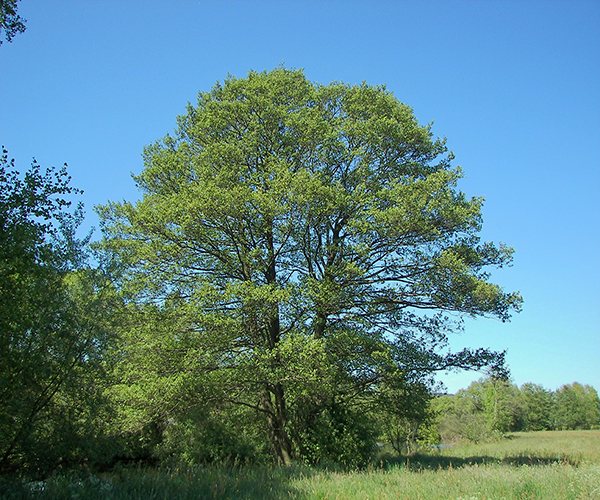
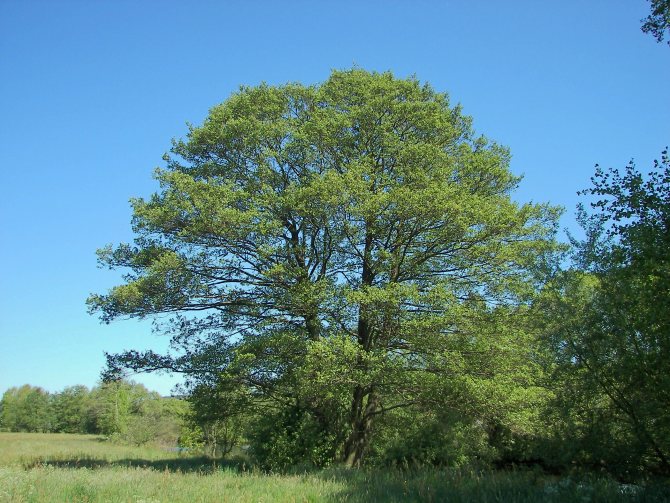
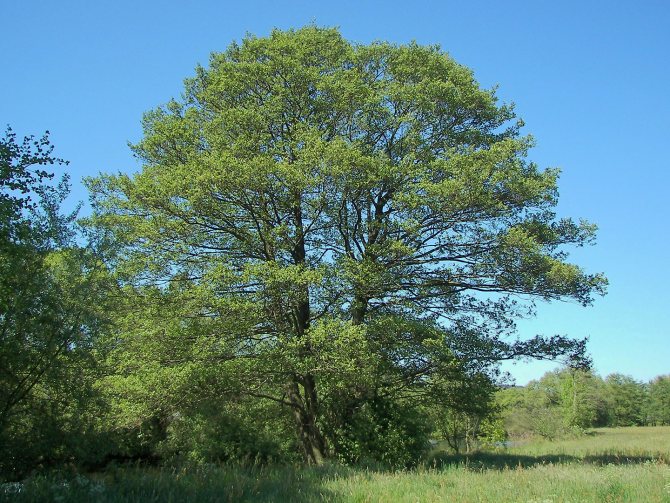
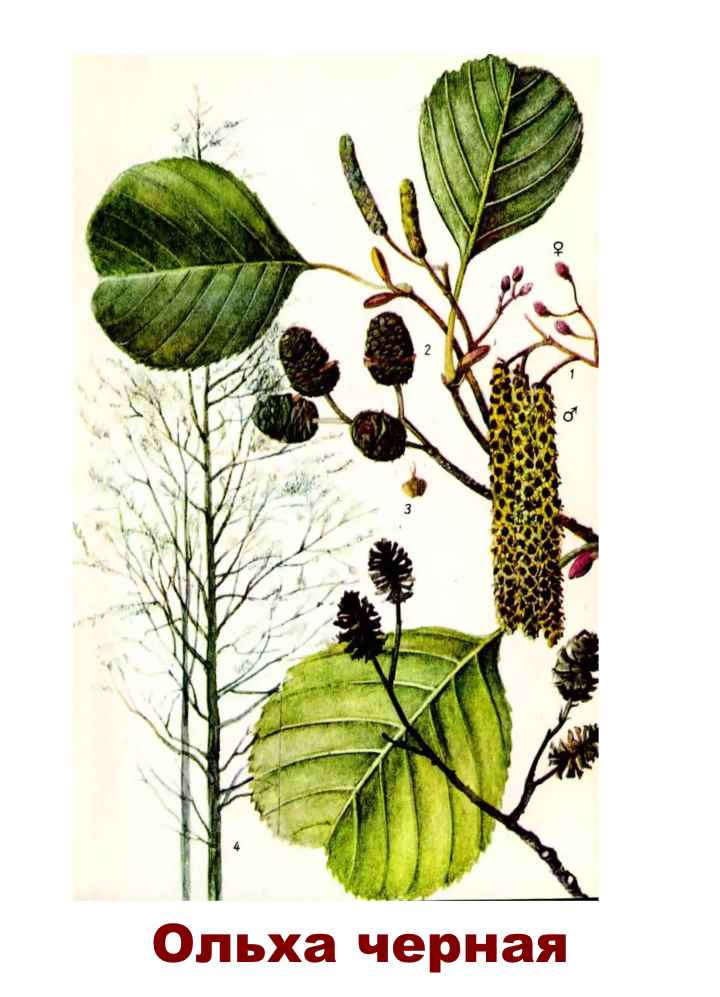
The tree is unattractive but extraordinary. It is called the harbinger of spring - it blooms when the snow has not melted yet. Flowering plant, belongs to the birch family. It opens in early spring, pollination occurs with the help of the wind. The trunk has a slender shape and smooth bark. The leaves are rounded, do not change color. So they fall green in the fall. There are more than fifty species of this plant, but two of them are considered the most common. So, we present - gray, black alder, description and photo, cultivation. Let's consider each representative in more detail.
Myths and legends
There are many myths and legends about this tree. He is referred to in Greek mythology. The first musical instrument of Orpheus was the alder pipe. The connection between the flute and alder can be traced in the name of this musician, which, according to some historians, is shortened from Orphruoeis - "growing on the river bank", thus indicating alder.
The banks of the caves of the sorceresses Sercea and Calypso, who held Odysseus, were overgrown with alder. In myths, there is no clarification of what species this or that alder was, but in nature there are many varieties. The fact that the tree has ancient roots is evidenced by the existence of a certain tribe of the Arverni - "alder people" who lived in the territory where the Celts lived.
Photo gallery
Alder growing areas
The alder tree grows in North America, where it has been called "alnus" since ancient times, which translates as "coastal". It belongs to the Birch family, as having earrings and cones. The places where alder grows are different. These can be areas with high humidity: rivers, streams, swamps, lakes. It feels good in the forest-steppe and in mixed forests, where aspen, birch, spruce and oak are present. There are various types of alder in the regions of Western Siberia and the Urals. The range of gray alder covers most of Europe, the species is found in Asia Minor and some oases of North Africa. In the Carpathians and the Alps, it can be found at significant altitudes above sea level.

Where does alder grow and what it looks like
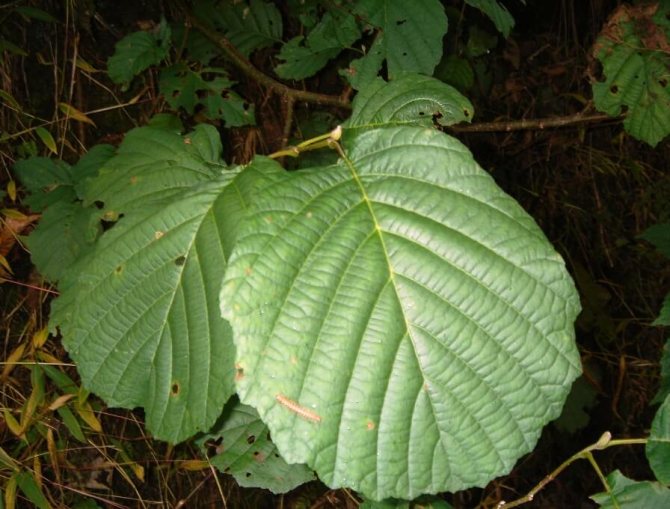
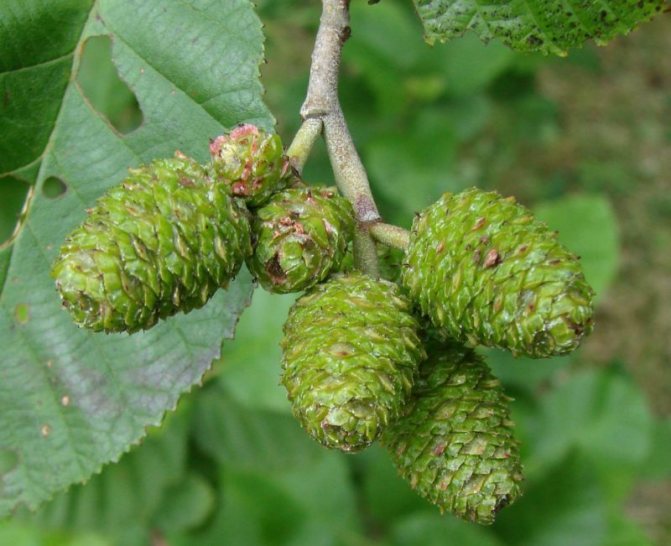
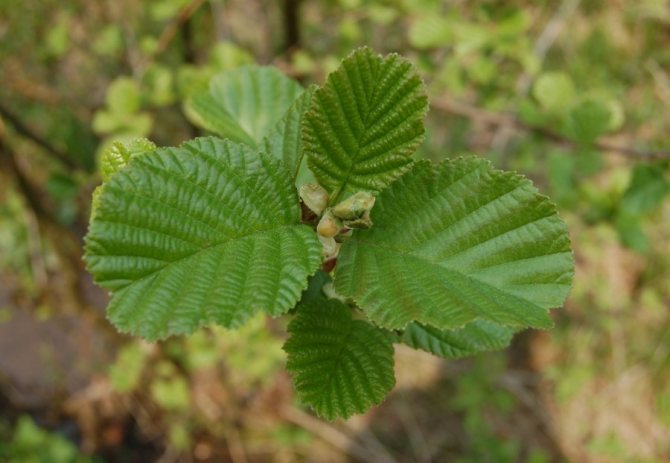
Botany classifies this tree with catkins in the birch family. Most often it can be found in areas with high humidity: near rivers, swamps, lakes. If we talk about Russia, then this tree species is most common in the region of the Urals, Western Siberia, in the steppe and forest-steppe zones. Spruces, birches, aspens, oaks can grow in their neighborhood. Graceful earrings on the tree appear in spring, at the time of flowering, and by autumn the fruits ripen in the form of small cones.
In total, there are about 40 species of alder. We most often have three varieties:
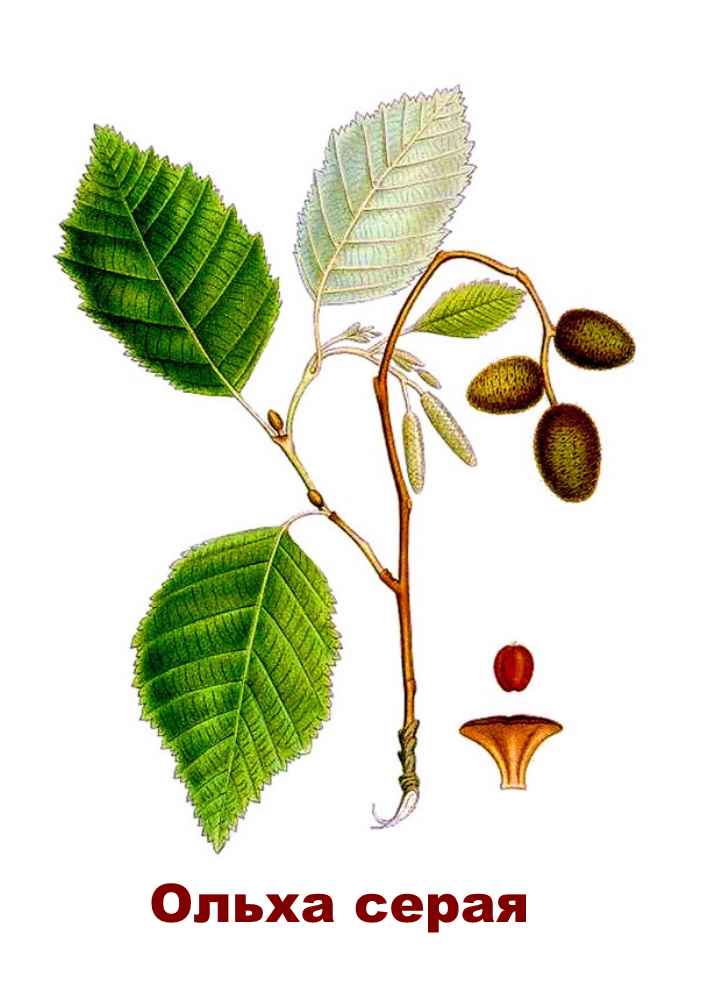
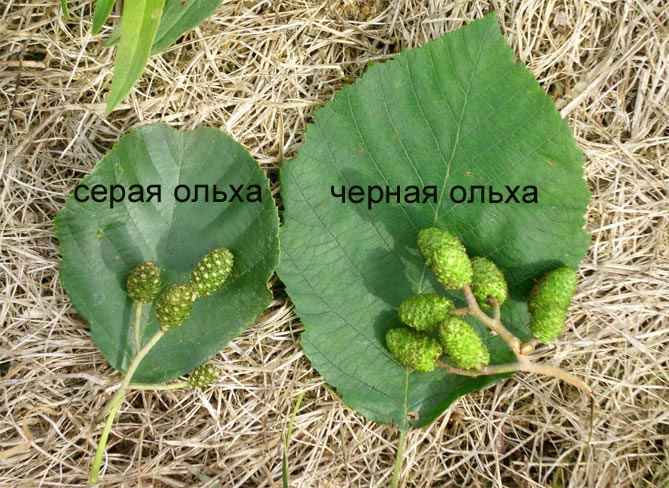
- Gray. The variety was named so because of the gray color of the bark and the same shade of the leaves growing on it. Its trunk is uneven, has many bends. The species grows in height up to 20 m. During the flowering period of alder, brown catkins appear on it. This variety loves light, therefore it grows more often in sunny places. These trees are not afraid of cold and winds, they can take root on rather scarce soils.
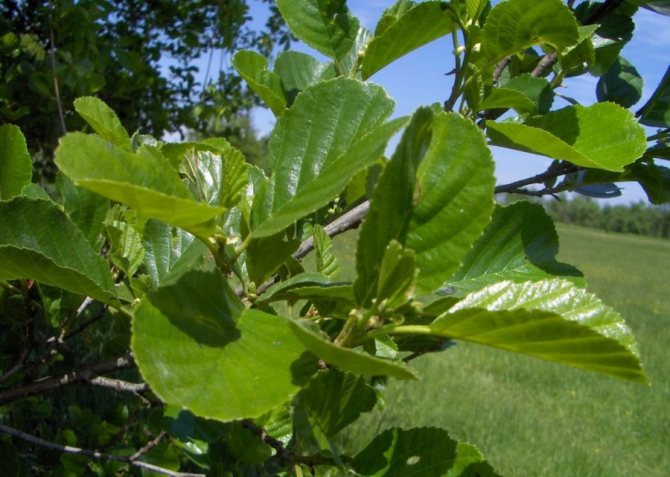
- Black alder has a dark bark with many cracks. Leaves are oval or rounded, have a notch. The trunk is branched. This variety reaches a height of 35 m. Flowering occurs with the formation of catkins in early spring.The fruits at the time of ripening are similar to the cones of small conifers. She likes to grow near rivers, you will not find her in wetlands. Black alder has beautiful, pink-tinted wood, so it is often used in production.
- Red alder has been cultivated since 1884. Grows up to 20 m in height. The tree has a light gray bark and dark red shoots. The leaves are large, pointed, with a tucked toothed edge. Cones are ovoid, medium-sized, collected in 6-8 pieces.
Alder species
In total, botanists have confirmed the existence of about 40 species of alder. The most common are:
- black alder, which is considered one of the best medicinal species;
- gray alder with ovoid leaves and superficial roots;
- white, with light gray bark and leaves with double serrate edges;
- red upright;
- shrub alder, rapidly growing.
In addition to the above species, in Siberia and in the Far East, you can find: Siberian, fluffy, Japanese, Italian, which are interspecific hybrids, and the established names are more related to the growing places of such alder species.
Natural enemies
Alder attracts many fungi and insect pests, from which they are unable to defend themselves. They get rid of fungi with the help of fungicides, insects are expelled with insecticides or folk remedies. To obtain environmentally friendly products from alder, it can be sprayed with biological protection agents.
Among the insect pests are butterflies, which lay their eggs under the bark, and leaf beetles, which eat the buds and leaves of the tree. You can use the same pesticides against them, or set sticky traps.
Alder tree: description
If we consider the features of the appearance, it all depends on the places of its growth, the species to which it belongs, as well as the soil on which it grows. A tree that grows in fertile soil can reach a height of up to 25 meters by the age of fifty. Black alder grows up to 35 meters. And what does alder look like on soils with poor fertility? It grows as a bush, living up to 60-70 years.
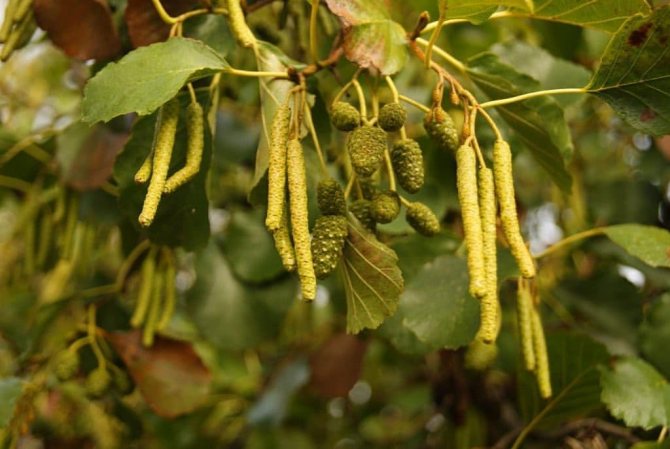
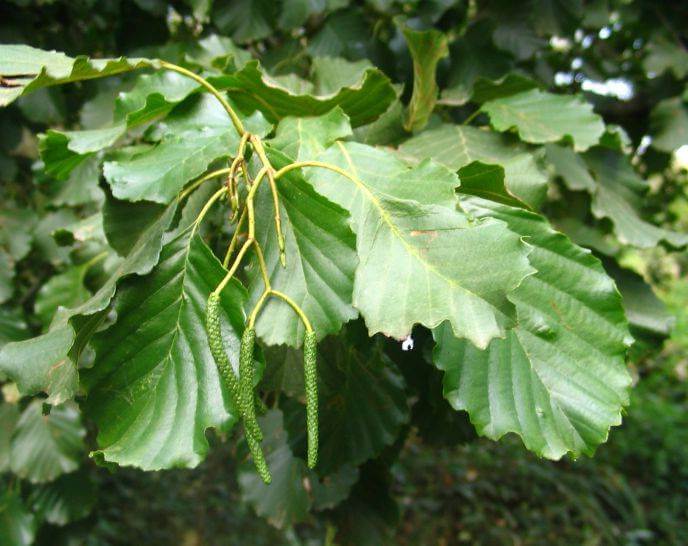
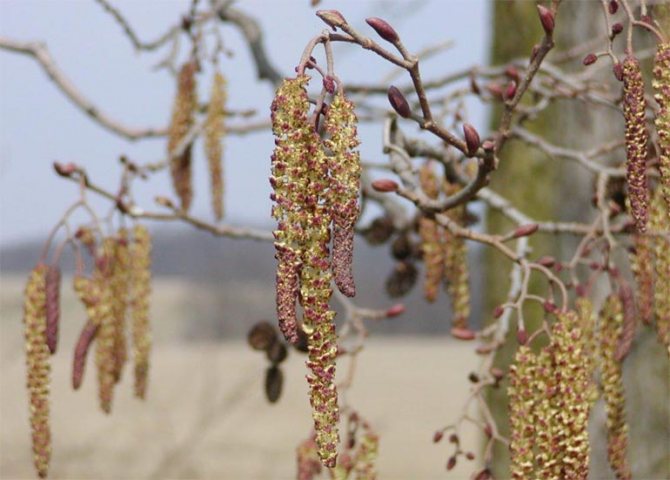
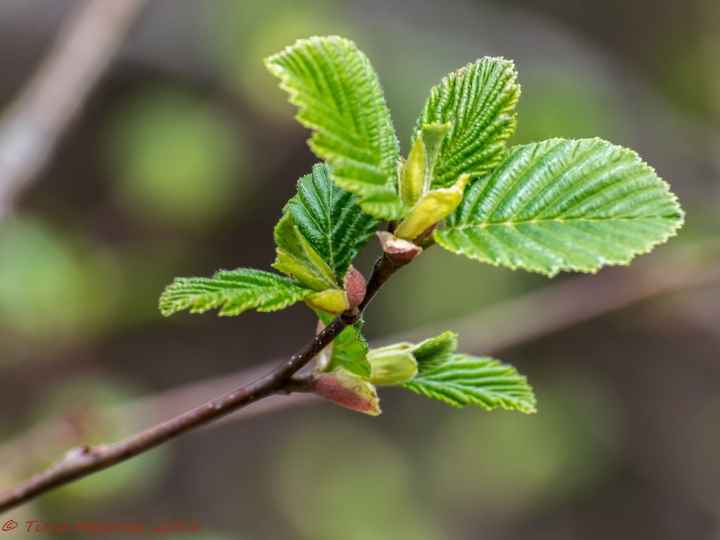
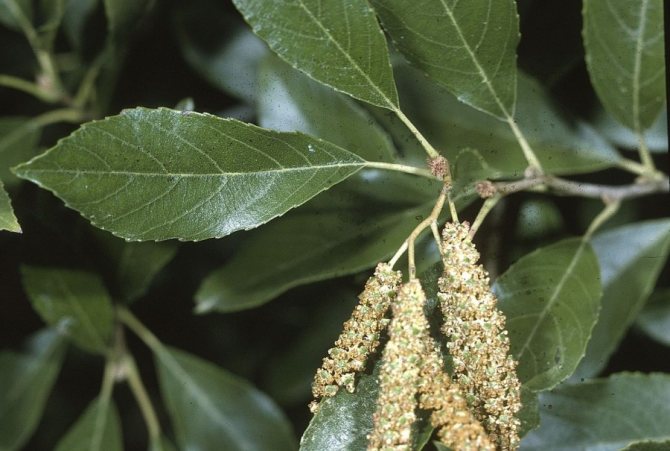
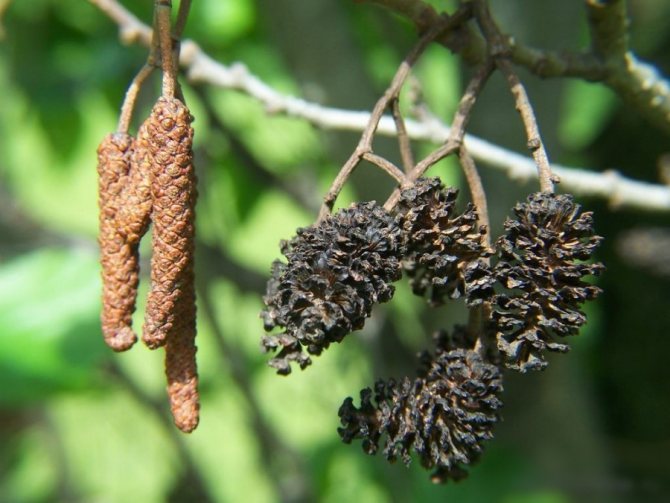
Alder has a lush crown. But it is not uniform, somewhat sparse due to the uneven arrangement of the branches. Alder is one of the first to signal that spring has come. This is manifested in the abundant flowering of the tree. It stands at this time adorned with beautiful earrings, which are divided into male and female. Female earrings are no more than 1 cm in size, and male earrings reach 5 - 9 cm in size. The article presents specific photos of alder trees and leaves that appear after flowering.
Collection and preparation of cones
A good time for harvesting cones comes at the end of autumn. Moreover, you can continue to collect them until March. The process of collecting cones itself has its own characteristics: first you need to carefully cut the ends of the branches with cones with a pruner, and then fruits are plucked from them... The cones that lie on the ground do not have the required properties, so they cannot be used. After harvesting, the cones are laid out in an even layer under a canopy or in the attic, where air must be provided, where the drying procedure is carried out. If it is warm enough outside, then you can dry the fruits in the open air, remembering to stir them from time to time. With proper drying, buds retain their beneficial properties for three years.
Fruit
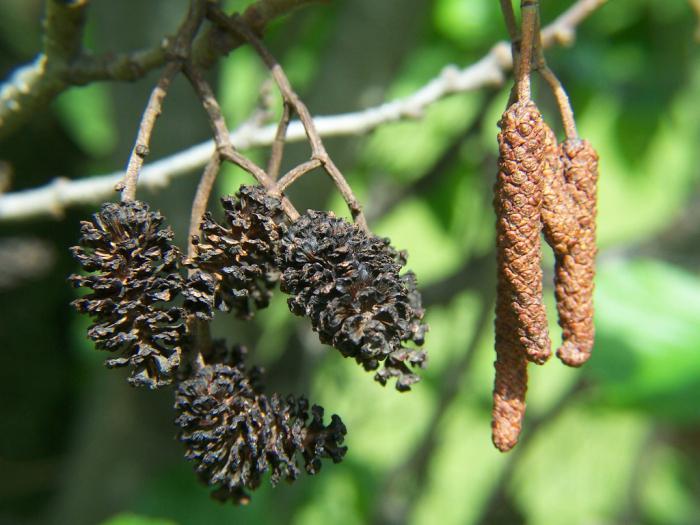
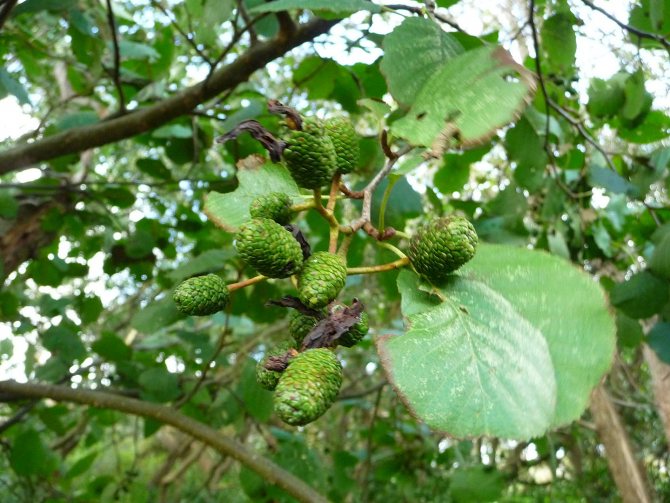
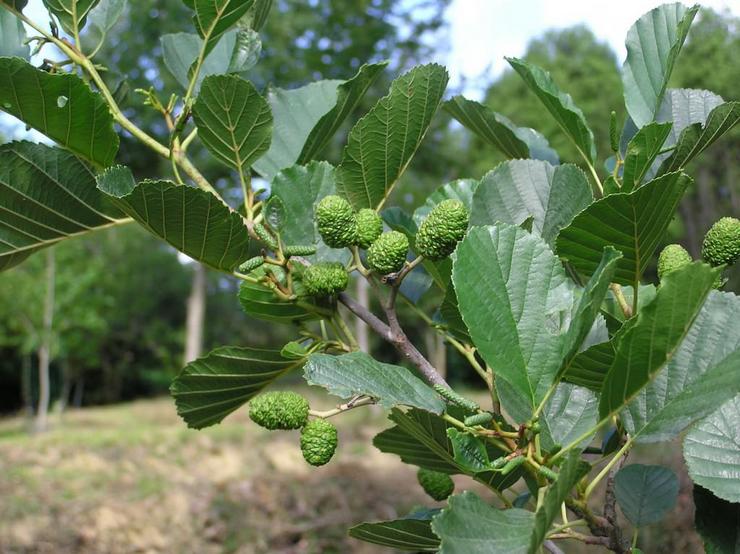
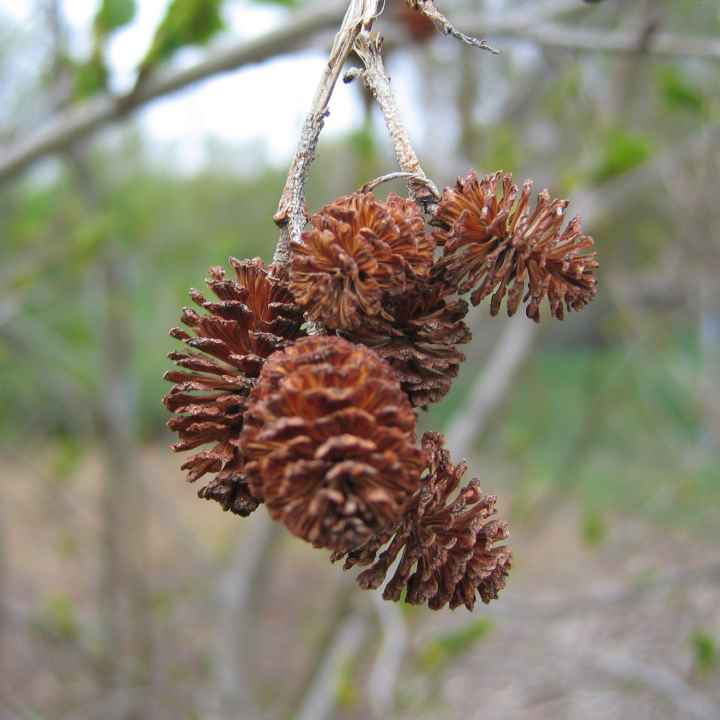
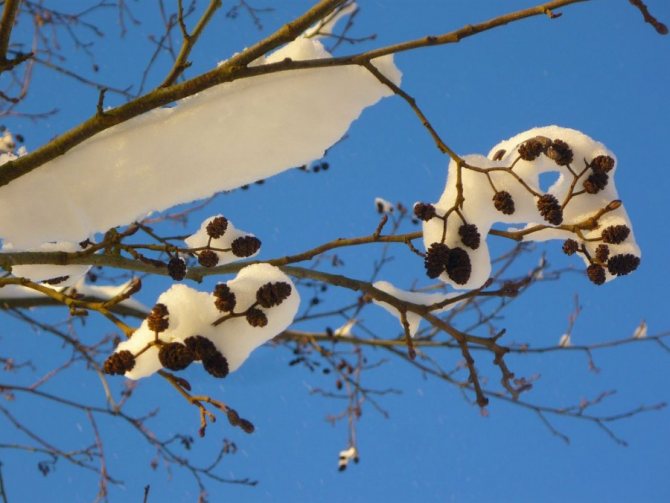
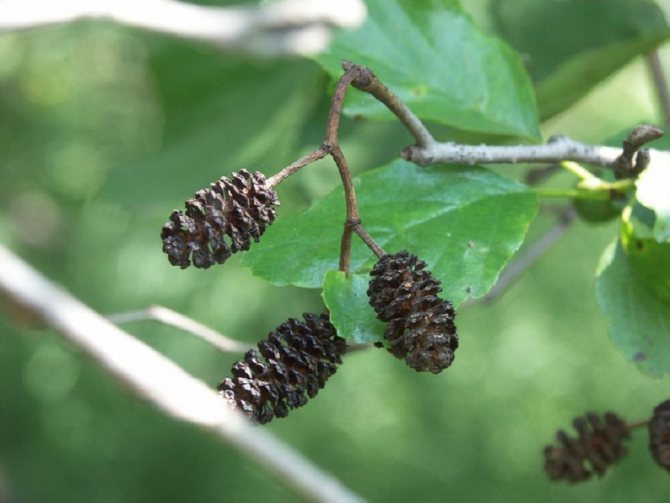
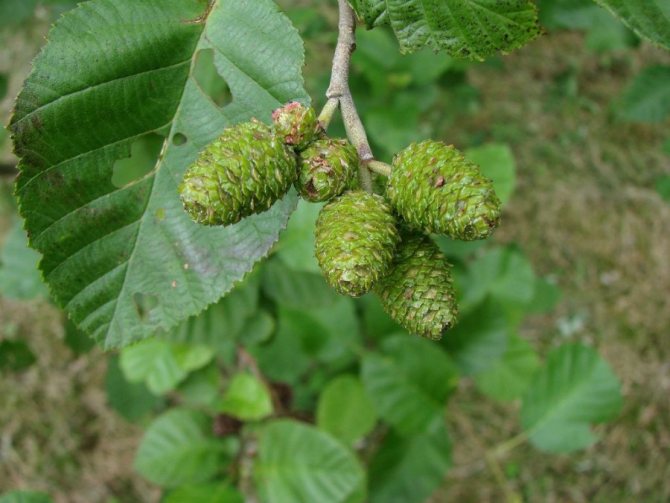
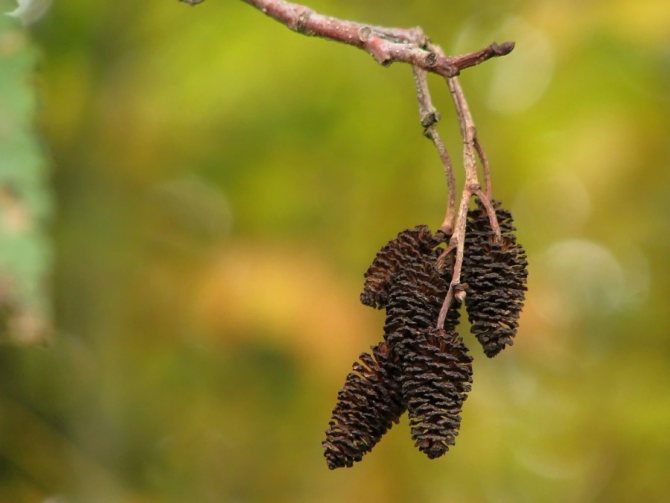
Alder cones of different sizes are fruits. Depending on its type, they are membranous and leathery, while others are wingless. Throughout the winter, cones hang closed on alder, opening only in March and sowing the soil with their seeds.
The cones can be harvested in late autumn and winter if the alder grows in the garden. When harvesting cones, they are cut with garden shears. The buds are dried at room temperature. Dried fruits turn brown or brown. A light aroma emanates from them. They have an astringent taste.
Alder in folk medicine
Alder leaves, bark, alder seeds, which are recommended to be collected in late autumn, have a healing effect. When harvesting, the cones are cut with garden shears, and then dried indoors at room temperature. If done correctly, the fruits will have a brown or brown color, light aroma and astringent taste. Leaves are harvested in early summer, and bark in early winter.
Due to the presence of essential oils, organic acids, tannins, alkaloids and other components, preparations based on alder fruits and leaves have a blood-purifying, bactericidal, hemostatic, astringent effect. Decoctions from the seeds and leaves of this plant give a diaphoretic and antimicrobial effect, reduce inflammation.
Infusion of alder fruits treat gastrointestinal disorders, the bark is used for enterocolitis and digestive disorders. Herbal decoctions cleanse the skin, heal wounds, eliminate nosebleeds, reduce allergies, and help with rheumatism.


The alder tree includes approximately 30 species, including:
- black (Alnus glutinosa);
- gray (Alnus incana);
- green (Alnus viridis).


Black alder
Alder blooms in April and is pollinated by the wind before the leaves, which have an oval or round shape, bloom. She prepared for the spring bloom the previous summer. It was at this time that male earrings are laid, which grow and form until late autumn. A supply of pollen is ready for winter. The fruits of this alder ripen by next spring. They are narrow-winged cones. This can be clearly seen in the photo of the alder tree and leaves.
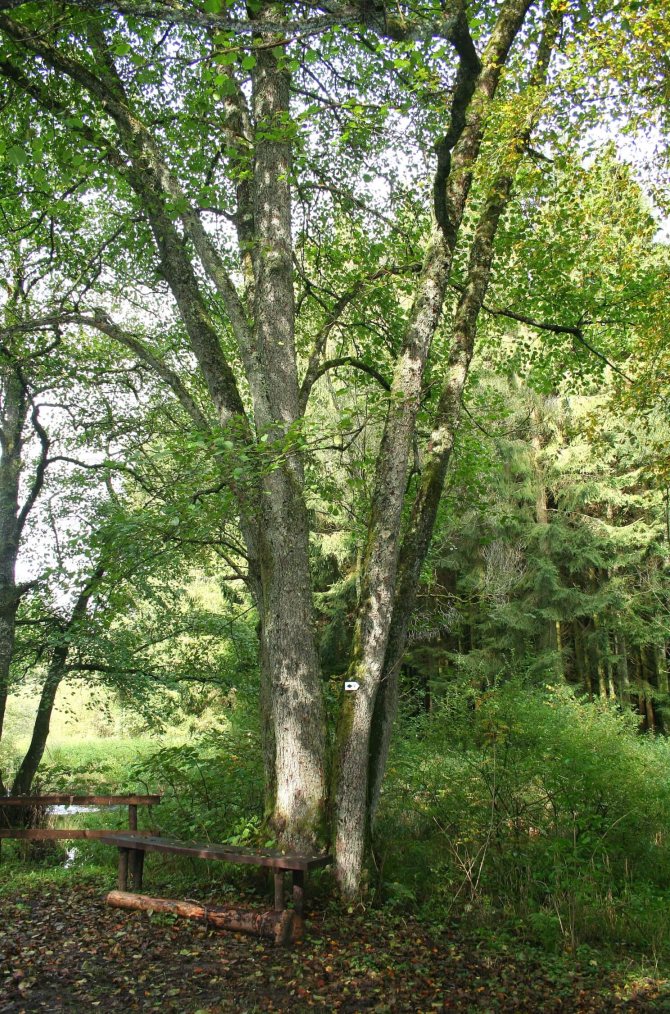
The bark is dark in color; old branches have a significant amount of cracks.


Black alder is found in North America, Europe, Ukraine and the Baltic countries. Loves wetlands. Sometimes black alder looks like thickets, especially in those places where there is a stream or a small river. There is even a sign among the people: "Where there is good alder, there is a heap of hay." This type of alder is included in the Red Data Books of Kazakhstan, Moldova and some regions of Russia. Black alder is quite often used by landscape designers to plant valley parks.
Black alder has a significant number of decorative species that differ in the shape of the leaf blade and the shape of the crown. What does these ornamental alder look like? For example, oakleaf has lobed leaves similar to those of an oak; in rowan-leaved foliage of the pinnacle-lobed type; royal has small, more deeply cut leaves. And all this is alder.
Etymology of the name [edit | edit code]
The Russian word "alder" comes from praslav. * ol'xa / el'xa (whence also Ukr.Vilha, Belorussian Volha, Bulgarian Elsha, Serbo-Croatian jóva, Slovenian jélša, Czech olšе, Slovak jelša, Polish Olsza, V-luzh wólša, N-luzh . wolšа) [6], ascending through the form *ălĭsā
/
ĕlĭsā
to the great-IE.
* elisos
[7] (compare German Erle elira / erila, English alder alor [8] [9]). Indo-European lexeme is derived from the root *
el
-,
ol
- associated with the designation of light [10] [11] or red / brown [12].
Generic name Alnus
is the Latin name for black alder (
Alnus glutinosa
), found even among the Roman writers Vitruvius, Pliny and others [13]. Through the form *
elsno
- (cf. lit. al̃ksnis, Latvian alksnis, Prussian * alskande) it also goes back to the common Indo-European name for alder *
haéliso / eha—
[7] [14]. For a long time in science there was a methodologically inconsistent point of view, expressed by Isidore of Seville, that the Latin name for alder comes from lat. álitur (ab) ámne -
river feed
or celtic
al
—
at
,
alis
—
water
,
lan
—
shore
- by habitat [15].
Scope of black alder
Characteristic in the description of this species of alder is the value of its wood. In ancient times, they knew that it is strong and does not lend itself to decay, so it was used for lining wells, making barrels and underwater structures. When wood is dried, cracks do not form on it. This makes it possible to make musical instruments from it, in particular, flutes and pipes.


In ancient times, shoes were made of wood and alder bark. Due to the pliability and softness of wood, it is used for the manufacture of sculptures and panels. After logging, alder wood changes its color from white to red. When it is treated with ammonia and drying oil, it acquires a beautiful ebb. Samples of decorative furniture are constructed from such wood. Amulets, talismans and amulets are made of alder, sincerely believing that they will help protect both the home and the person.
In folk medicine, alder bark and cones are used, which contain a large amount of tannins. With young leaves, purulent wounds are treated, and with diathesis, a decoction of black alder flowers is prepared. Alder earrings alcoholic infusions are used for constipation.
Gallothanin and even selenium
Cones contain tannins (6-34%), incl. gallotanin, alkaloids, phenolcarboxylic acids (gallic - up to 4%). The leaves contain, in addition to tannins, anthracene derivatives. The bark contains up to 20% tannins, flavonol glycosides, in particular hyperoside, steroids (β-sitosterol), triterpenes.
In addition, macroelements (mg / g) were found in seedlings: potassium - 5.8, calcium - 5.0, magnesium - 0.8, iron - 0.2. They concentrate selenium.
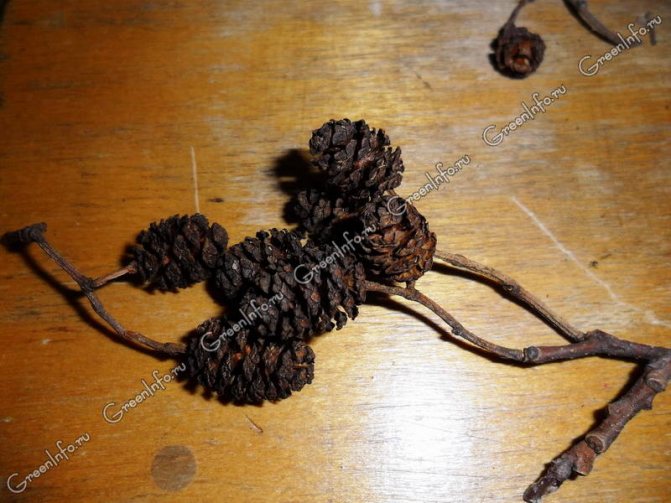


Medicinal alder fruit. Photo: Elena Malankina
Gray alder
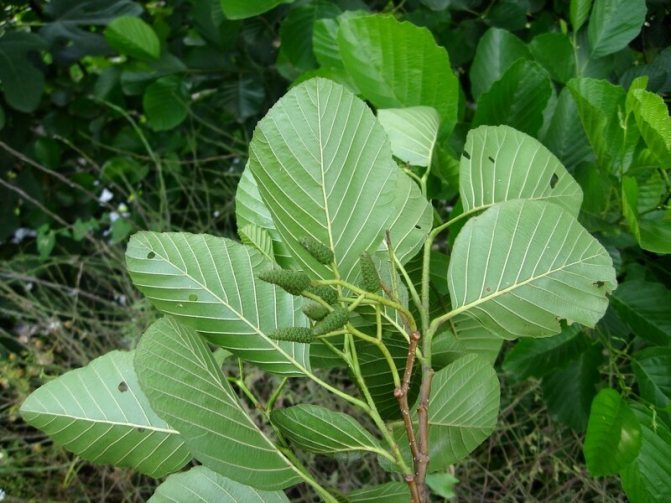
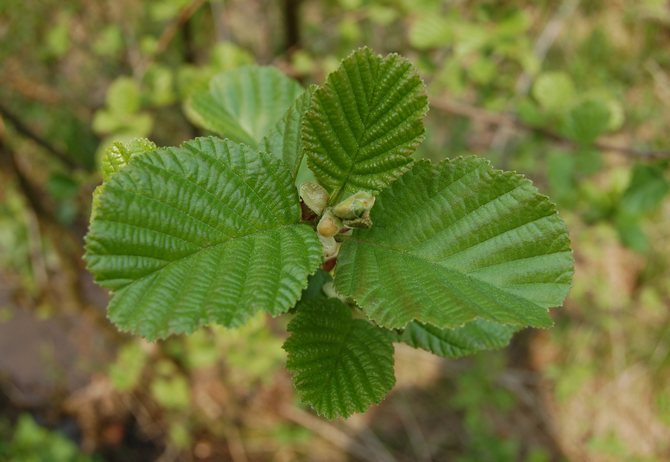
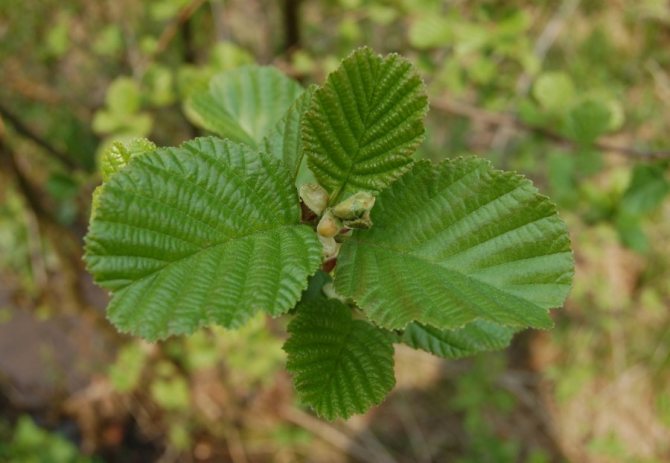
Trees of this species can be found on dry heights of the European part of Russia. This is a low species of plant, often having the appearance of a large shrub with superficial roots. Gray alder can often be seen on the edge of spruce forests and in fields that once served as arable land. Why is this type of alder named gray? This is most likely due to the color of the bark and the shade of alder leaves, which occurs due to the small edge, which gives silvery. Further in the article are photos of an alder tree and leaves, which are egg-shaped. The slightly pointed tip of the alder leaf gives it a similarity to a birch leaf. Gray alder blooms, like black alder, long before the leaves appear.


As mentioned above, gray alder has superficial roots. Microorganisms settle in them, which, absorbing gaseous nitrogen from the air, convert it into nitrogenous compounds. Thanks to this, gray alder is a natural creator of nitrogenous fertilizers. There is another interesting property of the tree: in the fall, alder leaves look green as in spring. The tree sheds unpainted crimson and gold leaves in preparation for winter. They remain green when they fall to the ground and rot very quickly, improving the topsoil.
The decorative forms of gray alder are varied. For example, blue alder, common in North America, is in the form of a bush or a short (6 meters) tree with bluish leaves, sometimes with a lower edge. Golden has the color of the shoots - reddish, and the leaves are pubescent and slightly yellowish.
There is a variety of ornamental gray alder called ugly. She has flat, creeping branches.
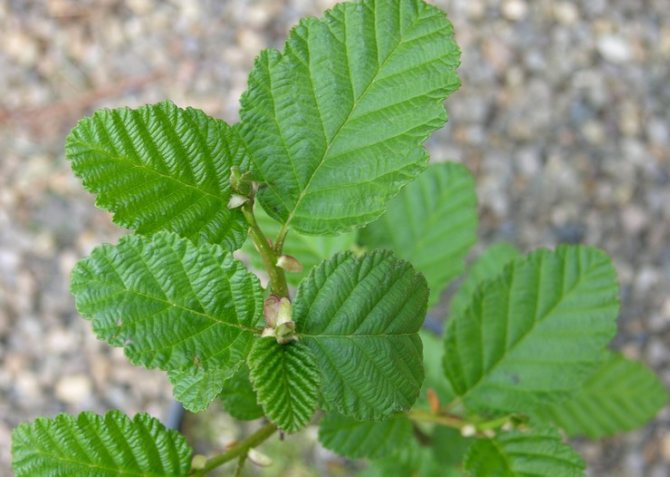
Green alder (Alnus viridis)
It is a very common shrub (rarely a small tree), with dense shoots. Reaches a height of up to 4 m. Creates numerous shoots bent in the form of a braid. Annual shoots are olive-green or red-brown, slightly flattened, pubescent.
| Photo of green alder | ||
| Earrings are male inflorescences. | Leaves are ovoid or elliptical, up to 6 cm long, pointed, with double carved edges. Veins are clearly visible, in the amount of 5-10 pairs, slightly pubescent in the corners. | The ripe fruit is a bump. The fruit is globular or ovoid, strongly lignified, resembles tiny pine cones in appearance. Contains nuts. They stay on the plant for a long time. |
The buds are convex, conical, covered with 4-6 purple-brown or greenish ciliated scales, sometimes slightly sticky. The plant is monoecious (separate male and female inflorescences appear on one plant). Before winter, rudiments of male and female inflorescences appear on the branches, which bloom only in spring.They bloom simultaneously with the development of foliage (April-May) and are wind-pollinated.
The plant grows especially abundantly along the streams. Prevents erosion and strengthens slopes. Its pollen sometimes causes allergies.
Origin: Found in North America, Europe and Asia (including Siberia and Kamchatka).
Scope of gray alder
The wood is used to make decorative ornaments and furniture. Red, brown and green dyes are obtained from the bark of the tree. Gray alder does not rot in water. Like black, it was used in the foundations of some medieval cathedrals. Many cathedrals and castles in Venice still stand on alder piles, like the watermills in Scotland. The gunsmiths of the Middle Ages knew a lot about alder wood. They valued wood as the best for coal, which was used to melt metal for swords.


Beekeepers know that alder pollen is an excellent food for bees. In folk and official medicine, alder is widely used due to tannins, vegetable and essential oils.
Infusions from lignified alder cones are used for all kinds of inflammatory diseases of internal organs, as well as dressings for non-healing trophic ulcers, eczema and burns. A broom made of twigs and leaves is an excellent bactericidal agent that tones the skin in a bath.
Application in construction
The wood of this tree is used not only independently, but also as a component in the production of chipboards, plywood, veneer. This is justified by its antiseptic qualities due to its astringent properties. Each type of alder has its own characteristics that determine the area of its application.
Black alder is considered the most sensitive to temperature extremes, so they try not to use it in the decoration of saunas and baths. What you need to consider when working with alder - this wood is quite soft and still requires processing from pests and moisture. Its main advantage is its long service life and the fact that the fibers have a beautiful texture. This species is used to make crafts, toys, paper, and is used as fuel.
Products made from gray alder are better suited for operation in humid conditions, this expands the scope of its application. This wood is also ideal for making eco-friendly toys, shoes and some turning tools.
Read also Jasmine effect on the body
Houses, saunas, baths
The advantages of this type of wood include the ability to get beautiful shades with the help of staining and even to imitate more valuable wood species. Alder board has healing properties, therefore it is well suited for interior decoration of houses, saunas and baths. The advantages of alder wood building materials are:
- resistance to deformation at high temperatures;
- lack of release of resinous and other harmful compounds;
- the ability to absorb moisture well;
- excellent sound and heat insulation properties;
- the fact that condensation does not accumulate on the surface of this wood;
- low thermal conductivity - this minimizes the risk of burns.
When building structures, it is important to take into account one nuance - alder boards should not come into contact with the ground.
Doors, laminate, furniture
Excellent interior doors are obtained from this solid wood. Thanks to various treatments, they can be used in any interior, while the price remains quite affordable. Alder doors are completely safe, besides they have antibacterial and anti-allergenic properties, they can be used even in children's rooms. They serve for quite a long time.
Alder laminate not only meets all technical requirements, but also has an attractive appearance. It can be considered as a substitute for elite parquet. Such floors do not get too dirty, are easy to clean, do not require a lot of time for maintenance and any special means for this.
For the manufacture of furniture, not only solid wood is used, alder is a part of plywood, chipboard and furniture boards. In operation, these types of materials give the best performance in terms of wear resistance, they do not form chips, are not subject to deformation. Alder furniture is lightweight, but quite durable.
It is important to know that when working with wood, it is better not to use nails, they can split the material when driven in. Screws are an excellent substitute in this case.
Italian alder
It grows in Italy and Albania. This is Alnus cordata - Italian (heart-shaped). The article presents a photo of a tree and leaves of an alder of this species, which is often confused with Alnus subcordata - heart-leaved. Italian alder has an ovoid crown. Her leaves are dense, smooth, oval in shape. The tree remains until December. Shaped like cherry leaves. The bark of the tree is dark brown.


Pests and diseases
lays the larvae in the shoots and bark of a tree.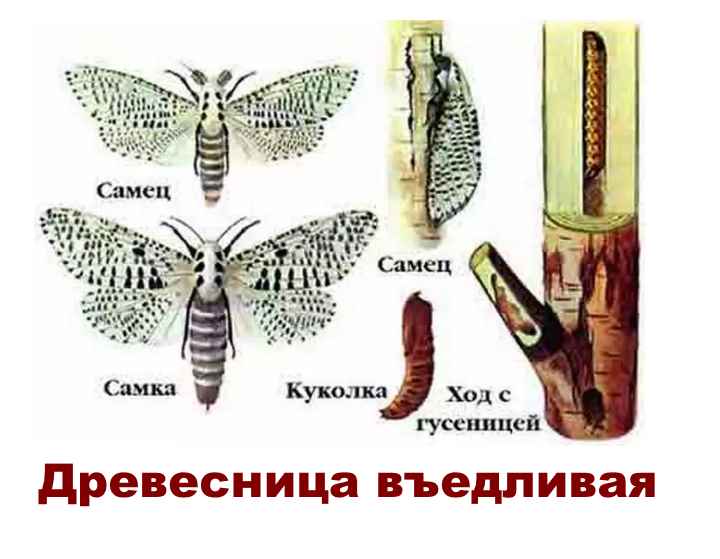

Corrosive arboreal- Tafrin mushroom - affects the female earrings of the plant, while leaf-shaped growths can be seen in the earrings. If the fungus appears, it is better to cut the branches and burn them.
- Fungal leaf disease - leaves become covered with spots and wrinkles. You can get rid of it by using special poisons.
- A disease common to alder may appear - heart rot, which affects most of the tree by the age of sixty.
Growing alder in personal plots
Many summer residents like to plant ornamental trees and shrubs on their backyard plots, turning part of the site into a piece of a fabulous forest. Alder is no exception, especially since its bark, fruits, leaves, pollen are good folk remedies that are always good to have “at hand”. You can plant ready-made perennial alder trees, small seedlings purchased from nurseries, seedlings from shoots dug out in places of growth, or wait for seedlings planted on the site of seeds of one or another type of alder.
Alder belongs to large-sized plants. They have a powerful root system, a height of more than 15 meters, and a well-formed crown. If a sufficiently mature tree is planted on the site, this process is laborious. Here you need a technique that will bring a tree and plant it in a prepared place. Planting can be done at any time, but the best option would be to plant alder in autumn and even winter, when the tree reacts least of all to temperature changes and is at rest.
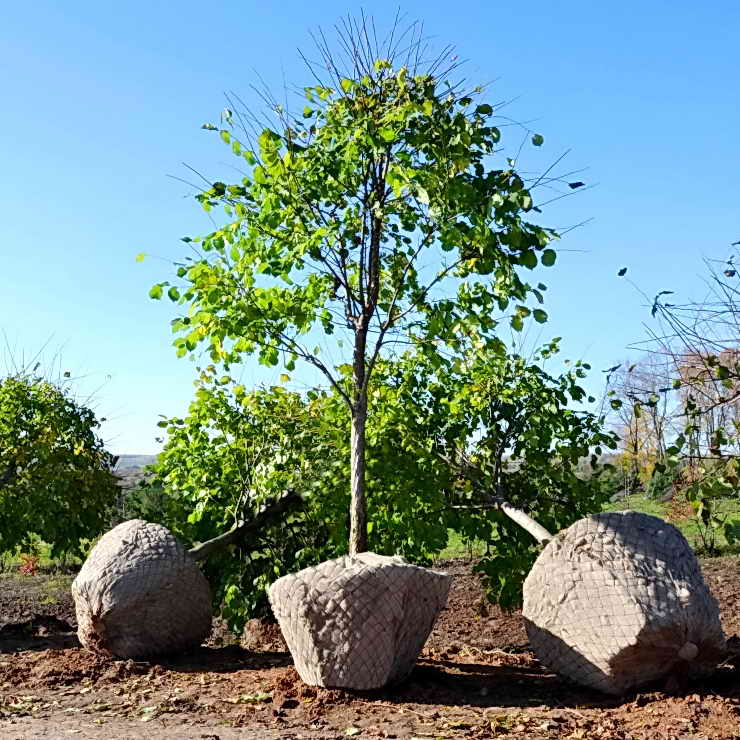


In central Russia, the landing time is from November to March. Caring for a tree planted in this way consists in intensive watering and loosening in the first year after planting.
In the nursery, you can buy shrubby alder, which reaches a height of 3 meters, or is formed in the form of a small tree, which rarely exceeds 10 meters. Shrub alder grows quickly, not picky about the soil, picky about moisture. Alder will transform even the most ordinary-looking piece of a personal plot, turning it over time into a cozy green corner.
Growing and care
Tree in the plant system
The tree is unpretentious to the composition and structure of the soil and can be planted even on sandstone.
In horticulture and forestry, alder is famous for:
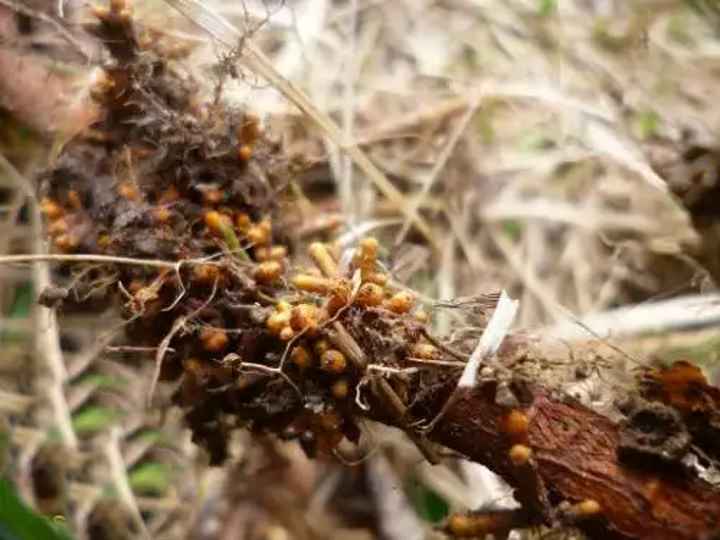


is a nitrogen supplier and fertilizes the near-stem circle, helping other plants to grow and feed,- has root nodule bacteria,
- the leaves are rich in nitrogen and are an excellent mulch and nutrient mass for the land and closely growing plants.
Seeds
Collection
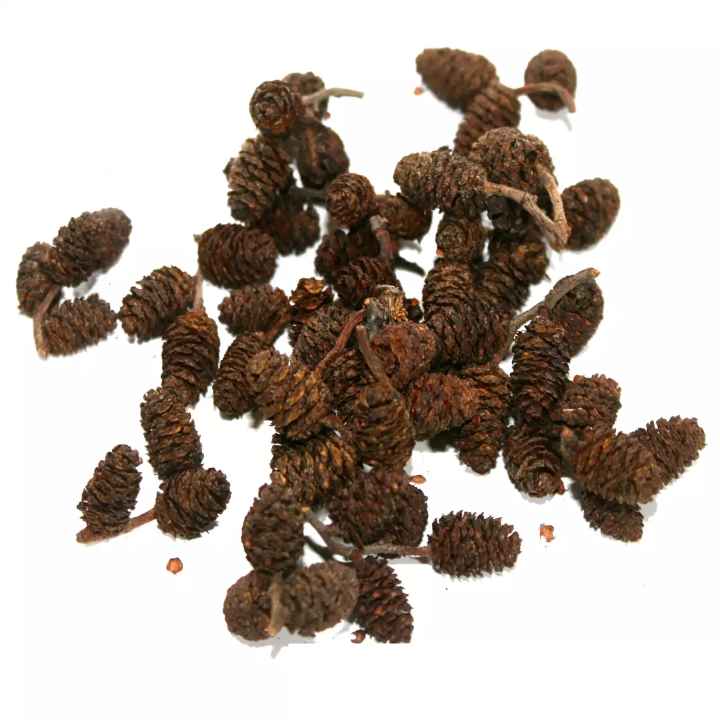


Alder cones are harvested in late autumn and stored in the fresh air until they are fully opened.
Separation of seeds is done using a sieve.
Storage
The seeds are stored in a refrigerator or basement at a temperature not exceeding 5 degrees.
Seeding
Seeds can be sown both in autumn and spring.But their shelf life is short, only 4 months, after which the germination of seeds begins to fall.
The soil
If alder is planted at home, then an earthen mixture is prepared from the following components:


sand;- sod land;
- peat;
- lime (only for gray alder);
- humus (only for black alder).
The seeds are sown in seedling boxes and moistened.
The tree grows quite quickly and during the season the seedlings, under favorable conditions, make an increase of several meters.
If the seeds are sown abundantly, then after a couple of years of planting they form an impenetrable jungle.
Watering
Watering the tree is recommended only in dry conditions. If the tree is not watered, it will try to grow deeper roots that can nourish the crown.


Rare artificial watering will still not be able to provide the tree with the necessary moisture and will slow down the development of the root system.
Although before the development of a meter in height, the seedling should be watered as often as normal seedlings.
Loosening
The trunk circle can be loosened, but then you will have to mulch the tree in winter.


To avoid this, you can plant lawn grass, green manures or flowers in the near-trunk circle and from time to time trim excess vegetation to ensure the protection of the roots and the formation of beneficial microorganisms in the soil.
Complete exposure of the trunk circle does not always have a positive effect on the health of the tree. Peat or wood chips are used for mulching.
Landscape use
The oval, openwork crown of alder with moving branches and quivering leaves looks very lively. Plants do not suffer from urban air pollution, so they can be planted along the road. Low trees or lush shrubs up to 3 m in height are usually used as hedges. They are planted in a ribbon method rather densely and regularly shape.
Large single-stemmed trees are used in single plantings or in a group over a large area. They are planted along paths and alleys. Also, alder can be used in compositions of shrubs and trees, combining plants with different colors and foliage structures.
Significance and Application [edit | edit code]
Wood [edit | edit code]
(the section is written based on the article Alder
in
Encyclopedic Dictionary of Brockhaus and Efron
, see the References section)
Alder wood is not durable, but has a fairly uniform structure, facilitating processing, and a beautiful reddish color. Smoother and thicker trunks are therefore used for crafts, for joinery and turning products, but the bulk of alder wood is used for firewood, which are usually valued 10-30% cheaper than birch.
Alder wood lasts a long time under water and therefore finds application for small underwater structures.
Alder coal was prized for making hunting gunpowder.
The peasants of Russia use alder wood to burn off soot in chimneys (especially after pine ones).
Alder shavings and sawdust are used for smoking meat and fish.
Alder wood is also used to make the body of electric guitars.
In medicine [edit | edit code]
Domestic pharmacopoeia are black alder and gray alder. In official and traditional medicine, infusions, decoctions of bark, leaves and seedlings are used as anti-inflammatory, antibacterial, astringent, hemostatic, wound healing, immunomodulating, anticancer agent.
Other uses [edit | edit code]
Alder bark is used for tanning and dyeing leather. Black, yellow and red paints are extracted from it [16].
Leaves and cones serve as medicinal raw materials [16].
Alder is a honey plant and a valuable ornamental plant. In the spring it is beautiful with long, hanging earrings, and in the summer with openwork, shiny foliage. In landscaping, black alder and gray alder are often used [16].
Alder improves the soil and is therefore used in forestry as an auxiliary breed. Alder can grow on poor, gravelly soils, clastic rocks. This property has been used for afforestation of waste dumps in Germany, USA, Estonia and Ukraine.
Alder foliage is used in autumn as fodder for livestock, primarily sheep [21].
Grapes
- In gardens and in private plots, you can choose a warmer place for planting grapes, for example, on the sunny side of the house, garden pavilion, veranda. It is recommended to plant grapes along the border of the plot. The vines formed in one line will not take up much space and at the same time will be well lit from all sides. Near buildings, grapes must be placed so that water flowing from the roofs does not fall on it. On level ground, it is necessary to make ridges with good drainage due to drainage furrows. Some gardeners, from the experience of their colleagues in the western regions of the country, dig deep planting holes and fill them with organic fertilizers and fertilized soil. Pits dug in waterproof clay are a kind of closed vessel that fills with water during monsoon rains. In fertile soil, the root system of grapes develops well at first, but as soon as waterlogging begins, it suffocates. Deep holes can play a positive role in soils where there is good natural drainage, permeable subsoil, or reclamation artificial drainage is possible. Planting grapes
It is possible to quickly restore an obsolete grape bush by the method of layering ("katavlak"). To this end, healthy vines of a neighboring bush are laid in grooves dug to the place where the dead bush used to grow, and sprinkled with earth. A top is brought to the surface, from which a new bush then grows. Lignified vines are laid on layering in spring, and green vines in July. They are not separated from the mother bush for two to three years. A frozen or very old shrub can be restored by short pruning to healthy aboveground parts or by pruning to the “black head” of an underground stem. In the latter case, the underground bole is freed from the ground and cut down entirely. Not far from the surface, new shoots grow from dormant buds, due to which a new bush is formed. Grape bushes, neglected and severely damaged by frost, are restored due to stronger fatty shoots formed in the lower part of the old wood, and the removal of weakened sleeves. But before removing the sleeve, form a replacement for it. Grape care
A gardener who starts growing grapes needs to study well the structure of the vine and the biology of this interesting plant. Grapes are lianas (climbing) plants, they need support. But it can creep along the ground and take root, as is observed in wild Amur grapes. The roots and the aerial part of the stem grow rapidly, branching strongly and reaching large sizes. Under natural conditions, without human intervention, a branched bush of grapes grows with many vines of various orders, which comes into fruiting late and yields irregularly. In cultivation, the grapes are formed, give the bushes a form that is easy to care for, providing a high yield of high-quality bunches. Planting lemongrass
Chinese schisandra, or schizandra, has several names - lemon tree, red grape, gomisha (Japanese), cochinta, kozyanta (Nanai), Kolchita (Ulchi), usimtya (Udege), uchampu (Oroch). In terms of structure, systemic relationship, center of origin and distribution, Schisandra chinensis has nothing to do with a real citrus plant with lemon, but all its organs (roots, shoots, leaves, flowers, berries) exude a lemon scent, hence the name Schizandra.The lemongrass vine, clinging or twining around the support, along with the Amur grapes and three species of actinidia, is an original plant of the Far Eastern taiga. Its fruits, like real lemon, are too sour for fresh consumption, but they have medicinal properties, a pleasant aroma, and this has attracted a lot of attention to it. The taste of Schisandra chinensis is somewhat improved after freezing. Local hunters who consume such fruits claim that they relieve fatigue, give the body vigor and improve vision. The Consolidated Chinese Pharmacopoeia, compiled back in 1596, says: “The fruit of the Chinese magnolia vine has five flavors and is classified as the first category of medicinal substances. The pulp of lemongrass is sour and sweet, the seeds are bitter-astringent, and the overall taste of the fruit is salty. Thus, all five tastes are present in it ”. Grow lemongrass
Beauty with brown earrings
Gray alder is one of the fairly common species of the birch family. It stands out for its large size, since it can grow up to 16 m. For its planting, they choose the banks of reservoirs and ravines, which are threatened with destruction. To obtain planting material, you can use young growth, cuttings or seeds.
The trunk of this tree has a characteristic gray color
, the leaves also look, brown earrings act as a decorative part. Therefore, seeing a tree that has these characteristics, know that you have an alder in front of you. Many people value this plant for its ability to withstand severe frosts and grow well in nutrient-poor soils and wetlands.
Distribution and ecology [edit | edit code]
Alder species are common in the temperate zone of the Northern Hemisphere. Some species enter South America, and in Asia reach Bengal and North Vietnam, but are found there only in the mountains. In the north, some species reach the forest-tundra and tundra, and in the mountains they rise to the subalpine belt. In Norway, gray alder is found throughout the forest zone, south of 70 ° north latitude. In the north, it is mixed with conifers, and to the south, it forms mixed forests together with beech and oak. In Great Britain, alder forests once dominated in humid places, but now, as a result of human economic activity, they have been destroyed. Black alder is a part of floodplain forests in Germany along the Rhine, Elbe, Weser and Danube valleys, in Hungary, in Romania in the Danube floodplain and delta, in the Sereti, Prut, Olta, Murisch valleys, etc. In Poland, black alder is found in deciduous plantations (3%), and gray alder is presented in them only as an impurity. On the territory of the former Yugoslavia, along the Danube, Drava and Morava, there is a strip of meadows and steppes with rare groves, which include black alder. Stands of black alder have been preserved in the valley of the Po River and on the island of Cyprus in humid places. On the coast and foothills of the western slopes of Lebanon, there are groves of eastern alder, both pure and mixed with downy oak, Alep and Italian pine, and eastern plane tree. In the Chinese province of Sichuan, alder grows along the beds of mountain rivers. In Korea, along the river valleys, there are groves of fluffy alder. In Japan, on the island of Hokkaido, in coniferous forests, you can find Japanese alder.
Alder prefers rich, moist, well-drained soil. It grows along the banks of rivers, streams, in grassy swamps, at the foot of hills. Alder can also tolerate soils of any richness and moisture and inhabit dry, poor, sandy and gravelly, as well as heavy, clay soils. Alder improves the soil due to the ability to nitrogen fixation, as well as due to the fact that it releases substances into the soil that have an inhibitory effect on pathogenic organisms and increase the populations of microorganisms competing with them [4].
Alder serves as an edifier of forest bogs, for example, black alder in Polesie, and bearded alder in Colchis. There it usually grows on high hummocks and is provided with stilted roots that strengthen the tree in unstable soil. In the subalpine belt of mountains, green alder forms shrub thickets.
Alder wood standards according to GOST
The type of alder already in the process of harvesting wood is determined by several parameters. These are the smoothness of the trunk, the number of knots and certain malformations, the most important of which are cracks, curvature of the trunk.
The variety of alder, harvested wood largely depends on where the harvested tree grows, and whether all the conditions for standard processing of wood are observed in the process of making sawn timber from it.
The price for alder wood and lumber made from it is estimated by experts at 4 points. The cost of this wood makes it possible to obtain from it economically profitable products used in various spheres of human life.
Harvesting, drying and medicinal properties of alder:
Healing properties
The alder tree is characterized by an amazing combination of three colors at once: fiery bark, emerald leaves, dark brown branches. According to national signs, this depicts the traditional trinity: fire, water and earth.


The black velvet light plant is perfectly trimmed, but it has one drawback - it is too fragile. Alder is a white tree, but when cut down, the color will turn brownish-red.


The vegetation in question is interesting for its beneficial properties for people and other vegetation. She fertilizes the soil with nitrogen. Its roots are made up of nodule formations, hiding places for bacteria and nitrogen helpers.


Small roots together with tree nodules eat catfish with pleasure. This is due to the following: the leaves fall and shed various animals that the fish brothers feed on. This is a tasty spot for fishermen.


Wood charcoal is also highly valued. It is designed to equip anti-chemical equipment, and alder chips are also used for smoking.


The next use is to get some decent paint. First, the bark is kept in water for two days, then filtered. If you keep the material in the solution for half an hour, it will turn brown.


People have been using this plant for medicinal purposes for a long time. Scientists studied it in 1942. Pharmaceuticals have mastered the techniques of making themelin.


Doctors prescribe medications containing alder extract for prolonged stomach ailments, inflammation of the small and large intestines.


Flower earrings are usually harvested in spring. With their help, creams are made for diathesis and eczema. At the dacha, many grow this plant, for preparations: jam from alder cones.


In rural areas, people will tell you how to harvest buds and leaves for certain diseases. Can be used for abdominal pain or colds. It is used for purulent-necrotic inflammation of the hair follicle.


Reproduction methods
Alder is propagated by seeds, cuttings and root shoots. The most common method is the seed method, and especially self-seeding. By the fall, ripe bumps begin to open and release the seeds. During November-March, they fall into the ground and undergo natural stratification. After that, during the period of snow melting, the seeds are saturated with moisture and hatch. When planting, the seeds are embedded in the melted soil to a depth of 2.5-3 cm. In the first year, only a small sprout is formed and a rhizome will develop. Gradually, the seedlings become stronger and rather quickly turn into a lush bush or small tree. Every year it will add 50-100 cm in height.
Young shoots often appear from the trunk. In just a year, their height can reach 1-1.5 m. In the spring, the offspring can be dug up and transplanted to a new place. It is recommended to keep a lump of old earth on the roots and not let it dry out.
In spring and summer, cuttings 12-16 cm long are cut from young shoots. They are rooted immediately in the open field. The best survival rate is shown by plants treated with a root stimulator. Cuttings should be watered regularly. By autumn, the plants will take root and grow strong enough for wintering without shelter.


Mushrooms associated with the genus Alder [edit | edit code]
Alder atelia [de] is associated with alder species (this is reflected in its name), which grows on the dead trunks of these trees [18]. Brown hypoxilon [de] settles on dry alder branches, very often it is found on dead young trunks [19]: 69, and on trunks and branches - concentric daldinia [en] [19] and saucer-shaped fomitopsis [19]: 109. On the bark of thick dead branches, radial phlebia is often found [en] [19]: 97. On deadwood, stumps, as well as on live weakened alder trees, a real tinder fungus grows [19]: 107, and on living trunks - a false tinder fungus [19]: 125.
Botanical description [edit | edit code]
Deciduous trees, sometimes shrubs. The life form can change depending on the conditions of the habitat [4].
Shoots are cylindrical, with an irregularly triangular, greenish core, rounded or oval lenticels.
Kidneys on legs, with two scales. Leaves are alternate, petiolate, simple, whole, occasionally slightly lobed, usually dentate along the margin [16], with early decaying stipules. Leaf shape - from almost round, ovoid, obovate to lanceolate [16]. The venation is pinnate. Folded foliation. Buds, leaves, and branches usually carry trichomes. The genus is very variable in pubescence and galliness, and these differences are both inter- and intraspecific [4].
Pistillate and staminate flowers of alder are monoecious. As a rule, staminate flowers are formed in the upper part of the shoot, collected by long catkins. Pistillate flowers are collected in small spikelets and sit in the lower part of the shoot [16]. Most species bloom in early spring. In some species, for example, the seaside alder ( Alnus maritima
) flowering occurs in autumn, in October - December. Flowering occurs before or simultaneously with the opening of the leaves, which promotes better wind transport of pollen. Inflorescences are laid during the growing season of the previous year, staminate - from mid-summer (5-6 months), pistillate - from autumn (1-2 months) [4]. Male flowers sit in three, rarely one at a time, on widened thyroid pedicels, spirally seating the rod of the catkins; the perianth is simple, usually four-leafed or four-incised; four stamens have short filaments and large two-celled anthers. Female flowers sit in pairs in the axils of fleshy scales, which by the time the fruits ripen, they stiffen and form a cone characteristic of alder, reminiscent of a conifer cone. A single flower is devoid of integuments and consists of a two-celled ovary with two threadlike columns. Pollinated by the wind. The period between pollination and fertilization is about 85 days. The seeds ripen by October [4].
The fruit is a single-seeded nut with two lignified stigmas and leathery, less often membranous wings, or wingless. Seed emergence begins in autumn and continues until spring. Their distribution occurs mainly by wind and water. Lignified cones remain on the tree for a long time after the fruit has fallen off [4].
Alder is spread by seeds, root suckers and shoots from the stump. The ability for vegetative reproduction in different species and individual specimens of the same species is different [4].
The main features of alder wood
Alder belongs to the group of deciduous plants from the birch family. This tree grows well and develops near river banks, in swamps and in high mountain areas. Depending on the environmental conditions of the alder, the type of soil, temperature changes, the plant can be either a tree or a low-growing shrub.
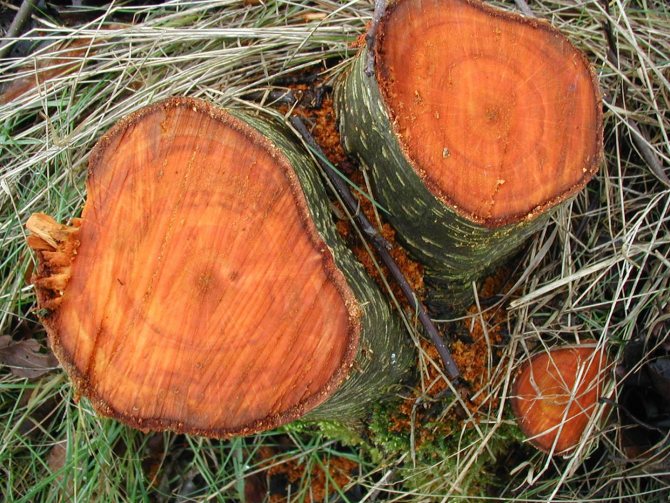
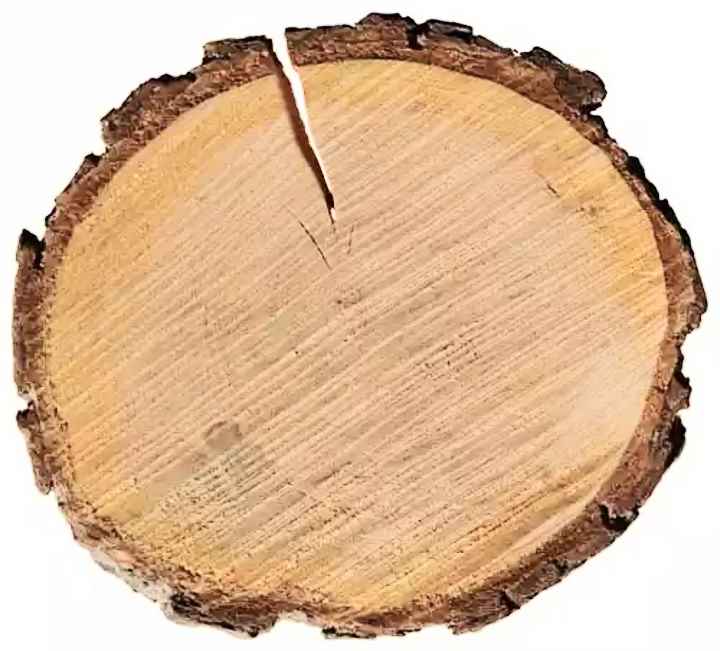
Alder wood does not have a central core in its trunk, due to which the color of its saw cut is uniform. After cutting, the cut of the tree is whitish in color, but after lying in the air it gradually acquires a yellowish-red color.
Alder wood is valued for a whole group of its main qualities:
- This tree does not rot under the conditions of its operation in water, and therefore, both in ancient times and now, it was widely used in the manufacture of piles and foundations of wells.
- Alder wood can perfectly undergo a wide range of joinery work. It is easy to cut, planed, products of various shapes are made from wood, craftsmen use alder blanks to create crafts that are unique in appearance.
- The special texture of alder wood harvested according to the standards allows it to be painted and processed using various paints, polishes, stains. Due to this valuable quality, wood of different types of alder is used as a material that imitates, that is, copies, more expensive tree species. That is, the practicality of alder wood from this side of its use in production can be estimated at five points.
- Alder blanks dry practically without warping, which ensures high economic efficiency of working with this type of treated wood.
Alder blanks are highly resistant to external mechanical stress and deformation. Among soft deciduous plants, alder rightfully occupies a leading position among trees that are highly resistant to decay in water.
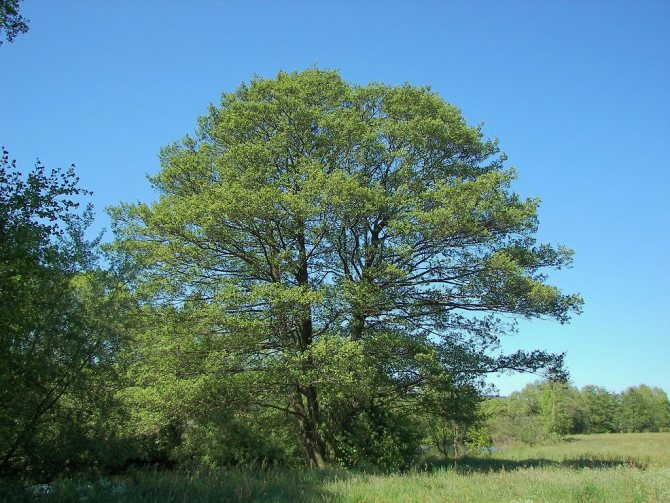
Photo of an alder tree