Leafy vegetables
| White cabbage Brassica oleracea Family: Cruciferous (Cabbage) |
| Red cabbage Brassica oleracea Family: Cruciferous (Cabbage) |
| Kohlrabi Brassica oleracea var. gongylodes Family: Cruciferous (Cabbage) |
| Broccoli Brassica oleracea var. italica Family: Cruciferous (Cabbage) |
| Brussels sprouts Brassica oleracea var. gemmifera Family: Cruciferous (Cabbage) |
| Savoy cabbage Brassica oleracea convar. capitata var. sabauda Family: Cruciferous (Cabbage) |
| Chinese cabbage Brassica rapa subsp. pekinensis Family: Cruciferous (Cabbage) |
| Cauliflower Brassica oleracea L. var. botrytis L. Family: Cruciferous (Cabbage) |
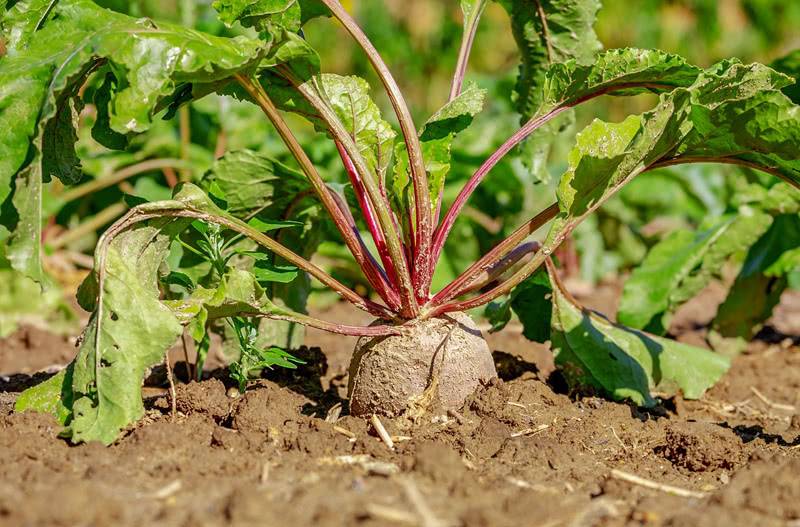
| Chard Beta vulgaris Family: Amaranth |
| Parsley Petroselínum Family: Umbrella |
| Dill Anethum Family: Umbrella |
| Basil Ocimum Family: Lamb |
| Marjoram Origanum majorana Family: Lamb |
| Savory Satureja Family: Lamb |
| Mint Mentha Family: Lamb |
| Melissa Melissa Family: Lamb |
| Oregano Origanum Family: Lamb |
| Tarragon Artemisia dracunculus Family: Asteraceae or Asteraceae |
| Sorrel Rumex Family: Buckwheat |
| Spinach Spinacia Family: Amaranth |
| Fennel Foeniculum Family: Umbrella |
| Lovage Levisticum Family: Umbrella |
| Watercress Lepidium sativum Family: Cruciferous or Cabbage |
| Endive or Chicory salad Cichorium endivia Family: Astrovye |
| Lettuce Lactuca Family: Astrovye |
Plant compatibility when planting in beds
When planting vegetables in the beds, the correct neighborhood of different representatives of cultures is observed. The gardener needs to be aware of which landing is most favorable.
Vegetables, list of plants by compatibility:
For the best harvest, onions are planted next to tomatoes, cucumbers, beets, radishes, parsley or lettuce. Refrain from the company of peas, beans and grapes. Garlic will not be the best neighbor. Despite many similarities, they often transmit diseases to each other, are competitors in terms of nutrients and moisture for the root system.
Read also Ginkgo biloba leaf extract
Carrot
The most suitable neighbor would be onions. These vegetables mutually repel the partner's pest. However, you need to be careful about watering. Carrots need more moisture. From this amount, the onion is capable of rotting. A good alternative is planting tomatoes, spinach, garlic, radishes, lettuce, or peas next door. Dill or parsley is an unsuitable garden companion.
Potatoes
It gets along with many vegetables. Exceptions are cucumbers, tomatoes and cabbage.
White cabbage
It goes well with salad, herbs, celery. Do not plant cabbage near tomatoes, strawberries and beans.
Garlic
Thanks to garlic phytoncides, it is a good neighbor for many. Its bactericidal properties will protect against fungal diseases. In the garlic society, potatoes, carrots, strawberries, beets, tomatoes, celery, cucumbers feel good. Do not plant legumes (beans, lentils) and peanuts nearby.
Tomatoes
Interact well with cabbage, radishes, beans.The neighborhood of potatoes and high-growth crops will be unsuccessful.
Cucumbers
Cucumbers are planted near onions, legumes, spinach, and garlic. Better not to be placed next to radishes, potatoes and tomatoes.
Beet
The best neighbors are onions, cucumbers, cabbage, zucchini, and lettuce. Mustard, corn, and beans are bad companions.
Eggplant
Compatible with peppers, onions, beans. At the same time, eggplants with peas and fennel have an unfortunate neighborhood.
Vegetable crops, a list of plants, photos and names of which are familiar to gardeners and summer residents firsthand, are one of the most popular in cooking. It's hard to imagine a diet that doesn't include vegetables.
They are baked, steamed, stewed, fried, frozen, canned for the winter. In order for the plants to please with a good harvest, you need to know the peculiarities of planting and combine them correctly. Therefore, you need to take into account not only the recipes, but also the basics of planting and care.
Useful information on how to properly plan the beds, what vegetables can be planted nearby - in the video:
The development of a plan necessarily precedes the implementation of any idea. This fully applies to the garden: the more carefully and thoughtfully the area allocated for planting is arranged, the more confidently you can expect a good harvest (of course, provided that the plants are properly taken care of).
Absolutely identical sites do not exist, and much depends on the terrain, soil and relief characteristics, on the location of the site relative to the cardinal points, special microclimate and much more. However, there are universal recommendations, adherence to which when planning a garden guarantees high yields in the future.
Before proceeding to the consideration of specific issues, it is necessary to study the specifics of agricultural technology of vegetable crops, their needs, the conditions necessary for their normal growth and development, since without this knowledge it is impossible to competently organize planting and crop rotation, take into account the compatibility of crops.
➣ Due to the mild climate, the largest number of types of vegetables is cultivated in Asia: more than a hundred in Japan, about eighty in China, about sixty in India, and about fifty in Korea.
Vegetable crops are extremely diverse. In Russia, about forty species of vegetable plants are grown, of which cabbage (white cabbage, Beijing, cauliflower), cucumber, tomato, eggplant, radish, radish, beet, turnip, rutabaga, pumpkin, watermelon, carrot, pepper, onion, garlic are most often cultivated. , celery, lettuce, dill, parsley, melon, zucchini. The rest are less common. Each of the listed crops has a number of unique biological characteristics, they all have different requirements for natural and climatic factors and methods of cultivation, and are used in food in different ways. Despite such a variety, vegetable crops can be combined into groups, since they also have common features. However, it must be recognized that within the framework of one classification it is impossible to take into account all their characteristics.
From the point of view of biology, vegetable plants belong to different families (Table 1).
Classification of vegetable plants based on their belonging to botanical families
| Botanical property | Vegetable crops |
| Cruciferous (cabbage) | Cabbage (white and red cabbage, broccoli, cauliflower, Brussels sprouts, kohlrabi, Beijing, Savoy), katran, watercress, mustard, radish, radish, etc. |
| Umbrella (celery) | Anise, coriander, carrot, parsnip, parsley, celery, cumin, dill, fennel |
| Nightshade | Eggplant, potato, pepper, tomato |
| Liliaceae (onion) | Onion garlic |
| Legumes | Beans, peas, soybeans, beans |
| Pumpkin | Watermelon, melon, zucchini, cucumber, squash, zucchini |
| Asteraceae (Compositae) | Artichoke, lettuce, scorzoner, Jerusalem artichoke, chicory |
| Buckwheat | Rhubarb, sorrel |
| Haze (swan) | Chard, beets, spinach |
| Bluegrass | Corn |
| Purslane | Purslane |
Knowledge of this classification is necessary for everyone who grows vegetables, as it helps not only to systematize plants, but also to plan correctly. crop rotation
and avoid growing related crops for a number of years in the same bed.
Vegetable plants can be divided into groups, taking into account the duration of their vegetative cycle (Table 2)
Classification of vegetable crops according to the duration of the life cycle
| Annuals | Biennial | Perennial |
| Plants, the vegetation of which is carried out in one year, begins with sowing seeds and ends with the formation of new seeds, are classified as annuals. In their life cycle, three periods are distinguished: 1) seed germination and development of cotyledonous leaves; 2) active growth of vegetative organs, the growth of green mass; 3) the formation of reproductive organs and the maturation of the plant. After the plant has passed these phases, it dies off. Annuals are eggplant, tomato, cucumber, squash, zucchini, zucchini, cauliflower, etc. | Biennial plants in the first year of growing season give a rosette of leaves and form roots, bulbs, tubers, heads of cabbage, from which peduncles appear during the second year. Seeds are formed and ripen in them, that is, the life cycle of plants such as carrots, beets, celery, parsley, white and red Brussels sprouts and Savoy cabbage is interrupted by a phase of physiological dormancy, which begins with the onset of naturally unfavorable plants for growth and development. -climatic conditions. Biennial crops are cultivated to obtain heads of cabbage and other vegetative organs. To obtain seeds, heads of cabbage, roots, bulbs are dug up, stored, and planted in the spring. | Perennial vegetables (asparagus, horseradish, rhubarb, sorrel, etc.) have a long vegetative cycle, which begins again with the arrival of spring. Like annual plants, they form a rosette of leaves and a root system in the first year, and productive organs in subsequent years. Like biennial vegetables, perennial vegetables go through a phase of physiological rest. |
Read also Average Pork Carcass Weight
Most amateur gardeners, when growing vegetable crops, most often distinguish them by the part that can be eaten (Table 3)
Classification of vegetable plants based on the use of certain vegetative organs.
From a scientific point of view, the presented classification is not entirely correct, since it cannot take into account everything. For example, in fruit plants, both mature (for a tomato, pumpkin, etc.) and immature (for a cucumber, zucchini, squash, etc.) fruits are eaten; in leafy - both leaves and other parts of plants (in Brussels sprouts, white and red cabbage, head lettuce - overgrown buds, in broccoli and cauliflower - inflorescences); in leafy and spicy flavors (in chard, spinach, sorrel, parsley, basil, etc.) - leaves; overgrown roots (carrots, beets), stems (kohlrabi), petioles (celery, rhubarb), etc. are used as vegetables.
In our article we will get acquainted with the cultivated plants of Russia. People have long been using them in their economic activities to obtain valuable nutrients and food.
Fruit vegetables
Solanaceae
| Tomato or Tomato Solanum lycopersicum Family: Solanaceae (Solanaceae) |
| Vegetable pepper or Capsicum peppers Family: Solanaceae (Solanaceae) |
| Eggplant or dark-fruited nightshade Solanum melongena Family: Solanaceae (Solanaceae) |
| Saraha edible or vegetable Saraha Jaltomata procumbens Family: Solanaceae (Solanaceae) |
Pumpkin
| Common cucumber Cucumis sativus Family: Pumpkin (Cucurbitaceae) |
| Zucchini Cucurbita pepo var. giromontina Family: Pumpkin (Cucurbitaceae) |
| Squash Patisson Family: Pumpkin (Cucurbitaceae) |
| Pumpkin Cucurbita Family: Pumpkin (Cucurbitaceae) |
| Edible chayote (Mexican cucumber) Sechium edule Family: Pumpkin (Cucurbitaceae) |
| Chinese bitter gourd or Bitter cucumber Momordica charantia Family: Pumpkin (Cucurbitaceae) |
| Lagenaria Lagenaria Family: Pumpkin (Cucurbitaceae) |
| Wax gourd Benincasa hispida Family: Pumpkin (Cucurbitaceae) |
| Cyclanter Cyclanthera Family: Pumpkin (Cucurbitaceae) |
| Luffa or Luffa Luffa Family: Pumpkin (Cucurbitaceae) |
| Trihozant Trichosanthes Family: Pumpkin (Cucurbitaceae) |
| Antillean cucumber or Watermelon cucumber Cucumis anguria Family: Pumpkin (Cucurbitaceae) |
| Melotria rough Melothria scabra Family: Pumpkin (Cucurbitaceae) |
| Doubtful tladianta (Red Cucumber) Thladiantha dubia Family: Pumpkin (Cucurbitaceae) |
Others
| Okra or Abelmos edible Abelmoschus esculentus Family: Malvaceae (Malvaceae) |
Composition secrets
It is difficult to overestimate the role of root crops in the life of every consumer. They are highly regarded not only by vegans, but also by those who prioritize healthy eating habits. There are certain food varieties that are grown to be fed to farm animals later. To process them for livestock, only the simplest feed cutter is required, because the products are given raw. Passing through the chopper does not deprive them of their original nutritional value.
But the biologically active composition of each vegetable can vary from species and other characteristics of the variety. An equally important role here is played by the growing area and the technological approach to plant care before harvesting.
The average statistical components for root crops that have not been affected by heat treatment include:
- about 90% water;
- amino acids;
- proteins;
- sugar-containing compounds;
- Omega-3;
- glycosides;
- phenolic substances;
- pectins;
- fiber;
- vitamins of group A,,,,;
- minerals like potassium, sulfur, iron, silicon, phosphorus, cobalt, copper, boron.
Collectively, this has made the underground parts truly rewarding for both adults and children. Their distinctive feature is their low glycemic index. In practice, this means that the selected tuber will block the sharp rise in blood sugar, which will be a useful find for those prone to diabetes.
Due to the small amount of calories on the background of food of animal origin, vegetables of this type will become indispensable in the life of those who strictly follow the figure. It is not for nothing that most dietary food schemes are based precisely on the fruit and vegetable base.
Adding advantages is the fact that their storage does not require special conditions. It is enough just to move the stocks to a dark place that is well ventilated and there is a low temperature. Basements and cellars are ideal solutions for this.
Often examples of various tinctures and decoctions for ailments of any organ affect the need to use just root vegetables. Moreover, they are boiled, ground, squeezed out and used in some other way, not only for internal consumption. Some recipes call for topical use when it is necessary to get rid of extensive burns or open wounds. Thanks for this should be antiseptic qualities, which have a beneficial effect on the regeneration functions of the affected organism.
But along with the great benefits, you should remember about the possible harm. Often it concerns the unscrupulous care of the future crop, when unclean gardeners add various chemicals to accelerate growth. Some, to achieve a good effect in a short time, even exceed the permissible dosage.
But even without this, ordinary carrots are able to "please" with the presence of arsenic and strontium. Because of this, the orange root crop should be bought only in trusted places so as not to purchase goods from an unfavorable ecological zone.
Leguminous vegetables
| Peas Pisum Family: Legumes (Fabaceae) |
| Beans Phaseolus Family: Legumes (Fabaceae) |
| Vigna, asparagus beans Vígna Family: Legumes |
| Winged beans Psophocarpus tetragonolobus Family: Legumes |
Application
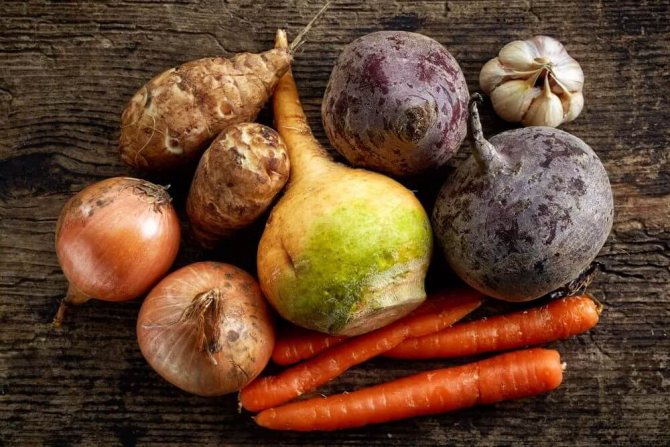
Root crops are an indispensable part of the diet of residents of different countries of the world. Russia is also included in this list, because vegetable crops are widespread here, and radishes, carrots and beets are especially popular.Since fruits are rich in vitamins, proteins, useful minerals and other elements necessary for the body, Russians happily consume them every day. Moreover, they cook them in different ways: someone prefers boiled vegetables, someone prefers fried food, and someone is just crazy about raw root vegetables.
Carrots, turnips, beets, and rutabagas are grown in the form of fodder fruits in Russia. All these products provide a lot of juicy mass, which contributes to improved assimilation by animals of rougher and more concentrated feed.

Root crops are often used in medicine. Indications for the consumption of a certain product are due to the beneficial substances contained in it. For example, most often carrots are used to treat hypovitaminosis, beets and turnips are used to improve the functioning of the digestive system, and radish is used as a diuretic.
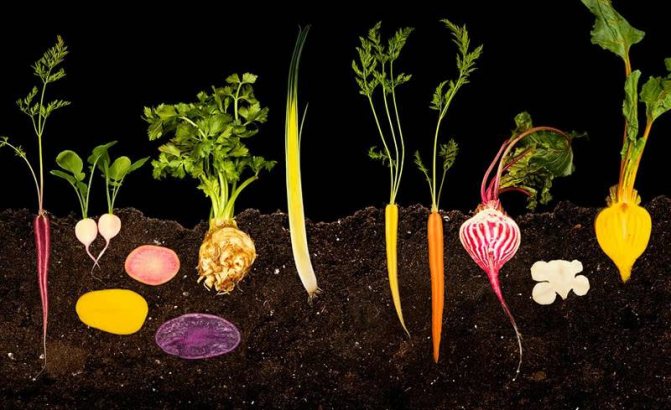
Root and tuber vegetables
| Potatoes Solanum tuberosum Family: (Solanaceae) |
| Carrot Daucus Family: (Umbrella) |
| Beet Beta vulgaris Family: Amaranths (Amaranthaceae) |
| Radish Raphanus Family: Cabbage (Brassicaceae) |
| Radish Radiculas Family: Cabbage (Brassicaceae) |
| Horseradish Ordinary Horseradish Armoracia rusticana Family: Cabbage (Brassicaceae) |
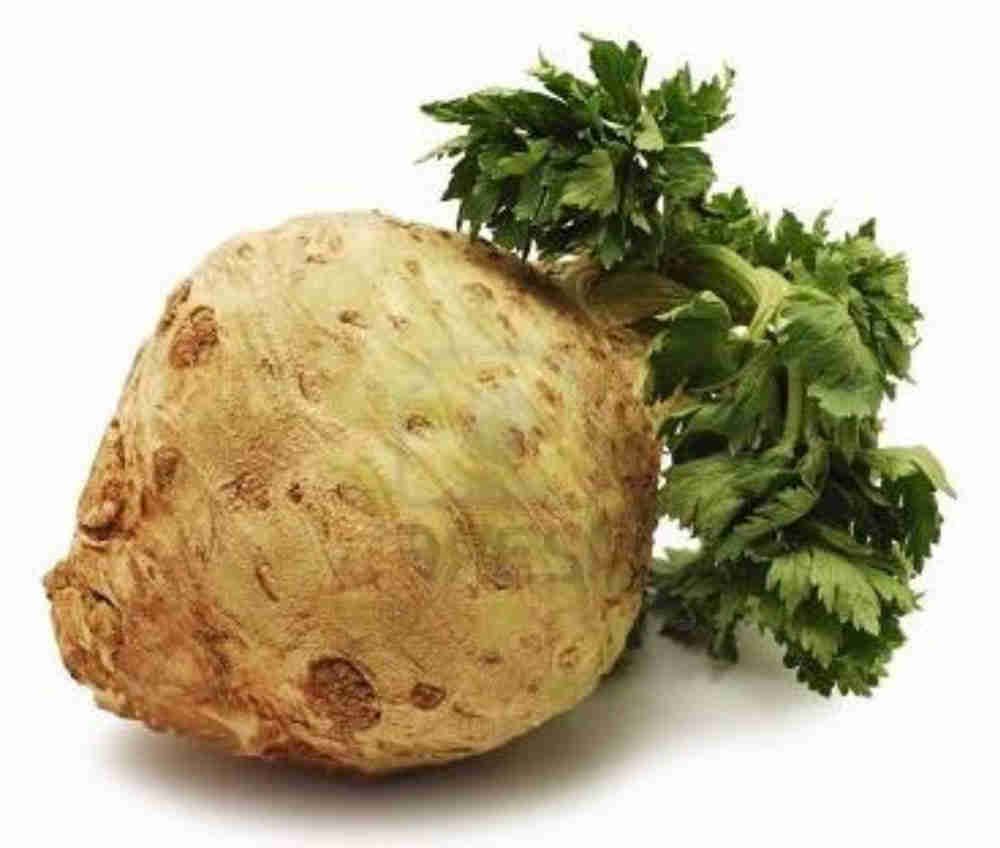
| Celery Apium Family: Umbrella (Apiaceae) |
| Ordinary parsnip or sowing parsnip Pastinaca sativa Family: Umbrella (Apiaceae) |
| Sweet potato Ipomoea batatas Family: Bindweed (Convolvulaceae) |
| Yams (group of vegetables) Family: Dioscorea |
| Edible cassava or Cassava Manihot esculenta Family: Euphorbiaceae (Euphorbiaceae) |
| Taro taro edible or Dashin Colocasia esculenta Family: Aroids (Araceae) |
| Yacon Smallanthus sonchifolius Family: Asteraceae |
| Jerusalem artichoke or Tuberous sunflower Helianthus tuberosus Family: Asteraceae |
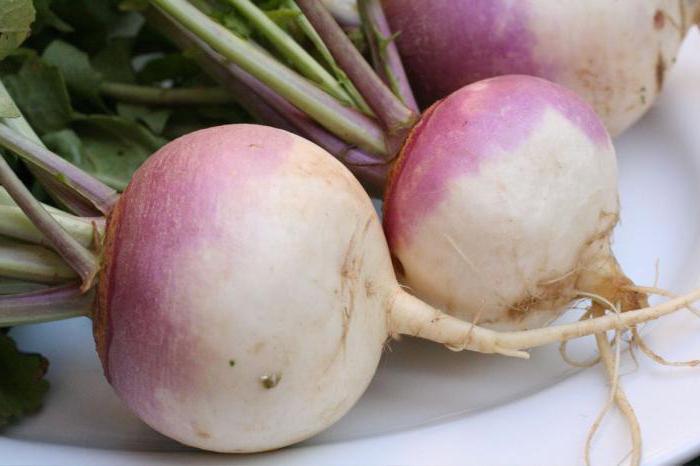
| Turnip Brassica rapa Family: Cruciferous (Cruciferae) |
| Swede Brassica napobrassica Family: Cruciferous (Cruciferae) |
| Hikama or Pachirisus cut Pachyrhizus erosus Family: Legumes (Fabaceae) |
| Chinese artichoke or Kindred purist Stachys affinis Family: Lamb |
| Scorzonera spanish or Spanish goat Scorzonera hispanica Family: Asteraceae |
| Goatbeard or Oat root Tragopogon porrifolius Family: Asteraceae |
| Burdock Arctium Family: Asteraceae or Compositae |
| Lotus Nelumbo Family: Lotus (Nelumbonaceae) |
| Tuberous acid or Oka Oxalis tuberosa Family: Sour |
| Tuberous nasturtium or Anyu Tropaeolum tuberosum Family: Nasturtium |
| Ulyuko tuberous NULLucus tuberosus Family: Basellaceae |
| Arrakacha edible Arracacia xanthorrhiza Family: Umbrella |
| Maca peruvian or Meijena Lepidium meyenii Family: Cruciferous (Cruciferae) |
Root functions
The modified, thickened roots of plants, called root crops, accumulate nutrients in their composition, thanks to which they are used for food and as medicinal plants. The performed function of root crops, in addition to the main one, is to obtain seed for subsequent reproduction of the culture.
If in the first year of life they are intended for use for their intended purpose, then left in the ground for the next year will provide seeds that meet all the characteristics of the variety. In the life of two-year-olds, it is due to the substances accumulated in the previous year that the roots will ensure the full growth of the testes. Roots are formed from the eyes located in the axils, and the growth of the aerial part of the plant begins, a flowering and fruiting stem develops. As a result, after the secondary cycle, the roots die off.
The role played by root crops in relation to the life of people is multifaceted. They are used in a wide variety of industries, using them for their intended purpose and as planting material.
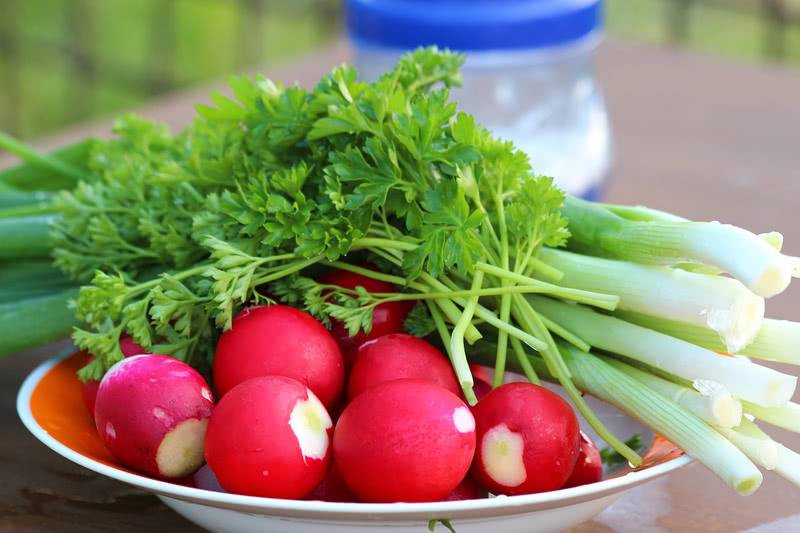
Fiber-rich roots perform many functions for the body:
- strengthen the immune system;
- restore vitamin reserves;
- improve metabolic processes and the work of the digestive tract.
Growing environmentally friendly products on your site is becoming popular. Agrotechnical methods do not require special skills.
Root plants are very light-requiring, the lack of sunlight leads to a decrease in yield. The exception is radish. It fully grows and develops even in shaded areas. Thanks to a developed, sufficiently powerful root system, vegetables tolerate drought more easily than other garden crops.
Reference! Radishes and turnips are not well tolerated in dry weather. Their protective shell thickens and stiffens, the softness loses its taste, the fibers coarsen.
Growing root crops is becoming a profitable and common business. The latest technologies and methods allow you to minimize financial and physical costs.
Bulbous and stem vegetables
| Bulb onions Allium cepa Family: Onions (Alliaceae) |
| Shallot, or Ashkelon onion Allium ascalonicum Family: Onions (Alliaceae) |
| Leek, or Pearl bow Allium porrum Family: Onions (Alliaceae) |
| Onion, or Fist bow Allium fistulosum Family: Onions (Alliaceae) |
| Slime onion, or Drooping bow Allium nutans Family: Onions (Alliaceae) |
| Sweet onion, or Branch onion Allium ramosum Family: Onions (Alliaceae) |
| Garlic Allium sativum Family: Amaryllidaceae |
| Asparagus Asparagus Family: Asparagus |
| Rhubarb Rheum Family: Buckwheat (Polygonaceae) |
| Sorrel Rumex Family: Buckwheat (Polygonaceae) |
Interesting Facts
In addition to basic information about what a root vegetable is, people will certainly be interested in learning something unusual about them. For example, among these products there are record holders listed in the Guinness Book of Records. This includes:
- radish (10 kg);
- carrots (5.839 meters);
- yams (35 kg).


Festivals dedicated to these particular food products are regularly held all over the world. The most famous event is the Mexican "Night of the Radish" held on December 23rd every year. In Russia, festivals of carrots and beets are held, as well as the "Underworld", where you can learn everything about root crops and truffles.
Tubers
This group includes only three plants - sweet potato, Jerusalem artichoke and the well-known potato. It makes no sense to describe the potato, but it is worth considering the first two representatives. The sweet potato is a food and forage crop, it is a herbaceous plant of the liana type. Its lashes can spread up to five meters from the root.


Jerusalem artichoke is also called "Tuberous sunflower" or "Earthen pear". It is a tall plant with very beautiful and large yellow flowers. Its fruits are used for food, which are somewhat similar in shape to pears.
The benefits of onions


Only by looking at the diversity of the composition of this root crop, one can immediately understand that one cannot do with the fight against colds alone. There are many other useful properties:
- prevents the development of cancer cells;
- has a tonic effect;
- disinfects the room;
- is an antifungal and antimicrobial agent;
- removes carcinogens and toxins;
- stops an asthma attack;
- reduces the manifestation of allergic reactions;
- improves appetite;
- stimulates the production of gastric juice;
- supports the work of blood vessels and the heart;
- cleans the blood;
- fights insomnia and improves sleep quality;
- prevents a heart attack;
- used for vitamin deficiency;
- has a calming effect;
- increases the tone of the body;
- reduces the risk of diseases of the hip joints in women;
- neutralizes toxins and binds free radicals;
- promotes digestion and absorption of nutrients;
- increases potency and prevents prostate cancer;
- helps with weight loss.
Onions are also used in cosmetology to improve hair growth, and it also brings them back life, shine, and nourishes the root bulb. Traditional medicine also uses the husk of the tuber. Decoctions, tinctures, compresses, baths, lotions, etc. are being prepared.
Salad


There are many types of salads in the world that are actively used in the preparation of various dishes.However, they are all divided into only two groups: leafy and cabbage. In leafy lettuce, the leaves grow freely and separately. Cabbage species are distinguished by the fact that as they ripen, the leaves curl, forming a head of cabbage. Depending on the specific species, it can be either very dense or loose.
Description of culture
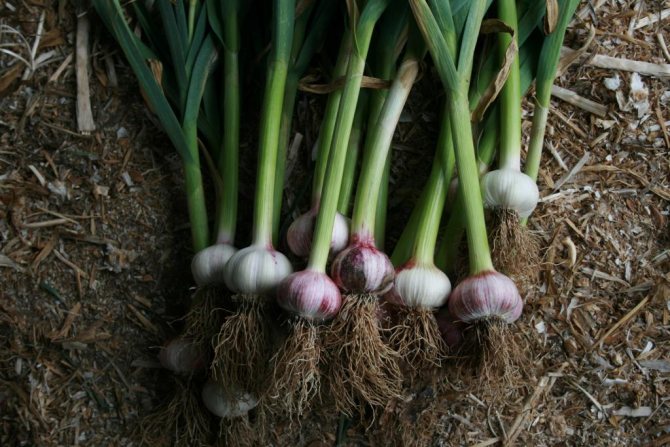
Introducing garlic, its main characteristics should be named:
- foliage is long, narrow, elongated upward;
- false stem formed from leaves;
- during flowering, an arrow of 0.6-1.5 m is formed, twisting at the end;
- the arrow forms an umbrella hidden in the membranous membrane;
- flowers are simple, white or light purple, six stamens;
- after flowering, a fruit with a small number of seeds is formed;
- the bulb consists of 2-50 "baby-cloves", covered with dense scales, they are round in shape, white, yellowish, purple.
Garlic can be arrowed or non-arrowed, as well as spring and winter.


Cabbage


This includes different types of cabbage: cauliflower, broccoli, kohlrabi, and so on. These are plants that differ from each other in the structure and shape of the fruit. Heads of cabbage form a strong, spherical head of cabbage, made up of large leaves. The kohlrabi fruit is hard, round, and tastes like a stump (core) of a classic head of cabbage. Broccoli does not eat fruits, but inflorescences, just like cauliflower.
How to store onions properly


The root crop is quite well stored for a long time. Everyone can achieve success in this. It is not so much the temperature and storage method that is important, but the correct preparation and harvesting of the crop.
You need to harvest about 3-4 months after planting, it depends on the variety. The weather should be dry. The tubers must be carefully dug up and folded, being careful not to expose them to physical injury. For example, don't hit the ground to shake off dirt.
Then the crop must be dried. It is best to do this on shelves under a canopy in one layer, but small volumes can be hung in a draft or even dried in the oven. It is important that the bulb does not dry out on its own and that its protective husk does not crack.
Then the greens need to be cut with scissors, leaving 6 cm from the tuber. The same must be done with the roots, it is important not to damage the bottom of the tuber. The surface can be cleaned of the first cracked scales and dirt. Then leave to dry for another two weeks.
After the deadline, you should choose only the most beautiful, strong and in no case damaged tubers. They are suitable for storage. Can be folded into wicker baskets, wooden boxes, nets for storing vegetables, fabric bags or nylon stockings. Ventilation holes are required. You can weave bundles, videos can be found on the Internet - this is the way of our ancestors and decoration for the room.
For the entire storage period, it is necessary to sort out the crop 2-3 times and discard the bad tubers. A cellar or basement is suitable for storage, the place should be cool and dark. It is better to choose a balcony in an apartment. There should be no high humidity. With these recommendations, some onion varieties can be preserved even until the next harvest!