Site requirements
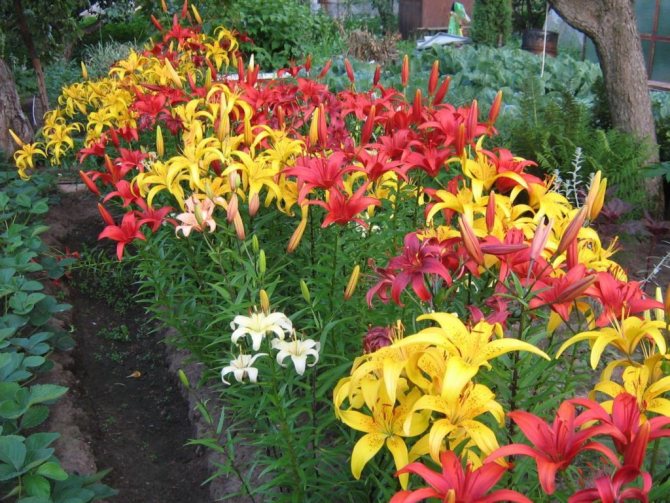
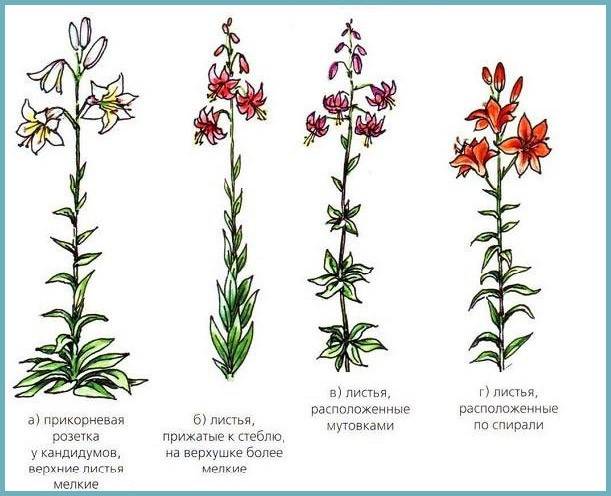
Unpretentious lilies still impose certain requirements on the location of the flower bed and the composition of the soil. These plants have several dozen varieties, and each has its own characteristic features. One variety requires a lot of sunlight, while the other, on the contrary, reproduces better in partial shade. You should pay attention to this even when buying seed.

The universal rule for planting lilies in open ground is the presence of good drainage on the site. Flowers consume a lot of moisture. It is necessary for the normal absorption of nutrients from the soil through the root system. But stagnant water in the flower bed will inevitably lead to the formation of mold and rotting of the bulbs.
For this reason, flat and straight areas should be chosen for the flower garden. Sometimes lilies are planted on a small hill. You should not break a flower bed in a place where groundwater is located close to the surface of the earth.
There are also special requirements for the soil intended for bulbous plants:
- 1. The soil in the flower garden should be good for air and moisture. You can increase drainage properties with ordinary river sand. Sometimes finely chopped peat is used for these purposes. Consumption of substances per unit area of the site depends on the type of soil. In too heavy clay soils, wood ash is additionally introduced, which not only structures the soil, but also enriches it with microelements.
- 2. Lilies grow well in a neutral environment. For some varieties, planting on slightly alkaline or slightly acidic soils is allowed. You can neutralize the soil by adding lime, ash and peat. The choice of substance and its amount depend on the composition of the earth.
- 3. Too much organic matter with a high nitrogen content can provoke premature development of the green mass of the plant. This negatively affects the vitality of the bulb. It will be rapidly depleted due to the consumption of nutrients necessary for the flower to survive the winter frosts and prepare for spring growth.


The flower bed must be protected from cold northerly winds. Drafts are bad for the bulbs. It is advisable that snow does not stagnate on the site in the spring. No other bulbous vegetables or flowers should grow in the location chosen for the lilies during the last 3 years. These plants are prone to the same diseases, so such a neighborhood is dangerous for ornamental culture.
Site selection and soil preparation
If the lilies grew in the same place, even with constant fertilization, the flower bed will have to be changed. Ideally, the remaining area should rest for at least 2 years. Until that time, it is better to sow siderates. Preparing a new garden plot doesn't have to be spontaneous.
- A year or two before the planned planting, the soil should be dug up and good humus added to it. To prevent weeds from growing on the site, you can use all the same green manure. They will also have a beneficial effect on the structure of the soil and will themselves become an additional fertilizer.
- Immediately before the start of transplantation, the site is cleared of the remnants of dry vegetation. The soil must be dug at least 15-20 cm deep and large lumps must be broken.
- Further, peat, sand and other additives should be distributed over the entire area, and dig it up again. So that subsequently the water does not slide to one side and the flowers grow straight, the future flower bed must be well leveled. All this must be done immediately before planting so that the soil does not have time to dry out.
The place of future transplantation of lilies is of great importance. Shade is undesirable on it, but it will be better if there are plantings of shrubs or other obstacles nearby - they will protect the tall and delicate stems from the wind. Lilies love the sun, so they should not be planted next to a wall of a house or a high blank fence.
It is better if the flowerbed is located on a hill so that water does not accumulate on it, because good drainage is important for lilies.
In addition to a good location, you need to attend to the condition of the soil. Clay and stony will not work - air exchange is difficult in it, and excess moisture will stagnate. In such an area, lilies will grow poorly, bloom poorly, and rot may form on their bulbs. To lighten the soil, to make it lighter and more loose, sand is introduced. The acidity of the soil is reduced by adding ash or slaked lime to it.
Read also Propagation of dracaena by cuttings at home video
In principle, you can improve almost any site, even the most inappropriate. To do this, you need to dig a hole or trench at least 30 cm deep. A drainage layer of small pebbles or broken brick is placed on its bottom. A pre-prepared soil mixture with a suitable composition is poured on top. The exception is swampy and lowland areas with excessive moisture.


Lily transplant: when is it better to do it
Transplanting lilies in spring
Lily bulbs are transplanted in spring and autumn, and both the spring and autumn procedure have both advantages and disadvantages.
The disadvantage of spring planting is that lilies in the current year may not bloom under unfavorable conditions. A dry spring complicates the growth and development of lilies, especially if you do not have the opportunity to organize watering. And species such as curly lily, Hanson, snow-white, Shovitsa, Canadian and one-brother generally do not tolerate spring planting.
Transplanting lilies in summer
Sometimes it becomes necessary to transplant lilies in the summer. The procedure is carried out by the transshipment method: the bulb is removed with a large earthen clod and planted in a previously prepared hole. As a rule, the transfer of lilies is tolerated well. However, without urgent need, it is better not to transplant lilies in the summer: when the biological rhythm of the plant gets lost, the negative consequences can be felt for several seasons.
Transplanting lilies in the fall
For most species and varieties of lilies, transplanting in early autumn is preferable. In areas with warm and late spring, the best time for this is September and October. LA hybrids and Asiatic lily bulbs can be replanted until mid-November. For the Urals and Siberia, the optimal time for planting lilies is from September to early October.
The timing of the transplant depends on how the summer season went: if during the flowering period the weather was not favorable for the lilies, and the bulbs consumed more nutrients than usual, they, accordingly, will need more time to recuperate. Dry weather can also delay the recovery of planting material. Under favorable weather conditions, the recovery of the bulbs after flowering is faster - from one to one and a half months, so the transplant can be started earlier.
Reproduction during storage
Winter is considered the most suitable time for lilies to breed. When performing this procedure, use the scales of the onions. The breeding process is carried out in several stages:
- Flakes preparation.First, they are engaged in preparatory work, during which all the scales are separated from the bulbs. This is done very carefully so as not to damage anything. You can separate them both manually and using a sharp blade.
- Soaking. The detached flakes are soaked in a fungicidal solution or in a manganese liquid. In this case, they should be soaked for about 40-45 minutes.
- Drying and storage. All soaked flakes are washed with water, dried and placed in a container filled with peat. After a month and a half, adult bulbs will sprout from them, which can be planted in a flower bed in spring.
- Planting. Before planting young bulbs, they are carefully removed from the pot of peat. Then they are placed in the dug holes and poured over with water.
Lily transplant: step by step instruction
Site preparation
Lilies are transplanted once every 3-4 years. Choose a bright, open area with fertile, well-drained and breathable soil. Some species, such as tubular hybrids or Asiatic lilies, may be comfortable in the sun or in light partial shade, but not under trees. Japanese, curly, calloused, reddish, gorgeous, golden, lovely and carniola lilies prefer to grow in partial shade, while long-flowered, dwarf, monochromatic, cuddly, Daurian, orange, Chalcedonian and drooping lilies need a lot of sunlight.
Dig the area to the depth of a shovel bayonet, remove the rhizomes of perennial weeds. In heavy soil, add peat and coarse-grained river sand for digging, add 8 kg of compost or humus per m² to podzolic soils, and 4 kg of compost per m² to leached chernozem. If necessary, you can add coniferous litter and leafy soil to the topsoil. And mineral fertilizers - phosphorus, potash and nitrogen - are applied to the soil of any composition. Never use manure as fertilizer!
As for the level of acidity, each variety has its own preference in this matter: in areas with neutral soil, most of the lilies can be grown, but species such as Martagon, Regale, monochromatic, bulbous, curly, umbrella, Tibetan and white lilies grow better on slightly alkaline soils, while lilies of David, Daurian, tiger, Maksimovich and Wilmott prefer slightly acidified soils. Too acidic soil is neutralized with wood ash, chalk or limestone
If the site is located in a lowland, where melt or rainwater can stagnate, make flower beds raised by 15-20 cm.
Preparation of planting material
Before planting, sort out the bulbs, discard rotten, soft and severely damaged bulbs. Clean the suitable planting material from dead scales, rinse in a solution of potassium permanganate or Fundazole, let the bulbs dry, and then sort them by size (parsing).
Planting bulbs outdoors
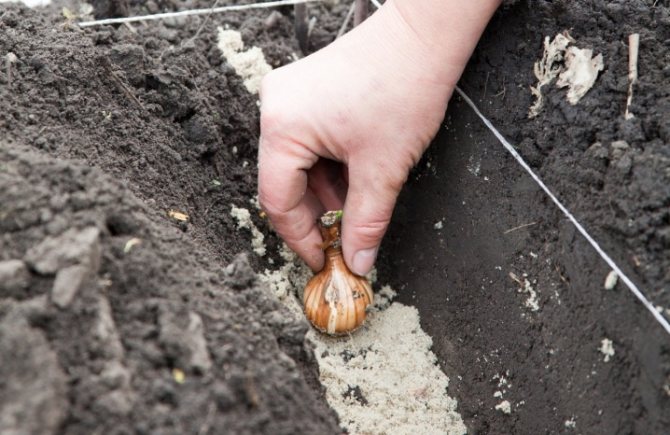
When planting lilies, a common scheme for all bulbous plants is used: the bulb is placed at a depth equal to three of its diameters, that is, the thickness of the soil layer above the bulb with a diameter of 5 cm should be equal to 10 cm.In heavy soils, the bulbs are planted at a slightly shallower depth, and in the lungs - slightly more than the scheme suggests.
For medium-sized lilies, a double-sided ribbon planting is used, when the bulbs are placed in a row at a distance of 15-20 cm, and between the lines they maintain a distance of about 25 cm.For low-growing lilies, it is better to use a three-line ribbon planting with an interval in a row of 10-15 cm and the same distance between lines. A single-line ribbon planting assumes a distance between the bulbs in a row of 5-10 cm, and between the lines - about half a meter.
Dig holes of the desired depth according to the scheme you have chosen, pour washed coarse sand mixed with wood ash into each mixture, plant bulbs in this pillow, spreading their roots and slightly pressing them into the sand, seal the holes with soil, water, and when the water is completely absorbed, cover the area with peat.
The right time
The frequency of replanting depends on the variety. The more the bulbs grow, the more often they need to be dug out, the children should be separated from them and planted again. For most varieties, an interval of 3-4 years is enough. However, when acquiring rare varieties of lilies, it is necessary to study their features in advance and take into account later. Some are best replanted every year (eg tubular).
There are two points of view regarding the timing of the transplant.
- Traditionally, all planting work is carried out in the fall. This is enough for the onion, which has completed all its tasks, to rest. An autumn planting will allow them to re-root. It is believed that such lilies will be healthier.
- If the weather conditions interfered with planting in the autumn months, or if you come across a variety for which wintering in a flowerbed is contraindicated, you can postpone the planting in the spring. Many growers consider this method more convenient - you do not need to insulate the plantings, and then clean them. In addition, even healthy and hardy bulbs can die from diseases or pests during wintering.


The exact timing of replanting can be calculated using the gardener's calendar. However, they also need to be adapted in accordance with the climate of the area. In spring, work can begin as soon as the frost stops and the soil warms up. For the southern regions, the second half of April is suitable, for more northern regions - early May. In autumn, these dates are shifted to the end of August and September, respectively. In addition, it is necessary to take into account the weather - in the Urals and in the Moscow region it will be very different.
Prolonged September rains can derail all plans and postpone the transplant until spring, and in the spring floods and prolonged frosts should be taken into account. A preliminary weather forecast for two to three weeks will help to adjust the plans.


When to plant lilies - in autumn or spring?
Perennial lilies are recommended to be transplanted once every 4-5 years, Asian hybrids can not be disturbed for 12 years. If the transplant is not done, the soil around the plant is depleted, the born, not separated baby becomes shallow, diseases and pests accumulate.
Among flower growers, there are enough supporters and opponents of planting lily bulbs in the fall, many prefer to divide and transplant plants in the spring.
They put forward the following arguments against late flower transplantation:
- in a frosty winter, there is a risk of bulbs freezing if the gardener has not taken care of sheltering the plantings;
- planting material extracted from the ground in the fall cannot be stored for a long time;
- young bulbs in a new place can be attacked by mice.
Nevertheless, you can find a lot of positive aspects in planting lilies in the fall:
- after flowering is complete, the bulbs are immersed in sleep, and the transplant is easier to tolerate;
- by the end of the growing season, the lily planting material gains good weight and accumulates enough nutrients;
- bulbs planted in autumn have enough time for rooting, and flowering for the next season will come earlier;
- by the fall, more babies will grow on the plant.
What time to choose for working with a plant is up to the gardener. It is necessary to take into account the climatic conditions of the region, the variety of lilies.
Features of cultivation and indications for transplantation
Depending on the variety, lilies grow in one place for up to 10 years. The flower is relatively easy to adapt to new habitats, with the exception of capricious oriental varieties. If garden lilies are not transplanted in a timely manner, due to the overgrowth of the root system, many children will be cramped, and the plant will suffer from nutritional deficiencies.The frequency of "moving" is dictated by the characteristics of the cultivated varieties:
- martagons grow well in one place for 8-10 years. American hybrids are adapted to similar habitat conditions;
- Asiatic lilies need replanting every year. For better development and beautiful flowering, you need to update the space for wayward garden beauties every two years;
- tubular varieties are also demanding on a fresh fertile composition and respond well to “moving” with a frequency of once every two years;
- individual subspecies of Asian and tubular varieties are able to reveal their decorative potential exclusively with an annual change of residence;
- other varieties of flower culture, as a rule, grow stably well in one place for 4-5 years.
One of the key indications for changing the place of growth of exotic flowers is that the risk of diseases in the new place is reduced by an average of 25%.
Benefits of transplanting garden lilies in the fall:
- a culture that has gained strength within 1.5-2 months after flowering, tolerates "moving" well, reacts positively to the renewed substrate, easily adapts and takes root;
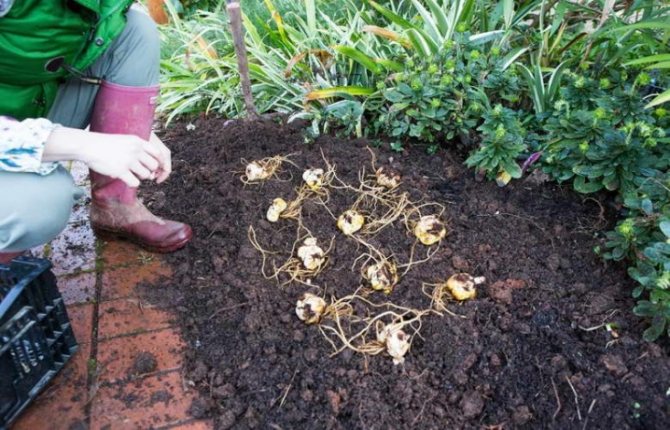
- autumn seating is ideal for decorating a flower bed of children that form near the bulb. If necessary, you can divide the bulb itself into several segments for reproduction of the variety you like;
- novice florists are recommended to plant flowers in autumn as a relatively comfortable and safe option for the survival of the culture.


Transplanting lilies in the fall is comfortable and safe for the survival of the culture.
Lily transplantation is usually accompanied by reproduction: the children are separated from the bulb and planted to grow new specimens. Under favorable conditions, young shrubs from bulbs bloom in the next season, a maximum of a year later. When propagated by seeds, the flowering of the culture is predicted only after 5-6 years.
The timing of planting lilies in the fall, what factors affect


The main factor that you should pay attention to when deciding when to plant lilies in the fall is the climatic conditions of a particular area and the region as a whole. On the vast territory of our country, the climate varies so much that the difference in terms of work can be up to 2 months.
The plant should have time to put down roots and begin to receive nutrition from the soil, before immersion in winter sleep. But the active growth of the stems and their emergence on the soil surface must not be allowed. Daytime air temperature should drop to +8 .. + 10 degrees, small night frosts will not harm the plant.
Depending on the region
Below is information on when to plant lilies in the fall, depending on the regions.
Moscow region and middle zone of Russia
It is necessary to start preparing the site for placing lilies in September. The planting itself is carried out in October, focusing on the weather. You need to be in time before the snow falls and the onset of severe frosts, but too early planting is useless - sprouts of lilies can appear on the surface of the earth and the winter cold will destroy them.
Leningrad region
The climate in the regions north of Moscow is damp and cooler. Autumn planting of perennial flowers occurs a couple of weeks earlier than in the middle lane.
Siberia and the Urals
The harsh winter and short, often rainy autumn make their own adjustments to the timing of planting lilies. In the Urals it is September, the whole month. Beds or flower beds with lily bulbs must be covered with spruce branches, sprinkled with wood shavings. In the spring, with the onset of warmth, winter insulation is removed.
For cultivation in the Siberian region, cold-resistant varieties of lilies are chosen. For subwinter planting, all adapted varieties for this region are suitable, except for Dutch lilies (delicate beauties are planted only in spring). August and September (depending on the weather) are good times to work with plants.
South of Russia
In a fertile warm land, the autumn planting of lilies begins in the second decade of October, and ends in November. Flowers do not need any sheltered for the winter, but watering the plantings can be useful - in the south, traditionally, there is a lack of moisture in the soil.
Ukraine
Perennial bulbs are placed in the soil from mid-October to late November. An additional guideline for the florist will be a decrease in the daytime air temperature to +10 degrees.
Belarus
The country's climate has much in common with the weather in central Russia. The timing of the autumn planting of lilies is the end of September and the beginning of October.
Advice! If the gardener incorrectly determined the planting time, he lowered the lily into the ground too early and it sprouted - you cannot leave the plant in this form for the winter. Stalk shelter will not work either.
The flower is carefully dug up along with a large clod of earth, placed in a bucket or box. The dug out lily is stored in a cellar or a cold storage room at a temperature slightly above 0. The plant is transplanted into the ground not earlier than May of the next year.
Depending on the variety
Each type of lily has its own characteristics of the development of the bulb, the time of onset of sleep. All this should be taken into account when choosing the date for planting lilies in the fall.
- Early autumn is suitable for transplanting king lilies, hybrids of the white plant variety, the Candidum lily.
- In October, it is time to plant oriental hybrids and tubular varieties.
- Asiatic lilies are so unpretentious that they can be transplanted at a convenient time for the gardener.

Lunar calendar
The location of the Moon in the sky in 2019 is favorable for working with plants on the following dates:
- August - from 1 to 9, 13-22, 27-31;
- September - from 1 to 6 (until 5 pm), 10-19, 23 and 24, 27-30;
- October - from 1 to 3, 8, 10-16, 20-23, 25-30;
- November - from 3 to 6, 8-12, 17-22.
Digging lily bulbs for the winter
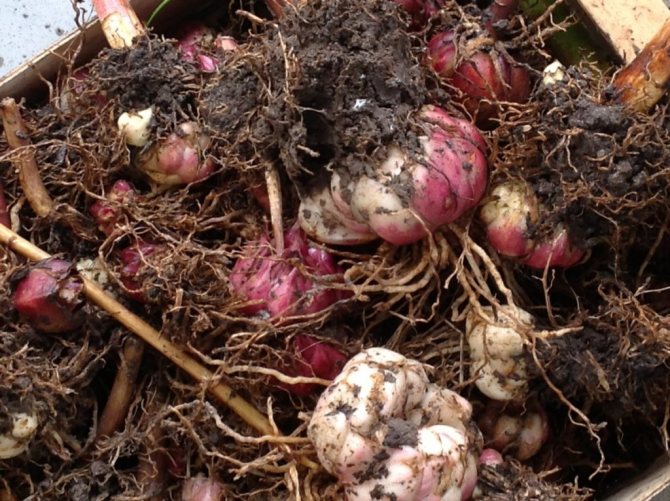
When planning how and when to dig up lily bulbs for transplanting to another place, take into account the following nuances:
- long-flowered, American and oriental hybrids react ambiguously to transplanting in autumn, as they are characterized by low winter hardiness properties. In growing conditions in regions with a difficult climate, including in the middle lane and the Moscow region, it is recommended to dig up the bulbs and send them for storage until spring planting. In the south, with mild winters, these thermophilic varieties tolerate transplanting well in the fall to another place;
- bulbs of unique specimens are dug up in autumn for storage in guaranteed comfortable conditions before planting in spring or transplanted for the winter in a greenhouse. A similar care option is also recommended in the case of crop varieties that do not have accurate information about the characteristics of winter hardiness;
- every autumn, bulbs of Asian hybrids are dug up for transplantation to a new place. Do not neglect the recommendations of experts and postpone the "move" of the flower to another area. Asian hybrids are characterized by fertility, they form many children, which necessitates an annual transplant. In the fall, it is important to dig up the bulb and separate the babies, otherwise they will grow tightly to the mother's base. Due to the large number of children, the plant lacks nutrients and moisture, the bush weakens, and decorative qualities deteriorate.
After digging up and separating the babies, the mother bulbs of Asian hybrids are transplanted to a new place, having previously been treated in a fungicide solution. Young offspring are sent for storage for the winter, in the spring they are planted in open ground.
How to store bulbs before planting in the fall

The ideal option would be to immediately immerse the lily bulbs in the ground immediately after removing them from the ground and taking the necessary measures (separation, disinfection). This option is possible if the grower transplants his own flowers to a pre-prepared area and can dig up the lilies before the transplant.
When buying bulbs from a store or if it is impossible to plant immediately, lilies must be properly preserved.
The bulbs themselves should be firm, with well-developed roots, and free from rot and mold. If there is mechanical damage on the scales, sprinkle the wounds with crushed charcoal.
To preserve the viability of lily bulbs, they are provided with a storage temperature in the range of 0 to +5 and high humidity. At home, the easiest way is to place lilies in a perforated plastic bag with a handful of damp peat or sawdust. The package is placed in the refrigerator in the vegetable storage box.
If at the dacha it is not possible to put lilies in the refrigerator, they can be placed in a cellar, a glacier. Some growers pack the bulbs in an airtight bag and lower them on a rope into a well. From such a "storage" lilies must be periodically taken out and allowed to breathe.
Further care
If the climate in the region is cold enough, then after transplanting in September-October, when the ground begins to freeze, the flowers need to be provided with good shelter for the winter. Spruce branches or dry foliage can be used as a covering material. The thickness of the covering layer should be about 10-15 cm. To prevent the wind from tearing the shelter, boards should be placed on top of it.
After the snow melts, the shelter should be removed. Next, the soil must be loosened and fertilizers added to it. Thanks to the first feeding, there will be a boost in crop growth. The recommended type of fertilizer is nitrogen-containing. Preventing the consequences of spring frosts, lily sprouts must be covered with a film.
On a note. If in the next season the culture does not bloom as brightly and luxuriantly as before, this is not yet a cause for concern. Lilies need to get stronger and grow up. To make this task easier for them, it is recommended to remove old buds, then the plant will not waste energy on their development.
So that the flowers do not lose their beauty and do not die, they need to be transplanted regularly. As it turned out, transplanting lilies is not at all difficult. The most important thing in this matter is to adhere to the rules and recommendations regarding when to transplant lilies, when to dig up lilies for transplanting, as well as the order and frequency of this event.
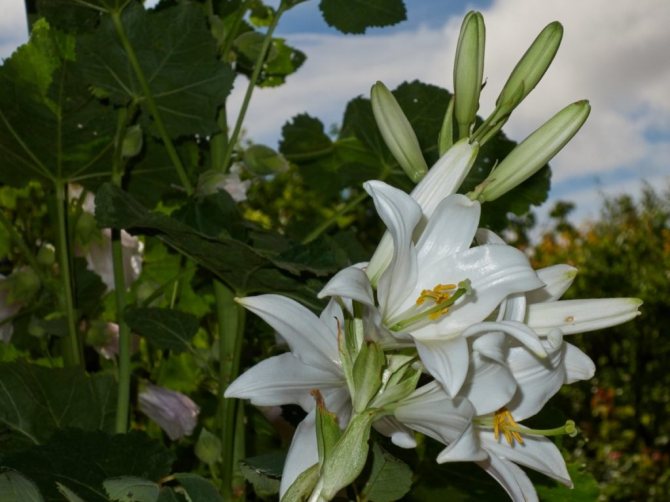
Lilies are striking flowers that "catch" at first sight with their purity, elegance and beauty. It is no coincidence that we enthusiastically admire the bright colors and enjoy the easily recognizable notes of the fragrance of the so-called symbol of chastity. Many growers successfully grow them in their summer cottages, diligently multiplying them. How often to replant lilies? When is the best time to transplant? What should be the new location in the garden? It is appropriate to recall all this to those who, with enviable persistence, decided to give the magnificent flowers even more of their time and energy.
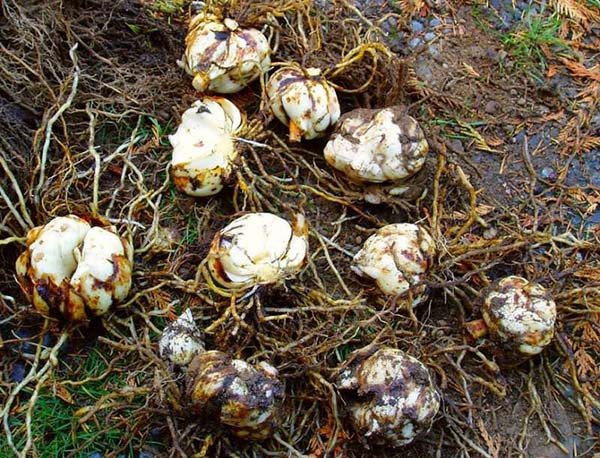


How to plant lilies correctly
Above we examined when to plant lilies in the fall, now let's take a closer look at how to do it correctly.
Soil preparation
3-4 weeks before placing the lily bulbs in the ground, you need to attend to the preparation of the soil for them. Lily places high demands on the structure and fertility of the soil.
- For flowers, choose a sunny, flat or slightly sloped area, closed from strong winds. When planting lilies near a fence or buildings, the bulbs are placed on the south or east side.
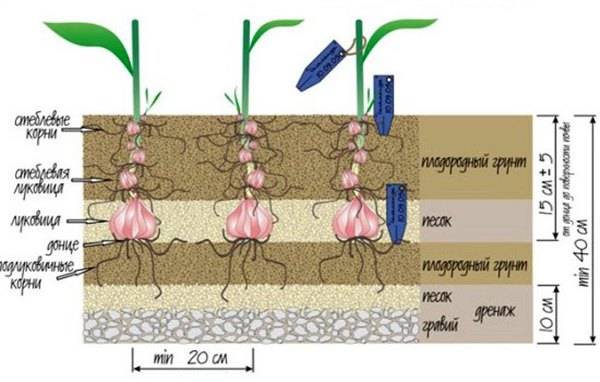
- The soil should be sufficiently loose and well-drained. Stagnant melt water in spring is detrimental to the bulbs. On soils with excess moisture, drainage grooves are arranged for rain and melt water, drainage is laid on the bottom of the planting holes from a layer of sand, gravel or expanded clay with a layer of 4-7 cm.
- The acidity of the soil for the lilies of the Asian, Oriental and American varieties should be higher than for the tubular lilies and Candida. You can acidify the earth with peat, adding wood ash and chalk will give the earth an alkaline reaction.
- The structure of the earth for lilies should be loose. A combination of sand, turf and humus is suitable. Admixture of clay is allowed no more than 20%.
- It is necessary to dig up the area on a shovel bayonet, carefully selecting the roots of perennial weeds.

How to plant lilies using sand
Preparation of planting material
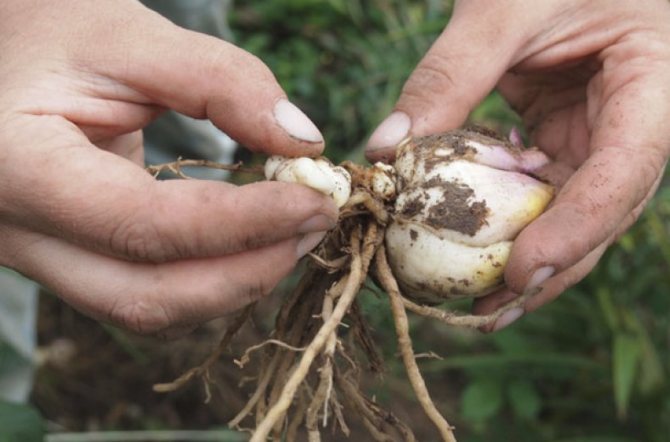
You can get a healthy, abundantly flowering plant only by planting healthy planting material. Even large and clean lily bulbs growing in their own area must be disinfected before planting.
Before planting, lily bulbs can be treated with a solution of foundation (2 g of substance per 1 liter of water) or karbofos in the same dosage. Florists use a bright pink solution of potassium permanganate or Maxim (according to the instructions). The soaking time of the bulbs is 20-30 minutes. The processed planting material is slightly dried in the shade, then planted.

Breeding methods for lilies
Step-by-step landing
The flower grower needs to decide at what depth to plant the onions. It depends on the type of lily and the size of the bulb.
- Low-growing varieties of flowers are buried to a depth of 7-10 cm, with intervals of 15-18 cm between bushes.
- Lilies of medium height are deepened by 12-15 cm with a step between the onions of 25-30 cm.
- Tall varieties are immersed in the ground 15-20 cm, the distance between plants is 30-40 cm.
The bulbs can be planted in individual wells or laid out in grooves. A 2-3 cm layer of sand should be poured on the bottom, it will protect the lilies from rot.
Advice. It is useful to mix sand with wood ash.
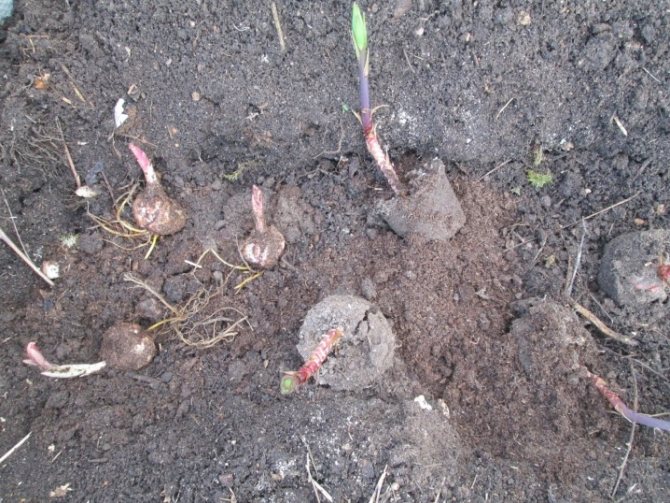
When planting lilies in the fall, it is important to carefully spread the roots of the bulb on the sides so that they do not bend up. The lily is covered with soil, gently pressing the ground to the plant with the palm of your hand.
Useful videos from Sadovy Mir channel
Below, the specialists of the Garden World channel will tell you about planting lilies in the fall.
Do I need to water after planting in the fall?
If the soil is dry and crumbly, the flower garden must be watered abundantly. After watering, it is useful to mulch the soil with a small layer of peat or shavings. Usually, this is required in the southern regions, where autumn is poor in rainfall.
What fertilizers to apply
The standard list of fertilizers for lilies is as follows:
- superphosphate 80 - 100 g per 1 sq. meter;
- potassium sulfate 50 g per square;
- 8 - 10 kg of rotted leaf compost or 5 kg of cow dung that has been in use for at least 5 years.
On light sandy soil, it is useful to additionally add 2 buckets of non-sour peat per 1 sq. meter, a sand-peat mixture is added to the clay soil, also 2 buckets.
Plant care after transplant
Autumn work in a flower bed with transplanted lilies consists in weeding and rare watering. In regions with heavy rainfall in the off-season, there is no need for additional irrigation of the plantings. In the case of dry autumn, the soil surface is compacted and periodically watered with sprinkling with a watering can.
Preparing lilies for winter
In climatic zones with early formation of snow cover, flower beds with lilies of autumn planting do not need additional preparation for winter. Also, garden flowers overwinter calmly without insulation in the southern regions of cultivation. In the absence of natural shelter during periods of little snow in the middle zone and Siberia, plantings require protection from frost and temperature extremes. To do this, use mulch, use different methods of warming in the fall, depending on the type of culture:
- oriental hybrids are affected by damp frosty weather, suffer from low temperatures. A dense layer of mulch of 15-20 cm is required with a cover of boards or film to protect the coating from the effects of wind;
- LA hybrids are insulated in autumn with peat or rotted sawdust in a layer of 10 cm, like the Asian varieties;
- Marchagon for the winter is mulched with a mixture of humus and wood ash. A similar preparation for wintering is suitable for tubular varieties and snow-white varieties of lilies.
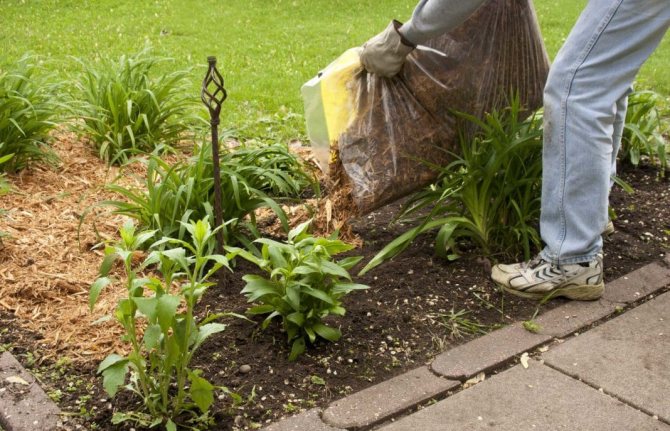


Mulching is part of the preparation of lilies for winter.
The thickness of the mulch, depending on the climatic zone of the growth of the culture, varies between 10-20 cm. In regions with severe winters, in addition to mulching, shelter is required to prepare lilies in the fall. Long-flowered varieties, American hybrids and oriental crop varieties need it. In this case, spruce branches, fallen leaves of forest species, boards are used as a shelter. The most effective method is considered when the mulch is covered with a layer of foliage or spruce branches and boards are placed on top, which are designed to ensure the integrity of the insulation "cake" and protect it from the effects of wind gusts.
To determine the optimal interval for mulching lilies for the winter, you should focus on the period of the onset of stable subzero temperatures. A layer of organic matter in the form of compost, rotted sawdust, needles, ash, leaf humus and rotted manure not only protects the bulbs from frost, but also improves the structure of the soil, contributes to the enrichment of the soil with nutrients.
How to transplant a flower
Having decided on the time of the transplant, you should start this procedure. It is necessary to prepare planting material, make holes and transplant lilies into them.
Preparation of planting material
If lily bulbs are stored indoors, remove them. When flowers grow in the ground, it is necessary:
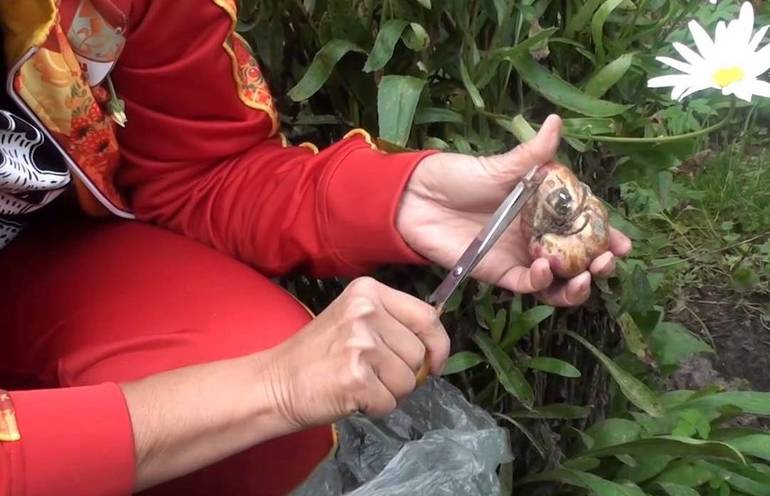


- Cut the stems of the plant almost to ground level.
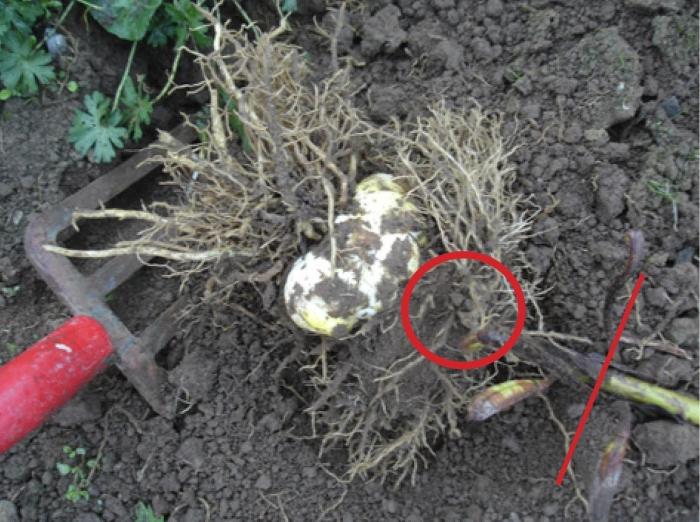
- Carefully dig the bulb out of the ground with a pitchfork or shovel, taking care not to damage the roots.
- To clear the hands of the lily tuber from the ground, rinse it with cool clean water for faster removal of the bulbs.
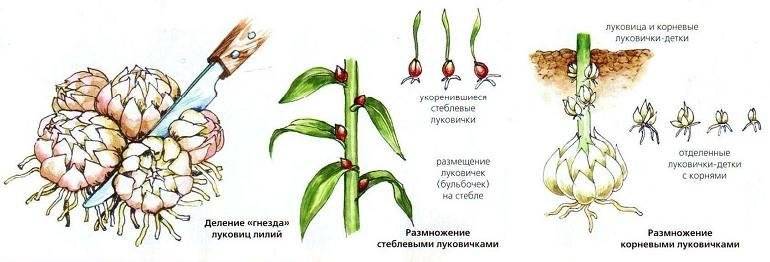
- Divide the bulbous nest carefully with a knife into separate onions, if it does not disintegrate on its own.
- Remove dead, damaged and dried scales, broken and too long roots, you need to leave healthy roots 10-20 cm.
- Place the planting material for disinfection for half an hour in a pale pink solution of potassium permanganate.
Digging holes
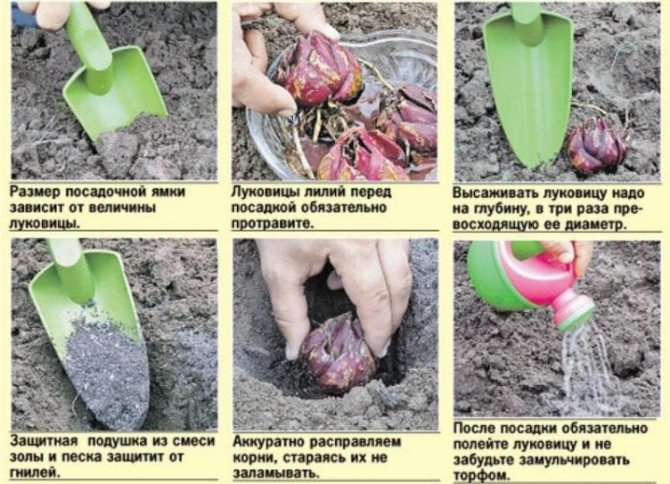
In the place where the lilies will be planted, they dig holes of the required depth, equal to three times the height of the bulb, adding to it at least 10-15 cm for the existing roots, the distance between the holes should be about 20-25 cm. After that, drainage is poured onto the bottom of the hole (8 cm) from broken bricks, pebbles, expanded clay. The drainage is covered with a layer of garden soil. River sand is poured on it with a slide, a flower bulb is placed on the top of the hill, the roots are straightened. Fill the hole with the plant with fertile soil.
Water the plantings abundantly with water, it is better to water it 2 times, the second time to do this when the water from the first watering is absorbed. Such moistening contributes to the disappearance of voids in the ground, better rooting of the bulbs. From above, the moist soil is covered with a layer of dry earth or a layer of mulch to prevent it from drying out.
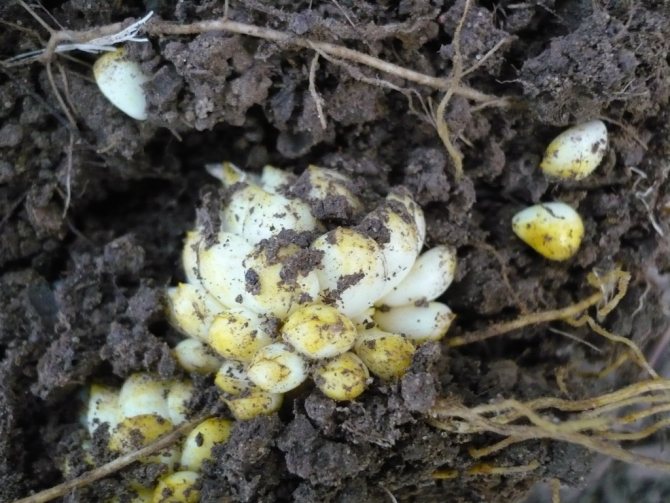
Reproduction of lilies by scales
We offer an excellent and economical way to propagate these luxurious flowers with scales. Carefully disassemble the bulb of the variety you like on the scales. They should be separated from the bottom very carefully. We etch the scales, strictly following the instructions for the product, the solution of which is used. You need to prepare a clean plastic bag and moss. It is better to use sphagnum - an excellent natural antiseptic. Any forest moss that grows nearby will do, too. It is always sufficiently moist, retains water for a long time, suppressing the occurrence of putrefactive processes, and will serve as a good environment for the formation of small bulbs. We put the scales in a bag, sprinkling them with layers of moss, close and store until spring in a moderately cool place. By spring, bulbs are formed on the scales, which will require growing. They will get stronger over the summer. And with good care, lilies from the scales will bloom next season.
How the transplant is transferred during the flowering period
When can lilies be transplanted if they are blooming: Experienced gardeners do not recommend disturbing the plants during flowering. This is an energy-consuming process for all ornamental crops without exception. During this period, all metabolic processes work like a clock. Digging up the tuber disrupts the nutrition of the lily, as a result of which the peduncles will die.
If the situation is difficult and there is no other way out, you will have to transfer the daylily during flowering, but try to follow all the recommendations so that the process goes without harm to the reproductive organs - roots and bulbs. Peduncles will probably wither at first after transplanting and fall off.
Asiatic lilies are considered the most hardy, therefore, with careful handling of the reproductive organs, they are sometimes transplanted at the time of flowering.
Further care
After transplanting, lilies lose some of their protective properties, therefore they need good care, which will differ depending on the season. There are rules here.
- In the fall, watering the bulbs is practically not needed. It is important to slightly moisten the soil after transplanting and fertilize with potassium and phosphorus. This is what will allow the bulb to take root and successfully endure the winter period.
- In the spring, there is still enough moisture in the soil, so frequent moistening is not required. In order for lilies to grow, nitrogen-containing fertilizers and saltpeter are needed. Do not add too many different additives, as well-prepared soil will provide the plants with everything they need.
- In the summer months, feeding is needed at the stage of budding and flowering. In the hot season, it is necessary to water the flower bed every day, in the morning or in the evening. It should be remembered that over-watering can be harmful. In addition, lilies need regular weeding. To provide oxygen access to the roots, the aisles should be periodically loosened. When cutting flowers for bouquets, it is necessary to leave a piece of the stem at least 15 cm for the bulb to develop further.
Lilies can be affected by infections and viral diseases. If the flower has stopped growing, its leaves turn yellow or become stained, action should be taken. For some infections, fungicides will help at first. But it will be better if the affected plant is removed or planted after treatment.


For information on how to properly plant lilies in spring, see below.
Why do you need a transplant and what will happen if you do not do it
Garden lilies are actively developing and blooming for the first 3 years after planting. Then the flowers begin to shrink. Thickened plantations do not allow young shoots to develop. The plant begins to age, wither.
A garden lily should be transplanted if it:
- stopped growing;
- covered with withered leaves, withers;
- gets sick with a fungal or bacterial infection;
- has grown greatly.
For each plant species, the frequency of transplanting varies. It is enough for American hybrids to change their place in the garden once a decade. Tubular and Asian varieties require annual replanting. Their bulbs multiply faster.
Preparatory stage
Before carrying out transplant work, prepare a place for lilies and the bulbs themselves.
Site selection and soil preparation
Lilies grow well in areas that are bright and open, but not blown by strong winds. Curly varieties can also grow in partial shade. The lily area should be located on a level or elevated area. Lowlands, which accumulate rain or melt water, are not suitable for this.


The soil in which lilies thrive best should be loose, humus, nutrient-rich, water and air permeable. Tubular lilies and the Candidum variety prefer neutral soil, all others prefer sour soil.
Before replanting lilies in the fall, prepare the soil for them. Work begins 2 weeks before transplanting: a plot is dug up to a depth of 0.4 m.If the soil is clayey, a bucket of river coarse sand and peat is poured into it for each square meter. m.Only peat is added to light soil. Mineral fertilizers are also applied at the rate of 5 kg of compost, 40 g of potassium sulfate and 90 g of superphosphate per 1 sq. m. Fresh organic matter cannot be introduced, not rotted manure can provoke outbreaks of fungal diseases.
Selection and processing of planting material
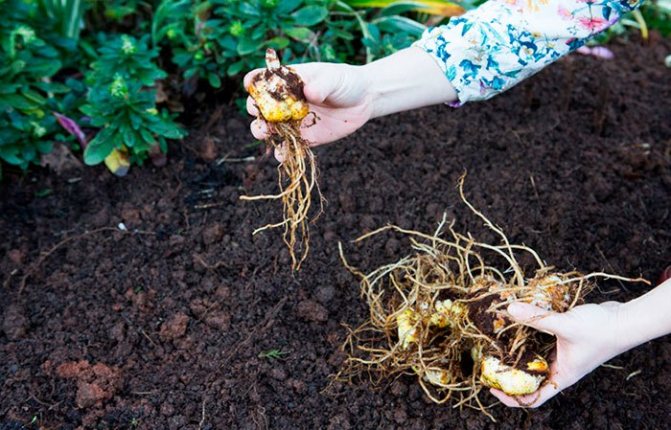
Lily plants are dug up for transplanting 30 days after flowering. With a pitchfork or shovels, they undermine them at a distance of 0.2 m from the stem. Raise the ground carefully so as not to catch the bulbs and injure the aboveground part. The stem is pruned, even if it has not yet dried up.
After they have finished digging up all the lilies, the planting material is examined and sorted at the same time. The best bulbs are selected for transplantation:
- healthy, firm, no soft areas;
- free from traces of diseases and various damages left by pests;
- 3-4 cm in diameter.


They are cleaned of dry scales and the roots are cut by one third with a knife or scissors. Root pruning causes the plant to form new, young ones. Then the bulbs are pickled in a dark pink solution of potassium permanganate for a quarter of an hour or in a solution of any fungicide, for example Fitosporin. Then they are dried in a shaded and well-ventilated area.
Frequency of the procedure
After what time periods the lilies need to be transplanted will depend on the selected flower variety. Transplant times for different varieties are as follows:


- species of Asian, oriental lilies, in which the onion grows rapidly, a large number of new heads appear, are transplanted every year;
- for tubular lilies that form many children, a transplant is necessary at least once every 2 years;
- lilies-marchons, American hybrid lilies in the next 8 years after planting, a change of place is not required;
- all other types of these flowers can not be moved to another area for 4-5 years.
Selection and processing of planting material
The least complications occur after bulb transplantation. But for this they need to be properly prepared.
- In order for the bulbs to have a good rest and stock up on nutrients, the peduncle is removed immediately after flowering, and after a few weeks, all remaining vegetation.
- Then you need to carefully dig out all the nests - that is, the mother's bulb and the overgrown babies. If the place for the flower bed has already been prepared and the transplant is planned immediately, you need to handle the roots as carefully as possible and in no case remove the soil from them. If you plan to keep the planting material until spring, all the dirt is cleaned, old, dead scales and roots are removed.
- After cleaning, you should start separating the children, while trying to separate the roots and not injure the old bulb. It is better to plant very small bulbs separately, since they will bloom only after two years, or even more.
- The remaining bulbs must be inspected. Their color depends on the variety; doubtful spots may indicate an incipient disease. The onion should be dense, full-bodied. If, when pressed, it crumples or fluid is released, it should be discarded from its landing.
- Then the planting material should be treated with a fungicide. For the purpose of prevention, you can also use the usual solution of potassium permanganate. The processed bulbs are slightly dried and start planting.


If the bulbs need to be sent for storage, they are dried in the shade outside and then placed in boxes in one layer so that you can view them and remove the spoiled ones. The signed containers are placed in a cool, dark place - a refrigerator, basement or cellar. If during storage the bulb has sprouted a little and there is little left until spring, it can be planted in a pot, and only then transplanted into the ground.
Varieties that are transplanted in summer
In summer it is possible to transplant the following early varieties of Asian hybrids:
- Bentley;
- Curitiba;
- Kogoleto;
- Fata Morgana;
- Gold Twin;
- Patricia Pride.
In warm climates, plants take root before the onset of frost and do not require additional shelter in winter.
The Candium lily variety has the earliest dormant period, which occurs in the two summer months - July and August. Before this period, it is necessary to have time to relocate the culture.





































