Features of nutrition and lifestyle
At different stages of the life cycle, food and lifestyle differ. Butterflies have a very short period of existence, depending on the breed, lasting from 4-6 to 10-12 and 20-25 days. Females are inactive, do not feed. During the production of silk, they do not leave the cocoon, dying in it. Males are more mobile than females, after fertilization they stop their life cycle.

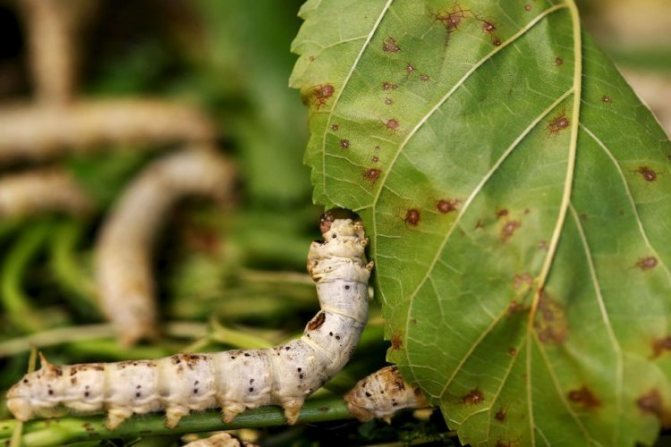
Caterpillars have a well-differentiated internal structure. In their digestive system, powerful jaws, pharynx, esophagus, goiter and intestines are secreted. This allows large quantities of mulberry leaves to be absorbed. There is a circulatory and excretory system, oxygen is transported by the respiratory system. The latter is of particular interest: on the sides of the body there are 9 respiratory openings (spiracles), from them there are branches of the trachea, which are divided into small tracheoles, ending in all organs of the larva.
Caterpillars hatched from eggs are very small, the weight of one individual does not exceed 0.005 g. Their distinctive feature is appetite and non-stop feeding, rapid weight gain.
The pupal stage lasts 12-18 days. The organism inside the cocoon is immobilized, food is not provided.
Spread
The natural habitat of the silkworm was the subtropical regions of Southeast Asia. This insect no longer occurs in the wild. It is grown artificially in many countries of the world. Sericulture centers are China, India, Central Asia, Italy, Spain, Hungary and France.
We suggest that you familiarize yourself with: Aphids on home flowers how to deal
Even flapping its wings with all its might, a domesticated butterfly can only travel a short distance through the air. Adults do not have a mouth apparatus, so they do without food for their entire short life. Males live 13 days, and females only 10 days.
Life cycle and reproduction
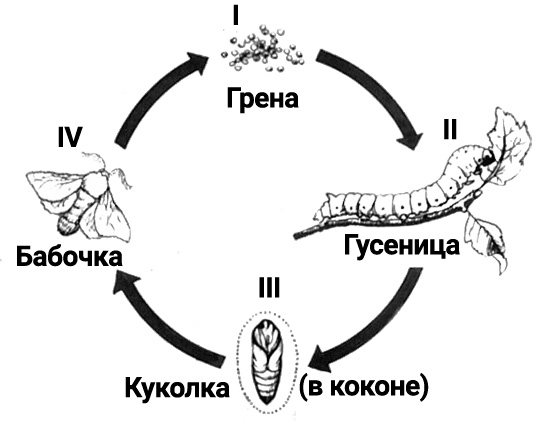
In the life cycle of the silkworm, four stages of development are clearly distinguished:
- egg (grena);
- caterpillar (larva);
- pupa in a cocoon;
- butterfly (adult, imago).

Silk producers from different countries choose breeds and hybrid forms of silkworms, differing from each other in physiological and economically valuable characteristics, and most adapted to local climatic and organizational and economic conditions. The fundamental difference between breeds is the annual number of generations of workers:
- one - monovolt;
- two - bivoltine;
- several are polyvoltine.
Let us consider in more detail the characteristics of each period in the insect's life cycle.
Egg
In the sericulture production cycle, masonry is called gren. In nature, the egg phase is hibernating (the state of diapause). The life processes in it are slowed down or stopped, the body is invulnerable to adverse environmental factors.
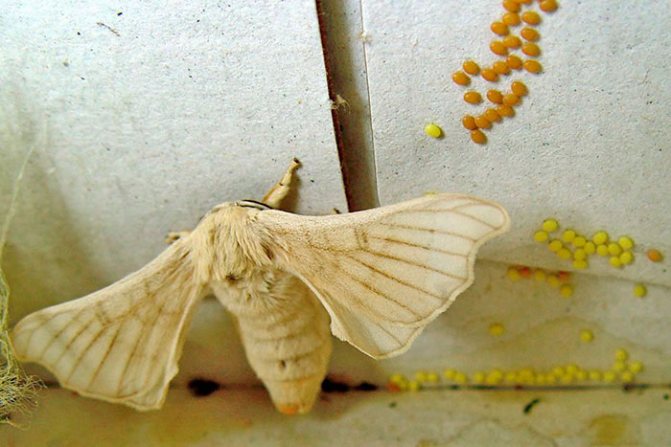


Silkworm eggs are very small, one gram contains 1500-2000 eggs. One female lays 500-700 eggs. The grenes are oval in shape, slightly flattened on the sides, have an elastic translucent shell - a white or light yellow shell. After laying, the eggs begin their development during the first two days, which externally manifests itself in a change in the color of the shell from light to pink and purple, and its hardening.
The optimum temperature for incubation (winter storage) is 2-4o C.Such conditions allow larvae to hatch simultaneously with the opening of mulberry leaves.
Caterpillar
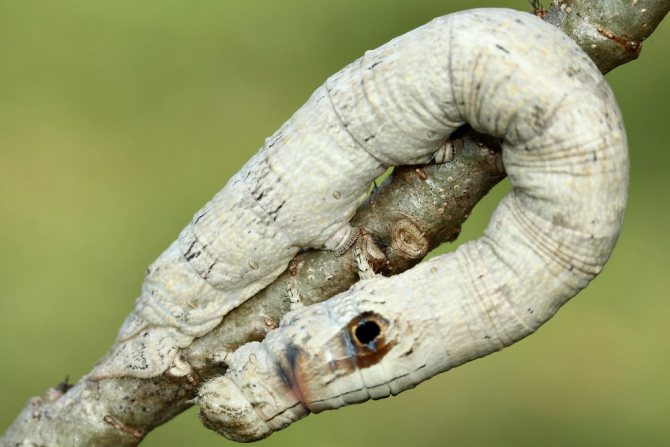
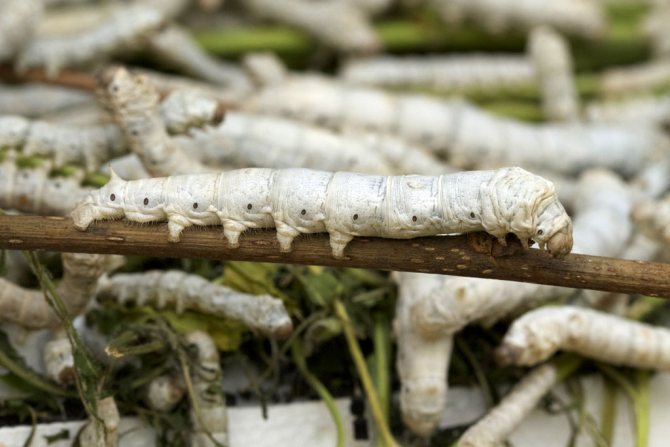
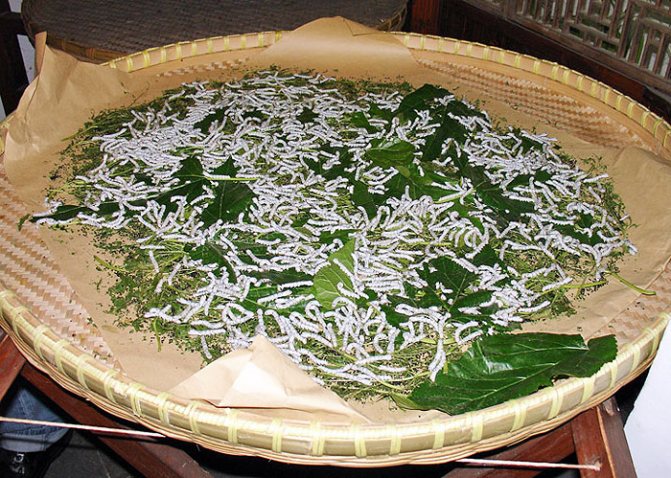
Silkworm larvae are called silkworms, but by their biological characteristics they are caterpillars. In appearance, their body is elongated, the head, chest and abdomen, ending in a corneous appendage, are clearly distinguished. Legs 8 pairs: 3 pairs of chest and 5 pairs of abdominal. Outside, the body is covered with a chitinous cover without pubescence - this is the external skeleton, muscles are attached to it.
In the development of caterpillars, five ages are distinguished, one more from the number of molts. The life span of an organism is 20-38 days. During this short period, the size of the body increases by 30 times, and the mass by tens of thousands of times. During molting, the caterpillar looks for an attachment site. For this, the abdominal legs serve her, the front part of the body is raised. The larva stops moving and goes into a state of complete rest or "sleep". Gradually, the old chitinous cover opens up, from which the head is shown first.
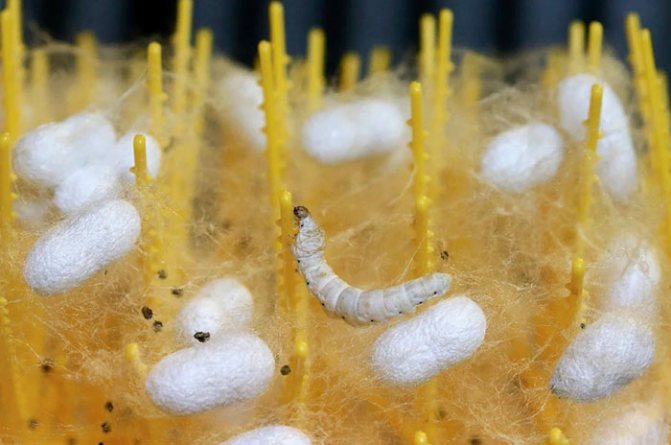


After molting, the return to enhanced nutrition is slow. It takes some time for the new cover to become harder and more durable. Along with this, the legs become larger, acquire hooks.
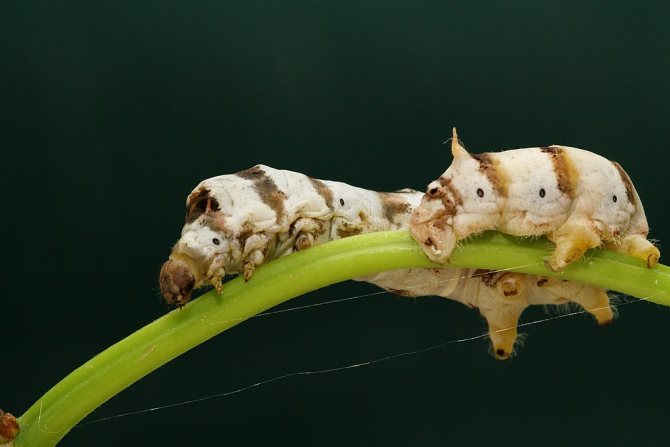
The color of the caterpillars varies according to age:
- at first instar dark brown or black;
- in the second, a light color appears on the chest;
- in the third and fourth - carpet coloring;
- in the fifth, white or light green.
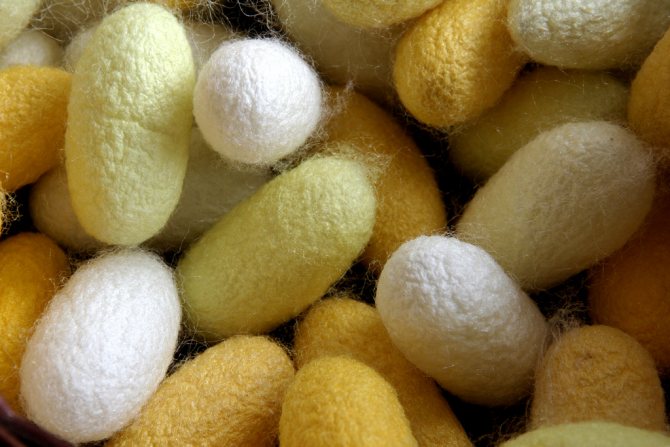
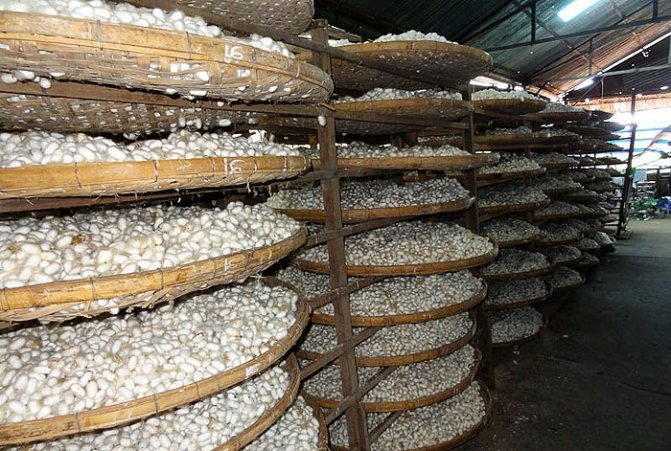
By the end of the fifth age in the body of the worm, more than a quarter of the volume is occupied by the silk-secreting gland - an organ capable of secreting silk fiber with one continuous thread. In medium-sized cocoons, the thread is from 300 to 900 m long, and the maximum - up to 1500 m. The centuries-old selection made it possible to isolate butterflies that give the most productive offspring. The average cocooning time is 3-4 days.
In the structure of the silk gland, the following departments are distinguished:
- fibrin isolation department;
- storage tank;
- excretory ducts (paired and unpaired).
In the unpaired duct, they find the so-called "wire drawing" - an insect's device, on the structure of which the thickness of the silk thread depends.
At the end of the fifth instar, which lasts 8-12 days, the caterpillars are completely covered with a cocoon, molting occurs inside, after which the caterpillar inside the cocoon turns into a pupa.
Chrysalis
The process of transformation of a caterpillar into a pupa - pupation takes 4-5 days. The pupa stage is a complex continuous process of quantitative and qualitative changes in the insect's body, lasting 12-18 days, as a result of which a butterfly emerges from the cocoon.
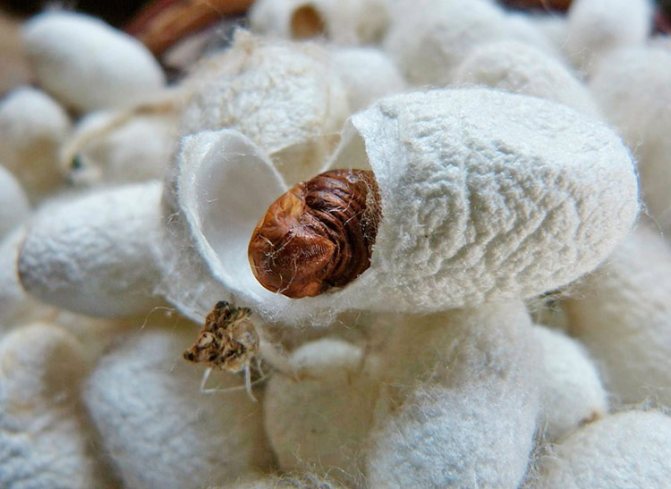


About a day before the release of the butterfly in the cocoon, movement and slight noise are noticeable. The future butterfly first sheds the outer covers of the pupa, then secretes a liquid that dissolves the adhesive sericin, with which the cocoon threads were glued. Butterflies emerge strictly from 5 to 6 in the morning.
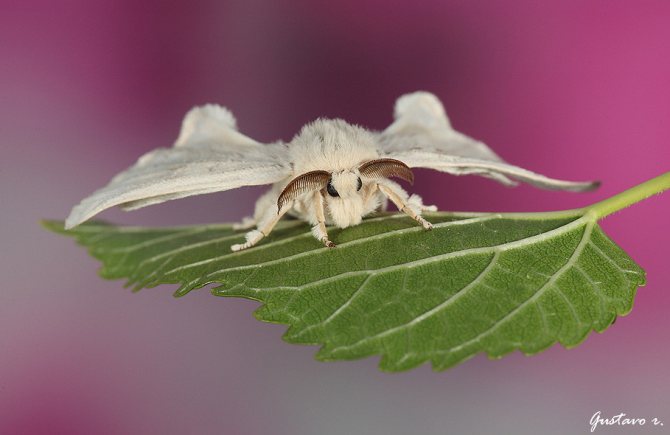
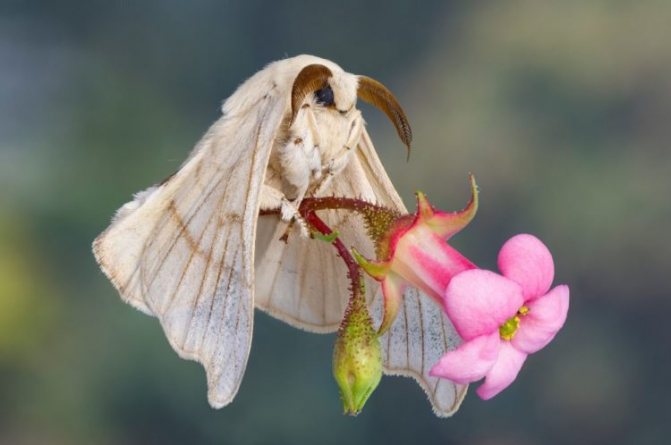
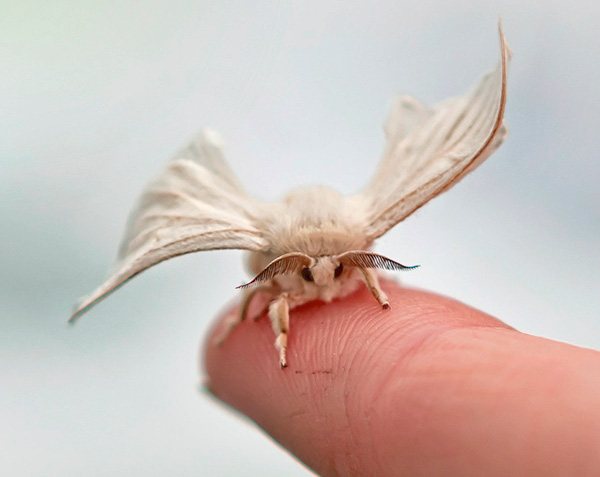
Silkworm butterfly
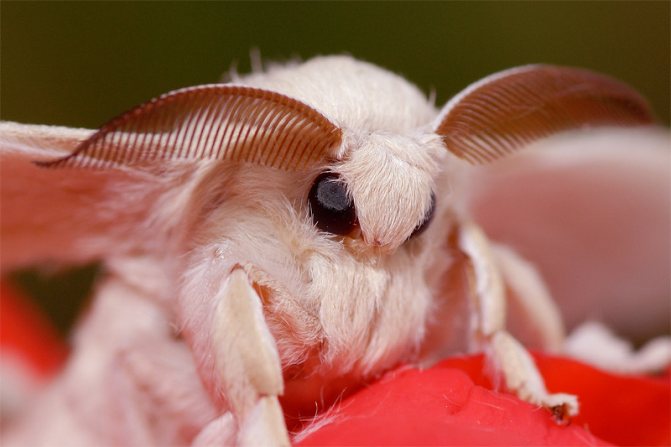
Butterflies look large, have pubescence on the body, hairy antennae with outgrowths in the form of comb teeth. The wings are white, when unfolded they reach 6 cm, the bands are slightly brown. The edge of the forewing has a distinct notch at the apex. During a short period of their life, butterflies lay in the bark of mulberry trees, where they hibernate.


Moth robot
Silkworm cocoons are a signature souvenir for Shengjie guests. But on the streets you can also find them in shops with street food - fried on skewers. Silkworms are also cooked in Korea: they are steamed or in oil with spices. These caterpillars are considered a delicacy in Vietnam, as well as in Japan, where the larvae are marinated from sake, soy sauce, sugar and other ingredients.
Eating on silkworms is beneficial, said scientists from Terami University in Italy.In their research, they concluded that they contain twice as much antioxidants as orange juice. Chinese biologists even suggested sending silkworms to space stations as a source of protein to feed astronauts. They argued that even the inedible part of these caterpillars - the silk thread - is saturated with protein. True, in order to completely feed the astronaut, 170 larvae will be needed, which are still unrealistic to grow in space.
peace


Photo: Depositphotos


A grasshopper sat in the meal: locust shells will enrich food for Russians
New functional dietary supplement will help with hypertension and atherosclerosis
Scientists have managed to find other uses for productive silkworms. Japanese scientists planted a caterpillar to control a robot (this experiment, according to their idea, could become the starting point for creating a device for detecting narcotic substances). Subsequently, it was repeated with a silkworm butterfly, hoping to find a new way to eliminate oil spills in the sea - the fault is the sense of smell of these insects, which can be triggered at a distance of several kilometers.
Types of silkworms
Other types of silkworms belong to other families. Most of them are pests of forest and fruit crops. Let's consider some of the varieties.
Pine
The pine silkworm is also called a cocoonworm, it belongs to the family of the same name. Caterpillars feed on pine, eat needles of different maturity, sometimes whole branches.
The butterflies are large grayish-brown, the wingspan of females reaches 8.5, of males - 6 cm. The color of the wings is largely adjusted to the color of the bark of the trees on which the cocoon moths settle. Butterflies can be recognized by a small white spot in the middle of their front wings.
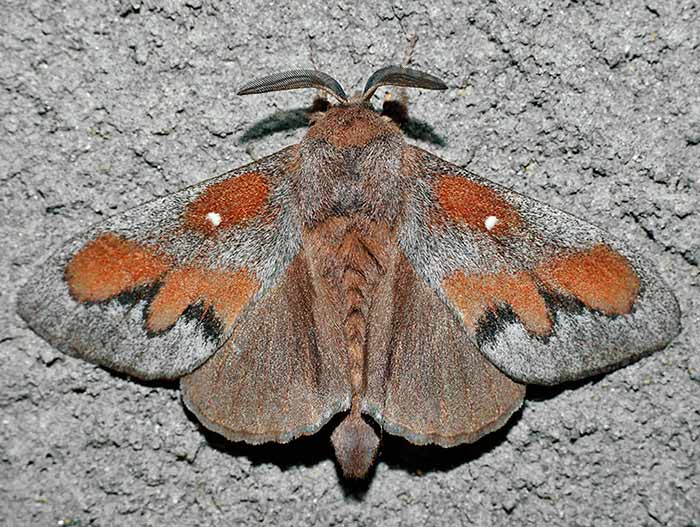


Caterpillars are shaggy, of a grayish carpet color, 6-8 cm long. Hair with a reddish tint, ring constrictions on the body. On the second and third chest constrictions, the cutouts are dark blue. The wintering stage is a caterpillar. Cocoons with pupae are gray, formed in early June on pine branches. Silkworms twine cobwebs around large branches. In nature, cocoon moths are eaten by cuckoos, their natural enemies are riders, microscopic mushrooms.
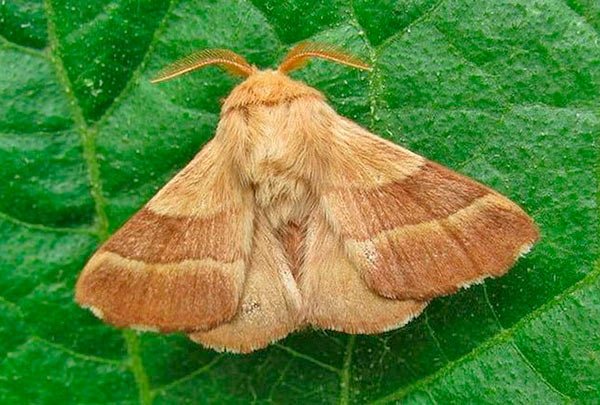
Ringed
Also belongs to the family of cocoons, widespread throughout Europe and Asia. It is a pest of forest and horticultural crops. The color of the butterflies is yellow-reddish-brown, 3-4 cm long. The caterpillar is dark with distinct yellow-orange stripes, covered with long hairs. Clutch of eggs is light gray in a ring around thin twigs.


Nun
A budworm butterfly, a typical nocturnal moth. Caterpillars prefer to feed at night, which makes them difficult to spot in gardens. Causes significant damage, eating leaves of apple, oak, birch, conifers - pine, spruce, larch. Juniper, yew, pear, privet, currant and gooseberry nuns are not exposed to invasions. The wingspan of butterflies is up to 6 cm, the color is gray with a typical dark pattern in the form of zigzag stripes. Antennae are black serrated.
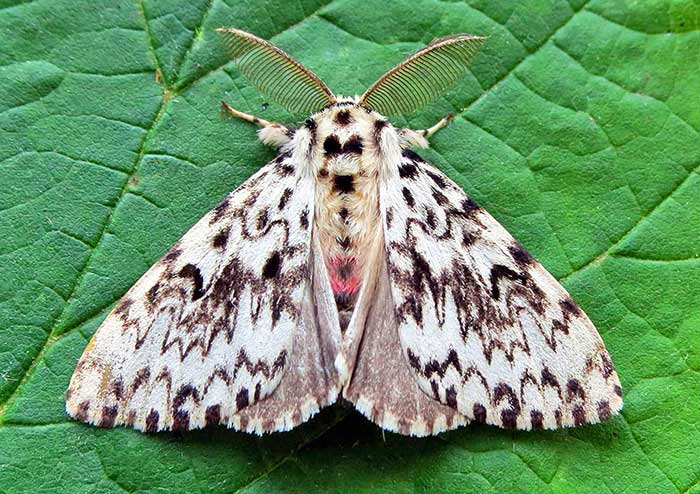


The caterpillar is densely covered with hairs with 8 pairs of legs, 6 cm long. On the back there is a black spot in the form of a heart, from which a dark stripe runs along the body. On the ninth and tenth ring constrictions, red warty spots are noticeable. Hibernating stage - eggs laid in the folds of the bark. Caterpillars are very voracious, they release cobwebs on which they can be carried by the wind and cause outbreaks in vast areas of forest tracts. Each outbreak lasts 7-8 years, after which the number decreases.
Unpaired
Belongs to the wolf family. Widely distributed in Eurasia, it was introduced to North America. Insect damage is the death of forest and fruit crops. Particularly striking are valuable tree species - oak and linden, plum, apple. Caterpillars do not eat pear, ash and alder trees.
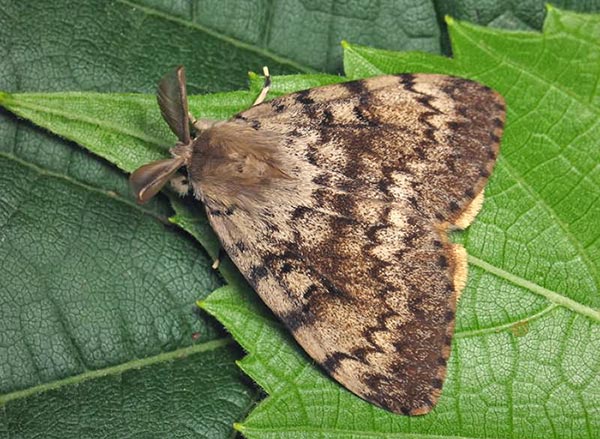


Butterflies of different sexes differ from each other. Females are large, with wings spread reaching 9 cm, light red or white. Males have a wingspan of up to 4 cm, they are brownish-yellow. They fly out in the second half of the summer, they fly low above the ground, after mating, they lay eggs in cracks in the bark on boles and trunks, stumps, fences. Therefore, trapping belts put on the trunks of fruit trees are effective against them.
The caterpillar is furry, 6-7 cm long with wart spots. The first five pairs of warts are blue, less noticeable, the back six pairs are distinct red. Clutches of eggs can be recognized by their shaggy reddish-brown coating. The eggs are very hardy.
Control methods
There are many effective ways to keep the gypsy moth out of your garden. The choice of a suitable one depends solely on the degree of damage to the tree and the size of the pests. So, with minor damage to the tree, it is enough only to collect the egg clutches (caterpillars) of the pest. It is necessary to carefully examine the entire tree (shrub) and, if caterpillars are found, carefully collect them (do not forget to wear gloves) in polyethylene, and then crush them. We do something similar with masonry. Only it is necessary not to collect, but to scrape from the surface of the tree into some bag, box and then destroy.
Take preventive measures in spring and autumn
The next method of pest control is traps. You can build traps from special glue rings for caterpillars by putting them on a tree trunk, or you can make effective traps with your own hands from burlap. At a height of about 1.5 m, wrap a piece of burlap about 30 cm wide around the trunk and secure it. Pull it partially down by grasping the top with your fingers. And every day, "armed" with gloves (thick enough) and a bag, collect and destroy the caterpillars.
Advice. If you live in a region where the gypsy moth is ubiquitous, try to additionally protect yourself by planting bushes / trees in your garden, the neighborhood with which the pest avoids: black / gray walnut, ash, tree, etc.
If, having accomplished all of the above, you have not been able to get rid of the pest, you can move on to "heavy artillery": biological and chemical preparations. The former are most often presented in the form of bacteria that enter the pest's body with food. As for chemicals, they are used extremely rarely and in moderation.
This concludes the consideration of the issue regarding the destruction of the gypsy moth at the site. Have a good fight!
The benefits and harms of silkworms
Weaving cocoons is not always beneficial. Mankind has been able to employ only the silkworm. Fabrics made from its threads are highly valued in the world market and have become a truly cultural value in many countries of the world - China, India, Pakistan.
Other types of silkworms are pests that cause irreparable damage to forests and gardens. Maintaining ecological balance in biogeocenoses, when the number of natural enemies does not decrease, helps to contain outbreaks of pest numbers.
GENERAL PROVISIONS

Nowadays, cheap synthetic fabrics have very much replaced natural silk, and yet products made from it, as before, remain popular.
As early as 4 thousand years ago, silkworms were bred in China to obtain silk. For a long time already this moth and its larvae cannot exist without human help. Adult insects have completely lost their ability to fly, and caterpillars would rather die of hunger than crawl to look for suitable food. For more than 2 thousand years, China maintained a monopoly on silkworm breeding. Any attempt to take out the grena (a clutch of silkworm eggs) was threatened with death. There was an ancient caravan route, which was called the "Great Silk Road".The fact is that silk fabrics were highly valued in the countries of Europe and the Middle East. And not only for the beauty of silk clothing. Most importantly, in such clothes, a person was less bothered by lice and fleas! This is why the silk trade has been the main source of income for the people of China for many centuries. In 552, the pilgrim monks managed to deliver silkworm corn to Constantinople. Then the Emperor Justinian issued a special order, which he ordered to engage in sericulture in the Byzantine Empire. China's monopoly on silk has come to an end. In Western Europe, silkworm breeding began in 1203-1204, when the Venetians, after the IV Crusade, brought silkworm grenade to their homeland.
Useful properties of silk thread
The productive ability of the silkworm is simply unique, in just a month it is able to increase its weight ten thousand times. At the same time, the caterpillar manages to lose "extra pounds" four times within a month.
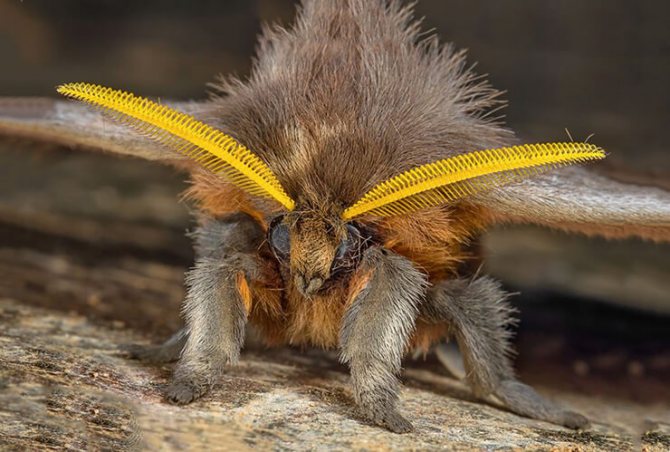


It takes a ton of mulberry leaves to feed thirty thousand caterpillars, enough for the insects to weave five kilograms of silk thread. The usual production rate of five thousand caterpillars yields one kilogram of silk thread.
One silk cocoon gives 90 grams of natural fabric. The length of one of the threads of the silk cocoon can exceed 1 km. Now imagine how much a silkworm needs to work, if on average 1,500 cocoons are spent on one silk dress.
Silkworm saliva contains sericin, this substance protects silk from pests such as moths and mites. The caterpillar releases substances of a sloping origin (silk glue) from which it weaves a silk thread. Despite the fact that most of this substance is lost in the process of making silk fabric, even the little that remains in the silk fibers will be able to save the fabric from the appearance of a dust mite.
Description
The wingspan of the silkworm is 40 mm. The body and wings are whitish in color. The body is thick and very hairy. The first pair of wings is sickle-curved.
The butterfly has three pairs of thin and delicate limbs. In individuals of both sexes, antennae are feathery, with two rows of fine bristles. In addition to the silkworm, the cocoons of the Chinese oak peacock moth (Antheraea pernyi) are also used for silk production. The products obtained from them are called scabies.































