighbors for honeysuckle
The culture enters the growing season early and also hibernates. During growth, the plant releases active components into the ground that not all plants like. It is important to choose the right choice for planting honeysuckle next to it. Good compatibility is observed with:
- pome fruits;
- stone fruit;
- black currant;
- gooseberries.
Pruning and shaping the bush
Pruning should be done in late fall or early spring when plants are dormant. Young bushes up to 3 years old need to remove only dead branches. On older plants, pruning is done annually to stimulate fruiting. Pruning correctly will help reduce shading in the center of the bush, improve the quality and quantity of fruit, reduce the risk of fungal diseases, and stimulate new shoot growth.
Did you know? In the past, it was believed that honeysuckle planted near houses can ward off evil spirits, and a branch of honeysuckle under the pillow causes pleasant dreams and improves mood.
Never remove more than 25% of a shrub in one season, as this can remove fruiting wood and reduce yields. Honeysuckle bears fruit on annual wood, and if there is no damage, the tops of the branches should not be cut off, since most of the fruit and flower buds develop here. Aim to leave 4–6 of the healthiest and most developed old branches and some strong young shoots.

New shoots will eventually replace old ones, which will ensure a balanced vegetative and fruiting cycle. Honeysuckle does not give root shoots, so there is no growth at the base of the bush. Rejuvenating pruning is done on old and unproductive plants. The shrub can be cut down 30 cm above ground level and allowed to grow back on its own roots.
Also read about how honeysuckle tolerates spring frosts.
Regrowth will be the same and even, which will rejuvenate the plant. Having mastered the methods and rules for planting honeysuckle, replenish your berry plantation with this useful multivitamin culture - and you can pick berries with the taste of forest blueberries right on the site, and the early spring flowering of bushes will add decorativeness to the garden landscape.
Honeysuckle pests
The list of insect pests in honeysuckle is not very large, but even the appearance of one of them does not bring joy to the gardener. The bush may be affected by:
- aphids - plants are treated with tobacco dust infusion with the addition of a soap solution (100 g of tobacco and 100 g of soap per 10 liters of water);
- scabbards - 2 times during the summer, the bushes are sprayed with Rogor or Aktellik;
- baby moth - spray the honeysuckle with Aktellik, Fitoverm or Karbofos in late summer or early autumn, when the moth lays eggs;
- miner flies - they spray the bushes with Inta-Vir, Decis during the summer.
Photo gallery: pests of honeysuckle


Scabbards attach to the young branches of the honeysuckle bush and suck the juice out of them


Miner flies lay eggs in honeysuckle leaf plates


From the eggs of the baby moth, amber-yellow caterpillars with a brown-red head appear, eating the leaves of the honeysuckle


Aphids feed on the sap of leaves and young shoots of honeysuckle
All insecticidal preparations are used strictly according to the instructions, observing safety measures.
Seedling and soil preparation
The plant is preliminarily examined, broken parts and dry roots are cut off.If the roots are too elongated, they are shortened to about 30 cm.
Honeysuckle has been growing in one place for many years, so the plot is prepared correctly:
- The earth is dug to the depth of the shovel bayonet with the formation overturned.
- Weed rhizomes are removed.
- 400 g of powdered slaked lime or dolomite flour is added to the soil if the soil needs to be deoxidized.
- The dug surface is tamped with a rake.
1-2 weeks before planting, they dig holes for shrubs 40 cm deep and 50-60 cm wide. The distance between them is maintained at 1.5 m.
Decorative honeysuckle: planting


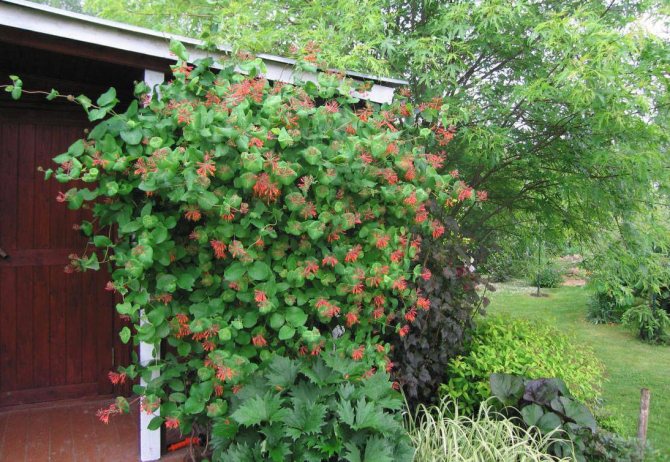
Noting the specifics of planting edible honeysuckle, do not forget about decorative varieties. Usually these are climbing vines, the length of which reaches several meters. They are used for vertical gardening of plots, decoration in landscape design.
Planting is not much different from planting edible varieties, but in order to quickly obtain shoots, shoots of ornamental plants are often buried in trenches. So from one shoot, several viable bushes are obtained.
The group includes many varieties that differ in appearance, distribution area. Plants are unpretentious, frost-resistant, differ from traditional varieties in the shape of berries. They are round and small, red, orange or black.
Attention!
The fruits of decorative honeysuckle should not be eaten, they are poisonous.
Among the most famous varieties, honeysuckle, honeysuckle, stands out with shoots up to 5-6 meters in length. Differs in a long growing period (up to 3 years), high frost resistance. Blooms profusely with bright orange or pink flowers. In sunny places, on supports (fences, gazebos) forms green curly walls.
Popular decorative varieties:
- Hekroth;
- Telman;
- Brown;
- Primorskaya;
- Gerald.
Autumn planting is recommended, seedlings are not pruned.
Description and features of honeysuckle
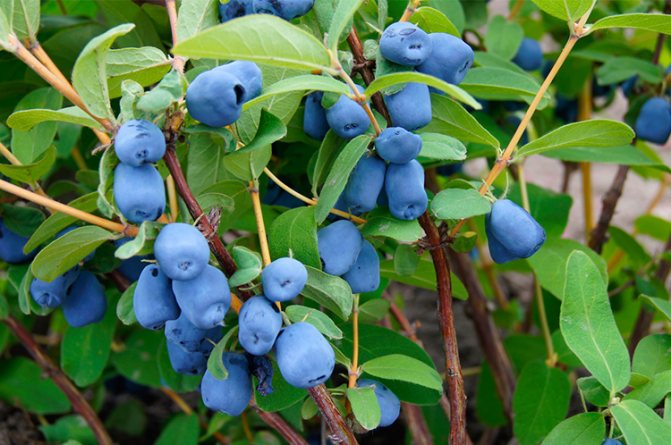
Honeysuckle is unpretentious. The berries appear in the first season. From one bush, you can get from 2 to 4 kg. The edible fruit has shades of blue, one of the first spring berries. They have a sweet and sour taste with a slight bitterness. They resemble blueberries and blueberries in appearance. Their characteristic features include a waxy coating, a weak aroma. The skin is very soft, delicate, quickly bursts.
Red and yellow berries are poisonous.
The plant is wild and cultivated. In any case, it is quite resistant to the effects of low temperatures and high humidity.


The honeysuckle root system is located close to the soil surface. Leaves are smooth and oblong. Flowers are considered cross-pollinated crops. An ovary can appear only if two assorted bushes were planted nearby. The maximum yield is obtained from plants over 15 years old. The flowering period begins in mid-May. Good pollination is facilitated by the appearance of a wonderful aroma.
If the crop is not harvested on time, the fruits may crumble. To prevent damage to them, it is recommended to pull a mesh cloth under the bush.
Fruiting
The average life span of honeysuckle is 20 - 25 years. The crop yield depends on age and increases up to fifteen years of age. The first harvest of honeysuckle gives at the age of 3-4 years.
If honeysuckle was propagated by cuttings, then the first fruits can be obtained the next year after rooting. The productivity of a shrub at the age of 7 years is just over a kilogram. An almost double increase in yield can be achieved by planting several varieties of honeysuckle nearby.


If the culture was planted with a seedling or cuttings, the first fruits can be expected in a year. In turn, seedlings begin to bear fruit only after 3-4 years, and only for 6-7 years more than 1 kg of berries can be removed from one bush. Yields will increase for another 10 years and then decline.Therefore, 20-year-old bushes are renewed, completely cutting off the shoots. The berries ripen by the end of June.
Testimonials
Peter, Moscow region
The first time I planted honeysuckle about 10 years ago, in the spring. And the bushes died due to the drought. Then he began to plant it only in the fall, they grow by leaps and bounds! There are no small berries, they bear fruit abundantly, they quickly take root, A couple of bushes grows in partial shade, and they bear fruit well. That's what it means - the right time to board.
Rose, Penza
My honeysuckle grows in a small shade, and in five years I realized that this is exactly what the culture needs. The soil is also important - light, loose, constantly slightly moist (but without moisture stagnation).
I planted all the seedlings in the fall, they took root well (I have Bakchar varieties). They all grow slowly, but the yields are excellent.
How to plant honeysuckle correctly
The culture, as already said, is unpretentious. But consider the following points when landing.
- The culture grows best in a well-lit area. Therefore, the place is chosen sunny, without drafts. Light partial shade is allowed, however, experts admit that the lower branches of the plant are in slight shade.
- The distance between the bushes should not be less than 1.5 m. It is also not advisable to plant a shrub next to or between large fruit trees, as they will greatly shade the bushes. In addition, they will still take most of the nutrients from the soil.
- The soil must be fertile and light so that the roots can develop quickly. Avoid lowlands and wetlands, high groundwater table. However, even in a dry place, honeysuckle will not grow well, since it especially needs moisture when pouring berries.
- It is best to buy seedlings from specialized stores or nurseries. Otherwise, you can buy something completely different from unscrupulous sellers. Be sure to ask the seller which variety you are buying, whether it is zoned for your area. For example, in the middle lane the climate is different than in Siberia. When warmth comes, the plant wakes up quickly, and with recurrent frosts, flower buds are affected by frost. And you can't expect a good harvest.
- Honeysuckle is a cross-pollinated plant. Therefore, never plant one plant, there should be at least 1-2 more plants nearby.


Growing and caring for honeysuckle in the middle lane
Proper planting and caring for honeysuckle in the spring significantly increase the chances of getting a good harvest.
The climate in different regions is different, so each has its own distinctive features in terms of growing shrubs.
Planting and caring for honeysuckle in the Moscow region is best done in the fall, not in the spring.
At this stage, the development of the root system slows down, the plant adapts faster. In the spring, a shrub is planted only in cases of extreme necessity.
Watering
For culture, it is necessary to create optimal conditions for active growth and development.
The shrub is watered abundantly during the period of fruit formation.
You need to water the plant every day, while at least 1.5 buckets of water are consumed per bush.
With prolonged drought, watering is increased, and during prolonged rains, watering is reduced or stopped for some time.
Fertilization
The yield directly depends on whether fertilizers are applied during its growth, development or not.
To feed the honeysuckle in the spring, organic fertilizers are used before planting. This helps to accelerate the development of the shrub.
If the soil is too acidic, add dolomite flour, lime.
In the first, second year of the shrub's life, fertilization is not necessary, since the necessary substances were introduced before planting. They will be enough for a couple of years. The following dressings are carried out as follows:
- In autumn, wood ash, compost, superphosphate are introduced into the soil.
- In early spring, fertilize with ammonium nitrate, urea. Dilute 15 g of beneficial substance per 10 liters of water.
- In the middle of summer, after fruiting, they are fed with nitrophos, nitroammophos.For 10 liters of water, 25-30 g of fertilizer are consumed.
Diseases and pests
Failure to follow the rules for caring for the plant, insufficient illumination can cause many problems.


The most common diseases of edible honeysuckle:
White spot is a fungal disease that often affects the plant. You can find out about its appearance by gray-brown spots with a white center on the leaves.
The situation is aggravated by high humidity. Spraying with Fundazol will help to cope with the problem;
Powdery mildew - represents a fungal disease. Greyish spots form on the leaves. Over time, powdery spots spread throughout the plant.
The disease spreads quickly when the shrub grows in the shade. The plant lacks light, soil drainage;
Drying of branches - fungi are the causative agents of the disease. Already in June, you can see how the branches begin to dry.
The disease can be detected by the reddish tubercles on the branches. For prevention, the plant is treated with Bordeaux liquid in early spring and after flowering.
Among the pests are noted:
- rose leafworm - brown butterfly. Its caterpillars eat the leaves;
- aphid - most often attacks shrubs. Aphids suck sap from the plant;
- gooseberry moth is a motley butterfly. Its caterpillars feed on the leaves of the bush.
Important! Processing edible varieties in the spring is unacceptable. There is a risk of chemicals getting into the ovary. In autumn, all damaged shoots are removed and burned.
Planting care and preparation for winter
In order for the honeysuckle, planted in the autumn, to take root safely, you need to take care of it:
- Pull up the weeds.
- Water regularly (as the topsoil dries up). In the heat, moisten at least once a week, pouring about a bucket of water onto the bush. If it rains constantly, then watering is not needed.
- Carefully loosen (1–1.5 cm) after each watering the soil under the bushes to improve aeration.
- To protect against frost, the root system is mulched by laying a layer of 8-10 cm of pine needles, straw, fallen leaves, etc.
When to plant honeysuckle?
The culture is characterized by an early growing season. However, at the same time, planting can be carried out in spring and autumn. Suitable planting dates for honeysuckle are as follows:
- spring - March-April;
- autumn - September-October.
At the beginning of the warm season, they do this as soon as the snow melts and the soil warms up slightly. This should be done before the buds bloom on the shoots. At this time, it is recommended to plant only shrubs grown in pots or containers. Planting and caring in the open field of honeysuckle has more positive results in the fall, since the plant ends its growing season early and therefore has a lot of time for rooting. Do this after the leaves fall. It takes a month and a half for full rooting.
Diseases and pests
Honeysuckle is a fairly young crop in our gardens and so far it has few pests. Its main enemy is the golden beetle, a golden-green beetle, the larvae of which eat up the bush from the inside. It is useless to fight the pest with the help of insecticides, since the bug flies away during spraying, and the larvae are not available for the drug. As a result, the branches of the culture dry up. The main method of struggle is cutting the affected shoots under the root and burning them.
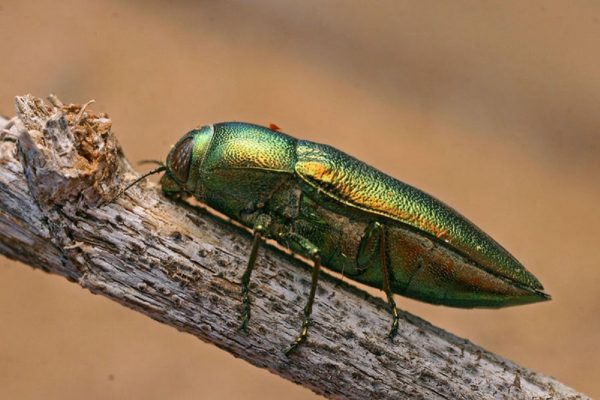


The average length of the Zlatka beetle is about 3 cm
In addition to goldfish, in some cases, the shrub can infect aphids, caterpillars, ticks, fingerwings. Among the diseases are mottling of leaves, mosaic-rezuha, as well as fungal infections like powdery mildew. During the fruiting period, it is impossible to use insecticides and fungicides, since the fruits will absorb the poison. It is better to replace them with folk recipes. Chemistry is used for prophylaxis in early spring, before the beginning of the growing season, or after harvesting.
Honeysuckle does not bear fruit - reasons
Several main factors are known, the impact of which negatively affects the crop yield.Consider why honeysuckle does not bear fruit:
- Lack of sunlight.
- The nascent buds were damaged by temperature extremes.
- During the flowering of honeysuckle, pollination did not occur for various reasons.
- Lack of nutrients and the appearance of various diseases.
- The wrong choice of variety, the wrong acquisition of a decorative look that does not bear fruit.


Conditions for good growth of honeysuckle
Honeysuckle is considered an unpretentious plant and does not require special care. It tolerates frost well, withstanding temperatures as low as -50 ° C. Even blossoming flowers are not afraid of spring frosts down to -7 ° С, and buds up to -14 ° С. The culture is distinguished by longevity and, in favorable conditions, gives excellent yields. It is grown in all regions of our country, from the south to the northern latitudes.


Honeysuckle is a wonderful honey plant
In general, the shrub can grow on any, it would seem, the most unsuitable poor soils, such as sandy or rocky. However, in order to get the most out of the edible varieties, it is better to plant the crop on fertile loose soils with deep groundwater. The acidity of the soil does not really matter, the main thing is that there is no waterlogging.
The site should be open, with maximum light during the day. Protection from the prevailing winds is necessary, as the berries are prone to shedding. Honeysuckle can grow in shaded, blown places, but then its development will be slowed down, and the taste of the fruit will leave much to be desired.
Video - comparison of varieties of honeysuckle
Reference! The taste of berries during their ripening period is influenced by the air temperature and the degree of soil moisture. It is noticed that in clear weather the berries are juicy and sweet, while the rainy summer makes them watery and sour.
Choosing a landing site
When choosing a place for a bush, you should consider the following:
- the culture bears fruit abundantly only in well-lit areas;
- honeysuckle does not tolerate drafts, winds, as fragile branches quickly break;
- likes to grow on fertile, slightly acidic soils.
Suitable places for planting are in small lowlands, but without stagnant water, with protection in the form of outbuildings or fences. Landings are closed from the north, from cold winds.
On soils with high acidity, before the autumn planting of honeysuckle, chalk or slaked lime is added in about 1-1.5 months (100-200 grams per square meter). On clay soils, a drainage layer is made in the pit.
Landing pit: preparation


The seedling pit is prepared in advance so that the soil has time to settle. With good care, berry trees grow in one place for up to two decades, so you need to take care of filling the soil.
The top layer of fertile soil is left, it will be needed to prepare the nutrient mixture. Its composition:
- humus (8-10 kg);
- potassium salt (30-40 grams is enough);
- superphosphate (standard rate 200 grams).
The components are mixed, add soil and fall asleep halfway into the pit. Then they cover it on top and leave it until the day of planting.
On a note!
On clay soils, sand, wood ash, turf soil must be added.
Pit sizes: in diameter - 40-50 cm, in depth - up to 30-40 cm.
Planting depth
It is important to plant the honeysuckle correctly in depth. A seedling is carefully placed in the pit, so that its neck is at ground level. Then carefully sprinkle the roots with the remaining nutrient mixture, soil. Planting is watered abundantly. After a while, the soil will settle, the seedling will slightly lower and its neck will be 4-6 cm below ground level. But this is done only on light soils. On heavy soil, it should not be buried, since the main roots can undermine.
It is advisable to mulch the plantings with peat or humus.
Selection of seedlings
Depending on varietal preferences, gardeners can choose for planting large or undersized specimens, winter-hardy or southern, decorative or fruit. When buying, they are guided by several criteria:
- the age of the rhizome does not exceed 2-3 years;
- the aerial part of the plant consists of at least 3-4 young and strong shoots, densely covered with small green buds;
- the length of the shoots is not less than 30 cm, they are flexible, without visible damage;


Variety with large berries - peeling of the bark is the norm for honeysuckle and is not a risk factor for planting;
- the plant is prone to cross-pollination, which is why shrubs of different varieties can transfer their best qualities to each other;
- attention should be paid to the fact that the seedlings are taken out of cuttings, layering, or formed by dividing the bush.
Plants derived from seeds lose their varietal characteristics over time, which is why the shrub, after a few years of fruiting, turns into a gray-gray wild plant.
When buying, experienced farmers are guided by the following parameters:
- The increased winter hardiness of the variety is important for the northern regions with long frosty winters. Otherwise, the seedling will freeze and dry out by spring.
- Unpretentiousness in seasonal care. Summer residents prefer to buy drought-resistant specimens. Southern varieties and hybrids of blue-gray wild plants do not need regular watering.
- The volume and height of the crown of an adult plant. Young seedlings are distributed at such a distance that the bush does not come into contact with other decorative inhabitants.
- Compatibility with other landings on the site. Some gardeners from honeysuckle lashes form fruiting hedges for the garden. Owners of suburban areas exhibit such plant structures in close proximity to single plants. The latter, due to the powerful root system, oppress the neighboring bushes, pulling moisture and nutrients onto themselves.


Flowering honeysuckle
Preparing seedlings for wintering


Honeysuckle - frost-resistant shrub
If after planting the seedling there is dry warm weather, water the bush once a week. Honeysuckle is a frost-hardy shrub and, with the right choice of planting time, overwinters without problems. To insure against poor rooting, the bush should be spud 10-15 cm in height with coniferous litter or just soil.
































