It is difficult to find a person who would not admire roses, their buds and fragrances. If earlier these plants were grown only in the southern regions of Russia, today these flowers are finding a new place of residence in the Urals, Siberia, Moscow region. Climbing roses, capable of curling on a trellis, also settled on the plots of residents of the Moscow region.
Often on the packaging it is written that the variety is winter-hardy. Inexperienced gardeners living in the Moscow region "peck" at him and do not cover the rose bushes for the winter. As a result, the flowers are irretrievably lost. After all, winter frosts and thaws destroy not only the buds, but also the root system. How to cover roses for the winter in the Moscow region, what covering materials to use, we will tell in the article.

Preparing roses for winter


Only healthy roses can overwinter with minimal damage. Before covering the bushes, you need to carry out a set of measures:
- feed with potassium-phosphorus preparations;
- cut out all thin and diseased shoots;
- remove foliage if possible;
- clean the soil under the bush from plant debris;
- carry out preventive treatment with copper sulfate.
Work on the shelter in the rose garden should be started no earlier than a stable minus temperature in the region of 5-7 ° frost is established. Depending on the region, this can be October or November. Earlier "warming" of the bushes will lead to the fact that they will start to hurt, especially if the heat returns and it rains.
When the shelter is being removed
It is important to build a protection for a climbing rose in time for the winter and also to remove it in time - a delay will lead to the plant damping out under the spring sun, and under an opaque cover the flower will also suffer from a lack of light.
It is necessary to open the bush gradually so that sunburn does not damage the whip.
In the Moscow region and in the middle zone of the Russian Federation, they do this in March, when the sun warms up during the day: they release the ends at the shelter or form air vents.
When the ground thaws and the average daily temperature is at least 4-5 °, all protection is removed.
How to cover ground cover roses for the winter
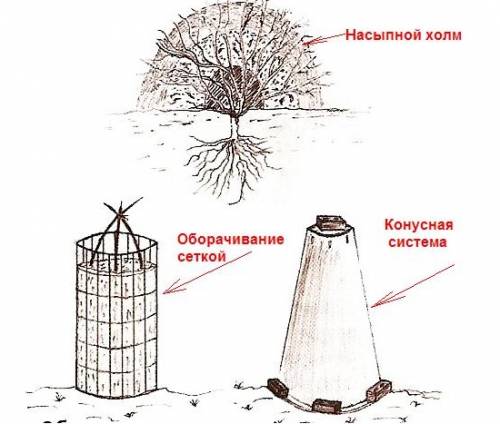
The shelter of rose bushes depends on the form in which they grow, or rather, on their height:
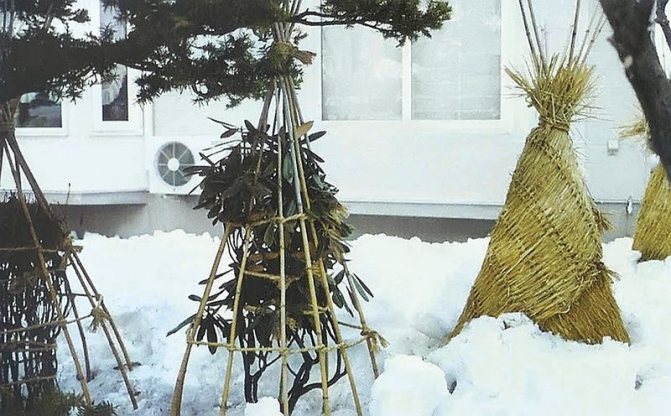
- Low-growing roses will be the least hassle. It is enough just to cover them with branches or spruce branches, and on top - with lutrasil. If desired, a metal frame is constructed instead of branches. Such a double cover will protect the shoots from contact with the tissue, and, consequently, from freezing.


- Medium-sized roses are already quite troublesome to "sprinkle" with branches - they have longer shoots. It will be more convenient to collect the bush, giving the branches a vertical position, and fix it. In this form, the roses can be wrapped with a tarp.


- Tall roses are best laid down neatly by bending them to the ground with metal staples. It is advisable to pre-cover the soil with spruce branches so that the branches do not lie on the ground. Above the bush, it is necessary to install the frame and stretch the agrofiber.


The use of a film as a covering material is permissible only if it is possible to open it frequently. The film does not allow air to pass through and without airing the roses will die. It is also worth considering that it breaks easily.
On warm winter days, when the thaw comes, any shelter must be opened slightly for ventilation. Otherwise, the bushes will mate. It is equally important to remove the protection from the roses in time. This should be done in early spring.
Video about caring for ground cover roses
One can only wonder at the variety of garden roses. One of the most unusual species is ground cover roses. Their main advantage is their rapid growth in width, because even in a short period of time they can cover the area with a fragrant carpet. Despite the small size of the flowers, lush inflorescences and almost continuous flowering throughout the season will provide the necessary decorative effect. Correctly carried out planting of ground cover roses will provide the necessary conditions for further development, and their unpretentiousness and visual appeal make these flowers the favorites of gardeners.


The choice of material for shelter
Today there is a large selection of materials that can be used to cover climbing roses for the winter. Each of them has its own advantages and disadvantages. Any gardener has his own preferences for the type of covering material.
Film
Plastic wrap is the most common covering material. Until recently, it was practically the only option. The film is sold in rolls and has a thickness of 0.03 to 0.4 mm.
Among the advantages of the film are the following:
- transmits sunlight well;
- reliably protects from precipitation.
The disadvantages of polyethylene are:
- quickly becomes unusable (service life one year);
- condensation accumulates under the film, which leads to the development of diseases and decay of plants;
- it is difficult for plants to breathe, as the film does not allow air to pass through.
Spunbond
Spunbond replaced plastic wrap. It is a polypropylene non-woven fabric. The characteristics of spunbond are several times higher than that of ordinary plastic wrap.
Among the advantages are:
- ease;
- transmits light;
- allows plants to breathe;
- allows moisture to pass through, which protects against condensation;
- very durable (it can be washed, glued, sewn).
Among the disadvantages are:
- Cannot fully protect against severe frost.
- Does not guarantee complete dryness of the soil and bushes under cover.
- May be damaged by birds or animals.
Sackcloth
Jute material or burlap is also a fairly popular plant cover for the winter. They are often covered with young heat-loving climbing plants. But this view is more suitable for protection from sunlight.


During cold weather, jute has many disadvantages. Among the most obvious disadvantages is the fact that the burlap gets wet from the snow and becomes an ice blanket. Mold often grows under damp burlap.
In addition, old material can serve as a source of various plant diseases. This is due to the fact that different bacteria and infections from different sources accumulate in old bags.
Cardboard
Sometimes cardboard is used as a covering material. It can protect well against wind and frost. But cardboard will poorly transmit sunlight and air. In addition, it gets wet easily from snow. It is best combined with a film.
Roofing material
Often, various building materials are also used to shelter climbing roses for the winter. The most common among them is roofing felt. It helps to protect not only from frost and wind, but also from rodents.
Most often, roofing material is used in combination with a film or spunbond and builds a reliable shelter for climbing rose bushes.
Spruce or pine branches
There are also more natural types of materials for covering roses. Spruce or pine branches, which are called spruce branches. This is a completely affordable and environmentally friendly type of shelter for the winter.
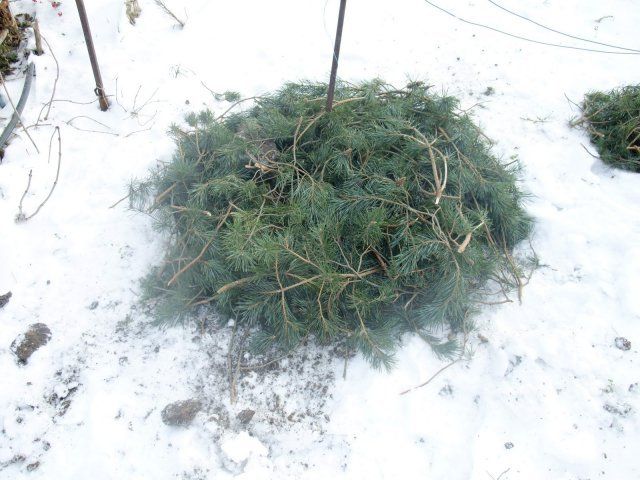


Lapnik protects well from frost and allows air to pass through. Before sheltering a climbing rose with them for the winter, it is imperative to dry the branches. Only healthy branches should be selected so as not to infect the rose bushes. In addition, spruce branches can reliably protect bushes from frost only after sprinkling them with snow.
Among the disadvantages of branches as a covering material, one can note the likelihood of branches getting wet and turning them into an ice blanket. In this case, the spruce branches will block the air flow, and air will not flow to the climbing rose. In order to avoid this, gardeners often cover the branches with foil, and then cover them with snow.
Basic requirements for the landing site
Conditions for growing roses are almost the same for all varieties. This should be a well-lit, open area, away from tall buildings and trees. For planting creeping roses, it is advisable to provide for a small elevation, which will save the plant from stagnant melt water in spring. Many varieties of ground cover roses are distinguished by rather long branches, up to two meters. They can be used to decorate verandas and gazebos like weaving varieties. These varieties also look attractive in flowerpots, among compositions of stones and other architectural delights.
The future landing site must meet the following requirements:
- Good soil aeration.
- Light shading during the sun.
- West or south-east direction.
- Enough room for further growth.
It is preferable to plant roses on black soil or light loam. Sandstones that are too loose do not retain moisture and nutrients well, so it is recommended to add a little clay to them. For heavy soils, it is best to use peat and humus as an additional ingredient.


It is necessary to allow the shoots to ripen
During the flowering period, the climbing rose looks divine; many growers want to extend this period of time. But they can make a fatal mistake. If the plant blooms before frost, there is a high probability of its death. Therefore, in August, it is necessary to completely stop the introduction of nitrogen-containing feeding substances.




Preparation and landing
It is advisable to carry out preparatory measures at least a month before planting roses. The soil must be dug up, all weeds and their rhizomes must be selected, and also fed with fertilizers containing nitrogen. The composition of the soil should be loose and nutritious, the reaction of the medium is from 5.5 to 6.5 pH. To alkalize acidic soil, use dolomite flour or fluff lime. If the reaction is alkaline, superphosphates are added to the soil.
Read also How to assess the condition of the house
It is best to plant ground cover roses in spring or autumn. For harsh climates, spring planting will be more beneficial so that the plant can take root properly before next winter. If the climate is mild and the winters are not so cold, ground cover roses are planted in the fall.
How is the landing:
- The size of the hole is determined by the root system of the seedling. When planting roses in a container, you must leave a margin of 8-10 centimeters on each side. For plants with an open root system, a place of 40 × 40 centimeters is usually prepared.
- The top layer of fertile soil from the hole is mixed with humus, peat and mineral fertilizers.
- The seedling is placed vertically in the hole. The surface of the ground should be at the level of the root bud. For container seedlings, the top edge of the potted soil can be used as a guide.
- The hole is covered with a previously prepared soil mixture, tamping it tightly at the roots. It is allowed to spill the earth with water so that there are no air voids inside.
- After planting, the plant is well watered, the topsoil is mulched with straw, dry grass or peat.This is a prerequisite, because with further growth of shoots it will be difficult to care for the root area, and this will save planting from weeds.
Before planting a rose from a container, it is imperative to water it well so that the earthy ball does not disintegrate. This will prevent root trauma and increase the chances of successful rooting. It is better to soak seedlings with an open root system in a stimulating solution for a day. Ground cover roses are planted directly from the water, preventing the root shoots from drying out.


Growing features


Even a novice florist can plant similar plants on his site and successfully grow them. Ground cover roses are kept according to the same rules as other flowers.
Choosing a landing site
Flowers are demanding on growing conditions. Factors affecting the growth of rose bushes:
- illumination;
- temperature regime;
- soil moisture;
- pH level;
- planting density;
- proximity to other plants.
Shrubs grow well, bloom profusely and for a long time in sunny areas, although in light partial shade they feel quite comfortable. It is advisable to choose such a place in the garden so that the sun's rays illuminate the plants only in the first half of the day, and in the afternoon they are shaded from the scorching summer sun, from which the foliage and color of the petals fade. Optimal soil moisture is equally important for flowers. It is most rational to place the rose garden on a small slope - so the level of humidity and evaporation will create the ideal proportion. It is even better if you raise the flower garden 40-50 centimeters from the total surface of the garden. Such placement will protect the flowers from frost, since it is known that cold air accumulates in the lowlands.
Important!
The slope of the site should be 7-11 degrees to the southeast or west.


Landscape designers prefer to place roses next to tall shrubs and trees. So the composition looks much more spectacular, and at the same time, tall neighbors create a saving shadow and protect from the wind. However, you should not plant seedlings too close to giant plants, since the latter will take all the nutrients from roses, thereby inhibiting their development and flowering. It is also impossible to place a rose garden near the walls of a house, a high, deaf fence - the root system in such places develops slowly, the shoots do not have the strength to grow, and few flowers are formed on such plants. In addition, roses planted "in the wrong" places often suffer from fungal diseases, since constant shade and poor ventilation create excessive moisture. Roses, on the other hand, do not tolerate excess water in the soil, because of which oxygen practically does not get inside, and the roots suffer from this in turn. Use a gravel pad to lighten the soil slightly. In addition, dense soils are highly acidic, which also affects the vitality of roses.
Attention!
The optimal acidity index for roses is 5.5-6.5 pH.
Roses are also temperature sensitive. If they are uncomfortable, then they immediately react, dropping the ovaries or stopping flowering. So, in the area of the flower garden, the air should be warmed up by 15-22 degrees. The optimum soil temperature is 17-20 degrees. If the soil is too overheated, the roses stop growing. Mulching with peat or sawdust will help to avoid such a situation. Too cold soil leads to freezing and death of the roots. Therefore, you should not rush to plant ground cover roses, but it is better to wait for the most suitable climatic conditions.
When planning a rose garden, it is important to know which plants have grown in a given area in past years. It is unacceptable to arrange a rose garden where roses or rosaceous ones have already grown - pear, apricot, irga, cherry and others. This rule is due to the fact that the soil here is very depleted.If there is no other place for laying out the front garden, then flowers can be placed in the place of the old flower garden, but on condition that the land to a depth of 50 centimeters will be completely replaced by a more fertile one.
Soil preparation


The best soil for ground cover flowers is loamy, well filled with organic matter and minerals, with high water and air permeability. In sandy soil, due to sudden changes in temperature, the roots suffer, the seedlings do not take root well and grow weak. You can saturate the depleted soil by adding "heavy" dense components - compost, peat, clay, turf. At the same time, too dense, clayey soil is diluted with sand, peat, humus, chicken droppings.
Roses are usually planted in April-May. In this case, preparatory work on the site begins in the fall. During the autumn deep digging of the earth (the digging depth is 35 centimeters), organic materials (compost, old manure or peat) and superphosphate or phosphate rock are introduced into it. Excess soil acid is neutralized with lime.
Important!
The introduction of fertilizers in advance of the planting procedure is necessary so that all the nutrients have time to be evenly distributed inside the soil.
Preparing seedlings for planting


Young rose seedlings are purchased in specialized nurseries. A high-quality seedling should have a highly developed rhizome with a large number of small shoots and at least three thick semi-lignified shoots with leaves and buds. Before planting, all the leaves are cut off.
Seedlings that grow in a container or pot, that is, with a closed root system, take root best of all. If the roots are in the open air, then they often dry out and become brittle, and this prevents their normal fusion with the ground. Some rose growers recommend planting roses in nets, but such a "container" does not always contain the roots properly - the root suckers often bend up and break.
Therefore, experts advise removing seedlings from the nursery and planting them with open roots. The integrity of the earthen coma can not be disturbed and roses can be planted using the transshipment method. To stimulate root growth, incisions up to 2 centimeters deep are made in several places.
If seedlings with an open root system are used for planting, then before planting the roots are shortened by 1/3 (up to 30 centimeters), and all incompetent shoots are also removed. If the roots are partially dry, they must be soaked in water for a day. Potassium permanganate can be added to the water for disinfection. Already before the disembarkation procedure, the roots are dipped into a clay-dung chatter, and the ground organs are treated with copper sulfate.
Landing dates


Groundcover roses can be planted in spring and fall. For regions with mild winters, it is preferable to plant flowers in open ground in the fall. In the central part of Russia and Siberia, roses are planted mainly in spring.
Spring planting
In spring, flowers are planted in April-early May, when it becomes warm enough outside and the soil warms up to optimal levels. If the weather does not allow the flowers to be planted on time, then the seedlings are placed in a bucket of moistened sand under a film cover. Roses are planted in deep pits, the bottom of which is covered with sand. The seedlings are placed on the inclined side of the pit. During spring pruning, the shoots are cut off the seedlings so that 2-3 buds remain on them.
Autumn planting
In autumn, it is customary to plant landscape roses from mid-October to the second decade of October, so that the seedlings have time to take root before the onset of frost. With this type of planting, the shoots of the seedlings are not cut off, but only slightly shortened. This is done in order not to stimulate plants for vegetation - in the autumn-winter period, the flower should be in a dormant state.
Technology of planting ground cover roses


Rose seedlings are planted in planting holes or trenches, which are dug in advance: if planting is done in the spring, then they are dug in the fall and vice versa. The distance between the holes must be at least 30 centimeters. The depth of the hole is 50-70 centimeters (roses have very long roots), the diameter is 50 centimeters. The bottom of the hole is drained with a layer of gravel (if the soil is dense) or a 10-centimeter layer of clay is laid (if the soil is sandy). The bottom of the planting hole is loosened so that the roots can easily penetrate into the soil layers. A couple of weeks before planting flowers, the wells are supplied with minerals and organics. On the day of planting, the hole is watered abundantly with water.
The bushes must be placed in the hole in such a way that all the roots look down, and do not bend up. To do this, a small mound is poured in the center of the hole and root suckers are laid out on its slopes. The earth is poured in parts, periodically shaking the handle so that all voids are clogged with earth. The root collar or the graft site should remain underground at a depth of 4-5 centimeters. From above, the surface is well compacted, watered with warm water and spudded to stimulate the formation of new roots. For the first 7-10 days, the planted seedlings should be under an awning - shading will contribute to better survival. As soon as a growth appears next to the bush, it is uncooked.
Best care tips
Groundcover roses are less demanding than other varieties. This gives a good chance to grow luxurious flowers, even for gardening beginners. At the same time, it is possible to achieve long flowering and active growth of bushes only if all the "whims" of the garden beauty are fulfilled. To do this, you need to know what conditions are necessary for this plant, as well as the useful nuances of successful cultivation.
Success secrets for ground cover roses:
- Top dressing should be carried out only the next year after planting. The frequency of mineral addition is determined individually. In general, it is necessary to use 5-7 dressings per season. Groundcover roses are also very susceptible to foliar dressing, which can be alternated with regular ones.
- In early spring, the bushes are fed with nitrogen fertilizers. For this, rotted manure, humus or ammonium nitrate are used. Before feeding, the plant is well watered.
- Before the formation of buds, sodium humate or potassium sulfate is added. This will give the plant the necessary strength to bloom. During flowering, fertilizers are not applied, this can damage the bush. After flowering, old buds must be removed from the plant, and then well fed with potash and phosphorus complexes. For re-flowering varieties, it is necessary to use at least two dressings with a break of 10 days.
- At the end of the season, three-fold feeding is carried out, the main purpose of which is to give the plant an additional margin of safety for a safe wintering. At the end of summer, organic matter is used, after two weeks - phosphorus complexes, after another two - potassium. It is important to finish feeding about a month before the onset of real frost, so the timing can be determined according to your climatic region.
- Roses are also pruned the next year after planting. This stimulates the formation of side shoots and an attractive bush shape. The cut points must be treated with garden varnish, and the bush itself is sprayed with Bordeaux mixture to prevent infection of the branches.
- A rejuvenating pruning of the bush is recommended about once every five years. To do this, all shoots are shortened to 20-25 centimeters, and the middle of the bush is thinned out. The disadvantage is the loss of decorativeness, but the next season the plant will thank the owner with lush flowering and active growth.
- Watering garden roses must be carried out with abundant, previously settled water. On average, each bush will need from 10 liters of water.At the same time, waterlogging is not allowed, as a result of which the plant can rot and hurt.
- Loosening the bush is desirable, but difficult for old plants. The root area is necessarily mulched, and care is carried out as far as possible. Strongly overgrown bushes are more expedient to simply spray and water, and loosening is carried out when pruning or feeding.
The video clip will tell you a lot of useful information about growing ground cover roses.
The meaning of cutting a flower
The climbing rose is a capricious plant. Therefore, it needs to be cut regularly. It is advisable to do this kind of care work in the fall.
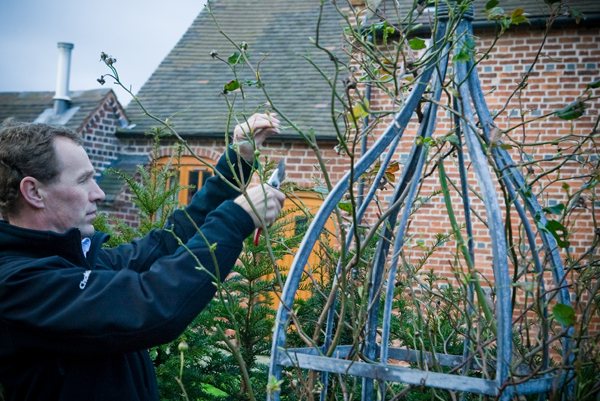


Cropping is required for:
- plant shoots renewal;
- removal of old and dried branches;
- thinning (the plant will grow evenly);
- good growth and flowering for the next season;
- even distribution of nutrients throughout the flower (top and bottom);
- increasing resistance to harmful insects and diseases;
- rapid cell division during the growing season.
Attention!
During pruning, experienced gardeners set the direction of flower growth in the right direction.




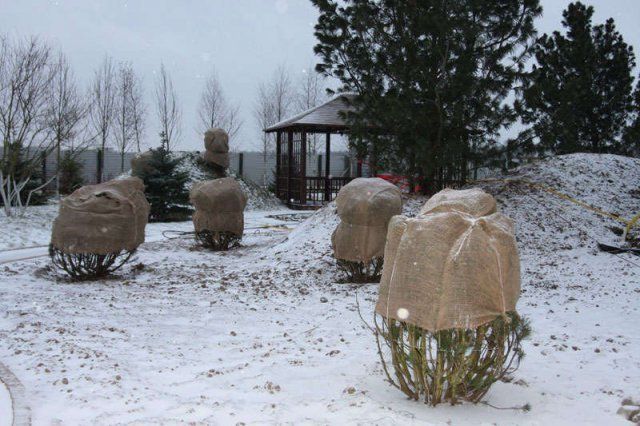
Shelter for the winter
An important condition for the preservation of planted ground cover roses is preparation for winter and reliable protection from frost. Many varieties of ground cover roses winter safely without additional shelters, but in case of unfavorable weather conditions, the plant may freeze, which will entail poor development and even death of the bush. To prevent this from happening, experienced gardeners recommend that you cover a ground cover rose for the winter.
It is quite simple to do this:
- Low-growing varieties are dressed up with spruce branches and dry branches and covered with a dense cloth or lutrasil on top. You can build an air shelter from metal arcs and agrofibre.
- Of medium height, the branches are loosely tied in an upright position, wrapped with a tarp or other suitable cloth. The root area is covered with sawdust.
- Tall varieties are laid on the ground, with pre-thrown branches and spruce branches. This will help protect the branches from rotting. An air shelter is being constructed on top.
Read also Green tomatoes for the winter as in the store
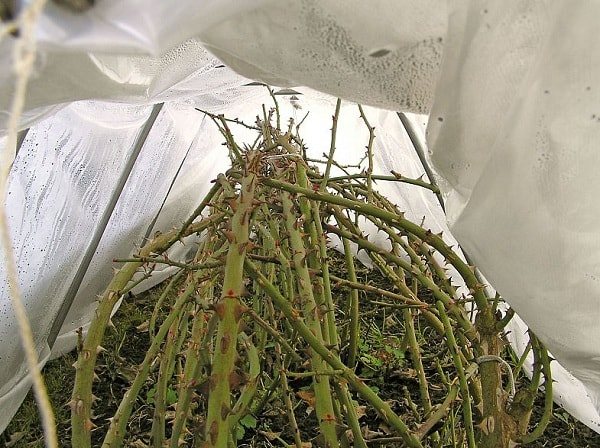


It is necessary to cover roses for the winter after the onset of the first frost, because in warm weather the plant can rot and rot. If warming has come, the shelter is ventilated during the day. Leaves are removed from the bush in advance and the branches are sanitized. It is also recommended to cut thin and weak branches, which, if dying from a cold snap, can be a source of infection for the entire bush. The shelter is removed in early spring, after which it is necessary to assess the condition of the bush, remove frozen shoots, spray the plant with Bordeaux mixture and feed.
The ground cover rose, the planting and care of the open ground of which are discussed in our article, are distinguished by their unpretentiousness, but they can decorate any area. They are often used in landscape design to "fill" empty areas, as well as in the design of garden compositions. Proper care and reliable shelter for the winter will provide the plant with a long life and excellent flowering.
Roses are deservedly considered royal flowers. Their beauty and fragrance cannot be compared with any other flower. In order for roses to bloom and delight with their beauty from year to year, they need proper care, including preparation for winter.
Reproduction of carpet roses


All varieties of these beautiful flowers reproduce mainly vegetatively - by layering, cuttings, dividing the bush, root suckers. When breeding ground cover species, gardeners most often use cuttings and layering, since these methods allow you to get new, well-developed bushes in a short time and without investment.
Layers
Roses creeping on the ground reproduce with the help of layering on their own - the lashes take root in the knee.If there is a desire to help them, then it will be enough to dig a long shoot together with the buds with earth, leaving the end of the lash outside. The twig in the ground is watered abundantly all summer. By autumn, the shoot will grow over its own root system. Then it is separated from the mother plant and transplanted to a new place or moved to a pot so that the young bush overwinters in more comfortable conditions.
Cuttings


You can increase the population of ground cover roses in your area by cuttings. To do this, cuttings 15-20 centimeters long are cut from faded one-year-old semi-lignified shoots. Each stalk should have a smooth stem, 2-3 internodes and the same number of buds.
Note!
Cuttings are cut from the middle of the shoot. The ends of the branches for grafting are not suitable, since they have not yet ripened, which means that such cuttings will require much more time for rooting.
Before rooting, cuttings are cleaned of thorns and leaves. The lower part of the twig is dipped in a growth stimulator and planted in a light nutritious soil consisting of sand, humus (or peat and compost). The cuttings are deepened into the ground by 2-3 centimeters, so that the lower bud is located very close to the surface. The cuttings are rooted in a small groove or nursery covered with a film on top. To activate growth, the microclimate of an impromptu greenhouse must be warm and humid.
If rooting was carried out in the spring (from cuttings prepared in advance), then the planting of roses for permanent residence is carried out in the fall with obligatory shelter for the winter. When grafting in the fall, young bushes are planted in open ground only next spring, as soon as the ground warms up enough. In the first year, it is necessary to remove the maturing buds and monitor the moisture and cleanliness of the soil.
Caring for roses in autumn
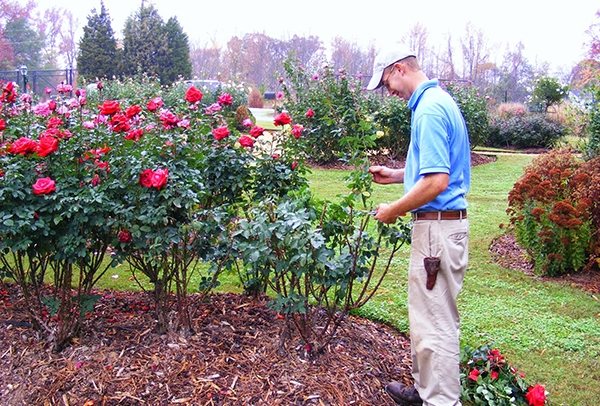


Caring for roses in the fall includes pruning, feeding and preparing the bushes for the winter period. Each type of roses requires a special approach and in each case, caring for them is different from the other.
Pruning
Roses for the winter need to be pruned in order to simplify the process of sheltering these plants, especially miniature, polyanthus, hybrid tea varieties and Floribunda roses, which quite often reach 2 meters in height.
There are several types of trimming:
- Short - shoots are cut to 5-15 centimeters from the ground. 2-3 buds remain on the stem near the ground. This pruning is well tolerated by densely branching polyanthus roses. Cascading roses in the first year after planting are pruned to 15 centimeters, and then pruning becomes more moderate.
- Medium - the shoots are shortened to 30-40 centimeters. 5 kidneys remain on them. This pruning is applied to hybrid tea, Floribunda roses, remontant roses, Pernetsian roses.
- Long - trimming the tips of the shoots. On cut stems 0.7-1 meter long, 8-10 buds remain. This is how park, climbing small-flowered, Bengal, Old English rose bushes are shortened.
- In climbing large-flowered and shrub roses, perennial shoots are cut by 1/3 to enhance the growth of young branches.
- Groundcover roses only require sanitary pruning.
- Bushes with small flowers do not need to be cut at all, the plants have enough pinching points of growth.
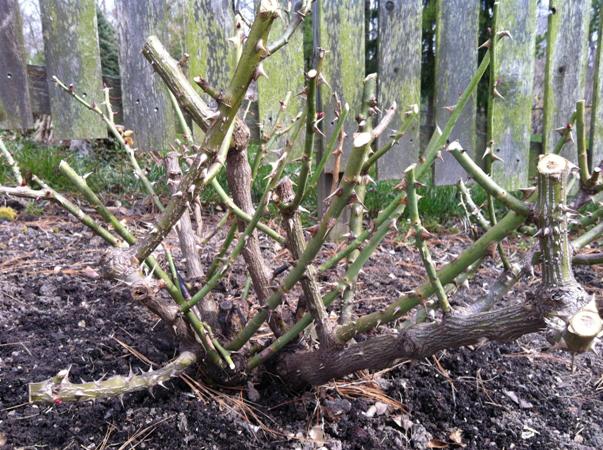


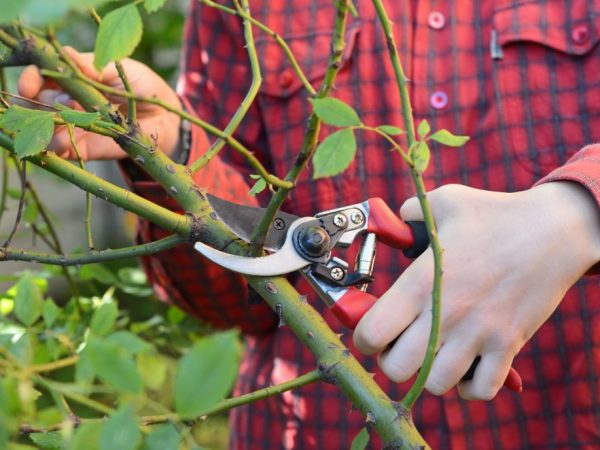
When pruning, the shoots are shortened with a pruner. The cut is made 5 millimeters higher from the bud growing on the outside of the stele. All cuts are made at an angle of 45 degrees. Weakened, damaged, not growing properly, crooked, dry shoots and light, not formed shoots are completely removed. The cut sites are treated with any antiseptic or wood ash powder.
If the plants are not pruned, their growth points are pinched. During the pinching, the buds and young, poorly developed shoots are broken, but not completely removed.They will then simply dry out and can be removed completely.
Top dressing
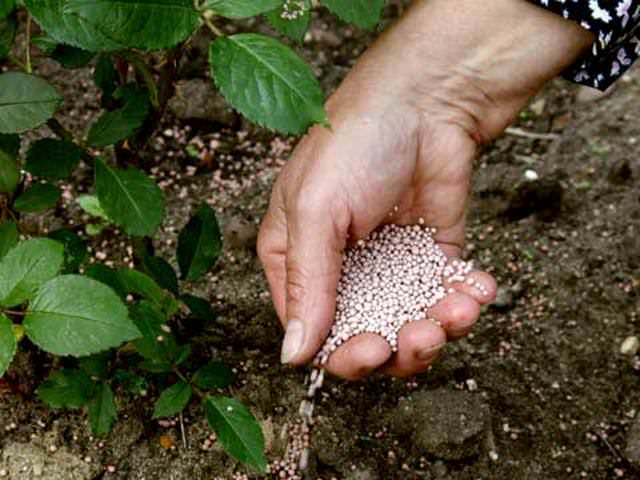


After the autumn pruning of roses, the plants need feeding. It is produced half a month after the removal of excess shoots. At the same time, one must not forget that from the beginning of flowering until the end of the season, nitrogen is excluded from the composition of dressings, which accelerates the growth of the green mass.
For feeding, 10 grams of potassium sulfate, 10 grams of magnesium sulfate, 25 grams of superphosphate and 2.5 grams of boric acid are taken per bucket of water. With a solution, the plants are poured under the root. Top dressing is carried out after watering the bush. The funds are enough for 3-4 square meters of planting. For foliar feeding, 15 grams of potassium monophosphate and 15 grams of superphosphate are used for 3 buckets of water.
A week after applying top dressing, the tops of the shoots are pinched, for faster lignification of the stems.
Top dressing after autumn pruning
In order to feed the rose one last time before the winter season, you need to wait 2 weeks after pruning. During this time, the state of the plant will become stable. The applied fertilizers must contain phosphorus and potassium. These chemicals strengthen the stems well. They also inhibit the growth of new shoots without provoking flowering.
After the last fertilization, the tops of the shoots must be pinned. It is useful for strengthening the main body of the plant.


The flower is very weakened in autumn. Therefore, it is best to apply groundbait in damp ground in the evening, when dusk falls. Such care will help the climbing rose to winter calmly and without injuries.
Preparing for winter by region


When the air temperature is below 0 degrees, the sap flow in the upper part of the rose bushes stops and the plants fall asleep. With warming, the sap flow of roses resumes and with a new cold snap, moisture on the stems freezes, and the ice that appears breaks the stems. The rupture sites are affected by microorganisms that cause disease.
To prevent this from happening, experienced gardeners are trying to prevent this situation and prepare flower beds with roses for the winter before the onset of stable cold weather. In each region, preparation for winter is carried out at its own specific time, which cannot be missed.
In outskirts of Moscow


Preparation of rose bushes for winter in the Moscow region begins in mid-September - early October. First, fertilizers are applied under the bushes, then irrigation and digging of the earth around the plants stop. Leaves are removed on the stems, pruning is done, and the roots are covered. With the onset of frost, the bushes are covered with a protective shelter.
Read also Double-glazed veranda attached to the house
Shelter of bushes is done in October. The dates may shift, depending on the weather conditions of the current year.
In the Urals
In the Urals, the preparation of rose bushes for winter occurs in late August - early September. The final shelter of roses is carried out no later than early October. By this time, the plants are completely ready for winter.
In Siberia
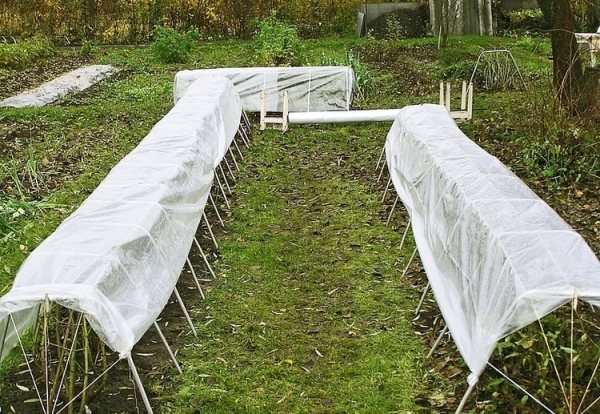


In Siberia, roses are prepared for winter based on the weather forecast. Preparation begins in August. In September, plants are covered with protective materials until spring. The snow in this region is an additional shelter from the cold, which additionally retains heat inside the cover materials that protect the bushes.
In the Leningrad region
In the Leningrad Region, preparation of roses for wintering begins in early September.
- In early autumn, flowers are cut and dry buds are cut off.
- In mid-September, the bushes are fertilized with potassium-magnesium dressings.
- By the end of September, yellowed leaves break off on the bush.
- Then the bushes are pruned.
- With the onset of stable frosts, the plants are covered with any covering material.
Tips from experienced florists


At the end of August, fertilizing with nitrogen fertilizers is stopped. Nitrogen stimulates the growth of new shoots that weaken the bushes. If young shoots appeared in September, they must be removed with pruning shears.
Potassium and phosphorus when feeding is applied around September 15th.
From the beginning of September, the watering of the bushes is gradually decreasing. It stops completely when the ground is completely frozen.
If the bush continues to actively develop and bloom, the process can be stopped by pinching the shoots and bending the stems around the buds.
After pruning, dry leaves under the bushes are raked up and burned so that infections and pests that have appeared on them during the growing season do not spread to the plants.
The shelter of the bushes must be treated with all responsibility, otherwise the plants may simply not withstand the long and frosty winter.
A thick non-woven material is used to cover the roses; when the bush is fully covered, it protects it from the cold and possible ailments. Such protection requires rather frequent replacement, since thorny shoots spoil the material and in the spring it becomes unusable.
A more budget option is spruce branches, special wooden boards or a box that can be used for more than one year.


Before the onset of winter, many novice gardeners think about how to properly cover climbing roses for the winter, and whether this procedure is necessary in their region. Regardless of the terrain, the bushes require preparation and some protection from the cold.
With frequent temperature changes, thaws and the absence of snow, even in a temperate climate, there is a likelihood of the death of the bushes. Having protected roses from cold weather, one can confidently expect a lush and bright bloom from them next year.
The autumn period is no less active time for gardeners. Many garden plants need protection for the cold season. So, for example, roses are very delicate and capricious flowers. Not all gardeners know how to cover climbing roses for the winter correctly in order to keep them blooming for the next year.
Features of preparing for winter different types of roses


Shelter of plants for the winter, after all the preparatory measures, is carried out at an air temperature equal to 5 degrees of cold.
Climbing
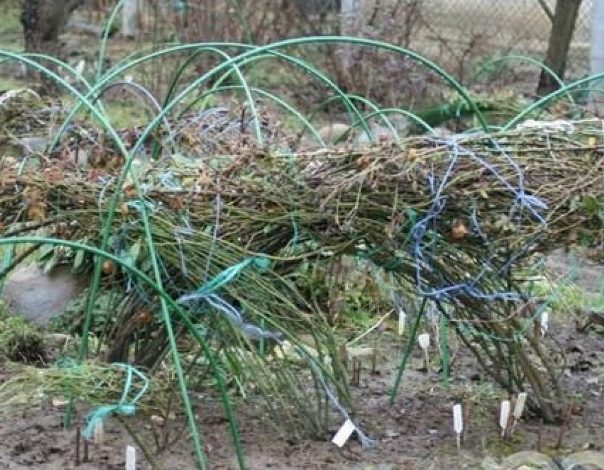


The land around the bushes is cleared of debris. Leaves break off the bushes. The branches of roses are removed from the supports, tied and treated with a fungicidal preparation. A sheet of roofing material, polystyrene or spruce branches is placed under the whip to protect the shoots from decay. A layer of sand or earth is poured on top.
Shoots bend over. With the onset of frost, the roses are covered with roofing material on top, the edges are fixed so that the shelter is not blown away by the wind.
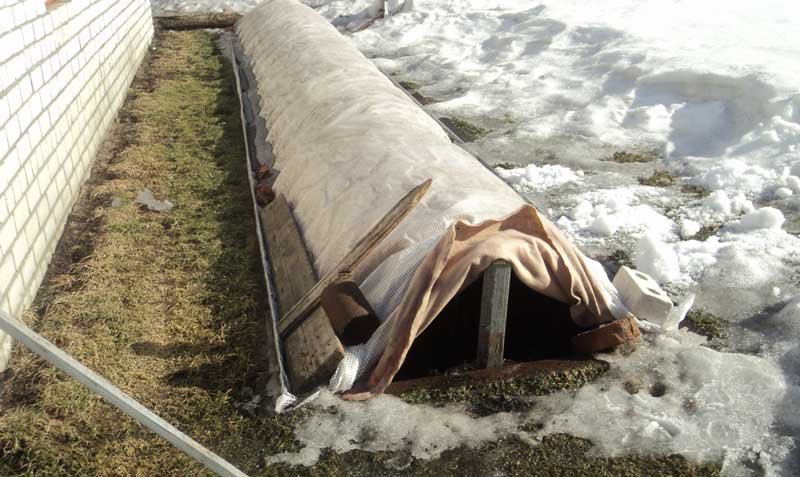
A more reliable and time-consuming option for sheltering climbing roses for cold regions is the shield method. For it, 2 wooden or plywood boards are taken, up to 0.9 meters wide and equal to the length of the bush. The structure is installed on top of the fixed branches. Wedges are driven into the ground to secure the roof against displacement. A film is stretched on top or spruce branches are laid out.
You can also use the bushes tying method for shelter. In this case, the shoots are covered with spruce branches and spunbond. The shelter is pressed down to the ground by boards, bricks and tarpaulins.
Floribunda
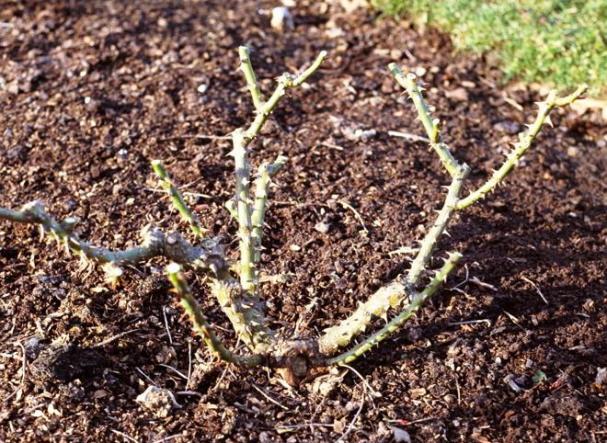


When preparing these roses, leaves are first cut from the bottom of the bushes. When pruning stems, 25-30 centimeters are removed from the total length. The lower part of the stems and the soil around the plants is treated with a 3% solution of copper sulfate or Bordeaux liquid. The ground around the bush is covered with a 15-centimeter layer of sand. The sand protects the roots from freezing.
Shoots are cut and treated with any pesticide. After that, they can be covered with any insulating materials, such as peat, compost, dry soil. High moor peat can be used for cover. The peat will keep the temperature constant and protect the bush from moisture. From above, the shelter is covered with specially prepared shields made of wood or spruce branches. Lapnik additionally protects bushes from rodents.
Tea-hybrid
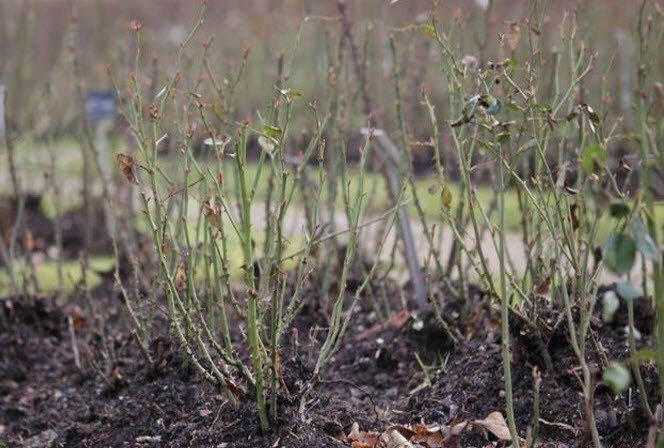


Hybrid tea varieties of roses require a gentle pruning of 10 centimeters.A protective frame is erected over the shortened shoots of roses when sheltered.
At the first frost, the remaining leaves and unripe stems are removed from the plants. Frames are formed from boards, plywood or boards. They are covered with agrofibre. The ends remain free. When frosty weather sets in, they close.
A film is spread on top of the covering material, which will protect the bushes from snow and moisture. The edges of the film are fixed from below with bricks or boards. This method of sheltering bushes is not used on too wet soils, since in this case moisture will collect inside the shelter, which will harm the plants.
Park
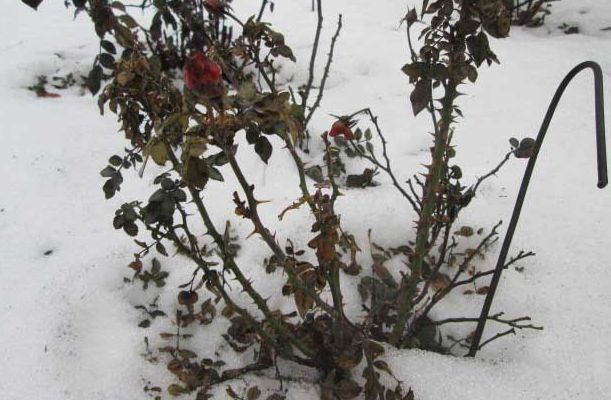


Frost-resistant park varieties are practically not pruned. Before wintering, for better flowering, all strong growths are shortened by 5-10 centimeters. In addition, damaged and dry stems are removed.
Before the onset of the first frost, the bushes are covered with peat or earth by 15-20 centimeters. The stems are bent to the ground. A frame of spruce branches or boards is formed on top, which is covered with a layer of kraft paper, burlap or spunbond, which will protect the bush from temperature extremes.
Groundcover
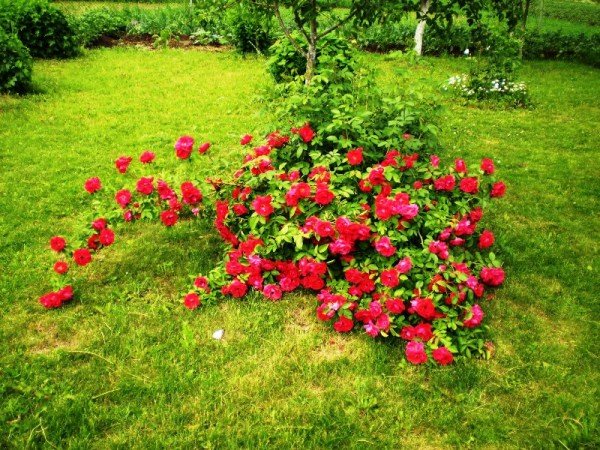


Ground cover roses require shelter if the region has frosty and little snowy winters. With a large layer of snow, the bushes winter well without additional devices.
Alternatively, to cover the roses above the bush, you can form a frame of arcs, and stretch agrofiber and a film with holes for air circulation on top.
When creating a structure, you need to make sure that it is stable and can withstand gusts of wind and the weight of precipitation.
Winter protection methods
Frameless shelters
If there is little or no snow at all, then it is enough to cover the rose lashes with covering material.
For the southern regions with mild winters, winding vines are not removed from the supports. The base of the bush is piled high (up to 30 cm), the branches are covered with spunbond and tied with ropes.
Where the snow cover is insignificant, shoots are laid on a layer of spruce branches, plywood, roofing material. The top is also covered with coniferous paws and a covering material is placed on top.
Frame structures
If there is a lot of snow, then a simple frameless shelter will not work - a snowdrift will press the covering material to the ground, the plant will not have enough air. To avoid this, a rigid structure is erected over the laid branches.
Basic requirements for the frame:
- It should provide a free space above the stems of at least 10-15 cm.
- Maintain the maximum snow depth observed in the area.
- Do not squeeze under the snow (have stiffeners at a short distance from each other).
Frames are constructed from wooden panels or planks, plywood sheets, rods, polypropylene pipes. The simplest design is of boxes covered with spunbond top.
Differences in pruning by cultivar
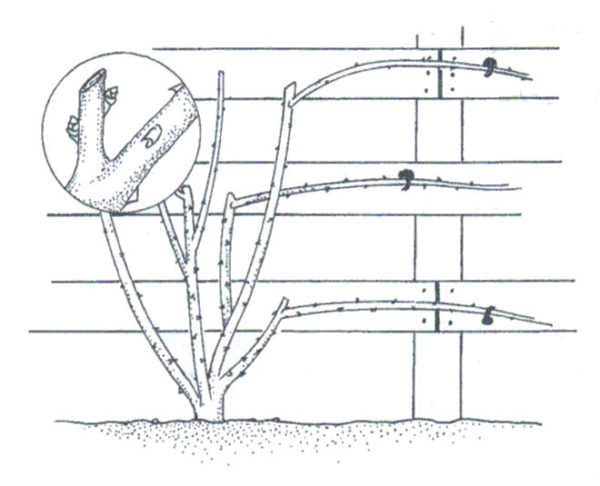

Pruning recommendations differ depending on the garden queen cultivar:
- Early flowering varieties - Excelsa, Dorothy, Perkens. From the purchased seedling, the affected roots are removed and all stems with a length exceeding 30 cm are removed, shortening them. Immediately after flowering, long shoots grow from the bush. Which you need to try to form horizontally. The next year, vertical shoots are formed on horizontal shoots, covered with buds. Blooming shoots this year must be removed. A climbing rose bush can be called fully formed for 2-3 years.
- In plants of the second group, basal shoots are poorly formed, therefore the old ones are removed only after the formation of new ones. After purchase, dry roots are removed from the seedling and long stems are removed. In the second year, the plant dissolves buds on young shoots.
- A group of roses with long, flexible stems. Blossom on last year's shoots. Care consists in pruning the plant after flowering, the cut should be done for 2-3 buds. Side shoots need to be tied, weak ones should be removed - the plant will not bloom on them.
- Pyramidal with vertical growth. After the purchase, the weakened and damaged shoots are pruned, the root ball is revised. Healthy stems provide support. After flowering, lateral shoots with buds are cut to the base. The next year, the flowers bloom on the lateral shoots of the last year, after flowering they are cut to a length of up to 15 cm at the base.
- Vigorous vigorous bushes with shoots up to 6 m long. Form horizontally and vertically. Pruning of old shoots is carried out annually. Side shoots are removed selectively.
Compliance with the rules of pruning will allow you to get lush bloom and see how the rose weaves and grows quickly in the next season. The main condition for the successful completion of the procedure is the temperature regime and proper wintering.
Completion of watering
Oddly enough, but roses do not particularly need abundant watering even during the period of active growth, since their homeland is the arid regions of the Mediterranean. They are able to develop such a powerful and deep root system that they will easily "extract" water for themselves from a depth of more than two meters.
Moreover, you should not intensively water the garden beauties with the approach of winter. In the conditions of the Moscow region, watering of roses is usually reduced from the second half of August in order to do without it by September, when the temperature drops to 8-10 ° C.
Important! In autumn, the ground around the rose bushes should not be damp. Excessive dampness is a source of disease.
Moreover, if September and October "indulge" with rains, especially prolonged ones, many gardeners even cover the bushes and the ground next to them with a film to prevent excess moisture. Most often, frame arcs of greenhouses and ordinary film are used for this.
When to prune
When considering the pruning process, it should be mentioned that climbing roses can bloom on last year's or young branches. This is the main condition that is taken into account when caring for a plant. Rambler give color only on last year's branches, therefore they are pruned in the fall after the completion of the vegetative cycle with flowering. In this case, dry inflorescences must be removed.
Read also: Caring for grapes before winter
Claymers bloom on young branches that are no more than 1 year old, therefore pruning is recommended in early spring after the air temperature in the daytime and at night is kept at around +2 degrees. Pruning at a time when night frost is possible is unacceptable, the frost will "grab" the slices and they will not give growth and flowers. Rot, which is formed as a result of fungal infection, is an equally dangerous problem, therefore, after formation, the plant must be treated with a fungicide.
Misconception 2: the warmer the shelter for roses, the better
Plants are well protected from the cold not by the non-woven material itself, but by the air gap between the bush and the shelter. Also an excellent insulation is a thick layer of snow. Therefore, the warmest shelter for roses is a solid frame (which will create a large cushion of warm air), covered with a white spunbond with a density of 60 g / m2, and on top of it - with snow.
The shelter frame can be built from wooden poles or boards, perforated plywood boxes, tall plastic vegetable boxes. Or buy a ready-made frame made of polymer tubes in a garden store.
Shelter terms in the Moscow region
So that the flowers do not die from severe frosts, which are inherent in the Moscow region, rose bushes must be covered. If the temperature is below freezing, it can significantly damage the young stems and the root system of the plant. This can cause the death of the rose. Adequate shelter will help the shrubbery gain strength and ensure a quiet winter.
The event itself for sheltering the plant is not particularly difficult, but you should still pay attention to some points.To begin with, you need to understand that you cannot cover a rose bush in the Moscow region ahead of time, otherwise it will rot and die. The event should be held when the temperature reaches -5… -8 ° C and remains at this level for 7 days.
Digging, fertilizing and hilling
The last loosening of the soil near the rose bushes is usually carried out in September, so as not to disturb the roots later, but to allow them to prepare for winter. They usually loosen with a pitchfork - this is less likely to damage the roots.
Simultaneously with loosening, the last fertilizing of the season with potassium sulfate is also introduced. It increases the winter hardiness of roses, and also promotes the ripening of their wood. Potassium sulfate is often successfully replaced with ordinary banana peel by dropping it into the ground.
One of the main points in preparing roses for winter is hilling them. It is better to do this before the first short-term frost in dry sunny weather. First, the remaining leaves are removed, if this has not been done before, then the bases of the bushes are sprayed with copper or iron-containing preparations to protect against fungal diseases.
Rose bushes are sprinkled to a height of 40-50 centimeters with dry earth, or earth with sand. If winters with severe frosts are expected, the bases of the bushes on top of the filled earth are covered with spruce branches.
Important! Sawdust is not used for hilling roses: they cake, damp, mold appears in them, or they freeze into a hard lump that can injure the stems.
It is best if, when hilling, do not rake the earth from the rose garden to the bushes, but simply add it. One bush takes about a bucket of dry earth or a mixture of earth and sand.


Do I need to cover park roses
The easiest way to prepare park roses for wintering. In fact, they are the same rosehip, only cultivated. Therefore, their attitude to winter is quite calm, they hibernate well without shelter, it is not even always recommended to add earth to them, since it will be difficult to get them out in the spring.
Experienced rose growers in the Moscow region still recommend arranging light shelters for them in the form of ordinary wooden boxes, which are filled with dry foliage.


Required inventory for pruning


To trim, you need the following set of tools and accessories:
- pruning shears of different sizes and strengths - for large, old branches, a massive one is needed;
- folding saw with the ability to change the angle of the blade;
- secateurs with one cutting end;
- teflon gloves (long);
- folding rake.
For convenience, you can buy knee pads. They are made from different materials. They can be called an indispensable thing for gardening.
Pruning shears of different sizes are essential for neat work. It is difficult to grab and chop without damaging a large branch with a small device. Working with young shoots requires caution, therefore it is better to work with a pruner with a thin blade.
In the Leningrad region
The weather in this climatic zone is unpredictable due to the constant influence of air masses of different nature. Wet cyclones from the sea coast are replacing cold air. In winter, severe frosts give way to thaws, and in summer the air temperature can drop significantly.