Growing grapes is a noble occupation, as is the grape plant itself. People have been growing these berries since ancient times. These berries have become so popular due to their beneficial properties and excellent taste. Farming has not died out in our time.
In the old days, growing grapes took a lot of time and effort, and not everyone could afford to grow such a noble plant. But today grapes can be found in many gardeners in the garden, with the development of technology, many varieties have appeared that are able to survive even in poor conditions.
What is grape plant formation

The life span of a grape bush is conventionally divided into three stages:
- growth, a set of vegetative power (lasts 5-6 years);
- active fruiting (25-50 years);
- weakening of growth, decrease in reproductive activity.
Fruiting and aging depend not only on the climatic conditions of the area, nutrition, care, but also the pruning of bushes. On liana-like plants, shoots appear in the most unexpected places, and to increase the number of bunches, it is required to form a bush.
Formation is the pruning of grape shoots according to certain schemes, which takes into account the variety, the characteristics of the bush, and other factors.
- stepchildren of no particular importance;
- diseased and deformed shoots;
- extra kidneys.
Thanks to the procedure, there is a redistribution of food, providing the main fruiting vines with the necessary elements.
Why do grape shaping
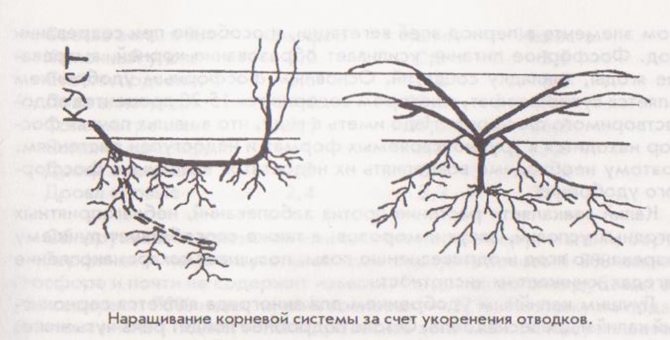
Forming grapes - artificial shaping of the bush. The shape of the bush must first of all ensure a high and sustainable grape harvest. It should also facilitate the care of the vineyard, promote the most rational use of land, light and air space, allow the systematic rejuvenation of the bushes by replacing dying sleeves or boles with new ones.
Formation of grape bushes created by trimming, garter, debris and installation of supports. With the help of a garter, they enhance the growth of the weak parts of the bush and retard the growth of fattening shoots. Correct placement of perennial and annual vines on a support can cause shoot growth in the places to be made.
The centuries-old grape culture has created a large number of different types of shrub shapes. In every growing area grapes certain systems have developed formations bushes that best meet the local soil and climatic conditions and biological characteristics of the varieties cultivated here. Local forms and shrub management systems should be especially considered when selecting formations for a home vineyard.
The choice of formations is more difficult in new areas of viticulture, where there is no experience and local forms of shrubs. Here you should give the bushes a shape that would help to eliminate or reduce the influence of unfavorable climatic factors. In areas where the grapes lack warmth and must be reliably covered for the winter, it is necessary not only to plant the bushes on a site well heated by the sun, but also to place the crown closer to the soil surface. When the crown is close to the soil, the reflected heat is used more fully and it is easier to cover the grape bushes for the winter.
The need to form vineyard bushes


Pruning bushes is a time consuming but important procedure for increasing crop yields. In addition, thanks to the formation:
- planting care is simplified;
- the risk of infections is reduced;
- the taste of berries improves.
Strong, sturdy bushes are able to withstand unfavorable loads, avoid freezing even in harsh climatic zones. Correctly pruned bushes produce more berries, and there is no difficulty in picking bunches.
Pruning grapes and forming the main fruit link
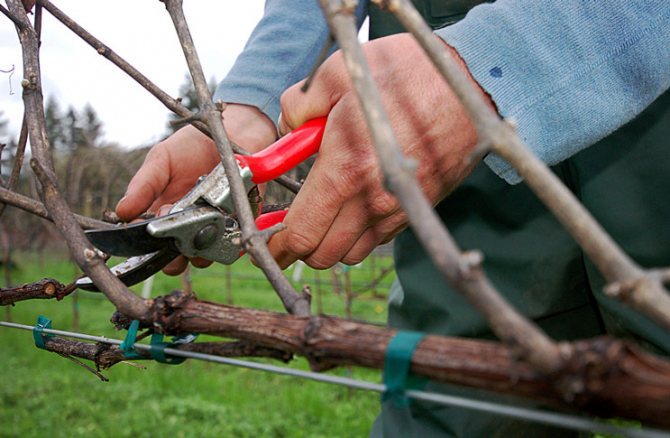
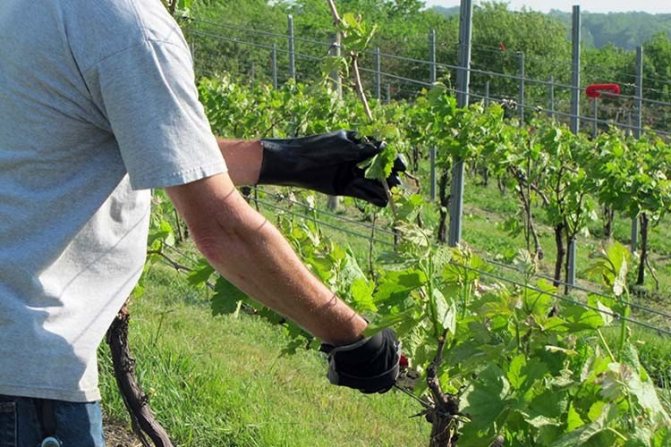
Next, it is worth considering the formation process itself. As you know, grapes have a different, but at the same time rather loose and porous wood, for this reason it is important to take the sharpest secateurs. Otherwise, all wood will be crushed, wounds will appear on the plant and a serious loss of sap can be noted.
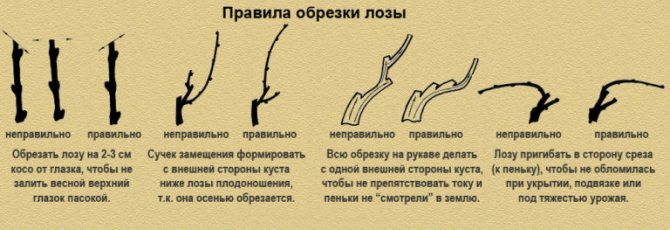
The sleeves must be cut not immediately above the kidney, but slightly higher, that is, the internode section must be cut. The kidney is very loose, and in the pores, frost can very quickly reach the kidney. Perennial wood is cut, like all other trees, that is, without any stumps.
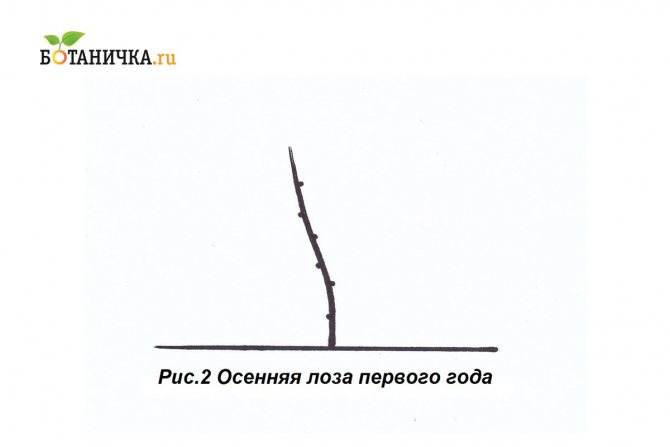
In the summer, among the main operations with grapes, the process of forming a fruit sleeve can be distinguished. Each of them should consist of two vines, one of which will be long, the other short. From the latter, green shoots will grow, which in a year will become vines. As for the long, green shoots will grow from it, which will bear fruit already in the year when pruning is carried out. So, the formation of grapes in the very first year of growing the fruit sleeve:
- Among the ripe fruit shoots, that is, vines, it is worth choosing the strongest ones, which are larger than a pencil.
- Then all this is broken down into pairs, and everything should grow as close as possible.
- One will be cut very short, you will need to leave literally 2 or 3 buds. The other length is equal to 8-9 buds.
- In the autumn of the second year of planting, a very long vine is pruned simultaneously with all the shoots.
- Already in fully grown vines, at the shortest one should choose the two strongest ones, and all the rest are removed. Formation occurs in about the same way - long fruit, short vegetative or substitute.
This operation must be repeated every year. This will guarantee a bountiful and more importantly stable harvest. At the same time, the bush will not overgrow, since a certain balance will be maintained every year. You don't have to do anything complicated with a fruit sleeve, even a novice gardener can handle it, since the type of formation - a sleeve, was disassembled step by step.
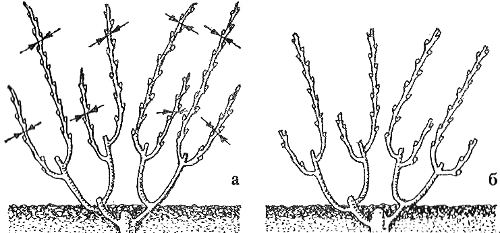

Formation of fruit links: a - on each arm, the lower vine is cut short (replacement knot), the upper vine is long (fruit arrow); b - after trimming
In the process of forming a fan, it is necessary to leave already two sleeves directed in different directions. in general, their number is determined based on the free area. Typically, one sleeve requires approximately 0.7 m per installed trellis. So, at a distance of 3.5 meters, you can even afford a fan of five sleeves. To form a shtambcordon, you will need to perform the following sequence of actions:
- One of the largest and most powerful branches is selected, the length of which is a meter or one and a half. On it, you need to leave about 5 pairs of vines, which will then serve as a fruit sleeve.
- Anything that grows below is clipped.
- A fruit sleeve is formed at the top.
- Certain substitutes for the stems should be left a little larger, but they must necessarily be small in length.
- If a stem is being conducted, then it is tied to a powerful support and until the thickest trunk is formed, which is able to withstand the load of crops and foliage.
One cordon is tied strictly parallel to the ground, at a distance of about 10-20 cm, which will provide effective ventilation of the lower part of the timber. This, in turn, will prevent the processes of decay, the appearance of mold, which is very important for winter.
Basic conditions for choosing a formation scheme


Shoots are cut according to certain schemes. Several options for removing branches of grape bushes have been developed and put into practice. The choice is determined by:
- the climate of the territory where the grapes are grown;
- type of soil;
- the speed of development of shoots;
- the main characteristics of a particular variety;
- the need for shelter for the winter.
They take into account the parameters of the accumulation of wood mass in bushes, soil fertility. On poor soils, where there are problems with watering, bushes with a small number of arms are grown. For fertile soils with abundant watering, any form is suitable, including those with numerous arms.
In cold regions, grapes require shelter in winter, therefore, the most suitable schemes for bending shoots are chosen. In central Russia, where winters with little snow and strong winds often blow, the bushes are completely covered. In the northern regions (Ural, Siberia, North-West), winters are colder and longer, so they practice their own pruning methods.
How to prune grapes in the spring
Most gardeners prefer to prune old grapes in the spring, for example, immediately after removing the winter shelter and attaching the vines to an arched structure or support.


Note: Some growers prefer to form the shrubs in the fall, when the buds begin to prepare for winter and the development of the culture slows down. In part, this makes sense, but in the spring you still have to pay attention to the bushes, at least after doing sanitary cleaning.
Spring pruning of covering and non-covering grapes has its advantages:
- Thinning the crown will help increase crop yields in the current season by 60-80%.
- Spring pruning helps to increase the frost resistance of the bushes, which is especially important when cultivating grapes in temperate and cold climates.
- By thinning the crown, pollination of the crop improves, the quality of the crop increases, and the plant itself is much less likely to be affected by fungal diseases and pests.
- A decrease in the number of shoots helps to correct the distribution of nutrients, since they will be spent not on the growth of green mass, but on the formation of fruits.
We advise you to read these articles:
When to plant strawberries in spring in Siberia
Planting eggplant seedlings in the 2020 lunar calendar
Planting dates for leeks in 2020 according to the lunar calendar
In addition, compliance with the optimal timing of spring pruning allows you to form a crown of the required shape and size, which is especially important for those who plan to grow grapes in small areas.

The description of the procedure would be incomplete without information on its shortcomings. First of all, spring pruning often causes stress in the bushes, and their development slows down for a while. Given this feature, the procedure is best carried out on healthy adult bushes. In addition, if pruning was carried out after the start of sap flow, there is a high probability of dehydration of the bush.
To reduce the possible harm from the procedure, you need to know how to properly prune grapes in the spring:
- The slices must be placed at right angles to speed up the healing process.
- Regardless of the purpose of pruning, it is imperative to remove all frozen, damaged shoots or branches with signs of disease.
- Pruning is considered correct, after which 7-12 buds remain on the bush.
- If you are pruning an old shrub with annual shoots, the latter should be cut too carefully so that the hemp is no more than 0.5 cm high.
- All shoots should be carefully examined.On the bushes, it is advisable to leave only branches with a diameter of about 6 cm. Thin or fattening shoots must be cut out.
Naturally, all manipulations should be carried out with a sharp and disinfected garden tool. So the cuts will turn out to be even and without burrs, and the resulting wound will quickly heal.
Features of the growth of culture


When choosing a scheme, the general characteristics of the culture are taken into account:
- The grapes lack fruit branches. Each branch can yield a crop under certain conditions, and the result depends on pruning.
- There are shoots of the first year (summer), biennial (usually clusters of the main crop are formed on it), perennial.
- The vine can be of the standard and non-standard type. The first is widespread in the southern regions, characterized by raised arms (fruit-bearing vines). The second type - the bush grows with fan-type sleeves; stakes (bowl) or trellises are used for supports.
- The stem is a perennial part, a shoulder.
- Sleeve is a perennial shoot located on the shoulder.
- Arrows or fruiting vines are biennial branches.
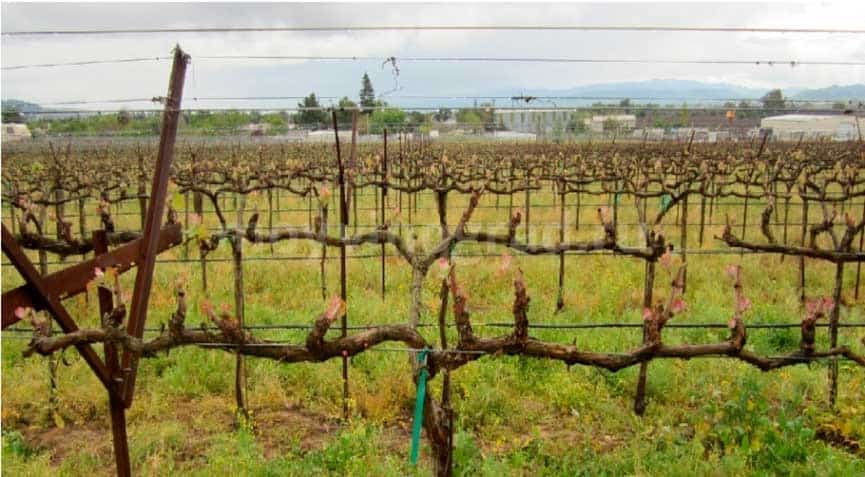
The location of the shoulders or cordons is different, depending on the climate of the region. One thing in common - they are located horizontally to the surface of the earth, while the height of the sleeve and shoulder is high, medium, low.
Formation types
Covering grapes for the winter or not is perhaps the main question that a future grower should ask himself. The method of forming a bush depends on the answer to it. In the conditions of a frosty winter, when the vines can die not so much from snow as from ice, a properly designed grape bush will be easier to cover for the winter.
The full formation of the vineyard usually takes about 3-4 years.
Forming can be:
- fan;
- standard.
In the standard form, the grape bush becomes like a tree. From one trunk, the trunk, secondary vines depart. This grape formation scheme is suitable for southern regions with warm winters.
Forming on a trellis
Formation of grapes in a sleeve (fan) way is used if it is necessary to tilt it to the ground during winter insulation. This method of formation involves the installation of trellises on the site. There are three types of tapestries:
- vertical;
- horizontal;
- combined.
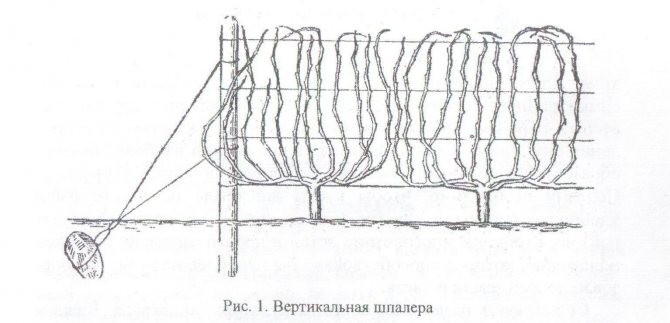

The vertical trellis provides for the formation of the vine upward along the wires stretched in several rows between the supports. The grapes are planted in rows. Shoots tied to a wire form rows of vertical trellises. A slight slope of 15-20 degrees can be provided for hanging bunches and better lighting.
A horizontal trellis is formed by constructing a horizontal grid from a wire, located at a height of 2.5 meters or more. Branches and shoots of grapes are placed on it. As the green shoots grow, they can be tied to the trellis, directing them in the right direction.
Such a trellis can be built over a parking lot, a summer cottage, a walkway.
How to transplant the phalaenopsis orchid at home
On the combined trellis, the sleeves are located both vertically and horizontally. This type is very effective. It turns out a kind of tunnels with walls and canopies. Shoots and leaves, striving for the sun, create a dense frame, within which clusters of grapes hang.
For aspiring wine growers, the formation process can seem time consuming. But having studied the correct molding scheme, many mistakes and difficulties can be avoided.
Basic schemes for the formation of a bush


The fruit plant is cut in certain ways, providing ventilation, a sufficient level of lighting, and the stability of the bush.
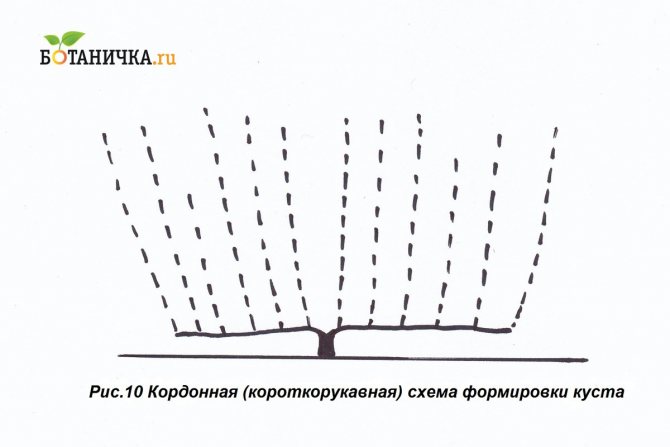
Sleeve scheme
Sleeve pruning plants have a short lifespan. But for plots of small area, this option will be convenient and most acceptable.
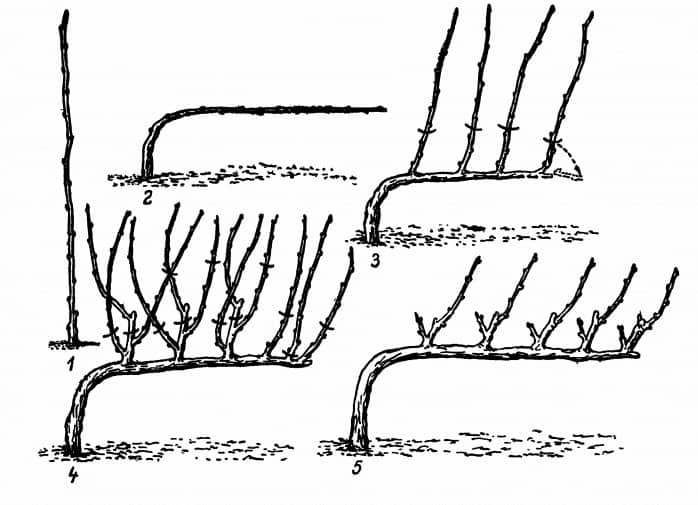
Suitable for regions with harsh climates, cold winters, strong winds. Parts of the plant are cut off annually, otherwise there is a nutritional deficiency and, as a result, the death of plantings. In the first season, all branches are removed, leaving only the strongest and most densely growing (long and short). The number of buds on the long one is 7-9, on the short one - 2-3 pieces. In the fall of the second year, the long branch is cut off. In the short, only strong arrows are left.
Fan shape
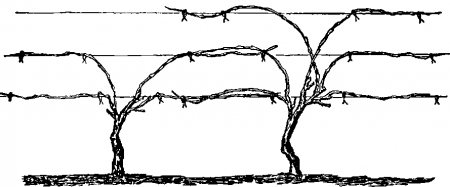

The scheme is similar to the sleeve one, but the gardener will have to grow at least 5-6 sleeves. The name was given due to the similarity of the resulting form with a fan, since there are more branches on the plant. Location - on both sides of the root.
In two seasons, it is required to grow two strong, powerful vines. The garter is vertical. On the support, the arrangement is fanned out, a couple of processes are left for lengthening. Large, medium and small vines are distinguished along the length.
The fan pattern is popular with winegrowers, as it is suitable for many varieties of culture. Faith is used when growing plants on trellises, stakes.
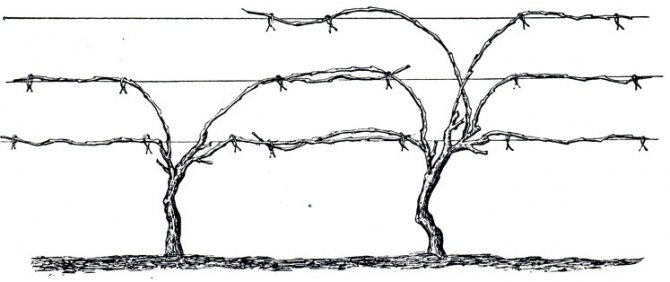
Cordon form


The time to create the shape of the bush is about four years. To begin with, the growing branches are thinned out, leaving a distance of 30 to 42 cm between them. Leave long sleeves, use all the vines.
It is necessary to grow a strong powerful stem in the first two years, then cut it off at a certain distance, tie it up arbitrarily to a support (trellis, trellis).
In the third year, they begin to grow arrows on the sleeve, thinning them out, removing weak and sick specimens. In the 4th year, they begin to work with the fruit link.
Using the Guyot scheme
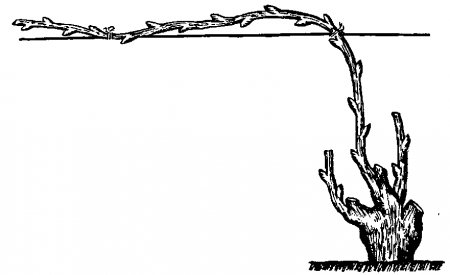

A relatively simple scheme for pruning a vineyard using the Guyot method. Using it, juicy, large groves are obtained, while the overall yield increases.
Forming options - with one or two arms. In the first case, they form a single small shoot with a well-developed fruit bud. When leaving two shoulders, two sleeves with stepsons grow.
Guyot with two shoulders is suitable for growing vineyards in poor soils, when the bushes are weak. Planting with one shoulder is practiced in dense patterns, where the distance between plants is 1-1.2 meters.
Moser formation


The scheme was named after the famous Austrian winegrower Lorenz Moser. Basically, the cultivation method is used in industrial viticulture, noting the intensity of the technology. In amateur gardening, the method has been modified to suit specific climatic conditions.
The essence of Moser's formation: the use of boles, height 1.2-1.3 meters. The system of green vines management has been changed, instead of a vertical arrangement, a free overhang is used. This gives a moderate growth of the vine, simplifies the care of the crop. The binding is done only for some branches to avoid twisting branches and falling bunches.
Bowl-type formation
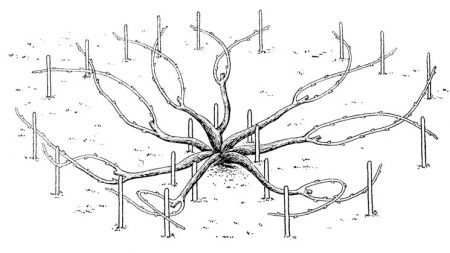

The scheme is used in the vineyards of the southern regions. The location of the sleeves, as well as the number, varies. The number depends on the vigor of the plant, the type and fertility of the soil. Most often, 3-6 pieces are left.
It is formed within 5-6 years. The scheme for the main stages is similar to fans, but the branches of all plants are left for growth.
Formation of VNIFS-1


The name of the scheme was received in honor of the research anti-phyloxera station, the employees of which proposed their own version of pruning the vine.
Short arrows are left on the sleeves that do not carry replacement knots. The distance between plants when planting is 2-2.5 meters. Intermediate anchors are made, on which the trellis wire is pulled. In the second season, all branches over a meter long are tied to supports. Weak shoots are left until the next season. Cut the vine for 3-4 eyes, after which they begin to create fruit links.
Stampless small fan


In the group of covering schemes, a promising method developed by the gardener D. Tokarev is popular. It is used in small areas when it is important to save space.
Plants are planted at a distance of 0.8-1 meters, leaving a distance of up to two meters between rows. Shelter gives protection, the grapes quickly renew.
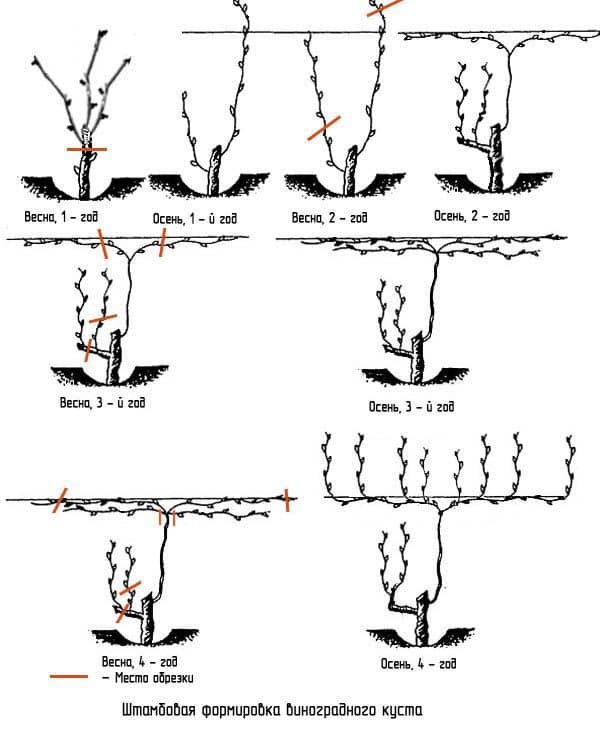
Formation of the trunk


The method is relevant for the southern territories, where the risk of freezing of the vineyard is excluded. It will take 5-6 years to fully form, then it is imperative to maintain the created shape of the plant.
The standard version allows you to solve many problems in plant cultivation. For example, with this method, grape plantings are less likely to be affected by infections and pests.
Forming work in the first year
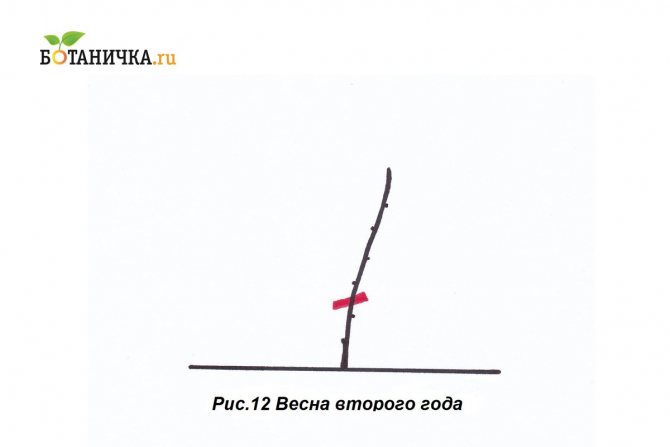
A single strong shoot is grown, defining strong branches on it. One branch is left to grow, the rest are cut off. For the winter, the grapes are wrapped, otherwise the whip will freeze.
Forming for the second year
The strong pillar of last season looks like a bole. A control pruning is carried out, leaving a branch of the desired size and complementing it with a distance of 2-4 eyes.
After the minting, two stepsons remain, which grow by about 30 cm over the summer.
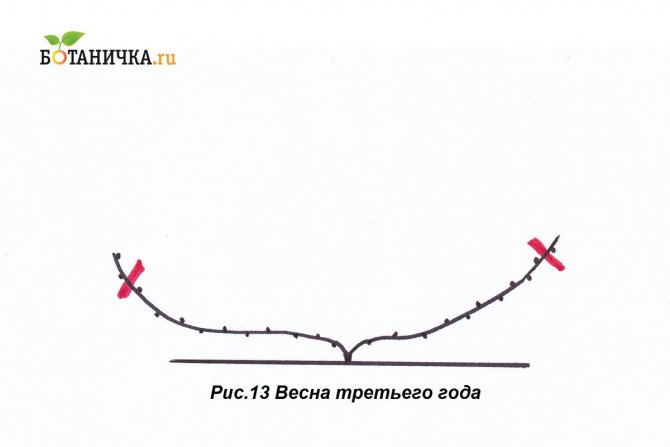
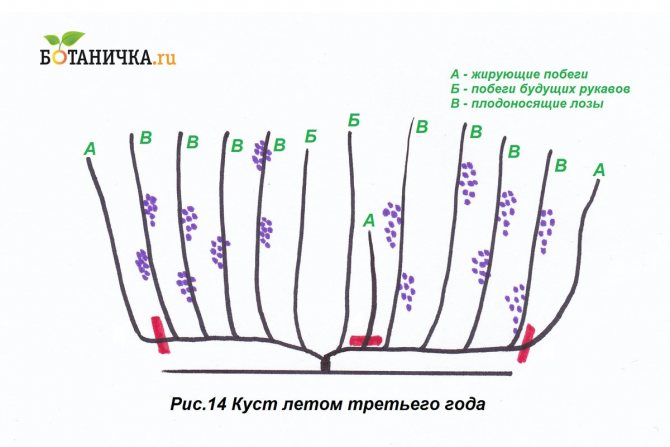
Forming for the third year
The stepsons formed on the second level are cut off. Only the upper buds are left, then the arrows that have grown from them are thinned out and tied up.
Forming for the fourth year
The shoot closest to the ground is cut off, leaving no more than three eyes. This will be the replacement stem. A fruit arrow is formed from the growing vine above, cut into 6-10 eyes.
Semi-fan shaping
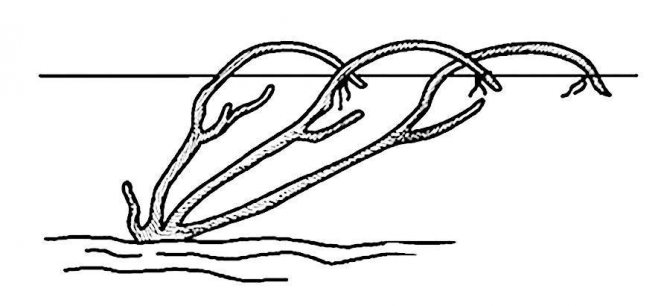

Semi-fan formation of the bush deserves to be used in areas of sheltering viticulture for vigorous grape varieties. It is a one-sided fan with two or three or more sleeves directed to one side of the row.
The creation of a semi-fan formation is in many ways similar to the creation of a regular fan formation. In the first 2 years after planting, two or three powerful shoots are grown on each bush, located at the very surface of the soil. When pruning at the beginning of the third year of the growing season, the shoots are shortened, leaving the entire length of the normally matured part (90-100 cm). Long-cut shoots are tied obliquely to one side with an L-shaped bend, which is fixed over the lowest wire of the trellis. All eyes from the base of the vine, with the exception of two or three upper ones, are removed. In this case, the lower peephole on the future sleeve should occupy an external position in relation to the crown of the bush.
In the future, as in the removal of the usual fan formation, pruning is carried out in order to create one or two fruit links on the sleeves. With good care, by the end of the third year, the bush should have at least two or three sleeves with fruit links.
Accelerated formation of vines


The schemes are used for the rapid entry of young vineyards into the fruiting stage. Views:
- method N.I. Sklyar;
- stepchildren's scheme (by F. Bashirov);
- method of scientific research institute "Magarach" (bending of a vine).
Green formation
Recommended on fertile soils and subject to agricultural regulations. In young plants, pinch the tops, then leave a couple of appeared stepsons. In the second year, replacement knots, fruit arrows, are created from these stepsons. A full harvest is obtained for 4 years.
Bending the vine


Strong shoots that have grown in the first year are cut off in the spring of the second year by 2-3 eyes. During the summer, stepchildren will appear from them.
In the third year, stepchildren are pruned in the spring:
- a couple of pieces for 12-15 eyes;
- the rest are cut into 2 eyes.
Long ones are tied to a support with the creation of a bend of the vine. The next year, those parts of the stems that yielded a crop are cut off. Shoots from a part of a curved vine are used to create a fruit link.
Forming on the trunk
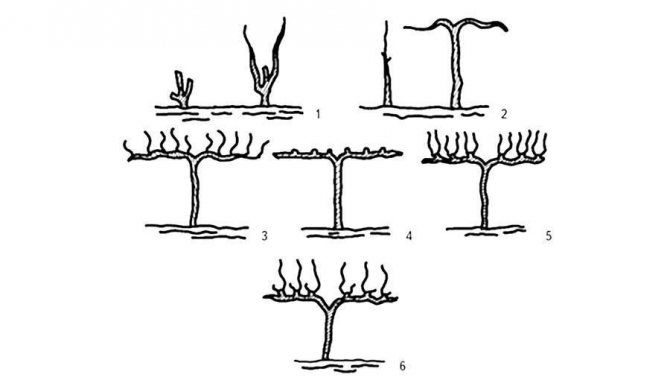

When creating a standard bush formation during the first and second years after planting, the seedling is cut into a twig with two eyes.When a fragment is broken in the second year, the two strongest shoots are left and, as they grow, they are tied vertically to the stake. When the shoots reach the first row of the wire (the height of the future stem), they are pinched 8-10 cm below the first wire. Of the developing stepchildren, only the top two are left, and the rest are broken off in time. Well-developed stepchildren are laid horizontally on the lower trellis wire. In the third year, weak shoots are removed. Two stepsons on a stronger shoot are cut into six to seven eyes to form shoulders. Repeated removal of the resulting shoots and stepchildren is carried out on the trunk. In the fourth year, if necessary, the shoulders are lengthened using two extreme shoots; horns and fruit links are formed on the remaining shoots of the shoulders.
With a strong development on a young bush of two standard vines, two stems are formed with one shoulder on each. Two-stem forms of bushes enter full fruiting earlier than single-stem forms.
Forming methods with trellises


In the south, vineyards are often grown on trellises. Equipped with two-plane structures, due to which the yield increases by 20-40%.
It is required to follow the rules for planting plants, placing the seedling in the hole so that the lower bud is 10-12 cm above the ground surface. The popular scheme is fan-shaped with sleeves, without a standard.
How to choose a shaping for a beginner
A novice winegrower should immediately decide on the method of forming, as well as covering the culture. If frost-resistant varieties grow in the vineyard, then they do not need to be covered. When planting a plant, you need to take into account the distance between the bushes themselves and between the rows. If these parameters are large, then the vineyard will be powerful and yield a large harvest.
Important! If you do not form a bush, then shoots will grow on it, and there will be no strength left for the formation of fruits.
If a novice wine grower lives in the northern regions of Russia, then he needs to use only one of the proven methods by experienced wine growers:
- horizontal cordon;
- fan;
- sleeveless head-type form.
Formation - horizontal cordon
If the territory allows you to make a distance between the bushes of three meters, then you can use a cordon trimming or a six-arm fancordon. At a distance of two to two and a half meters, a fan-shaped four-arm grape formation is used. When the bushes are planted at a distance of one and a half meters from each other, then only a two-arm fan or a stemless, sleeveless capitate method is suitable here.
Formation on gazebos


Schemes:
- multi-sleeved with the formation of a trunk;
- multi-sleeves without a stem;
- vertical cordon.
Used only for varieties that tolerate low temperatures well. The grapes are planted near arches, awnings, arbors.
The length of the main stem is at least three meters. All lateral shoots are cut to 6 eyes. In autumn, the main stem is cut by 2/3, the side ones - up to two buds.
When to do shaping
Formative pruning is carried out in the spring before the juices begin to move, around March. If you prune at a time when the buds are already swollen or begin to bloom, and the vine begins to ooze with juice, the bush, having received stress, will most likely dry out.
Did you know? According to ancient Greek legend, people learned about the benefits of pruning for the vine thanks to the donkey. The animal nibbled on some of the shoots, after which the vine began to bear fruit better.
Grape varieties requiring shelter for the winter are also pruned in the fall. This is necessary to make it easier to remove the vine from the trellis and cover, protecting the fruit shoots from freezing.
Terms and rules


Pruning plants throughout the life of the vineyard. In this case, the first years form bushes, and then maintain a given shape. Of all the agricultural techniques, this one is considered the most difficult.
- Spring. Form a bush to increase productivity, ease of planting maintenance.
- Fall.Plants are prepared for wintering, sheltering in the cold period. Also, by removing unnecessary, diseased shoots, they ensure plant health.
Cold snap damage
Spring frosts, often coinciding with the period of budding, can destroy not only young shoots and buds, but also annual vines. If this happens, prune shortly from last year's branches to stimulate the growth of new shoots from the dormant buds.
If the greens and inflorescences have suffered, then in order to wake up the dormant buds, shortening the annual shoots will be enough. This will partially restore the crop. If only the tops of the branches are damaged, as well as a small number of leaves and inflorescences, it is not necessary to carry out special pruning.
Testimonials
I use my own method on my site, I call it cordon. I remove the thin shoot, and tie the strong one to the trellis. On it I will leave shoots after about 28-30 cm. Then they will be cordon horns. All other stems are removed.
During the season we get a cordon with several horns on it. The length is about two meters. We leave a strong vine for fruiting in the current season. Usually I make 5-6 shoots, one bunch grows on each. There will be only one cordon left for next year.
Ivan, Voronezh
I am using the fanned way. I leave the distance between the bushes no more than 1.2 meters. In the spring, when tying, we do so that the first eyes on the fruiting vine are higher. They will receive good nutrition, and then in the fall it is easy to choose a vine for fruiting from them. Remove all others. Then there is no need to grow a replacement knot.
Long pruning of ripe vines
In the first 2 years after planting, two to four well-ripened shoots are grown on the bush, extending from the underground trunk at the very surface, and even better - 10-12 cm below the soil surface. When pruning, highly developed shoots leave 8-15 eyes, and on underdeveloped ones - 2-3 lower eyes. Long-cut shoots are tied obliquely to the bottom wire of the trellis with the formation of a well-defined bending angle. When the buds swell in the obliquely tied parts of the vines (future sleeves), the eyes break out, with the exception of two or three located below the bend. The eyes are left on the horizontally tied parts of the vines.
At the next pruning, the fruiting horizontal parts of the vines are cut off. Shoots that develop below the bend are used to form fruit links, and those grown on short-cut vines at the base of the bush are used to form new fan arms.
When removing boles, they act in a similar way with the only difference that long-cut shoots intended to create a bole are tied not obliquely, but vertically to the trellis wire and let them grow freely. In the third year, two shoots are bent in opposite directions on the first wire and cut into six to seven eyes after bending. When a fragment is broken on the horizontal part of the vine, green shoots are removed through one, and on the vertical - all developing shoots. In the fourth year, the shoots left on the shoulders are cut into knots with two eyes. In the future, horns with fruit links are created.
Tags:
Why do you need the formation of a grape bush
During the process, the bush is freed from old, sick or weak and sterile lashes. This gives the vine the opportunity to develop and grow strong promising shoots, not to waste nutrients in vain.
During the procedure, the bush is significantly thinned out, which allows the sun's rays to warm up and illuminate all parts of the plant, and especially the pouring bunches of fruit. A properly formed bush is well ventilated, and this is one of the measures for the prevention of fungal diseases that develop in a humid environment. A correctly distributed load on the vine is a guarantee of excellent fruiting, large berries with excellent taste.


Are the bushes frozen during the winter?
First, check the condition of your kidneys. Make incisions on the eyes, moving from the base of the branch to the top: if the buds are green, then they are healthy. But black or dark brown color indicates damage. Count the damaged kidneys and calculate what percentage of the total volume of the eyes they make up.
If less than 80% of the buds die, leave more buds on the fruit links than with normal shaping. Also, the harvest can be obtained from additional shoots on the fruiting branches that you left during the autumn pruning.
If annual shoots were frostbitten or more than 80% of the buds died on the bush, a two-stage sanitary pruning will help. Before buds bloom, remove frozen shoots and damaged sleeves. When greenery appears, complete sanitary pruning by removing unnecessary growth.
If 100% of the kidneys are damaged, check the condition of the stepsons - they are more frost-resistant and have a better chance of surviving the winter. If the buds of the stepchildren have died, try to form fruit links from shoots (shoots developing from the underground part of the stem) or tops (fattening shoots of a grape bush growing from buds on perennial branches).
Look at how the core is colored on the cut: its bright green color indicates a good condition of the shoot, slightly brown indicates minor damage. But shoots with a dark brown core must be removed.
When the entire above-ground part of the bush dies, a cut is made "for a black head." To do this, dig in the bush to a depth of 25-30 cm and cut down the entire above-ground part above the healthy node. Then cover the stump with earth (5 cm layer), and soon young shoots will begin to grow from the trunk. Leave the strongest of them, and remove excess growth. This will give you a healthy new vine.
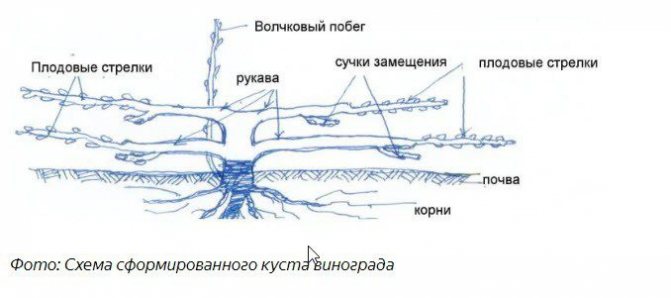
Formation scheme
Schemes can be different; growers choose the more suitable one, depending on the variety and region of cultivation.
Main types:
- with and without sleeves;
- with different lengths of lashes;
- capitate type on a stem or without a stem.
Sleeveless
The sleeveless or capitate scheme is good because the vine in this case takes up a minimum of space. It is easy to remove from the support and cover; you can leave less distance between bushes, saving space.
Technology:
- Install a trellis with one plane and four rows of wire, the lowest one at a distance of 25 cm from the ground.
- The backbone is a perennial bole, shortened almost to the surface of the soil, on which 3-4 eyes are left.
- Growing lashes are shortened by the same 3-4 eyes.
- When the main shoots of the vine get stronger, they leave about 3 of the most promising for fruiting. They are shortened, leaving up to 18 buds.
- After fruiting, for the winter, these shoots are cut with the segment on which they grew.
- The next year, green lashes are sent up the trellis.
By fan
According to experienced winegrowers, the fan version is the ideal method for dummies. The process does not require complex calculations and special skills.
Multi-sleeve trimming
For fast-growing grape varieties, a fan of 6-8 arms is formed, for weak-growing ones - 3-4 arms.
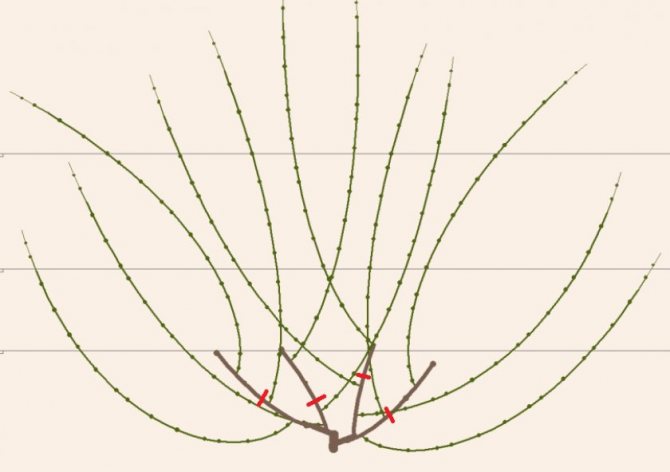

Technology:
- A grown bush with 4-5 shoots of at least 1 m in length is shortened to the desired length.
- The lashes are tied vertically on the trellis. The lower wire on the trellis is at a distance of 45-50 cm from the ground surface.
- During the season, annual lashes are shortened, leaving 2-3 untouched for fruiting.
- The objective of the method is to build up 2 shoots with fruit links (4-5 buds) on each of the left sleeves.
- Subsequently, the upper shoots are cut into 4-5 eyes, and the lower ones by 2-3.
- The length of the sleeves depends on the quality of fruiting and varietal characteristics. It is advisable for fast-growing ones to leave long whips; bushes that yield large yields - about half a meter.
One-sided long-arm fan
The method requires a sufficient amount of moisture.
For a garter on a trellis, the wire is pulled in a certain step:
- 1st row - distance from the ground surface 15 cm;
- 2nd row - distance from the lower ligature 70 cm;
- 3rd row - half a meter from the 2nd ligature;
- 4th row - at a distance of 40 cm from the previous row.
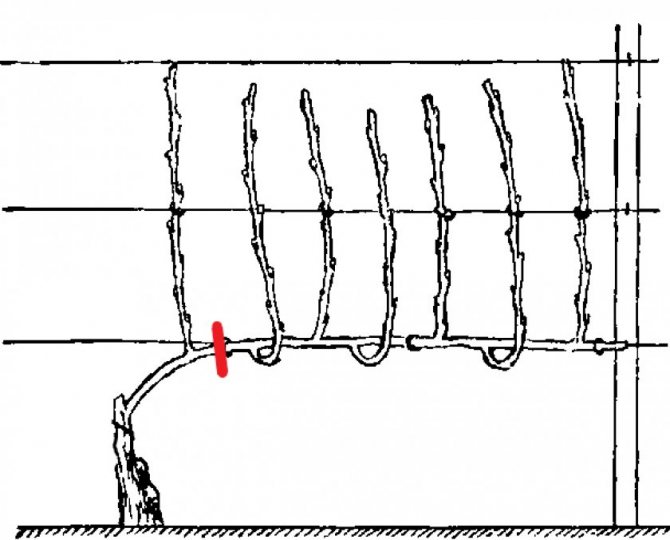

On the vine, no more than 3 sleeves are left up to one and a half meters long. With a garter, they are oriented so that they become one-sided. When growing, you need to achieve several lashes on each sleeve. The distance between bushes when choosing this pruning method should be 1–1.2 meters. In the fall, all whips that have finished fruiting are cut off. Leave one, with the thickest base, to form fruit arrows for the next year.
Types of grape formations
In amateur viticulture, all kinds of forms of bushes are used - from the smallest to the largest, which is due to the variety of conditions and methods of growing grapes (near walls, fences, on open flat areas and slopes, etc.). The main differences in the shape of the bushes are associated with the construction of the aerial part of the crown skeleton and the distribution of annual growth.
The most common formations of grape bushes are: - covering - fan-shaped with one or more perennial branches. They can be short- and long-sleeved, one- and two-sided, one- and multi-tiered; - semi-covering - combined forms with a covered lower tier; - non-covering - standard, cordon, arbor and decorative. They are used mainly in areas of uncovered grape culture and in the cultivation of frost-resistant varieties.
Each of these types of formations has its own characteristics and differs in the removal technique. The formation of bushes begins from the first year of planting and, depending on the created form and cultivation conditions, continue for three to six years.
When choosing a formation, one should take into account the planting site and the method of placing the bushes. At the same time, the wall culture of grapes, formations for covering balconies, verandas, courtyard grounds, the formation of alleys and other places are of particular importance.
Additional tips for beginners
Novice winegrowers are unlikely to know some of the subtleties that can play an important role.


A few helpful tips:
- The first pruning is done in the first year of planting.
- All instruments must be disinfected.
- If a mistake was made in the timing and the vine began to ooze, you need to treat the cut with the "Artificial bark" preparation.
- After pruning, immediately update the vine supports so as not to waste time on this when active crop care begins.
- Fruit arrows are recommended to be tied horizontally.
- The breakdown of unpromising shoots begins in the head of the bush.
- The four-arm cropping pattern can be done in steps: 2 sleeves per year.
- On a fan of 2 sleeves, it is easier to distribute the load in bunches, which is recommended for beginners.
So, the advantages of the fan-shaped method of forming grapes are obvious: the bush is not thickened, it is open to lighting, it bears better and more fruit. With very little effort, you can significantly improve your expected yield.
Formation by years
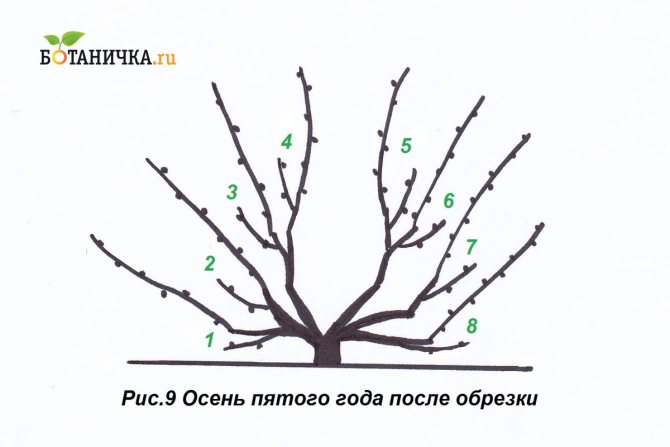
A young grape bush enters the fruiting period in the third year after planting. In order to get a good harvest, you need to carry out your own agrotechnical procedures every year.
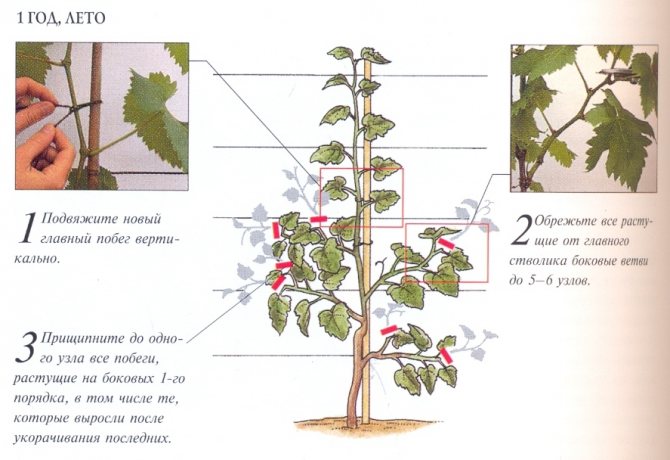
First
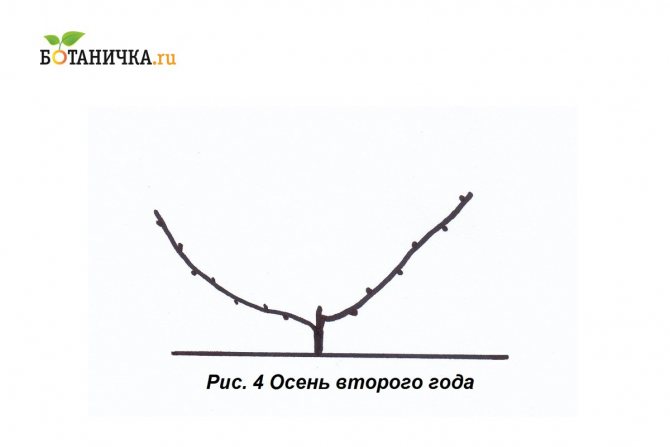
In the first year, only one strong and strong vine needs to be grown. This will be the shoulder from which the sleeves will grow. The shoulder is the basis of the entire fruiting part of the vine. It is recommended to grow the second shoulder only the next year, since a young bush may not have enough root strength to feed two strong vines at the same time. This article will tell you about the characteristics and description of the Codrianka grape variety.

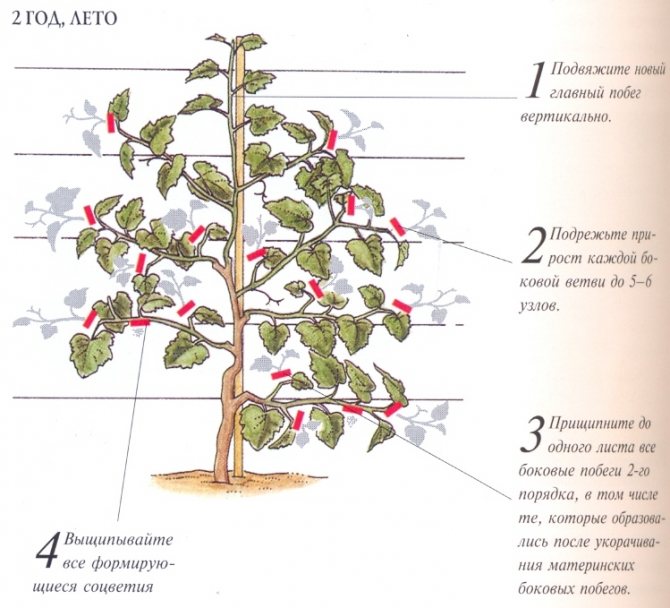
In the second
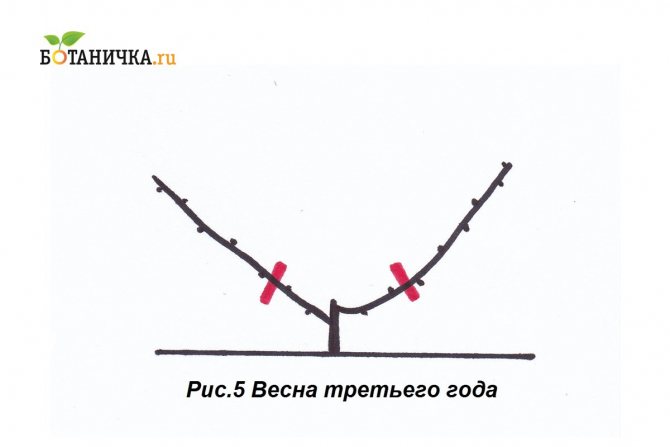
After the vine has successfully overwintered, it can be tied to the bottom wire of the trellis.This is done in the spring, when the positive temperature has already stabilized. On a tied shoulder, in the second year, three sleeves should be grown. They should grow from the upper shoulder buds, and the distance between them should be about 80 cm. In the fall, each vine must be laid on the shoulder, having previously cut it by 80 cm. Three sleeves will be enough for the further development of the bush.
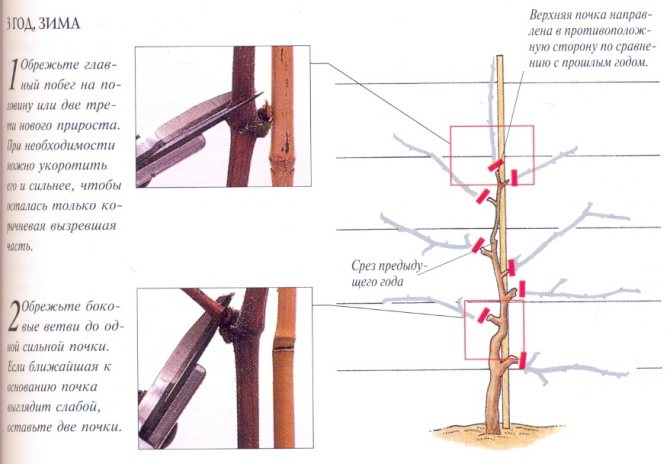
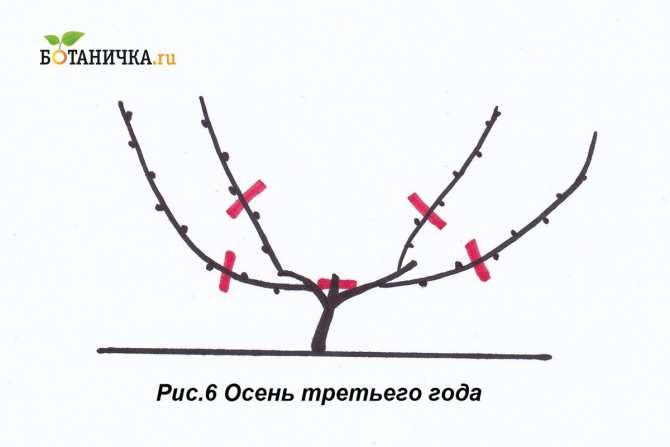
On the third
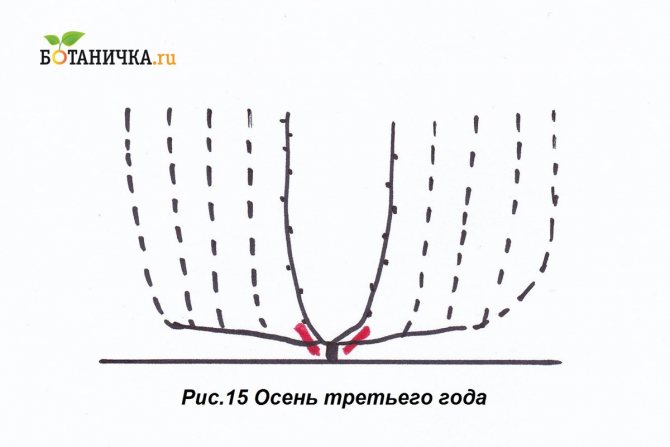
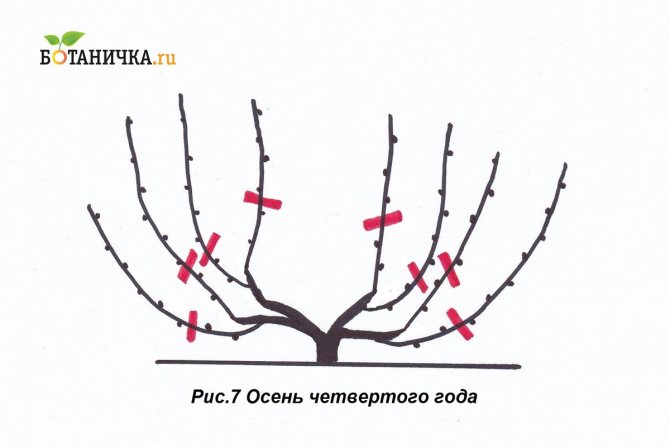
In the third year, the grape bush enters the fruiting period. After flowering, a bunch of berries and yield are formed on the vine. Spring buds that hatch on the shoulder should be removed, leaving them only on the sleeves. Several inflorescences can form on the vines, of which the most developed should be left, and all the rest should be removed. Usually the lowest inflorescence is the strongest. In the third year in the fall, you need to cut off the vines on which there were bunches of berry. After that, the sleeve will be formed as if in two parts. This is part of the sleeve of last year and part of the vine of the current, third year, on which there were berries. After all the operations, in the fourth year of grape development, a bountiful harvest can be expected.
You can learn how to properly prune grapes in autumn here.