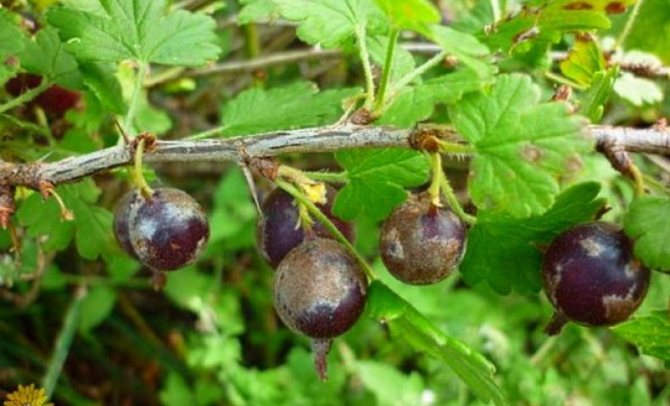
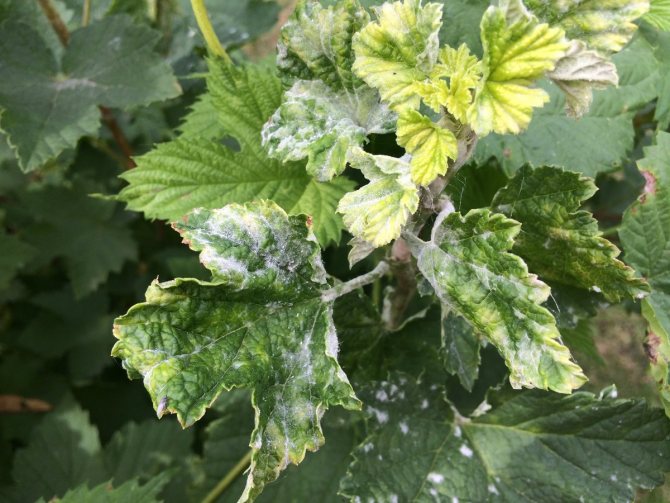
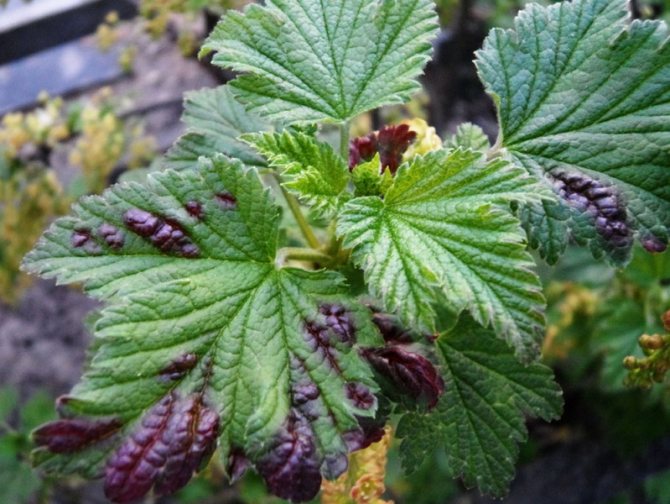
Often in the summer, when the gardener collects the long-awaited crop of currants, he notices unpleasant changes in the appearance of the plants. The color of the leaves changes, young branches grow poorly, and some berries remain unripe.
It is at this time that the most appropriate time for fungal infections to flourish. A particularly common and destructive disease is powdery mildew on currants.

Application methods
To combat the disease, you will need strong acting agents. However, a lot also depends on the observance of the rules for caring for currants, the nature of the treatment with fungicides.
The fungus prefers dampness, abundant watering, excess nitrogen in the soil, shade. Elimination of these conditions and adherence to certain recommendations when treating with fungicides significantly increase the chances of recovery. Read about the varieties of bristle tomatoes here.
Root treatments
Traditionally, nitrogen preparations are applied in the spring, since nitrogen stimulates plant growth and helps to increase the yield. But if an infection has occurred, the stimulation should be abandoned.
Instead of nitrogen, potash and magnesium fertilizers are applied to the trunk circle of the bush.
All last year's leaves and branches on the ground are collected and burned. The earth is dug to a depth of 15 cm. Learn how to grow indoor tomatoes here.


After spring watering, be sure to mulch the trunk circle to reduce evaporation.
Foliar
For a better harvest, currants of Rovada, Alpine, and other varieties are sprayed with urea or carbamide solutions in the summer. However, if the bushes are infected with powdery mildew, foliar feeding should be completely abandoned.
Spraying
The fungus loves high humidity. Accordingly, you will have to give up spraying the bushes, no matter how sad they look in a dry summer. Maximum sun is what kills powdery mildew.
Instead of spraying with water, drip irrigation is recommended. And so that the plant does not discard the existing ovaries due to weakening, it is better to carefully cut the currants in the spring.
The only permissible spraying of infected currants with water is carried out in the earliest spring before the snow melts.
Disease harm
Powdery mildew on currants gradually weakens the currants and kills them. If you do not follow the appropriate treatment steps, then the following signs of damage appear in the currant:
- all young and growing parts of the currant are primarily affected by the fungus and slow down development: the point of growth, twigs, buds, petioles, leaves;
- young branches affected by infection grow poorly, become thinner and bent, do not ripen and often dry out completely;
- berries remain unripe and become unsuitable for food;
- shoots are deformed, internodes on them become short;
- the bush ceases to bear fruit;
- the currant becomes sensitive to frost, its winter hardiness is greatly reduced;
- the plant lacks nutrition due to weakened photosynthesis, the leaves on it become smaller, become ugly.
Processing stages
The fight against the fungus should be started in early spring. Some gardeners prefer chemical products, some use folk remedies.In practice, it is better to combine, since chemical preparations, for all their effectiveness, are poisonous and it is no longer possible to process currants with them, for example, after the formation of the ovary.
Processing is carried out in accordance with the recommendations, but, as a rule, it consists of several stages:
- spring - includes both spraying the bush and processing the trunk circle. Several procedures will be required depending on the duration of the drug;
- summer involves spraying with chemical compounds before the berries ripen and processing with biological ones as needed. In any case, the procedure is repeated at least 4 times;
- autumn - includes the removal of old branches, infected leaves and shoots and their burning. The trunk circle is completely cleared of leaves. If necessary, add phosphorus-potassium fertilizers or wood ash.
Spring
The largest list of works is carried out in the spring.
- Even before the snow melts, the currant bush is irrigated with boiling water. The tops of the shoots are dipped into a container of boiling water. The procedure should take a minimum time, therefore it is performed very quickly.
A very good way to reduce the risk of the appearance or recurrence of the disease is to replace the upper fertile soil with new humus. This option brings very good results, since mushroom spores winter in the soil.
- To destroy the fungus, the trunk circle under the bushes can be treated with a solution of tansy.
- In early spring, before the buds swell, the currants are sprayed with a solution of copper sulfate. At this moment, water-charging spring watering is also carried out.
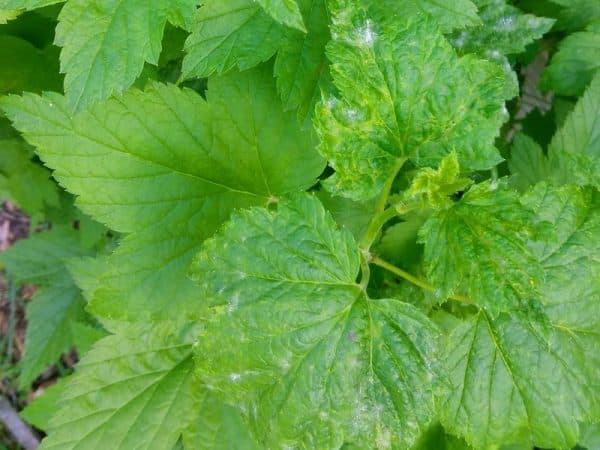


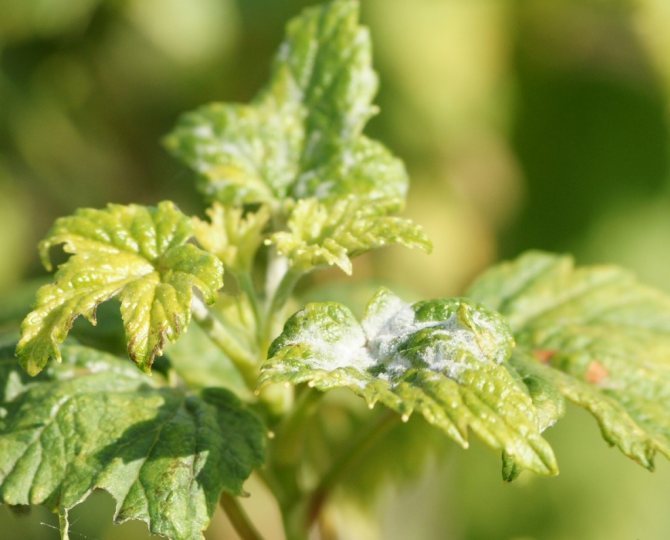
Until the leaves appear, it is unclear whether the bush is infected or not. But if whitish spots are found on young leaves, treatment should be started immediately.
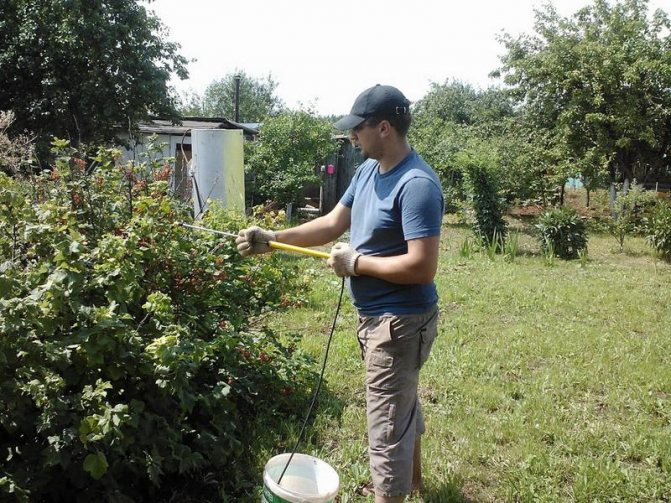
- Spraying - with biological or chemical agents is performed immediately. It is best to catch it before flowering, as this reduces the risk of disease and berries. One treatment is not enough, since the fungus is very resistant to the action of fungicides, so the currants are sprayed at least 3-4 times in accordance with the instructions for the preparation.
Typically, spraying occurs before flowering, during flowering and immediately after. When the berries begin to ripen, it is advisable not to treat the currants with chemical fungicides, since they are poisonous. Biochemicals can be used until the end of summer. However, procedures with their participation have to be repeated much more often. Find out if you can freeze leeks for the winter by following this link.
Spraying requires either a very good powerful spray gun or a soft brush. It is necessary that the preparation falls on both sides of the leaf, so the processing must be carried out very carefully.
Chemical and biochemical preparations
For the treatment of powdery mildew, 2 types of synthetic drugs are used: biofungicides and chemical ones.
Biochemical
They destroy the fungus through several unusual mechanisms. For example, fungal biofungicides contain a culture of a parasitic fungus that multiplies on the spherotek and, in the end, suppresses its vital activity. Bacterial drugs include bacteria that can actively destroy the shell of the fungus, releasing antibiotics and amino acids.
This option is practically harmless to human health. You can process bushes with it at any time, including when the berries are ripening. However, biofungicides have a fairly short duration, are water-soluble, and are easily washed off by rain. Accordingly, the spraying procedure has to be repeated often: usually once every 5-7 days. This article will tell you about growing and caring for Suvorov onions.
Chemical
Usually they are pesticides of various kinds. They are toxic substances: spraying is carried out only in a respirator, glasses and closed clothing.Fungicides are very effective, but you cannot get carried away with them, since drugs contain heavy metals, and the latter tend to accumulate.
Chemicals last much longer. On average, to get rid of the fungus, you need up to 3 treatments per season. Systemic is preferable, since they prevent infection, and not only protect the plant from fungal spores. But, if the disease has affected only a small area or even neighboring bushes, it is preferable to use protective fungicides: such a drug covers the shoots and leaves with a layer of active substances that prevent infection, but at the same time it is not absorbed into the leaf plate or ovary.
It is important to pay attention to the composition of the drug. So, in the spring, preference is given to dithiocarbamic acid, since it stimulates plant growth to some extent. In summer, it is better to use copper-containing preparations.
Processing should be carried out in calm dry weather, preferably in the evening, when the sun is not so active.
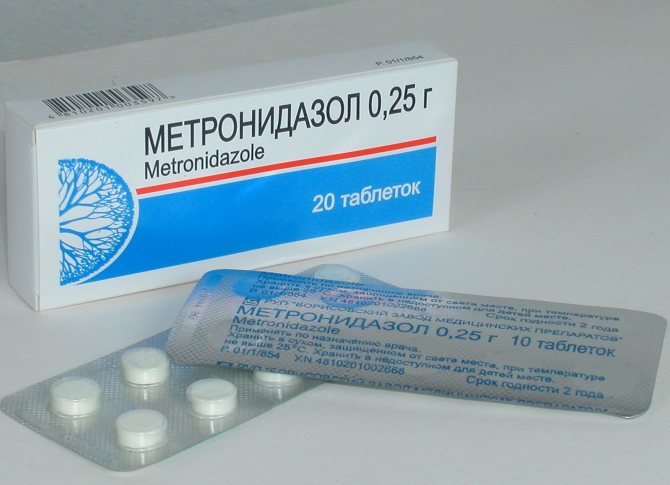
Metronidazole
The better known name is Trichopolum. It is an antibacterial medicinal product sold in pill form at the pharmacy. The medicine is used to treat various fungal diseases in humans, such as trichomoniasis, gingivitis, gynecological ailments.

It turned out that the drug is also quite effective against powdery mildew and late blight.
For spraying, 3 tablets of trichopolum or metranidazole are dissolved in 500 ml of water and the plants are sprayed. The first time they do this, as soon as traces of the disease are found. If the first procedure is carried out before flowering, the effect will be higher.
Spraying is repeated in late May-early June, when fungal spores begin to spread. If, after a week, powdery mildew is still found on the currants, then the plant is treated with trichopolum every day until complete recovery. It is also recommended to water the plants with metronidazole solution.
The drug does not affect the fruit in any way. Berries can be safely eaten after washing.
Boric acid
Boric acid is usually used as a foliar dressing in cases where the garden crop lacks boron.


Treatment with a solution of the substance stimulates the growth of berries, makes the pulp more juicy and fleshy, so black currants are periodically sprayed with this preparation.
Boric acid is used against powdery mildew together with potassium permanganate: 2 g of each substance is dissolved in a bucket of water - 10 liters. Then add 40 drops of iodine to the composition and spray the plants as a protective biofungicide.
The procedure is carried out after the appearance of the leaves. If necessary, repeat during flowering, after and during the formation of the ovary.
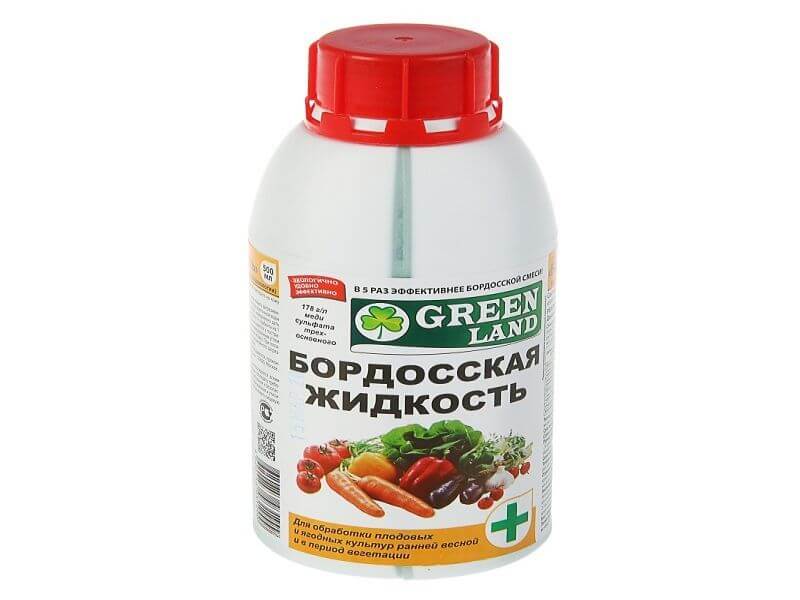
Bordeaux liquid
Bordeaux liquid is a mixture of slaked lime, water and a solution of copper sulfate. It was first used in vineyards, and today it is used as one of the most versatile remedies for combating fungal diseases.
A big plus of the remedy is the duration of the action. 1 spraying is enough for a month. The drug cannot be washed off with rain. So there is no need to repeat spraying after every thunderstorm.
- As a preventive measure, both fruit trees and berries are treated with a 1% solution of Bordeaux liquid in early spring, before the buds begin to swell.
- If the currant is infected, but partially, but in general the bush is healthy, then 3 procedures are carried out: before the blooming of the leaves, at the beginning of the growing season and after flowering.
- If powdery mildew has affected all the bushes, then the number of treatments increases up to 6 times. The last spraying is carried out no later than 2-3 weeks before picking the berries. It is impossible to exceed the maximum number of procedures: copper does not accumulate in the plant, but in the ground. Its excess weakens the currants, it grows more slowly and gives a much lower yield.
Bordeaux liquid is a contact pesticide.To get the maximum effect, the plant should be treated very carefully.
Bordeaux liquid is incompatible with organophosphate pesticides, therefore, when using various preparations for powdery mildew and scab, you need to monitor the composition. Work should be carried out only in protective clothing, goggles and a respirator, since copper-containing preparations pose a significant threat to humans.
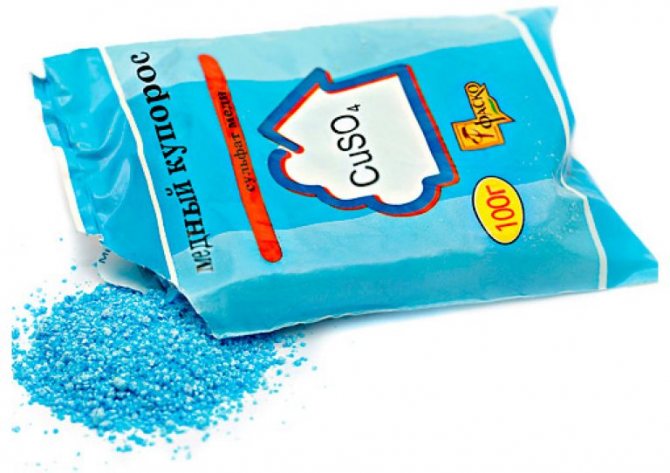
Copper sulfate
A simplified version of Bordeaux fluid. Depending on the purpose, 1% and 3% solutions are used. As a rule, solutions of lower concentration are prepared for spraying shrubs.


Copper sulfate is used to treat currants in the spring before bud break. This is a standard preventive measure, since the substance is effective in killing many fungal diseases.
With a total infection of a shrub, the solution is also used for treatment, just like Bordeaux liquid, boric acid. However, the duration of the solution is shorter, so the treatment is repeated every 10-14 days until the fruit is formed. In total, no more than 4 procedures are allowed.
You can also use a copper-soap emulsion. To do this, prepare a soap solution: 50 g of laundry soap is dissolved in 10 liters of water, and then a 1% solution of copper sulfate is added to it - 200 ml. The resulting composition is sprayed with currants every 7 days.
HOM
Alternative to Bordeaux liquid. This is a very strong copper-containing preparation. The currants are sprayed with a 0.4% HOM solution, that is, 40 g per 10 l of water.
HOM can be mixed with fufanon and decis - 1 bottle each. Thus, a complex treatment for fungal diseases is carried out.


Spray currants with HOM once - before flowering.
Speed
A chemical fungicide based on difenoconazole from the triazole class. A broad-spectrum drug used against fungal diseases such as powdery mildew, spotting, coccomycosis, moniliosis. The speed inhibits sporulation, which leads to a decrease in the intensity of the infection and to its complete disappearance.
The speed takes effect 2 hours after spraying. Rain, wind and temperature do not affect the result of exposure.
The drug is diluted with water - 2 ml per bucket, and the plant is sprayed. For a shrub, 2 procedures are enough with an interval of 10-12 days if it is a preventive treatment, and after 8 days if the currant is already sick. In extreme cases, 3 spraying is allowed after the same period.
Fitosporin
It is a bacteriological biofungicide that inhibits mycelium growth. The drug is used both as a prophylactic agent and for treatment. However, when infected, phytosporin is effective only in the first stage of the disease.
Fitosporin should be activated. For this, the contents of the package are diluted in a small amount of water and left for 5-6 hours. During this time, the solution turns into a suspension. A tablespoon of such a suspension is added to 10 liters of water, and the plants are sprayed with the resulting composition. Currants are processed 1 time in early spring.
If the bushes do get sick, re-treatment does not make sense. It is recommended to use a more potent remedy.
Fungicides
For the treatment of currants, both organic and inorganic fungicides are used. Organic does not include heavy and hazardous metals like mercury and copper. They are very easy to prepare - just dilute the powder with water and combine with many other pesticide formulations.
Inorganic ones are more dangerous, as they include metals, and the latter tend to accumulate in the soil, which is harmful to the plant. However, inorganic drugs are the most potent agents, so if the garden is heavily contaminated, you have to use them.
Fundazol
Broad-acting fungicide. The active substance is benomyl: it disrupts the division of nuclei in cells and thereby prevents the growth of the fungus.Fundazol performs this function for 3 days, and then becomes an ordinary protective drug for another week.
Fundazole is used to treat not only leaves and shoots, but also the soil. Apply the drug in the form of a solution - 1 g of the substance per 1 liter of water. The first processing is performed when an infection is detected, the next one - after 10-14 days. Both 3 and 4 procedures are allowed, while maintaining the specified time interval.
Topaz
Penconazole-based fungicide. Unlike many other chemicals, it works well with other fungicides and insecticides. It is produced in the form of ampoules or in vials of different capacities.


Topaz is the most popular powdery mildew remedy. It is very sparingly consumed, acts for 2-3 weeks, is well tolerated by plants and does not cause poisoning.
The composition inhibits the growth of mycelium within 3 hours after spraying.
For the procedure, 2 ml of topaz is dissolved in a small amount of water, and then the composition is diluted in 10 liters. Currants are treated with such a solution for prevention and at the first signs of an illness.
For prophylaxis, top dressing is carried out during the growing season and repeated after 12-14 days. If powdery mildew does not appear within 20 days, then the fungus does not threaten the currant.
When treating already infected bushes, the interval between treatments is reduced to 8 days. For spraying 1 bush, 1.5 liters of working fluid is enough. 3 treatments are allowed.
Do not spray currants with topaz during flowering.
Previkur
Systemic drug for the fight against true and downy mildew, based on prolamocarbofosethyl.
The drug penetrates the leaves, accumulates in them and destroys the mycelium. In addition, Previcur has a stimulating effect on the growth of leaves and berries.
For the procedure, 5 ml of Previcura is diluted in 1 liter of water and the plant is sprayed. Care must be taken to wet the composition of the sheet from one side and the other.
Watering the ground around the currant with a solution of the drug is also effective - 3 ml per 1 liter of water.
Re-processing is performed after 10-14 days.
Plants should be sprayed in the evening or morning when the sun is inactive.
Vitaros
Not the most suitable preparation for processing currants. Destroys almost any type of fungus. It stays on the surface of the processed material for a long time. It was originally intended for grain disinfection.
To spray currants in 10 liters of water, dissolve 2 ml of the drug - a capsule. Vitaros has the form of a suspension, therefore, first it is dissolved in a small amount of water, and then the composition is already diluted to 10 liters.


The bushes are sprayed with Vitaros before flowering.
External signs of the disease
The disease is common throughout the country. It affects many deciduous plants: gooseberries, strawberries, delphiniums, eggplants, apple trees.
The spread of spores of the fungus occurs from other diseased plants through the air, through the ground in which the fungus hibernated. An outbreak of infection occurs in the early summer months.
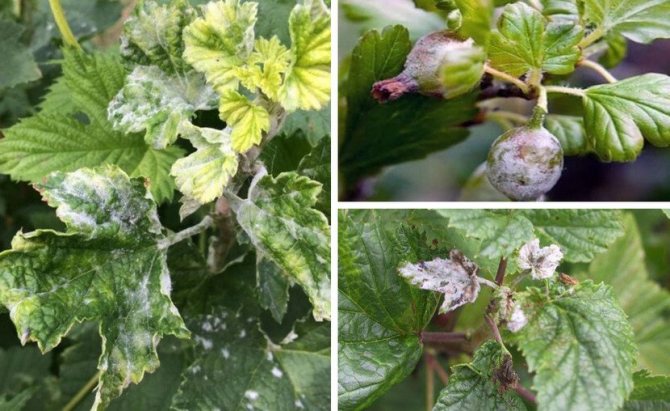
The most favorable time for the development of mycelium occurs in July-August. The fungus infects leaves, young shoots and even berries. The growth of the infection is favored by:
- maximum air humidity;
- poor illumination of currants;
- fungus-infected bushes growing nearby;
- surplus nitrogen fertilizers.
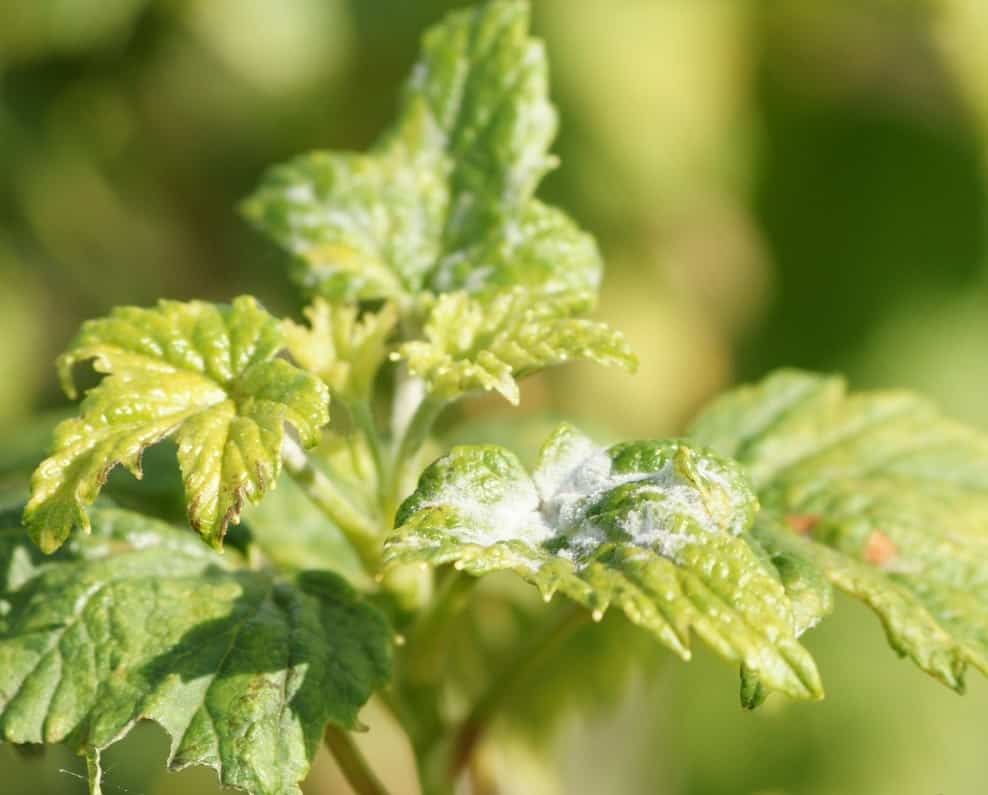
Leaves on currant bushes are covered with a whitish spider web of mycelium in just a couple of days after heavy rain. The growth rate of the infection is incredible.
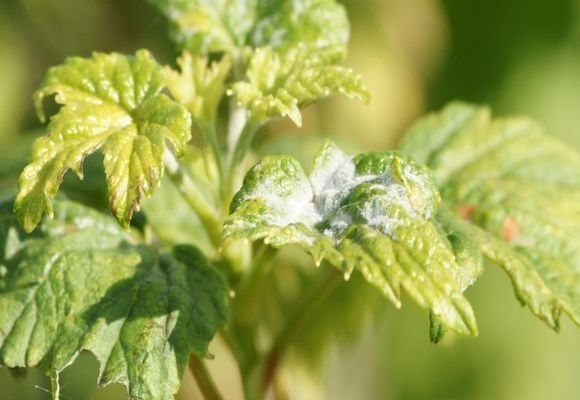


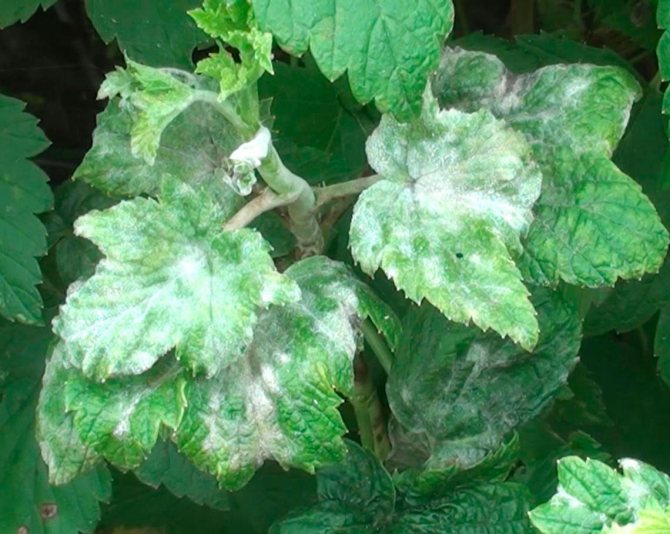
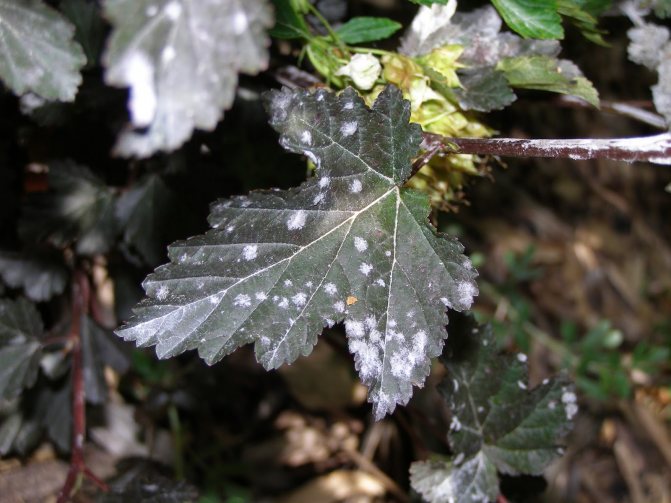
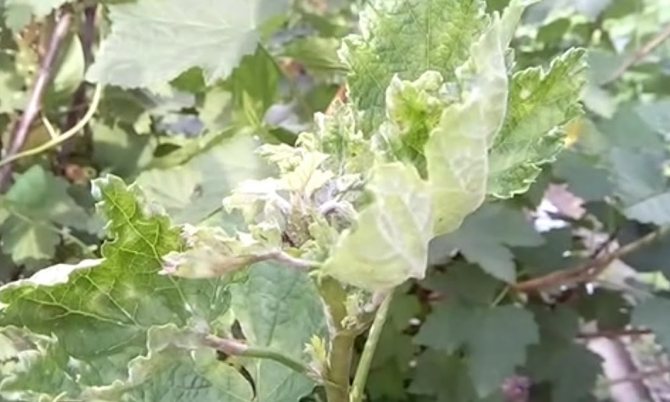
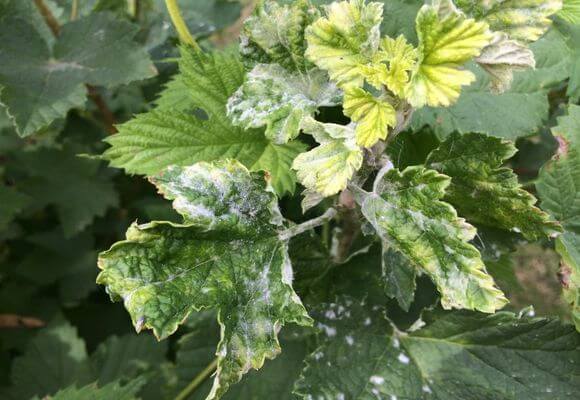
Powdery mildew on currants or powdery mildew is easily recognized by its characteristic difference - the appearance of a whitish coating on the leaves, reminiscent of flour powder. It appears after the flowering of the currant.
At first, the plaque only slightly covers the leaves with a spider web and is freely washed off and peeled off.But gradually the plaque thickens, the color becomes dirty, spores grow on it in the form of black dots. The bloom changes color to a gray-brown color. At this stage it is no longer possible to remove it from the surface of the plant.
Important! During the season, the mycelium produces more than 10 generations, ensuring recurrence of infection in the garden.
The fungus waits out the winter on dry leaves and fallen fruits. At the beginning of the season, intact spores re-infect the currants that had recovered last year.
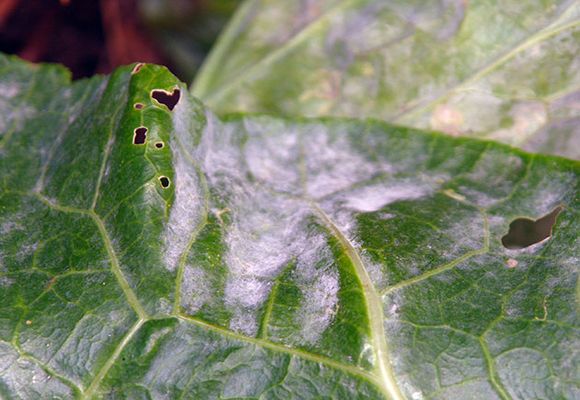


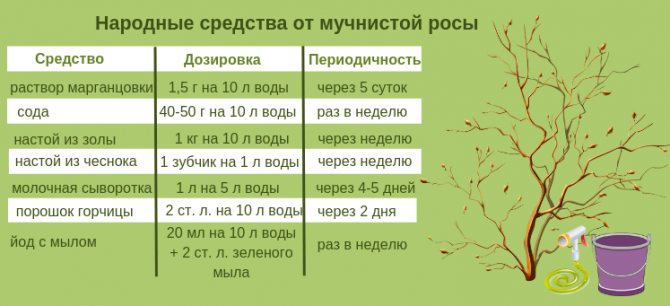
Folk remedies
To combat powdery mildew, various folk remedies are also used. Most of them are of natural organic origin, easily decompose in the soil, do not pose a danger to humans or animals.
The common disadvantage of such formulations is low efficiency and water solubility. Rain and even strong winds completely neutralize their effect. Accordingly, the processing has to be repeated more often.
- Baking soda - more precisely, a soap and soda solution. Mix 50 g of baking soda or soda ash, the same amount of grated laundry soap and dissolve in 10 liters of hot water. After the liquid has cooled, the bush is sprayed with it, making sure that the leaves are processed on both sides. The procedure is repeated a week later, until the powdery mildew disappears.
- Kefir and whey - fermented milk products give a good result, especially at the initial stages of the disease. 1 part of whey or kefir is dissolved in 10 parts of water and the plants are sprayed 3 times in a row. The procedure is repeated every 3 days. The products form a film on the surface of the leaf, which prevents the fungus from multiplying. In rainy weather, such a film is immediately washed off, therefore, after rain, spraying is repeated unscheduled.
- Potassium permanganate - a strong disinfectant, quite suitable for combating fungi. For currants, ½ teaspoon of potassium permanganate is dissolved in 10 liters of water and the plants are processed three times. The procedure is repeated every 5 days.
Potassium permanganate is effective only in the initial stages of powdery mildew.
- Soap solution - Soap is included in several options for combating fungus. For example, a soap emulsion obtained by mixing a 1% solution of copper sulfate and a soap solution (50 g of soap per bucket of water) is an extremely effective preparation. The emulsion is sprayed with currants 3 times every 7 days.
A soap-ash solution is prepared as follows: 1 kg of wood ash is poured into 10 liters of boiling water and insisted for 1-2 days. Up to 50 g of soap is added to improve the adhesion of the composition, after 2 days the currant is sprayed with the solution. The procedure is repeated twice in 7-10 days.
- Field horsetail - 100 g of fresh grass is poured into 1 liter of water and insisted for a day. Then the infusion is boiled for 2 hours over low heat, cooled and filtered. The infusion is stored in the refrigerator. Before spraying, the infusion is diluted in a ratio of 1: 5 and the currants are treated with it. 3-4 procedures are performed in 5 days.
Reasons for defeat
Despite the fact that the ash fungus is often found in the soil, its activation and development of the colony is possible only under certain favorable circumstances:
- Lack of sunlight associated with weather conditions or the wrong place for planting currants.
- Lack of heat or excess moisture.
- Improper watering - both too frequent and rare, but abundant.
- The close arrangement of the bushes when disembarking.
- High content of nitrogenous substances in the soil.
Infection of currants most often occurs with frequent alternation of rains or humid cloudy weather with warm sunny days, when the humidity does not have time to drop to 50-60%.
Infection with a fungal infection is possible from:
- affected nearby bushes or culture representatives from neighboring areas;
- water for irrigation, which could get spores of the microorganism;
- touching a sick plant, and then a healthy plant.


Preventive measures
To reduce the risk of powdery mildew, the following guidelines should be followed:
- for planting, the most disease-resistant varieties are selected. It is better to purchase seedlings in a proven nursery;
- purchased seedlings are necessarily treated with copper-containing preparations;
- when planting, you need to maintain the distance between the bushes. Closely planted plants shade each other, dry out for a long time after rain, which creates suitable conditions for the reproduction of the fungus;
- insecticide treatment also helps against powdery mildew, since insects are often its carriers;
- weeds should be destroyed, leaves and infected branches should be removed and be sure to burn them;
- pruning and lightening the bush provides good light and quick drying after rain, thereby reducing the risk of developing fungus.
Powdery mildew on currants: a description of the problem
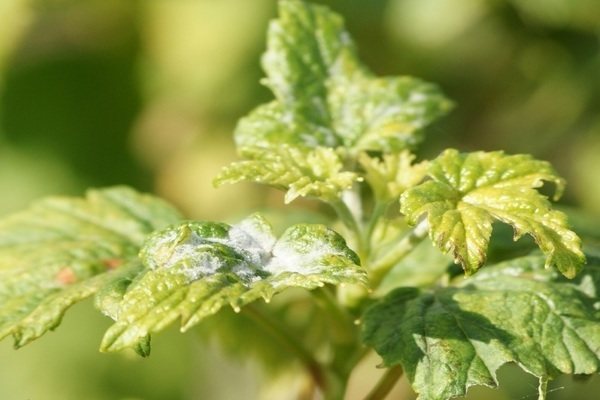


Powdery mildew is the popular name for a fungal disease caused by a microscopic fungus called Sphaerotheca mors-uvae. The causative agent of this disease is activated in mid-spring (in April or May), when, after the winter "rest" spent on the shoots and buds of a currant bush, microscopic spores of this fungus are spread everywhere by the wind. Further, in the presence of suitable weather conditions (moderate heat and high humidity), mycelium begins to develop from these spores at the beginning of summer. The risk of developing this disease increases if your currants have been infested with aphids, caterpillars, or other pests that damage the foliage. Too close "neighborhood" of plantings inside the garden will also be a favorable factor for the development of powdery mildew.
conclusions
- Powdery mildew or berry death is one of the most severe fungal diseases of the currant. Infection in the first year deprives the owner of 80% of the crop.
- Today, there are no varieties of currants that are completely resistant to powdery mildew. However, among the zoned varieties, you can always find the most resistant ones: they respond better to treatment and recover faster.
- The most effective drugs for combating the mealy race are chemical fungicides. However, these substances are toxic and require strict compliance with all rules for use.
- Less effective, but much safer biofungicides. Such preparations work for a shorter period, so the currants have to be processed much more often.
- Also, folk remedies are used for the treatment of shrubs: infusions of field horsetail, a solution of potassium permanganate, soap-ash emulsions.
- An obligatory element of the fight against powdery mildew is compliance with the rules of care: pruning bushes, timely disinfection, preventive spring treatment with copper-containing preparations, and so on.
When to plant cucumbers for seedlings according to the lunar calendar, this material will tell.