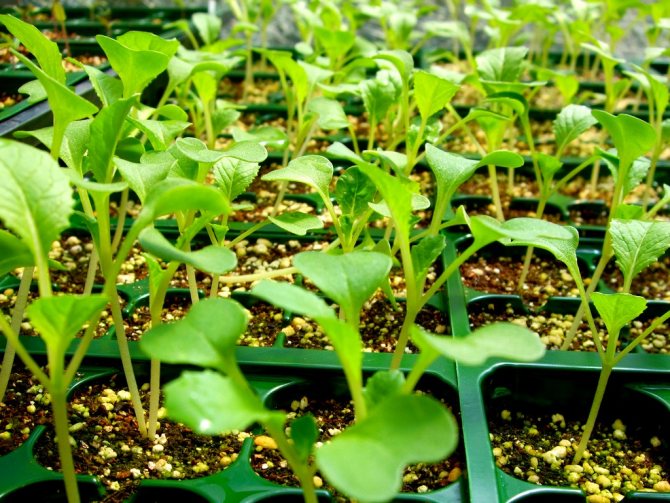
Cutting is one of the methods of vegetative propagation of plants, and for some plants it is the only method of propagation. One of the main features of cuttings is that plants grown from cuttings retain all their parental properties.
Let us consider in more detail the reproduction of plants by green cuttings:
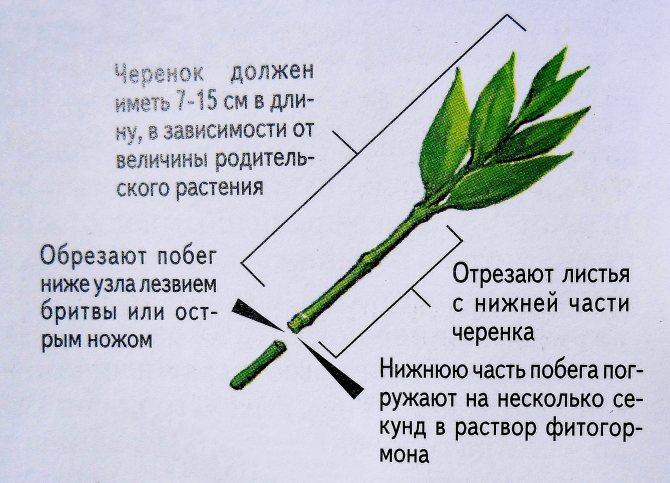

Green cuttings are cut from mother plants that are 5 to 10 years old. For difficult-to-root plants - in two-three-year-olds. Choose healthy and robust plants.
Cuttings are made in June - early July. But do not forget that each plant has its own characteristics and timing for the successful rooting of cuttings. The most easily rooted cuttings of plants such as maiden grapes, clematis, privet, mock orange, actinidia, honeysuckle, hydrangea, lilac and many others.
- 2 Prepare cuttings for plant propagation by cuttings in the following way
- 3 Planting cuttings
- 4 Care of cuttings
- 5 Terms of plant cuttings
5.1 Video: "Cutting plants with Sergei Glazinov"
- 5.2 Video: "Cutting Plants with Pavel Trannoy, Part 1"
- 5.3 Video: "Cutting Plants with Pavel Trannoy, Part 2"
Propagation of indoor plants by cuttings
Propagation by cuttings (vegetative method) is the most popular among flower growers. A stalk is a part of a plant that is specially cut off. She has the ability to root and grow. In floriculture, several different types of cuttings are distinguished, namely: stem, leaf, apical, and middle.
Propagation by apical cuttings

This method is used for all ampelous plants, as well as for touch-me-not and balsam.
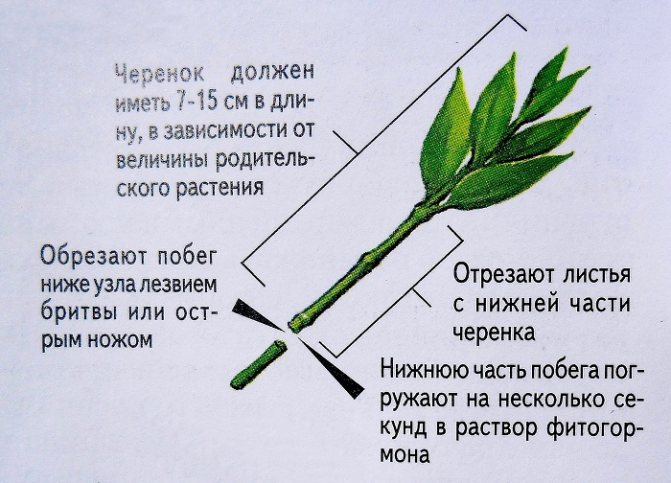
To obtain this kind of cutting, cut off the part of the non-lignified stem, which is located at the top. On such a cutting, there must be developed leaves in the amount of 2 to 4 pieces. You need to step back a centimeter below the knot and make a cut. It is on this node that the roots appear first. To make rooting faster, it is recommended to treat the cut with growth stimulating agents (phytohormones).
For rooting, the cuttings are planted in a soil mixture for young plants, and then watered. Cover the container with plastic wrap to keep the humidity high.
Propagation by stem cuttings

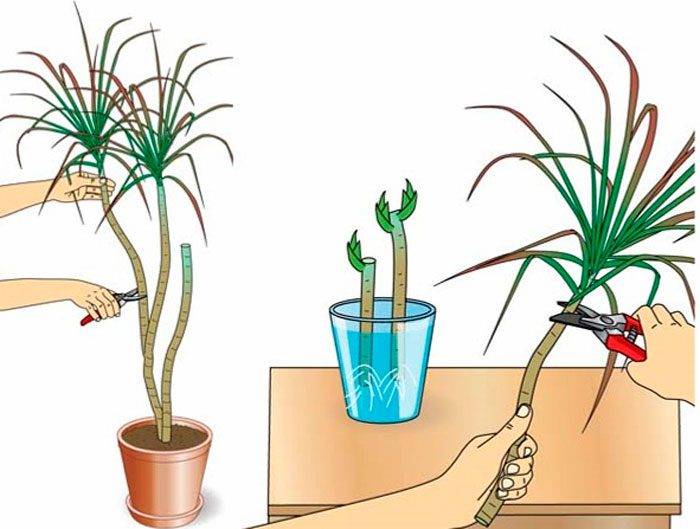
Ficus, geraniums, all succulent plants, as well as cacti can be propagated by stem cuttings.
This type of stalk can only be cut from a healthy plant, and the cut must be made slightly below the node.
Which stalk should consist of 3 or 4 nodes and leaves should be present on it. Pay attention to the cut, it must be fresh and even. There should be no flowers or buds on the handle. If desired, the leaves from the bottom can be torn off. Rooting is carried out in moist soil, which contains a lot of sand, or a soil mixture for young plants is used for this. After the roots appear (after about 3-4 weeks), the plants are transplanted into an ordinary soil mixture. Most cuttings are rooted simply by dipping them in a glass of water.
If you propagate succulent plants or cacti in this way, then the cutting should be left for several days in the open air for drying before planting for rooting. At the same time, the place of the cut should become tightened, and the edges of it should be bent inward. This will avoid the appearance of stem rot. After planting, the soil is slightly moistened with a sprayer (do not watered).
Cuttings of geraniums, as well as succulent plants, are not covered with a film during rooting. All other plants need high humidity at this time, so they must be covered with foil.
As a rule, it is recommended to place the cuttings in a well-lit and warm enough place. It should be borne in mind that they must be protected from direct sunlight.
As a rule, such cuttings are propagated in spring and summer, when the plant is growing intensively. But there are plants that are best propagated in this way in the last summer days, for example, geranium, fuchsia.
The middle stalk is considered part of the stem. Cut it off from the middle or bottom of the shoot. As a rule, such cuttings are used for propagation of Tradescantia.
Propagation by leaf cuttings
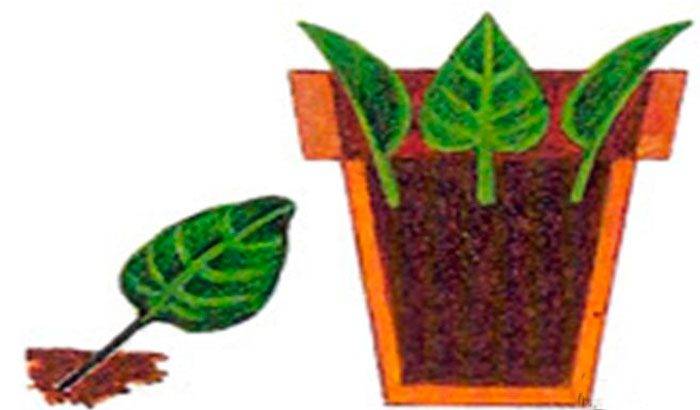

Bushy begonia, gloxinia, uzambara violet (Saintpaulia), peperomia can be propagated by leaf cuttings.
Reproduction of Saintpaulia is carried out with whole leaf plates with cuttings. A strong healthy leaf with a handle of a decent length should be cut off from the plant, then it is planted in a special soil mixture. When daughter plants are formed on the leaf plate, they will need to be separated and planted separately.
Succulent plants propagate directly with leaf plates. So, for the reproduction of streptocarpus, sansevieria and gloxinia, part of the leaf is used. It is necessary to plant the leaf in the soil in such a way that only a small part of the leaf rises above the soil surface. In the case when the particles of the leaf plate are too small, they are laid out on the surface and slightly pressed into the substrate.
Prepare cuttings for plant propagation by cuttings in the following way
- Cuttings are cut, the length of which is 8-12 cm, with two or three internodes.
- With a sharp knife or pruner cut the base of the cutting at an angle of 40 degrees at a distance of 0.5-1 cm from the kidney, the upper cut is made straight above the kidney. All the lower leaves are cut off, and two or three leaves are left on top of the cutting. If the plant is broadleaf, then the leaves on the cuttings are cut in half.
- Next, the cut cuttings are placed for a few minutes in a fungicide solution to a depth of 1.5-2 cm. After that, extra drops are shaken off the tip of the cuttings. Then the tip is dipped into a growth stimulator parasail (for example, root or root).
Reproduction by layering


Climbing, as well as ampelous plants with long shoots, for example, ivy, chlorophytum and others, can be propagated by layering.
This type of reproduction differs in that a young plant is formed without being separated from the mother plant.
After sprouts appear on rather long shoots, they try to fix them with a wire or hairpin on the surface of a special soil mixture. Rooting is pretty fast. A young plant should be separated when its root system is formed, and it begins to grow by itself.
Terms of plant cuttings
| Plant | Cutting time | Rooting percentage | Duration (days) |
| rose flower | Budding-beginning of flowering | on average, 83.9%, in some varieties up to 100% | from 10-15 to 28 |
| Lilac | Fading phase | up to 90-100% | |
| Clematis | Budding-beginning of flowering | 40-100% depending on the grade | 25-30 |
| Chubushnik | Attenuation of shoot growth - beginning of flowering | up to 90-100% | 15-25 |
| Spirea | Early to mid-June | from 30 to 100% in different species | 12-25 |
| Forsythia | First half of June | up to 70% | 20-30 |
| Viburnum | Flowering period | 100% | 14-21 |
| Cotoneaster | End of June - beginning of July | 100% | |
| Action | Early June to mid-July | 100% | 17-25 |
| Privet | Mid June - early July | 80-90% | 14-21 |
| Derain | Mid June - early July | 100% | |
| Honeysuckle | End of shoot growth | 100% | 11-20 |
| Hydrangea | June July | 80-100% | 20-23 |
| Rhododendron | July-September | 72-76% | 50-70 |
| Actinidia | June July | 36% | |
| Scumpia | End of June - beginning of July | 100% | 20-30 |
| Barberry | June | 33-100% | |
| Colquitia | Early July | 46% | |
| Weigela | 100% | ||
| Euonymus | 45% | 45 | |
| Currant | 83% | ||
| Chaenomeles | 100% | ||
| Cotoneaster | up to 100% | up to 28 | |
| Keriya | up to 100% | ||
| Kuril tea | 100% | ||
| Juniper | 70-90% | ||
| Thuja | June | 30-60% | 30-60 |
| Spruce | June July | 50% |
Video: "Cutting plants with Sergei Glazinov"
Video: "Cutting plants with Pavel Trannoy, part 1"
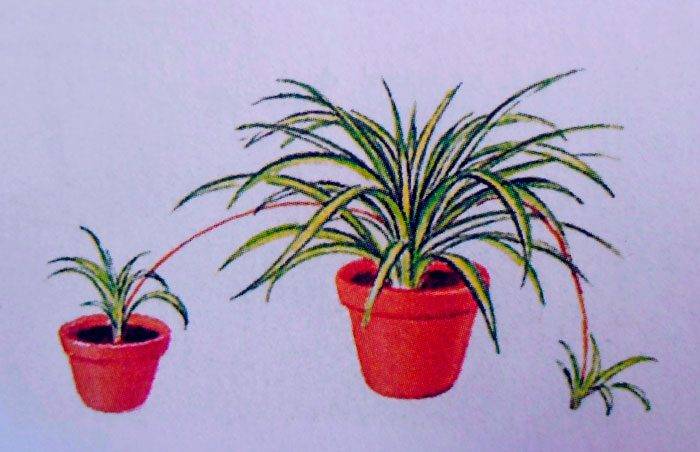
Reproduction by offspring
Bulbous and bromeliads, as well as cacti can be propagated by offspring.
The daughter plant that develops from the base of the mother is the offspring. After such plants develop well, they are separated from the mother with a sharp knife or with your hands, while trying to make a cut closer to the main flower. We must try to ensure that the separated offspring has many of its own roots. The separated offspring are planted in an individual pot, and they are provided with the same care as for cuttings.
Small bulbs appear on the mother bulb plant. They must be carefully separated and placed in a separate container. They usually bloom after 1 or 2 years.
Planting cuttings
- Greenhouses or greenhouses are used for planting cuttings. If there are few cuttings, then they can be planted in small pots of several pieces, depending on the size of the cuttings.
- A layer of soil (10-15 cm) is placed on the bottom of the pot, mixed with sand. The second layer on top is coarse clean sand (3-5 cm).
- With a thin stick (for example, a pencil), holes are made in the soil with a depth of 2.5-3 cm. Then the finished cuttings are placed vertically in them at a distance of 4-7 cm from each other. With the same stick, tamp the soil around the base of the cutting.
- The cuttings are carefully watered from a watering can with a fine sieve. For planting, a mini-greenhouse is built from a film. If the cuttings are planted in a pot, then you can wrap it with a transparent bag on top, and secure it with an elastic band at the bottom, at the base of the pot. Thus, you get a mini-greenhouse that you can leave on the windowsill at home.
All planted cuttings must be shaded !!!
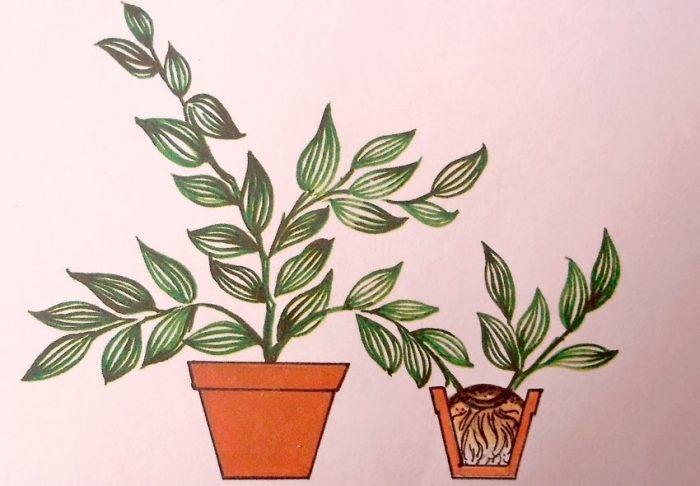
Reproduction by children


You can propagate degremona, Kalanchoe, degremon bryophyllum, Kalanchoe tubule.
As a rule, children with their own roots develop at the tips of the leaf plates of these plants. Separate them with your fingers, while you need to be very careful not to damage the delicate roots. They are planted in containers filled with moist earth mixture. When the flowers grow, they should be planted in separate pots.
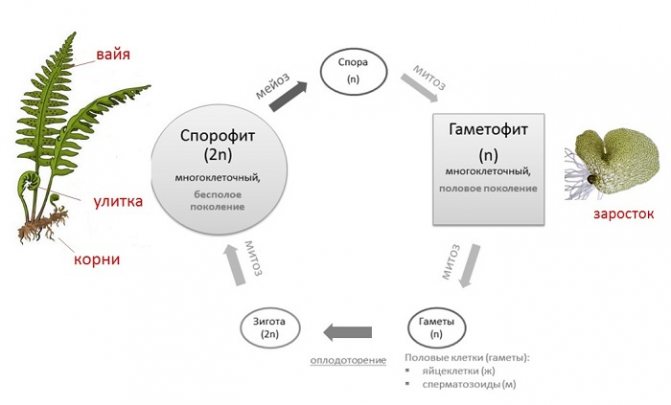
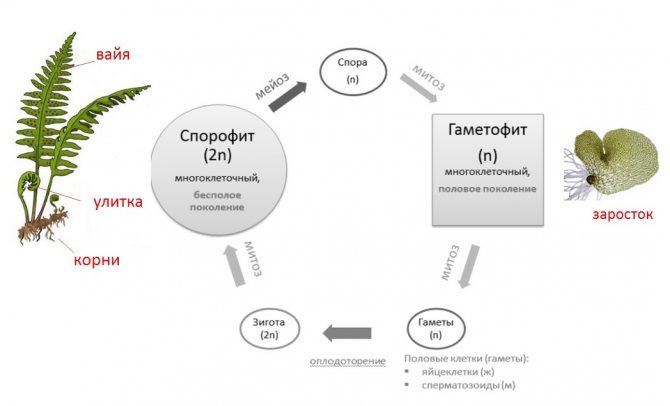
Alternation of generations
In plants, there is an alternation of sexual and asexual generations:
- the sexual generation grows from the spore, the gametophyte, which reproduces by gametes;
- from the zygote a sporophyte grows, an asexual generation that reproduces by spores.
Externally known to us spore plants are asexual generation. The sexual generation of spore plants is called an outgrowth and is a small, not similar to sporophytes, plants.
Sexual reproduction of spore plants depends on the availability of water to move gametes.
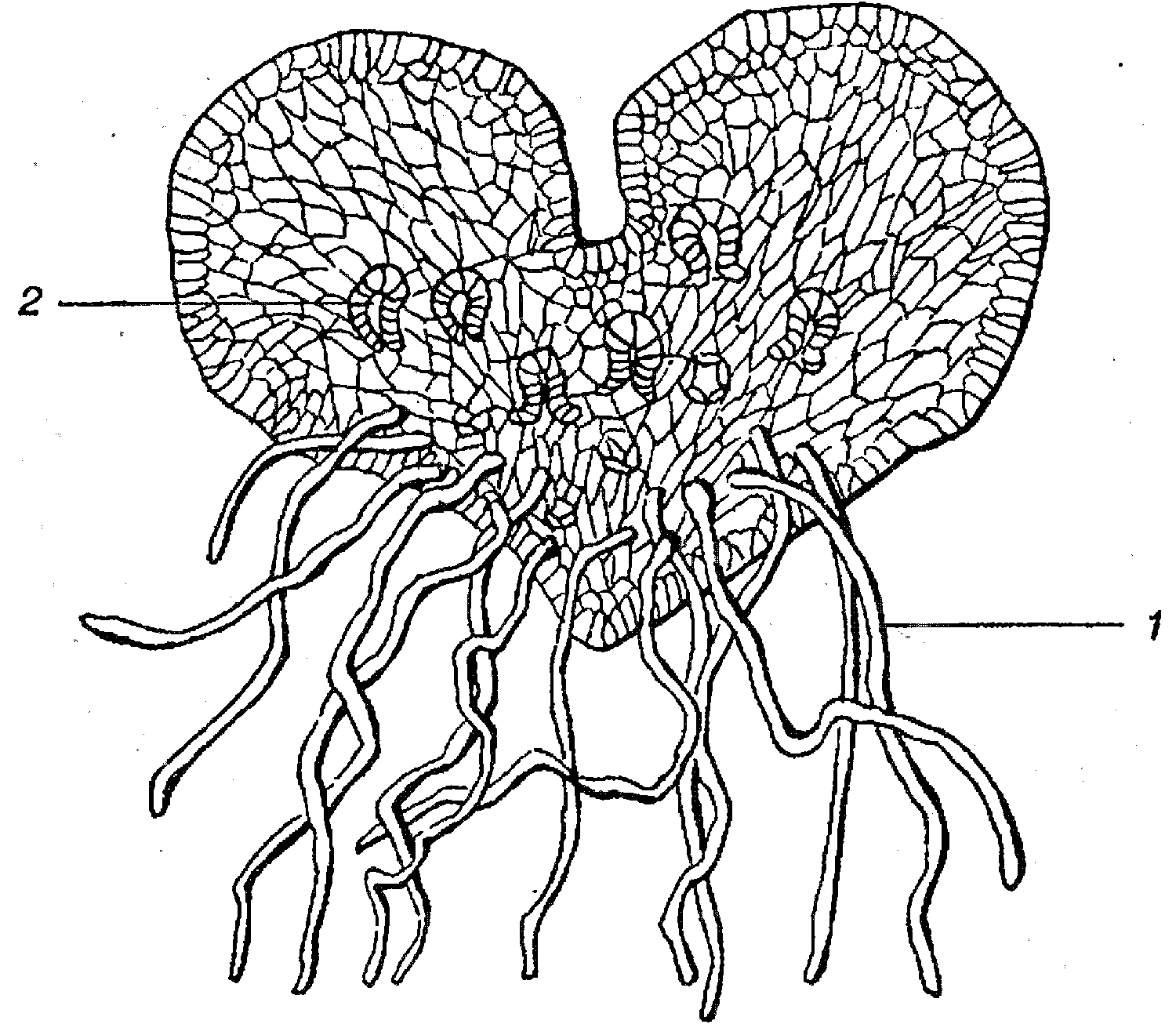
Fig. 3. Fern overgrowth.
Seed plants also have an alternation of generations, but outwardly it does not manifest itself. The gametophyte develops at the expense of the sporophyte and inside it. So, in gymnosperms, the development of gametophytes occurs inside closed female cones, and in angiosperms, inside a flower.
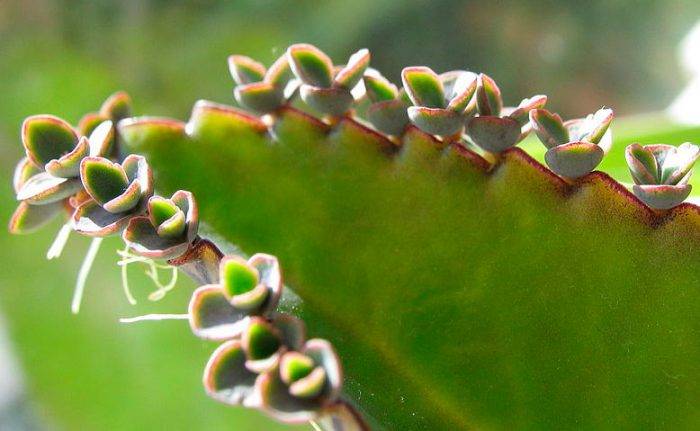
Mustache reproduction


You can propagate a mustache for an episode, braided saxifrage, chlorophytum, tolmiya.
At the ends of the shoots of such plants, small daughter plants (whiskers) appear.In the event that they have roots, then the mustache is simply carefully separated and planted in a moist soil mixture. A mustache without roots must be rooted in the same way as when grafting.
Reproduction of spore plants
Spore plants are plants that are characterized by spore reproduction.
Spore plant organisms are:
- Lower: algae;
- Higher: mosses, moss, horsetails, ferns.
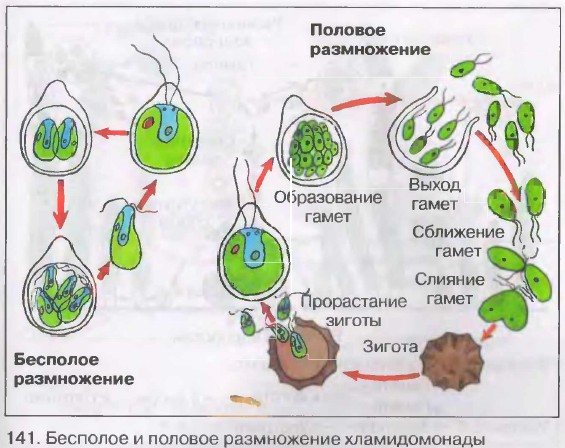
Reproduction of algae.
- Vegetative: algae reproduce in such a way that parts of them are accidentally separated from the mother's body due to strong currents or the influence of animals;
- Spore: spores of algae are mobile with flagella (zoospores) and motionless; inside the mother cell, a lot of spores are formed, which then go outside into the aquatic environment;
- Sexual: sexual reproduction is activated only when unfavorable conditions occur for adaptation to changing external conditions; gametes from the gametophyte converge in the aquatic environment and form a zygote, from which a new plant is formed.


Reproduction of algae:

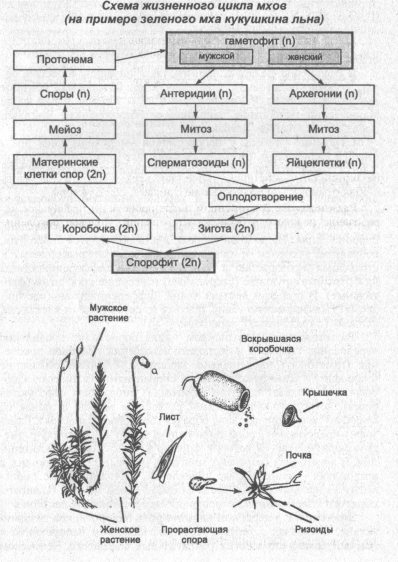
Reproduction of mosses. Moss has a pronounced alternation of generations. The dominant generation is the gametophyte. In the cuckoo flax, in wet weather, sperm from the male moss travel to the egg cell on the female moss. The former zygote becomes a sporophyte - a box on a leg. There, spores are formed, which are then thrown to the ground. Male and female mosses - gametophytes - grow from them.
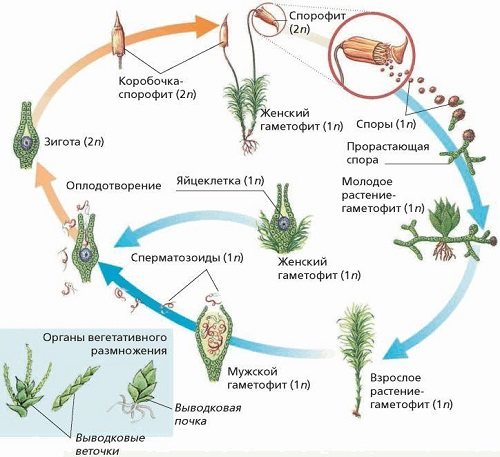

Moss Life Cycle:
Reproduction of lymphoids. The dominance of the sporophyte over the gametophyte is already noticeable in the life cycle of lycopods. On the green organism - sporophyte - sporangia are formed with many spores inside. The spores form the gametophyte of plants, which is called an overgrowth in lymphoids. There the male and female genital parts are formed, which produce gametes. They merge in wet weather to form a sporophyte.

Life cycle of lymphoids:

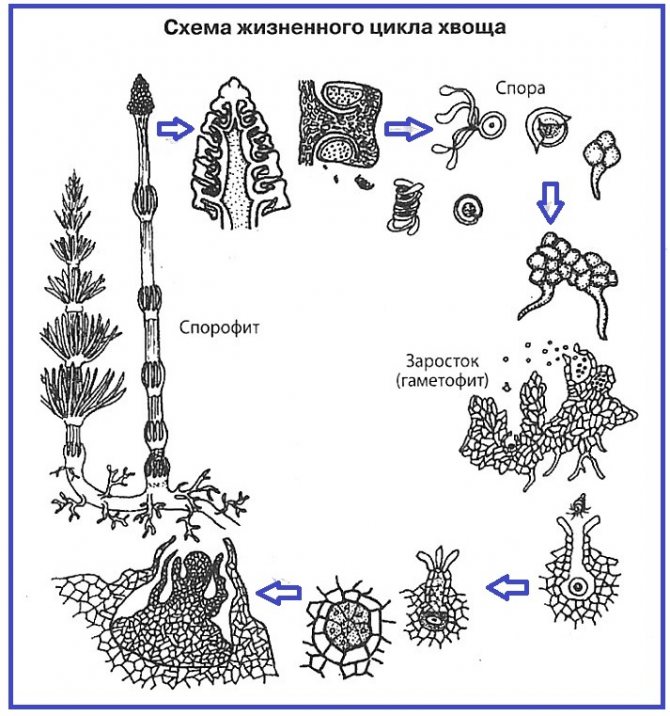
Reproduction of horsetails. Further, in all plants, the sporophyte will be the dominant generation. The reproduction of horsetails repeats the reproduction of lycopods. Spores are formed on the sporophyte, from which an outgrowth - gametophyte - grows with female and male gametes.
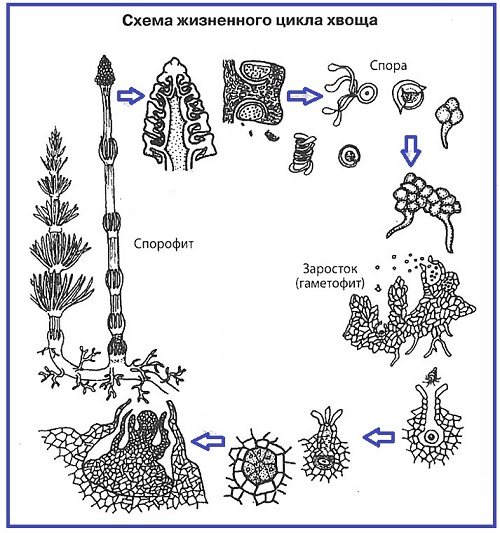

Horsetail life cycle:

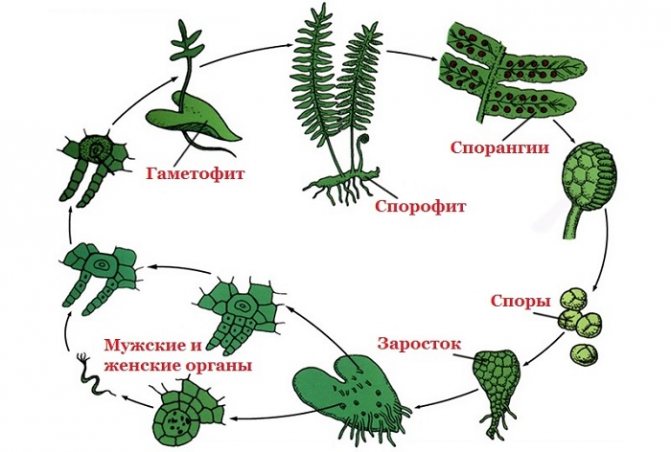
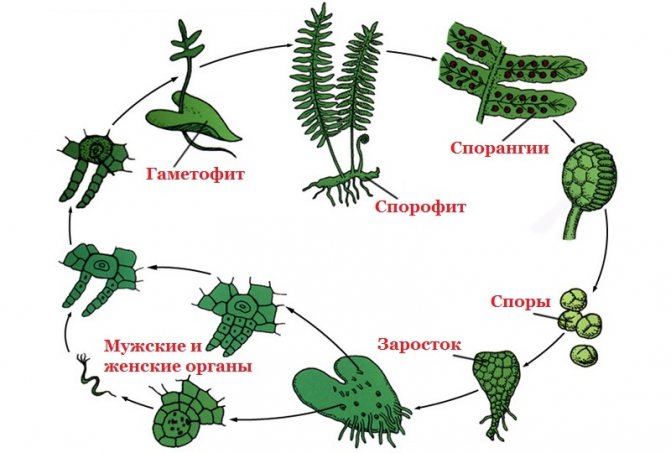
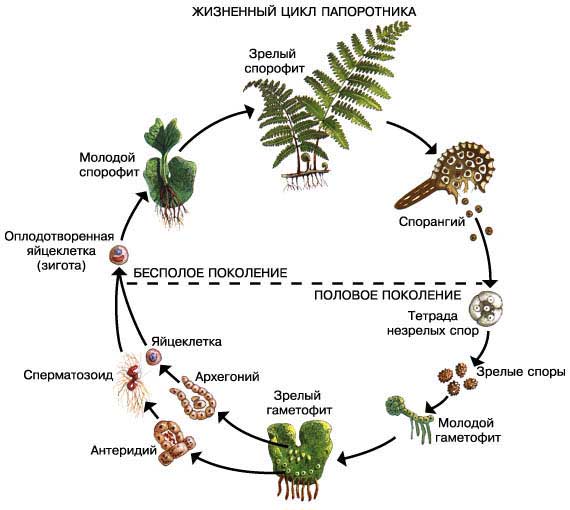
Reproduction of ferns. The dominant generation of ferns is also sporophyte. Sporophyte is a plant with leaves, on the underside of which brown tubercles are formed - sporangia. Spores form a gametophyte - an outgrowth. Male and female cells are formed on it. When fertilized, they create a zygote, from which a sporophyte develops.
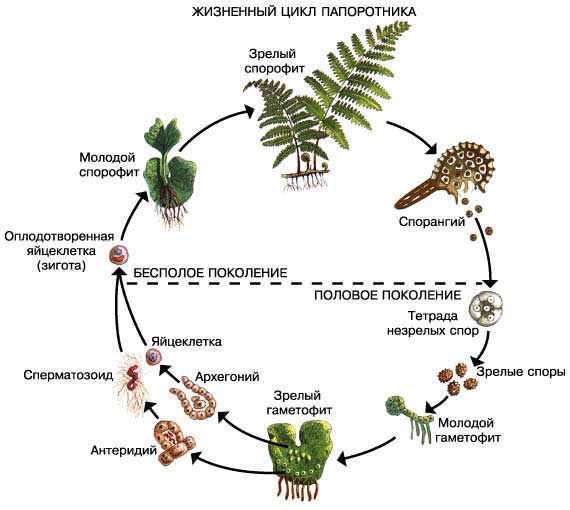

Fern life cycle:

Thus, the reproduction of lower and higher spore plants is different. The lower spore plant organisms are characterized by a choice between asexual or sexual reproduction. Both types of reproduction are rare. Higher spore plants are characterized by a change of generations with a predominance of gametophyte (mosses) or with a predominance of sporophyte (moss, horsetails, ferns).
Reproduction by division


You can propagate violet, arrowroot, asparagus, fern, sansevieria, calathea.
When growing, these plants are able to form rosettes (small daughter bushes). In this regard, such a plant can be divided.
It is recommended to propagate by division in spring or June. The mother plant is removed from the ground, the soil is removed and the daughter part of the plant is carefully cut off or broken off. In this case, you need to cut where the daughter and mother flower are connected. The cut should have a healthy growth point, as well as developed roots. They are planted in a moist soil mixture. Before a young shoot appears and full rooting occurs, the soil must be constantly moist. And the plant also needs to be protected from direct rays of the sun.
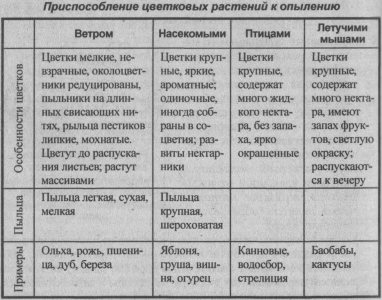
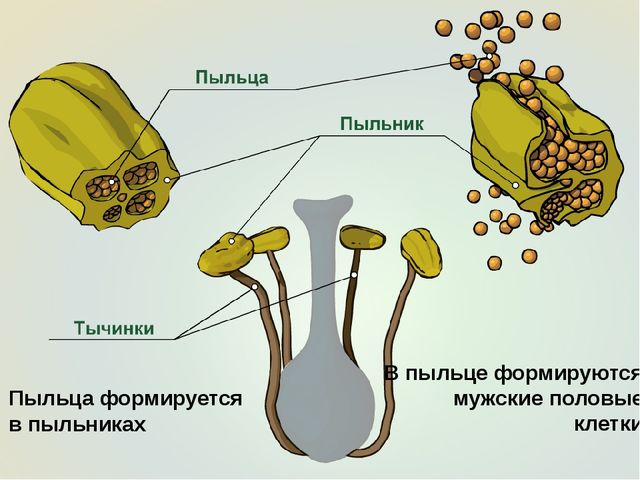
Pollination of plants
❖ Pollination - transfer of pollen from the anthers of the stamens to the stigma of the flower pistil; typical for seed plants. It occurs with the help of wind or insects, as well as humans (for breeding or production purposes).
❖ Pollination methods:
■ self-pollination - occurs in one bisexual flower and does not depend on weather conditions and intermediaries (example: barley);
■ cross-pollination: pollen is transferred to the stigma of the pistil of another flower of the same or a different plant (examples: rye, corn). Cross-pollination of plants increases the level of heterozygosity of the offspring, which makes it possible to better adapt to constantly changing environmental conditions.


Reproduction by spores
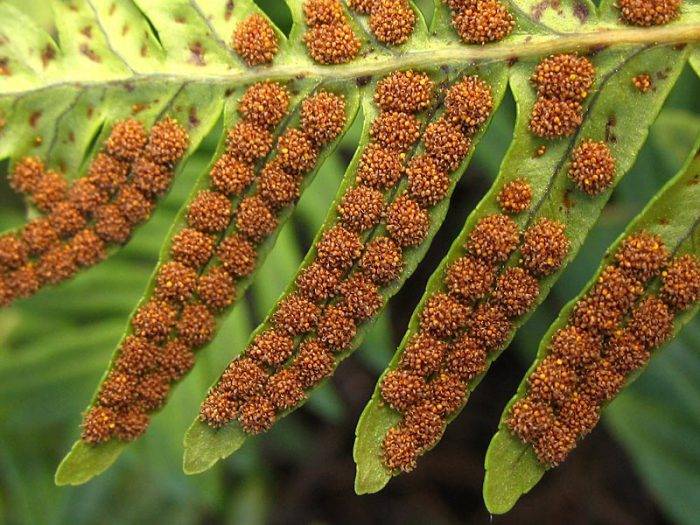


Fern can be propagated by spores.
This method is quite difficult, but fern lovers can try it.
With proper care, spores appear on the seamy side of adult leaf plates. If desired, such disputes can be bought in the form of mixtures of different or one type. To plant spores, you need special soil, which includes crushed brick chips and peat mixture.
The substrate is poured into a pot, which should be small, low and wide. Smooth its surface and compact slightly. After that, spores are evenly distributed on the surface of the soil. Cover the pot with glass on top, and then place it in the water poured into the container. To improve the result, instead of tap water, it is recommended to use thawed or rainwater (it is softer). Spores should be placed in a dark and warm place, while making sure that there is always liquid in the container. The first shoots can be seen after about 4–5 weeks. You should remove the cover from the pot after 4–8 weeks, after the seedlings get stronger. Grown plants need a pick, which is made in special trays for germinating seeds. The grown seedlings need to be planted in separate pots.
Care of cuttings
A suitable temperature for normal rooting is 20-25 degrees.
During rooting (and the rooting time for each plant is different, see the table below), the cuttings are periodically sprayed with warm water 2-4 times a day. When spraying, an epin solution can be added to the water, which promotes faster root formation.
After a certain time, callus begins to appear at the end of the cutting, and then the roots themselves.
After that, the buds of the cuttings come into action, shoots begin to appear. After the shoots grow a little, the cuttings begin to harden. To do this, once a day, the greenhouses are opened for a while (if the pot, then the package is removed). With normal growth of shoots, young plants are ventilated more often and for a longer time. And then the greenhouses are completely opened (approximately the end of August - the beginning of September).
If the cuttings are well rooted, then (in deciduous trees) in the fall they can be planted in a permanent place in the garden. If not, then it is better to leave it in a greenhouse until spring.
In slowly growing conifers, it is better to leave cuttings in a greenhouse for growing for 2-3 years.
Seed propagation
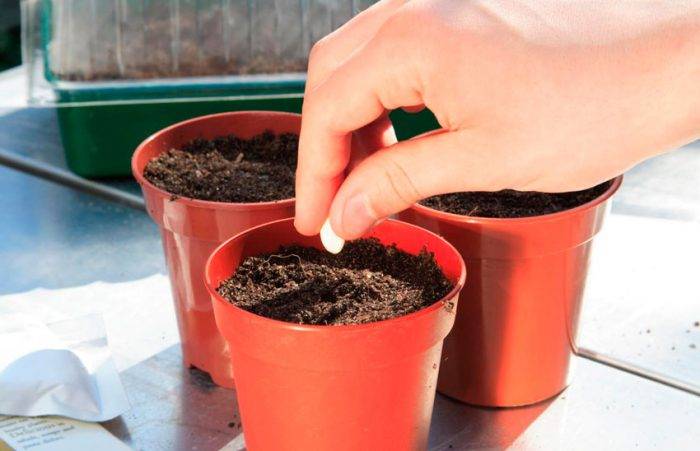


Seeds can propagate several types of cacti, primrose, fuchsia, cyclamen, coleus.
Houseplants are rarely propagated by seeds, because this is a rather complicated method. However, if you wish, you can still try to grow a spectacular plant from a tiny grain. Also, thanks to this propagation method, it is quite possible to get a new plant shape (for example, with a different color). It is recommended for beginners to choose annual plants for the first sowing, as they are relatively easy to grow.
In March – April, seeds of rapidly germinating plants are sown, and in the last winter weeks, those that germinate for a long time. If there is a thick skin on the seeds, they will need preliminary preparation, so they can be doused with freshly boiled water or placed in a liquid for several days.You can also treat the seeds with aloe juice. This will speed up germination as well as bring flowering closer.
Before sowing, the soil must be warmed up in the oven. A dredge mix consisting of sand and peat, which are taken in equal proportions, is suitable for this. You can add a small amount of vermiculite. A ready-made soil mixture intended for growing seedlings is also suitable for sowing.
Fill the pot or tray with soil, level the surface and compact slightly. Spread the seeds over the surface of the substrate (not thickly) and sprinkle them on top so that they look slightly out. Water with a watering can with a strainer or a sprayer. Cover the container with glass or foil on top. Provide the seedlings with the required temperature regime, as well as the desired level of lighting (this information can be found on the package).
Taking care of the planted seeds is easy enough. They only need to arrange systematic ventilation, as well as ensure regular watering with a sprayer. After the seedlings appear, the shelter is removed, and the container is placed in a well-lit place.
Seedling picking


In order for the plant to have powerful roots, the seedlings must be dived. As a rule, this procedure is carried out 1 to 3 times. There are flowers that do not need to be dived, and some, on the contrary, need to be dived 5 or even more times. The first pick is made after the formation of 1–2 true sheets. With each subsequent transplant, a substrate is used that is more saturated with nutrients.
You can use a peg, pencil or pen to make a hole for a seedling. Insert it to the required depth and then pull it out. After that, you can plant the seedling, while the soil mixture should be wet, and watering after planting must be done with a sprayer. To make the seedlings take root faster, they are sprayed with a solution of phytohormones, and then covered with glass or film.
All plant propagation methods
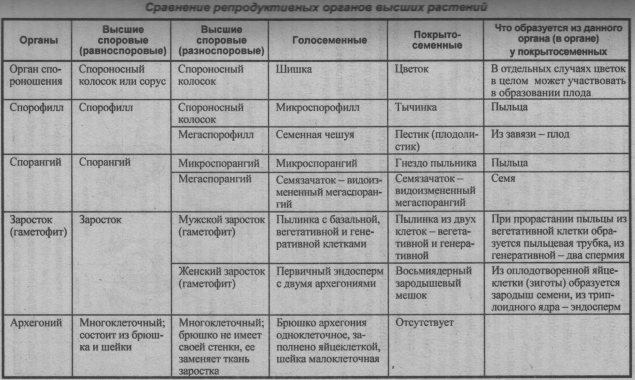
Sexual generations of plants
In the life cycle of higher terrestrial plants, sexual and asexual generations alternate naturally (see, for example, diagrams).

< Asexual generation presented sporophytes. Sex generation presented gametophytes.
Sporophyte - the organism of asexual diploid generation of plants, on which disputes... ■ Sporophyte is formed as a result fertilization - the fusion of the egg with the sperm (or sperm) and the subsequent development of the zygote and embryo. ■ Sporophytes are the predominant organisms in all higher plants (except mosses).
❖ Gametophyte - a haploid organism of the sexual generation of plants in which gametes are formed. ■ The gametophyte can be bisexual, ie. can carry male (antheridia), and female (archegopia) organs of sexual reproduction (gametangia), and same-sex - male or female. ■ After the sexual process, a zygote is formed from the gametes, from which the sporophyte develops.
Features of the structure of gametophytes: ■ with isomorphic generational change gametophyte individuals are outwardly indistinguishable from sporophyte individuals; ■ with heteromorphic generational change individuals-gametophytes differ sharply from individuals-sporophytes.
Gametophytes of mosses and ferns: ■ mosses - leafy plants; ■ ferns - overgrowths.
Gametophytes of higher plants: ■ male gametophyte - pollen graingrowing in pollen tube with education sperm; ■ female gametophyte -, haploid multicellular endosperm from archegonium (in gymnosperms) or seven-celled embryo sac (in angiosperms).
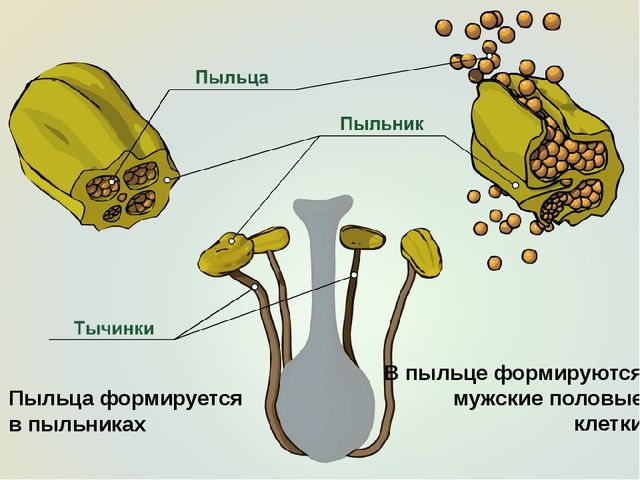
Pollen - a set of pollen grains (dust grains) formed in anther nests (microsporangia) of holo- and angiosperms.In gymnosperms, it is formed in the sporangia of anther (male) cones, in angiosperms, in the anthers of stamens.
Pollen grain - male gametophyte of the seed plant; begins its development from a microspore in a microsporangia and exhausts it after pollination, i.e. after transfer to the pollen chamber, the ovule (in gymnosperms) or on the stigma of the pistil (in angiosperms).
The pollen grain is covered sporoderm, the outer layer of which (exine) has high strength and resistance to external factors, and the inner layer (intina) consists of fiber and pectin substances. By the time of pollination, a pollen grain consists of two (or more) cells - one generative and one (in angiosperms) or several (in gymnosperms) vegetative cells.
The vegetative cell gives rise to pollen tube, and the generative divides to form two sperm, which are delivered through the pollen tube to the archegonia of female outgrowths (in gymnosperms) or to the embryo sacs (in covered-nominal ones).
Pollen production: a diploid mother cell of a microspore present in the pollen sac (sporangium) of the anther of the flower macula, meiotically divides into four haploid cellsmicrosporeswhich after mitotic divisions turn into two-celled pollen grains.
❖ Embryo sac formation (occurs in ovulelocated in the pistil of a flower):
■ the diploid maternal cell of the megaspore, which is present in the ovule, meiotically divides into four haploid megaspore cells, three of which are destroyed;
■ core the fourth megaspore, the most distant from the pollen entrance, three times mitotic divides (8 daughter nuclei are formed); three daughter nuclei remain at each of the poles of the megaspore and are separated by thin cell walls, separating into polar cells, and two nuclei (one from each pole) move to the center of the megaspore and then merge, forming diploid central cell nucleus;
■ one of the three cells at the pole closest to the pollen gate becomes ovum, and its two adjacent cells are companion cells;
■ the entire formed system of seven cells is embryo sac... Three cells of the embryo sac located at the pole opposite to the pollen passage (antipode cells), take part in providing the system with nutrients for some time, and then die off.
Possible mistakes


The plant should not be placed above the heating system, as the hot air will burn the foliage.- It is impossible to transport a flower in winter without appropriate shelter.
- Starting from April, you cannot put a flower in a place where there is a direct sun, since its rays will burn the foliage.
- Do not overdry a clod of earth to a desert state. The ground should be moderately moist.
- Without top dressing, there will be no abundant flowering in the summer.
Time suitable for breeding at home
The features of the entire plant world indicate that the best time for reproduction is spring and spathiphyllum is no exception. In the spring, even the mistakes of a beginner grower may not cause much harm to the plant. Although the same mistakes made in autumn or winter can lead to a sad experience - the death of a plant.


So, based on the experience of flower growers, we can say with confidence that the best time for the reproduction of spathiphyllum is spring and early summer. The main thing is to transplant before flowering.
Interesting! If your "Women's Happiness" does not bloom, then sometimes this may indicate that the flower has not been transplanted for a long time and the children have not been separated from it. Many gardeners noted that if the plant has not been divided for a long time, then the lower part begins to "bare", and the spathiphyllum itself ceases to bloom. If the separation of children occurs, then the flower begins to actively build up the green mass.
Cutting methods


There are three types of stem cuttings:
- Lignified.
- Semi-lignified.
- Green.
Different plants are propagated by different types of cuttings. So lignified, for example, propagate grapes, conifers, poplar and willow. This type of cuttings is usually harvested in spring or late autumn, i.e. when plant growth has not yet begun or has already stopped. Typically, the length of cut shoots for these cuttings is 250-300 millimeters. In this case, it is important that there are at least 3 nodes with buds on the shoot. When they are planted, 2-3 buds are left above the ground, after which new shoots and leaves are expected to appear. If the cuttings were harvested in the spring, then they can be planted almost immediately. They will quickly take root. If the sprouts were harvested in the fall, then they are first placed in wet sand, after which they are left to be stored in a cold room until spring.
As for semi-lignified cuttings, they are stem fragments with unripe wood and leaves. This is the most common method of grafting. The photo below shows an example of such a cutting. They are usually harvested during the budding period, after which they are immediately planted in a place prepared in advance. Such cuttings propagate, for example, lilacs, shrub roses, clematis, mock orange, tamarix. The length of such shoots is 80-140 millimeters. They should have at least 3 kidney nodes. When planted, they are deepened by 35-45 millimeters. The leaves from the buds, which will be immersed in the ground, are cut off. Such cuttings are used if reproduction by lignified shoots was unsuccessful. They take root better, but are more sensitive to low temperatures, due to which they may even die. Therefore, for the winter they are recommended to be transplanted into a pot.


Green cuttings are used primarily for the propagation of indoor plants. Nevertheless, if certain requirements are met, then with the help of such shoots, some shrubs and even trees can be grown. Harvesting green cuttings is usually carried out during the period of active plant growth. As a rule, this is May or early June. A prerequisite is the presence of at least one bud on the sprout. Therefore, shoots with an apical bud are usually used. Although, sometimes cuttings taken from the middle of the stem, with several axillary leaves, are suitable. If the leaves are too large, then a part is cut off from them so that less moisture evaporates. Stem cuttings cannot propagate plants in which growth occurs at the expense of one apical bud, for example, a palm tree. It is not yet possible to propagate by green cuttings an annual flowering plant without a stem, such as a fern. Because their shoots usually die off after flowering.
What plants are propagated by green cuttings?
The question of whether it is possible to propagate a particular plant with a cuttings is of primary concern to novice gardeners. Indeed, not every plant lends itself easily to vegetative propagation.
It depends on the ability of the perennial to quickly form adventitious roots. Green cuttings of the following popular ornamental crops will take root more or less well:
- Actinidia
- Barberry
- Euonymus
- Privet
- Weigela
- Hydrangea
- Action
- Derain
- Spruce
- Honeysuckle
- Viburnum
- Keriya
- Cotoneaster
- Clematis
- Colquitia
- Bloodroot
- Juniper
- Rhododendron
- Rose (small-leaved varieties and species)
- Lilac
- Scumpia
- Currant
- Spirea
- Thuja
- Forsythia
- Chaenomeles
- Chubushnik
Propagation of angiosperms
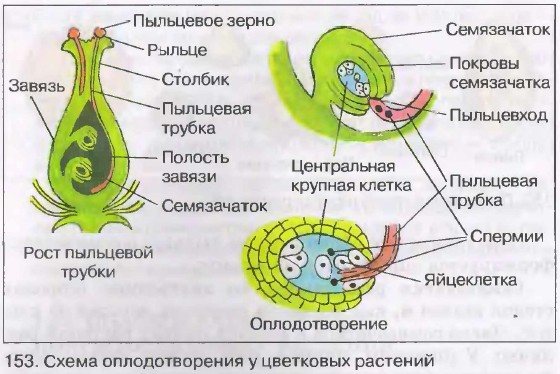
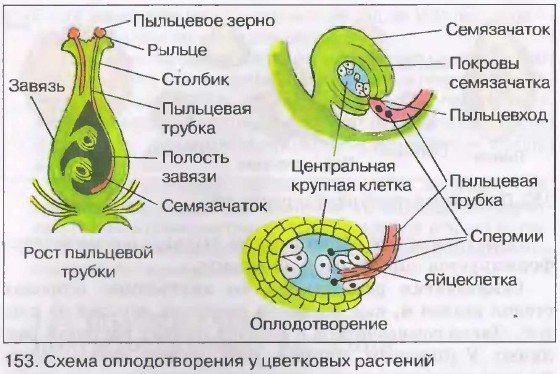
Angiosperms are the pinnacle of evolution. For reproduction, they have developed special organs: a flower and a fruit. The bright flower attracts pollinating insects, which facilitate the transfer of pollen between plants. The pericarp fruit protects fragile seeds from adverse effects.
Male and female gametophytes in angiosperms are strongly different:
- Male.The male gametophyte is called pollen and is located on the anther of the stamen. It is a ball with a two-layer shell: the outer one is uneven and the inner one is smooth. Irregularities are needed for better fixation of pollen. There are two cells under the membranes: vegetative and generative.
- Female. The female gametophyte is called the embryo sac and is located in the ovule of the pistil. It has a micropyle inlet for pollen. Opposite the micropyle is the ovum, and in the center is the central cell.

Male gametophyte:

Female gametophyte:
The process of transferring pollen is called pollination. Pollination of plants happens:
- Self-pollination: pollen falls on the stamens of the same plant organism (peas, beans); high probability of pollination, but little variety of offspring;
- Cross-pollination: pollen falls on the stamens of another plant (corn, watermelon); high diversity of offspring, but low probability of pollination.
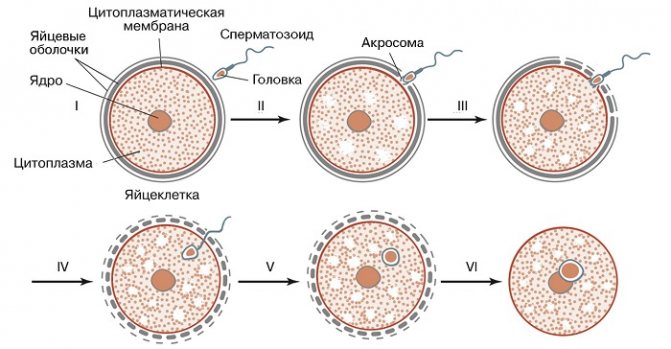
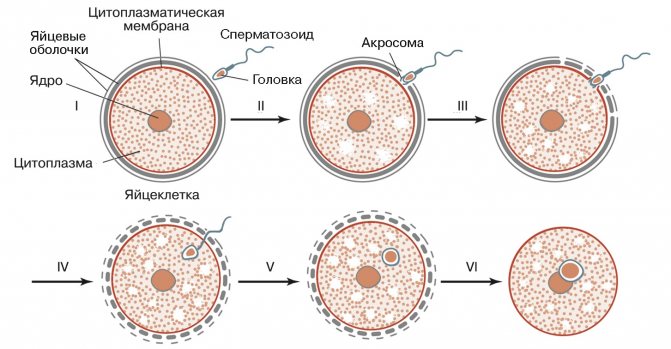
By means of pollinating insects (zoophilia) or wind (anemophilia), the pollen is separated from the stamen and flies over the stigma of the pistil. The vegetative cell lengthens and becomes a pollen tube. It grows and makes its way to the embryo sac. The generative cell is divided into 2 immobile sperm. One of them connects with the egg, forming a zygote. The second unites with the central cell, further forming the endosperm. This process is called double fertilization, that is, two sperm fuse with two cells.

Double fertilization:

Further, an embryo develops from the zygote, which is surrounded by an endosperm with a supply of nutrients. The fetus is gradually formed.
FAQ
Why transplant a plant annually?
This must be done in order for the plant to bloom profusely in the summer. In this case, the pot should be exactly the size of the root system of the spathiphyllum.
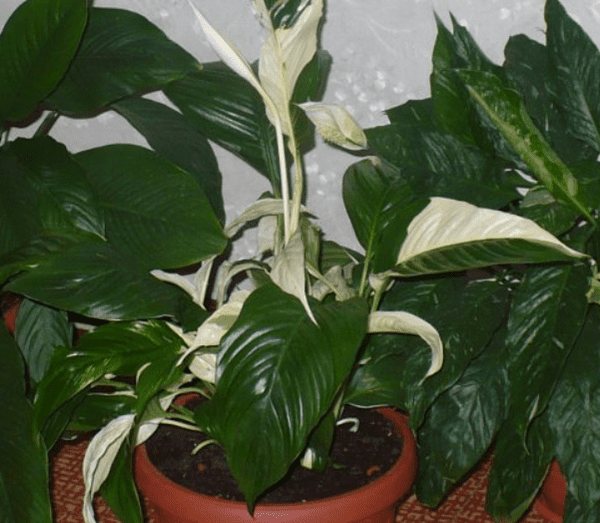


Why remove dead plant parts when dividing the rhizome?
They are removed, as there may be infections in their sinuses and this will be visible when removed. Also, when decomposing, they can harm the plant, and what is important is the appearance of the plant. Decayed and dry parts of the leaves will not add beauty to it.
What do the brown edges of the leaf mass of spathiphyllum indicate?
This indicates that the indoor air is very dry. This can be corrected by placing the container with the plant in a wide pallet on expanded clay. The brown tips will not turn green, but it will stop them from appearing in large numbers on the bush.
Examples of plants that can be propagated by certain layers
Horizontal and arcuate layering reproduce: currants, including ornamental, gooseberries, grapes - fruit, Amur and maiden, chokeberry, yoshta, clonal rootstocks of all fruit crops, hazel, junipers, yews, spruce, fir, forsythia, wisteria, wood pliers, all spiraea, honeysuckle (Tatar , shiny and curly), mock orange, action, weigel, lilac, barberry, lemongrass, actinidia, magonia, hydrangea, cinquefoil, clematis, colquitia, privet, cotoneaster.
Vertical layering almost all plants reproduce, except for conifers.
Apical - plants of the genus Raspberry.
Air - for any plants that are problematic to bend to the ground, or when you want to immediately get a fruiting plant, for example, a lemon.
Features of planting children


First of all, when propagating a plant, you need to have the necessary soil at hand.
Since in its homeland a flower grows in fallen leaves and rotting branches with a small amount of charcoal, then at home you need to have a similar soil at hand.
You can purchase soil for orchids and add a little deciduous soil there, or immediately purchase soil for Aroids.
We must not forget that the earth must be loose and let water pass well, feeding the root system.
The capacity where the flower is planted must be accurately matched to the root system, since the spathiphyllum will not bloom in a large pot until the roots are completely entwined with a clod of earth.
Also, in a large pot there is an opportunity to fill the roots of the flower, and as a result, get rot on the roots.
Important! It is necessary to plant a flower so that the root collar is at the same level.
In what conditions do you need to grow cuttings


The ability of freshly cut cuttings to form a root system largely depends on temperature and climatic conditions. Root formation is influenced by many chemical processes. At elevated temperatures, various reactions are more active, therefore, roots appear faster under such conditions.
if the entire stalk is warm, then nutrients will also be spent on the growth of the tip, which can lead to the fact that the stocks of necessary substances in the stalk are used up faster than it has time to root normally. For this reason, when growing shoots, the air temperature must be kept at a low level in order to retard the growth of the tip. To accelerate the emergence of roots, the temperature in which the lower part of the cutting is contained, on the contrary, should be increased.
The temperature regime for growing depends on the quality of the cuttings and on their response to water loss. For green shoots, it is recommended to keep the temperature around 20-21 degrees. A fogging unit can be used to create these climatic conditions. As for lignified cuttings, they usually multiply in open, well-heated ground. Even if the weather is freezing outside, you need to make sure that the air temperature does not drop too low.
Semi-mature, herbaceous, and evergreen shoots require moist and warm conditions to reproduce, which can be created in a variety of ways. For example, place in pots in which the cuttings will be grown in the substrate. In this case, the containers will be covered with plastic wrap. A vessel with water is installed next to them. You can use large-diameter pots for the same purpose, which are filled with wet peat. But there is a chance to harm the plant by excessive moisture. In addition, under such conditions, the sprouts can be damaged by fungal diseases, which, in turn, can lead to their death. It is best to grow them in cold greenhouses and chambers, as well as in special closed containers.
Seeds
The propagation of indoor plants by seeds is carried out less frequently than in other ways. This method is more complicated, laborious and time consuming. Growing from seeds has other features as well. Many varieties of perennial indoor flowers lose their attractiveness and specific characteristics during seed reproduction. As for annuals, they reproduce quite easily by seeds. It is a little more difficult to grow cacti, saintpaulias, ferns by seed method.


When propagated by seeds, the grown plant may change the shade and shape of the leaf plates, the color of the flowers.
Preparation
The main condition for the successful reproduction of plants by seeds is their freshness. For seeds of most plants, germination decreases during long-term storage. Sowing time is determined by the rate of germination: for fast germinating seeds, the optimal planting time is March or April.
Seeds with a hard shell (palm, camellia, asparagus and others) must be prepared for planting in advance. Seed treatment is carried out in various ways. Can:
- scald the seeds with boiling water;
- soak in water for 3-5 days;
- file the skin with a file, cut with a knife;
- soak the seeds in aloe juice.
Before sowing, the soil for disinfection is poured with boiling water 1-2 times. The pots or trays are then covered with a suitable soil substrate (usually a mixture of peat and clay).It is better not to sow seeds in ready-made commercial soil for indoor flowers. Large amounts of nutrients contained in such soil inhibit the germination process.
Sowing


When planting a small number of plants, seeds are sown in pots, otherwise it is more convenient to use a tray.
- On a tray. The soil mixture poured into the tray is leveled with a plank or other improvised means, slightly compacted. Seeds are evenly distributed over the surface, sprinkled with a thin layer of soil (the thickness should be equal to the size of the seeds). A sieve can be used to distribute the soil evenly over the surface. Then the crops are evenly watered, the container is covered with glass or placed in a greenhouse.
- Into the pot. High-quality drainage is laid out on the bottom of the pot (fine gravel, coarse sand, pebbles), and the soil mixture is poured on top. The soil is leveled, tamped. Seeds scattered over the surface are covered with a layer of soil. Watering is carried out using a spray. Then the pot is covered with foil or glass, placed in a greenhouse.
If the sowing of small seeds was carried out, the distance between the soil and the glass should be about 1 cm, when planting large planting material - 1.5–2 cm.
Care
Crops need to be provided with periodic bottom watering or spraying, regular ventilation, and removal of condensation from glass or film. After the emergence of shoots, the glass can be removed, and the container with the shoots can be moved to a brighter place, but only with diffused lighting.
Seedling picking
A pick is necessary to form a strong root system. The procedure is usually carried out 2-3 times, and in each case a more fertile soil mixture is taken. Pry the seedling with a pointed peg, lift it slightly, transfer it to another container with wet soil, spray it, place it under glass for a couple of days.


Some plants need to be dived 4–5 times, and there are species that cannot stand this procedure at all.
After the seedlings are well rooted and germinated, they are transplanted into pots with suitable soil and placed in a permanent growing area.
Why can cuttings take root badly?


There may be several reasons. Let's list the most common:
- Unhealthy stems were taken for harvesting.
- When planting, untreated tools and dishes were used.
- Blunt cutting tools were used. To get sharp and even cuts, the knife must be sharpened well enough.
- Poor quality soil with poor air and water permeability was used. It is advisable to use peat mixed in half with pre-calcined river sand for this purpose.
- Adequate moisture was not maintained until roots emerged. For this, you can use the spraying method. Rooting under film or glass will also be helpful.
- There was insufficient lighting, or, conversely, the sprout was in direct sunlight.
- Poor thermal conditions were present. It is best for planted cuttings to maintain a temperature of 21-24 degrees. In this case, it is desirable to provide heating in the zone of formation of new roots.
Reproduction methods


Each houseplant has its own way of reproduction.
There are many ways to breed indoor plants:
- offspring;
- children;
- layering;
- dividing the bush;
- stem cuttings;
- parts of a leaf or leafy cuttings;
- seeds.
Most often, the reproduction of indoor plants is carried out by cuttings and the seed method.
Features of asexual reproduction
In nature, angiosperms reproduce asexually. Plants have learned to adapt to adverse conditions, and they do not reproduce in the same way. Variants with which asexual occurs the formation of daughter specimens in nature and during cultural cultivation:
- disputes;
- shoots;
- cuttings;
- layering;
- root shoots;
- tubers;
- creeping mustache;
- thalli or pieces of the body (in algae);
- bulbs;
- air bulbs;
- leaves;
- roots.
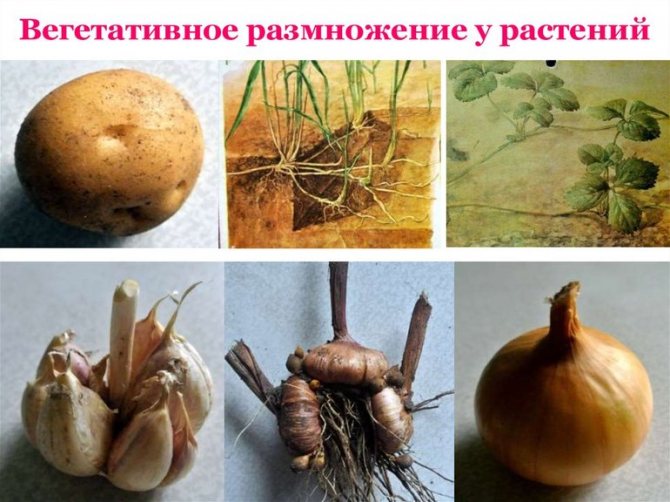


Gardeners and florists choose those methods that are characterized by high survival rate and allow you to get offspring with minimal labor and time.
When selecting, they use special diagrams and tables that are compiled by employees of the research institute. A part of a plant is considered a separate organism from the moment when it can independently carry out vital processes.
At this time, the young specimen can be separated from the main one and transplanted to a suitable place.
The plant obtained as a result of separation has the same species and varietal characteristics as the parent. It can be considered a clone. The advantage of this dilution is accelerated development of a seedling, flower or bush compared to growing from seed. Fruit or vegetable crops form generative buds earlier and yield faster harvest.
Indoor and garden plants grown from tubers, shoots or leaves, tolerate adverse factors better, and suffer less from diseases and pests. In addition, when reproducing from seeds, it is not always possible to preserve varietal characteristics, and as a result of cloning, they remain unchanged.
When is rooting of green cuttings carried out?
The ideal time for vegetative propagation of perennials is usually considered the beginning of summer (June - first half of July), when the plants are in the phase of active growth and they have enough strength to form roots. However, the specific timing of harvesting cuttings depends not only on the genus, but also on the species, and sometimes the variety of the plant.
May June
In May-June, cuttings of most shrubs are harvested, which bloom in spring or early summer.
June July
June-July is the “hottest” season for green cuttings. In the first half - mid-summer, conifers are cuttings, as well as many summer-flowering shrubs.
July August
In the second half of summer, it is not too late to start grafting those shrubs and trees that are capable of growing a new root system in a short time.
Green cuttings of lilac and clematis
In lilacs and clematis, the timing of cuttings is tied to the flowering period and the type of plant.
Benefits of plant propagation by layering over cuttings
The reasons why a gardener needs to propagate a plant can be very different:
- I want to plant a few more of the same plants or even create a hedge or a living wall (in the case of vines);
- fear of losing a single plant in case of adverse conditions;
- the desire to transplant a large bush to another place, but due to its large size, this event looks dubious;
- the need to replace an aged plant, etc.
But grafting, although not a very difficult science, but in some cases requires special preparation: a substrate (for example, clean sand), moistening, greenhouses with ventilation and the possibility of shading, containers, the use of phytohormones, and of course, some experience for cutting and preparation cuttings. And most importantly - supervision: humidification, airing, shading. So that the cuttings do not dry out, do not sop, do not catch some kind of fungal disease ...
People who have a lot of experience in grafting or are doing it professionally, perhaps, say: "That's me too, problems!"
Read more about grafting in our article Summer grafting of trees and shrubs - myths and real experience.
Of course, there are plants that are very easy to cut (root quickly even in water and also take root well). For example, cinquefoil, weigela, action. And you will have to tinker with others, but success is still not guaranteed.
This, oddly enough, is the Japanese quince (which reproduces well in itself by root suckers), tanning skumpia, conifers and even some types of spirits. The survival rate of cuttings is only 30-50%.
Sad, huh? In addition, any cuttings will require supervision in any case, and their rooting time is from 10-14 (in the fastest) to 60-120 days.
And the layers sometimes even turn out by themselves, if the branches lean too close in the ground. Therefore, before starting propagation by layering, check if you have any ready-made rooted shoots?
Or, instead, use existing root suckers, like those of a self-rooted lilac or quince. Moreover, they must be removed in any case, so as not to weaken the mother plant.
Important! In the case of Japanese quince, plants planted from offspring usually do not produce large fruits, although they bloom beautifully. So, if your goal is fruits, then it is better to tinker with cuttings, make layers or buy a varietal plant in the nursery.
Rooting of cuttings usually begins in the spring and takes place throughout the summer, while the growing season continues. In the end, you can just leave the branches to root until next year.
Layers are separated in spring or autumn at the usual time for planting and transplanting shrubs.
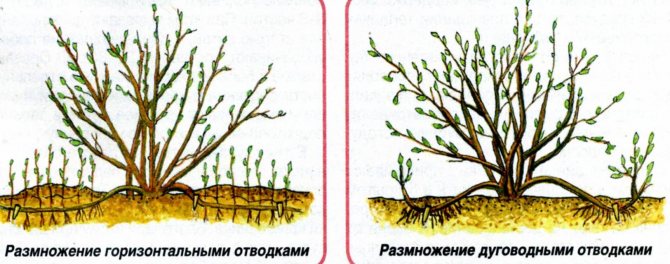
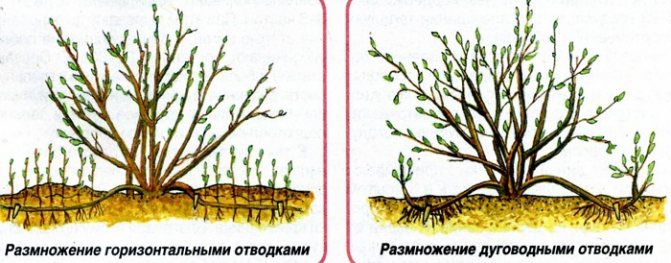
Layers are horizontal, vertical, arcuate, apical and even airy.
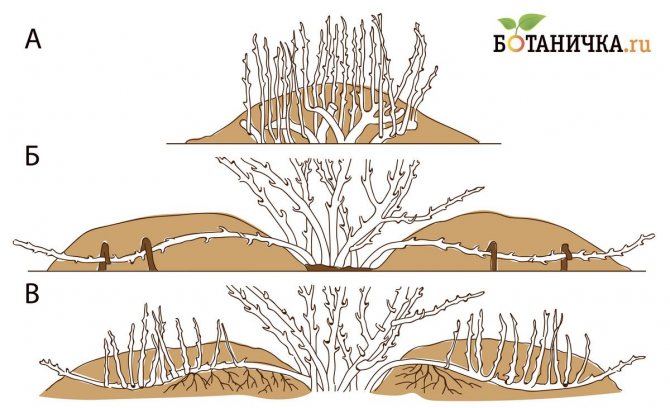

Fig. 1. Reproduction of plants by layering: a) vertical; b) horizontal; c) rooted horizontal layers
Reproduction of plants by arcuate layers
Arcuate cuttings are used for plants with not very flexible stems, or if you want to get a more developed plant at once. In this case, only one plant is obtained from each cut. The technology is the same as for horizontal layers, but in this case, the shoot is bent in an arc and pinned only in one place into a hole with humus. The end of the shoot is left in the air, tying it to a peg to get a more or less straight seedling.
Leaves are also removed only in the place that is intended for rooting. You can also overtighten it slightly to stimulate root formation by limiting the supply from the mother shrub slightly or by ringing the bark and making an incision.
A pebble is inserted into the incision so that it does not close. The use of phytogromone will also not be superfluous. Rooting can also be carried out in a technical pot of the appropriate size, dug into the ground and filled with humus. This will facilitate the process of transplanting the layering.
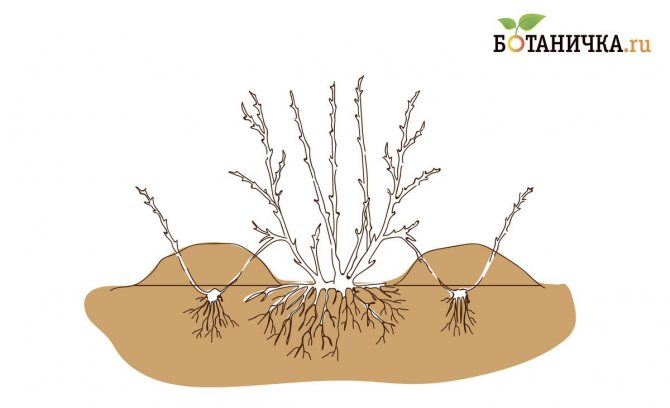

Fig. 3. Reproduction by arcuate layers
Reproduction of seed plants
Seed plants are also called gymnosperms. These plants are characterized by seed reproduction. Unlike spore plant organisms, gymnosperms reproduce not with the help of spores, but with the help of seeds. Unlike angiosperms, gymnosperms do not protect seeds with special formations - fruits.
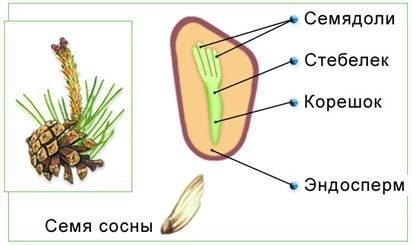
Female and male plant seeds can be distinguished with the naked eye: female seeds are much larger, since they carry a supply of nutrients that are enclosed in the endosperm. The female seed consists of the embryo, endosperm, and dense seed coat. Male seeds are more like pollen.
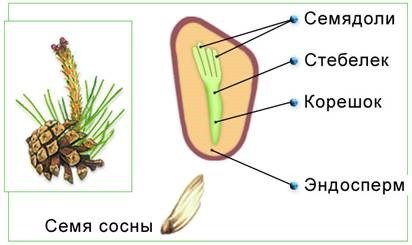

Pine seed structure:

It is customary to consider the reproduction of gymnosperms on the example of Scots pine. Pine is a monoecious plant organism, that is, both female and male cones are located on the same plant.
- Female cones: red, sitting on top one at a time; on the scales of female cones, two ovules develop, in which the eggs are located;
- Male cones: yellow-green, small, gathered in groups; on the scales of male cones, two pollen sacs develop, in which pollen and air-filled bubbles are located to facilitate flight.


Pine cone structure:


The pollen flies out of the male bump and meets the female. This is the pollination stage. The scales of the female cone are connected so that the pollen grains do not fly back. The pollen becomes a pollen tube, forming immobile, flagella-less sperm. They connect to the egg.A seed grows from the formed zygote. The cone lignifies, opens, freeing seeds for further spread.
In the life cycle of gymnosperms, sporophyte predominates. Sporophyte is an adult plant. It forms inside the seeds of the cones and then germinates when it hits the ground. Gametophyte - cones.
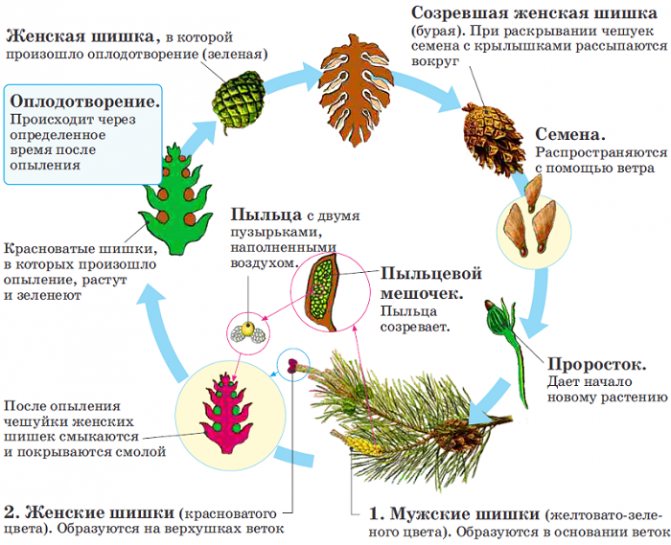

Life cycle of gymnosperms:
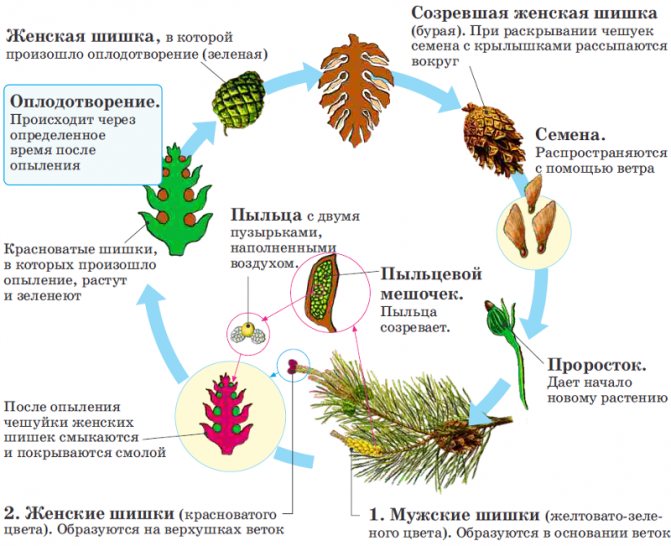

Also, vegetative reproduction is rare in seed plant organisms.
Vegetative propagation
Vegetative reproduction occurs with the help of vegetative organs: root, shoot. Unlike sexual reproduction, vegetative reproduction gives rise to identical individuals without diversity. This lowers the chances of survival in changing environmental conditions.
The cells of the parenchyma, the main tissue, are involved in vegetative reproduction. These cells are not specialized, therefore, in the process of development, they can give rise to any organ.
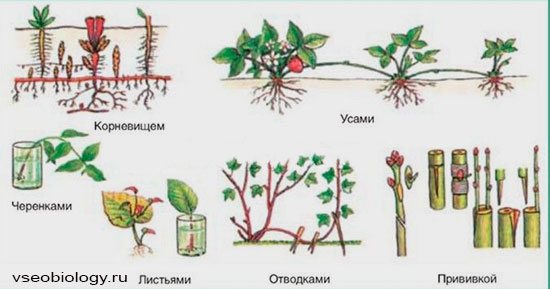
For vegetative propagation, plant organisms have developed a variety of ways:
- Horsetails and ferns reproduce by rhizomes - modified shoots;
- Gymnosperms reproduce by cuttings and cuttings;
- Angiosperms also reproduce with the help of modified parts: whiskers (strawberries), rhizomes (wheatgrass), tubers (potatoes), bulbs (onions).
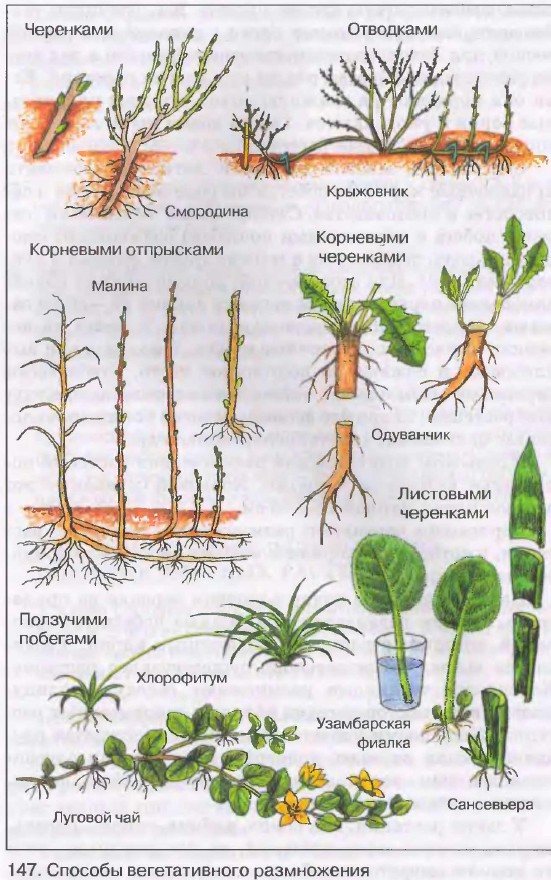

Vegetative propagation methods:
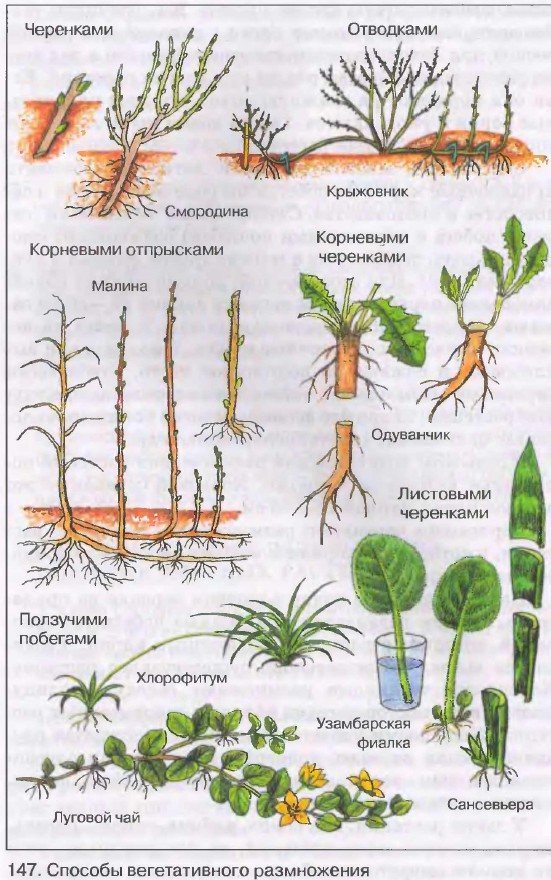

Vegetative propagation represents the development of new plants from various vegetative organs (stems, rhizomes, bulbs, leaves) or parts thereof.

Vegetative propagation is very widespread among all groups of ornamental plants, with the exception of annuals and true biennials (plants with a two-year development cycle), which do not vegetatively reproduce in natural conditions. All the variety of vegetative reproduction can be subdivided into natural and artificial.
Natural vegetative reproduction was formed during the long evolution of plant species and is a hereditary trait. This type of reproduction, both in vivo and in culture, is carried out using the following vegetative organs:
- rhizomes (cannes, irises, lilies of the valley, peony); mustache (strawberry, chlorophytum);
- bulbs (tulip, daffodil, hyacinth) and bulbs (bulbs that form in the axils of a leaf or inflorescence - white, bulbous, tiger lily); corms (gladioli, montbrecia);
- tuberous root (dahlia, daylily, chistyak);
- stem tuber (gloxinia, cyclamen);
- brood buds (bryophyllum and in such open field plants as bulbous bluegrass, hairy sedum, snow saxifrage).
Artificial vegetative reproduction can be divided into several basic techniques:
- division,
- grafting,
- layering,
- vaccinations.
Reproduction of flowering plants by corms.
The corm is an underground thickened stem that stores nutrients. Corms are formed in gladioli, montbrecia, acidantera.


Every year, a new daughter corm is formed at the base of each stem. The multiplication factor is thus in direct proportion to the number of stems. Under natural conditions, plants that form corms reproduce in this way, but if it is necessary to increase the number of newly formed organs, they resort to special methods (planting upside down or dividing the corms into parts). When propagating corms, it is very important to ensure that the source material is not contaminated. Usually, secondary shoots are formed between the new corm and the decaying old one - small daughter corms. Their number depends on the type of plant; in gladiolus, for example, up to 50 of them are formed.
Corms are dug out 40-45 days after flowering.During the autumn digging, corms are collected, dried (drying time - 3 weeks) and stored until planting in boxes or gauze bags at a temperature of 4 ... 10 ° C and an air humidity of 60
Propagation by bulbs.
The bulb is a modified, usually underground shoot of plants with a short flat stem (bottom) and fleshy colorless leaves (scales), adapted for storing nutrients. There are two types of bulbs, scarious and tiled, which differ in the way the scales form.
Filmy bulbs, such as those of daffodil and tulip, have succulent thickened scales, which are filmy leaf sheaths that cover each other and form almost closed concentric circles around the growth point. Each scale-like leaf develops an axillary bud.
Scaly leaves of scarious bulbs are very large and cover almost the entire bulb; they are not as easily detached from the base as the scales of tiled bulbs. Therefore, until new plants are formed, the incised scaly leaves of the scarious bulbs should be left undivided from the bottom. This principle is used in two breeding methods:
- cutting out,
- notching the bottom.
Cutting the bottom. A notch is made at the base of the bulb (cut out the bottom), the rest of the bulb remains intact.
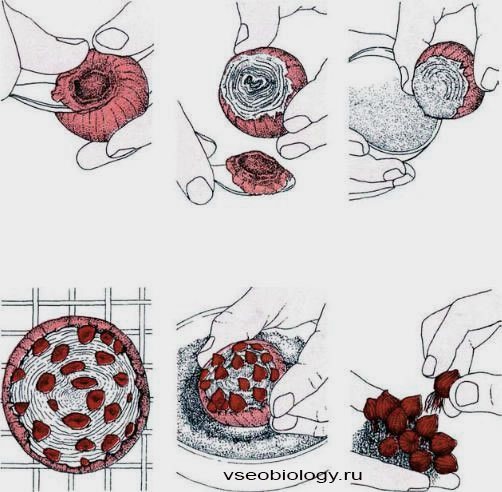

After about two to three months, young bulbs are formed on the cuts of the scales. Now the mother's bulb (again inverted) is planted in a pot so that the babies are barely covered by the substrates. In the spring, the bulbs will start to grow and form leaves, and the old bulb will gradually collapse. At the end of the season, young bulbs are dug up and planted. The size at which the plants can bloom, the bulbs will reach in 3-4 years.
Cutting the bottom of the scarious bulbs. The difference from the previous method is that instead of cutting the bottom on the bottom of the onion, only a few are made; cuts up to 0.6 cm deep. On a large onion, 4 cuts are usually made at right angles to each other, on smaller ones - it is enough to make 2 cuts. The cut onions are placed in a dry, warm place (21 ° C) for a day.
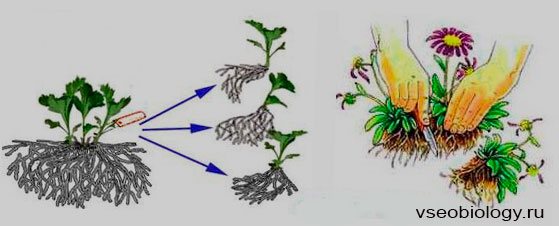
Dividing the bush
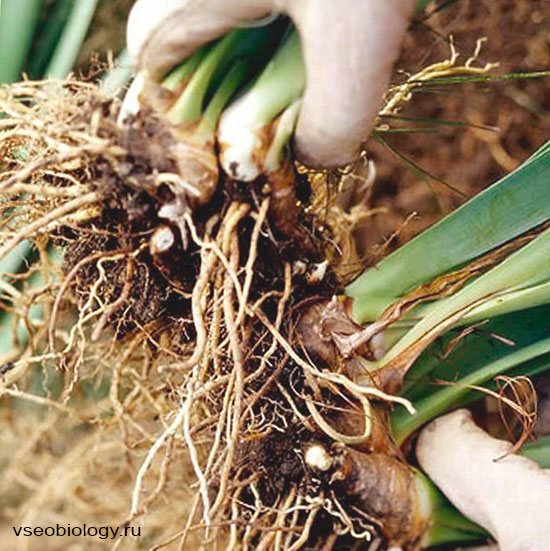


This is an easy way to reproduce. Usually, rhizomatous plants are propagated in this way, especially strongly bushy and forming a large number of aerial shoots coming from roots or rhizomes (phlox, spirea, perennial chrysanthemums, some varieties of lilac, rooted chubushnik, and from protected ground plants - aspidistra, asparagus) Sharp shovel, pruning shears or with a knife, the dug out bush is divided into equal parts so that each of them (delenka) has roots and at least two or three shoots or buds. If necessary, the roots, shoots, annual branches are shortened.
Plants blooming in early spring are recommended to be divided and planted in autumn; blooming in summer and autumn is best divided in autumn and spring.
The formation of suckers is sometimes artificially induced. On this day, in the spring, the bush is pruned from two opposite sides, and by the fall, dense growth is formed in the pruning places, which can be used for dividing, grafting, etc.
Division of root growth. Natural formation of root shoots is typical for lilacs, cherries, rose hips. From the dormant buds of plant roots, young shoots are formed, which later form their own root system.

At the end of the growing season, the root system of the shoots is separated from the mother. After several weeks, when young shoots are already growing completely independently, they are dug up and transplanted.
Division of rhizomes. Many ornamental plants (royal begonia, iris, canna, lily of the valley, mint, kupena, peony, sansevier, etc.) are propagated by dividing rhizomes.
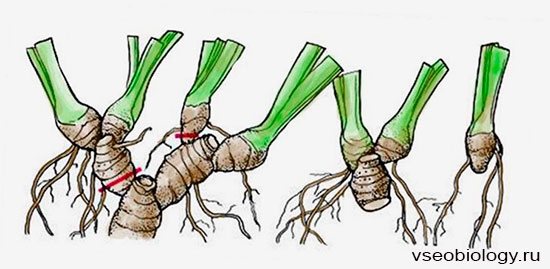

Rhizomes can grow in two ways.For example, in the garden iris, the apical bud develops into a peduncle, and growth in the horizontal plane is carried out due to the lateral bud. In the next season, this formed lateral shoot forms its own apical bud, which forms a peduncle, and the plant continues to grow horizontally, laying new lateral buds. In a different; In the case, for example, in mint, the growth of the rhizome is carried out due to the prolonged functioning of the apical and sometimes lateral buds, which usually give flowering shoots. The rhizomes of different plants may differ in other ways: the rhizome of asparagus, for example, gives a very insignificant annual increase, and the rhizome of mint is characterized by rapid and prolonged growth, due to which the shoots spread over a large area in a relatively short time.
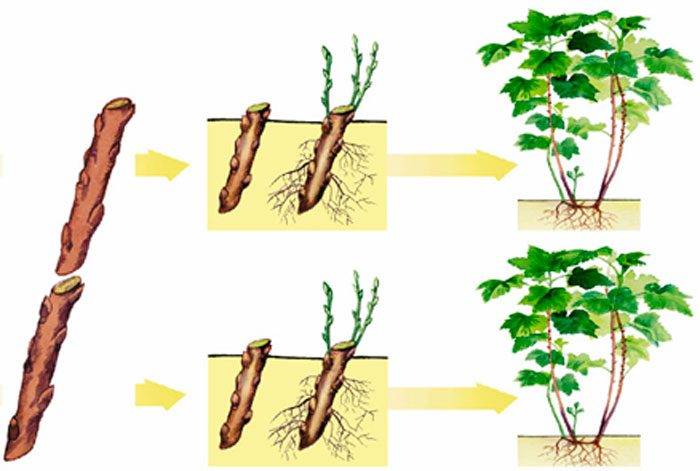
Cuttings - a method of vegetative propagation by rooting certain parts of the plant. A stalk is a section of a stem separated from the mother plant with leaves and buds (less often a root or leaf). Cuttings can be:
- stem,
- root,
- leafy.


The quality of the cut also affects the survival rate of cuttings: it should be very even, smooth. Therefore, cuttings are cut with a sharp instrument so that there are no roughness and lacerations, which contribute to the development of various diseases. Then the cuttings are rooted in a sandy substrate, which is poured with a layer of 4-5 cm on top of the nutrient mixture in greenhouses or pick boxes in greenhouses. The cuttings are planted obliquely so that the lower cut is in the sand and does not touch the ground, and the upper bud is located at the level of the sand surface. When planting cuttings in greenhouses, the distance in rows should be 3-5 cm, and between rows 5-8 cm. Up to 100 cuttings are placed in one dive box.
The rooting time of cuttings of different plants is not the same. Cuttings of geranium, carnations,, lupine, delphinium, mallow, sedum, phlox take root quickly (on days 6-3) Shrubs - roses, lilacs, viburnum - take root for 20-24 days, and most conifers - spruce, cryptomeria fir, araucaria - 3-4 months after planting and even after 6 months.
Gloxinia, violet, ficus, primrose, etc. are propagated by leaf cuttings. In these plants, when the leaves are rooting, adventitious roots and buds are formed, from which the stem develops.
Layers unlike stem cuttings, they are shoots that are rooted without separating them from the mother plant. Therefore, the rooting process is not difficult.


When propagating beautifully flowering shrubs (rose, lilac, hydrangea, clematis, spirea, etc.), horizontal, vertical, arcuate, air layers are used.
Horizontal layering. Young shoots are placed in shallow grooves, pinned and, as the shoots grow, spud 2-4 times per season.
Arcuate layering. After preliminary pinning, part of the shoot is added dropwise.
Vertical layering. If you cut off a young tree, vigorous stump growth appears. When the shoots reach 8-10 cm in height, the first hilling is carried out (necessarily with nutritious soil for 2 / 3-3 / 4 of their length), the second - when the shoots are 15-18 cm long, the third, when their length reaches 45-50 cm. at the end of September, the land is removed, the rooted shoots are cut off and planted in a nursery or in a permanent place.
Air layering. In this way, yucca, aralia, rhododendron, dracaena, agave, echeveria are propagated. This method is used in cases where the plant is very elongated and it is necessary to reduce its height. At a certain height, the leaves are removed, and the stem is covered with moss. Then, below the resulting root system, the stem is cut off, and the plant is transplanted into a new pot.


Graft consists in transferring part of one plant to another and merging them, which allows you to preserve the varietal characteristics of the grafted plant. Propagated by grafting roses, lilacs, azaleas, cacti.
The plant or part of it to be grafted onto is called the stock, and the part to be grafted is called the scion. The graft can be a bud with a small piece of bark and wood (eye or shield or stalk. There are many ways of grafting (budding, grafting with butt, grafting, etc.). Grafting is one of the methods of vegetative propagation of plants. It consists in transplanting buds or cuttings - a scion - of one plant to another, called a stock.Inoculation in floriculture is applied to roses, azaleas, cacti, Camellias, rhododendrons, citrus fruits and some other plants.
Reproduction by lashes, or mustaches. Indian strawberries, saxifrage, tradescantia, chlorophytum, nephrolepis and some other plants give more or less thin creeping or hanging stems ending in new small plants. The latter take root easily, developing into independent plants.
Plants from test tubes


Many people know about the existence of plants from test tubes, but it is difficult to call this method simple and affordable. Microcloning can be classified as vegetative propagation, but using microscopic pieces of tissue. Microclonal plant propagation at home is possible, but practically unavailable. Vegetative propagation of indoor plants in this way requires not only knowledge and skills, but also special nutrient media and equipment. However, nothing is impossible, and there are a huge number of successful examples of home experiments.
Growing under sterile conditions on nutrient media allows you to solve the problem of germination of orchid seeds. In such conditions, there is no need for symbiotic mushrooms, which supply the microscopic seed with everything necessary, and the seedlings are clearly visible after a few months.
Any of the selected breeding methods allows you to get a new copy of your favorite indoor plant, but good results can be expected only with the optimal method and proper care. Before proceeding with reproduction, it is worth studying the specific features of the plant.


Do you want to increase the number of your indoor plants and not spend a penny on it? Or grow a spectacular flower to present as a gift? Or do you want to change the old plant for a young one? Reproduction of indoor plants can help in all of the above cases. And floriculture is also a great way to entertain your child and instill useful skills in him.
Currently, most of the indoor plants are bought in a specialized store, but sometimes it is much more pleasant to admire a beautiful flower grown by yourself. Many people believe that the reproduction of indoor plants is only to tear off a leaf and place it in a glass filled with water for rooting. But this is far from the case. There are many different ways to do this.