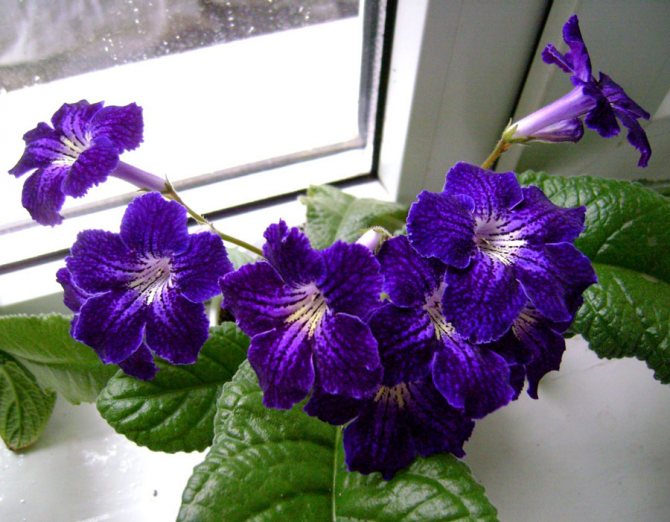
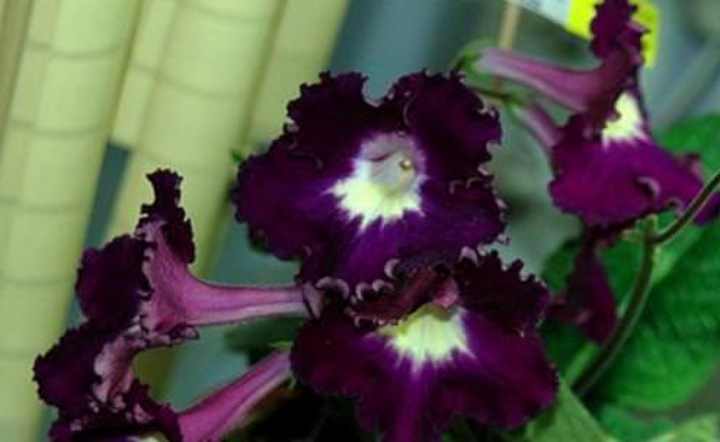
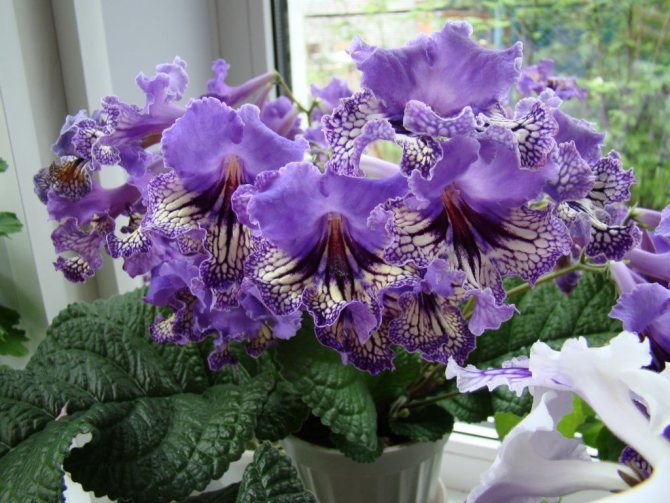
Streptocarpus (Streptocarpus) is a creeping plant, characterized by abundant flowering and original inflorescences, resembling an elongated bell in shape. It belongs to the Gesneriev family and is the closest relative of the Uzambar violets. But in comparison with them, it is more hardy and unpretentious in care, which adds fans among flower growers and amateurs.

Description of streptocarpus


The rosette herb belongs to the Gesneriaceae family (Streptocarpus). More than 105 species of streptocarpus found in the wild have been described. Some of them, about 30%, are adapted for rooting on rocks - lithophytes, the rest are epiphytes that develop due to symbiosis with other plants. You can watch the video how the slope looks like, on which the bushes have blossomed. It is very beautiful - at an adult bush, sometimes 100 flower-buds bloom at the same time.
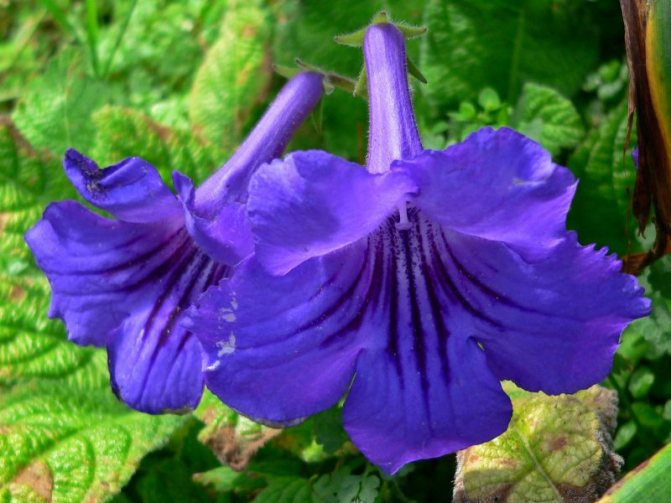
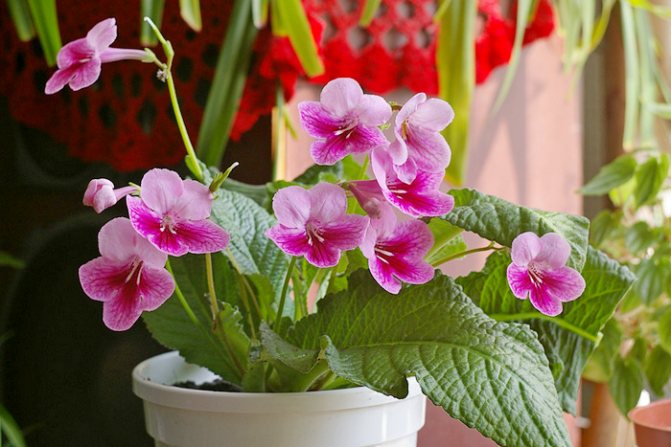
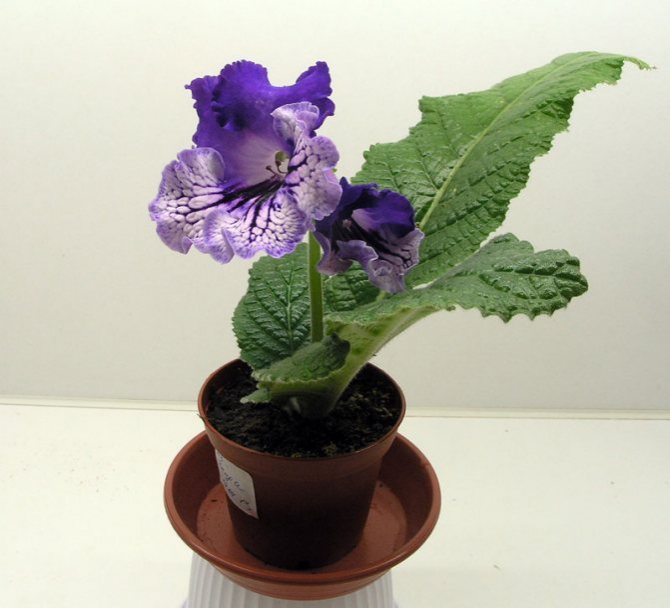
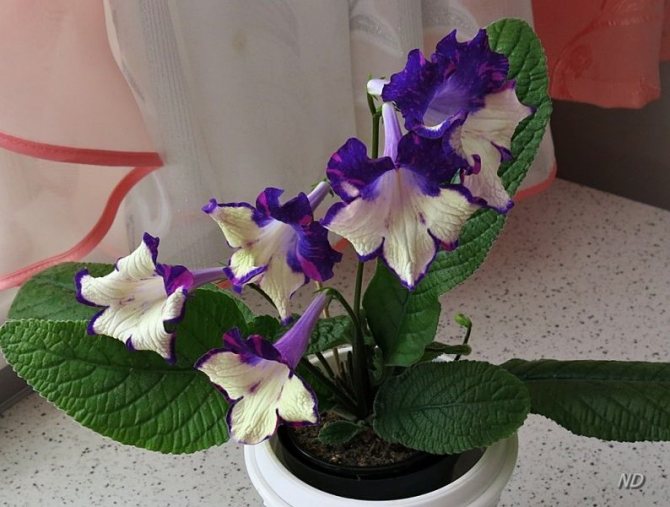
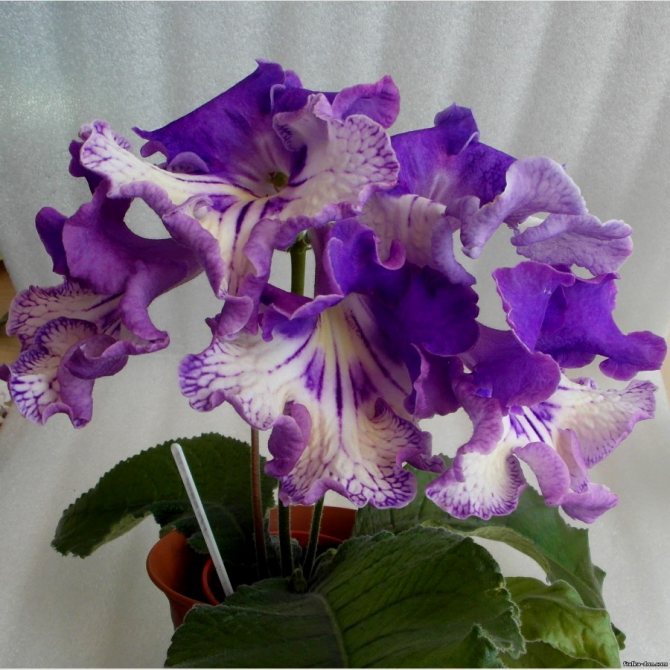
Plants differ in the size and color of the petals. But there are also common signs. You can see in the photo that all species and varieties of streptocarpus have a wide rosette, from which elongated green wrinkled leaves on short petioles, covered with a short down on the front side, rise. Peduncles can be up to 25 cm in length - each has many buds. Each variety has its own color of petals, they can be monochromatic, with dots, stripes, complex interweaving of patterns. In order for flowers to bloom on time, competent care is needed.
Streptocarpus - what kind of flower is it, what family it belongs to
Streptocarpus belongs to the Gesneriev family. Plants of this family can be perennial and annual. In nature - herbaceous shrubs with flowers with 5 petals and fruits in the form of a spiral seed capsule.


Pink streptocarpus
Brief description of why it is called that, origin story
The homeland of the plant is Asia, Africa, the island of Madagascar. It has been popular for about 150 years. It has densely pubescent, wide and long leaves. The edges of the petals of flowers can be wavy, there are double forms. The plant has about 130 species, which have a different structure of leaves and flowers. Hybrid forms have large inflorescences (from 4 to 8 cm).
Interesting information! The fruits of the plant are 2- and 3-fold, twisted in the form of a long spiral or box. Thanks to this unusual form, streptocarpus acquired its name.
Plant features
Feature of culture in the form of fruits. They look like a spiral-curved seed capsule. Due to this shape, the plant received the name "streptocarpus", which in Greek means "twisted box". The leaves are elongated and collected in a basal rosette. The size reaches 30 cm. The number of leaves depends on the type of flower. One variety of streptocarpus has many leaves, while the other has only one. The color is green and variegated.
Streptocarpus flowers are of three types:
- terry;
- semi-double;
- simple.
On a note. The diameter can vary from 2 to 9 cm in diameter. The smaller the size of the flower, the greater their number in the peduncle.
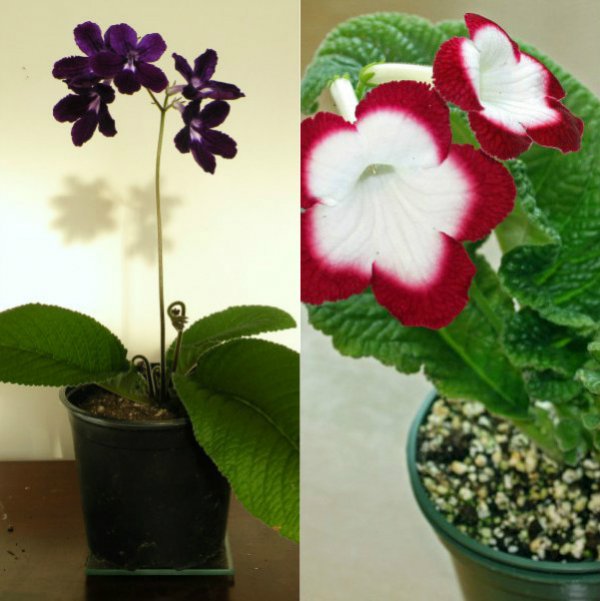
The color of the flowers is replete with variety. Each grower can plant a plant in the following colors:
- white;
- yellow;
- all shades of red and blue;
- lavender;
- velvety purple;
- black.
There are hybrids with bicolor petals covered with dashes, dots or patterns. You can grow varieties with a fancy color of 3-4 flowers. The shape of the petal is different, but the edges are wavy or rounded.
Streptocarp flowering lasts from spring to autumn. If you provide the flower with additional lighting, then it will delight with its colorful flowering all year round. This is achieved by leaving up to 10 peduncles from the axils of each leaf, on which several flowers can concentrate.
Description
Streptocarpus "Jana" during flowering.
Streptocarpus have the form of a rosette of large, fleshy oblong leaves of a dark green color. The length of one leaf can reach 25 cm, and the width - 7-8 cm, while the stems of the plant are very short and covered with fluffy pile. In the center of the rosette there are beautiful, bright, bell-shaped flowers with curved petals.
The plant is distinguished by abundant flowering - one specimen can throw up to hundreds of buds. At the same time, the color of the flower is very diverse - from white and blue, to purple and dark purple.
Streptocarpella is loved by gardeners, both professionals and beginners. If you are lucky enough to get to the exhibition of these indoor plants, the impressions will be the most vivid. The most popular varieties are those that combine two or three colors.
You can see specimens with two or three petals in a strip or dot, with a fringed or corrugated edge. One of the most common types of streptocarpus "Jana". The size of flowers and their number on one bush may be different.
Growing and care
The small homeland of the plant is the tropics of South America and Madagascar. But they do not grow in the depths of tropical forests, but on the slopes of mountains, in woodlands. It is cool in these places at night. That is why streptocarpus is easy to grow on a windowsill. They do not require greenhouse conditions, they will not die during temperature extremes, with changes in humidity and from short-term drafts.
Attention!
The only exception is sensitivity to water hardness.
To ensure stable flowering, it is worth adhering to the recommendations from experienced florists.
- Observe the temperature regime. In summer - 22-25 ° С, in winter - 15-25 ° С. There is no need to open the window, just put it closer to the glass. In the summer, they open a window or put a flowerpot on the balcony.
- Humidity. If the conditions of the tropics are created, then everyone who lives in the apartment will suffer. Therefore, you can limit yourself to 50-70%, but periodically spray the flower with warm water after sunset.
- Lighting. It can be both natural and artificial (phytolamp). In the warm season, flowers are placed on the northern windows, in winter - on the southern ones. If the sun is bright, cover the glass with a light cloth.
- Watering. Water does not come straight from the tap. It should be defended for a day, allowed to warm up to room temperature. Moisten the soil at the edge of the pot so as not to splatter the leaves, or fill the pan.
When dry, watered in small portions, little by little, in order to prevent root rot. Moisture mode is selected independently, analyzing the quality of the soil.
Important!
The surface of the ground is dry, the leaves have slightly lost their turgor - it's time for watering. After 10-15 minutes, when the soil is saturated with water, the elasticity of the leaf plates will be restored.
Lighting
If you are going to grow streptocarpus on a windowsill, keep in mind that this plant is afraid of the direct sun. So, either shade or place where there is no direct sunlight. You yourself will notice when the straps is uncomfortable - he will hang his "ears".


Streptocarpus grows well under artificial light. If you give them a daylight hours of 10-12 hours, then they will bloom.
In summer, in natural light, flowering is more abundant. In winter, plants do not bloom without lighting.
Landing
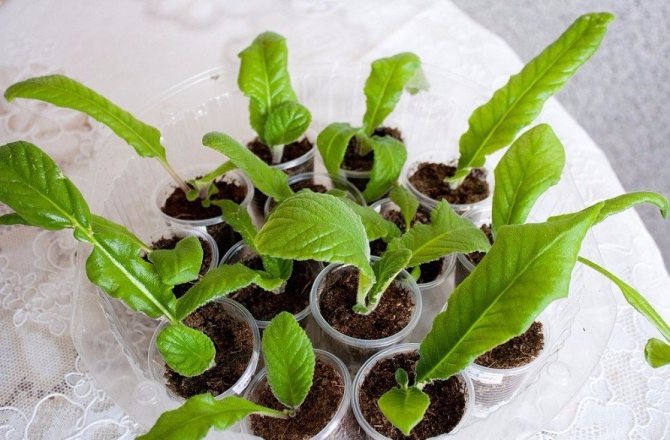
The ideal time for sowing streptocarpus for seedlings is the end of January - beginning of February. This process is painstaking and does not tolerate haste. Small bowls are prepared for future seedlings, on the bottom of which drainage is performed. Soil or a ready-made substrate is poured onto the drainage layer, then the soil is moistened.
Seeds are planted in the soil superficially, they are not covered with earth from above and do not deepen into it, although sometimes sprayed from above from a fine spray. After planting, the container is covered with plastic wrap or glass on top to provide a greenhouse effect. The dish is removed to a warm place, where the temperature is approximately + 21-24 degrees.
Reproduction methods
Dividing the bush
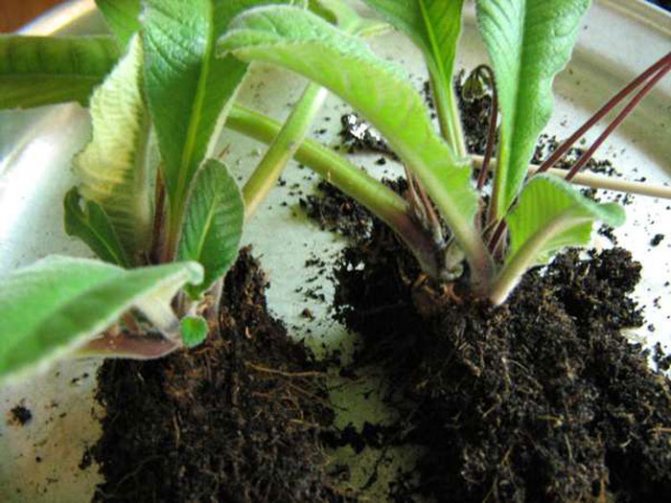


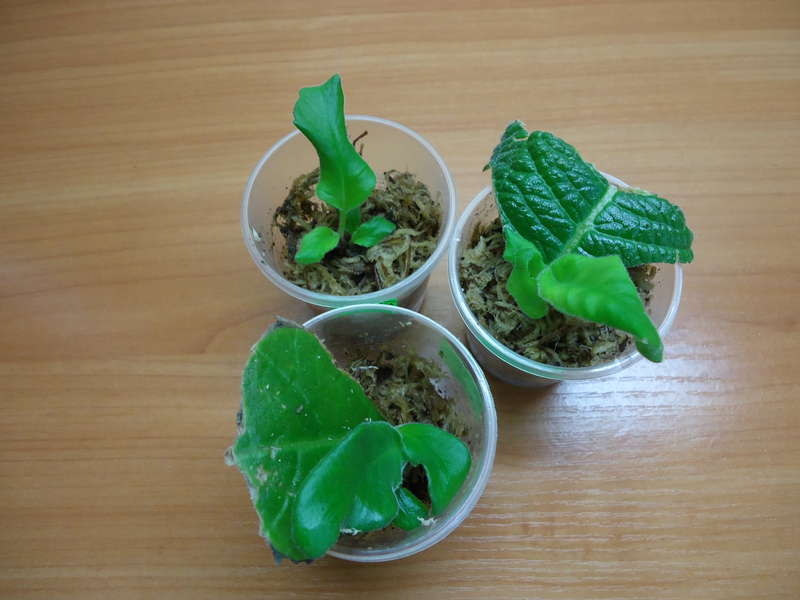
It is possible to propagate by dividing the bush a highly overgrown streptocarpus. To begin with, the substrate in the pot is watered with a small amount of water, then the bush is pulled out of the container, and the remaining soil mixture is removed from the root system. Then a sharp instrument is taken, with which part of the thick root with foliage is separated. Leave the cuttings for a while in the fresh air so that the cut points dry well, then they must be treated with charcoal powder. The prepared pot is filled 2/3 with fresh substrate, then a cut rosette is placed in it and sprinkled with soil mixture to the level of the root collar. Next, the substrate must be slightly compacted, and the bush must be watered with lukewarm water. In order for the division to take root better, the pot is covered with cellophane on top. You can also speed up rooting and activate the growth of young foliage by shortening large leaf plates in half, or they can be cut off altogether. After a little time, the bush that has grown from the cut will begin to bloom.
Growing from seeds
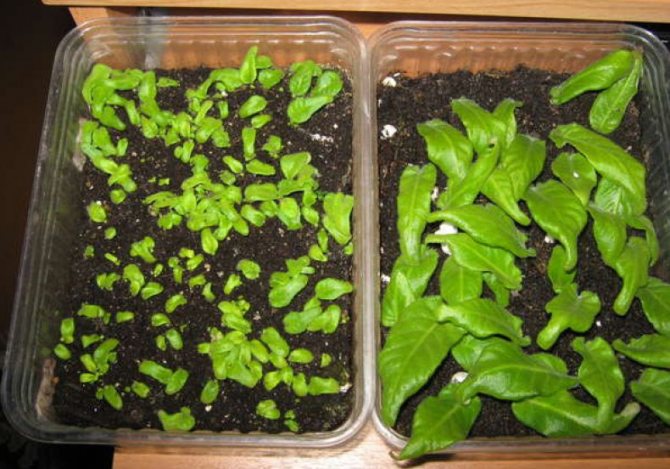


Seeds are sown in a small container, while they are evenly distributed over the surface of the substrate. Then the container is covered with glass on top. Crops need bottom watering through the pallet, they also need to provide systematic ventilation, the lighting should be bright, but diffused, and the air temperature should be constantly about 21 degrees. In order for the temperature not to drop, you need to put a piece of paper on top of the glass. However, it is better to keep crops not on the windowsill, but under the lamps. After 6 weeks, the cover needs to be moved slightly and then removed completely. For the first picking of seedlings, a container is used, which should be slightly larger than the old one, while the distance between them should be increased only slightly. In order not to injure the seedlings during the dive, they must be transplanted carefully. To begin with, you need to lightly knock on the walls of the container, then carefully pry the plant with a needle and, holding the foliage with your fingers, transplant it into a new container. The substrate is slightly compacted, then the transplanted seedlings are watered, after which the container is placed on a pallet and transferred to a warm place, while on top it is covered with glass or film. Individual pots are used for the second pick. In order for the plants to develop better, it is recommended to feed them.
Seeds can be sown several times a year, and this can be done at any time of the year. Thanks to this, you can get bushes that will bloom at different times.
Cuttings
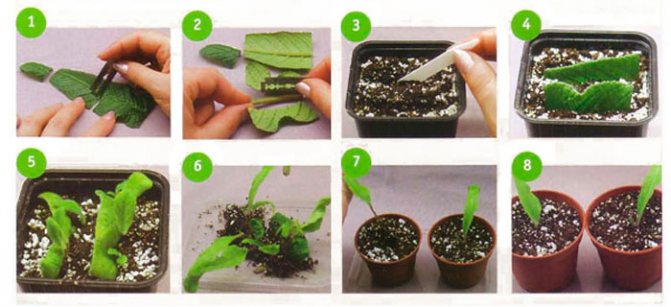

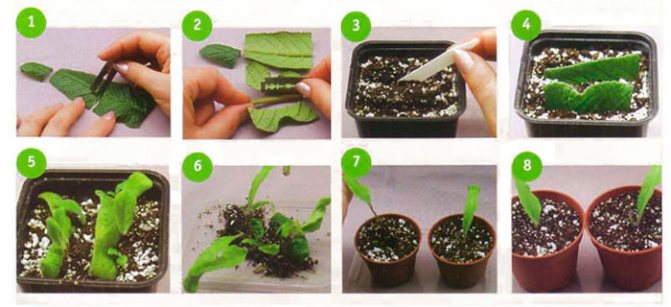
A young leaf plate that is well developed and absolutely healthy (there are no signs of disease or harmful insects) must be cut off from the bush, and then the petiole must be cut with a sharp blade. After the places of the cuts are dry, the leaf stalk must be planted in a small pot, while it is placed vertically. Then it is sprayed with a solution of a fungicidal preparation, and the container is covered with a film on top. After that, the pot is removed to a well-lit and warm place. After 4-6 weeks, young shoots should appear.After the plant grows a little and gets stronger, it needs to be transplanted into a permanent pot. If bushes of streptocarpus of various species are cultivated, then it is recommended to stick labels on the pots with the name of the variety.
For reproduction, you can also use part of the leaf plate. To do this, the sheet is laid with its front surface on a board, after which, using a sharp blade, it is divided into strips, the width of which should be 50 mm. It is necessary to cut the leaf plate perpendicular to the median vein. The lower and uppermost parts of the leaf plate must be thrown out, and the remaining segments are planted in the grooves with the base of the cutting down at an angle of 45 degrees. A distance of at least 30 mm should be kept between the cuttings. They must be sprayed with a solution of a fungicidal preparation, then the container is covered with a transparent bag on top and removed to a humid place where the air temperature should be from 20 to 22 degrees. Watering the cuttings is carried out through the pallet, and they also need daily ventilation. Young shoots will appear from the ground after 6-8 weeks.
For reproduction, you can also use the longitudinal part of the sheet plate. To do this, the leaf is laid on the board face down, and then the median vein is separated with a sharp blade. In the resulting two parts of the sheet plate, the places of the cuts must be sprinkled with coal powder. After that, they are planted in grooves with a cut vertically downward, deepening them by 1/3 of the height of the leaf petiole, then the substrate is slightly compacted, after which it is watered, and the container is covered with a film from above. The container is rearranged in a well-lit and warm place. Young plants will appear along the entire leaf plate from side veins. On the seamy surface of the plate on the median vein, it is necessary to make twenty-millimeter cuts every 2 cm. Then the leaf cutting with the seamy surface is pinned to the surface of the moistened substrate, after which it is sprayed with a fungicidal agent. From above, the container with cuttings must be covered with glass, and then it is transferred to a well-lit place, protected from direct sunlight. After the young shoots appear, the shelter must be slightly moved.
When the grown and matured bushes are transplanted into individual pots, their first few days will need to be covered with a transparent plastic bag. After the shelter is removed, the plants must be looked after in the same way as for the adult specimens.
Diseases and pests
With proper care, streptocarpus blooms for a long time. But if the buds do not form, the leaves begin to dry and fly around, the plant needs help. Withering is caused by: violation of the irrigation regime, high or insufficient humidity, thickening of the green part and the invasion of pests.
To stop parasites, you can carry out preventive spraying with Fitoverm in the warm season. In a glass of settled water, dissolve 2 ml of the drug, apply to the leaves with a spray bottle (spray with a brush) once every 7-9 days. You can use Kleschevit and Aktofit.
Aphid
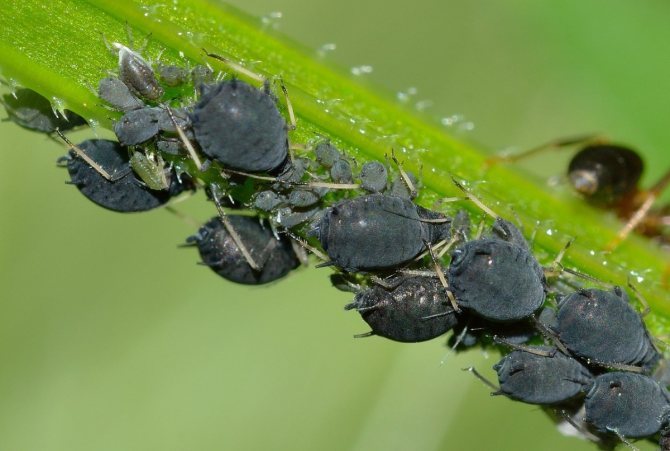


Twisted leaves and white scales on them - the remains of cocoons - testify to pest infestation. The main reason weakening streptocarpus is too abundant moisture. To kill the insect, the plant is sprayed with Iskra Bio (dilution ratio - 10 ml: 1 l of water). Processing is carried out 3 times, with an interval of a week.
I don't want to use chemicals in the apartment, you can use homemade recipes:
- Husks or 1 tbsp. l. finely chopped onions are insisted in 1 liter of water for 8 hours.
- To make an infusion of dried orange peels, pour 100 g of 1 liter of water and leave for 3 days.
Sprayed with the same frequency as Iskra, that is, once every 7 days. If there are children or pets at home, preference is given to such products.
Thrips
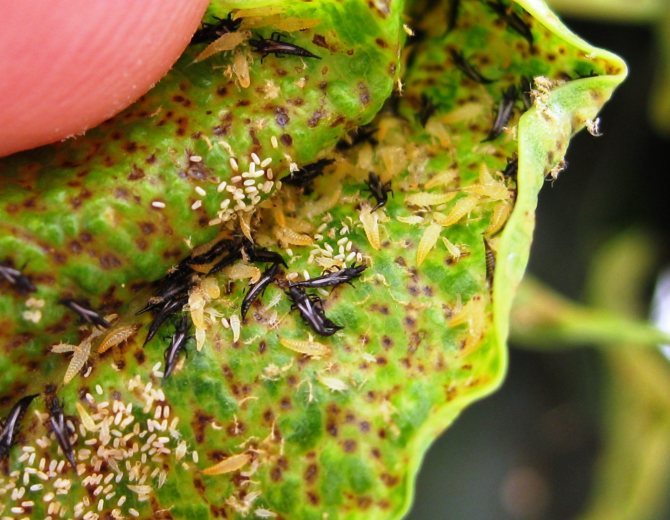


This insect, especially if you didn't have to encounter it, is difficult to see. Infection is noticed by drying brown buds, rapid fall of flowers, empty anthers, crumbling pollen. Acarin, a low toxicity drug, can be used to kill thrips.
Problems when growing streptocarpus, pests, diseases
Cultivation of Cape primrose can be accompanied by a number of problems, the appearance of which negatively affects its condition.
| Manifestation | The reasons | Remedies |
| Withering | Lack of moisture. | Timely watering. |
| Yellow and falling leaves | Lack of nutrients. | Feeding with complex fertilizers. |
| No blooming, pale color and size reduction | Lack of light, inappropriate conditions. | Providing correct lighting, temperature, change of location. |
| Cramped pot. | Transplant with division of the rhizome. | |
| Abundant watering. | Reducing the frequency of watering, you need to let the earth dry out. | |
| Drying of the tips of leaves and buds | Dry air. | Spraying water around the flower. |
| There is not enough room in the pot. | Transfer. | |
| Rusty coating | Strong watering. | More rare watering. |
| Excessive concentration of nutrients. | Planting in a peat environment, feeding every 2 weeks. | |
| Small leaves instead of flowers | Lack of light. | Improved lighting, up to 14 hours a day. |
| Black petioles | Much moisture and cool. | Warm place, less watering, you need to dry the ground. |
| Blurry yellow or colorless spots | Burn after direct sunlight. | Remove from the sunny side, rearrange to windows with diffused light. |
It is important to know about the main pathogens that cause certain diseases of streptocarpus. Understanding the cause of the disease will help in its further treatment and restoration of the flower.


| Disease / pest | Manifestation | Remedies |
| Root rot | Fungal brown spots on the leaves, black slimy roots. | Remove from the container, wash the roots and cut off the blackened parts. Soak the remaining plant in 0.25 g of manganese per liter of liquid. Plant in a container with a new substrate. Water for 4 months with a solution of 0.5% Skor, Bayleton, Maxim. |
| Gray rot | Light brown, fluffy spots, overgrown with light gray bloom. They arise in damp and cool conditions. | Remove damaged parts, sprinkle the sections with charcoal, chalk or cinnamon powder. Drizzle with diluted 0.2% Fundazol, Topsin-M. If there is no result, treat with Horus, Teldor 2-3 times (according to the instructions). |
| Powdery mildew | Whitish spots on leaves, flowers and stems. | Wash off plaque with a brush soaked in soda solution, cut off too disfigured areas, sprinkle with wood ash. Sprinkle the earth with Benlat, Fundazol. You can repeat it after a week, and then add a weak manganese solution up to 3 weeks. |
| Thrips | Silvery lines on the seamy side of the sheet, light spots and small black sticks. | Remove all corollas and infected leaves. Wipe the rest and spray the soil with Aktara, Spintor, Karate, and another 2-3 times a week later. Wrap in polyethylene for a couple of days, airing. |
| Spider mite | Almost transparent cobwebs, on the seamy side there are spots of them. | Water well and leave for a couple of days under polyethylene next to a container with chopped onions, garlic or turpentine. If it does not help, treat 3-4 times with Fitoverm, Apollo, Omayt, changing the preparations. |
| Shield | Spots of different tones of brown along the veins on the seamy side of the leaf plate. Increase and redden over time. | Lubricate each build-up with oil, acetic acid, kerosene, and after a few hours remove insects. Apply onion gruel to the affected areas. Every week, water the soil a couple of times with a solution of Admiral, Fufanon, Permethrin. |
| Whitefly | It looks like a small moth, lives on the wrong side of the sheet and takes off when touched. | Use duct tape, insect fumigator. Replace the top couple of centimeters of the substrate.Spray the ground with infusion of pepper, tobacco or mustard. Or take Fitoverm, Bitoxibacillin, Bankol. |
| Aphid | Small green insects, sticky bloom on the plant and deformation of its individual parts. | Clean aphids from surfaces with a brush or cotton wool. Put dried orange peels and herbs on the ground. Or use Biotlin, Fury, Iskra-Bio. |
| Weevil | Wingless small beetles of black color, gnaw at the leaves starting from the edges. | Carry out treatment with Fitoverm, Akarin, Aktellik or another insecticidal preparation, and repeat after a week. |
Thus, at the first signs of a disease, it is worth carefully examining the plant for pests. If there are any, it is worth isolating the diseased streptocarpus from uninfected flowers. For prophylaxis, it is allowed to process them with Fitoverm, following the instructions of the instructions.
Possible problems
Like most plants, streptocarpus can become ill during active growth and dormancy. The main reason for this is non-compliance with the rules of caring for him.
- If the plant is sick with gray rot, then it suffered from the cold or received mechanical damage. Spots appear on leaves, shoots and flowers, and then mold. Save streptocarpus with a fungicide.
- Fusarium indicates excessive watering and a low temperature that is not suitable for the flower. Cuttings and peduncles begin to rot, and then the roots. If the roots are sick, it is almost impossible to save the plant.
- Drying and deformation of leaves, the appearance of a white bloom, the loss of decorativeness of the plant speaks of its disease with powdery mildew. This happens in high humidity, drafts and sudden temperature changes. An urgent need to treat the flower with a copper-soap solution.
- If growths appear on the leaves, and the foliage itself begins to curl, this says about the attack of aphids. Spider mites appear when the room is hot and dry. They get rid of each insect with their own preparation.
- If the plant is attacked by thrips, they will feed on its juices, which will lead to a loss of decorativeness and growth arrest. It is necessary to get rid of pests with Aktellik or Akarin.
For information on how to grow streptocarpus from seeds, see below.
All rights reserved, 14+
Use of any material without our prior written consent is prohibited.
Watering streptocarpus
Watering the straps should be done carefully. They dry up quickly, but don't like the bay. Their root is small, and with excessive watering it quickly decays.
If you spilled the soil well, do not forget after 20 minutes. drain excess water from the sump.


The roots of streps are close to the surface, so you need to pour water from above carefully, without eroding the substrate.
You can also water in the pan if that's more convenient for you, but do not forget to drain the excess water.
It is better to underfill streptocarpus than to overfill. If you delayed watering, and the leaves wilted, do not be alarmed: after watering, they will restore turgor.
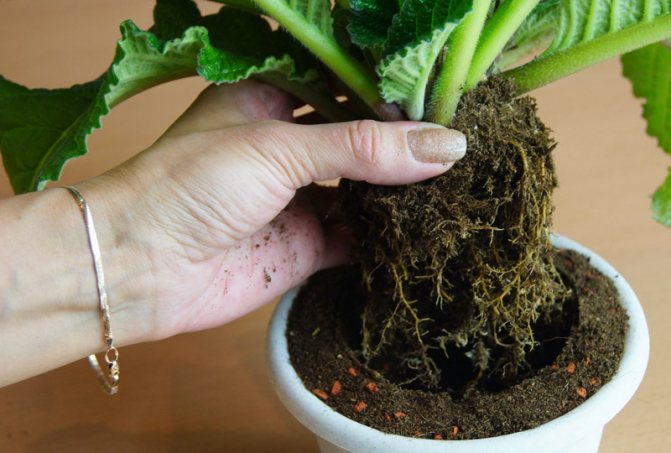
Transplant rules
It is necessary to change the place of deployment not only in case of diseases. The root system grows rapidly, therefore it is necessary to transplant often: while the plant is developing, once a year, an adult flower - once every 3 years. The composition of the soil for streptocarpus - humus, crushed dried bark, oven-calcined soil (or turf), coarse clean river sand and peat are mixed in equal amounts. You can use another mixture - peat, vermiculite, turf and sphagnum. It is important to ensure stable drainage.
The pot is chosen 5-10 cm higher than the previous one. River pebbles or ceramic balls are laid on the bottom, then the prepared soil. With each transplant, the substrate is changed. For lush flowering, streptocarpus need feeding - potassium, phosphorus, nitrogen. Fertilizers are applied 1-2 times a year, focusing on the development of buds.
During transplantation, the bushes are planted. The easiest way is division.The earthen ball is abundantly moistened, the plant is taken out of the pot, the rhizome is cut into several parts with a sharp knife. Remove the dry parts, sprinkle the slices to dry, with crushed charcoal. Plant a bush in a new pot, add soil, lightly crush and moisten.
Transplant after purchase and during reproduction
A good time for transplanting is the beginning of spring, when the culture is just beginning to grow actively. With a winter planting, it will be more difficult for her to root.
After purchase, the bush is carefully examined. With an overgrown root system, it must be transplanted into a new, more voluminous container. After the procedure, the first fertilization is carried out after 2 months. The soil must be regularly loosened and watered (as the upper layers of the substrate dry).
Important! Adult specimens need to be moved to a new container every 2-3 years, young ones annually. With the growth of the root system, the procedure can be carried out more often.


Transplant from a small pot
Reproduction and planting at home
The process of planting and growing crops requires compliance with the following conditions:
- Transplant newly acquired young specimens 2 weeks after purchase. To do this, use a transparent container. This will allow you to monitor the development of the root system in the future.


For successful cultivation, plant the flower in shallow containers. This will ensure lush flowering and green mass build-up. The more points of growth a plant has, the more it will release peduncles.- Young specimens must be looked after correctly. First, such plants must build up green mass, and only then bloom. So it is recommended to cut off the formed peduncles.
- Correctly selected temperature regime, air humidity and systemic irrigation will allow you to grow and reproduce a beautiful decorative flowering culture.
Recommendations for planting and germinating seeds
Seed propagation is called generative. This process is simple, but it involves the observance of certain recommendations:
- The planting material is sown on top of a wet substrate. It consists of perlite, crushed peat and vermiculite, taken in equal proportions.
- The seeds can be mixed with sand. It should be dry and fine.
- After sowing, carefully sprinkle the planting material with water from a sprayer. Cover the container with polyethylene.
- Place the container with seedlings in a warm and bright place.
- It is necessary to wait for shoots in 12-14 days.
- Ventilate the mini greenhouse every day to avoid condensation.
- As soon as the seedlings have 2 leaves, then you can start picking. To do this, prepare a nutrient substrate: peat, crushed moss, leaf soil, vermiculite, perlite: 3: 2: 2: 1: 1. Instead of the prepared substrate, a purchased one, intended for Saintpaulias, is also suitable.
Reproduction of streptocarpus by seeds:
Growing features
Soil selection
The root system of streptocarpus is large, consisting of many small roots, expanding in breadth. This property determines the choice of container for growing. For the plant, wide, but low pots are suitable, the size of which should fully accommodate the roots, which will avoid rotting of the root system.
The best option would be to use ceramic, best without glaze, flowerpots. You can also use clay, but sometimes the roots grow into the walls of such vessels, which greatly complicates the process of plant transplantation.
It is better not to choose plastic containers for growing streptocarpus, since the root system in them will develop worse.
In nature, streptocarpus grow on light soils. Therefore, the soil for planting should be good for air and water. If you choose from ready-made substrates, then a mixture for Saintpaulias is quite suitable. The development of the plant will noticeably improve if the mixture is diluted with high-moor peat. It will act as a baking powder and fertilizer at the same time.The optimum pH of the potting mix should be between 5.5-7.
Those growers who want to prepare the soil for growing streptocarpus on their own can mix three components in equal proportions: peat, vermiculite and perlite. This combination will facilitate planting and caring for the plant.
A suitable option is also a mixture of peat, garden soil, charcoal, sphagnum moss. The components should be taken in proportions of 3: 3: 0.5: 1. It is imperative to sterilize the potting mix in a water bath for an hour and a half after drawing up the potting mix. This time will be enough for the complete destruction of pathogenic microorganisms and pests that can cause diseases and cause the death of the plant.
It is important to know that these flowers are not planted in the garden.
Location and lighting
The plant grows well under artificial light. Sunny places and access to fresh air provide streptocarpus with conditions close to natural. The main thing is that the room where the plant grows is not too hot, but at the same time there should be high humidity. It is in such conditions that wild species live.
In the hot period, the flower will feel as comfortable as possible on the western and eastern windows. On the north side, the light will not be enough, and on the south side you will have to protect it from direct sunlight.
Strong heat and drafts are hardly tolerated by streptocarpus. In the summer, you can take the plant out into the fresh air, and bring it indoors at night.
To ensure year-round flowering, streptocarpus should be additionally illuminated with fluorescent white fluorescent lamps. Daylight hours for these plants should last at least 12 hours. Streptocarpus should be placed about 20 cm from the lamp. In the absence of an additional light source, the plants will be dormant for 2-3 months.
Temperature, humidity, watering
The plant is thermophilic. The optimum ambient temperature for it is + 22 ... + 25˚С.
In winter, streptocarpus should be left in rooms where the temperature is maintained within + 14 ... + 15˚С.
As for irrigation, water should not be in excess: in nature, streptocarpus feed only on sedimentary waters. Excessive moisture in the soil layer can lead to root rot. Thus, in the period between watering, the earthen lump should have time to dry out a little.
In order to understand how much moisture your plant needs, you should monitor the condition of the leaves, which, with an insufficient amount of moisture, begin to fade. After watering, their shape takes on a normal state.
When grown under artificial conditions, streptocarpus is best watered with rainwater. In the absence of such, filtered or simply settled tap water is a little warmer than room temperature. The best watering option is through the pallet. Bottom watering should be done from time to time. But the main thing here is not to overdo it, so as not to bring the plant to decay.
Air humidity for keeping streptocarpus requires high. In no case should the leaves be sprayed with water or wiped with a wet sponge. It is only necessary to carefully humidify the air, preventing moisture from getting on the leaves. The plant feels comfortable next to moss or containers filled with wet pebbles.
Fertilizers and feeding
Streptocarpus should be fed with fertilizer every two weeks, but do this carefully, using ¼ of the recommended fertilizer concentration for a flowering houseplant.
Streptocarpus needs potassium, phosphorus, nitrogen in equal proportions. These substances promote the growth of leaves, provide abundant and stable flowering. You can use ready-made liquid mineral fertilizers specially designed for flowering plants.
Fertilize only completely healthy plants.
Nutrients are introduced into the pre-moistened soil.
In winter, when the plant is at rest, you can not feed it, limiting yourself to only scanty watering.
Transfer
In order to ensure long-term flowering, streptocarpus should be transplanted into a new nutrient-rich substrate every spring or summer. In order for the leaves to be strong and large, fertilizer should be applied between transplants. During the transplanting process, it is necessary to properly prepare an earthen lump: it should be slightly damp, and the earth should not stick to your hands. If the soil is too dry, mechanical damage to the root system can be caused, which will affect the general condition of the plant.
When replanting streptocarpus, it is necessary to ensure that the plant petioles do not touch the substrate. To fix the position of the plant, a little sphagnum moss should be placed on the surface of the soil layer, it is allowed that it slightly covers the lower leaves of the streptocarpus.
Pruning
If the streptocarpus has reached a large size and takes up a lot of space, the large side leaves can be cut off. However, this is undesirable. The fact is that the abundance of flowering directly depends on the state of the bush. The good flowering is due to the healthy and strong leaves that nourish the flowers. Pruning leaves is not without consequences, as the photosynthetic surface is reduced and the production of nutrients is reduced. It is only necessary to remove infected parts of the plant, weak leaves and growth points, as well as faded flower stalks.
Winter care
It is necessary to start preparing streptocarpus for the winter period in advance, back in September. First, the flower is transplanted into new soil, which has an identical composition with the soil used to grow the plant. Partially remove old roots and leaves, after which the streptocarpus is watered. Top dressing is not required in winter. The optimum temperature for wintering is about + 15˚С. With the onset of the dormant period, watering of the plant should be significantly reduced.
Reproduction


You can increase the number of plants on the windowsill during transplantation, but there are other ways to expand the flower garden. For example, using leaves. Cut off the elastic sheet plate, lay it out on the cutting board with the wrong side. Draw an imaginary line perpendicular to the central leaf vein 4-5 cm above the cutting, and cut off the rest with a sharp knife. The cutting is sharpened, and the "blank" is planted in a previously prepared substrate or immersed in water 0.5-1 cm.
Attention!
Reproduction of streptocarpus
Various methods are used for breeding varieties. Vegetative methods allow the characteristic features of the mother plant to be fully preserved. Growing streptocarpus through sowing seeds is a rather long process and the result may not always be predictable.
Reproduction of streptocarpus by dividing the bush
Together with the transplant in the spring, the plant is propagated by dividing an adult bush (2-3 years) into parts.
- The roots are freed from the soil, carefully untangled, separated by hand or with a sharp, sterile knife.
- The damaged parts of the root are removed, the places of the cuts are sprinkled with activated carbon.
- To create a new outlet, young shoots (children) with good roots are selected, planted in moist, loose soil.
- To preserve moisture, new plants are kept under a transparent cover in diffused sunlight until engraftment.
Reproduction of streptocarpus by cuttings
Streptocarpus can be propagated by other vegetative parts of the plant: children without roots remaining from division, whole leaves with petioles and their parts.
- They are immersed to a shallow depth in water until roots form, in moist soil or moss.
- Places of cuts are processed, as well as when dividing a bush.
- After the roots appear, the cutting is transplanted into a pot with the chosen substrate.
Growing streptocarpus from seeds
Most often carried out during breeding work to obtain unique traits.
- A streptocarpus flower at home is sown in shallow containers filled with vermiculite, peat and perlite.
- To distribute small seeds evenly over the surface, they are mixed with sand.
- After sowing, the soil is moistened with a spray bottle.
- To retain moisture and create a greenhouse effect, the container is covered with glass or transparent film.
- Until the seeds germinate, the temperature is maintained at 22 - 25 ° C, regular ventilation and condensate collection are carried out. Under favorable conditions, seedlings will appear in 10-14 days.
- The shelter is removed, but the humidity is kept high.
Toaster breeding method
- For this method, leaves are used from which the central vein is cut.
- The sections are treated with charcoal, dried and buried in the soil by about 5 mm.
- While maintaining optimal humidity, small children will sprout in 1.5 months, which are transplanted into pots at the age of 3-4 months.
Highlights in seed propagation
To get a healthy plant that will delight the eye, you must adhere to certain rules and recommendations. Only in this case can you be sure that all efforts will not be in vain.
Landing dates
The ideal time for planting seeds is February - April. It is at this time that the sun begins to warm up, which will contribute to the rapid growth of the flower.
How to choose seeds
Today, you can buy streptocarpus seeds at any flower shop. A huge variety of varieties allows you to choose a plant to your taste. Typically, the seeds are packed in a paper bag. Be sure to pay attention to the date, buy only fresh material.
Landing technology
Planting streptocarpus seeds is a painstaking process that should be approached with great care and accuracy.
Initially, it is necessary to prepare shallow bowls, at the bottom of which drainage must be done. Peat mixed with sand is poured over the drainage.
Streptocarpus seeds are very small, so it is customary to sow them on the surface. You do not need to cover them with soil from above. Before planting, it is necessary to moisten the substrate, that is, sow the seeds already on the moistened soil.
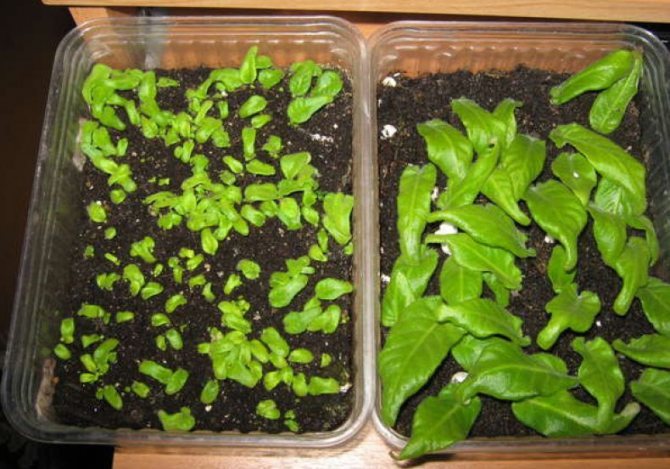


After the seeds are in the bowl, cover the container with glass or film. The dish should be in a warm room with an air temperature of at least 21 ° C. From time to time, you should ventilate the container, since they need fresh air for the rapid growth of seeds. You need to water the seeds from the pallet - when the soil is moistened from above, the seeds will simply be washed out.
When real leaves begin to grow, you can make the first pick. To do this, you need to pick up a larger container, plant the plants so that they do not interfere with each other's growth. After distributing the seedlings, they are watered, covered with foil again and left in a warm place.
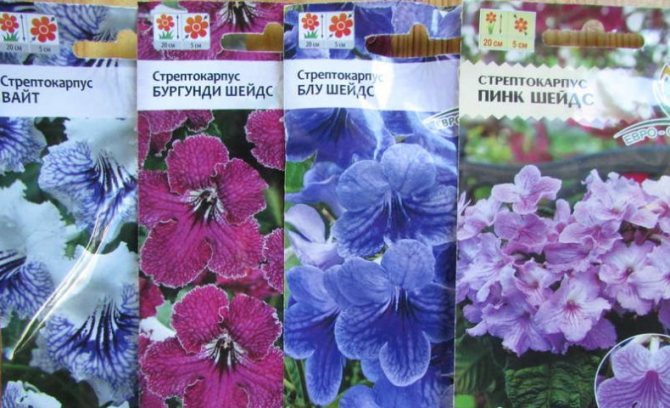


Streptocarpus species


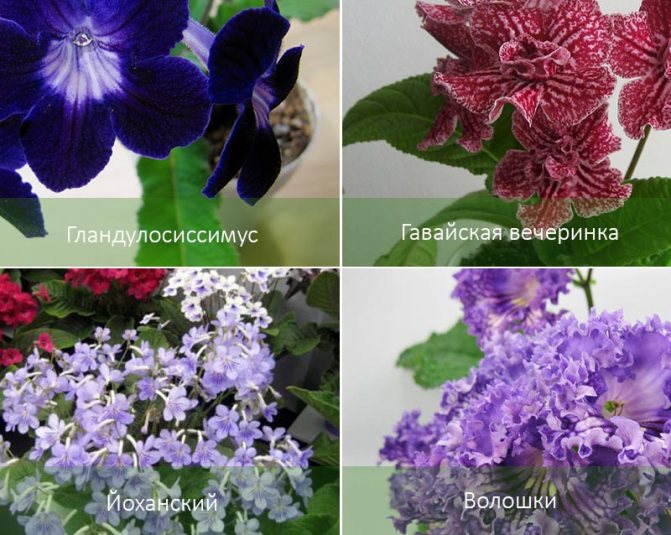
Taking care of a tropical plant is not difficult. Just how to understand the variety of colors and colors? Breeders have already bred more than 1000 varieties, but they do not stop experimenting yet. Streptocarpus species that are still found in the wild are also popular:
- Rocky - perennial with a dense woody base, oval, relatively small dark green leaves and purple flowers. The length of the bells reaches 12-14 cm.
- Royal - with bright purple petals covered with stripes and strokes. The leaves are large, long, up to 25 cm, covered with long dense fibers.
- Stele-forming - unlike other species, it has a long creeping stem adjacent to the rock. The buds are down, the inflorescences are pale blue.
- Pickaxe - can be recognized by its appearance.It differs from other streptocarpus with oval-shaped leaves, green above, red below. The size of the bush in the wild is impressive - the height can reach 1 m.Up to 20 buds are located on the peduncle. This plant is an annual, it dies after flowering, and the next year it germinates from seeds.
At home, such bushes are rarely grown. They can be seen in greenhouses or while traveling on the slopes of the Andes.


Types and varieties
Streptocarpus never ceases to attract the attention of breeders. Thanks to their painstaking work, new varieties have been bred to date.
Rocky streptocarpus (Streptocarpus saxorum)
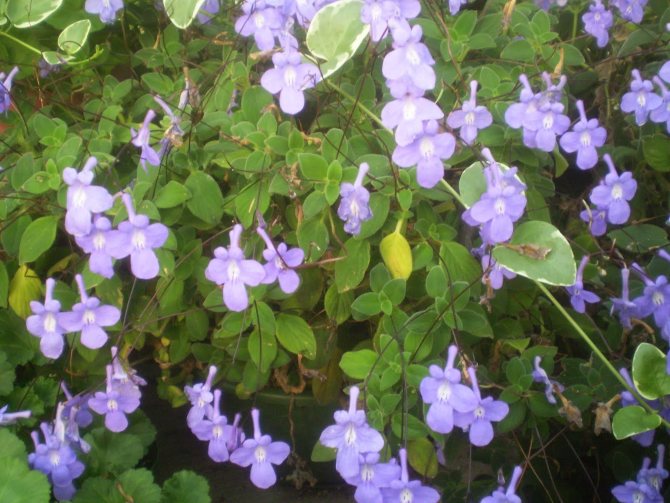


Rocky streptocarpus (Streptocarpus saxorum)
Due to its external similarity, this plant is sometimes called "fake violet". To grow this species in artificial conditions, it is required to observe a certain temperature and humidity regime.
In nature, streptocarpus grows in Tanzania and East Africa. A perennial plant has a woody base. This species is distinguished by hanging stems and small leaves of a grayish-green color. Several peduncles appear from the sinuses, the length of which reaches 7 cm.
The flowers are small, bell-shaped, the funnel is white, the petals have a purple frame around the edges. The flowering period lasts, as a rule, from March to October, but in a warm, sunny climate, with sufficient light, rocky streptocarpus blooms even in winter. In this case, the dormant period falls in November.
Streptocarpus royal (Streptocarpus rexii)
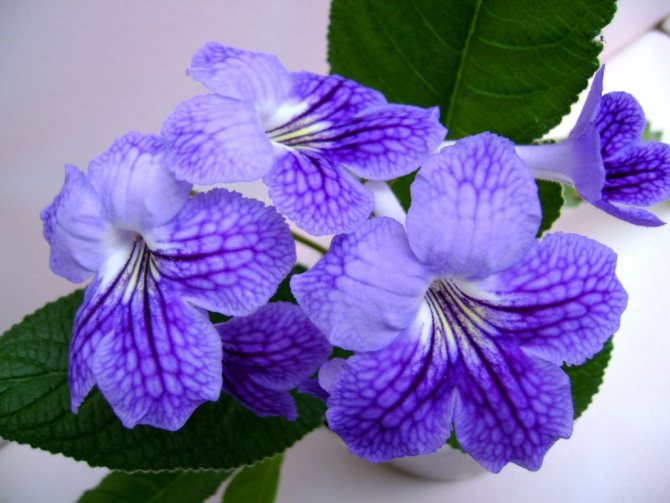


Streptocarpus royal (Streptocarpus rexii)
It is distinguished by drooping leaves, which can reach 25 cm in size. Leaves are wrinkled, long, hard, usually light green. Flowers are small, solitary, up to 2-2.5 cm in diameter. Blue flowers with red or brown stripes in the pharynx, rise on stalks 14-18 cm long. This species feels good indoors.
Streptocarpus royal - the ancestor of domestic species, appeared in Europe in the 19th century. It was he who became the ancestor of hybrid samples.
Streptocarpus stele-forming (Streptocarpus caulescens)
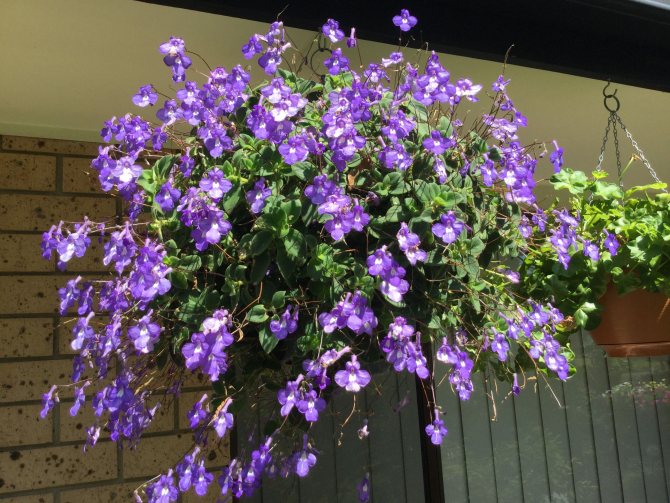


Streptocarpus stele-forming (Streptocarpus caulescens)
The stem of this species grows in length from 40 to 60 cm. The plant has flowers of pale blue drooping shape.
Streptocarpella Kirk (Streptocarpus kirkii)
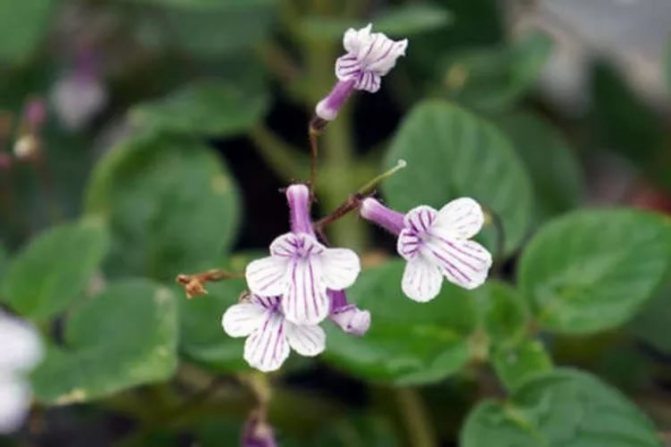


Streptocarpella Kirk (Streptocarpus kirkii)
Ampel plant grows up to 15 cm. Inflorescences are small in size and in the shape of umbrellas. The color of the petals is light purple.
Streptocarpus wendlandii
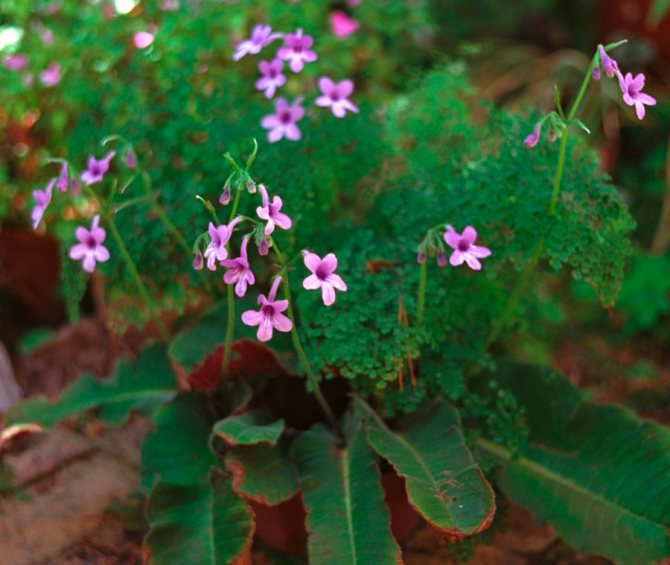


Streptocarpus wendlandii
A distinctive feature of the species is only one wide oval leaf. The wrinkled leaf grows up to 90 cm in length and sinks under its own weight. Remarkably, the top of the leaf is green and the bottom is reddish-purple. The peduncle can consist of 20 purple flowers. This species reproduces only by seeds. After the flowering period, the plant dies.
Streptocarpus hybrid


Streptocarpus hybrid
Due to the variety of hybrids of amazing beauty, streptocarpus turns into an object of admiration and collectible. The breeding of this plant is now on the rise. Various varieties can be found not only among experienced, but also among novice flower growers.
The varieties bred by domestic breeders have already gained worldwide recognition.
Streptocarpus Bird
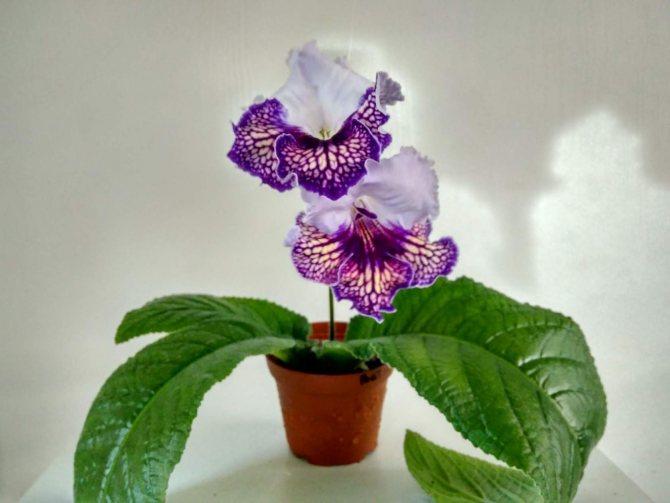


Streptocarpus Bird
When blooming, it forms large flowers with an unusual color: the upper petals are white, while the lower ones are decorated with purple veins and specks of lemon color.
Streptocarpus Crystal Lace
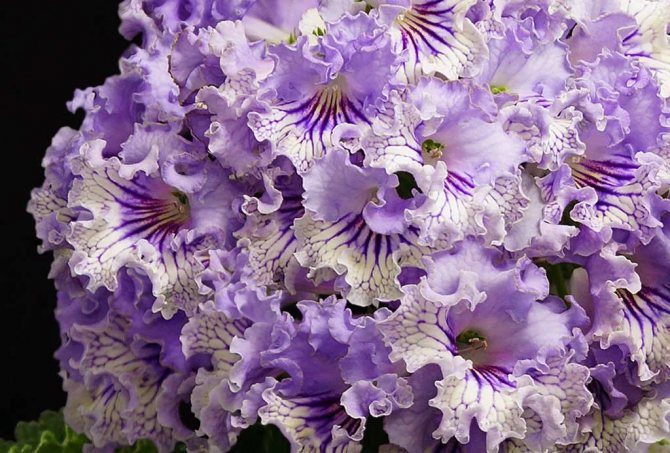


Streptocarpus Crystal Lace
An ornamental plant during flowering pleases the owners with flowers with complex colors of delicate shades. In turn, the flowers are located on short peduncles.The delicate flowers reach a size of 6.5 cm and are surrounded by tough leaves.
Streptocarpus Black Swan
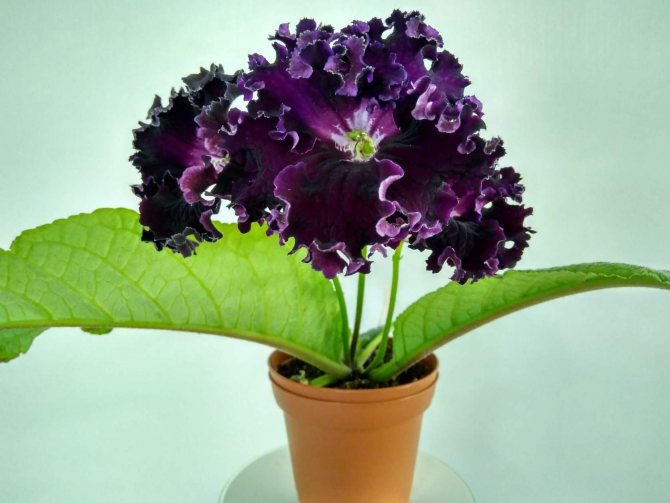


Streptocarpus Black Swan
It has flowers with openwork edges of dark purple color.
Streptocarpus Caramel
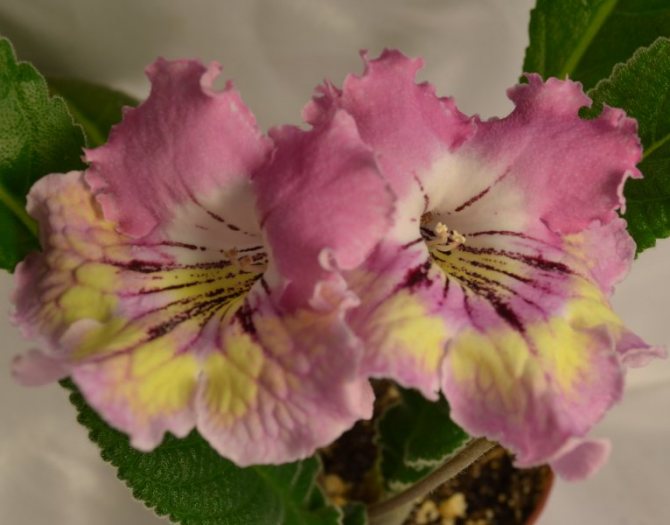


Streptocarpus Caramel
It blooms with the formation of flowers of an unusual color. The pink-lilac upper petals and yellow lower petals are decorated with dark red veins emerging from the neck of the bud.
Streptocarpus Eternity
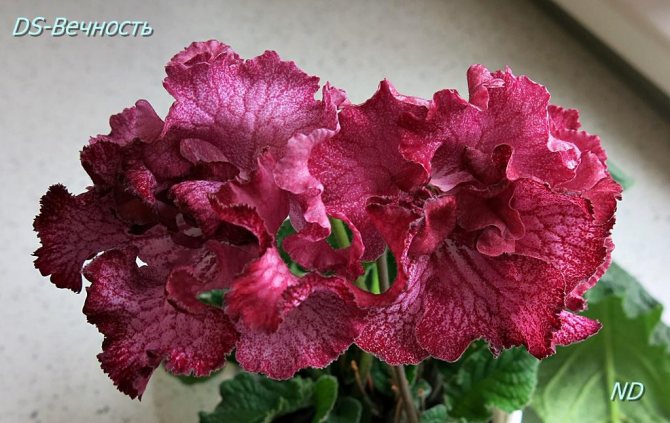


Streptocarpus Eternity
It has large red-terracotta flowers, reaching a size of 10 cm. The edges of the flowers are wavy and darkened, in some places their color may approach black. By their appearance, the flowers of this variety resemble a carnation. Peduncles of streptocarpus Eternity are tall, but rather strong, do not bend under the weight of flowers.
Streptocarpus Maple Syrup
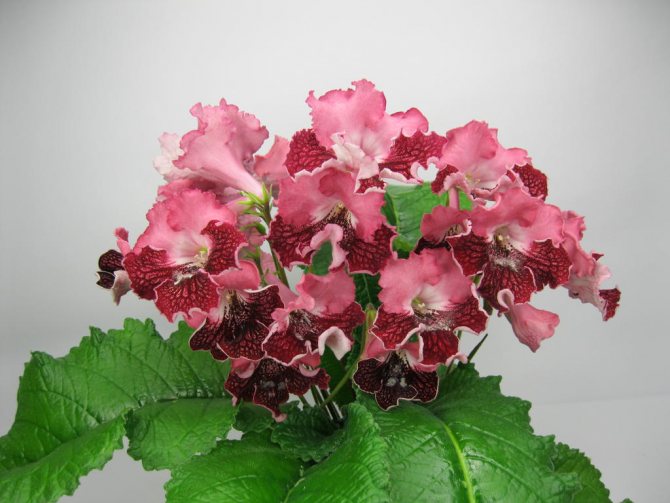


Streptocarpus Maple Syrup
A very unpretentious variety that will delight with constant flowering. It has rather massive peach-pink flowers with burgundy lower petals with a wavy edge.
Streptocarpus Shake
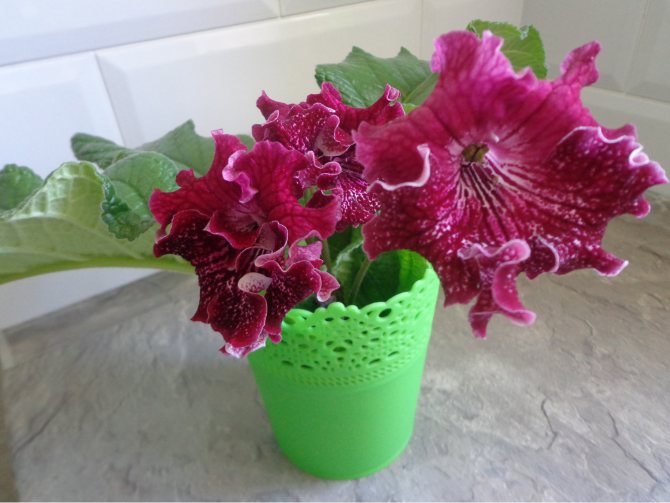


Streptocarpus Shake
During the flowering period, it forms large, up to 8 cm in diameter, pomegranate-colored double flowers with white dots. Flowers are arranged on strong peduncles.
Streptocarpus Picnic
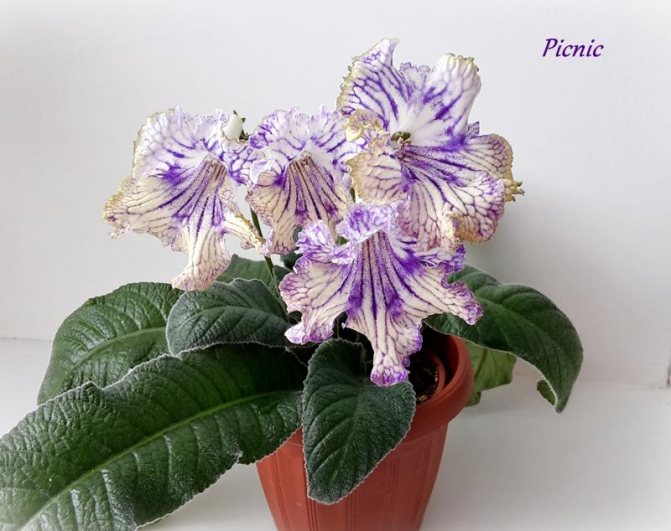


Streptocarpus Picnic
Differs in large flowers with a wavy edge. The two upper petals are blue-white, and the lower three are blue-yellow. The petals are pierced with violet rays emanating from the white neck.
Streptocarpus Cockade
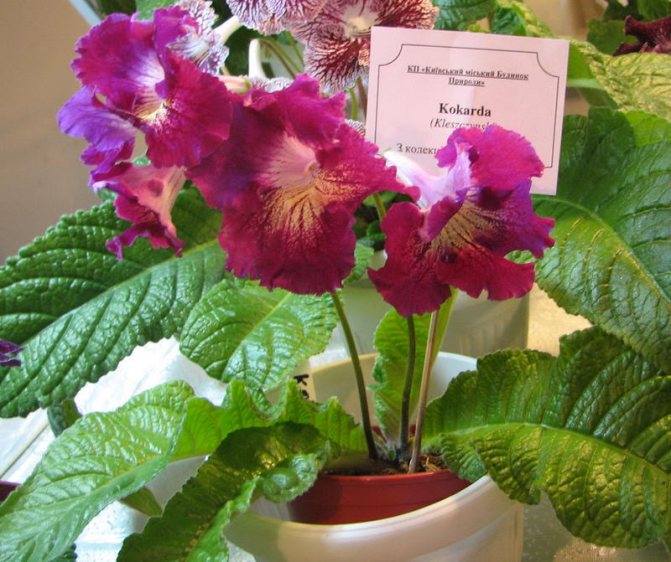


Streptocarpus Cockade
It has large bright flowers of a non-standard form for streptocarpus in the form of a star. The upper part of the flower has three petals, and the lower one has two. The color of the petals is crimson, sometimes with a bluish tint. Several yellow rays emerge from the neck onto the lower petals.
Streptocarpus German
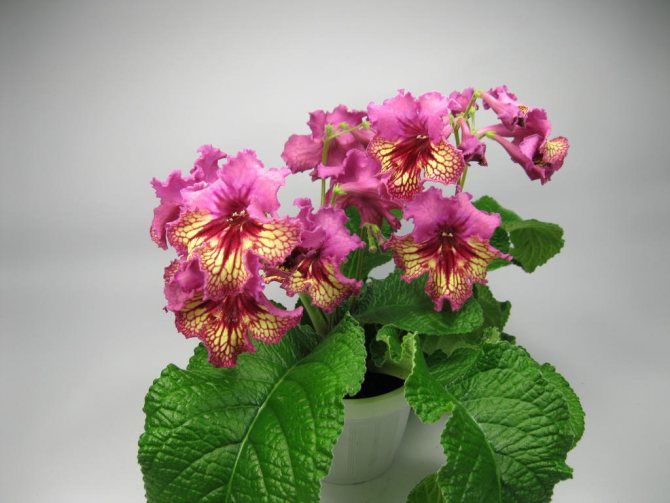


Streptocarpus German
It has flowers up to 7.5 cm in diameter. The two upper petals are fuchsia. The lower petals are yellow with burgundy veins and fuchsia lace edges.
Streptocarpus I want and I will
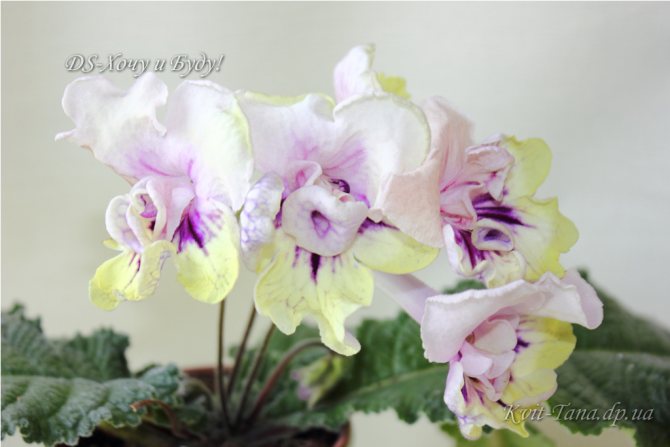


Streptocarpus I want and I will
It has large flowers with pastel transitions from pale lilac to pale yellow. Bright violet rays emerge from the neck. Flowers do not fall, but at the moment the buds open, the plant becomes capricious, requires increased attention from the florist.
Streptocarpus Kalahari
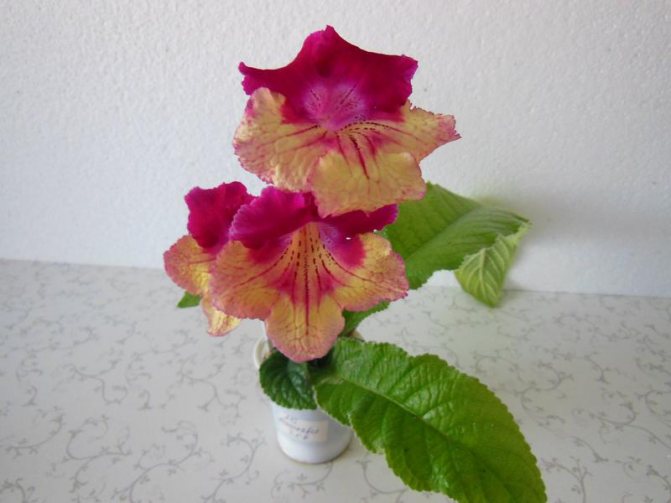


Streptocarpus Kalahari
A very beautiful variety with large flowers reaching a diameter of 8 cm. The color of the petals changes from yellow to red. Peduncles are strong, do not bend under the weight of the buds.
Streptocarpus Fifa
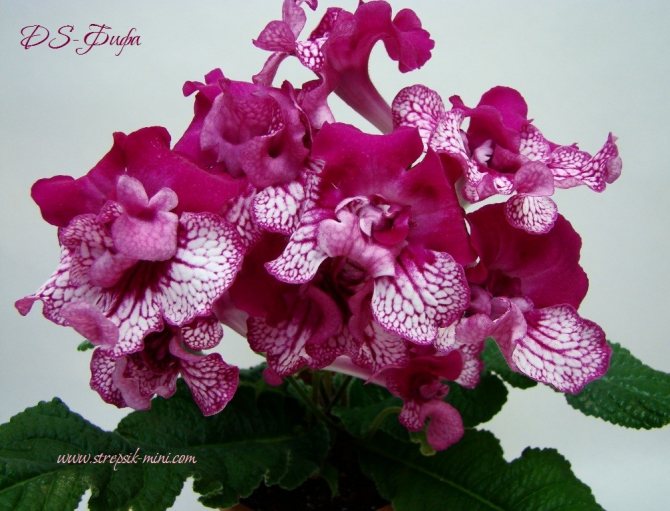


Streptocarpus Fifa
It has elegant crimson flowers, the lower petals are covered with white spots. When flowering, it forms many flowers, which almost completely cover the leaves of streptocarpus.
Streptocarpus Margarita
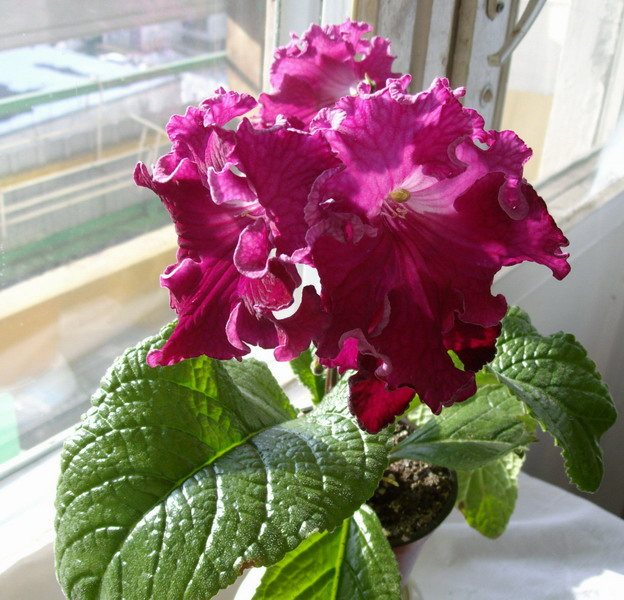


Streptocarpus Margarita
It has large crimson flowers with openwork edges.
Streptocarpus Chicken
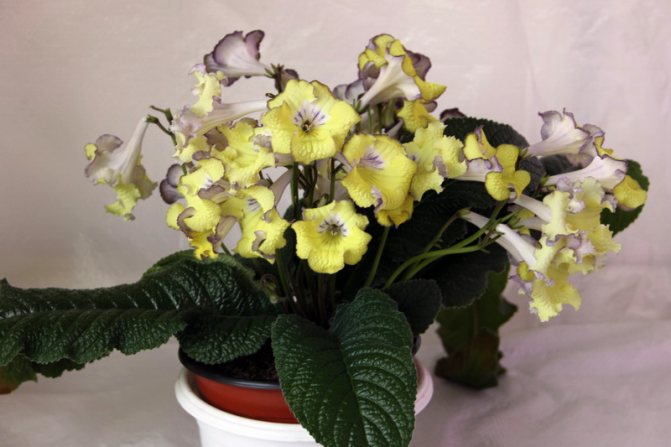


Streptocarpus Chicken
It stands out in bright yellow flowers with ruffled purple edges. Violet rays emerge from the neck.
Streptocarpus Arabesque
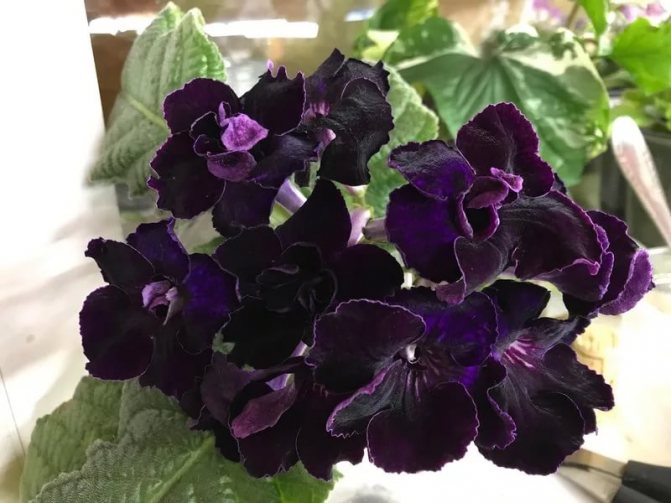


Streptocarpus Arabesque
It has dark purple flowers with an openwork edge with an even darker shade.
Streptocarpus Joy


Streptocarpus Joy
It has three lower yellow petals with purple edging. The upper part of the flower is purple-crimson. The plant looks very compact and neat due to the fact that the flowers are turned to one side.
Streptocarpus Mozart


During the flowering period, the plant will delight flower growers with beautiful large flowers up to 10 cm in diameter. The lower petals are yellow with a purple edging, pierced with purple rays coming out of the neck. The upper petals are purple in color.
Follow-up care of sprouts
30 days after the first pick, the second must be done.
It is required to properly prepare the substrate. To do this, you need to mix:
- leafy soil - 2 parts;
- sod soil - 1 part;
- sand - 1 part;
- bone meal - 1 tbsp. the spoon.
After the second pick, about a month should pass, only then can the plants be planted in separate pots. From this point on, streptocarpus can be looked after as adult plants. Brief recommendations for flower care:
- Pay attention to the lighting: the flower loves clear weather and sunlight. During the summer months, in hot weather from 10:00 to 16:00, it is better to move the pot to a more shaded place.
- Maintaining the temperature regime is very important for the plant. If the temperature is more than +25 ° C, you can forget about flowering. The optimal indicator is + 18-23 ° C.
- The ideal air humidity is 60-80%.
- Watering is recommended with purified water. It is worth moistening when a light crust has formed on the soil surface.
The Gesneriev family can boast of such an original representative of the flora as streptocarpus. Outwardly, it is a rather attractive rosette plant with a dense, shortened stem. And if the wild fellows of a flower can be 2-2.5 cm in diameter, then indoor, hybrid specimens have a diameter of up to 4 cm, and taking into account the bend of the petals - up to 8 cm. Growing streptocarpus with seeds at home is an exciting activity for experienced flower growers. It is necessary to observe the agricultural techniques of culture with precision. You can carry out timely care and choose a primer for flowers, based on the advice of specialists. The original flowers of streptocarpus can be used for landscaping a room and office. They often decorate the space of the patio and outdoor terrace with a country house. Look at streptocarpus in the photo, illustrating all the external attractiveness of this culture:


Varieties of indoor plants with names, what they look like
At the moment, there are about 130 plant varieties. Most of the streptocarpus species are suitable for growing and care at home.
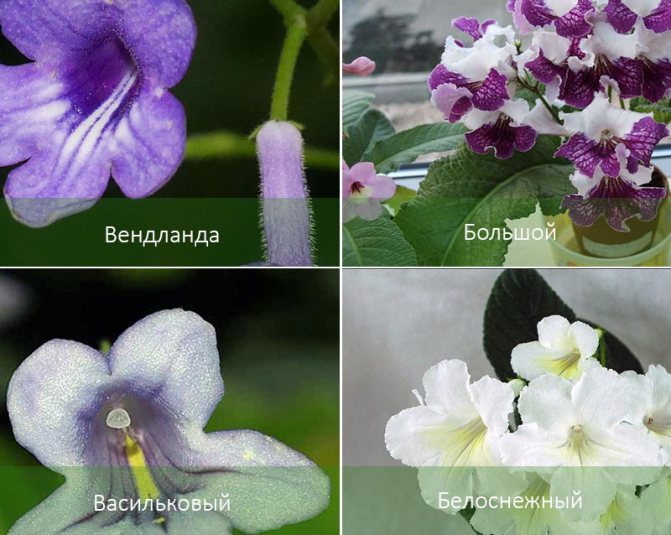
Snow-white streptocarpus (Streptocarpus candidus)
The plant has a rosette structure, wrinkled leaves. Many people note that white small flowers exude a honey smell. Their length is 2.5 cm. Flowers with yellow stripes and small red spots in the fauces.
Streptocarpus large (Streptocarpus grandis)
Large streptocarpus is a plant with a single leaf, the length of which reaches 40 cm and width - 30. On a half-meter stem, there are flowers of a light lilac shade. In the pharynx, the color is darker.
Streptocarpus cornflower blue (Streptocarpus cyaneus)
The rosette plant has stems 15 cm in length. Each of them has a pair of pink flowers with purple stripes and a yellow core.
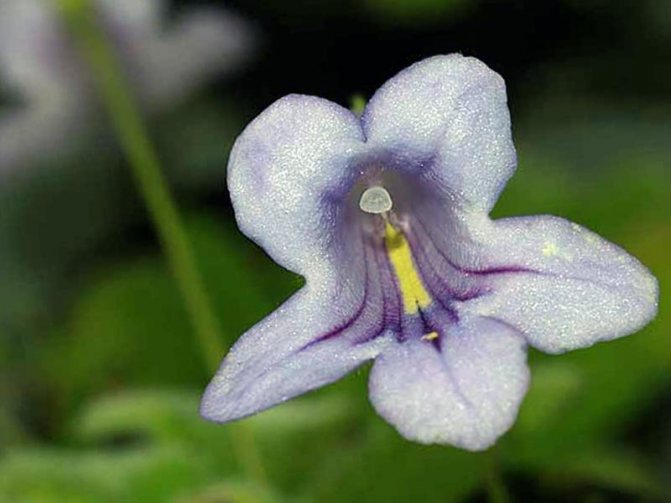


Cornflower-blue streptocarpus
Streptocarpus wendlandii
Wendland originated from South Africa. Its leaf is dark green in color with lighter veins and measures 90x60 cm. The flowers are located on long peduncles about 5 cm long. The purple funnel-shaped corollas in the pharynx have white stripes.
Rocky streptocarpus
The plant of this variety lives in most cases on mountain slopes and embankments near the sea coast. The appearance of the inflorescences resembles a crocus - it has lilac-purple flowers on green peduncles.
Important! This species is resistant to drought and bright sunlight.
Streptocarpus from seeds (master class)


Streptocarpus is a flowering plant from the Gesneriaceae family, which is very popular today among collectors and indoor florists. Streptocarpus is unpretentious in growing and caring for it, like some of its other brothers. Indeed, to date, many varieties of streptocarpus have appeared with flowers of various shapes and unusual colors. And this is due to the fact that flower growers have studied the methods of care and reproduction of streptocarpus. There are several ways to propagate this plant. This is the division of the bush, propagation by leaves and seeds.I do not take into account the meristem breeding method, since this method is used by professionals. In this article, I will tell you how to sow streptocarpus seeds and how to care for seedlings. I want to warn you right away that when streptocarpus reproduces by seeds, parental signs are not always transmitted to children. But this is an excellent breeding method for obtaining new colors, flower shapes, and the only way to get new varieties. Streptocarpus seeds are very small, slightly larger than a speck of dust.


Freshly harvested seeds have the best germination. The seeds that I sowed were collected from the streptocarpus varieties of Yulia Sklyarova. The best time to plant streptocarpus seeds is early spring.
She sowed seeds in a plastic box with a lid.


At the bottom of which perlite was poured, vermiculite is also suitable,


moistened it and poured the prepared substrate from the Jiffy tablet on top, which contains all the necessary substances and trace elements for germination and rapid development of seeds.
How do I prepare a Jiffy tablet for planting? Jiffy tablets are sold in sizes 3.6 centimeters and 5 centimeters in diameter. I like the big ones more. I noticed that there are small ones with a large fraction and with a large addition of coconut.


I prepare the tablet for planting as follows: I put it in a container and fill it with warm boiled water without removing the mesh.


Someone is pouring boiling water, I think that this should not be done. Boiling water kills all living microflora, both good and bad. When the tablet absorbs water and swells, I squeeze out the excess water.


Do not squeeze hard, the soil for streptocarpus should remain moist. I release the substrate by cutting the mesh,


I loosen it a little with my hands and put it in containers for planting plants.
Flower diseases and their treatment
Most often, streptocarpus is exposed to the following diseases:
- Sulfur rot. The disease develops due to the long stay of the plant in dampness and at low temperatures. It manifests itself as a gray fluffy bloom on the leaves, in the place of which holes appear over time. It is necessary to remove all affected areas of the leaf.
- Powdery mildew. The disease is easy to identify by a whitish bloom that forms on flowers, young leaves and peduncles. Disease can be avoided with good ventilation in the room.
The following pests are dangerous for the flower:
- Aphid. Small insects that have a green or orange color and feed on the lope of plants. These parasites multiply quickly. Excess moisture or, conversely, excessive dryness provoke the appearance of aphids.


Mealybug. Colonies of pests form a white mass, it is not easy to fight them, like with aphids.- Weevil. A wingless insect with a black body and a sharp head covers the larvae near the base of the stem. The pest eats the leaves of the plant, leading to its wilting and death.
- Fly sciriada. Pests crawl on the ground and eat thin young roots, thereby damaging the entire root system.
- Thrips. The size of the pest is 2 mm, it leaves pale spots on the flowers, provokes pollen to fall off. It is difficult to detect them, they will be noticeable if you shake off the flower on a sheet of paper.
You can find out about common diseases and pests of streptocarpus, methods of their treatment, as well as see photos of plants here.
When caring for streptocarpus, it is necessary to make enough efforts to fulfill all the conditions necessary for the successful growth and development of the flower. However, all of them will pay off when the plant will thank the grower with a long, lush flowering and impeccable health.
Forum of florists Frau Flora
- Registries
- ↳ Registers of varieties and species of plants
- Conference and users
- ↳ Conference work
- ↳ Everything about the work of the forum
- ↳ Photo Tutorials: How to Use the Forum
- ↳ Let's get to know
- Identifying green strangers
- ↳ Identifying indoor plants
- ↳ Define garden plants
- Indoor floriculture
- ↳ Adenium
- ↳ Adenium - varieties and hybrids
- ↳ Adenium from seeds
- ↳ Agrotechnics of adeniums
- ↳ Diversity and features of adeniums
- ↳ Ahimenes
- ↳ Ahimenez Serge Saliba
- ↳ Ahimenes other breeders
- ↳ Species Achimenes
- ↳ Intergeneric hybrids involving Achimenes
- ↳ Achimenes agrotechnics
- ↳ Vegetative propagation of Achimenes
- ↳ Seed reproduction of Achimenes
- ↳ Breeding Achimenes
- ↳ Diversity and features of the Ahimenes
- ↳ Ahimenez news and events
- ↳ Pests and diseases of Achimenes
- ↳ Begonias
- ↳ Begonias - classification and characteristics
- ↳ Eternal flowering begonias (Semperflorens begonias)
- ↳ Tuberous begonias
- ↳ All about tuberous begonias
- ↳ Begonias Elatior (Rieger-elatior types)
- ↳ Rhizomatous begonias (Rhizomatous begonias)
- ↳ Royal begonias (Rex Cultorum begonias)
- ↳ Shrub-like begonias
- ↳ Cane-like begonias
- ↳ All about decorative leafy begonias
- ↳ Other begonias
- ↳ Bougainvillea
- ↳ Bougainvillea by variety
- ↳ All About Bougainvillea
- ↳ Hibiscus
- ↳ Hibiscus by varieties
- ↳ All about hibiscus
- ↳ Hippeastrum
- ↳ Hippeastrum by varieties
- ↳ Species hippeastrum
- ↳ Agrotechnics of hippeastrum
- ↳ Variety and features of hippeastrum
- ↳ Hippeastrum from seed
- ↳ Gloxinia and Sinningia
- ↳ Gloxinia varieties
- ↳ Varieties of Height T. Yu.
- ↳ Varieties Lapinskaya V.V.
- ↳ Varieties Slyusar E.V.
- ↳ Varieties Statsenko E.A.
- ↳ Varieties Tkachenko N.A.
- ↳ Industrial varieties
- ↳ Gloxinia of unknown breeders
- ↳ Gloxinia of other breeders
- ↳ Simple Gloxinia Varieties
- ↳ Tidei (Shoes)
- ↳ All about gloxinia
- ↳ Variety names, terminology, classification
- ↳ Seed Gloxinia
- ↳ Photo lessons about gloxinia
- ↳ Reproduction of gloxinia
- ↳ Problems with the reproduction of gloxinia
- ↳ Agrotechnics Gloxinia
- ↳ Problems of agricultural technology gloxinia
- ↳ Growing Gloxinia Online
- ↳ Questions about gloxinia
- ↳ Photos of flowering seedlings
- ↳ All About Gloxinia Breeding
- ↳ Interesting about gloxinia
- ↳ About gloxinia in surveys
- ↳ Gloxinia pests
- ↳ Diseases of gloxinia
- ↳ Sinningia
- ↳ Varieties of micro- and mini-sinning
- ↳ All about micro and mininning
- ↳ Species synningia and their cultivars
- ↳ Cacti and succulents
- ↳ Agrotechnics of cacti
- ↳ Variety of cacti
- ↳ Caudiciform and pachycalculous plants
- ↳ Other succulents
- ↳ Schlumberger varieties
- ↳ All About Schlumberger
- ↳ Coleria
- ↳ Coleria by varieties and types
- ↳ Coleria - cultivation and reproduction
- ↳ Coleria - variety and features
- ↳ Orchids
- ↳ Agrotechnics of orchids
- ↳ Variety of orchids
- ↳ Pelargonium
- ↳ Species and primary hybrids of pelargonium
- ↳ Scented Pelargonium
- ↳ Star Pelargonium
- ↳ Zonal Pelargonium
- ↳ Cactus and Clove Pelargoniums
- ↳ Royal Pelargonium
- ↳ Pelargonium Angels
- ↳ Pelargonium Zonartica
- ↳ Pelargonium Unicums
- ↳ Pelargonium Formosuma and Medusa
- ↳ Ivy Pelargonium and Ivy are hybrids
- ↳ Rosaceae and tulip pelargoniums
- ↳ Pelargoniums of unknown origin
- ↳ Agrotechnics pelargonium
- ↳ Variety and features of pelargonium
- ↳ Pests and diseases of pelargonium
- ↳ Primulines (Khirit)
- ↳ Smithians
- ↳ Saintpaulia
- ↳ Saintpaulia Korshunova E.V.
- ↳ Saintpaulia K. Moreva
- ↳ Saintpaulia Evgeniya Arkhipova
- ↳ Saintpaulia B.M. and T.N. Makuni
- ↳ Saintpaulia T. Pugacheva
- ↳ Saintpaulia N. Puminova
- ↳ Saintpaulia N. Skornyakova
- ↳ Saintpaulia A. Tarasova (Vialkovod)
- ↳ Saintpaulia of other breeders of Russia
- ↳ Saintpaulia Svetlana Repkina
- ↳ Saintpaulia Elena Lebetskaya
- ↳ Saintpaulia of other breeders of Ukraine
- ↳ Saintpaulia Holtkamp
- ↳ Saintpaulia Ma's (O. Robinson)
- ↳ Saintpaulia Sorano and LLG
- ↳ Saintpaulia P. Hancock
- ↳ Saintpaulia breeders of other countries
- ↳ Minisenpoly Rob's (R. Robinson)
- ↳ Minisenpola McDonald
- ↳ Minisenpoli Sorano and LLG
- ↳ Minisenpoly H. Pittman
- ↳ Minisenpoly N. Berdnikova
- ↳ Minisenpoly A. Kuznetsov
- ↳ Minisenpoly of breeders of Russia and Ukraine
- ↳ Minisenpoli of other breeders
- ↳ Saintpaulia trailers
- ↳ Saintpaulia Chimera
- ↳ Variety and features of Saintpaulias
- ↳ Agrotechnics Saintpaulia
- ↳ Seed Saintpaulia
- ↳ Problems, diseases and pests of Saintpaulias
- ↳ Streptocarpus
- ↳ Petr Kleszczyński Streptocarpus
- ↳ Streptocarpus Dimetris
- ↳ Streptocarpus Kabanova and Trofimenko
- ↳ Streptocarpus N. Pavlyuk
- ↳ Streptocarpus Paramonovs
- ↳ Streptocarpus by Yulia Sklyarova
- ↳ Streptocarpus D. Demchenko
- ↳ Streptocarpus CF
- ↳ Streptocarpus of other breeders of Russia
- ↳ Streptocarpus of other breeders of Ukraine
- ↳ Streptocarpus breeders of Japan
- ↳ Streptocarpus David Thompson
- ↳ Streptocarpus R. Robinson
- ↳ Streptocarpus R. Dibley
- ↳ Streptocarpus breeders of other countries
- ↳ Agrotechnics of streptocarpus
- ↳ Vegetative reproduction of streptocarpus
- ↳ Seed streptocarpus
- ↳ Photos of streptocarpus seedlings
- ↳ Diversity and features of streptocarpus
- ↳ Problems, diseases and pests of streptocarpus
- ↳ Fuchsia
- ↳ Fuchsia varieties
- ↳ All about fuchsias
- ↳ Hoyi
- ↳ Khoi species and cultivars
- ↳ All about hoys
- ↳ Cyclamens
- ↳ Varieties of cyclamens
- ↳ All about cyclamen
- ↳ Seed Cyclamen
- ↳ Species cyclamen
- ↳ Episodes
- ↳ Discussion of grades of episodes
- ↳ All about episodes
- ↳ Families
- ↳ Acanthus
- ↳ Amaryllidaceae
- ↳ Aroid
- ↳ Bromeliads
- ↳ Vervain and Lamb
- ↳ Other Gesneriaceae
- ↳ Commeline
- ↳ Kutrovye
- ↳ Gully
- ↳ Malvaceae
- ↳ Maranth
- ↳ Euphorbia
- ↳ Root
- ↳ Asparagus
- ↳ Fatty
- ↳ Mulberry
- ↳ Other families
- ↳ Plants from seeds and seeds
- Garden
- ↳ Ornamental garden
- ↳ Garden flowers
- ↳ Trees and shrubs, including conifers
- ↳ Bulbous, tuberous, rhizome
- ↳ Roses
- ↳ Fruit garden and vegetable garden
- ↳ Vegetable garden
- ↳ Fruit garden
- ↳ Plot and garden - general questions
- ↳ Landscaping
- To help the florist
- ↳ Plant care
- ↳ Everything for growing plants
- ↳ Fertilizers and stimulants
- ↳ Botanical primer
- Pests and diseases
- ↳ Pests
- ↳ Insecticides and acaricides
- ↳ Diseases
- ↳ Fungicides
- Green Planet
- ↳ Informative and interesting
- ↳ World Gardens and International Exhibitions
- ↳ Botanical gardens, arboretums, arboretums
- ↳ Forum about nature
- ↳ Flower Shows
- ↳ Contests and flora shows
- ↳ Past contests and flora shows
- ↳ Completed contests and flora shows
- Brags
- ↳ Show off indoor plants
- ↳ Show off garden plants
- ↳ Archive of brags
- Buy - sell - exchange
- ↳ Flower fair
- ↳ All about the Forum Fair
- ↳ Collective plant orders
Streptocarpus (Streptocarpus) or streptocarpella is a beautiful indoor flower from the Gesneriaceae family. The homeland of the plant is the island of Madagascar; in the wild, it can be found in South Africa and Asia. In total, about 130 species of flower have been recorded, it gets along well at home and can serve as a decoration for any greenhouse or garden. Streptocarpus got their name due to the unusual shape of the seed bolls.
After the flower of the streptocarpus withers and the seeds ripen, the capsule curls into a bizarre shape. Translated from the Greek "streptus" is a twisted spiral, "karpos" is a fruit, a seed. For the first time in Europe, the flower became known in 1818 thanks to the botanist James Bowie. Then it was named “Didimocarpus rexii”, but very soon it was renamed “Streptocarpus rexii”. The plant is known under this name even today. If in the wild you can find more than a hundred of its varieties, then more than a thousand cultivated hybrids are known.
Disease prevention
Indoor streptocarpus from seeds, just like plants grown from cuttings or by dividing rhizomes, can be affected by diseases and pests at home. The only reason for this may be illiterate care and violations of the agrotechnical rules of this plant.
- In dry indoor climates, there is a risk of thrips settling on streptocarpus. Affected plants dry out very quickly and die. To kill these parasites, insecticidal solutions are used.
- Low air humidity is an excellent environment for the appearance of not only thrips, but also scale insects. Actellik will help get rid of these insects.
- With an excess of moisture in the soil, aphids may appear. In the fight against it, not only repeated treatment of plants with a chemical preparation will be required, but also a complete replacement of the soil.
- Most often, streptocarpus affects fungal diseases, from which these flowers are rarely saved. If the plants are provided with the necessary growing environment and competent care is provided, then they are not afraid of any diseases and pests.