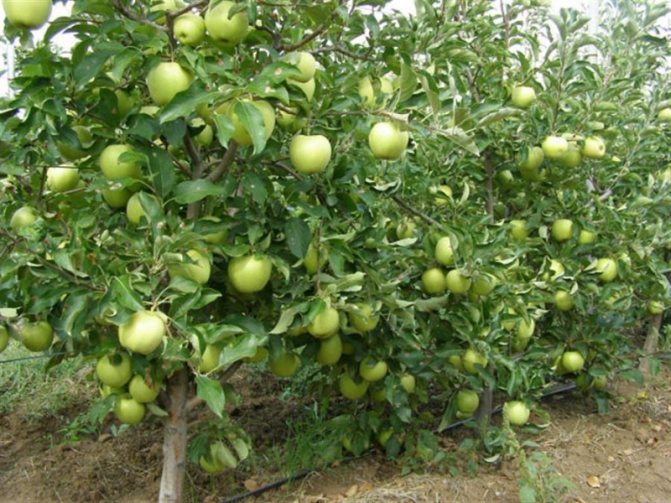
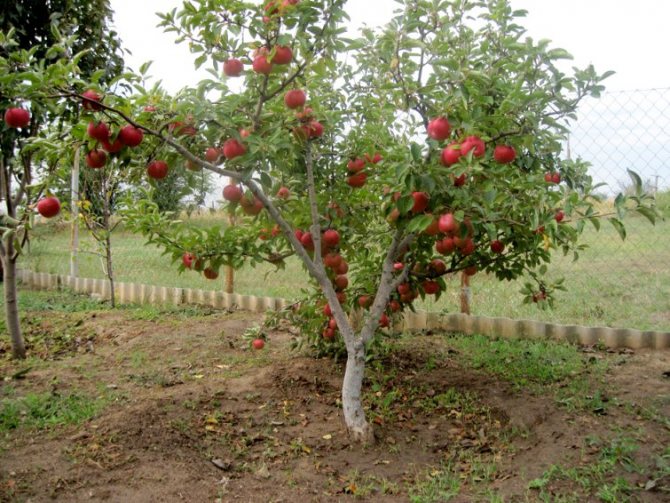
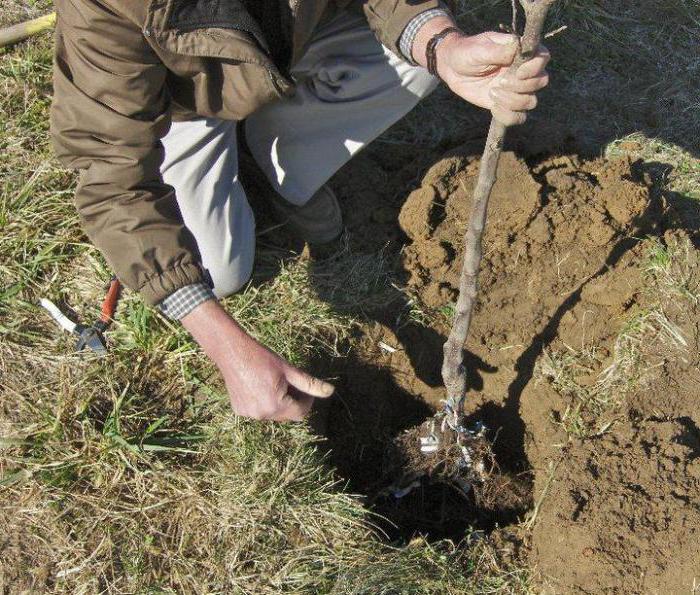
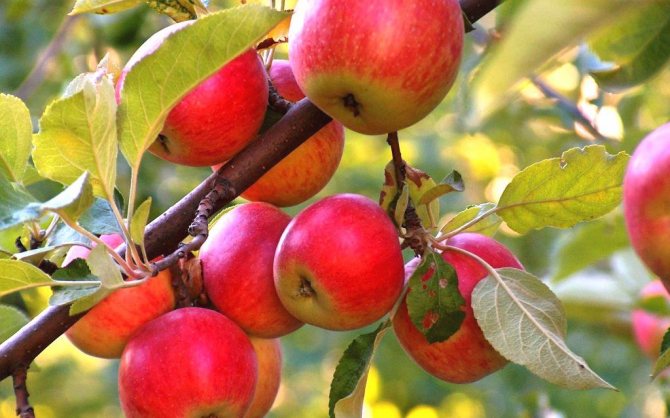
Apple trees are one of the most common fruit crops for cultivation in the CIS countries, and many gardeners are increasingly paying attention to the dwarf varieties of these trees.

The main argument in favor of such species is the ease of harvesting. In addition, dwarf and semi-dwarf apple trees have other advantages over classic varieties.
However, regardless of the variety, dwarf apple trees require special attention in matters of planting, cultivation and care, which is necessary for the long life of the tree and active fruiting.
What are dwarf trees for a garden
Dwarf trees are low-growing fruit crops grafted onto a dwarf rootstock, the total height of an adult tree does not exceed 3 m. Earlier fruiting and a long lifespan make this type of tree advantageous for growing in a small private garden. The most common dwarf trees for the garden today include the following crops:
- The apple tree is the most popular among gardeners. The number of dwarf apple varieties successfully grown in the past few years allows you to choose the color, taste and ripening of the fruit. The apple tree is the easiest to care for, the least demanding on soil and lighting.
- Pears are the second most popular, they are more difficult to take root, some difficulties can be caused by growing a dwarf scion. On the positive side, it is incredibly resistant to disease and harsh weather conditions.
- The peaches grown in the dwarf garden reach a height of only 1.5 meters. They give a high degree of survival rate, resistance to disease and frost. The best varieties for today are "UFO" and figs "Sweet Cap".
- Plum bonsai have gained popularity due to their resistance to disease and their ability to ripen even in cold regions.


Mandatory procedures in summer and autumn
Regardless of the unpretentiousness of the dwarf rootstock apple trees, there are certain procedures that must be carried out in the summer and autumn.
With a closer look at the necessary steps in the summer, the following points are highlighted:
- soil moisture tracking;
- control of insect pests (folk and chemical agents);
- the use of dressings, primarily foliar on the gland;
- taking into account the need for supports for branches with fruits.


Most dwarf apple varieties ripen during the summer to fall transition, so most of the harvest needs to be harvested in September and October depending on.
Also during this period, such a number of procedures are carried out:
- cleaning the near-stem area from the volunteers;
- sanitary pruning of shoots;
- the use of mineral fertilizers;
- loosening the soil to drive out pests from the tree area;
- chemical treatment of the tree itself from pests.


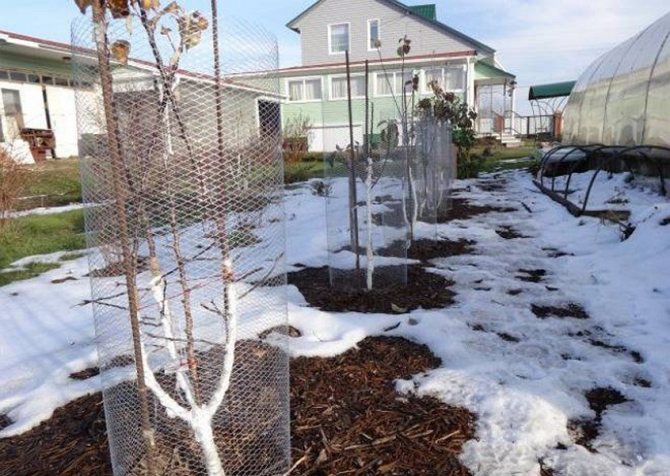
In the late autumn, it is recommended to additionally cover the soil with a mixture of soil with opal foliage, which will provide additional insulation of the root system in severe frosts.
Planting dwarf fruit trees in the garden
The key to successful long-term fruiting of a dwarf garden is the correct planting of trees. Everyone can choose a suitable way of obtaining seedlings, the ideal option is to buy two-year-old trees already prepared for planting.If desired, they can be grown independently using the dwarf scion grafting method. The best result can be achieved using as a scion:
- Budagovsky's red-leaved paradise for an apple tree;
- Quince C for growing pears;
- Felt cherry for peach or plum.
The laying of a dwarf garden, as in the case of planting standard fruit trees for the garden, can be carried out in the fall (at the end of October) or in the spring (depending on the region, before the buds begin to swell).
In any case, soil preparation begins in the fall, in the first half of October. The choice of location plays an important role for the cultivation of dwarf trees, the root system of which is high and does not deepen more than a meter. To maintain the ideal humidity regime, the best place will be where the groundwater lies close to the surface. The site itself should be well lit by the sun and, if possible, be protected from strong winds; the presence of a fence in the garden saves the situation perfectly.


The chosen place for planting dwarf trees for the garden is fertilized in advance with mineral and organic fertilizers. Ideally, this should be:
- Manure (compost) per 10 kg;
- Superphosphate 50 g;
- Potassium salt 35 g;
- Dolomite flour (limestone) 300 g.
The quantity is indicated per 10 m2 of land when mixed at a depth of the planting layer (25-30 cm). The quantity and composition can be adjusted individually, depending on the quality of the soil and the varieties of the selected plants.
A few days before planting, a hole is dug that is suitable in size for each individual variety of bonsai for the garden. Immediately before planting, a mound is poured in the center of the recess, on which the tree will be placed.
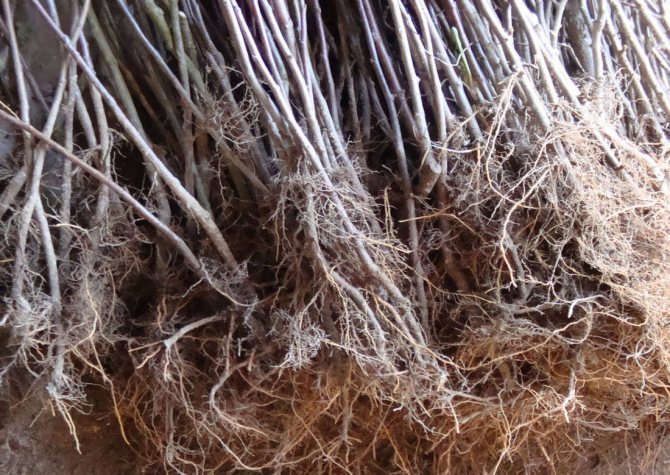
Each seedling is carefully examined, all damaged or dried roots are cut to healthy tissue. It is recommended to pre-place it in a bucket of water for 30-40 minutes to saturate the root system.
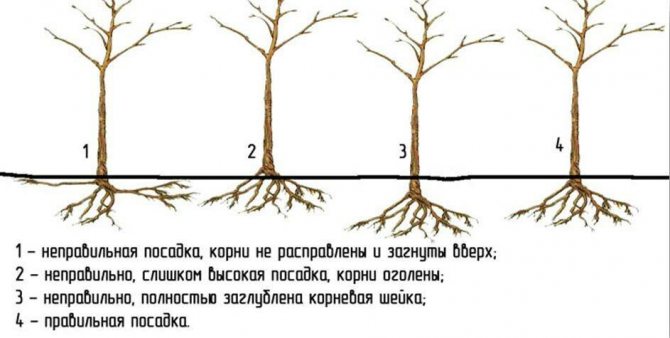
The prepared seedling is set on the top of the mound, the roots are gently straightened and covered with prepared soil mixture. When planting, special attention should be paid to the root collar of the plant, it should be slightly higher or at the level of the soil. When it deepens and is covered with earth, the tree may not take root, hurt or even die.
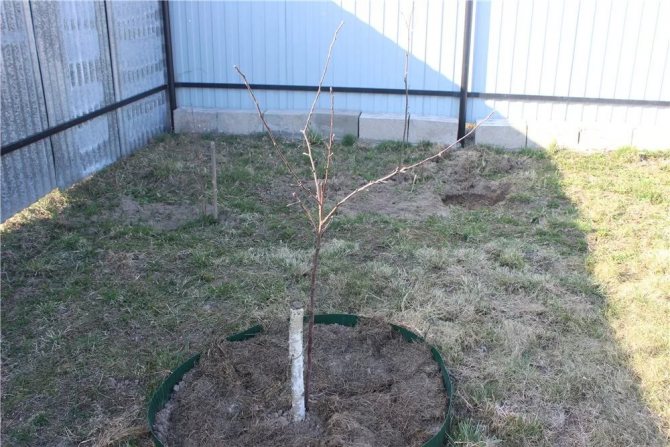
After burying, the soil is carefully compacted, the tree is watered and mulched. For the convenience of watering and guaranteeing the flow of water to the roots of the plant, it is recommended to make a root roller up to 10 cm high with a hole diameter of 60-70 cm.
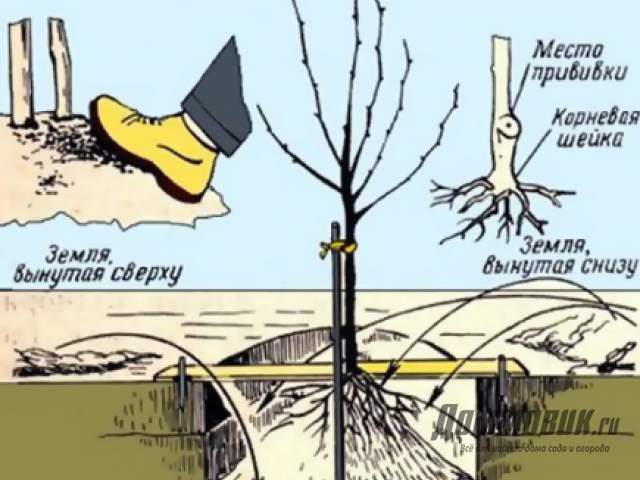

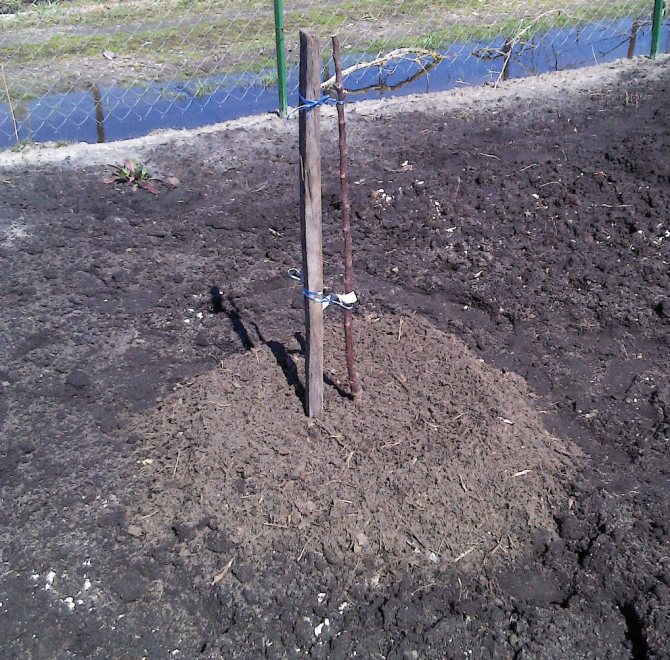
When planting fruit trees in the garden, it is important to observe the distance between seedlings, it should not be less than 2 m. Dwarf trees do not have a developed root system and need reliable supports. A peg and a wide elastic band to secure the trunk without risk of damaging its tissues will be the best option.
Growing apple trees on dwarf rootstocks


If you want to plant apple trees on a dwarf rootstock, the best choice is to purchase a finished seedling from a trusted seller.
However, in this case, you should also pay close attention to the inspection of the purchase.
After purchasing a seedling, you should take into account such a number of requirements for protecting the roots, when transporting the plant and when finally planting it on the site:
- The roots are wrapped in a wet cloth to keep them moist and provide temporary nourishment to the tree. If a long-term transportation is planned, then the humidity must be monitored and refreshed from time to time.
- A plastic bag or cropped eggplant should be put on top of the fabric to ensure long-term moisture retention. Alternatively, many people use cling film, but it is inconvenient in terms of maintaining the integrity of the roots.
- The roots should be expanded immediately before planting, regardless of the constancy of the place.Otherwise, the roots can be overdried and subsequently broken, which will lead to the death of the seedling.


Sometimes, the tree is purchased in the fall, but planting is planned only for the spring season.
In such a situation, you should prepare a temporary place of detention - a tub, a large pot or a small place on the site.
Planting a dwarf apple tree in autumn
It is recommended to plant dwarf apple trees in the fall from the second half of September to mid-October.
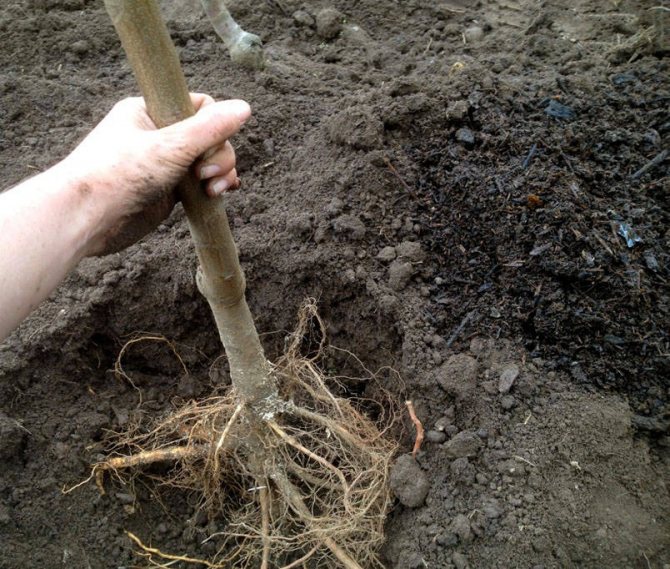


At this time, the flow of juices through the plant has not yet been completely stopped, but has already slowed down significantly.
For disembarkation, you must take into account the following points:
- The site is well lit or in partial shade, since the apple tree requires a sufficient amount of sun, and it will not break through on its own with a dwarf size.
- It is imperative to protect the landing site from excessive drafts and gusts of wind - the root system deepens weakly and does not have a central core, unlike wild apple trees and other species.
- The location of groundwater is assumed to be no closer than 1.5 m, otherwise the root system may be frostbitten from excessive moisture in the winter or it will get wet in the spring.
- Be sure to fertilize the soil before planting. This is due to the fact that the root system has its own weaknesses and does not go deep into the ground, so it collects food in the nearest area.
Important! It is impossible for the roots to come into contact with the fertilizer mixture, as the roots may suffer from some aggressive components.


It is obligatory to tie a young tree to an auxiliary support and mulch the surface under the plant with peat or humus.
The last nuance will allow you to maximize the moisture content of the soil to feed the apple tree on a dwarf rootstock.
How to plant a dwarf apple tree in spring
Planting dwarf apple trees in the spring season can only be during the period when the soil has already thawed, and the buds on the trees have not yet woken up.


Pits for this planting option have been harvested since last year, before the start of frost, they are filled with a mixture of fertilizers with fallen leaves and soil.
This will speed up the process of mixing fertilizers with the soil, and will give it time to compact.
The further process should be carried out according to the following algorithm:
- To ensure the safety of the root system from fertilizing additives, a small hill (up to 20 cm) in the center of the pit should be filled with ordinary clean soil.
- After the formation of the required elevation, a supporting element - a pole - is driven in the center of it.
- The tree must be placed strictly in the middle of such a mound, and the roots are spread over its entire surface.
- When the root system is distributed, the hole is covered with soil to a level that is determined by the grafting site. The inoculation is located 3 cm above the ground.
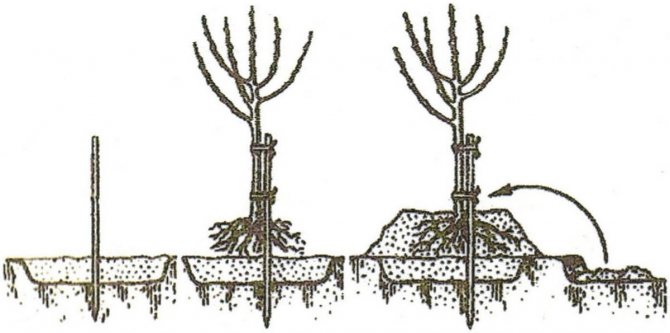

After planting a dwarf rootstock in early spring, a shortening pruning of the branches should be carried out immediately.
In the case of further care, for older trees, such a procedure is more of a preventive and crown-forming nature.
Such an early procedure is explained by the fact that the procedure must be performed before the start of sap flow.
Rules for caring for bonsai for the garden
To grow a healthy dwarf garden in your backyard, you need to provide the trees with proper care.
The basics of a bountiful harvest and healthy fruit trees in the garden will provide:
- Timely pruning. During the formation of the crown, one should be minimal, throughout the further life of the plant - on demand.
- Watering is the key to the health of a bonsai, being practically on the surface, its roots hardly get moisture. Timely moistening followed by mulching that is not adjacent to the trunk will help to get a rich harvest.
- Removing weeds is a desirable item in bonsai care.
- Loosening of the soil should be considered carefully. It is desirable for better moisture penetration, but must be carried out carefully due to the high occurrence of roots.
- Additional fertilization is carried out regularly, depending on the type of plant.
- Regular whitewashing of the trunks will protect young dwarf trees from harmful insects and rodents.


Subject to the simple requirements for planting and caring for dwarf trees, you can grow a full-fledged garden with a set of various varieties of fruits in a small area of the personal plot.
How to distinguish a bonsai seedling from a regular one
The easiest way to grow dwarf apple trees from seedlings, which can be bought ready-made in a specialty store or market. The main thing is not to confuse dwarfs with other varieties. Distinctive features of planting material for growing mini-trees:
- in the field of vaccination (the junction of the neck of the seedling and the trunk) should be a pronounced protrusion;
- root system - fibrous, with small roots;
- good roots usually elastic, fresh;
- on the ground part of the seedling there should be no areas with dry bark, injured branches;
- large kidneys there are two-year-old dwarf seedlings;
- the trunk should be smooth, have no ramifications;
- maximum stem height - 50 cm.
Read how to plant an apple tree here.
For the tree to grow well, properly transport its seedling to the planting site.
The planting material is transported in a damp cloth, the twigs are fixed to the trunk with twine. Try to plant the variety as quickly as possible. This article will tell you how to plant an apple tree correctly.
Popular species and varieties
Among the popular dwarf and semi-dwarf fruit trees, dozens of popular varieties are distinguished, which differ in terms of fruit ripening.
Apple trees
The most popular apple stock is the M9 stock. It is especially good for industrial horticulture. In our area, such early maturing varieties of low-growing apple trees are popular:
- "Candy". Apples of this type have a yellow-green, striped color, firm and juicy flesh. Ripen in August, weighing on average about 120 grams;
- "Wonderful". Fruiting begins in the fourth year after planting. It is characterized by frost resistance and high yield. The apples are large, yellowish, with red barrels, flattened, round. It tastes like honey;
- Melba. Super early grade. Fruiting begins in the second half of July, the yield is great. Fruits are medium in size, juicy with a caramel flavor. Among the shortcomings, one can note the frequent defeat by scab;
- "Suislepskoe". Less popular dwarf. It bears fruit after three years. The color of the apples is pink-yellow, striped. Fruit weight - from 100 grams.
The following species are classified as mid-season, autumn:
- "Autumn striped". The fruits are large, weighing up to 200 grams. The color is bright yellow, the taste is sweet and sour. Apples of this kind lend themselves well to storage at low temperatures in basements and cellars;
- Zhigulevskoe. The most resistant to weather conditions and diseases variety. Produces red-orange fruits in the second half of September. Possesses high commercial characteristics;
- Sokolovskoe. The variety is high-yielding: one tree gives 80-90 kilograms of greenish, sweet-sour apples with grainy pulp. The plant is a natural dwarf.
Did you know? According to the observations of archaeologists, the apple tree is the first tree cultivated by people, the fruits of which were eaten as far back as 6500 BC.
Winter, or late-ripening undersized apple trees include varieties:
- "Bogatyr". The variety is tolerant of sudden weather changes, but requires increased attention: in order for the apple tree to bear fruit regularly, it is necessary to carry out frequent pruning of branches. Fruits are elongated, red-yellow, sour;
- "Snowdrop". Fruits have a conical rounded appearance, yellowish color and red barrel, sweet and sour taste. The apple weighs 150 grams.
- "Moscow necklace".The species is quite new, but already quite popular. Fruits are bright red with pinkish pulp and have a sweet and sour taste;
- "Grushevka Podmoskovnaya". The tree begins to bear fruit in the sixth year after planting. Differs in rather small white fruits. Possesses good preservation and productivity.
Also, the varieties of apple trees that are no less popular include:
- "Ottawa";
- "Aroma de Vare";
- Earley Mac;
- Airlie Geneva.
Check out such varieties of apple trees as: "Aport", "Rudolph", "Bratchud", "Red Chief", "Spartan", "Mantet", "Currency", "Semerenko", "Orlovim", "Northern Sinap" and " Orlik ".
Pears
The most common types of undersized pears among gardeners are mid- and late-ripening:
- "Grand Champion". A variety with a high yield, the fruits are large, weighing up to 250 grams. The pulp of pears is oily, very juicy and sweet. Also resistant to frost;
- Veles. Round shaped dessert pear. The color of the fruit is greenish. The weight of one pear is 180-200 grams;
- "Parisian". Fruits of winter ripening, sweet and sour taste, rather large. In color - green-yellow, with a protruding redhead.
It is good to plant a pear near the place where it previously grew: plum, cherry or sweet cherry.
Plums
- Blue Free. A very winter hardy species of miniature plum. Differs in early maturity. The fruits are inky black and oval in shape.
- "Chachakskaya". Late ripening plum tree. The pulp of the plum is creamy and has a sweet and sour taste.
- "The president". The most unpretentious plum tree. The harvest gives quickly, a lot and with high quality. Has high commercial characteristics. The fruit is oval in shape, sweet in taste.
It will be useful for you to learn about: recipes for harvesting plums for the winter, making plum wine, and also read how to dry plums.
Peaches
The maximum height of dwarf peaches is about two meters.
- Sweet Cup fig peach is considered the most widespread. The variety is winter hardy, very fertile. Fruits with whitish flesh and sweet taste.
- UFO is another kind of miniature fig peach. Very disease resistant species. The fruits are extremely sweet, large and juicy. A great option for industrial gardening.
Apricot
- Earley Red Orange. A very early variety of low-growing apricots. Apricots are large, light orange, with a red barrel, sweet in taste. Market variety, has high transportability and storage rates.
- "Hardy". Late variety of apricots. It is very common in our area due to its resistance to low temperatures and drought. The fruits are large, with an easily detachable stone. The skin is thin, the pulp is rich orange, juicy, sugar-sweet.
- "Crimean Cupid". Medium late grade. Apricots are large and compressed, weighing up to 100 grams. Light orange in color, with a sour taste. Very aromatic.
Did you know? Queen Elizabeth II of England begins her breakfast with two plums grown in her own garden at Holyrood Palace. The variety of these plums is called "Brompcon".
conclusions
- Dwarf apple trees are small in size and high in yield.
- The easiest way to plant trees is with seedlings.
- All varieties on sale are divided into summer, autumn and winter varieties. Also read about the Chudnoye dwarf apple tree.
- When buying a seedling, pay attention to a number of specific characteristics that distinguish ordinary seedlings from dwarf ones.
- Planting in the ground is recommended in the spring so that the trees grow well, use fertile soils, and regularly apply top dressing.
Are there any downsides?
The organization of a dwarf garden is not without its drawbacks.
Initial investment
The cost of purchasing planting material is several times higher than when planting a pair of ordinary trees. Also, dwarf varieties are more expensive in themselves than cuttings of simple fruit trees.
Difficulty leaving
The difficulty here is not in the events, they are the same as in an ordinary garden, but in the frequency of their holding. And it is often difficult to set aside enough time.
Life span
Low-growing varieties of trees live almost two times less than an ordinary garden, which means that their fruiting period is shorter.
The need for supports
The shallow roots of low-growing species forces the gardener to purchase supports for each tree. It is impossible to predict from what the tree will bend or fall: from the severity of the fruit or from the wind.
Important! In the process of choosing a place for a garden, pay attention to the future neighbors of your trees: if a maple, linden or oak grows nearby, the place is more than suitable. If the adjacent territory is planted with alder, sedge and horsetail, the acidity of the soil is increased and it is not suitable for fruit crops.
Cultivation of a low-growing garden
A bountiful harvest, healthy and neat trees are the aspirations of every gardener. For these purposes, it is necessary to adhere to some requirements for the cultivation of dwarf plantations. Let's consider them in more detail:
- Carefully remove weeds around the tree and keep it clean.
- To prevent the formation of a crust on the soil, it must be slightly loosened and applied with nutritious mulching. It is advisable to use ½ or ¾ decomposed compost as mulch.
- For regions with dry weather and fast drying soil, the soil needs to be protected and valuable moisture is retained inside. For this, a hay litter is suitable.
- Mulch of any type should be at least 60 cm from the trunk of the dwarf seedling, and the outer boundary should end with the circumference of the crown of the tree.
- Do not use the mulching technique in particularly wet seasons, as well as on overly heavy soil.


How to plant and care for basic rules
Dwarf trees can serve not only for planting in the garden, but also as a decoration for the home. Such babies are planted in a tub and at any time can be transferred to the open ground.
Landing
The most optimal time for planting fruit crops is autumn. Temperature regimes and a long period before the beginning of the growing season contribute to root engraftment and the growth of the root system as a whole. The soil should be plowed and level, marked out for planting seedlings. Planting holes should be 60-70 centimeters deep and about a meter wide. When laying planting material in the pits, mineral and organic fertilizers should be added, which will significantly accelerate the formation of additional shoots. Before planting, the seedlings are inspected, sorted and pruned. The planted stalk should be in the ground at the level of the graft; you should not sprinkle the graft itself with earth. Upon completion of planting, the trees need to be shed well.
Important! If improperly done in the process of planting and caring for a stunted garden, trees can change their variety, going to the roots of the rootstock.
Care
Unlike ordinary fruit trees, dwarf trees are more demanding on the soil, so you need to monitor its condition: conduct regular watering, fertilize. Loosening will be inappropriate here, since young tree roots are shallow. As the garden develops, the garden maintenance activities may change slightly. So, over time, it is necessary to carry out pruning, preventive treatments, organize supports and cover the garden for wintering.
Harvesting
The most pleasant thing in the process of growing an orchard is, of course, the time of harvest. The collection takes place at different times: it all depends on what types of plants you will be planted - early, mid or late ripening. The process itself is quite easy and fast, due to the size of the trees. Like any other occupation of a gardener, planting and growing a dwarf orchard takes a lot of time and effort.But the payoff is worth it: the yield of such plantings exceeds the yield of ordinary gardens, and most importantly, you will be able to get fruits much earlier.
Important conditions
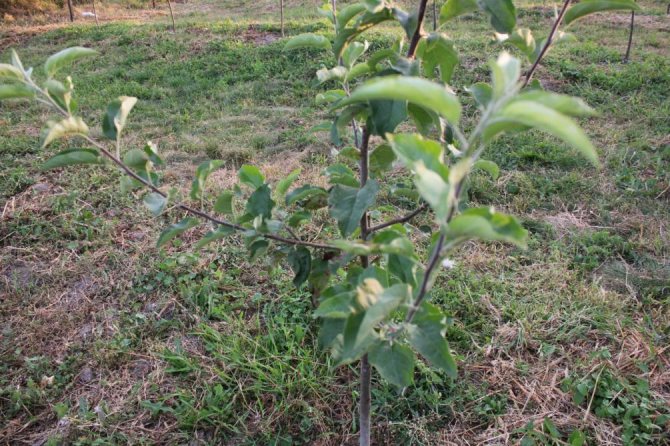


Biennial apple tree sapling
Planting material purchased for planting an apple tree in the fall must be planted in the soil as quickly as possible. Long-term storage can lead to overdrying of the roots and further death of the seedling. Plants 1 - 2 years old take root well. Such young specimens should be chosen in nurseries. In plants of three or more years old, this process takes longer.
The deepening for planting trees is prepared in advance. You should take care of the timely introduction of nutrients. The plant must receive all the components necessary for growth. After planting, the seedling must be watered abundantly. This should be done using a watering can with a wide nozzle. It will help to moisturize the soil well and compact it in a way that is optimal for the normal growth of the apple tree.
Tall tree varieties should be planted at least 4 meters away. For dwarf apple trees, the distance between the trees is about 3 meters. This condition is very important for normal rooting and further growth of apple trees in any region.
The area for breaking an orchard should not be above the pipes of communications. In addition, when choosing a land, you need to take into account the level of occurrence of groundwater. If the distance is less than 2.5 meters, such a site will not work. The roots of apple trees must develop in a comfortable environment and have freedom of movement and growth.
The best time for planting in autumn will be dry and warm days, when the air temperature during the day is kept at + 10 ° С, and at night it does not drop more than + 5 ° С. In such conditions, the root system of the fruit tree develops very quickly and well and the plant will quickly be ready for wintering.
Fruit trees
Almost all fruit trees are represented by traditional tall and dwarf varieties. Below are the features of the most popular crops.
Apple tree
Dwarf and columnar varieties of apple trees are distinguished separately. First of all, they differ in the external features of the trunk. The bonsai is outwardly completely identical to the classic one, it differs only in height. Columnar varieties practically do not form branches, there are no clear branching.
On sale you can find apple trees reaching heights of up to 1.5-3 m. More than 1,000 varieties are known, which are usually classified as they ripen. The most famous varieties of dwarf and columnar apple trees: Candy, Chudnoe, Zhigulevskoe, Autumn striped, Carpet, Snowdrop.
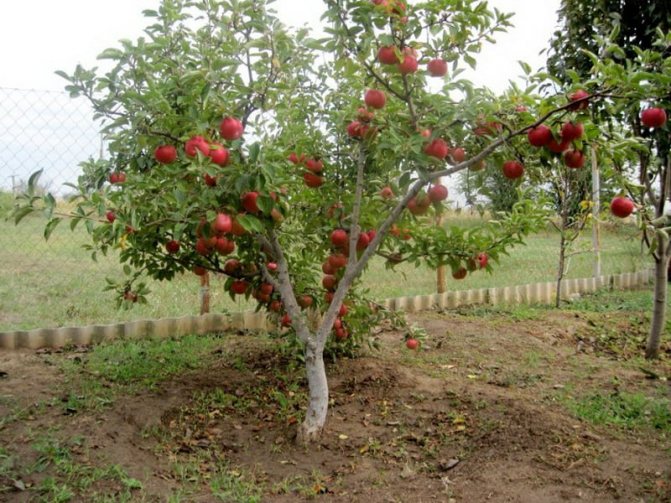


Pear
In the scientific literature, they are called pears on a dwarf rootstock, they have a small height, reaching 1.5-3 m. They have a high yield, the fruits are in no way inferior to tall varieties. Fruiting is possible as early as 4 years from the date of planting.
As in the case of apple trees, dwarf and columnar tree species are distinguished separately. Popular varieties: Velesa, Bere Gardi, Otechestvennaya, Parizhanka, Rossoshanskaya beautiful.
Plum
Dwarf varieties are distinguished as a separate species of the Plum family. Externally, they can be represented by a recumbent or upright deciduous shrub, the height of which does not exceed 2 m. In horticulture, dwarf plums are obtained using a special technology of planting and rootstock (table grafting or on a garden bed).
The plant is characterized by slow growth, fruiting occurs only 3-4 years after planting. Usually, the tree has a weak frost resistance, it is not recommended for planting in the northern regions. Famous varieties of dwarf plum: Blue Free, Chachakskaya, President.


Peach
They are displayed only with the help of a dwarf rootstock. Plant height does not exceed 2 m, it is sensitive to temperature conditions and humidity.
Not recommended for cold summer regions. They have developed foliage, so regular shaping is required.Popular varieties of dwarf peach: Sweet Cap, UFO.
Low-growing varieties of this culture are obtained using a special dwarf rootstock. As a result, a tree of small stature is formed, which fully retains the yield indicators. They often have a sweeter taste and a higher weight of the fruit. Notable varieties: Hardy, Crimean Cupid and Earley Red Orange.
Diseases and pests ways to deal with them
The list of the main diseases of the dwarf rootstock fully corresponds to a similar list for tall varieties of apple trees and includes the following names:
- "Witch's Meter" (polypheresis);
- powdery mildew;
- muxosed;
- dying off of branches;
- rubberiness;
- flattened branches;
- tsitosporoz;
- tinder fungus;
- common cancer;
- pome fruit rot;
- bitter rotting fruit;
- mosaic ringing;
- scab;
- rust;
- black cancer;
- vitreousness of the fruit.
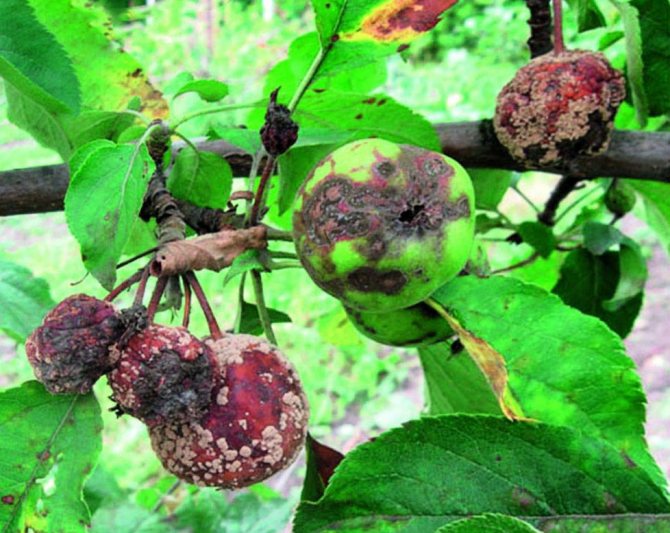


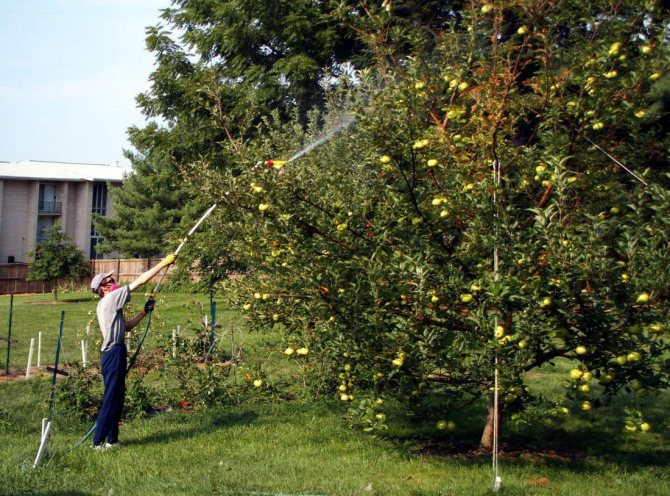
To eliminate fungal infections of apple trees, the following group of agents and compositions is successfully used:
- Skor;
- Topaz;
- Horus;
- Kvadris;
- Fundazol;
- Ridomil.
It is also allowed to use copper sulfate, Bordeaux mixture and colloidal sulfur. In the case of viral lesions of a tree, there are no direct methods of influencing the disease, therefore, the affected area of the tree is indirectly cut off and processed with copper sulfate.


If the tree begins to recover from the disease, then it can be grown further.
But, if the disease continues on the healthy part, the apple tree should be completely uprooted and burned.
Among pests, the following representatives are the most dangerous for apple trees, both dwarf and tall:
Table of the main pests
| apple aphid; | apple moth; | rowan moth; | mole leaf roll; |
| currant leaf roll; | bluehead scoop; | copperheads; | red apple mite; |
| western unpaired bark beetle; | tube wrench; | sawfly; | hawthorn; |
| fruit moth; | moth and skinned; | oakleaf and ringed silkworms; | scabula comma-shaped. |
Such a list of individual pests is largely due to their universality in terms of defeat - they attack not only apple trees, but also an extensive list of other fruit crops:
- Pear;
- Plum;
- Sweet cherry;
- Apricot;
- Bird cherry;
- Cherry plum;
- Willow;
- Peach.
And this is not a complete list of possible neighbors for a dwarf apple tree, which can become a source of another pest.


To eliminate them, insecticides are usually used, which must be sprayed not only on the apple tree, but also on all fruit crops present on the site.
Decorative types and varieties
Among dwarf trees, there are not only fruit and berry crops, but also ornamental plants. They do not form a crop, but are distinguished by beautiful flowering, shape and foliage.
They are actively used for landscaping household plots, city parks. They respond well to shaping, suitable for creating a variety of decorative compositions.
Thuja
An unpretentious and very decorative tree for planting outdoors. Dwarf representatives grow up to only 1.5 m, they are frost-resistant and resistant to diseases and pests. Among the varieties, you can find plants with a pyramidal, oval or spherical crown shape.
The plant looks harmoniously next to undersized deciduous and coniferous shrubs. Western thuja Brabant and Wagneri are the most famous representatives of this culture, forming a miniature tree.


Decorative maples
This is a low-growing, unpretentious tree, known for its beautiful deciduous crown. It looks especially decorative in autumn, when the leaves turn yellow-red. It grows up to 3 m in height, responds well to shaping. The most spectacular dwarf types of ornamental maple are Canadian, Holly and Platan.
Magnolia
An exotic flowering tree that forms a fairly voluminous shrub. With proper care, dwarf varieties only grow up to 4 m in height. Magnolia looks especially decorative during flowering. During this period, the plant is completely covered with large buds up to 15 cm in length.
They exude a delicate aroma with vanilla-citrus notes. Magnolia is very whimsical to care for, not suitable for beginners.


Spruce conic
A variety of ornamental Canadian spruce, it is the result of natural mutation. The plant is represented by a coniferous tree growing up to 1.5 m in height. It has a pronounced conical shape, soft blue-green foliage.
Reacts well to shaping, suitable for creating hedges. The main disadvantage is very slow growth, in one year the spruce adds only 2-3 cm. This is an unpretentious plant, it can grow even in frosty winters and cold summers.
How to plant correctly?
When planting any crop on the site, you must strictly follow the recommendations of gardening specialists at every stage. This is the key to getting the expected results. Otherwise, what will later grow on the site may turn out to be too unpredictable or the result will disappoint the gardener.
The choice of planting material
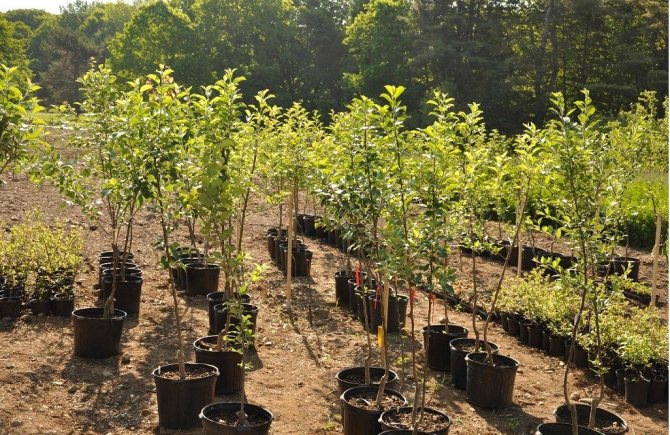


Apple seedlings in the nursery
The purchase of a young tree should be carried out in a proven nursery. As a last resort, you can purchase a seedling in a large, well-known store, having previously studied the independent reviews of ordinary buyers. They approach the choice very responsibly and make it according to several criteria at once.
There are seedlings on sale with an open root system and a closed one. The second type is much less whimsical to care for and takes root pretty quickly on any soil. In addition, you need to get expert advice about the varieties presented. It is best to purchase exactly those apple trees that grow and bear fruit best in a particular climate.
Agronomists give a number of general recommendations that will help with the choice of a seedling:
- In the lower part of the trunk of a young tree, there should be a trace from the vaccination, it should not be too large, the bark should remain in place, this is a guarantee that the plant is not a wild game;
- all parts of the plant are intact and intact, with no pests or obvious signs of disease;
- you should not buy seedlings older than two years of age - 1 - 2 years is the optimal age for planting material;
- the height of the plant should vary from 1 to 1.5 meters - a tree that is too tall and abundantly overgrown, most likely, was overfed with nitrogen, uncontrollably applying fertilizers, such a plant will not overwinter after planting on the site, weak and frail trees have received improper care and will also be unviable;
- the root system should be small (about 20 - 25 cm), the processes are elastic and strong, without visible damage.
In recent years, dwarf and columnar apple trees have become very popular. They are small in size, due to which they are compactly located on the site. At the same time, they give a rich harvest and are relatively unpretentious in care. You can also transplant in the fall, but all work must be completed by the end of September. And you can start planting only after the tree slows down all its life processes and sheds some of the foliage.
Preparation of planting material
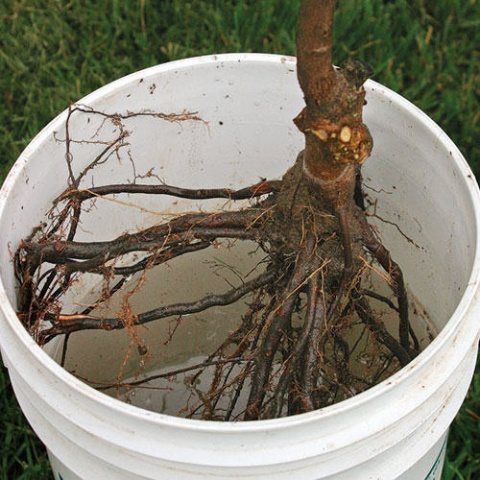


Inspection of the root system of an apple tree seedling before planting
Preventive measures will not harm any seedling, especially a tree with an open root system. The first thing to do is to wash the roots from dirt and old adhering earth. Then the roots are carefully examined and, if necessary, all damaged, dried out or painful-looking parts are removed, trimming them to a healthy area.
After that, you can dip them in a clay mash. A few hours before planting, you need to place the roots again in water or Kornevin's solution and only then plant them in a previously prepared place.
Site selection and preparation
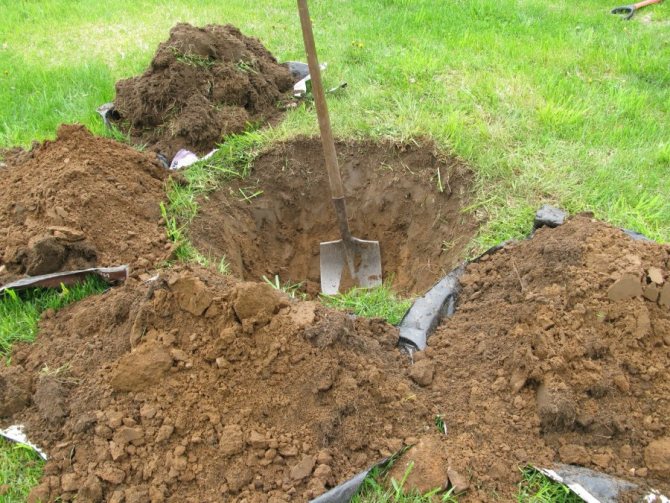


Preparing a pit for planting an apple tree seedling
This point of preparation must be approached with all responsibility. This should be a comfortable habitat for the apple tree so that it develops well and gives rich yields. With the wrong choice, the fruit tree will feel bad, not grow and give meager apple yields.
There is a set of rules to be followed when choosing a place:
- the site should be open to sunlight, not shaded;
- there should be a barrier from the northern part to protect the plant from the piercing cold wind in winter and drafts;
- it is important to retreat a sufficient distance from structures and other plants;
- too moist soil or marshy area is not the best place for an apple tree.
Neutral acidity, a good fertile layer and the availability of oxygen are the key to the correct development of the apple orchard. Light loam or black soil is suitable, this is an excellent soil option for apple trees.
The preparation of the pit should be done in advance, ideally a month before planting the planting material. The site is cleared of debris, dirt, old leaves and grass. Then they dig a hole, throwing the fertile layer aside.
The dimensions of the recess in the ground directly depend on the type of plant:
- tall varieties need a pit with dimensions (WxD) 100 * 80 cm;
- medium-sized - size 90 * 70 cm;
- undersized (including columnar apple trees) - 80 * 60 cm.
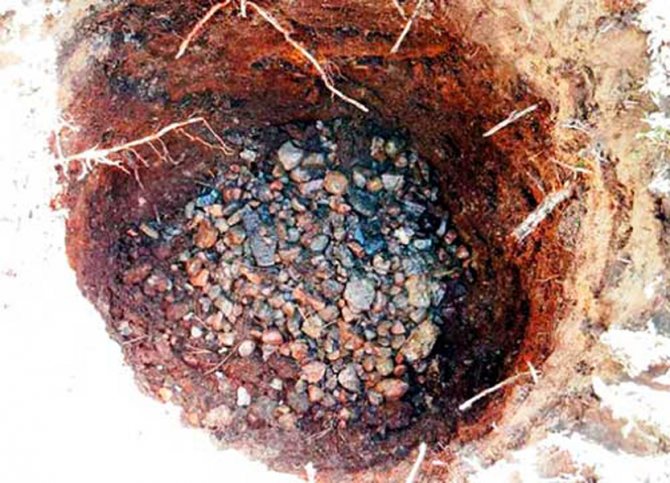
Seedlings of container growing, the roots of which are closed, are planted in a small depression. The volume of the hole should not exceed 2 - 3 times the size of the root bunch of the plant. If the soil is too heavy or the groundwater is too high, it is necessary to make a drainage layer.
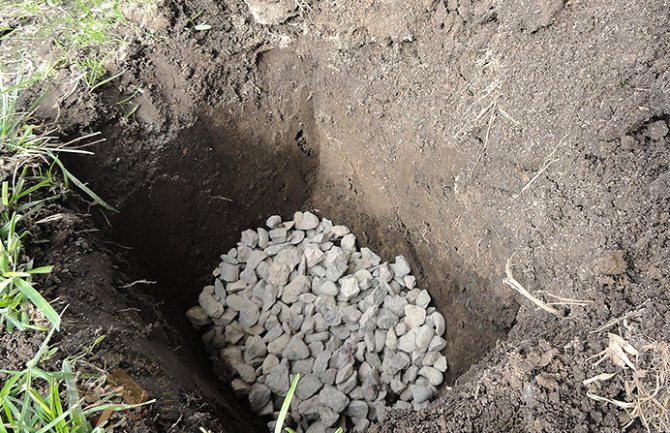


Preparing drainage before planting an apple tree
To design the correct substrate, you need to fill in broken brick on the bottom of the hole. The thickness of this layer is about 15 cm. After that, the pit is filled with a layer of fertile soil mixed with nutrients.
To compile the nutrient composition, you need to mix the removed fertile soil layer with a bucket of compost or humus, and add fertilizer. Potassium sulfate in the amount of 70 g and superphosphate in the amount of 100 g will be an excellent starting composition for a young tree.
The preparation of the pit involves filling it with a nutrient composition. We leave enough space for a comfortable location of the seedling. After filling with soil with fertilizers, the pit is carefully spilled with water so that the earth settles in a natural way.
Planting planting material

Scheme of planting an apple tree seedling in autumn
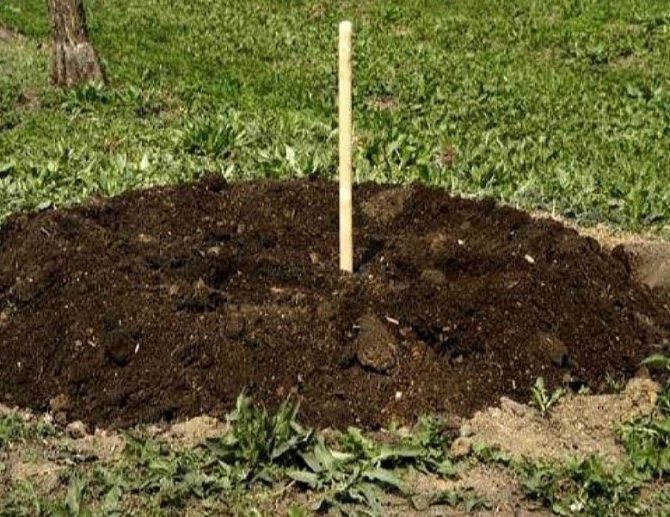
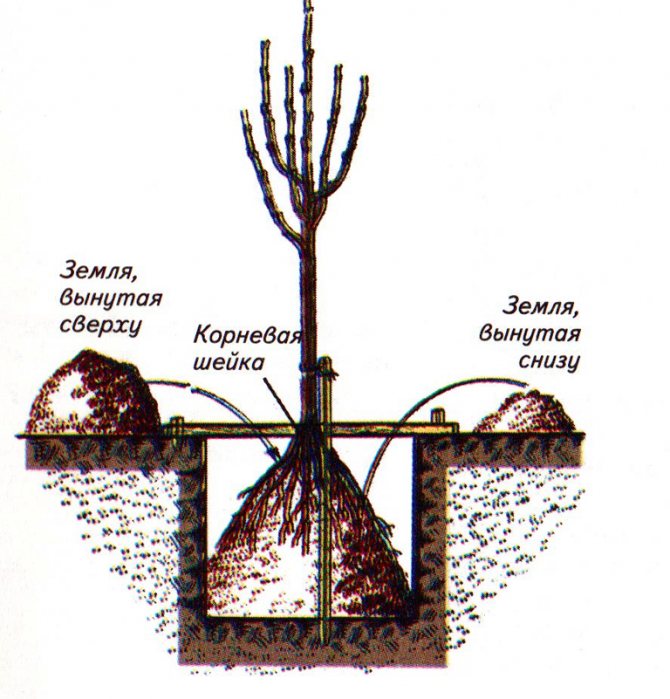
In the pit, a mound is made of loose earth and a peg is placed in its center. It will serve as a support for the planted seedling. Then a seedling is also installed in the center, and its roots are straightened along the entire perimeter of the pit. After that, you can start filling the pit with soil. Do not forget to constantly shake the seedling to fill all the voids with soil, so the plant will root well in the ground and will sit tightly in the ground.
The root collar, after falling asleep with earth, should protrude 3 - 5 cm above the surface. If the collar is drowned deeper, the plant will die. Its high location above the soil surface is also not recommended. The roots will be too exposed to weather conditions, they can freeze in winter and dry out in summer.
After planting the seedling, the soil around is compacted with your hand, or gently stepping on with your foot. Then they form a near-trunk circle, making a small roller around the tree at a distance from the trunk, its height is about 10 cm, for watering. Then the planted tree is watered. In total, you need to add about 3 to 4 buckets of water, but this should be done gradually, pouring out a small amount and waiting until it is completely absorbed.
Benefits of dwarf gardens
We will start, as usual, with the positive aspects, thanks to which such green areas have gained some popularity all over the world:
- Early entry into fruiting. This is a very important indicator for both industrial and private gardening, because we plant fruit crops on the site not at all for beauty, but for a bountiful harvest. So, an ordinary fruit tree begins to bear fruit 5-6 years after planting. For more than ten years, it has been increasing and stabilizing the yield, and only by the age of 17-18 years of life, it begins to give a constantly plentiful harvest, that is, the time of full fruiting begins. For dwarf pears and apple trees, the situation is slightly different. Their first fruiting occurs 3-4 years after planting, but they can begin to give a full harvest in 8-10 years. Simple mathematics helps to calculate that dwarf trees begin to give full harvest almost 10 years earlier;
- Simple plant care. Standard fruit trees reach a height of 7-9 meters and a crown width of 5-8 meters. If we take some special varieties, then these figures may increase a little more. This is the main reason, because at the level of human growth, only a small part of the crown, and its main part is much higher, respectively, it is very difficult to harvest, cut or process a tree at that height, and for this you have to use a special tool or even equipment. If we consider dwarf trees, then there are no such problems. The whole complex of care can be provided directly from the ground, since the height of such apple and pear trees is, on average, about 2.5 m. Harvesting, cutting off unnecessary shoots, and spraying will be much easier;
- The feeding area of dwarf trees is another rather significant advantage over tall trees. The calculation here is also very simple. In a tall tree, this area can reach 40-48 m2, in some varieties, and more. If you take dwarf trees, for example, apple trees, grafted on the paradise, then you can feel a significant difference in the food area, because it is only 8-9 m2. The conclusion suggests itself: on the area of a standard tall fruit plant, 4-6 dwarf plants can be grown;
- Productivity is the most significant advantage that you can rely on when choosing. Professional gardeners, breeders and agronomists have repeatedly proved the fact that the yield of dwarf crops is much higher than the yield of tall fruit trees. It is worth noting the quality of the fruit, which grows larger and closer to the standards.


This list of benefits allows us to draw some conclusions that work exclusively towards low-growing gardens.
Dwarf trees can be grown as independent plants, or as compactors among tall fruit crops.
If you mix planting, this will not affect the quality of fruits of various varieties and types of fruit trees, and even, on the contrary, you will be able to grow much more individual varieties of fruits on a plot of the same area, and consistently receive high-quality fruit products from them.
> Dwarf conifers in the garden (video)
Features of crown formation
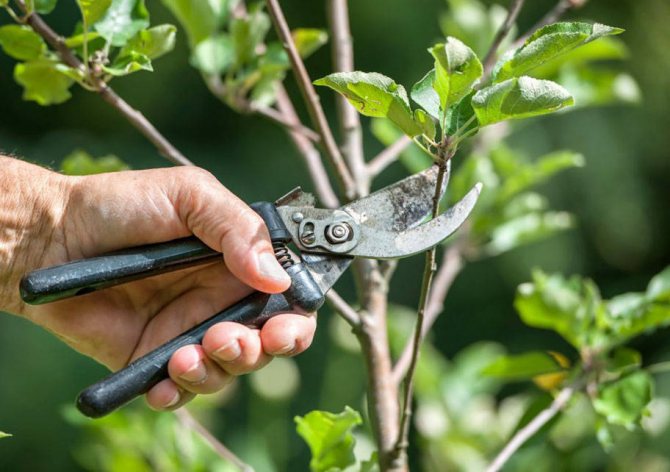


The independent development of the apple tree is possible, but this approach can lead to a decrease in yield and the gradual death of the tree.
One of the most important factors in this matter is the competent formation of the crown.
In the spring, attention is paid to rejuvenating pruning, and in the fall, the main one is sanitary, which is carried out exclusively after the harvest.
How to prune a dwarf apple tree
Crown-forming pruning for a dwarf or semi-dwarf tree is carried out according to the same principles with tall apple trees, adjusted for a reduction in terms.
The main options for forming a crown are the following types of apple pruning:


dwarf pyramid;


slender spindle;


loose palmette;


flat spindle.
The most common is pyramidal pruning, as it allows the formation of a tree about 2.5 meters high with approximately the same length of branches (about 1 m).
This allows you to free up space, make the tree more attractive in appearance and provide free space and the amount of juice for the formation of fruits.
Pruning a dwarf apple tree in spring
Sanitary and crown-forming pruning requires a thorough approach and taking into account the norms for application to trees.
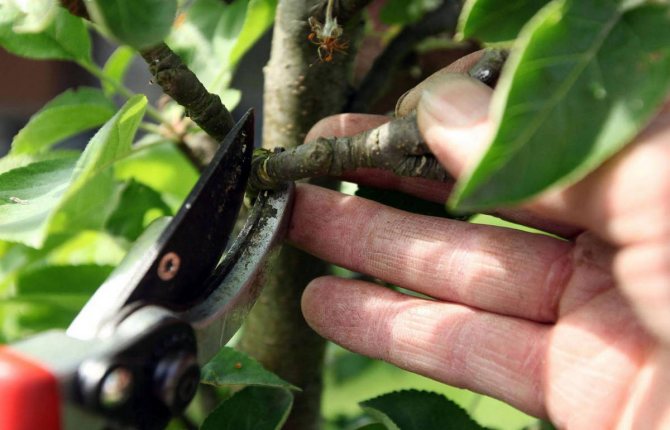


The differences in these moments are large, since sanitization does not imply the elimination of living and healthy parts of the shoots, but the formative one is largely based on the effect on the growth centers, some of which are removed.
In the spring, the priority is the sanitary pruning of the crown, which implies the elimination of all branches that have a certain number of damages:
- broken:
- improperly growing;
- frozen;
- sick;
- dried.
In addition to sanitization, it is necessary to carry out a formative one, which implies the following series of annual actions:
- The first pruning necessarily requires shortening the plant up to 50 cm, taking into account the cut for the bud opposite to the graft. Thus, at the end of the season, there will be 4-5 main shoots on the tree, the central and highest of which is skeletal.
- In the second year, the central branch-guide is cut by 20 cm, taking into account the cut on the side opposite to the left kidney. This maintains the vertical direction of growth of the main part of the tree and forms its skeleton.
- Further pruning of the center conductor implies an annual opposite pruning of 20 cm until the desired apple tree height is reached. After that, all the growth of the central part of the tree is eliminated, which will allow maintaining a certain level.
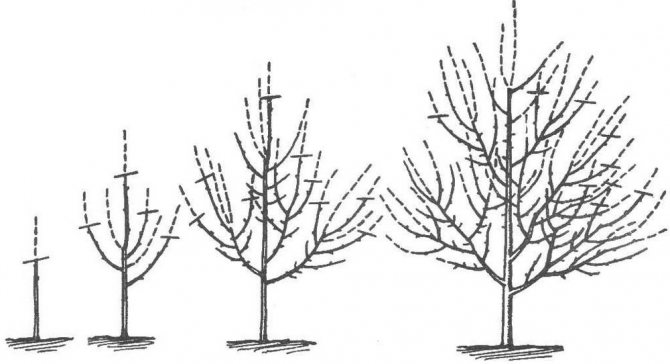

During the formative pruning of a dwarf apple tree into a pyramidal shape, lateral shoots must be shortened by 3 leaves during the summer and all branches of the second order must be cut to the first leaf from the base.
Pruning a dwarf apple tree in the fall
In the process of harvesting, quite often the branches of the tree are damaged, which ultimately requires corrections.
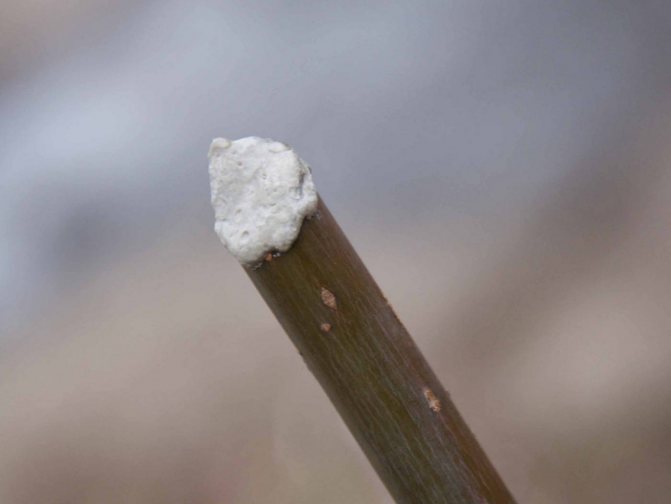
Sanitary pruning of dwarf apple trees in the fall season requires attention to the following branches:


- dry forest;
- kinks;
- diseases;
- competition;
- damage by pests.
When the thickness of the cut branch is over 7 mm, it is necessary to process the cut area with garden pitch to close the duct.
Attention! A temperature that has dropped to -5 ° C is an indication that trimming is prohibited. This is due to the fact that the apple tree at such temperatures becomes rather fragile and, accordingly, there is a risk of causing significant damage to the tree by accident.
Disadvantages of undersized trees
Unfortunately, there are a number of disadvantages when growing a dwarf garden:
- Serious upfront costs. Naturally, when planting it, much more planting material is required than when laying an ordinary orchard, and this increases the initial costs several times, which can shake the budget;
- Life span of plants. Dwarf and semi-dwarf varieties on rootstocks live much less than vigorous fruit trees, and you should take this fact into account when planting single specimens in the country or when laying an industrial-scale garden;
- Support costs. Many dwarf fruit tree varieties have a shallow root system, and therefore trees can be particularly affected by hurricane winds, erosion, or even during a high harvest, when there are a lot of fruits on the branches and a small tree can simply fall on its side under their total weight. For this reason, experts recommend installing supports, preferably under each individual tree, since it is almost impossible to predict which plant can roll or fall;
- Loss and variety changes. If planted incorrectly or simply deeply, dwarf trees can lose their properties and completely move to the roots of the scion;
- Care. We have already said that caring for such a garden is much easier than for rich plantings of vigorous fruit trees, but it is worth noting the fact that grooming procedures should be performed much more often, which also makes its own negative adjustments to the gardener's regime and schedule. And this is watering, and pruning, and fertilization;
- Weakness of some varieties. There are a certain number of varieties of dwarf trees that do not tolerate severe frosts, so you need to seriously think about the correct choice of planting material or the constant wrapping and covering of vegetation from frost;
- The need for frequent pruning. This is not a whim for the formation of the crown or the original look of the garden, but a natural requirement for a miniature green space. All trees in it, in particular those grafted on paradis, require constant pruning. This will save your crop from chopping and losing its presentation, and the garden itself from breaking branches.


As you can see, there are many shortcomings in the dwarf garden, but here it is worth knowing that many of them are fixable. And, if this is the case, then before laying the garden, you will only need to correctly determine the planting material, and also clearly follow all the requirements for planting.
Dates for planting seedlings
Planting seedlings before winter is a long-term investment in your plot. After a few years, usually already in the second growing season, the apple tree produces a certain amount of fruit. They can be consumed fresh or used in various preparations.
For the harvest to be really rich and tasty, you need to choose the right timing for planting seedlings in the garden. The favorable period for planting primarily depends on the climatic conditions of the region where the gardener is located. For example, in the Moscow region and in the Urals, the weather is completely different and frosts come at different times. This moment must be taken into account.
Experienced gardeners note that the main condition that must be met when planting young apple trees is at least 3 weeks before the first frost. During these days, the root system will have time to adapt and develop at a sufficient pace to survive the winter.
The average date for planting apple seedlings in Russia is from the end of September to 15 October. But the gardener needs to carefully monitor the temperature outside and select the timing of disembarkation individually.
There are general recommendations for the regions:
- Moscow region and Central Russia - in the regions of the central part of the country, the first frosts begin in November, gardeners are engaged in planting seedlings on the site from September 20 to the end of October;
- Leningrad region - this northern part of our country is distinguished by a harsh winter with strong winds and an early onset of frost, planting is carried out in September, without delaying and applying a sufficient amount of fertilizers, since the lands here are poorly supplied with nutrients;
- Siberia and the Urals - here experienced agronomists advise planting seedlings in the spring, this is explained by too harsh winters and the early onset of cold weather, but the Urals are spread over vast territories, so in the southern regions it is possible to plant seedlings in the soil in autumn, but this must be done no later than mid-September.
In addition to general recommendations, the gardener will not hurt to monitor the weather conditions that are outlined outside the window. In recent years, the temperature at different times of the year is too variable and can be harmful to young plantings of fruit trees, even if they are planted at the recommended time.
Features for different regions
Planting apple trees in each region is carried out according to the same scenario. The differences are only in the timing of the autumn planting. They are strongly influenced by the climate of the region of cultivation.On average in the country, work is performed from the last days of September to the third decade of October.
We are often asked questions about when is the best time to plant apple trees in the Moscow region. In this region, planting of apple trees begins in the third decade of September, and this work must be completed no later than October.
Landing in the Leningrad region is performed during September. The soils in this region are depleted, so fertilizers are indispensable.
In southern Russia, the planting period can be safely extended until the start of November, because frosts there occur at the end of November.
In the regions of Siberia and the Urals, winter is characterized by severe frosts. Saplings are not always able to survive such a winter without loss. Therefore, in these regions, planting is postponed until the spring.
Why buy dwarf apple trees
Dwarf apple trees appeared in my garden by accident. It happened 6 years ago, when there was still no garden, but there was a bare area in the South Ural steppe. It is blown by all winds, sometimes squally, with summer droughts and winter frosts down to -40 ° С.
In general, whoever has been on virgin soil at least once will understand that growing an apple tree in our area is not an easy task, but quite feasible, you just need to approach the matter responsibly. Which I did.
The sad experience of my parents helped, namely, every time my father bought seedlings from visiting sellers from unknown nurseries. These are such trucks, covered with an awning, usually stand on the roads or drive up to the markets. Their seedlings look very solid, the photos are beautiful and all the varieties are described correctly, but ...
No matter how much the father bought these same seedlings, nothing good has grown. Either they died in infancy, or, having waited for their fruits, disappointment awaited us. Then there were attempts to instill something worthwhile, but that's another story.
In a word, I decided to go the other way and forbade myself to even look in the direction of these visiting guest performers. I found a local fruit nursery, which is located in the north of our region, which means that the climate there is even sadder than ours. In general, what you need.
And when I was already delighted and tuned in to purchase apple trees, it turned out that this nursery grows only dwarf and semi-dwarf apple trees, and pears too. I was not ready for this, or rather, I did not even think that apple trees could be like that. I read the literature and made an order.
Fertilizing bonsai
Dwarf trees are perennial plantations that develop rather slowly. The growth of new shoots and branches is proportional to the formation of root shoots that go into the soil. Experienced gardeners use compost manure, decomposed compost mixes, or a combination of both to grow a strong and healthy tree.
Such fertilizer must be placed in a ring into the soil, but not close to the tree trunk, as this can harm the plant's nourishing roots. Place the compost around the diameter of the crown circumference, similar to the rules for mulching. At the same time, spraying the tree in autumn and spring is permissible, so that it pleases with harvest and health.
A guide to planting a low-growing garden can be seen in the fragment:
Meet the most popular dwarfs
The most popular types of dwarf apple trees are Chudnoe, Bradchud and Land. It is not possible to instill them on your own, so you should seek help from specialists. For example, to the nursery.
- Wonderful. The variety is late summer and has a high yield. Convenient in that it can be grown in any soil, and therefore throughout all the territories of Russia. Its main characteristic features are height (no more than 3 m), stem (small), medium-sized fruits (their weight reaches 150 grams, have a blush on a green-yellow peel).
The grains of the apples of this variety are small, and the pulp is very juicy. Taste qualities for an amateur - sweet and sour.Harvesting takes place at the beginning of September, but up to 70 kg can be harvested from a dwarf alone.


The fruits are perfectly stored. If stored properly, they will last more than 60 days. The tree itself is unusually resistant to frost. It is rightfully called the miracle pollinator of all varieties and types of dwarf apple trees. To make its pollination more successful, it is better to plant Sverdlovsk Anis nearby.
- Bradchud. Its height reaches 2 meters. The crown can have a diameter of up to 3 meters. The leaves are very large and therefore it is impossible to confuse Bradchud with another variety. One apple can weigh 150 g. But there is also the smallest weight - 100, and the largest - 250. The variety is also noticeable by the fruit: a shovchik will be visible on one of the sides. The skin is dry and free of dust or waxy coating. It is greenish-yellow in color, but it has a peculiarity - a large purple spot on half of the fruit.
The grains of apples are large, and the flesh is very juicy and white. Taste - sweet and sour. Full ripening occurs only in late September - early October. Since the species is considered winter, the fruits can be stored until spring. At the same time, they do not deteriorate at all, but retain a delicate pleasant taste and aroma.
- Grounded. Unlike previous varieties, it has small fruits. The weight reaches a maximum of 110 grams. The shape is slightly flattened, and the apple skin is oily. The fruits are very juicy and sweet and sour in taste. They are not stored very long (up to 50 days), but are well suited for preserves, juices and jams. The main advantages of the variety are that it is compact and takes up little space. This is very convenient for planting in small areas. Also tolerates frost well. The growing season is maximum 150 days.
Each variety is unique and beautiful. Among the mass of varieties and types of dwarf apple trees, you can choose the one that you like.
How to grow a dwarf apple tree: tree propagation
One of the ways to create low-growing orchards is to grow fruit trees on a seed stock with an intermediate insert of a low-growing stock from the number of dwarf forms adopted in the zone. Such trees grow somewhat stronger than directly on the dwarf rootstock itself (by 10-15%). The yield in the first years of fruiting is inferior to the yield directly on the rootstock. Then it levels out and often becomes taller.
Insertion of a thin rootstock, due to the fact that it retains the stem origin, is more resistant to low temperatures. It can withstand a drop in temperature without significant damage to 20-25 ° C of frost, while the roots of this rootstock die already at a temperature of 14-15 ° C. Trees with an insert are better fixed in the soil, but this deficiency is not completely eliminated.
Weak rootstocks reproduce, in contrast to vigorous ones, not by seeds, but by vegetative means. There are many ways of vegetative propagation.
Reproduction by vertical layers. With this method, the rootstocks are grown on a mother plantation. The laying of the mother liquor is carried out either by layering, or by grafted (winter grafting) plants. After planting a bonsai, the aboveground part of the cuttings is cut off, leaving 7-10 cm above the soil surface. In the fall, the aerial part is cut off almost to the ground, leaving 1–2 cm. In the spring of the next year, after the shoots have grown to a height of 18–20 cm, hilling is carried out. After one and a half to two weeks, the hilling is repeated and the mound is brought to a height of 18-20 cm. In the fall, before the onset of frost, the rooted layers are separated from the bushes. Before the separation, the leaves are scrubbed, the shoots are removed, the shoots are undone and the shoots are cut off with a pruner at the base by 0.5 cm. Then they are sorted, tied into bundles and sent to the top area or to the basement in plastic bags for winter vaccination.
Reproduction by horizontal layers. This is a more productive way of obtaining thin rootstocks than vertical layers.Unlike the first method, the shoots are not cut into a stump, but in the fall they are laid in furrows along the row and pinned. Further, hilling and other work when growing dwarf trees is carried out at the same time as on the mother liquor of vertical layers.
Arcuate layers are a way of accelerated reproduction of low-growing rootstocks. The eye of the clonal stock during budding in the 1st field of the nursery is grafted simultaneously with the cultivar just below it. Sometimes this peephole is turned over, so that when the shoot grows back, it immediately makes a bend and it is easier to bend it into the ground. When a vegetatively propagated shoot grows back, it is folded back into loose soil. By the fall, along with the one-year-old, they also get a cut of a weak rootstock.
Propagation by lignified cuttings. Lignified cuttings are a byproduct of the reproduction mother liquor. In the experiments of many researchers with kilchev, treatment with growth stimulants, it was possible to achieve rooting of 40-70% of cuttings. Good results were shown by winter grafting of a weak root of any apple rootstock (from the waste of desktop grafting) into the base of the cutting. In this case, the rooting rate can be increased to 75-85%.
Propagation by root cuttings. The roots are harvested in the 3rd field of the nursery when cutting the root system of seedlings. They can also be harvested in the garden. After heat treatment and growth stimulants, cuttings about 10 cm long are planted in the beds.
Breeding methods for dwarf trees for the garden are shown in these photos:
By maturity
In the same way as tall apple trees, dwarf and half-dwarf apple trees are divided by ripening period into:
- early;
- medium;
- late.
Summer
The best varieties of early (summer) ripening:
- Melba;
- Candy;
- Wonderful.
These varieties are known to most gardeners.
Autumn
Among dwarf varieties of medium (autumn) ripening, gardeners value the following varieties:
- Sun;
- Zhigulevskoe;
- Carpet;
- Autumn striped;
- Grounded.
Winter
Of the late (winter) varieties, the most common are:
- Bogatyr;
- Golden Delicious;
- Arbat;
- Legend;
- Moscow red;
- Brother of the Wonderful.
Bratchud is a variety that was bred quite recently, but has already managed to prove itself well and receive positive reviews.
Seedling preparation
For better survival, some manipulations are performed with the acquired seedlings. Usually performs root trimming, stem shortening, root soaking.
Root pruning
Seedlings with an open root system are inspected. Too long roots are slightly trimmed so as not to bend them in the hole. The dried and broken parts of the roots are removed.
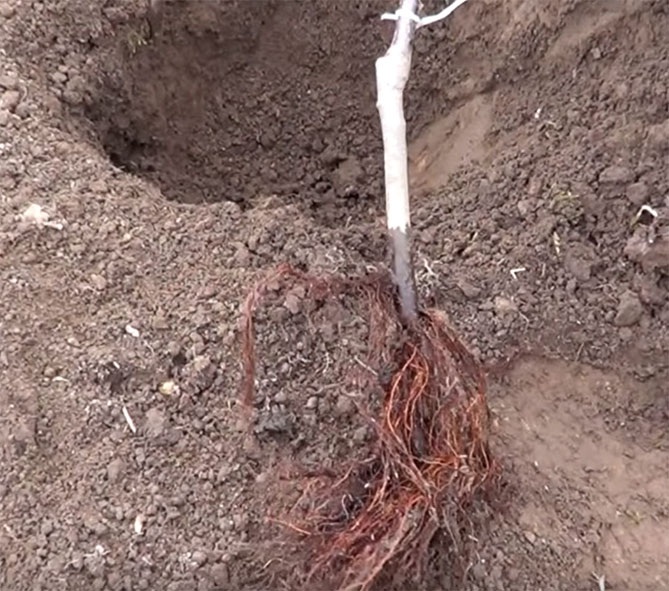


Trimming the aboveground part
Before planting, the seedling is shortened so that its height does not exceed 0.9 m. The branches extending from the grafting site and 40 cm higher than it are cut off completely. Other branches are made shorter by 2/3 of the original length.
Advice! If you have a choice, it is best to purchase a seedling that has not been pruned. So there will be confidence that he is not grown more than permissible.
Soaking roots
Planting rules require soaking the roots in water for one hundred percent rooting. They should be there for about a day. A little heteroauxin and a pinch of potassium salt are added to the water.
By zoning
Experienced gardeners know that it is impossible to grow a heat-loving apple tree in a region with harsh winters. The entire assortment is strictly zoned, that is, it is recommended for cultivation in certain regions. In addition, many clonal rootstocks are only compatible with varieties that can be grown in specific areas. Therefore, when buying a dwarf seedling, you should pay attention not only to the apple variety, but also to the characteristics of the rootstock itself and its compatibility with the scion.
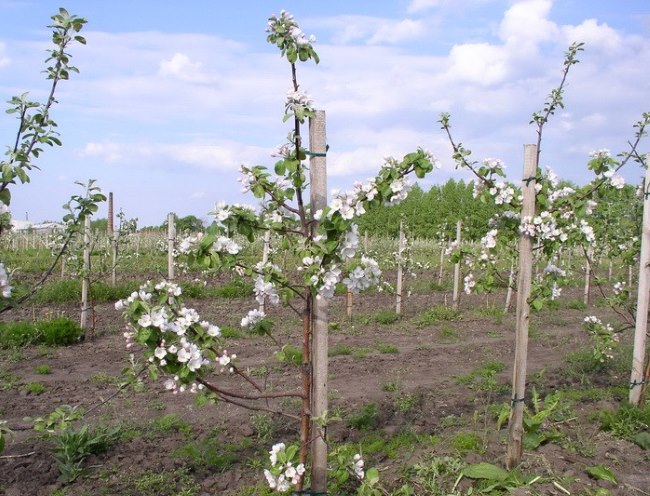


Apple tree varieties with dwarf stock.
For Central Russia
In Central Russia, there are often dry summers, and winters are mild and little snow.Therefore, the main desirable quality of seedlings is drought tolerance.
| Rootstock | Compatible apple variety |
| R 22 | Bogatyr, Zhigulevskoe, Sinap Orlovsky give a record harvest |
| 62–396 | All assortment recommended for the Central belt and the Moscow region |
| 54–118 | Champion, Melba, varieties of Russian selection for the Middle Strip |
| Kid Budagovsky (76-6-6) | With all varieties of Russian breeding, recommended for the Central strip |
| 57–491 | With all varieties of Russian selection, recommended for cultivation in the Middle Lane |
For Siberia
Siberia and the Urals are distinguished by long cold winters, so the seedlings should have excellent winter hardiness and frost resistance.
| Rootstock | Compatible apple variety |
| Kid Budagovsky (76-6-6) | With all varieties of Russian selection, recommended for growing in Siberia |
| 60–160 | Bogatyr, Gift to Grafsky, Welsey, Winter Medunitsa, Uslada and other varieties recommended for growing in Siberia |
| AT 9 | Used on seed stocks of local varieties as an intercalary (stem) insert |
For the Urals
| Rootstock | Compatible apple variety |
| Kid Budagovsky (76-6-6) | All assortment of Russian selection, recommended for growing in the Urals |
| 60–160 | Wonderful, Bogatyr, Solnyshko, Bashkir handsome and other varieties recommended for growing in the Urals |
| AT 9 | Recommended for use as an intercalary insert |
For the North-West
In the Northwest, winters are unstable, there is a lot of precipitation, a shallow layer of fertile soils, and a high level of groundwater. These are extremely unfavorable conditions for growing fruit trees. Therefore, dwarf seedlings must be winter-hardy, very resistant to various fungal diseases arising from dampness.
| Rootstock | Compatible apple variety |
| 75–11–280 | Sinap Orlovsky, Bashkir handsome, Autumn striped, Uslada, Kovalenkovskoe and other Russian varieties recommended for the North-West |
| 60–160 | Bogatyr, Welsey, Sinap Orlovsky and other varieties recommended for cultivation in the North-West |
| Kid Budagovsky (76-6-6) | Bogatyr, Welsey, Idared and other varieties recommended for the North-West |
| AT 9 | Used as an intercalary (stem) insert |
All about planting species


To plant a dwarf apple tree, you need to know its exact variety. Each of them has a different care and fit. So, for example, there are varieties for autumn, for winter. A dwarf apple tree is a little more difficult to care for than another variety of this tree.
If you want to independently get a wonderful tree by grafting, then this process is laborious and highly complex. Still, it's easier to go to the nursery and buy your favorite cutting. Only choose a nursery with positive customer reviews, so that the reputation is checked repeatedly. It is also not worth buying in the markets, since most often there are no bratchud dwarf apple trees on it. Unfortunately, to get to the nursery, you need to cover a distance of several thousand kilometers. They are found in places that are safe for plants.
Some people have repeatedly purchased from the market and were satisfied with the result. If there is a desire, then you can check, only you need to approach the choice of a cutting with all responsibility. Very often you can confuse wild animals with varieties of dwarf apple trees.
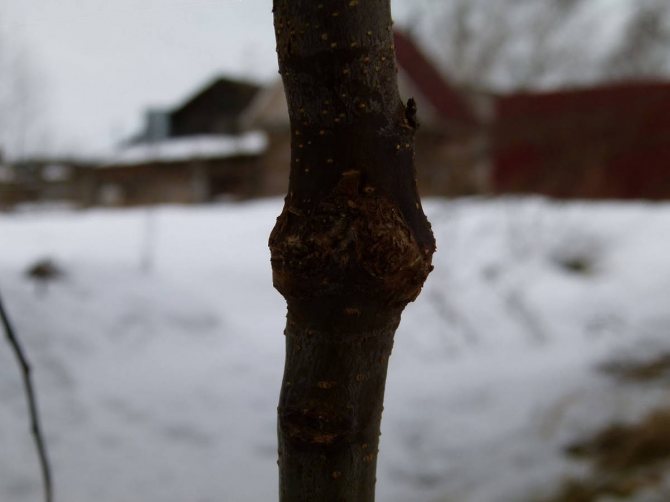
- The root collar and the stem of the seedling, to be precise between them, should have a wedge-shaped protrusion. It should be clearly visible, since this is the vaccination site.
- On a two-year-old dwarf rootstock, there are about 4 well-developed branches. But no less. The branches should have large buds (usually at the ends), the height is 45-50cm. The root system of dwarf apple trees is very elastic and has several pieces of roots.
- Consider the wild: the branches are many and sharp; no kidneys are observed, the root is pivotal.
Advice. After purchasing a seedling, it is necessary to wrap the root in polyethylene, but first in a wet cotton cloth.This is necessary so that the roots do not dry out or get damaged during the move to the planting site. The branches are shortened before planting.
disadvantages
Growing dwarf fruit and ornamental trees has a number of disadvantages. There are such disadvantages:
- the cost of purchasing planting material is significantly higher, dwarf varieties are more expensive, more seedlings are required;
- requires more frequent planting care;
- all low-growing plants are able to grow in one place for a limited period of life, the growth period is almost half that of traditional varieties.
In addition, for some dwarf trees, it is necessary to erect a support to protect against a strong gust of wind. Such plants have less winter hardiness; when grown in cold regions, shelter must be carried out.
Gardeners reviews
Diagnozstroitel
So I got the opinion that on a personal farm, an apple tree on a Dwarf rootstock is a waste of time and money. An apple tree, one and a half meters high, cannot produce more than 5 - 6 kg of apples even in a good year.
Liberty
We planted a dwarf apple tree .... the apple tree is like an apple tree, only its growth is small, 2.5-3 meters in height. We have "White filling", the yield depends on the year. Usually so - everyone has a lot of apples and we have a lot ... ..
Dwarf apple varieties recommended for the regions of Russia
What kind of gardens will grow in the 21st century? Many will answer that these are tall trees on which different varieties of several types of fruits grow at the same time. But in fact, gardens have prospects, for years the trees are grown on dwarf rootstocks.
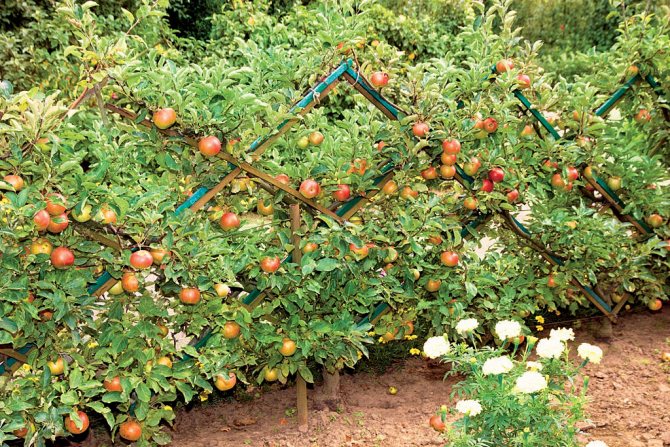
Why? These trees do not take up much space. At the same time, they give a surprisingly large yield. They are planted so that they rest on special supports. In modern gardens, trellises are arranged - these are pillars with a wire stretched between them. The branches of small trees are supported on supports.
Such a modern garden is somewhat surprising at first, but getting into it, any visitor admires the variety of varieties growing in a small area. Therefore, it is worth talking about dwarf apple trees for a summer cottage or a backyard garden.


Dwarf apple tree: reviews
Inna Petrovna: “For a long time in my garden popular varieties of dwarf apple blossom and delight with a good harvest. I have a large garden, trees are planted in rows, it is very convenient to till the soil, water as needed and harvest. The trees are not tall, it is easy to reach out and pick the apple. Even my grandchildren are very happy to help me in the harvest ”.


Yulia Nikolaevna: “Among the favorites of varieties of dwarf apple trees, I have the“ Chudnoe ”variety. The tree is low, compact, unpretentious. I watch in the heat so that the soil near the trunk does not dry out, I put in top dressing on time. Grooming is not difficult at all, as well as harvesting. I planted my first tree 3 years ago and this summer I have harvested my first crop! Apples are sweet, fragrant, just to eat, and to make juice for kids. By the way, apples of this variety lie for a long time and do not spoil. The apple tree, though small, barely reaches 2 meters, but strong and hardy, is not afraid of frost in our area. "
Victor Petrovich: “Recently I planted several saplings of a dwarf apple tree in my dacha; my neighbor in the dacha donated the saplings. He planted it for himself and gave it to me, he praised it, he says expect a big harvest soon. It's too early to think about it, I try to monitor the soil, apply fertilizers so that the tree develops well. In the meantime, a neighbor treats apples from his garden, he has a large garden and many different varieties of dwarf apple trees. By the way, it is very convenient to harvest, I helped him this year. The apples are bulk, strong, very aromatic and tasty. "
Dwarf apple trees. Video:
Features of fruit trees on a dwarf rootstock
Fruit trees on a dwarf rootstock are characterized primarily by their early maturity: early entry into fruiting and a rapid increase in the size of the yield.
A distinctive feature and great advantage of such plants is their small size. In the middle lane, their height is 3-3.5 m (on dwarf rootstocks) and 4-4.5 m (on semi-dwarf), while on vigorous seed stocks, trees often reach a height of 6-7 m (without appropriate shaping and pruning ). When caring for dwarf apple trees and other low-growing trees, labor productivity is significantly increased, especially in tree pruning, harvesting, and pest and disease control. Practice has shown that pruning 100 low-growing trees is easier than 10 vigorous ones. A lot of labor costs (up to 60%) are spent on harvesting. The rate of harvesting fruit from vigorous trees is 300-400 kg, from weak trees 1000-1200 kg, that is, labor productivity increases 3-4 times. Fruits on dwarf trees are of higher commercial quality. Their size, according to the observations of many researchers, increases by 10-15%. Due to better illumination, the color of fruits on dwarf trees improves, more sugars, ascorbic acid accumulate, and acidity decreases. When harvesting from dwarf trees, the number of pressing on the fruits is reduced by 2-3 times and the amount of fallen at hand, which improves the commercial quality of the crop. It is necessary to note the following moment.
During the period of strong winds, less fruit falls from dwarf trees in an orchard than from vigorous ones. This is due to the fact that near the ground, the intensity of the wind weakens, and small trees sway less.
In gardens on dwarf rootstocks, the ripening of fruits is accelerated by 7-10 days, which is very valuable for summer varieties - they are delivered to the consumer earlier. For varieties of the autumn and early winter ripening period, this is undesirable, since the keeping quality of the fruits worsens during the storage period. However, for deep winter apple varieties, such as Kutuzovets, Volzhskoe Zimnee, Severny Sinap, no decrease in the shelf life of fruits was noted. Fruits from semi-dwarf plantations are stored in the same way as from vigorous ones.
In a dwarf garden, fruit trees on a weakly growing rootstock have a number of features in their development in comparison with vigorous ones. They spend 60% of the products of photosynthesis for the formation of the crop and 40% for the growth of the entire tree, while on vigorous rootstocks it is the opposite. This is due to the high productivity of dwarf trees.
One of the features of trees on low-growing rootstocks is an earlier end of growth processes. This contributes to better preparation of trees for overwintering.
It should be noted that the recovery of frost-damaged dwarf fruit trees in the garden is faster. The recovery period is more intensive due to the fact that such crops are capable of producing crops not only on ringlets and twigs, which require two years to recover, but also on a one-year increment.
Dwarf trees respond more quickly to growing conditions than vigorous ones. Under unfavorable conditions of growth (drought, cold), the activity of the cambium slows down, but with the onset of favorable conditions, growth processes are more active. This makes dwarf plants more responsive to all agricultural techniques (watering, fertilizing, loosening the soil).
The root system of dwarf plants carries little water. The water conductivity of the roots of vigorous rootstocks is much higher. This biological feature of the root systems of vigorous rootstocks contributes to the development of a powerful skeleton, through which water flows relatively easily over long distances.
As you can see in the photo, in dwarf fruit trees, the volume of the root system is 2-3 times less than in vigorous ones:
It is densely branched, and the bulk of the roots lies in the surface layer of the soil (0-60 cm). However, individual roots go into the soil to a depth of 2.5-3.0 m, they provide the plant with water, especially in the hot, dry season.Dwarf trees have few thick skeletal roots. They do not anchor plants well in the soil. The fragility of the rootstock wood, the lack of a sufficient number of skeletal roots makes the trees unstable in the soil. Such plantings need additional support.
The root system of semi-dwarf fruit trees is stronger and more powerful, goes deeper into the soil, and the trees are well anchored in the soil. They do not need additional support.
Water with soluble mineral salts is absorbed by the active suction roots. They appear when the soil warms up to 4–5 ° C and form a large suction surface, 2–2.5 times larger than the leaf apparatus. Under these conditions, the tree grows and develops normally.
The parenchymal tissue is well developed in the roots of weak trees. The bark of dwarf plants occupies a large area. More nutrients accumulate in the parenchymal tissue. A densely branched fibrous root system with a large supply of nutrients is able to regenerate faster in case of damage. According to numerous observations, the roots of dwarf rootstocks when planting seedlings of dwarf fruit trees in the garden or layering in the nursery grow 3-5 days before bud break. This ensures high survival rate and good plant growth in the year of planting. In practice, trees on dim clonal rootstocks tolerate transplanting painlessly and often give an increase in annual shoots of up to 40-50 cm per year of planting. In trees grafted onto vigorous seed stocks, leaves bloom before root formation. This leads to a decrease in survival rate and to weak growth in the year of planting, especially in dry years.
One of the features of low-growing trees is that they use water more economically compared to strong-growing trees. This is due to the fact that the leaves evaporate less moisture, they have more bound water, the sucking force of the cells and the osmotic pressure are higher. They can more actively absorb hard-to-reach moisture from the soil on the verge of a dead stock.
Dwarf trees, having a more branched root system, which assimilates the top fertile layer of the soil, are more resistant to functional diseases.
The winter hardiness of fruit dwarf trees for the garden largely depends on the rootstocks, as well as on the grafted varieties and conditions that develop in the period preceding overwintering. Most southern rootstocks are not hardy enough. They can withstand temperatures down to -10 ... -11 °. This is clearly not enough for the conditions of the middle lane. New rootstocks of V.I.Budagovsky's selection 54-118, 57-233, 57-490, 62-396, 57-366, 57-476 can withstand a temperature drop to -14 ... -16 ° С, that is, at the level of Anis seedlings, Moscow pear trees.
When planting a dwarf garden, it must be borne in mind that the life cycle of low-growing trees is shorter than vigorous ones. However, in a shorter period of a garden's life, dwarf plantations produce the same number of fruits as vigorous ones over a longer period. Hence, there is a clear advantage on the side of low-growing gardens. In addition, they make it possible to quickly update the assortment, improve agricultural techniques, taking into account the achievements of science and advanced production experience.
Check out what a dwarf garden looks like in these photos:
When to plant an apple tree in autumn: optimal timing
If you plant a seedling of any fruit tree at the most favorable time, then it will take root more safely and faster, it will develop normally, and in the future it will bear fruit more successfully. The culture we are talking about is no exception. When is it better to plant an apple tree in autumn, in what month? The main guideline when choosing the optimal planting dates in the fall: two to three weeks must be left before the onset of frost... During this period of time, the seedling will be able to safely adapt to new conditions in the open field, to take root.If you plant it close to the first frost, then it simply will not have enough time for rooting, the tree will freeze and die.
The timing of planting an apple tree seedling in open ground in different regions of Russia is different:
- In the middle lane - end of September and first half of October;
- In Siberia, the Urals, the Leningrad region - it is best to plant during September;
- On South - the procedure can be performed throughout October.


When choosing a specific time, one should not forget about the weather conditions. The most suitable air temperature for rooting in the fall:
- in the daytime - 10-15 degrees Celsius;
- at night - + 5 ° C.
It is these temperature conditions that are most optimal for the procedure in the autumn. The main thing is that t is not lower!
Varieties and varietal features of dwarf apple trees
Gardeners, characterizing an apple tree, must indicate the ripening period: summer, autumn, winter. Belonging to one type or another depends on the rootstock. It is he who is responsible for the indicators. The stock is only a support on which a particular variety grows.
Varietal traits of tall apple trees are inherited in a dwarf version.
| Apple variety | Ripening period | Productivity and characteristics of fruits | Notes (edit) |
| Candy | Summer (early), usually acquire consumer maturity in the 20th of July | Fruit weight 110 ... 130 g. |
Yields up to 60 kg per tree, in record years can yield up to 120 kg.
The color of apples is reddish, visible from afar
The attached video gives the characteristics of the grade "Glory to the Winner".
Summer cultivation and autumn care


In the summer, it is necessary to carry out two main activities: watering (watch the soil) and treatment from insects that harm the plant.
Top dressing is next in line. It is carried out only for the first year, and then on demand. The most commonly used foliar method. It is simpler and more convenient. Just add the necessary elements along with watering. Iron is especially important for the apple tree. It is never enough for a tree.
As the fruit ripens, start preparing the branch supports. Dwarf apple trees are very fertile, there are many apples on them. This can cause branches to break. In addition, many fallen fruits appear. They must be removed immediately, as they attract the attention of insects. Also, due to the volunteer, pathogenic microbes appear that can destroy the tree.
Harvesting begins in the autumn. After that, it is necessary to carry out all the work to prepare for the winter cold and hibernation. Here you should prune for sanitation, remove fallen leaves and carrion residues, be sure to apply fertilizer. Closer to cold weather (mid-October) - treatment against pests and fungal diseases (Bordeaux liquid or Nitrafen). To prevent the trunk from freezing, it should be treated with lime, wrapped in cotton cloth and polyethylene. And the higher the better. Still, in the middle of winter, uninvited guests - hares can visit.
Advantages and disadvantages of planting an apple tree in the fall
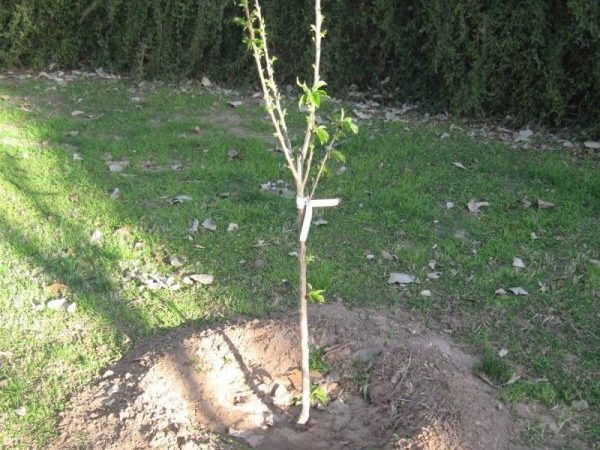


Planting an apple tree in autumn
Planting work is always early spring or autumn. For decades, novices and aces have argued about when to plant. Disputes from scratch end when everyone weighs for themselves the pros and cons of planting dates.
Benefits
What attracts gardeners to rooting trees before winter? After all, it is these terms that have traditionally been considered optimal.
The autumn planting period has a number of significant advantages:
- at the end of the season, nurseries have the richest selection of healthy seedlings. And in the spring, buyers are offered planting material that overwintered in containers, left over from the autumn sale;
- a seedling in a dormant state will take root faster: it does not need to spend energy on growing foliage, trying to bloom;
- summer residents from the southern regions with early hot springs, low-rain, sultry summer find it more difficult to leave a seedling that needs to take root in such conditions;
- in the spring, an apple tree planted before winter immediately begins a new growing cycle.
Autumn planting works are preferred by residents of the south, Central Russia, Central Russia, Western Siberia. The more severe the climate, the more often the planting is transferred to the spring. Although in the zone of risky agriculture, they try to guess with the timing so that it is not too late to plant an apple tree in autumn, but also not to rush to planting.
disadvantages
The disadvantages of autumn work with seedlings are associated with risks. It is impossible to predict what the weather will be like, how long the heat will last, how soon the frost will come. Forecasters are wrong. Gardeners are at risk.
Autumn planting problems:
- planting too early - to stimulate vegetative processes instead of a state of rest;
- to plant too late - the seedling will not have time to grow roots, which means it will not overwinter;
- sudden warming or cold snap are factors that reduce the chances of rapid establishment and hibernation;
- young trees must be covered for the first winter;
- if mistakes are made during planting, it will become clear only by the middle of summer, when it is better not to touch the rooted tree;
- during the winter and with melt water in the spring, insufficiently compacted soil in the planting pit sags, pulling the root collar. With spring planting, this is corrected immediately, until the apple tree has overgrown with new roots.
But the last two problems are the result of mistakes in preparation and landing. If everything is done right at once, these risks do not threaten the young tree.
Description
Dwarf fruit treesI are stunted fruit trees grafted onto a dwarf rootstock. The height of adult dwarf crops reaches only 2-3 meters. Such dwarfs live from 20 to 30 years, and they begin to bear fruit already from the third year from the moment of planting. They are very demanding on soil and moisture, because their roots are shallow.
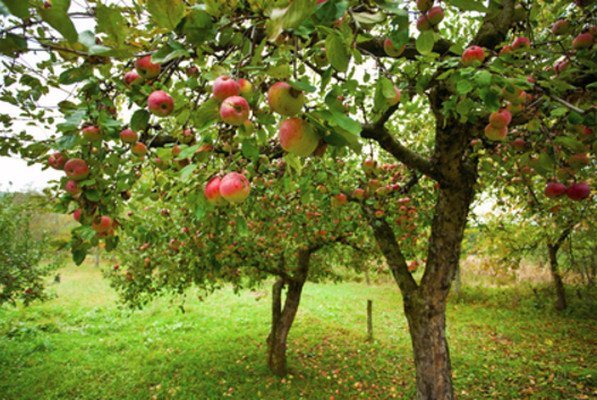


Characteristics and description of undersized culture
A dwarf apple tree is obtained if a varietal cuttings are grafted onto a clonal dwarf stock. The resulting undersized tree retains all the characteristics of a varietal donor, except for height. Its crown shape resembles a tall culture.
Height and branching of the crown
The dwarf apple tree grows up to 2.5-3 meters in height. Its crown shape is the same as that of an ordinary tall apple tree. Skeletal branches alternately extend from the trunk at an acute or right angle to the sides and up. Crohn - spherical, spreading, branched, requires pruning and shaping. The branches lean down under the weight of the fruit. Leaves are oval, with a sharp tip, serrated at the edges, long-petiolate. The bark is light brown, with many lentils and streaks.
Features of the root system
Dwarf apple trees have a superficial fibrous root system. The roots are highly branched, they go down only 0.60-1 meters deep. Low-growing trees are planted in an area where groundwater is at a depth of 1.5 meters. The roots of dwarf trees will not get to them. True, the superficial root system makes the tree weakly resistant.


It is advisable for dwarf apple trees to install a support that will support them in strong winds. Before wintering, the trunk circle can be mulched with humus and peat in order to protect the roots near the surface from frost.
Flowering and pollinators
Dwarf apple trees are often self-fertile, but they need pollen from other apple trees to increase yields, so at least 6 different apple varieties are planted in the garden. For pollination, apple trees of a related species are selected, blooming at the same time. Trees are planted not far from each other. Pollination occurs with the help of insects. Apple trees bloom in April-May.
Productivity from one tree
Dwarf apple trees can bear fruit for 15-25 years. Almost 60 percent of the nutrients are used for the formation of the crop and only 40 percent is used for vegetative growth of trees. The apple yield of one adult tree is 35-70 kilograms.Fruiting occurs 3 years after planting.
See also
What to do if the apple tree drops the fruits before they ripen and the main reasons
To read


How to save a seedling if planting late
The first frosts are about to occur, and a suitable seedling has been purchased, but not planted. Planting will have to be postponed until spring. The situation is not uncommon.
- To save the planting material, you need:
- Dig a trench as long as a seedling, 10-15 cm deep on the south side, up to 40 cm from the north.
- Cover the bottom with a layer of fallen leaves.
- Wrap the apple tree in a non-woven fabric.
- Place the tree with its roots in the deepest part, with the crown towards the south. Leave the tips of the shoots above the ground.
- Fill up the trench with earth and peat.
- Pour a thick layer of fallen leaves, sawdust on top, cover with spruce branches.
- As soon as the snow melts, the ground begins to thaw, the seedlings are taken out and prepared for planting.
If the winter is very harsh in the region, the trench is made deeper.