- 28 October, 2018
- Houseplants
- Irina Maskaleva
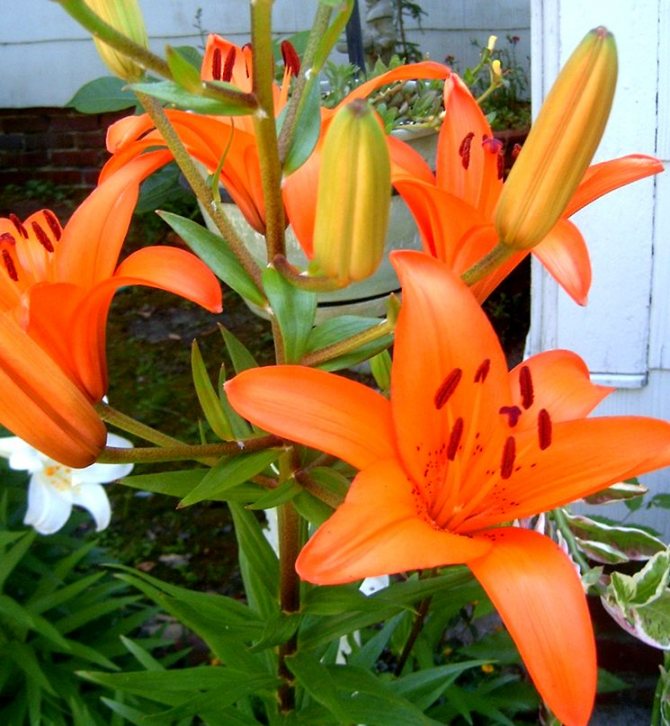
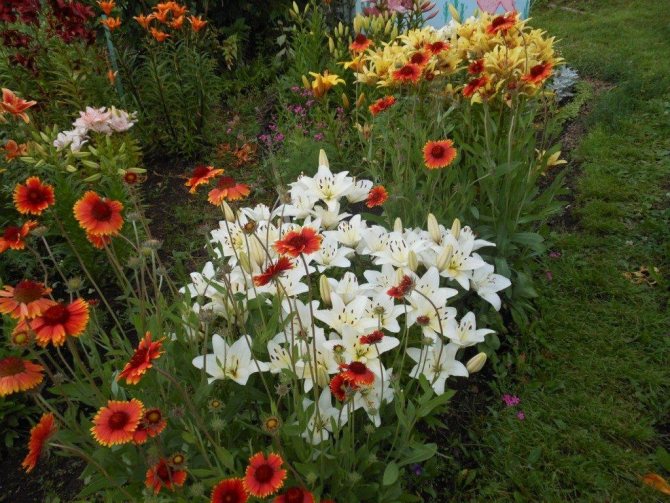
Lilies have bright green foliage and large, beautiful flowers with a fragrant scent. At home, mostly compact varieties are grown. In lilies, you can adjust the flowering time so that it pleases with its buds at the desired time. These plants can become a beautiful and original interior decoration.
Lily: characteristics of the species
Lily (Lilium) is a perennial flowering crop that belongs to the Liliaceae family. The stems of the plant are straight and tall (some varieties reach 1.5 m in height), with small glossy leaves. Flowers can be of different shapes: cup-shaped, funnel-shaped, star-shaped or bell-shaped. However, they always consist of 6 elongated petals and the same number of stamens.
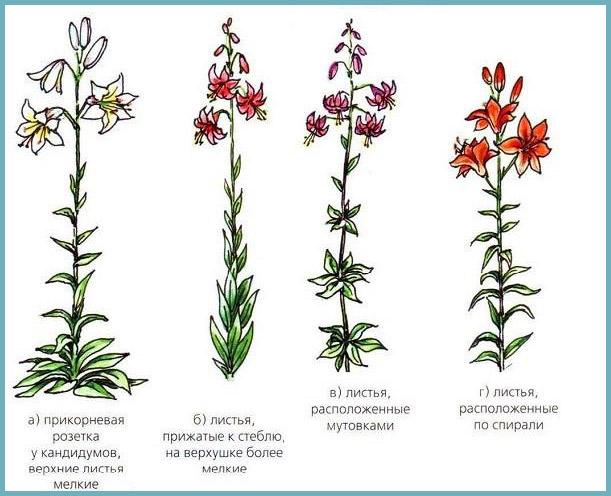
Scheme: types of lilies according to the structure of the stems
Although the word "lily" literally means "completely white", the flowers of modern varieties can have different shades: yellow, orange, red, lilac, lilac, pink. Varieties with a combined color are very popular among summer residents.
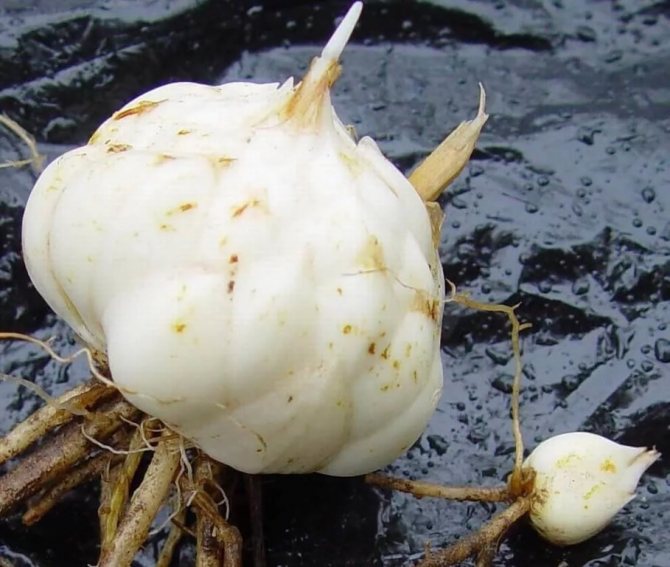
The underground part of the plant is a single-tiered (less often two-tiered) root system and a bulb. It is the bulb that is the source of nutrients for the culture, as well as the reproductive organ of the species. About the cultivation of other types of bulbous plants - hyacinths, tulips.
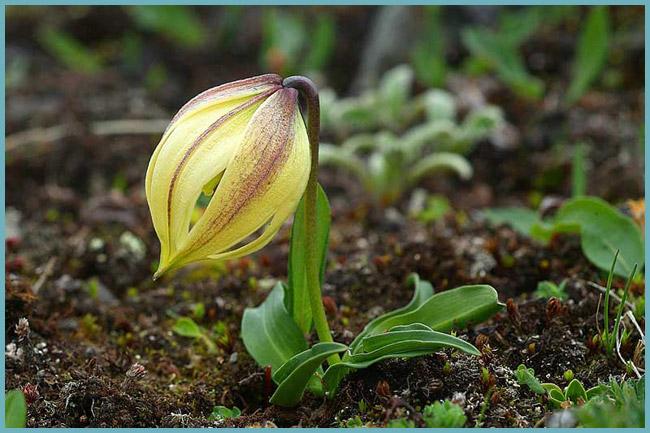


Wild lily - the predecessor of hybrid varieties
Planting capacity
The planting capacity is selected taking into account the size of the plant that will grow in it. The pots should be deep enough as indoor lilies need room to grow their roots. In addition, about 5 cm is left from the edge to the surface of the soil. Such an indent is needed for further filling of the earth, since additional roots are formed during the growth of lilies. The preferred container height is 30-45 cm.If one bulb is planted with a circumference of 10-12 cm, then the diameter of the container should be 20-23 cm.When three or four bulbs are planted together, the diameter of the pot is 23-25 cm.The distance between future flowers should be 5 cm. Drainage holes are required in the container.
When to plant a lily
As you know, lilies can be planted both in spring and in the middle of autumn - it all depends on the wishes of the grower.
Autumn planting is considered the most favorable. A low temperature and a sufficient amount of moisture will allow the plant to adapt and take root normally, thus reducing the stress level of the crop. That is why it is better to plant lilies in the southern regions of Russia in October.
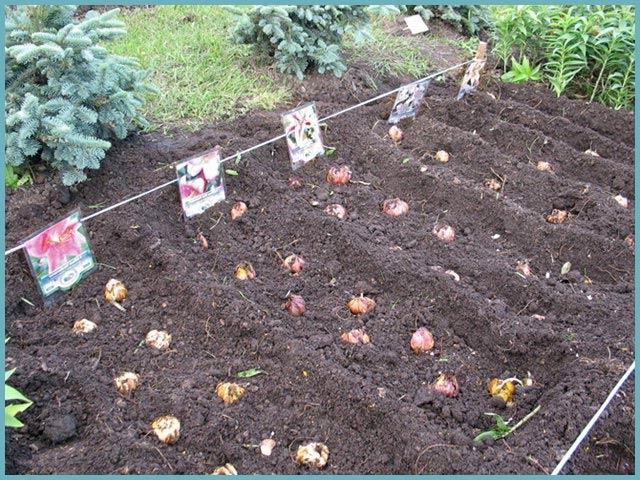


Preparing for planting lilies in open ground
However, it is worth noting that most varieties of lilies require exactly spring planting - study the characteristics of the variety you have chosen.
Problems when growing indoor lilies
Often lilies refuse to release buds or their greens turn yellow and dry. This occurs not only due to illness, but also due to improper care. Common causes of problems are temperature drops, insufficiently moistened soil and air, lack of nutrition, inappropriate packaging, and lack of a dormant period.
Why does the indoor lily not bloom


Indoor lily without flowers
The buds may not appear for the following reasons:
- Lack of moisture in the ground, air. Care - water more often, spray the plant.
- Changes in temperature, which leads to rotting of the bulbs. Keeping lilies in a room with a constant mild climate will help to avoid this.
- Lack of light, fresh air. The solution is to move the lily to a well-ventilated area with bright, diffused light.
- Too wide a pot in which children grow, green mass. The solution is to transplant a lily into a smaller container.
- Lack of a dormant period. Leaving - move the pot to a cool, shaded place in the fall.
Why do lily leaves dry


Dried leaf of home lily
This problem is the most common. A change in the color of the foliage indicates the following:
- Autumn has come, so the yellowing of the greenery is natural. Caring for lilies at home is traditional - preparing for rest, keeping the flower in the cold.
- Damp foliage can be exposed to direct sunlight, causing burns. You need to move the pot to a room with diffused light, water or spray the plant in the evening or early morning.
- Dry air. Care - place a humidifier and a container of water next to the lilies. In addition, the flower pot can be placed on moistened stones, expanded clay, moss.
- Lack of nutrition leads to disruption of the process of photosynthesis, the suspension of the production of chlorophyll. When plants are actively developing, saturate them with complex compounds. When leaving, mixtures with a high content of potassium and iron are especially recommended: 2 tsp. citric acid + 7-9 g of ferrous sulfate + 3 liters of cool water.
Choosing a place for planting lilies
Before planting a crop in open ground, carefully select a place to grow it. The plant grows well in sunny places that are protected from the wind (if you want to plant a lily near your house, observe which side of the sun is on most of the day).
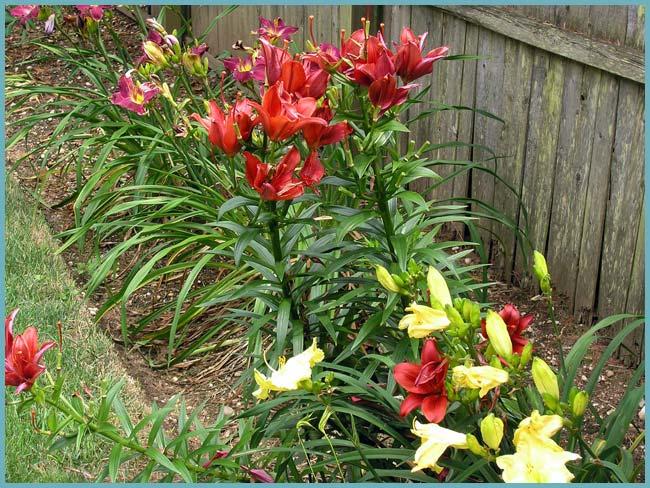


Any sunny spot on your backyard is suitable for planting lilies.
When the site is selected, dig up the soil and remove any remaining roots of other plants (especially weeds). Lilies can be planted in the same flowerbed with other flowering plants - the culture will not feel bad from this. The main thing is that the "neighbors" are not too tall and do not create a lily shadow. For this reason, you should not plant under trees or bushes.
Planting seeds
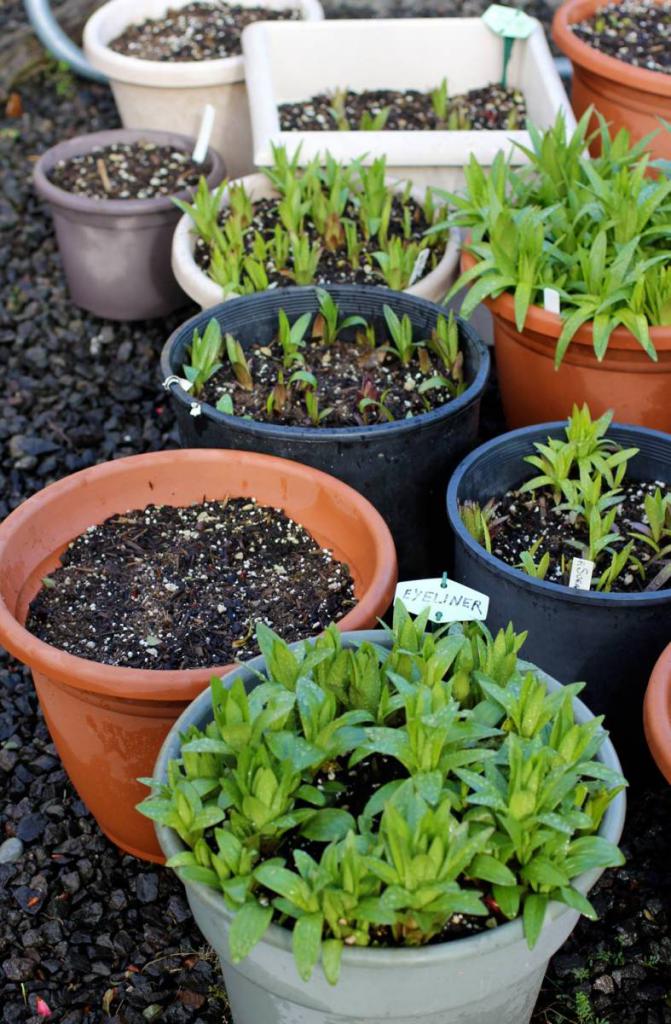
The size of the lily seeds is 0.5 x 1 cm. The seeds are left in the refrigerator. Then they are scattered over the sand. The gaps between them should be 1 cm. After that, a small layer of sand is applied. Carefully water and cover the seed containers with foil. Seeds must not be poured. The germination temperature is maintained at 20-22 ° C. The sprouts appear in about three weeks.
Pots with small plants are taken out to a lighted place. Their daylight hours should be 12 hours. Small lilies are protected from direct sunlight. When two leaves appear, they are seated in separate pots.


Soil preparation
Lily does not tolerate drought well, so the soil in which it is planted should be good at allowing moisture to pass through. Most lily varieties like fertile soils with high moisture permeability. Although breeders have also developed varieties that safely tolerate dry and even swampy areas. However, heavy loamy soils and salt marshes should be avoided when cultivating crops.
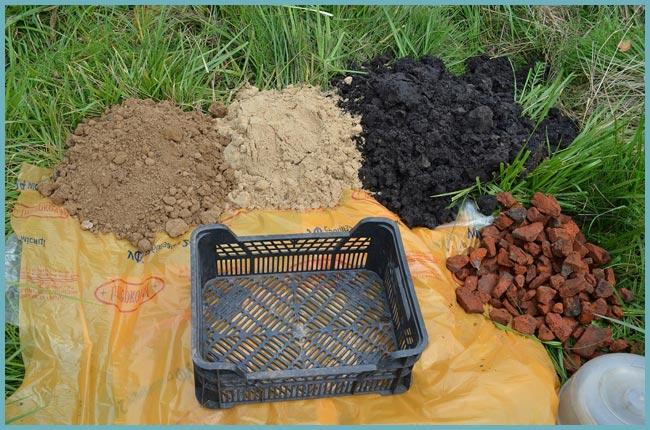


The optimal soil for planting lilies should consist of layers of gravel, sand and fertile soil.
Whatever the type of soil, it should be remembered that fertilizing the lily is still necessary. Peat fertilizers, humus or rotted compost (1 bucket per 1 m2) are suitable for feeding.If the soil is dominated by sandy impurities, then a good option for improving the quality of the soil would be phosphorus-potassium dressing, which is applied before planting the plant (100 g per 1 m2).
Important! Having well fertilized the soil when planting plants, you will provide them with comfortable conditions for growth and development for the next 2 - 3 years.
By the type of environment, the soil for lilies should be alkaline or slightly acidic. Too acidic environment is not suitable for the plant, therefore it is neutralized with wood ash (also ensures proper drainage of the soil), limestone or chalk (200-300 g per 1 m2).
Plant care after planting
Plant care consists in timely fertilization of the soil and regular watering. In practice, such actions do not take much time and do not require special skills, which is the advantage of growing such flowers.


Water for watering lilies should not be ice cold
In order to ensure the normal development of flowers, it is important that the sun shines on the bulb head and the stem remains in the shade. To comply with this condition, especially if there are other plants in the vicinity of the lilies, it is worth planning planting ahead of time.
Abundant watering is required for the plant during the period of active growth (until July). In the dry season, any moisture will only benefit the lilies, but you should not moisten the soil too often, because this is bad for the root system. From the second half of the summer period, the frequency of watering is significantly reduced. At the same time, moisture is required for lilies until the end of November, albeit in minimal quantities.


When watering, you need to make sure that drops do not fall on the flowers.
Top dressing for lilies should be applied at the very beginning of March, when the shoots have not yet begun their active growth. A whole complex of ready-made fertilizers is added to the soil, which includes up to 15 useful microelements (35 grams per planting square).
Additional feeding will be required by the plant during the period of bud formation, and when the lilies have completely bloomed, fertilizers based on potassium and phosphorus (25 grams of sulfate and 15 grams of superphosphate per square meter) are applied to the soil so that the bulbs can recover.


An important point! If the plant is young, it is necessary to remove the buds while they are still forming. Thanks to this, the lilies will be able to strengthen and will delight them with their flowers next season.


Lily fertilizer detailed diagram
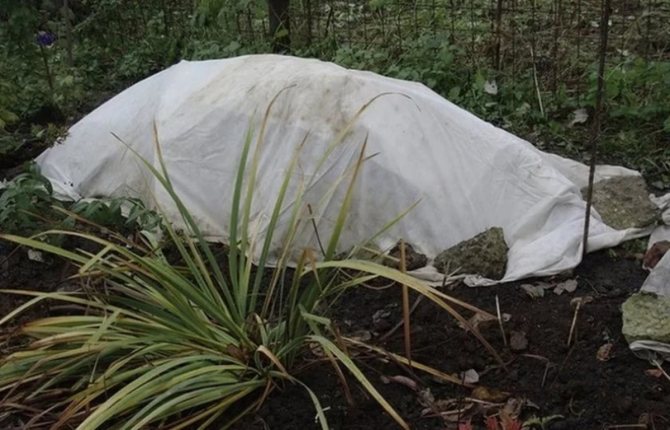
In the process of growing lilies, gardeners have to face some difficulties. So, all oriental hybrids are thermophilic, they do not tolerate frost well. To protect such plants from freezing, it is necessary to cover them with a film already in the middle of autumn. But the main difficulty is that they must be constantly ventilated under the film (but only in the absence of high humidity in winter).
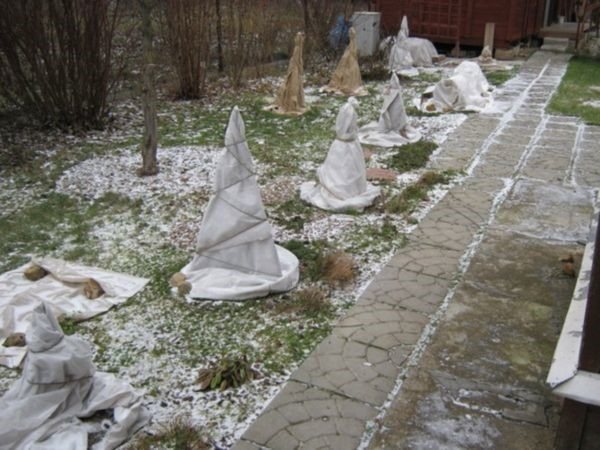


The winter shelter should be tapered.
You should not plant bulbs in various depressions of the soil and on slopes, because, as a rule, excessive moisture accumulates in such areas as a result of precipitation. In such conditions, plants will not be able to survive for more than one year. And also some gardeners note that the shoots of lilies begin to fade when planted on elevations. This is often due to overheating, so choose a flat surface for planting the bulbs.
Organic fertilizers, in particular manure, are often used as plant nutrition. However, it should not be forgotten that the excrement of animals and birds may contain pathogenic microorganisms that pose a danger to flowers. That is why such dressings are used only in minimal quantities and with extreme caution, diluting with water.


You can purchase ready-made fertilizer complexes
An important point! The stems of lilies grow quite long, which is why they can break off under their own weight. To prevent this, special props are installed.
Planting lilies in open ground
If you decide to plant lilies in the spring, then you should do this when the frosts have already receded, but the dry period has not yet begun. For each region of the country, the optimal time for planting lily bulbs in the ground will be different.
Prepare lily bulbs for planting as follows:
- sort the bulbs, removing spoiled planting material;
- the most viable specimens are completely cleaned of flower scales;
- rinse the bulbs in a solution of potassium permanganate or foundation (this will get rid of harmful bacteria).
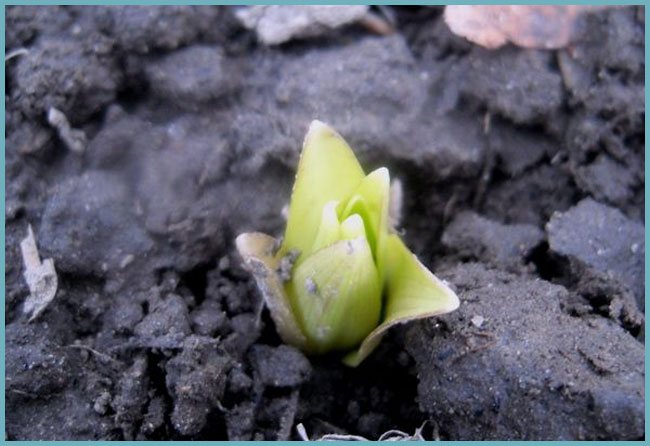


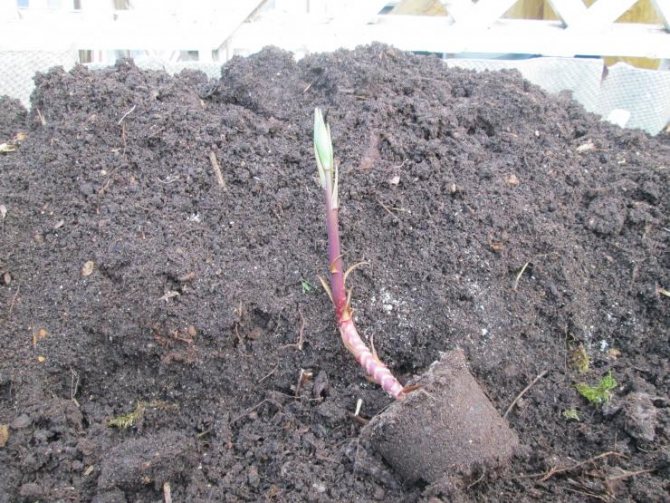
Lily sprout
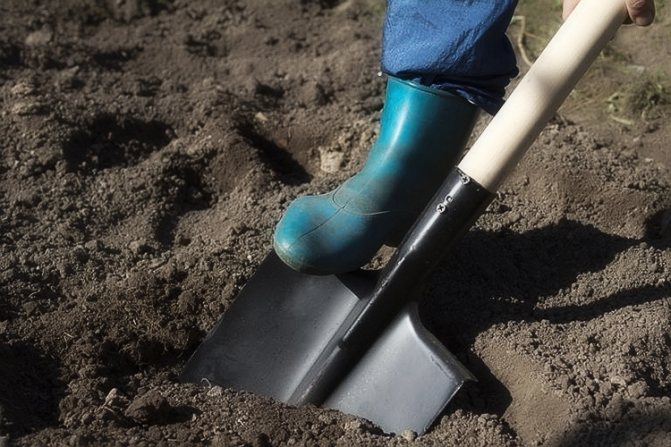
The planting depth of the bulb is determined depending on the type of soil:
- in heavy soils, small bulbs should be planted to a depth of 5-6 cm, large planting material - at 13-16 cm.
- if the soil is loose, it should be planted 2-4 cm deeper than in the previous example.
Important! Only good quality bulbs with an intact root system are allowed.
After planting is complete, the plants should be fed with organic and mineral fertilizers. If you planted lilies in the fall, then cover the flower bed with dry leaves and an additional layer of soil. This will allow the planting material to avoid freezing.
Buying bulbs
The process of acquiring bulbs requires the same responsible approach as transplanting, propagating or caring for them. In particular, when making a choice, you need to know the following rules in order to avoid possible mistakes:
- The main and mandatory requirement is obtaining information about which specific group the favorite and purchased variety belongs to, since in the future all other processes will depend on this, including planting, leaving or preserving for the winter. If it is not possible to obtain such information, then it is recommended to choose a different type of lily.
- If the purchase of oriental hybrids is carried out, then it is necessary to clarify the flowering period, since it can vary significantly between different varieties included in this group.
- Check the bottom of the bulb for damage before purchasing.
- Bulb size also matters since the largest specimens form rather large flowers already in the first season. In this case, the diameter does not matter at all, since the size is usually measured exclusively in height.
- The purchase process itself is recommended to be carried out before the start of the planting season. This is due to many factors, including at this time a wide range of bulbs are available that have not yet been damaged by buyers at the time of selection.
- After making a purchase, it is recommended to carry out the processing of the bulbs, to protect them from various sucking parasites.
Care principles
Maintaining optimum soil moisture is the first thing you need to watch out for. Watering is carried out as the soil dries up (accordingly, in dry periods, watering is done more often, and in rainy periods, watering can be excluded altogether). Use the root watering technique (called strip irrigation): surface irrigation can harm lilies. If necessary, fertilizing can be applied along with watering.


If the summer is rainy, then the lily need not be watered.
In the first year of life, the plants are rather weak. Therefore, in order to improve their development, remove all the buds: the lily will spend too much energy on flowering and, having weakened, will not be able to endure the winter frosts. But in the second and third years after planting, the plant will bloom profusely. Usually, in the fourth year, the flowering intensity decreases - this means that the culture needs feeding. Closer to the fifth year, flowers are divided and transplanted.
Advice! Do not forget to create support for the lilies: these crops often break under the weight of their own stems.
Hello dear readers!


As I promised, in this article I want to invite you to familiarize yourself with several of the most common ways lily breeding
... Lilies can be propagated both by seed and vegetatively.
Reproduction of lilies
seeds are more complex and troublesome, it is usually used by breeders when developing new varieties.
And among amateur flower growers, vegetative propagation methods are more common. Let's take a look at them.
Reproduction and transplantation of lilies
Lilies are propagated by dividing the bulbs. The procedure is carried out at 4-5 years of growth of the lily: the thickening of the bulb nests by this time is fraught with the cessation of flowering. The lily bulb is divided and each part is planted separately. Care for transplanted bulbs is required the same as for plants in the first year of life. Under favorable conditions, the divided bulbs will bloom within a year.
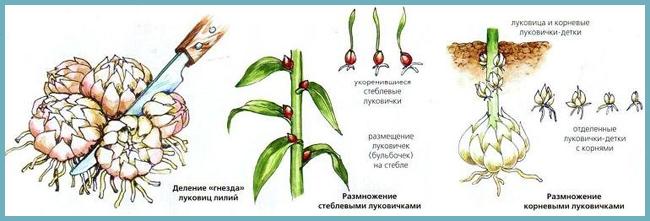

Schematic: breeding species of lilies
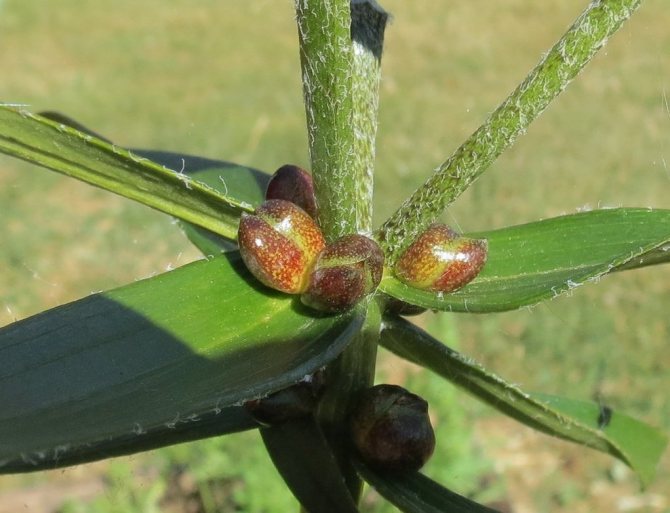
Some varieties of lilies produce baby bulbs. They are attached just above the base of the main bulb. Such bulbs should be carefully separated and planted for growing. These plants will bloom only 2-3 years after planting.
There is also a more complex method of reproduction of lilies - with the help of scales. Small loose growths are carefully separated from the base of the mother bulb and planted in a special sand bed. If the flakes were planted in the spring, then by the fall, bulbs are formed from them.
Pests and diseases
There are a number of pests that can harm lilies, among the main species are:
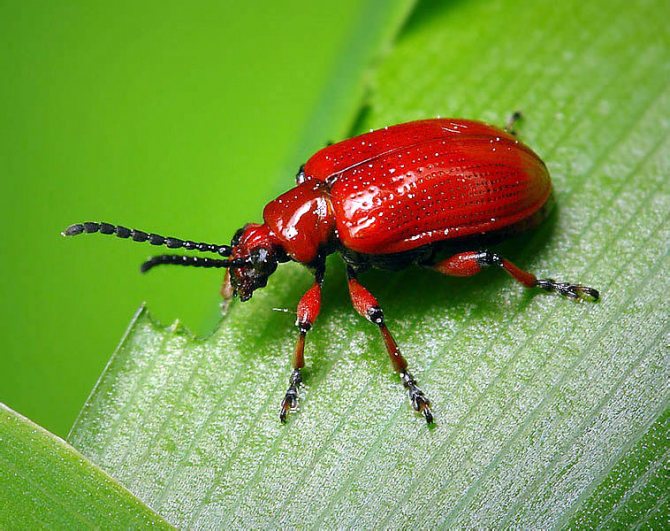


Onion leaf beetle
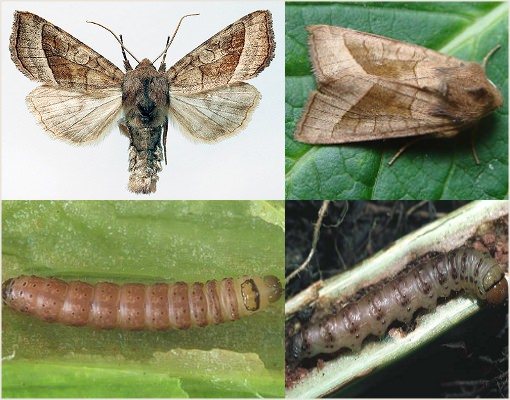


Potato scoop
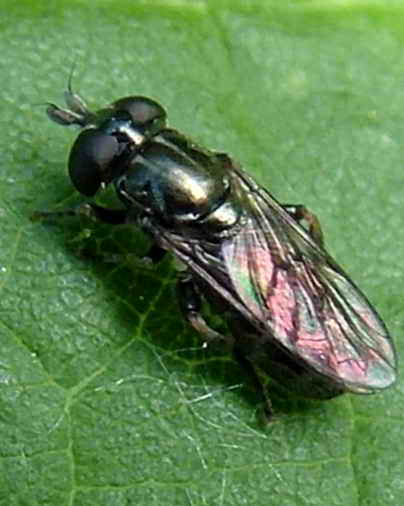


Onion hoverfly
- Onion leaf beetle eats foliage, and its larvae skeletonize it. Outwardly, it looks like an oblong orange beetle with red legs. To combat it, it is necessary to eliminate all weeds, as well as collect all the pests noticed.
- Potato scoop Are caterpillars that eat stalks. To prevent the appearance, it is necessary not only to eliminate weeds, but also to remove their remnants from the flower garden.
- Onion hoverflies - these are greenish flies with a metallic sheen of the body, its larvae feed on bulbs. To combat them, it is necessary to discard the infected bulbs and treat with a 30% solution of karbofos.
The predisposition to disease depends on the variety of lilies, but they are all susceptible to the following ailments:
- Penicillosis on lilies Rust, expressing in colorless spots on the foliage, which then lead to yellowing.
- Gray rot, capable of affecting any part of the lily, outwardly manifests itself in the appearance of round brown spots.
- Penicillosis expressed in the appearance of a green bloom and decay of the plant.
All of these diseases are of the fungal type, the fight against them is carried out both by agrotechnical methods and by treating plants with fungicides.
Popular groups of lilies
When choosing lilies for planting in the country or in the courtyard of a private house, you should pay attention to the following groups of hybrid plants:


Asiatic lily (left) and Candidum lily (right)
- Asian hybrid lilies. Unpretentious winter-hardy varieties, have cup-shaped flowers of white, pink, orange, yellow, as well as multicolored colors.
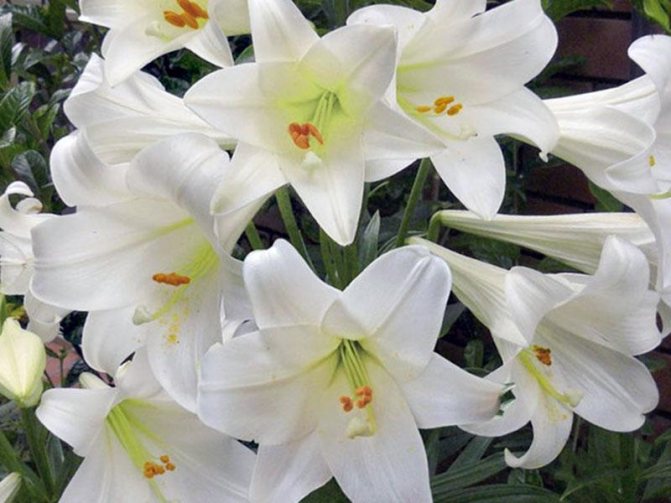
- Candidum. These varieties are capricious to growing conditions. Flowers have a funnel-shaped or tubular shape, the color is snow-white or yellow. Unlike the previous group, the flowers of these varieties have a strong aroma.


American lily (left) and oriental lily (right)
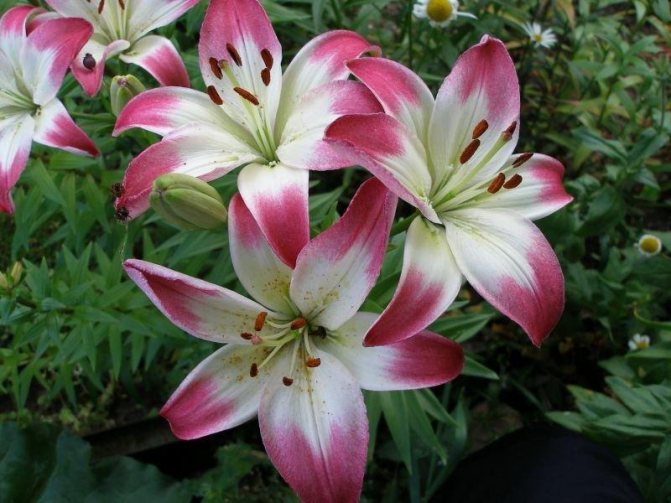
- American hybrid lilies. The varieties are well suited for breeding in central Russia. They are distinguished by moderate demands on growing conditions. The flowers are turbid with pink or lilac color and bright red dots.
- Oriental hybrid lilies. The varieties are quite resistant to external factors, but at the same time they are highly susceptible to viral and fungal diseases. Flowers of various shapes and colors. Suitable for breeding in the middle lane and southern regions of Russia.
Each of the four groups of lilies includes many varieties with similar characteristics. Choose a group based on the planting conditions and climate in your region. The variety is determined solely at the discretion of the gardener.
Care during growth and flowering
Indoor lily for home care requires certain conditions during the growing season and flowering. When the bulbs germinate, organic feeding is carried out. A week later, phosphorus-potassium fertilizers are applied. Additionally sprayed with growth stimulants 2 times a week. When the lilies grow up to 10 cm in height, soil is poured into the container. Complex mineral-organic fertilizers continue to be applied weekly. In the warm season, young plants can be taken outside. For this, the lilies are hardened, gradually increasing the duration of their stay in the fresh air from half an hour to 10 hours. If the temperature is kept below 10 ° C at night, the flower buds will not develop well.
General care rules:
- In the process of growth, lilies are tied up or substituted for them, since their flowers are large and heavy.
- Water the plant often, avoiding excessive moisture. You can check the ground with your hand.
- Lilies love to be sprayed. It is impossible for the buds to get water, otherwise the flowering period will be shortened.
- The soil should be loosened by adding humus to it.
- It is necessary to weed the soil from weeds.
Various varieties of indoor flowers of lilies have their own characteristics in care:
- Asian hybrids are considered the most unassuming. These plants have a long stem. The petals are monochromatic or painted in two or three colors, often interspersed. They love the sun and partial shade. When growing them, you need moderate soil moisture. They have a fairly stable immunity. These flowers are odorless, so many people prefer to keep them at home. Includes five thousand varieties.
- Lilies Martagon (curly) - tall plants with turban-shaped drooping flowers. They grow on almost any soil, shade-tolerant. Frost resistant. They have good immunity. In total, about 200 varieties are classified as curly lilies.
- Snow white hybrids include plants with white and cream flowers. They require a lot of attention and knowledge in care. They smell good. Poorly tolerate cold. Susceptible to disease. This group is made up of about 30 varieties.
- Long-flowered lilies have large, elongated flowers. They have a strong aroma. Not hardy. Popular as indoor plants. Currently, low varieties have been bred, reaching 40 cm. They are susceptible to pests.
- Oriental hybrids can be purchased in stores in bloom. They have large flowers. They love warmth and sun, loose and light soil. The group includes 1300 varieties.


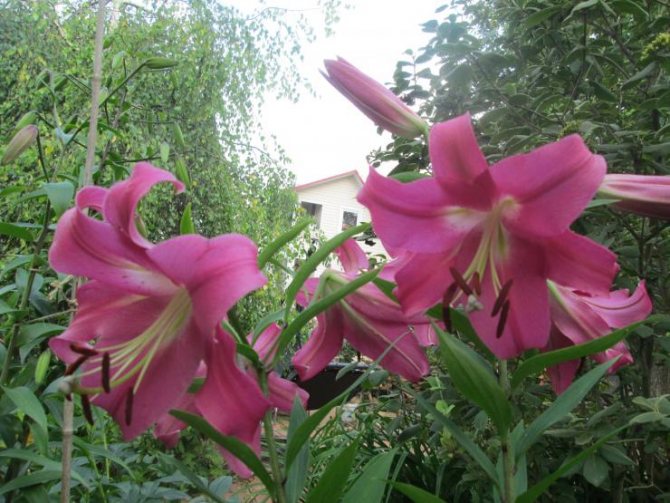
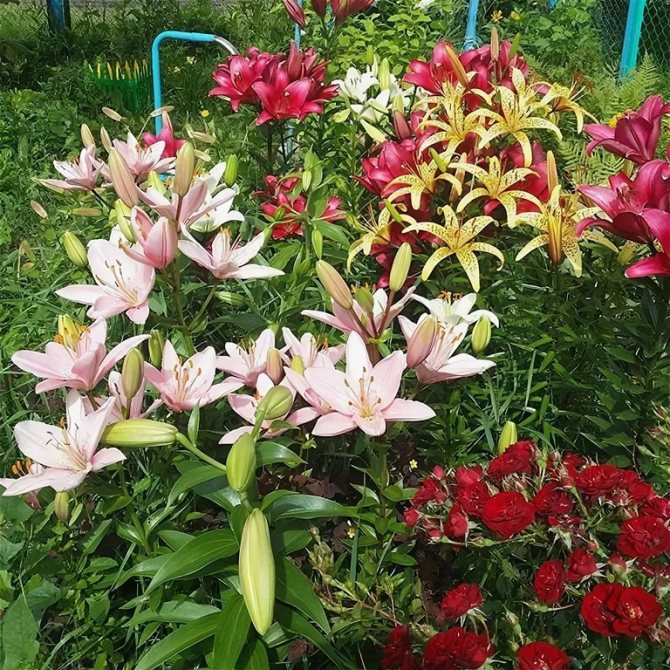
Lily varieties: photo
Fertilization rules
It is customary to fertilize lilies with dressings containing phosphorus and potassium (examples are given above) directly at planting. In the spring, it is recommended to feed the plants with ammonium nitrate, which is a nitrogen fertilizer. This is especially necessary if the lilies turned out to be undersized last year. In summer, it is advisable to feed with ash, superphosphate, potassium magnesium for lush and bright flowering. Top dressing is done at least four times per season.
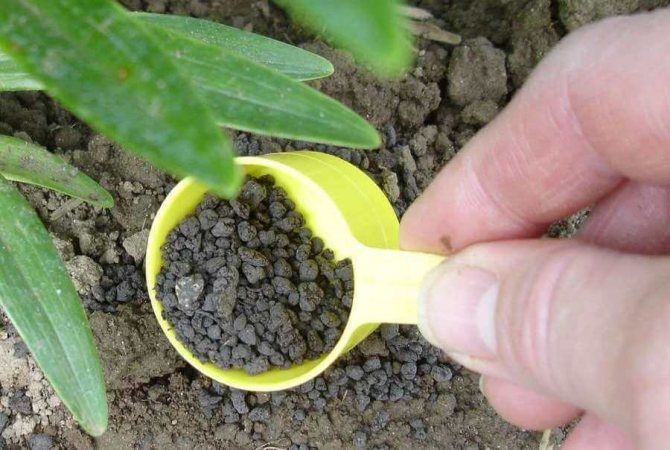


Photo: <>
Combination with other plants in landscape design
Tall lilies are very often planted in separate islands in the same tone, or vice versa, mixing variegated varieties. Miniature subspecies will be favorably planted in the form of a low-growing curb.
A good solution would be to plant undersized violets or marigolds next to chic peonies or verbena, which will cover the roots of the lilies and help retain the necessary moisture, and after the lily has faded, they will cover the ugly wilting stems.
In the background, a good solution would be to plant astilba or evergreen juniper, fern or variegated hosta. All of these plants need partial shade that a growing lily can provide.
No one will dispute the opinion that any lily and any rose, for example a floribunda rose, will look great together in plantings.
All varieties of lilies have their own individual characteristics, both in decorative terms and in climatic, and they just need to be taken into account during their placement in the landscape. After all, they differ not only in color, but also in height, flowering time and period, care and planting features.
Features of agricultural technology in different regions of Russia
It is no secret that climatic conditions differ in different regions of Russia, and therefore the inhabitants of the regions take care of plants in different ways. For example, if a garden lily is grown in northern regions with severe winter frosts, then in the winter it will have to be dug out of the ground and planted in pots until warming. Gardeners from other regions do not need to dig up and replant the bulbs.


Florists living in the southern part of the country have to water their plants more often in summer due to drought. In other regions, there is no such problem, and therefore they moisten the soil less often. Experts do not advise the inhabitants of Siberia to plant lilies on the street because of the constant frost. In such climatic conditions, it is better to grow them in greenhouses where the above-zero temperature is maintained.
Reproduction methods
Lilies are propagated in several ways:
- bulbs
- seeds,
- scales.
The most common is bulbs. It is recommended to plant them on average for 4-5 years of life. If lilies grow in one place for a long time, the bulbs become smaller, flowering worsens.
The bulbs are separated from each other by hand. Each is planted separately. With proper care, they will bloom next year.
If propagated by seeds, then they need to be harvested after the seed pods turn brown. Store seeds before planting at a low but positive temperature. The maximum storage period for seed is 3-4 years.
New plants can be obtained from bulb scales (small loose growths). They are carefully cut, transplanted into moist sand or peat, and placed in a warm place. After a few months, young bulbs will form from them, which can be planted in the soil.
Lilies have brown leaves: what to do
The appearance of rusty and brown spots on greenery is due to the defeat of the plant by a fungal disease.
- At first, the spots cover the edges of the leaves, they look wet. Over time, dry up, move to the stems, buds.
- If the disease was noticed at the initial stage, you can try to save the lily. If the plant is completely damaged, there will be no flowering.
Note! In order to prevent brown spots, flowers are treated with such agents as zircon, epin. Processing is carried out in cloudy weather on dry foliage.
Frequent loosening of the soil near plantings, especially in rainy weather, will reduce the risk of disease.
If brown spots are already visible:
- the affected leaves are removed, burned;
- the completely affected plant is cut off, a stump is left no higher than 5 cm;
- lily and the place of growth are sprayed with Bordeaux liquid or other means containing copper;
- mineral fertilizers (phosphorus, potassium) are applied at the root;
- sprinkle the plant with ash.
If the disease manifests itself annually, then the place for growing lilies is not suitable, it is time to change it.
How to cut flowers correctly
Usually, lilies are not cut and left to bloom in the flowerbed to strengthen the bulbs and ensure abundant flowering for the next year. But sometimes you want to make a bouquet and decorate a room or living room with lilies.
To reduce the negative impact of pruning, you need to learn how to cut flowers correctly:
- cut lilies only in the morning hours or with the onset of dusk; during the day, you can cut flowers only in cloudy weather;
- use a sterile tool for cutting; alcohol or a pharmacy iodine solution is used to process the knife;
- do not cut off the stem at the very base, leave a third of the stem and adjacent leaves for proper nutrition of the bulbs;
- cut at an angle, after watering or rainfall, the water will not stagnate on the stem.


How to process lilies
Overgrown plantings, weeds, lack of care for flowers lead to diseases. Caring flower growers begin the fight against diseases, insect pests from the time of planting.
The most effective method of protection is prevention. Plants need to be inspected more often in order to notice the disease or insects that have flocked to the juicy stems of lilies in time.
Pest control
There are up to a dozen dangerous lovers of lilies. The most common ones are:
- curling leaves indicates a spider mite. Sprayed with phytoverm, actellik;
- the squeak beetle is clearly visible on the leaves. Against him, flowers are sprayed with decis, karbofos;
- lily fly lays eggs in buds. Processing is required three times. Apply karbofos, ditox;
- The bear eats roots, bulbs, damaging them, leaving numerous holes in the ground. Thunder or grizzly preparations are poured into them. The same funds will help against the larvae of the May beetle (crustacean)
Note! Start processing immediately, until a lot of pests have developed. There is a wide selection of insect repellents and bulbs in the shops. Instructions for the use of drugs are indicated by the manufacturer on the packaging.
Preparing lilies for wintering
In order for lilies to survive the winter, it is necessary to prepare them for wintering in advance. In a few months, it is necessary to strengthen the root system so that it can cope with winter frosts. To do this, at the beginning of September and in October, more potash-phosphorus fertilizers are added to the ground. Florists advise feeding the soil with potash dressings and superphosphate.
See also
Is it necessary to dig lilies for the winter, preparing a shelter, when to cut and how to storeRead
To make fertilizers better absorbed, the area is periodically watered with heated water. In mid-October, watering the flower beds completely stops so that the bulbs do not start to rot due to high humidity. In the fall, lilies are sprayed with copper sulfate 2-3 times to protect them from the development of fungal pathologies.
In early November, flower beds with planted lilies are insulated. As a covering material, dried fallen leaves, wood twigs or sawdust are used. The shelter is removed in early or mid-April, when there is no frost.


Seed selection
You need to start planning your front garden or flower bed with lilies by choosing varieties. The harmonious combination of size, height and flowering time will allow you to enjoy a luxurious flower garden all summer long.
Varieties for planting
The International Botanical Classification identifies 9 main groups of lilies:
- Asian, more than 5 thousand hybrids, winter-hardy, unpretentious. Flowers are odorless.
- Curly, about 200 varieties. The inflorescences are graceful, elongated, reminiscent of a candlestick tilted downward.
- Snow-white, only 20 varieties. Large, boiling white, sometimes with delicate yellow veins, petals with a strong aroma. Capricious, demanding on the climate and care.
- American, there are 150 subspecies. Leaders in brightness, there are incredible shades. A distinctive feature is the dark contrasting dots on the inner side of the calyx.
- Long-flowered, more common among the inhabitants of greenhouses and nurseries. Very susceptible to infections and parasites. Inflorescences are long, elongated, inclined with the core to the ground.
- Tubular, thermophilic varieties with large, incredibly fragrant flowers.
- Eastern, the most numerous varietal group, numbering more than 1,000 subspecies. Plants love warmth, careful care, and require careful protection from disease.
- Interspecific hybrids are popular with flower growers, as they combine the advantages of other groups. The most in demand are LA hybrids, OT hybrids and LO hybrids. The corolla of a lily can be up to 30 cm in diameter. They are more often used for forcing.
- Natural varieties are often inferior to garden relatives in beauty and size, but play a key role in obtaining new varieties.
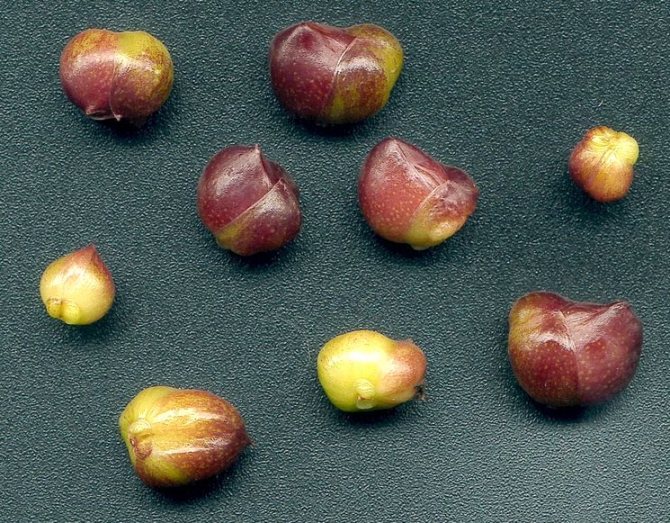
Bulb quality
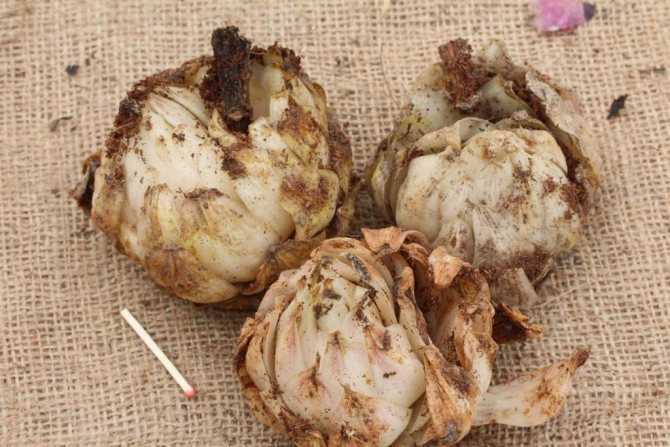
When buying, you need to meticulously inspect the bulbs.


The weak and spoiled will not germinate, and the infected can spread pathogens throughout the garden and cause unpleasant hassle.
When choosing a lily, you need to pay attention to:
- The bulb was firm to the touch, juicy, without any signs of rot, trauma, black spots and soft areas. If there is noticeable damage, most likely, the rules of transportation and storage have been violated, which means there is a great risk of death.
- Small shoots and fresh, not dry roots were visible. Such plants are more viable. The size of a living root system should be at least 4-5 cm.
- The size of the onion was as large as possible. Planting material from 14 cm in diameter will give powerful shoots and large inflorescences. Smaller ones will gain strength for a year or two, and those with a diameter less than 3 cm will bloom at all only 2-3 years after planting.
You should pay attention to the material with a high sprout. Probably, these bulbs were not planted in the ground and they missed one growing season. After rooting, they will begin to grow actively and will not survive the cold weather.


Planting rules for various varietal groups
The ancestors of ornamental garden lilies originally grew in various regions of the planet: from cold, harsh Siberia to steppe Central Asia, in the mountainous regions of the Caucasus and in the tropical Amazon foothills. From them, modern varieties have inherited preferences for soil acidity, size, growing season and sensitivity to cold and disease.
In order not to be mistaken with the choice of a hybrid, you need to know their features.
| Group | Location and ground | Landing dates | Popular varieties |
| Asian | Well-lit area with no close groundwater. Loves slightly acidic well-drained soils, fertilized with peat or humus. It is possible to plant different varieties in the form of a pyramid, where undersized pixies are placed on the lower tier, and large tangos on the upper tier. | End of August - beginning of September |
|
| Oriental | Free, well-heated and sunlit areas on the south and southeast side. There should be no plants with a powerful root system in the neighborhood. Moisture stagnation should not be allowed, so slopes are ideal. Loose soils, neutral in terms of pH, into which ash, humus, peat, and mineral fertilizers are preliminarily introduced. | August |
|
| Tubular | Well-lit areas, inaccessible to wind and drafts. Loose, fertile neutral or slightly alkaline soil is suitable. | End of August - beginning of September |
|
| Curly (Martagon) | Spacious light areas of the garden without the threat of waterlogging. You need sandy or loamy, additionally loosened soil of slightly acidic and neutral pH. The plant is quite large, so it is better suited for single plantings. | End of August - beginning of September |
|
| Snow white | Sunny warm areas in the southern part of the flower garden, well protected from the wind.Prefers fatty fertile soils saturated with nitrogen and potassium, rather moist and loose. In September, the plant is cut and the bulb is dug up for winter storage. | Planted in the spring after the end of frost. |
|
| LA-hybrid | Well-lit flower beds and front gardens with sandy and loamy soils, lightened by river sand, peat, deciduous humus and ash. Slightly acidic or neutral. | Mid September to early October |
|
| OT-hybrid | The sunny side of the garden, while the flowers should be placed in such a way that the tops with inflorescences are in the sun, and the stems at the root in the shade. Loves loose, fertile, well-drained soil. | Beginning of September |
|
Do I need to dig lilies for the winter
Depends on a number of reasons:
- if you want to propagate the plant;
- the variety has poor frost resistance;
- the flowers show signs of the disease (the stem turns black, rot appears);
- the lilies began to grow smaller.
There is no consensus among experienced florists whether it is necessary to dig up the bulbs. But once every 5 years, when it is necessary to dig up the lilies, it is imperative to transplant them to a new place.
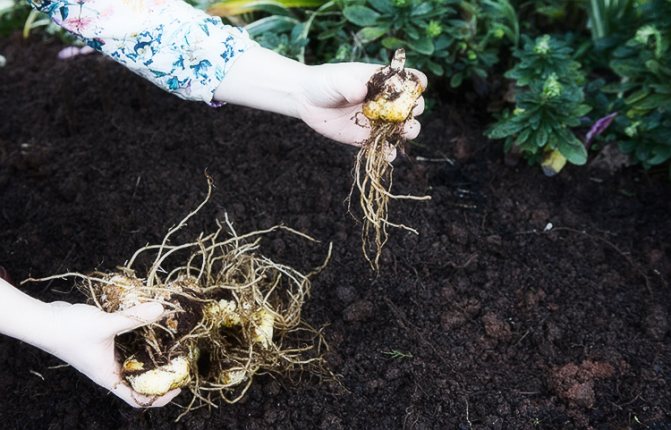
Collection and storage of planting material
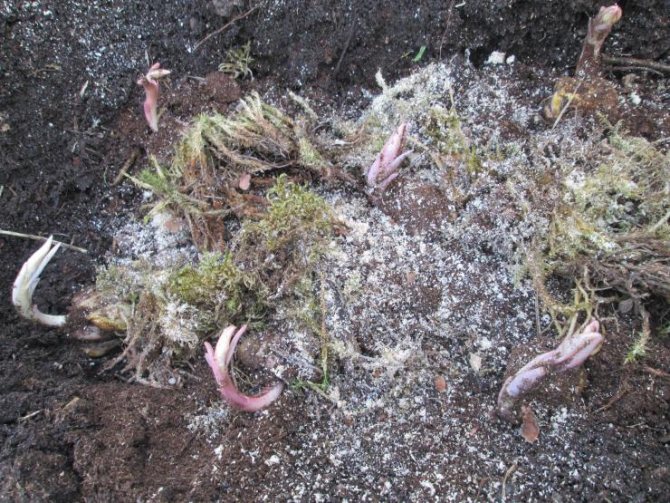
The dug out bulbs are carefully examined, sorted, processed:
- wash off dirt with warm water;
- diseased and damaged roots, dried scales are cut off;
- disinfect with potassium permanganate (weak solution), basezol or karbofos;
- dried in a place inaccessible to the sun;
- placed in containers (wooden or plastic), covered with sand, sawdust.
Planting material is stored in a cool room, for example, in a cellar at a temperature not exceeding 4 ° C.
If there are few bulbs, they are stored in the refrigerator, but first in a film, then wrapped in a wet canvas cloth.
Note! Some gardeners, for reliability, leave half of the bulbs to winter in the ground, dig up the other half.
Why do lily leaves turn yellow
Foliage turns yellow for a number of reasons. The main thing is insufficient care. Others:
- lack of water. You need to water the flowers on time, especially on hot days;
- too frequent planting also causes yellowing of the leaves, the plant does not have enough oxygen and nutrition;
- excess water is also harmful, as a lack, due to which the foliage turns yellow;
- there is not enough or too much fertilizer;
- flowers are hungry for iron;
- from fungal, viral diseases, the leaves turn yellow.
It is possible to protect lilies from yellowing if the cause of their occurrence is established.
Lilies have faded: what to do next
Gardeners who decide to leave flowers for the winter in the ground, cut the stems of the plant, feed, cover.
Pruning lilies after flowering
If you cut off the stems without waiting for drying:
- the bulb will stop growing;
- the flower will not receive proper nutrition;
- winters badly;
- will not give a lush bloom next year.
Important! Dried stems are removed and those on which a capsule with seeds has begun to form, which takes away nutrition from the plant.
Flowers are cut obliquely with alcohol-disinfected tools: pruning shears, scissors.
The most popular varieties of hybrids:
Lilies OT-hybrids
Abbreviation for Oriental - Tubular
Terry lily
Pretty Woman - (Lilium Pretty Woman). It grows almost up to a meter in height. Large inflorescences creamy white with a delicate pink.
Anastasia (Lilium Anastasia) Intricately curved leaves of a rich emerald color. Countless flowers of a bright pink hue, with a white spot at the base and a greenish stripe on it.
Robina (Lilium Robina) In blooming vyde in a height of 1.5 m. Large green leaves with dark areas, Flowers purple-red with a yellowish core.
Scheherazade (Lilium Sheherazade). A giant variety of almost 2.5m.Multiple flowers of a reddish-burgundy hue, edging and a light cream-colored core. Blooms in late summer.
Honeymoon Large but delicate slightly yellowish flowers.
Shocking Pure red flowers are edged with a rather thick golden yellow stripe.
Lilies LA hybrids
Burgundy lilies
The abbreviation stands for Longiflorum Asiatic longiflorum
Frey or Freya (Fray) beautiful golden yellow flowers.
Ercolano (Ercolano) delicate inflorescences of lemon shades with white splashes.
California (California) exquisite cherry color large flowers with green stems.
Brindisi is a tall subspecies, growing 1-1.3 m. Large flowers not of a monochromatic pink color.
Fangio (Fangio) tall lilies up to 1.5-1.6 m. With a deep dark red beetroot color all over the petal.
Lilies A-hybrids
The abbreviation stands for Asiatic Lilies
Tiger
Tiger lily (Lilium lancifolium "Citronella".) Or lanceolate. On a pure yellow background, orange-brown splashes are scattered, petals fancifully twisted outward.
Red Twin. Terry red lilies are not clouded in another tone of a pure shade, with stamens a little darker in color. Blooms early in June - July.
Fata Morgana from a row of yellow lilies. Terry soft yellow multiple flowers interspersed with brown dots in the neck. Blooms in late June or early July.
Ceres. The Asian lily is hybrid with a beetroot-crimson color, which is shaded in a light tone to the edge of a double petal.
Elodie. Double pink lilies. The pink tone lightens to the edge to pallor. In the center is a point of languid tone.
Lilies O-hybrids
The abbreviation stands for Oriental or Oriental Lilies.
Siberia white lily. Highly frost-resistant variety with snow-white inflorescences, with a slightly greenish center.
Lily Carolyn Tensen Huge snow-white inflorescences with a touch of some waxiness, looking slightly to the side. The foliage is light green.
Lilies LO-hybrids
The abbreviation stands for Longiflorum Oriental
Triumphator (White Triumphator), snow-white flowers with a crimson gradient in the center of swirling petals.
Lancon (lilium lankon). With drooping inflorescences of a beautiful pink shade with a large blotch on all petals of burgundy dots.
Lilies T-hybrids
Royal
The abbreviation stands for Tubular Lilies
African Queen has strongly curled orange petals with darker spots on the outside. Dark emerald leaves.
Lily Royal Regale Album (Album) The flower is snow-white with a yellow core and richer in yellow stamens. They do not grow tall, only up to 1 meter.
Pink Perfection Smoky lilac-pink large tubular inflorescences.
Damson Pink flowers with an unexpected shade of fuchsia on tall stalks.
Rare lilies
Black Beauty (lilium black beauty). Purple tall lily more than 1.5m tall. On the surface of each petal, burgundy dots are scattered.
Lily Henry (henryii). A multi-flowered lily with numerous small flowers (about 7 cm each), orange-apricot in color, with a brown speck. A short "beard" grows at the base of each petal.
Scarlet Delight A rare beauty with burgundy flowers. A light green middle with a white edging comes out from each petal. The outer part of the petal is several tones lighter.
Dwarf lily
It also tolerates frost well, enchants with its miniature beauty and fragrant flowers.
Advice!
In order not to throw money down the drain, decide on the varieties that suit your region. For example, when choosing varieties of lilies for Siberia or for planting in the Urals, remember that Asian or LA hybrids will definitely be suitable, again with them at the base.
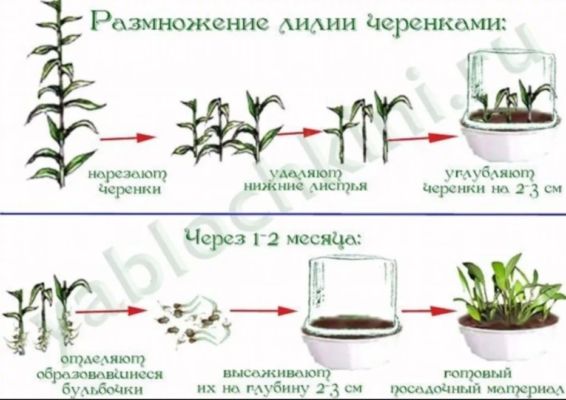
How to propagate lilies after flowering with cuttings from a bouquet
And the last way to propagate is by cuttings or leaves.Thus, you can get a new root from your own lilies or from those donated in a bouquet. Although from the latter, the probability of rooting the cuttings is relatively lower. But why not give it a try? Moreover, there is little trick in this process. So, to obtain planting material, you must:
- Choose a sturdy, healthy plant. Or use the bouquet as quickly as possible.
- Using sharp scissors, cut off the medium large leaves from the stem.
- Plant the leaves in a greenhouse with nutritious soil.
- Wait for rooting. As a rule, 1-2 out of 5 leaves from a bouquet take root, 3-4 from a garden plant. It depends on the fact that flowers for bouquets are grown on hormones and stimulants, which cannot but affect their reproductive performance.
- The rooted leaf should be planted in an individual greenhouse and wait for the formation of new leaves from a tiny onion.

Healthy and strong flowers are the pride of a gardener. But this is not the result of a series of accidents, it is the result of rather painstaking work. I hope the tips from the article will help you. Let your flowers delight you and your guests.
Author of the publication
offline 58 minutes
Seat selection


The flower loves sunlight and prefers to grow in open sun beds, with minimal exposure to wind. The land must be thoroughly loosened to remove weeds and grass.
Lily feels great in the company of other flowers, but they should not exceed the height of the plant and block it from sunlight. The flower should not be darkened. Otherwise, such a neighborhood will only be preferable.
It is important to note that planting a lily in the shade of trees or fertile shrubs is strongly discouraged. The sun's rays will be blocked and instead of a beautiful stately plant, a thin and incapable of living like a royal flower can grow.
Dates of spring and autumn planting
Even experts are not able to say unequivocally when it is better to plant lilies. In the spring, as well as in the autumn planting, there are advantages and disadvantages.
Spring planting
The advantage of spring planting is the safety of the planting material. The risk of bulbs getting wet, rotting and freezing is minimal. Oriental varieties and tubular hybrids are planted in early spring in March, just after the snow melts. Tibetan and tiger species are planted in the last week of March, and terry hybrids in the first week of April, but, of course, the timing depends on the growing region.
Autumn planting
Autumn planting is preferred by most flower growers, as it has its advantages:
- lack of summer heat;
- no need for regular watering;
- pests are not a threat;
- lilies bloom earlier;
- saving time in spring, when there is a lot of work on the site.
In the fall, planting dates can be adjusted. The bulbs are planted in late September - mid-October. The main thing is that before the onset of frost there must be at least a month so that the bulbs have time to take root.


Why do lilies fall off their buds without blooming
There are many factors affecting the dropping of buds:
- water scarcity. Flowers are lacking especially on hot days and get rid of buds, some of the greenery;
- fungal disease. Because of him, the flowers also shed their buds, which did not have time to open;
- botrytis (gray rot), spotting. Excess moisture causes rotting of all elements of the flower. The buds rot;
- nematode. Because of this worm, the buds dry out, the foliage begins to fall off, as the insect drinks the juices of the plant;
- lily flies, fire beetles.
When the first signs appear, you need to find the cause and treat the plants so as not to lose their flowering.














































