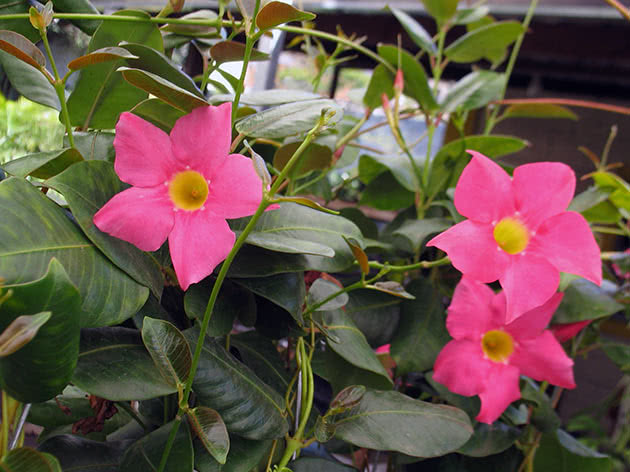
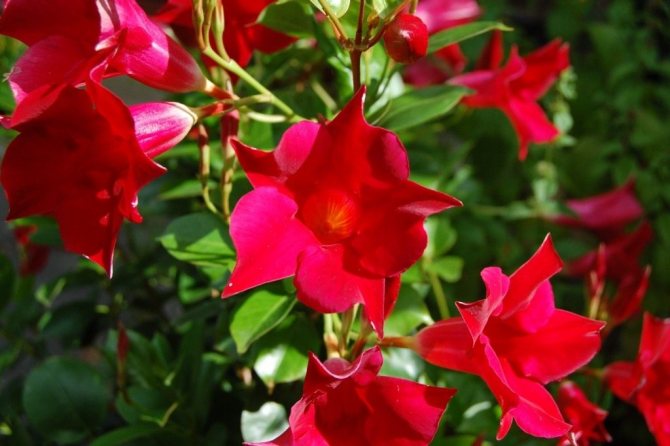
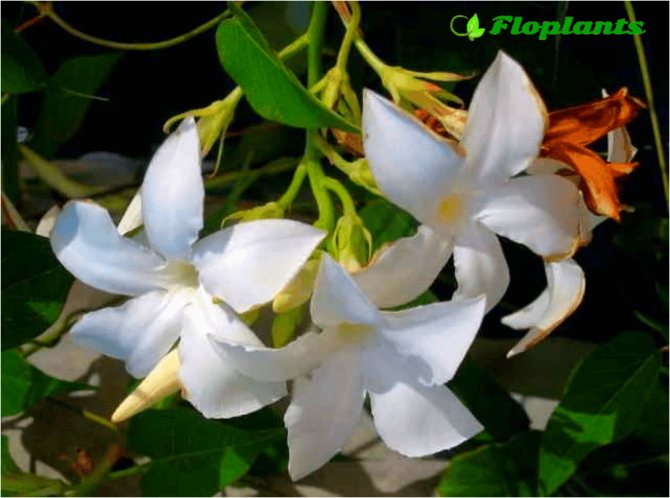
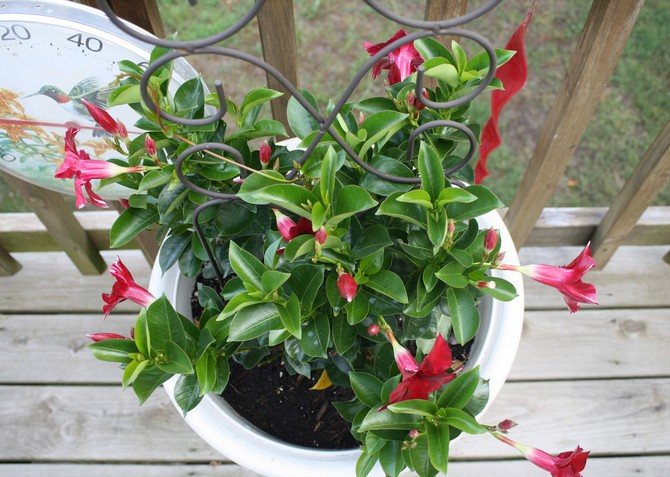
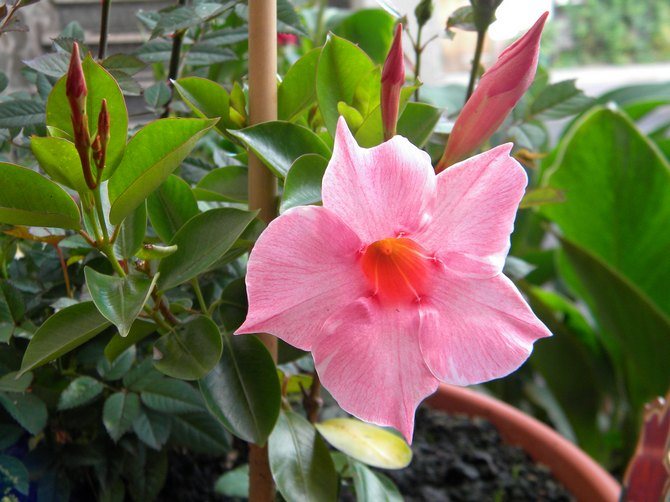
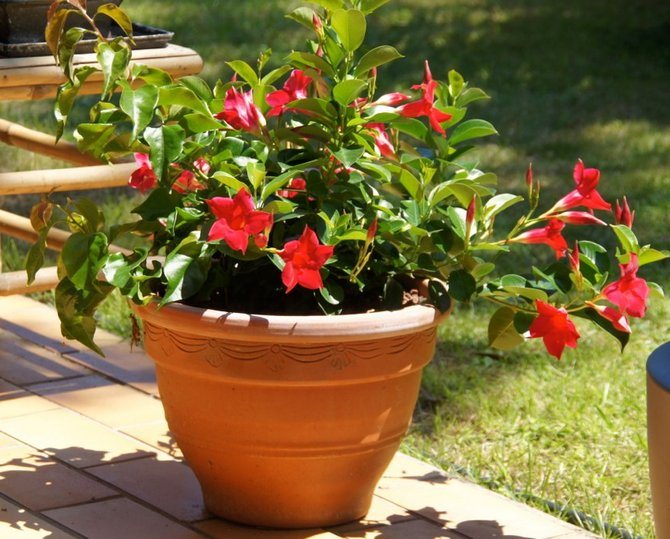
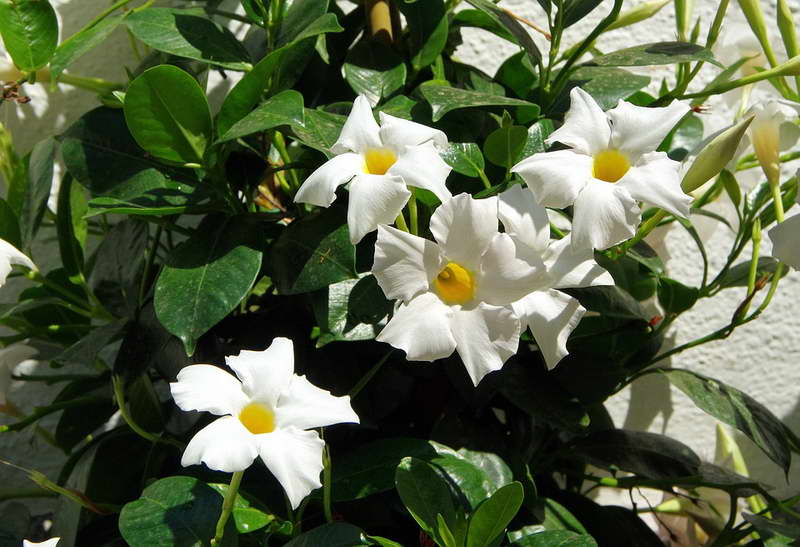
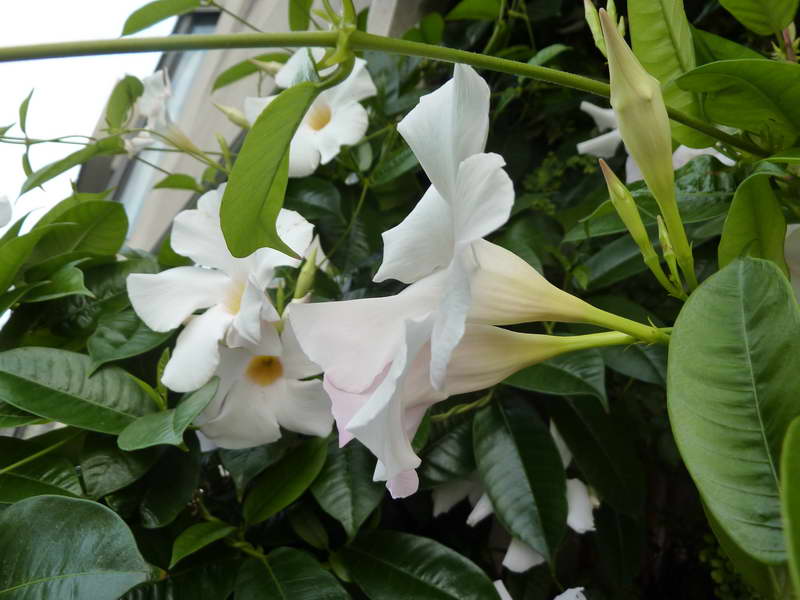
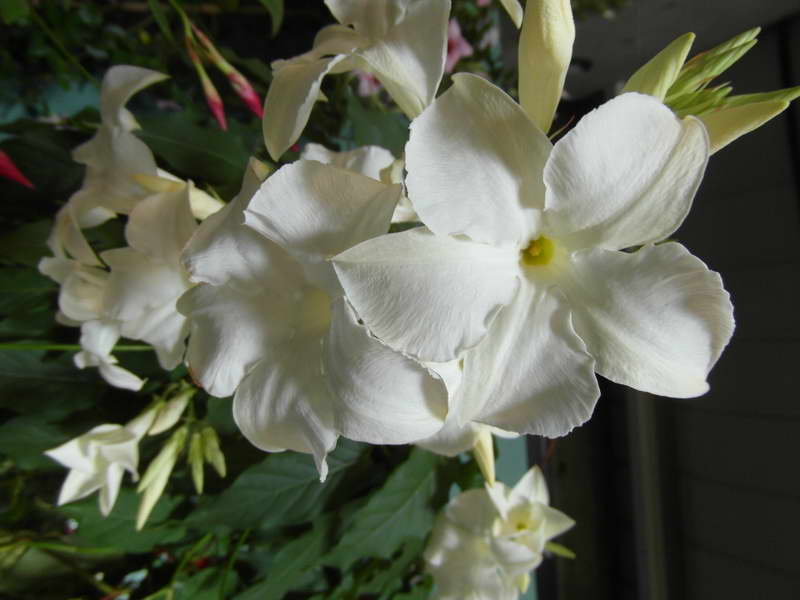
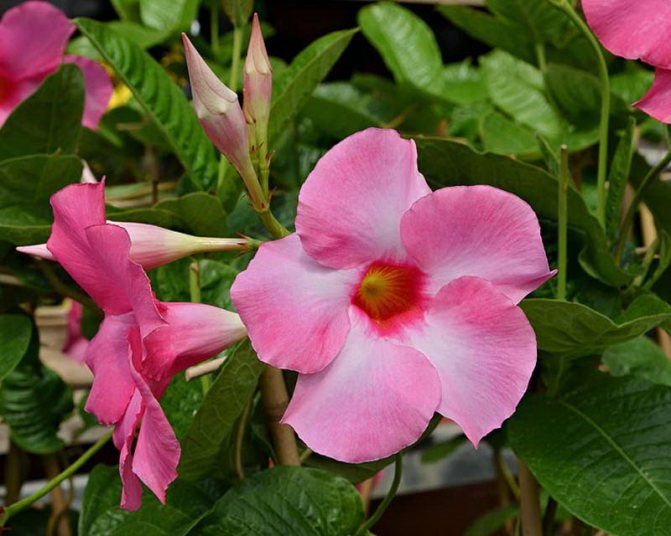
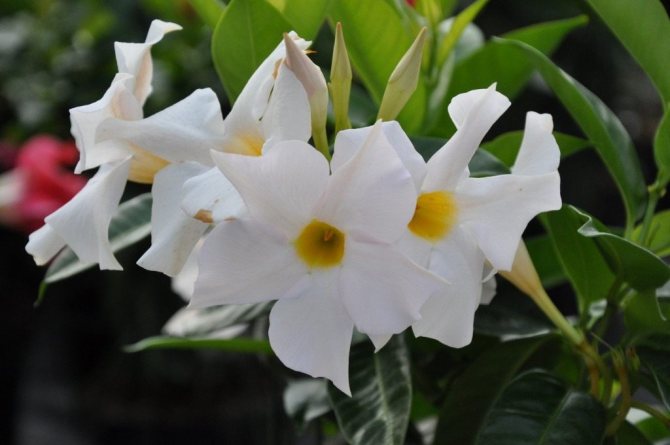
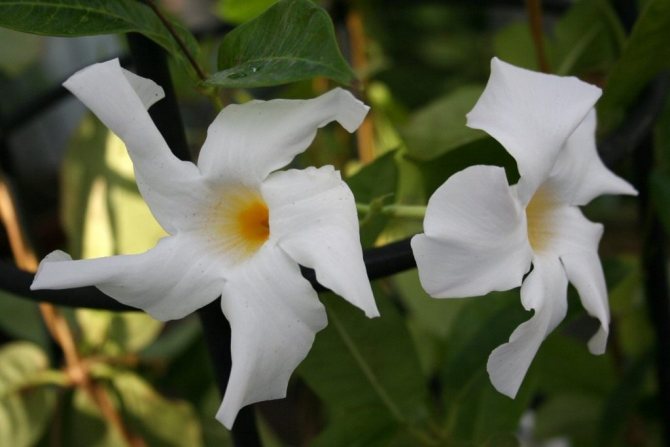
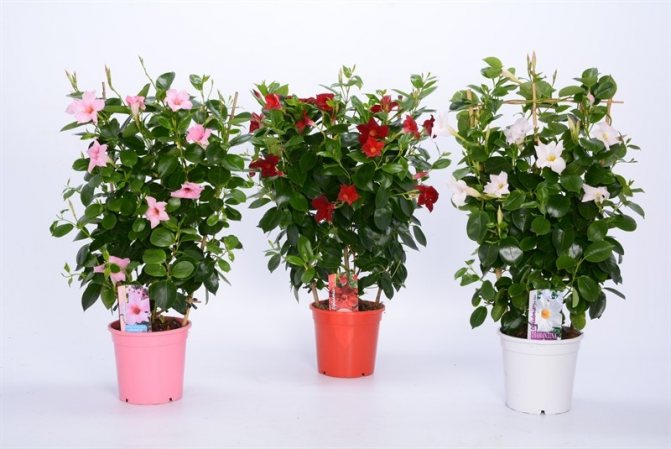
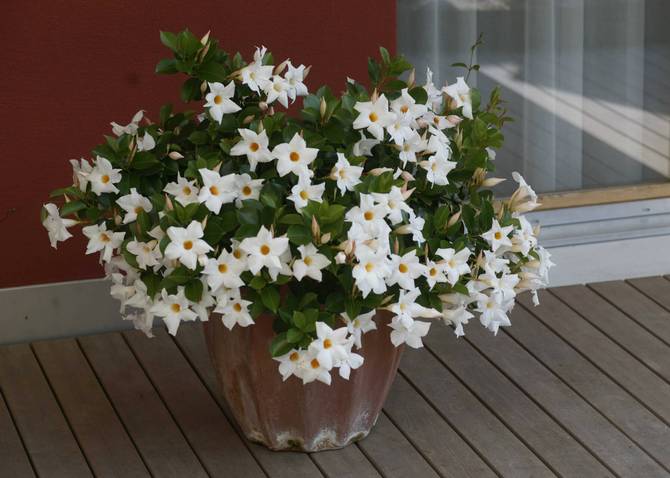
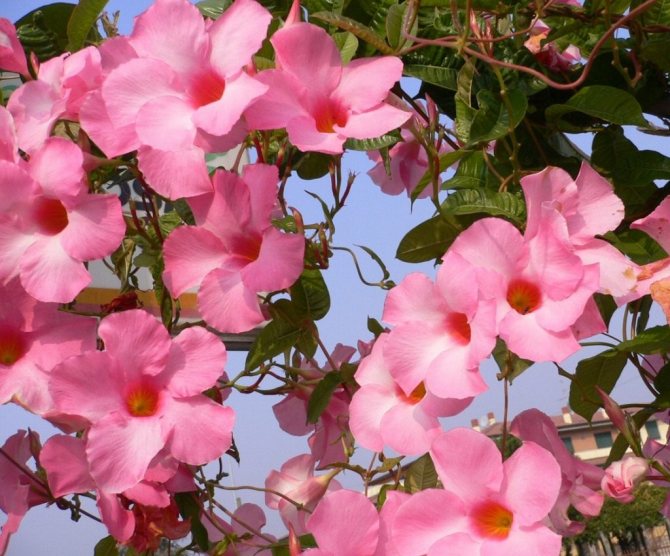
It has another name - diplomatic, and among the people you can hear about it as a Bolivian rose or Chilean jasmine.
Originally from the Mandeville region of South and Central America.
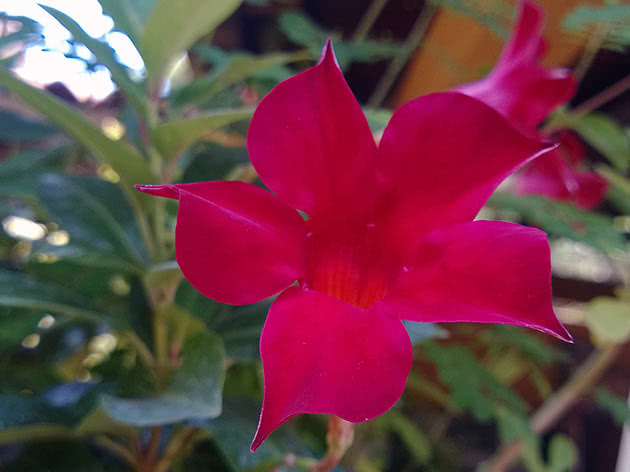
The plant blooms all summer with flowers from white to bright red shades.
Planting and caring for a diploma
- Bloom: abundant and long lasting from late March to November.
- Lighting: bright diffused light of the east and west windows.
- Temperature: during the growing season - 18-26 ºC, during the dormant period - 12-15 ºC.
- Watering: abundant, 2-3 times a week, after the soil in the pot dries out to a depth of 1-1.5 cm. In the heat, watering is sometimes carried out 2 times a day. Watering has been reduced since September.
- Air humidity: high: the plant is kept in a glass display case or on a pallet with wet pebbles.
- Top dressing: from March, liquid nitrogen fertilizing is introduced into the soil once a week, but as soon as buds begin to form, solutions of potassium-phosphorus complexes will be required, which are applied with the same regularity until August.
- Cropping: regular, in autumn, at the end of the growing season.
- Rest period: not pronounced, but falls in the autumn-winter period.
- Transfer: as needed, when the pot becomes small. Adults do not bother with transplantation, but simply replace the top layer of the substrate in the pot.
- Reproduction: seeds and cuttings.
- Pests: mealybugs, whiteflies and spider mites.
- Diseases: powdery mildew.
Read more about the cultivation of diplomas below.
Pruning
Pruning diplodenia is a very important step in plant care. Without this procedure, the vine will grow strongly. It is best to prune the plant at the same time as the spring transplant or preparation for wintering. For a positive result, you need to adhere to the following requirements:
- Remove antennae that may have formed during the time the flower was in a shaded place.
- Do not touch the young shoots, as it is from them that new buds will appear.
- Do not prune during flowering.
Diplomatic flower - description
Diplomatic flower is a fast-growing, evergreen and abundantly flowering liana with a curly woody stem and opposite bright green, oval, glossy leathery leaves, from which white milky poisonous juice oozes when broken. Home-grown diplodesia are grown in the form of a compact bush or climbing plant. The fragrant, funnel-shaped, five-petaled Mandeville flowers can be white, pink, crimson or red. On an adult plant, up to 80 flowers can open at the same time, not withering for more than a week.
How to choose a healthy plant in the store

Healthy, flowering plant
Give preference to young diplomacy. Do not buy it during flowering. It cannot be moved and transported, at this moment it is fragile and sensitive. It is important to find a healthy specimen. This is a bush with a dense small crown, shiny leaves, flexible vines of the correct shape. Don't buy outwardly unhealthy Chilean jasmine. If it has pale leaves, spots, streaks or cobwebs.
Pay attention to the capacity and condition of the soil.The incommensurate dimensions of the container, a dry or waterlogged substrate indicate a violation of the rules for care. Perhaps the exotic is fraught with hidden diseases.
Home care for diploma
Cultivating a Diploma at Home
Growing a Mandeville involves creating conditions for it close to tropical: the lighting must be bright, otherwise the vine will not reach the peak of its attractiveness. Eastern or western window sills are most suitable for the plant. You can keep the diplodemy on the south window, but on condition that in the afternoon it will be protected by a light curtain from the sun's rays, which can damage its leaves.
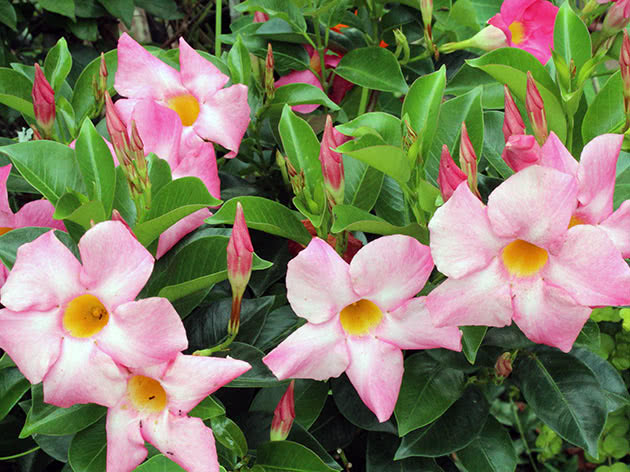


The optimum temperature for diplosing is 12-15 ºC in winter and 18-26 ºC in summer, although if the temperature rises higher, the plant will not die from this: on the contrary, the color of the flowers will become brighter and more saturated. Mandeville needs fresh air, so tune in to frequent ventilation of the room, however, drafts will not benefit the plant. In summer, the flower can be kept on the balcony, veranda and even in the garden, protecting it from direct sunlight, drafts and gusts of wind.
- Jasmine (Jasminum) - care, photos, types
Since dipladenia is a climbing plant, it needs reliable support and regular pruning. The support should be one and a half times higher than the adult diploma: as the shoots grow, climbing the support, they will gradually master it.
Watering the Diploma
Like any other representative of the tropical flora, the diplodenia vine needs abundant watering. The principle of moistening is approximately the following: as soon as the soil in the pot dries out to a depth of 1-1.5 cm, the flower is watered with warm water. This usually happens 2-3 times a week, but in heat and drought, watering is carried out 1-2 times a day. Since the beginning of autumn, watering is reduced, however, care must be taken that the indoor diplopia does not begin to lose leaves from a lack of moisture. Keep in mind that diplodenia does not tolerate lime, therefore, the water for irrigation must be defended or filtered with a filter, and once a month a little citric acid or fresh lemon juice must be dissolved in it so that the water tastes slightly sour.
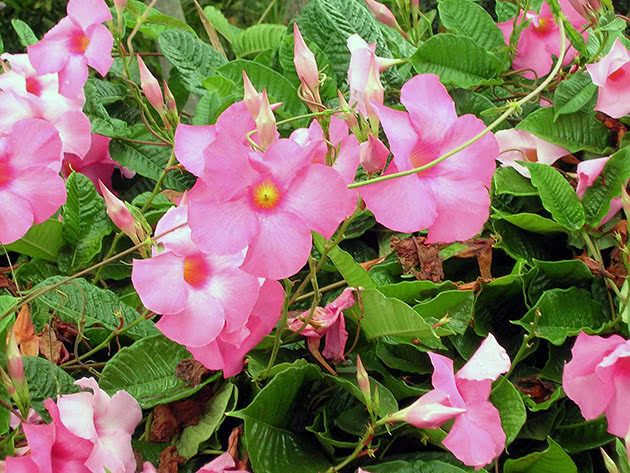


As for the humidity of the air, this indicator should be at a high level all the time, so it is best to keep the plant in a glass display case, but if you cannot create such conditions, place the flower on a pallet with wet small pebbles or expanded clay or place a pot with diplodenia in a large planter, filling the space between the walls of the pot and the walls of the planter with moist peat or sphagnum. Diplomacy also responds well to daily spraying of leaves with warm water, especially during bud formation and flowering.
Fertilizer diplodenia
Caring for Mandeville involves mandatory feeding. To grow leathery glossy leaves, the diplodenia plant needs nitrogen fertilizers, but as soon as the flower begins to form buds, it will need potassium-phosphorus fertilization. Fertilizers are applied in liquid form once a week from March to August. In winter, Mandeville is not fed.
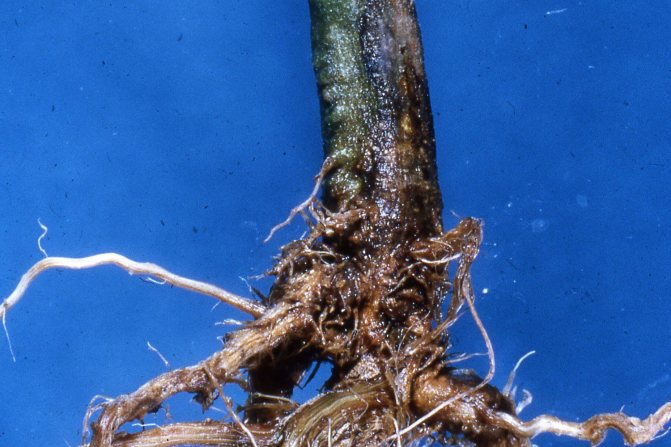
Diplomatic transplant
The diplodenia plant prefers fertile, loose, moderately acidic soil. The optimal soil composition for this plant is a mixture of equal parts of sod land, sand, humus, leafy soil and peat. Sand can be replaced with fine expanded clay or perlite: the looser structure of the substrate better provides air access to the roots.
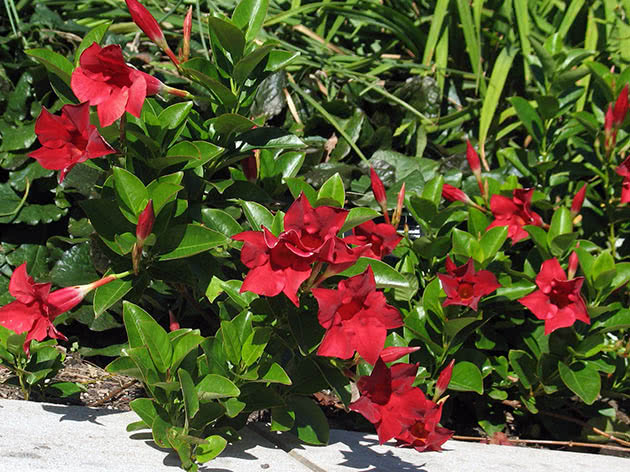


Mandeville is transplanted in the spring as needed, when the old pot becomes cramped and roots begin to hang from the drain holes. It is advisable not to disturb adult plants with a transplant; it is better to replace the top layer of the substrate with a fresh one every spring.
Pruning a Diploma
Diplomacy grows very quickly, and if you do not cut it, it will arrange for you thickets, like in the jungle.Diplomatic flowers are formed exclusively on the shoots of the current year, which is why the plant needs regular pruning, which is carried out in the fall, at the end of the growing season. The old unbranched shoots of the Mandeville are shortened by two-thirds, and the branched ones by a third or half the length after the fork. That is, from unbranched stems only a third of the length is left, and from branched ones - a third of the length after the fork. Autumn pruning of diplosing promotes successful wintering and the growth of new shoots in the next growing season.
Diplomas in winter
How to care for a diploma in winter? In late autumn, the plant enters a dormant period, which lasts until spring. At this time, the temperature in the room should not be higher than 16 and not lower than 12 ºC. The plant is pruned, and the watering is greatly reduced: during the winter, the Mandeville is watered only three days after the soil in the pot is completely dry. In the spring, when the plant begins to show signs of awakening, it is moved to its usual conditions, the watering regime is gradually resumed and fertilizing begins.

Growing difficulties
Diplomas are demanding in their care. The slightest flaws in agricultural technology can cause the development of a disease or the spread of pests.


Diseases
The most common problems:
- Rhizome decay - as a result of stagnant water or the use of soil contaminated with a fungus, the process of decomposition of plant cells begins. They correct the situation with an urgent transplant with the removal of the old earthy coma and damaged roots.
- Rare not abundant flowering - provoked by a lack of light. The way out of the situation is to change the location or install phyto-backlight.
- Drying foliage - the cause is dry air or burns from direct sunlight. All damaged leaves must be removed, the moisture regime adjusted and the plant shaded.
Reproduction of diploania
Reproduction by seed method
The cost of an adult plant is quite high, but flower shops offer seeds of different varieties of diplodesia, and a florist who is not afraid of difficulties can save a lot by growing a Mandeville from seeds. Seed germination is carried out under bright diffused light at a temperature of 22-28 ºC in a loose and light weakly acidic substrate, placed in a dish with drainage holes: the soil should be moist, but the possibility of stagnant water should be excluded. However, even if all these conditions are met, it can take from 2 to 4 months to wait for seedlings, and all this time you will need to water the substrate and remove condensation from the coating. When the seedlings develop two true leaves, they are dived into separate cups with drainage holes and with soil of the same composition, and then they are seated in permanent pots.
Propagation of diplopia by cuttings
Mandeville cuttings are carried out from mid-spring to mid-summer. The tops of young shoots are used as planting material in spring, and in summer, segments of mature, lignified stems are used. We remind you that the leaves and stems of the plant contain poisonous sap, so all work should be carried out with gloves so that the sap does not get on the skin and mucous membranes.
Diplademia cuttings are rooted in cups with a moist soil mixture consisting of equal parts of sand and peat. A little dry sphagnum moss can be added to the substrate. The cuttings are deepened to the first pair of leaves, after which they are placed in a greenhouse and kept at a temperature not lower than 25 ºC. It is better to water the cuttings through the pallet. Rooting usually lasts about a month, and as soon as the cuttings develop roots, they are planted in pots.
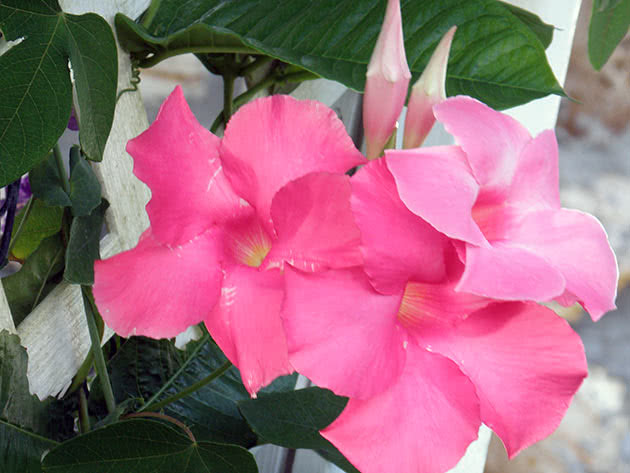


In some cases, rooting is carried out simply in water, and when the roots of the cuttings reach a length of 1-2 cm, they are transplanted into the substrate.As a rule, propagation by cuttings is quite successful, but sometimes double plants do not want to form roots, and then they have to resort to growing double varieties from seeds.
Diplomacy pests and diseases
Dipladenia leaves turn yellow
Yellowing leaves of diplosing in summer are a sign of too dry air, but if it happens in winter, check to see if your vine is freezing. Another reason for yellowing of leaves can be a disease or occupation by pests.
- Jasmine (Jasminum) - care, photos, types
Dipladenia leaves fall
Mandeville leaves turn yellow and then fall for the following reasons:
- irregular, insufficient or excessive watering;
- the room temperature is too low.
Monitor your plant and look for the cause of the problem at the first changes.
Diplomatic pests
Pests can occupy a diplomatic property due to its weakening by improper or insufficient care, for example:
- irrigation with low-quality water;
- growing in soil infected with larvae or fungi;
- content at too low temperatures or insufficient lighting;
- poor hygiene: your plant is covered in dust.
Most often in such conditions mealybugs, whiteflies and spider mites settle on Mandeville.
Whiteflies usually infect plants that spend their vacations in the open air, therefore, before introducing a diplophene into the house in the fall, be sure to inspect the back of its leaves: this is where these flying pests resembling moths are hiding. If the plant is infected, treat it with an insecticidal preparation - Aktellik, Aktara, Fitoverm, otherwise the whiteflies brought into the house from Mandeville will very quickly move to other indoor flowers.
Mealybugs are sucking insects that feed on the cell sap of the leaves and shoots of dipladenia and infect it with viral diseases. Signs of infestation with worms can be a drooping appearance, leaves that have lost their turgor, deformed buds, insects that look like small mosquitoes flying around the flower, as well as white lumpy formations in the soil and small oval white bugs on the plant itself. You can eliminate pests by applying a tincture of garlic for the treatment of diplodenia: the head is passed through a press, poured with a glass of boiling water, infused for 4 hours, after which the areas affected by the worms are washed with this infusion. Of the chemicals, Applaud, Phosphamide and Bi-58 are the best for dealing with worms.


Spider mites are the most dangerous pests, and they are not insects, but arachnids. Mites appear on the plant in conditions of low air humidity. If brown or black dots appear on the leaves of diplodenia, carefully examine the flower: mites, like other pests, settle on the underside of the leaves. Another sign of the presence of mites is the finest spider webs. Wipe off the leaves of the Mandeville with slightly acidified water with a small addition of soap, and if this does not help, you will have to treat the flower with an acaricidal preparation, for example, Fitoverm. And the main thing that will need to be done is to increase the air humidity in the room.
Diseases of diploidia
The most dangerous disease for Mandeville is powdery mildew, which covers the ground organs of the plant with an untidy whitish bloom. The causative agents of this fungal disease are destroyed with a 1% solution of colloidal sulfur: all affected areas are lubricated with this agent, and after a day the plant is washed under running water. It is unlikely that you will be able to cope with powdery mildew in one go, so tune in for 2-3 sessions.
Testimonials
Elena, 35 years old: “I brought this flower from Italy. I transplanted it a couple of weeks after arrival. Dipladenia grew superbly and bloomed well, but in the fall it rapidly began to throw off the leaves. The flower died. My second attempt at planting a flower was also unsuccessful.Despite the fact that I bought the plant in my city, with the same climatic conditions. Unfortunately, expectations were not met, the plant also bloomed, then the leaves began to fall off, and the root rotted. I held it for a couple of weeks, but I had to throw out the plant. For the third time, I was in no hurry to transplant a plant. Until the plant dries. This time I planted the plant in acidic soil. Maybe she really did not guess right with the soil, or she transplanted it early. "
Anna, 45 years old: “The flower is magnificent, with bright flowers like bells, it grows rapidly in the summer, the plant has covered the entire window on the balcony in almost a week. All that was needed was support and watering, and so practically no care, more and more he gave fresh sprouts. From time to time needs watering, pruning to renew. Then the plant gives fresh shoots, and flowers appear mainly on new ones. In autumn, watering must be reduced, pruning must be done. It is recommended to always wear gloves when pruning, the plant sap is toxic. "
Types and varieties of diploma
There are not so many types of diplomas grown in culture. Here is some of them:
Dipladenia brilliant (Dipladenia splendens)
- evergreen climbing plant, which in culture is usually grown as ampelous. The stems of this species are pubescent at a young age and densely covered with oval leaves up to 20 cm long with a pointed apex and a cordate base. With age, the stems, reaching four to five meters in length, become bare, the leaves on them become less and less. The flowers of the brilliant diplodemy are bright pink on the outside and white on the inside, up to 10 cm in diameter, collected in 6 pieces in a loose racemose inflorescence. Bracts are purple;


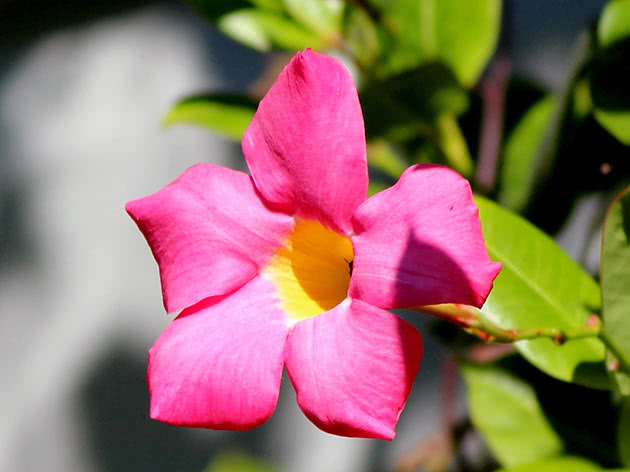
Bolivian Dipladenia (Dipladenia bolewiensis)
- a thermophilic liana from Bolivia, the most common plant in the culture of the Mandeville genus. Long shoots covered with bright green ovoid leaves 5 to 8 cm in diameter brought fame to this species. On axillary peduncles, a cluster of 3-4 white flowers up to 5 cm in diameter with a cylindrical tube, saucer-shaped limb and yellow throat is formed;
Excellent Dipladenia (Dipladenia eximia)
- an evergreen plant with smooth reddish stems covered with rounded ovoid bright green leaves 3-4 cm long. The flowers of a plant up to 7 cm in diameter with a tube up to 5 cm long and a red calyx are collected in a brush of 8 pieces. The corolla of the flowers of this vine is usually red-pink;
Dipladenia sanderi
- a fast-growing indoor vine with smooth stems, thick oval leaves 5 or more centimeters long with a slightly pointed tip and racemose inflorescences located in the axils, consisting of 3-5 bright pink flowers with a yellow throat up to 7 cm in diameter;































