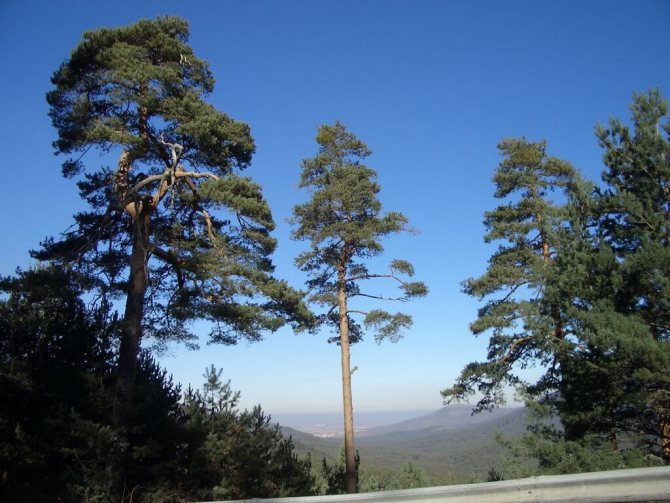
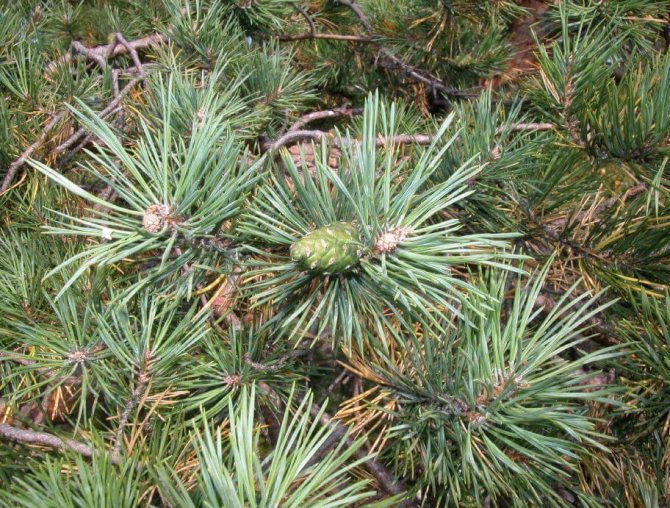
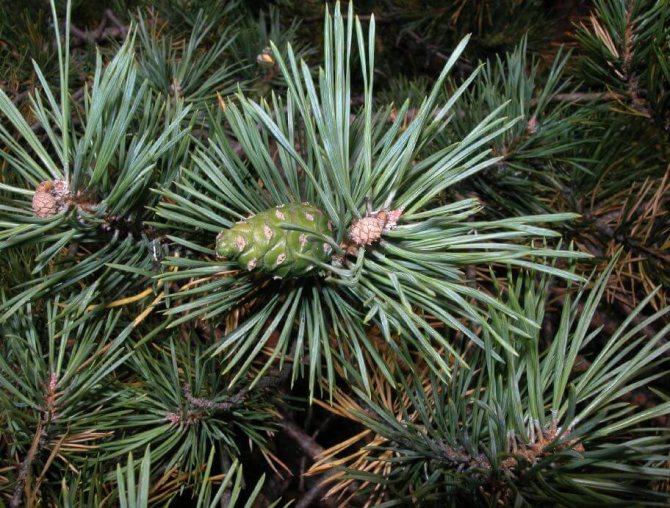
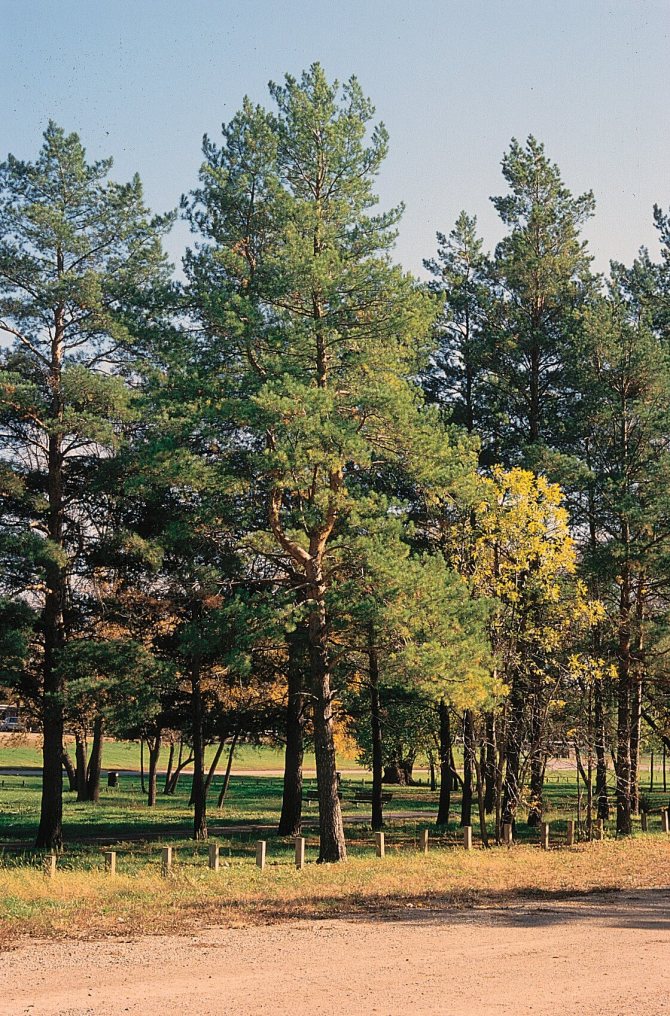
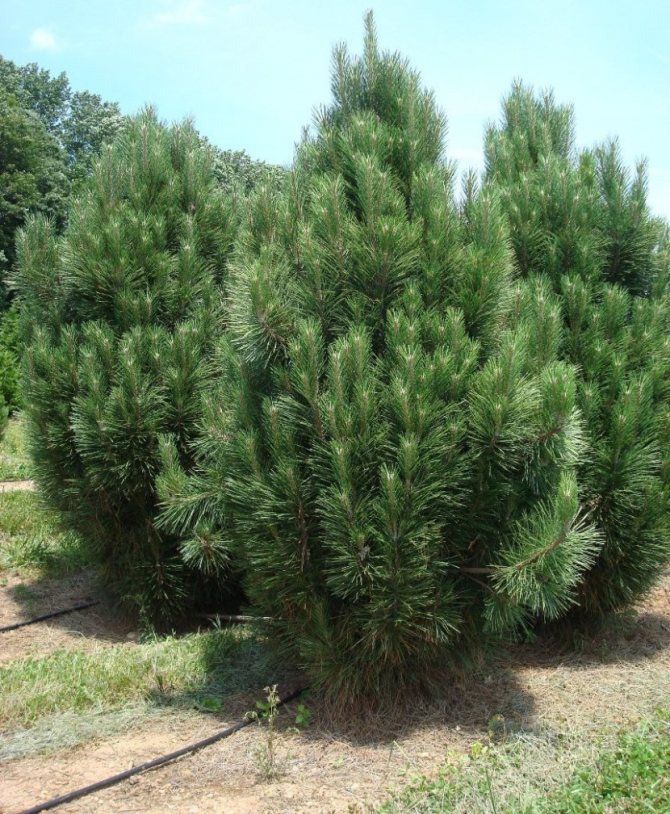
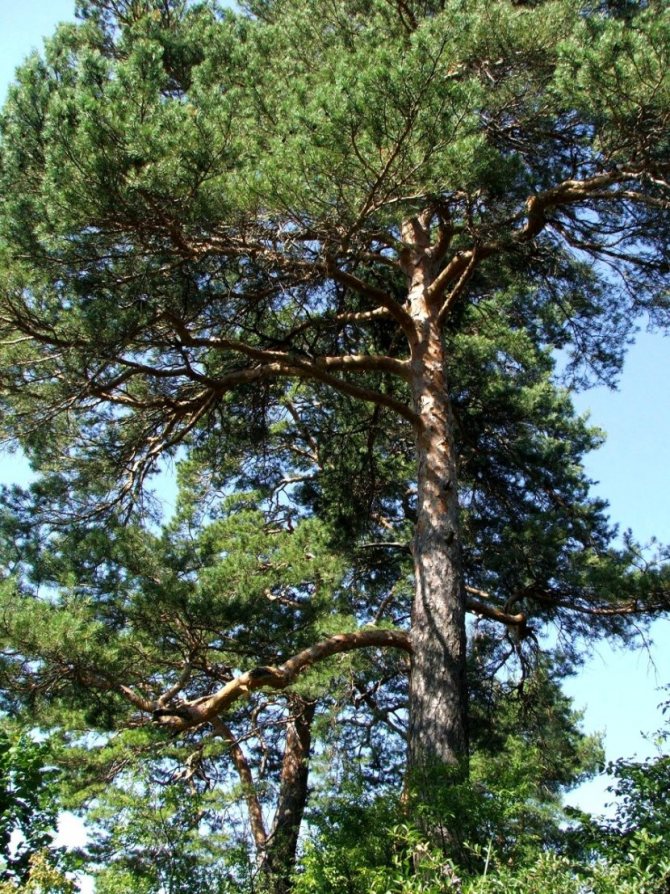
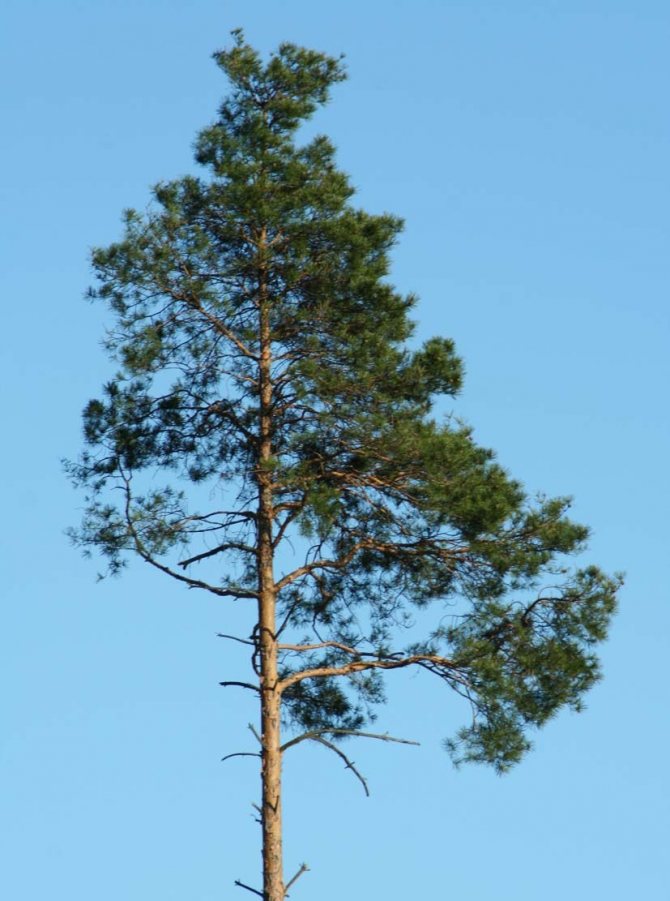
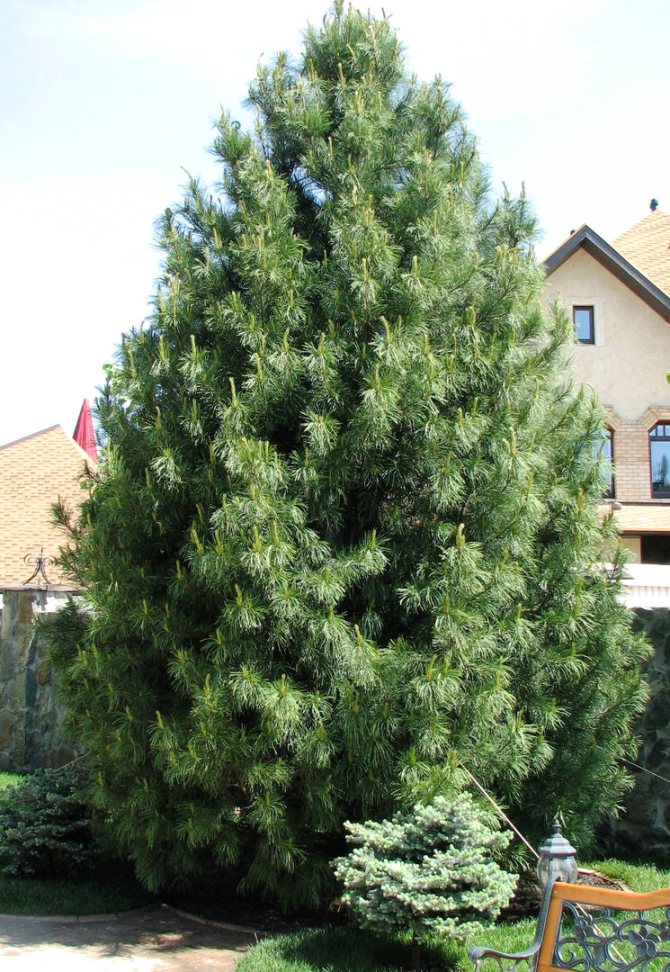
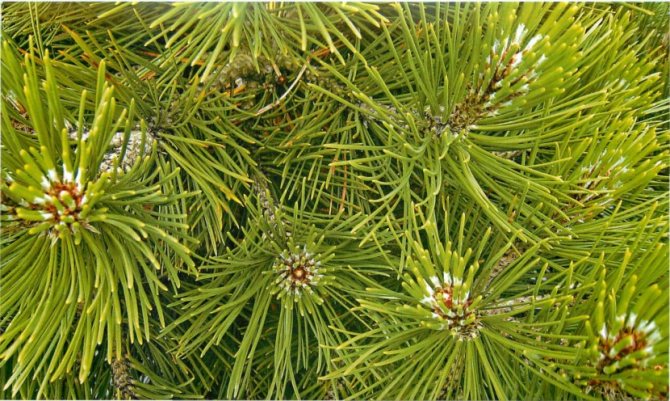
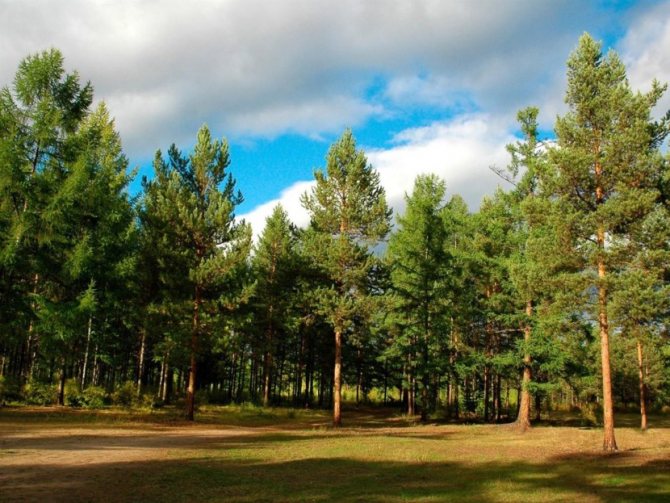
For people who are tired of the quick change of elegant green foliage to yellow, from the problems associated with the annual collection and burning or disposal of leaf litter and the need for constant and annual pruning aimed at creating a beautiful appearance of the tree, we recommend planting conifers on their site, specifically - Scots pine, which we will talk about today.
Scots pine (Pinus sylvestris).
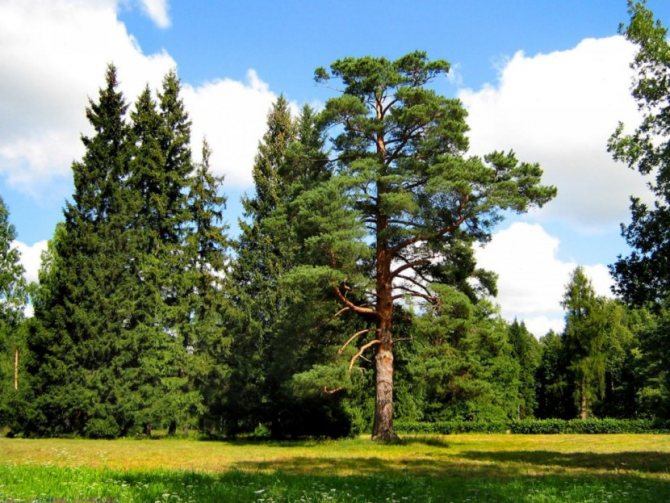
Pine, like most conifers, remains decorative throughout the year. Scots pine (Pinus sylvestris) is perhaps the brightest representative of the pine family, and it not only possesses a chic and lush crown, but is also the source of a very pleasant and revitalizing aroma of pine needles.
However, taking into account all the advantages of Scots pine as an ornamental plant, we still do not observe the presence of this culture at every site. Of course, if the plot is small, this is one thing, but it so happens that for some reason there is no Scotch pine on rather large areas. Perhaps it is not often possible to find Scots pine on the site because it is believed that it is difficult in agricultural technology, but in reality it turns out completely wrong.
Conifers: general information
Conifers are one of the divisions of the plant kingdom, represented by trees (most often), as well as shrubs and elfin trees. They grow practically all over the world, but dominate only in one natural zone - the taiga. There are two main distinguishing features of this unit:
- The leaves are usually long, thin needles.
- Seeds develop in specific shoots - cones.
Conifers are the oldest plant group on Earth. Their remains are found in different parts of the planet and date back 60-300 million years ago. Some of them have already become extinct without a trace, such as, for example, Wolcian or Cordaite. The features and appearance of these plants can be judged only by the discovered fossil fragments.
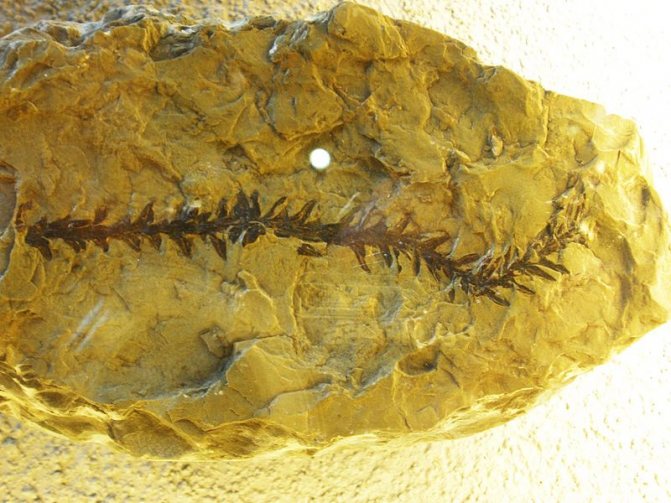

Photo gallery
Conifers: examples
Typical representatives of the order of conifers:
- yew;
- sequoia;
- Pine;
- spruce;
- cypress;
- larch;
- cedar;
- juniper;
- fir.
Of all the listed plants, spruce, pine and larch are most often found on the territory of Russia. Where do these trees grow?
- Spruce is widespread in Europe, Asia and North America, widely represented in the vastness of Siberia and the Far East.
- Pine has filled the temperate latitudes of Europe and Asia, it also grows in Southeast Asia and North America (from Alaska to Yucatan).
- Larch occupies vast areas in Russia, in particular, in its Siberian and Far Eastern parts.
So, we found out where pines, spruces and larch trees grow. Next, we will dwell in more detail on the botanical description of the pine, talk about the distribution and main types of this tree.
Features of the root system
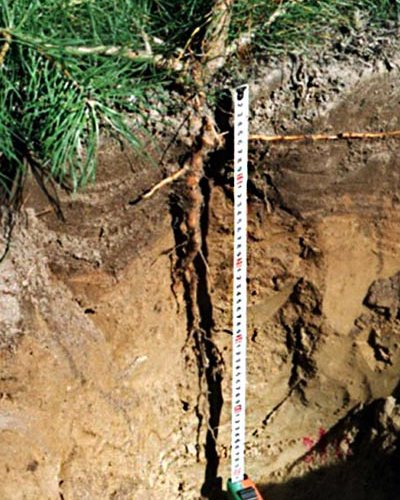


If we are talking about a tree such as Scots pine, its description will not be complete enough without a story about the root system. Unlike many other trees, it is plastic in pine and its shape, like the shape of the crown, depends on the growing conditions. There are four main types of root systems found in this plant:
- developed taproot and several lateral branches
- strongly pronounced lateral with a weak rod
- dense network of short roots that do not go deep into the soil
- practically superficial developed root system.
The looser and well-drained soil in the area where Scots pine grows, the stronger the taproot. On very dense soils, for example, on stones with a small amount of soil, the tree is forced to form a kind of "plate" capable of holding a heavy crown and a high trunk, especially under strong wind load. In addition, since the main function of the root is to supply the plant with water, a root system widely spreading in all directions is characteristic of areas with deep groundwater.
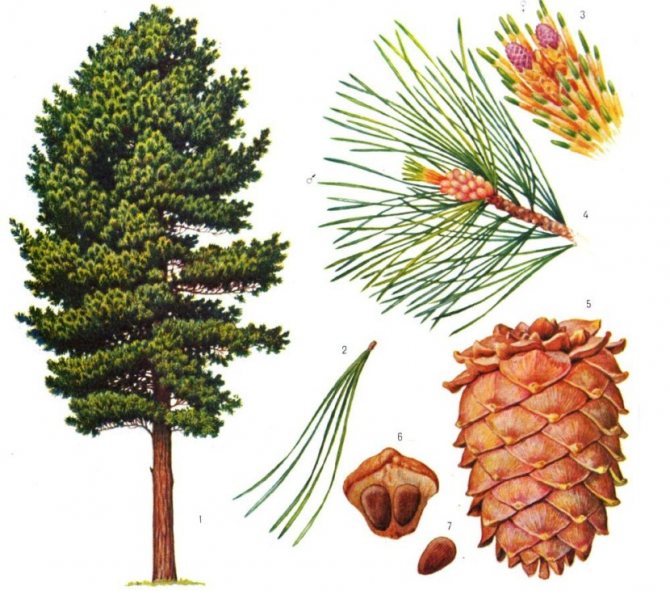
Pine tree: botanical description
Pines are a family of conifers with over 130 species. In Latin, their name sounds like Pinus. It is believed that this name comes from the Celtic word pin, which translates as "resin". Pine trees really emit a fairly large amount of resin, generously enriched with phytoncides.
Pine wood is quite dense and soft at the same time. In terms of strength, it is second only to larch. It has a pleasant color, which darkens with age (and unevenly).
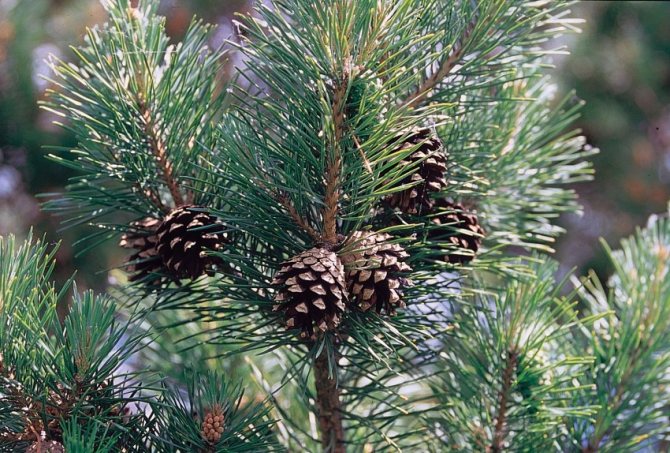
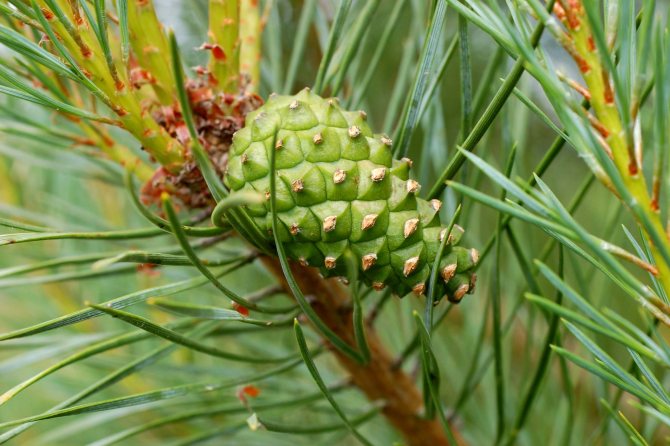
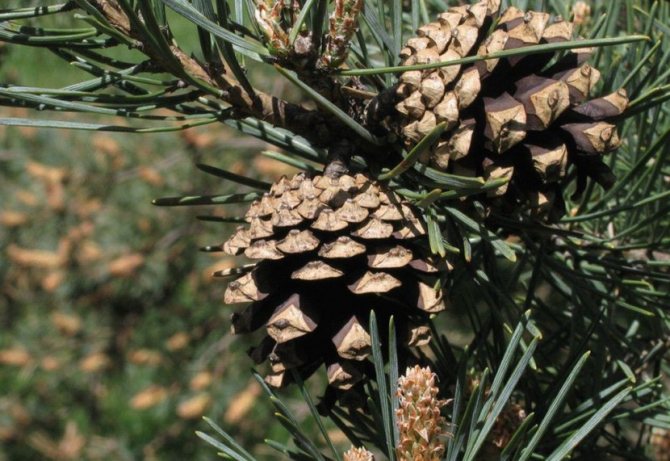
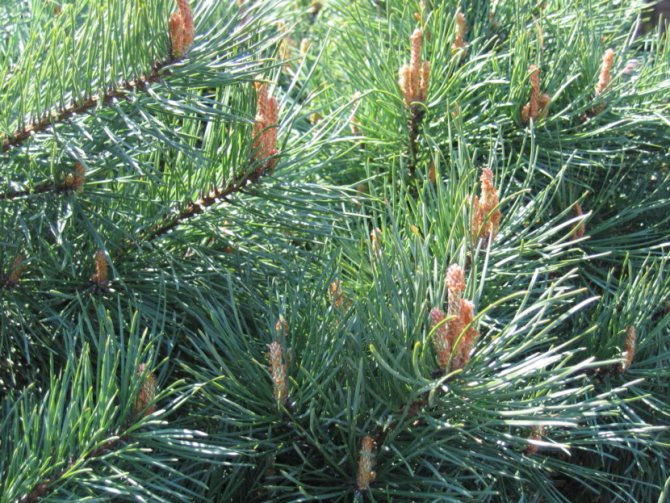
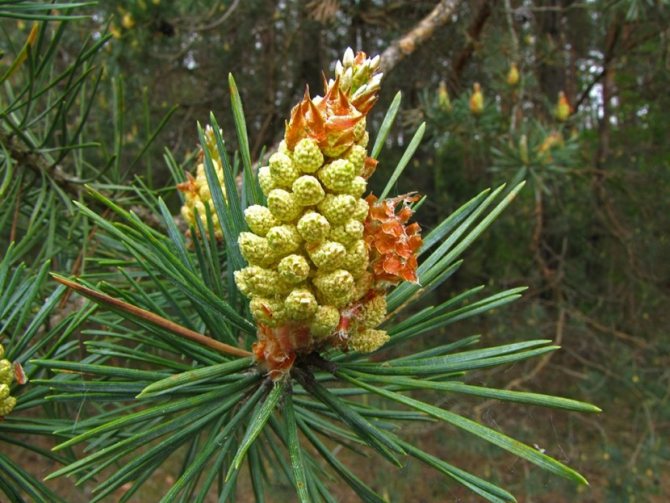
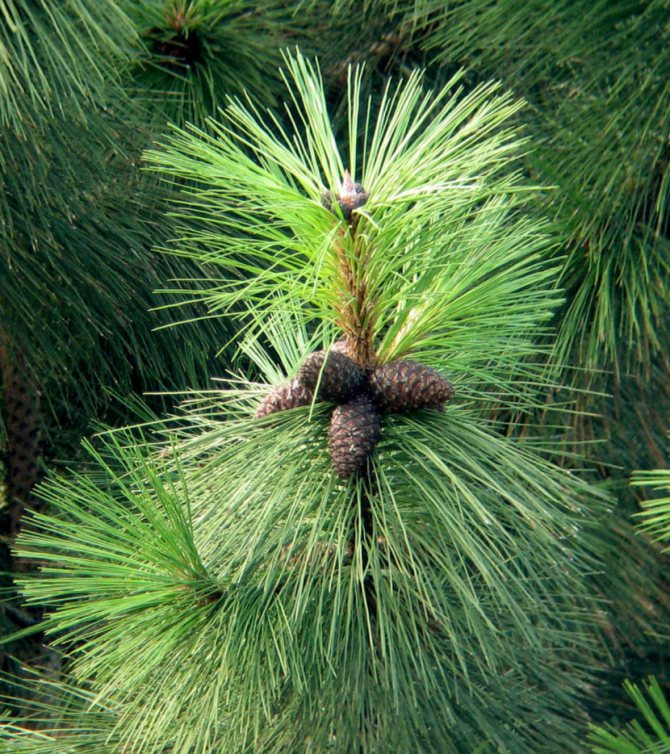
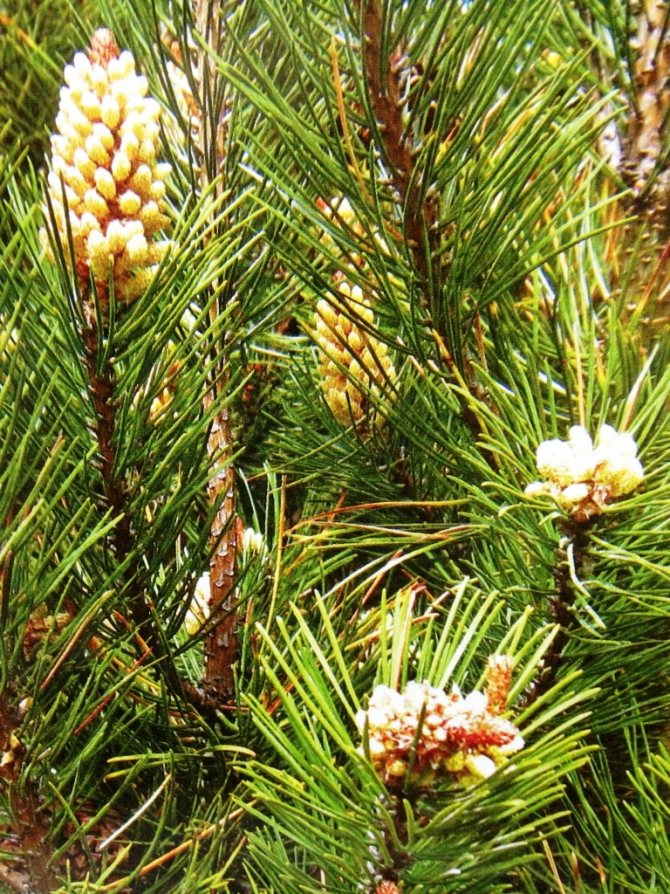
Pine shoots are of two types: long and short. Leaves (needles) are thin and elongated (5-9 cm in length), as a rule, collected in bunches of 2-5 pieces. Cones are oblong or ovoid and consist of tightly closed scales. During the period of maturity of the plant, these scales open, exposing the seeds.
Diseases and pests
Cultivars are generally resistant to the most common pine diseases: cancer and Schütte disease.
Ailments appear on the needles - it becomes brown-red, becomes covered with spots, stops growing. Pine is treated with foundationol during the entire growing season for cancer and Bordeaux liquid for Schute's disease. Aphids, scale insects and bugs are isolated from pests. Parasites are fought with the help of insecticides, for example, Actellika.
While watching the video, you will learn about growing pine from seeds.
Pine becomes infected with diseases and pests relatively rarely, but periodically inspect the ephedra and, if damaged, take action. Otherwise, the culture does not present any difficulties either in care or in planting. It grows slowly, but always pleases with a pleasant pine aroma and a beautiful crown.
Attention super FLY!
Conifers
Interesting to read:
- Mountain pine: a plant for lazy gardeners
- Fast-growing conifers: types, names, descriptions and role in the garden
- Siberian cedar gum - basic information
- Pine Mugo Pumilio: description, planting, care and cultivation features
- How long can a tree live and how to determine its age
- Thuja: its types and methods of cultivation
- Spectacular cypress - planting and care
- Low-growing apple trees for the Moscow region: varieties and their description
- Spruce "Konika" - care and cultivation in the garden. The story of the offspring of the Canadian spruce
Distribution and main types of pines
Where do pines grow? In their natural environment, the area of their distribution is wide enough (see map below). Pine forests are found in different parts of Eurasia, from equatorial to circumpolar latitudes. In the tropics and near the equator, pines are found mainly in the mountains. These trees grow in North America (including the Caribbean islands), as well as in northern Africa (in the Atlas Mountains).
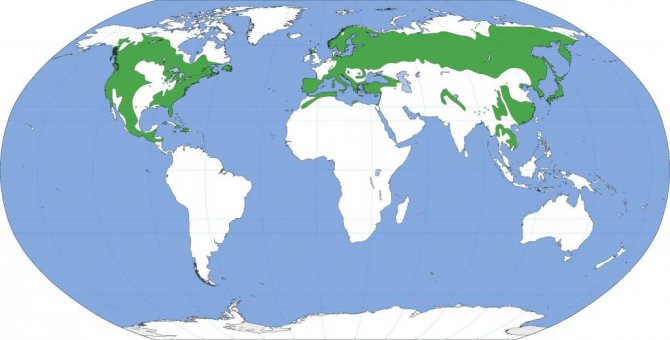

What is the name of the forest where the pines grow? The popular name of the pine forest is boron. True, sometimes this word also denotes spruce forests. In the pine forest, as a rule, there is no undergrowth, but mountain ash, juniper and other low shrubs are often found. Pines are often mixed with aspen or birch.
In the Northern Hemisphere, botanists count over a hundred different species of pine trees. About half of them are cultivated.Among the most famous and common types:
- Scots pine.
- Siberian cedar pine.
- Pine black.
- Weymouth pine.
- Mountain pine (or European).
MYTHOLOGY


In East Asia Pine was considered a true "tree of life", which even in old age looks green and fresh. For this reason, pine has always been highly valued as a symbol of a long life and a happy marriage. In China, pine (sung) symbolizes winter and long life, as well as hope and good fortune. In Chinese art, pine is a symbol of inviolability, since it retains its needles even in cold weather; in addition, the paired way of existence of this tree symbolizes a married couple. “With her calmness, she lengthens her life” (Confucius). Pines were also planted on graves to drive away evil spirits. Old trees were especially revered. "
In Japanese culture, the pine is considered “one of the three friends of winter, along with bamboo and the plum blossom, and is called matsu-no-ke. On New Years, the Japanese lay pine branches around their doors to attract good luck, as the pine tree is considered to be the temporary home of the gods descending to earth. In Japan, it was believed that when descending to earth, the gods descend to the tops of pines (and other tall trees) growing in the mountains, which connect the earth with Takama no hara - the abode of the gods in the sky.
Pine, cypress and willow held a special place in the ritual life of the Koreans. Pine and cypress were especially revered - "they were associated with the idea of royal ancestors." Since ancient times, there has been a custom in Korea to plant pines and cypresses on graves "to give the spirit of the deceased strength and thereby save the body from decay.". The coffins were made of pine boards in order to preserve the remains of the deceased, and the memorial tablets were made of cypress. “A staff made of pine in mourning rites symbolized mother earth” and “with its help the shaman (mudan) divined and spoke on behalf of the deceased. The pine acted not only as a receptacle for the soul, but also (in poetry) as the embodiment of the deceased himself. "
In the Buryat mythological tradition, the cult of family groves and trees is known. The Buryats believed in the origin of the human race from a tree, in the existence of a mother-tree and a father-tree. According to legend, the soul of a shaman lived in a pine tree - a shaman tree. "The bones of the shaman after his death were to be walled up in the same pine."
It is known that in different cultures the formation of a shaman proceeded in different ways, but the election always depended on the choice of the ancestor spirits. When the future Khakass shaman was convinced that “the spirits of the shaman ancestors want to see him as their successor,” he had to make a journey to another world, to the land of his ancestors, where he was to be endowed with miraculous power. “The road led him to a mountain, on top of which a pine tree grows. Only the one who carves a sign on a pine tree can become a true shaman, so the traveler took care of decorating the tree with his own mark. " Having passed all the tests of the dangerous path, the candidate reached the land of his ancestors, where he passed the last test and became a shaman.
Used materials:
- Hans Biedermann. Encyclopedia of symbols:
- Myths of the peoples of the world, vol. II;
- Yu.V. Ionov. About the cult of trees in Korea // Myths, cults, rituals of the peoples of foreign Asia:
- L. Zhukovskaya. Forms of manifestation of the cult of nature in the pantheon and rituals of Lamaism // Religion and mythology of the peoples of East and South Asia;
- V.N. Basilov. Chosen of spirits.
- Willow. Part 10
- Apricot
- Quince
- Acacia. Part 1
- Acacia. Part 2
- Acacia. Part 3
- Alchemy tree
- Orange. Part 1
Pine in culture, literature and folk art
According to an ancient Greek legend, the pine is the embodiment of the dawn nymph Pitis. Once she turned into this tree in order to hide from the evil god of the north wind Boreas.
Pine is quite widely found in the visual arts, in particular in Russian.Thus, the image of a tree can be seen on the canvases of Ivan Shishkin, Fyodor Vasiliev, Paul Cezanne, Camille Corot and other prominent artists. Perhaps the most famous painting depicting pines can be considered the work of II Shishkin "Morning in a pine forest".


Mention of these trees is often found in the literature. Here, for example, is an excerpt from the fairy tale "Artel Peasants" by the classic of Russian and Soviet prose Konstantin Paustovsky:
“Varya woke up at dawn, listened. The sky was slightly blue outside the window of the hut. In the yard where the old pine tree grew, someone sawed: zhik-zhik, zhik-zhik! They were sawing, apparently, experienced people: the saw went loudly, did not jam. "
There are many folk proverbs and sayings about pines. Here are just a few examples:
"Where the pine tree has grown, there it is red!"
"In winter, the pine looks greener."
"Getting lost in three pines."
"From the apple tree - apples, and from the pine - cones!"
In addition, there are many children's riddles with the mention of this tree. Here is the most popular one:
“Where did the old pine grow? Where did the red squirrel live? What has she got for the winter? " (Answers: in the forest; in the hollow; nuts).
Distribution and habitat [edit | edit code]
A widespread tree in Eurasia, starting from Spain and Great Britain and further east to the Aldan River basin and the middle reaches of the Amur in Eastern Siberia. Scots pine grows in the north up to Lapland, in the south it is found in Mongolia and China.
Forms clean plantings and grows together with spruce, birch, aspen, oak; undemanding to soil and soil conditions, it often occupies areas unsuitable for other types: sands, swamps. Adapted to various temperature conditions. It is distinguished by its photophilousness, it is well renewed in felling areas and fires, as the main forest-forming agent, it is widely used in forestry practice in all climatic zones. In the north of the range it rises to an altitude of 1000 m above sea level, in the south up to 1200-2500 m above sea level.
Where do pines grow?
Pine is a truly unique tree. After all, she knows how to adapt to a wide variety of environmental conditions. You can meet this tree both on the marshy northern plains and on the rocky cliffs of the Crimean peninsula. However, in mountainous areas, pines, as a rule, rarely rise above 800 meters.
Where do pines grow best? If we talk about the geological aspects of the territory, then this tree successfully settles on both sandy and rocky substrates. Some pine species have even adapted to clean chalk deposits. However, these trees grow best on well-drained sandy loam or loamy soils.
Often, in those places where pine trees grow, there is a significant excess of moisture. In this regard, they are also quite unpretentious. Pine trees adapt perfectly even to marshy conditions. As a rule, they are the first to "master" those lands that are unsuitable for all other trees, gradually fertilizing them with their own needles.
So, we found out in what natural conditions representatives of the pine family grow. And now it is worth talking in more detail about some types of pines. In particular, about those that can be found on the territory of our country. In addition, it will be useful to find out which pine tree grows where.
Comments (8)
Anna
07/29/2017 at 02:30 |
My dream is a pine tree near the yard. But I always thought that she would not grow with us. I will definitely try to plant this year, it is a pleasant aroma, the needles can be used for a bath, etc.Reply
Julia Expert Plodogorod
06.12.2018 at 21:09 |
Hello Anna! Pine is a completely unpretentious tree, but several conditions should still be met so that it is beautiful and healthy. The soil should be sandy with good drainage. Do not plant conifers close to your home, they can begin to erode the foundation with roots.At first, in order for the seedling to take root, one must not neglect watering. An adult tree is watered only in especially dry summer heat.
If the winters in the region where you live are very cold, then in the first few years of life, it is better to cover the pine tree with agrofibre and make sure that the snow does not break the branches. It is still better to remove fallen needles, despite the beneficial properties, fungal diseases can begin to multiply in it. As a preventive measure, it is better to treat the tree with fungicides several times a year, otherwise it will certainly start to hurt.
Reply
Svetlana
11.02.2018 at 18:50 |
Parents planted a pine tree in the country when I was still little. It has been growing for a very long time, I already have a son, and the pine tree is now no more than 2 meters. Nobody looked after her especially, it grows without fertilizers.
Reply
Julia Expert Plodogorod
22.01.2019 at 21:56 |
Hello Svetlana! The growth rate of a pine in the first four years of its life is about 10 centimeters per year. From five, the minimum growth rate per year is 30 centimeters, and from ten from half a meter to a meter. If the specified parameters are met, then everything is in order. But if your tree is growing more slowly, then there is a possibility that the conditions are unfavorable.
In this case, we recommend feeding the pine tree and checking if it has parasites or is infected with a disease. In any case, we recommend carrying out preventive spraying, since some fungal diseases affecting conifers are dangerous for other crops that grow in your garden.
It should not be ruled out that the pine variety that grows on your site is considered decorative and, in principle, does not differ in high growth. To determine if this is the case, it is worth comparing the appearance of your pet with the descriptions of the pine varieties.
Reply
Maria
21.01.2019 at 08:26 |
A pine tree grows beautifully on our site, for 8 years already. It adds a little. She took root remarkably in the corner of the garden, almost did not get sick. A place with diffused sunlight, shaded in the afternoon.
Reply
Julia Expert Plodogorod
22.01.2019 at 22:22 |
Hello Maria! If your pine has been ill at a young age with some kind of disease, then you need to take measures so that this does not happen again, since many problems are very difficult to get rid of.
To protect against fungal diseases, it is imperative to remove fallen needles and other debris from under the tree. It is best to burn it. Some gardeners find it helpful to mulch the soil with fallen needles, but the risk of developing fungus in it is much higher than the intended benefit. And in order to create a layer of mulch, a lot of materials are also suitable, for example, sawdust. In addition, we recommend spraying with Bordeaux liquid two or three times a year, stem injections and the use of immunostimulants.
From diseases that provoke deformation of branches, yellowing or russeting of shoots, planting on hills, adherence to the rules of fertilization, moderate watering and prevention of waterlogging will help. It is important that the initial planting material is healthy and strong. In addition, the pine tree must have enough space of its own to ensure air circulation around the trunk.
It is imperative to carry out pruning for the purpose of sanitation, removing diseased and dry branches, and also in early spring to spray with prophylactic agents in order to get rid of pests that have overwintered in the ground or on the plant itself.
Reply
Elena
03.11.2019 at 01:20 |
I planted three Mini Pugs in the yard. They do not require special care, the first years they fed and watered periodically. And as they grew up, I began to do it much less often. Trees look very beautiful both in summer and winter.
Reply
Julia Expert Plodogorod
05.11.2019 at 00:50 |
Hello, Elena! Although it is a truly unpretentious culture, it still requires proper care.The decorativeness and health of the plant depends on this.
You rightly pointed out that the most intensive care is required in the first years of life. At this time, you can use nitroammophosphate fertilizer. Also, young plants need to be moisturized often and abundantly enough. It is better to use non-cold water for this. Otherwise, the roots that have not completely taken root will receive a cold burn.
For Mini Pug specimens of any age, loosening is important. This improves oxygen access to the roots. And the absence of weeds will protect the ephedra from pests, and also make the planting more well-groomed. Alternatively, mulching can be used. For the described culture, peat or old sawdust is best suited.
Another important part of grooming is pruning. At the beginning of spring and at the end of autumn, you can carry out a refurbishment. To do this, you need to carefully examine the plant, remove dried or damaged places. Also, frozen areas and those that have stains or plaque are subject to removal.
The formation is carried out in order to slow down the growth of the Mini Pug, to make it more compact. Although this is a hardy culture that almost does not lend itself to disease, we recommend using only clean and disinfected instruments for all manipulations. They must be sharp, otherwise there is a risk of harming the conifer.
Of the pests, the appearance of pine hermes is possible. This pest feeds on plant juices. Signs - white and light gray down on the crown. This pest is dangerous not only because it inhibits the plant. When coniferous immunity falls, it becomes susceptible to a number of other diseases.
Hermes to some extent resemble aphids, but they most often affect conifers. In case of breeding such uninvited guests on the Mini Pug, we recommend that you immediately begin treatment with Calypso, Confidor Maxi, Mospilan preparations.
The plants described are quite cold-resistant, but sometimes they suffer from drying out. This happens in the spring. The reason is not in the disease, but in the fact that the culture cannot yet actively absorb moisture, since the earth has not warmed up, and the crown is already exposed to sunlight.
In this case, there are several options. You can moisten the plants with warm water or cover them from the rays of the midday sun. If the front garden is large, we recommend using a diffuser mesh.
Reply
Scots pine
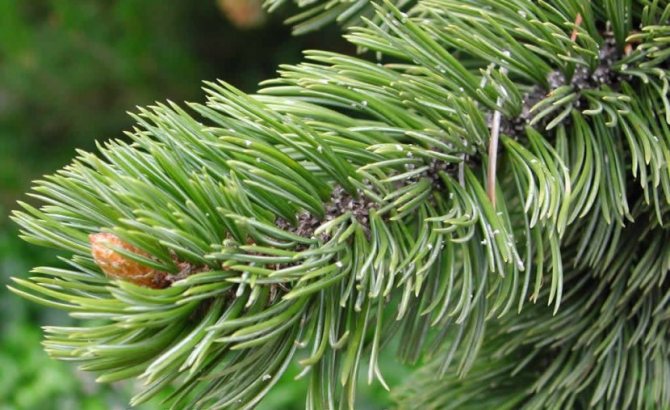
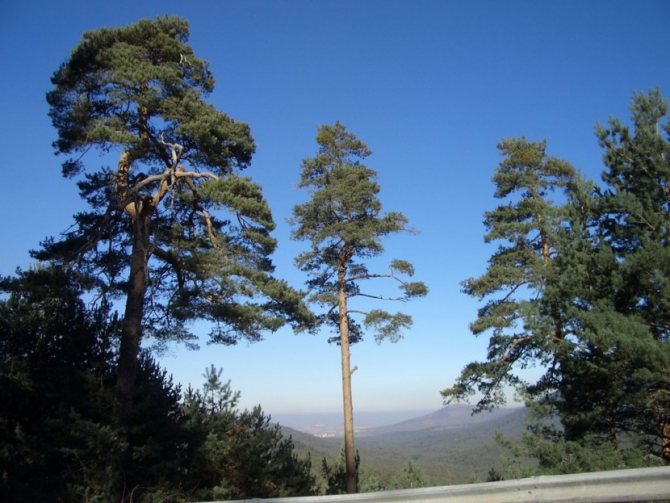
Pinus sylvestris is the most common species of the pine family. This is a light-loving and fast-growing tree, reaching a height of 30-50 meters. The crown is transparent and highly raised, often with a flat top. Bark color: light brown, reddish. The trunk, as a rule, is straight with a diameter of 0.5 to 1.2 m. The needles are quite long (up to 6-9 cm), bluish-green, slightly curved.


The distribution area of the tree extends in a rather wide belt from Central Europe to the Far East. Where does Scotch pine grow? It can be found on the loose sands of Mongolia, and in the bogs of Polesye, and in the mountains of the Caucasus. The tree adapts well to various natural and climatic conditions. However, it feels most comfortable in soils of light texture.
Scots pine grows rather quickly. Lives 300-600 years.
Reproduction of pine
Pines can be propagated by grafting, cuttings and seeds. As a rule, pine vegetative propagation methods are reliable and faster results. But most often such a tree is propagated by seeds.
Growing pine from seeds


Well-ripened fresh seeds are used for sowing. Collecting cones should be carried out in the last days of October or in the first - November, during this period the seeds in them will already be fully ripe and suitable for sowing. It should be borne in mind that the cones must be plucked from the pine, and not collected from the ground. They will need to be thoroughly dried, for this they are laid out in the room on a sheet of paper or cloth, while placing them next to the heating device. Seeds can be easily removed from well-dried buds.For storage, they are poured into tightly closed glass jars, which are removed in a cool place. 8-12 weeks before sowing, the seeds must be sorted out, after which they are poured into a container filled with water for a while. Floating seeds are recommended to be collected and discarded. The same seeds that drowned must be stratified. To begin with them for 30 minutes. placed in a solution of potassium manganese, which should be painted in a faint pink color. Then they are washed and kept in clean water for 24 hours, then they are combined with moistened sand. The mixture is poured into a nylon stocking, which is removed on the refrigerator shelf for at least 4 weeks.
Sowing seeds is carried out in the second decade of April. The substrate should be light, but not necessarily nutrient-dense. So, for sowing, you can use river sand, which needs to be calcined for a third of an hour in an oven heated to 200 degrees. The container is first filled with sand, then a two-centimeter layer of sawdust is poured on top, on the surface of which the seeds should be evenly distributed, with the pointed tip pointing downwards. Each seed needs to be slightly pressed into the substrate, after which its surface is covered with a layer of fallen needles, the thickness of which should be 10-15 mm. Crops are watered abundantly with a spray bottle, after which the container is covered with a film on top. The first seedlings, as a rule, are shown already in April, but may be a little later. Crops need systematic ventilation and watering, and condensate accumulated on the film must also be removed in a timely manner.
After the first seedlings appear, the container must be transferred to a warm and well-lit place, which must have reliable protection from drafts. During the formation of the second pair of needles in the plants, they will need to be transplanted into a real soil mixture for pine trees. Planting seedlings in open soil is carried out after 2-3 years in the spring, while a distance of 0.3-0.5 m should be kept between them. you also need to try not to shake off the microsea from them, on which the normal growth and development of the tree depends. The root of the seedling must be carefully trimmed, after which it is immersed in a chatter box consisting of humus and garden soil (1: 2), so much water is added to obtain the consistency of thick sour cream. Then the pines are planted in holes, which should be prepared in advance. Watering the seedlings in the school garden is done once every 7 days. When the trees are watered, the soil surface should be loosened around them, and all the weeds should be pulled out. And in the second year in the spring, before the sap flow begins, the pines should be fed by adding 25 grams of superphosphate, 0.5 kilograms of rotted manure and 10 grams of potassium nitrate per 1 square meter of the garden to the soil. Fertilizers must be sealed to a depth of ten centimeters. 4 years after transplanting into a school, the seedlings can be planted in a permanent place, they do this in spring or early autumn.
Propagation of pine by cuttings
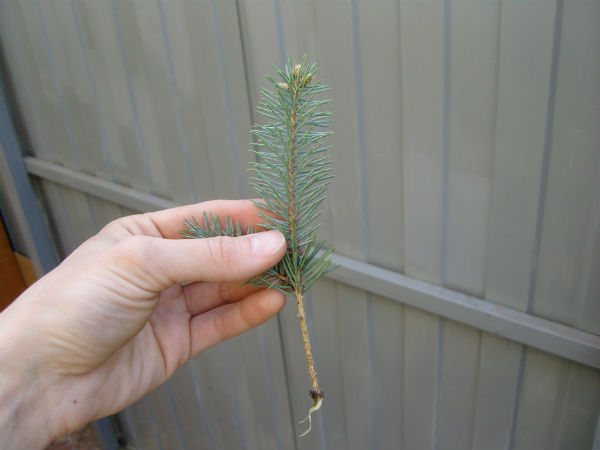


Cutting of this culture is recommended to be carried out in the autumn. Lignified cuttings are cut, the length of which can vary from 80 to 120 mm, they are taken with a heel (with a piece of wood from the branch on which the cutting was located). To prepare them, you should choose a cloudy day. Cuttings are cut from the apical lateral shoots of the middle part of the crown, which are facing north. Cuttings should not be cut off, but with a strong, quick movement down and to the side, tear off with a piece of wood and bark (heel).
Before planting the cuttings, their heels will need a little deburring and needling. Then the cuttings should be kept for 4-6 hours in a 2% solution of Fundazol, potassium manganese (dark pink) or Kaptan.And shortly before disembarkation, the heel and the lower edge of the segment must be treated with a solution of Epin, Kornevin or Heteroauxin. Cuttings are planted in a soil mixture, which includes humus, leaf earth and sand, taken in equal parts. They are planted at an angle, and then covered with a transparent cap on top to create the greenhouse conditions necessary for rooting. Every day the cuttings should be ventilated, and condensation should be removed from the hood. For the winter, the container with cuttings is recommended to be removed to the basement, and in the spring time it should be transferred to the street. Cuttings will take root after 1.5–4.5 months, while young shoots and roots will grow at the same time. With the onset of next spring in the month of May, the cuttings need to be watered with Kornevin's or Epin's solution. Planting pines in open soil can be done after another 1 year.
Reproduction of pine by grafting
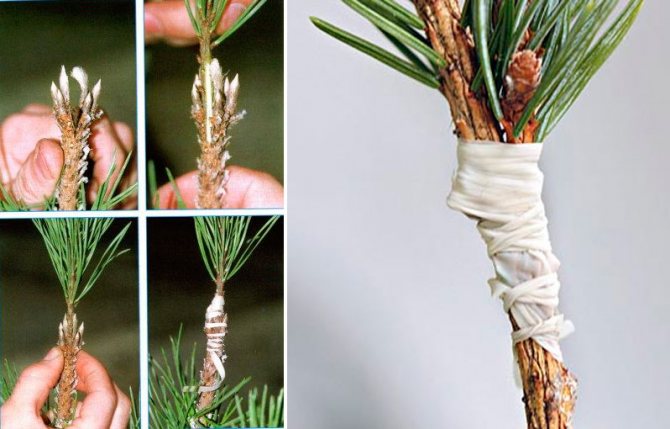


As a rule, only gardeners who have experience in this matter are propagated by grafting a pine tree, but if desired, a beginner can also do this. The grafting in the butt has a very important advantage, namely, thanks to this method, the scion stalk is guaranteed to retain all the varietal characteristics of the parent plant.
As a rootstock, you can take a plant whose age is from four to five years. And the scion is cut with growth, the age of which is 1–3 years. All needles must be cut off from the cutting; they should remain only near the bud, which is in the upper part. At the rootstock, you need to cut off all lateral buds and cut off long shoots.
Vaccination should be done in the spring, as soon as sap flow begins, or in the middle of the summer period. In the spring, the pine is grafted on last year's shoot, and in the summer - on the shoot of the current season.
Siberian cedar
Siberian cedar pine (most often referred to simply as cedar) is a majestic coniferous tree with a dense crown and a powerful trunk. Its branches are located tightly to each other and are covered with soft and long needles (up to 12 cm), which are collected in bunches. The shape of the cones is elongated ovoid, the color is purple at first, and later brown. Cones contain seeds (“nuts”) that are eaten and used to make pine nut oil. One cone can hide from 30 to 150 of these nuts.


Where does cedar pine grow? The tree is widespread in the forest belt of Western Siberia (from 48 to 66 degrees north latitude). Within Eastern Siberia, the upper boundary of its range is noticeably shifting to the south. Cedar is also found in the forests of Mongolia and northern China, grows on the slopes of the Altai Mountains (up to 2000 meters). On the territory of the Arkhangelsk region there are artificial plantings of Siberian cedar, planted in pre-revolutionary times.
How to contain the growth of pine trees on the site
In order for the trees not to grow too high on the site, it is necessary to maintain the height of the pines within the permissible limits, so that they do not create a lot of shade and do not interfere with other plants.
The growth of the crown in height and width is due to the annual appearance of young shoots, which are formed on the tops of the branches of the previous year in the form of 2-3 new buds.
In the spring they give young shoots, colloquially called "candles". By pruning or plucking them off, the growth of the tree is held back and its size is regulated.
In order to contain the growth of the pine, it is necessary to start pruning when 3-4 levels of strong branches have appeared on the tree. Already 1 year after planting the seedling in open ground, you can start forming the crown.


How is pruning done
To do this, break out the longest "candle" in the bunch of new shoots, which is the main shoot of the next season and is responsible for the continued growth of the pine in height.
The rest of the shoots are shortened. Depending on what result you want to get, pinch off 3 or 4 parts from the tops. The shorter the shoots, the better the crown will develop and the slower it will grow.
The growth of side branches is regulated in a similar way. Remove the main "candle", and pinch the rest.
It is not recommended to use pruning shears for pruning, as it can severely damage the plant. Young needles begin to turn yellow, and the decorative qualities of the pine deteriorate. It is best to do this with your fingers, gently pinching off excess shoots. This method is used by the Japanese, who are the progenitors of such a culture as bonsai. Regardless of the height and number of shoots on the tree, they slowly and carefully pinch them with their fingers.
When pruning a pine tree, make sure that all the shoots are the same length. Even if the branches are too short, they must be pinched, as this promotes the formation of new young buds.
Weymouth Pine
A slender and extraordinarily beautiful tree with very high quality wood. The branches extend from the trunk strictly horizontally and are covered with thin, soft and long needles. In the 18th century, the wood of the white eastern pine (as it is also called) was actively used for the construction of ships of the British Navy. Nowadays it is widely cultivated in forestry.
The natural range of Weymouth pine is limited to North America. In particular, the tree is common in the northeastern United States and southeastern Canada. It is also found in Mexico, Guatemala and the islands of Saint Pierre and Miquelon. In the mountains it rises to a height of 1500 meters.
What is mycorrhiza
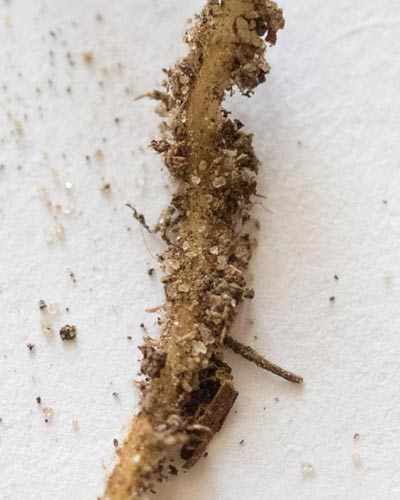


Transplanting pine trees from the forest is often unsuccessful for one reason: when a tree is transferred to a new place, the formation, which plays an important role in the life of the tree, is disturbed. This formation is mycorrhiza - a symbiosis of fungal hyphae and tree roots. In such an alliance, for the most part, mutual benefit reigns.
Although pine grows quickly, enough carbohydrates are deposited in its roots, which are necessary for fungi to reproduce, unlike, for example, poplar. Mushrooms, in turn, improve the saturation of the plant with micro and macro elements. In particular, the concentration of potassium increases by 75%, and nitrogen by 86%. The best benefit for the tree is seen in the study of the absorption of phosphorus, which was absorbed more actively by 234% in pines with mycorrhiza than without it.
It is also curious that fungi that settled on the roots of pines and formed a kind of caps are able to protect the root system from pathogenic fungi, bacteria and viruses. And due to the fact that hyphae germinate not only near the tree, but can stretch for tens of meters, there is an exchange of nutrients between neighboring pines.
In a stressful situation, many trees, including Scots pine, can form phytoalexins, natural antibiotics. It turned out that mycorrhizal fungi can stimulate pine to synthesize these substances and, thus, activate the plant's immunity.
The symbiosis of fungi and roots is in balance until a certain point. If the tree is weak and begins to die, then the fungal hyphae penetrate deep into the root and destroy it, accelerating its death. At the same time, if the mushroom cannot withstand the influence of some unfavorable factors, the pine begins to dissolve and "digest" it, absorbing all the nutrients. Thus, in nature, the strongest survive, capable of giving good offspring.
Bunge pine
Perhaps, in the whole pine family, the Bunge pine (Pinus Bungeana) boasts the most exotic appearance. It got its name in honor of the Russian botanist Alexander Bunge, who first described it back in 1831.
The tree stands out for its unusual bark. It is initially greenish in color. But with age, its scales begin to flake off, and the bark becomes grayish-white. The tree rarely exceeds 30 meters in height. The pine needles are tough, dark green, the cones are resinous, brown.
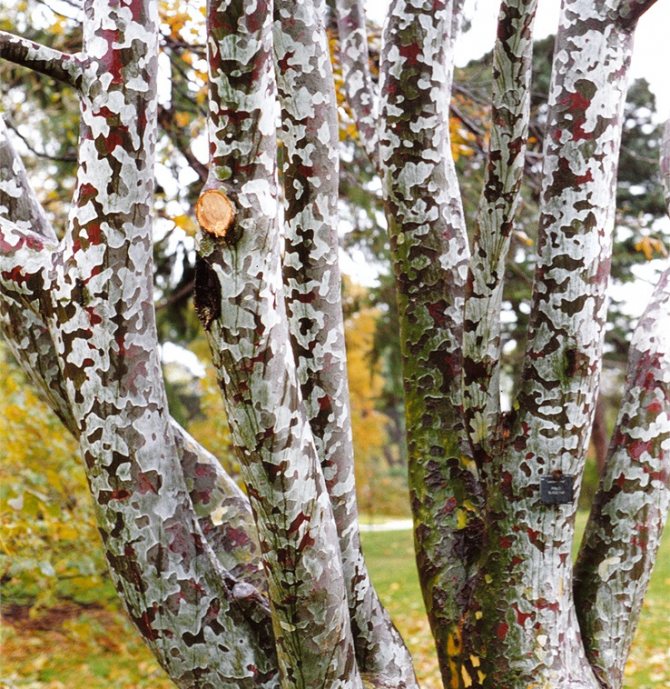


Bunge pine grows in central and western China. The tree is actively planted in parks and gardens, and is used for landscaping city streets and squares.
Witch's broom on the crown of a pine tree


The crown of the pine sometimes forms the so-called "witch's broom". These formations arise from dormant buds, which the tree needs as a reserve to restore the lost parts of the crown. The witch's broom appears in the form of many thin branches of short length with short needles. Thus, a cluster is formed that resembles a ball.
The reason for the appearance of the witch's broom has not been finally clarified, however, the processes occurring in this case are well studied. Under the influence of viruses, bacteria or other factors, mutations appear like a cancerous tumor, which lead to the proliferation of plant tissues.
In pine, these mutations can lead to the formation of viable forms, which is used in breeding and landscape design. A witch's broom is grafted onto the trunk of a young pine tree and, as a result, an interesting dwarf pine tree with a rounded crown is obtained. Such varieties are capable of bearing fruit, and some of the seedlings also inherit the mutation, while others grow into ordinary tall trees.
Economic use of pine
Scots pine wood is most widely used by man. It is distinguished by its special hardness, density and high tensile strength. In particular, the following building materials and substances are obtained from it:
- construction logs and beams;
- shipbuilding and deck ridges;
- railway sleepers;
- plywood;
- cellulose;
- rosin;
- tar;
- turpentine, etc.
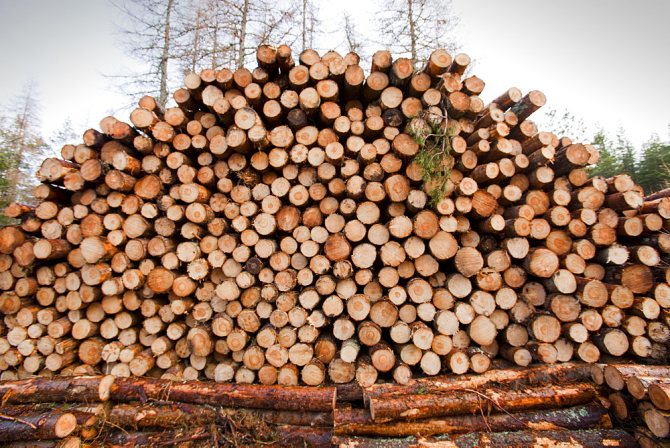


Pine is also known as a medicinal plant. In folk medicine, almost all parts of this tree are used - buds, needles, bark, resin, seeds. So, needles contain a number of vitamins and have an excellent bactericidal effect. Turpentine oil is widely used for arthritis, rheumatism and neuralgia. Pine tar is used to successfully treat skin conditions such as psoriasis or eczema.
Coniferous plant pine
Scotch pine forms a number of forms, which differ in the structure of the crown, color and shape of the cones. There are varieties with a weeping and pyramidal crown. The color of the needles in young shoots can be golden, whitish or silvery. The bark is scaly or lamellar.
The pine plant has a wide range, which extends over different, from an ecological point of view, areas, therefore the species is characterized by a large number of ecotypes. To date, ecologists distinguish more than 30 such ecotypes. For example, the Angara pine growing in the basin of the river. Angara is an ecotype of Scots pine. The study and observation of Scots pine seedlings of various origins grown in the same conditions shows the difference in plants in their ability to drought and cold resistance, to growth, and resistance to diseases. Also, these plants may differ in morphological characteristics, such as: crown shape, length of needles, structure of the trunk, etc. However, all these characters are prone to changes and are not used to isolate the species.
Features of growth and growing conditions for pine
Pine tolerates severe frosts and low air humidity. The tree is highly resistant to industrial pollutants. The only thing the pine tree desperately needs is natural sunlight. Therefore, it should be planted in open, unshaded areas. Sandy or sandy loam substrate is best suited for planting. In the case of planting in "heavy" soil (for example, black earth or loam), additional drainage of the site will be required.
Pine seedlings are usually planted in late April or early September. To do this, a meter-long hole is dug and a mixture of soil, turf and river sand is poured into it. You can also add some nitrogen fertilizers (about 35-40 g). The optimum age of the seedling is 3-5 years. When planting in the ground, it is extremely important to ensure that the root collar of the young tree is at ground level.
In the first five years of its life, a pine sapling gains, at best, ten centimeters per year.Thus, a five-year-old tree does not exceed half a meter in height. In the future, the annual growth of pine increases to 25-60 cm per year, and after ten years of life of the tree - reaches 80-100 cm per year. In a thirty-year-old pine, the growth in height slows down and the process of trunk expansion begins.
For garden and summer cottages, it is recommended to choose decorative and miniature forms of pine trees with crowns of original forms. This could be:
- Weymouth Pine Radiata.
- Pine Aurea.
- Mountain pine Dwarf.
Pine tree care
You need to take care of the tree only in the first two years after planting. In the spring, a full range of mineral fertilizers is applied. Seedlings are rarely watered, 1-2 times a week up to 30 liters of water under the root.
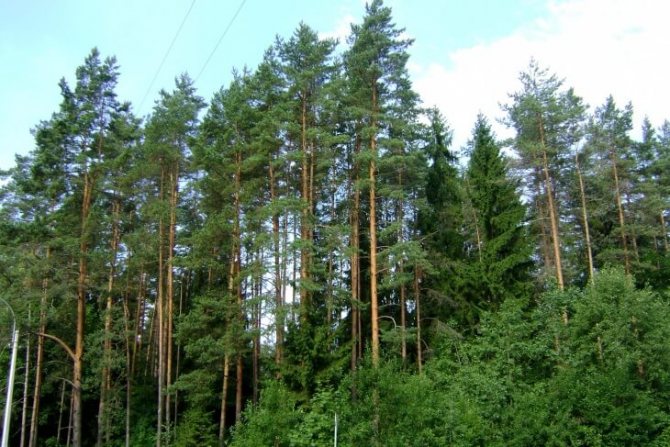


Pine forest
After 3 years of life, you don't have to worry about watering. An adult plant is not fed or watered - from 5 years of age. It is not recommended to remove coniferous litter. It forms the mulch that the tree needs to retain moisture and provide nutrients.
Some species are covered with spruce branches for the winter, the overgrown crowns are tied up so that the snow does not break the branches. In spring, young seedlings are shaded from direct sunlight. Do this up to 5 years of age. In the first year of life, the soil around the tree is weeded and mulched.
Crown trimming is done only when forming decorative figures. For a more lush crown, spring shoots are pinched by 1/3. The rest of the pine does not require much maintenance.
Expert opinion
Yulia Yurievna
I have a large garden and vegetable garden, several greenhouses. I love modern methods of plant cultivation and soil mulching, I share my experience.
Ask a Question
We would like to note that although litter is a natural mulching agent, it is still better to remove it. The fact is that fungal spores often develop in it, which subsequently infect a coniferous plant. It is especially dangerous to leave such debris in preparation for wintering. It is better to use sawdust, humus or peat instead of coniferous litter. They will also help to retain moisture and heat in the soil, but without harm to the plant. As for pruning, do not forget that its main purpose is not only crown formation, but also sanitation. It is imperative to remove dry, diseased, growing inward or thickening branches.
Where can you find pine in Russia?
Pine is one of the main forest-forming species in Russia. There are 16 of its species within the country. Scots pine is the most widespread. In general, pines occupy about 15% of the area of all forests in Russia. They often reach a height of 50-70 meters. Where does pine grow in Russia?
Pure pine forests are widely represented in Siberia (usually on sandy or stony soils). To the south of the conventional line Bryansk - Kazan - Ufa, these trees are extremely rare and dotted, forming only small pine forests and groves. However, in the mountains of the Caucasus and Crimea, they are ubiquitous.
In addition to Scots pine, Siberian cedar is widespread in Russia, and Korean cedar is also common within the Amur Region. The latter is distinguished by more elongated cones and seeds.
Pine trunk and crown
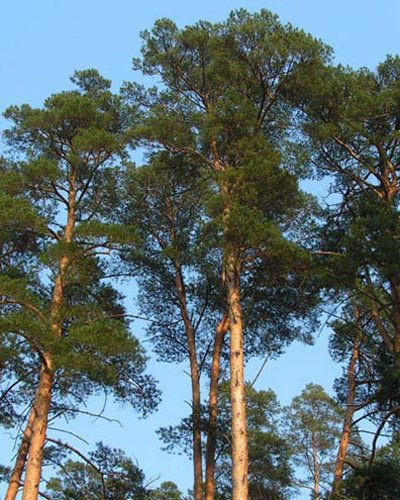


The trunk is covered with scaly bark, and in the lower part these scales form thick plates. The outer layer lags behind quite easily - this is a kind of protection against insect pests that lay their eggs or hibernate under the bark. The trunk is covered with a scaly bark of a brown-beige color, and in the lower part these scales form thick plates. The outer layer lags behind quite easily - this is a kind of protection against insect pests that lay their eggs or hibernate under the bark. Under the influence of the wind, trees sway, partially shedding bark scales, exposing the shelter of pests. The branches are green in the first year, and then turn brown. The branches are green in the first year, and then turn brown.
The wide legs of Scots pine consist of horizontally arranged branches, the needles on which are arranged in pairs and have a length of 3 to 9 cm.The edges of the needles have small teeth, the upper part of the needle is convex, the lower one is concave, forming a groove.
Scots pine crown diameter varies depending on the age and conditions in which it grows. In adult plants, the length of the lower, oldest branches can be up to two meters. As a rule, if the competition between tall plants is small, they do not shade each other, the crown width is larger. Conversely, if a pine tree grows in a dense forest, then it grows taller, as it seeks to receive more sunlight.
Still, the "Green Japanese Pine Branch"
Hello my dear friends! After a little reflection, I decided to change the name of my magazine. Now its full, real and final name is "Green Branch of the Japanese Pine". I think this is correct. Both in meaning and in the content of my blog. After all, I already wrote that my blog is dedicated to the topic "Japan". And Japan is inextricably linked with nature, with the colors of nature, with greenery. The pine tree is traditionally a symbol of Japan. A symbol of longevity, overcoming, strength, wisdom and beauty. "Green Branch of the Japanese Pine" is an original, authentic name with a lot of meaning. But the name "Green Branch" is not very informative. In addition, the entire Internet is replete with the names of the Green Branch.
But you really want to be recognizable, the one and only!
How to open pine cones at home
The cones are harvested still unripe, unopened. Place in a shallow dish and cover with a regular sifter to prevent the birds from chewing on the seeds.
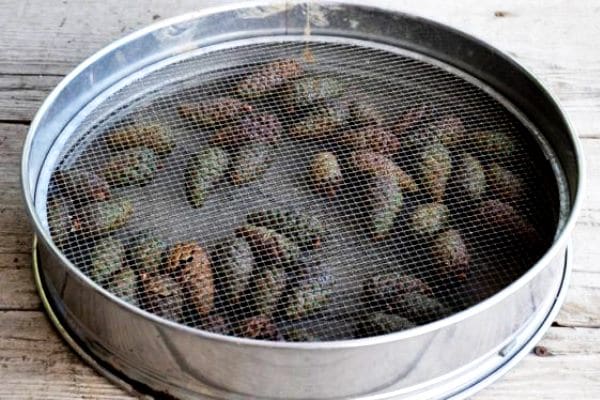


Immature buds
The buds should remain dry throughout the ripening period, as this will speed up the time it takes for the flakes to open. After about a week, the buds are fully ripe, darken and open.
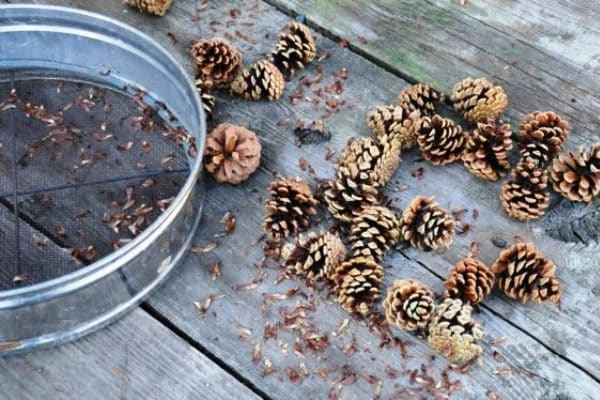


Pine seeds
The seeds fall out on their own.
Taxonomy [edit | edit code]
- Pinus binatofolio Gilib.
- Pinus borealis Salisb.
- Pinus cretacea Kalen.
- Pinus ericetorum thore
- Pinus erzeroomica Calvert ex Gordon
- Pinus fominii Kondr.
- Pinus frieseana Wich.
- Pinus genevensis Carrière
- Pinus genovensis Garsault
- Pinus hagenaviensis K.Koch
- Pinus krylovii Serg. & Kondr.
- Pinus lapponica (Hartm.) Mayr
- Pinus montana Hoffm.
- Pinus mughus Jacq.
- Pinus resinosa savi
- Pinus rigensis Loudon
- Pinus rubra Mill.
- Pinus tartarica Mill.
Varieties [edit | edit code]
In different parts of the range, scientists have identified varieties of Scots pine, as well as morphological and ecological forms - ecotypes that are characteristic of certain growing areas.
Currently, scientists are considering 3 valid subspecies of Scots pine:
- Pinus sylvestris var. hamata Steven - grows in the Balkan Peninsula, in northern Turkey and the Caucasus, at an altitude of 500-2600 m above sea level.
- Pinus sylvestris var. lapponica - grows in Norway, Sweden, Finland and the adjacent territories of Russia north of 65 ° north latitude (north of Karelia and the Murmansk region). On the Solovetsky Islands in the White Sea, its growth is up to 30 m [7]. The needles are shorter and tougher. The seeds are yellowish brown. Often forms a creeping shrub form [8].
- Pinus sylvestris var. mongolica Litv. - grows in Mongolia, northwestern China and southern Siberia, at an altitude of 300-2000 m above sea level. It occupies large territories in Transbaikalia, in other places it prefers dry and sandy soils. A tree 42 m high grows in the Sokhondo nature reserve in Transbaikalia [7].
Ecotypes [edit | edit code]
Due to the wide range of Scots pine, extending over significantly ecologically distinct areas, this species is characterized by a very significant number, up to 30 distinguished by ecologists, ecotypes. For example, in the basin of the Angara River, the Angara pine, an ecotype of Scotch pine, grows.
The formation of distinctive ecotypes in natural conditions contributed to the emergence of a large number of scientific synonyms of the species, which currently have the nom status. illeg. or nom. inval. and are not used in taxonomy.
How to properly place coniferous shrubs in the garden and on the site
To maintain the attractiveness of the garden, the generally accepted rules are followed:
- a flower bed with dwarf coniferous bushes is located in a spacious area;
- the lowest plants are planted in the foreground in the curbs;
- near reservoirs, deciduous, better weeping forms are planted to coniferous bushes;
- variegated varieties are planted pointwise, surrounded by specimens that do not change the color of greenery.
Original compositions
Often conifers form. Tall and medium-sized junipers, thuja, cypress trees are modeled, creating interesting examples of topiary art. Everyone chooses from a variety of garden ensembles:
- in the alleys, evergreen shrubs alternate with deciduous ones;
- low mountain pines are combined with ground cover junipers and creeping perennials;
- red-leaved barberries and tubular nandines create bright contrasts with evergreen shrubs;
- junipers are excellent partners for ferns, dwarf ones are also used as an ampel culture.
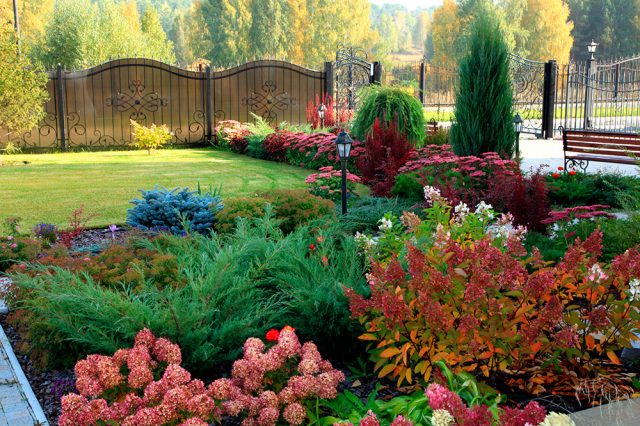


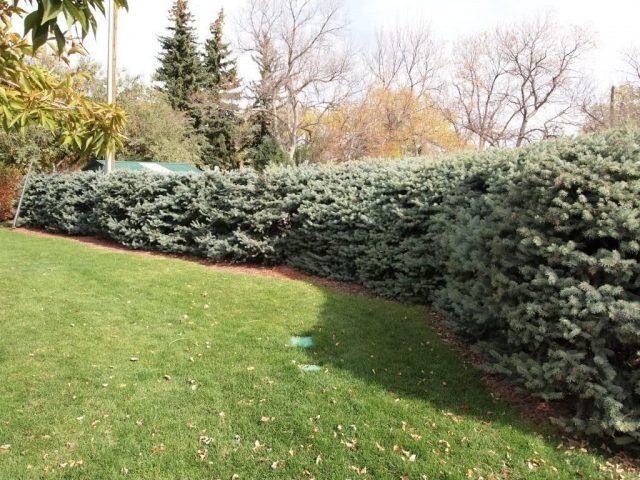
Hedge
The division between garden zones is made from bushes of different heights: low, medium or high. Usually the hedge is trimmed. Sometimes tall and medium-sized plants are planted alternately. The most dense coniferous hedge is planting shrubs in 3 rows in a checkerboard pattern.


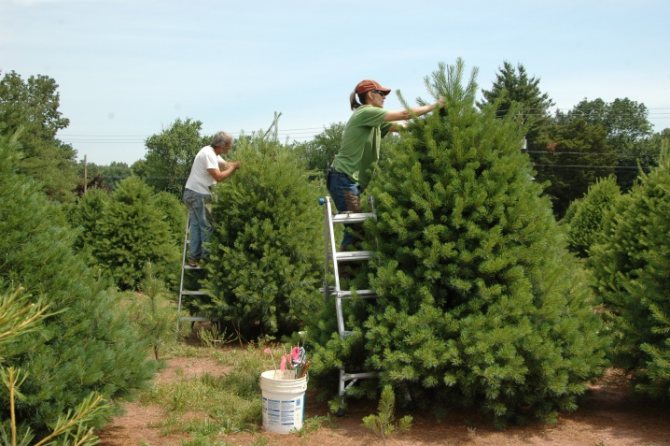
How to stop the growth?
The growth of pine in height can be a real problem, because the tree grows very quickly, and this is not always good, especially for a small suburban area. It is quite possible to limit the growth of a tree if you know how to do it correctly. You can get a spreading crown and a shorter trunk by adjusting the central shoot.
Adjusting the growth of a pine is done simply by pinching the upper shoot, popularly called a candle. This can be done on seedlings that have already formed 3 levels of branches. Very young plants should be pinched only in cases of extreme necessity, but it is better to wait until they are 4-5 years old. The procedure is carried out in spring or autumn.


For information on how to care for a pine tree, see the next video.


Scots pine (Pínus sylvéstris) is a tree common throughout Eurasia, from Scandinavia to China. In Russia, it grows everywhere, as part of coniferous and mixed forests. Pine has been actively used in landscape design since the first half of the 19th century.
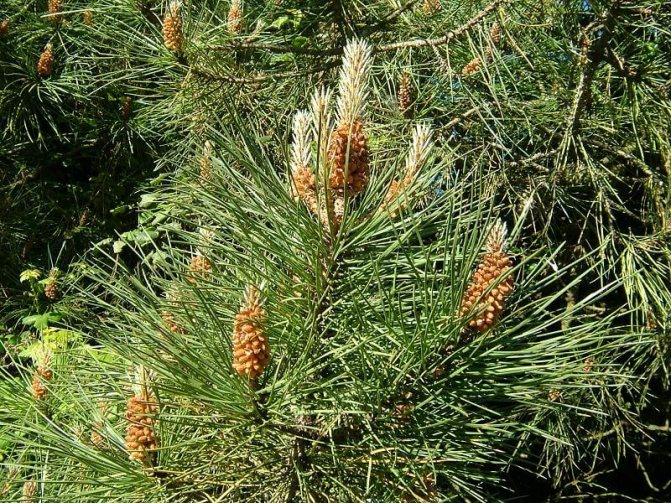
Scotch pine, according to the old classification, belonged to gymnosperms, that is, it does not have flowers and the seeds are not located in the container - the fruit, but openly. Now they are referred to the Coniferous department. Seeds - lionfish with a long wing, are formed in ovoid female cones, which are located in the upper part of the crown. Male spike-shaped strobili are formed at the base of young shoots.
The healing properties of pine
Possessing great vitality, the pine contains a storehouse of healing riches. And needles, and juice, and buds, and wood - everything in the pine heals, heals, goes into action. The pine needle extract is used for life-giving baths.
Pine sap - resin, - containing rosin, is a raw material for the manufacture of ointments, plasters. Turpentine obtained from it is an excellent external remedy for neuralgia, rheumatism, gout. Pine inhalation cures the most persistent cough and laryngeal catarrh by acting as an antiseptic.
The tar used in the treatment of skin diseases - scabies, eczema, neurodermatitis also has a disinfecting effect.
The shortened apical shoots of pine (buds), which must be harvested in February - March, before they start growing, have expectorant and disinfectant properties. The healing properties of pine are used for colds, bronchitis and even tuberculosis.
Some pine species have large, edible seeds that are rich in fatty oils and proteins.
Video: Pine cones, harvesting
Next, you will learn what types of pines are, and what are their features.
Coniferous shrubs in garden landscaping
The endurance and expressiveness of the silhouette of coniferous shrubs, most of which are amenable to formation, provide plants with high popularity for building various multi-style garden compositions:
- low and medium height are positioned as attention points on spacious lawns;
- creeping and dwarf specimens - an indispensable element of rockeries, rock gardens;
- bright green plants of short stature often serve as a strict backdrop for bright flower beds;
- densely planted tall bushes form a division into zones and decorate the walls of buildings and fences;
- dwarf conifers are often grown as container crops.
Photo of pine


Cherry - description of the main varieties, planting and care rules + 68 photos

Peach - cultivation, reproduction, diseases and varieties + 81 photos
- Cedar tree - description, cultivation, types of cedar and its beneficial properties + 77 photos
Views
What types of pine trees are best to plant on the site?
back to menu ↑
See also: How to make garden paths in the country with your own hands? (80+ Photo options for great ideas) + Reviews
Norwegian
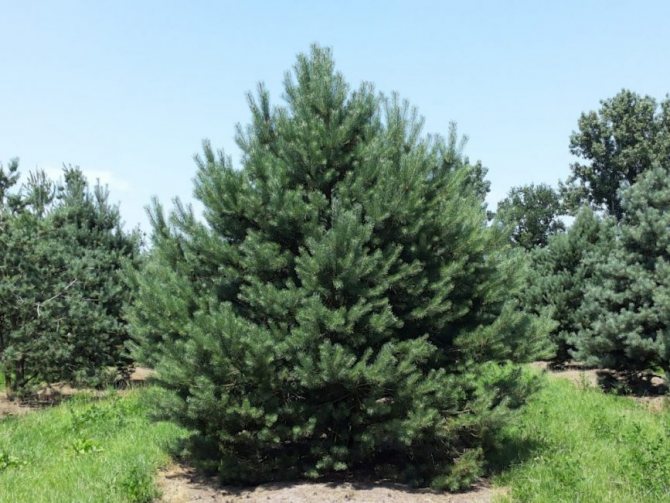


Norwegian pine A champion in unpretentiousness, but this breed is very expensive.
back to menu ↑
See also: [Instructions] How to effectively deal with moles at their summer cottage: modern and folk remedies |
Black
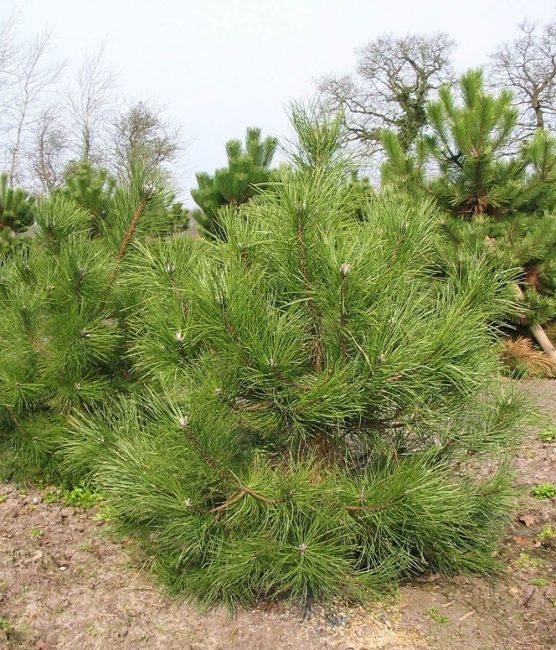


Pine Black It looks beautiful, retains a rounded crown, but is very moody, young growth burns out from the bright sun, and it should be shaded, it is also afraid of frost over 20 degrees.
back to menu ↑
See also: Peat tablets: how to use it correctly, the device of a mini-greenhouse for seedlings (20 Photos & Videos) + Reviews
Mountain
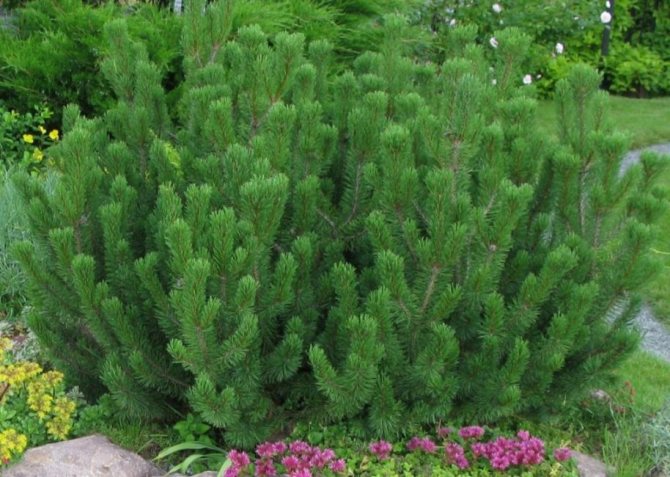


Mountain pine These are low-growing trees with a spreading crown and an impressively curved trunk. Favorite trees of landscape designers, especially recommended when creating a Japanese garden, ideal for compositions in a small area. It is best to choose varieties with shorter needles, in these varieties the bunches consist of two, not five needles, they are more unpretentious. The varieties Gnome, Pumilio, Pug do not suffer from pests, are decorative and lush, although they are very expensive.
There is a good version of Mugo Magnus, it grows from two to four meters, it is very easily formed not only by a tree, but also by a bush or soil cover. Mountain pines are compact, fluffy and branchy, do not take up much space, like other species, growing up to 20 meters, the only minus is that they take a very long time to grow.
back to menu ↑
See also: May lily of the valley: description of the plant, species, cultivation on your site and care, medicinal properties (55 Photos & Video) + Reviews
Cedar


Cedar pine Sold as seedlings, can also be grown from pine nuts. For cultivation, you will need ordinary pine nuts (not hardened), the cones are harvested in February or March, the nuts germinate well. Cedar pine also grows slowly, and gives cones only at the age of 60 or more.
True, sometimes in nurseries they sell already grafted seedlings of two meters, which begin to bear fruit in ten years. Simple cedar pine is beautiful, slender, and grows quickly. Of the minuses, it is worth noting the susceptibility to its attacks by pests, in the spring such a tree can be attacked by a beetle beetle, which climbs under the bark, which causes the tree to die.
back to menu ↑
See also: Almonds: description, planting a tree or shrub in the open field, caring for it, benefits and possible harm + Reviews
Ordinary


Scots pine This plant is most commonly sold, but you can also grow it yourself from seed or dig up a young pine tree. Pine reproduces by self-sowing, there are always many small pines under large trees.
One-year-old pines often get sick from the "black leg"; in order to avoid this, it is recommended to water them with a solution of phytosporin. He loves the sun very much, and in the shade it stretches out and throws off branches, so that the trunk remains bare, grows very quickly.
back to menu ↑
See also: Sedum: species and varieties for growing at home and outdoors. Rules for planting and caring for a succulent plant (110+ Photos & Videos) + Reviews
Common Vatereri


Scots pine Vatereri A beautiful plant, needles of a spectacular bluish color, grows up to three meters, very stable, but also expensive.
Pine is a wonderful and healthy tree, with a wonderful smell, quite unpretentious and does not require care in its adult form. A very light-loving plant, it becomes high in the shade, the trunk may become bare from below, and the branches are not fluffy, but planted in the right place for a long time remains a beautiful and spectacular decoration of the site.
Pine needs a lot of space to grow, so nothing will grow around the perimeter at a distance of five meters, so it is best to plant dwarf decorative varieties in small areas.
See also: TOP-35 Most unusual and amazing plants in the world | + Reviews
Trees that grow fast
Trees that have a high growth rate grow in different parts of the earth. They can be divided into the following groups:
p, blockquote 3,1,0,0,0 ->
- very fast-growing - in a year they grow by about 200 centimeters (white acacia, paulownia, white willow, black poplar, silver maple, eucalyptus, warty birch);
- fast-growing - the growth is about 100 centimeters per year (rough elm, common spruce, European larch, elm, plane tree, walnut, common pine);
- moderately growing - only 50-60 centimeters per year are added (Amur velvet, prickly spruce, hornbeam, Virginia juniper, field maple, silver linden, Caucasian fir, rock oak).
For these tree species, indicators are presented that appear in the phase of active growth, when the tree is young.
p, blockquote 4,0,0,1,0 ->
How to grow pine from seeds at home
Pine propagation is carried out using seeds. First of all, it is necessary to separate the empty and viable seeds. The material is poured over with water and left for 24 hours. Empty seeds after this time will remain on the surface of the water, and ready-made germinations will sink to the bottom.
Before planting in the ground, the seed must be cold stratified. The seeds are placed in a plastic bag with wet sphagnum moss or a damp paper towel and stored in the refrigerator for 3-4 weeks at a temperature of 2-5 ̊С.


Seed stratification
If a bag fogs up from the inside a few minutes after placing it in the refrigerator, it means that there is enough moisture in it.
It is sown into a mixture of equal parts of peat moss, sand and vermiculite to a depth of 1 cm, moistened with a weak solution of potassium permanganate using a spray bottle and covered with a film. The container is kept in diffused sunlight and the moisture of the substrate is maintained.
After emergence, the film is removed.
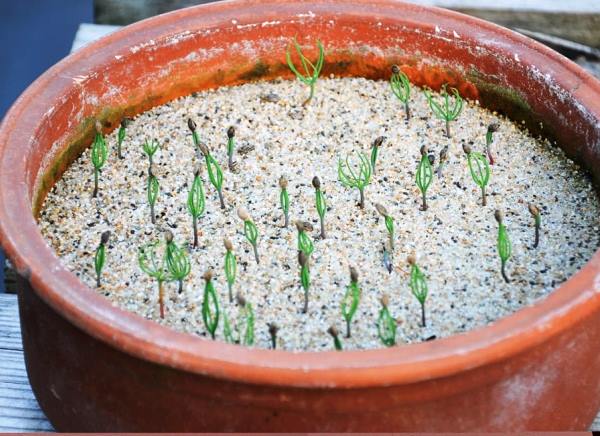


Pine seedlings
Watering is carried out after the top layer of the soil has dried. The grown seedlings dive into separate pots with fertile soil. They are planted in open ground at the end of spring and the first winter is well insulated.
Pine application
Pine wood is a valuable material that has been used by man for many centuries. One cannot do without it in the construction of private houses and backyard buildings, and wood is used both as the main and as an external finishing material. Pine wood is used to produce durable, beautiful and inexpensive furniture, parquet and veneer. Pine wood is indispensable in the construction of some types of bridges and railway tracks, where it is used in the form of manufactured piles and sleepers. Wood wool is produced from pine wood, and pine firewood is considered one of the best in terms of heat output.


Create a conifer garden design: pine. Part 1.
Create a conifer garden design: pine. Part 1.
When creating the design of your garden, you always want it to be for a long time and at minimal cost. In my opinion, pine is a suitable material for creating great compositions. Below I have selected the most interesting varieties that you can use.
First, let's start with a general description of a plant like pine.
Pine belongs to the pine family and is an evergreen coniferous plant, the appearance of which varies from dwarf shrubs to forest trees up to 75 m high; in most species, the height is 15-50 m and the trunk diameter is up to 2 m. Pine trees reach such dimensions, depending on the type and conditions at the age of 70-100 years, in young trees the crown is conical and in mature trees it is flattened although it can remain quite dense and compact, there are also many dwarf or slow-growing forms that look good in rock gardens or extensive landscape compositions ... Some pines are used as decorative, others, especially Scots pine, as windproof. Most pines prefer acidic soils and dry places, some well tolerate thin, infertile or waterlogged soil. All of them are common in the temperate and subtropical zones of the northern hemisphere to Central America and Indonesia, only the Merkuza pine comes south of the equator.The assortment of species and varieties is rich and can satisfy any gardener, for example, Bunge pine, European cedar, Cultera, Dense-flowered, Bosnian, white-brown , Montezum, mountain, small-flowered, drooping or Mexican, weeping, pine, Italian pine, Weymouth dwarf pine, white eastern, ordinary, forest.
Plant pine trees in a permanent well-lit place in the second half of autumn, the soil is preferably acidic and well-drained; do not use lawn mowers and trimmers at the base of the trunks - they can damage the roots of the pine trees located at the very surface.
Reproduction - sow seeds in early spring under glass or later in open ground, replant seedlings to a permanent place, at least after 2 years. As for varietal plants, in the fall, plant with cuttings half a pencil in diameter, the optimal thickness of the rootstock is twice that.
Regarding pruning, then it is rarely required - we remove the frail lower branches. In most pines, pruning them deforms the natural conical shape of the crown.
About pine diseases, you can write a lot, they are amazed by real mushrooms, late blight and rust. Among insects, Hermes, sawflies, and pine silkworm caterpillars are dangerous (the latter species have brown larvae about 2 cm long, which seriously harm pine plantings by eating their young apical shoots). Advice - fight insects with insecticides.
Now let's look at interesting pine varieties, from the point of view of design and decorativeness, but I want to say right away - this is my point of view, in fact, there are a lot of varieties:
Japanese pine Compacta - Pinus parviflora Compacta


Originally from North Korea, needles, crown and fruits are of interest, growing zone 3 is suitable (see at the end of the article). Compacta is a short tree or, more often, a shrub. An adult plant grows up to 3 m. The crown diameter is the same or slightly less. It grows more slowly than the original form, adding about 10-12 cm annually.Skeletal shoots are long, thick, slightly curved, branching strongly, especially at the ends far from each other, grow evenly, diverge from the center at an angle, directed to the sides and up ... The crown is symmetrical, moderately dense, oval or broadly pyramidal, with an indistinct apex. The needles on old shoots are about 5-6 cm long, slightly curved, colored bluish-green, and on young ones they are very short, bright green, tightly pressed. Young growth stands out in contrast against the background of old needles. Numerous cones, collected in large groups, serve as an additional decoration for the plant. Features of cultivation: Pine grows slowly, It can grow both in the sun and in a shaded place. Undemanding to soils, grows on any moderately nutritious and moist garden soils. Moderate winter hardiness.This Compacta variety can become a solitaire (single planting) on the lawn, decorate a rocky, heather or Japanese garden, retaining wall, slope and forest edge. Regarding pruning and disease as well as reproduction - see general description above.
Japanese pine Tempelhot - Pinus parviflora Tempelhot


Native to North Korea, Tempelhot is a short tree. An adult plant grows up to 2.5-3 m, with a crown diameter of no more than 1.2-1.5 m. It grows relatively quickly, adding 8-10 cm annually. The trunk is slightly curved, thick. Skeletal shoots are also thick, straight, whorled on the trunk, branching moderately and only at the ends, far apart from each other, growing unevenly, extending from the center at an almost right angle horizontally, and only the upper shoots are directed to the sides and up. The crown is slightly asymmetrical, conical or broadly conical. The needles are long, thin, very dense, straight or slightly crescent-curved, painted in an elegant silvery green color. Young growth differs slightly from old needles. The plant is light-requiring, but it can grow in a small shade, while decorativeness does not suffer. Soils are desirable nutritious, moderately moist, drained. Zone 4 is suitable for cultivation. Good winter hardiness. This elegant tree with a beautiful crown can be planted at the edge of the forest, in a rocky, heather or Japanese garden, alone on a lawn, included in a mixed group that forms a free-growing living wall.
Japanese pine - Pinus parviflora


Japanese pine, of course, grows in Japan, and can also be seen in North Korea. In nature, this is a relatively short tree, no higher than 10-12 m with a crown diameter of about 9-11 m. It grows rapidly, on average, the annual growth is 20-25 cm. Young trees have a dense, pyramidal crown, with age the skeletal branches begin to grow larger spread out to the sides, and the crown becomes wide-pyramidal, and then umbrella-shaped or almost flat. The needles are relatively short (no more than 4-6 cm), strongly bent, twisted and form peculiar tassels at the ends of the shoots. On young shoots, the needles are pure blue or bluish-white, and on last year's gray-green, needles are collected in bunches of 5 pieces. Begins to bear fruit at the age of 8-10 years. Cones can be either single or collected in bunches, beautiful ovoid, up to 10 cm long and 4 cm wide, persist on a pine for 6-7 years. Japanese pine is unpretentious, ready to grow on a wide variety of soil types, undemanding to either the nutrient composition or the acidity of the soil, it can grow both in the open sun, without suffering from sunburn, and in moderate shade. The level of illumination does not affect the decorativeness of the plant. Japanese pine and its decorative forms grow well in containers. She could rightfully become a universal coniferous plant in the garden, if not for the very low winter hardiness. Zone 5A, since the natural species can only be used in landscaping gardens located in areas that are not subject to excessively low winter temperatures (not lower than -25-28 ° C). Numerous garden forms of Japanese pine are distinguished by their modest size, they winter well even at low temperatures, covered with snow.
Black Pine Jeddeloh - Pinus nigra Jeddeloh


This pine comes from Italy, but it can grow in zone 4, since the frost resistance is good. Jeddeloh is a short tree. An adult plant grows up to 2.8-3 m with a crown diameter of about 1 m. It grows relatively quickly, the annual growth is 12-15 cm. The trunk is straight and even. Skeletal shoots are very short, branching strongly at the ends, far apart from each other, growing expressed unevenly, departing from the center at an almost right angle and directed to the sides. The ends of the shoots rise up. The crown is formed asymmetric, openwork, sparse, conical or pyramidal.The needles on old branches are very long, thin, sharp, tough, often twisted, located radially, colored dark green, and on young ones they are short, bright green, pressed tightly. The plant is selected a place illuminated throughout the day. Undemanding to soils, can grow on any moderately nutritious and moist, drained garden soils. For a tree with such an unusual, spectacular crown, it is desirable to provide an all-round view. It can be planted alone on the lawn, in the front area of the garden, and can be used to decorate a rocky, heather or oriental garden, the edge of the forest, or a retaining wall.
Scots pine Waterreri - Pinus sylvestris Watereri


Came to us from the Northern Hemisphere, Watereri is a dwarf, often multi-stemmed tree or shrub popular in landscaping. An adult plant reaches a height of no more than 3-4 m, rarely more. The diameter of the crown is about 3 m. It grows rapidly, annually adding from 20 to 30 cm in height and 10-15 cm in width. Skeletal branches are long, thick, strongly branched at the ends, grow evenly from the center, depart at an almost right angle and directed to the sides. The ends of the shoots are slightly bent upwards. The crown is dense, symmetrical, at first spherical or rounded, then it becomes wide-conical or pyramidal, with an indistinct apex. The needles on old branches are long, moderately dense, thorny, crescent-curved, often twisted, arranged radially, painted in a rich green color with a bluish tinge, and on young ones they are short, tightly pressed, painted in a bright grassy green color. The plant is light-requiring. In shady places it develops poorly, the crown becomes sparse. Moderately nutritious and moist, drained, loose soils are required. Grows well on sandy loam. The plant can be planted in the front part of the garden, alone on the lawn, at the edge of the forest, and included in a free-growing hedge. Winter hardiness is high, in zone 3 it will grow well.
Scots pine Globoza Viridis - Pinus sylvestris Globosa Viridis


Another representative of the Northern Hemisphere - Globosa Viridis - a dwarf tree or bush-like form, reaching a height of 1.5 m with a crown diameter of 1.2-1.3 m. Skeletal shoots are short, thick, strongly branching, especially at the ends, grow evenly, depart from the center at an almost right angle, directed mainly to the sides and slightly upward. The lower branches lie on the ground, and the trunk is not bare, even in older specimens. The crown is formed symmetrical, very dense, dense, at first flattened-spherical, then becomes ovoid or oval with an indistinct apex. The needles are long, stiff, dense, slightly crescent-curved, sometimes twisted, colored dark green. Young growth is one tone lighter. Pine grows slowly. The plant is light-requiring. In shady places, the shoots are unnecessarily stretched to the sides, and the crown becomes loose. Moderately nutritious and moist, drained soils are desirable. Grows well even on poor sandy soils. Absolutely does not tolerate waterlogging of the soil and the compaction of its upper layers. High winter hardiness, grows well in zone 3. This elegant, attractive plant will be appropriate in a rocky, heather and Japanese garden, on a retaining wall, slope, forest edge. May become a tapeworm on the lawn.
Mountain pine mugus - Pinus mugo var. Mughus


Var. mughus is a widespread shrub in nature. Grows in the mountains - from the Eastern Alps to the Balkans. The height of an adult plant is usually 1.5-2 m, but you can find specimens that have reached the mark of 3 m. The diameter of the crown is about 1.5 times larger. It grows relatively slowly, the annual growth is 6-8 cm. Skeletal shoots are short, thick, numerous, of different lengths, growing unevenly. In young specimens, they depart from the center at an acute angle, are directed slightly to the sides and mainly upward, and the crown is formed almost spherical or oval, asymmetric.Over the years, the shoots begin to move away from the center at a large angle, some spread, and the crown becomes prostrate, sometimes even cushion. The crown at a young age is dense, thick, then it becomes openwork. The needles are long (up to 4-4.5 cm), tough, thick, crescent-curved, sometimes twisted, colored dark green. Young growth is slightly lighter. During flowering, the plants are highly decorated with the creamy yellow anthers of numerous male inflorescences. The shrub is light-requiring, although it can grow in a light shade, the crown becomes more spreading. It does not have special requirements for soils, but it grows poorly on acidic soils. High winter hardiness, zone 2. The large size of the shrub suggests its use in large gardens. They can decorate slopes, forest edges, retaining walls, and include them in freely growing hedges.
Wallichiana Pine Denza - Pinus Wallichiana Penza


Wallichiana Pine is a fast-growing, large, tall tree native to the Himalayas. In its native mountains, this tree reaches a height of 45-50 m, and in culture it is not higher than 20-25 m. The annual growth is about 25-30 cm. The crown is very beautiful, even, symmetrical, pyramidal, the lower part of the trunk is not bare, branches lie on the ground. The needles are very long (up to 18-20 cm), thin, sharp, hanging on old shoots, collected in 5 pieces, painted in a bluish-silver color. On young shoots, the needles are shorter, stand upright. Cones are light brown, up to 25 cm long. Denza is the most popular and widely used form in landscaping. Often goes on sale under the name Denza Hill (Denza Hill). An adult plant grows up to 4.5-5 m with a crown diameter of 2.5-2.8 m. It grows rapidly, adding at least 20-25 cm annually, in favorable years up to 30 cm. The trunk is straight, even. Skeletal shoots are long, thick, highly branched, far apart, grow evenly, directed to the sides and up. The crown is formed regular, symmetrical, dense, conical or broadly conical. The needles are slightly shorter than that of the original species, thin, densely located on the shoots, hanging down beautifully, colored bluish-green with a slight silvery tint. Young growth is slightly lighter. It grows quickly, is unpretentious, grows on a variety of garden soils, very light-requiring. However, it also has a drawback - insufficient winter hardiness, so this is zone 5a and with a stretch 4. Perfect for decorating slopes, forest edges, walking paths. Can be grown on alpine slides, rocky, heather and Japanese gardens.
European cedar pine Pygmea - Pinus cembra Pygmaea


European cedar pine, or European cedar, is ubiquitous in central Europe. In nature, it is a moderately tall tree, rarely exceeding the 20-25 m mark. It grows very slowly, but after 30 years the growth rate increases. The crown is dense, dense, conical or ovoid. When the trees are standing close, the trunk from below may become bare. The needles are long (up to 6-8 cm), straight, soft, collected in 5 pieces, painted in a bright green color with a slight bluish tinge, on the inside - blue-white. Young cones are purple, mature ones are reddish-brown, 6-8 cm long. Seeds are edible nuts. The breed is unpretentious, grows on any moderately nutritious, sufficiently moist soils, prefers drained loams. Photophilous, but shade-tolerant, very hardy. For cultivation, zone 3 is suitable. Variety Pygmaea is a dwarf tree no more than 1-1.2 m in height with a crown diameter of 50-60 cm. It grows slowly, the annual growth is about 3-5 cm. Skeletal shoots are very short, thin, moderately branching. grow unevenly. In young specimens, the branches are far apart from each other; with age, the crown becomes denser, acquires a wide pyramidal shape.The needles are long, thin, with a pointed tip, sometimes slightly twisted, painted in a spectacular blue-green color. The young growth is bright grassy green, contrasting against the background of old needles. The plant is light-requiring. In shady places, the crown remains loose, and the needles do not acquire their elegant tone. Soils are desirable nutritious, moderately moist, drained, ideal loam. Winter hardiness is high, therefore zone 3. The tree will bring brightness to the composition on an alpine hill, in a rocky and heather garden, on a retaining wall and slope, at the edge of the forest and in the coastal zone of the reservoir. But the Alba variety is a tall tree, not less than 15-18 m. The diameter of the crown is about 7-10 m. It grows rapidly, the annual growth is 20-25 cm. The trunk may be slightly curved. Skeletal shoots are long, thick, branch mainly at the ends, grow unevenly. In young specimens, the branches branch off from the center at a slight angle, directed to the sides and up. The crown is formed asymmetric, broadly pyramidal, with a vaguely defined apex. Over time, skeletal shoots descend, are arranged horizontally, and the crown becomes wide-spread, umbrella-shaped. The needles are long (7-9 cm), thick, flat, slightly twisted and sickle-curved, of an unusual gray-blue color. Young growth from old needles is practically indistinguishable. The plant is light-requiring. It develops poorly in the shade, moreover, a green tone appears in the color of the needles. Soils are desirable light, well-drained, moderately moist, ideal sandy loam. Winter hardiness is high, therefore zone 3. This beautiful, majestic tree can be planted singly on the lawn, to decorate the edge of the forest area. Alba's rather large dimensions suggest its use in large gardens. Choose an open, lit place for the plant. The slightest shading leads to a thinning of the crown, while the trunk is gradually bare from below. Undemanding to soils, grows well on any garden soils. Well, if we return to the European pine, then this low tree looks beautiful in the form of a tapeworm on the lawn, at the edge of the forest zone, in the front part of the garden.
Pine Banks Compact - Pinus Banksiana Compacta


Pine Banks is a resident of the eastern regions of Canada. The further north the plant moves, the more squat its crown becomes. If usually the height of an adult pine reaches 15-20 m (sometimes 25 m), closer to the north it takes the form of a bush. It grows slowly. The tree is often multi-stemmed, with a compact, sparse, asymmetrical, oval crown. The needles are tender, strongly curved, twisted, collected in 2 needles. Cones are conical in shape, slightly curved, on the shoots, as a rule, are arranged in pairs. The plant is light-requiring, undemanding to soil. Resistant to pathogens and frost-resistant. Compacta is a dwarf bush-like form of the Banks pine. An adult plant reaches a height of about 1.5 m with a crown diameter of 2-2.5 m. It grows relatively quickly, adding 12-15 cm annually. Skeletal shoots are long, thick, serpentinely curving, grow unevenly from the center, are located mainly horizontally some branches lie on the ground. The crown is asymmetric, wide, flattened-rounded, and with age it becomes more and more flat. The needles are short, flat, radially extending from the shoot, slightly crescent, densely covered branches, painted in a rich green color. Young growth is one tone lighter. The plant is light-loving, but can grow in light shade. Soils are required moderately moist and nutritious, drained, with a neutral or slightly acidic reaction. Perfect for decorating slopes, forest edges, walking paths. Can be grown on alpine slides, rocky, heather and Japanese gardens. High winter hardiness, zone 2.
Japanese pine Glauca - Pinus parviflora Glauca
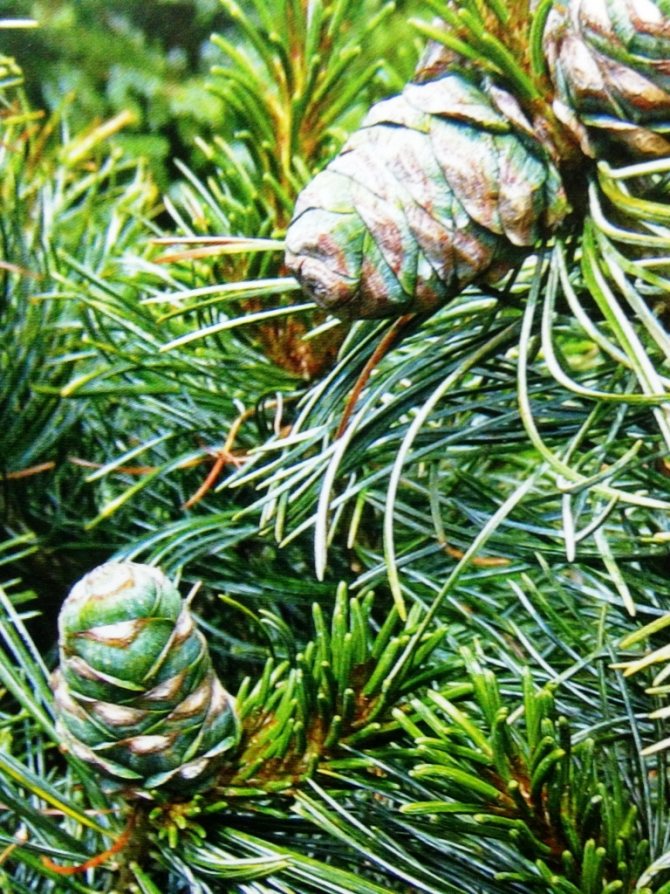


A small tree from North Korea came to us - Glauca.Height does not exceed 1.8-2.5 m with a crown diameter of about 1.5 m. It grows slowly, the annual growth is 10-12 cm. Skeletal shoots are thick, often slightly curved, strongly branching (mainly at the ends), far from each other from a friend, grow expressed unevenly. The crown is formed asymmetric, openwork. In young specimens, the skeletal branches branch off at an angle, directed to the sides and up, the crown is pyramidal or wide-pyramidal. With age, the branches lie horizontally, and the crown becomes broadly spreading, umbrella-shaped. The needles on old shoots 5-7 cm long, rigid, crescent-curved, bluish-green with a silvery tinge, and on young ones it is much shorter, painted bright green, loosely adherent. Cones are numerous, very long (up to 10 cm), young bluish-green, mature brown. Glauca is shade-tolerant, but grows better in open places. Grows well on garden soils of any type, with the exception of heavy and excessively moist. An elegant plant for decorating alpine hills, rocky, heather and Japanese gardens, retaining walls, slopes, forest edges. May be a tapeworm on the lawn. Moderate winter hardiness, zone 5a.
Black Pine Pygmea - Pinus nigra Pygmaea
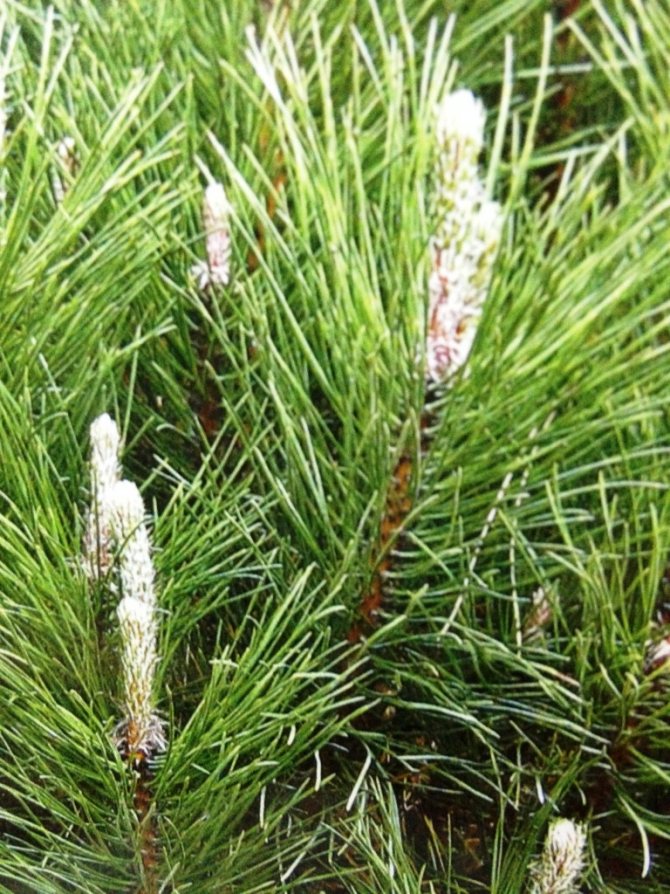


Pygmaea is a natural dwarf form found high in the mountains of Italy. It reaches a height of no more than 1.8 m. The crown diameter is the same or slightly larger. It grows very slowly, the annual growth does not exceed 4-6 cm. Skeletal shoots are short, thick, weakly branching, but numerous, grow unevenly, tightly pressed against each other, depart from the center at an angle, directed slightly to the sides and up. The crown is formed dense, dense, asymmetrical. In young specimens, it is wide-pyramidal, with a pronounced apex, but over time it flattens, to a greater extent spreads to the sides and becomes broadly oval. The needles on old branches are very long, thin, sickle-curved and twisted, radiate out radially, painted in a rich green color, and on young ones they are short, very sparse, slightly lighter colored, tightly pressed. The plant is sun-loving, the most open places, illuminated by the sun throughout the day, are selected for it. It is undemanding to soils, it can grow even on poor, moderately moist garden soils. Good winter hardiness, zone 4. Looks great alone on the lawn and in rocky, heather and Japanese gardens, on retaining walls, slopes, forest edges.
Scots Pine Suecia - Pinus sylvestris Sueccia
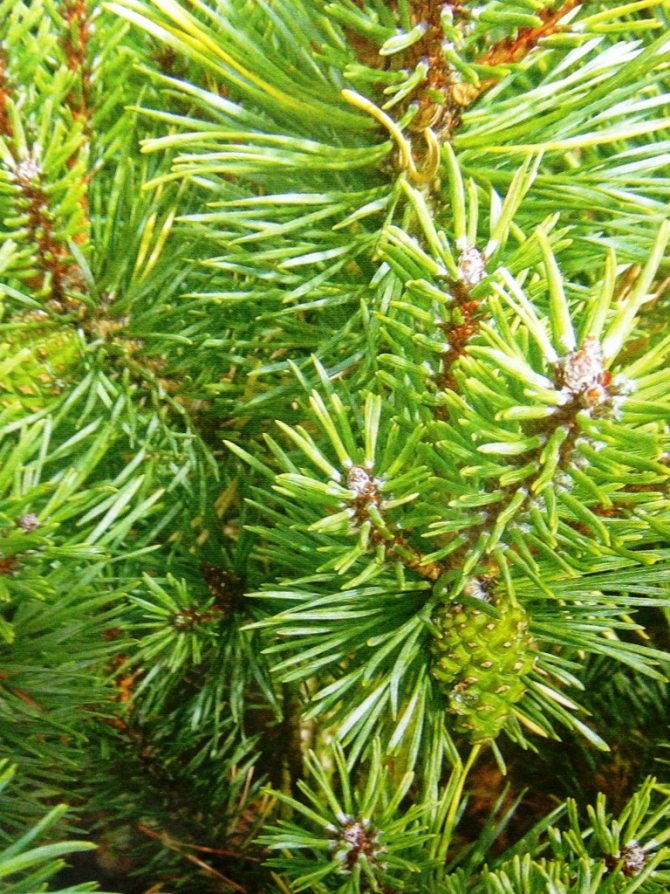


From the Northern Hemisphere came to us - Sueccia bonsai, reaching a height of 3-4 m with a crown diameter of no more than 1.5 m. It grows relatively quickly, the annual growth is 15-17 cm. The trunk is sometimes slightly curved. Skeletal shoots are short, thick, far from each other, are whorled on the trunk, grow unevenly over the years, but towards the final formation the crowns are leveled, branch very moderately, depart from the center at a slight angle, directed to the sides and up. The crown is symmetrical, openwork, conical or broadly conical. The needles are of medium length, thick, dense, dense, sickle-curved, often twisted, painted in a bright green color. Young growth is slightly lighter. Good frost resistance, zone 3. The plant is photophilous, but it grows in a very light, delicate shade, while decorativeness does not suffer. Soils are desirable nutritious, moderately moist, drained. This tree can become a tapeworm on the lawn, used in the design of a rocky, heather or Japanese garden, retaining wall, forest edge, become part of a free-growing hedge.
Balkan Pine Select - Pinus Flight Select


It is easy to guess that the Balkan pine, or Rumelian, comes from the Balkan Peninsula. In nature, it reaches a height of 18-20 m with a crown diameter of 4-5 m.The crown of the tree is beautiful, dense, dense, narrow-pyramidal, with a clear silhouette. The barrel is not exposed from below. The needles are sticking out, dense, straight, dark green or green with a bluish tinge, up to 7-10 cm long. Cones are numerous, erect, elongated (up to 12-15 cm), light brown. The seeds ripen in the fall and quickly fall to the ground. Resistant to rust and the scourge of conifers. The root system is deep. In culture, this species has been used for about 150 years, but few garden forms are known. Select is a low, beautiful tree. An adult plant grows up to 5-6 m with a crown diameter of about 2-2.5 m. It grows relatively quickly, adding up to 20-23 cm annually. The trunk is even, straight. Skeletal shoots are straight, short, grow evenly, depart from the trunk at an acute angle and are directed mainly upward. In young specimens, shoots branch moderately, then branching intensifies. The crown is formed regular, symmetrical, narrow, conical, with a beautiful, well-defined silhouette. The needles are long, straight, tightly pressed on young shoots, radially located on overwintered branches, dense green. Young growth is one tone lighter. The plant is light-requiring. In shaded areas, the shoots are unnecessarily stretched to the sides, and the crown loses its beautiful silhouette. Soils are required moderately nutritious, slightly moistened, ideal loam or sandy loam, moderately dressed with organic fertilizer. High winter hardiness - zone 4. This tree is in demand for landscaping small gardens, looks great in rocky and Japanese gardens, on retaining walls and edges, as part of free-growing hedges.
In any case, if you are a big fan of pine, then you need to take into account not only its decorativeness, and sometimes suppress the desire "I WANT", but if you cannot suppress it at all, then first learn about the plant more, how it grows, where is better growing, its size, agricultural technology, and everything else. Since a large pine tree in a small garden will not be relevant, but its dwarf forms are just right.
As promised, here is the information on the growing zones:
Zone 1 - Central Siberia
Zone 2 - Southern Siberia
Zone 3 - Lapland.
Zone 4 - Moscow region, most of Russia, northern and mountainous regions.
Zone 5a - St. Petersburg, Vladivostok, Minsk, Kiev, central Russia, the Baltic countries.
Zone 5b - Northeastern Poland, western Ukraine, southern Sweden, southern Finland,
Zone 6a - Eastern Poland, Slovakia, central Sweden, Southern Norway
Zone 6b - Central Poland, eastern Hungary, Czech Republic.
Zone 7a - East Germany, western Poland.
Zone 7b - East Holland, Denmark.
Zone 8a - Central Holland, Belgium, northern and central France, northern England
Zone 8b - Maritime Holland, Western France, northern Italy, central England.
Zone 9 - Southern France, central Italy, Portugal, southern England.
Zone 10 - Southern Italy, southern Spain, central Greece.
Zone 11 - North Africa.
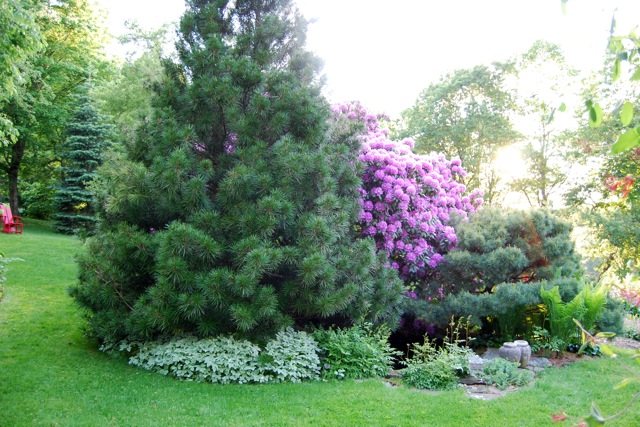


I wish you inspiration when creating compositions from conifers such as pine. Good luck to you.
The advantages of growing coniferous shrubs on the site
Evergreen shrubs are often the winning choice when planning your garden. Conifers are quite unpretentious, they take root well in various parts of most of the country. Green shrubs of original forms at different times of the year are successfully perceived aesthetically, as a bright color spot. Most conifers have undeniable advantages:
- the possibility of placing in the sun, in partial shade or even in the shade;
- undemanding to the type of soil;
- the plasticity of the crown - the disposition to pruning or shearing;
- the release of aromatic medicinal compounds into the air - phytoncides;
- minimal maintenance is required.
Pine buds
When walking in the woods or in your garden, pay attention to young buds, they smell wonderful resin.These buds contain pine pollen, which has a healing effect on the body.
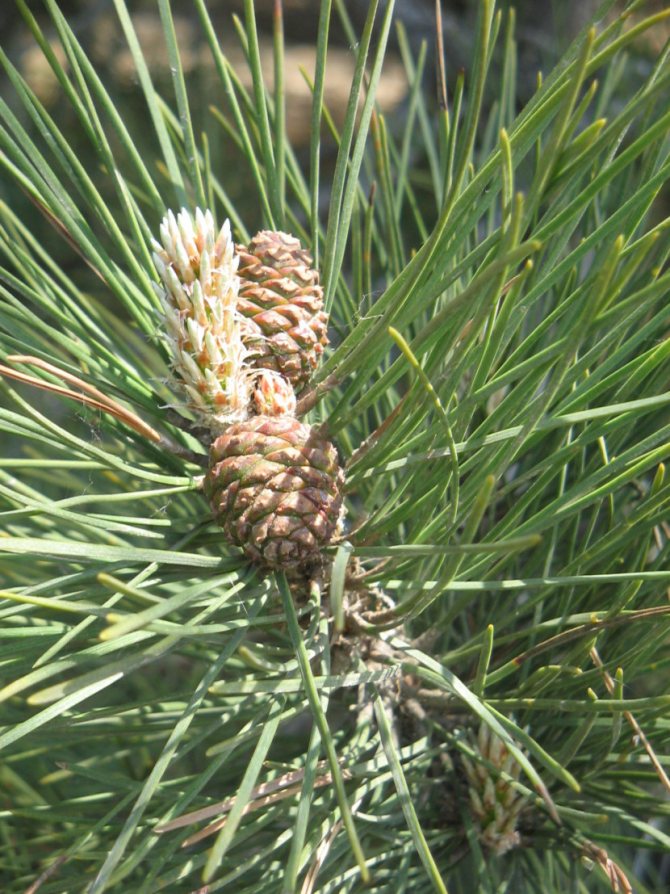


You can collect these anthers and make homemade pine honey. He will help you in the treatment of cough, tuberculosis pathologies, because this is a ready-made set of trace elements and vitamins, a good substitute for going to the pharmacy.
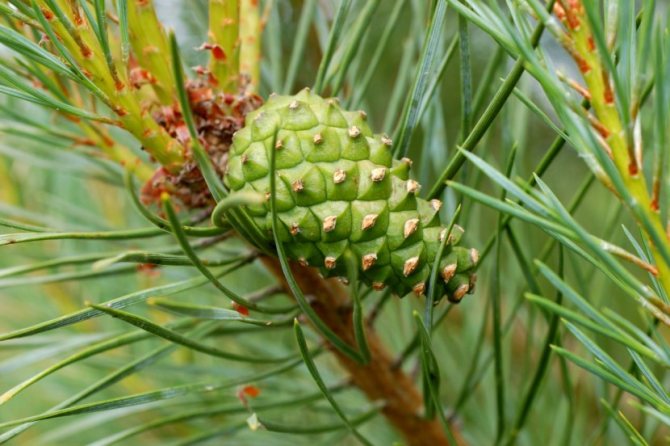


Cooking this honey is very simple, the kidneys can be covered with sugar or added to the ready-made honey. This will keep your body in good shape in winter, but you need to take care of this from spring, since at this time the kidneys are the youngest.
Interesting Facts
In different countries of the world, the coniferous tree serves as a symbol of life and fertility, longevity and immortality, adherence to principles and loyalty to duty. The Japanese sages considered a pine tree covered with snow to be a symbol of a happy noble old age.
Some interesting information about pine:
- In the list of the oldest uncloned trees on the planet, Methuselah, an intermountain bristlecone pine, is in first place, its age is about 5000 years. To preserve the ancient tree, its exact location is hidden.
- The tree heals itself by producing sap. The resin quickly heals wounds and prevents infection.
- In folk medicine, different parts of the plant are used: buds and cones, needles and shoots, resin and pollen.
- The Lambert pine, which grows in western North America and reaches 82 m in height, has cones up to 60 cm in length. The resin of this tree is rich in sugars, for which the locals called it sugar pine.


- Some species, united by the name pine pine, produce edible nuts. However, scientists note that in a biological sense, these are not nuts, but seeds, and true nuts are produced by a tree of another genus from the pine family - cedar.
- Before the advent of metal, pine wood was indispensable in shipbuilding.
- The tallest ship pines grow on the southern coast of the Baltic Sea.
Gardeners reviews
- Examine the roots carefully when buying... Otherwise, you run the risk of discovering rotten elements and you will have to destroy the earthen lump in order to remove all the damaged processes. After that, the plant may not survive.
- For a plant to survive the winter well, many factors are needed.... Most often, pine suffers from winter thaws, when there is a big difference between day and night temperatures. It is better to cover the crown to avoid trouble.
- In winter, small Japanese pine trees in pots are located on a glazed balcony on the sunny side.
MEET JAPAN!
Good day! My name is Nina Mingaleeva!
I live in St. Petersburg!
During my student years, I was carried away by the study of the Japanese language. The teacher of the course taught us not only the Japanese language, but also gave a lot of information on the history, culture, literature, cinema of Japan. He told Japanese tales and legends. Introduced the outstanding works of the Japanese epic.
"Nihonbashi Bridge in Edo" - Hokusai ("Thirty-six Views of Fuji")
There were trips to the House of Cinema, where we watched a retrospective of films by Japanese filmmaker Akira Kurosawa. A wonderful director! I loved his films!
Reading the works of Japanese writers, I noticed that there are writers who subtly feel the beauty of life and nature. Their vision was close to my attitude. Even if they wrote about sad things. I especially liked Yasunari Kawabata, Yasushi Inoue, Junichiro Tanizaki, Kobo Abe and others. In their works, they managed to convey the subtle and beauty-sensitive nature of the Japanese, who was not overcome by the hardships of life. I'm also interested in Japanese painting. Peculiar, in a popular fashion, organically combined with nature and with other phenomena of life.
I have always loved to travel, however, I did not even dare to dream of a trip to Japan. And yet - my dream has come true! I went on a sea cruise around the Japanese islands. It was an unforgettable trip! I have put a story about this journey in 14 parts on the pages of my magazine.
The trip to Japan left an indelible impression on my soul! Everything was unusual for us - culture, aesthetics - this is a mixture of Asian life with ultra-modern technologies! Ancient monuments of architecture, medieval castles, hot springs, magnificent nature! Everything was great!
And here, on the pages of my magazine, I wanted not only to share my impressions of that old trip, but also to tell about a mysterious country - Japan, about everything that I love and that is interesting to me.
To come in
Economic value and application [edit | edit code]
Using wood [edit | edit code]
Scots pine wood is very resinous and durable, used in housing and hydraulic engineering, in joinery and carpentry, for the manufacture of veneer, plywood.
Pine sawdust is used as a raw material for the production of hydrolysis alcohol.
The high resinousness of wood prevents the receipt of cellulose from it.
The stock of wood in middle-aged pine forests of I-III bonitet is 330-600 m³ / ha [9].
Roots, very flexible when fresh, become firm and elastic when dry; various wicker utensils are made from them, for example, wicker vessels [3].
Raw materials for the chemical industry [edit | edit code]
Pine is the source of many substances and products widely used by humans.
Resin is a sap formed in resin passages that penetrate wood and bark in the horizontal and vertical directions, and is extracted by tapping; it is a valuable raw material for the chemical industry. The collected resin is melted and filtered, freeing it from water and impurities. The refined resin is called turpentine. During distillation with steam, about 25% of the essential oil, called gum turpentine, is distilled off from the resin, after purification of which purified turpentine oil is obtained. After distilling off the essential oil, a resin remains - rosin. Turpentine and rosin can be further processed to obtain varnishes, solvents, fragrances, adhesives, chandeliers and other products. The amount of resin and turpentine depends on the age of the trees, the nature of the soil and climatic conditions. Rosin obtained during the processing of resin is used in the soap-making, paper, rubber and paint and varnish industries, as well as for rubbing the bows and strings of musical instruments.
When dry distillation of wood and stumps, first, turpentine of the best quality is obtained, then technical, tar and wood vinegar. Coal remains in the distillation boiler.
Medical use [edit | edit code]
Scots pine buds (lat.Turiones Pini) are harvested as a medicinal raw material in winter or early spring (February - March), cut with pruning shears or knives in the form of crowns with the remainder of the stem of about 3 mm, dried in attics or under canopies with good ventilation, spreading thin a layer on paper or fabric (cannot be dried in attics under an iron roof and in dryers [10]). It is used as a disinfectant, antitussive, diuretic agent in collections and for baths.
Pine needles (lat. Folium Pini) are harvested in the form of "legs" on felling sites during felling. Needles contain up to 1% essential oil, up to 0.2% ascorbic acid, resin, tannins [10]. Pine oil (Oleum Pini) is obtained from pine needles, young shoots and cones, which is part of the Pinabin and Phytolysin preparations used as anti-inflammatory and antispasmodic agents and for kidney stones. The oil is used for inhalation for lung diseases and for air freshening in office and residential premises, hospital wards, kindergartens, schools, and saunas. Pine extract is produced from pine needles for strengthening baths.
The cleaned sap of Scots pine - turpentine (Latin Terebinthina communis) is used for the production of plasters. Purified turpentine oil (turpentine) (lat.Oleum Terebinthinae rectif icatum) is widely used in medicine.
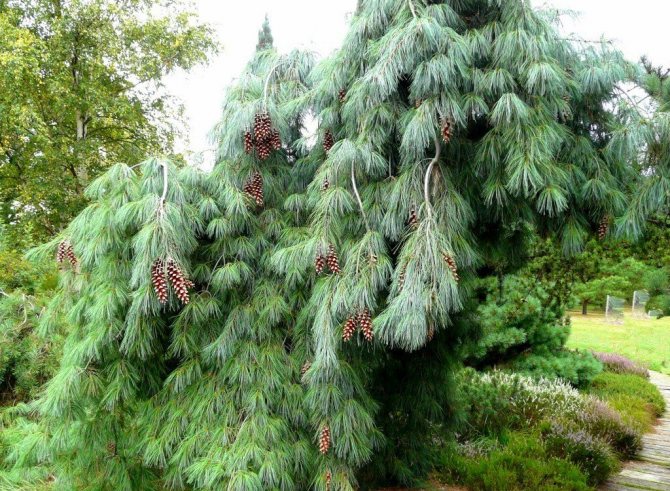


All types and forms of pines have exceptional healing properties. Moreover, remedies can be obtained from needles, and from juice, and from buds, and even from wood. Despite the fact that the agricultural technology of growing pine is not at all difficult, they are rarely planted in small household plots, since these trees are large enough, not very suitable for group plantings. On this page you can find photos, names and descriptions of pine varieties, as well as learn about their cultivation.
Benefit
For those who have a plot of land, and who decide to replace the garden with a gazebo and a clearing for barbecue, pine can become the optimal coniferous tree. Coniferous resin fumes and phytoncides improve air, and a dense crown can protect buildings from dust, heat and wind.


Squirrel on a pine tree
In addition to its decorative qualities, the tree is also very useful. Its bark, shoots, resin, needles heal the body, increase immunity and are a good prevention of pulmonary diseases. A vitamin fortifying drink is prepared from the kidneys and needles, it is useful for colds and other diseases, joint diseases and diabetes are treated with bark.
The resin is used for wound healing and disinfection by phytotherapists, it can even be chewed if the gums hurt, with periodontal disease and other diseases of the mouth. Many animals feed on seeds - squirrels, chipmunks and some birds, so different animals, nimble squirrels and birds can settle on the site.
back to menu ↑
See also: Fir: description and characteristics of the 10 most popular species, varieties, planting and care (50+ Photos & Videos) + Reviews
Habitat
Asia and Europe are the habitat of pine trees. The plant can be found in Great Britain, Spain, CIS countries, Mongolia, China. On poor and arid lands it forms pine forests, and on fertile lands it forms part of mixed forests.
The tree has no requirements for moisture and soil composition. Most often it grows on sandy loam, peat, sod, and podzolic soils. Occupies areas unfavorable for other crops - swamps, sands. Forms pure and mixed forests. Its neighbors can be birch, spruce, oak.


Scotch pine most often grows on sandy loam, peat, sod, and podzolic lands.
Scotch pine distribution: the greatest concentration in Siberia, the Caucasus, in the regions of the Lena River, Angara, Irtysh, Ob, Oka. The area of distribution in Siberia covers more than 5 million square kilometers.
The healing properties of Pine
Pine is used as an expectorant, diaphoretic and diuretic. Pine has analgesic properties and kills disease-causing microbes in the body.
Sap - a thick light yellow liquid flows out of the damaged branches and trunks of the Pine. Possessing antibacterial properties, it prevents harmful microorganisms from entering the trunk.
If in the forest with injuries and scratches there was no first-aid kit with you, instead of a plaster, you can apply clean Zhivitsa to the wound. It is also able to relieve toothache, which is why resin is used in some regions to make medicinal chewing gum.
Has an antibacterial effect burning tar smoke... Rooms, cellars and salting barrels are “fumigated” with smoke.
For pain in the joints and muscles, a different component of the resin is used for rubbing - turpentine.
Planting a pine tree
When to plant a pine
The best pine seedlings are three to five year old trees with a closed root system: the roots of a young pine tree die in the open air in 10-15 minutes. It is better to purchase planting material in specialized nurseries located in your area. Before planting a pine, you need to lower the container with the roots of the seedling for three hours in water. It is necessary to plant pine in open ground in early autumn (from late August to mid-September) or in spring (from late April to early May).
How to plant a pine tree
A pine pit is dug about a meter deep.If the soil on the site is heavy, it is necessary to lay a layer of expanded clay or broken brick 20 cm thick in the planting pit for drainage and sprinkle it with sand. An earthen mixture is prepared in advance: 2 parts of the fertile topsoil are mixed with 2 parts of sod land and 1 part of sand or clay. Add 50 g of Nitrofoski or 100 g of Kemira-wagon to the soil mixture and mix everything thoroughly. An additional 200-300 g of slaked lime is added to the acidic soil.
Pour the soil mixture into the hole, then very carefully remove the seedling from the container, being careful not to destroy the earthy ball, lower the tree into the hole and fill the remaining space with the soil mixture, adding it gradually and immediately tamping it slightly. After planting, an earthen dump is made around the tree so that the water does not spread during irrigation, and 2 buckets of water are poured under the seedling. After the water has been absorbed and the earth has settled, the root collar of the seedling should be at surface level. If you are planting a large size, then its neck should be 10 cm above ground level: over time, it will be where it should be.
When planting several trees on the site, keep a distance of at least 4 m between them, although an interval of 1.5 m is enough for low-growing pines.
Description and characteristics of pine
The height that a tree reaches during its life span varies from 35 m to 75 m.With this growth, the average trunk diameter reaches about 4 m.However, when grown in unfavorable conditions, or in swampy areas, the height is limited to only 1 m. The pine loves sunlight very much, thanks to it it can reach such large sizes. It blooms in late spring, during this process, cones appear. However, they are all different in their shape and shades.
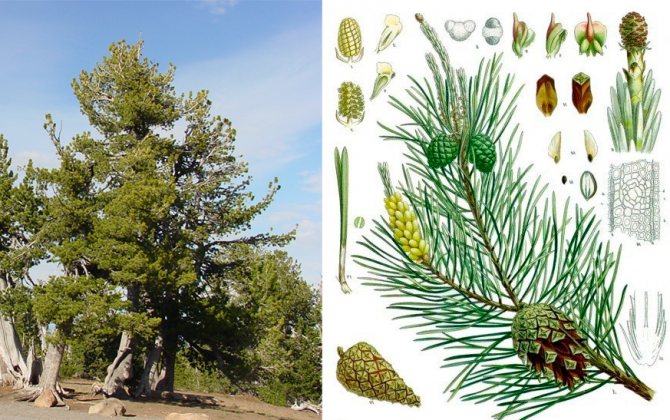


Pine is widely known for its appearance, which gives it numerous, woody shoots covered with needles. The needles themselves are smooth and hard, moreover, sharp.
Her life expectancy is no more than 3 years. The length of individual specimens can reach up to 20 cm. The tree is unpretentious to the soil. The root system directly depends on the place of planting. If the soil is wet, the roots spread along the surface, going down only 2-3 m deep.If the soil is dry, they penetrate down already by 7-8 m.In this case, the radius of the root system is about 10 m.However, preferences for the type of soil are still there is. Pine gets along better in sandy soil.
Signs
Often, people planning to plant a coniferous tree on their site are faced with a mass of accepts, and change their mind. According to ancient Slavic signs, it is not recommended to grow spruce and pine in or near the house, it is believed that these types of trees can "survive" the owner from the house. But other signs, on the contrary, say that pine, birch and oak are very good and energetically strong plants, but spruce and aspen are not.
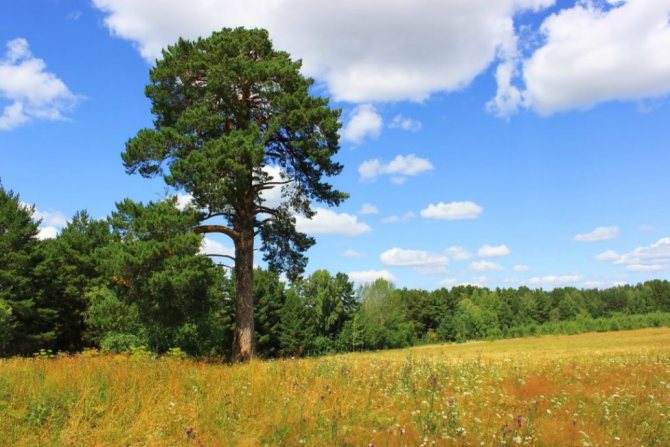


Freedom-loving tree
Having scrolled through many different sources, I still managed to find out - from the point of view of medicine, the coniferous smell strongly tones up, and can provoke an increase in pressure in hypertensive patients. Coniferous plants have great energy, they perfectly heal various diseases of the human respiratory system, and have a positive effect on the psychological state of people. But ... They bring such benefits only if they grow in free, unrestricted conditions.
If the coniferous tree is cramped, then it seems to begin to conflict with the tenants of the house, literally "dominate" - then seemingly groundless conflicts and quarrels can really arise. Therefore, conifers should definitely not be planted close to a residential building, but in an open place, or along paths. In this case, the house and its residents will really receive the necessary support from the plant protector. It is believed that the sharp needles of conifers protect from the evil eye.
back to menu ↑
See also: Derain: description, types, rules for planting and caring for a plant in the open field, reproduction (75+ Photos & Videos) + Reviews
Caution danger
Previously, houses were predominantly wooden, and such a wary attitude towards conifers can be explained by the fact that, due to their resinousness, they burn very well. A tall pine tree could be struck by lightning, and the fire could easily spread to housing. Even now, according to fire safety rules, you cannot plant them closer than ten meters from buildings. In addition, conifers have very powerful long roots, and an adult strong tree is quite capable of destroying the foundation of a house, being planted next to it.
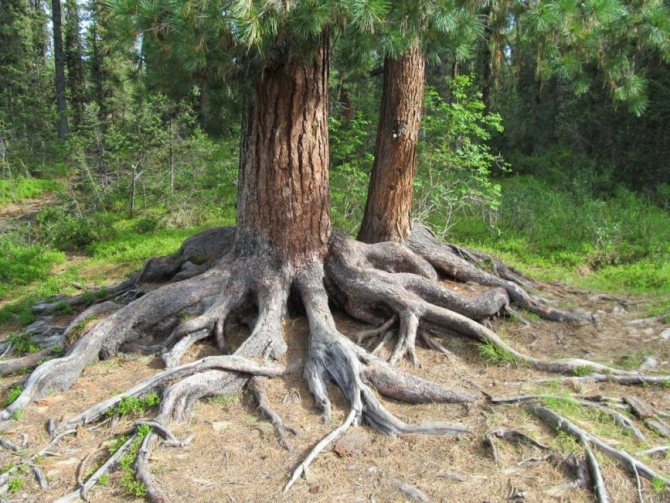


Mighty roots
The root system of spruces and pines is located close to the surface of the earth, so an adult tree is even capable of destroying paths with its roots and turning out entire layers of earth in the yard. These trees absorb a lot of moisture from the soil, in arid places they do not take root at all, and if they have already grown, then other plantings simply do not survive within a radius of 5-6 meters.
Superstitions and omens that came to us from antiquity are no longer relevant today, but many continue to believe in them. In this case, it is better for too suspicious owners not to plant conifers on the site.
back to menu ↑
See also: Euonymus: Description of the plant, species and varieties, cultivation, planting in the open ground and care, reproduction (65+ Photos & Videos) + Reviews
the image of the Pines
The Evergreen Pine is a symbol of immortality and vitality. Even in winter, when nature is asleep, this beautiful green tree reminds us that spring is coming soon.
In old times Pine branch was considered magical. The Western Slavs kept the branch for a whole year and only on New Year's holidays was it replaced with a new one. She guarded the peace and well-being of the hut and was a kind of amulet against evil forces. And now in the villages you can find Pine spruce branches, standing in a vase as a decoration.






















































