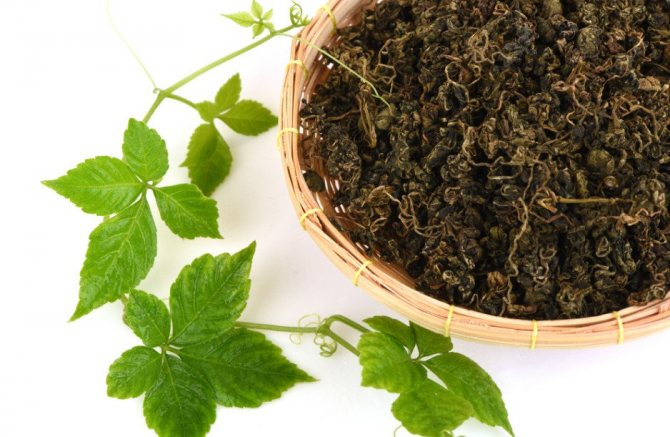
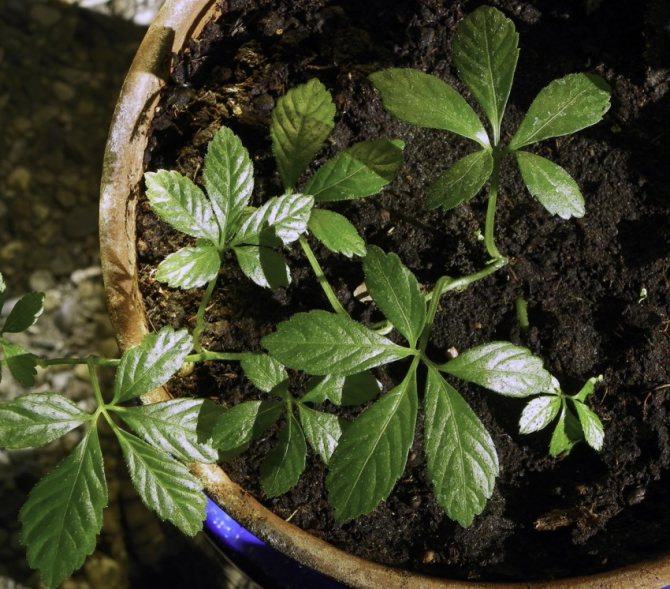
Growing gynostemma
Gynostemma is a dioecious plant, in order to set seeds, you need two vines of both sexes.
It is possible to distinguish the sex of a gynostemma only during flowering: male panicles are longer than female ones, also in male flowers the stamens are longer and pistils are reduced.
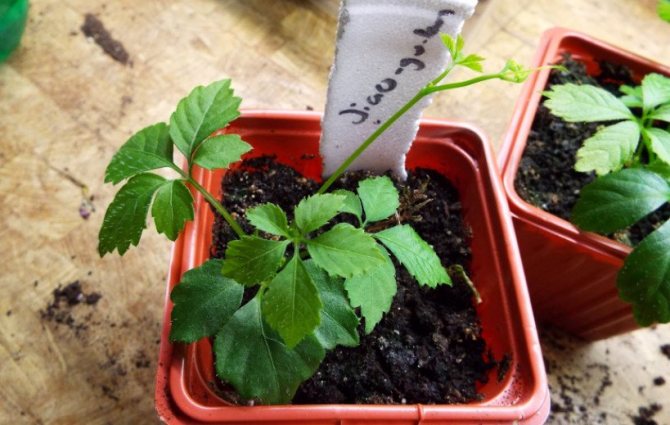
Gynostemma is a small plant, therefore, having planted with seeds, it is better to renew it with cuttings that take root well.
Before sowing, soak the seeds in warm water for a day, then they are sown in compost in pots to a depth of 2 cm.

Growing features
When the seedlings grow up, support them.
Gynostemma prefers rich, drained moist soils. Choose a place for it protected, sunny. It is useful to cover the roots with compost. In dry conditions, spray the vine in the morning with water to increase the humidity of the surrounding air. Watering should be done regularly to keep the soil moisture even.
Gynostemma is not resistant to cold; in winter, keep it on a light windowsill, without additional lighting.
Reproduction of gynostemma by leaf cuttings
A more labor-intensive method is to propagate gynostemma using a leaf with a shank. To do this, you need to cut a long branch and choose a developed and healthy shoot. Then, above the sheet plate, make an oblique cut from left to right and another one under the sheet, having previously retreated 1.5 centimeters. The resulting seedling should be planted in the ground, deepening it to the leaf plate.
After planting the cutting, the ground must be watered with a root solution and press the soil around the shoot. Then the area around the seedling must be covered with compost. Until the plant takes root, you should monitor the temperature and moisture content of the soil mixture.


Application in traditional medicine
In China, where traditional medicine is still highly trusted, gynostemma has been used as a medicinal plant since the 13th century. The Chinese love to brew tea from the leaves and believe that it is this tea that brings longevity. This traditional Chinese medicine is primarily recommended for physical and emotional stress. Today, the herb is included in many dietary supplements and tea mixtures.
In addition, the plant helps to get rid of many diseases, tone the body, relax the nervous system, turn on the inhibition of aging processes, improve metabolism, cleanse the body, and improve the saturation of cells with oxygen.
The beneficial effect of the plant includes the digestive, immune, nervous, cardiovascular and reproductive systems.
Among lovers of oriental medicine, food supplements from ashwagandha are popular to strengthen the nervous, cardiovascular systems, and overall health of the body.
Long-term use of drugs based on gynostemma as part of complex therapy can improve the patient's condition with such diseases:
- diabetes mellitus, since it has the effect of lowering blood sugar;
- hypertension, due to the ability to stabilize blood pressure;
- obesity, as it helps to improve metabolic processes and normalize weight;
- atherosclerosis, because it removes bad cholesterol from the blood.
Gynostemma is also used as a prophylactic agent against:
- blood clots;
- malignant tumors;
- the development of hypertension;
- stroke;
- heart attack.
Traditional healers advise healthy teas to be drunk by athletes to increase physical activity and endurance, people whose work is related to mental work, or those who are engaged in heavy physical exertion.
Did you know? In addition to brewing tea, gynostemma leaves are also used in Asian cuisine as a sweetener and seasoning for various dishes. The first mentions of this culture describe just its nutritional qualities and use in case of hunger or lack of food. They date back to 1406 and are contained in the Chinese treatise Medical Aid for Malnutrition.
Reviews of doctors and patients
Gynostemma five-leafed is not used in domestic pharmacology, but has found widespread use in folk medicine. According to doctors, Jiaogulan is not a medicine and cannot replace drug therapy, but this plant can be used as a prophylaxis for many diseases. After the course of taking Jiaogulan, patients noted an improvement in well-being and sleep, and resistance to stress. It is noticed that if you take drugs based on Gynostemma five-leafed while losing weight, the process goes faster due to better metabolism.
Gynostemma five-leafed from the Pumpkin family is a climbing liana that naturally grows in the countries of Southeast Asia, China and Japan. Over the past decades, it has been actively studied in Europe and other regions of the world as a valuable medicinal plant, although it has been used in traditional Chinese medicine and as a food product since 1400. Decoctions are prepared from its leaves and teas are brewed, which have a pronounced tonic, anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, immunomodulatory, adaptogenic effect.


In eastern countries, the plant is called Jiaogulan, Jiaogulan, Jiao Gu Lan or Qiaogulan, which literally translates as "climbing orchid." Gynostemma five-leafed does not require special care and can be used for decorative purposes to decorate garden plots. The plant, due to its amazing healing properties, is also known as the herb of immortality or the herb of longevity, southern or cheap ginseng.
Spread
Gynostemma is widespread in China, India, Malaysia, Vietnam, Korea, Japan, Bangladesh, Sri Lanka and other Asian countries. It grows in forests, among clusters of shrubs, along road sides, and occasionally occurs in the mountains at an altitude of up to 3000 m above sea level.
Gynostemma is planted in the open field as a ground cover plant covering vertical surfaces. At home, it is also planted in flowerpots as an ampelous culture, while its shoots droop down. By the way, when the gynostemma was brought to the Europeans, at first they used it only as a room culture and only after a while they transferred it to the flower beds in the gardens.
Ampel plants are decorative flora with hanging shoots and climbing stems that look great in hanging pots and boxes. These are verbena, lobelia, fuchsia, pelargonium, dichondra, petunia.
Content
- General information
- Varieties and types
- Gynostemma planting and care in the open field
- Watering the gynostemma
- Soil for gynostemma
- Gynostemma transplant
- Fertilizer for gynostemma
- Flowering gynostemma
- Pruning gynostemma
- Preparing gynostemma for winter
- Gynostemma seed cultivation
- Reproduction of gynostemma by leaf cuttings
- Gynostemma pests
- Gynostemma diseases
- Gynostemma five-leafed beneficial properties
- Contraindications to the use of gynostemma
- Conclusion
Beneficial features
Gynostemma is credited with the following healing properties:
- anti-lipid;
- fortifying;
- immunomodulatory;
- sugar reducing;
- antioxidant;
- anti-aging;
- calming;
- tonic;
- hematopoietic;
- anti-inflammatory;
- adaptogenic.
Did you know? Top most expensive teas in the world include a ginseng drink called Tienchi. It sells for $ 17 per 100 grams. It is believed to be very beneficial for the human body. To make the drink even more useful, gynostemma leaves are mixed with it.
Disease and pest control measures
In general, diseases and pests rarely affect this vine. However, if you do not follow the rules of agricultural technology, certain problems can still arise.
In particular, with stagnant moisture, powdery mildew, white and root rot, and bacteriosis may appear at the roots. In the first three cases, it is enough to simply remove the damaged parts and spray with a fungicide. If the liana is struck by bacteriosis, it will have to be dug up by the roots and burned.
Of the pests on gynostemma, aphids and spider mites are most common. To combat these pests, spraying with insecticides is carried out, however, after such treatment, it will not be possible to eat the leaves and stems of the crop.
Gynostemma five-leafed - the most famous species
Five-leaf gynostemma grows in China, Vietnam, southern Korea and Japan, India, Bangladesh, Laos, Indonesia and other Asian countries. In Russia it is also known under the trade names "jiaogulan", "jiaogulan".
This vine is evergreen, herbaceous or semi-lignified. Distributed in forests, shrubs, lowlands, roadsides, also occurs on mountain slopes about 3000 m above sea level
The shoots of Gynostemma pentaphyllum are climbing, angularly furrowed, usually glabrous, occasionally pubescent.
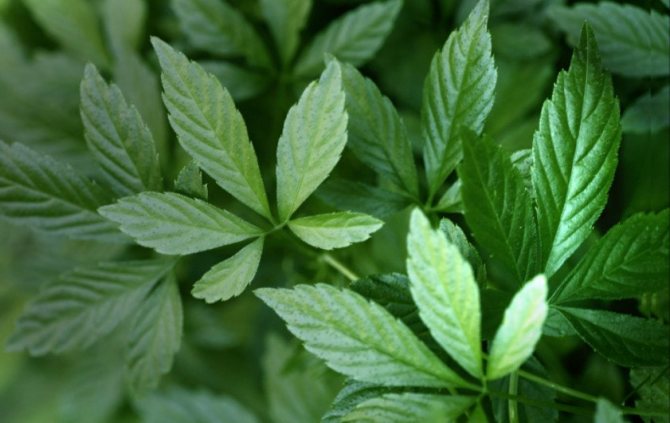
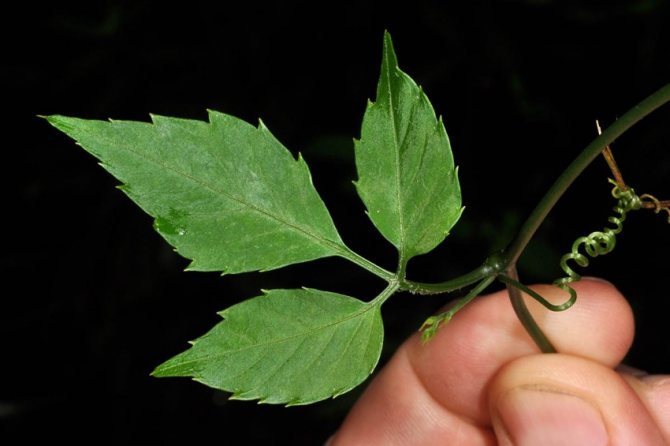
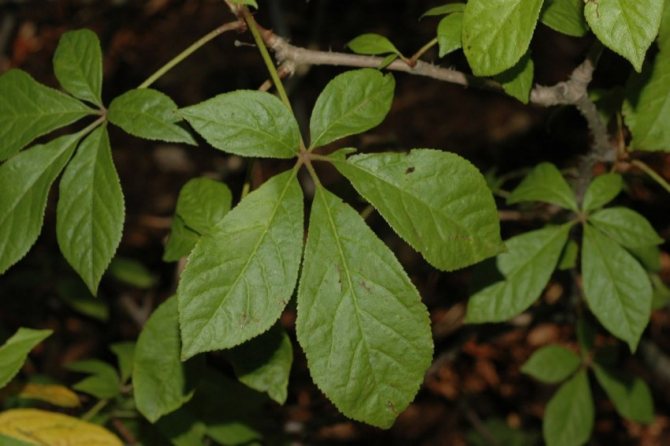
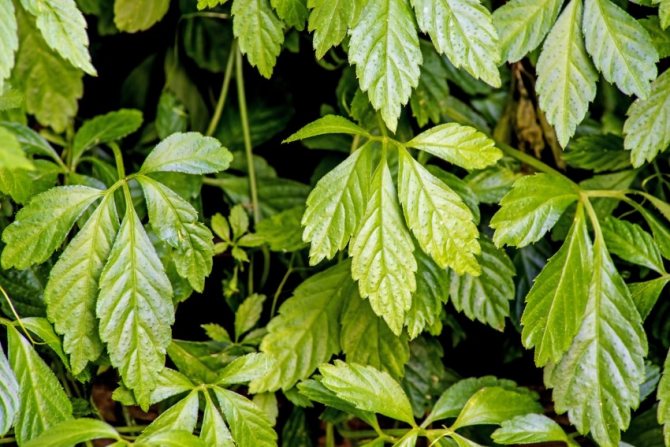
Shiny leaves growing on long petioles are located opposite to the shoots. In shape, they are similar to girlish grapes: finger-shaped, usually consist of 5, less often 3, 7, 9 lanceolate leaves with jagged edges.
We also recommend reading: Temperature regime for potatoes
Gynostemma blooms once in July. The flowers are inexpressive, pale green or white, forming axillary panicles. The berries are pea-sized, black, with 2 seeds.
Description
Gynostemma is a vine species known in botanical circles as Gynostemma pentaphyllum. In ordinary life, you can find the following names - cheap, southern ginseng, jiaogulan or jiaogulan. But the most popular is the "herb of immortality"
Belong to the genus Pumpkin, at the base it has woody shoots. The leaves are large, consisting of diamond-shaped lanceolate toothed leaves (there can be from 5 to 9), reminiscent of wild grapes. The leaf of the gynostemma is dense, bright green, changing its color to crimson by autumn.
Gynostemma, a climbing plant that drives out long whips and tendrils, with which it clings to supports. Braids trees, trellises and any vertical supports, transforming them into a dense green carpet.
It blooms with small white and light green male and female flowers, collected in panicle brushes up to 15 cm long. After flowering, forms edible fruits, small black berries with a small number of seeds inside (usually 2 or 3). The flowering period is 1.5 months, from mid to late summer.
"Grass of Immortality" is unpretentious, calmly endures cold winters and survives at a temperature of -18 0C, if properly and well insulated.
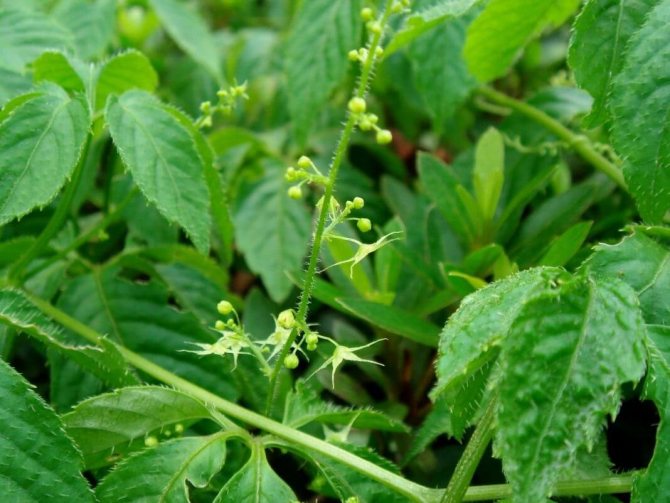


Bloom
Gynostemma five-leaf tea
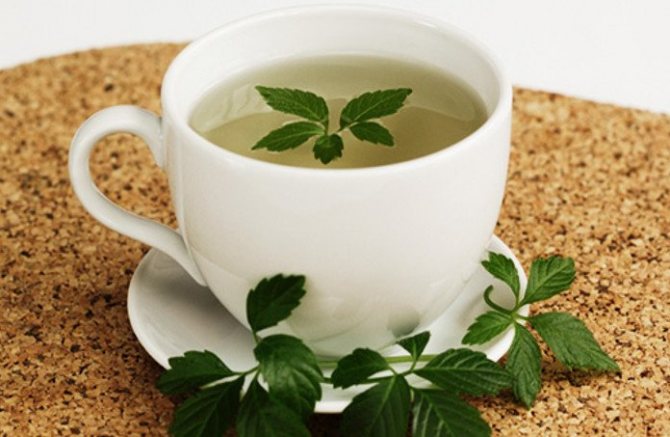
Unlike other herbs, broths are not prepared from gynostemma five-leafed, but its leaves are brewed in the form of tea. Tea:
- 2-3 tsp fresh or 1-2 tsp.dry leaves of gynostemma;
- 250 ml hot water.
Tea from this unique plant has a pleasant sweetish aroma and taste with a little astringency.
Brew the gynostemma with not very steep boiling water, let it brew for 5 minutes - the tea is ready! The same leaves can be brewed repeatedly up to 6 times, but the finished drink cannot be stored - the tea should be drunk immediately, and a new portion of gynostemma should be brewed for the next tea party.
How to use
Jiaogulan is used in medicine in 4 types: medicinal extract, tea, capsules and alcohol infusion. Each of them has its own characteristics and rules of use:
Extract. Sold in powder form in packs of 100 g. One box of Jiaogulan is enough for several courses of treatment. Take an extract of 0.5 g three times a day before meals, stirring it in warm water. During the weekly treatment course, you need to drink 20 servings of half a gram.
Herbal tea. Gynostemma has a pleasant tart taste, and a small amount of honey can be used to sweeten it. As a preventive measure, tea is drunk 2 cups a day; during the treatment of the disease, the number of servings can be doubled. To prepare a medicinal broth, you need to bring water (250 ml) with dried grass (1 teaspoon) to a boil and keep on low heat for 5 minutes. When the tea has cooled to a comfortable temperature, you can drink it before eating. The course lasts up to 3 months.
Alcoholic infusion. To prepare the medicine, you need to pour 50 g of dry grass with 500 ml of vodka and leave the bottle in the dark for two weeks. When the funds are infused, they filter it and drink a teaspoon from 1 to 3 times a day.
Capsules. Take a course for a week twice a day, one capsule half an hour before meals. It is advisable to take Jiaogulan no later than 4 pm.
The choice of the form of the drug depends on personal preference and health status. It is advisable to consult a doctor before taking Gynostemma five-leafed. The therapist will suggest the appropriate dosage and duration of the course, taking into account the state of the body.
Gynostemma care


Watering should be frequent, regular and abundant. As a rule, it is carried out once every 1–1.5 weeks, while it should be borne in mind that the soil near the plants should be constantly slightly damp (not damp). If there is a prolonged drought, then every evening or morning the foliage of such vines must be moistened from a sprayer, for this they use lukewarm water. When the bushes are watered or it rains, the surface of the soil around them must be loosened, as well as all the weeds.
In the first year of growth, the gynostemma does not need to be fed, since it will have enough of those nutrients that were introduced into the soil when preparing the site for planting. In subsequent years, it is recommended to feed such a liana with Kemira's solution, while under 1 bush it is necessary to add from 30 to 40 grams of the drug. This complex fertilizer contains all the nutrients that are needed for the normal growth and development of such a crop. In the case when foliage is used throughout the season for the preparation of various dishes (salads, soups, etc.), then it is only necessary to feed the bushes by the root method; in this case, it is strictly forbidden to spray the foliage with a nutrient solution.
Gynostemma has a relatively low frost resistance. The bushes can withstand a drop in temperature only to minus 18 degrees, but if they are covered with a layer of snow, they will endure the winter quite well. When growing such a plant in regions with practically snowless winters, lianas will need shelter, for this they are covered with spruce branches or with a thick layer of loose leaves. When growing this crop in regions with frosty winters, it is recommended to remove the bush from the soil in autumn and plant it in a pot.Until the onset of spring, the plant is kept in a well-lit room, while the heating devices should be at a sufficiently large distance from it. The bush must be provided with the same care as for any other plant that has a dormant period.
Preparing gynostemma for winter
The culture can withstand frosts up to 18 degrees and can hibernate without any problems under high snow cover without shelter. However, with snowless or too cold winters, the root system without shelter can freeze out.
To avoid this problem, you should cut off the ground part of the plant at the end of October and cover it with a layer of dry foliage, spruce branches or peat. In the spring, when the threat of frost has disappeared, the gynostemma is opened and its green shoots begin to grow and curl again.


Procurement of raw materials
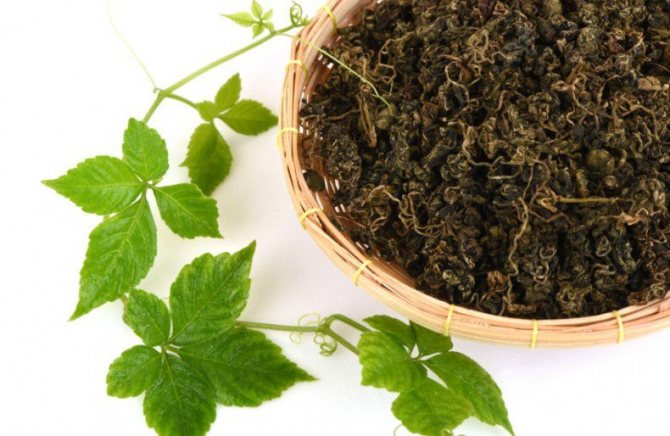
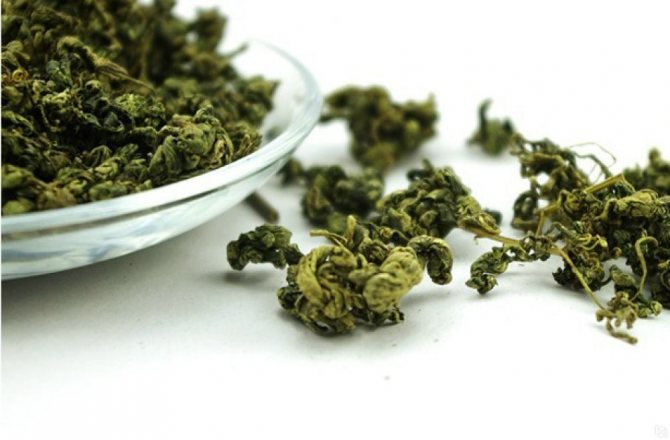
Jiaogulan leaves are harvested in the summer. They are torn off, cleaned of impurities and damaged leaves, laid out on paper or natural fabric in a thin layer and dried in the shade in the open air for 10-14 days, periodically turning them over. After drying is complete, the raw materials are packed in suitable sized cloth bags, glass jars or plastic containers. Store the finished raw materials for a year in a dry place.
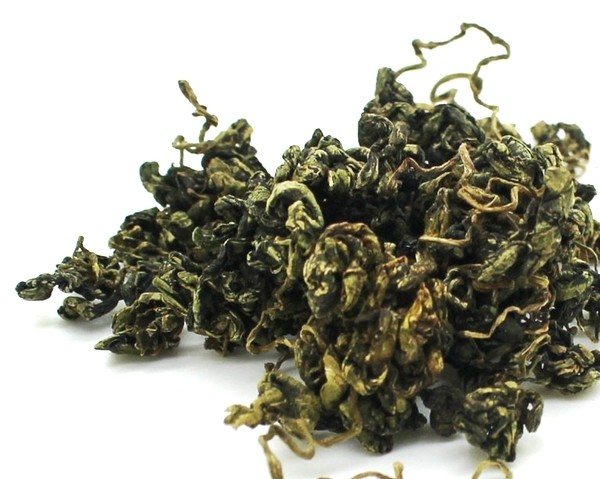


Dry leaves of gynostemma quintuple
Despite the fact that gynastemma can be successfully grown at home, for use for medicinal purposes it will have less valuable useful properties than raw materials that grow in their natural range. The same applies to plants grown in greenhouses on an industrial scale. However, such a plant can still be used for making tea or salads. The quality and chemical composition of the jiaogulan herb depends on the region of growth.
General information
In the wild, the branches of the culture are lignified. The plant's leaf plates are large, finger-shaped, and divided into five separate lanceolate leaves with finely toothed edges. In the summer they have a dark green tint, and in the fall they turn red. Outwardly, gynostemma resembles wild grapes.
The flowering time of the plant is in July and lasts until the end of August. Inflorescences are small, having a racemose-paniculate shape of a white or olive shade. With the onset of the first frost, the ground part of the culture dies off before the onset of warmth. Throughout the growing season, the branches and foliage of the plant can be cut and medicated teas made from them.
Gynostemma is grown as a ground cover that braids vertical surfaces. In the past, it was used only as an ampelous home culture, however, at the beginning of the twentieth century, the plant was transferred to garden beds.


Chemical composition
For medicinal purposes, the leaves and, less often, the seeds of jiaogulan are used. Many compounds useful for the human body have been found in the composition of the plant:
- saponins;
- flavonoids;
- polysaccharides;
- proteins;
- amino acids;
- vitamins (B1, B2, E, C);
- minerals (Se, Ca, Zn, Mg, Mn, Fe, etc.).
Gynostemma five-leaf contains more than 80 types of saponins of various structures, 4 of which are the same as in ginseng known to every medicinal plant. At the same time, in the ginseng itself, the number of saponins reaches only 28.
Important: In jiaogulan, unlike other plants of the Pumpkin family, there is no compound cucurbitacin, which is characterized by an unpleasant bitter taste and nonspecific toxic effect on the body.
Precautions
Contraindications for gynostemma pentaphyllum include individual intolerance or allergy to the plant. Also, you cannot use it for pregnant, lactating women and children due to the lack of a sufficient number of studies confirming its safety for these categories of people.
As with any medicinal plant, you should consult your doctor before taking tea or other medicinal products from jiaogulan. It is necessary to treat this plant with caution in patients with hypertension, renal failure, sleep disorders.
Video about the medicinal properties of gynostemma five-leafed:
All materials on the site are presented solely for informational purposes. Before using any means, a consultation with a doctor is MANDATORY!
Share with your friends:
Gynostemma five-leafed, known in China as Jiaogulan, is not for nothing called the herb of immortality. This exotic plant, which can be easily grown in your own garden or even at home, has many beneficial properties. In terms of the amount of active substances, Jiaogulan can be compared with ginseng.
How to collect and store gynostemma
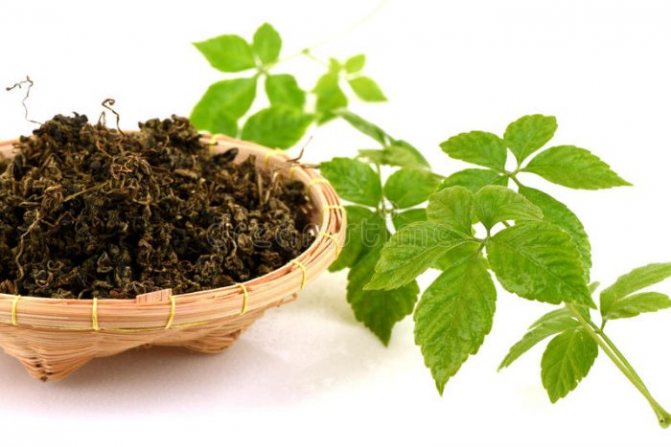


Gynostemma foliage is collected throughout the summer. The collected leaves must be dried. Fresh stems, as well as leaves, are suitable for making soups and salads, while the dried leaves make a very healthy tea.
The collected stems and foliage must be spread out in a semi-dark well-ventilated room or under a canopy outside for drying. After the raw material becomes brittle, it can be considered completely dry. The crushed raw materials are removed for storage in a dry room, first they are poured into bags or paper boxes, as well as into glass or ceramic jars with a tight-fitting lid. Ripe gynostemma berries are very sweet and edible.
Varieties and types
Gynostemma Five-leafed - the homeland of the plant is China. The culture has branched, thin, mustache-like shoots, reaching a length of 8 meters. The leaf plates are medium, compound-palmate with serrated edges on long petioles. In summer, they have a dark green tint, and with the arrival of autumn, the color changes to red. The plant blooms from July to August. Inflorescences are small, collected in large clusters of white or olive shade. After flowering, small round black fruits with seeds in the middle are formed.


In the family of this culture, there are about twenty species, among which there are gynostemma blumei, cissoides, pedatum, siamicum and trigynum... Since the plant is rarely found as a domesticated garden specimen, there is no information about its varieties.


Application methods
The most popular remedy for gynostemma quintuple leaf or "herb of immortality" is leaf tea. This drink has a pronounced tonic effect on the body, therefore it is recommended to use it in the morning. Jiaogulan tea is characterized by a pleasant spicy-sweet herbal aroma and a sweetish slightly tart taste with a slight bitterness.


Jiaogulan tea
Making tea
To make tea from jiaogulan, you can use both fresh and dry leaves of the plant. At the same time, in order to get the maximum benefit, it is important to follow the cooking technology exactly. It is better to take water for tea purified through a filter or bottled, and not from the tap. A drink is prepared at the rate of 2 tsp. fresh or 1 tsp. dry plant leaves in 250 ml of water. The optimum temperature for brewing tea is 80 - 85 ° C. After the leaves are covered with hot water, they are infused for no more than 3 minutes, and then filtered and the resulting drink is drunk. This tea should be consumed after meals. The same leaves can be brewed several times, but each time it will be necessary to increase the infusion time. Naturally, the taste and medicinal value of the plant will decrease after each infusion.
Tip: When preparing tea, it is not recommended to use steep boiling water for brewing, as in this case the taste of the drink will acquire more bitterness.
[collapse]
Contraindications to the use of gynostemma
There are no contraindications to the use of gynostemma, so it can be safely used by everyone.However, for those people who have an individual intolerance to the plant, it is better not to take funds based on it.
Hypertensive patients should be careful when drinking tea from jiaogulan, as in some cases it contributes to an increase in blood pressure. For those who suffer from insomnia, it is necessary to drink tea based on the plant no earlier than four hours before going to bed.
Future and lactating mothers should not take gynostemma-based products, since it is not known how they will affect their body.


Jiaogulan Jiaogulan Improves Cardiovascular Function
Angelica herb medicinal properties and contraindications
Diseases of the heart and blood vessels are the first and foremost cause of premature death in the world. As a result of these diseases, 17.3 million people die in the world every year. In 2013 alone, nearly 800,000 people died in the United States.
Most of the causes of heart disease are directly related to atherosclerosis, or thickening and hardening of blood vessels, up to blockage. Atherosclerosis is a disease of the arteries resulting from the deposition of plaque in the lumen of blood vessels, mainly composed of white blood cells and lipids such as cholesterol and triglycerides.
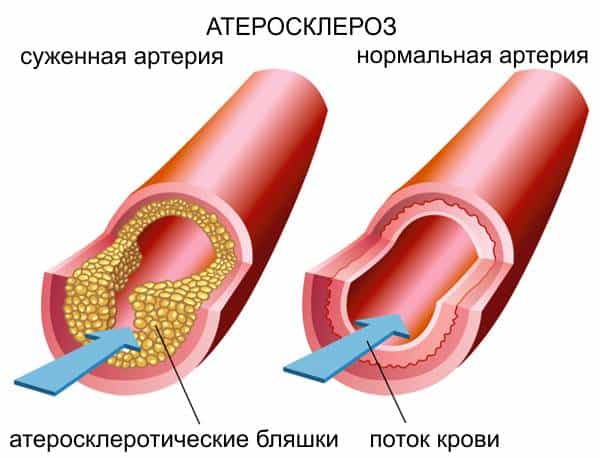

The process of development of the disease begins with damage to the inner lining of the arteries and endothelium - by the deposition of fats and cholesterol. As a result, rounded dense formations or atherosclerotic plaques appear, which impede normal blood circulation. All subsequent processes occurring in the arteries reduce the strength of the vascular walls. In addition, over time, dense scars form, as a result of which the walls of the arteries lose the elasticity necessary to maintain normal blood pressure. Risk factors for the disease can be high blood pressure (hypertension) or exposure to free radicals, such as from smoking.
Damage to the inner lining of arteries and endothelium has a twofold adverse effect.
First, it leads to lower nitric oxide production, which in turn leads to low nitric oxide levels, which causes narrowing of the arteries, increased blood pressure, plaque formation, more damage to the arteries, and less nitric oxide production. This destructive process leads to serious heart disease.
Second, when arteries are damaged, over time they lose their elasticity and become more rigid. Thus, attracting more "bad" cholesterol and leukocytes, which then accumulate in the walls of the arteries, forming a plaque.
Ultimately, when the plaque breaks down, a blood clot forms (a process called thrombosis) that can completely block blood flow and lead to heart attack, stroke, or embolism.
A heart attack or ischemic stroke occurs when blood flow to a part of the heart or brain is blocked by a blood clot (thrombus). If this clot completely blocks the blood flow of the arteries that supply blood to a part of the heart muscle or brain, then that part will cease to function. This process is fatal or, in the case of a stroke, loss of the ability to perform normal functions such as the ability to speak or walk.
In another type of stroke, a hemorrhagic stroke is a rupture of a blood vessel in the brain. The most common cause is uncontrolled high blood pressure.
Other complications caused by atherosclerosis include peripheral arterial disease, kidney disease, and erectile dysfunction.
What is really amazing about Jiaogulan is that the plant counteracts each of the individual causes of atherosclerosis mentioned above, and therefore eliminates all the complications of atherosclerosis in the beginning.
Jiaogulan Jiaogulan protects and strengthens the nervous system
Jiaogulan protects, enhances the function of the central and peripheral nervous system, mainly due to its antioxidant properties, the ability to regulate the production of nitric oxide.
Nitric oxide plays an important role in learning and memory by helping nerve cells in the brain communicate with each other. It is involved in the release of neurotransmitters, development, neuronal repair, synaptic plasticity, and regulation of gene expression.
At normal concentrations, nitric oxide protects nerve cells from damage and death. However, at high concentrations, it becomes toxic to nerve cells.
Excess nitric oxide in the nervous system is associated with Alzheimer's disease, Parkinson's disease, multiple sclerosis (MS), amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), Huntington's disease, depression.
In addition, free radical exposure has been shown to play an important role in the development of neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer's and Parkinson's disease.
In light of this, it should come as no surprise that Jiaogulan helps prevent Alzheimer's and Parkinson's, which are the 6th to 14th leading causes of death in the United States.
Gynostemma five-leafed has been shown to improve brain functions such as memory, attention, coordination, and thinking in human and animal studies, especially in the elderly. The plant is also able to protect the brain and memory from damage caused by alcohol, free radicals, as well as damage to cognitive impairment from ischemia-reperfusion syndrome and hypoxia due to stroke.
The plant is also able to protect the brain and memory from damage caused by alcohol, free radicals, as well as damage to cognitive impairment from ischemia-reperfusion syndrome and hypoxia due to stroke.
A study of elderly patients with cerebral infarction (a type of ischemic stroke) found that taking Jiaogulan for a 12-week course improved their cognitive function to the level of normal elderly people who did not experience heart problems. In addition, its positive effects exceeded those of Piracetam (a popular nootropic drug that improves brain function), which was used in a control group of patients.
Jiaogulan can prevent damage to the brain and nervous system caused by the consumption of the popular dietary supplement E621 - Monosodium Glutamate.
The herb has been found to increase excitability, brain stability during sports competitions. The research team of Guiyang Medical College has tested more than 300 professional athletes, including the Chinese national figure skating team. All tested athletes reported that taking Jiaogulan, before the competition, increased energy, concentration, improved reflexes, and reduced nervousness.
Other benefits of Jiaogulan for the cardiovascular system
The plant prevents myocardial disease (cardiomyopathy), protects the heart muscle from damage in diabetes. Jiaogulan protects against spasm of the coronary vessels, arrhythmias, pressor reaction (an increase in blood pressure in response to various internal or external conditions, for example, the influence of drugs, mental stress), ventricular tachycardia.
Jiaogulan is beneficial for people with chronic heart failure as it increases the efficiency of the pumping function of the heart. Due to this, the heart pumps blood well, delivers more oxygen and nutrients to the organs, without additional stress.
Uses
Borago - cucumber herb
The plant is used in folk medicine, typically as an herbal tea, but may be used as an alcohol extract or in dietary supplements. It has not seen widespread use in traditional Chinese medicine (TCM), being adopted only in the past 20 years, because it grows far from central China where TCM evolved; consequently, it was not included in the standard pharmacopoeia of the TCM system. Before then, it was a locally-known herb used primarily in mountainous regions of southern China and in northern Vietnam.It is described by the local inhabitants as the “immortality herb”, because a large number of elderly people within Guizhou Province reported consuming the plant regularly. In the European Union, jiaogulan is considered a novel food following a 2012 court ruling that prohibited its sale as food.
Effects on glucose metabolism
Mechanism
Gynostemma five-leafed (90% hypenosides), when exposed to α-glucoside, has an IC50 of 42.8 μg / ml (exceeds 53.9 μg / ml of acrabose). Is able to reduce the absorption of carbohydrates; the degree of inhibition is unknown, since fecal analysis was not performed Saponins of gynostemma pentafilia have an inhibitory effect on the PTP1B enzymes (a negative regulator of insulin signal, which is a therapeutic target for the treatment of type II diabetes), depending on the concentration, including hypensapogenin A (IC50 23uM), B (IC50 24.
5 μm), E (IC50 13.1 μm) and G (IC50 19.7 μm). Hypenapogenins F (IC50 49 μm) and 3β-hydroxyethio-17β-dammaranic acid (24.5 μm) are less effective, while (20S) -3β, 20,23ξ-trihydroxydammaran-24-en-21-y acid-21 , 23 lactone (IC50 5.3 / -0.
4 μm), by competitive inhibition with a Ki value of 2.8 μm; this effect is comparable in effectiveness to corosolic acid (IC50 7.5 /-0.6 μm) and ursolic acid (3.6 /-0.2 μm) .22) These compounds have been structurally modified (into compounds that do not occur naturally in southern ginseng) in more powerful inhibitors (thanks to the new structure);
have a fairly low IC50 value of 0.27 μm. Southern ginseng compounds are comparatively effective inhibitors of PTP1B, they promote the uptake of glucose by cells, while maintaining the function of the insulin receptor.
At least natural compounds have moderate potential. The compound of gynostemma pentaphyllum, known as phanoside, is capable of inducing insulin secretion, the process can occur depending on the concentration in the tissues of the pancreas of healthy subjects, and in diabetic patients with high and low glucose concentrations.
It was noted that the action of phanoside at low glucose concentration is not blocked by any of the added agents, which may be associated with the facilitation of insulin exocytosis (like many standard mechanisms of KATP channel closure, calcium influx and PKA / PKC activity proceed independently of phanoside).
Research
Taking 100 mg / kg hypinosides for 9 weeks did not significantly reduce blood glucose levels in streptozocin-induced diabetic rats. A study in db / db mice using low (0.
0025% hypenosides per feed weight) and a high dose (0.01%) for 5 weeks, noted that high doses reduced fasting blood glucose by 13.2% (not as effective as rosiglitazone, which lowers glucose by 57%);
Compared to the diabetic-controlled group, fasting blood glucose levels were elevated in all tested groups.23) It was noted that high doses have a short-term effect on fasting blood glucose levels (injections of 200-300 mg / kg;
oral intake 1500 mg / kg). During the experiment, non-drug diabetics were given 30 mg of gliclazides for 4 weeks, then they were divided into a group taking gynostemma five-leafed, and a group taking placebo (green tea catechins).
In the group taking 3 g of gynostemma quintuple leaf twice a day (18% saponins), there was a subsequent decrease in blood glucose and HbA1 levels, and the improvement in insulin sensitivity was insignificant.
A study was conducted on the effects of tea made from 6 g of gynostemma leaves. five-leafed, in combination with standard diet and exercise, in type II diabetics. The southern ginseng group had a greater decrease in fasting blood glucose over 12 weeks (5-fold compared with placebo; 3 / -1.
8 mmol / L), HbA1c (2%; placebo 0.2%), and decreased insulin sensitivity. One study found high doses to temporarily lower glucose levels, but two studies in humans showed that taking tea made from Gynostemma quinqua leaf can enhance the effects of medication and exercise.
Jiaogulan kaufen - Was gibt es zu beachten
Jiaogulan ist in den letzen Jahren sehr in Mode gekommen, wodurch es im Handel mittlerweile recht viele Produkte des Heilkrauts gibt.
Große Nachfrage haben vor allem frische Jiaogulan-Pflanzen, die es mittlerweile in vielen Pflanzencentern, Baumärkten und teilweise auch in größeren Supermärkten zu kaufen gibt. Achten Sie beim Kauf darauf, ob die Pflanze von Schildläusen befallen ist. Diese sind meist auf der Blattunterseite als kleine weiße und flache Punkte erkennbar. Weiterhin sollte die Erde nicht ausgetrocknet sein.
Wesentlich schwieriger ist es Samen von Jiaogulan zu bekommen. Dies liegt u.a. daran, dass es verhältnismäßig schwer ist, gesunde und kräftige Pflanzen aus den Samen zu ziehen. Gelegentlich gibt es Saatgut bei Onlinehändlern sowie auf einigen Online-Marktplätzen.
Diejenigen, die an Jiaogulantee aus getrockneten Kräutern trinken wollen, müssen auf Alternativprodukte zurückgreifen. Tee oder Teemischungen, die aus Jiaogulan bestehen, dürfen derzeit nicht in den Verkehr gebracht werden. Verantwortlich hierfür ist die Novel Food Verordnung, die es untersagt, neuartige Lebensmittel aus anderen Ländern direkt in den Verkehr zu bringen. Dies gilt auch dann, wenn durch Studien ein Risiko beim Verzehr minimal ist oder ausgeschlossen werden kann. Bevor Jiaogulankraut wieder als Tee im Handel käuflich ist, muss ein Inverkehrbringer zunächst ein teures Zulassungsverfahren durchführen. Viele Händler umgehen diese Verordnung, in dem sie beispielsweise Potpourri oder Jiaogulan zur Dekoration verkaufen.
Literaturnachweise:
- : Hou, J. et al. (1991): Effects of Gynostemma pentaphyllum Makino on the immunological function of cancer patients. In: Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Vol. 11, S. 47-52
- : Mishra, R.N. und Joshi, D. (2011): Jiao Gu Lan (Gynostemma pentaphyllum): The Chinese Rasayan - Current Research Scenario. In: International Journal of Research in Pharmaceutical and Biomedical Sciences, Vol. 4, S. 1483 - 1502, ISSN: 2229 - 3701
- : Sriwanthana, B. et al. (2005): Immunomodulatory Effects of Gymnostemma pentaphyllum Makino on Human Immune Cells. In: Traditional Medicine and Nutraceuticals (Acta Hort), Vol. 6, S. 165-169
- : Chavalittumrong, P. et al. (2007): A phase I trial of Gymnostemma pentaphyllum Makino in healthy volunteers. In: Songklapakarin Journal of Science and Technology. Vol. 29, S. 83-93
- : Huyen, V. T. T. (2013): Clinical Study - Gynostemma pentaphyllum Tea Improves Insulin Sensitivity in Type 2 Diabetic Patients. In: Journal of Nutrition and Metabolism. Vol. 2013, S. 1-7, doi: 10.1155 / 2013/765383
- : Wang, Z. et al. (2019): Anti-diabetic activity evaluation of a polysaccharide extracted from Gynostemma pentaphyllum. In: International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, Vol. 126, S. 209-214, doi: 10.1016 / j.ijbiomac.2018.12.231
- : Zhang, X. et al. (2018): Protective effects of dammarane-type triterpenes from hydrolyzate of Gynostemma pentaphyllum against H2O2-induced injury and anti-hepatic fibrosis activities. In: Phytochemistry Letters, Vol. 25, S. 33-36, doi: 10.1016 / j.phytol.2018.03.010
Collection and storage
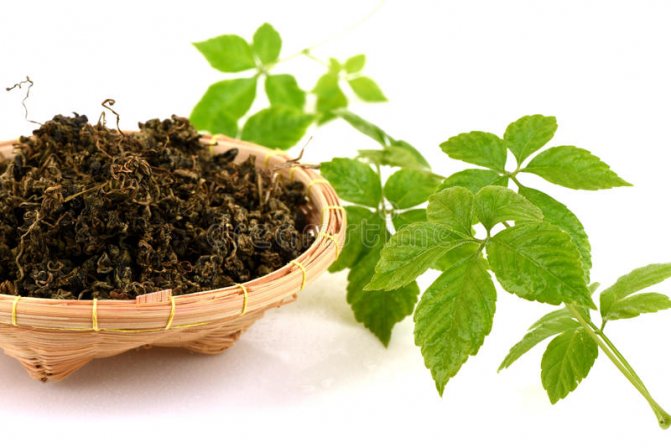
This vine will delight you with its fast growth. You can harvest the entire warm season. Fresh gynostemma leaves are used in salads and first courses, you can also brew healthy and tasty tea (Figure 5).


Figure 5. The leaves of the plant are eaten fresh and dried
You can dry the leaves in reserve. This should be done in a dark place until it dries completely, when the leaves break easily. Then you can grind them or store them in a dry, tightly closed container. This way you can indulge in tea all year round. By the way, the berries are also edible and even tasty.
Side effects
Despite the many benefits, there are some side effects:
- Pregnancy: Due to its adaptogenicity, this herbal tea affects hormone levels, which can pose a threat to the baby. Therefore, pregnant and lactating women are advised to refrain from consuming it.
- Blood clotting disorders: this plant contains substances that have a depressing effect on blood clotting and blood pressure. If you are taking medication, have problems with blood clotting and blood pressure, or have surgery in the near future, refrain from using this remedy.
This herbal tea is completely non-toxic. Even when consuming the extract of this plant in large quantities, only minor side effects are possible.
Sources:
- Wonder Herbs: A Guide to Three Adaptogens
- Adaptogens: Herbs for Strength, Stamina, and Stress Relief
- europepmc.org
- acs.org
- academicjournals.org
- en..cn
Cooking recipe for beauty and treatment of various ailments
Gynostemma five-leaf is part of many dietary supplements and medicines, dietary supplements and slimming teas. However, if you wish, you can purchase tea based on just one component and brew it yourself for beauty and health improvement. Here's the correct recipe:
- Rinse a clean teapot with boiling water, pour raw materials into it at the rate of 1 tsp. in a glass of water. The water should not be boiling, but hot - cooled down to a temperature of 80-85 ° C. Stir the contents with a wooden stick and drain the water after half a minute. Pour again the same amount of water and the same temperature, let it brew under the lid for about 10 minutes. When the drink acquires a light lemon color, it means that it is ready to drink. You can improve its taste by adding mint, oregano, thyme. For women, it is useful to add lemon balm for beauty and well-being.
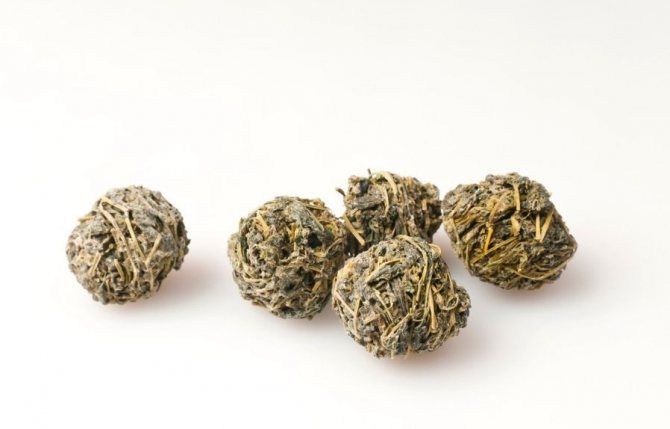
You can enhance the effectiveness of the drink if you brew it for a longer time - 15-20 minutes. You can use the same raw materials and repeatedly, but simmer it in a teapot for 25-30 minutes. When choosing tea, be sure to pay attention to the color of the leaves - it should be of a natural green hue, but the shape can be any - the usual tea leaves, balls or even twisted spirals.
Moreover, the stronger the tea is twisted, the stronger and richer the infusion will be. Drink it regularly, but in no case replace it with traditional therapy for existing diseases. Drinking tea can supplement it, but not be used as a substitute for the main treatment.