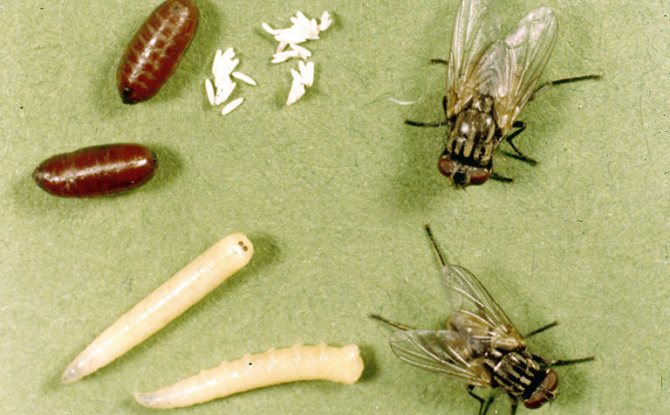
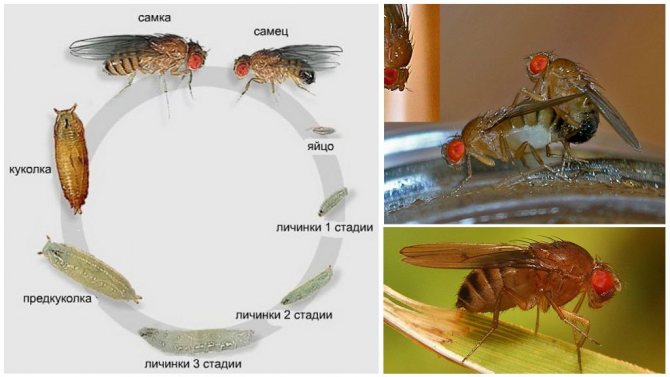
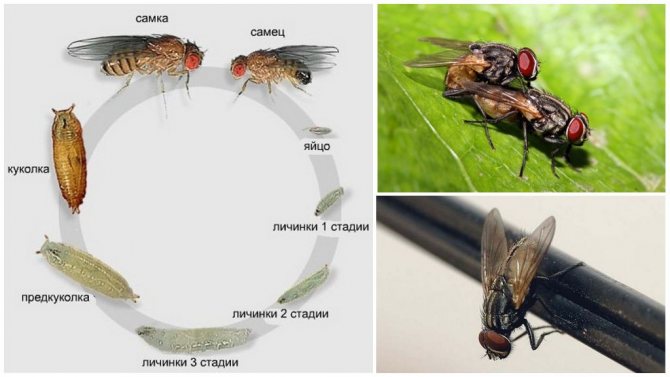
How long does the housefly and its street relatives live? Let's compare the lifespan of different species of these insects.
The average life span of a fly is short - only 2-4 weeks, sometimes a little more if the living conditions are as favorable as possible. But during its short life, this insect manages to breed several generations of offspring, so sometimes it seems that the same individuals live unimaginably long.

Project "The structure of a fruit fly on the example of a children's handicraft"


Model of a fly from scrap materials.
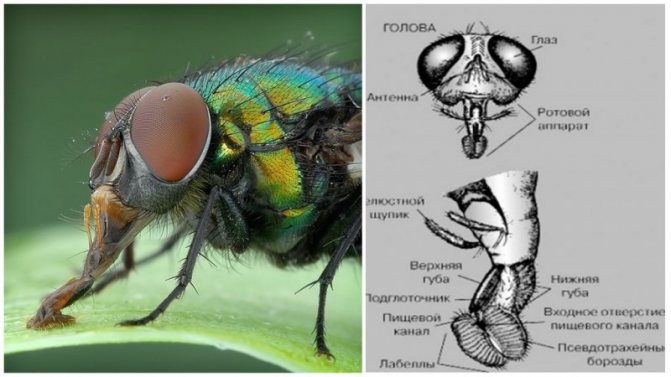
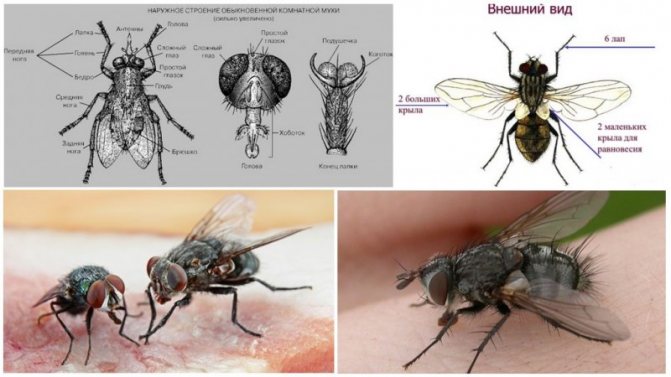
The body consists of three sections: head, chest, abdomen.
- The head contains what we call the brain, although other parts of the insect's body are also responsible for storing information and controlling movement. The mouth apparatus is also located on the head, the eyes are usually oval in shape and short antennae responsible for the sense of smell.
- The chest is the middle part of the body and can be compared to one large muscle. Attached to it are three pairs of legs and wings. The leg consists of several segments, at the end of each limb there are claws. They help to cling to surfaces.
- The internal organs are located in the abdomen. Fruit flies, like any insect, do not have lungs, but they have holes called spiracles located under the chest and abdomen.
We propose to complete a creative task that will allow you to create a model of a fly with the help of scrap materials, as well as study its structure in detail.
What we need:
- 2 oval balloons and 1 oblong balloon;
- a piece of clear plastic;
- old newspaper;
- 2 cups flour
- water;
- 1 tbsp. l. salt;
- Bowl;
- 8 bottle brushes or 8 bristled wire (2 of them short);
- acrylic paints;
- permanent markers;
- insulating tape;
- Super glue.
Experiment progress:
- To create a mock-up of a fly, find its picture on the Internet and study it in detail.
- Inflate one balloon for the head, a larger second balloon for the chest, and a third balloon even larger for the abdomen.
- Use duct tape to attach the head to one side of the chest and the abdomen on the other.
- Toss in a bowl 2 cups flour, 1 tbsp. l. salt, 2 cups water until a homogeneous liquid mass without lumps.
- Tear the newspaper into strips about 1.5 cm wide and, dipping them into the flour mass, carefully wrap the balloons completely.
- Let dry for 1-2 days.
- Glue 2 short wires to your head with superglue - you get antennas. Glue 6 long wires in pairs to the place on the chest where the legs grow from the fly.
- Cut wings out of plastic, draw patterns on them. Then glue them on top of your chest. Leave the balloons intact inside.
Output:
- Why did you make the layout of the front sight? What did you understand in the process of constructing the fly? What would you change during the experiment and in the layout itself to improve it?
- This project allows you to create a model of a fruit fly in a playful way and study its structure. Children are interested in creating something new with their own hands, and the fly created by you and your child will be a worthy decoration for the house or a good gift to close relatives.
Historical reference
It entered service in the Soviet army in 1972 after numerous tests. The predecessor of the RPG-18 is the RKG-3 anti-tank cumulative grenade.Purpose - fighting tanks, infantry fighting vehicles, self-propelled artillery installations and other types of armored vehicles, eliminating enemy forces in rooms, buildings and structures.
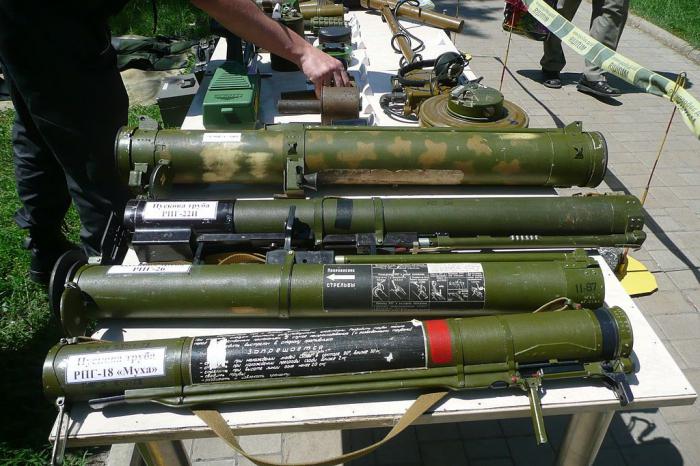


The expediency of creating a new anti-tank gun is quite understandable, because the fire capabilities of the predecessor hand grenade of the RKG-3 type are minimal. Initially, the Fly RPG-18 grenade launcher was designed on the basis of the American M72 anti-tank grenade launcher. It was this weapon model that was used as a model for the development of the Soviet RPG-18.
Project "How does a fly see?"


For the experiment, you will need plastic tubes.
There are many types of eyes in the insect world. Fly eyes are complex, consisting of a large number of lenses. Such a structure allows you to see the world from a wide viewing angle, but, at the same time, objects are not clearly visible. The fly's vision is different from how animals and even many other insects see.
Thanks to this experiment, you will be able to get closer to understanding how a fly sees the world around it. Surely, it will be informative and also very unusual.
What we need:
- 12 plastic straws;
- Scotch.
Experiment progress:
- Collect the straws together.
- Secure them well with tape.
- Bring one end of the bundle to your eye and look through it with your other eye closed.


Bring one end of the bundle to your eye and look through it with your other eye closed.
Output:
- It is difficult to look through such a beam. This is roughly how you might see if you had compound or compound eyes.
- When multiple lenses work simultaneously, the clarity of vision is lost in most insects with complex eyes. Faceted eyes help insects see, but their vision is not as clear as that of humans.
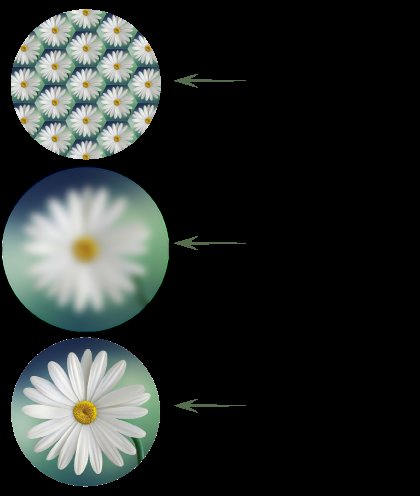


As the fly sees, insects and humans. - Have you ever seen, in movies or on TV, how the world is shown through the eyes of an insect? The picture above shows how different types of eyes see. The image above shows what insects usually see, but now you know that it looks much more like the image in the center. The bottom image shows the clarity and resolution of the human eye as opposed to the center image.
What are they
Each species of flies belongs to the order Diptera; they are distinguished from other relatives by large faceted eyes, which provide a view of almost all 360 degrees. Depending on the variety, they can have a different cycle of life, reproduction and nutritional patterns. Their oral apparatus is also different:
- Licking;
- Piercing-sucking;
- Cutting-sucking.
There are subspecies that do not require nutrition at all, and therefore they do not have a mouth apparatus. Each fly has the so-called zhuzhuli - symmetrical reduced wings placed in the thoracic segments. It is they who hold the creature in the air, while emitting a characteristic buzzing sound, thanks to them it is extremely difficult to catch the fly with your hands.
Fruit Fly Lifestyle Project


Experiment on phototaxis, geotaxis and chemotaxis in fruit flies.
The fruit fly often becomes the object of study of ethology, a science that studies the innate behavior of all living organisms. The same type of behavior of one type of organisms, which is their response to an external stimulus, is called taxis. In this experiment, you will explore phototaxis, geotaxis, and chemotaxis in fruit flies.
Observing chemotaxis should be especially fun as you can test any product.
What we need:
- 4 tall empty plastic bottles;
- scissors;
- transparent tape;
- Drosophila flies (wild-type Drosophila);
- refrigerator;
- clean table;
- black thick paper;
- funnel;
- cotton wool;
- sugar;
- salt;
- baking soda;
- fresh fruit (unripe and overripe);
- vinegar;
- water;
- other products to explore.
Experiment progress:
- Before starting the experiment, it is necessary that the Drosophila flies slow down a little. To do this, place them in the refrigerator for 15-30 minutes;
- Give fruit flies a few minutes to rest between experiments;
- Now we need to connect two bottles: Using scissors, cut off the bottom of all plastic bottles;
- Insert one bottle into the empty bottom of another bottle; Secure them with tape;
- Close the necks with cotton wool;
- Make an identical second camera.
Phototaxis experiment
- Attach black paper to one side of the first camera;
- Carefully run 6-20 fruit flies inside through one of the necks;
- Lay the camera on its side;
- Wait about 20 minutes;
- Count how many fruit flies are in the lighter part of the bottle. Subtract this number from the total to determine how many are in the dark part;
- Write down the results.
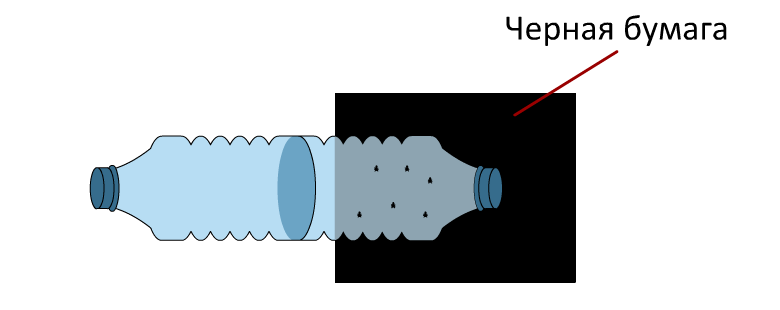

Fly phototaxis experiment.
Geotaxis experiment
- Introduce 6-20 fruit flies into the second chamber;
- Hold this camera upright for 10 minutes;
- Count the number of fruit flies in the bottom half of the bottle;
- Compare this number with the number of fruit flies in the top half of the bottle;
- Write down the results.
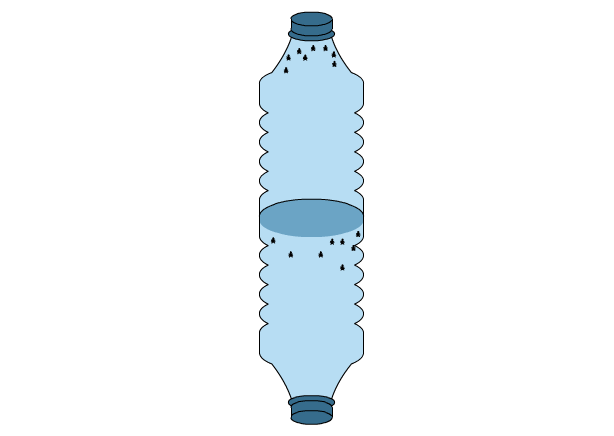

Fly Geotaxis Experiment.
Chemotaxis experiment
- If you plan to use dry substances such as baking soda or sugar in your next experiment, first dissolve a spoonful of each in water;
- Drop 5-10 drops of the substance you are interested in on separate cotton balls;
- Place a cotton ball soaked in one of the test substances on one end of the bottle. The other end of each chamber should be covered with a cotton ball soaked in water only. Consider why a cotton ball soaked in water is used;
- After 10 minutes, count how many fruit flies are on each side of the chamber;
- Write down the results.
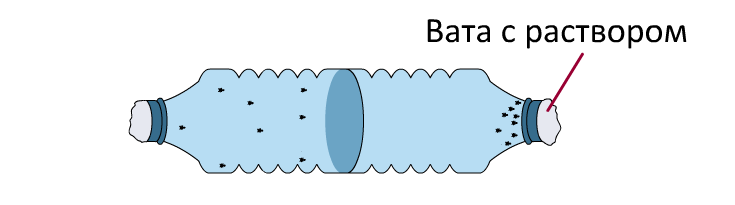

Fly Chemotaxis Experiment.
Output:
- Drosophila more often show positive phototaxis, in other words, move towards light;
- They show strong negative geotaxis, they like to move up;
- During the chemotaxis experiment, you will notice that fruit flies prefer sugary foods and vinegar, which can be found in rotting fruits, their favorite food.
About the benefits
In an apartment or a private house, flies are unwanted guests. Even if these are safe indoor flies, it is not known why spinning in the space under the chandelier, sitting down on tasty products, they annoy the home owner with one fact of their presence. Some of them are not threatening and even beneficial, but others can infect you with a dangerous disease. In total, there are about 75 thousand species that can be used to bring benefits:
- The hoverfly larvae cleanse the plants of aphids;
- Larvae of certain species are used to treat gangrene.
All of them are an integral part of the existing biosphere. While some people would be happy to eradicate all the flies in the world, their absence will seriously disrupt food chains and lead to ecosystem disruption. Their larvae and the adult flies themselves serve as food for various animals, buzzing insects help plants to pollinate, accelerate decomposition and even eat bugs and caterpillars.
Project "Products attracting fruit flies"


Fruit waste container.
This experiment will help determine which foods are most attractive to fruit flies. It is best done in warm weather. Let's determine which foods in the compost are the most attractive.
What we need:
- 4 plastic containers with lids;
- drill;
- protective glasses;
- the soil;
- red worms;
- vegetable waste in the form of salad and celery;
- fruit waste in the form of banana peels and apple cores;
- newspapers or white paper;
- kitchen scales;
- notebook;
- pencil.
Experiment progress:
- Take 2 plastic containers and ask an adult to help you drill holes in the bottom of one of them. The diameter of the holes is about 0.6 cm and the distance between them is about 12 cm. Place the container with holes in the container without holes. Repeat with 2 other containers;
- Spray the paper with water, shred it and fill both containers halfway;
- Place about 450 g of worms in each container;
- Label the containers “vegetables” and “fruits” and add the same amount of the appropriate waste to them;
- Place them in shade on opposite parts of your home or garden;
- Monitor each container daily for the next 2 weeks;
- The fruit container will attract more fruit flies;
Output:
- Why do you think the flies chose the fruit container? What attracted them? How would you improve this experiment, what would you change?
- Drosophila feed on plant sap, rotting fruits, and in the absence of them feed on rotting vegetables.
Vital activity of adults


Fly activity
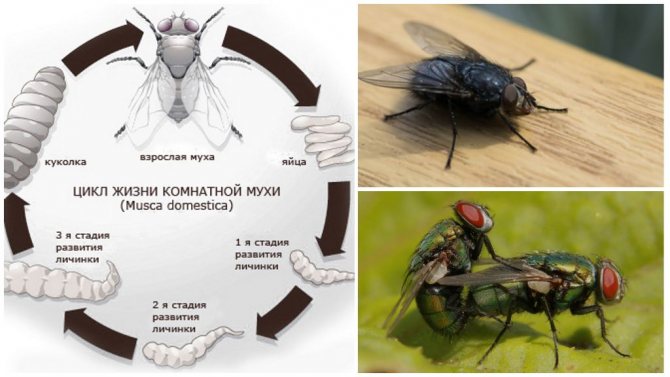
The life of a fly after birth begins with fertilization. The main task of the female is to lay eggs, she does this with a regular frequency. In some species of this family, the female lives without food, the energy reserves are still sufficient for those that the insect received as a larva.
Among flies, there are wildlife inhabitants, synanthropic species that live in close proximity to humans. Distinguish between settlement, semi-settlement, pasture. The latter are attached to livestock, the larvae develop in litter, feces, or on the body of the animal.
Where village or city flies live - in a person's house, apartment. They feed on food leftovers, crumbs, waste in the trash can, as well as sweat particles. Towards the end of summer, a flare fly appears in the human house, which hides from the night cold. This insect feeds on blood, so a person often feels painful bites on himself.
On a note!
Semi-village flies include meat flies, cadaver flies. These insects are large in size, with a shiny body with tints of blue and green. The food source is decaying meat, vegetables, feces, and manure. From time to time they can fly into a person's house, which is very undesirable. Meat flies are carriers of many diseases. The most common of these is intestinal infections, the most dangerous is leprosy.
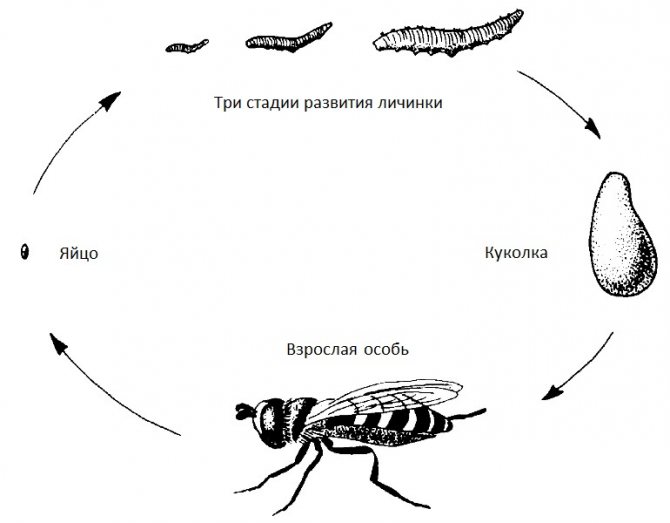
Fruit Fly Life Cycle Project


Banana jar for catching fruit flies
This experiment will provide an opportunity to observe the reproduction of Drosophila. It aims to refute the theory that decaying fruits are produced by living organisms. We can confirm that rotting food attracts fruit flies, which lay eggs on it, from where the larvae emerge.
What we need:
- overripe banana;
- one glass liter jar;
- large elastic band;
- magnifier;
- paper towel;
- wingless fruit flies (optional, can be purchased at the pet store).
Experiment progress:
- Peel a banana, place it in an open jar and leave it outside or near an open window;
- After a couple of hours, you will find tiny fruit flies crawling around the banana. You need to catch some fruit flies for this experiment to work. If your banana hasn't been hit by any fruit flies, try waiting a couple more hours or, if you're doing an experiment in the winter, you can order wingless fruit flies from the pet store.
- Cover the jar with a paper towel.
- Secure the paper towel with an elastic band.
- Using a magnifying glass, observe the fruit flies and see if you can identify males and females.
- While keeping the paper towel intact, watch the fruit flies every day for at least ten days using a magnifying glass.
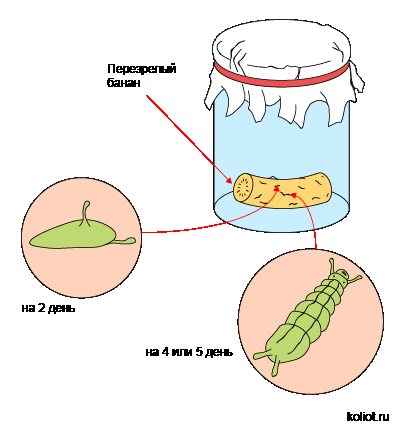

The first stages of development of fruit flies. - At first, you will be able to notice tiny white wet spots on the surface of the banana. These are the eggs that the fruit flies lay. After a couple of days, you should notice small white worm-like creatures on the surface of the banana. Since Drosophila flies are also flies, these cute little white worms are called grubs.
- These larvae are busy eating the tunnels in the banana all day and all night. Four or five days later, the larvae will attach to the inner wall of the jar, forming structures similar to large grains of rice that will darken after a couple of days. Tiny flies should emerge from the banana in about ten days. If your family doesn't get tired of this decaying banana, you can watch this generation of flies mate and lay eggs, repeating the life cycle.
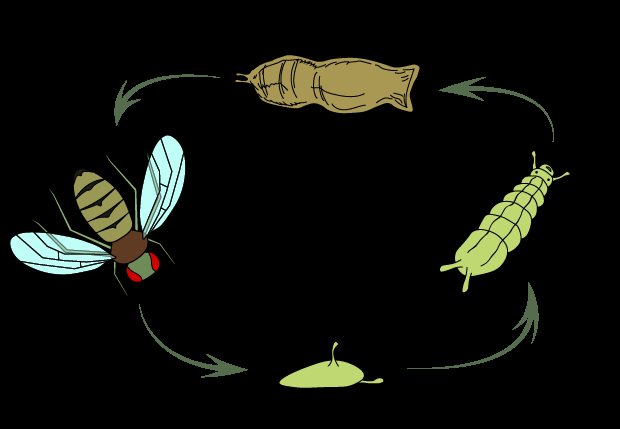

The life cycle of a fly.
Output:
Fruit flies are insects and, like all insects, they go through various stages of their life cycle. The fruit flies you catch lay their eggs, and these white wavy larvae that you observed are the second stage in the development of a fruit fly called larvae, just like caterpillars are the larval stage of butterflies and moths. The small specks were the third stage in the life cycle of the fruit fly, called pupae. The spots darkened as the legs, wings, and heads of the flies developed. To date, it has already been established how many Drosophila midges live. Their lifespan depends on the ambient temperature. It is about 10 days at 25 ° C and about 18 days at 20 ° C. The female lays eggs in the rotting fruit. The larvae appear in 24 hours and grow for 5 days, feeding on microorganisms and fruit. Then the larva enters the pupal stage for another 3 days, from where the adult emerges.
Repeat the experiment, leaving the jars at different temperatures. How does temperature affect fruit fly behavior? Where do fruit flies come from?
Lifestyle
The housefly, of course, is a subspecies of the common wild fly, which over time became so addicted to, albeit unsafe, but such a convenient and vicious cohabitation with a person, that by itself it branched off from its native taxon and formed a new one. This is how house flies appeared - regulars in kitchens, balconies, verandas and rooms.
These insects live mainly in those houses and apartments, where there is always something to profit from. They are attracted by the smells of something edible, especially rotten fruits, vegetables, meat products. They have a licking-sucking apparatus, so they do not pose any danger to a person from the point of view of a bite.
Domestic flies reproduce very quickly and easily, and are able to create a considerable problem for a negligent owner, having arranged a real invasion under favorable conditions for them. After all, flies appear in the home environment most often under conditions of "sanitary liberalism" on the part of the owners, you should not forget about this.
In this case, it is necessary to take measures in order to reduce the number of spread flies at least to an acceptable minimum, but this is a slightly different story.
By the way, about the lifespan of house flies. It ranges from two weeks to a month. If no one tries to shorten the life of a fly, the life span of an annoying parasite largely depends on the temperature parameters of its habitat.
The acceptable range is 10-40 degrees. At lower temperatures, closer to zero, the fly begins to seek refuge for the winter. At minus degrees, the insect dies.
Project "Life Cycle of a Butcher Fly"


Place a piece of meat inside the jar and observe.
In the experiment with flies and meat, we will be able to see how the life cycle of the gray meat fly proceeds. Many children are often drawn to study insects, you just need to make this process safe, interesting and educational.
What we need:
- a small piece of raw meat;
- margarine container;
- a tool for punching holes in the container lid.
Experiment progress:
- Take a container and pierce several holes with a diameter of about 0.6 cm in the lid.
- Place a piece of meat inside.
- Close the lid and leave the container outside.
- Observe at the same time every day.
- Write down when and where the first eggs, larvae, and flies came from. Compare your results to the life cycle of a gray blowfly.
Output:
Reproduction of blowflies occurs as follows: females are viviparous and lay the larvae on decaying flesh, where they spend 5-10 days. After that, they move into the soil and pupate, from where adults appear on the fourth day, which live 5-7 days. Forensic entomology knowledge about how long flies can live at different stages of life is used to determine the time of death in homicide investigations.
Surviving the cold
Insects are creatures dependent on solar heat. When cold weather sets in, they try to hide in cracks where they can spend the winter. The colder the winter, the fewer individuals will survive. Usually, either larvae in the ground or pupae overwinter. For most flies, the situation is similar. An adult insect rarely experiences winter.
The insect cannot fall asleep for the winter. It falls into a daze, from which it can come out even in the middle of winter. The sun's rays only need to heat it up. This explains the appearance of single individuals in apartments even in the middle of winter. But such a "winter" fly is doomed to perish.
Most species live in natural conditions and common flies create the main problem for people in the apartment. They are brownies or indoor. When considering the development cycles of flies, it is better to focus on this type of insect, since it is unlikely that anyone is interested in the distant and infertile tsetse or the hunchback bee living in the apiary.
We suggest that you familiarize yourself with: How to get rid of mice in an apartment forever
Project "Influence of ultraviolet radiation on flies"
This experiment serves to educate students about the growth, reproduction of fruit flies, the basic physical characteristics of these flies, how they are fed and kept, and their short life cycle, making them excellent candidates for genetic experiments. The duration of this project about flies is about 2 months. This period includes the experiment itself, collection, registration, data analysis, summing up the results of the experiment. Through this project, you will be able to determine if UV radiation will cause mutations in flies.
What we need:
- fruit flies;
- agar agar;
- 5 kg of bananas;
- fork;
- large measuring cup;
- water;
- large magnifying glass;
- small plastic spoons;
- 2 bowls;
- 4 glass bottles;
- gauze;
- paper towel;
- camera with a magnifying lens;
- ruler;
- access to ultraviolet radiation with a power of 2920 A (Angstrom) (you can contact a dental clinic or local chemical laboratory).
Experiment progress:
- Write down the problem you are going to investigate.
- Create data tables to record observations.
- Prepare all materials.
- Prepare a banana feeding medium for fruit flies. Dissolve 15 g of agar in 480 ml of water, bring to a boil. Mash the bananas, weigh 500 g of banana pulp, add to the agar, from where the resulting mixture is bottled. Cut the towel into strips, place 2 strips in each bottle. Now close them and tilt them to increase the surface area. When the mixture hardens, start the fruit flies. Cover each bottle with cheesecloth. At the end of the 2 weeks, repeat this procedure and transfer the fruit flies to new bottles.
- Use a magnifying glass to study fruit flies, write down the characteristics: body color (gray or black);
- eye color (red or pink);
- wing length;
- floor.
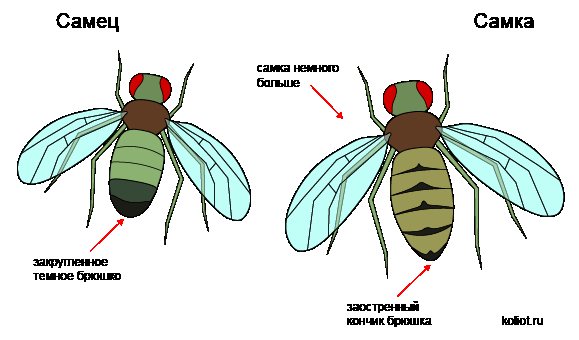

Distinctive features of the male and female flies.
- a clear statement of the problem;
Output:
You can evaluate what you did and describe what you would do differently if you had to go through this project again. Something went wrong? What has been successful? What advice would you give your classmates when repeating this experiment?
In this experiment, children will not only gain knowledge about the nature of fruit flies, but also become familiar with basic learning processes, such as the importance of controlling the experiment, determining the dependent and independent variables, collecting data, graphing data and the ability to make correct judgments, and justify their conclusions. They take on the role of scientists and learn to act independently.
Description
The soaring fly got its many names due to the fact that adults soar over flowers like a hummingbird or a hawk moth. Larvae can be voracious predators of small insects, especially aphids, and all aphid-eating species belong to the subfamily Syrphinae.
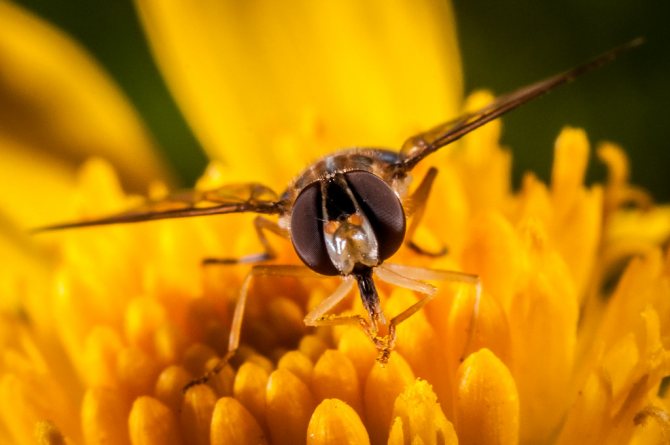


Flies are common in many crops affected by aphids and other small soft-bodied insects.