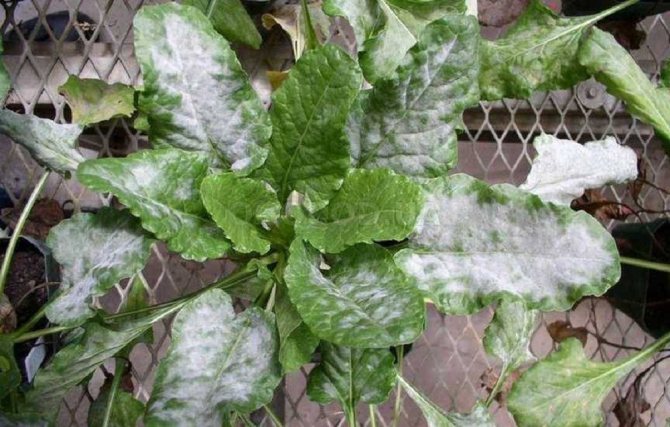
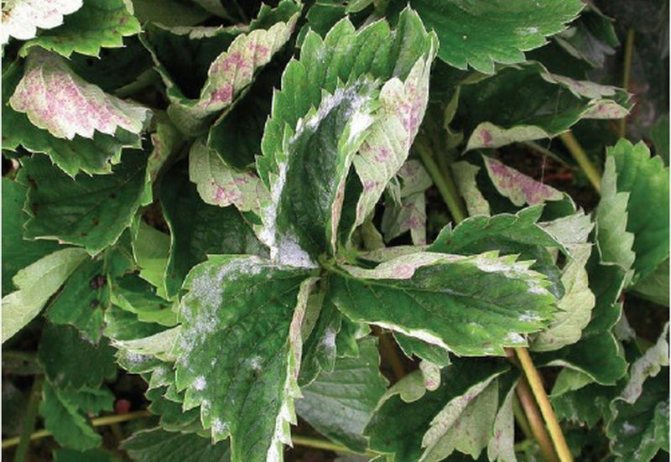
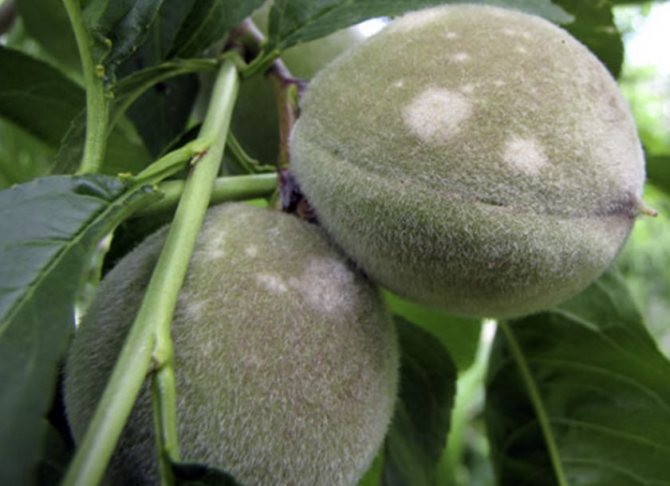
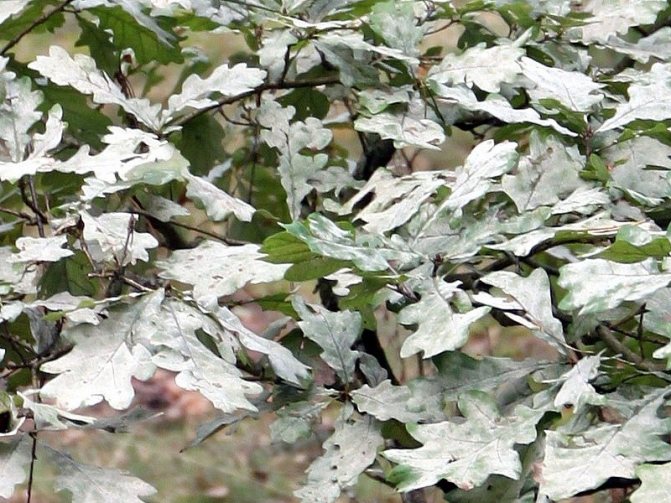
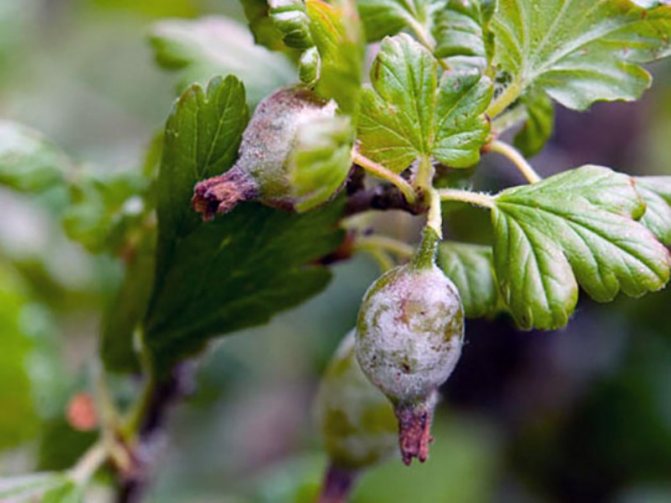
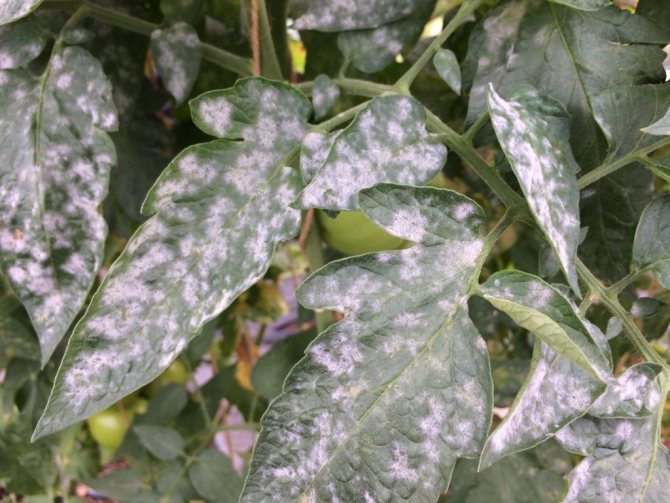
Powdery mildew is a fungal disease of plants. It is generated by parasitic fungi that live on green parts, most often on leaves.
It is dangerous in that it causes exhaustion, decay, and subsequently the death of the plant. Powdery mildew can affect not only indoor flowers, it also affects garden fruit bushes, adult strong trees.
Often, the disease is very difficult to treat and it is not possible to save the plants.
Advantages and disadvantages
Chemical processing methods have more disadvantages than advantages:
- phytotoxicity (plant growth is inhibited);
- the ovary may fall off;
- decreased immunity in plants to pathogens;
- environmental pollution;
- possible negative consequences of contact with various elements in the soil;
- destroy useful ethnofauna;
- after a few years, the pests develop resistance to fungicides and become resistant to subsequent treatments;
- bad effect on pollinating insects.
The advantage is one, but weighty: the drugs quickly and efficiently eliminate the focus of the disease and prevent its appearance for the entire season.

Signs of infection


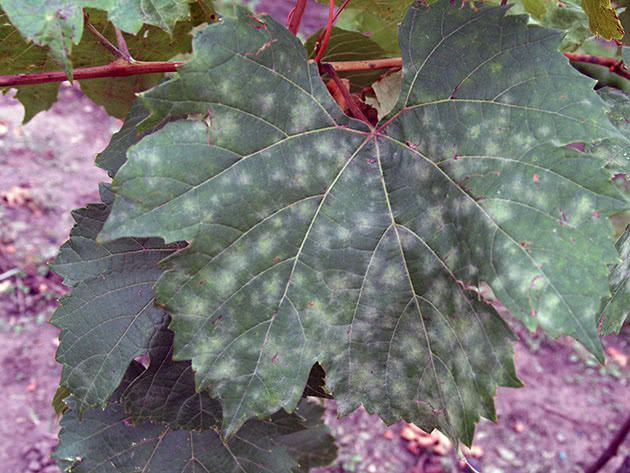
It's easy to guess that the plants in the garden are affected by powdery mildew. This infection has several characteristic manifestations. Symptoms are easily visible. Among the main features are:
- the leaves of the plant at the first stage are covered with a white bloom, resembling a powder, which is easy to confuse with dust;
- gradually, an increasing area of plantings is covered with such a bloom;
- the growth of bushes slows down;
- the affected foliage becomes withered and turns yellow;
- young leaves grow noticeably deformed;
- if you look closely, you can see ulcers on the leaves in those places where the mycelium was attached;
- without timely treatment, infected plants die.
If you periodically inspect the plantings, you can notice the development of the disease in time. Preventive measures will help to avoid infection.
Important!
Infusion of garlic and mustard solution are good against powdery mildew.
Signs of the appearance of a fungus
The main sign of powdery mildew infection of flowers is a whitish bloom on the leaves. With the naked eye, a person can see only spots randomly located on different parts of the plant. When viewed under a microscope, the filaments of the fungus are clearly distinguishable - mycelium, resembling a dense cobweb. The mycelium gradually covers all parts of the plant, disrupts the processes of photosynthesis.


As a result of the reproduction of spores:
- the plants look depressed, they stop growing;
- the leaves are deformed, turn yellow and gradually die off;
- buds freeze in development, do not bloom;
- new shoots are formed twisted, defective.
What is dew
What is dew in terms of physics? This is excess moisture "precipitated" (condensed) from the air. Dew droplets form on surfaces colder than air. These are usually the tips of leaves or blades of grass, insects, or even water pipes.
Dew most often falls in warm, calm, clear weather, in summer or early autumn.


The first frost in the fall often turns dew into frost.
Dew can be morning, evening and night.Each of them has its own specific healing properties, which are well known to traditional healers. Well, and an ordinary person knows how pleasant it is to run barefoot at dawn in a meadow, the grass of which is covered with life-giving dew drops! And to wash with morning dew - what could be better?
In ancient legends and myths, among different peoples, dew drops were often attributed to miraculous properties that rejuvenate and heal from ailments and evil magic.
And the ancient Greeks even had the dew goddess Ersa, the daughter of the thunderer Zeus and the moon goddess Selene.
By the way, until the eighteenth century, it was not known exactly what dew was and it was considered a consequence of rain.


These little dewdrops are the source of life in arid deserts.
In some places, dew drops collected by special devices, condensers, can form a whole lake, because up to two hundred liters of them are collected per night!


And what is dew from the point of view of art? An endless source of inspiration for many: poets and composers, artists and photographers. In the photo, dew drops often look like jewels on the cobwebs and wings of dragonflies, etc.
Reasons for development
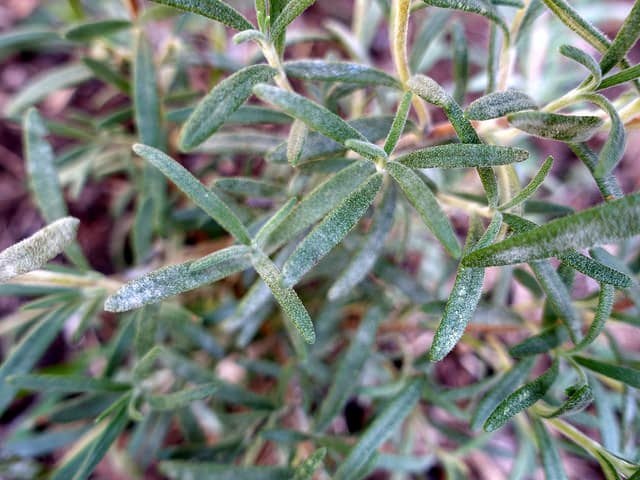


Rosemary and other horticultural crops can become infected with powdery mildew in a number of ways. Fungal spores can persist in the soil for a long time. But they are not active in hot sunny weather. If the plant receives enough moisture and nutrients, then it has strong immunity and is not susceptible to infection. The fungus is activated in cool and damp weather, when the sky is overcast.
In a soil oversaturated with nitrogen, the causative agent of the disease feels very good. When plants are planted too densely, they too become an easy target for powdery mildew. Violates plant immunity and improper watering. Water the rosemary evenly, do not overfill it or overdry the soil. Fungal spores can enter the beds by air or water. It is easy to infect plantings if you do not disinfect tools and wash your hands. In some crops, radical pruning in the spring can cause a decrease in defenses.


Common methods of struggle
The most difficult thing is to treat fungal plaque in the active, advanced phase. Moreover, forecasts can be disappointing. Therefore, experts recommend not to start the disease and get rid of it in the early stages of its onset. Better yet, take preventive measures. In order to minimize the risk, it is advisable not to flood the plants, but when planting, use a special scheme designed for the free passage of air masses between plants.
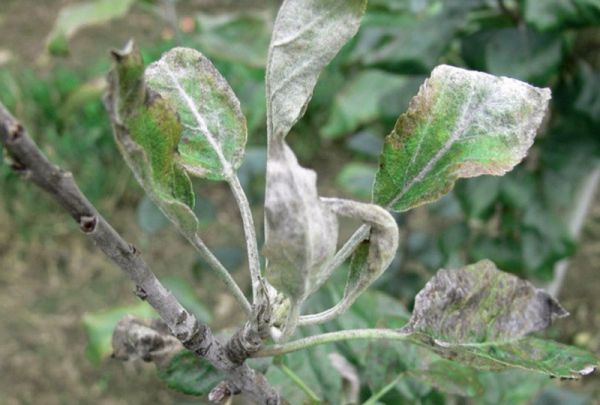


Powdery mildew of apple and pear
Fruit trees need rejuvenation. This procedure, if carried out correctly and without excessiveness, will allow you to get rid of the thickening of the crown and thereby prevent the manifestation of powdery mildew. To prevent fungal spores from remaining in the ground, you should regularly remove debris and the remnants of foliage and flowers on the site. It is important to avoid the development of weeds that form dense growth and obstruct free air circulation.
Types of indoor plant diseases
Flower indoor crops are susceptible to various diseases. For example, a white, velvety coating may appear on the leaves or buds. It is a disease called powdery mildew caused by a special kind of fungus. The development of the disease is facilitated by stagnant water, a sharp drop in temperature and irregular watering. The affected leaves must be removed, the temperature and watering regime must be adjusted, and the culture itself must be treated with a fungicide (three times with an interval of 10 days).
The most common illnesses include (picture 1):
- Mycosis (gray rot) causes the formation of mold, after which the leaves simply rot. The disease appears with an increased level of humidity, too dense content and insufficient ventilation. It is possible to fight mycosis with fungicides only if the lesions are small. But most often the flowerpot is simply thrown away.
- If the leaves are covered with black sootquickly forming a crust, this means that the culture is damaged by the black. Plaque does not directly harm, but spoils its appearance and interferes with photosynthesis. Fighting fungicide plaque is pointless. The only way to eliminate it is to regularly wipe the leaves or rinse them in the shower. You can use a mild alcoholic solution or beer.
- Late blight also cause mushrooms. Stems and leaves are covered with purple-brown spots, wither and gradually die. Too intense watering or a dense substrate can provoke the disease. It is useless to fight late blight, and the affected specimen is simply thrown away along with the substrate. In order to prevent the appearance of the disease, flowerpots should be planted only in a specially prepared soil mixture, and in winter the room should be regularly ventilated.
Sometimes adjacent leaves begin to wilt and turn brown. This process is caused by a special fungal disease, with which it is practically useless to fight. The affected flower must be thrown away as quickly as possible so that the fungus does not spread to neighboring crops.


Figure 1. Common diseases of indoor plants: 1 - powdery mildew, 2 - gray rot, 3 - black soot, 4 - late blight
Another sign of the disease is cinnamon or black spots on the leaves. It can be scab, cercospora or anthracnose. As it is, the usual spraying with fungicides helps, but if the leaf tissue begins to die off, all damaged parts will have to be removed. Bordeaux liquid is considered the most effective remedy, which can be used not only for medicinal, but also for prophylactic purposes.
Viral
Some crops infect viruses. Leaves begin to discolor or deform. There is no effective method of struggle, so a diseased flower must be destroyed so that it does not infect other crops.
The most common viral diseases of indoor flowers include (picture 2):
- Mosaic - the leaves are covered with spots of various colors and shapes, which form a bizarre pattern. At the same time, the mosaic does not cause serious harm, but it can spoil the appearance.
- Jaundice - a dangerous viral disease, since the affected culture quickly begins to wither, wither, stops growing and dies. A cure for jaundice has not yet been developed, so it is better to destroy the infected flower immediately.
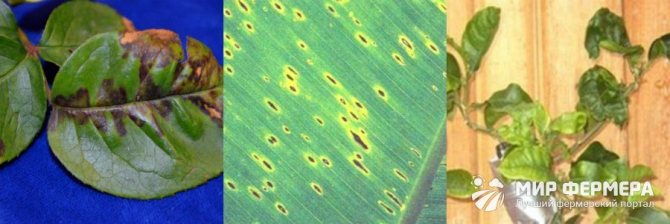

Figure 2. Signs of viral lesions
There are also varieties that are not susceptible to disease at all. These include aspidistra, caladium, cyperus and many others. Examples of such crops are shown in Figure 3.
From the video you will learn how to properly deal with the most common diseases of indoor plants.
Bacterial
Bacterial diseases are also dangerous for domestic crops, as they not only slow down the growth of the plant, but also spoil its appearance. There are several types of diseases in this group.


Figure 3. Examples of disease-resistant crops: 1 - aspidistra, 2 - caladium, 3 - cyperus
The most common bacterial diseases are (Figure 4):
- Rot especially often affects varieties with fleshy leaves and stems. High humidity and excessive use of nitrogenous fertilizers can be provoking factors.
- Withering first affects the stems, gradually switching to the leaves.
- Spotting manifested by the formation of dead areas on the leaves. Unlike the fungal spot, the bacterial spots have clear contours.
- Bacterial cancer provokes the formation of growths on the roots and young shoots.As the disease spreads, the culture weakens and gradually dies.


Figure 4. Bacterial diseases of indoor flowers: 1 - rot, 2 - wilting, 3 - spotting, 4 - bacterial cancer
To combat bacterial diseases, it makes no sense to use chemicals, since they are not effective enough. In case of severe damage, the plant is destroyed along with the soil and the pot, but it is much more effective to take preventive measures and use fertilizers sparingly.
Fundazol
Produced in powder form, the drug is another broad-spectrum fungicide, i.e. used against many fungal diseases of the lawn.
Its antifungal effect is based on the suppression of the multiplication of fungi by the active substance (benomyl) due to the violation of nuclear division in their cells.
This therapeutic effect of the drug against powdery mildew lasts for 3 days after treatment, then a protective function remains for another week.
The tool can be used both for spraying and for watering the lawn. For this, 1 g of the drug is diluted in a small amount of water, then liquid is added to a volume of 1 liter.
If it is necessary to make several treatments, an interval of 10-14 days is left between them.
Fundazol
Mr. Summer resident informs: prevention of powdery mildew on indoor plants
Getting rid of powdery mildew is not easy, so it's easier to focus more on prevention. Simple tips will protect plants from other diseases and parasitic insects.
- Preventively spray with a solution of potassium permanganate (potassium permanganate) or sulfur. They are sold at regular pharmacies. This procedure is especially important during the period of warmth and long daylight hours, namely from May to September. One such spraying per month is enough for the plants to be protected.
- The risk group includes indoor flowers in a stuffy room, or vice versa, standing in a draft. It is necessary to create a comfortable environment for green pets to keep them healthy.
- Avoid too humid climate, which may arise on the balcony during prolonged rains or with the onset of cold weather. Do not overflow or dry out the soil.
- Remove wilted leaves and flowers in time to prevent rotting.
- Prevent the appearance of scale insects and aphids. They are carriers of other diseases and weaken the immunity of plants.
For the same reason, do not use land taken from summer cottages, humus, purchased soil without heat treatment. They can be infected.
Prevention of infection
The best plant protection is prevention. The most effective solution is to organize the right pet care. It is he who will provide crops with maximum resistance to infection. Two simple rules of content can be followed not only by professionals, but also by novice gardeners.
- Inspection. We check the plant regularly. This will help to notice changes in appearance and development in time. We pay special attention to the inspection of leaves and peduncles.
- Care. We apply fertilizers with phosphorus and potassium on time. We adhere to the correct watering regime. We remove the fallen, dried leaves from the ground. We carefully transplant it into a new pot, select the soil taking into account the type of plant. We carry out pruning and other maintenance procedures. We maintain the required indoor climate. We do not overmoisten, do not overdry the air.
It is useful to periodically spray indoor crops with drugs for prophylactic purposes, which will help to avoid sudden infection. Their choice depends on what kind of crops will be processed. It is necessary to act according to the manufacturer's instructions in order to avoid the death of the green "friend". Flowers donated or just purchased should be quarantined for some time.
We must not forget that powdery mildew is dangerous and insidious. Even if you managed to overcome it, you do not need to relax. She can return within a year.Almost all popular indoor flowers can suffer from infection. Species with soft and delicate leaves are especially vulnerable. These are Kalanchoe, violet, begonia, gerbera.
Folk remedies in the fight against powdery mildew
Folk remedies are available, found in almost every home and will not cause any harm. They can also be used for prophylaxis. Several recipes for spray mixes:
Ash + soap
For a liter of warm water, take 100 g of sifted wood ash. Stir and insist for about a week, shaking occasionally. At the end of the period, the liquid is drained, trying not to raise the sediment. To it add 50 g of shavings of laundry soap, wait for complete dissolution. You can use liquid soap. This solution is sprayed on the plant daily for a week.
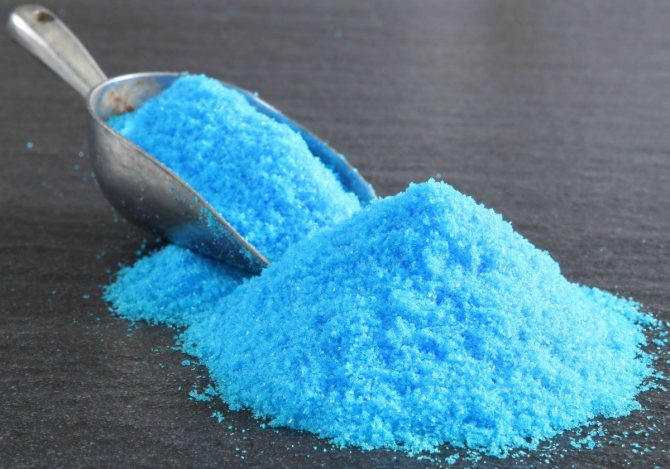
Copper sulfate + soap
50 g of soap, prepared in the same way as in the previous recipe, is dissolved in 5 liters of warm water. Stir copper sulfate powder (5 g) separately in a glass of water (250 g). Gradually pour into soapy water in a thin stream. Spray damaged flowers every other day until powdery mildew symptoms disappear.
Mustard
Stir mustard powder (2 level tablespoons) in 10 liters of water. In a day, the infusion is ready. They can water the soil and spray the ground parts of the plant. It is best to alternate between the two for 10 days.
Milk
You will need sour milk, curdled milk or, even better, milk whey. Dilute with water in a ratio of 1: 3 and treat plaque on indoor plants once every three days for two weeks. This method is good in that the solution can be used immediately, without insisting, and you can always prepare a new portion.
Disease prevention
Powdery mildew is able to live in the soil for 10 years without showing itself.
Preventive measures will help prevent the development of the disease. So:
- Every year from the end of May to the beginning of September, it is necessary to spray with sulfur or manganese solution. The best option would be 4-5 sprays during the specified period.
- Ventilate the premises frequently, but avoid drafts. Avoid stagnant air.
- Do not leave flowers on the balcony during rainy periods when the humidity rises.
- Do not use soil from summer cottages for indoor flowers. It can be infected with a fungus.
- Limit the use of nitrogen fertilizers. Plant immunity is strengthened by phosphorus or potassium supplements.
- Avoid the appearance of aphids or scale insects. These pests are carriers of ashtrays.
- Remove dried leaves and damaged leaves, buds and shoots.
- Avoid stagnation of water on the leaves and in the soil.
- Do not allow the soil to dry out.
5 / 5 ( 2 votes)
Causes provoking the onset and development of the disease
Powdery mildew spores live in the ground and await the most favorable moment to settle on living vegetation and begin to multiply. They show their activity under certain conditions:
- violation of the watering regime (excessive or frequent moisture, especially in cool weather);
- densely planted or malformed bushes, due to which the sun does not penetrate in and there is no ventilation;
- an incorrect quantitative ratio of nitrogen and phosphorus-potassium fertilizers, when an excess of nitrogen causes rapid growth of foliage (it becomes juicy, pampered and susceptible to disease);
- optimal temperature and humidity conditions for the pathogen (humidity 80-90%, temperature 15-170 С).
To prevent powdery mildew from developing rapidly on roses, timely measures are taken to combat it, trying to avoid excessive moisture, and adjust the composition of nutrient mixtures.
It will be useful to read:
Black Spot and Methods of Controlling It Basic Description of the Disease Black spot is caused by the fungus Marssonina rosae, which, when it gets on plants ...
Biological products for powdery mildew on indoor plants
Biological drugs are less effective than chemical drugs. But they are less harmful. They are safe both for the flower itself and for humans and everyone who has contact with the plant.
Their action is based on living bacteria, which naturally fight against the mycelium of the fungus, suppressing and oppressing it.
The most common and affordable drugs are: Fitosporin, Alirin, Gamair, etc.
Apply strictly in accordance with the instructions. To achieve a lasting result, the treatment with biological products must be repeated several times.
Treatment
What to do and how to process the planting if signs of powdery mildew are noticed in the garden or in the garden? Immediately start treatment:
- remove all affected leaves and shoots (with a whitish bloom, yellowed, lost turgor);
- bushes are cut off from flowers, leaving the main stem, since conidia of the fungus can be on all shoots;
- in containers or on flower beds, the top layer of soil is replaced;
- thinned out plantings;
- remove all leaves, shoots, plant debris from the surface of the beds;
- planting is treated with medicinal compounds. Spray abundantly, completely wetting the stems, shoots, leaves. The soil is cultivated so that the top layer is moistened.
The cut parts of the plants are burned. It is not permitted to use plant residues for compost pits. Fungal spores are tenacious, a favorable environment is created for them in the compost, and in fact, such fertilizer will serve as a source of spread of infection.
Chemical remedies for powdery mildew at home
The harmful effects of fungicidal (chemical) preparations are well known. They are resorted to only in extreme cases, when the disease is severely neglected, but you do not want to lose a particularly valuable specimen from your home collection.
In order not to suffer from the use of toxic agents, you need to carefully study the recommendations for the use and use of personal safety measures.
At home it is allowed to use: Topaz, Fundazol, Vitaros, etc.
The complex of using different means


The most tangible effect is provided by the complex use of various means. The fight must be fought in all directions.
Severely affected plants are treated with fungicides. The effect is fixed with biological products. And for prevention, they use folk recipes.
It is important to use gloves and even special clothing for any contact with a sick plant. Otherwise, the grower himself risks becoming a carrier of spores of a harmful mycelium if, after contact with an affected flower, he touches healthy plants.
How to deal with fungus
There are several ways. The first (and easiest) - mechanical... This is a method with the minimum cost of the budget, which implies only your participation. Also, there are folk methods and chemical... The latter are not particularly trusted by experienced gardeners, since many chemicals have a hazardous factor on humans, animals and the plant itself. However, this is the most effective method of all the above, since only it is guaranteed to destroy pests.
Read also: Room primrose, home care rules
But folk methods are very fond of gardeners and just holders of indoor plants. After all, you make all the infusions, spray solutions yourself, which means that you are sure of what is included in the composition.
- Amistar EXTRA... A highly effective chemical, certainly not on a budget. For a 5 liter canister in stores, on average, they take 15-18 thousand rubles. A wide range of actions, not only fights the pest, but also has beneficial properties on the plant (regulates water balance and much more).If the pesticide is used strictly according to the instructions, no phytotoxicity occurs.
- Vitaros... This drug specializes in protecting bulbous flowers. The average cost is 12-15 rubles. Completely destroys the infection in two days. It not only fights pests, but also creates a protective barrier against subsequent possible infections.
- Acrobat MC... Produced in the form of granules (price per 1 kg - 1.5 thousand rubles, for 10 - 14 thousand rubles). A systemic fungicide, it does an excellent job of eliminating the fungus, it acts not only as a therapeutic, but also as a protective drug. It is not phytotoxic; if necessary, it can be used together with other drugs. With strict adherence to the instructions, there are no problems with subsequent attacks of the fungus.
- Fundazol... Sold in powder form, 60 rubles per 10 grams. Watering plants requires only 1 gram per liter of water. Therefore, the consumption is correspondingly small. For the complete destruction of powdery mildew, it is necessary to carry out 3 treatments. This fungicide is the real subject of controversy. Some holders of indoor plants claim that there is no need to use it at home, they say it is too toxic. Others, on the contrary, fell in love with it for its high efficiency and rapid destruction of various kinds of infections.
How to carry out the treatment with chemistry?
Don't forget about safety
First, prepare the territory. Leave only those plants that are subject to processing, remove others away. Mix the drug with water strictly in the proportions indicated in the instructions (each drug has its own recommendations for each species / family, pay attention to this). Then spray thoroughly. Even if only the leaves or some specific part are damaged, it is necessary to process the entire plant completely.
Don't forget about your own appearance. Closed clothing should be worn to prevent possible skin contact. If the chemical does get on your skin, immediately rinse the area with copious amounts of water, and if you accidentally swallow a tablet, drink activated charcoal, 2 liters of water and induce vomiting.
If there are signs of poisoning, consult a doctor immediately, it is better to call an ambulance.
Fighting powdery mildew on indoor plants at home: means and methods
A sick flower becomes a carrier of infection, therefore, immediately after the symptoms of powdery mildew are detected, the pot or pots with a flower must be isolated and contact with other indoor plants in the room limited, otherwise the disease can spread quickly.
For the same reason, purchased or donated indoor flowers should be quarantined for up to 10 days.
Immediately before treatment and during procedures, the plant maintenance regime should be changed. For this, the following rules are observed:
- Remove all affected leaves, buds, stems. Also cut off the lower leaves and branches that are in direct contact with the ground.
- Remove the top of the soil and replace it with a new one.
- Thoroughly wash and disinfect the tray or pots used to collect excess moisture when watering.
- Reduce watering and do not spray the plant while using medications.
- Do not apply top dressing. With a successful end of the disease, subsequently, in order to prevent, abandon nitrogen fertilizers, replacing them with phosphorus-potassium fertilizers.
- It is better to choose a place for keeping a plant in quarantine well-lit, but not hot and ventilated.
Means for powdery mildew on domestic plants are used by different:
- chemical;
- biological;
- folk.


Prophylaxis


It is easier to prevent damage to indoor plants than to deal with an already developed disease. You need to pay attention to the trees and bushes growing under your windows.If you find signs of disease on them, take urgent measures to protect the potted flower, since fungal spores are carried by the lightest breeze.
- Pollinate flowers with sulfur during the summer.
- The period when buds appear is most vulnerable to overfeeding with nitrogenous fertilizers, leading to possible trouble.
- Potash and phosphorus feeding will increase the resistance to the pathogen.
- Plants will benefit from airing the room, however, avoid cold drafts.
- Spraying with milk whey every two weeks will bring benefits in preventive actions. Before the process, it is necessary to dilute it in the ratio of one part of the product to three parts of water.
- Place the pot in a lighted place.
- Use complex flower fertilizers regularly.
- Examine your pets more often, wipe the leaves from dust, and remove faded ones.
What are the signs of powdery mildew
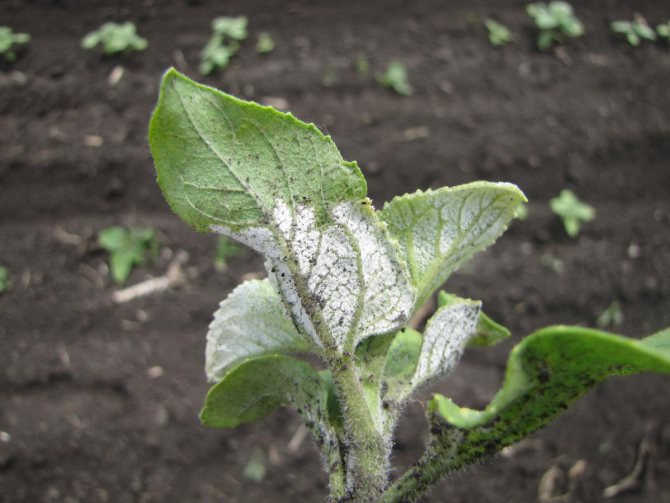
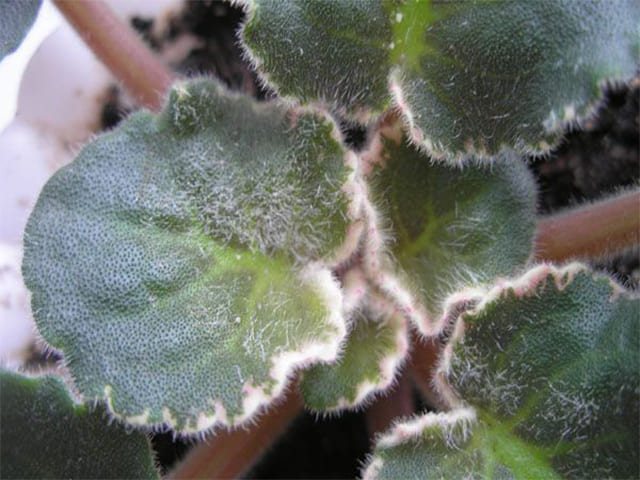
Infection of indoor plants with the disease is accompanied by the appearance on young leaves, pedicels, branches of white bloom in the form of small spots. After that, brown fruits grow on it, which contain spores of mushrooms.


Belle is easy to spot. Its diameter is 0.2-0.3 mm. The parasite spreads from leaves near the surface of the soil, then spreads to all flowers.
Symptoms
Powdery mildew is easy to define, as it has rather characteristic symptoms. It begins with small white spots on the top of the leaf. Gradually, the spots increase and cover the entire leaf as a whole, move over the entire aerial part of the plant. As the disease progresses, the spots become larger, denser and whiter: the bushes look like they have been doused with lime mortar. And upon closer inspection, the leaves seem to be covered with the thinnest layer of cotton wool or cobwebs - this is the white mycelium of the fungus, consisting of numerous conidia collected in chains.


What is typical for any pathogen of powdery mildew - the pathogen can strongly suppress plants, the leaves turn yellow noticeably, necrotic spots appear on them, but shrubs and trees never begin premature leaf fall, and the plant does not die. To explain this is simple: mealy fungi are obligate parasites that live in the host's body and exist as long as the plant is viable. At the ends of the mycelium of the mealy fungus there are formations - haustoria - branches of hyphae, penetrating into the leaf cell and absorbing nutrients. But if the plant dies, the mushrooms will also quickly die, and therefore they do not completely deplete it.


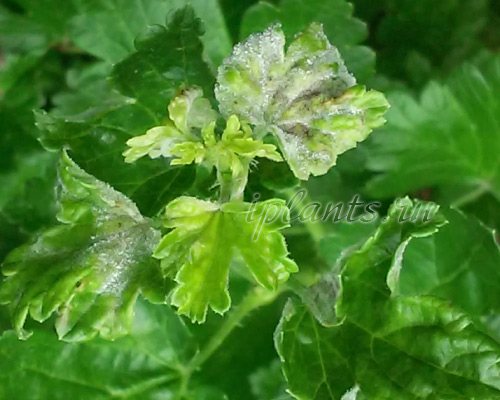
In fruit plants, the growth of the bush is disturbed, the wood on maturing shoots does not ripen, as a result the plants suffer greatly from frost, especially for grapes. In addition, the spheroteka very quickly moves from leaves to ovaries and fruits, you can be left completely without a crop, since berries and fruits affected by a white bloom are unsuitable for food.
With vegetables, the situation is more complicated - since tropical plants consume a huge amount of nutrients for the growth and formation of fruits, very often they simply cannot cope with the infection and die. Powdery mildew is a serious threat to cucumbers and tomatoes.
Causes of defeat
- stagnant humid air in the room;
- sharp temperature fluctuations;
- contact of a sick seedling with a healthy one;
- excess nitrogen, giving an abundance of greenery;
- unventilated room;
- abundant watering.
The danger of the disease lies in its rapid spread, in the complexity of treatment. A diseased plant loses nutrients. The processes of respiration, photosynthesis and evaporation deteriorate sharply. The leaves dry up and die off. Infected young shoots do not develop.
Climatic conditions.
Powdery mildew spores spread mainly in the first days of summer, as they went through the winter recovery period. After that, abrupt changes in climatic conditions become ideal conditions for full-scale infection. Infection of plants, in general, passes with an abrupt change from a hot day to a cool evening. It is then that a white bloom appears on the leaves. In such comfortable conditions, the fungus spreads. Due to the wind, the fungus migrates from plant to plant, quickly settling on the lower part of the leaves and stem. A striking example here will be the situation when oak powdery mildew, on one single tree, becomes a hotbed of infection for all nearby plants. Getting on the plant, the fungus begins to actively spread over the area of the object of infection, while releasing microscopic droplets of liquid. That is why this fungus is called dew.
In general, like any fungus, powdery mildew is adapted to any conditions. This feature of the evolutionary development of all fungi makes them terrible neighbors. An independent fight against powdery mildew will take a long time and sluggishly, it is much more effective to use the help of professionals.
Description of the disease
Powdery mildew is classified as a fungal disease provoked by the activity of pathogenic microorganisms. Depending on the agricultural culture, a certain class of pathogenic fungus can become a provocateur of the disease:
- Uncinula necator - Affects vines
- Erysiphe graminis - prefers to parasitize on grain crops;
- Sphaerotheca mors - Dangerous for fruit bushes and all trees;
- Erysiphe cichoracearum, as well as Sphaerotheca fuliginea - fungi that infect pumpkins, squash, squash;
- Sphaerotheca pannosa - a parasite on flower crops.
Signs
The early signs of a fungal infection are the formation of soft leaves, stems, young green shoots, as well as flowers of a white fluffy bloom on the surface. The spread of pathogenic fungi begins from the soil, therefore, the signs of the disease are more noticeable on the lower structure of the plant. Over time, pathogenic microorganisms "capture" the entire plant.
The neoplasms are "collected" in spots of various sizes. Often, gardeners try to erase the whitish bloom, but the spots reappear. After the fungal spores mature, small droplets of liquid form on the surface of the white spots.
The next stage is the compaction of the whitish plaque. It acquires a rich grayish hue, and small black dots form on its upper part.
What is the danger?
Affected by a fungal infection, agricultural crops, shrubs and flower plants lose their decorative qualities. Dense plaque on the leaves disrupts photosynthesis, and the plant becomes weak and lifeless.
Young diseased shoots turn black, rot and die off. Flowers with symptoms of powdery mildew, are not able to stay on the peduncles for a long time, they prematurely fall off.
Weakened agriculture is not capable of producing a full-fledged crop. Fruits formed on diseased plants are deformed and do not grow to their normal size. Affected crops lose their frost resistance, most often such plants cannot survive the winter and die.


A favorable environment for pathogenic fungi
Microorganisms exhibit the greatest pathogenic activity under the following conditions:
- in moderately warm weather (+25 degrees) and an air humidity of more than 70% - such climatic conditions are observed during prolonged summer rains;
- with a constant change in temperature conditions;
- after an incorrectly performed plant pruning procedure;
- if the soil is oversaturated with nitrogen compounds;
- with thickened plantings;
- with improper soil moisture (when overdrying or, conversely, waterlogging of the soil is constantly observed).
Powdery mildew disease: where does it come from?
Spores of powdery mildew fungi are frequent inhabitants of the soil, but they do not always show their parasitic nature. When it is warm, sunny weather, the plant is watered and fertilized during the time, nothing shines to the fungi. They begin to cling to the "owner" and develop if:
- outside is cool (15.5-26.5 ° C), damp (humidity 60-80%), cloudy (for example, during the rainy season). The weather conditions have a particularly great influence on outdoor and balcony plants; when grown in rooms, they are not so noticeable;
- there is a large amount of nitrogen in the soil;
- vegetable plantings are thickened;
- irrigation regime is not observed. For example, a plant is often watered without waiting for the top layer of the earth to dry out. Or, on the contrary, they regularly dry out the earthen lump, and later fill it in. All this leads to a violation of immunity and, as a result, the appearance of powdery mildew.
In addition to these external conditions, already "awakened" spores can fall on flowers:
- by air (from infected trees or plants);
- through irrigation water (if spores got there);
- through your hands (if you touched an infected plant, and then touched a healthy one).
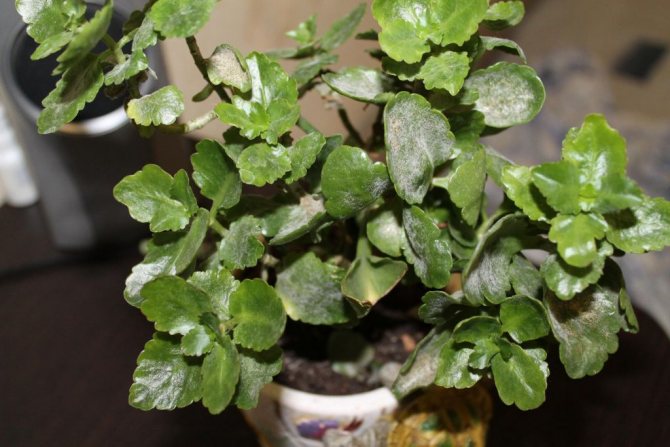


Powdery mildew is capable of completely destroying a plant in a short time.
Why is powdery mildew dangerous?
Up to 60% of affected plants die. Malicious spores spread very easily and the disease is difficult to treat.
Here are just some of the consequences of powdery mildew damage:
- The hindered process of photosynthesis, due to which the plant as a whole suffers.
- Lack of nutrients.
- Slowdown in growth.
- Blooming oppression.
- Dying off of leaves and buds.
Very often decorative flowering indoor plants with large flowers and leaves, such as gerbera, violet, chrysanthemum, etc., suffer from this disease.
Powdery mildew should be distinguished from downy mildew (peronosporosis). They look almost the same. With downy mildew, only the back of the leaf is covered with bloom.


Downy mildew
Very soon it turns yellow and then turns brown. Methods of dealing with them are different.