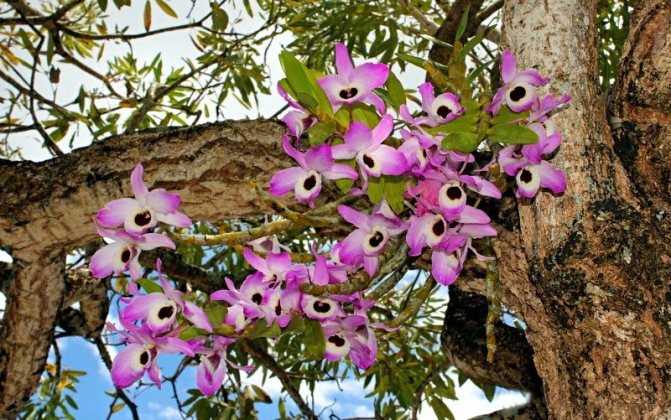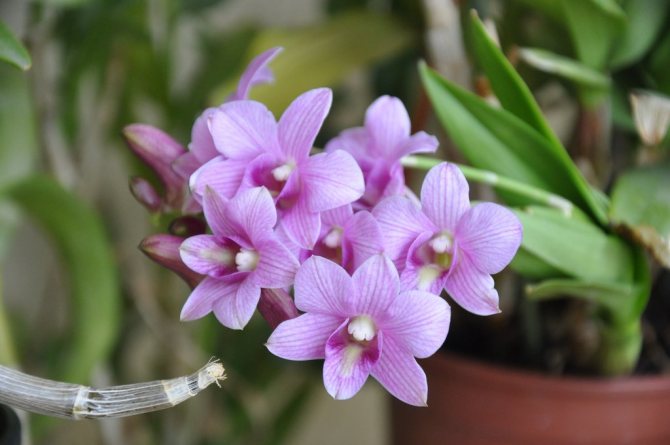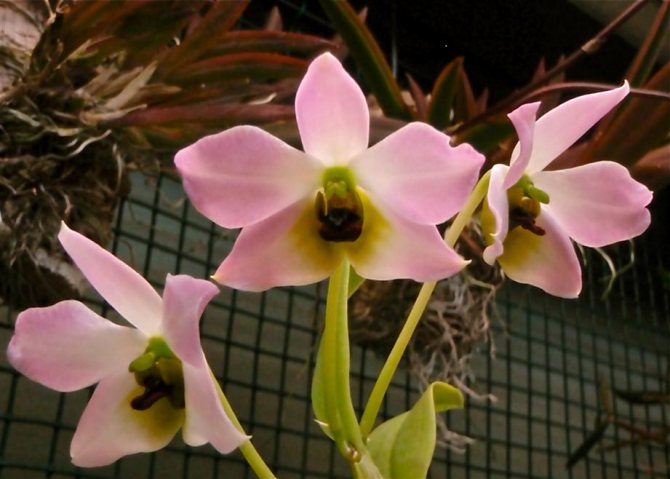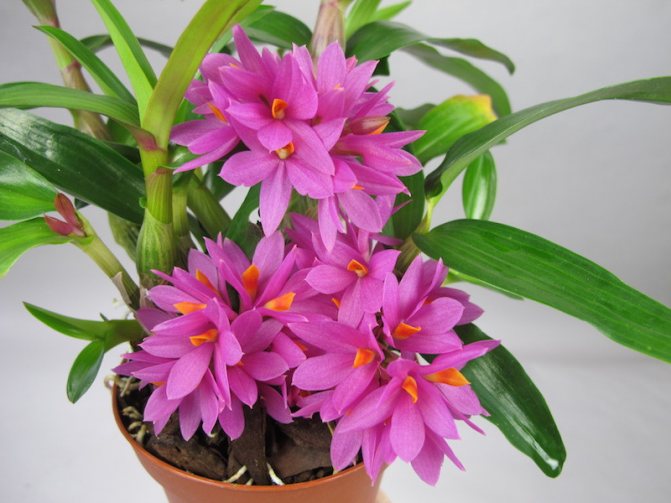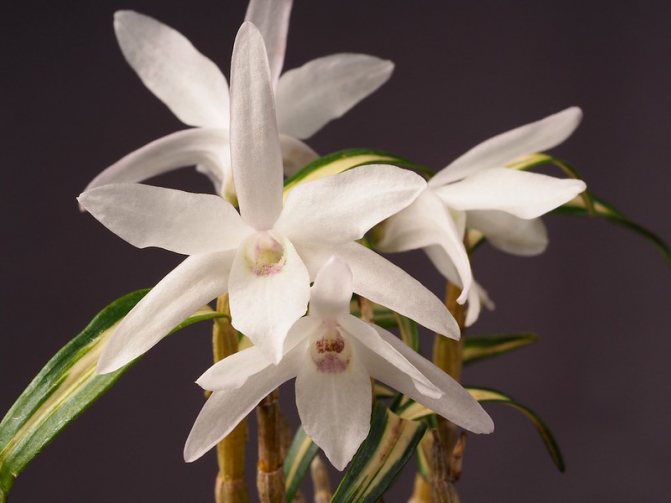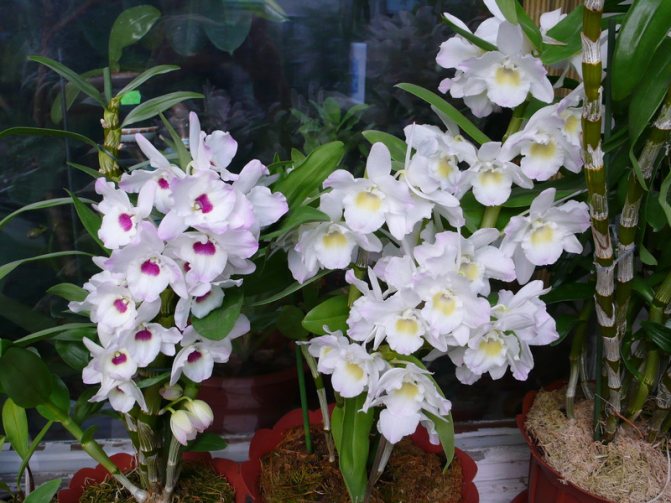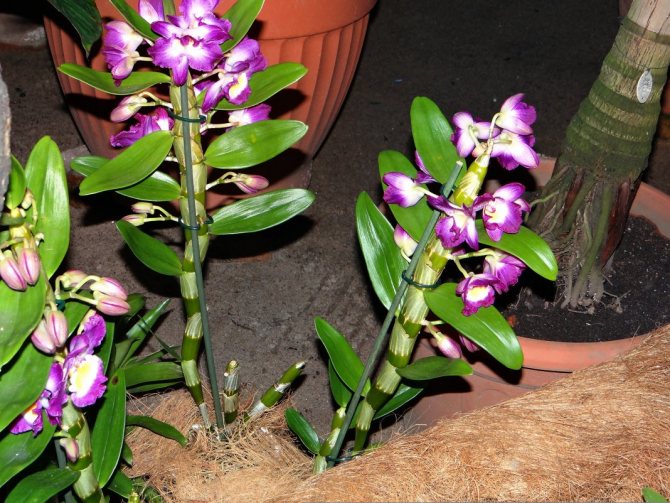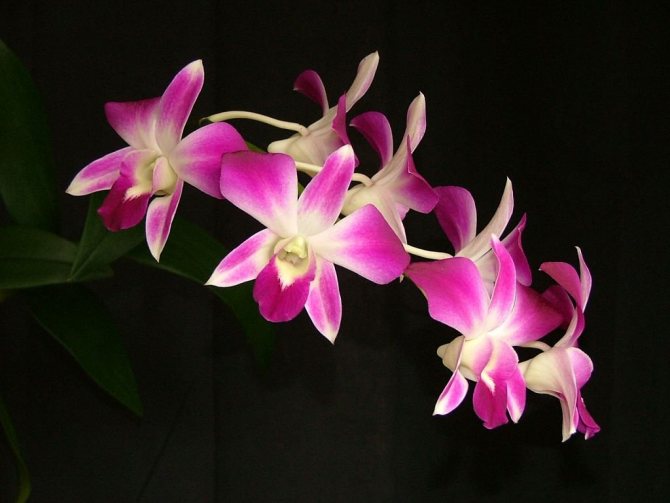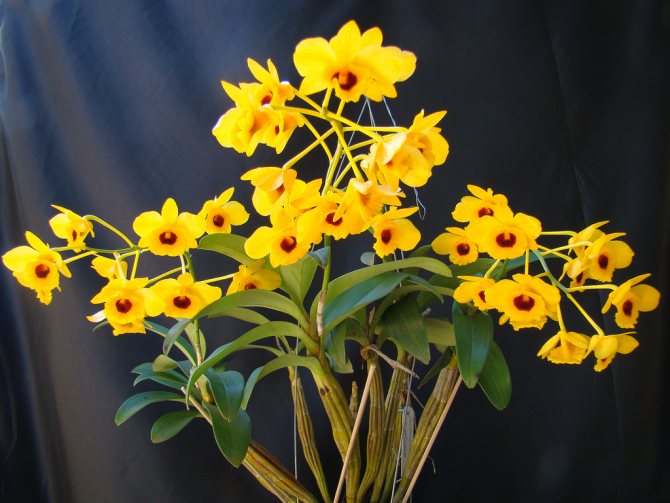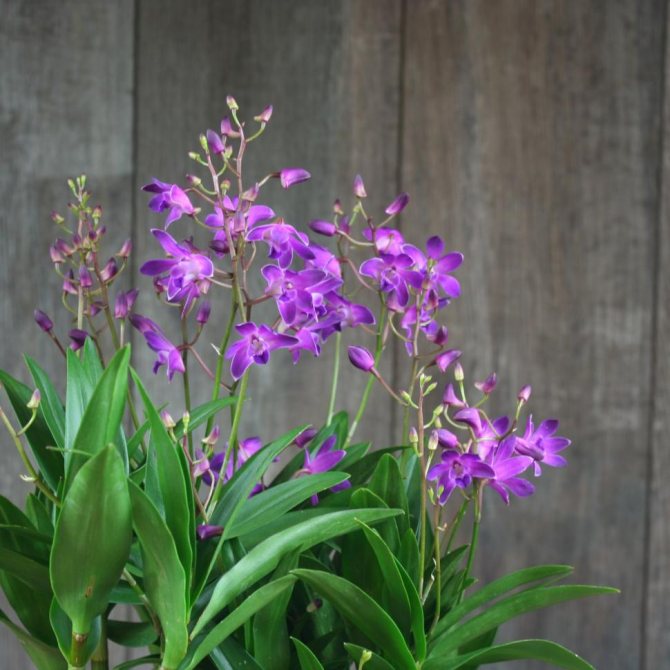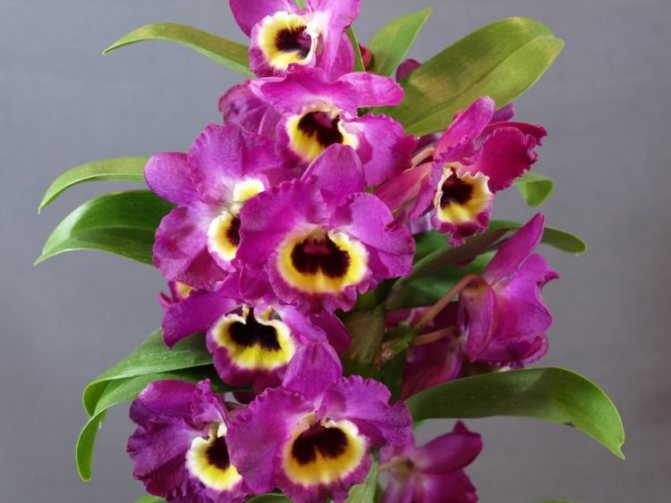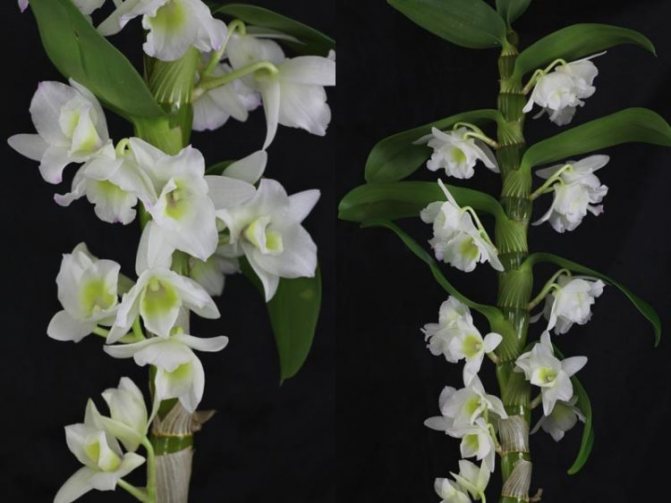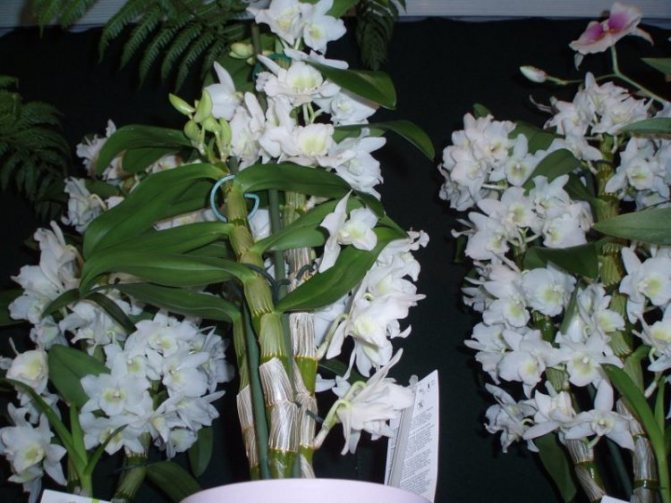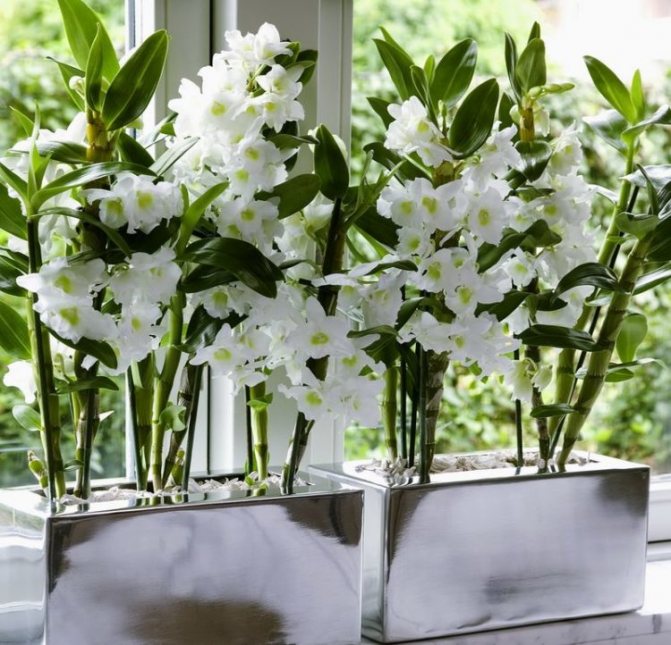
Dendrobium (Dendrobium Nobile) is an epiphyte plant of sympodial branching. Family - Orchidaceae. Homeland: the tropics of Southeast Asia, China, the Philippines, Japan, the islands of the Malay Archipelago, Australia, New Guinea, New Zealand, the islands of Oceania. As a rule, hybrid plants are grown in culture.
Flowers have a smell. Coloring - white / pink / dark purple and other shades. Flowering period: autumn / winter / spring / summer. The budding period stretches for three months. Dendrobium (Nobile) flowers cover the pseudobulb almost its entire length.
Description of the plant, external characteristics
It is almost impossible to confuse this species with other orchids because of its original appearance.
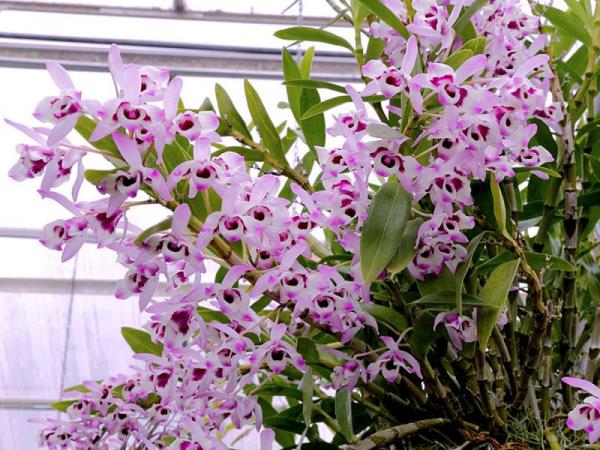


The number of leaves on an adult plant
The main difference between dendrobium is the absence of a root rosette... Its dense and tough (leathery) leaves grow along the stem on both sides. Their shape is elongated or belt-like, the size is 7-10 cm. Each shoot grows up to 6-7 leaves.
Height of an adult plant
Under natural conditions, dendrobium is stretched up to 1 meter in height... The domestic orchid of this species is a bush with a height of about 60-80 cm.
Diameter and type of flower
Orchid petals are ovoid, while sepals are stretched in length.


Dendrobium flowers are collected in groups of 3-4. Them diameter reaches 10 cm (usually 5-8 cm)... The number and size vary depending on the age and variety of the plant. On the shoot, up to 50-70 flowers bloom at the same time.
Maximum peduncle length
Another distinctive a feature of dendrobium is a peduncle, the length of which is no more than 2-5 cm... Therefore, in the photo, and on the plant itself, during abundant flowering, they are practically invisible.
Photos of different varieties
Himezakura
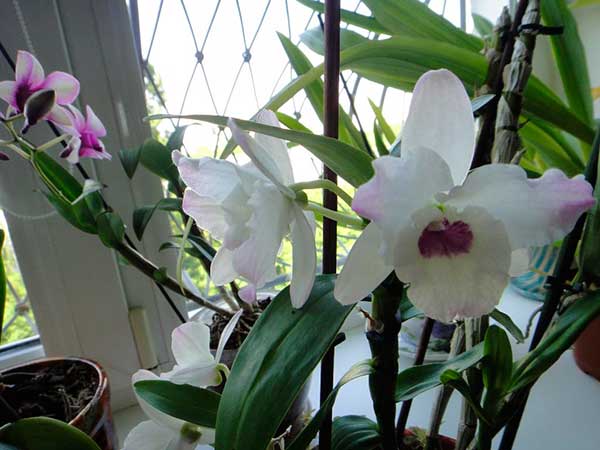


New Century


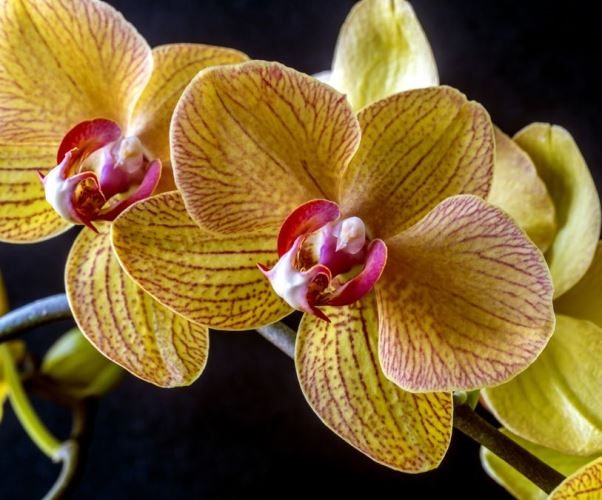
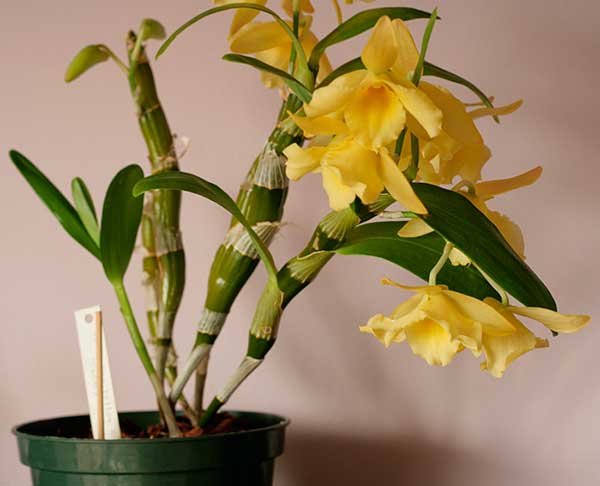
Yellow song


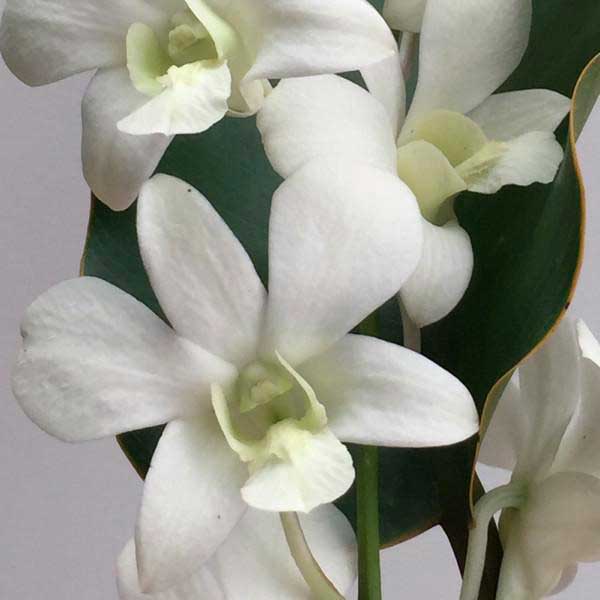
Bon white


Jade green
Important to know when buying
To avoid many problems with dendrobium, especially for beginners, choosing the right plant when buying will help.


- Healthy young orchids have green root tips... This indicates their growth. If only green dots are visible, but the leaves of the plant are not sluggish, then the dendrobium is in a dormant stage, or has recently "woken up". This is also considered the norm.
- The foliage of a healthy plant is bright green. and a smooth glossy surface. Too bright and too large leaves are the result of applying a large amount of fertilizer. Such an orchid may not bloom at all in the next 2-3 years. In addition, overfed dendrobium is at risk of pests and diseases.
- A flower in a dry substrate will endure transportation easier and adapt faster in a new place, so you should not buy orchids immediately after watering.
They also approach the issue of buying a flowering plant with special care. In order not to get trapped, you need to choose an orchid, most of the buds of which have not yet blossomed.
When to have a scheduled transplant?
Experts consider the most favorable time for a transplant - start of growth.
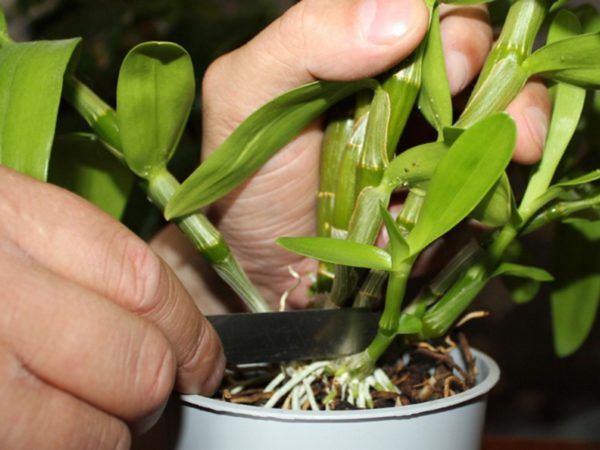


The Dendrobium Orchid should be transplanted during the start of growth.
Before starting the procedure, you should stock up on fresh substrate, a new pot and tools for removing rotten parts of the root system, which must be disinfected without fail.
After removing the faded orchid, you should carefully remove old soil... In order to thoroughly clean the roots of the orchid, you should rinse them under warm water.
IMPORTANT! Before transplanting, you should carefully examine the flower for the presence of parasites and diseases. Next, you need to dry the plant for 8-10 hours. The bottom of the new pot should also be treated with an antiseptic.
Growing dendrobium
Rational home care - the guarantee of longevity and health of a flower, so you need to know what he loves and what he may not like.
Lighting and location


Dendrobium is photophilous, but direct sunlight is destructive for him... Therefore, when choosing a place, preference is given to windows facing east or west.
If there is no choice, and all windows face south, then the orchid will need "Protective shield" in the form of light curtains or blinds. But a flower placed on the north side will need additional lighting. The optimal length of the day for this plant is at least 12 hours daily..
Most of all, dendrobium needs sunlight with the active development of new shoots. As a rule, this is the last decade of August and autumn months.
Temperature
The most comfortable temperature regime for dendrobium nobile and most other varieties is 22-28 ° C in summer and 15-20 ° in winter... But the plant can quite easily tolerate warming up to 32 ° C (only with sufficient humidity).
During flowering, for a more active flow of the process, the orchid requires an average daily temperature drop of 5-10 ° C... It can be provided, for example, with good evening airing of the room. Turning off the heating, spraying the plant, or damp cleaning nearby surfaces will also help change the temperature.
Watering
The frequency with which you need to water your dendrobium depends on the environment.


In the spring and autumn periods, for example, it is enough to do this every 10-15 days. In the summer - 2-3 times a week. BUT in winter there is no need to water the plant at all... The procedure is resumed only after the young flower shoots appear.
The substrate will help you navigate this issue. Drying it "says" that the flower needs moisture.
Advice! The degree of heating of the water should be 2-3 degrees above room temperature. You can take filtered, well-settled or boiled.
Humidity
The birthplace of dendrobium is the tropics, therefore the orchid needs high humidity... Its minimum indicator in the room where the flower grows should be 40-50%. The optimum moisture content in the ambient air is 50-80%.
Priming
The easiest option is to buy a special substrate. But if you wish, you can prepare the soil yourself.
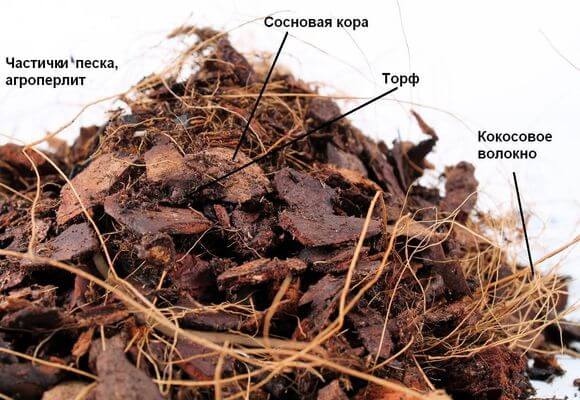


Pieces of old pine bark are used as a basis, ranging in size from 1 to 3 cm. Mixed with it:
- charcoal (not very coarse);
- fern roots (if available);
- fellam (bottle corks can be used);
- coconut fiber.
If the orchid is on the south side, it is recommended to add a little sphagnum moss to the substrate, which will retain moisture.... For flowers growing on northern windows, it is permissible to add small pieces of styrofoam to the ground. Moderate amounts of peat are also a good addition.
Transplant rules and pot selection
Dendrobium does not require spacious containers - he will be quite comfortable in a pot, where the distance between the walls and roots is only 2-2.5 cm.
Having bought a new flower, it is worth replanting only next spring.... Further "expansion of the living space" of the orchid is made after 3-4 years.
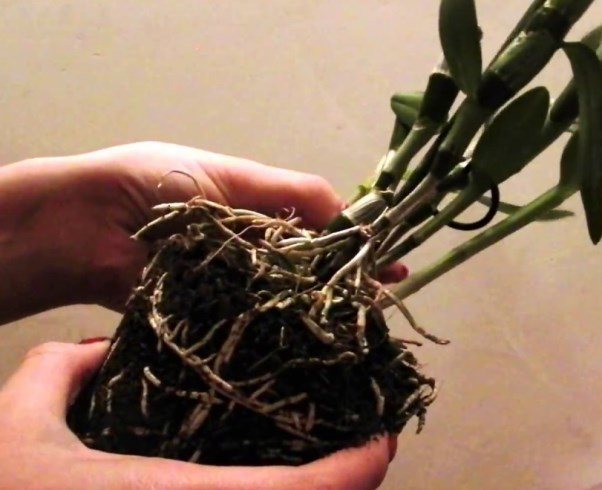


You should hurry up only in certain cases, for example:
- If the substrate has completely turned into dust and can no longer serve as a support for the flower.
- When the root system has grown a lot and there is no room for soil in the pot.
- If a brown coating appears on the lower part of the plant, the tips of the roots begin to rot.
Transplant the orchid after the flowers have fallen... But if there are traces of disease or decay, it is not worth waiting for the plant to fade.
The process is performed according to the following algorithm:
- Preparing the pot... Its walls should be high enough so that, in addition to the soil and the plant itself, there would be room for a drainage layer 3-4 cm thick. The best option is a container made of clay or plastic with a sufficient number of holes. In this case, the transparency of the pot does not really matter.
- Drainage laying... It is prepared from sufficiently large, heavy and sterile stones. Together with them, you can put large pieces of pine bark.
Caution! Expanded clay, which is usually used for these purposes, contains calcium, a salinizing substrate. Therefore, it is better not to take it.
- Flower transfer... After removing the plant from the old pot, its roots are completely cleaned of the substrate. All damaged parts are cut off with a sharp knife, and the wounds are treated with activated carbon. After the sections are dry, the flower is placed on the drainage layer, the substrate is added, without falling asleep at the same time with the young shoots.


At least 2-3 cm should remain from the ground to the edge of the pot... There is no need to tamp the soil when transplanting an orchid, it is enough to slightly shake the pot so that it is evenly distributed and fills the voids.
After the procedure, the flower is placed away from bright lighting for 3 weeks.... But all this time it is necessary to keep the ambient temperature within 20 ° C. The plant should not be watered for the first three days after transplanting.
Top dressing
From the substrate used, dendrobiums cannot extract the required amount of substances necessary for growth and development. Therefore, the flowers are regularly fed. For this, exclusively liquid fertilizers are used.
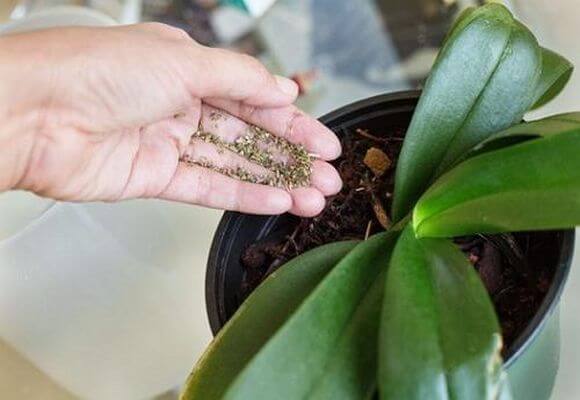


Top dressing can be root and external. The first is done by adding fertilizer to a pan with water. The second - when spraying plants with a spray bottle.
In both cases, special mineral additives are used for orchids, but they are diluted in different concentrations.
So, with root feeding, the dosage of the drug is reduced by 2 times against that indicated by the manufacturer, and when spraying - 5 times. During the growing season (April - September), dendrobium is fed twice a month.
Attention! Nitrogen fertilizers promote shoot growth but reduce the likelihood of flowering. Therefore, they should be replaced with phosphoric ones after the children are half-grown.
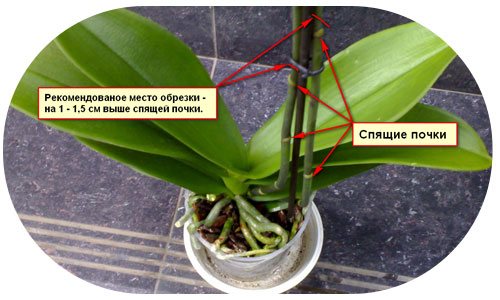
Pruning


During flowering, dendrobium should not be disturbed by pruning. Wait for the end of flowering.
Even if you are a perfectionist, do not rush to cut off the faded leafless stems.
We remember that they have stored nutrients in themselves to ensure the growth of young shoots.
The stems are subject to pruning in two cases:
- severely wrinkled, yellowed and dried stems - they have exhausted their resource and take away living space from young shoots.
- Obviously rotting, damaged pseudobulbs - to prevent the spread of infection to the remaining bush.
Features of care after flowering
Preparation for this important stage begins when the plant has completely bloomed and the old pseudobulbs wither (not just turn yellow, but dry out!)
The withered shoots are cut off and the wounds are sprinkled with crushed coal. After that, the pot is removed in

a room with a suitable temperature (16-20 ° C during the day and 10-12 ° at night) and reduce watering (gradually stop it altogether).Also, during this period, dendrobium does not need feeding.
Closer to spring, you need to closely monitor the plant. As soon as flower buds appear in the internodes of the shoots and flower stalks begin to form, the orchid should be taken to a warmer room in the sun (returned to its original place).
At the same time, watering is resumed and fertilization begins.
Growing geography


The distribution area of dendrobiums is the tropical forests of Southeast Asia, starting from the Himalayas, as well as Indonesia, Oceania, Australia, New Zealand.
Some of the species are found on the South American continent. Most dendrobiums are epiphytes, some are lithophytes.
Dendrobiums are protected by law, the export of orchids from nature is prohibited by the international CITES convention.
Reproduction
There are several ways to breed dendrobiums. All of them are quite lightweight and will not present difficulties even for novice florists.
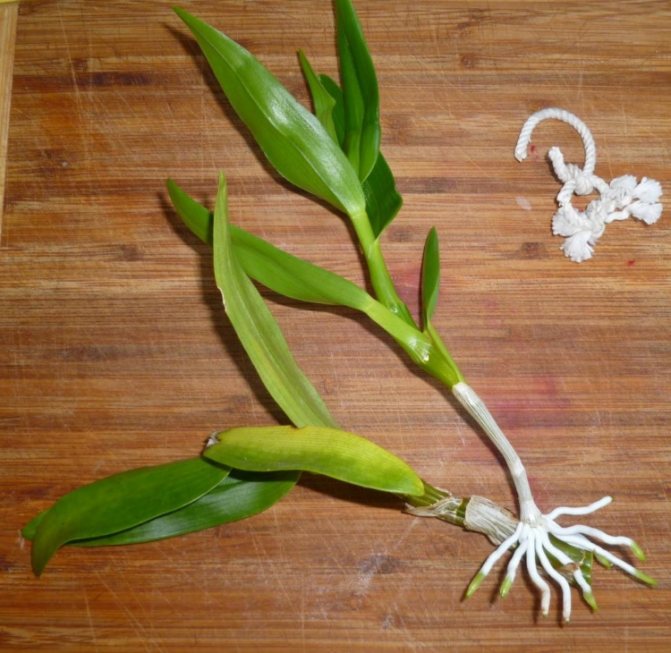
With the help of children
The simplest option is reproduction kids... In this case, the sockets that have appeared on pseudobulbs instead of flowers are used as seedlings. A slightly grown and formed baby is cut off with a sharp knife, the wound is allowed to heal in the air, treated with coal and planted in slightly moistened soil.
At first, a young plant will need greenhouse conditions., for which the pot is tightened with polyethylene or covered with a glass jar. After the dendrobium has taken root, the flower no longer needs a greenhouse. Further, a young orchid is looked after in the same way as for older ones. The first flowering of a transplanted plant can be expected in a year.
Cuttings
The second way to propagate dendrobiums is by cuttings. It is carried out as follows:
- An old pseudobulb with which the leaves have already fallen is cut under the root.


- Divide it into several parts using transverse cuts, making sure that each has at least 2 dormant kidneys.
- The sections are treated with charcoal.
- The cuttings are placed in a container filled with a sphagnum moss substrate. Close tightly, thereby creating a greenhouse environment.
- The container is placed in a warm place (temperature not lower than 22 ° C) with sufficiently bright diffused light.
- As needed, the substrate is moistened, and the container is ventilated so that rot does not form inside and mold does not appear.
If everything is done correctly, children will begin to grow on the cuttings after 3 weeks. Once the roots have reached a length of 5 cm and the plants are strong, they can be placed in pots of regular orchid substrate.
Watch a video on how to propagate an orchid by cuttings
By dividing an adult plant
Only fully formed, healthy orchids with a sufficient number of children are suitable for this method. Part of the plant is separated from the mature bush during the next transplant using a sharp instrument, the sections are processed and left in the air in partial shade for a day.
After the wounds are dry, a new bush is placed in a container of a suitable size with a ready-made substrate.
With the help of a young pseudobulb
For reproduction, a shoot that has never flowered is used. It is cut from the mother bush and placed in a container filled with sphagnum moss. The container is removed to a warm and bright place (22-25 ° C) and left until children are formed on the pseudobulb. This usually takes about 4-5 weeks.
After the young sprouts get stronger and acquire their own root system with a length of 3-5 cm, they can be transferred to separate pots with orchid substrate.
What to do with a faded pseudobulb?
Pseudobulba is a storage organ that feeds new shoots, providing favorable conditions for their growth.
Each false bulb blooms only once.
Experienced flower growers note that if only the upper part of orchids has faded, under the right conditions of care you can ensure flowering on the other part of the plant.Cutting off pseudobulbs is not recommended, it can be harmful.
It is necessary to wait not only for the end of flowering, but also for the moment when leaves will begin to falland the false bulb will begin to dry. Only in this case is it recommended to cut the pseudobulb.
Diseases and other problems
In some cases, dendrobium may lose its attractiveness and exhibit a number of symptoms that cause concern among florists. Sometimes these "bells" are only part of the normal life process of an orchid, but they can also indicate the development of a disease in the plant.
Dendrobium leaves turn yellow
The yellowing and falling foliage of an outwardly healthy flower is a natural process. Old leaves, which have ended their life cycle, are falling off. The latter is on average about 2 years old.
Dendrobium withers
Shrinkage of shoots during the formation of new pseudobulbs and during the dry period is also a common and normal process, so you should not panic too much.
How to save dendrobium if it turns yellow and withers


Not always yellowing leaves and wilting trunk - this is natural. If at the same time you pseudobulbs become flabby, wither, this may indicate that the plant is damaged by pests, for example, scale insects.
To get rid of insects and help the orchid to recover, you can use laundry soap... The plant is thoroughly washed with it, after which it is treated with 0.15% actellik solution.
Soap baths can be carried out as a preventive measure.
Root rot
The reason is excessive watering... If the problem is not eliminated in time, the rot will move from the roots to the stems, the plant will begin to wilt. Also, this problem can be caused by excessive enthusiasm for mineral dressings. In both cases, in order to prevent the orchid from dying, it must be urgently transplanted.
Dendrobium trunk rots
Rotting occurs due to waterlogging of the substrate, or as a result of the ingress of water between the leaves and the trunk. To prevent such a situation, after spraying such places are recommended to get wet with a napkin, removing excess moisture.
If the plant still has rot, it is necessary to urgently cut off all damaged areas, treat the wounds with charcoal or activated charcoal, and spray the entire orchid with a fungicide solution.
Dendrobium is cracking
Cracking on pseudobulbs is caused by:
- excess nitrogen fertilizers;


- a sharp temperature drop, coinciding with watering a flower;
- severe hypothermia;
- lack of moisture.
They also result from mechanical damage. If, in addition to cracks, the plant has no other problems, restorative procedures should be carried out.
These include the rejection of nitrogen fertilizers (replace them with potassium-phosphorus additives), optimization of the air temperature and irrigation regime.
Why might this not be happening?
Why Dendrobium Nobile may not bloom:
- The soil in which the flower grows is more than 3-4 years old.
- The plant lacks mineral salts.
- Pests have started.
- The conditions for keeping the orchid have been violated.
- If the peduncle has not formed, and the children continue to appear. The reason lies in the lack of light and high temperatures around.
- Has not bloomed for more than 1.5 years. The plant has a constant lack of light and there is no rest period.
- Only the blossoming flowers begin to dry. Causes: pests, high temperature or excess moisture.
Fact... An orchid may not bloom if ordinary snails are bred on it.
Berry Oda dendrobium may not bloom for a very long time. This is due to the fact that one of the flower development cycles has been disrupted.
In total, four development cycles are distinguished:
- Vegetation. The emergence of new shoots.
- Development of new pseudobulbs from new shoots.
- Rest period. Peduncles are laid.
- Bloom. Blossoming time.
Therefore, in order to remedy the situation, the following must be done so that the plant throws out the arrow:
- Arrange additional lighting.
- Lower the temperature.
- Limit watering.
We also have useful articles on replanting the Dendrobium orchid and on the causes of yellowing of the leaves and on how to combat this problem.
General information
In the wild, the orchid grows in the Philippines, Japan, New Zealand, China and Oceania. The culture has over 1200 varieties, differing from each other in the variety of colors, the shape of the inflorescences, leaf plates and flowering time.
Dendrobium, in comparison with other orchids, reaches a length of only 70 centimeters, and its stem consists of cylindrical pseudobulbs. The leaf plates are lanceolate. They are placed on the stem alternately. Peduncles grow from their sinuses and contain from one to four variegated inflorescences with a pleasant aroma.
It is quite simple to grow this unusual orchid, the main thing is to create a suitable microclimate for it and take proper care of it, then it will delight the grower with its decorativeness and bright, unusual inflorescences.


Do I need to fertilize?
During periods of active flowering, fertilizers may not be applied. It is recommended to fertilize with a balanced complex after flowering with the beginning of the growth phase (summer time) and continue until autumn. For rapid development and full formation, use nitrogen fertilizers. In general, nobile dendrobiums belong to rather unpretentious plants, well adapted to growing and breeding in the middle lane. By learning from this article what to do with these orchids after flowering and at each phase of the life cycle, you will ensure proper care and the possibility of early re-flowering.
Table: seasonal requirements of the Noble Orchid for keeping conditions
| Season | Lighting | Humidity | Temperature |
| Summer | Bright, but no direct sunlight | Watering is abundant, but with drying of the substrate, the plant needs high humidity. | During the day: +25 C, at night: 3-5 degrees lower |
| Winter | Moderate | Humidity is moderate. During the rest period, watering stops altogether. | In the afternoon: + 15-16 C, at night: + 10-12 C |
How to transplant - step by step instructions
Next, we will tell you step by step about transplanting a dendrobium orchid.
- Removing a plant from a pot. In order to painlessly get the orchid out of the pot, you need to soak it in water for 10 minutes. Carefully, taking the leaves by the rosette, gently pull the earthen ball.
- Root rinsing and disposal of excess substrate. The orchid should be put together with the remaining substrate in a container with a solution of epin and succinic acid for 30 - 40 minutes. This procedure is performed to prevent diseases and viruses.
- Examination of the roots and removal of diseased processes. When the substrate is wet, remove it. Old moss can be removed with tweezers in accessible places. Use a clean, clean knife to cut out the old, dead roots. Examine for rot. Remove rotten scions immediately so that the infection does not spread.
- Drying the plant after washing. Treat the renewed, peeled flower root well with 3% hydrogen peroxide solution. Sprinkle the "wounds" with crushed charcoal. Place the orchid on a clean dry cloth. You can use a lamp for extra warmth and light.
- Planting dendrobium in a new pot:
- Treat the pot, especially if it is not the first time it is used. The size of the pot should not be large, because you cleaned the root, thinned it out. The roots should be comfortable in the pot.
- At the bottom of the pot, put some drainage material - pebbles, chopped wine corks, chopped shards.
- Lower the orchid in the center of the pot, place the roots loosely, sprinkle with the substrate lightly, without pressure and compaction.
- The roots will adapt and position as they please.


Watering. Immediately after planting, place the orchid in a well-lit area with diffused, soft light. Moisten the room. Do not water the flower for 2 - 3 days, let the roots "grab".
Dendrobium is a tropical crop, watering should be moderate, but frequent, and its watering conditions should be as close as possible to the conditions of the natural habitat of the orchid. In the summer you need to water more often, the temperature is higher, the evaporation is greater.But in winter, watering is reduced to a minimum, transferred to a "dry" mode. Can be watered with a warm shower during summer to freshen the leaves. After a shower, dry well with a cotton swab or ear sticks of the axils of leaves, buds of growth, so that there is no stagnation of moisture.
Watering during irrigation is only purified and only warm, otherwise the roots will freeze and rot.
Important! It is necessary to boil the substrate, thereby disinfecting.And the bark, when treated with boiling water, will become softer, from this the soil will be loose, and not compressed.
What should not be done in any case?
- Peduncles and pseudobulbs should not be cut off, the dying off should take place naturally.
- When transplanting into a new pot, do not deepen the root. The voids in the pot are filled with the substrate.
- When replanting, place the roots so they don't clump together or intertwine.
Germination of cuttings
It is quite realistic to transplant dendrobium with stem fragments, where there are several internodes:
- Cuttings 10 cm long are treated with charcoal.
- Moss - sphagnum moss, which is moistened in advance, is placed in plastic bags.
- In each of these "greenhouses" are placed 2 cuttings.
- Store small cuttings at 22-24 degrees, ventilate the greenhouse daily and water the moss.
- Organize diffused and bright light.
- After 14 days, when the first roots grow, transplant the plants into pots.
- After you decide to transplant the dendrobium into another pot, young orchids will bloom in a year and a half.
Which pot to choose?


Clay pots are great for dendrobiumproviding the necessary stability to the flower. Plastic containers and special orchid baskets are also suitable.
The size of the pot should accommodate the root system of the plant and there should be no more than 1-2 cm of free space around the edges. If you choose a small pot, the roots will not have enough space, they will begin to crawl out of the container and can be injured.
Correct selection of soil
It is better to buy a special dendrobium substrate in the store.
Disinfect the substrate before planting - soak or boil.
Dendrobium substrate composition:


Drainage - pieces of styrofoam, pebbles, clay shards.- Moss - sphagnum is essential to retain moisture.
- Foam chips to allow the substrate to pass through well.
- Large pieces of bark are superimposed on the drainage bottom layer.
- Small pieces of pine bark are used for the main substrate mix.
A little about the signs


According to Eastern philosophers, there are many signs associated with the presence of this mysterious flower in the apartment.
- It is believed that for married couples, Dendrobium Nobile will bring peace and well-being to the house. If the couple is in a civil marriage, then the appearance of this flower can lead to strife and, even, to a break in relations.
- It is not advisable to place an orchid in the bedroom. It is believed that the flower will take away the strength from the owner, he may become depressed.
- The plant has a negative effect on people with an unstable psyche.
- In creative people, it helps to awaken inspiration and new strength.
- She gives women cheerfulness and prolongs youth.
- The presence of a blooming orchid Dendrobium Nobile in the house is a talisman against guests with bad intentions and any ill-wishers. If such a person appears as a guest, the orchid will worsen his well-being and force him to leave your house.
The color of orchid petals also has an effect.
- The red and purple-flowered orchid species are believed to help break bad habits.
- Yellow and orange orchids contribute to an active lifestyle, bring success in financial affairs.
- White and pink flowers relieve depression and bring the state of mind into harmony.































