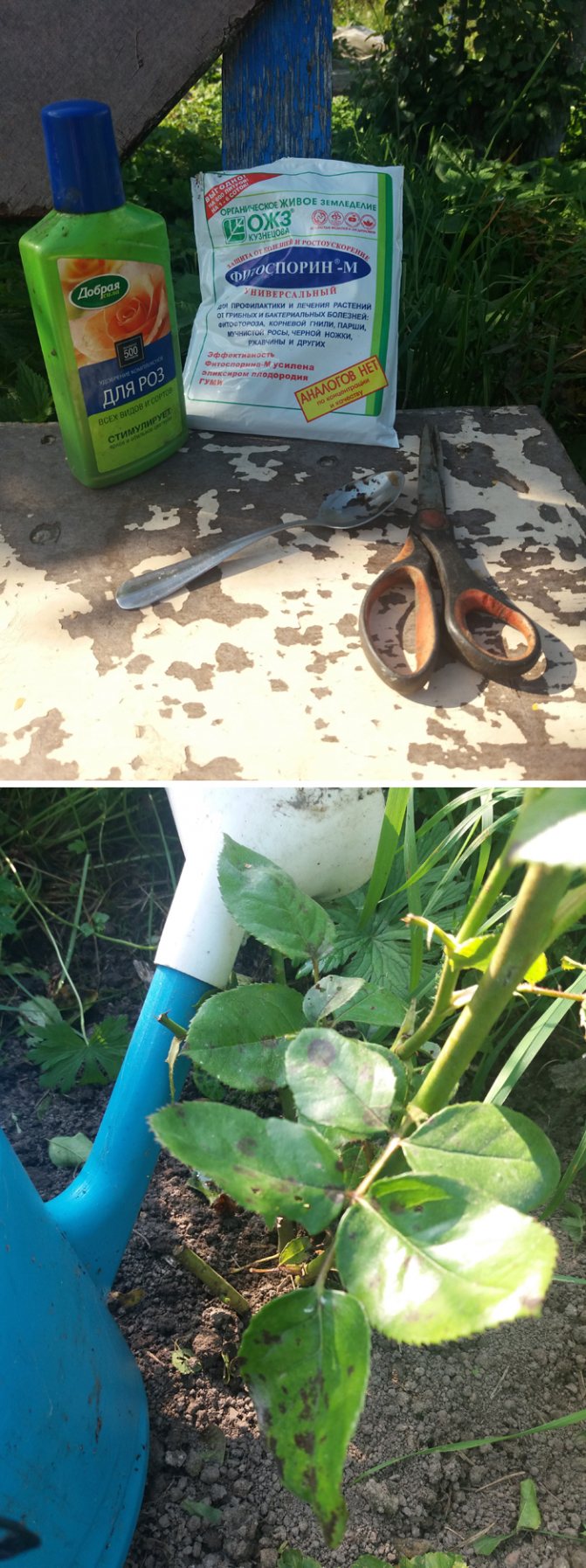
Diseases of roses negatively affect the appearance of the plant. They are debilitating and, in severe cases, can be fatal. In order to avoid these troubles, each owner must be able to properly protect their garden roses. In the material of the article, we will tell you in detail about what types of lesions there are and how to treat roses from diseases. If the slightest signs of a pathological process are detected, treatment must be started immediately. Experienced gardeners know that it is better to spray roses with special products than to allow further spread of the disease. Since preventive measures allow you to preserve the beauty of the plant and lengthen the flowering period.
Fungal diseases
Powdery mildew
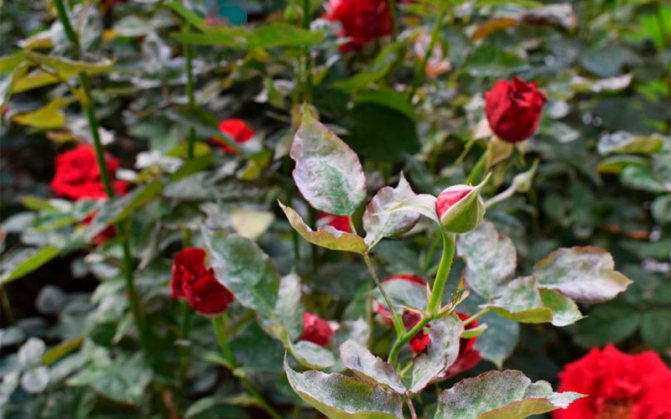

Fungi begin their harmful vital activity in early summer in warm, damp weather with sharp jumps in daytime and nighttime air temperatures.
The disease is detected by the appearance of a white bloom on the leaves of the rose. These stains resemble scattered flour and are easy to remove. Biologically, they are a colony of Sphaeroteca pannosa spores.
Have questions? Ask and get useful advice from professional gardeners and experienced summer residents. Ask a question >>
With downy mildew, dark spots appear on the underside of the leaves, then spread throughout the plant. If nothing is done, then brown dots appear on the affected leaves. Then the leaves curl, wither, fall off. At this stage of the disease, flowering stops.
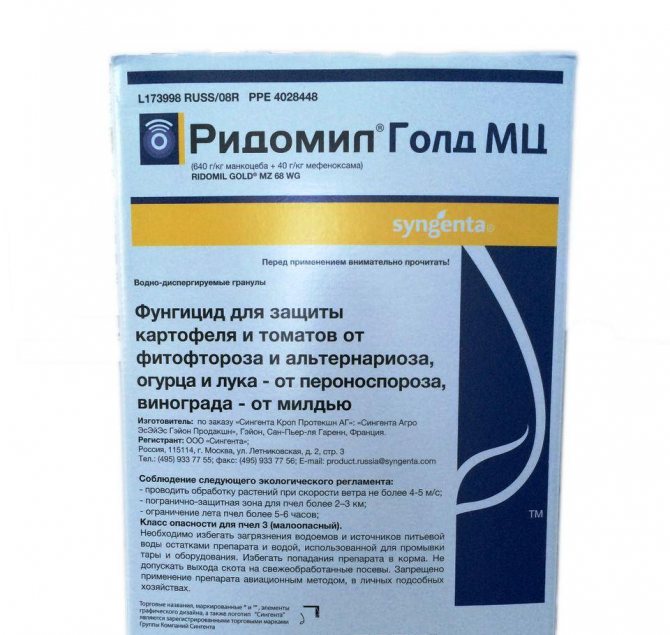
For the treatment of powdery mildew, systemic drugs are used. For the queen of flowers, the fungicide Fundazol is suitable. The solution should be sprayed with roses three times with a break of 10 days. After two weeks after the last spraying, it is imperative to treat the diseased bush with biofungicide. A good drug is Fitosporin M. Summer residents also use Topsin-M.
Rust
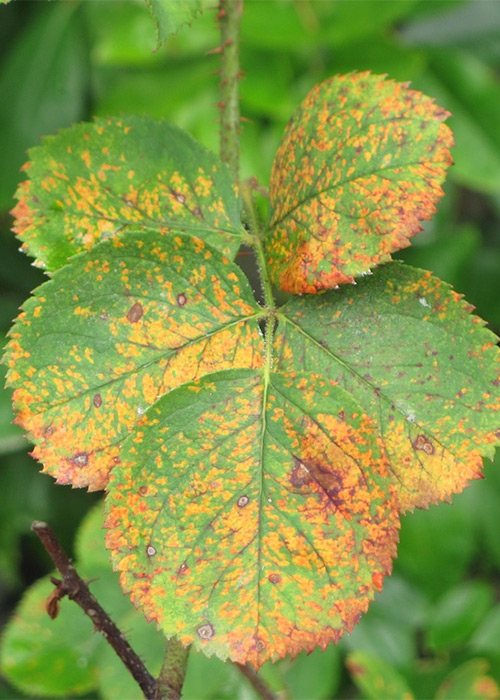


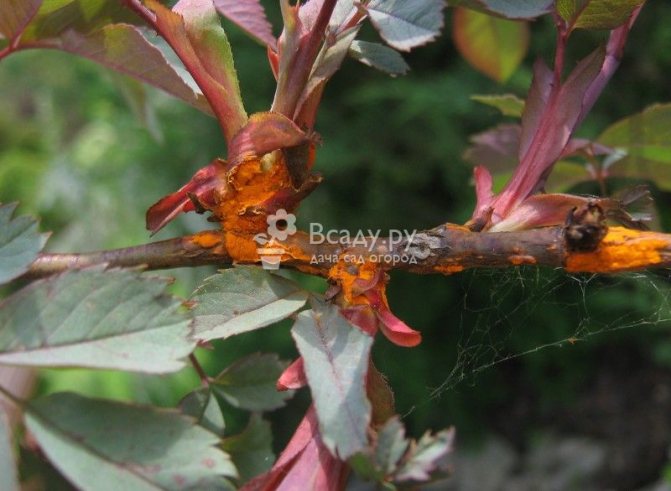
Fungal disease can occur in mid-June. The causative agents of rust are Phragmidium disciflorum fungi. It is manifested by the appearance of bright red dots on the leaves or branches of the rose. If the rose is not treated, then these points will begin to multiply, merge into single dark brown spots. The whole bush can die from rust, and not just individual branches.
Rust progresses in wet weather. Also, an excess of nitrogen in the soil stimulates the development of the disease.
In order to avoid the appearance of rust, rose bushes and the ground around them should be treated in early spring with a 1% solution of copper sulfate. In late autumn, the treatment should be repeated, but with a solution of ferrous sulfate. Its concentration should be 3%. It is also worth treating roses with a 1% solution of Bordeaux liquid before and after flowering.
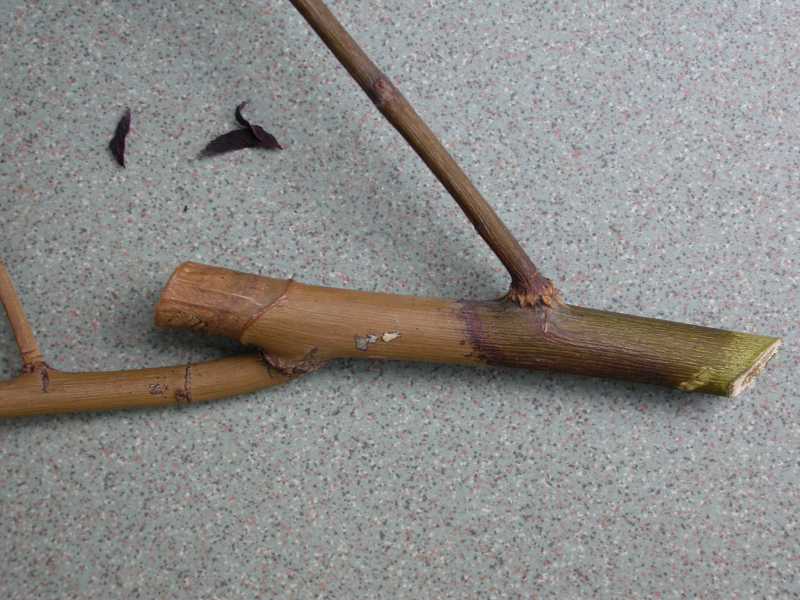
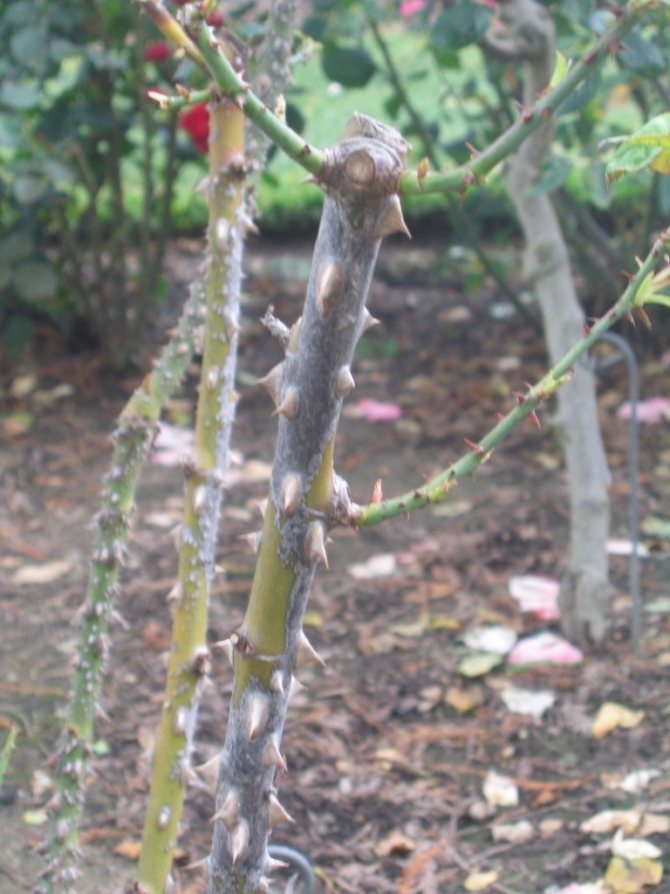
Bark necrosis


This type of disease is manifested by the affected areas of the cortex. Their color differs markedly from natural. If you do not notice the symptoms and do not start treatment, then the bark cracks and dies. A depression appears at the site of the crack.
The causative agents of necrotic diseases are pathogenic bacteria and fungi.
Infectious burn
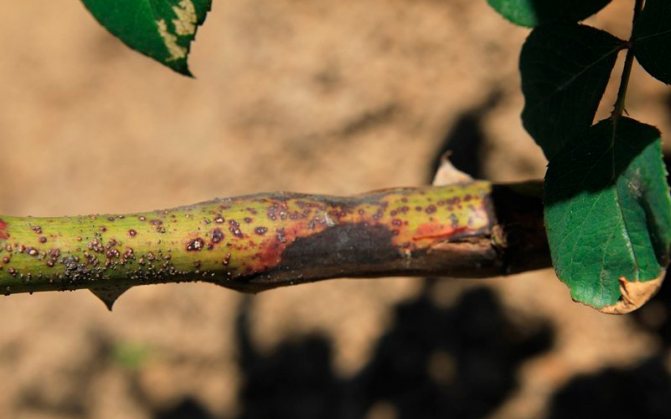


Stem cancer of the bark of roses arises from the vital activity of fungi. They love musty damp air, they also thrive in the soil in winter, if the rose bushes are covered with a film. When the soil freezes, the development of fungi stops, but they do not die.When the soil thaws, the fungi reactivate.
An infectious burn is initially detected by the appearance of red-brown spots on the branches of a rose. Also, in the early stages of bark cancer, instead of mottling, brown or black bands around the stem may appear.
Further, tubercles begin to appear on the surface of the stems. They contain fungal spores. Under their influence, the bark begins to lighten, small ulcers appear on its surface. Later, the bark cracks and the stem dries up.
Unfortunately, this disease is not treatable. Do not cover roses for the winter with plastic. It is better to use natural materials or garden fabric for this.
Common (European) cancer
The causative agents of common rose cancer are fungi from the genus nectria. They often end up in our gardens along with imported seedlings.
A sign of an incurable disease is the appearance of longitudinal cracks in the bark. The presence of an overgrown uplifting callus along the cracks is characteristic. This word translated from Latin means corn. Biologically, it is a neoplasm.
Such calluses often appear on old stems at their bases. As the disease progresses, they appear on young shoots. The affected stems gradually wither and dry under the influence of the disease.
Diplodious necrosis of the cortex


Bark disease is manifested by the appearance of multiple shallow longitudinal cracks on the bark along the stems. At the same time, the color of the bark changes, it becomes dark chestnut. Later, small bumps appear, in which spores of the fungus develop. After a short time, the stem dries up completely.
Favorable conditions for the occurrence of this disease are damp musty air due to the excessive density of the bush. Also, fungal spores enter the bush through a working tool that has not been disinfected for a long time. Excess nitrogen in the soil can also cause necrosis.
The disease cannot be treated. All affected stems must be removed and destroyed in a fire.
Tubercular necrosis of the cortex
This also incurable disease arises from the influence of the fungus Tubercularia vulgaris. It is manifested by the appearance on the surface of the stems of pink-red tubercles, inside which spores of the fungus develop. Later, the bark changes its color to brown and dies off.
Diaport stem cancer
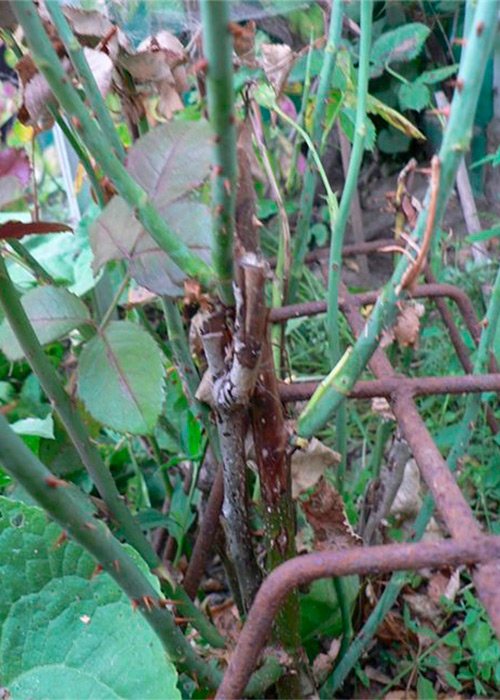


Diaport cancer occurs under the influence of the fungus Diaporthe umbrina. When the disease appears, areas of purple color appear on the bark, which soon begin to swell. The bark of the affected stem darkens, acquires a light brown color.
Later, at the site of the bulges, the bark cracks, and to its entire thickness. Further, pycnidia (fungal colonies) begin to form in these cracks. They look like small black bumps that gradually grow.
As such, there is no cure for this disease. The diseased stems have to be burned.
For prophylaxis, roses are sprayed with universal 1% solutions of copper sulfate or Bordeaux liquid.
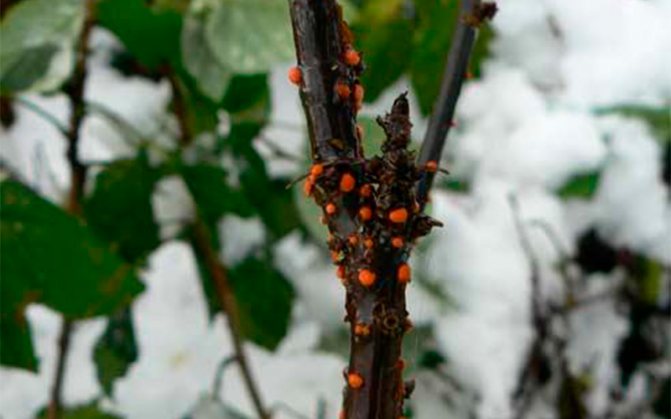
Cytosporosis
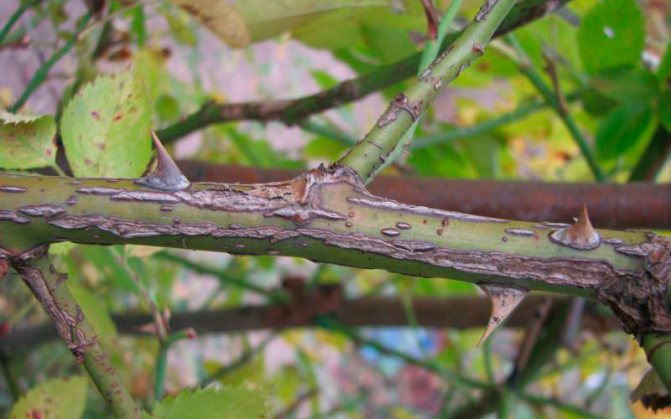


Cytosporosis is caused by the fungus Cytospora rosarum. From the disease, the bark on the branches begins to pee, brown tubercles form on it. In the spring, fungal spores are selected from them and begin their destructive activity. The spore colony looks like golden or red blobs.
Plant spores are carried by rain or harmful insects. Under the influence of these microorganisms, the leaves wither, and then the branches dry out.
Cytosporosis is also not treatable. When it appears, it is necessary as quickly as possible, without waiting for drying, to cut off all affected branches and burn. All cuts must be covered with crushed charcoal.
To prevent the disease in early spring, before the buds begin to swell, spray the rose bushes with a solution of the product containing copper.
Shrinking branches
The branches on rose bushes can dry out from the effects of various types of fungi. From their vital activity, the bark acquires a brown color. At the same time, stromas appear on it in the form of colonies of fungi, the disease begins to progress from this. How to treat a rose?
There is no recipe for this disease. However, subject to the rules of caring for roses, it never arises.
These include:
- spraying bushes in early spring and late autumn with a 1% solution of copper sulfate, Bordeaux liquid or a solution of the same concentration of Abiga-peak;
- timely pruning of dry branches;
- cleaning and burning fallen leaves;
- correct feeding.
Gray rot
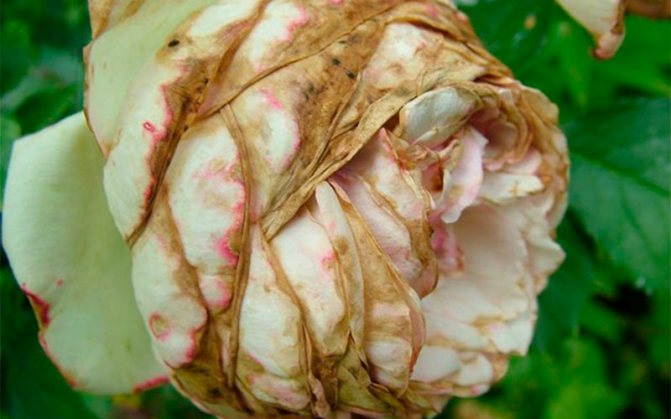


Gray rot on roses is caused by the fungus Botrytis cinerea. Its name is botrytis. Floribunda rose is most susceptible to gray rot. Also, tea rose hybrids are not resistant to this disease.
Gray rot is manifested by the appearance of small brown dots on the branches. These spots grow rapidly, merging into single large spots. At the same time, a gray bloom appears on the flower petals. The flower from this loses its former beauty. The spot can even cover the entire branch. After this, the foliage on the affected branch begins to wilt and fall off.
It is not possible to cure a rose from gray rot. When it appears, all diseased branches must be burned.
It is worth saying that only weakened bushes are affected by gray rot. Therefore, you need to care for roses carefully.
For the prevention of this disease, it is advisable to carry out spring and autumn spraying of the bushes with a 1% solution of copper sulfate, and in the summer to prevent excessive density of the bushes. When insects appear, it is worth sprinkling the bushes with insecticides, because pests just contribute to diseases.
Favorable conditions
The development of black spot on the leaves of a rose can be facilitated by factors that do not depend on a person, for example, wet weather or a large amount of rainfall. Also the reproduction of the fungus is affected by the lack of air circulation and the strong thickening of the shrub.
Also, experienced gardeners recommend finding out in advance the complete information about the acquired variety, including resistance to black spot. If the plant is immune to the disease, then the risk of infection will be minimized, otherwise the fungus can comfortably multiply on the leaves of the rose.
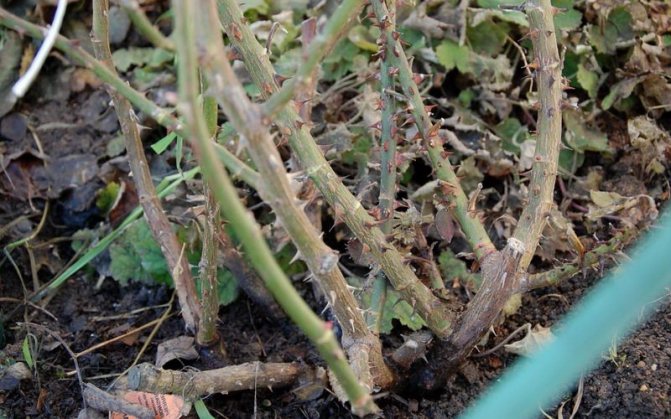
Root rot
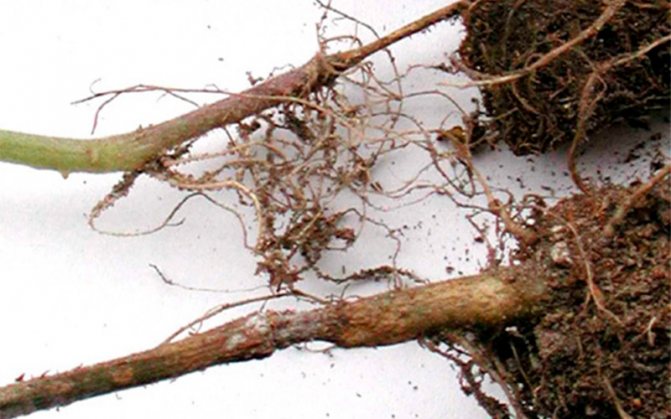


Root rot on roses can occur from the effects of various types of fungi. It is impossible to notice the onset of this disease for obvious reasons. When external signs appear on the aboveground part of the plant, it is too late to save the rose - its root system is already affected by fungi.
Only preventive measures and careful care can prevent root rot disease.
White sclerocial rot
This disease is caused by the vital activity of the sclerotinia sclerothiorum fungus. It always affects only young rose roots - they can no longer absorb nutrients from the soil. If you dig up a sick bush, you can see that all the young roots on it are wrapped in a white bloom, like cotton wool.
Already in the initial stage of the disease, wet spots appear on the leaves. Next comes the active wilting of the foliage, and behind it the rapid death of the entire bush.
If you start treatment in a timely manner, then the bush can often be saved. The essence of the treatment consists in watering the soil under the bushes with an aqueous solution of Fitosporin-M, Gamair or Alirin-B.
A good prevention is the treatment of the roots of seedlings with Baktofit. Also, do not plant flowers in heavy soil and lowlands.
Prevention and precautions
For the prevention of rose diseases, the following recommendations must be observed:
- select unpretentious shrub varieties with the necessary resistance to cold and rain;
- inspect seedlings for infestation and treat with biofungicides before planting;
- choose loose soils for planting, well-lit and ventilated areas of the garden;
- keep the distance between shrubs;
- process roses every 2-3 weeks, regularly loosen the soil and cut off the shoots;
- do not plant plants in lowlands and with shallow waters;
- pour fertilizers and water under the roots;
- feeding and wrapping should be carried out in dry weather;
- spray shrubs with vitriol solution after spring pruning;
- disinfect instruments with chlorine and iodine-containing agents, and wash fabric gloves at high temperatures.
Bacterial diseases
These diseases are caused by unicellular pathogens. Chemicals are used to destroy them. The most popular for these purposes, judging by the reviews of flower growers, remains an aqueous solution of copper sulfate.
Bacterial cancer
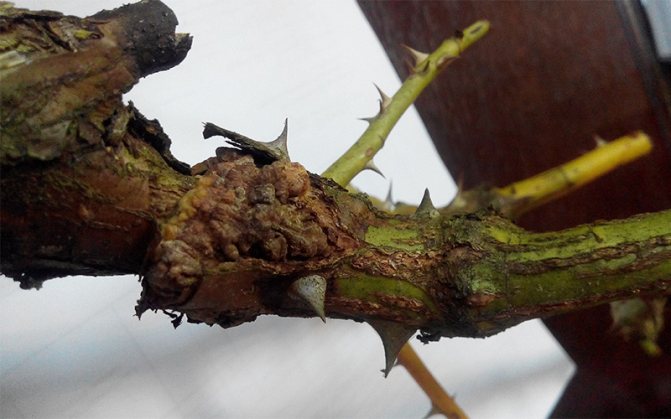


At the beginning of the disease, soft gall growths appear on the roots of roses. After some time, the growths begin to harden, and then rot. Further, the bush slowly fades, dies.
If, at the first sign of wilting, a bush is dug out of the ground, then it can be saved. To do this, remove all growths. After that, the entire root system of the bush must be immersed in a 1% solution of copper sulfate for 5 minutes and the plant must be transplanted to a new place.
The bacteria will safely live in the soil in the place where the diseased bush grew for at least another five years. If you plant a rose or other plant there again, they will get sick again. Therefore, the soil should be thoroughly disinfected at least twice. The first time after removing the bush, and the second time in early spring.
The disease also affects the stems. It flows like this:
- round brown spots appear;
- areas of the bark dry out, exfoliate, ulcers are noticeable in their place;
- moist brown spots appear on the leaves, which soon become holes;
- in rainy weather, all the leaves on the stem turn black and crumble;
- branches dry out.
It is possible to save a rose from bacterial cancer if the disease is detected early. The first step is to cut off all affected branches and burn them. All places of cuts should be lubricated with linseed oil. After that, the entire bush must be sprayed with a 5% solution of copper sulfate.
Treatment of an infectious burn
Remove diseased shoots without damaging the ulcers on the stem; Clean small wounds to a healthy base, using a paper knife is most convenient. Cover with garden pitch; Before budding, it is important to prevent rose disease, treat the affected bush with 3% Bordeaux liquid, this will destroy the spores so that the pests of roses do not spread them; Spray the infected shoots every week with the HOM fungicide until they are cured.


Viral diseases
Viruses are microorganisms that can grow inside plant cells. It is impossible to save the affected cell, just as it is impossible to detect the first signs of a viral disease. This is indicated by experts in the videos. When signs of disease are found on the stem or on several, and this, according to the description, is the amicable wilting of the leaves, this means that the disease is already rapidly progressing, it is too late to treat the rose. Nothing remains, except for removing the affected branches from the bushes.
The main danger of viral diseases is that they are detected too late.
A good prophylaxis against infections is spraying the bushes with an aqueous solution of Inta-Vir or Karate.
Striped leaves
This disease is triggered by the rose streak virus. When it appears, brown rings and a border along the leaf veins appear on the leaves. At the same time, streaks and brown spots appear on the branches of the rose. At this stage of the disease, flowering and growth of young shoots stops.
Viral wilting
The causative agent of the disease is a virus.Its harmful activity leads to a stop in the growth of shoots, a strong thinning of the leaves, the cessation of flowering, and the complete drying of the bush.
Jaundice
Tea, climbing and ground cover roses develop jaundice when exposed to microplasma. The infection is carried by leafhoppers and leaf flies. Shortly after infection, the veins on the young leaves of the rose begin to turn yellow. Further, the leaves rise upward, and begin to fade. Then the entire leaf plate turns yellow. Already at this stage of the disease, the entire bush is weakened, usually dies
Rose leafhopper: description and treatment of roses from the pest
Below you will find a description of the leafhopper rose pest and learn about the fight against it at their summer cottage.
Rose cicadas... The larvae of the rose leafhopper settle on the underside of the leaves, sucking out the juice. The upper surface of the leaves changes color, they turn white, acquiring a marble color. With a large number of pests, damaged leaves fall prematurely. Roses growing in warm, sheltered places especially suffer from leafhoppers.
The pest itself is a small white-yellow insect with two pairs of wings, which in a calm state fold over the back like a roof. The length of an adult insect is 3.5 mm, width is 0.7 mm.
Look at the photo - this rose pest resembles an apple leaf:
The larva is white or pale yellow with a wedge-shaped pointed abdomen. The length of the larva is 2 - 3 mm, the width is 0.8 mm.
Eggs overwinter on branches at the base of the buds and in forks. The larvae appear during bud break. They develop during May-June. Unlike the larvae of aphids and leaf beetles, they are very mobile: disturbed, they quickly escape to the opposite side of the leaf.
At the end of June, the wing buds appear in the larvae, and they turn into nymphs. In early July, leafhoppers fled, and adult insects appear. Winged leafhoppers, like larvae and nymphs, settle on the underside of the leaf, sucking the juice out of them. After fledging, the adult leafhopper leaves the leaf on which it fed and flies off to the grass and other plants or branches.
On leaves damaged by leafhoppers - whitish with a marble color - white skins remain on the underside after molting of larvae and nymphs.
In addition to roses, leafhoppers damage rose hips and other plants from the Rosaceae family.
How to treat roses from these pests in order to protect the plants?
In the fight against the pest, use the same drugs as for the fight against aphids. When spraying roses from pests, make sure that the underside of the leaf is carefully covered with a solution of poison.
Mottling
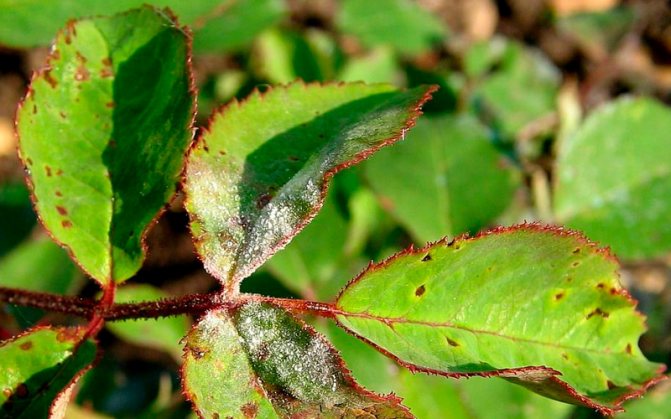


Any kind of spotting occurs on roses under the influence of various types of pathogenic fungi. These fungi penetrate the structure of the plant and feed on its sap there. From this, the roses quickly wither and die. Little remains of their former beauty, as we see in the photograph.
There is no separate drug for treating spotting. It is possible to destroy fungi using an aqueous solution of fungicides, both systemic and contact action. Unfortunately, these types of fungi are able to adapt to the action of any drug. Therefore, when spraying the bushes, the means have to be alternated.


Cercosporosis is one of the types of spotting.
Spider mite on roses: photo and how to get rid of it
Spider mite on a rose is especially dangerous for roses in dry, hot summers. Optimal conditions for its development are temperatures + 29 ... + 31 ° with air humidity below 35%. Under such conditions, the number of ticks rapidly increases, because every 10-15 days a new generation of the pest appears.
As you can see in the photo, the spider mite on the rose sucks the cell juice from the leaves, as a result of which small light spots (pricks) appear on them, the leaves turn yellow, dry up and fall off:
How to get rid of spider mites on a rose using spraying?
The most effective in the fight against spider mites are: Fufanon and Iskra-M. Spraying roses in the presence of a tick must be repeated after 10-12 days until its harmfulness decreases. If you use Tiovit Jet or colloidal sulfur in the fight against powdery mildew, then these drugs inhibit the reproduction of mites.
Non-communicable diseases
Sunburn
Sunburns occur in the spring on young shoots. The burnt leaves turn bronze-brown, but they do not always fall off. The only way to save young shoots from sunburn is to shade the bush on sunny summer days.
Physiological aging
This disease cannot be prevented, but it can be delayed. Aging of a rose is a natural process. The old bush is weakening, which is also natural. The first sign of aging of the bush is a strong thickening of the root collar. After that, the beauty of the rose's appearance is lost. This applies to both flowers and leaves. Old bushes are highly susceptible to all types of diseases inherent in roses. The only way to prolong the life of roses is by proper cultivation.
It is better to remove aged bushes in time, as they will become a source for the disease of young bushes.
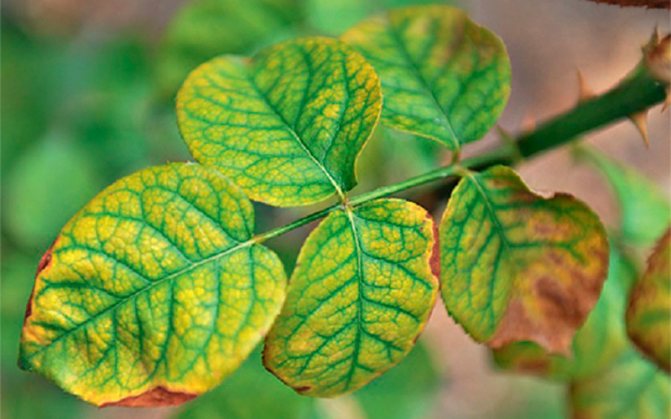
Chlorosis
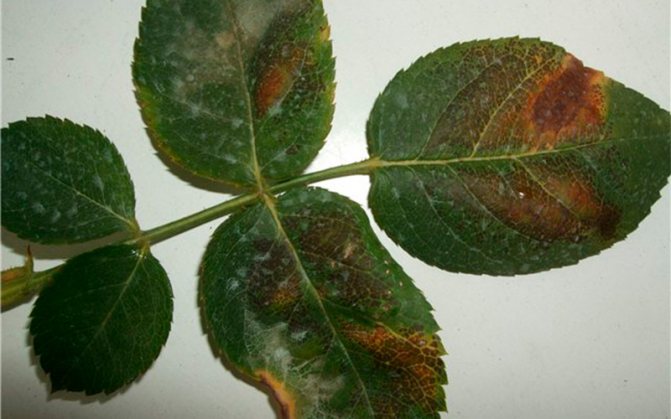


Chlorosis is manifested by yellowing of the leaves, but the veins remain green on them - look at the photo. Chlorosis occurs due to a violation of the correct course of chlorophyll synthesis in the leaves. This often happens when there is a lack of iron in the soil, as well as from an excess of organic matter or lime in it.
To combat the disease, it is necessary to shed the soil under the rose with an aqueous solution of iron chelate.
The same symptoms are characteristic of iron and manganese deficiency.
Phosphorus deficiency
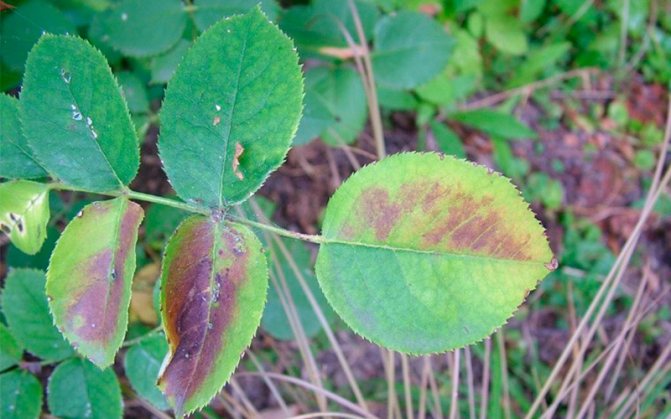


The disease arises from a lack of phosphorus fertilizers in the soil. Due to the lack of their leaves, they noticeably decrease in size, and their lower part acquires a red color. Such leaves fall prematurely, and the flowering of roses becomes sluggish.
You can enrich the soil with phosphorus with an aqueous solution of superphosphate.
Nitrogen deficiency


With a lack of nitrogen fertilizers, the leaves on the roses become elongated, narrow. Red dots appear on the upper half of them. You need to immediately enrich the soil with nitrogen. For roses, an aqueous solution of ammonium nitrate is used. To prepare 10 liters of solution, one tablespoon of the drug is required.
Potassium deficiency
With a lack of potassium, the leaves of the rose first turn red-purple, then they become smaller and crumble.
Replenish potassium complex mineral fertilizers with a high potassium content. To prepare 10 liters of solution, one tablespoon of the concentrate is also required.
Calcium deficiency
With a calcium deficiency, the root system weakens. Following this, the bush does not receive enough nutrients. From this, the plant weakens, the leaves begin to curl, crumble. At the same time, the buds do not open.
The rose will be saved by immediate feeding with calcium nitrate.
Magnesium deficiency
With a lack of magnesium in the soil along the central vein of leaves, foci of decay appear. Then light spots form on the leaves. Leaves fall off prematurely.
It is best to increase the magnesium content in the soil with complex mineral fertilizers with a high magnesium content in them. To prepare 10 liters of solution, use no more than one tablespoon of fertilizer.
Locking the root system
When the root system is locked, yellowing first occurs on the leaves. Then they begin to fall off, and the roots rot. The bush dies quickly.
There is no cure as such. The rose needs to be transplanted to another place, after cutting off the rotten roots.
Chlorosis
Chlorosis usually makes itself felt when the soil of the plants lacks the elements they need. For example, such as iron, manganese, zinc, magnesium, boron, etc. Chlorosis infects almost the entire leaf of roses except for the veins, so usually the leaf turns yellow, leaving the veins green.
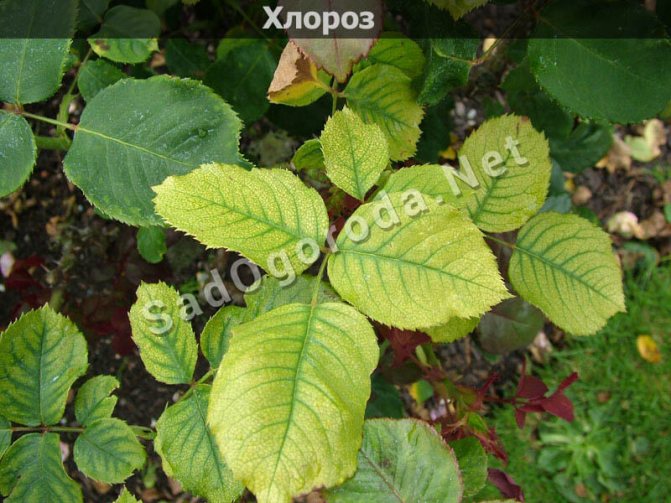


The disease begins to spread from young leaves, affecting more and more, after which the leaves begin to fall off profusely. In order to start fighting the disease, you need to understand what exactly the plant lacks, and then add all the necessary substances to the soil.
Useful Tips


- Plant disease-resistant, easy-care rose varieties. For example, Topaz.
- Do not set up a rose garden on flooded grounds.
- Do not plant bushes close to each other.
- Cut dried stems off the bushes regularly.
- Water and fertilize at the root.
- Perform foliar feeding of the bushes in the evening in calm warm weather, but in such a way that the leaves and stems of the roses have time to dry completely by night.
- Once every two weeks, do a preventive spraying of the bushes with an aqueous solution of biofungicides.
- The tool with which you worked when caring for roses must be disinfected with a weak solution of potassium permanganate.
- The soil around shrub roses should be free of weeds or fallen leaves.
- Before covering the roses for the winter, treat them with a 3% solution of ferrous sulfate.
- Do not use polyethylene for insulation.
- Do not be lazy to do the spring treatment of roses. To do this, you need to cut off all the dried stems from the bushes, spray the bush with a 1% solution of copper sulfate.
- In summer, follow the rules for fertilizing the soil.
As you can see, the list of rose diseases is huge, and their photos are impressive. However, you should not be afraid of this. Provided proper care of the flower garden, knowledge of the description and methods of treatment, the queen of the garden will bloom luxuriantly.
Olga Danilina
New varieties of garden roses


Breeders from all over the world are constantly trying to develop new varieties of plants that will be less whimsical to conditions and habitat. Disease Resistant Roses mark these with the ADR sign... Of course, he cannot guarantee in any way that everything will be fine with this particular type of garden shrub. But the quality mark is awarded only to those varieties that have the best characteristics.
Most of the garden shrubs marked with this quality mark are quite rare, and some are well known in many countries around the world. Among them you can find: densely double, non-double, ground cover and flower beds.
The most resistant varieties include the following types of garden roses:
- non-double "Escimo",
- bud cover "Crimson Meidiland",
- floribundas "Cherry Girl", "Novalis",
- climbing "Apricola" and many others
If you follow the simple rules of care and proper feeding of the plant, you can avoid the appearance of diseases of garden roses. If you see the first signs of illness, take action immediately. This approach will allow not only to quickly heal your flower, but also to protect the entire garden from infection with pathogens. There are now many varieties of garden roses that are disease resistant. But this does not mean that the flowers will not need care.
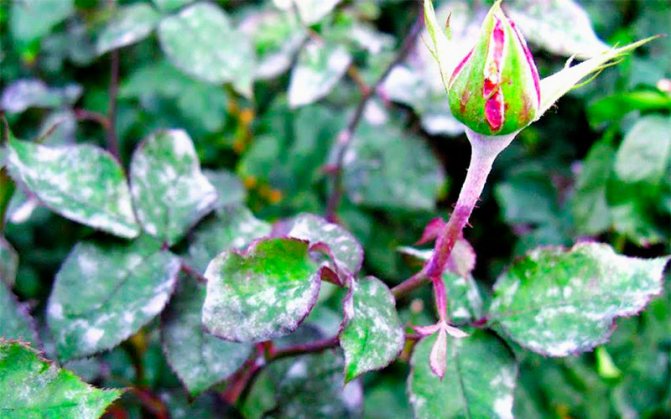
Powdery mildew or rose conidiosis (Latin Sphaerotheca pannosa)
It is caused by a fungus that infects leaves and shoots, less often flowers and buds. For the development of spores (conidia), warm weather (from 20 degrees Celsius) and a high level of air humidity in summer are favorable. The fungus is transferred through the air, water during watering and rain, insects. Powdery mildew affects almost all ornamental plants, fruit and vegetable crops, so it is important to start fighting the disease in time.
Signs of rose infestation, disease and treatment
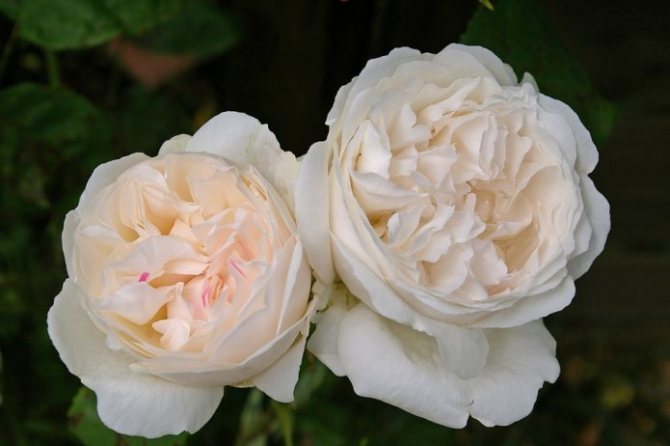
- The leaves of roses are covered with dark red spots, in the future the leaf plate is deformed, dries and disappears;
- The shoot is covered with loose pustules that look like pads. Fungal spores ripen in them.
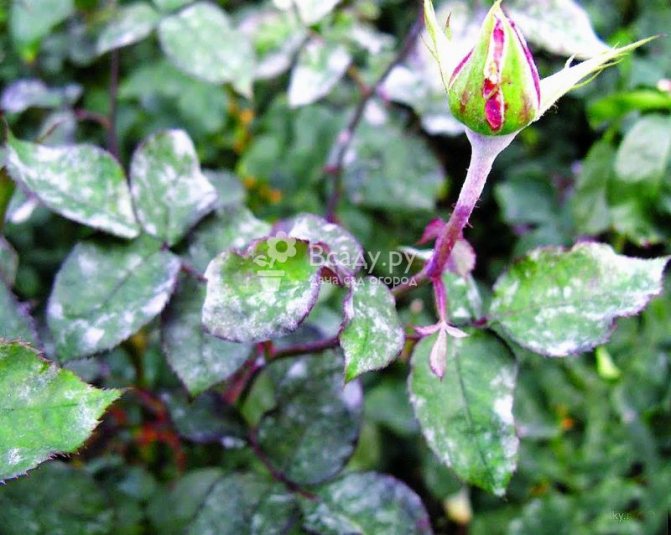


Signs of rose disease - powdery mildew on the shoot and leaves
How to avoid powdery mildew infections
- Thin bushes and prevent planting from thickening;
- Do not overfeed with nitrogenous fertilizers, observe the timing of their introduction (until mid-summer);
- During the formation of buds, treat with fungicides ("Topsin-M", "Baylon", "Fundazol");
- Every 2 weeks spray the rose bushes with a 10-day infusion of mullein;
- From mid-July, top dressing with potassium sulfate.
Preventive actions
In order to avoid or at least reduce the risk of black spot disease, you need to take certain preventive actions.
Optimal growing conditions
Before planting rose bushes in your area, you need to think not only about where they will look more beautiful, but also about where it will be safer for them:
- bushes should be planted in areas well warmed by the sun;
- the soil should be light, not retaining moisture;
- water should not accumulate under the bush;
- you should not plant roses too tightly to each other or to other plants;
- produce moderate watering.
External examination of the bush
It is important to inspect the bushes periodically. Indeed, a disease detected in time will make it possible to get rid of it faster and prevent it from spreading.
Removing weeds and loosening the soil
Timely removal of weeds will reduce the spread of pathogens and allow the sun's rays to better warm the soil. Loosening the soil under the bushes also helps to dry the soil and allows oxygen to get to the roots of the bushes.
Feeding rationing
It is imperative to feed rose bushes, while you should adhere to certain norms. Top dressing with potassium is carried out from spring to autumn. The first feeding is carried out at the end of May, the second at the beginning of June, the third at the end of July, then in the middle of August and at the beginning of September.
Top dressing with liquid agents is carried out only at the root. It is impossible to carry out processing in the evening and at night.
Treatment for diseases and insects
Such treatments must be carried out in a timely manner, since diseases and insect attacks significantly reduce the immunity of roses. And in the future, shrubs become more vulnerable to black spot and other fungi.
Timely prune
Affected shoots should be removed immediately after opening the bushes from wintering. Trim them to healthy tissue. Sections are treated with garden pitch.
Disinfect the instrument
After each cut off pink branch, the pruner is treated with alcohol, vodka or a strong solution of potassium permanganate. Other alcohol-based or chlorine-based solutions are also suitable.
In the fall, harvest dry foliage and dig up the soil
In autumn, dry foliage must be removed; it can become a shelter for pests and fungal spores. They also remove the topsoil and dig up the area around the bushes. Foliage and soil removed must not be sent to the compost heap to avoid contaminating it. Better burn them.
Cercosporosis, septoria, sphacelome
As already mentioned, they belong to the same group of diseases along with black spots. The difference between them is only in their manifestation:
- Cercosporosis manifests itself as bright rusty-brown spots, up to 6 mm in diameter. The causative agent of the disease is Cercospora rasiola;
- Septoriasis looks like whitish "freckles" with a black rim on the leaves of the flower. It appears as a result of damage to the plant by the fungus Septoria rosae;
- Schaceloma appears due to the activity of Sphacelomarosarum and is small specks of crimson or black color. Cercosporiasis Septoria Sphaceloma
Prevention of treatment also requires handling and careful maintenance.
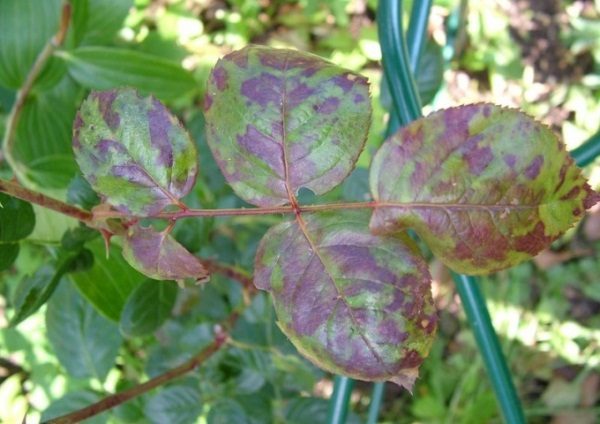
Symptoms
Usually, the disease begins to manifest itself in the second half of summer, it is also possible that several outbreaks of spotting occur in one season. The parasitic fungus attacks the soft, green part of the rose, namely the leaves and young shoots.
Experts identify the following signs of black spot:
- bush stops growing and develop;
- dark spots on the leaves can reach 15 centimeters in diameter;
- shape of spots resembles the sun;
- disease develops from the bottom up;
- gradually a few small spots combine into one;
- affected leaves turn yellowroll up and fall off;
- bushes thin out sharply, the colors are formed much less.
Specialist recommendations
Black spot on the leaves of a rose poses a serious threat to the rose hips growing nearby, so they should be transplanted at the farthest distance from the rose bushes. On the site there should be no varieties with low resistance to fungal infections.
One way or another, the main preventive measures to prevent the development of black spot are:
- Spring spraying.
- Removing foliage from shrubs before wintering.
It should be noted that no rose variety is 100% resistant to this disease. Therefore, absolutely all varieties of culture can get sick. Depending on the degree of resistance to pathology, roses are divided into two categories:
- susceptible (in particular climbing, tea varieties);
- weakly receptive.
Most modern hybrid varieties are highly immune to black spot.
Reference. Thanks to preventive measures, even vulnerable varieties can be significantly improved by increasing their resistance to fungus.
Well-chosen neighbors for roses will help to some extent protect the culture from diseases and parasites. The fact is that the latter often secrete substances on which the fungus is actively developing.
These plants include:
- lavender;
- oak sage;
- lemon catnip.
Rose black spot is caused by the fungal infection Marssonina rosae. The danger of pathology lies in the very rapid spread of spores, from which it is very difficult to protect healthy plants. You can maximally protect a delicate culture from the appearance of black spot with the help of competent and comprehensive flower care. In the event that the infection with the fungus has already occurred, it will be difficult to cure the plant: it will take a long time to fix the problem, using various means, alternating them and combining them in accordance with the recommendations specified in this article.
Black spot is one of the most common fungal diseases in roses, so it is important to know how to treat it. When affected by this infection, rose bushes quickly lose their attractiveness, as the disease progresses rapidly. This means that you also need to react immediately.
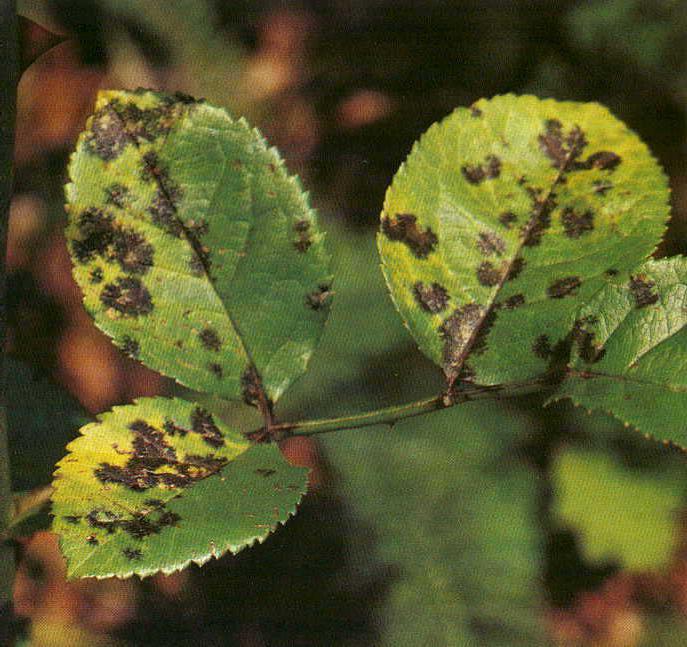
Reasons for the appearance of black spots
To carry out effective treatment of any disease, it is necessary to know the cause of its appearance, which must be eliminated as soon as possible.


Black spots on the leaves of a rose
There are several reasons why black spot appears on the leaves of a rose.:
- If as the landing site for the rose was chosen low or a very thickened area, the evaporation of moisture will be greatly slowed down, as a result of which the fungus will multiply and spread as quickly as possible;
- In warm and damp weather mushroom spores become active, and roses begin to become covered with spots;
- Incorrect feeding (lack or excess) can also cause the development of the disease;
- It is also very important take good care of flowers and stop any provoking factors in time.
What can a florist do to prevent rose infestation?
- Roses are whimsical flowers that require proper care. Do not forget about pruning them, this procedure makes them resistant to external factors.
- It is important to remove the dried parts of the rose bush in time and burn them. It is better to do this at a distance from the flower bed.
- It is important to constantly weed and loosen the root area.
- If the summer is too rainy, you can sprinkle the soil around the roses with ash.
- Experienced gardeners spray roses with special compositions, as well as infusion of horsetail, mullein.


- Do not forget about the treatment of garden tools with disinfectants.
- And, of course, the landing place for the queen of flowers! It shouldn't be shaded.
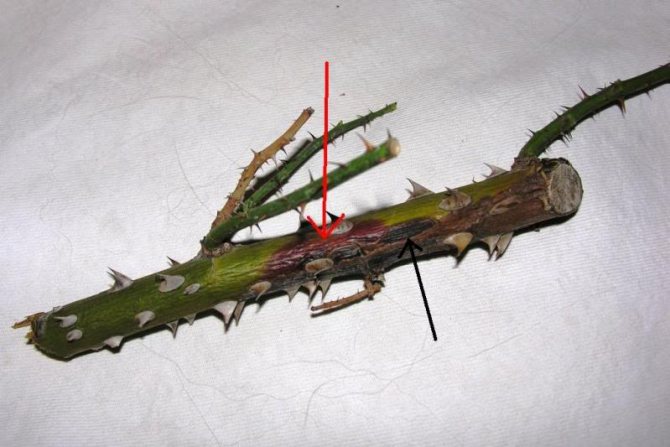
Stem cancer
Stem cancer
The reasons. Infection of a flower with cancer can occur as a result of rain, a contagious insect, poor soil and is often due to external damage from gardening tools. As a result, the bark begins to die off, and on the shoot the lesions become brown or yellow. The leaves dry up and curl, but stick to the stem.
Treatment. Infected shoots and stems should be cut immediately with disinfected garden shears. A solution of 3% zinc sulfate is usually used for processing. For the complete destruction of the disease, regular frequent treatment (2–4 years) is required.
Mosaic
Mosaic
The reasons. A virus that appears during the cultivation of roses. The disease begins to manifest itself clearly only in hot and dry weather. Represents yellow patterns on the leaves of the plant. The carrier of the infection is aphids or infected garden tools. The disease is so strong that it can easily be transmitted by contact of the roots.
Treatment. Rarely leads to the death of the plant. To avoid disease, it is necessary to carefully examine the seedlings. You can get rid of the infection only with the help of heat treatment in a specialized laboratory.
Gardeners reviews
nikke
Mulching helps a lot, I tried two options: hay around the roses, planting a ground cover in the "feet to the roses". The result - both methods helped out great, the state of emergency was not so rampant, it was much less pronounced.
viola2
I advise planting roses in full sun and not crowded: whatever chemistry I've tried, nothing really helped. I tried ash and green soap too - zero result. Rather, after processing, the speed of the emergency seems to slow down, and after the first rain, everything starts at twice the speed.








![Black spot on roses: how to treat? - basic methods [2019]](https://bgn.imadeself.com/wp-content/uploads/chernaya-pyatnistost-na-rozah-chem-lechit-osnovnye-metody-20192.jpg)