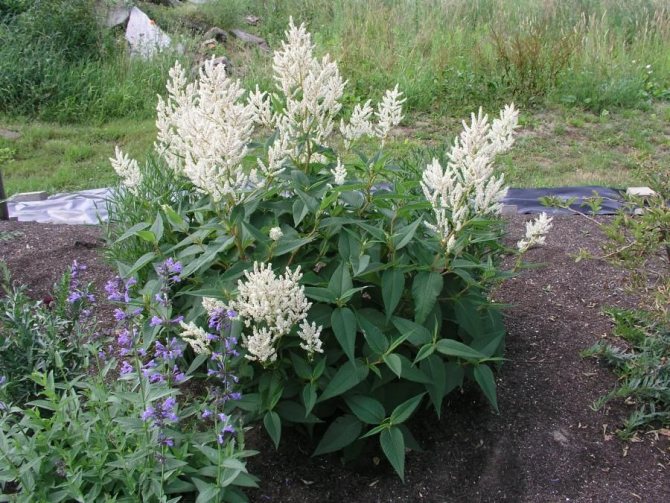
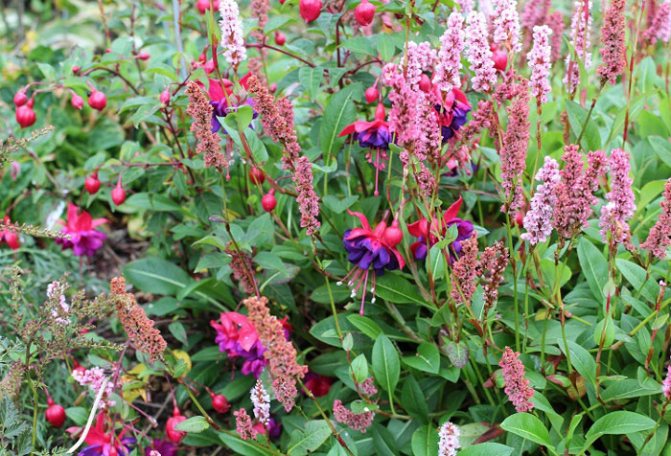
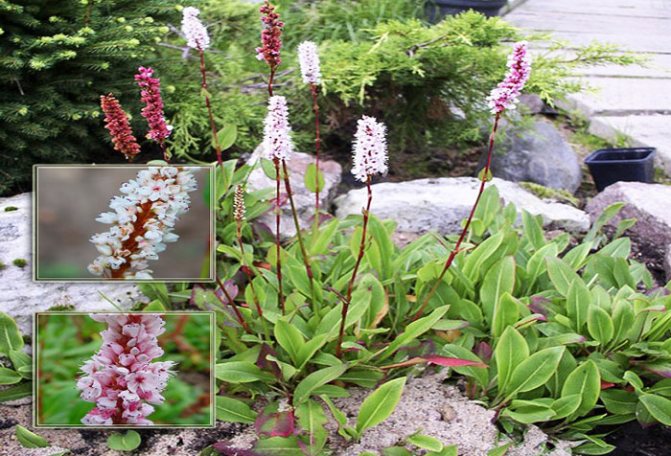
Highlander Aubert is a perennial plant that is often grown at home or in the countryside. Some consider it to be the grass of the field. This is partly true, but the plant is widely used in landscape design. The main advantage of this flower is that it does not require special care and planting. A photo of the Highlander Aubert demonstrates his simplicity and pleasant sophistication. It is not surprising that this plant has won the hearts of many gardeners.

Description
The homeland of the Highlander Aubert is the Far East, Siberia, China and Japan. It grows on rocky slopes, gravel and mountainous areas. Today, there are about 300 varieties of this plant. Among them there are annual and perennial flowers. In nature, you can see shrubs and vines. Highlander Aubert grows in almost all parts of the world. At the same time, he can feel great both in a meadow and on the banks of a river, in a forest or in high mountains.
Highlander serpentine properties
Snake mountaineer is used in the preparation of dietary supplements and herbal preparations. The herb is valued for its high content of tannins, about 30%, free polyphenols, oxyanthraquinones and vitamins A, B, C.
In addition to the above elements, buckwheat contains protein, starch, catechin and calcium, as well as acids: ascorbic, gallic and elaidic. The plant is rich in flavonoids: hyperoside, rutin, avicularin. Gorletz is widely used for the manufacture of anti-inflammatory drugs and dietary supplements aimed at combating diarrhea.


Highlander snake is used to treat the nasopharynx and oral cavity, by rinsing and irrigation. Its anti-inflammatory effect is comparable to that of oak bark. Buckwheat has an astringent, hemostatic and soothing effect. When taken orally, a decoction of the coil has an antioxidant and calming effect on the body.
In addition to oral administration, decoctions of knotweed snake are used in the form of lotions and compresses to relieve inflammation, stop bleeding, accelerate the healing process of damaged areas, relieve redness and swelling.
Appearance
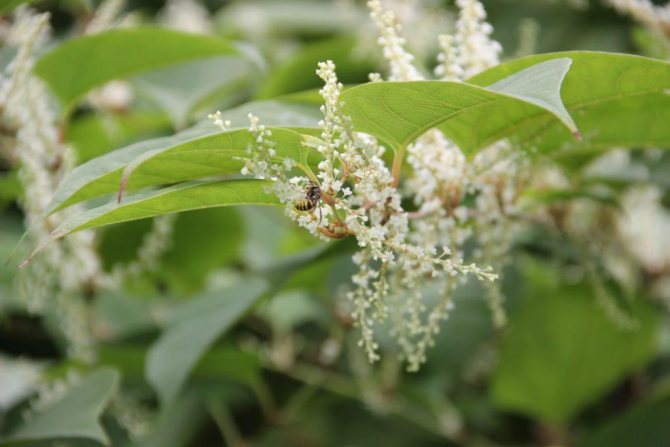
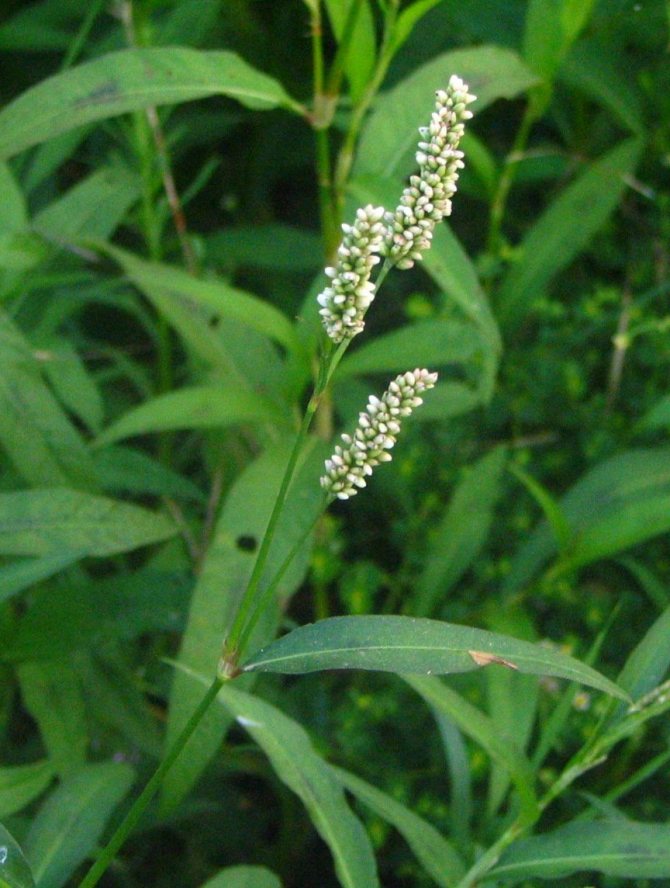
This plant is distinguished by erect or outstretched stems that can curl slightly. The leaves of the Highlander Aubert are simple. If we talk about flowers, they are rather small, collected in few-flowered curls, although they are often collected in racemose inflorescences. The fruit is a small nut, which contains up to 100 seeds.
The height of a perennial plant of the Highlander Aubert can reach 30-40 cm. Sometimes long hairs can be seen on the grass trunk, and sometimes it remains completely naked - it all depends on the type of subspecies. The length of the flower's leaf plates is about 2.5 centimeters. They are rather sharp in shape, wedge-shaped. Flowers are located at the tops of stems or branches. In this case, the inflorescences practically merge with the vegetative part of the stem. The perianth can be white or pink.
Views
Ayanskiy (Aconogonon ajanense)
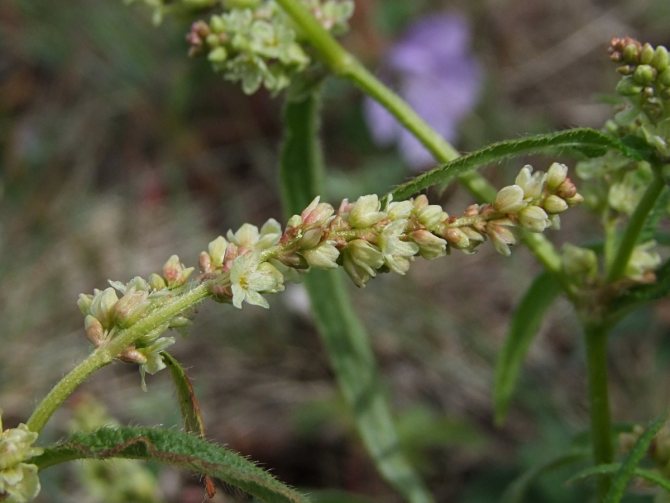


Photo:
This species is found in Siberia, the Far East and China - most often on mountain slopes and embankments. Reaches a height of 35 cm. The branches are directed in different directions, and the stem is covered with small hairs. The leaves are elliptical in shape, and pointed at the edges.The base of the leaf is broadly wedge-shaped. Flowers are collected in clusters, which are located at the top of the main stem. The perianth is white.
Auberta (Polugonum aubertii)
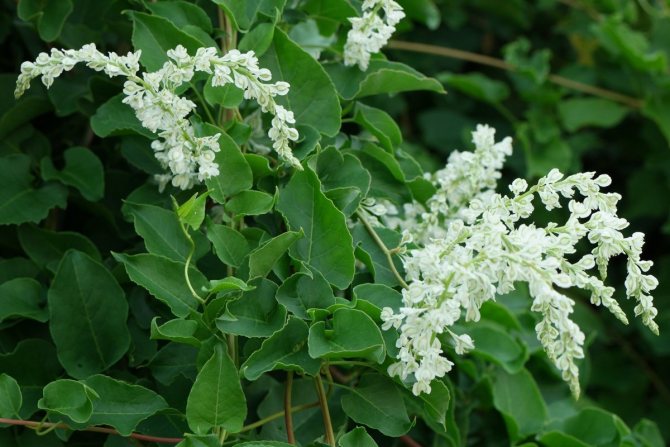


Photo:
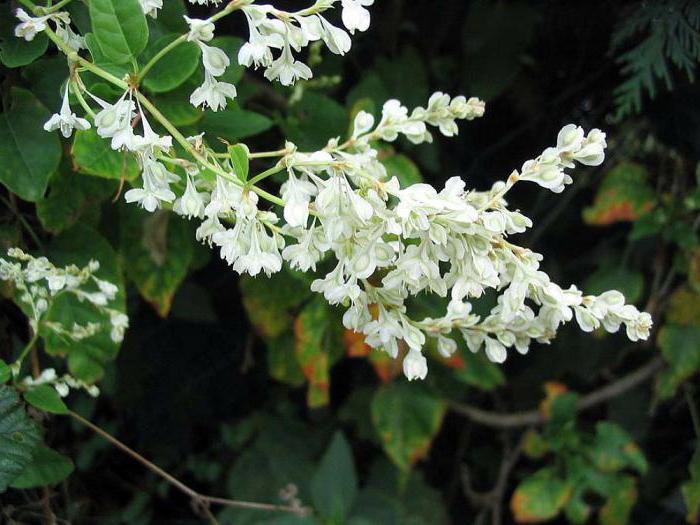
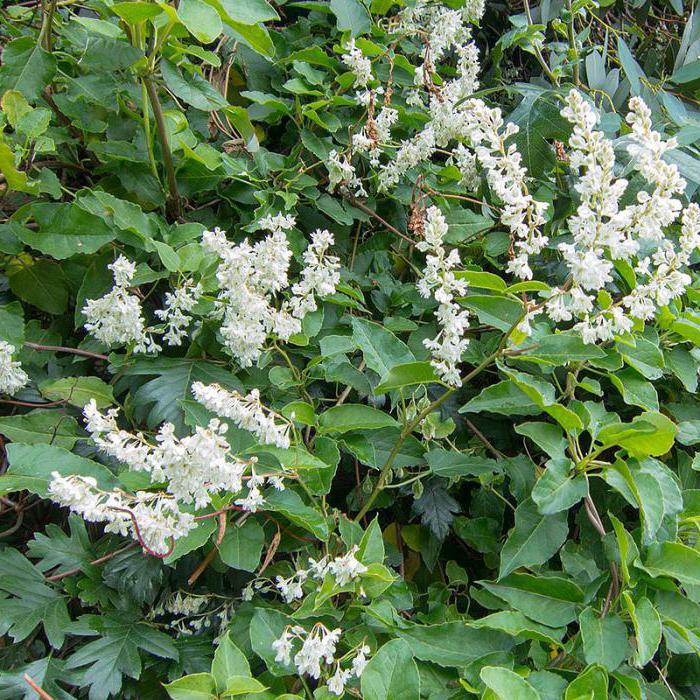
The western part of China is considered the birthplace of the Aubert species. It is a low curling shrub vine. The stem and shoots harden slightly. The leaves are ovoid with carved edges. The ombre effect is also observed - from red to green. The clusters above the shoots are composed of small, light green or pink flowers. White fruits are small and inconspicuous. This species reproduces by seeds. It grows mainly on chernozems and moist soils. Can develop in partial shade. It is appreciated by gardeners all over the world - it is used to form hedges.
Alpine (Polygonum alpinum)
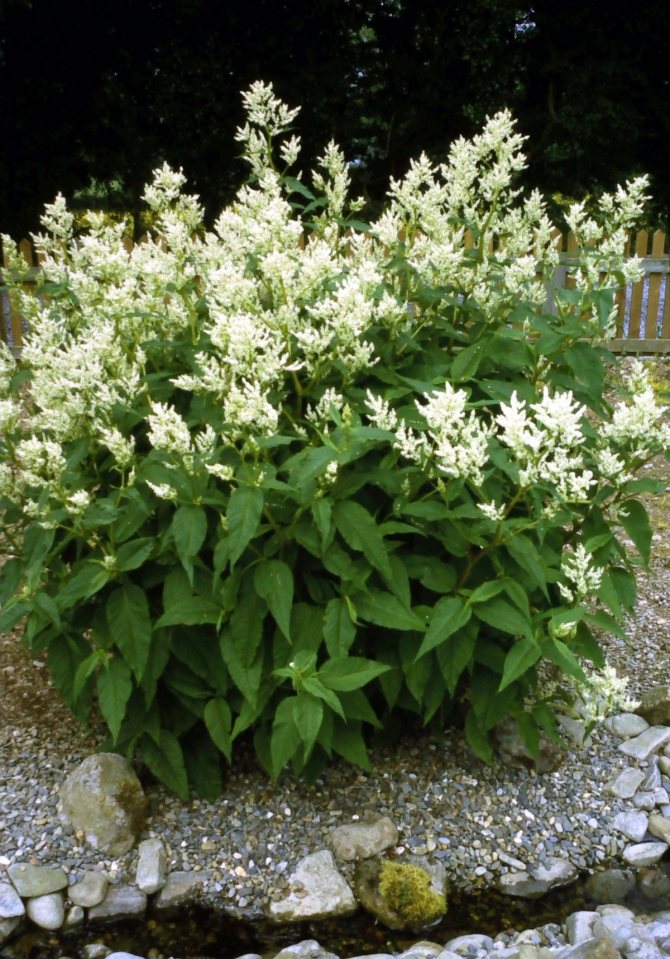


Photo: <>
It grows in mountain meadows and steppes of a temperate climatic zone. It looks like a large bush 1.5 m high. The stems are branched, and the leaves are pointed. Flowering peaks in mid-summer. Multiple flowers form paniculate inflorescences. The Alpine mountaineer is frost-resistant, so it does not need to be covered. In fact, it is an unassuming weed.
Lingonberry (Polygonum vaccinifolium)
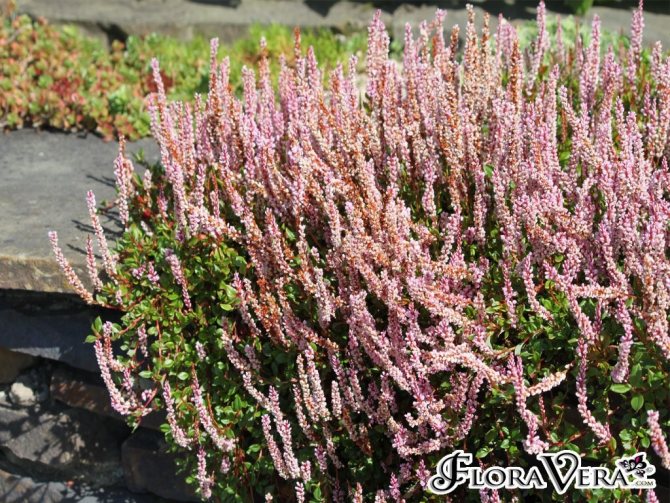


The homeland of this species is the Himalayas. It is a creeping plant 15 cm high. The stems are woody and have many branches. Leaves are ovate, narrowed at the ends. Flowering occurs in August. Lingonberry Knotweed is resistant to cold weather, but requires protection from excess moisture.
Oriental (Polugonum orientale)
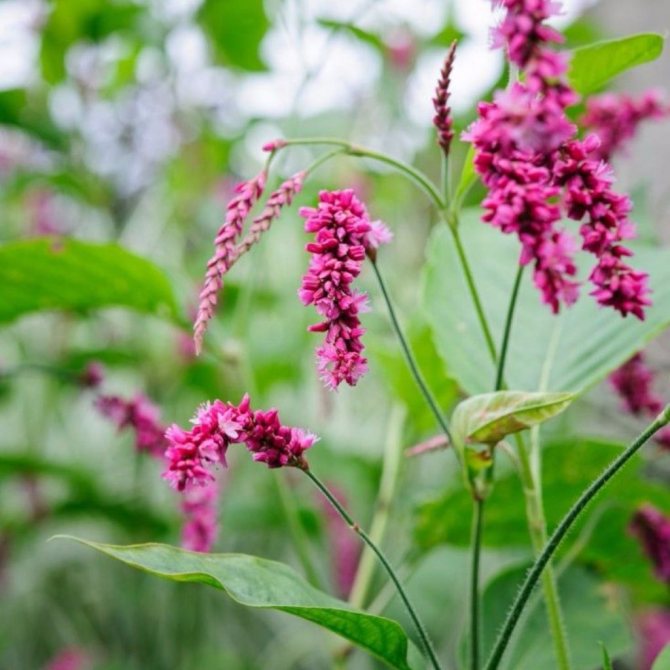


Photo: <>
Grows in India. It is an annual herb up to 2 meters in height. He is picky in soils, since for a full-fledged existence he needs moist, nutritious lands with deep cultivation. It is used to decorate walls, fences, as well as to create mixborders (combined flower beds).
Weyrich (Polygonum weyrichii)
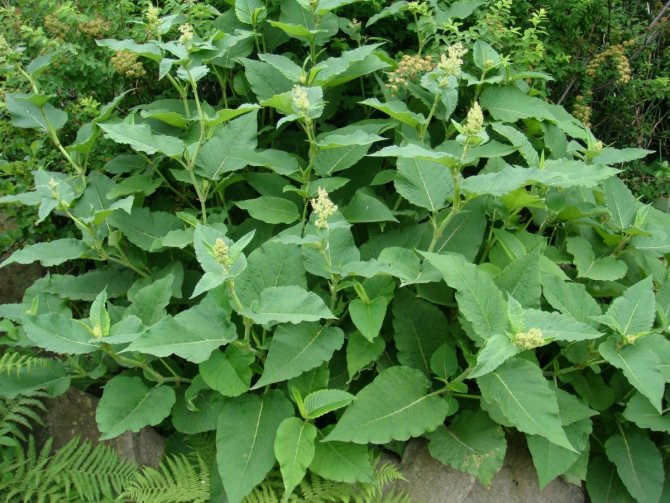


Photo: <>
This wild species of highlander grows in the Kuril Islands, Sakhalin and Japan. Creates high and strong thickets. Weirich's stems are branched, and the leaves have an oval elongated shape. The roots are tenacious and creeping. The inflorescences are formed by small white flowers. Blooms in late summer. It is frost-resistant, so no shelter is required. This species is rather unpretentious, but prefers highly fertile loamy soils. It is used to decorate fences.
Virginian (Polugonum virginianum)
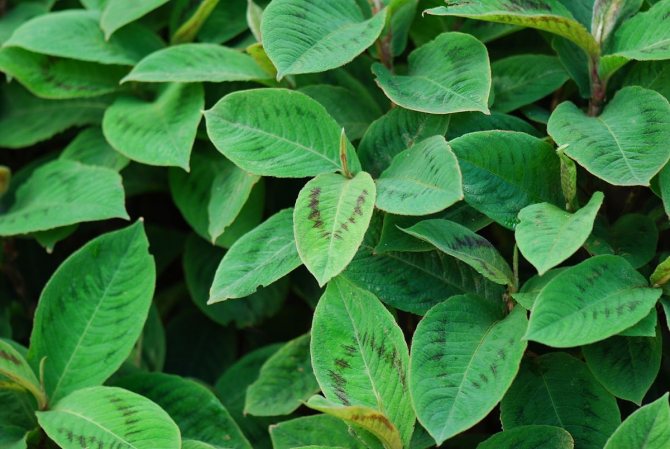


Photo:
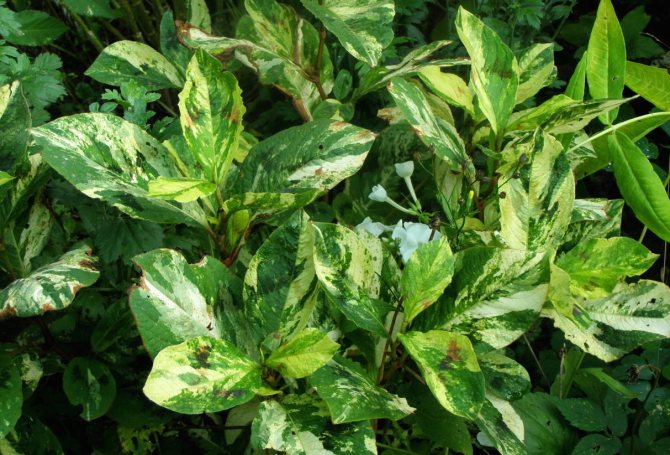
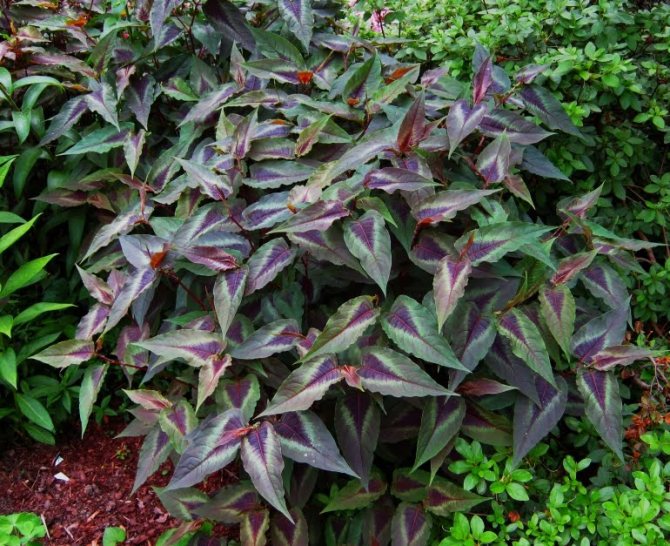
A fairly beautiful perennial species of a mountaineer. The flowers are white with a greenish tint, but the multi-colored foliage is considered the main advantage. Therefore, it is highly regarded among gardeners. In order for the leaves to show themselves to the fullest, the plant must be planted in sunny places. Slight partial shade is acceptable. Virginia knotweed grows mainly on moist soils, but tolerates dry periods well.
Capitate (Polugonum capilatum)
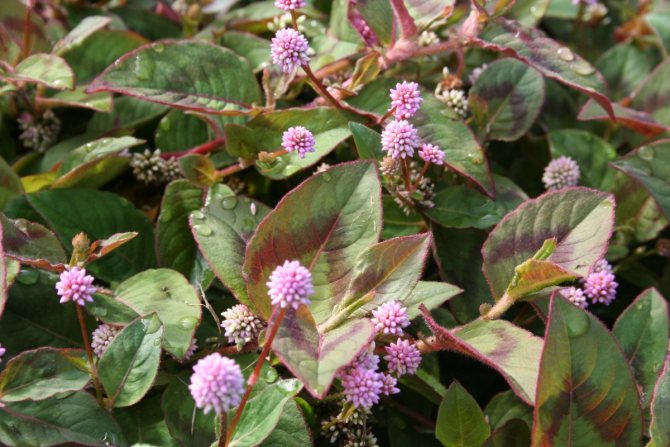


Photo:
The capitate mountaineer is a rather rare and unknown species, but this does not prevent him from being beautiful. Refers to annual plants. It has a unique ability - it grows very quickly. This species loves warmth and moisture. In the shade, the leaves fade, and the plant becomes less elegant. This knotweed is spread on the ground, its height is barely 15 cm. Small rounded inflorescences consist of pinkish flowers. Performs a decorative function from the beginning of summer until the first frost. The capitate knotweed is bred by both seeds and cuttings. They can arrange a mixborder or a vase in the garden, from where shoots will beautifully descend.
Viviparous
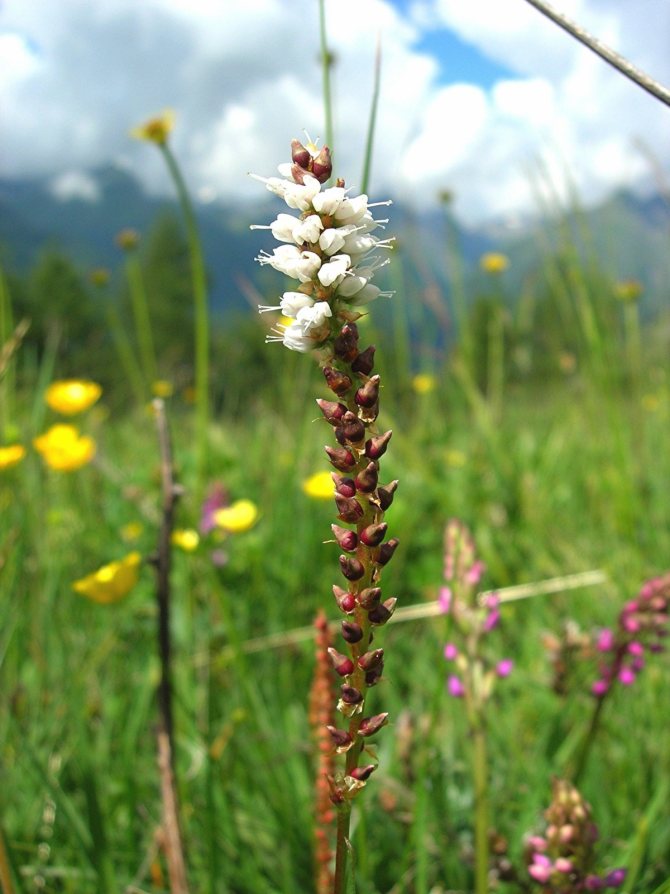


Photo: <>
Distributed in the mountains of Europe, Asia and North America (Alps, Carpathians). It is found in temperate, tropical or subtropical climates and can grow up to 50 cm. Prefers meadows, marshlands and forests, as well as tundra and mountain slopes. For development, it needs moist fertile soils. It tolerates winter well, but if there is no snow, then it is better to cover the plant.The stem is straight and the leaves are curled. Inflorescences are narrow and loose. The fruits have 3 sides.
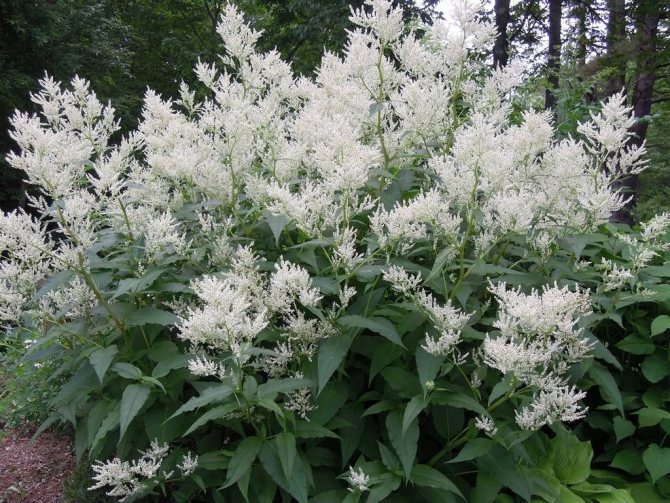
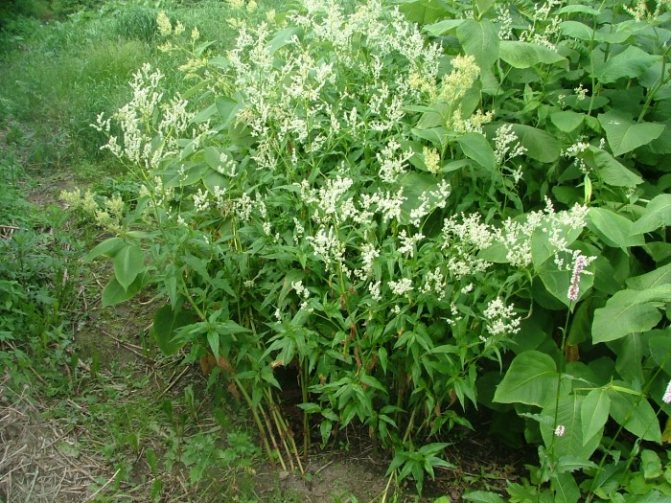
Variable (Polygonum polumorpha)
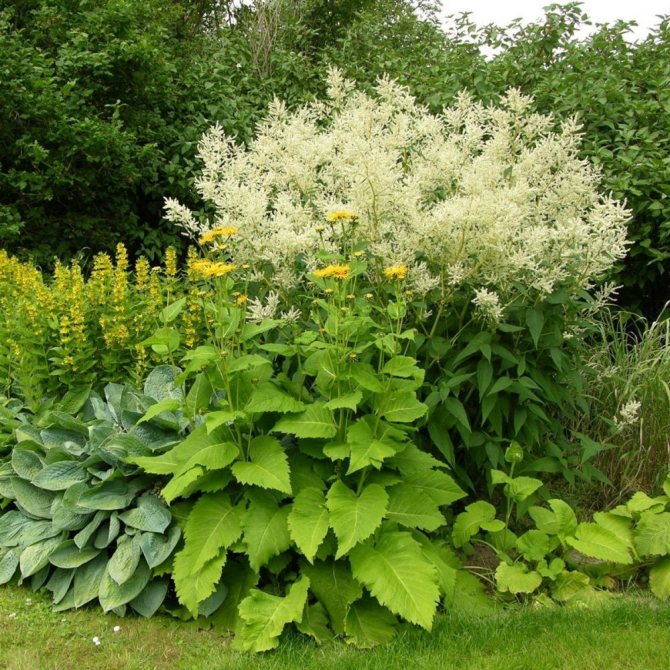


Photo: <>
This species came from East Asia, so it will feel good in our latitudes. Height under 2 m, a branched stem with large inflorescences and tenacious roots distinguish the Variable Knotweed from other species. Blooms all summer with white flowers. Unpretentiousness in the choice of soil and weather conditions, help him to easily endure the winter. Long oval leaves are located on the bush, which gives the plant volume. With the help of a mountaineer, tall hedges are created in the country, which exude a pleasant aroma with hints of spices.
Spread wide (battering ram)
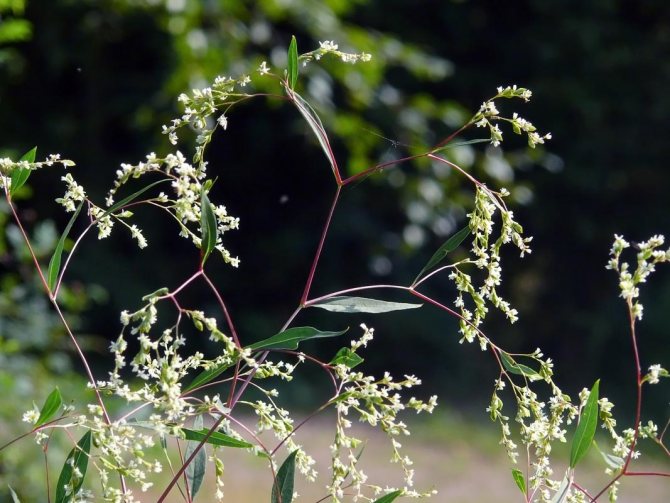


Photo:
This perennial species is characterized by a large number of stems 1.5 m high. The main advantage is its appearance. A large openwork bush that combines burgundy stems, whitish flowers and elongated green leaves. Peak flowering at the very beginning of summer. Loves drought, since the main places in which it grows are steppes and dry fields. The middle zone of Russia is also suitable for the development and wintering of the Spread Highlander. The properties of the root system do not make it possible to transplant it to another place. It is widely used in the creation of lawns and mixborders.
Sakhalin
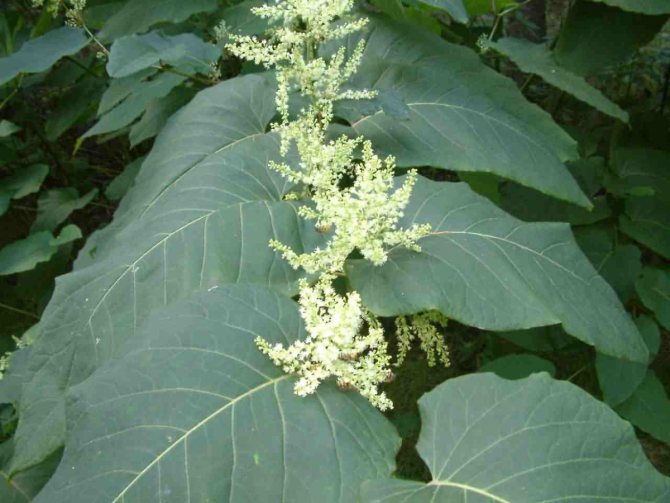


Photo:
Polygonum cachalinense grows in the Kuril Islands, Japan and Sakhalin. It is a perennial with a tenacious root. The stem is erect, brown or greenish. It reaches a height of 3m. Large leaves are located on a short petiole. Light cream flowers are formed into inflorescences. Blooms in the middle of summer. The fruit is a nut with three sides. The Sakhalin Highlander is used to decorate and mask outbuildings. It is capable of rapidly expanding and capturing significant territories, so you need to use restraints.
Small-headed (Red Dragon)
The homeland of this species is China. It is not an aggressive, slow growing perennial. Height up to 90 cm. Carved red leaves are located on reddish shoots. Small-headed knotweed is unpretentious, therefore it can grow even on clay soils.
Japanese
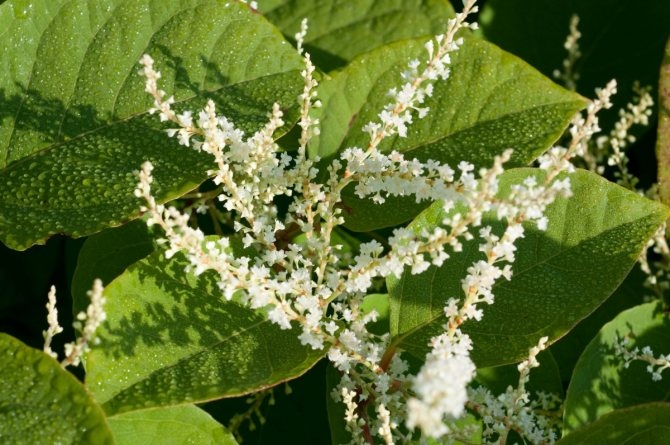


Photo:
Polygonum cuspidatum is considered a weed. Due to the lack of chlorophyll, additional feeding is required. Grows well in a shaded area on damp ground.
Highlander disadvantages
Gardeners very often scold the plant for being too aggressive, which manifests itself in the fact that the mountaineer "wants to live" very much, therefore it creeps out almost throughout the suburban area. Sometimes it becomes impossible to control its growth: even if the plantings of the Highlander Aubert are minimized, this does not change the situation.


In just one season, this plant can throw out new shoots several meters beyond 1 bush. This brings a lot of inconvenience, since in this case, gardeners have to constantly weed out the shoots that spread throughout the site. That is why it is not recommended to plant the plant in a small garden. The highlander loves large spaces, so that he has a place to roam!
Description and features
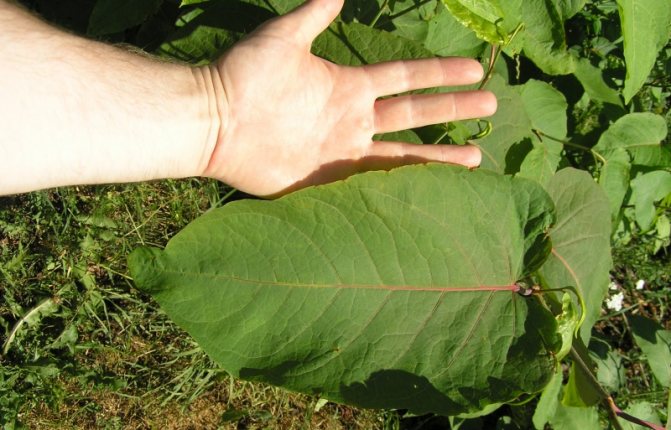


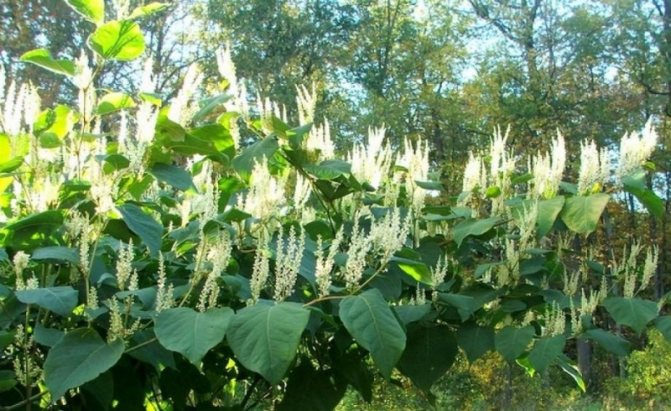
Highlander grows on Sakhalin. It has a smooth, hollow stem inside. The plant is erect, in the upper part it branches. The internodes are thick, thus the Sakhalin mountaineer resembles bamboo. It has a powerful rhizome that is well developed. The roots are deep, they spread over a long distance. This leads to the fact that the thickets of the mountaineer fill the site.
Buckwheat has large heart-shaped leaves. Their edges are slightly wavy, below each leaf is pubescent. In length they reach 30 cm, and in width - 25 cm. In summer they are green, red spots are clearly visible on them. In the autumn, the color changes, they turn red-brown.
Siberian bamboo makes delicious soups and salads, but it can be used not only for human nutrition, but also as animal feed.Buckwheat is a honey plant, so bees flock to its flowers.
Plants in the garden are planted to form a decorative hedge. In the middle lane, the height of the bushes reaches 3-4 m, it is easy to close buildings with them. At the summer cottage, the mountaineer quickly braids the pergolas, but it must be borne in mind that it is growing rapidly. Creeping rhizomes produce layering, as a result, the site turns into impassable thickets.
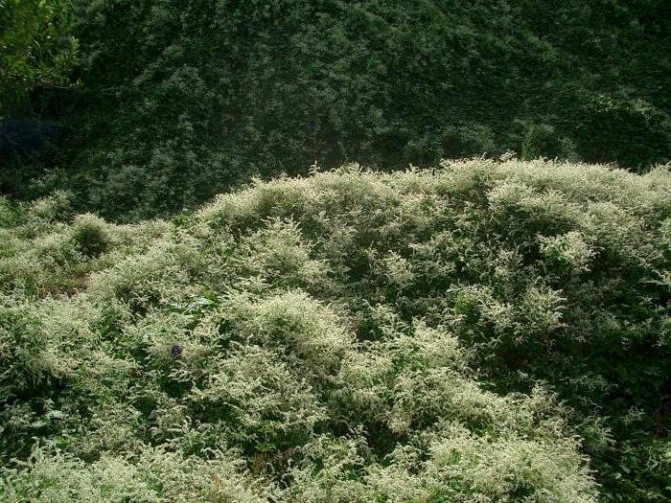
Highlander Aubert: photo, planting and care
As mentioned at the very beginning of the article, knotweed does not require special conditions for growing. Moreover, this feature applies to all types of plants. The same goes for the rest of the characteristics and properties of the flower.
If we talk about the winter hardiness of the Highlander Aubert, it is worth noting that it is perfectly capable of adapting to cold conditions, so it is ideal for growing in harsh climates. Among other things, this plant grows well and develops in partial shade, it is not negatively affected by high humidity.
However, like any other plant, it is best planted in more fertile and moist soils. Loamy soil is considered the best. It is enough to look at the photo of the Highlander Aubert to understand how well he can grow on such fertile soil.


If we talk about oxidation, then it is better to choose slightly acidic or neutral soil. Pests do not bother this plant, which looks very much like a huge weed. By the way, that is why it is very often called knotweed. This name "clung" to it due to its amazing ability to spread over large areas in the shortest possible time.
Highlander related photos and descriptions of the plant
Botanical name: Persicaria affinis / Polygonum affine / Bistorta affinis
It is a complex perennial plant that grows under ideal conditions up to 75 cm in height and 90 cm in width. It has slender stems, with oblong or triangular, ovoid, bright blue-green leaves, alternatively described as spears and extending up to 15 cm or more. The pink summer flowers resemble the delicate flowers of a bottle and extend up to 12 cm. The Knotweed is often visible from a distance, pink flowers grow on many stems, it can be found in grassy glades, in the forests of the northern hemisphere. The root is dark brown to black on the outside and is usually "S" shaped. Slice it up to see the rich red color that results from its high tannin content.
The Latin words "bis" mean "twice," and "torta" means "twisted," a reference to the twisted and creeping nature of this plant. The old local name with a literal Latin translation is “written twice”. The related highlander is also called Adderworth, Serpentine Weed, Serpentine, Easter Giant, Patience Dock, and Red Feet. Further reference to the plant can be found using terms such as serpentaria, columbina, dracunculus, and even dragon snake. The old medieval classification of the Highlander related belonged to the peach (Persian) because of the peculiar leaves.
It can be found in the Northern Hemisphere, including Northern England, Southern Scotland, Northern Ireland, Northern Europe, Siberia, Japan, and Western Asia to the Himalayas. Because of its beautiful flowers, this plant is loved by butterflies and bees, and is most often grown as an ornamental garden decoration. Until the 20th century, it was cultivated as a culinary and medicinal plant.
Secrets of caring for the Highlander Aubert
When planting, it should be borne in mind that during the summer he needs to provide moderate watering. If the soil water table is too low, it is recommended to water the plant as often as possible. If necessary, the mountaineer can be fertilized, however, even without this, it will bear fruit perfectly.
Highlander tolerates drought well, but excessive waterlogging makes him feel uncomfortable.
Remember that young plants do not tolerate frosts quite well, so they need to be covered for the winter. If, in the fall, severe cold came and the leaves of the mountaineer died, then its stems must be cut off immediately. Sometimes the foliage of the plant begins to turn yellow with the arrival of autumn, therefore, upon arrival at a suburban area in the spring, it is worth removing all brown and wilted leaves.
Care


Photo: <>
Basic rules of care:
- High-quality plentiful watering in the heat (a slight excess of moisture is allowed, but the constant presence of the roots in damp soil is not acceptable);
- Not all species can tolerate frost, so cover before warmth. If the leaves are wilted, cut off the stems;
- The yellow and brown leaves should be cut at the end of winter;
- If you grow Japanese or small-headed mountaineers, then it is better to get a greenhouse;
- Continuous fertilization of the soil is necessary for the supply of nutrients.
Breeding methods
By and large, this plant does not need artificial reproduction, since it grows beautifully on its own. However, if such a need still arises, you can use any of four methods: use seeds, cuttings, dividing the rhizome or bush.


Keep in mind that each subspecies has its own preferences. As a rule, seeds should be sown in late spring, immediately after the frost has receded. In this case, the seeds can either be immediately placed in the ground, or they can be pre-germinated in boxes.
If we talk about the highlander Aubert, then this plant prefers grafting. Let's consider in more detail the features of this procedure.
Reproduction
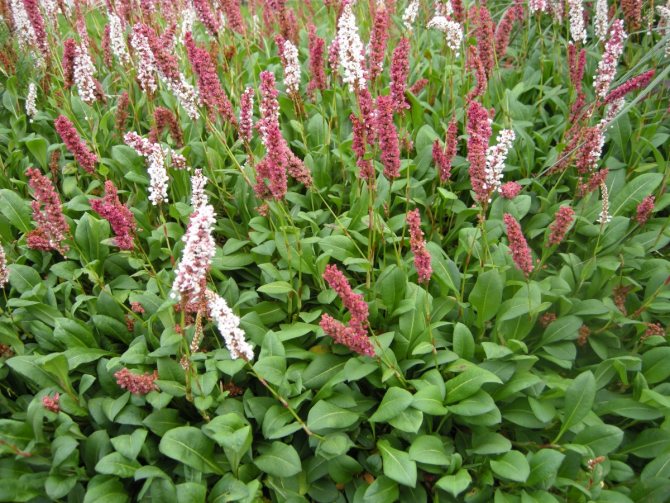


Photo:
Highlander can propagate by seeds and cuttings. Each species has its own method. Seed propagation is suitable for the snake, oriental and splayed mountaineer. They are planted by the end of winter in boxes or open ground. Cuttings are also prepared towards the end of spring. Two nodes should appear. A cutting is planted in a warm bed. The lower node should be at a depth of 2 cm. The top is covered with a film, and for the winter it is dug up and stored at a temperature of about 2 ° C.
Highlander cuttings
Cuttings can be done both in spring and summer. Plants must be planted at a distance of 20 to 60 cm from each other. It should be borne in mind that replanting new shoots is often not required. By the way, on one site they can live up to 10 years.
In order to carry out the grafting procedure, it is necessary to prepare the source material. Branches with at least two nodes should be used as branches. Also, the cuttings must be treated with Kornevin.
After that, you need to prepare the bed that you want to insulate. It is necessary to ensure that the temperature of the earth is slightly higher than the environment. In this case, the rooting of the new plant will take place much faster. In order to organize high-quality insulation, it is necessary to put a little horse manure in the base of the ridge, sprinkle it with fertile soil and sand mixed with peat in an equal ratio on top.
The landing is pretty straightforward. The lower knot of the prepared cutting must be buried 1-2 cm into the ground, then covered with polyethylene or other material in order to create the necessary microclimate around the plant. For the winter, the plants must be dug up and stored at a temperature of no more than +2 ° C. After that, the finished shoots can be safely planted in the spring.
Landing
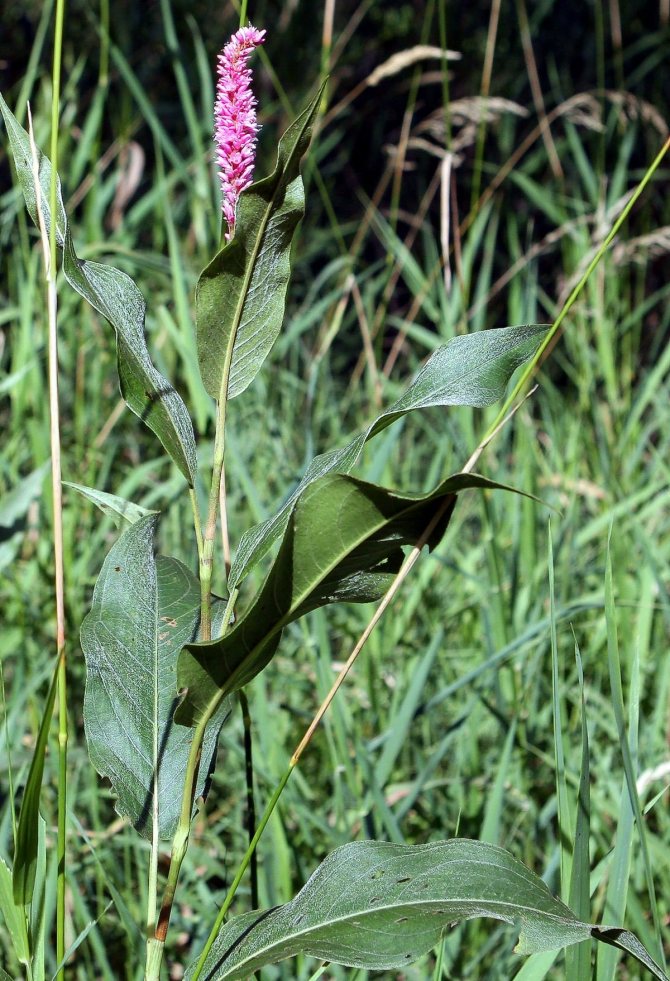


Photo: <>
Landing in open ground is done with the onset of heat. The adaptation is fast. The soil must be loose. Treat the cuttings with “Kornevin” and store them for several hours in a room with a temperature of 23 °. At first, the plant needs regular, but not excessive watering. Plant to a depth of 1-1.5 cm. After planting, cover with foil to maintain the microclimate.
On a note
As has been said repeatedly, this plant is quite actively spreading throughout the suburban area, however, there is a special trick, thanks to which you can avoid the aggressive occupation of the fertile territory. To do this, it is necessary to create limiters up to 30 cm deep around the knotweed.
Please note that in conditions of severe drought, or, conversely, high humidity, flower clusters may form on the stems of plants. In this case, outwardly, the plant will look a little more modest and graceful.
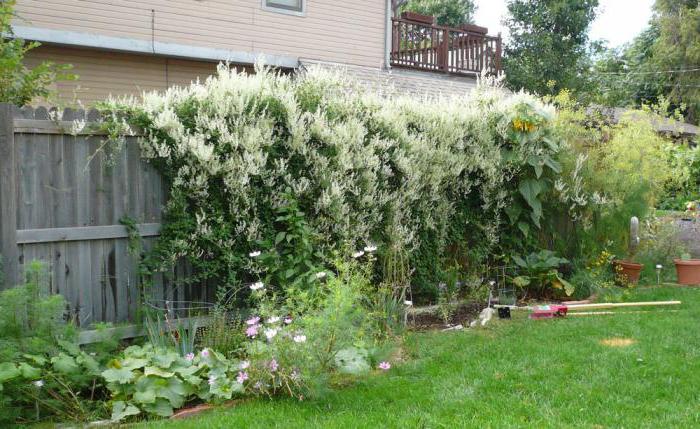


If we talk about the root system of the mountaineer, then it is distinguished by increased creep, so the flower spreads not only above the ground, but also under it. That is why it is necessary to weed not only the upper parts of the unwanted processes, but also to thin out their rhizomes. However, this disadvantage can turn into an advantage if you need to quickly plant greenery on an unseemly garden plot.
Landscape designers are very fond of this plant, as it can be used to create decorative fences and other living fences very quickly.
Perennial vines
They are no less interesting than their herbaceous relatives. Lianas "take in bulk": with the beauty of green-velvet leaves and touching graceful whitish inflorescences, a contrasting color would be clearly superfluous.
Baljuan Highlander
Abroad it is called "Russian liana", or "mile per minute", or "silver lace liana". He comes from Western China, Tibet, Tajikistan.
Highlander Baljuan, photo by the author
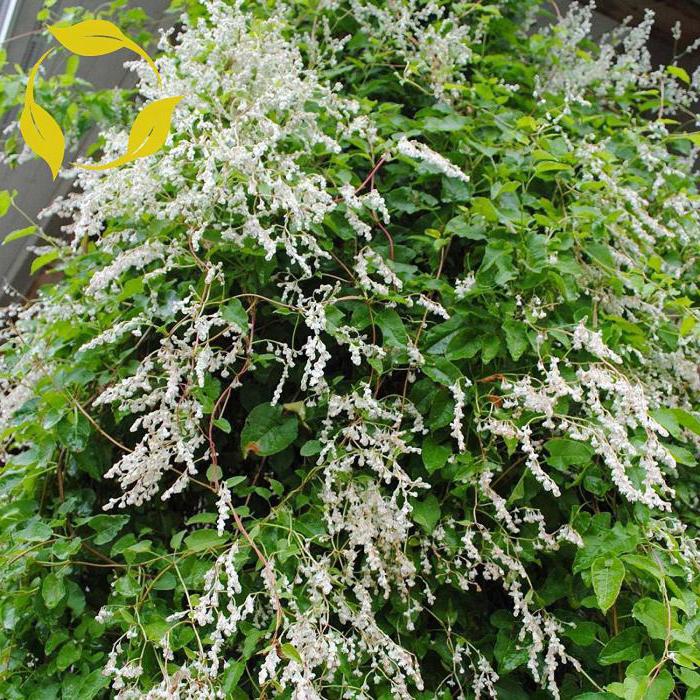
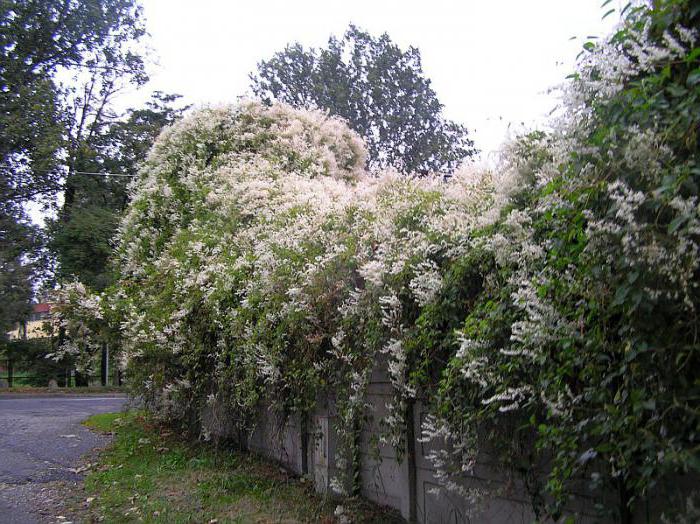
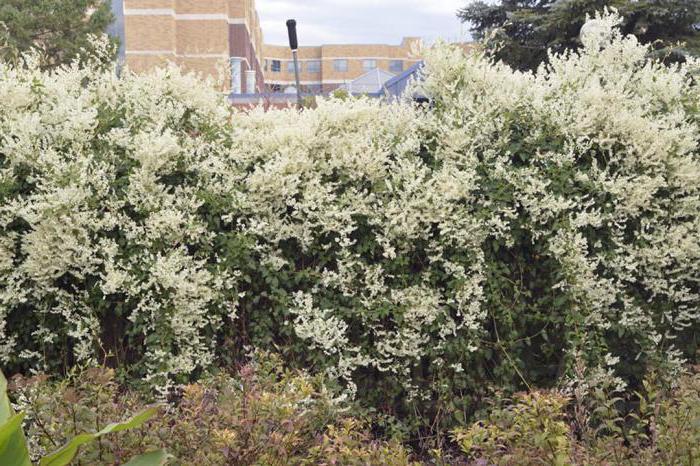
Highlander Baldzhuan, or Fallopia Baldzhuanica (Fallopia baldschuanica, syn.Polygonum baldschuanicum, Bilderdykia baldschuanica), with fallopia being the priority "name". Oval leaves up to 8-9 cm long are first red, then bright green. Small creamy white fragrant flowers, collected in dense, abundant panicles, cover the vine from mid-summer to autumn, giving it an amazing resemblance to clematis Clematis paniculata... It grows quickly: during the season, the shoots are extended by 30-90 cm. Winter hardiness: withstands -34.4 ° C. A semi-shaded place is ideal for her. Looks better, more luxurious on well-drained loams with constant moisture; less aggressive on poor soils; withstands drought, trampling. Supports required. Pruned every year from late winter to early spring; rejuvenate at the end of winter, leaving a few centimeters, then long shoots are shortened as needed.
The Baljuan highlander gives a dense, lively green covering for trellises, fences, walls; can also be used as a ground cover plant, decorating not only the ground, but also old stumps; suitable for strengthening the soil on slopes. When settling a highlander in the country, you must remember that you will have to control its growth. It is impossible let him go to live trees.
Highlander multiflorous
He comes from Central and South China, Korea. In the Nikitsky Botanical Garden, it has been growing for a long time at the old Stevenovskaya greenhouse. In China, old copies are "worth their weight in gold": in the Celestial Empire, they believe that a 100-year-old foti (root) preserves a youthful face, a 200-year-old gives a slender figure, and a 300-year-old gives immortality.
Highlander multi-flowered, photo by the author
Polygonum multiflorum, or Rhinotria multiflorous, multiflorous fallopia (Polygonum multiflorum var. Hypoleucum, syn. Reynotria multiflorum var. Hypoleucum, Fallopia multiflorum var. Hypoleucum) - herbaceous liana 2-4 m high. Beautiful dark green leaves 3-7 cm long, arrow-shaped, with a wavy edge. Flowers are small, greenish-white, collected in short dense panicles up to 10-20 cm long, bloom in summer and until mid-autumn. In traditional Chinese medicine, it is known as a tonic and anti-aging agent. The extract promotes hair growth. Toxic.
Highlander Obert
Another buckwheat liana, which because of its violent growth is called "curling lasso". He comes from China, Tibet.
Highlander Obert, appearance. Flowers. Highlander Obert, or Fallopia Obert (Polygonum auberttii, syn.Fallopia aubertii, Bilderdykia aubertii) in the southern regions it grows up to 12 m high.In central Russia (in a tub) it gives shoots up to 5-7 m.All summer its lively light green cover is beautiful, from July decorated with creamy-white fragrant panicles 20 to 40 long see In bloom, this highlander is a "bee field", and small fruits in the form of nuts are a delicacy for birds.
Decorative form:
- ‘Lemon Lace’ - rare golden yellow leaves on red shoots, less aggressive.
Highlander Obert Lemon Lace. She's in garden design. Highlander Oberth is more thermophilic than the previous species, so he is removed from the supports and covered like roses; tubs for the winter are brought into a frost-free room. The critical winter minimum fluctuates between -15 ° C. In the open field, a sunny or semi-shady place is selected for it. During growth, watering is plentiful; responds well to top dressing (until August), in a tub - weekly. Requires support and trimming of long shoots that are knocked out of the desired contour.
Perfect for decorating walls, gate posts, gates and gazebos. Highlander flowers are beautiful in a vase.
Blanks and storage
As a rule, it is customary to collect the mountaineer from the second decade of June until the end of autumn. It is advisable to perform this procedure during a drought period, at the moment when the plant begins to bloom. To do this, it is necessary to separate all unnecessary parts from the knotweed and dry it in the open air. In this case, it is recommended to avoid direct sunlight.
It is best to dry the plant in the attic. This type of room has enough fresh air, and the sun does not dry it out. If necessary, you can use special drying devices. In this case, the temperature regime must be set no higher than 45-50 ° C. Ready-made shoots are stored in woven bags or cardboard boxes. So the mountaineer retains all its properties for almost two years. It is not recommended to use dried herb after such a long storage period.
Medicinal properties
Much of the traditional medicinal benefits of Highlander have been derived from the high tannic acid content combined with the presence of gallic acid, gums, and starches. Highlander is known to be highly astringent, which helps in contact with bodily tissues and reduce mucus. The plant can also help with some digestive problems such as:
- diarrhea;
- reducing mouth irritation by reducing swelling;
- if necessary, softening and lubricating bodily tissues;
- act as a mild diuretic;
- in wound healing as direct application;
- and it also has a hemostatic effect that can help reduce internal bleeding.
However, no clinical trials have been conducted to investigate the efficacy of the Highlander related.
Traditionally, boiled roots were used to make wine, which was then used to treat dysentery and diarrhea, inhibiting vomiting, controlling excessive menstruation, and treating inflammation of the mouth and throat. During Shakespeare's time, the Highlander sibling was used to treat nasal polyps. It was also widely used as a mouthwash and had a good reputation as a useful herb for "fixing loose teeth."
The plant also contains oxalic acid, which is not a direct toxin. However, when consumed in large quantities, it binds large amounts of minerals and nutrients to make them inaccessible to the body. This leads to mineral deficiencies and can cause serious problems. Cooking herbal ingredients reduces the oxalic acid content, similar to the need to cook sorrel and rhubarb.


The tannins in this plant can absorb and reduce the effectiveness of certain drugs by binding them in the stomach.Take your medication at least one hour before consumption. Also note that consuming the Highlander sibling can aggravate rheumatism, gout, arthritis, and kidney stones.
Culinary use
The related highlander is traditional for food, so in Russia, Iceland and Siberia, plants were consumed as a food source during famine. However, this is not one of the main reasons for the popularization of the plant. All parts of the Highlander are edible and can be used in cooking. The rhizome is known to have a high starch content and is considered very tasty and nutritious. It was used during times of famine to provide a high calorie intake when other foods were unavailable.
The reddish roots can be treated like potatoes and used in soups, stews, or simply roasted. They can also be dried and ground into powder for use in making bread flour. The roots should be immersed in water before drying to reduce the tannin content. The leaves taste bitter, although the young leaves are not so bitter and can be used as a substitute for spinach. Knotweed is the main ingredient in the "bitter lean pudding" made for Easter in Northern England.
The use of knotweed in everyday life
According to reviews, the highlander Aubert has been successfully used as a useful feed for livestock. This plant has a huge amount of nutrients, which is why it is used along with clover and alfalfa.


In ancient times, the ground parts and roots of plants were used to give fabrics a yellow tint. Today this unique plant is used in the production of wine products or liqueurs. When it comes to cooking, young knotweed is suitable for making salads or making vitamin soups. In some Central Asian countries, highlander is used as a filling for pies, and some peoples use this herb to clean dishes.
Planting and reproduction of a plant
The homeland of the shrub is the southern part of the island, which is why it is called the Sakhalin mountaineer. It is easy to grow a shrub, it can be propagated as follows:
- Bury part of the bush in the ground. After a while, buds will appear, and later a lush bush will form in their place.
- Reproduction by shoots that are taken from the root. First, the rhizome will strengthen, it will take a year, and then all the forces will be spent on the development of the bush.
- Reproduction by seeds.
If the latter option is chosen, the grower should temper them in a cold place. Planting before winter is permissible, but it must be borne in mind that they will germinate only at a temperature of + 20 ... + 25 ° С.
Plants can be grown anywhere on the plot, they thrive in the shade and bright sun. The mountaineer is not picky about the composition of the soil, but does not like excess fertilizers.
Weeds do not grow where buckwheat is planted, so you don't have to weed. A perennial is not planted next to fruit trees and berries, because a large bush takes away nutrients from them. The plant rarely gets sick, it is resistant to pests, so it can be grown in any climate.
Healing properties
Highlander contains a huge amount of tannins, silicic and ascorbic acids, carotene. Thanks to this, the herb is considered healing. It is used in the treatment of inflammatory processes in the stomach, liver and kidneys.
Also in folk medicine, a tincture from a mountaineer is widely used. It is used to remove stones in urolithiasis. In addition, this plant is actively used in the form of decoctions, powder, tinctures, extracts, etc. Scientists have proven that this unpretentious plant has a lot of useful properties.
Beneficial features
ethnoscience
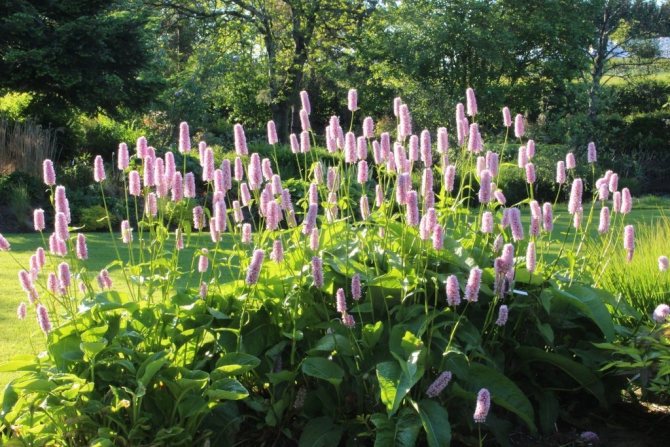


Photo:
Highlander Serpentine can help with diarrhea, sore throat and mouth. Highlander root is used for bleeding, cholelithiasis and urolithiasis. The inflammation caused by cystitis can be relieved. In eastern countries, it is even used for douching and treating tumors. Has a sedative effect.
Cosmetology
Means, which include a mountaineer, will help normalize the water balance of the skin and get rid of burns and dermatitis. A decoction from the roots will eliminate sweating of the feet and corns.
Supplements
The young leaves and stems of the mountaineer snake are edible. Dried root powder is added to bread and alcoholic beverages.
What types of highlander are often grown in suburban areas
In addition to the Highlander Aubert, other varieties of grass are also grown in the gardens. Very often on a suburban area you can see a related highlander. Outwardly, this plant is not very tall, as a rule, it spreads a little along the ground. You can also find the double-twisted knotweed, which is also called the snake knotweed. Japan, China and the Himalayas are considered its homeland. It is also suitable for harsh climates.


All varieties of this plant are distinguished by their attractive appearance and unique unpretentiousness. They can be successfully used as components of a design composition or in the form of separately planted plants. In addition, the vines of the Highlander Aubert tolerate pruning very well, so you can give the plant any shape. All procedures for the decorative shaping of the grass carpet can be carried out at any time of the year. The highlander is distinguished by great vitality, therefore such procedures do not have a negative effect on him. However, do not forget to limit its growth in a timely manner. Otherwise, after a few years, this plant will fill the entire area and displace other flowers, so take care of at least minimal care - the Aubert Highlander is very aggressive in growth.
Growth conditions
The Knotweed can be grown in a wide variety of soils, even where the land does not need good drainage. It grows very well in humid areas near large streams, ponds or the edges of small streams, but it may need to be controlled in these areas. Because if left to grow unattended, it will spread on a large scale. As long as water is supplied, the plant will tolerate warm conditions, but its northern hemisphere origins allow it to withstand temperatures as low as minus 25 C.


Knotweed will grow in full sun and partial shade, but if your garden is very warm or hot, choose partial shade. When there is not enough water, the plant will not flower well, so it is better to provide moist soil. If the conditions are too dry, the plant will dormant for a while. Pink flower buds appear in spring and summer, or from November to March in Australia, for example. The seeds ripen from February to April. Roots can be dug up in the fall for drying (cut long roots in half) or for current use. Leaves are best picked and used when young.
To grow the Knotweed, you can sow the seeds in the spring when the temperature is 18-24 ° C, directly in the ground or in trays if you are in cold regions. Seedlings can be potted and planted in the garden when the ground is warm enough. Seedlings can be taken from 21 to 60 days, but if not, cultivation can be done from seed, which is a fairly simple method. In warmer areas where there is no true cool season, it may be helpful to adjust to the seasons by refrigerating the seeds for a period of time. Mature lumps can be split so they can be planted elsewhere in the garden, or simply to support growth.
Growing
The easiest way to grow a mountaineer is from rhizomes brought from natural thickets in early spring or late autumn. Planted in fertile soil and without weed competition, the plants grow rapidly. They are much larger and more spectacular than in the meadow. It is preferable to choose a wet area, you can even slightly shade.
Care consists in weeding and, if there is a lack of moisture, in watering. The roots can be harvested for medicinal use from the third year after planting. It is better not to dig up the whole plant, but only to separate half. Then the beauty will be preserved, and valuable raw materials are collected.
Main selection criteria
When choosing plants for an alpine slide, it is recommended to pay attention to the following key criteria:
- Location of the rock garden. It is recommended to choose sun-loving plants if the structure is located in the sun. For a slide placed in the shade, shade-tolerant specimens are more suitable.
- Duration of flowering. For a rock garden, plants that are distinguished by long flowering are more suitable, since they allow you to preserve the decorativeness of the slide from spring to late autumn.
- Aesthetic color compatibility. It is desirable that the selected specimens are combined with each other in shape, shade of leaves and flowers.
- Individual plant needs. Before planting, it is recommended to study the requirements of the selected specimens for the type of soil, humidity and lighting.
Highlander breeding
Shrubs reproduce:
- Seeds. After flowering and ripening of the fruit, a seed capsule is formed. The fruit of the mountaineer, resembling a nut, having reached its ripeness, opens, the seeds spill out, falling into the ground, germinate, forming a new bush.
- By dividing the bush. If an adult bush needs to be divided, then with a sharp blade of a shovel, cut the main bush in places where younger shoots have taken root. Dig them out, along with an earthen lump. So they transfer the bush to a new place, after watering the soil well, they plant it, if necessary, fertilize it with rotted manure.
- Creeping branches. If, in the process of growth, large and large branches have reached the soil, then the germination of roots in places of contact with the ground is possible. Due to the high moisture content of the soil, the plant, once on the surface of the earth, lets young roots through the deciduous sinuses. After a while, a bush is formed, suitable for transplanting to a new place.
- Cuttings. In the summer, when the plant develops, you can cut off the apical stalk, up to half a meter long, stick it into the ground and water it well. In two weeks, young shoots may appear, the root mass will already be developed. In the fall, woody cuttings are used for these purposes.
Collection and preparation for the winter
Preferred harvesting is carried out in late summer, early autumn.
Rhizomes of mature plants are dug up, then dried, peeled, washed and cut into small pieces.
The cut raw materials are dried (in an oven, in the sun or in a dryer) and then crushed. Such raw materials can be stored for about two years, it has a pinkish or brownish tint and does not have a pungent odor.
To understand which rhizomes will benefit and which will harm, carefully examine its surface when removing the snake root. A healthy Knotweed root on a fracture is always with a pinkish tint, curved serpentine, without signs of rot and mold.
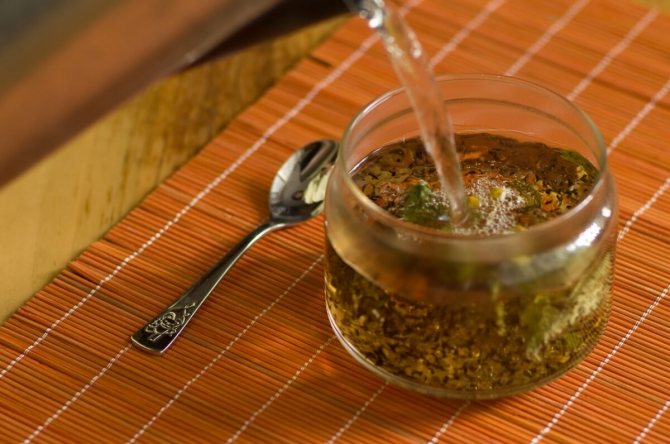


The rhizome tastes bitter and astringent, odorless. If the rhizome has a bloom of mold, black kinks, or a rotten smell, then it is better not to use such a specimen for harvesting, it will not be useful.
It is worth noting that prolonged drying of the mountaineer root leads to the destruction of trace elements and a devaluation of the usefulness of raw materials.
The prepared raw materials should be stored in fabric bags in a cool place.
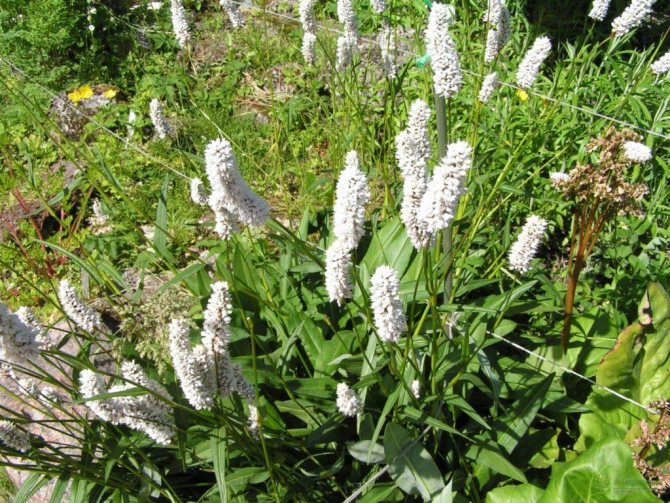
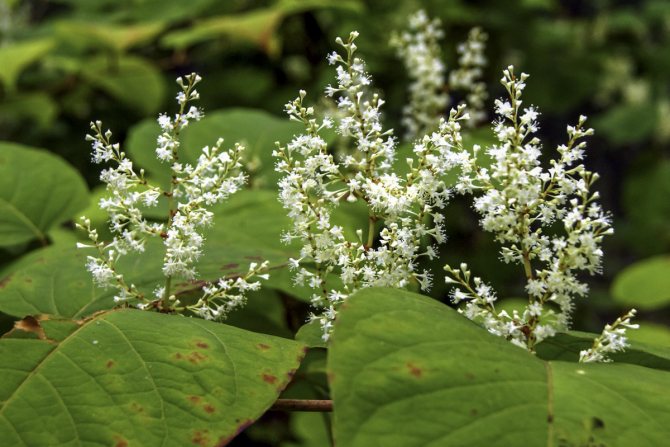
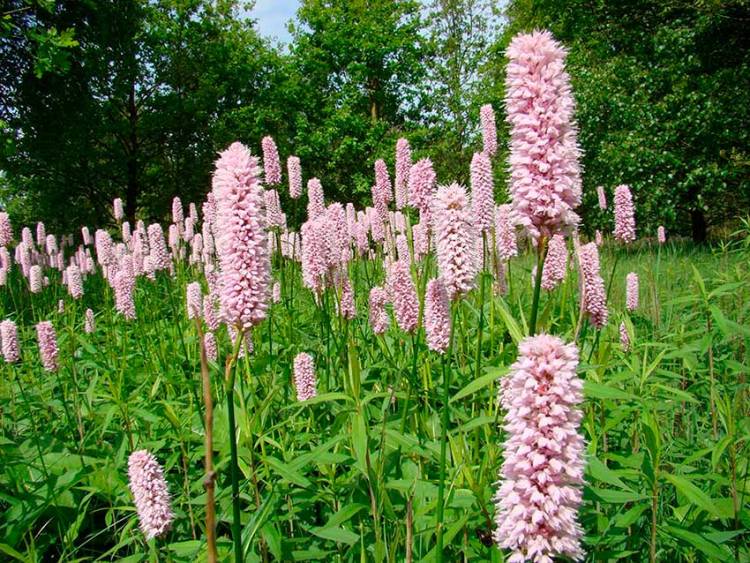
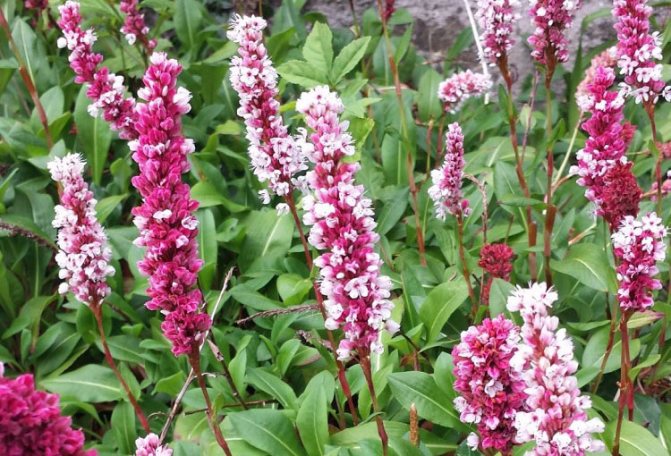
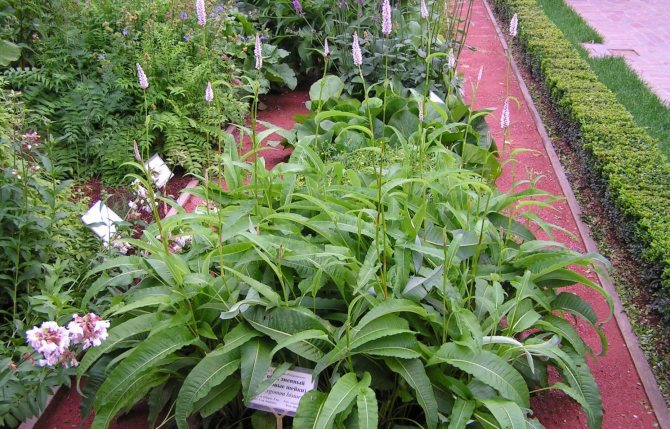
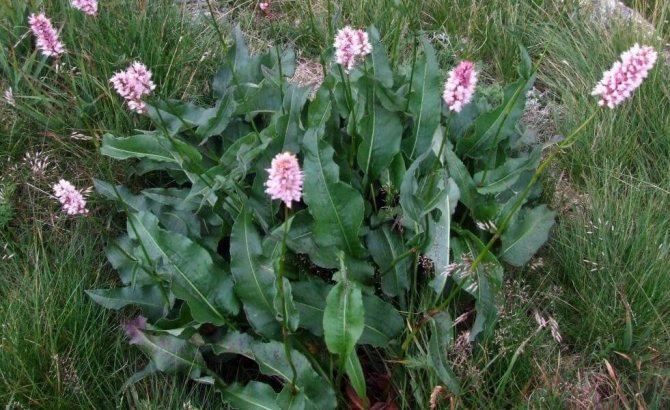
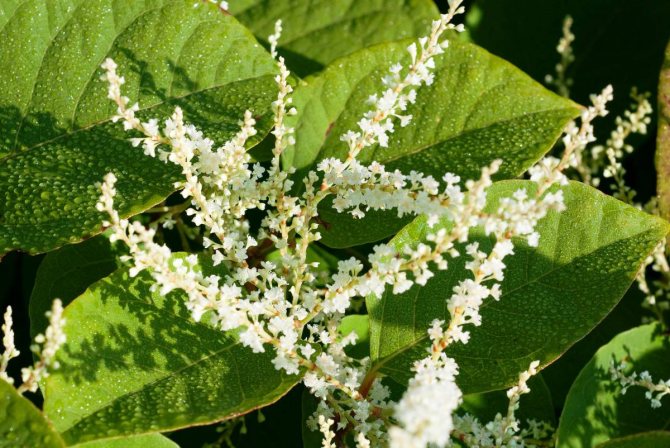
Highlander serpentine (Polygonum bistorta) is a perennial herb from the buckwheat family with a thick, shortened, strongly curved rhizome of dark red color, with numerous thin roots, for which it is sometimes called serpentine. At the break it is brownish-pink, like the body of a boiled crayfish. Actually, this is where the popular name came from - cancerous necks. The snake mountaineer differs from other species of this numerous genus, in addition to the characteristic appearance of the root, by a dense dense spike-shaped inflorescence. Therefore, there is practically no danger of confusing him with other highlanders.
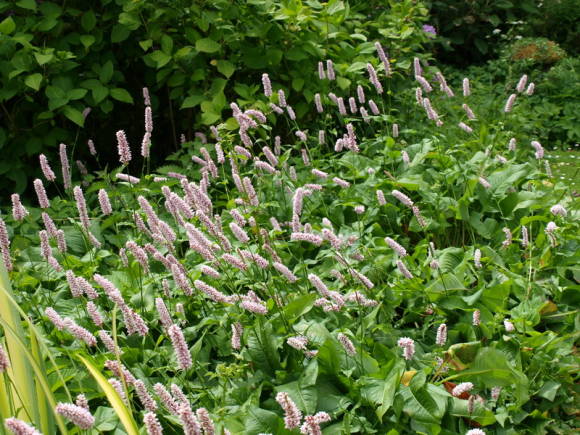


Stems 30-100 cm high, erect. Basal and lower stem leaves - with long winged petioles, oblong or oblong-lanceolate plates with a rounded or cordate base; the upper leaves are lanceolate or linear, sessile, with a slightly wavy edge. The inflorescence is a dense, dense, cylindrical spike, later it begins to resemble a brush due to the elongation of the peduncles. The flowers are small, pink, sometimes white. The fruit is ovoid or oval, triangular, shiny, dark brown or greenish brown nut. Blossoms in serpentine mountaineer in May - June, fruits ripen in June - July.
In Russia, snake mountaineer is found from the Kola Peninsula to Lake Baikal. It grows in floodplain meadows, herbaceous swamps, in sparse forests, on their edges and clearings, more often on peaty soil, sometimes in thickets of bushes. In the mountains, it occurs in moss and shrub tundra, in subalpine and alpine meadows. Therefore, it is an extremely unpretentious plant that can grow on waterlogged soils.
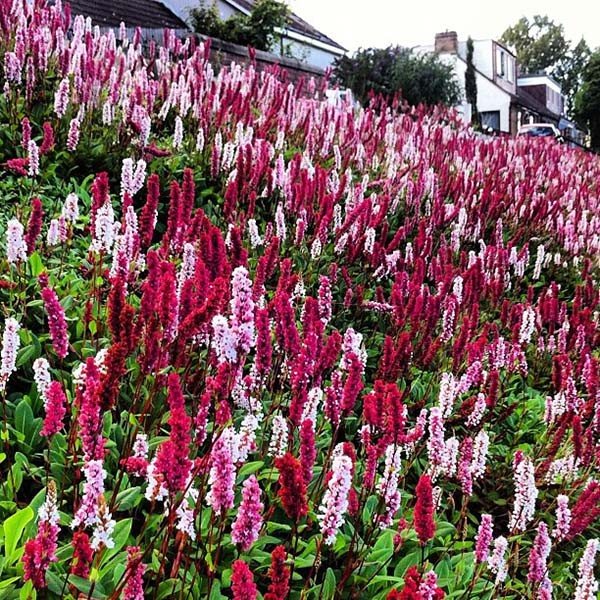
And on the site it can be placed not only near the reservoir, but also in any wet place. When grown in a mixborder or as a curb plant, it grows much larger and more showy than competing with other plants in the wild. Mixed plantings of white-flowered and pink-flowered plants look very impressive. If a prolonged, warm autumn happens, then the highlander has time to bloom again.
Highlander serpentine application
Buckwheat roots have long been used in folk Tibetan and Chinese medicine, treatises of the 11-14 centuries for the first time brought to modern man the benefits of this herb. The most valuable raw material was considered to be the ground rhizome of the mountaineer snake, which was widely used to treat many diseases associated with suppression of immunity.
As a basis for the preparation of medicinal raw materials, Tibetan medicine used the rhizome of the snake mountaineer at least 16 years old, it was this age of the plant that was considered balanced and optimal for the production of medicinal infusions.
Broths based on buckwheat are used to prevent gastrointestinal disorders, used in the fight against enterocolitis, diarrhea, gastritis, duodenal ulcers, cholelithiasis, dysentery, urethritis, urolithiasis, upper respiratory tract infections and hemorrhoids.
To combat the above diseases, a decoction was prepared: 50 gr. raw material was poured in 200 ml. boiling water and infused for about an hour. The drug was used up to 4 times a day, on an empty stomach.


In addition to decoctions, the rhizome of the snake knotweed is used in the preparation of raw materials for compresses, the crushed raw material of the fresh root of the plant, mixed in equal parts with the crushed ginger root, is applied to abrasions and weeping wounds, and is also used to treat fungal infections.
Alcohol tincture on the mountaineer snake is used to alleviate the condition in the climatic period in women and to suppress profuse uterine bleeding in girls. This tincture also perfectly copes with diseases of the oral cavity and nasopharynx: gingivitis, stomatitis, periodontal disease and sore throat. Compresses with snake mountaineer tincture are used for furunculosis and eczema.
The herb infusion can also be used for douching in the treatment of vulvovaginitis, as well as for any inflammatory processes in the body.
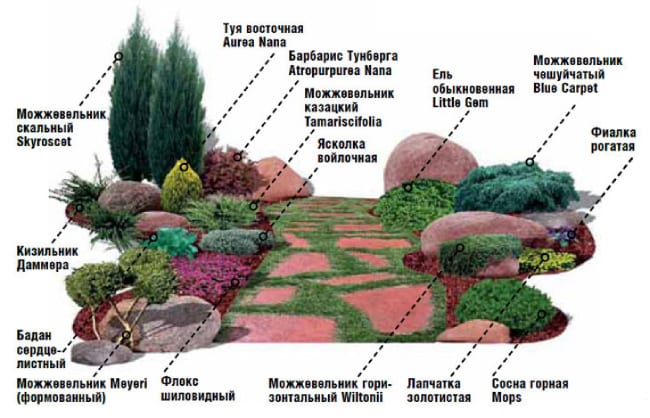
Recommendations for the placement of plants in the rock garden
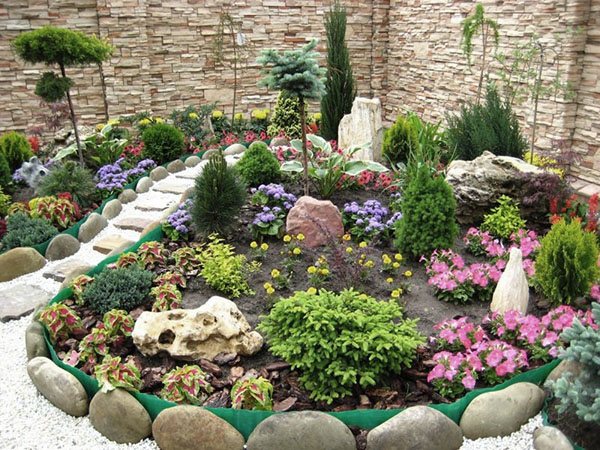


A successful combination of plants in a rock garden
Plants in the rock garden are recommended to be planted in tiers so that they look harmonious. It is advisable to plant moisture-loving and shade-tolerant specimens at the foot of the slide. In this place, cereal plants and saxifrage take root well and look. On the middle tier, it is recommended to place specimens that calmly tolerate the lack of lighting (lumbago, primroses). Stonecrops can be planted in between upright plants. On the upper tier, it is desirable to place perennials and annuals, for example, Iberises. To make the alpine slide brighter, you can add creeping thyme to its top. It goes well with the rock alyssum, which has yellow flowers.
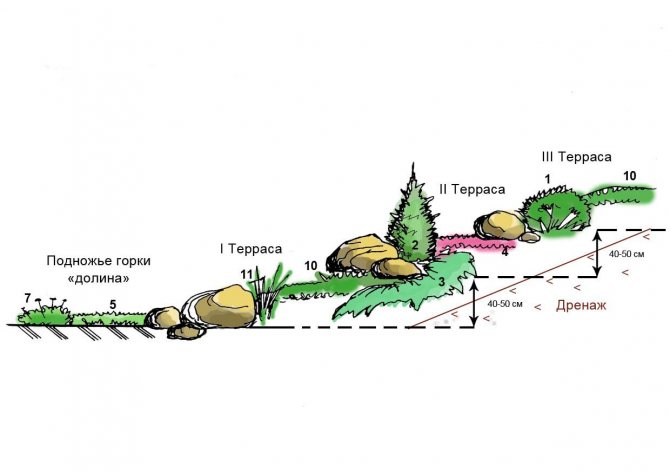

Plants in a rock garden should be arranged in tiers
Small trees and tall plants are recommended to be planted primarily at the foot or in the background. They look good near large stones. It is recommended to divide the tiers with undersized specimens or stones.
Photo: approximate color schemes

Tall plants and trees are recommended to be placed in the background.


A perennial herbaceous peony looks good on the upper tier.


Herbaceous plants and shrubs such as thyme and plantain are best placed at the foot of the rock garden
Features of growing a highlander
- The soil for the highlander. Shrubs grow in any soil that is well fertilized and loose.
- Watering. The plant is very moisture-loving and therefore, whenever possible, the roots are mulched as much as possible to retain moisture. Watering is done frequently and abundantly.
- Pruning. Prune the plants several times. Dried branches are harvested in the spring. During the development of the deciduous mass, the shrub is slightly thinned out. In the process of growth, they form the correct shape so as not to harm nearby growing plants and the bushes look well-groomed, and not wild-growing.
- Landing. When breeding highlander shrubs with seeds, they must first be prepared. For the winter, the seeds are placed in a refrigerator for stratification. In early spring, they are sown in garden cups or boxes to obtain seedlings. After the seed has sprouted, with dense sowing, they dive, sow in separate glasses one by one sprout. This is kept for up to one month, until the root system takes root well and the shrub develops. When warm days come, the plant is planted out of the boxes in a permanent place, before that it has been well loose and fertilized the soil. Water abundantly and enjoy the lush flowering already in the first year after planting.


Highlander CHANGE - VIDEO
Peacarium / Highlander volatile. Overview, characterization of persicaria / polygonum polymorpha
ORDER QUALITY AND CHEAP SEEDS AND OTHER PRODUCTS FOR HOME AND COTTAGE. PRICES ARE BOTTLE. CHECKED! JUST LOOK FOR YOURSELF AND BE AMAZED HOW WE HAVE REVIEWS. GO >>>
Below are other entries on the topic "Cottage and garden - do it yourself"
- Highlander plant - varieties and species, planting and care: Cultivation of different types of highlander I must say ...
- Planting strawberries: master class and photo: How to plant strawberries correctly - ...
- How to cut shrubs correctly: Cutting and shaping shrubs - ...
- How to plant roses correctly - a master class from a PROFESSIONAL: CORRECT PLANTING OF ROSES What can be ...
- Planting phloxes - master class and photo: HOW TO PLANT PHLOCKS CORRECTLY In September ...
- Do-it-yourself summer house-temporary house in the country: How to build a house for guests ...
- DIY hedge for bushes: FENCE FOR SHUSTERS IN THE GARDEN ...
Subscribe to updates in our groups and share.
Chance meeting


Literally the next spring, my neighbor, who considers herself to be in the category of people who knows better than anyone what others need, with the most solemn air presented me ... a highlander's spine. True, it was a different species - the polygonum polymorpha (Polygonum polymorpha), but nevertheless I did not feel the joy of the gift.Seeing a slight annoyance on my face, my neighbor added fuel to the fire: “Don't be afraid - it will quickly grow!”. I couldn’t tell her that this is what I’m afraid of!
In the year of planting, flowering occurred in the middle of summer. The bush has reached the size of a meter with a small one, and clearly did not spoil the overall picture of my "natural garden". But the most important thing is that he did not crawl out for the third of a square meter allotted to him!
Related article
Garden design in your country house
Advice and feedback from experienced gardeners
The basis of my alpine slide is the clay left over from digging a well. There is a plus in it - it inhibits the rapid growth of conifers and shrubs, keeps them within certain limits, so to speak. The assortment of my "upper" tier (everything has passed a sufficient test of time and various winters): mountain pine, lavender, fescue, dwarf bearded iris, many rejuvenated various varieties, stonecrop, subulate and spread-out phlox, saponaria (soapwort) - the simplest, creeping, on one of the peaks sits a barberry of an indefinite variety out of a box with an indication of the size of 40-170 cm, it spreads a little, does not want to grow in height at all - for 5 years it has never froze, conic spruce and blue dwarf juniper - do not burn, do not freeze and dry up.
mogileva
In the summer, my alpine slide looks no worse than in the spring. True, the colors are a little smaller, but there are many green rugs and all kinds of decorative foliage: tenacious, sedge, heuchera, sedum, cineraria, bergenia, rejuvenated, thyme, juniper, woolly purse, etc. The ground cover rose has grown very well. Blooms profusely, brightly, pleasing to the eye. Carpathian bells are also blooming. So the slide is constantly changing colors and does not lose its decorative effect. Of course, provided that all protruding and faded, dry peduncles (sedum, tenacious, edelweiss, etc.) are constantly removed.
Yulichka
The plant is ideal for a rock garden from the southern side - armeria. It is blooming now. It grows without problems. In order not to disappear, the main thing is to divide during the time It doesn't grow in my rock garden, but I try to keep it dry and put sand-stones. Yaskolka and sisyurinchia can also be identified there. Yaskolka grows remarkably, covering large areas. Reacts calmly to trimming and excess removal.
LenaMir
For an alpine slide, I can offer Turkish carnation, rejuvenated or stone rose and periwinkle. All flowering plants. The carnation has many varieties, I have three of it. The stone rose shoots out arrows, and pink flowers bloom on them, very beautiful. Well, periwinkle, as far as I know, has at least two species, and blooms somewhere in May with blue flowers.
Vitalinka
Declaration of love
The next year was a turning point. I, of course, watched the "gift horse" with particular passion, but the highlander both behaved and looked beyond praise. In May, bright green shoots with attractive leaves appeared. The growth was extremely rapid: by mid-June the bush had reached one and a half meters in height and was clearly not going to stop. A week later, numerous grayish-white inflorescences appeared, similar to clenched fists. In July, the development of the plant reached its climax: the two-meter bush was covered with caps of snow-white flowers, exuding a clear honey aroma, which was felt from a distance of several meters. By the way, the flowering of the highlander changeable lasts almost 2 months, and everyone who comes to my garden at this time, without fail, dips his nose into fragrant inflorescences. This is understandable: not only is the smell very pleasant, but also the flowers are just at the level of an adult's face.
Application
In ornamental gardening, an unpretentious and rapidly growing mountaineer is widely used in mixborders, rock gardens, for decorating buildings and fences, and strengthening the coastal zone of ponds.
Large specimens of the plant form powerful, abundantly flowering bushes that look spectacular on the lawn.The weaving forms of the mountaineer are planted near the arbors and arches, with long stems braiding around the supports, creating green walls. Low-growing forms look great under trees and shrubs, as part of an alpine slide composition.
CHARACTERISTIC CHANGE IN A FLOWER - PHOTOS AND IDEAS
Application in medicine


Knotweed stems and leaves contain the following nutrients:
The Sakhalin Knotweed plant is useful, it has bactericidal and tanning properties. The substances it contains are believed to have anti-inflammatory and anti-cancer effects.
Highlander broth has diuretic properties, it is used to treat kidney stones. It makes the blood cleaner, stops it when bleeding. Acting as a mild laxative, it relieves hemorrhoids.
Taking the drug in lower concentrations can relieve fever. It is an effective diaphoretic. It also tones the human body, stimulates sexual activity. The broth has proven itself well in the treatment of rheumatism, it helps with cholecystitis and nervous disorders. Bamboo is used to prevent the development of gout.
The Sakhalin mountaineer helps to get rid of the headache that occurs with high blood pressure. To do this, fresh grass is pressed, the resulting mass is applied to the back of the head.


Even though the climbing plant is a mountaineer and not as spectacular as, for example, wisteria, it still takes its rightful place in country gardens. Rather, this vine is suitable for garden plots decorated in a landscape style.
Its natural beauty will become a worthy framing of the perimeter of the territory, it will shade bright annuals, and will serve as an excellent background for any floristic compositions.
Perennial decorative vines - the most numerous group of all climbing plants. The value of perennial climbing plants lies in the fact that they, like other vines, occupy small areas when planting where there is no place for trees or shrubs.
Their long shoots, densely leafy with leaves of various structures and colors, covered with magnificent flowers, and then no less decorative peculiar fruits, cover a large area, provide shade and protection from the sun, create a unique decorative effect.
The description and photo of the highlander, as well as tips for growing a plant in the country, are presented in this material.
PROBLEMS AND SOLUTIONS
The thin shoots at the top of the bush are broken - this can happen in very strong winds or rain. A squally wind can pretty much ruin the appearance of our giant. Agree, a plant with inflorescences hanging down does not look very neat. In this case, there is only one recipe - pruning broken peduncles to the height of the scrap. Do not be afraid! The volatile highlander responds well to such a "haircut". Even if you cut the entire bush at its peak to a meter height, it will bloom again in three weeks.
Highlander is not susceptible to diseases and pests.
Popular in the Moscow region species and varieties
Alpine mountaineer is a branched semi-shrub, up to 150 cm high. The foliage is bright green, ovoid, the roots are powerful, creeping. It blooms in July with white flowers, collected in large paniculate inflorescences. Well worth the cut. The plant is winter-hardy and unpretentious, grows rapidly, crowding neighbors.
Highlander Weirich - powerful, unpretentious plants, up to 200 cm tall, form dense thickets. It blooms in August with small white flowers.
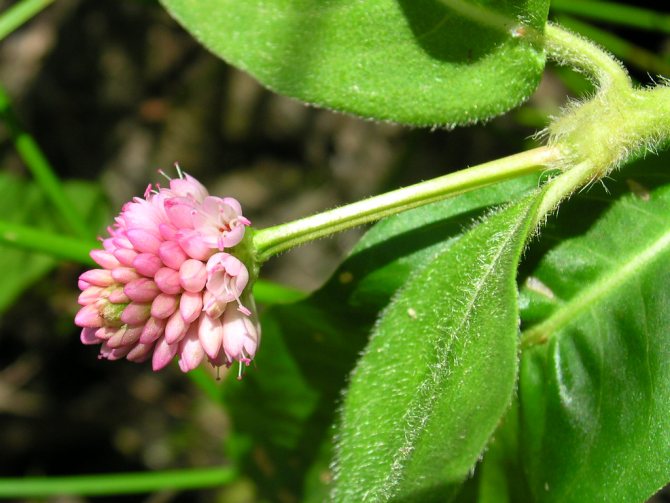
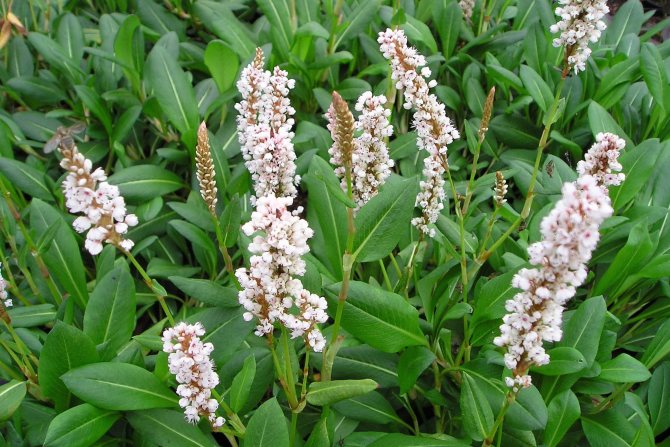
Knotweed is a ground cover variety of peaches, with a stem height of up to 25 cm. Flowers are small, bright pink, sitting in inflorescences-spikelets. Blooms in May. It tolerates drought and shade well, but in a snowless winter it can freeze slightly. Varieties:
- Darjeeling red (hot pink);
- Donald Lones (deep pink flowering turning to red).
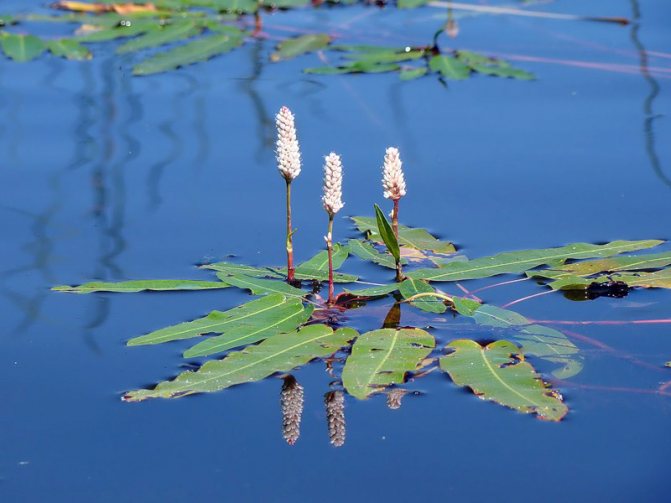
Highlander amphibian - used mainly to decorate the shores of reservoirs.The perennial grows partially submerged in water. The leaves are elongated, shiny, float on the surface of the water. Inflorescences are elongated, candle-shaped, pink. Flowering begins in July and lasts until frost.
The serpentine mountaineer is also placed along the banks of reservoirs. The plant is perennial, up to 130 cm high. Pink inflorescences resemble reed arrows. Blooms in June. The most popular variety is Superba, with pink candle inflorescences, peduncle height up to 90 cm.
Highlander Aubert is a compact liana (up to 40 cm in height), grows well in partial shade, and loves moist soils. Carpal inflorescences: pink, white or yellow.
Bindweed Highlander is an annual with a curly stem and shoots.




































