Description
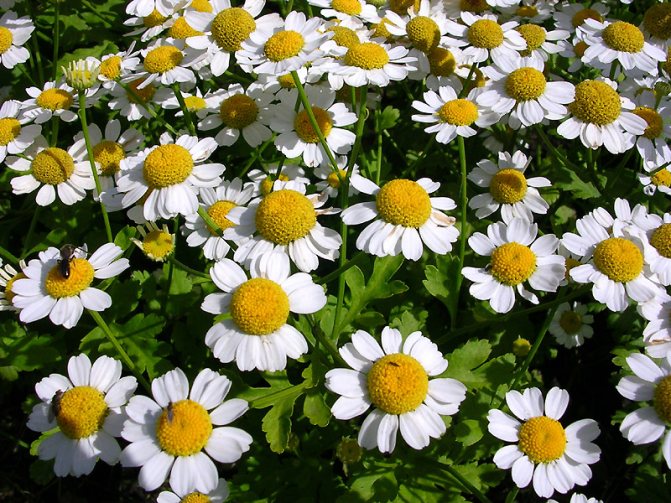
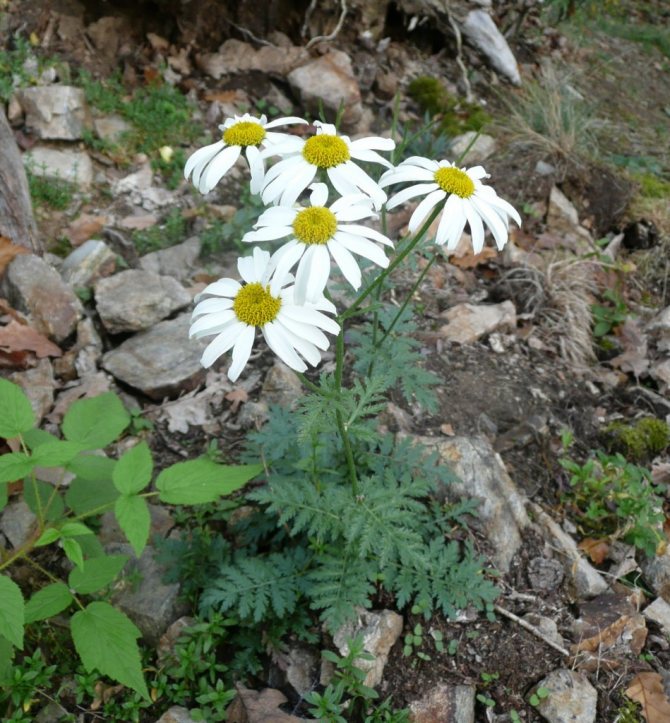
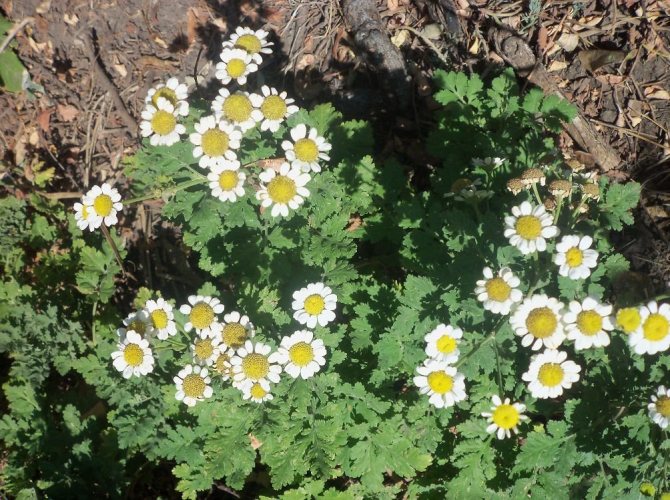
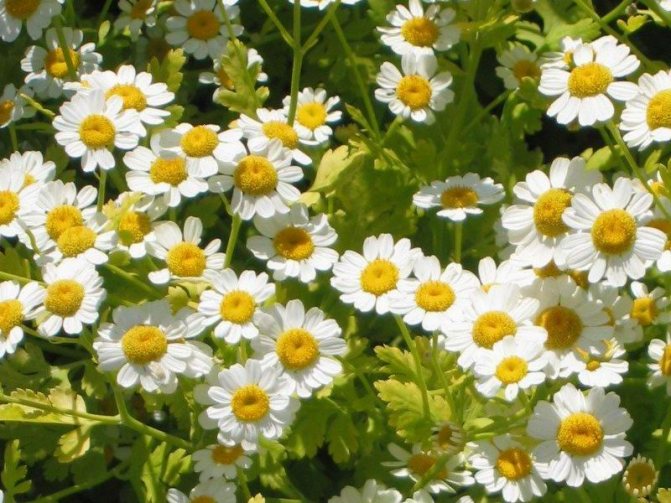
The pyrethrum has a root system with a fibrous structure. Erect shoots grow 50-70 cm in height. Juicy green leaves are pinnately dissected. At the base of the bush, they form a dense rosette. On the shoot, there are alternately only a few smaller leaves.
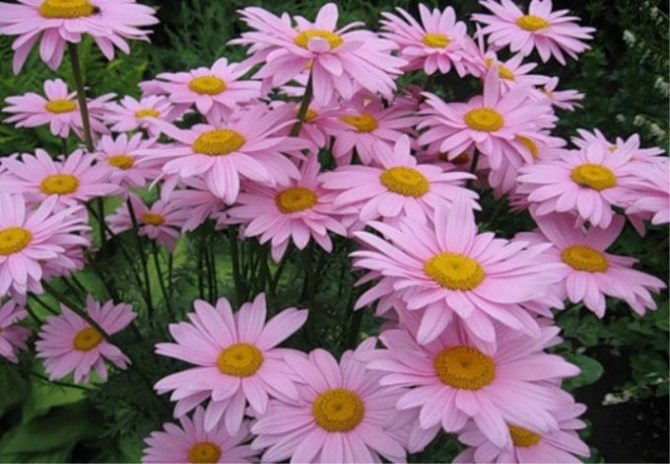
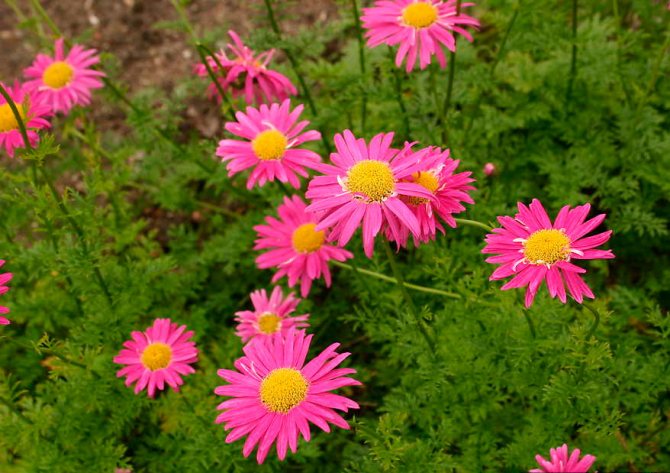
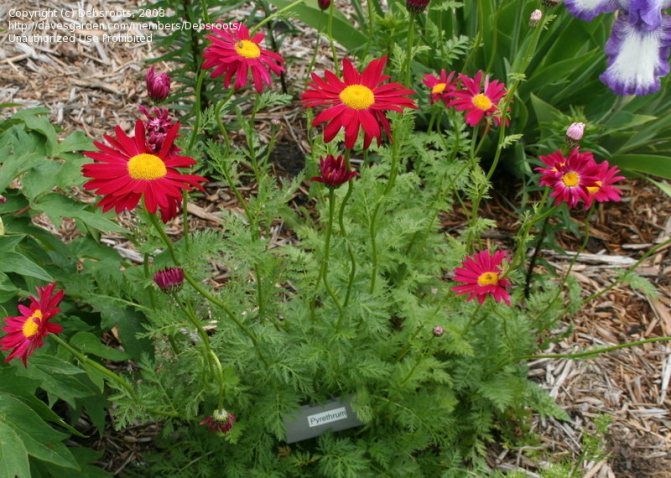
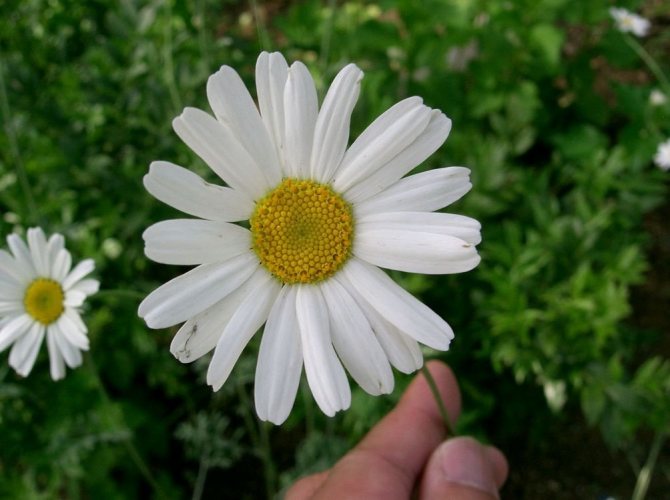
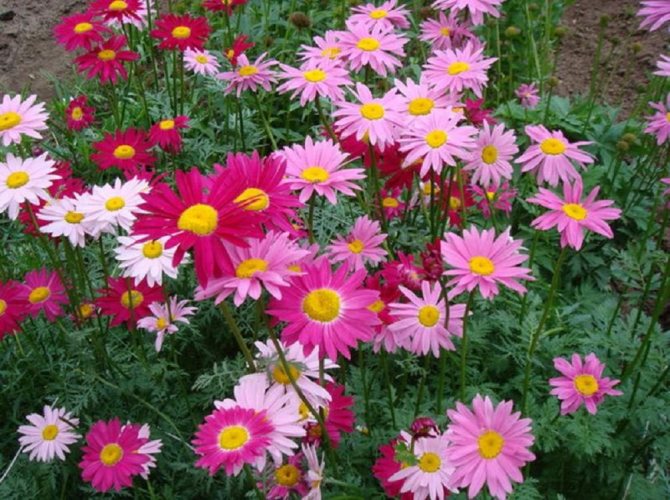
Inflorescences-baskets appear on the tops of the shoots. They are quite large, 3-6 cm in diameter. Narrow petals surround a core of reed and tubular flowers. The reed ones are located along the edge and are painted in a pinkish tone, the tubular ones are in the very center and have a yellow tint. The color of smooth petals can be white, yellow, pink, lilac or crimson. Flowering time is in the summer months of June and July.
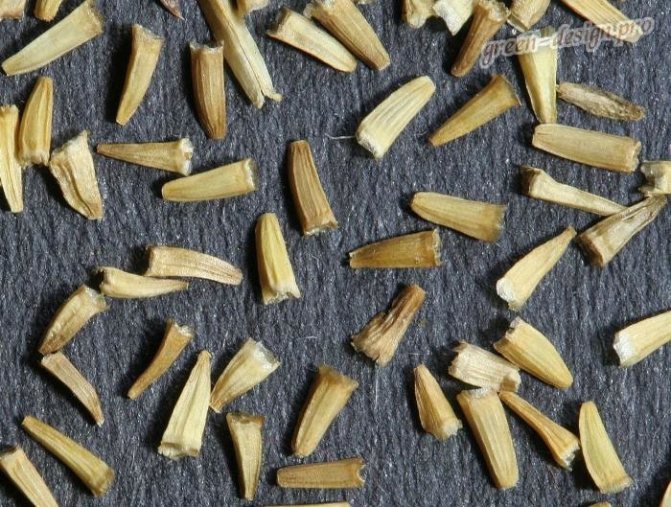
Achenes of light brown color consist of a crown of a lobed or toothed structure with ribs. The seeds are small and elongated. Do not lose germination for 3 years.

Appearance
Necessary conditions for growing
Chamomile-like pyrethrum is an unpretentious plant. Planting is done every year or the bushes are left as a perennial. In the latter case, it is especially important to choose suitable growing conditions. Culture loves light and warmth, protection from drafts.
As an annual, it is permissible to plant a flower even in the northern strip of Russia and in the Urals. A correctly selected and prepared planting site will greatly simplify further care, and will have a beneficial effect on the decorative qualities of the bushes.
Climatic conditions
Natural culture is common in warm climates. At the same time, unpretentiousness and the ability to withstand unfavorable factors makes it possible to plant in regions with mild winters, where it is permissible to carry out the cold season without additional shelter. Otherwise, preparation of plants for frost is required - mulching the soil surface with a thick layer of natural material.
Location and lighting
Pyrethrum is a thermophilic plant, therefore, when planting, it is recommended to choose the southern side, well lit and warmed up by the sun. Seating in partial shade is possible, but not desirable.
Strong shading negatively affects the decorativeness of the bushes - the shoots are stretched, the leaves become smaller, the flowers are almost not formed.
Soil requirements
The plant is unpretentious to the composition of the soil, the main thing is to refrain from waterlogging. To do this, when planting, you should avoid lowlands and areas with groundwater flowing close to the surface.
The root system develops well in a light substrate, therefore, it is advisable to plant on sandy loam or add coarse sand. Fertile chernozems help the plant to release large inflorescences with a beautiful aboveground mass.
Variety of species
About 100 species of pyrethrum are known, and about 50 have become garden-spread.
The most popular ones are:
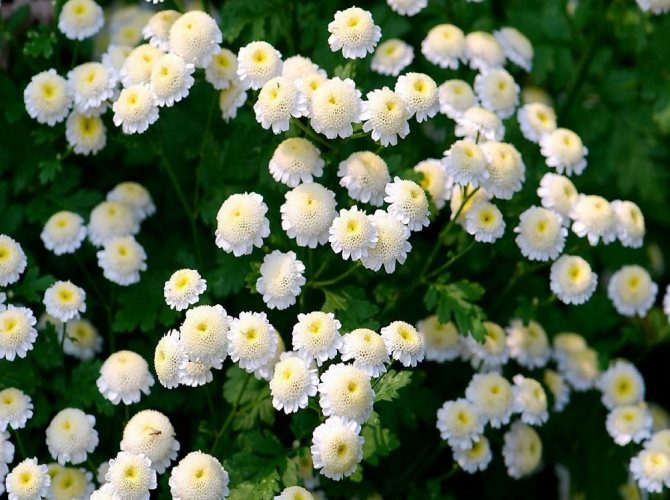
- Feverfew with dense shoots branching at the top. The bush and leaves are similar to chrysanthemums. The leaves are deeply dissected, pale green. A bush 50 cm high is decorated with inflorescences with a lush, pompom core. The flowers of pyrethrum are white and yellow, 2-3 cm each, as in the photo of flowers. The species is represented by several varieties: • White Stars - a compact small plant 25 cm high blooms with snow-white, pompom inflorescences. • Gold Ball is a dense, dwarf bush with double yellow flowers.• Schneebal is a compact plant with white, double inflorescences. • Virgo has spherical, white buds.


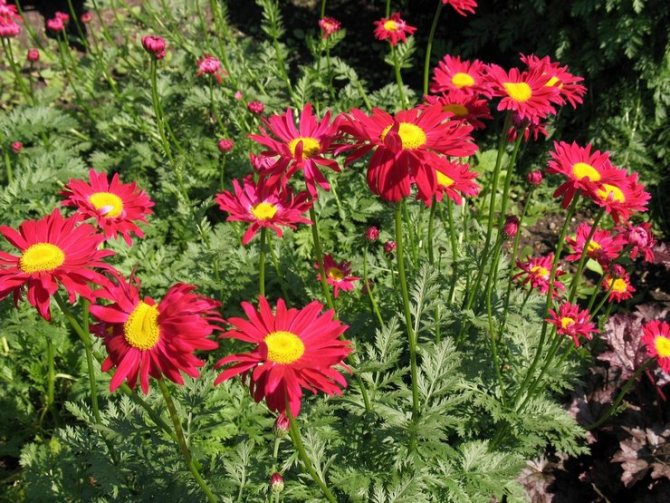
Maiden - Pyrethrum pink It is considered a perennial with a branched stem 60-70 cm high. In the lower part of the upright processes, light green foliage of a dissected type is collected. Single inflorescences with pale pink long petals. The size of the basket with a yellow center is 6 cm. It blooms in June and pleases with flowers for a whole month. The homeland is located in the Transcaucasus, where during the flowering period it covers the mountain slopes. Varieties: • Brenda with bright pink double-type flowers. • Kelway Glorious blooms with scarlet, full buds. • Atrosanguinea has deep red, large flowers with a yellow center. The bush is tall, branched. • James Kelvey is a 60 cm high bush with red flowers.


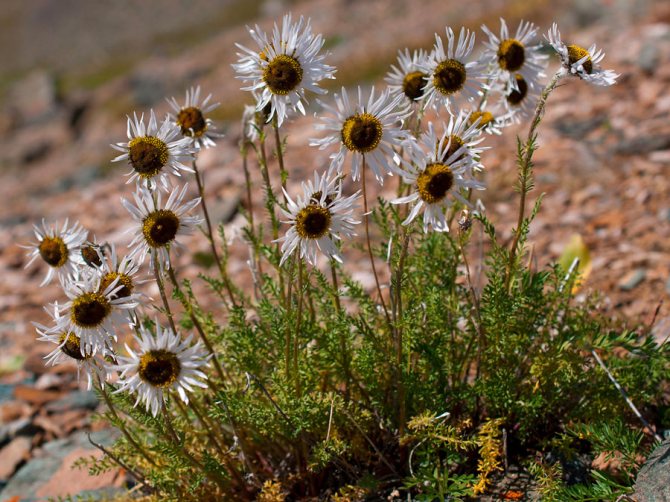
Pink - Large-leaved pyrethrum refers to tall species. Its height is 1-1.5 m. The bush with weak branching is covered with pinnately dissected leaves. Scallet inflorescences are large, 10 cm in diameter. Petals are white, small.


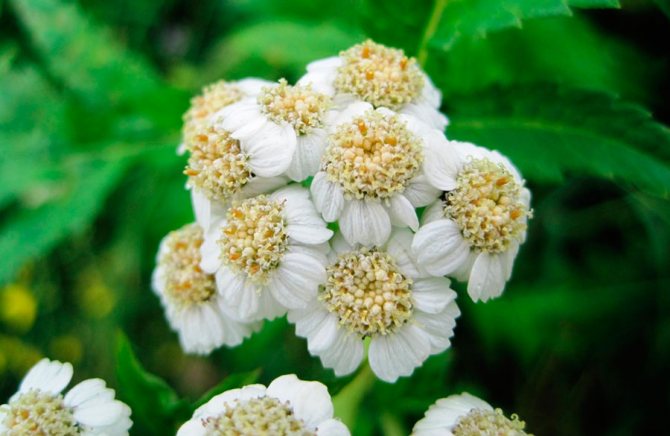
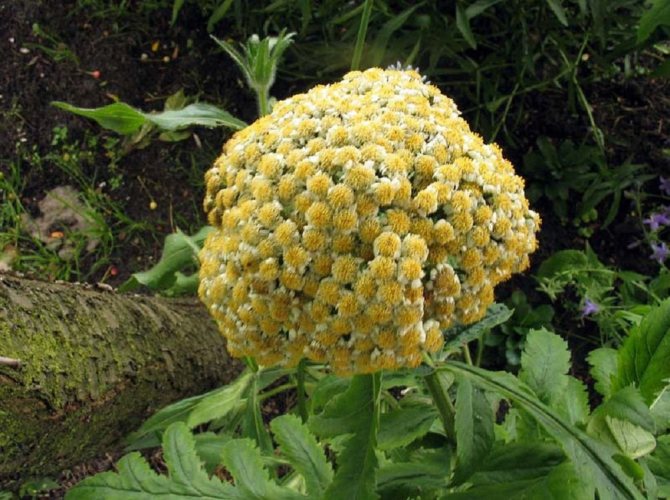
Large-leaved - Pyrethrum scutellum found in the foothills of Altai, in the Caucasus and in Eastern Europe. Single-stemmed rhizome plant. Pinnately dissected or pinnate leaves in the root part grow on long petioles. Stem leaves are sessile, with a similar structure. During the flowering period, many corymbose baskets appear on high, pubescent legs. The flower has a spherical bed and white petals.


Shield - Balsamic pyrethrum grows in the Caucasus. The height of the plant is 1.5 m. At the beginning of flowering, its flowers are white, and at the end they turn brown-red.


Balsamic
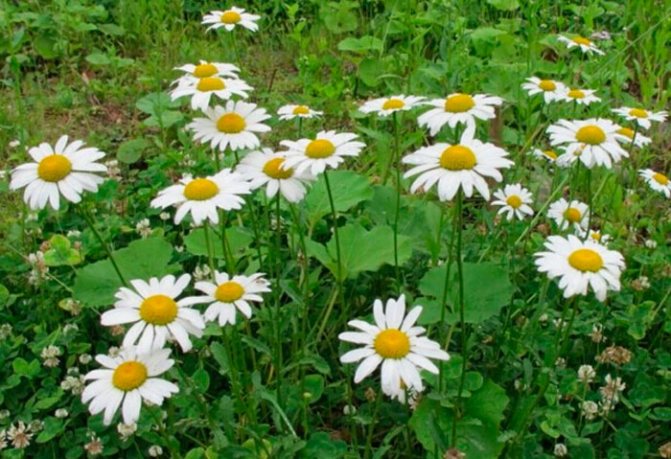
Feverfew maiden or Dalmatian chamomile (Persian chamomile): appearance and description
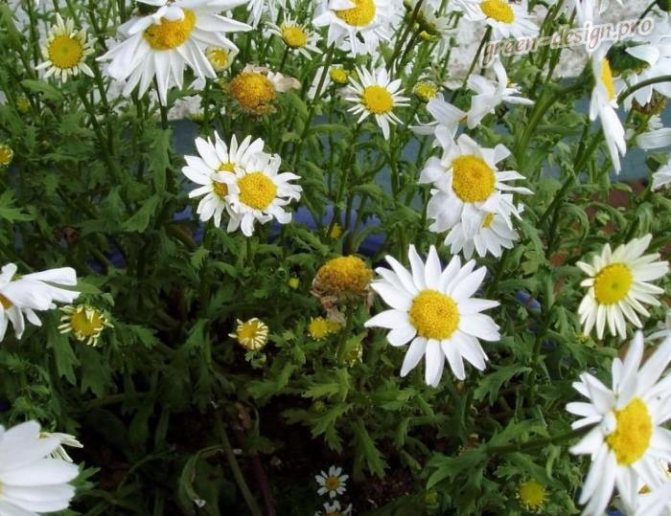
A perennial flowering plant combines the qualities of a common field chamomile and a sophisticated chrysanthemum. Thanks to the bright color of the inflorescences, the flower will become a real decoration of the personal plot and garden. The plant has strong immunity, so it practically does not get sick. It is unpretentious in leaving, even a novice gardener can grow it.


Appearance of feverfew maiden
Blossoms of Persian chamomile Robinson with large white flowers. This type is considered the most common. Depending on the type and variety, the height of the bush can fluctuate between 15-60 cm.
Leaves are medium in size, have a pinnately dissected shape, rich green color. Visually, the inflorescences resemble baskets collected in the upper part of the bush.
Important! Feverfew has a repellent effect on bed bugs and fleas.
Use in landscape design
An unpretentious plant resembling a Dalmatian chamomile is used by designers in landscape design to decorate lawns and flower beds. Attractive compositions can be created in combination with doronicum, dolphinum, poplar and bells.
Note! It is better to plant plants in sunny areas, but if this is not possible, the flowers will bloom in shaded areas, but not so abundantly.
Reproduction methods
For the propagation of pyrethrum, seeds, petioles and division of the bush are used.
The easiest way to get new bushes is with the help of seeds, of which a sufficient amount ripens annually. It should be borne in mind that the flowers are pollinated and the seedlings will not retain varietal characteristics. Even from seeds extracted from the same fruit, inflorescences of different colors will grow.
Sowing seedlings are carried out in the first half of March. Small containers are filled with a mixture of peat and sand. The dive is carried out after the appearance of at least 2 leaves. They are planted on a flower bed in May. In the first year, you should not expect a friendly flowering. Only part of the bushes will bloom.
You can sow pyrethrum seeds directly into open ground. This is done in the spring when the soil warms up. Fortified seedlings are planted with an interval of 20-30 cm between the bushes.
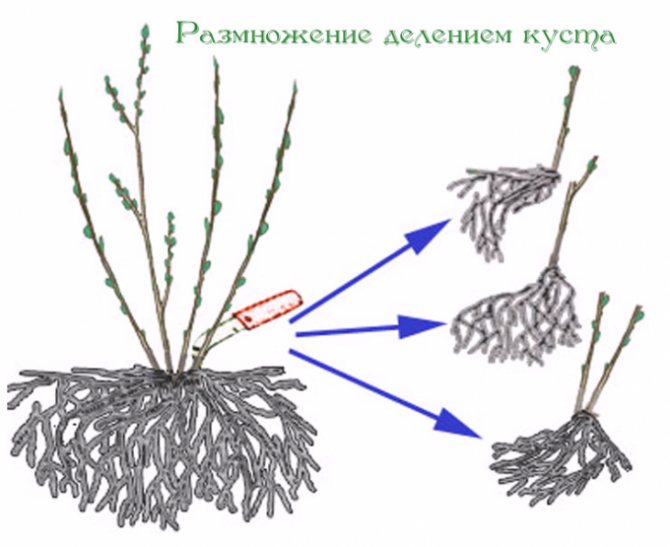
Bush division and cuttings
In feverfews, the bush is actively growing with lateral shoots. The bush grows and must be divided every 3-4 years. After flowering, the bush is removed from the ground and cleaned from the ground. The division is carried out by hands. The parcels should be large. They are immediately placed in holes and watered.
Cuttings are cut from young, basal processes. This can be done from May to August. For rooting, they are placed in partial shade in a nutritious, airy substrate. It is constantly kept moist, and to reduce evaporation, the cuttings are covered with a film. Airing and irrigation is done regularly. Rooting will take place after 2-3 weeks. Then from can be transplanted into the garden.


Seeds
Use in landscape design
The culture is suitable for planting in flower beds, on alpine slides, borders. Dwarf varieties of perennial pyrethrum are used as a ground cover plant. Brightly colored inflorescences look spectacular in rabatkas and mixborders. The variety is ideal for a country-style garden. It takes root well under trees, next to shrubs. Landing on balconies and terraces is possible.
Suitable neighbors for feverfew:
- cloves;
- cosmeya;
- bell;
- basil;
- digitalis;
- doronicum;
- delphinium;
- daisy;
- poppy;
- Felice.


Care requirements
The plant requires a minimum of attention, which will delight busy growers. The area for feverfew should be lit and sunny. In partial shade, the bushes stretch out more.
Any soil composition is suitable, except for heavy and marshy ones. The composition of the acidic soil is improved by adding ash. The fertile land will provide large and vibrant flowers. There should be no stagnation of water in the area for feverfew.
Removing dry inflorescences will preserve decorativeness and prolong flowering, and there will not be self-seeding yet. In feverfew, you can get a second flowering, if all flower stalks are cut off immediately after the first. For higher grades, a garter is required.
Feverfew is not recommended to be kept in one place. The roots actively grow and intertwine, and the soil becomes impoverished over time. A transplant is needed every 3-4 years with the simultaneous division of the bush.
The flower is cold-hardy and winters well in the soil. With the onset of cold weather, the stems are cut off, and the bush is covered with peat, dry leaves, spruce branches.


Watering and feeding
Pyrethrum is drought-resistant. They need watering only on hot days. Otherwise, the leaves lose their turgor, and the earth cracks. Moisture is important for flowers even at the time of flowering.
New plantings are immediately mulched with peat or cut grass. Mulch protects against moisture loss, crusting and annoying weeds.
Fertilizer is applied 2-3 times a season. Adding mullein is beneficial for flowering and growth. The first feeding is done in the spring, before the buds open. When flowering is over, fertilize with a complex fertilizer. In late summer and early autumn, the bushes are watered with herbal infusion.
Useful properties of pyrethrum


The healing properties of pyrethrum
Even in ancient times, the collected leaves and stems of herbs were used to stop various inflammations, bring down fever and relieve a person from headaches. Feverfew acts on the body like aspirin. The culture first gained recognition in England in the 17th century, when local healers learned to use perennial plant materials as a remedy for headaches. At the end of the last century, the British managed to find out that feverfew was able to cure migraines, and since such a disease was common, the flower quickly gained confidence and popularity. Even many young people often suffer from migraine attacks. Dried and powdered raw materials act no worse than medications. The reason for this effective effect lies in parthenolide. This substance is able to block serotonin produced by the thyroid gland.The accumulation of the aforementioned breakdown product in the body is a source of migraine.
The medical analogues of pyrethrum Lizurite and Metisergide also cure migraines, but their use often causes negative consequences and impairments. The job of feverfew is to prevent the production of serotonin. The use of the herb prevents blood vessels from forming blood clots, and the production of histamine stops. Perennial leaves are prescribed for the treatment of arthritis, rheumatism, delayed menstruation, asthma. The medical course for the treatment of psoriasis, dermatitis and various allergic rashes includes the use of pyrethrum.
Diseases and pests
Diseases overwhelm feverfew extremely rarely, if a diseased plant is adjacent to it in the garden. And pests are trying to bypass this perennial side. The only exception is the black aphid, which is sometimes found on the stalks of pyrethrum. To combat it, you must use special preparations sold in any gardening store or remove the plant from the flower bed.
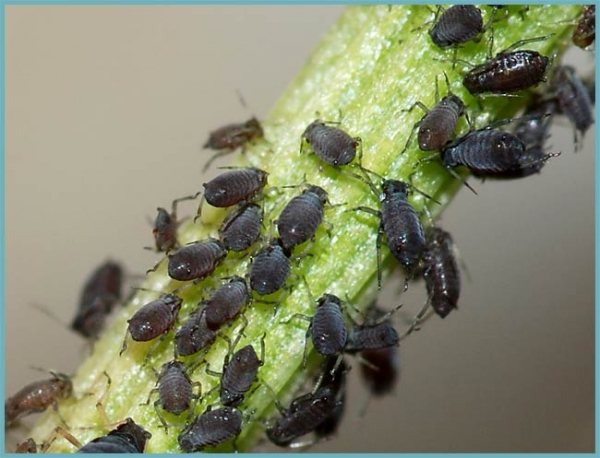


Black aphid