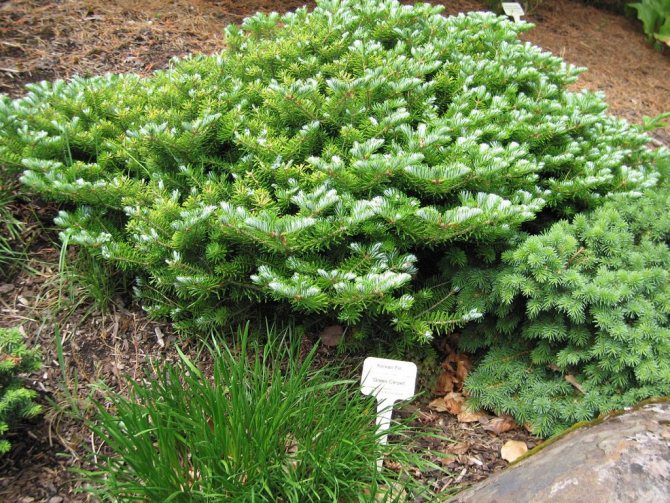
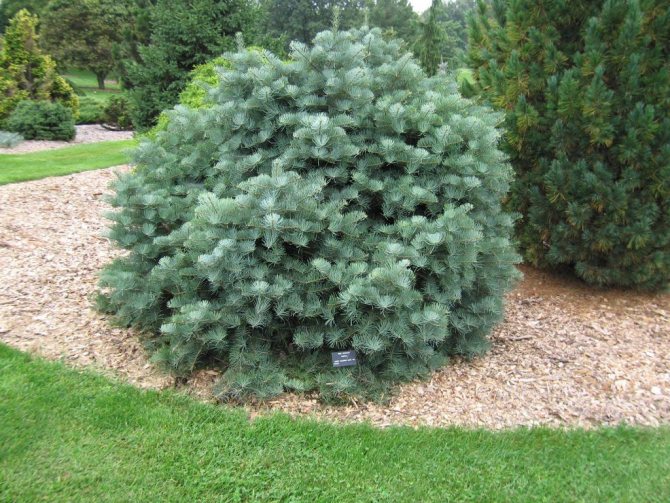
If at the dacha and the plot there is an additional free space that is not occupied for utilitarian needs, then such a beautiful plant as a fir will greatly decorate it (both that notorious "place" and the entire plot as a whole). Despite the fact that fir and fir oil, based on their beneficial properties, are the leaders in terms of frequency of use in traditional medicine recipes, planting fir on the site will rather bring only aesthetic pleasure. I think no one needs to brew her needles from scurvy in modern Russia, (with all its disadvantages in the field of medicine) still will not arise, and fir oil in pharmacies is not so expensive. We ourselves, having sorted out a bunch of essential oils for the sauna, now use only fir.
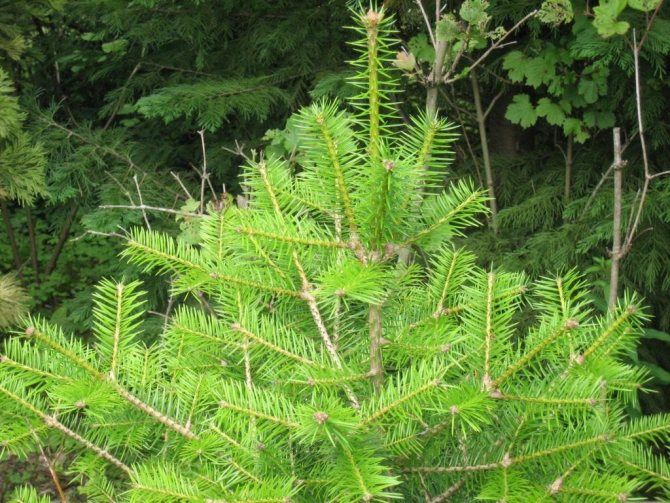
The main plus of fir for use in the landscape design of the site is needles that do not fall off for a long time, which does not become "rusty", that is, does not turn red. The crown of the fir is soft and dense, easily tolerating formation.
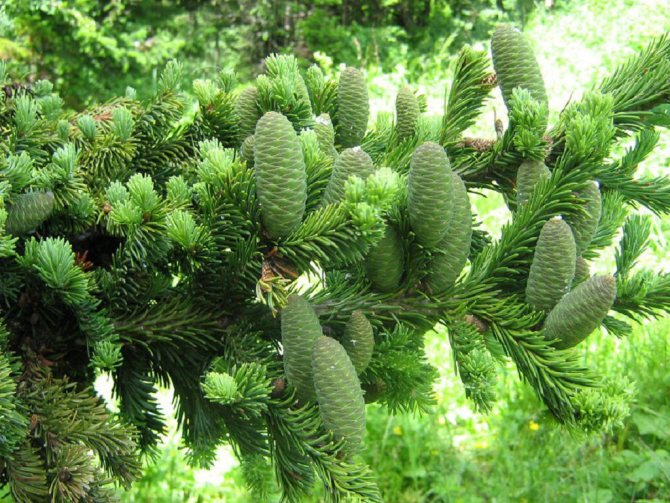
Fir (Latin Aies) belongs to the Pine family (Pinaceae), the genus includes about 50 species distributed in the temperate zone of the Northern Hemisphere. Most often used as holiday trees Nordmann fir, noble and balsamic... Christmas wreaths and garlands are made from fir branches.
RARE PLANT SEEDS FOR YOUR GARDEN - FREE SHIPPING. PRICES ARE VERY LOW. THERE ARE REVIEWS
A neat, well-defined crown, most often of small diameter, dense branches located almost from the very base of the trunk, shiny dark green needles give the fir attractiveness and decorative effect.
These trees have long been used for park plantings, mainly for country ones, since the city air has a bad effect on the appearance of coniferous beauties.
Strict firs are good along the front alley. They also look great in group plantings by themselves or in combination with birches, maples, mountain ash. Firs make excellent hedges around the edges of the site. A single fir can decorate the lawn or the surrounding area. Dwarf forms look great in rock gardens.
In plantings, firs perfectly coexist with other large conifers (spruce, pine, larch), and their dwarf forms - with low counterparts, ground cover flowering perennials, heathers, erik, rhododendrons.
Brief information about the variety
- Color: the top of the needles is emerald and shiny, and the bottom is covered with whitish stripes.
- Height: 25-35 m.
- Crown diameter: 10-15 m.
- Distribution regions: Far East, China, Korea, North America and Japan. It is successfully cultivated in all regions of our country.
- Landing features: scheme - 1x1.5 m. Likes to grow in a sunny place with shading at lunchtime.
- Immunity: High frost resistance and good disease resistance.
- Life span: 200-250 years.
Where does balsam fir grow
Most of the varieties of balsam fir grows in Canada, USA, the range extends from the shores of the Pacific to the Atlantic Ocean. After the introduction of some varieties to the territory of Russia, good growth rates were observed in all forest loamy zones of the country. In the taiga and the middle climatic zone, the plant reproduces independently on a large scale.However, fir cannot be found in the forest-steppe or steppe zones - the soil is of poor quality.
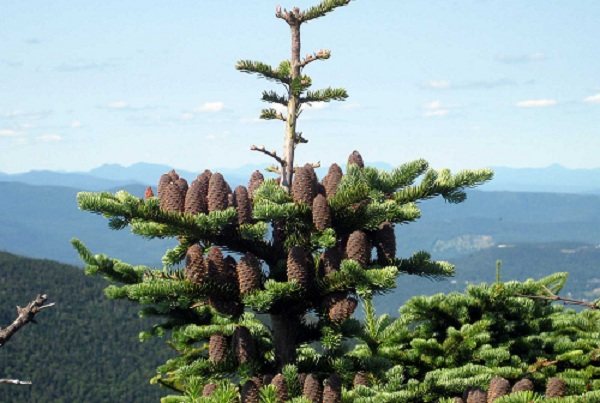

Description of varieties
Balsam fir (abies balsamea) belongs to the Pine family. It has several successful hybrid varieties that differ in shape, color and size.
Piccolo
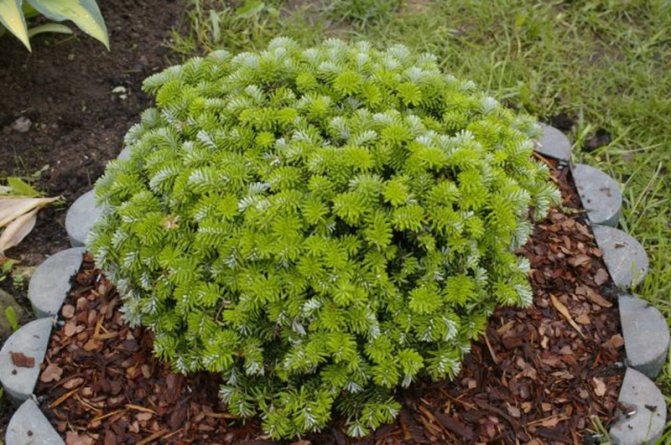
Miniature compact ephedra 30-50 cm high with a spherical crown and emerald needles. Young needles have a rich light green tone, ripened dark green.
The Piccolo variety is often planted as a tapeworm in containers or tubs. They are used in creating various compositions on alpine slides, in mixborders, rockeries and rabatkas.
Due to its miniature size, fir can be grown on a tiny garden plot without losing its decorative effect.
Nana
Dwarf plant Nana (nana) in the form of a bush - height from 0.5 to 1 m, width - 2 m.
The crown is spherical with spreading, dense branches growing horizontally. The needles are of an emerald tone, short, on the lower side contain 1-2 pronounced stripes of a bluish tint.
The description of fir includes several advantages:
- slow growth;
- good shade tolerance;
- high frost resistance.
The plant is suitable for single and group planting, looks good in rocky gardens, is an excellent decoration for terraces, gazebos and roofs.
Some people use the variety to create compact hedges along fences or outbuildings.
Diamond
Another unique variety is Brilliant fir.
An adult tree reaches 0.3-0.5 m in height. It grows very slowly, therefore it is often used for cultivation as a pot crop. The annual growth is 3-4 cm.
Possesses a cushion-shaped compact crown with densely spaced shoots. Young needles of light green color, later become a rich green hue. The length of the needles varies from 10 to 20 mm.
Ornamental shrubs are readily used in the creation of rock gardens, gardens of different styles.
Hudsonia
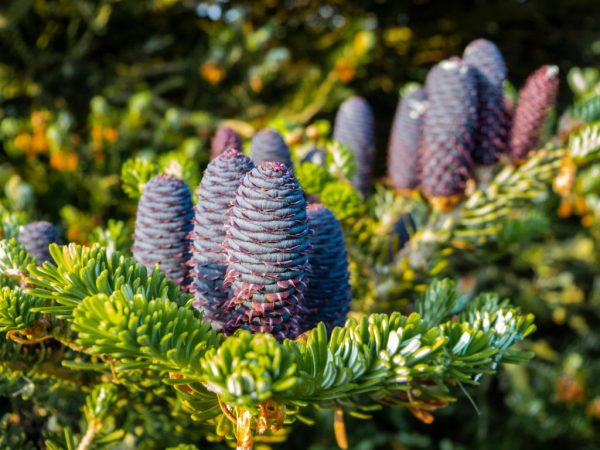


Fir will decorate your garden
One of the most popular dwarf mountain species. In its natural environment, it is a compact slender tree 15-20 m high with a beautiful pyramidal crown.
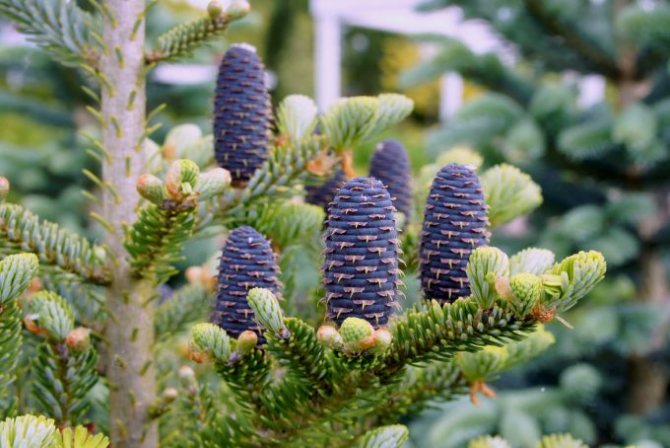
Skeletal branches densely cover the trunk to the bottom. Emerald needles, with a sheen, thornless, contain silvery-whitish stripes on the underside. Young cones berries of a purple hue, after ripening, become chocolatey.
This culture forms a superficial root system, so a windless area with little shading is chosen for planting it.
The description of the cultivated form is slightly different:
- height about 1 m;
- diameter - 1.2-1.5 m;
- slow growth - the annual growth is 5-7 cm;
- needles are short, flat, bicolor pointed at the tips - emerald above with a black tint, below - bluish-green, young needles - light green;
- shoots not too long, thick, densely covering the central conductor;
- the crown is often asymmetric, wide and rounded.
Refers to frost-resistant and shade-tolerant varieties. Used on alpine slides, to create rocky, heather, Japanese gardens.
Kiwi
Fir abies kiwi is a dwarf shrub up to 0.5 m high. It has a beautiful rounded crown with emerald, dense, short needles. Young growth of a bluish-blue hue.
This ephedra is readily used in rocky and heather gardens, small compositions - rabatki, rockeries. This variety is suitable for growing as a pot crop.
Dwarf species
Kiwi is a rather miniature bush, not exceeding half a meter in mature age.
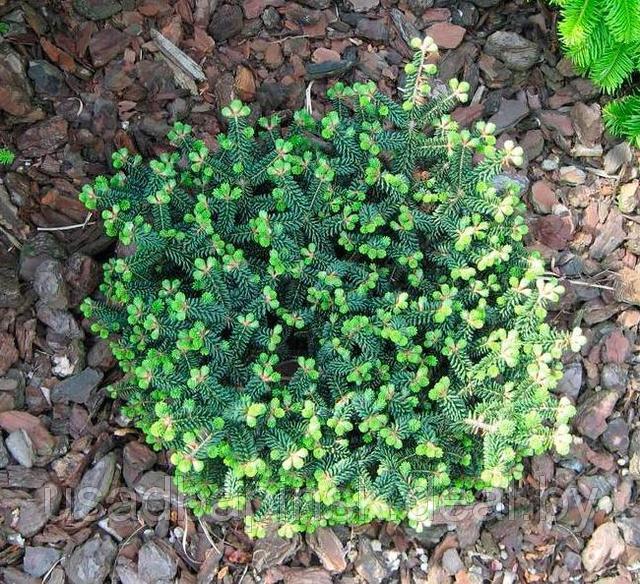


Hudson is a mountain fir of miniature volumes with dark green needles.


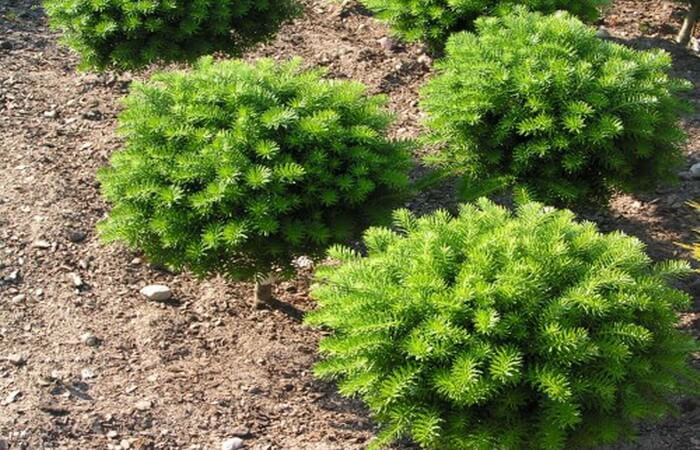
Fir Nana is a small bush up to a meter in height with a rounded crown, with branchy shoots.


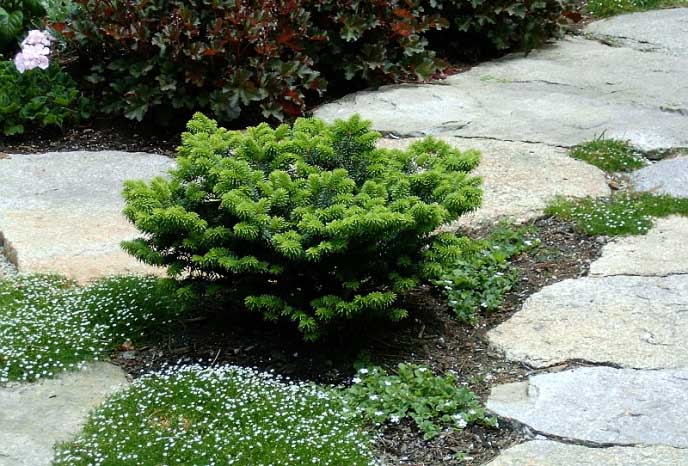
Green Globe is a tree with a height of up to a meter. The needles are green. With the onset of spring, it acquires a yellow tone at the ends of the processes. Crown in the form of a ball. She is usually not cut.


general characteristics
In nature, balsam fir is a giant tree reaching 25-35 m in height.
The crown is of the correct conical shape, densely covered with skeletal branches hanging to the ground, the circumference is from 10 to 15 m.
The central conductor and adjacent shoots have a smooth gray-brown bark. The needles are long - from 15 to 25 mm, blunt, two-colored - the upper side is emerald, shiny, the lower one with whitish stripes. The needles have a comb-like arrangement.
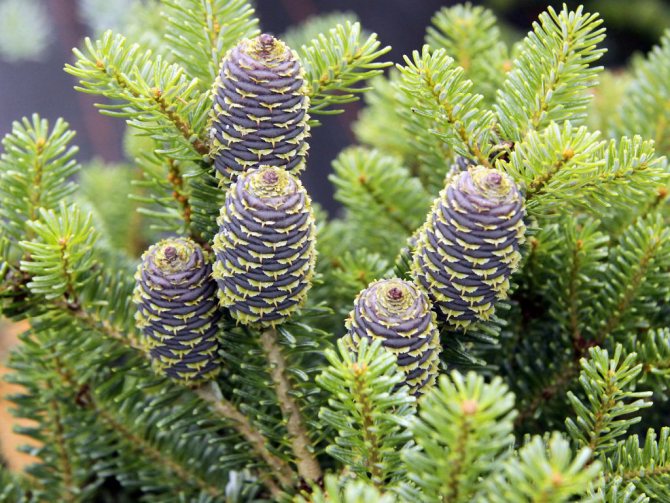
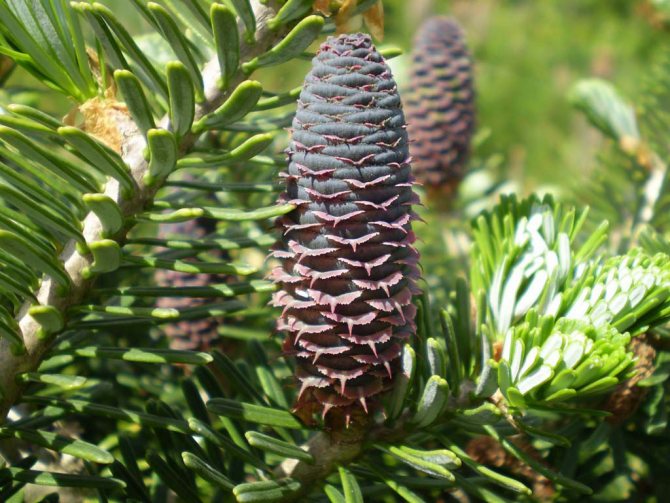
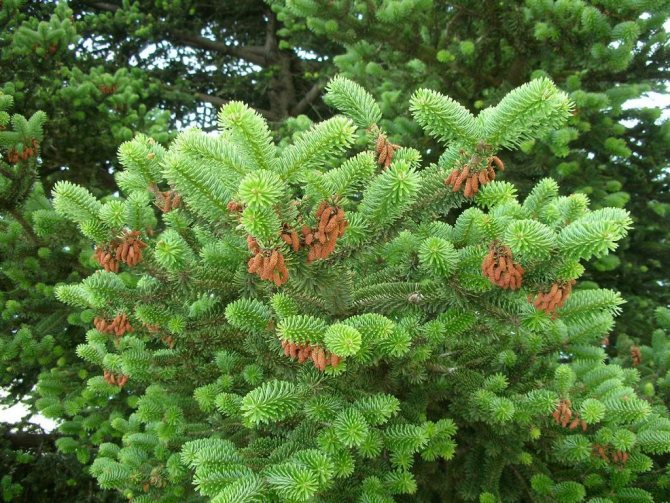
The cones are oval-cylindrical in shape, 10x2.5 cm in size. At the beginning, they are dark purple, when fully ripe they acquire a chocolate tone.
This culture has a superficial, branched root system. Refers to long-lived conifers - life expectancy varies from 200 to 250 years.
Growing regions
The evergreen plant is widespread in the forest zone of the Far East, China, Korea, North America and Japan.
Almost all varieties have good winter hardiness and frost resistance, therefore they are successfully cultivated in all regions of our country.
Care features
Balsam fir is characterized by sufficient shade tolerance and frost resistance, which greatly facilitates plant care. However, in too harsh climatic conditions, under the influence of return frosts, freezing of the trunk of a fir is often observed.
The plant does not need decorative pruning at all and is able to form an attractive crown on its own. Sanitary pruning, which allows you to remove old and injured branches, is carried out in the spring, before the start of active sap flow.
Despite the relative drought resistance, balsam fir is very responsive to regular watering. In addition, it is recommended to carry out weekly sprinkling of the plant crown in the summer. It should also be remembered that the shallow root system makes the plant unstable and can be damaged by strong gusts of wind.


Landing rules
Anyone can grow one of the above varieties of fir, the main thing is to choose high-quality material, a suitable place, soil and provide the plant with timely care.
Seedling selection criteria
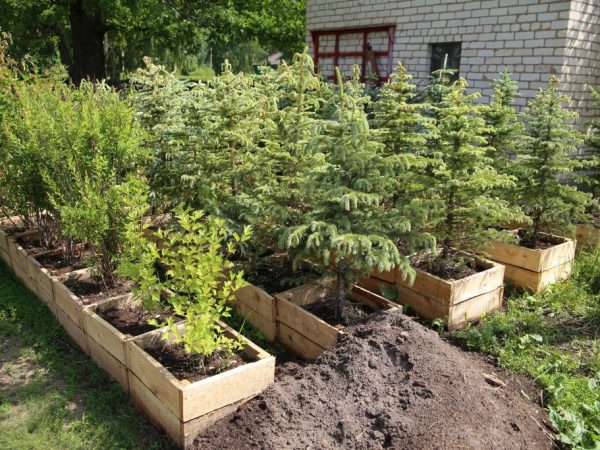


It is recommended to buy seedlings in nurseries.
You need to purchase this ephedra with all the varietal characteristics of the mother plant in a specialized nursery. At the same time, the selection criteria are observed.
- Take copies that are at least 4 years old, because too young have weak roots, and after transplantation they may not take root in a new place.
- Buy bushes with a closed root system - they are easier to transfer stress during planting on the site, and the roots, shrouded in earth, are protected from drying out. Alternatively, you can purchase a seedling in a container or tub.
- When buying, you should carefully examine the crown - it should be alive, with bending shoots and needles of a uniform green color. Any spots - yellow, black or reddish tones, as well as mold - are signs of infection and non-viability.
The optimal time for planting is late April or early May in regions with a cool, harsh and changeable climate.
In the south, balsamic fir is planted in the first decade of September, so that it has time to take root and take root before the onset of stable frosts.
Site and soil preparation
This plant tolerates shade well, so you can plant it near fences, walls of a house or outbuildings.
It is important that the ephedra is protected from the scorching sun and strong winds, which quickly dry out the soil and root system.
Any type of soil will do, but with good drainage.
- If you plan to land on loam, you need to add a couple of buckets of sand, vermiculite or other drainage material 1 m².
- When planting on sandy loam, add clay in the same amount.
The site must be flat, not swampy, otherwise the plant will quickly rot and die. A soil with a slightly acidic reaction is suitable - within 5-6 units.
At a higher rate, any deoxidizing material is introduced - slaked lime, dolomite flour, calcite or chalk at the rate of 350-400 g per 1 m².
The landing pit is prepared two weeks before the planned landing. The approximate dimensions are 70x70x70 cm. If the earthen lump is larger, then its dimensions are increased.
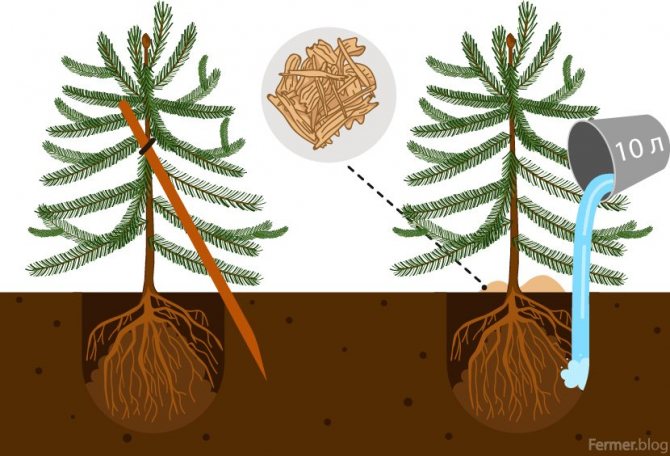
The pit is spilled with water - 25-30 liters. After the moisture is absorbed, drainage is introduced - half a bucket of broken brick, pebbles or rubble. Then, ½ the depth is filled with a fertile earth mixture of sand, humus, peat and clay soil in a ratio of 1: 1: 3: 2.
Additionally, you can add 300 g of nitroammophoska and 10 kg of coniferous sawdust. After a couple of weeks, as the nutrient components settle, you can start planting the plants.
Landing technique
When planting in groups, it is necessary to follow a certain scheme, so the conifers can fully develop and not compete for moisture, nutrients and space. A distance of about 1 m is maintained between seedlings, the distance in a row is 1.5 m.
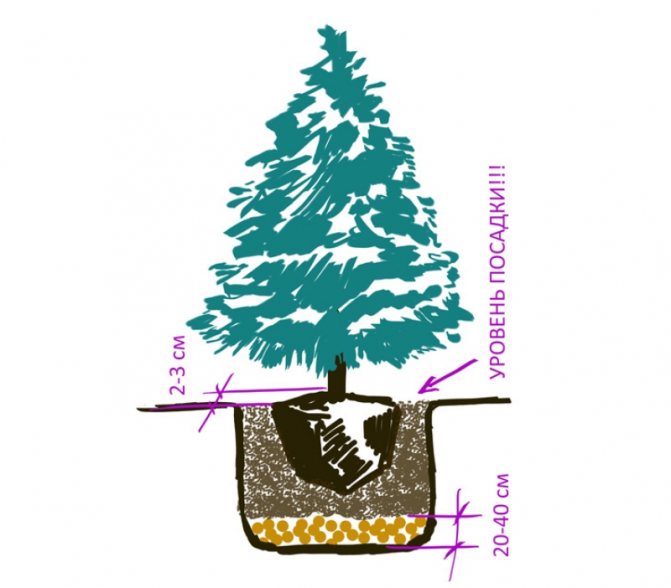
The earthen ball is placed in such a way that the root collar is 5-6 cm above the soil surface. It is sprinkled with the remaining soil mixture, tamped and watered.
In order to avoid rapid evaporation of moisture, it is necessary to mulch with a thick layer of coniferous sawdust or peat.
When to replant fir
Planting trees on the site begins in early spring before bud break. They will form roots if the air temperature rises above + 5 ° C. They can be planted in the same way in the fall - in September or October. Fir trees will take root, calmly endure winter and in spring they will give new growth of branches.
To a new place
If the tree was planted incorrectly and after a while there was a need to transplant it, then they do it either in the spring before bud break, or in the fall. The criterion for starting planting is the air temperature. No frost should be expected on the soil. Sure, the tree can be transplanted in the summer, but conifers do not tolerate planting in the summer heat and will hurt.


In winter, the tree is also not disturbed. Fir, unlike deciduous trees, do not fall into a state of complete dormancy. This means that a poorly rooted root system will not be able to receive moisture from the soil necessary to support the needles. Therefore, postpone planting until spring.
From the forest to the site
Fir reaches a height of 60–80 m and a trunk diameter of 3.5 m. Therefore, no one transplants mature trees. But you can always take a small seedling from the forest and plant it on the site. This should be done in March before the tree starts active sap flow. Fir will grow for over 200 years, so it is better to choose the right site right away.
Important! Young forest firs should be planted on the site on the same day they were dug up and brought home.
When replanting, try to take as much soil as possible from the forest in which the tree grew. It contains mycorrhizal fungi. They form a single system with the roots, processing phosphorus and other difficult-to-digest substances, and in exchange receive photosynthetic products from the tree.


For planting, choose a fir no higher than 0.7-1 m in the forest. It is advisable to take one that grows separately, and not in a group.
Such trees are considered more resistant to disease and will adapt better to a new location. To reproduce later the planting in natural conditions, you can mark the cardinal points on the trunk with a marking tape. And when planting in a permanent place, unfold the tree in the same way.
The fir is dug in and removed together with the soil. The diameter of the crown of a 70 cm tree will be about 25-40 cm. Then the roots, together with the soil, are dipped into a wet burlap.It is necessary not to damage the branches during transportation. It is also forbidden to drag a tree by the trunk so as not to break it.
Care requirements
Balsam fir grows well and pleases with its decorativeness all year round, if it is provided with timely and proper care.
Watering
In the first months after planting, it should be regular but moderate.
Moisturize once a week, the consumption for a young tree is 5 liters, provided that the summer is hot and dry. Moisture-infused conifers will rapidly grow root system and green mass.
From the age of four years, the frequency of watering is reduced to three times per season. The amount of water for one copy is 25-30 liters.
It responds well to frequent sprinkling - it is carried out in the evening to avoid burning the needles and no more than 1 time in three days.
Loosening and mulching


Loosening helps the roots get oxygenated
For this tree, a surface loosening procedure is carried out to a depth of 5-6 cm.
This operation is necessary to maintain the moisture and air permeability of the soil, as well as to ensure full access of water and oxygen to the roots. During it, weed shoots are removed, weeded between the rows.
Mulching provides protection against drying out of the soil and prevents the growth of unnecessary vegetation among the conifers. Peat, pine sawdust or wood chips are used as mulch.
Top dressing
With good nutrition, fir grows beautiful and healthy.
The first time fertilizer is given a year after planting - one of the nitrogen-containing preparations is used: a solution of urea, nitrophoska or ammophoska at the rate of 20 g per 10 liters of water.
The liquid nutritional composition stimulates the growth of roots and green matter. It is brought in in early spring before bud break.
The second time, you can feed with a mineral complex of 15 g of superphosphate and 10 g of potassium sulfate in a bucket of water.
This fertilizer increases the immunity against diseases and the winter hardiness of the crop. Fertilized one month before the onset of stable autumn cold weather.
The growth and development of fir is positively influenced by foliar nutrition with drugs in a hylate form - Quadris, Epin or Geterauxin. Irrigation of the crown is carried out three times per season in the evening hours.
Pruning
This tree naturally has a beautiful and compact crown, but if you want to make it thicker or trim the edges, an easy cut is allowed - 2-3 cm in length of all shoots. Otherwise, the needles will not tolerate stress and will die.
Basic care includes annual sanitary pruning, which is done every spring. Cut out all branches damaged by frost, winds and diseases, as well as dried and growing parts.
To avoid infection, use a sterile sharp object - a pruner, a knife. After the operation, irrigate with a solution of copper sulfate or Bordeaux liquid to protect against infections.
Shelter for the winter
Regardless of the region of cultivation, adult firs from the age of three years do not require insulation, since they have good frost resistance.
Before wintering, they can be covered with a thick layer of peat or pine chips.
Young trees need to be protected from severe frosts and harsh winters:
- mulch the near-trunk zone with peat or sawdust;
- press the skeletal branches to the central trunk, fix with twine, wrap with burlap or cover with spruce branches.
Under a breathable covering material, the seedlings will safely endure wintering and will not wipe out until spring. The shelter is removed when the threat of recurrent frosts has passed.
How to properly transplant fir on the plot in the fall
For planting in the fall, you will need to choose a cloudy day in September. It is advisable that after the end of the process it starts to rain. There are not many rules for replanting fir.
You will need:
- prepare the site and the pit;
- bring a seedling from the forest along with the soil;
- prepare materials: broken bricks for drainage, sand, compost.
While you prepare for planting, place the tree you brought back neatly on its side to avoid damaging the branches.
Choosing a landing site
Fir trees grow in a shady area. But you can also choose sunny. The main thing is that when the tree reaches its optimal height, this does not interfere: it does not create a thick shadow in the garden, does not close the windows, does not interfere with communication systems.


There must be a distance of at least 10 m between the growing fir and the nearest building.
The same applies to fences and other structures, including sidewalks and driveways, where the largest roots can eventually cause deflection of flat sections of the track, alleys. Groundwater should be lower than 2 m from the surface to exclude stagnant water and root rot.
2 weeks before planting, you will need to prepare a hole. For this, the site is dug up. Remove weeds. The depth of the hole will be about 60 cm. And the width will depend on the size of the root system.
Important! Also note that all conifers are susceptible to burns, including fir. Therefore, the area should be shaded naturally after 3 pm.
Soil preparation for replanting fir
Good soil is the key to successful tree growth. If it is poor, just supplement it with organic fertilizers. Heavy and clayey - complete with sand. The goal is to create as much fertile and useful soil as possible that can be rooted.
therefore the size of the planting pit will always be 2-3 times larger than the diameter of the seedling root system... Remove weed roots and rocks larger than your fist from the soil. You can leave those that are smaller by placing them in the drainage layer.


Planting a tree:
- Dig up the site.
- Dig a hole to a depth of 0.5–0.7 m.
- Be sure to lay drainage on the bottom. It can be pebbles, stones, broken bricks. The thickness of the layer is 15–20 cm. It is necessary to limit the contact of the roots with excess moisture.
- Now fill the hole with a mixture of leaf soil or compost mixed with river sand. This is necessary to increase the nutritional and water-holding properties of the earth. Also add 10 kg of sawdust and 200 g of nitroammophoska to the composition.
- Stir and pour into the bottom of the hole in a slide. Now place a seedling on it and add the earth brought from the forest.
- Straighten the roots on the sides of the earthen cone and begin to cover with soil mixture. According to the result of planting, the tree should be at the same level as it grew in the forest.

The trunk circle can be mulched after completion of work. This will help retain moisture in the soil and inhibit weed growth. Mulch will also protect the soil from overheating in hot weather and frost in winter. The height of the layer is 10 cm. It should be located around the tree, but not up to the trunk of 15 cm, to prevent the root collar from wetting with water.
Reproduction
You can get a large number of new seedlings in two ways - by seeds and using cuttings.
The first method requires a lot of patience, some knowledge and is not always effective. It is more often used by breeders to obtain new hybrid forms.
Cutting is one of the most successful and proven options by many gardeners.
Preparation and landing


They are engaged in cuttings in the spring.
Shoots are cut in the spring - an adult and healthy tree from three years old is used. The apical parts are cut off with a piece of lignified bark. The optimal length of the segments is 15-20 cm.
In the lower part, they are freed from processes, needles, sprayed with one of the growth stimulants, planted in a moist and loose substrate of peat and sand mixed in the same amount.
Basic care
Sprinkle with warm water, cover with a transparent film and put in a warm place with a temperature in the range of 20-23 ° C.
When kept at home, the plantings are periodically ventilated, watered, loosened and freed from weeds.
Rooting will take 60 to 90 days. The success of the process can be determined by the new buds on the cuttings. Then the shelter is removed, the seedlings are transferred to a room with a temperature of 15-18 °, they continue to moisten, loosen.
Transplantation to the site is carried out after a year and a half of germination at home. Usually this procedure is carried out in the second half of September, so that the conifers have time to take root and take root before the onset of the first cold weather.
How to care for fir after transplant
Despite the fact that conifers are unassuming in growing conditions and in care, they still need the attention of a gardener.
After planting fir you need:
- watering;
- fertilize;
- loosen the soil after watering;
- mulch;
- carry out sanitary pruning;
- fight pests.
Did you know? Conifers do more than just decorate the garden; in winter they provide the birds with vital protection from rainfall and icy winds. Therefore, gardeners recommend planting about 1/3 of conifers on the site.
Proper watering
Water newly planted fir quickly, saturating the soil with 1 or 2 buckets of water. It is necessary for the soil to become moist, but not liquid. Excess water flushes nutrients into the lower layers of the soil, where plant roots cannot reach them yet.
Continue watering weekly for the first year of growth. The exception is moments of drought. If the topsoil is dry, water, regardless of when the previous watering was. Mature trees can be watered less often - 1-2 times a month.


Evergreens never completely cease their livelihoods. Therefore, you will need to start irrigation from early spring and continue it until late autumn. The last watering is carried out 2-3 weeks before the onset of frost.
For trees planted near the track, sprinkling is periodically carried out. This helps to remove dust from them. But you need to do this in the morning so that the moisture has time to dry out and the needles do not get burns from the daytime sun.
Diseases and pests
This type of ephedra has a high immunity against diseases and parasites; it is rarely possible to spot Hermes (a type of aphid) on its crown.
The massive awakening of females occurs at the beginning of spring, so you need to have time to carry out preventive treatment with Antio or Rogor - 20 g of substance per bucket of water. Irrigate in the evening and early in the morning twice with an interval of 7 days.
The same funds are used for medicinal purposes not only for Hermes, but also for other pests of fir - pine cone leafworm, fir shoot moth.
Of diseases, rust is annoying. Signs of a fungal infection are the massive appearance of reddish or orange spots on the bark of the trunk and skeletal branches. All damaged organs are cut out, fallen needles are collected under the needles.
Places of cuts are covered with garden pitch, and the crown is irrigated with a solution of Bordeaux liquid of 2% concentration.
If a stellate or chive is found, the affected specimens must be dug up and burned.
Beneficial features
Medicinal fir oil is extracted from almost all types of fir, but the most valuable and effective is the oil of Siberian and balsamic fir.
In Canada, balsam fir is very popular and is used as a source of healing Canadian balsam. Such a remedy has anti-inflammatory, bactericidal, disinfectant, analgesic, antispasmodic, warming, antirheumatic and antiarthritic, as well as general stimulating properties.
You may also be interested in the article on the solid color fir.


Testimonials
Due to the high decorativeness of balsamic fir, it is very popular among gardeners in different regions of the country.
- Many people appreciate it for its unpretentiousness, good resistance to frost and the ability to maintain decorative properties throughout the year.
- Successful cultivation by cuttings allows you to get a large number of new plants with all the varietal characteristics of the mother bush.
- Compact in size, the bushes are perfectly combined with almost all the vegetation in the garden, without oppressing their decoration and growth.
Reproduction methods
First of all, beginners need to focus on tree propagation. This can be done in three ways:
- Seeds.
- Cuttings.
- Saplings purchased in nurseries.
The first two methods are rather complicated, and there is no guarantee of a positive outcome. For this reason, buying seedlings from shopping malls and nurseries will be the best option. Usually the soil in pots, in which the tree grows, is impregnated with long-term fertilization. For this reason, replanting fir on the site will not be difficult.
Popular: Useful decoration of parks and areas with ash tree


Preparing fir for planting
In order to grow a healthy tree, it is important to start with a competent approach to the process. This means the preparation of planting material and soil, the correct choice of a planting site with optimal conditions for growth.
Selection of seedlings
It is recommended to buy seedlings in nurseries or special points of sale. It is better to consult a specialist on site regarding the acceptability of a particular variety. Here, the climatic features of the region where the plant will be grown are taken into account. It is preferable to choose frost-resistant types of fir (for example, Siberian, balsamic or subalpine). You should not buy rare decorative forms that are thermophilic. There is a high probability of their death in the first year after landing.
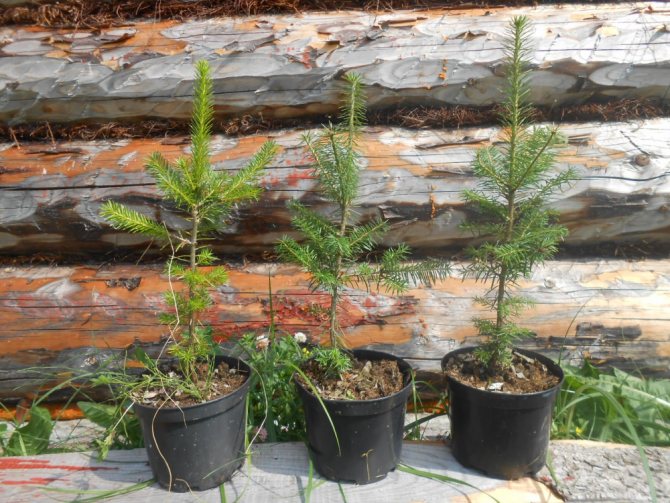


It is recommended to buy fir seedlings in containers, as they root better outdoors.
When choosing seedlings, they pay attention to their appearance. Any damage, signs of disease and dry branches are unacceptable. It is more rational to buy copies of 4–5 years old. The soil in containers must be clean and moderately moist.
Location


Fir will transform any site if you choose the right place for it
Ideally place the fir in partial shade, which is especially important in the first years of life... The tree will not die from exposure to direct sunlight, but it will grow weak. Fir does not tolerate drought - it begins to wither and lose the attractiveness of the crown. But a strong wind is not terrible for this ephedra, so a single landing is possible. As for frost resistance, it differs by varieties. But all young trees suffer from recurrent night frosts, which are not uncommon in central Russia.
Firs love clean air, gas pollution and dust can destroy them. Therefore, suburban estates are an ideal place for growing conifers.
Fir severely depletes the soil as it grows. Because of this, there should not be any fruitful crops near the tree, which from such a neighborhood will experience a lack of macro- and microelements. Falling needles oxidize the soil, which is contraindicated in many plants. And also take into account the height of the tree in perspective. So there should be no wires over the site. You cannot plant an ephedra close to buildings - it is optimal to indent at least 15 m.
The soil
For all firs, fertile and loose soil, moderately moist, is preferable. If the soil is heavy and clayey during planting, it will be necessary to lay drainage in the form of rubble or broken brick.
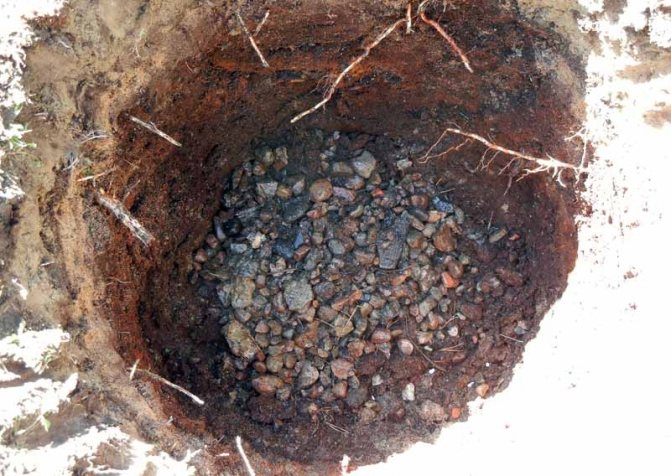


If the soil is clay, then drainage is poured at the bottom of the planting pit
Optimal soil mixture for fir:
- leaf compost - 3 parts;
- peat (humus) - 1 part;
- river sand - 1 part;
- clay - 2 parts.
Landing dates
Fir is a resistant plant that takes root well at any time of the year. The tree is able to withstand drought and frost, so it can be planted in spring, summer and autumn, starting in late March and ending in mid-October. According to experts, as well as gardeners who have already acquired this charming coniferous plant, the best time to plant is April or September.
Did you know? Unlike other conifers, fir is capable of propagating by layering. Its lower branches touch the ground and take root.
It is advisable to plant fir in cloudy weather, and if in hot summer, then in the evening, after sunset. It is best to plant when the weather is cloudy or rainy.
Fir tree - description
Fir is a monoecious plant, evergreen, thermophilic and shade-tolerant. Its root system is powerful, pivotal, deeply embedded in the ground. Fir bark in young years is thin and smooth, with age it becomes thick and cracked. The crown is conical, starting right at the base of the trunk - this is how the fir differs from other conifers. Fir branches are arranged annularly horizontally, fir leaves are flat, whole-edged soft needles, narrowed at the base into a short petiole.
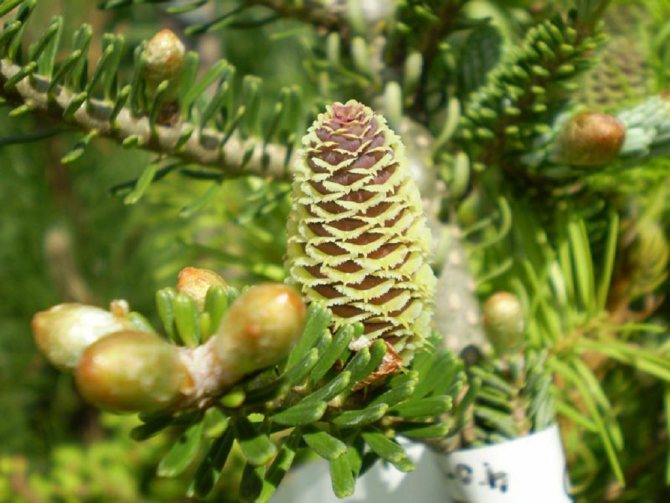
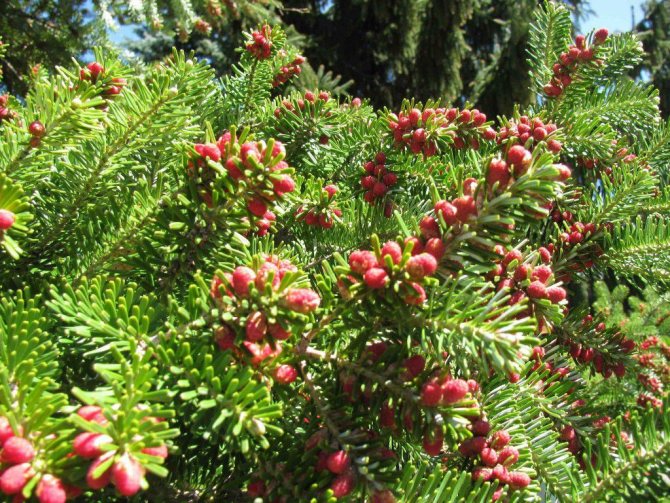
Fir needles do not acquire a dirty red hue in winter, as happens with many other conifers; from below each fir needles are decorated with two white stripes. On the reproductive branches, the needles are pointed, on the vegetative shoots - with a slightly notched or rounded tip. Male flowers look like cone earrings, while female flowers look like ovoid, cylindrical or ovoid-cylindrical, sticking up cones (another difference between fir and other conifers, whose cones usually hang). Female fir cones consist of a rod, on which cover scales sit, inside which there are fruit scales carrying two ovules. Fir trees are pollinated by the wind.
- Gynostemma: properties and contraindications, cultivation and use
When the fir seeds ripen, the scales on the cones become woody and fall off, freeing the winged seeds and leaving only the rods on the tree. In culture, in one place, fir can live up to three hundred years.


When the fir blossoms


Fir grows slowly and in the first years of life it adds only a few centimeters in height.
Flowering occurs in spring in May.
The purple female cones mature throughout the summer and fall off in September. When all the seeds leave the bud, it completely crumbles.
The average age of Fir trees ranges from 300 to 400 years. The tree begins to bloom at about 60 years of age.
Use in landscape design
In landscape design, balsamic needles are used to complete the image of a thematic or classic style of garden composition. With the presence of an evergreen tree, a harmonious atmosphere appears on the site even in the winter season. Trees are often planted in front of summer cottages using a single planting pattern or by combining the plant with other dwarf varieties. For example, the Brilliant fir variety has an original crown shape and small growth, which makes it possible to compactly place several trees in front of the house or along a garden path. These trees are combined with other pine species: cypress, boxwood, juniper, thuja. Pine needles are popular in northern, English, or minimalist garden landscapes.
Fir information
The birthplace of fir is the Caucasus and North America. And since it has many different types, it has become popular with gardeners. If the plant grows in its natural environment, then it can grow up to 8 meters up, but decorative varieties can only sometimes reach at least 2 meters. The shoot of the plant has a hard bark with small cracks or is completely smooth, a taproot, but very strong, this allows it to sink to the required depth. The needles of the plant are flat, soft and arranged in a spiral on the stem, in some varieties - comb. A grown tree in a container differs from street one, by the color of the needles and the appearance of the top. Basically, such firs are bred at home as:
- Nordman or Caucasian;
- Fraser;
- Erect;
- Golden;
- Sizaya.
Ornamental plant varieties can grow for a couple of centuries, and in a natural setting for about 800 years.At the same time, a plant planted in open soil grows by 30 cm per year, but in a container it grows only by 6 cm per year. Fir for planting and subsequent care is undemanding, so most gardeners plant it on their summer cottages. At the time of flowering, male, similar to catkins and female, with cones that grow up inflorescences are formed on the plant. They are pollinated by the wind and will give ripe seeds in the same year.
Is it possible to grow a fir in a pot
For growing fir in a pot, dwarf breeds, which are now available to everyone, are ideal.
When purchasing a tree, be sure to consider its cold resistance.
If the fir pot will spend a lot of time on the balcony or in the garden, its frost resistance should be slightly higher (by 1-2 zones) than in the region.
The best option is to plant fir seeds. To do this, they are harvested at the very beginning of the ripening of the cones. Sow in spring or autumn. After the sprouts appear, they are seated in separate containers.
Dwarf fir can also be propagated vegetatively, using cuttings with apical buds, only such a seedling will grow for a very long time and will take root in 8-10 years.
Is it possible to plant a felled fir
Felled conifers can stand in water or wet sand for quite a long time. At the same time, the plant often begins to release fresh needles, young cones appear on it. This behavior of the tree is considered by many to be proof that, under certain conditions, a full-fledged root system can be grown on a felled fir and then planted in open ground.
However, it is not. Still, it will not work to bring the felled fir back to life. Conifers are rather poorly cuttings, and even small twigs with a heel can not always be rooted. An adult fir tree, after cutting, is guaranteed to die, which can only be delayed by constantly feeding it with water.
Botanical description
Fir is an evergreen perennial in the form of a tree or shrub. Its pyramidal crown can be translucent or dense, narrow or spreading. The height, depending on climatic conditions and species, is 0.5-80 m. The rhizome is mainly pivotal, but it is located shallow (up to 2 m from the soil surface). Young trunks and branches are covered with smooth gray-brown bark, which becomes covered with vertical deep cracks over the years. The branches grow ring-shaped, almost perpendicular to the trunk, or have an ascending character.
On young shoots needles and resinous buds are located. The needles are flat, not too stiff, narrowed at the base. They have solid edges and 2 white stripes at the bottom. Needles grow comb-like, in two planes. The needles are arranged singly and are colored dark green, sometimes bluish-silver. Their length is about 5-8 cm.
Fir is a monoecious plant. She dissolves male and female bumps. Male strobiles resemble catkins and grow in groups. Due to the large amount of pollen, they acquire a straw yellow or reddish color. Female cones, cylindrical or ovoid, grow on erect rods pointing upwards. The length of each is 3-11 cm. The covering scales are attached to the rod. Initially, their color is dominated by pinkish-purple shades. Over time, the lignified scales turn brown. Already in the fall of this year, small winged seeds ripen under them. In September-October, the cone crumbles completely, and the seeds fly away. Only the rods are preserved on the branches.
Recommended varieties for summer residents
If there is a plot of more than 6 acres, landscape designers recommend planting 1 large-sized coniferous plant and several dwarfs. Fir, spruce, berry yew, pine are chosen from massive trees. The tree is planted at the gate or in the center of a well-kept lawn. From undersized species, they form compositions on a flower bed, at curbs, near a playground.


Fir branch with dense needles
Selection of varieties:
- Sabalpine Argentea is native to the United States. Reaches 15 m in height and 2 m in width. At a young age, they are distinguished by active growth, giving an increase of about 15 cm per year. Crescent needles of blue-green color remain on the branches for up to 9 years. During the ripening period, the cones acquire a red-violet color, in late autumn they become brown, and fall off in winter. In landscape gardening compositions, the variety is used to create hedges and composite compositions. The main advantage of Argentina is its resistance to spruce and fir diseases and aggressive conditions.
- A diamond is bought in most cases for an alpine slide. Low-growing bushes (0.5 m) with a green crown fit into woody-floral compositions and set off the lush color of other plants. Differs in average frost resistance, moisture-loving, not afraid of direct sunlight and strong wind.
- Prostrata is a dwarf variety intended for the southern regions of Russia. Its height does not exceed one and a half meters, and its width varies from 1 to 2 m. Young plants and new shoots on mature trees can freeze over in winter. To avoid deformation of the crown, it is covered with insulation or insulated with sawdust.
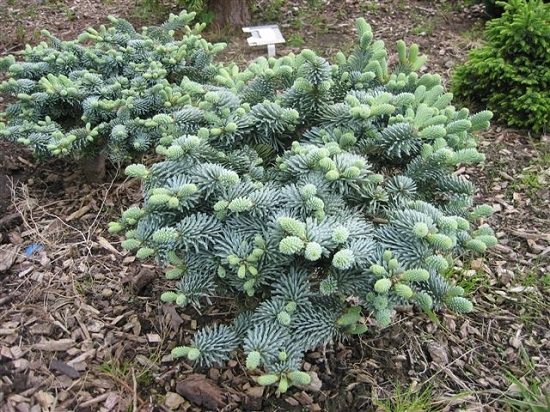


Fir Prostrata - Kiwi is a precious dwarf emerald that never loses its decorative effect. It grows up to parameters 50 * 70 cm. Short and soft needles form a dense crown with a light whitish bloom. To focus on the bush, the tree trunk circle is sprinkled with deciduous bark, boulders are placed next to it.
Blue Glauka, variegated Variegata and neatly creeping Prostrata successfully take root.
Choosing a landing site
A plot with suitable conditions for a crop is the key to successful fir cultivation. The plant feels good next to a reservoir, while waterlogging of the soil, constant waterlogging should not be allowed. This perennial has a powerful root system that goes deep into the depths, therefore, the close passage of groundwater will lead to decay and death of the tree. You can plant a seedling in an orchard, on an alpine slide (decorative varieties), take it to the country. The main thing is to choose the right place so that you do not have to transplant.
Fir characteristic:
- shade-tolerant;
- winter hardy;
- hygrophilous;
- a young tree requires protection from strong winds and drafts;
- does not tolerate gas pollution and smoke from large cities;
- prefers drained, fertile soil.
On a note! The spring sun and dry air damage the shoots, but when favorable conditions are created, the damaged crown is restored.
Lighting for fir
The breed grows in the wild in shady forests, so it feels good in partial shade and shade conditions. When planting a single plant, it should be borne in mind that direct sunlight can provoke a burn of the needles. At the same time, an open area, where there is the possibility of a little shading of young seedlings, will allow the fir to develop well, promote rapid growth, and accelerate seed production. In the forest, seed material is formed after 60-70 years, with single plantings after 30 years.
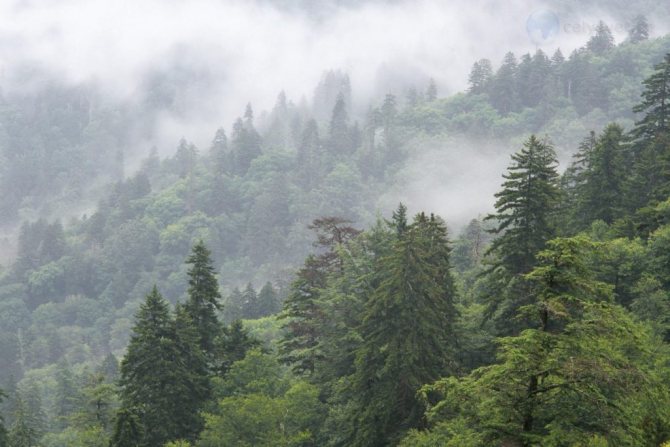


The breed grows in the wild in shady forests, so it feels good in partial shade and shade conditions.
Is fir picky about soil?
The culture needs a loose, nutritious, slightly acidic soil that is good for air and moisture. The soil must have a sufficient amount of essential nutrients, so it must be fertilized before planting. Heavy clay soil, close flow of groundwater require the arrangement of a drainage layer. When growing on sandstone, it is recommended to coat the bottom of the pit with clay.
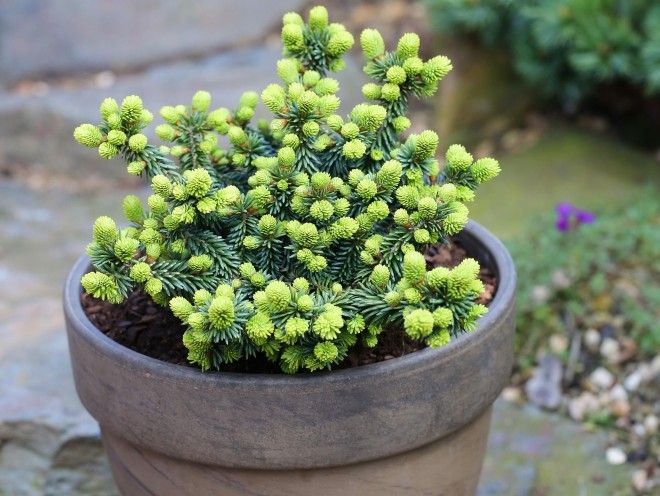
Balsam fir at home
For a small summer cottage, another option is suitable - growing dwarf forms in a pot. Balsam fir Piccolo, Hudzonia, Kiwi and others will do. For convenience, you can make a stand on wheels, which will simplify the movement of the container around the site.Remember that the soil freezes in a pot faster than outside, so it is better to bring trees indoors in winter. To control the height and formation of the crown, pruning is carried out regularly. It is advisable to spray the fir in the summer, watering is carried out moderately at the root.


What is interesting in fir for our gardeners and summer residents
Fir is an evergreen coniferous tree from the Pine family. It can be from 50 cm to 70 m in height, depending on the species. Only in nature can you find gigantic trees. And mainly medium-sized specimens are cultivated. The tree has a superficial root system. At a young age, the trunk is covered with a yellowish-gray smooth bark, but over the years it coarsens and forms seals that contain resin.
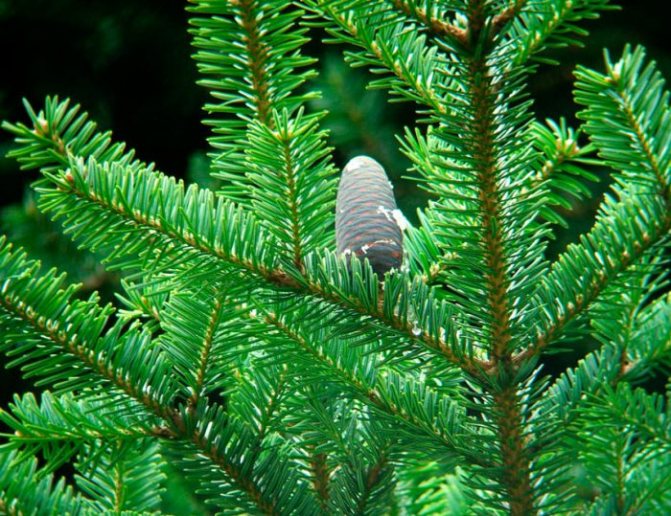


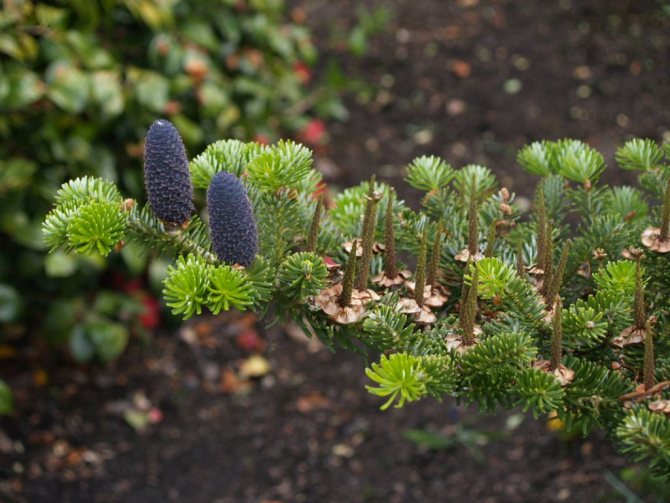
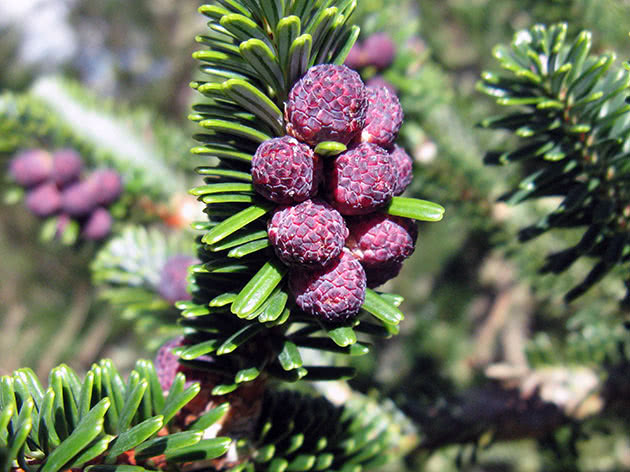
Fir has soft needles and standing cones of a bluish-purple hue
The crown of the ephedra is conical, and its base practically touches the ground. Unlike other representatives of this family, fir needles are soft and do not prick. Another individual feature is the horizontal arrangement of the branches. On them, egg-shaped cones with female and male spikelets grow vertically upwards. The first flowering and fruiting in fir occurs after 25 years. And on average, she can live up to 200 years.
Is it possible to bring out a tree in a flowerpot
For breeding a plant in a flowerpot, dwarf forms are perfect, which everyone can now acquire. When buying a tree, you should definitely take into account its frost resistance. If the fir in the container will stand on the balcony or in the garden for a long time, then its cold resistance should be about 2 zones higher than in the area. Important! Fir in a container will freeze faster than in open soil. The best solution for planting fir is to choose seeds. Therefore, they need to be prepared at the beginning of the ripening of the buds. It is possible to sow them both in spring and in autumn. And as soon as the sprouts sprout, they can be transplanted into individual containers. A dwarf plant, perhaps, can also be bred vegetatively, using cuttings with an apical bud, but this sapling will grow for a long time, and take root only after about 10 years.
How to plant a fir: step by step instructions with a photo
You can transplant seedlings from containers to a permanent place at any time during the spring and autumn period.... And the planting of fir in spring (early) or early September is intended for plants with an open root system aged from 5 to 10 years. It is advisable to carry out the procedure on a cloudy day after rain.
Sequencing:
- Dig a hole 50–70 cm deep and 50 cm in diameter. Additionally, the bottom is loosened by 10–15 cm.

A hole is dug under the fir planting so that the root ball can fit freely in it. - Drainage from crushed stone or brick chips is poured.
- The hole is half filled with nutritious soil mixture, a layer of sawdust and complex mineral fertilizers is laid on top (the first - 10 kg, the second - 200 g).
- Leave the hole for 2 weeks to shrink the soil.
- Then a mound is made in the center, on which the seedling is placed and the roots are carefully spread on the sides.
- Fill in the free space with the remaining earthen mixture. In this case, the root collar is left open.
- After the completion of the work, the fir is abundantly watered and the root space is mulched with peat with pine chips.
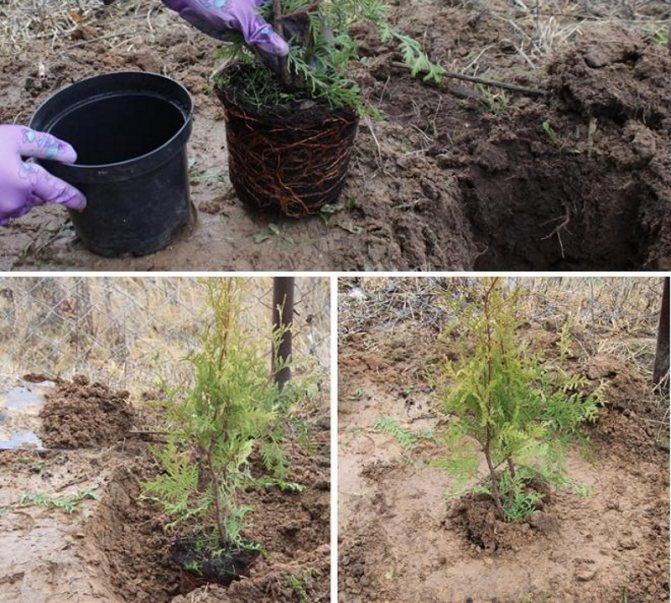


If a seedling is transplanted from a container, then it is placed in a pit along with an earthen lump.
If several trees are planted, then they are distributed depending on the desired result. The following schemes exist:
- alley - arrange seedlings in a row at a distance of 4–5 m from each other;
- chess - plant trees in the shape of a square with an interval of 3 m;
- group - keep the distance between landings from 2.5 to 3.5 m.
Fir alone will look no less impressive. Then it is recommended to surround it with companion plants:
- birches;
- maples;
- juniper;
- firs.
Shade-loving flowers will feel good next to the fir.
Description
When developing in natural conditions, the height of the tree reaches 20 meters. Moreover, the trunk diameter of an adult culture is 80 centimeters. The trunk of the fir is smooth and brown in color. The shape of the crown is made in the form of a regular cone, the branches are numerous, thin, often touching the surface of the earth. The color of the needles is dark green.
The needles of a balsamic plant are placed on the branches in even rows, there are identical partings between the needles. Individual needles up to 25 millimeters in length. The end of the needles is blunt or with a notch, so the green mass of the fir seems to be soft. The name "balsamic" culture got its name from the characteristic coniferous aroma.
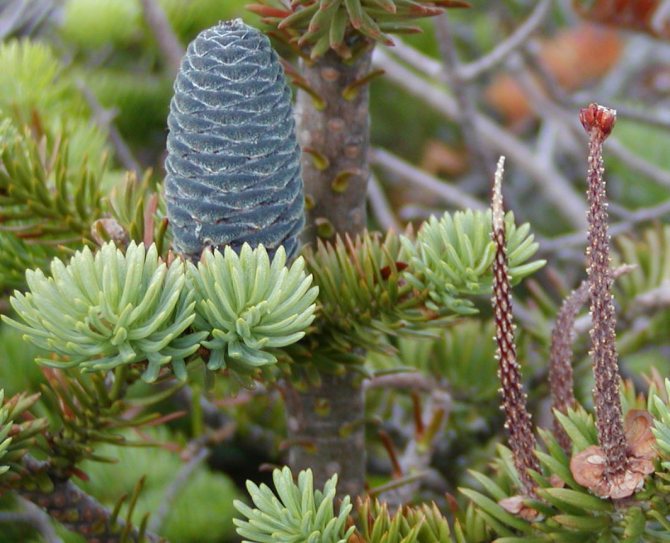


Young buds are purple or blue with a violet tinge.
Abies balsamea buds have a standard oval shape. Young fruits are purple or blue with a violet tinge. After a while, the bumps turn brown. The fruits are arranged vertically on the tree at the very top of the crown. The seeds ripen in the first year, with the arrival of autumn they are released from the sinuses of the cones.
The root system of a balsamic culture is located in close proximity to the surface of the earth. Fir develops at a slow pace, after 10-15 years the plant stretches upwards by 1.5 meters. It is noticed that some specimens of pine trees live in natural conditions for up to 300 years.
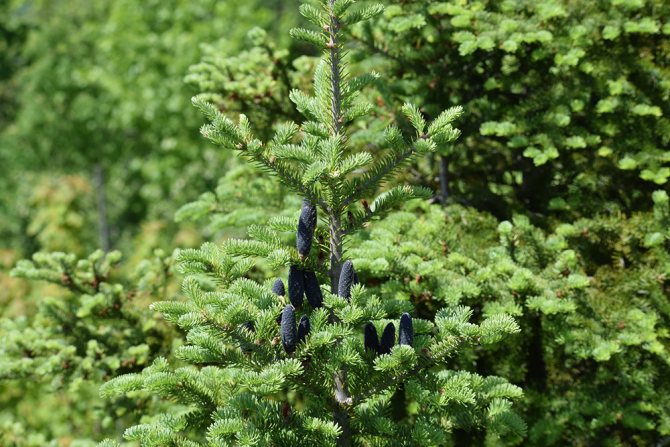


Some specimens of pine trees live in natural conditions for up to 300 years.
Growing area
The natural area of balsamic fir is the territory of the countries of North America. It was from this place that the tree began to spread throughout the world. The culture grows successfully even in the middle latitudes, in the northern part of Russia. Prefers a cool climate, tolerates the influence of negative temperatures. Fir easily takes root in any conditions, coexists with other trees, and quickly forms forests in open areas.
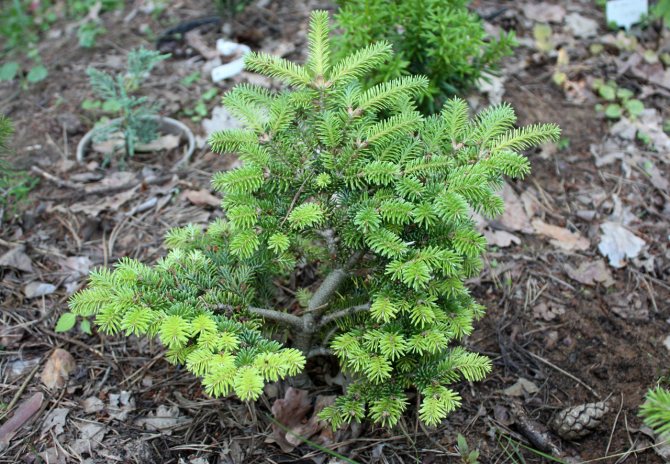


Fir prefers a cool climate.
Balsam fir - reproduction
Subject to the technology, summer residents are excellent at getting their own seedlings of coniferous plants in any quantity. If you like balsam fir Kiwi or another tree of this type, then use cuttings or seed propagation. The first method is faster and allows obtaining varietal seedlings 100% identical to the parent tree.
Fir cuttings:
- In the spring, in a cloudy season, 5-8 cm cuttings are cut from young trees on a one-year growth.
- Branches with one upper bud are chosen.
- It is better not to cut the breeding material in a sector, but to cut it off with your hands with a small "heel" (a piece of bark).
- Burrs are removed from the heel.
- For 6 hours the material is placed in a solution of "Fundazole".
- Composition for grafting balsam fir - humus, sand and leafy earth (1: 1: 1).
- After planting, the vessel with the handle is closed with a transparent plastic cap.
- For the winter, the containers are transferred to the basement.
- Normal roots appear on the fir only in the second year, in the first season callus is formed.
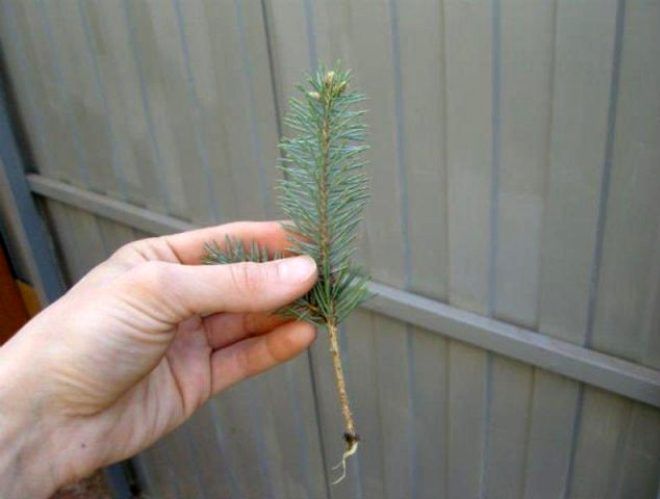


Seed propagation of fir:
- Unripe buds are dried.
- The seeds are removed.
- Stratification of seeds is done in the refrigerator.
- Sowing material in April.
- Sowing soil - sod land with sand.
- The crops are covered with foil.
- Germination period - up to a month.
- Transplanting a fir from a school for the second year.
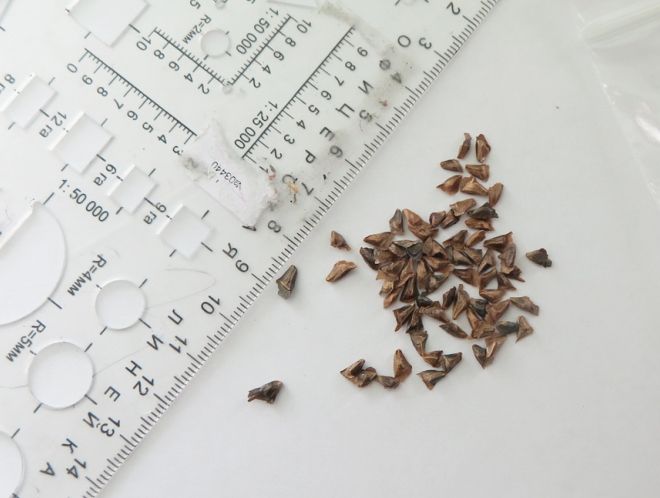


Siberian fir photo, medicinal properties, application.


Siberian fir (Abies sibirica).
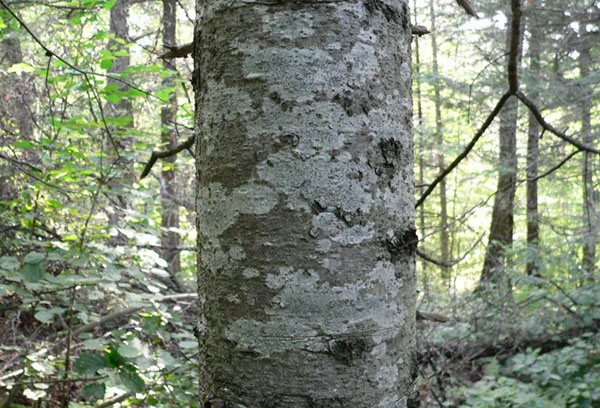
Description. An evergreen monoecious tree of the Pine family (Pinaceae) up to 30 m high. The root system can be different, depending on the soil. On damp soils, it is shallow, in this case the trees are not resistant to the wind, and can be felled by it.
On dry soils, the root system has a taproot and lateral roots that go deep down. This enables the tree to be wind-resistant. Siberian fir has a beautiful narrow pyramidal crown with a sharp top, which is preserved even in old trees.
The barrel is ribbed at the bottom, cylindrical at the top. The bark is dark gray, thin, smooth, with thickenings (nodules), which are filled with a transparent fragrant resin "fir balsam". The branches are thin, so in freely growing trees, they can go down almost to the very ground.
The needles are flat, dark green, shiny, soft, not prickly, fragrant, up to 3 cm long, 1-1.25 mm wide, with two whitish stripes below. Each needle lives for 7-10 years.
Male cones in the form of yellow spikelets with pollen are located at the top of last year's shoots. Pollen grains with two flying air sacs, thanks to which pollen can be transported over a long distance. The female cones are located vertically upward at the bottom of last year's shoots. Unripe cones are brownish-red, mature - light brown, ovoid-cylindrical, 5-8 cm long, 2-4 cm wide. Siberian fir blooms in May - early June.
At the end of September - October, the seeds ripen and crumble together with the scales, and sticking cone rods remain on the branches. This distinguishes fir from other conifers. Siberian fir is widespread in Western and Eastern Siberia, in the Urals.
It is part of the taiga along with other conifers. Fir is a thermophilic, frost-resistant plant that prefers moist air and rich moist soils. Unlike larch, pine, spruce, it does not tolerate deep and prolonged freezing of the soil. Fir is grown as a garden and park culture in the northern, middle parts of the forest, forest-steppe zones. Fir propagates mainly by seeds. The life span of a tree is 150-200 years.
Collection and procurement of raw materials. For medicinal purposes, buds, young shoots, unripe cones, needles, fir resin are used and harvested. The buds are harvested before they begin to bloom. They should be tightly closed. The kidneys are used raw and dried. They are dried in a dry room, spreading on the fabric in a layer of no more than 4 cm, stirring often. Store in closed jars. Unripe cones are harvested in June - August. Cones and needles are used fresh.
Young shoots are harvested from May to the first decade of June and used fresh. The resin is harvested in dry weather, during the growth of young cones (June - August). To form a larger number of nodules (thickenings filled with resin), they beat on the surface of the trunk with a wooden mallet.
At the site of the blows, over time, nodules of significant sizes are formed. The lower part of the nodule is pierced with a pointed tube and squeezed into a jar. Turpentine is made from sap. From fresh young shoots, immature cones, needles, an essential oil is obtained, from which camphor is made.
The composition of the plant. Buds, immature cones, young branches, needles contain essential oil (0.6-3.2%), tannins, ascorbic acid, carotene, tocopherols.
The essential oil contains bornyl acetate (30% —60%), camphene (10%), free borneol, (10%), alpha-pinene, beta-pinene, bisabolene, santen, dipentene, felandren. Zhivitsa is a solution of resin (rosin) up to 70% in essential oil.
The healing properties of fir. In scientific medicine, camphor preparations are widely used - camphor oil, camphor alcohol, camphor ointment, an alcoholic solution of camphor and salicylic acid.
A solution of camphor 20% in oil for injection (Solutio Camphorae oleosae 20% pro injectionibus) is used in the form of injections to stimulate the respiratory center in pneumonia and other infectious diseases, in the complex therapy of acute and chronic heart failure, collapse, in case of poisoning with hypnotics and narcotic drugs.
Available in ampoules of 1 or 2 ml. Camphor alcohol 2% and 10% (Spiritus Camphoratus) is a topical preparation with local irritating action. It has a local irritating, antiseptic effect, stimulates the nerve endings of the skin, reflexively improves the trophism of organs and tissues.It is indicated for inflammatory diseases of the musculoskeletal system (rheumatism, arthritis), as well as for the prevention of pressure sores. Available in bottles of 50 ml. Camphor oil 10% (Oleum Camphoratum 10%) for external use is used for myalgia, rheumatism, arthritis, bedsores.
When coughing, warm camphor oil is rubbed into the chest and back (clothes should be warm and warming). For colds, you can take a warm bath with this oil (7-10 drops). Camphor ointment 10% has the same indications as camphor oil. In homeopathy, camphor preparations are used to treat vomiting, diarrhea, fainting, epilepsy, urinary retention, diseases that are accompanied by a feeling of coldness in the body.
Application in traditional medicine. Galenic preparations of Siberian fir have expectorant, diuretic, disinfectant, analgesic, blood-purifying properties.
In folk medicine, an infusion of young shoots or a decoction of fir buds is prescribed internally for inflammation of the upper respiratory tract, bronchitis, pulmonary tuberculosis, stomach ulcers, cystitis, rheumatism, gout. A decoction of needles is considered an effective prophylactic and therapeutic agent for scurvy. Outwardly, a decoction or infusion is used as a gargle for sore throat; compresses - for frostbite, varicose veins; sitz baths - for women with lingerie, foot baths - for sweaty feet with a bad smell.
Dosage forms and doses. Broth of fir buds. 1 tablespoon (10 g) dried kidney per glass of water.
After boiling, cook over low heat for 5 minutes, remove from heat, filter after 20 minutes. Take a third of a glass of 3 r. a day after meals.
Preparation for wintering
Most of the fir varieties cultivated in the regions of central Russia are quite cold-resistant. However, young specimens need shelter for the winter. It is recommended to cover the trunk circle with peat or spruce branches about 12-15 cm thick.


So that young trees overwinter safely, they are covered with any non-woven material.
Mature trees winter well without insulation, but in spring they should be covered with non-woven material to protect them from direct sunlight.
Plant care
Fir is not particularly whimsical, but you still need to take care of it, especially in the first years of life. Necessary measures:
- The first summer after planting in the country, the seedling is watered 2-3 times a month. After its complete rooting, it should be moistened only in steadily hot weather. And so the fir has enough natural precipitation.


Adult conifers have enough natural rainfall, so they are not watered - The soil is systematically loosened in the trunk circle to a depth of no more than 15 cm and at the same time weeds are removed. You can mulch this space with peat with sawdust (layer thickness - 5–7 cm), without covering the root collar.
- For the first 10–15 years, the tree is not pruned, but the crown is allowed to form on its own. The only thing is permissible to cut dry and diseased branches.


Fir does not really need artificial crown formation, but sanitary pruning is necessary - 2-3 years after planting, the tree is fed for the first time. To do this, use the mineral composition "Kemira-universal" (powder consumption - 100-120 g per landing), which is scattered in the near-trunk space.


Fir seedlings can be fed with bark, ash and peat
Is it possible to grow fir in an apartment
There are no particular difficulties in growing fir at home, since these trees take root well in almost any natural environment.
Do not be afraid that the fir in the house will be too hot. Having a southern or even subtropical origin (fir is native to the Caucasus and Central America), plants generally have good tolerance to a wide range of temperatures (from -30 ° C to + 35 ° C). They are able to do without water for quite a long time, and it is much easier for them to endure droughts than excessive waterlogging.
Types and varieties
The distribution area of fir is the forests of Eastern and Central Europe, Asia, Siberian taiga, the Far East, North Africa.
Scientists count about 50 species of fir, from dwarf trees about half a meter high to forest giants, reaching a height of 80 m. Let's get acquainted with the species that are often found in cultivated plantings.
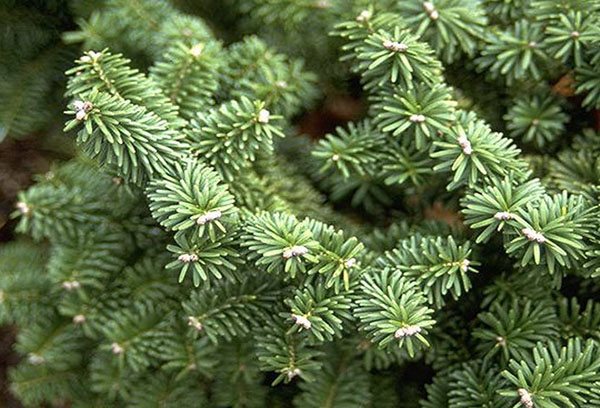


Balsamic
A native of North America, it is characterized by shade tolerance, frost resistance. The height reaches 25 m, the trunk diameter is up to 1 m.The soft needles are green, the length of the needles is up to 3 cm.
- In the design of summer cottages, the dwarf variety of balsamic fir Nana is of interest. It is a tree up to 50 cm in height with a spreading - up to 2.5 m in diameter - crown. The branches are horizontal. The needles are dense, the lower part of the needles is yellowish.
- Another popular dwarf variety - Hudsonia, is interesting in the color of the needles: thick, to black, dark green in the upper part and with a bluish tint in the lower.
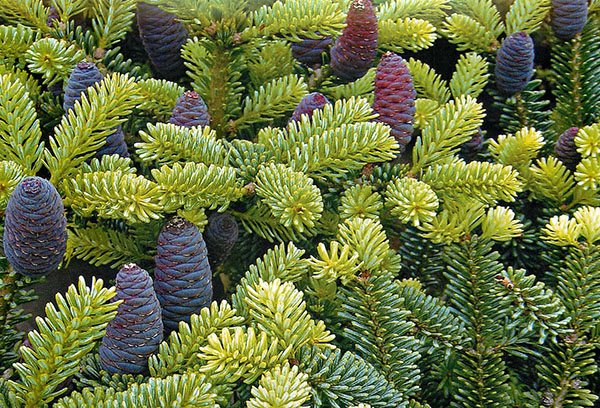


Korean
Originally from the Korean Peninsula, it prefers to grow in high places. It grows in height up to 15 m with a trunk diameter of up to 80 cm. The crown is conical, the branches are covered with hard needles, slightly curved. The color of the needles is dark green, silvery at the bottom. It is notable for its 7-centimeter pink-purple candle cones. Popular in Russia in urban landscaping.
- Piccolo is a dwarf variety used to decorate rocky areas and terraces. Its height is only 30 cm, but the crown grows up to one and a half meters, dense. The needles are tough.
- In urban landscaping, the Blue Standard variety is popular - up to 8 m high, with a crown diameter of about 3 m. It is interesting in the color of cones - from green to deep purple.
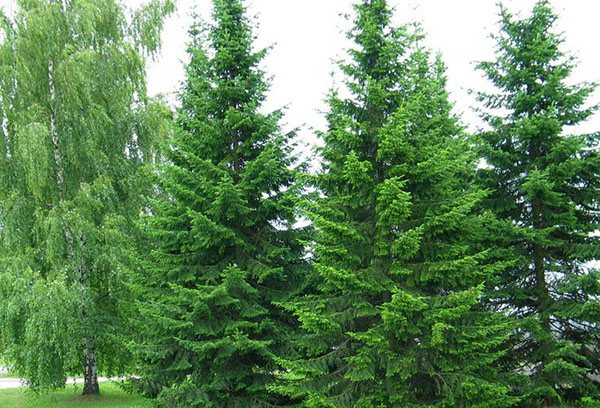


Siberian
In its natural environment, it grows only in the forests of Siberia, a protected species. The height of the trees reaches 30 m, the crown is narrow, pyramidal in shape. The needles are short, up to 3 cm, narrow, soft. Siberian fir is rarely used in landscape design.


Monochromatic
High, up to 60 m, tree with a powerful trunk. The crown is conical, needles with variable color - from bluish to gray-green, with pronounced yellowness in autumn. Drought and frost resistant species.
For landscape gardening, varieties of single-color fir have been bred:
- Violacea, up to 8 m high, with a wide cone-shaped crown, the color of the needles is white and blue;
- Compact (Compact Glauka) is a shrub dwarf fir, suitable for decorating Japanese gardens, rockeries, alpine slides.
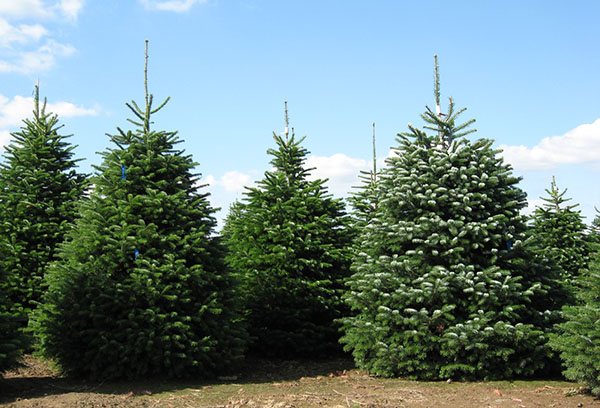


Caucasian (Nordman fir)
Endemic species, widespread in the Caucasus, partially grows in Turkey and the Middle East. A powerful tree 60 m high, with a two-meter trunk diameter. The color of the needles is dark green, with a silvery tint, the needles are down.
- Interestingly, the so-called Norman fir is a Nordmann fir grown especially for the Christmas holidays. Such trees are appreciated for their appearance - neat, symmetrical, fluffy branches, needles of an even green color.
- Golden Spreader is a compact dwarf fir, slow growing. The needles are golden yellow in color. Recommended for alpine slides.


White-brown (budscale)
Growing territory - mountain ranges of the Far East, Northern China. The crown is conical and pyramidal. The color of the needles is dark green. Frost resistant, durable in urban environments.


Fraser fir
Fast-growing, shade-tolerant tree up to 25 m high, native to North America. Interesting with long silvery-green needles.
- For small areas, the variety Prostrata is suitable, which forms a creeping shrub.
The species diversity of fir is not limited to those listed, for the description, those are selected that do not cause much trouble when grown in the country.


Fir in winter
Fir in autumn
Fir trees, recommended for planting in the middle lane, tolerate our winters well, however, young plants must be covered with spruce branches, and the trunk circle should be mulched with peat or dry leaves with a layer of 10-12 cm.


Wintering fir in the country
Adult plants hibernate without shelter, however, at the end of winter, you need to cover the fir with non-woven material to protect them from the spring sun - they can be severely affected by its rays that are too bright at this time.
Diseases, pests and methods of dealing with them
Fir trees are distinguished by their endurance, but still they, like others, are attacked by pests and get sick. Dangerous pests are:
- fir hermes;
- pine cone fire;
- bark beetles;
- wireworm;
- shoot moth.
If the needles of the tree begin to turn yellow, this indicates an attack on it by fir hermes. The females of the insect are activated in early spring, therefore, at the beginning of the season, a massive spraying of trees with Rogor or Antio liquids should be carried out. The solution is made in the proportion: for 10 liters, 20 g of the drug is taken.
Insecticides also stop the reproduction of shoot moths, bark beetles and pine cone moths. The processing is carried out during the period of caterpillar emergence and is repeated after 2-3 weeks.
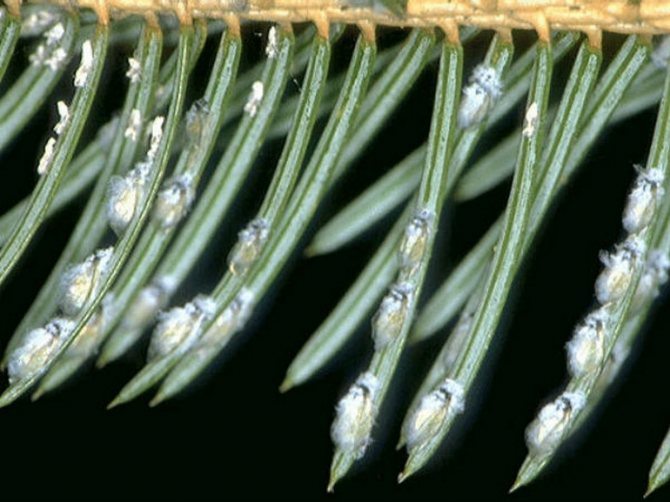


Fir hermes is considered one of the most dangerous species of aphids, and if you do not start the fight in time, the tree will die.
The most dangerous diseases for fir are:
- root cancer;
- browning;
- rust, or rust fungus;
- brown shute.
Diseases can be avoided by spraying the crown with pesticides and applying cold and hot fog. In case of yellowing of the needles and the appearance of fungi, it is recommended:
- remove affected branches;
- process the cuts with garden pitch;
- burn the remote branches and needles;
- spray the crown with 2% Bordeaux liquid.
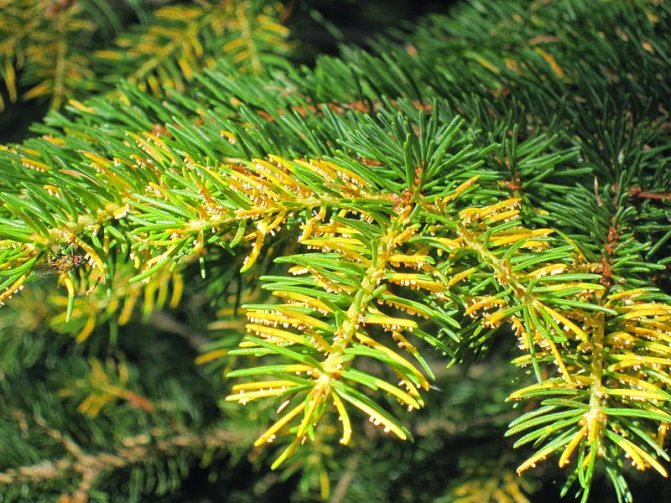


The causative agents of diseases can be non-observance of planting conditions, seedlings already acquired by sick, lack of moisture, attack of pests
How to dig up a fir
To remove a tree from the site (the reasons may be different - it is old, sick, or you just need to free up space), it is worth remembering that it not only needs to be cut down, but also to get rid of the stump and roots. For quick removal, you can use special equipment, but if this is not possible, you will have to tinker. You can get rid of wood mechanically or chemically. The first involves cutting down the trunk, digging in the earth around the root in a radius significantly exceeding the diameter of the trunk. On light soils, they resort to washing out the soil under the roots of the pressure of water.
In this case, it is worth taking care of the drainage of excess liquid from the root pit and constructing a drainage gutter. Bare roots are cut down with an ax or with the help of a winch they are taken out of the ground. If there is no way to resort to it, then the stump is swayed and twisted with a crowbar. You can also try to split it and remove it in parts. A longer method is chemical. For him, in the fall, deep holes are made in the remaining stump with a drill with a large diameter, they are filled with granules of "Urea" (urea), poured over with water and tightly wrapped with polyethylene.
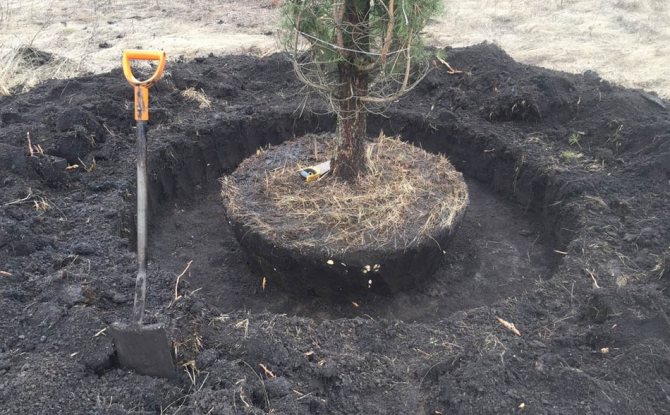


The result does not depend on you, it can be observed already next spring or in a year. This will make the wood softer and the stump easier to remove. Also, this method is harmless to the surrounding plants. Also, table salt, copper and iron vitriol, herbicides are used as chemical extermination. But such methods should be treated with caution, since they can harm the surrounding plantings, and the latter option is suitable only if the vacated space is not planned to be used for planting.
Learn how to transplant a fir to a new location.
The course of action is the same as for the urea method. It is possible to grow fir from seeds at home, although this will take time and some effort.This method is suitable if you need to get a lot of seedlings, but it does not guarantee the safety of varietal characteristics. It is quite difficult to get rid of an adult tree, therefore, the choice of a place should be taken with special care, since fir are long-lived plants.
Korean fir and balsamic - differences
Due to the presence of many types of conifers, gardeners often confuse plants, buying a re-grading from unscrupulous nursery growers. There is balsam fir, monochromatic, mountain, Caucasian, Greek and others. Due to its high decorativeness, the Korean variety of abies koreana is often found on sales next to the North American relative of abies balsamea, so it is advisable to know its main differences:
- The crown of the Korean fir is conical or spherical.
- The bark is reddish or ash-chestnut in color; in the old tree it is covered with cracks.
- The needles are two-colored - the underside is silvery, and the top is emerald.
- The needles are saber-shaped, up to 2 cm, soft.
- Fruits are lilac-purple, growing vertically.
- The dwarf plant abies koreana is slow-growing, 0.3-7 m high.
- Wild forms of Korean fir are tall (up to 15 m).


How to plant a plant at home
Before purchasing a growing fir, you need to carefully remove it with roots from the container in order to make out the rhizome. Like the plant itself, they must be fresh, and the earth moistened. It will directly depend on how you followed the instructions for caring in the store, it is so much easier to grow a plant at home. Important! You should buy trees only with an open root system - small and young saplings will better get used to containers. The older the plant, the more difficult it will be for it to endure the stress of the dive. Most stores offer to purchase a plant planted in a special substrate. Fir will not survive in this soil for a long time, so it is necessary to avoid these acquisitions. Saplings need to be purchased only with a lump of soil, these trees grow from seeds and are packaged from the manufacturer with a view to acquiring minimal stress during subsequent transportation. After transplanting into a new container, it is necessary to irrigate the soil well. To do this, it is advised to place the container in a sink, bucket or container of water for a couple of hours. After this procedure, the excess water should be removed through the drainage holes. Then the container with the plant should be placed in a decorative flowerpot. If the volume permits, you can pour a layer of expanded clay on the bottom and pour a little water to increase the humidity level.
Growing fir as a business
The constant demand for ornamental coniferous trees makes it possible to consider growing fir in the country as a way of earning money. However, fir can be used not only as an element of landscape design. Fir brooms are very much appreciated by lovers of bath procedures. From the needles of this tree, infusions and oil are obtained, which are used in the treatment of many diseases and are an excellent prophylactic agent. From fir, camphor is obtained, a substance widely used to treat infections of the respiratory tract, lymph nodes and other diseases.


Fir wood is not inferior in quality to pine or spruce. Therefore, it can be used in construction, as well as for the manufacture of various wooden fittings, decorative elements, joinery, furniture.
How fast the fir grows
The growth rate of fir, like other plants, depends on the variety, location and soil, care and fertilization. Since your plant is grown from seed, there is no definite answer on how the tree will grow. The first 5-6 years it will be small, because the root system is growing, then it will increase.
You will be interested to know how fir differs from spruce.
It is worth noting that outdoors and in a pot, the same cultivar will grow differently.So, if it is characterized by an annual growth of 30-40 cm, then on the site it will add about 20 cm in height, and in a container of 5-6 cm, in order to calculate the growth rate of a particular tree, you can take measurements of length once a year in one and the same time.







































