Category: Garden plants
Plant paprika (lat.Capsicum annuum) belongs to the species of herbaceous annuals of the genus Capsicum of the Solanaceae family, widely cultivated in agriculture. A native of the vegetable pepper from Central America, it came to Europe in the 15th century and, despite the exacting care and increased thermophilicity, quickly became the most popular garden plant. Today there are about 2,000 varieties of capsicum, but most of them belong to the sweet pepper subspecies, and others - to the bitter pepper subspecies. In this article we will tell you about how to plant peppers, how to dive peppers, how to water peppers, how to fertilize peppers, how to grow pepper seedlings and when to plant sweet pepper seedlings. Bitter pepper will be the topic of a separate article.
Preparation for growing pepper seedlings, planting seeds and further care
Pepper is a thermophilic crop with a rather long growing season, therefore, planting seeds in open ground is impractical even in warm southern regions. The time for planting seeds depends on several factors:
- Type of variety. Seedlings of early maturing peppers are considered suitable for planting at the age of 60-65 days, later varieties require 70-75 days.
- Place of cultivation. When cultivated in temperate climates, peppers are transferred to heated greenhouses in the last decade of April, and in ordinary ones - in the second half of May. In open beds, seedlings are planted in early June. In the south, the dates are shifted 10-15 days ago, in more severe regions - on the contrary, forward.
- Picking. If it was carried out, the seedlings need about 12-15 days more to form. In general, this is an undesirable procedure for peppers. The roots of the seedlings are very weak, there is a high risk of their death.
Most often, pepper seeds are sown for seedlings in late February or early March. They do not differ in very good germination, therefore, rejection and preliminary preparation are necessary. When buying seeds, pay attention to the date of manufacture. If they were harvested more than two years ago, mass shoots can not be expected.

When choosing pepper seeds, pay attention to the date of collection and the expiration date
To select viable seeds, they are immersed in a salt solution for 7-10 minutes (2 tablespoons per liter of water). Those in which there are no embryos quickly float to the surface.


Immersion in brine is a simple and reliable way to reject seeds that will definitely not germinate.
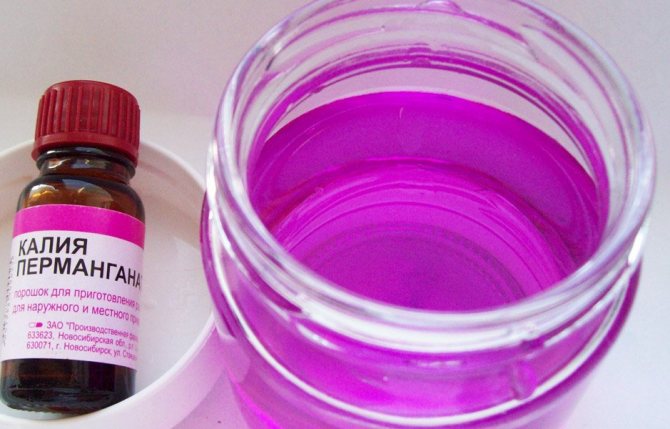
The next stage is disinfection. To prevent the development of diseases, pepper seeds are kept in a bright pink solution of potassium permanganate for 5-6 hours. Biofungicides (Alirin-B, Bayleton, Fitosporin) give a similar effect. Processing time is reduced to 20-30 minutes.


Potassium permanganate solution is one of the simplest and most affordable disinfectants
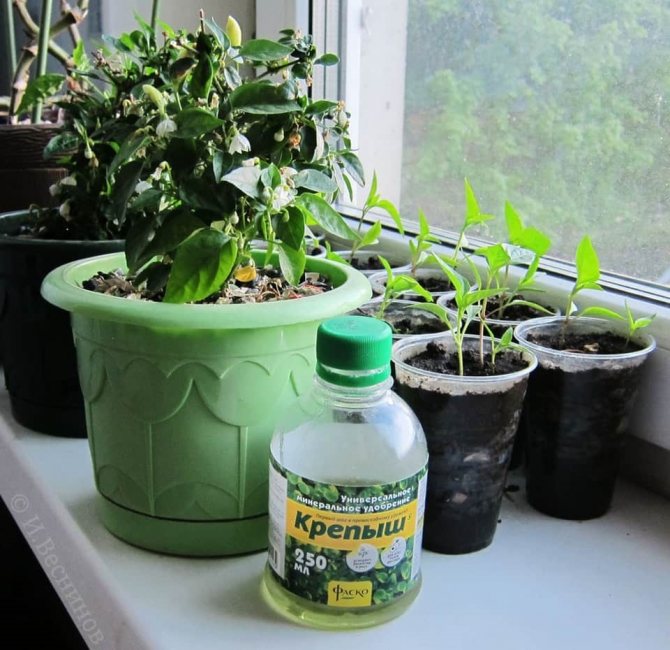
Seeds begin to germinate a week before sowing. The easiest option is to wrap them in damp gauze or cotton wool and leave the container on the battery. Germination increases if water is replaced with a solution of a biostimulant, purchased (Epin, Heteroauxin, Kornevin) or natural (honey, aloe juice). In the same way, "shock therapy" works on pepper.The seeds are covered with wet sand or peat, during the day they are kept on a radiator or windowsill on the sunny side, and put in the refrigerator at night.


Sprouted pepper seeds have better germination, seedlings appear faster
A less common method is bubbling. Seeds in a linen bag are immersed in water at room temperature and a regular aquarium compressor is turned on, saturating it with oxygen. Processing time is about a day.
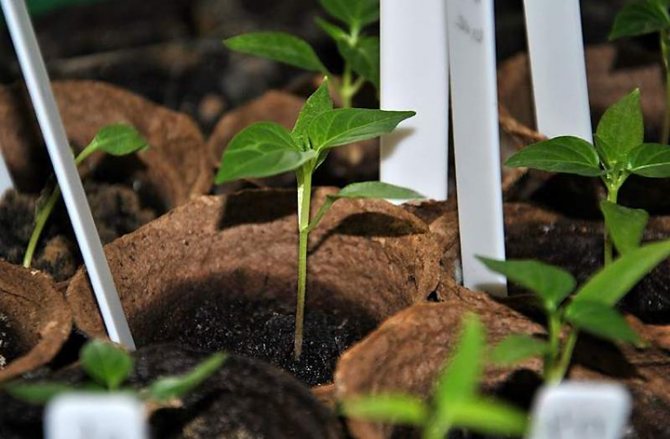
Pepper does not tolerate picking too well. Therefore, it is better to immediately plant the seeds in separate containers with a volume of about 150 ml. For them, both purchased soil for Solanaceae, and a self-prepared mixture of humus, peat crumbs, rotted sawdust and sand (4: 2: 1: 1) are suitable. Any substrate is pre-sterilized.
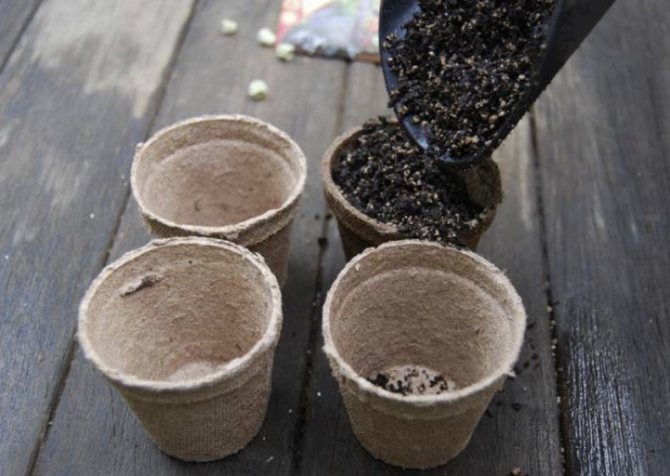


Peat cups for seedlings are convenient because the plants can be transplanted into the ground right with them
Seed planting takes place according to a simple algorithm:
- In the bottom of the container, make holes for water drainage, pour a little expanded clay or other drainage material, fill it with soil by about two-thirds.
- Water the substrate moderately, compact the soil a little. Wait until the water is absorbed.
- Plant two seeds in each cup with an interval of 2-3 cm. Sprinkle on top with a mixture of humus and sand (1: 1), creating a layer no thicker than 1 cm. Sprinkle with water from a spray bottle.
- Create a "greenhouse effect" in any way: cover the containers with glass, foil, put them in a mini-greenhouse. Remove the shelter daily for ventilation for 5–7 minutes, spray the soil every 2–3 days.
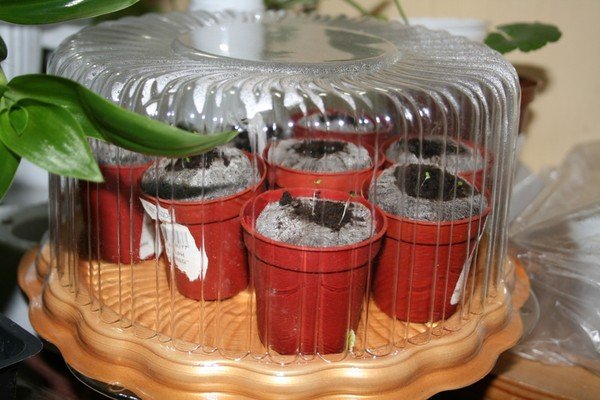


A home "greenhouse" can be created from many available tools; the main thing is that it maintains high humidity and the desired temperature
- Before emergence, remove to a dark place, providing bottom heating and a constant temperature of 25-27 ° C. Seeds germinate unevenly, it takes 7-15 days.
- After that, move the containers to the brightest place in the apartment. Remove the film. Reduce the daytime temperature to 23–25 ° C, and the nighttime temperature to 16–18 ° C. Provide 9-10 hours of daylight hours. Light up if necessary.
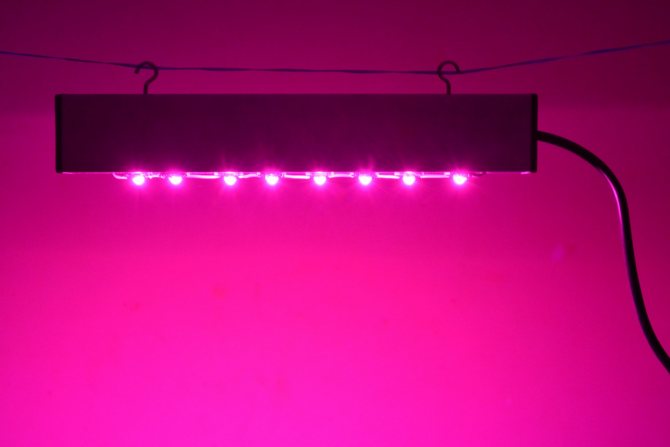


For supplementary lighting of seedlings, it is better to use special phytolamps, but ordinary fluorescent lamps are also suitable
Collection and storage of peppers
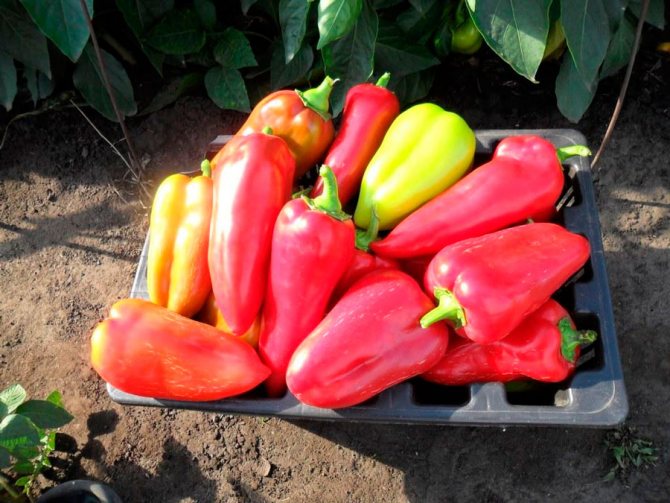
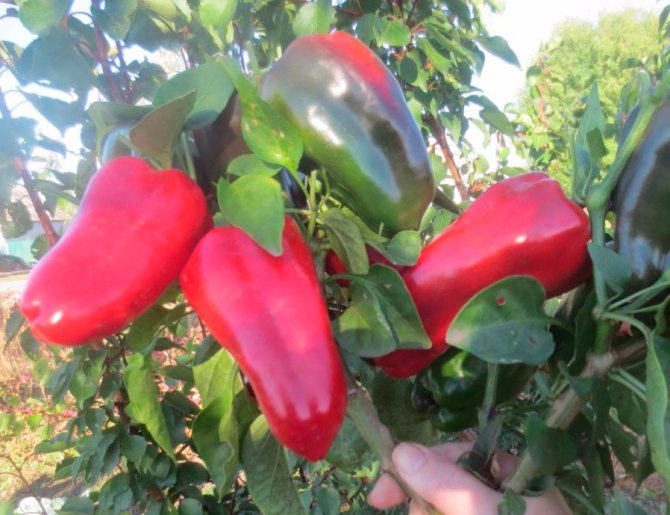
Pepper has two types of ripeness - technical and biological (or physiological). At the stage of technical maturity, all peppers are usually green in color - from dark green to greenish-whitish hue. If the peppers on the bush are yellow, red, orange, lilac or brown, then we can say that they are already at the stage of biological maturity, which means that the fruits removed from the bush must be used immediately - canned or eaten, since they are stored such peppers for a very short period of time.
The fruits harvested in a state of technical maturity under suitable conditions can be stored for up to two months. The time difference between technical and biological ripeness is 20-30 days. The readiness of the pepper for harvesting is determined by the crackling of the fruit when you lightly press it. And one more landmark: peppers are harvested at about the same time as eggplants and tomatoes.
Usually, the first fruits are harvested in early or mid-August, and peppers continue to be harvested until frost. That is, ripe fruits are removed selectively every 5-7 days. To keep the pepper better, it is cut off along with the stalk. During the growing season, three to five harvests are carried out. Before the onset of frost, all fruits are removed from the bushes, and their further ripening takes place indoors, after sorting by size and degree of ripeness.


Before storing the fruit, the stalk is cut off, leaving a segment of only 1-1.5 cm. Only healthy thick-walled fruits that do not have mechanical damage are suitable for storage. Thin-walled varieties are stored in the refrigerator.Juicy-walled varieties can be kept in plastic bags with a thickness of at least 120 microns, preferably with a perforated membrane on the side wall. Peppers keep better if each fruit is wrapped in paper. Peppers can be stored in baskets, shallow boxes with 1-2 rows or on shelves in the basement with a temperature of 8-10 ºC and an air humidity of 80-90%.
Since peppers quickly absorb odors, make sure nothing in your basement grows moldy or decays. Keeping peppers in the right conditions keeps them fresh for one and a half to two months. Bell peppers can be stored for up to a month in the refrigerator at 9-10 ºC. Many housewives prefer, after washing the fruits and removing the testes, fold the peppers one into the other and store them in the freezer all winter so that at any time they can cook their favorite dishes or add a slice or two to borscht or salad.


Those fruits that are not suitable for storage can be processed. They make excellent marinades, aromatic winter salads, borsch dressing.
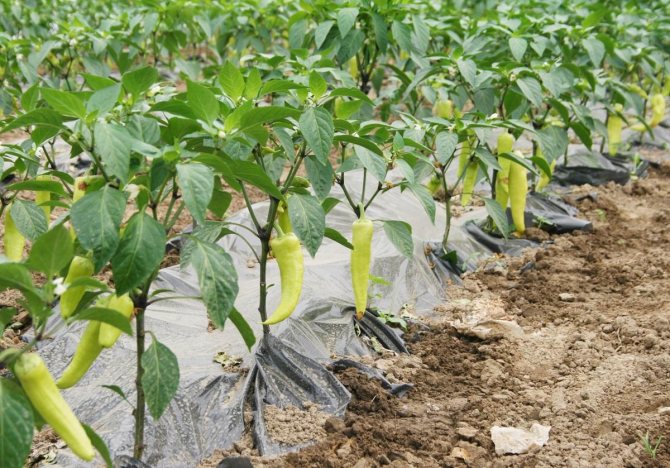
Growing pepper in a greenhouse
Agrotechnology for growing peppers in a greenhouse is not much different from what is required for a culture in an open field. But there are some nuances:
- Change the top 10 cm of soil annually, and every 4–5 years - completely.
- Every autumn, clean the garden from plant debris, disinfect the substrate by spilling a solution of potassium permanganate or any fungicide.
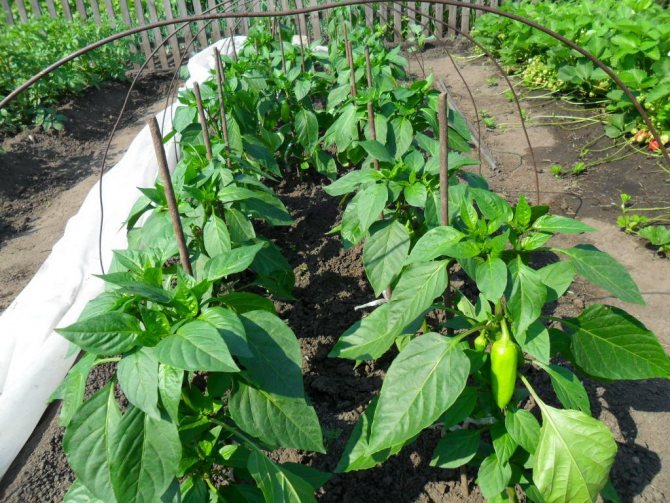
- Tie plants more than 0.5 m in height to a wire stretched under the ceiling so that they do not collapse under the weight of the fruit. Pepper in the greenhouse is more productive than in the garden.
- When the weather permits, open doors and windows. Stale air is a suitable environment for many pests and fungi.
- Peppers in greenhouses and greenhouses are more susceptible to sunburn. To prevent this, in extreme heat, spray the glass from the inside with a solution of slaked lime.
- Maintain a constant temperature of 25-28 ° C and a humidity of 70-75%. Sudden changes negatively affect yields. At rates up to 20 ° C and above 32 ° C, pollen becomes sterile; at low humidity, flowers and ovaries massively crumble.
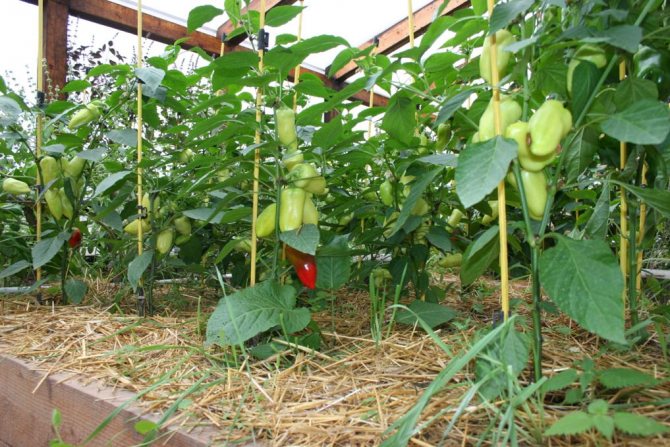


Growing sweet peppers in a greenhouse for many regions of Russia is the only way to get a harvest.
Video: recommendations for cultivating pepper in a greenhouse
Pepper care
How to grow pepper
Growing pepper in the open field involves timely watering, weeding and loosening of the site, garters and feeding the plants. Professionals recommend removing the central flower from the first branch on each bush - this should increase the yield of the pepper. Also, to increase the yield, the bushes are formed into 2-3 stems, for which it is necessary to promptly remove the resulting lateral shoots - stepchildren. They do this in hot and always humid weather. No more than 20-25 fruits can be left on one plant.
When planting seedlings of high varieties of pepper into the ground, drive in a peg right next to each seedling, to which, if necessary, you will tie a bush.
For successful pollination of pepper, it is necessary to attract pollinating insects to the site, for which the bushes are sprayed with boric-sugar syrup, dissolving 2 g of boric acid and 100 g of sugar in a liter of hot water. And refuse to treat the garden with pesticides from the moment the pepper blooms, otherwise the insects pollinating the pepper may die.


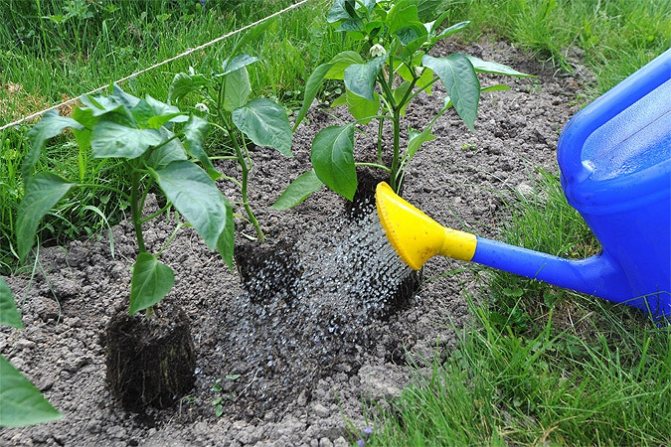
Watering the pepper
After planting in open ground, the seedling looks somewhat sluggish, but this is quite natural, therefore it is very important not to overdo it with soil moisture at this time. Before flowering, you need to water the pepper once a week, and during the period of fruit formation, you will have to water it twice a week at the rate of 6 liters of water per m². After watering, you need to very carefully loosen the soil between the rows, taking care not to damage the superficial root system of the plants.
Watering the pepper is carried out with warm, settled water from a watering can by sprinkling. From a lack of moisture, pepper slows down growth and can shed flowers and ovary. To keep the soil moist, experienced gardeners recommend mulching the area with pepper with a ten-centimeter layer of rotted straw.
Pepper dressing
After dressing in the seedling stage, pepper in the open field is fertilized twice with a solution of chicken manure at a concentration of 1:10, and foliar dressing is also used with a solution of a tablespoon of nitrophoska in a bucket of water. Twisted pepper leaves with a dry border around the edges will tell you that there is not enough potassium in the soil, but do not use potassium chloride as a fertilizer - pepper does not tolerate chlorine.
From a lack of nitrogen, the leaves acquire a dullness, a gray tint and gradually become smaller, and from an excess of this element, the plant sheds ovaries and flowers. When the pepper lacks phosphorus, the underside of the leaf plate turns deep purple, the leaves rise up and press against the trunk.
Due to the lack of magnesium, sweet pepper leaves become marbled. Be attentive to the plant, and you will be able to help it in time by adding the necessary top dressing.


Pepper processing
The fight against diseases of peppers during the period of fruit ripening with pesticides is undesirable, since all the beneficial properties of the plant are leveled by nitrates and other chemicals harmful to humans absorbed after treatment. With proper care and adherence to agricultural technology, the type of problems with diseases or pests should not arise in pepper, but if they do appear, let's consider what measures will help get rid of them and at the same time keep the quality of the fruits at a high level.
The nuances of growing pepper in different regions
Conditions in central Russia, in principle, are favorable for growing early and mid-season varieties of pepper both in the open field and in greenhouses. But occasionally in this region, returnable spring frosts are possible, plantings must be protected from the cold.
In the Urals, Siberia, the Far East, the only way to cultivate pepper is in a greenhouse or in warm beds. They choose varieties specially zoned for these regions. The main danger for peppers is temperature extremes. Summer is short here, therefore, already in the last decade of July, it is recommended to remove flowers, small ovaries and pinch the top of the main shoot of the bush so that the peppers have time to ripen before the cold weather.
Caring attitude
The first days after the transplant, the growth of pepper slows down, the leaves are lethargic and omitted. Within a few days, when the bushes take root, a strong stem will begin to develop. Outdoor pepper care is accompanied by regular watering, soil fertilization, and weed control.
Growing and caring for peppers in the open field should be accompanied by proper, regular watering. The first watering is carried out at the time of disembarkation, and then after 5 days. If the weather does not indulge in rains, then watering until the first fruits appear, it is recommended every week. During rapid fruiting, watering is reduced. As soon as the first crop is harvested, and new flowers appear on the plants, the previous watering regime is resumed.


As soon as the height of the plant reaches 35 cm, pinch the top. Thanks to this, new side branches will go. In order for the flowering to be abundant and to form many ovaries, remove the flower that is in the center.
Throughout the time when the bell pepper grows, you need to pluck off excess leaves and twigs. This allows better access of sunlight and air to the stem.
Pepper loves soft, well-loosened soil. Therefore, a hard crust should not be allowed. During loosening, the soil is enriched with oxygen, the plant grows faster, and the activity of beneficial bacteria improves. At the same time, weed control is being carried out. The first loosening should be carried out no deeper than 6 cm.In the future, it is useful to loosen the soil after each watering or rain.
See also
Planting, care and cultivation of pepper Spark on the windowsill at homeRead
Since peppers are thermophilic plants, they can hardly endure adverse weather surprises. You can protect peppers from frost as follows. Shelters are constructed from cardboard, warm cloth over the beds. If cold nights last for a long time, it is better to cover with plastic.
Hot peppers in the open field
Gardeners plant bitter peppers much less often than sweet ones. But there is nothing supernatural in its cultivation. The requirements for growing conditions and soil are the same as for bell peppers. But he is more prone to sunburn, so shading is desirable in extreme heat. The plant is thermophilic, lowering the temperature to 2-3 ° C is destructive for it.
Bitter peppers are grown as seedlings; they are transferred to the ground at the age of 40-50 days (height is about 15 cm, the presence of 5-6 true leaves). With proper care, the height of the bushes reaches 1 m, the plants are powerful. The planting scheme is 40–45 * 50–60 cm. Another possible option is the square-nesting method (two bushes at the corners of a 70 * 70 cm square). The stem of the plant is weak, immediately fix it on a support.
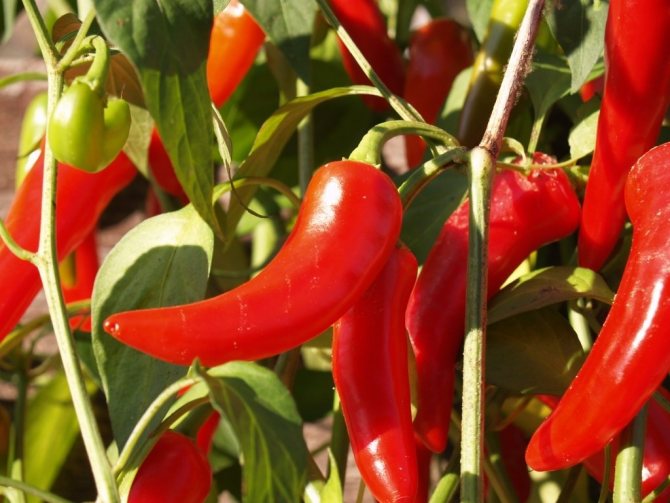


Bitter pepper bushes take up a lot of space in the garden, but at the same time they have a very good yield.
To stimulate the branching of the plant, pinch the top of the central shoot at a level of 25 cm. After the fork, 4–6 of the most developed branches are left. The rationing of the crop is recommended. On one bush, 25–27 large fruits ripen, the rest of the ovaries are cut off.
Bitter peppers need daily watering, especially during flowering. In extreme heat, the soil is moistened even twice a day. When choosing fertilizers, pay attention to the presence of phosphorus and magnesium in the composition. Top dressing is carried out every 2.5–3 weeks.
Video: how to grow hot peppers in the garden
Additional nutritional components
Bulgarian pepper cultivation is not complete without the introduction of nutrients. The frequency of fertilization should be once every 12-14 days. You need to fertilize the plant at least three times. Peppers need nourishment especially acutely during flowering and fruit formation.
The first feeding with nutrients occurs 14 days after planting. During this time, the peppers take root and get used to the new place. The best formulations at this stage are those containing mullein. Water is added to the manure in a ratio of 1: 5, insisted and stirred with water 1: 2 before watering.
When flowers appear, you can use the following recipe based on herbal infusion and mullein. Nettle, plantain and dandelion leaves are poured with water, mullein is added and infused for a week. Add the prepared solution to the root of each bush. Watering can be repeated every 2 weeks. The nutrients obtained in the course of this top dressing contribute to the activation of growth and better fruit formation.
To attract insects that pollinate during the flowering period, you can use a solution with sugar. Sugar and boric acid are dissolved in water. The resulting composition is sprayed with bushes. As a result, ovaries form faster.
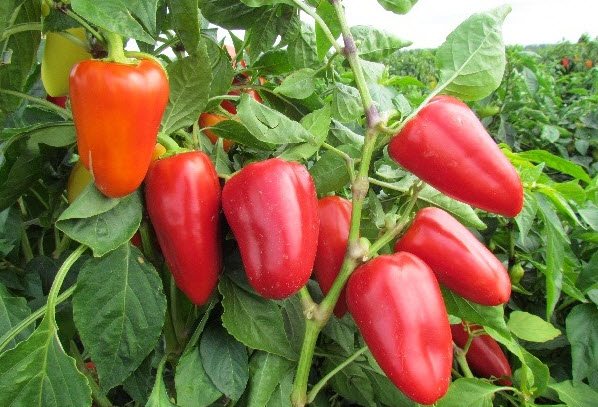


During the formation of the fruit, you can take care of it with a fertilizer based on chicken manure and nitroammophoska. The components are mixed and left to infuse for the whole week. Fertilizer is transferred to the garden bed between the rows.
Bell peppers can be treated with nettle infusion. An infusion of nettle alone stimulates the growth and development of pepper. Young nettle is best suited for infusion. It contains magnesium, iron, potassium and other essential micronutrients.The stems are crushed and insisted in a barrel of water, covered with a lid for two days. Before feeding, the solution is diluted with water in a ratio of 1:10.
Before applying organic or mineral fertilizing, the beds should be watered with plain water. Such care will evenly distribute nutrients and avoid scalding of the root system.
The agrotechnology of growing pepper does not allow the use of fresh manure as fertilizer. Manure contains a lot of nitrogen, so the risk of an overabundance of this element increases. The stem and leaves begin to gain mass and strength, and fruiting stops.
Decorative pepper at home
The peppers on the windowsill look very cute and will be a valuable addition to your home garden. There are also perennial varieties that yield crops for 8-10 years. They choose varieties with compact, low (up to 50 cm) bushes - Ogonyok, Aladdin, Poinsettia.
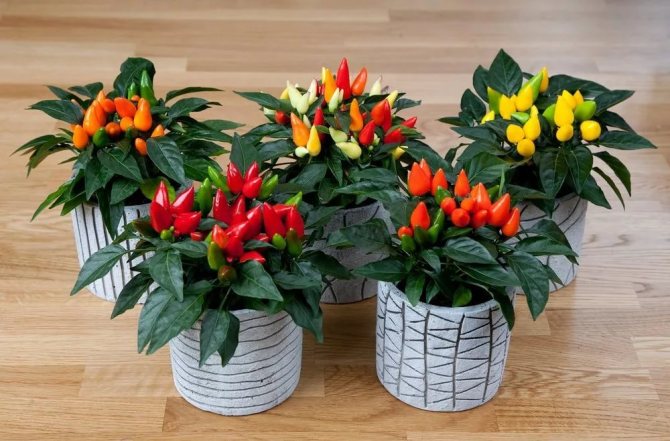


Homemade peppers are most often grown for the sake of the harvest, but there are also purely decorative varieties.
The optimum temperature for plants in winter is 18–20 ° C, in spring and autumn around 25 ° C. In the summer, it is useful to take the pots out to the balcony, it perceives fresh air and natural temperature changes favorably. The container is kept in a place well-lit by the sun, but not in direct light, if necessary, supplemented with light.
Seeds, soaked for an hour or two in a solution of a biostimulant, are planted in a pot with a volume of about 5 liters in February, this will avoid further transplants. A drainage layer is required at the bottom. The soil is shop soil for Solanaceae. You will have to wait 2-3 weeks for seedlings. When 3 pairs of leaves appear, pinch the top to stimulate branching.
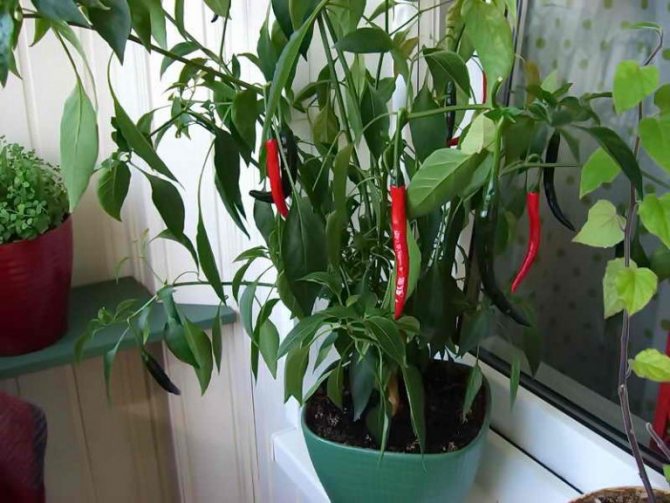


If you provide the pepper with the right conditions, proper care and choose the right variety, the plant will delight you with a harvest for more than one year.
Water the plant every 2-3 days, spray it weekly with a spray bottle. In winter, spraying is stopped, watered once a week. Fertilizers from March to October are applied every 15–20 days, complex feeding for Solanaceae is used. After the first fruiting, the tops of all shoots are pinched, those that are knocked out of the general configuration are cut off completely. In perennial varieties, each shoot is shortened by half at the end of autumn every year.
Video: cultivating pepper on the windowsill
Site preparation
You should choose and prepare a site for pepper in the fall. Well-prepared soil is a guarantee of normal growth and fruiting of plants for the next year. The ideal place is the beds on the south side of the house or outbuildings, which are in light shade in the afternoon. This arrangement provides protection from both wind and leaf burns in the July heat. Peppers should not be planted where tomatoes, potatoes, eggplants and other nightshade crops have grown in the previous three years. The best predecessors of pepper are considered to be legumes and pumpkin crops, cabbage, melons and green manures.


Preparing a bed for pepper
The soil for the pepper should be neutral or slightly acidic. On beds with acidic soil, plants take root for a long time after transplanting, develop poorly, almost do not bloom and do not bear fruit.
Advice! It is very easy to check the acidity at home: you need to take a little earth and moisten it with ordinary table vinegar. If no reaction follows, the soil is acidic and needs liming, but if bubbles appear on the surface, this indicates neutral acidity.


How to determine the acidity of the soil


Plants-indicators of soil pH
So, if the soil in the selected area is acidic, slaked lime (1 glass per square meter) or wood ash (1.5-3 kg) is added during digging. If the soil is neutral, you need to add rotted organic matter (from 5 to 10 kg per m2) and dig up the beds to a depth of 20-25 cm.In the spring, potash-phosphorus fertilizers are additionally applied at 40 g per square meter, the soil is well loosened and leveled.
Cultivation of black peppercorns
In nature, black peppercorns are a curly long (up to 15 m) liana. The plant is very thermophilic, temperatures below 10 ° C are destructive for it, therefore in Russia its cultivation is impossible even in the southern regions. The vines have large, hard leaves, the fruits are twisted in bunches. Unripe peas are green, gradually they turn red.
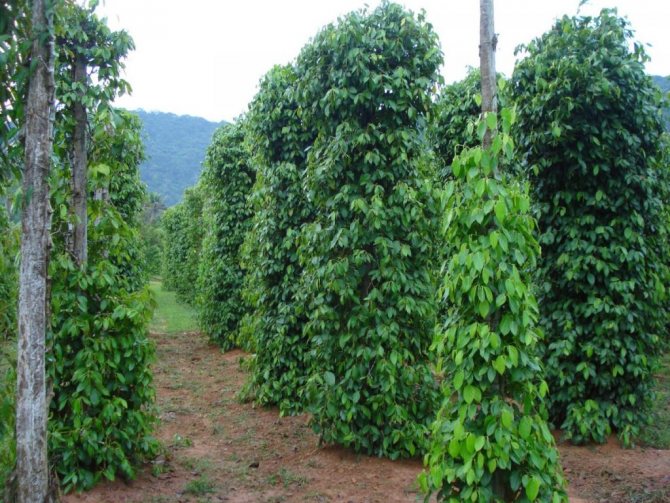


The Russian climate for the vine on which peppercorns grows is definitely destructive
You can try to grow this pepper at home. An ordinary spice, which is sold in the store, is suitable for planting. Pay attention to the expiration date, a year or less must pass from the date of collection. The procedure is carried out in May-June. Suitable soil for orchids.
The conditions for the plant are the same as for ornamental paprika. Plants are watered as the soil dries up, mineral fertilizers are applied twice a month during the active growing season. The transplant is carried out every two years, the length of the vines is regulated by pruning. The first crop is harvested in 2-3 years.
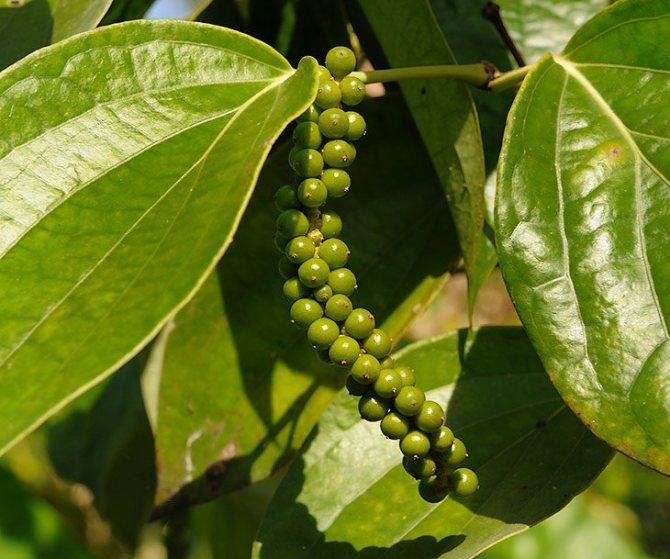


Few people know, but the well-known spice before collection and packing in bags looks exactly like this; black, white, green and pink pepper are obtained from peas
Small whitish "grains" on the wrong side of the leaves are normal for a plant, and not some kind of exotic disease.
Video: how peppercorns grow in natural conditions
Vegetable pepper - description
Sweet pepper, or paprika, is an annual vegetable that is naturally a perennial shrub. Its leaves are simple, petiolate, collected in a rosette or single, the color of the leaves, depending on the variety and variety, can be of different shades of green. The flowers of the pepper are axillary, large, collected in a bunch or single, with a white, purple or greenish corolla. The fruits are false, hollow polyspermous berries of yellow, red, brown or orange color of various shapes, weights and sizes.
Non-standard ways of growing pepper
Planting pepper in barrels saves space on the site. The bottom of the container is removed, several drainage holes are made. It is half filled with soil in layers about 10 cm thick, alternating with turf, ordinary soil and raw materials for compost. The bush is planted in early May. The lower leaves are cut off, covered with a layer of earth about 10 cm thick, covered with a film. When the pepper grows up, the procedure is repeated. And so several times, until the barrel is filled with the substrate to the brim. After that, the film is removed, the plant is looked after as usual.
The Chinese method allows you to get more powerful bushes. Seeds are planted in "cassettes", a layer of soil no more than 6 cm thick. When the 7th true leaf appears, the tops are pinched. Bushes slow down growth by an average of 3 weeks, during which time the root system is developing. Fruits on such plants ripen 2.5–3 weeks later than usual, but the overall yield is higher. After planting, the soil is covered with a thick (6–7 cm) layer of mulch.
Problems arising
If it was noticed that the leaves change shape, color, the stems look sluggish, or other signs have appeared, often the reason is a lack of mineral components:
- with a lack of potassium, the leaves curl, and their tips dry and turn yellow;
- it is time to apply nitrogen fertilizers when the leaves have lost their rich green color and turned gray;
- if the leaves are pressed against the stem and have acquired a bluish tint, it means that there is not enough phosphorus;
- white spots indicate magnesium deficiency;
- leaves and ovaries fall off with an excess of nitrogen.
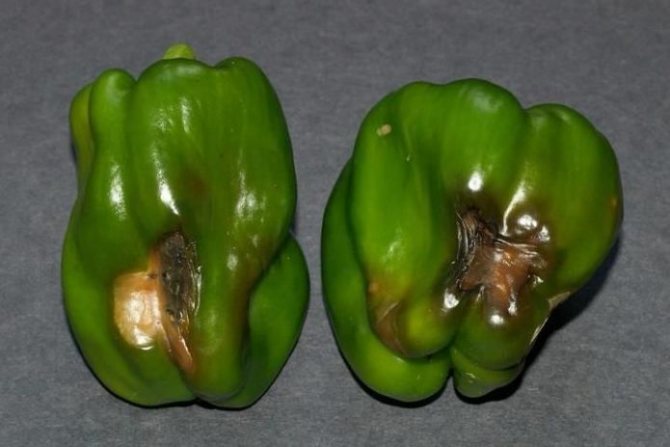
For the cultivation of sweet peppers, you need to create conditions. With improper care, he is exposed to the development of various diseases.The most common disease is blackleg, which develops in too moist soil. You can notice the problem by the dark bloom of the stem that runs near the ground. If you do not take action, then all the roots succumb to rotting and the plant dies.


To reduce the risk of developing a black leg, seeds are planted only in treated soil, only strong, healthy seedlings are transplanted into open ground. The distance between the bushes must be large, this will reduce the rate of spread of the disease. In addition, closely planted bushes will poorly transmit air and light.
Phytophthora is a fungal infection that affects the green part of the plant. You can tell by the appearance of brown spots on the stem and leaves. To avoid this disease, care must begin with seeds. Before planting, they are soaked in potassium permanganate, foliar spraying of seedlings in open ground with protective solutions is carried out. You should also avoid the neighborhood of pepper with tomatoes and potatoes.
Another common fungal disease is white rot. The lower part of the stem is covered with a whitish bloom, while the inner part of the stem turns black. As a result, the stem loses its strength and the plant dies. To avoid the problem, pepper seedlings are transplanted into the ground well warmed up by the sun. Do not forget to remove flabby leaves in time and water the bushes only with warm water. At an early stage of the onset of the disease, you can try to get rid of it with a solution with wood ash.
Diseases and pests: prevention and control
Diseases and pests that attack peppers are typical of all Solanaceae.
Table: diseases, pests of pepper and methods of dealing with them
| Name | Signs | Control methods |
| Gray rot | "Wet" gray-brown spots on stems and fruits, covered with a "fluffy" gray coating. | Severely affected plants - remove and disinfect the soil, at the first sign - use Fundazol, Acrobat, Ordan, Skor (according to the instructions). |
| Bacterial wilting | Rapidly growing yellow spots on the leaves, drops of whitish liquid on the sections. | Treatment with any fungicides in the early stages, in the later stages - the destruction of the plant. |
| Late blight | Brown spots on leaves, stems, fruits, in dry weather the plant dries quickly, in rainy weather it rots. | Treatment with Gamair, Alirin-B, Ridomil-Gold, in case of massive defeats - Bravo, Quadris. |
| Fusarium | Yellowing, curling leaves, brown stem base, fruit decay. | Treatment with Fundazol or Topsin-M. The drugs will not cure the disease, but they will slow it down enough to harvest. |
| Mosaic disease | Mosaic pattern on the leaves interspersed with light and dark green, beige, yellow. | There are no cure measures yet. The best prevention is competent agricultural technology. |
| Aphid | Small insects dotting the inside of the leaves, the tops of the shoots, the buds. | At the initial stages - spraying with any infusions with pungent odors (onion, garlic, tomato tops, wormwood, needles), in case of mass infection - with general-action insecticides (Aktara, Mospilan, Tanrek). |
| Spider mite | A thin cobweb surrounding the plant, small yellow spots on the leaves. | Treatment with acaricides (Neoron, Omite, Apollo). |
| Slugs | Large holes in leaves and fruits, sticky silvery marks on the surface. | Surround the bases of the stems with sand, needles, ground nut or eggshells; in case of a mass invasion, use the preparations Meta, Groza, Slizneed. |
Photo gallery: diseases and pests typical of pepper


It is useless to treat gray rot that has entered far away, remove the plant from the garden
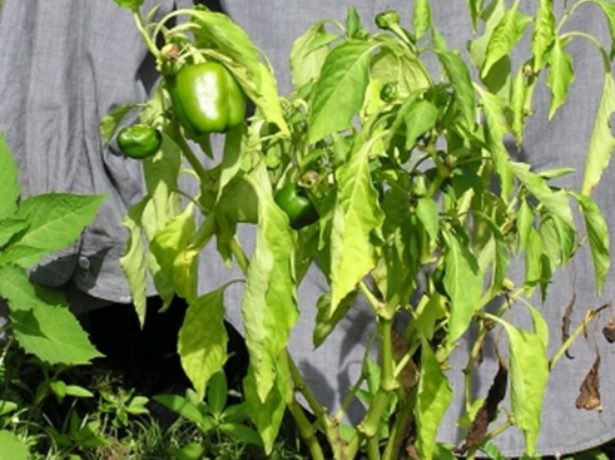


Bacterial wilting of pepper develops very quickly, it is very difficult to notice it at an early stage.
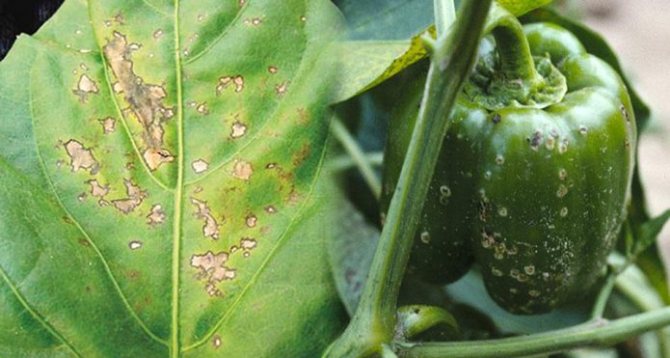

Late blight of pepper makes the fruits unfit for food
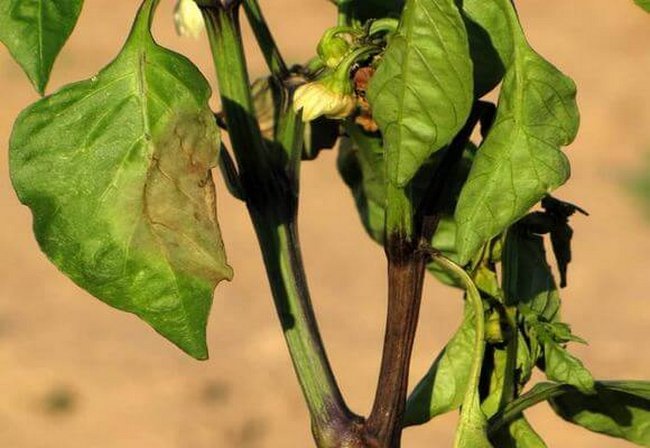


Fusarium pepper blight is a dangerous disease for all Solanaceae, bushes die in a matter of days
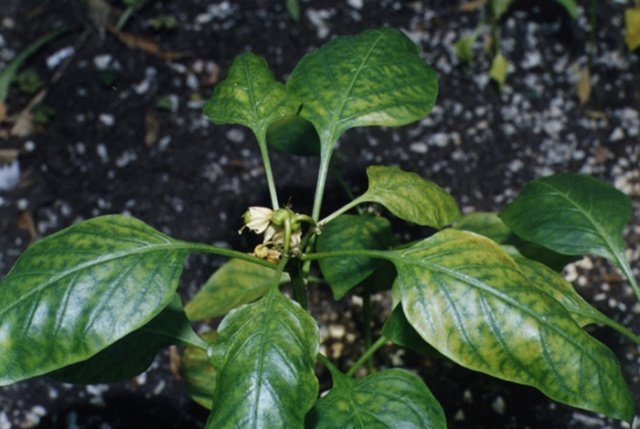


Pepper mosaic disease is caused by a virus, how to deal with it is not yet clear


Aphids are one of the most "universal" garden pests; they will not disdain pepper either.
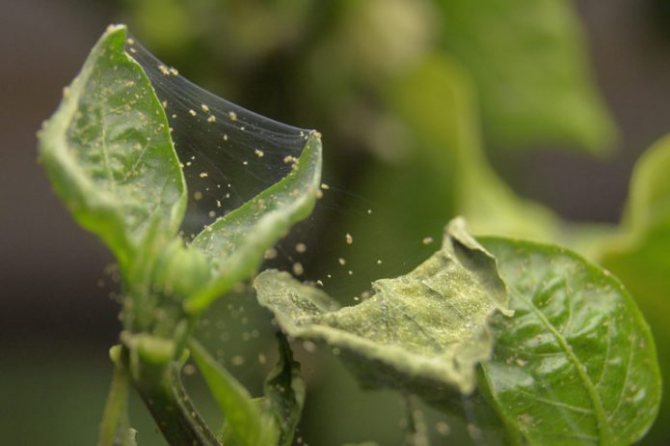


A spider mite is not an insect, folk remedies are ineffective in the fight against it, it is better to immediately use suitable preparations
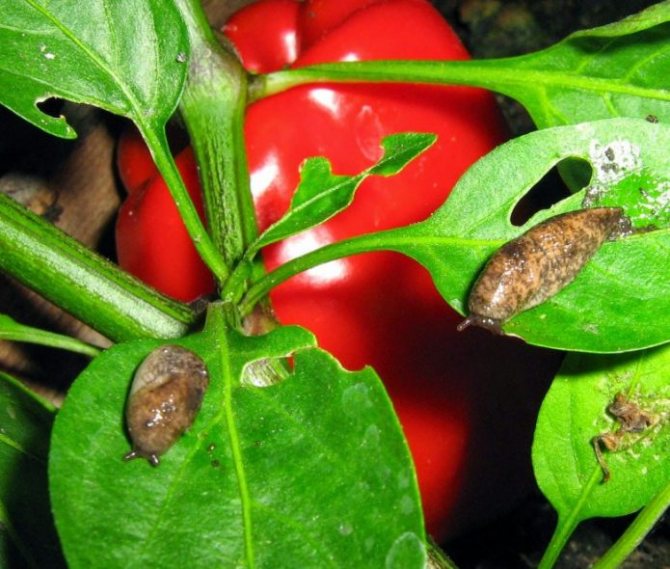


Of course, the slugs will not kill the plant, but I no longer want to eat the fruits damaged by them
Getting seeds
When harvesting, it is necessary to take care of the gene pool for the next season, because the germination of seeds from plants grown with their own hands, in compliance with all the rules of plants, reaches almost 100%. The core is extracted from the selected, most beautiful and large pepper, the seeds are separated from it. The seeds are naturally dried and stored in cotton bags for three to four years.
And a little more about selection.
Important! Although pepper is a self-pollinating plant, cross-pollination is also possible. Therefore, when growing different varieties of sweet peppers, it is necessary to isolate the plants that are left for seeds.
How to choose the right variety
Many gardeners deciding to grow pepper are faced with a variety of varieties that can be purchased, and the question immediately arises what to choose?
An interesting fact: all varieties have differences not only in color, but also in the shape of the fruit.
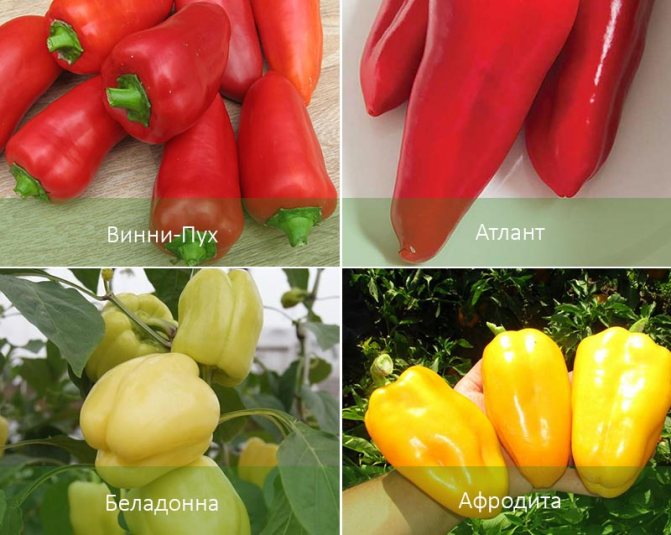
There are elongated, cuboid, spherical, curved and other shapes. By weight, there are varieties weighing more than 190 grams, and in length they can reach 30 cm.The color of the fruits depends on the stage of ripening and can be either light green or purple, but ripe specimens are colored more diversely and are found in red, yellow, orange, brown, etc.
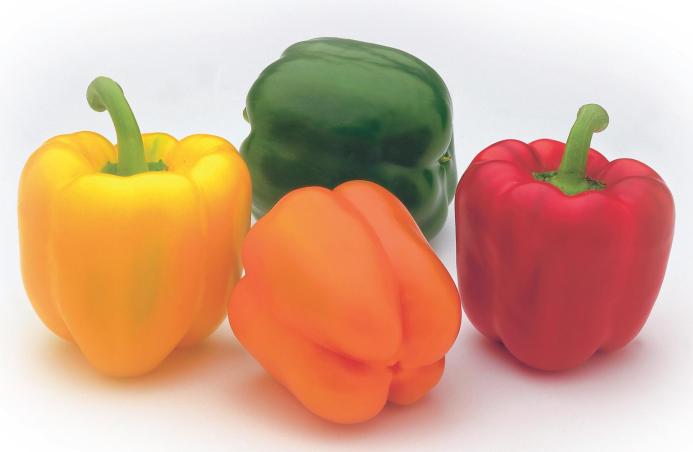


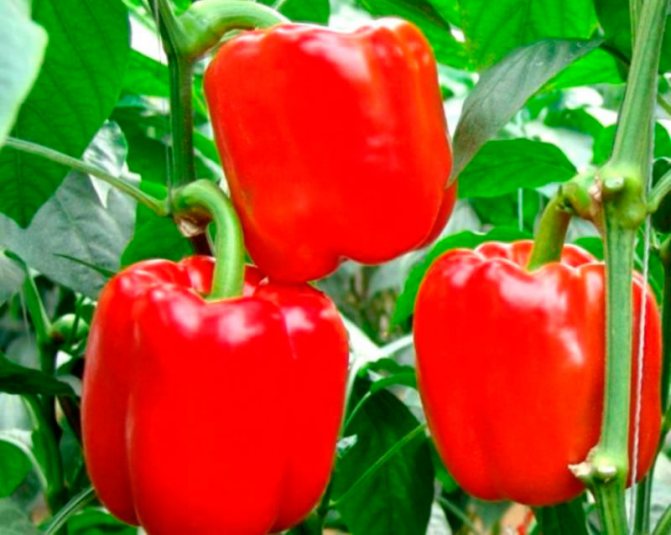
Bell pepper varieties
For greenhouse cultivation, gardeners most often choose the following varieties:
- orange miracle - refers to early maturing hybrids. The fruits are cube-shaped and bright yellow in color;
- alenushka - a hybrid culture with fruits in the form of a pyramid and red color;
- Buratino - is an early ripe hybrid variety with fruits - elongated cones, with smooth skin and red color;
- tenderness - peppers have a delicate pulp, have the shape of a pyramid, red. It is an early maturing variety;
- Astrakhan - the culture is characterized by coarse pulp, conical shape, is a mid-season variety.
Tall varieties need support
Tall sweet peppers need to be tied. Low-growing varieties of pepper can not be tied up, but the presence of a support contributes to uniform ripening of fruits, easier care and high-quality harvesting. Traditional wooden pegs are used to create the support. The plants themselves are protected by other high-growth crops. The wind through such protection will not blow so much. We form a bush - we increase the yield of a vegetable


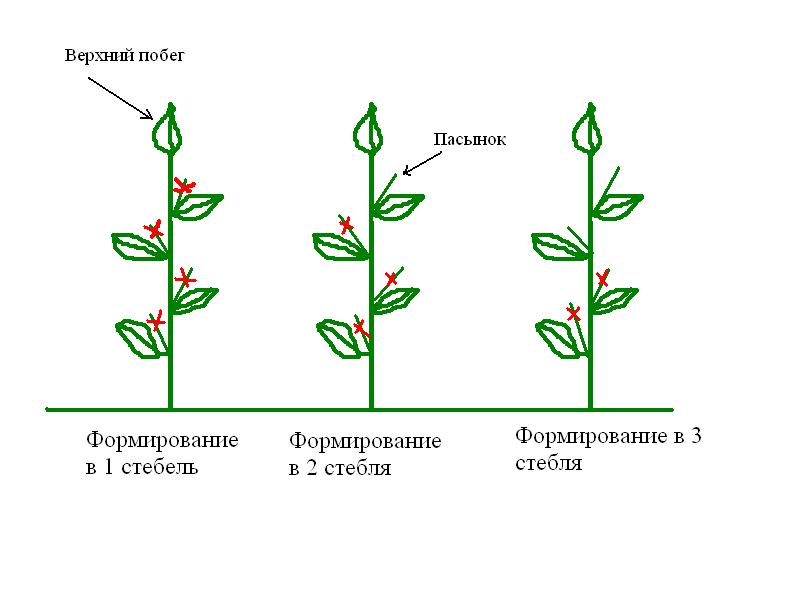
Formation of the plant is very important for obtaining high yields. Many breeders believe that it is impossible to get the most out of a plant without a properly designed form. Bush formation methods:
- They create a skeleton of a bush: in the first fork, only the two strongest shoots are left. On skeletal shoots, 2 branches are also left, one of which will grow vertically, and the second directed to the outside. It is recommended to remove internal shoots. When properly shaped, a pepper bush can grow up to 1.2 m in height.
- The skeleton of the bush is created: two shoots are tied up in a vertical direction. In each node, 1 external shoot is left. With such a formation, it is necessary to plant the plants at a distance of up to 50 cm, install supports and pull horizontal strings. The bush is able to rise more than 2 m in height.
Tillage and fertilization process
To cultivate the soil should begin in autumn, immediately after harvesting the vegetable plant preceding the pepper. To begin with, it is worth chopping up plant residues.If the fields are littered with annual weeds, it will be necessary to stubble the soil in one or two tracks to a depth of 6-10 centimeters using disc cultivators.
If the fields are clogged with root weeds, additional stubble cultivation is required to a depth of 10-12 centimeters using plowshares. If we are talking about the southern regions, then it is optimal to carry out additional stubble cultivation to a depth of 16-18 centimeters. After these procedures, mineral and organic fertilizers must be applied to the site.
Organic fertilizers are applied under the plow in the autumn season. In the spring, manure can be used if it is rotten. Fresh manure and chlorine-containing fertilizers are contraindicated under pepper plants.
If the amount of nitrogen fertilizers exceeds the permissible norm, then the plants form a continuous vegetative mass, due to which the yield of fruits and their quality is sharply reduced.


Seeds need to be prepared for sowing
Features of choosing a suitable variety


Given the huge variety of species, it is often very difficult to choose seeds for planting, giving preference to any variety. In this case, it will not be superfluous to determine the main selection criteria:
- hybrid or variety?
- ripening period;
- place of growth;
- color, size and shape of the fruit.
Before making a choice, you need to study the main characteristics.
Novice gardeners do not always understand what is the difference between a variety and a hybrid. Let's try to understand this issue.
Variety - these are selected the best specimens, breeders are working to improve the taste and yield, taking into account the place of growth. The advantage of varietal peppers is the ability to harvest seed on your own.
Hybrid varieties obtained by crossing different varieties.
They have several advantages:
- immunity to fungal diseases;
- abundant fruiting;
- great taste.
The disadvantage is the impossibility of self-harvesting of seed.
Important! The seed bags of the hybrids are marked with F1.
Selection by maturity
Experienced gardeners recommend planting varieties with different ripening periods on the site. Thus, you can provide yourself with this useful vegetable for a long period.
Pepper has different ripening times:
- early (ripens 2.5-3 months);
- middle (112-120 days);
- late (reaches maturity after 145-150 days).
Selection by place of growth


An important role in the choice of seed is played by the place of cultivation:
- open ground;
- heated and unheated greenhouses;
- film shelter;
- windowsill or balcony;
Early maturing and medium varieties are most suitable for growing outdoors:
- "Kapitoshka";
- Avangard;
- "Boatswain";
- "Orion".
For heated greenhouses, hybrid tall varieties with large fruits are suitable. They are distinguished by the duration of fruiting and high productivity. For these purposes, the following varieties are suitable:
- Atlant;
- Alyonushka F1;
- "Cardinal";
- "Prince Silver".
In an unheated greenhouse, it is best to plant early ripening peppers on seedlings:
- "Actor";
- "Mastodon";
- "Nafanya";
- Nice F1;
- "Jubilee Semko F1".
Under a temporary film cover, it is better to plant varieties of early and medium ripening periods:
- Ether;
- F1 Adept;
- Baliko F1;
- Wonder Giant F1;
- Chelubey.
For growing in an apartment, and growing on a balcony, the following are suitable:
- Jalapeno;
- Hungarian yellow;
- Maikop 470.
Selection according to the shape of the fruit


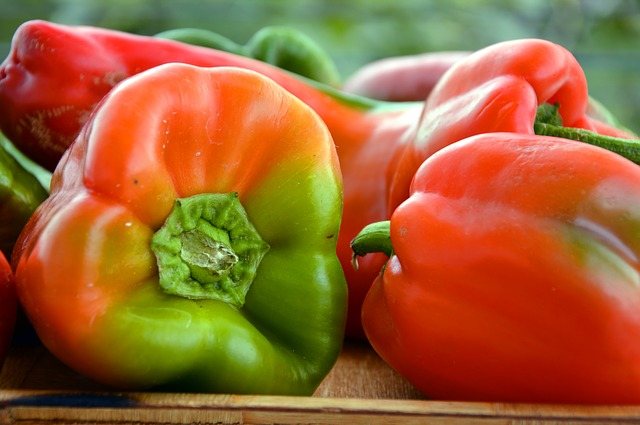
Shape and color are important factors when choosing a variety.
Peppers can take the following shape:
- spherical;
- cylindrical;
- oblong;
- conical;
- proboscis;
- heart-shaped;
- prismatic.
The color range is quite varied - from pale yellow to dark purple. The weight of each fruit can vary from 25 to 650 grams.
Possible problems with seedlings and ways to solve them
| Problem | Cause | Remedies |
| Seeds did not sprout, or rarely sprout | 1. Poor quality seed 2. Low air and soil temperature. | Raise the room temperature to 26-27 degrees |
| Real leaves are not formed | Lack of lighting | Organize additional lighting with fluorescent lamps |
| Pulling seedlings | Excessive nitrogen | It is recommended to use nitrogen-containing fertilizers in limited quantities during the first feeding |
| No ovaries | 1. High humidity. 2. The temperature is too high. 3. A sharp drop in temperature. | Treat the plants with the "Ovary" preparation. |
| Falling flowers | 1.Dry soil. 2. Excess nitrogen. 3. Low temperature | Timely watering. When the temperature drops, cover the seedlings with polyethylene. |
| Decay of fruits | Prolonged cold snap | Treat plants with Uniflor-Bud |
| Darkening of the stem | Disease of a plant with a black leg as a result of waterlogging of the soil. | Replace the soil, treat the plants with Fitosparin |
In order for the seedlings to be strong, healthy, and can please with a generous harvest, it is necessary to follow the recommendations for planting and care, as well as timely take preventive measures to prevent fungal diseases and pests.
Description, conditions and technology of cultivation
The description of bell pepper should start with the fact that its homeland is South America, from where the seeds were brought to Europe by the Portuguese at the beginning of the 16th century. Gradually, the vegetable culture gained popularity and spread throughout the continent. Sweet pepper came to Russia from Bulgaria in the 17th century, receiving the characteristic prefix "Bulgarian" to its name. That is why the vegetable is called Bulgarian.
The culture in Latin is called Capsicum (capsicum) and belongs to the nightshade family. This group includes potatoes, tomatoes and eggplants. These plants can coexist successfully in the same greenhouse and help each other develop successfully. It is better not to plant next to cucumbers, squash and zucchini. It is not easy to create suitable conditions for the cultivation of bell pepper in the conditions of central Russia and the Moscow region: the construction of a film shelter will be required. An alternative can be the choice of a suitable early maturing variety, which will have time to give a full harvest before the onset of early autumn drops in night and day temperatures. The fact is that bell peppers are a heat-demanding culture. For successful growth, development, flowering and fruit formation, an average daily temperature of at least +18 ° Celsius is required. As a predecessor crop, it is better to choose legumes or vegetables, under which a large amount of organic fertilizers is applied (cucumbers, zucchini, potatoes, herbs).
Modern technology of growing bell peppers dictates the conditions for irrigation. This is a crop that is demanding on soil moisture. However, it absolutely does not tolerate the systematic wetting of deciduous mass. Therefore, watering is carried out exclusively at the root. Adequate sunlight is required. Does not tolerate shading. However, in order to prevent the risk of sunburn on foliage, thickened plantings should be carried out. 12-15 roots can be planted per m2. This will affect the yield for the better, since the plants will protect themselves, or rather their neighbors.


How to fertilize bell pepper
Experienced gardeners say that the best option for feeding peppers is active mulching with freshly cut grass. Moreover, the thicker the layer of mulch, the better. And then the inhabitants of the soil will do everything for you. By processing mulch, they will nourish the soil with organic matter that your garden needs.


It is not the plant itself that needs to be watered, but the grass spread out in a layer on top of the soil. For mulching, there is one rule: you cannot dig up the ground together with mulch, otherwise putrefactive processes will begin to form, which will lead to diseases of the pepper.The mulch should be on the surface of the garden until the end of the season. More details in the next video.
Active mulch (video)
How to grow bell peppers
The first thing to start with when growing bell peppers is to learn the theory. After all, each culture has its own character and makes its own special requirements for the gardener. To get a good harvest, you have to learn and work hard. And it will be very disappointing if our gaps in knowledge of how to grow bell peppers lead to the death of a plant or a lack of harvest.
How to grow bell peppers so that the harvest will delight the gardener with both the quantity and quality of the product?
First rule: warm.
The main thing you should know about pepper is that it is a very thermophilic plant. Therefore, bell pepper grows only at temperatures from + 18 ° C to + 25 ° C. When the thermometer reading drops below + 18 ° C, the development of the pepper slows down. And at a temperature of + 13 ° C, it stops altogether.


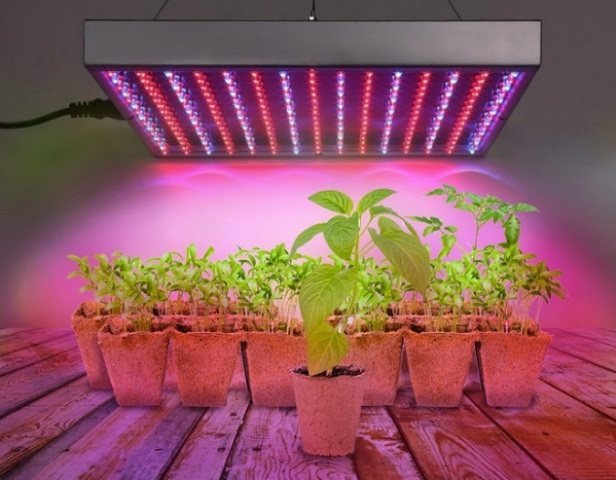
Second rule: light.
Also, bell peppers need a fairly large daylight hours for development. Gardeners begin sowing pepper in January (if a heated greenhouse is available) or in February (if transplanting to an unheated greenhouse or greenhouse is planned). With such an early sowing, additional supplementary lighting of the plants will be necessary. Pepper does not even tolerate partial shade. Phytolamps are best suited for supplementary lighting of seedlings.


Why start sowing so early? In order for the pepper to be able to give the maximum harvest, which can be grown before the first cold weather. In addition, there are late ripening varieties of pepper. They are also sown early (in January).
It is desirable that by the time of planting the plants are strong, but do not begin to bloom. This happens approximately 70 days after sowing. Therefore, I plant sweet peppers from February 10 to 20, choosing medium and early ripening varieties.


For the lazy: if you do not want to bother with highlighting the pepper, then sowing pepper in the first week of March is optimal for you. At this time, it is already quite light during the day, and the thermometer is slowly creeping up. But in this case, you should choose an early ripening pepper variety.... Otherwise, you run the risk of not waiting for the harvest or getting a small return. You can read all the information about the ripening dates (early, middle, late) on the package with the seeds.
Well, we will start growing pepper with seedlings. So how to grow bell pepper seedlings?
How to grow correctly: choosing and preparing a site for planting
The main criteria and recommendations for the selection and preparation of soil on the site:
- It is worth giving preference to sunny, well-heated areas that have protection from cold winds;
- It is optimal to use the beds after cucumber, cabbage, carrots, onions, zucchini. Poor predecessors include tomatoes, eggplants, and potatoes. It is not recommended to grow peppers for two years in a row in the same area;
- You should not grow a crop on sandy and clay soils, in lowlands, as well as in areas that are characterized by stagnant moisture. With an increased level of acidity, lime is introduced into the soil in the fall;
- High beds are prepared for planting, this will allow the root system to stay warm. The beds are made out in the west-east direction;
During spring digging, humus, compost and superphosphate are introduced into the soil.
- It is quite effective to grow a pepper crop in "warm beds" using biofuels. To prepare it, they dig a trench 40-50 cm deep. Manure mixed with chopped straw or compost is placed on the bottom. A soil layer is laid on top of this mixture. A few hours before transplanting seedlings, the soil is spilled with hot water so that the biofuel begins to generate heat. The root system of the culture, due to being warm, will be protected from minor cold snaps.In addition, the bottom layer will serve as an additional source of plant nutrition.


Qualities of "adult" seedlings


Knowing how to grow pepper seedlings, what competent agrotechnical measures are necessary, taking care of our young pets, we will be able to grow strong seedlings that will successfully turn into adult, healthy plants.
And for a successful transplant into the garden, they must meet the following characteristics:
- The seedlings are 60-80 days old.
- The height of young peppers should be 17-20 cm.
- Healthy plants must have 7-10 well-developed leaves.
- They can have small buds and a strong stem 3-4 mm thick at the roots.
Our seedlings will be ready to move to their permanent place of residence when the soil in the garden warms up to + 14 ° -16 ° C (in the root layers it is 10-15 cm deep).
And when there is no longer the threat of sudden frosts (as a rule, this period falls on the end of May-beginning and mid-June).
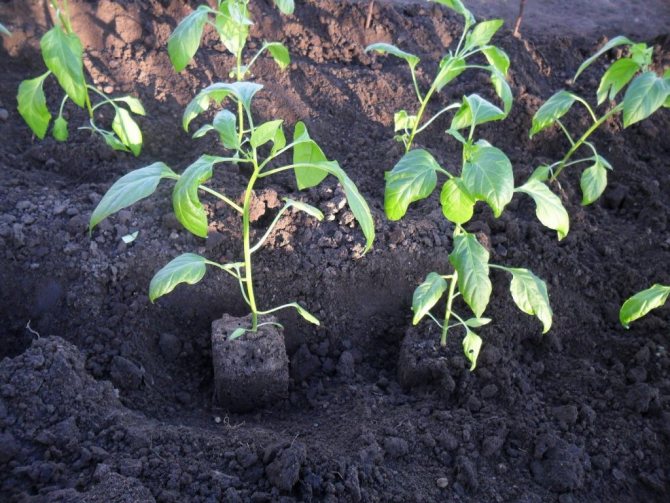
Before planting, young seedlings should be well watered to reduce possible root injuries.
We got acquainted with the traditional method of growing sweet pepper seedlings.
But I want to invite you to watch a few videos of Yulia Minyaeva about another method of growing seedlings - "in a snail". I liked it very much. I will try to plant some of the seedlings using this method.
See you soon, dear readers, and success in growing strong and healthy seedlings!
How to prevent hypothermia of plants?
Immediately after transplanting, pepper seedlings should be protected from frost. Tents made of wooden blocks, cardboard, burlap and other materials will be an excellent protection of plants from possible frosts. These tents are used to shelter plantings at night, with the onset of the morning the shelter is opened. In the presence of prolonged cold weather, a portable temporary film shelter is used.


How to grow bell pepper seedlings


Planting seedlings according to the lunar calendar
Many gardeners adhere to the lunar calendar to choose the day of planting a vegetable. Each year is different days, but the rule is one - you need to land when the Moon is in the constellation of the fertile signs (Pisces, Cancer).
What you need for seedlings
So, to sow seeds, you will need:
- the soil;
- pots or boxes;
- planting material.
Planting material, seeds, can be selected in any specialized store. Of course, with a huge number of multi-colored labels, eyes run up. What should you pay attention to when choosing varieties? How to choose bell pepper seeds?
How to choose pepper seeds


First of all, you need to start with the choice of seeds, because the quality of seedlings and fruits depends on their quality. The choice of seeds depends on the area where you live. It is better to choose zoned breeding. For the regions of Siberia and the Urals, special marks should be on the seed bags: “Tested in Siberia”, etc. Also, note what is written about the ripening period. If you have a heated greenhouse, you can of course opt for a late-ripening pepper. But if you are going to plant peppers in an unheated greenhouse or on an open garden, then the choice should be on early and mid-season varieties. There are no special selection criteria for the southern regions, since bell peppers come from warm regions and grows and ripens well there.
Seed treatment before planting
After the seeds for planting are purchased, they need to be carefully examined. Sort out damaged or too small seeds. They should not be used for sowing. Next, you should make the treatment against the fungus. Store seeds are traditionally processed in advance, homemade seeds will need to be soaked for 25 minutes in a pink solution of potassium permanganate.
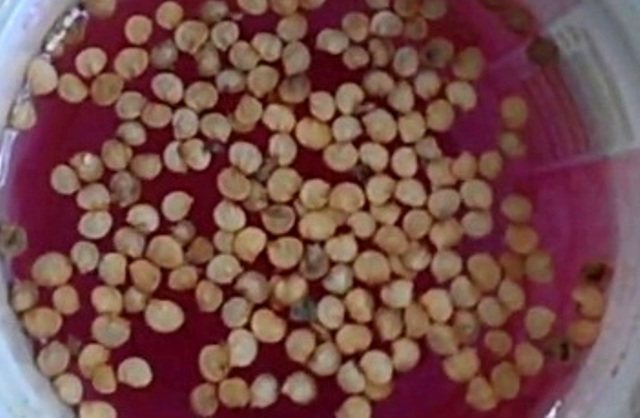


Processing pepper seeds with potassium permanganate
In addition to traditional potassium permanganate, such preparations as "Maxim", "Vitaros" are suitable for processing.They can also be purchased from specialized stores. Dissolve the drug in water, and wrap the seeds in a cloth bag and dip in the solution.
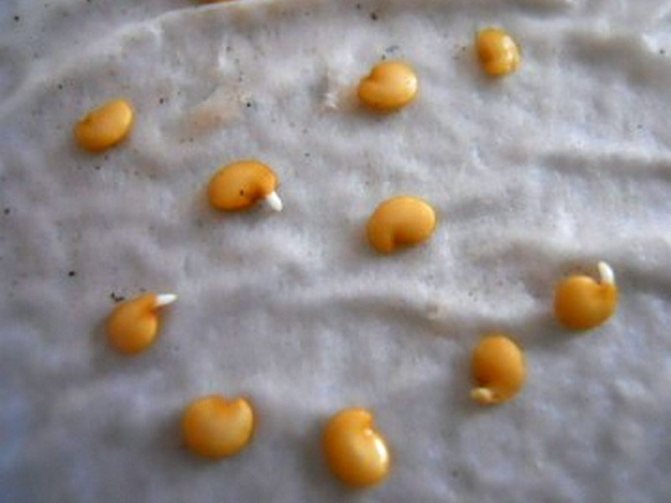


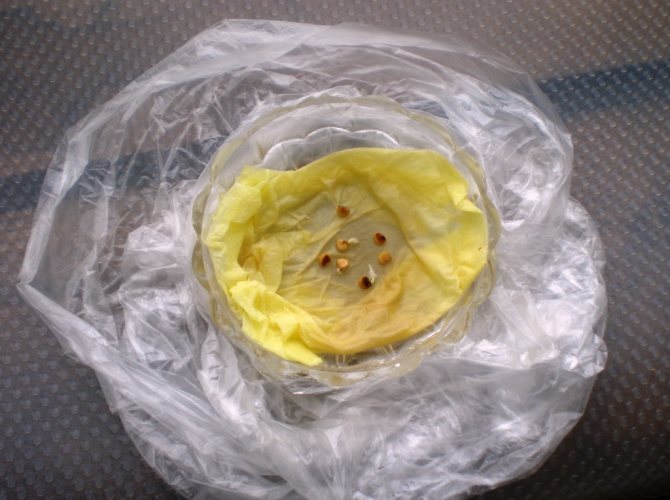
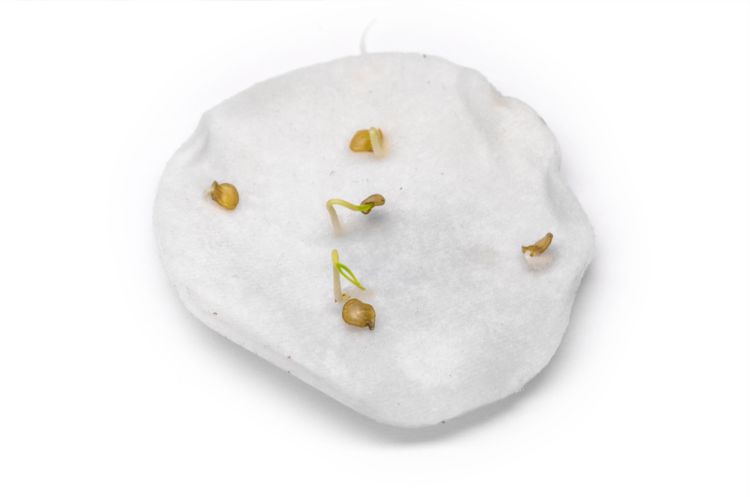
Pecking pepper seeds
After that, put the seeds on a damp cloth, which you place in a very warm place (+ 25 ° C - + 30 ° C), covered with a transparent lid to create a greenhouse effect. Wait for the seeds to start pecking and sow them in the soil. It is very convenient to carry out the initial sowing in peat tablets. And when the sprouted pepper seedling gets stronger, without damaging the roots, place it together with the tablet in a more spacious pot, filling the space with specially prepared soil for pepper seedlings.
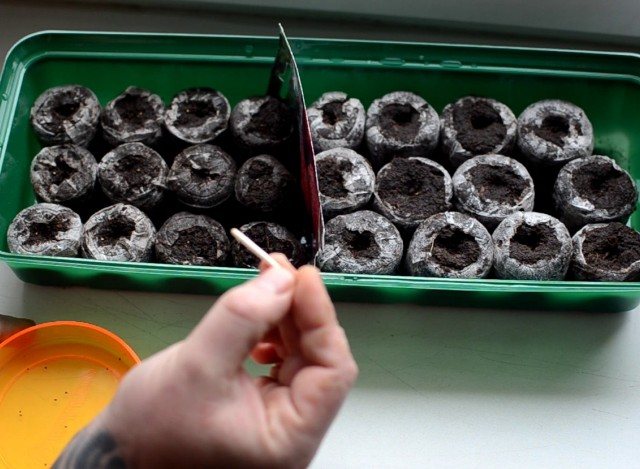


Sowing pepper in peat tablets