Home care for decorative leafy begonias
Landing
All manipulations with the plant are desirable spend early springwhen it is just beginning to start growing. The fact is that planting and transplanting slows down development for some time, because begonia is under stress from changed conditions. It is important to consider this and bring a new plant from the store to your home or office. Shop begonia was grown in greenhouse conditions in compliance with all the rules, and at home it is forced to adapt in a new way.
Priming

The soil is used slightly acidic or closer to neutral... It should be loose and fertile. Leafy earth and humus are taken, they are pre-disinfected. Sand is added to this mixture. It is also recommended to add perlite or vermiculite to improve the quality of the soil.
Pot
The container for deciduous begonia is taken wide, but not deep. Okay plastic pots will do, it is easy to remove the plant from them when the need for a transplant arises. Holes must be made at the bottom of the pot - this provides additional air access to the roots and the outflow of excess water
Watering
For watering, the water is defended or boiled. Water only when the top layer of the earth is dry. Experts determine the need for watering by changing the weight of the pot. You can gradually pour water from the pan until the top layer darkens.
In the summer, a frequent intake of moisture is required, in winter it is less frequent and always after the top layer of the soil has dried to a depth of at least 1 cm.
Avoid excessive moisture intake; it is better to water the begonias less.
Air humidity


Prefers moderate humidity. If the air is too dry, there is a high probability ofthe appearance of a spider mite, and at high humidity - there is a risk of decay of roots and leaves. Spraying begonia is not recommended. To increase the humidity of the air, containers with water are placed next to the pot or the begonia is placed on a wide pallet, into which moistened expanded clay is poured.
Temperature
Prefers a moderate temperature from 18 to 25 degrees. It is undesirable to place the plant next to cold drafts and radiators. In the summer they put in a cool place.
Location
Begonia loves light, but it should be diffused. Bright sun will burn the leaves and make them pale or increase the amount of green pigment, reducing variegated spots. Lack of lighting will affect growth and reduce the variegation of foliage.
The begonias do not like a sharp change in location, however, in order for the foliage to grow evenly, the plant can be slowly turned relative to the light source.
Landing requirements
First, let's describe everything in general terms. In principle, planting any ornamental plant is troublesome, but when planting our guest, who is also called an "unpretentious foreigner", strict requirements should be observed. For example, germination associated with freezing of tubers may become a nuisance. When buying, you should pay attention to the presence of rot on the glomerulus... Small roots can be removed from the tuber. It should be processed in a special liquid.
TIP: Fungicide is an excellent treatment agent, see packaging for dissolution proportions. Processing takes 20 to 40 minutes.
The pot should not be deep, as the roots will not be long in the future. Drainage must be laid at the bottom of the pot. Drainage should not fill more than 10% of the pot volume.
The ground must be loose and also have a lot of air.... You can buy such land in specialized stores. Debris such as pebbles or sticks must be removed. It is not necessary to accept the land, the looser it is, the better. It will not be superfluous to add vermiculite. It is not necessary to deepen the tuber much; relatively speaking, the tuber sits "shoulder-length". Until the begonia has matured, watering is carried out along the edge. Do not cover with dishes to create excess moisture.
Watch a video about the transplant of hogweed begonia:
Reproduction
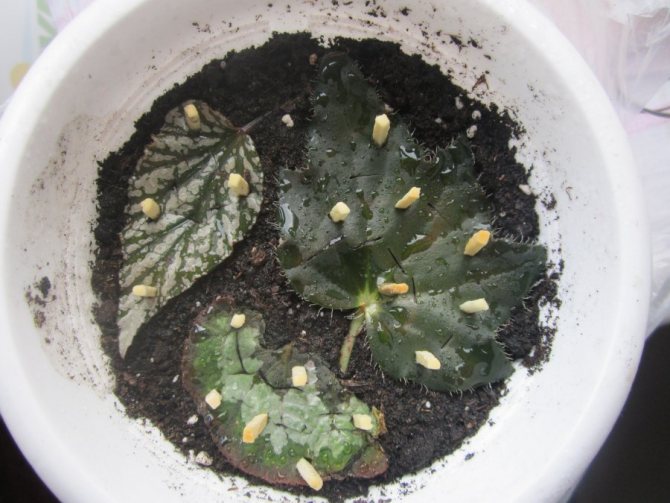
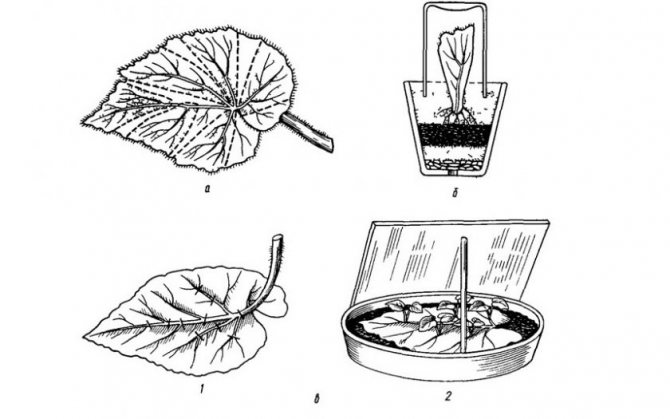
Most types of domestic begonias reproduce easily. Take a small stalk about 5 cm long, set in a glass of clean water. The best time for this is spring. Leaves are used instead of a cutting, they are cut with a sharp knife, the cuts are disinfected with charcoal. Reproduction is also available in parts of a leaf blade, cutting it so that a central vein remains on each piece. After that, the pieces are laid on loose soil, sand or perlite, pressed against them, and covered with a bag or jar on top.
Cuttings are planted after rooting in small pots or plastic cups. It is impossible to plant immediately in a large container - the soil in such a pot dries out for a long time, which can lead to the death of a young specimen.
Transfer
Every spring, the land is renewed and the plant is replanted. If it has grown a lot, and the roots have become cramped, then they take a pot slightly wider than before. A drainage layer is poured at the bottom, for which they take expanded clay or brick chips. The roots are cleaned of old soil, the plant is placed in a new pot and carefully sprinkled with earth, sometimes tapping the pot so that the soil lays down evenly. After that, the begonia must be watered, and the excess water is removed from the pan.
The soil


The soil, as for all other begonias, should be loose and enriched with various trace elements. Peat and black soil can be added to the ground in a one to one ratio... You can buy the soil at any flower shop, or mix it yourself.
Adult begonia is not particularly whimsical to the soil, but when planting and germinating, the soil must be loose, have a large supply of oxygen, and must also be enriched with mineral and trace elements. Soil is one of the most important factors in the beauty of your begonias.
Features of care in the winter
In winter, most plants are dormant. Watering is reduced.
The amount of light in the winter decreases, so the begonias are placed closer to the window or artificial lighting is added.
Protect the plant from exposure to cold air and radiators. Carefully monitor the watering regime, its excess hi to decay of the root system.
Also read on our website about such varieties of begonias: Krasnolistnaya, Bauer, Mason, Barshevikolistnaya, Cleopatra, Royal, Spotted, Collar.
Indoor plant description
There are both annual and perennial grasses, shrubs or shrubs with a creeping or tuberous thickened rhizome (read about tuberous begonias here). The leaves are most often asymmetric, they have a pretty beautiful color, especially in domestic species. Flowers are irregular, unisexual, monoecious. The perianth leaves are unequal, brightly colored. The fruit, like the rest of the species, has the shape of a box. It was first discovered in 1864. Named after a friend of the scientist, Michel Begon.
Diseases and pests
Too humid air and excess watering in winter will lead to powdery mildew: plaque appears on the leaves, and they die off.
In dry air, the edges of the leaves dry out and turn brown. With a lack of lighting, the leaves stretch out, become small and pale.
In the summertime, aphids can attack begonia, which was accidentally brought from the street. The appearance of a spider mite is also likely - it loves dry air. To remove pests, Actellik is used, which is sprayed on the plant.
Begonia - This is almost an ideal plant for keeping at home or in the office. It looks great in green areas and conservatories.
Decorative leaf begonia purifies indoor air and helps fight harmful bacteria.
Features of appearance
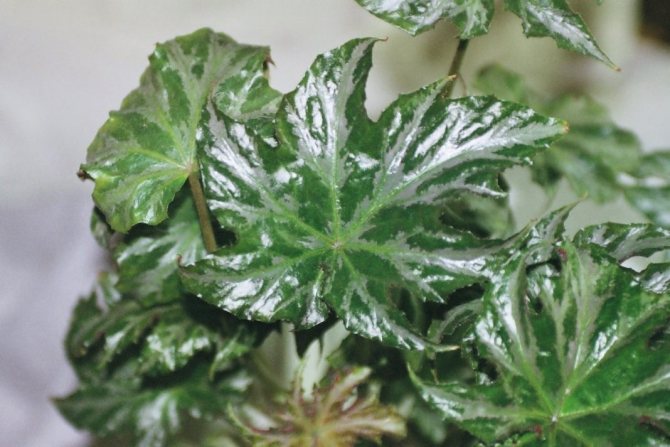
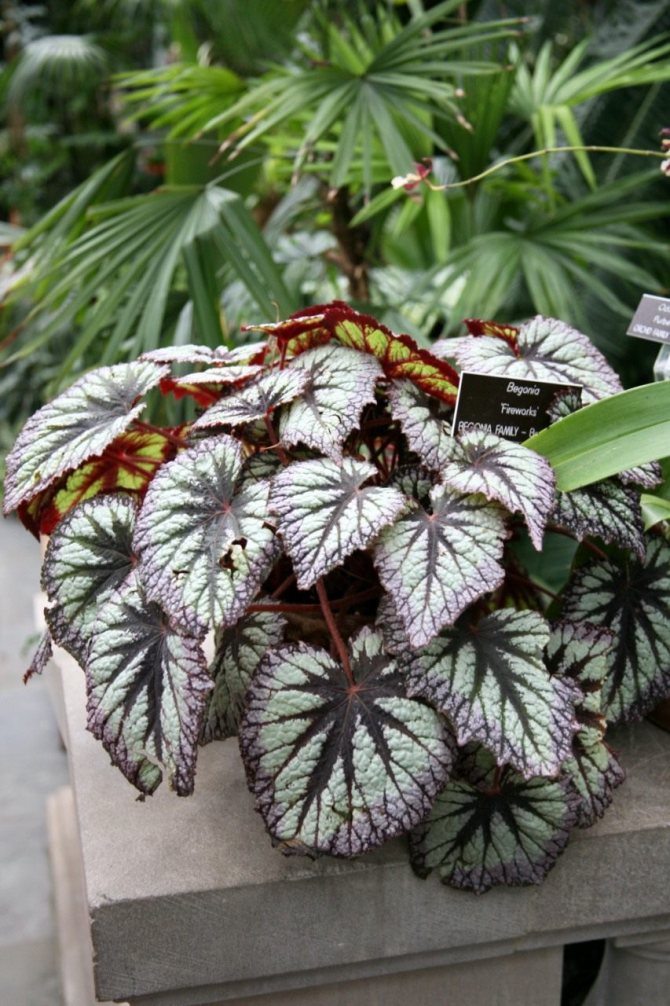
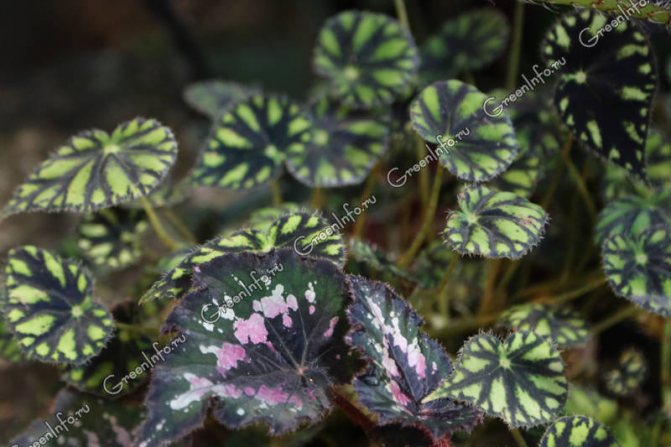
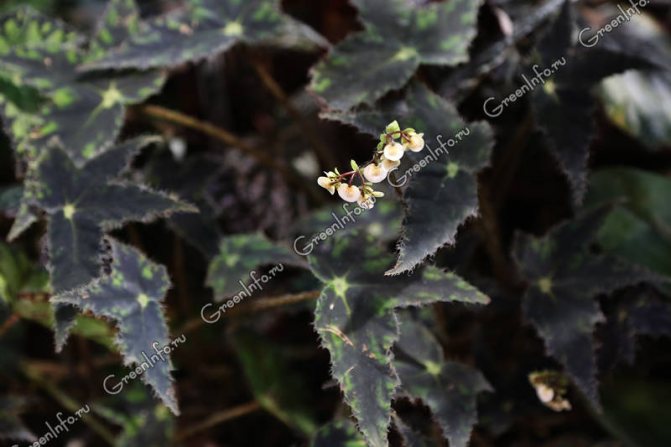
On long erect stems there are large asymmetric leaves with serrated edges, reaching an average of 15 cm in length and 10 cm in width. The main color is dark green, with an olive tint, on which contrasting white spots located throughout its surface. Sometimes the leaves have a purple tint. On the reverse side, the leaves are purple (you can find an overview of begonias with bright red leaves here).
Begonia Diadem blooms with delicate pale pink flowersalmost white. In order for the bush to form correctly, it must be periodically rotated.
Photo
Below you will see a photo for caring for decorative leafy begonia at home:
Planting rules and tips


For indoor Begonia, a shallow pot 3-4 cm in diameter larger than the rhizome of the plant is best suited.- Planting (as well as subsequent transplanting) is best done in the spring, before intensive growth begins.
- The plant can be watered immediately after transplanting.
- The plant needs to be transplanted annually while maintaining the entire root ball.
- Begonia can also be planted outdoors. But it is worth remembering that Begonia Diadem is a rhizome plant; during cold weather it must be transplanted into a pot and kept indoors.
- It is better to plant Begonia at the end of May in order to exclude the possibility of a sharp cold snap.
- It is advisable to fill the planting hole with a ready-made soil composition.
- If, after planting, it suddenly gets cold or it rains, Begonia should be covered with polyethylene or lutrasil for protection.
- For the first few weeks, the plant can be fed with fertilizers to give the Begonia a quick strength.
- In extreme heat, the plant may well stop growing. In this case, you just need to increase the frequency of watering and monitor the soil.
- At the beginning of October, Begonia can be dug out, but before that it is necessary to cut off the stems, leaving only a small part (about 3 cm).
Lighting and location
For Begonia Tiaras, direct rays of the sun are destructive; diffused light or partial shade is best suited. Indoor Begonia should be placed on a windowsill with darkened glass, or in a place where the sun does not reach.
Important! Begonia is sensitive to temperature changes. The climate in the kitchen is the least suitable, as the plant will be constantly exposed to temperature changes from the stove and refrigerator.
Soil requirements
First, a third of the pot is covered with drainage (pebbles or expanded clay), and then 2-3 cm of charcoal to avoid root rot. The soil mixture can be bought ready-made, or you can make it yourself... This will require:
- sheet land (2 parts);
- river sand;
- high-moor peat;
- humus (can be replaced with coniferous and sod soil).
The soil should be slightly acidic (pH: 5.0 to 7.5).
The potting soil must be sterilized before use. To do this, put the mixture in a water bath and, after boiling, keep on low heat for 1.5 hours.
Brief conclusions
- All the beauty of decorative leafy begonia lies in lush, bright leaves of various shapes, colors and sizes.They vary according to the specific plant species.
- It is best to propagate a flower by cuttings, this process does not take much effort, which cannot be said about sowing seeds. You can also grow a culture by dividing a bush, it is carried out during a flower transplant.
- Planting new seedlings or replanting existing plants should be in the spring, before growth begins. This will reduce the stress the flower experiences from changing conditions.
- In the process of caring for a crop, you need to remember that it needs a moderate temperature and diffused lighting.
- Water the plant abundantly during the warm season. Air humidity should not be lower than 60%, and top dressing is applied regularly. Don't forget about sanitary pruning in the spring.
Useful video
In this video, in 2 parts, the care of decorative leafy Begonia is described:
If you find an error, please select a piece of text and press Ctrl + Enter.


For many years begonia was one of the most popular plants in indoor floriculture - its unusual carved leaves adorned the windows of the houses of many of our compatriots. Unfortunately, at the beginning of this century, begonia was undeservedly forgotten.


Let's talk about watering


From spraying, let's move on to the related topic of watering plants. To make begonia delight you with lush foliage, it is best to water it through a pallet. At the same time, it is possible to avoid the ingress of water on the surface of beautiful carved leaves, and waterlogging of an earthen coma in a pot.
In winter it is watered moderately, in spring and summer - abundantly, avoiding stagnation of water.
Optimal growing conditions
In order for indoor flowers to develop harmoniously and delight with the variegation of their large foliage, they need to create conditions close to the area. We are talking about the appropriate temperature and humidity conditions, as well as lighting and soil composition.


Ground requirements
The quality of the substrate is one of the most important factors that determine the growth of the plant, therefore, for planting home begonias, loose and nutritious soil with excellent water and air permeability is preferable.
In the case of self-preparation of the earthen mixture, it is recommended to combine equal parts of fertile chernozem (extracted from a depth of 20 cm), deciduous soil and high moor peat. In order to prevent the rapid evaporation of moisture, it is advisable to add a little vermiculite to the soil mixture. And do not forget about the drainage layer, which should not exceed 10% of the planting capacity.
Keep in mind that young seedlings have special requirements for potting soil, so when rooting, do not tamp the top layer. The more loose it is, the better the sprout will develop.
Lighting and daylight
It is better to place the begonia pot in a well-lit area with diffused rays.... For this, it is not necessary to choose the sides of the southern orientation, since the plant is afraid of the scorching sun. He will be comfortable in rooms with windows facing east and south-west.
If the flowerpot is in partial shade, its foliage will acquire a thicker color and be covered with brown-red veins. This arrangement does not harm the splendor of the begonia crown and the size of its leaf plates. It is desirable that the daylight hours for a plant last at least 12 hours, otherwise its biomass will lose its volume and fade.
Temperature and humidity
In conditions of excessive heat or cold, it is impossible to achieve a luxurious appearance of the flower. In the first case, the tips of its leaves will dry out and begin to curl, and in the second, the flowerpot will stop its development and may die altogether.


The optimum temperature for the harmonious development of the culture is + 18 ... + 22 ° С with a humidity of 60%. It is important that in winter, when the period of stagnation begins, the thermometer in the room does not fall below the minimum mark. Otherwise, cold-sensitive begonia will disappear.
In the warm season, especially in hot weather, it is recommended to spray the air near the plant, protecting it from water. Drops falling on foliage and inflorescences are fraught with the appearance of not aesthetic brown spots.
Keep in mind that this variety is moisture-loving. But a sense of proportion is of colossal importance. With excess moisture, rot quickly develops on the roots of the flower, and it is far from always possible to save it. Experienced flower growers advise periodically humidifying the air in the room or placing a container filled with water near the pot.
Signs of trouble
Leaves turn pale, shoots stretch out - the result of insufficient light, especially in winter. It is necessary to organize additional lighting during the short daylight hours.
The edges of the leaves turn brown and dry - dry air and overheating. Limit exposure to direct sunlight and provide humidification.
Leaves brighten, brown drying areas appear on them - sunburn. It is necessary to reduce the "dose" of direct sunlight.
Growing problems
Begonias are affected by aphids, red spider mites, scale insects, and sometimes mealybugs. The tubers can be affected by the weevil.
Signs of the appearance of a tick: cobweb, bite marks, deformation of young leaves. When they appear, the plant is treated with acaricides (Neoron, Fitoverm) at least three times, evenly wetting the upper and lower parts of each leaf plate. It is important to observe the dosage, processing times and safety rules indicated on the package. Insecticides are used to control insects. The principle of application is the same.


Among the fungal diseases of begonia, gray and root rot, powdery mildew are more common. They are manifested by the appearance of wet spots on the trunk, tuber, roots or leaves; white bloom. To save the plant, all damaged areas are removed by sprinkling the cuts with crushed charcoal. The bush is treated several times with Fundazole or Copper Chloride.
| External manifestations | The reasons | Remedies |
| Brown spots on the leaves that are covered with a gray bloom | Gray rot | Cut off damaged parts, separate the infected bush from healthy plants. Treat with fungicide. |
| Room begonia leaves dry | Air humidity too low. | Place the pot on a tray of damp sphagnum. |
| Begonia leaves fall | If the stems are thin, and the internodes are long, the reason is a lack of light. If the leaves curl, the plant is hot. If they rot and wither, then subsidence is caused by excess moisture in the soil. | Observe agricultural practices. |
| Buds fall off | Too dry air or excess moisture in the soil. | Increase the moisture around the bush without spraying the leaves. Water the plant as recommended. |
| Begonia does not bloom | There may be several reasons: lack of light and fertilizers, non-observance of the rules of agricultural technology. | Fertilize the plant regularly, provide it with bright, diffused light. Follow the care instructions. |
This plant is sensitive to violations of agricultural technology and immediately reacts to them. The most common cause of death of begonia is insufficient or excessive watering.
Rhizome begonias
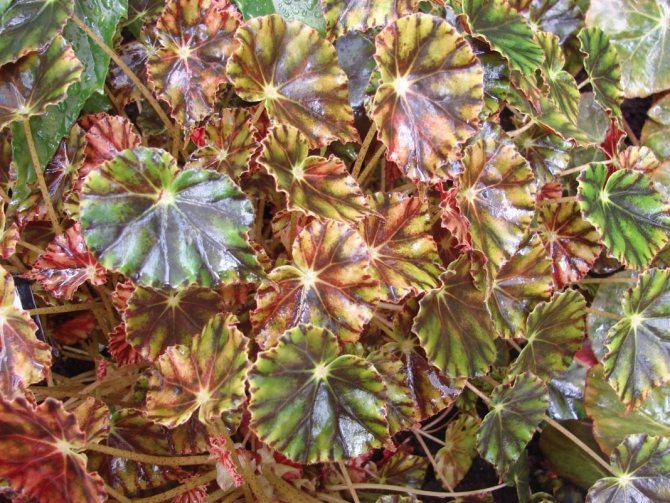
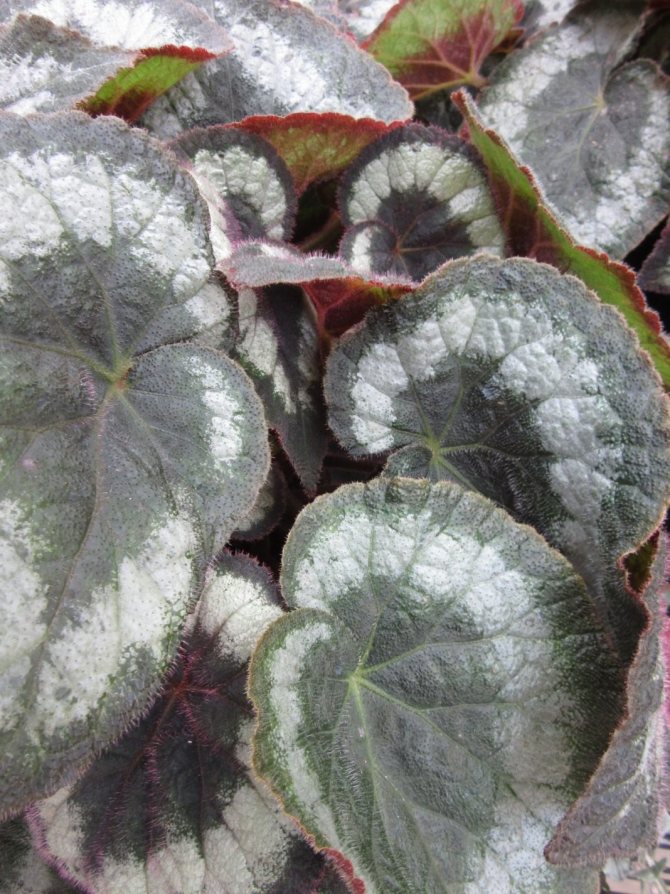
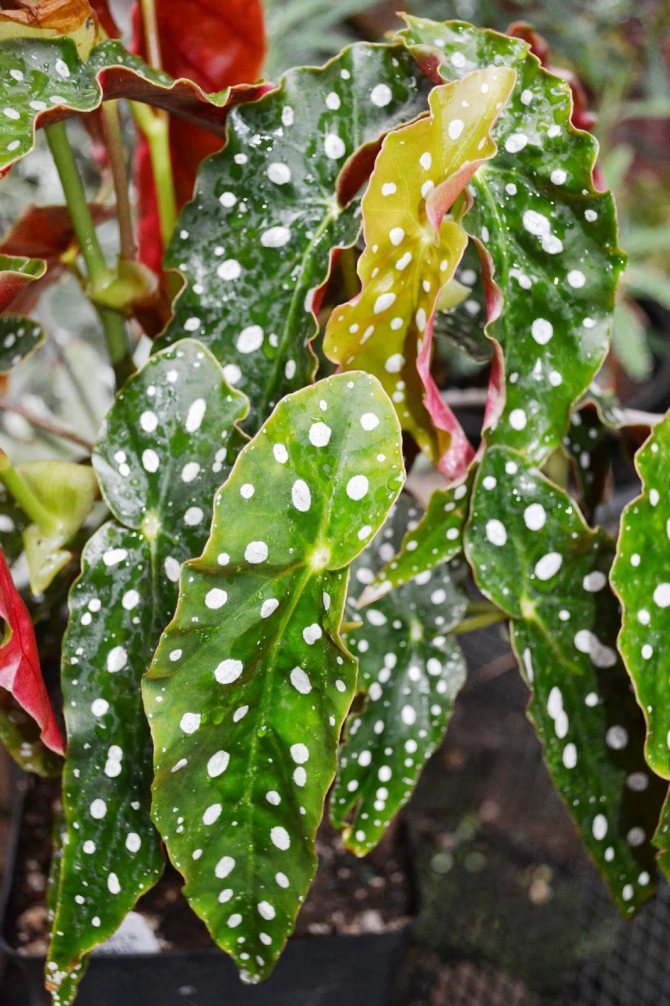
Rhizome begonias (Rhizomatous Begonias), or as they are often called, rhizomes are one of the largest groups of begonias. This includes species and varieties that have stems modified into growing on the surface of the soil or underground rhizomes. There are varieties with partially erect stems. Rhizome begonias are grown mainly for interesting leaves of various shades of green, black, silver or purple, often with intricate patterns. The shape of the leaves is also varied, rounded or stellate, with spirals in the center of the leaf, a fringed or hairy edge. In texture, the leaves can be smooth, shiny or rough, covered with hairs.
With the beauty of the leaves, some varieties are close to royal begonias (Rex-group).But just because there is no royal begonias (Begonia rex) in their pedigree, they are classified as rhizomatous.
In addition to decorative foliage, many varieties also have bright, impressive flowering. Most species bloom in spring, they need a period of short days to set flower buds, others bloom all year round, and then large inflorescences can completely cover the leaves. The flowers are most often white, pink or red, some varieties are yellow.
Among rhizome begonias, miniature begonias are not uncommon, but there are also quite large ones. Many varieties are shade-tolerant and are quite content with a not very bright location. Some of them are quite unpretentious, in warm climates they can be grown outdoors, others are so capricious that they grow only in florariums.
The variety of species and varieties is so great that it will satisfy every taste. Here are some common types and varieties of rhizome begonias:


Begonia Mason
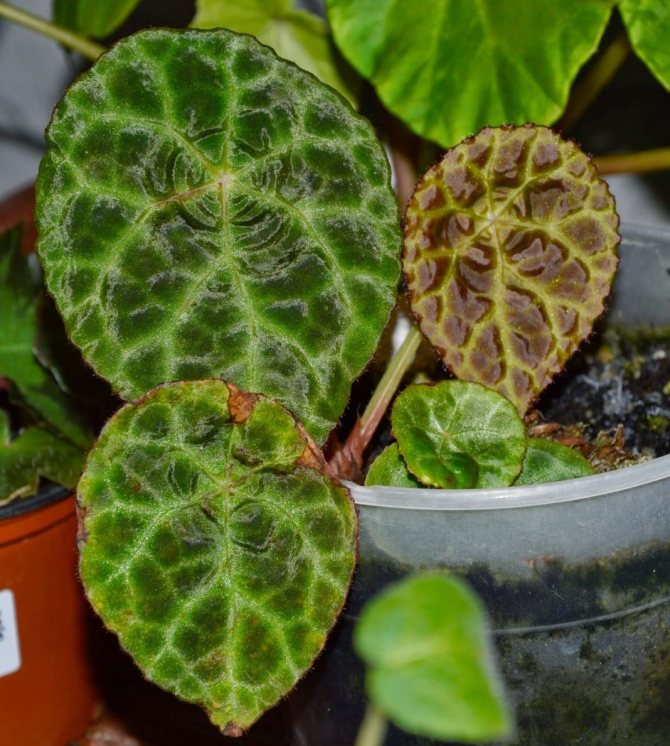
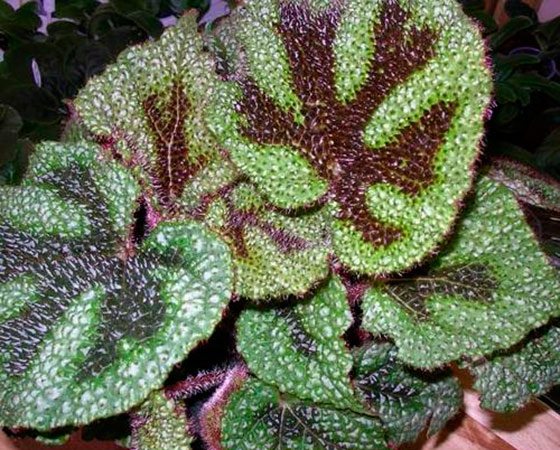
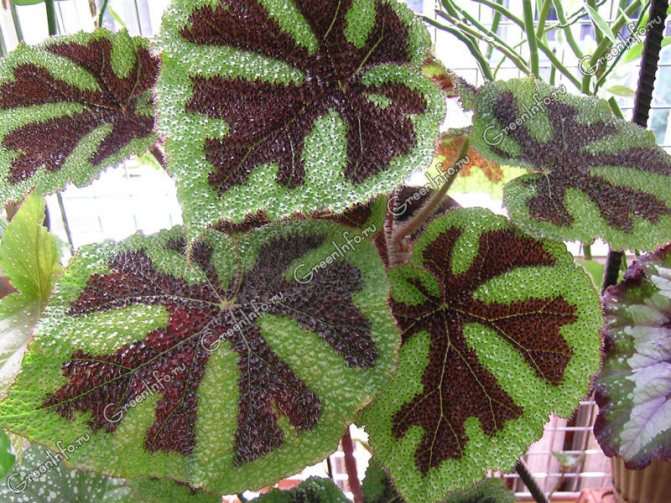
Begonia Mason (Begonia masoniana) was brought by L. Maurice Mason to England in 1952 from Singapore. Its homeland is China or India. The plant is about 45 cm tall with heart-shaped leaves. The leaf surface is hard and wrinkled, covered with pimples with red bristles growing from them. The edges of the leaf are serrated and hairy. On the light green background of the leaf there is a characteristic brown pattern along the veins in the form of a cross, which gave the name to the plant - begonia Iron Cross.
Red-leaved begonia, or Fista (Begonia x erythrophylla, syn. B. feastii) does not occur in nature. This is one of the earliest hybrids, obtained in 1845 in Germany from crossing Begonia manicata X B. hydrocotylifolia. This is a rhizome begonia about 30 cm tall, with dark green glossy rounded thyroid leaves up to 6-7.5 cm, covered with white hairs along the edges, red on the underside. The petioles are red and covered with hairs. Pink flowers on long peduncles appear in late winter - early spring. The variety is easy to maintain. On the basis of this begonia, decorative varieties were bred, such as:
- Begonia Buncha (Begonia x erythrophylla Bunchii) - with small rounded green or burgundy leaves. The edges of the leaves are very fringed, which gives the variety a special appeal. Small pink flowers in loose racemes on long peduncles appear in spring.
- Begonia Helix (Begonia x erythrophylla Helix) - has smooth, shiny chocolate-black leaves. The base is twisted into a "snail". The reverse side of the sheet is red.
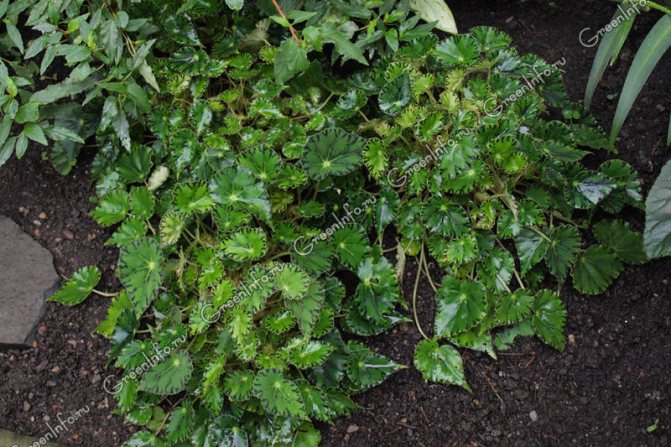


Begonia Bauer
Begonia Bauer (Begonia bowerae) is native to Mexico. It is a small plant about 25 cm tall with a creeping stem. The leaves are medium-sized, heart-shaped, emerald green with black, purple-burgundy or brown spots along the edges. The edges of the leaves and petioles are covered with hard hairs. The flowers are light pink, collected in loose drooping inflorescences. The original species is rarely found in collections, but it served as the basis for breeding many varieties:
- Begonia Tiger (Begonia bowerae Tiger) is a miniature variety reaching a height of 10 cm. The stem is creeping, branching. Numerous small, up to 2.5-4 cm, velvety oblique-heart-shaped leaves are covered with a tiger pattern: wide brown stripes run along the veins on a green background. The leaves are covered with small villi along the edge. The leaf stalks are also spotted.
- Begonia Cleopatra (Begonia bowerae Cleopatra) is a plant up to 20-30 cm tall, with creeping, ascending branching stems. Leaves up to 7-10 cm, palmate-lobed, reminiscent of maple, wavy, with an uneven edge, covered with numerous villi. Depending on the lighting, the upper side of the leaf is dark olive or bright green in color with chocolate spots along the edges, the lower side is lighter, with burgundy spots. It blooms from late winter to June with white or pink flowers collected in a brush.
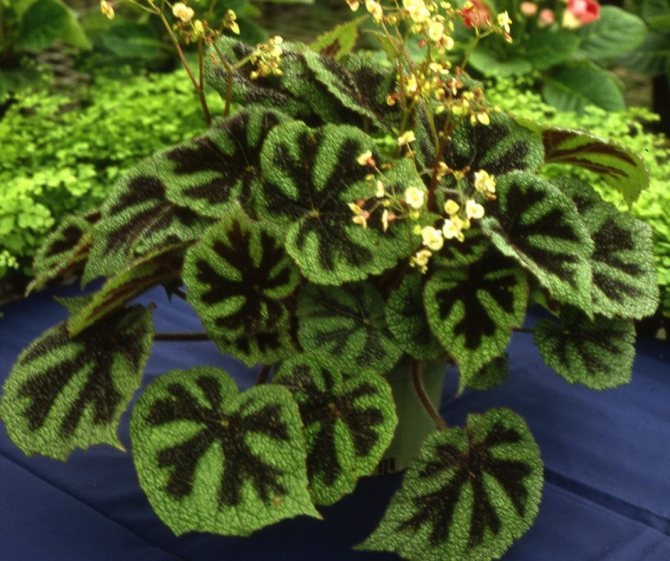
- Begonia Black Velvet (Begonia bowerae Black Velvet) resembles the Cleopatra begonia in habit, but the leaves are velvety black, with a small green star in the middle.
|
|
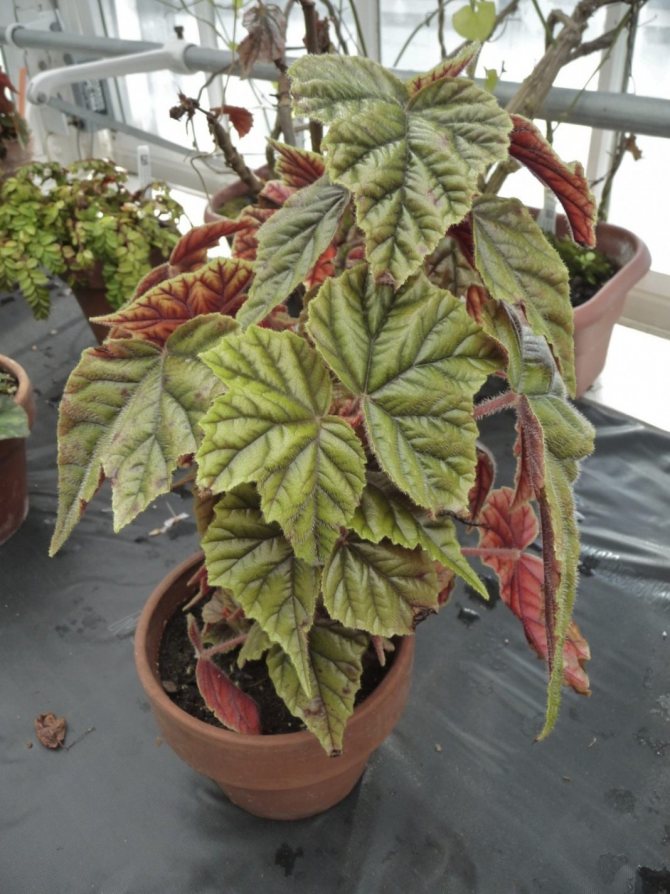
Begonia hogweed (Begonia heracleifolia) - native to Mexico, was first described in 1830. Often found under the name Star Begonia. It is a herbaceous plant with a height of 40-50 cm with a thick creeping stem.Leaves up to 25 cm, finger-dissected, hairy, coarsely toothed at the edges, dark green above, with lighter stripes along the veins, reddish below. Leaf petioles up to 30 cm long are covered with soft dense hairs with a bunch of narrow fringed scales at the top. This begonia has many varieties, gave rise to many new varieties and is one of the parents of the castor-leaved begonia.
Tick-borne begonia (Begonia x ricinifolia) - one of the oldest hybrids, obtained from crossing the hogweed begonia with the peponoliferous begonia (Begonia heracleifolia x B. peponifolia).
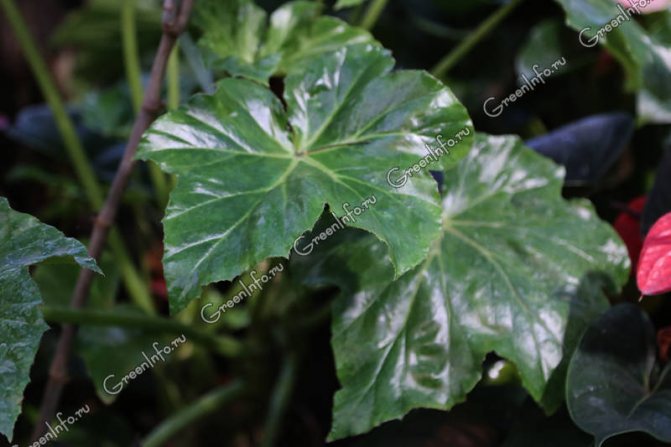


Tick-borne begonia
Powerful plant 1-1.5 m high with a creeping stem covered with white pubescence. The leaves are large, up to 35 cm in diameter, asymmetric, with large teeth along the edge, on long petioles. The color of the leaves is from bronze-green to copper-brown above and reddish below. The leaf is covered with brownish villi. The flowering of this variety is quite decorative: small white or pinkish flowers are collected at the top of a long, up to 1 m peduncle. Flowering can last from spring to autumn.
Begonia Griffith (Begonia griffithiana) - originally from the Himalayas. This is a small herb up to 40-50 cm high, with a thick rhizome. Leaves are ovate, pointed, oblique at the base, with large teeth along the edge, pubescent on both sides with violet-red hairs. The center of the leaf and the strip along the edge are olive green, the rest is bright silver.
Goegian begonia (Begonia goegoensis) - rhizomatous begonia with characteristic ovoid, without notch at the petiole, leaves. The leaves are silky, dark green, with a beautiful pattern in the form of a web of light veins on the upper side. The underside of the leaf is reddish, with sparse hairs. Petioles of leaves are faceted, square in cross-section. The flowers are small, pink.
Begonia salt mutata (Begonia soli-mutata) is a short species from Brazil with a thickened underground rhizome and fleshy creeping shoots. The leaves are petiolar, reniform in outline, brownish-dark green, with a light green pattern radiating from the center along the veins, covered with small pimples and velvety to the touch, with a red edge along the edge. It blooms with tiny white flowers.
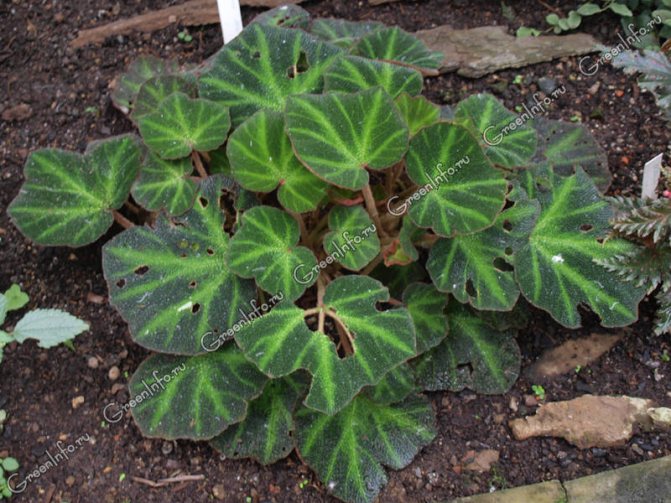


Begonia salt mutata
Imperial begonia (Begonia imperialis) is native to the humid forests of Mexico. Rhizome begonia with ovoid, rough pubescent leaves, serrated at the edges, about 12 cm long. The upper side of the leaf is bright green with a pattern of olive-silvery spots along the main veins. Many varieties have been developed that differ in the color of the upper side of the leaves, from monochromatic to very contrasting striped or speckled.
Begonia hatakoa (Begonia hatacoa) - syn. red-hearted begonia (Begonia rubro-venia) is a native of the shady rainforests of East India. Plants with a thick creeping rhizome and thin short shoots. The leaves are whole, oval, elongatedly pointed, 10-20 cm long and 3-8 cm wide, finely toothed along the edge, dark green above, with white spots, covered with hairs, pink-purple below. Petiole 8-20 cm long, covered with purple hairs. The flowers are whitish; the petals are covered with reddish strokes on the outside.
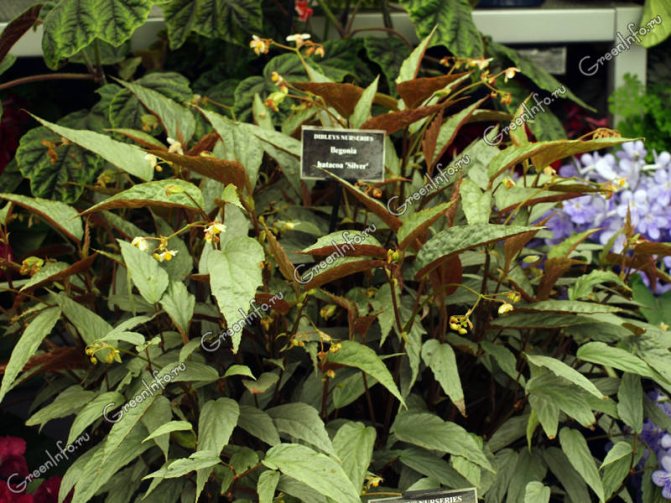


Begonia hatacoa Silver
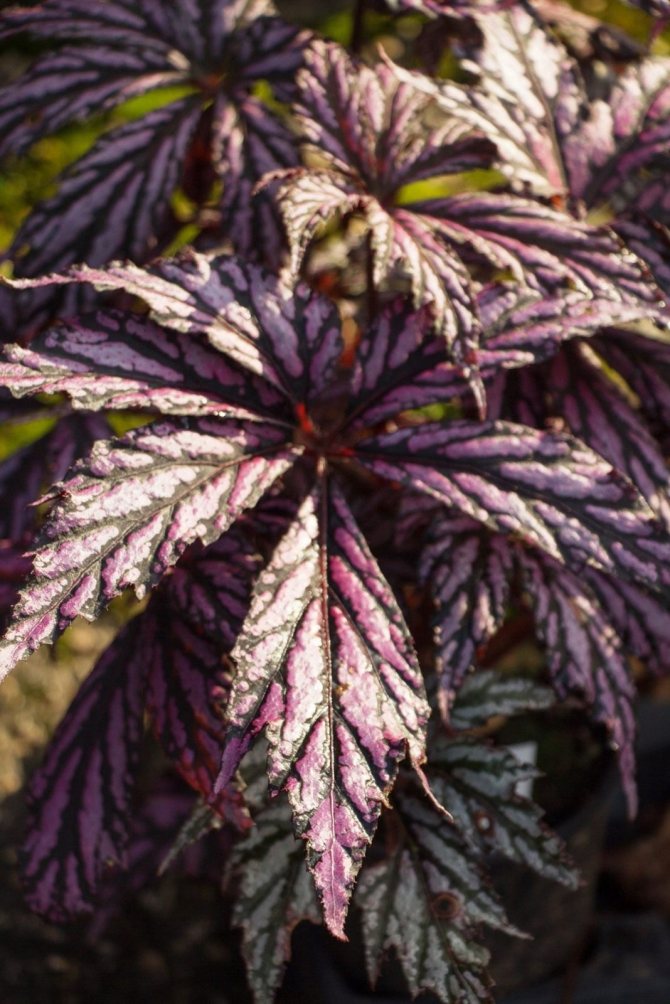
Begonia royal (Begonia rex) was discovered in India, in the state of Assam, and introduced into culture in the middle of the 19th century. The leaves emerging from the creeping rhizome have a magnificent brown-silver pattern. Today, numerous spectacular hybrid varieties obtained by crossing royal begonias with other species and varieties of begonias also appear under this name. Not all of them are rhizome, but they are similar in growing conditions.
More information about this group - in the article Royal begonias, or Rex begonias.
About growing rhizome begonias - in the article Peculiarities of growing rhizome begonias.
Photo: Rita Brilliantova, Maxim Minin
Botanical description and history of origin
It is a herbaceous perennial plant. It reaches a height of 60 centimeters, and some growers argue that this begonia can reach up to a meter. The shape of the leaves is asymmetric, finger-shaped. The edges are very serrated. Begonia was discovered by the French botanist Charles Plumier, who later began to investigate his find and named it after the organizer of the search expedition, Michel Begon. The homeland of this flower is considered to be South and Central America, where they grow in tropical forests on old dried trees, less often they can be found on mountain slopes and cliffs.
On a note. Foliage dimensions: length - about 15 centimeters, and width - about 12 cm. They are attached to long cuttings. Stems are erect.
Room temperature
It is necessary to ensure a stable air temperature so that there are no sudden changes. You should also monitor the level of humidity, after all, this is a "miracle" from the tropics, and therefore dry air has a detrimental effect on the growth, condition and color of the leaves.
In this case, it is required to comply with the norm, not to allow waterlogging, otherwise the begonia branches will begin to rot. The best option for winter, when working heating systems "dry" the air, is to put flower pots in a tray with slightly moistened sphagnum or gravel.
Spraying is useful, but it must be carried out carefully and correctly so that drops of water do not fall on the leaves, but form a cloud around the plant. Water is used only heated, settled or filtered.
You will have a constant temperature and normal humidity in your room, the begonia leaves will be rich in color, bright, beautiful.
Cultivation of tuberous and decorative flowering species
Tuberous and ever-flowering hybrids attract us with bright, abundant flowering, which, under favorable conditions, can last all year round. This variety of begonia flowers has special properties, caring for them is somewhat different from the decorative deciduous counterparts.
Some aspects of care
Flowering varieties are more susceptible to lack of light than deciduous varieties. In too shaded places, the stem and peduncles stretch out, the leaves turn yellow, dry, the flowers fall off.
Another unfavorable factor is heat and open sunlight. Newcomers to floriculture often wonder why begonia leaves curl, not even suspecting that this is a common sunburn.
Begonia tubers are prone to decay. Therefore, watering is preferable in the pan and in moderation. Varieties with glossy leaves can be sprayed and even bathed.
The flowering process is very energy intensive and requires good nutrition. Regular fertilizing with mineral and organic fertilizers is required, which contain calcium and phosphorus. They stimulate budding, give flowers a rich color.
To prevent the plant from stretching too much, you need to pinch the upper shoot, forming a bush. Tuberous begonias have fragile stems and can break under the weight of the inflorescences, so it is recommended to tie them up.
Important! In November, a dormant period begins in room tuberous begonia and lasts until about February. At this time, it may remain green, but if the plant is old, then there is a high probability of leaf shedding. In this case, the stems must be cut, and the tuber must be transplanted in the spring.
Reproduction
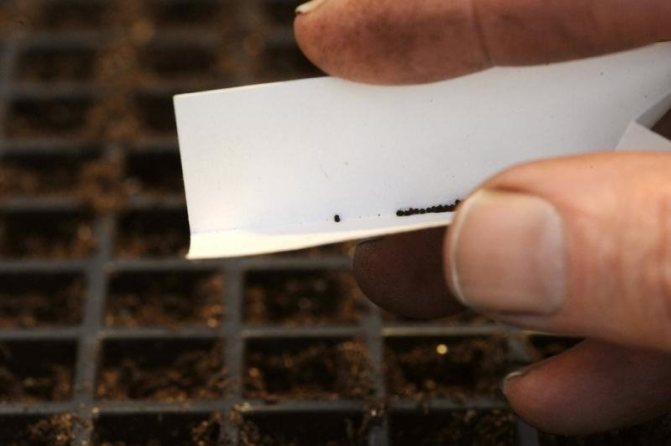
Along with grafting, this type of culture is propagated by tubers. Planting material is acquired or used by an old tuber in order to rejuvenate the plant. It can be germinated in its entirety or divided into several parts (by the number of buds).
The substrate for planting is taken lightweight - based on peat and leafy soil, a baking powder is added - perlite, moss, sand. Drainage is laid on the bottom - expanded clay, pieces of foam.Before planting, the tuber is disinfected in a solution of manganese or fungicidal preparations (Maxim, phytosporin) for half an hour.
Tuber germination takes place in several stages. First, it is placed in a pot in such a way that only the root part is in the ground, the top with the buds is not sprinkled. When the sprouts hatch and grow up to 3-4 cm, the tuber is covered with a substrate, leaving green shoots on the surface.
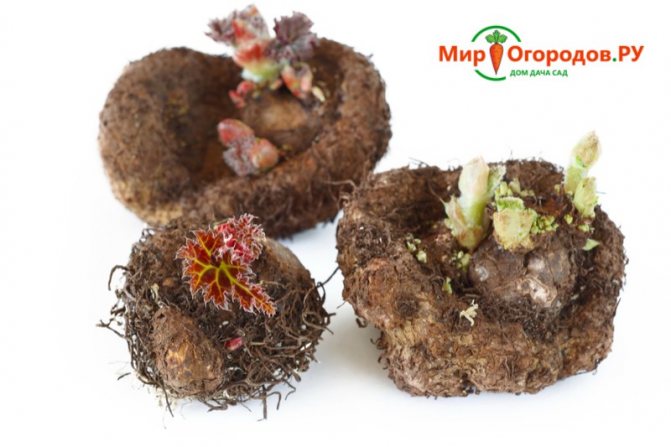


Tubers with swollen buds and sprouts
You need to know the enemy
The list of "opponents" of begonia should include:
- dry air (we described in detail how to water and spray);
- powdery mildew;
- mold;
- gray rot;
- aphid;
- Putin mite.
In fairness, let's say that these plants are quite unpretentious, they are resistant to diseases and pests, but if some kind of attack happened, then improper care and non-compliance with the regime are most often to blame.
They get rid of mold and powdery mildew with special compounds, after removing all plaque from the leaves. But in the fight against pests, infusions of ordinary garlic, chamomile or tobacco help well.


I think you are convinced that not so much hassle is required when growing begonias, but this flower will thank you with magnificent colorful greenery.
Transfer
Young ornamental-leaved begonias grow quickly, and they become cramped in an old pot. Therefore, transplant each year in mid-spring to a larger container. For older cultures, hold this event as needed. How to transplant begonia:
- Moisten the soil under the flower well one day before the procedure. Then the plant is easier to get out of the pot.
- Lay a layer of expanded clay or other drainage material on the bottom of the new container and sprinkle it with a substrate.
- Remove the begonia carefully from the pot. Examine its roots and remove any damaged or dried out growths. Treat the places of cuts with a solution of potassium permanganate.
- Place the flower in a container and cover the voids with the prepared substrate. When doing this, do not add soil to the top of the pot.
- Moisten the flower well. If the soil has settled after drying, then add some more substrate to the pot and water the plant again.
The transplant is stressful for the plant, so at first it needs gentle care. Apply fertilizer for the first time 30 days after the event.