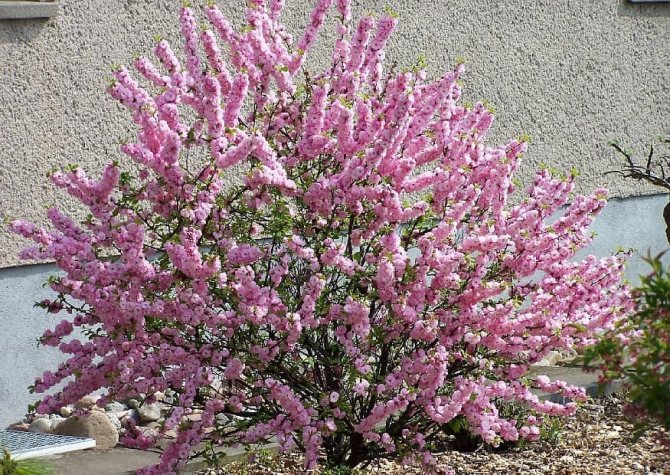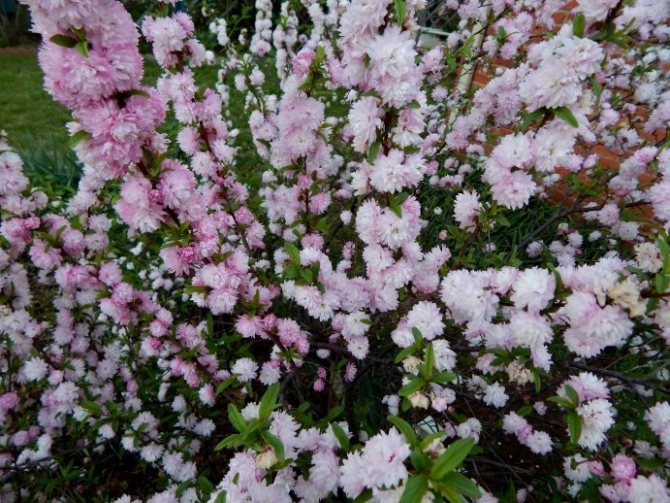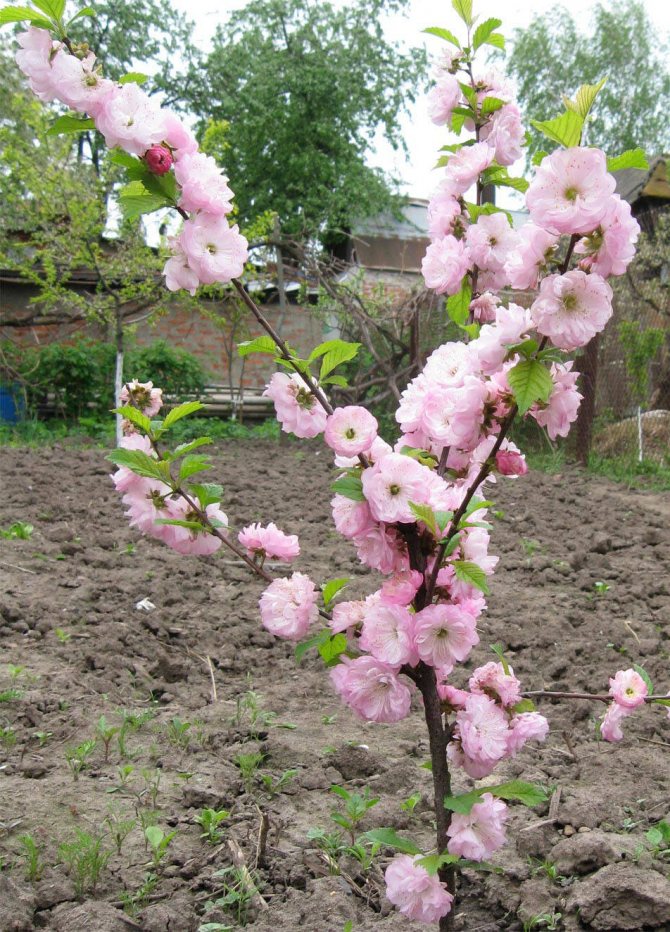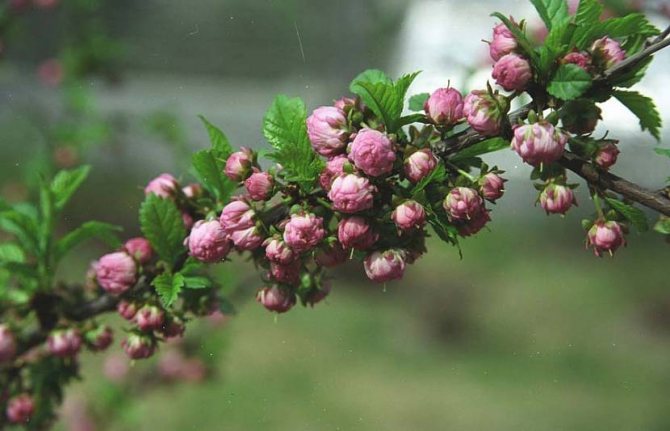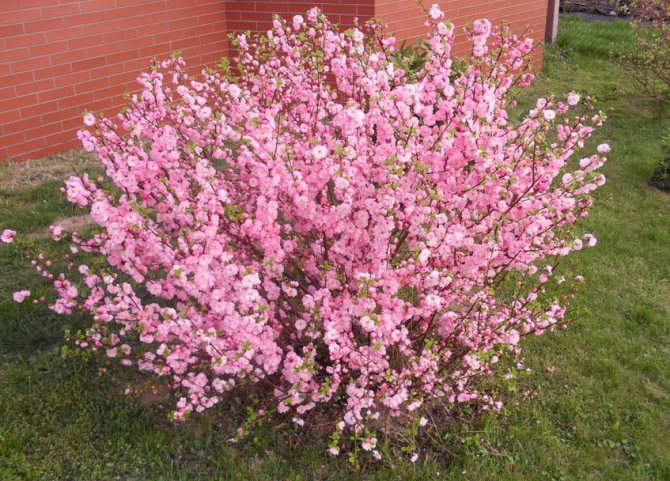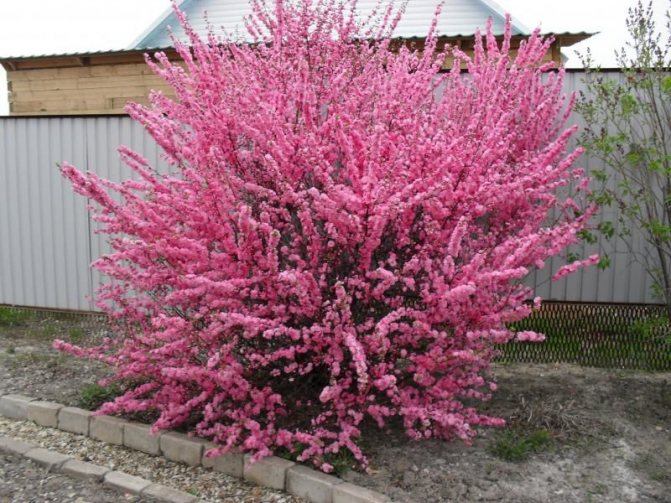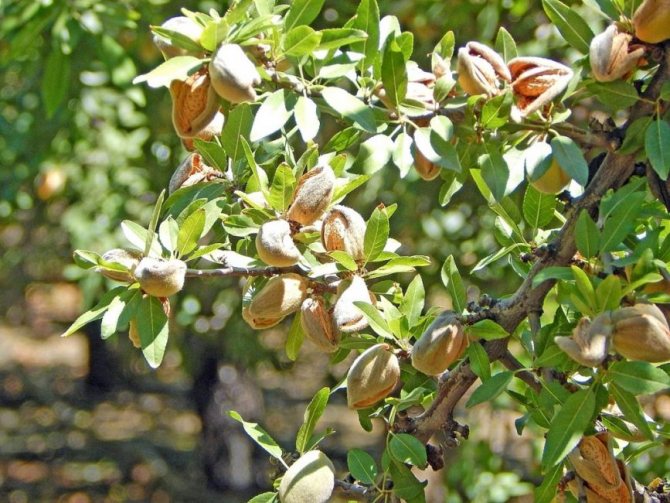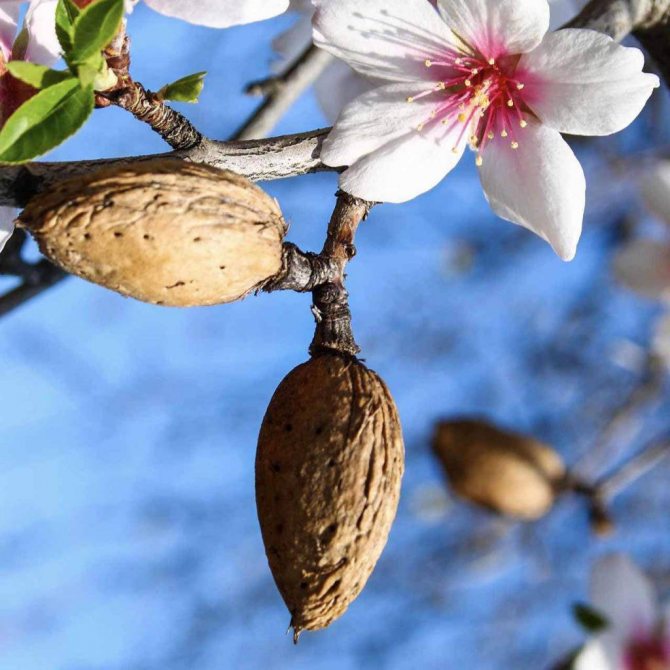
Almonds (Amygdalus) - a shrub or small tree from 1 to 6 m tall, famous for its spectacular flowering. Common almonds (A. communis) have been cultivated as a nut crop since ancient times. Low (up to 2 m) species of almonds are graceful, beautifully flowering shrubs, which are of interest as ornamental plants.
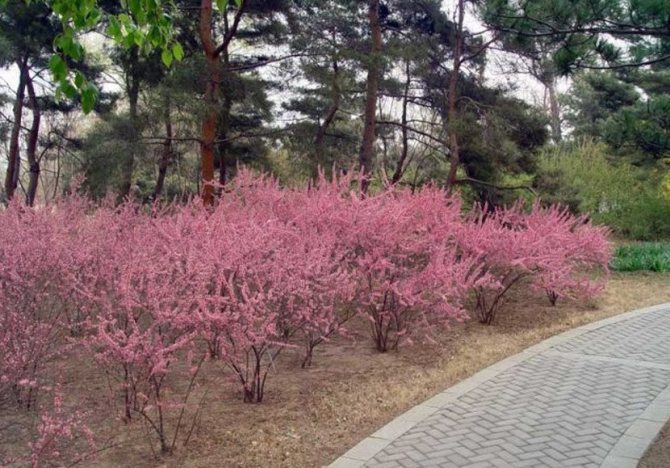
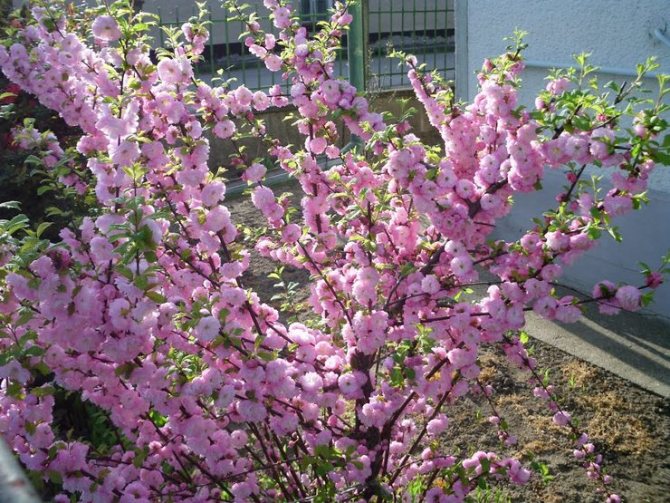
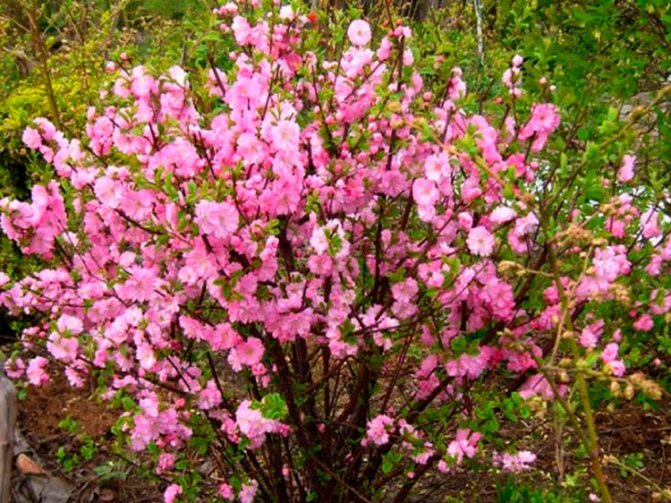
Such is the ornamental plant almond low, steppe, or bean (A. papa), which is small in size (up to 1.5 m in height). In spring, simultaneously with the blooming of the leaves, the bushes are covered with delicate, modest, but numerous pink flowers. At this time, the plant literally catches the eye. But even after flowering, thanks to its compact crown and graceful leaves, the bean tree looks attractive.
Another winter-hardy almond - Georgian (A.georgica) grows up to 1 m in height, has bright pink flowers.
Of the undersized ornamental almonds, the legume is perhaps the most resistant to adverse conditions. This type of ornamental almond shrub is winter-hardy, easily tolerates drought, but requires a lot of sun. Almonds are propagated by seeds and numerous shoots.
general description
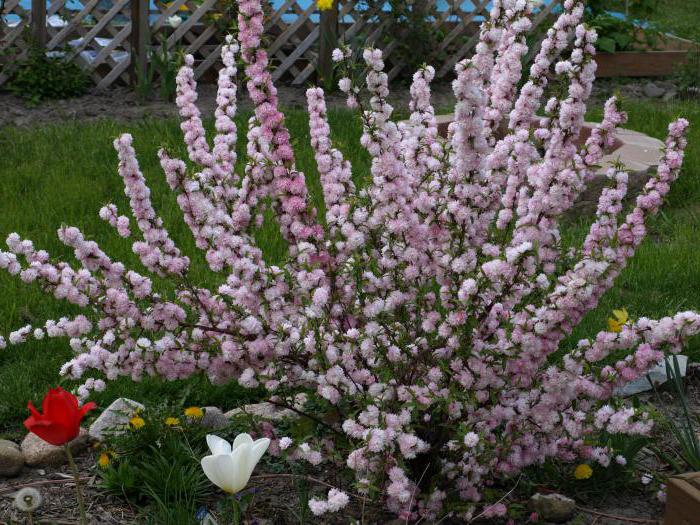


Many novice gardeners are interested in the question: is the almond low - is it a tree or a shrub? We will immediately dispel all doubts. This type of almond is a shrub. It belongs to the pink-flowering family and, with proper care, grows for many years. The bush can reach one and a half meters in height. The leaves are medium in size with an oblong dark green color. When the flowering period begins in early spring, the bush is covered with small pink flowers. Despite the fact that this plant came to us from the south, it tolerates frost perfectly and therefore immediately became a favorite among local flora lovers. Due to the fact that this is a southern plant, it also tolerates dry periods when there is no rain for a long time. This is mainly due to the special structure of the root system. The bush has strong main roots that go far into the ground and from there take moisture to feed the plant. There are also small branches of the roots, but the main roots still carry the main function. The fruits of the bush appear in the middle of autumn in the form of nuts. The nut is about six centimeters long and has a delicate aroma and pleasant taste.
Decorative almonds in landscape design: how a plant blooms (with photo)
Low almond is very popular in landscape design, which is suitable for small open areas and rockeries. In the background of a mixborder, it will become a bright spring accent, and then a good backdrop for perennials.
Even before the time when they began to plant decorative almonds in our area, this plant grew in the vast expanses of the Mediterranean. Little by little, the shrub began to spread and filled the territories of countries such as China, Czech Republic, Slovakia and others. In the middle lane, the cultivation of almonds is now by no means a rare phenomenon, since many plant species are well adapted to our climatic conditions. By the way, the three-lobed almond is a favorite among local gardeners due to its frost-resistant qualities and the beauty of flowering.The indisputable advantage of this shrub is also the fact that even novice gardeners can cope with it.
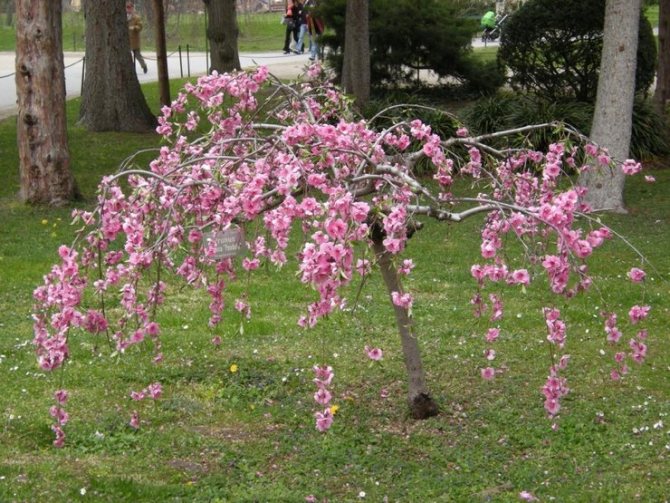
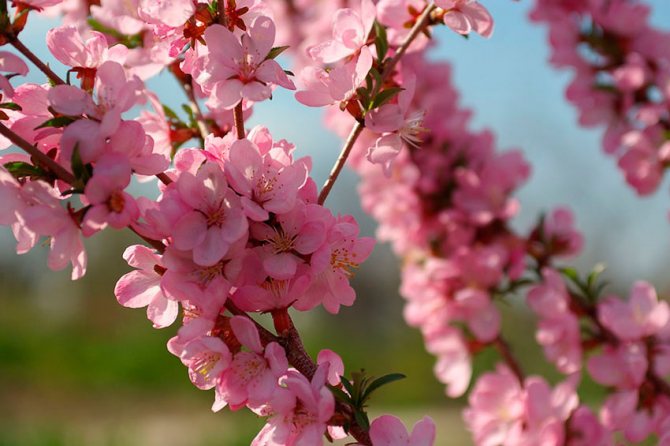
But it will not be possible to see the long-awaited results of their labors right away. When asked how almonds bloom, experts smile mysteriously and answer: "Unbelievable." Only this splendor can you observe only four years after planting the plant. This is its peculiarity. However, believe me, it's worth it: terry flowers of white or pink shades of stunning beauty will decorate your garden and fill with a wonderful aroma.
Take a look at the photo of how almonds bloom: this magnificent plant will decorate your garden for many years if you take care of it and provide a favorable environment for existence:
By the way, some believe that almonds are translated from Greek as "beautiful tree." Well, it is quite likely, since a riot of colors - purple, snow-white, flaming - cannot be conveyed by a single picture. Approximately 20 days a year, this plant allows itself to admire in our area - at the very end of April and until mid-May.
Varieties and types
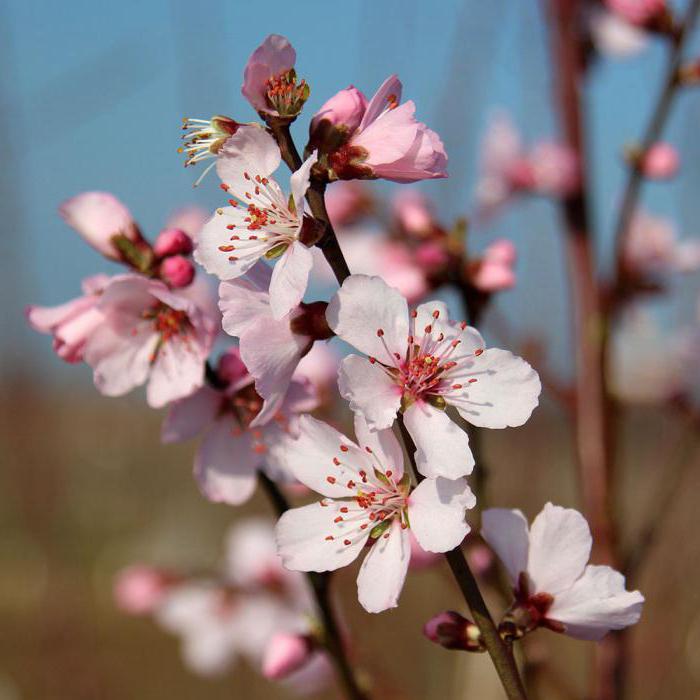


Low almond (bean) has many different names, but they all refer to the same species: low, steppe, dwarf, bean. But there are other types of almonds that I want to remember:
- Georgian,
- ordinary,
- petunik,
- three-bladed.
These species differ in that they grow not only in the form of bushes, but also grow into full-fledged trees, sometimes reaching three meters in height. Further, the shape and tone of the leaves, as well as the color of the buds, differ. Today we are interested in low almonds, and it is about him that we want to tell in detail. Indeed, in order for this shrub to grow and develop correctly, you need to know everything about how to plant it, how to care for it and deal with possible problems.
Description and flowering of an ornamental shrub
The almond tree reaches a height of 4-6 meters, and the shrub 2-3 meters. The rhizome consists of 3-5 skeletal roots, which are able to penetrate deep into the soil, thereby protecting against drying out.
The plant is quite branchy, while it consists of two types of shoots, which include shortened generative and elongated vegetative ones.
Dark green leaves are attached on brown petioles and have a lanceolate shape with a pointed tip.
An interesting feature of the almond is that it begins to bloom in March or April, much earlier than the time the leaves bloom.
Flowers such a plant consists of 5 petals painted in white or light pink. On average, the diameter of one flower is 2.5 centimeters.
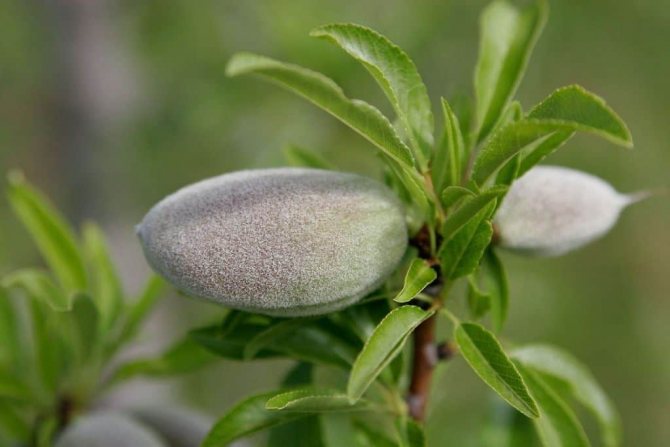
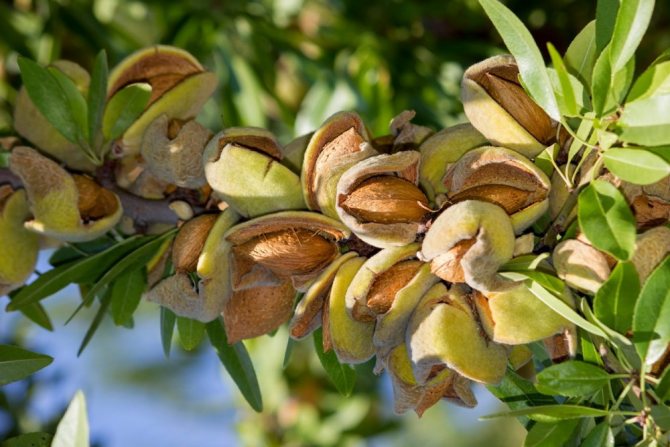
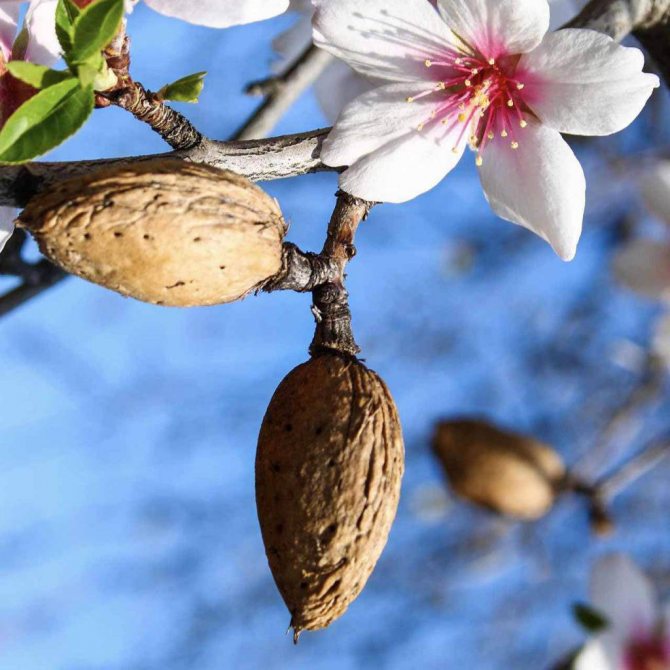
Almond fruit Is a dry and velvety drupe with a leathery and fleshy green pericarp.
After drying, the pulp is very easily separated from the oval-shaped edible bone and is 2.5 - 4 centimeters long. It is characterized by the presence of a large number of furrows.
The first fruiting occurs in the 4-5 year of the tree's life., but in full force it appears only for 10-12 years. With good care, the shrub bears fruit for 30-50 years.
Besides getting fruit almonds are also grown for decorative purposes... The pink or white foam of the flowers of such a tree not only decorate the garden in early spring, but also exude a unique aroma.
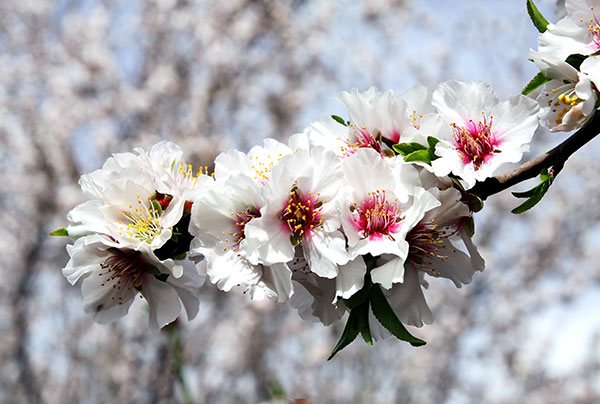


Almonds bloom in March-April with white or light pink flowers
Almonds are a plant that needs to be pollinated beforehand. There are two types of trees:
- the former need cross-pollination, therefore, at least 3 pollinators are planted next to the fruiting almonds, the flowering time of which must coincide;
- the latter are pollinated by bees, therefore, it is desirable that 2-3 hives stand next to the plant.
Initially, it was believed that almonds can only be grown in the southern regions, but with the development of scientific technology, breeders have developed varieties that, with proper shelter, can survive even the most severe winter.
Landing
Low almonds, described here, prefer a location in direct sunlight or, in extreme cases, where there is light shade. It is categorically impossible to plant a bush in a draft and in a place where the wind is constantly walking.
Having chosen the right place for planting, take care of the preparation of the soil. The acidity level should be around 7.5. If you want to create the most favorable conditions for the bush, then make a mixture of ingredients such as leafy earth (three parts), humus (two parts) and sand (one part). Next, you need to add lime or dolomite flour at the rate of 300 grams per bush. When planting several bushes, you need to leave a distance of about one and a half meters so that later the plants do not interfere with each other. In each hole, good drainage must be created so that there is no stagnation of water. This can be done with rubble or brick fragments, as well as sand. The whole process is as follows:
- We dig a hole of such a size that all the roots fit freely into it.
- First, we place a drainage layer on the bottom, which should be about twenty centimeters.
- Pour five centimeters of sand onto the drainage layer.
- We fill in the prepared soil and plant a bush there so that the neck of the root is above the ground.
Content
- Listen to the article
- Description
- Planting almonds When to plant
- Planting in autumn
- How to plant in spring
- Almond care
- When to trim
- How to propagate
- Beneficial features
Care secrets
Dwarf almonds require attention and proper care from their owner, so we recommend that you follow the following tips.
- Watering the plant should be moderate. The bush requires the most moisture during budding, but water stagnation at the roots should not be allowed. If the soil where the almonds grow is sandy, then you need to water more often. In order to understand when to water the bush, assess the condition of the soil and the degree of its dryness. After watering, be sure to loosen the soil to allow air to reach the plant's root system.
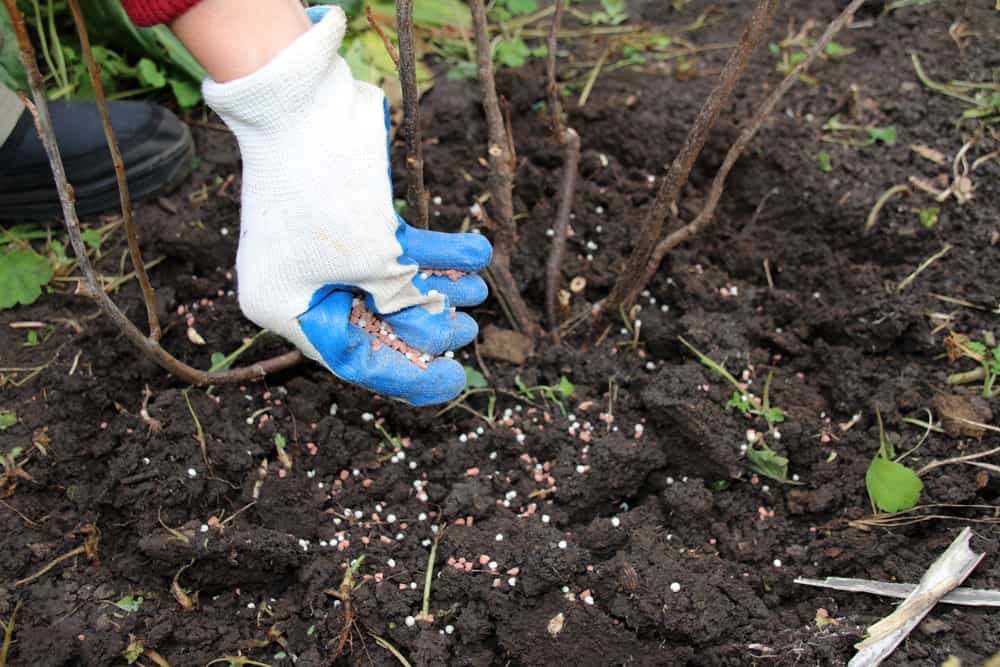
- Do not forget that the plant needs strength for growth, which means that it needs to be fed in the form of mineral and organic fertilizers. This is recommended in early spring. Mullein works well for this purpose. Then, in the summer, you can add superphosphate. It has a good effect on the quality of wood and yield. It is enough to take thirty grams for one bush. In the fall, you can feed with fertilizers containing potassium.
- At the beginning of spring, it is imperative to prune the shrub to maintain the correct shape. This helps to strengthen the roots and make the shrub more lush. It is necessary to remove all unnecessary branches, including those that grow towards the center of the bush.
How to care for decorative almonds
Let's take a closer look at how to grow almonds so that they fill the territory of your garden with a divine aroma and does not suffer from a lack of care and attention.
Growing and caring for almonds follows the same scheme as for any ornamental plant: the shrub should be watered, fed with fertilizers, cut and protected from any pests.
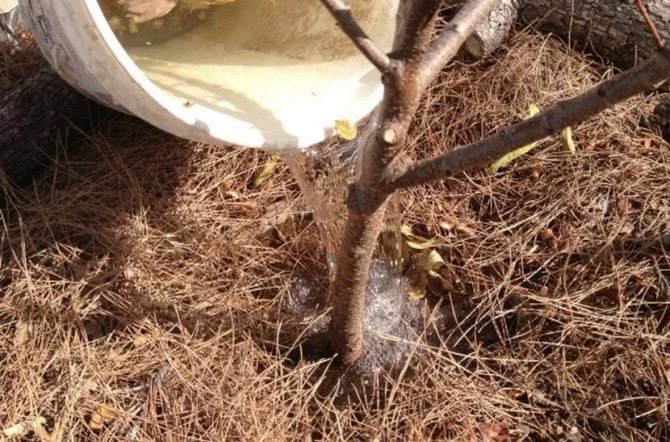
First, about watering. As you remember, stagnation of water in the soil of this tree is contraindicated. Therefore, it is necessary to water the shrub no more than once a week. In this case, just a bucket of clean water is enough.
Another feature in the conditions of growing almonds is that after watering the bush, it is imperative to thoroughly loosen the soil. You should deepen into the soil by 7 cm if it is a seedling, but for adult specimens, indulge in this procedure at a depth of at least 9 cm.Remember that the rest of the time - not only after watering - the area around the bush must be cleared of weeds.
Any plant needs to be fed. Therefore, when wondering how to care for almonds, remember that he needs in the spring, for example, feeding in the form of manure or mullein, but in the autumn period you need to add either superphosphate or potassium to the soil around the shrub.
Pay attention to the photo of a decorative almond, which is fed with nutrients in a timely manner: it gives a lush color and is protected from all diseases:
But in order to give the shrub a proper aesthetic appearance, caring gardeners trim their "pet". Pruning decorative almonds involves several stages: in the spring, for example, a sanitary haircut is carried out. With its help, the plant gets rid of sick, broken and those branches that thicken the crown. But shaping - a haircut that helps to give the crown the desired shape - occurs after the flowering of the shrub. By the way, in the eighth year of life, ornamental trees must get rid of old branches.
You should pay special attention to the cultivation and care of almonds in the middle lane: firstly, since our winters are characterized by very low temperatures, it is necessary to protect the shrub from frostbite. Cover the seedlings with either straw or dry foliage.
Do not forget just to make sure that the root collar does not rot and rot under this insulating layer. The situation is much simpler with already adult specimens: they are rarely sheltered for the winter. Just remember that winter-hardy types of almonds such as three-lobed, Georgian, steppe and Ledebour are the most suitable for our region. They tend to recover quickly after the winter cold.
Since you have already understood that frosts, in principle, do not pose a particular threat to this plant, you need to be on the lookout for another kind of danger - pests and diseases. A common disease is moniliosis, a type of fungal infection.
Most often, the fight against this scourge is to prevent it. This is why we said that almonds need regular nutritional support and appropriate soil. But if trouble does occur, use a variety of fungicides for the war against moniliosis - for example, the same foundation.
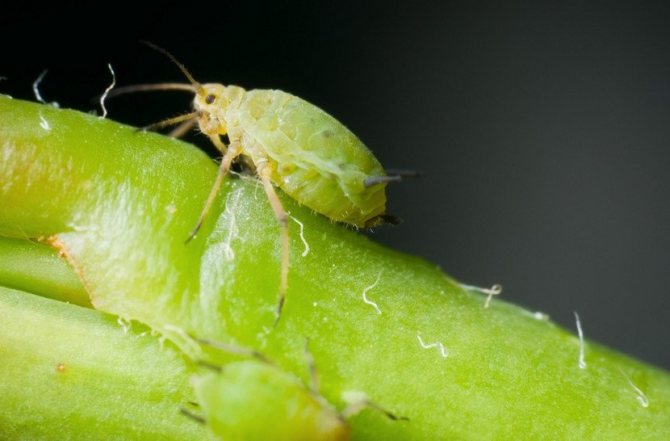
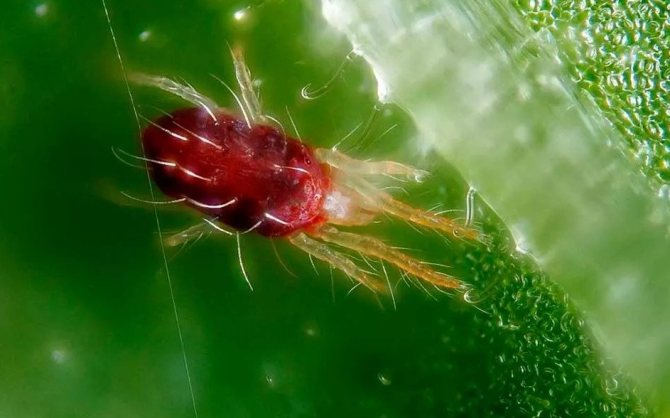
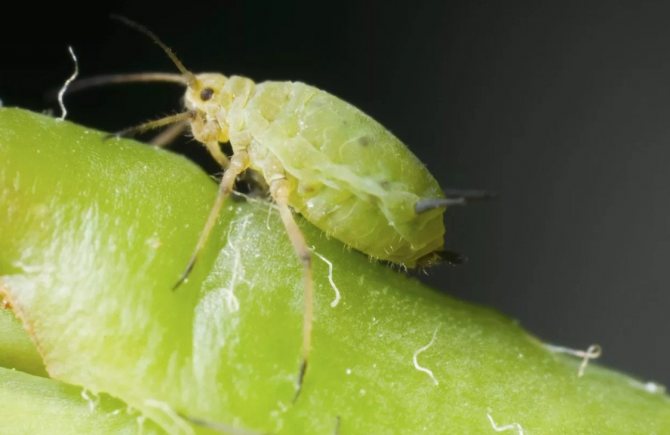
But in order to get rid of such creatures as ticks, cotyledons, leaf rollers and, of course, aphids, you should use a set of insecticides. One of the suitable options is Zolon. It is better to use Akarin for cleaning spider mites.
Plant propagation
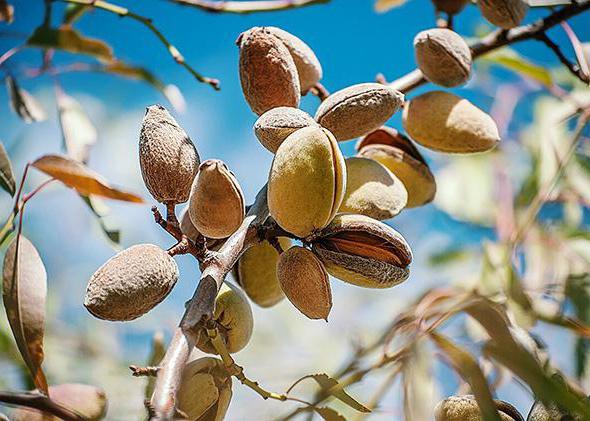


Low almonds can be propagated in ways:
- seminal,
- cuttings,
- vaccination,
- with the help of overgrowth.
The first method is that the seeds are planted in the ground at the beginning of spring, before that, having loosened the site and added fertilizer there. This should be done when the weather is warm. In this case, you will quickly get strong seedlings.
With the cuttings method in the middle of summer, you need to cut off a cutting with several nodules, place it in a solution that stimulates root growth for several hours. Next, you need to plant it in the soil, leaving a couple of nodes above the ground. With the onset of cold weather, the stalk must be sheltered from the cold.
The last two methods are also quite simple. An escape from the root must be dug up and transferred to a prepared place with the desired soil. And for grafting, you need to take branches that are already well ripe and graft them on trees such as a peach or plum.
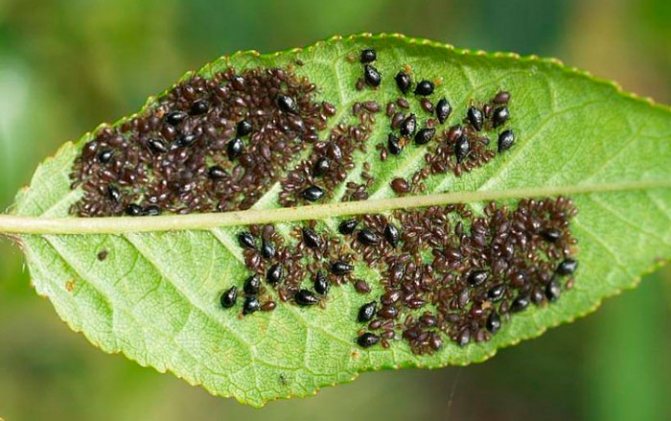
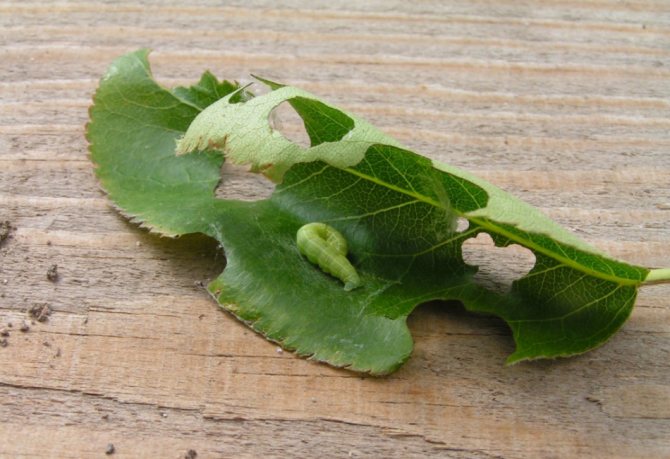
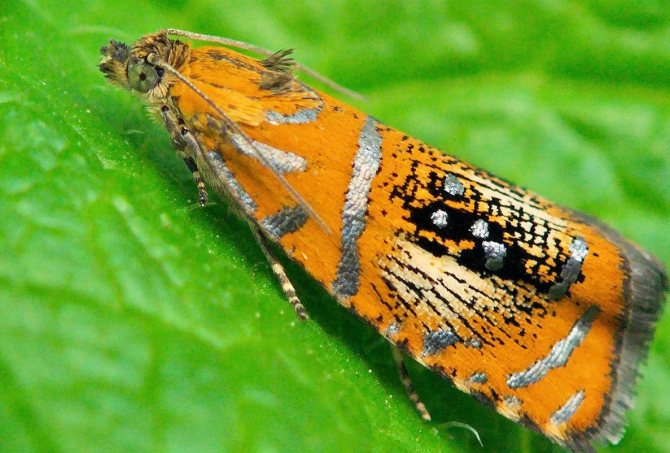
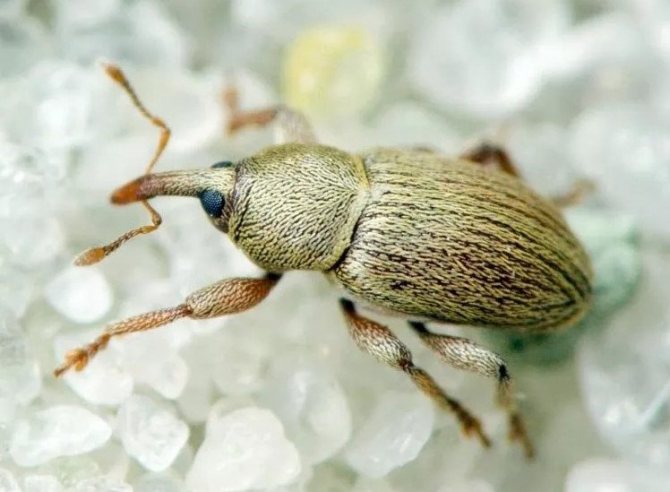
Pests and diseases of low steppe almonds
Diseases of almond shrubs are common in horticulture. It is impossible to protect low almonds from the influence of pests, but to reduce their negative impact is real. Diseases appear due to the following parasites:
- spider mite;
- almond seed-eater;
- aphid;
- leaf roll.
Light spots appear on the diseased plant, dark cinnamon outlines form on the stems. The flowers begin to look not very presentable, and the leaves begin to crumble.
You can help the steppe bean with soapy water. It should be applied several times a day with an interval of 2 days.
The nitrophene action will be beneficial before the flowers bloom. It will protect the shrub from the effects of the leafworm.
Low almonds can be cured of fungal diseases by treatment with fungicides: "Topaz", "Skor", "Fundazol", "Kuproksat". Insecticides (actellik, fufanon, zolon) will help eliminate insects. You can destroy spider mites by treating almonds with solutions of castor oil, acarin or agravertine.


Fundazole will help with fungal diseases
Pest control
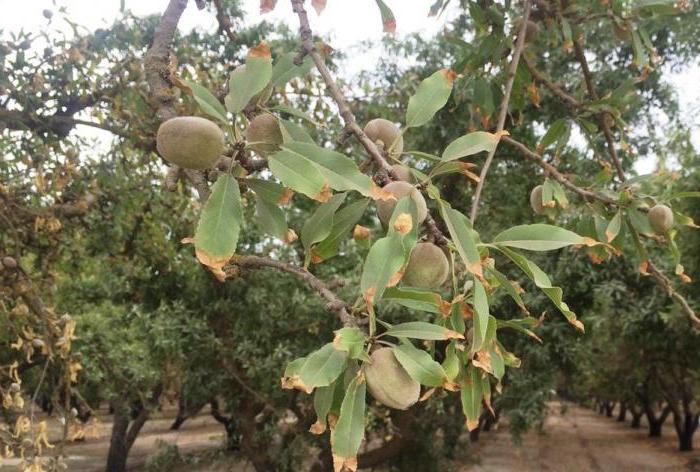


The shrub has average immunity to attacks from various insects, so it needs help. To do this, it is necessary to carefully monitor the condition of the almonds and, at the first sign of a problem, immediately begin to fight the pest.
- The leaves began to curl up into a tube? So a leafworm has visited you. In this case, you need to spray the bush with a 2.5% nitrophene solution if the process began before the buds appear, and chlorophos with a concentration of no more than 0.3 percent will help to destroy the caterpillars.
- Aphids are a frequent visitor to the almond bush. You need to deal with it in the standard way, spraying the plant with a solution of laundry soap, making a mixture of 200 grams of soap per ten liters of water.
- The application of a lime layer on the tree trunk saves from the bark beetle. It is recommended to add glue to the mixture to prolong the life of the protective agent.
Almond pruning
When to prune almonds
Almonds need formative and sanitary pruning, and mature trees require a rejuvenating treatment. Sanitary pruning is carried out in early spring, before sap flow begins, and in autumn, when the almonds enter a dormant period, and formative pruning is done after the almond has flowered.
How to prune almonds
An almond crown is formed like a plum, apricot, peach or nectarine - three tiers of skeletal branches are removed. Immediately after planting the seedling, it is cut off at a height of 120 cm, while the stem at the tree is formed with a height of 50-70 cm.
When thinning pruning of fruit-bearing trees, thickening crown and improperly growing branches are removed. When flower buds freeze, annual shoots are shortened.
Pruning almonds in spring
After winter, even before the buds begin to bloom, frozen annual growths are shortened in almonds, cutting them to healthy tissue, and broken, diseased or deformed branches and shoots are removed. After the end of flowering, they begin the formative pruning of the tree. On a seedling planted in autumn or spring, there are usually at least three branches located at a distance of 15-20 cm from each other - they are shortened to 15-20 cm, and new tiers of skeletal branches are laid on the central conductor for the next 2-3 years, which should be one from another at a distance of 20-30 cm.
The shoots that are unnecessary for the formation of the crown are pinched several times over the summer, and those that are needed are shortened no later than July, as soon as they reach 50-60 cm in length. In the second and third years of almond growth, unnecessary shoots are cut out, the rest are shortened. Upon completion of the formation of the crown, the central conductor is cut so that the last skeletal branch of the almond is 55-60 cm below the conductor.
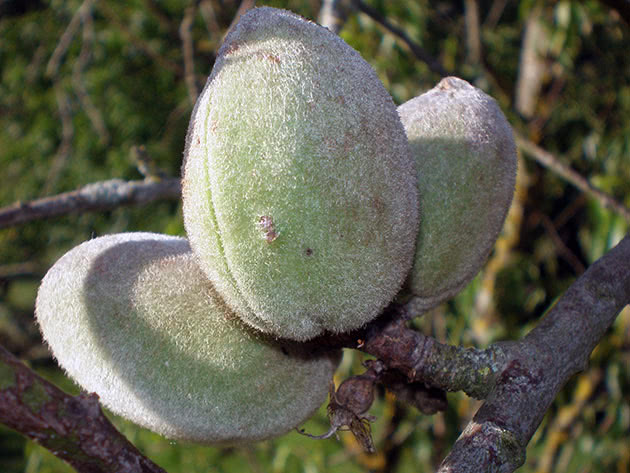


Trees that have entered fruiting with a formed crown almost do not need pruning, you just need to cut fat shoots into a ring, and shorten broken ones to 3-4 eyes.Annual shoots that do not interfere with the correct development of branches do not need to be cut.
Pruning almonds in the fall
In autumn, after leaf fall, they carry out sanitary pruning of trees and shrubs: cut dry, broken, diseased and thickening shoots and branches. If you have to cut or saw down a thick branch, do not forget to process the cut with garden pitch, and if for some reason you did not have time to prune the almonds before the beginning of winter, transfer sanitary pruning to spring.
- Apple tree columnar: planting and care, pruning and varieties
Application methods


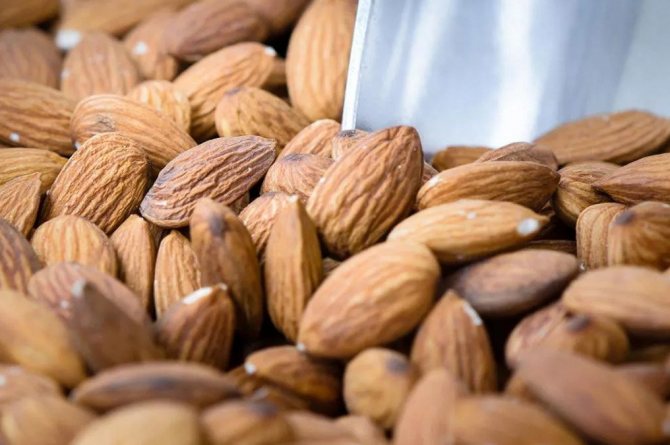
Steppe almonds are attractive not only for culinary specialists with their fruits, but also for landscape designers, as well as for cosmetologists. The nuts themselves are used in food in various dishes. The nut contains a large amount of vitamins, minerals and other beneficial substances. Moreover, it is simply delicious. Also, various drugs are made from it in folk medicine in the treatment of diabetes mellitus, asthma, anemia and other diseases. Almond oil is widely used in cosmetology as part of masks, creams, shampoos and gels. And the beautiful bush itself is used in the design of private plots and public areas in combination with other bushes and flowers.
Specific traits
The Latin name of the plant is Amygdalus nana, it is also known as low almond or legume.
His homeland is the steppes, forest edges and slopes of ravines in Siberia, Asia and Eastern Europe. Gradually, from the wild, a rare handsome man began to be planted in gardens.
- The height of the shrub is about 1.5 m. The crown is neat, ovoid or spherical in shape.
- The bark is brown, often tinged with red.
- The root system is fragile.
- The leaves are long, but narrow, leathery, rich green.
- The flowers are 2-3 cm in diameter, the flowering tree lasts about a week. In this way, almonds resemble sakura.
- Fruits are egg-shaped, up to 2 cm long, ripen by the beginning of autumn. The fruits are rich in vegetable oils, which are used for cosmetic purposes, and the kernels are added as a spice to meat dishes, but eating them raw is dangerous to health.


Eating raw steppe almonds is dangerous to health
Steppe almonds are suitable for growing in almost any, including very poor, soils, in cold or arid regions and in industrial cities.
Germination of seedlings from seed
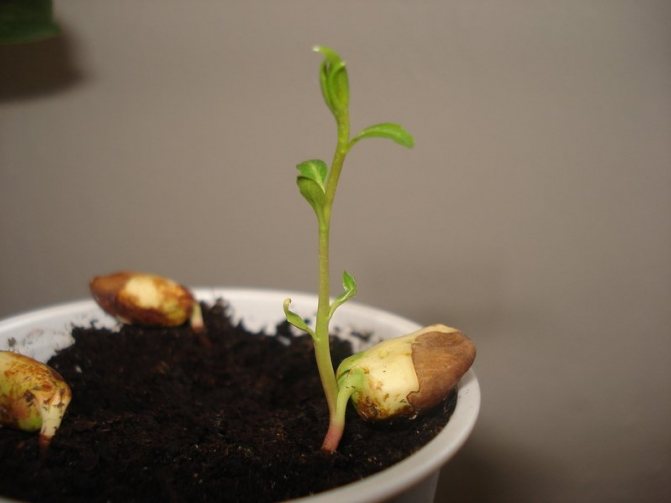
Under natural conditions, almonds propagate by seed. This is a rather lengthy process, but this method can be used to obtain a stock for a varietal cuttings, if it is not available at the summer cottage. Fresh, unprocessed almond seeds are used for germination. It is important that they do not have traces of rust, rot, mold.
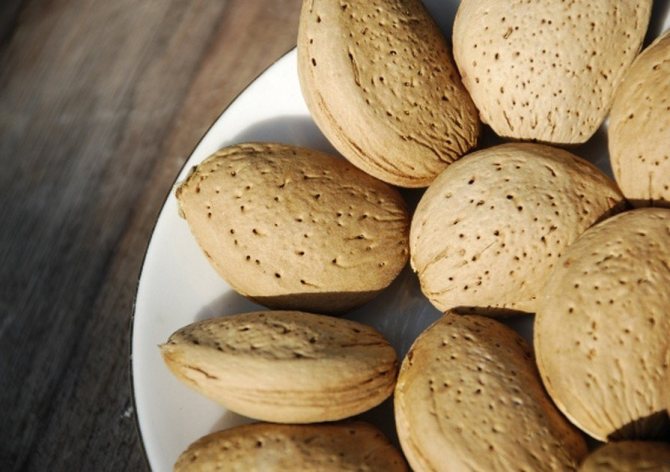


Under natural conditions, almonds propagate by seed.
For planting in spring, seeds must first undergo a stratification process - soaking for 6–8 hours in a growth stimulator and subsequent storage for 3–4 months at a temperature of 2–5 ° C (for example, in the vegetable compartment of a household refrigerator).
Sow the seeds as follows:
- grooves with a depth of 8–10 cm are made in the soil with an interval of 50 cm;
- with a distance of 10-12 cm, holes are made in the furrows, where 2-3 seeds are placed, burying them into the ground by 3-5 cm (then a stronger seedling is chosen for cultivation).
Germinated seedlings need standard care - watering, weeding, loosening the soil. When the plant reaches a height of 30 - 50 cm, all its branches located at a distance of 10 cm from the root collar are cut off. After that, the seedlings are transplanted to a permanent place.
Planting seeds in the open ground in autumn is not recommended, as the seeds can be destroyed by rodents.
Fertilization
Almonds do not require frequent fertilization. While the tree is young, you can feed it 2 times a year - in spring and late autumn.And a newly planted seedling does not need to be fed at all in the first year of life, because it will have enough of those fertilizers that the gardener brought into the planting pit.
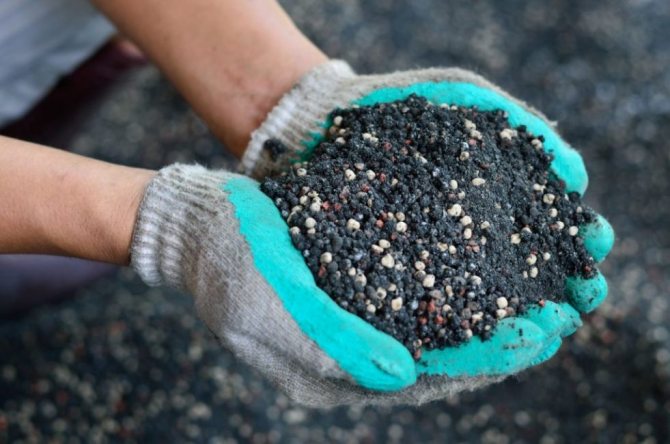


In the spring, nitrogen fertilization is necessary
Almond feeding is carried out according to the following scheme:
1 In the spring, before the first watering and loosening, nitrogen fertilization is applied to the trunk circle. You can use nitrate for this, at the rate of 20 g of the drug per 1 bucket of water.
2 In the fall, when the site is being digged, a complex of fertilizers is introduced into the almond tree trunk - 1 kg of compost or humus, 20 g of potassium sulphide, 20 g of double superphosphate.
back to menu ↑
See also: Pine in the yard: secrets of growth, folk signs, tricks of planting in the open ground and caring for it (55+ Photos & Videos) + Reviews
Shelter for the winter
Shelter for the period of cold weather is necessary for all plants, regardless of age or where the almonds grow. If the garden is located in the southern strip, insulation for almonds is not so critical, but it is better to keep young seedlings all the same. Of course, if the tree has already "grown" by 4-6 meters, it will not work to cover or insulate its branches, but you can try to take appropriate measures regarding the trunk.


It remains to pull the insulation over the frame - the bush will not freeze
Experts recommend insulating even frost-resistant varieties, such as Steppe Almond, aka Low, Russian, Bobovnik, or Almond. Some varieties of this frost-resistant species are bushes, not trees, but the taste and benefits of the fruit do not get worse from this.
To protect the plant from the cold, you can take the following measures:
- In early August, remove the apical buds on the shoots. Thus, it will be possible to accelerate the lignification of the shoots and they will better tolerate frosts.
- Cover young (required) and adult (highly desirable) plants 15 cm or more with breathable material - bunches of straw or a bunch of dry leaves. You just need to make sure that the covering material is not sick, since humidity during a thaw or early spring can contribute to the infection of the tree with pathogenic microorganisms. With the first snow, you can begin to form snowdrifts around the tree trunks.
If the crown of young trees consists of relatively bending shoots, they can be collected "in an armful", tied with twine and wrapped in agrofibre. On a more spreading and more elastic crown, you can try to throw lutrasil.
Harvesting and storage of crops
When the almonds ripen, the oval shell of the fruit begins to crack along the lines, after which it is easily separated. Inside there is a bone up to 30 cm long, oval-elongated or drop-shaped, beige or brownish.
Harvesting of the ripe crop begins in late July. The bones are freed from the pericarp and dried in the sun. If unrefined grains are harvested, they can be stored in cloth bags. Choose a storage place that is dark and well ventilated.


Growing
Almonds are an ornamental shrub that a novice gardener can easily grow. Some of its varieties are standard, having lanceolate leathery foliage with serrated ends and straight thin branches that create a spherical crown shape. Almond blossoms often begin 5 years after planting. Together with pink fragrant flowers, densely enveloping the branches, leaves open in April-May. Flowering lasts up to 3 weeks, attracting bees. Its fruits are inedible nuts, covered with a shell.
Reproduction
In the wild, ornamental almonds are propagated by seeds. Cultural varietal shrubs are bred by the vegetative method - budding, dividing, stump shoots, cuttings, layering, seeds.
Kidney vaccination
Budding is carried out in July-August. Ornamental almonds are grafted on plums, cherry plums, apricots.
- choose a strong one-year-old seedling with a root neck thickness of at least 1 cm and a well-developed bud;
- a T-shaped incision 10 cm above the root collar is made on the rootstock;
- a vegetative bud cut off with a heel from a bush of the required variety is inserted into it.
The vaccine is wrapped with a film, which is removed after a month and a half. The engrafted bud grows actively starting in the spring of next year. A shrub or tree is formed from the resulting shoot, which is transplanted to the chosen place.
A simple breeding method for further cultivation of almonds. The overgrown shrub is divided into the required number of parts and planted.
Breeding with stump shoots
After pruning the plant, many young animals appear. When its roots are strengthened by the next year, the shoots are planted from the mother bush.
They are harvested in the summer, planted as seedlings. For this, cuttings with 2-3 nodes are chosen. When landing, only one node is left above the ground. Plants cannot survive the first wintering without insulation. Cuttings are covered with dry foliage, sawdust, straw.
Shoots are taken to the side, bent, fixed, covered with earth. After a year, roots appear on the layers. After their strengthening, the layers are cut off from the mother bush.
They are planted in the fall in a hole 8 cm deep.If planting is carried out in the spring, the seeds undergo a 4-month stratification and buried 6 cm in the soil.


Decorative almonds are unpretentious in planting and care, but it should be borne in mind that they are photophilous, they cannot stand shade and drafts. You need to choose a planting site on the south side of the garden in a sunny or slightly shaded place. It is planted in late autumn or in spring, when warm weather comes and the risk of frost during the growing season passes.
The shrub grows poorly on acidic saline swampy soils. The place reserved for planting is cleared, removing weeds. When planting one individual, you should not count on fruits. The plant is cross-pollinated. If a summer resident wants to see decorative rounded fruits on almonds, he needs to plant at least two bushes at a short distance.


A pit is dug 30 cm deep. A drainage is poured into the bottom - a mixture of sand and gravel. The roots of a one-year-old seedling are neatly laid out in a circle and covered with earth. Before planting, the roots can be dipped in a clay chatterbox. The soil is enriched with compost, sand and leafy soil. The trunk circle is watered with a bucket of water. When the soil settles, a support is installed so that the few roots of the plant can gain a foothold. Mulching is carried out with dried soil or peat. In this case, it is necessary to avoid getting mulch on the tree trunk.
Planting and care includes watering, loosening, feeding, pruning ornamental almonds.
Water it as needed to avoid drying out the earth. During flowering, the soil moisture must be monitored especially carefully. Lack of moisture leads to rapid flowering. A bucket of water when watering a bush is enough. If the soil is very wet, there is a risk of root rot. After that, the soil is loosened and weeds are removed.
In the spring, the near-stem zone is flavored with organic matter - mullein, ammonium nitrate, urea. In the fall, potassium sulfide with double superphosphate is added per square meter, 20 g each.
Ornamental almonds, like all plants, when planting and caring for them, need spring sanitary pruning of the shrub immediately after flowering. Sick, dry, crown-thickening branches are removed. Places of cuts are treated with garden pitch. A shaping haircut is carried out if necessary. The branches that interfere with each other are cut off, choosing the one that is more advantageous in the crown. A young seedling in the second year is reduced to a height of 1.2 m. Within 4 years, a crown is formed in the form of a bowl. Then the bush is thinned out.


Preparing for winter
In August, the apical nodes are cut off from the plant for early lignification. This helps the bush to survive frosts without freezing the shoots.Young seedlings are covered with dry foliage, and adult plants can do without insulation.
The almond bush is susceptible to various diseases.
- Gray rot. For salvation, all affected branches are removed and burned after flowering. Then the plant is treated with fungicides.
- Curly foliage. Diseased leaves are plucked, burned, and healthy ones are treated with Bordeaux liquid.
- Rust. Almonds are sprayed with sulfur powder.
- Moniliosis. Every 2-3 weeks, the plant is treated with Bordeaux liquid.
The shrub can be overcome by aphids, plum moth, leafworm, spider mite. All of them are destroyed by insecticides. For prevention, you can use chemicals that will protect the garden area from pest attacks in advance.
Common almonds
Has no particular decorative value. Divided into sweet almonds and bitter almonds. Sweet nuts are used in the food, cosmetic and pharmaceutical industries. Bitter contains poisonous hydrocyanic acid and is not suitable for consumption. It grows up to 3-8 m. The thermophilic tree with reddish branches resembles a sweet cherry. After pink or red flowering, it is covered with oblong foliage.
Read also: Sea buckthorn buckthorn - cultivation, care and use
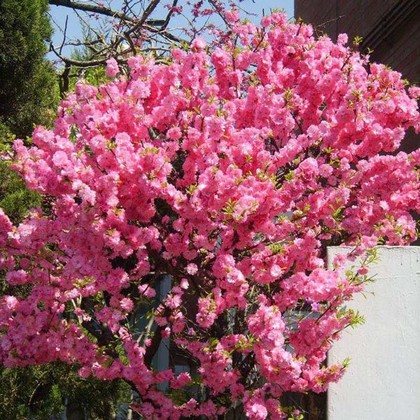
Georgian almonds
Fruiting from the age of seven. Frost-resistant, growing up to 1 m. It blooms in a bright large pink color. Produces bristly fruits surrounded by leaves. Loves slopes, edges, hollows.


Ledebour almond
The plant has large, long, dark green leaves. Violent pink bloom begins earlier than other species and lasts almost 3 weeks. Fruiting from 10 years. It is grown mainly in Altai.
Low almonds (Bobovnik)
In the wild, it is found in the lowlands of Siberia and Asia. Gray erect branches form a spherical crown, abundantly covered with narrow leathery foliage. It appears at the same time as pink flowers. Blooms for 1-2 weeks. Undemanding to soil, frost-resistant, light-loving plant. It tolerates any pruning well. Propagated by layering, seeds, grafting. Grown as a cultivated plant in the middle zone in white-flowered and Gessler forms with large pink flowers. Its famous varieties include:
- White sail - almond covered with small white flowers;
- Anyuta - with bright deep pink flowers;
- The dream is of a delicate pink color;
- Mediator - created by Michurin, with a pale pink color. Possessing high frost resistance.
Almond Petunnikov
In the wild, it grows on slopes with rocky ground, forming impassable meter thickets. Straight shoots are strewn with shortened twigs of a light fawn color. Long leaves with pointed tips appear after flowering. The frost-resistant plant, calmly tolerating drought, pleases the eye during flowering and during fruiting.
Almond Luiseania or Three-bladed
A bush with a spreading crown, covered with fertile dark gray shoots and foliage that appears on the branches in bunches. The flowers are dark pink, sometimes red, and grow in pairs. Flowering takes place from the beginning of May and lasts 2-3 weeks.
Several varietal species of Luiseania have been bred:
- Captivity is a wide spreading two-meter shrub with double pink flowers. After ten days of flowering, the branches are covered with dark leaves.
- Kievskaya. A bush or tree reaching 3 m. Pink flowers with a delicate aroma attract honey bees for a week.
The three-lobed almond has a lot of hybrids and varieties that are radically different not only in the type of flowers, but also in the duration of the flowering period:
- Svitlana is a variety bred by Ukrainian breeders with light flowers;
- Tanyusha is a densely flowering almond. Shrub with double, twisted petals;
- Ruslana is a hybrid with simple pale pink flowers that turn white towards the end of flowering;
- Snows of Uimura - pale pink double color, towards the end acquiring a creamy shade;
- Hybrid No. 3 - pale pink flowers growing on long peduncles. Almonds are similar to sakura when blooming.
Reproduction of almonds from an adult tree
Cultivated almonds can be propagated vegetatively - by separating cuttings, shoots, offspring from the mother plant with their subsequent development to a whole organism.
Cuttings
For this method, planting material is prepared in the second half of June:
- semi-lignified cuttings with two nodes (15 -20 cm long) are cut from the tops of the shoots of the current year;
- cuttings are immersed in a growth stimulator for 16 hours;
- a soil mixture of equal parts of sand and peat is poured into containers or boxes;
- cuttings are planted in planting containers and for further rooting for 20-30 days are placed under a film in a cold greenhouse;
- after this time, the cuttings are transplanted into open ground for growing.
Root shoots
With the help of intensive pruning, the active appearance of young growth around the almond tree or bush is achieved. In the second year of life, when the root system is fully formed in the offspring, they are separated from the mother plant and transplanted to a permanent place. Further care for them is carried out in the same way as for annual seedlings.


Cultivated almonds can be propagated vegetatively - by separating cuttings, shoots and offspring from the mother plant
Layers
For reproduction by layering, the most flexible shoots of the lower tiers are chosen. They are laid on the ground, fixed in several places with wooden or wire pins and covered with a layer of earth 15–20 cm thick. For better rooting, the shoots are watered throughout the season, the soil around them is loosened, and weeds are weeded. After the root system of the cuttings has developed well (usually after a year), they are removed from the main plant.
Budding
To preserve the characteristics of the variety, vegetative propagation is used - budding on the stock. To do this, you can use any type of almond, including bitterseed almonds. The operation is carried out in mid-July - early August.
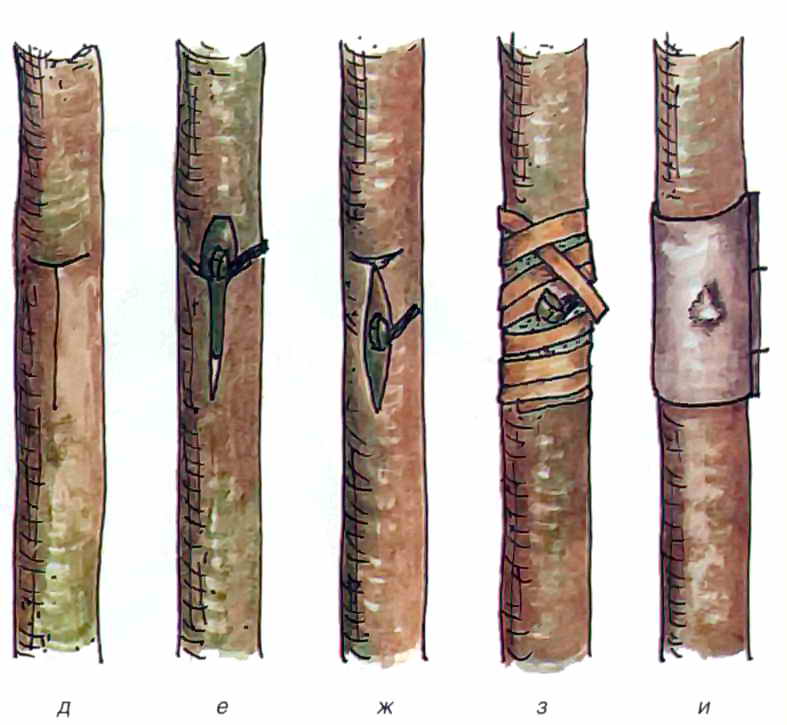

To preserve the characteristics of the variety, vegetative propagation is used - budding on the stock
- Choose a stock - an annual well-developed seedling with clearly formed eyes and a root collar thickness of at least 8 mm.
- A vegetative bud (scion material) is cut from the desired tree together with a layer of bark.
- Having retreated from the base of the stock to a height of 10 cm, a T-shaped incision is made on the trunk, into which the scion is inserted.
- The budding site is tightly tied with a film or tape, leaving the kidney outside.
- The harness is removed no earlier than after 1.5 months.
The eyepiece, which has grown to a height of 10 cm, is spud up and this operation is periodically repeated. The emerging shoots on the stock and the oculant must be removed.
Is it possible to grow almonds in your garden
Almonds, both fruiting and ornamental, are not exotic plants. Subject to the terms and rules of agrotechnical work, growing almonds on a personal plot does not present any particular difficulties.
A mistake that novice gardeners often make is that they do not ask the manufacturer or seller whether the selected variety is adapted to a specific climatic zone, what is its dormancy and flowering time.


Subject to the terms and rules of agrotechnical work, growing almonds on a personal plot does not present any particular difficulties.
For a plant, it is not so much low temperature values that are dangerous, but its sharp drops. Almonds have a short deep dormancy phase, the buds are able to move forward during winter thaws. The frosts that followed the warming ruin the generative buds, flowers and ovaries, which leads to a sharp decline in the current year's harvest. Even in the southern regions, for successful cultivation of almonds, it is better to choose varieties with a long dormant period, blooming in late March - early April.
Timely formative and health-improving pruning of the crown and shoots is important for good fruiting. This operation is carried out after the almonds have flowered: the frozen, dried branches and shoots that thicken the crown are cut off.
Harm and benefits of fruits
Any fruit that grows on the ground has a large number of positive and negative properties. For example, almonds are recommended for:
- blood purification;
- removing bile;
- increasing potency;
- calming the nerves.
Almond fruits can cause allergies
Milk is also produced from this nut, which is excellent for cleansing and softening the skin.
Also, doctors were able to prove that it is almonds that perfectly stimulate the work of the human brain.
But this fruit can also harm the human body, for example:
- causes allergies;
- the nut contains a lot of fat and calories;
- the fetus is poorly digested by the body.
Many gardeners know that the almond bush is not only beautiful when it blooms, but also smells very good. To all this, you can also add the divine taste of the nuts themselves.
But in order to make the purchase of this nut for planting, it is recommended to contact a specialized store.
Today, the cost of almonds fluctuates. This is due to the fact that there is some financial instability on the territory of our country. But, despite this, gardeners are increasingly planting almond bushes on their plots.
Almond preparation for wintering
Almonds should be prepared for winter in summer. First of all, the gardener needs to pinch the tops of the branches to allow them to lignify faster and not freeze in winter.
Young bush should be covered with dry leaves and lutrasil to a height of 15 centimeters from the ground. It is also necessary to ensure that the root collar does not begin to rot under the snow.
There is no need to cover adult bushes and trees, they are frost-hardy, and even if some branches freeze, the culture will quickly recover in spring.


Where to plant - practical and aesthetic aspects of site selection
Considering that almonds grow very tall, they should be planted where it is spacious. If you plant it too close to other plants, then over time, its crown will shade all the space around.
Also, when choosing a site for planting, it must be borne in mind that this plant bears fruit only with cross-pollination. Therefore, at least two or three more almond trees, pollinating varieties, will have to be planted around the first almond. If the neighbors already have almonds growing, the plants still do not get pollinated, since they must be very close to each other.


Arrangement of trees
The best place for planting a tree is a sunny (partial shade is allowed), protected from winds and drafts. If the gardener ventured to plant almonds in the shade of tall buildings or trees, the tree's growth process will be slowed down, and the productivity of the plant will be low.
Soil for almonds:
1 Suitable - black soil, loam or sandy soil. Well air and water permeable, with deep groundwater. The plant thrives on calcareous soils with a PH of 7.7.
2 Unsuitable - acidic or saline, chloride or with a high groundwater table.
You also need to make sure that the tree fulfills its decorative role - why hide such beauty from eyes in the far corner of the garden? A group of 3-5 plants will look great along the fence, which will also protect the trees from the wind.
back to menu ↑
See also: Raspberries: how to care for them to have a good harvest? In spring, summer, autumn and winter: features of watering, feeding, pruning of shrubs and its remontant varieties





















































