From early spring to the onset of the first frosts, summer residents have to take care of their plots. Throughout the season, they use many different drugs to combat pests and fungal diseases, to feed plants and to fertilize the soil.
Dear Readers! For you, we have created communities in social networks, in which useful articles and interesting ideas are published several times a day! Subscribe and receive useful content in a convenient format!
Nowadays, hardware stores sell many different preparations for gardening needs. But there are also proven folk remedies, from the use of which the effect is no worse.
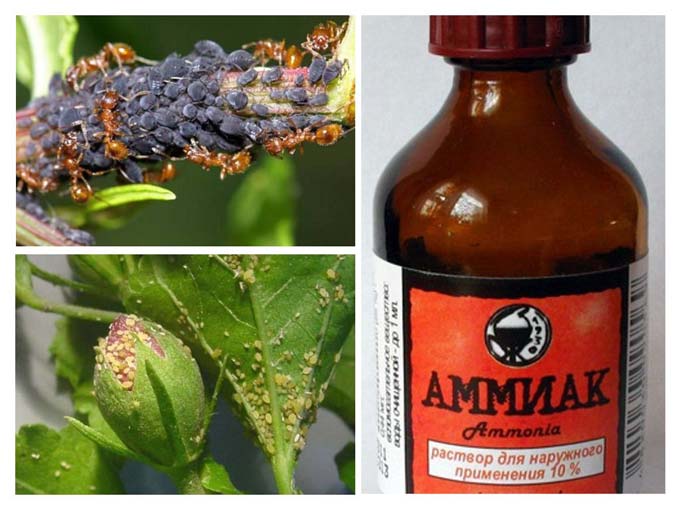
Today we will talk about the most common ammonia, which is found in almost every first-aid kit. You will find out how it will be useful to you in a subsidiary farm, and what pests it will help to fight.
Characteristics and chemical properties of ammonia
Ammonia is a diluted ammonium hydroxide with varying concentrations of ammonia, the most popular 10% option can be found in any pharmacy, 25% is also often found, but it is sold only in specialized fertilizer stores. In this case, ammonia is a gas that has a high level of solubility in water, depending on its temperature, with an increase in temperature, its solubility decreases.
This drug is a transparent, liquid solution with a specific smell of ammonia, unpleasant for humans and animals. From the point of view of chemical composition, this is a very simple concentrate, popularly called ammonia.
This substance is used in the following areas:
- Agriculture;
- chemical industry;
- medicine, the most popular remedy for fainting;
- antiseptic;
- cleaning of copper alloys.
The use of ammonia for indoor plants
An affordable and cheap option for nitrogen fertilization can be confidently called an ammonium solution, which is sold in pharmacies and specialized stores. Since all flowers need nitrogen directly from the soil, they need such feeding for normal development. When using ammonia as a top dressing, plants quickly receive the nitrogen necessary for the production of chlorophyll, since the agent is immediately absorbed without additional processing.
Ammonia is widely used by flower growers in the form of a mixture of different concentrations, it is perfect for such colors:
- lily;
- geranium;
- nasturtium:
- clematis;
- violet.

Also, this type of dressing can be used for deciduous types of home flowers.
The second option for the widespread use of this substance among amateur flower growers is its use to increase the resistance of plants to various pests and diseases, since ammonia liquid has a positive effect in the fight against various pests and diseases.
The use of ammonia for plants
Ammonia is actively used in agriculture as a fertilizer for garden and vegetable garden plants. The positive effect of alcohol is that it activates the growth and development of plantings.
Signs of a nitrogen deficiency in plants:
- the leaves turn yellow or turn pale below, become small and lifeless;
- crops bloom poorly and form an ovary;
- the resistance of seedlings to unfavorable weather conditions, a decrease in air temperature decreases.
Ammonia repels harmful insects, protects greens from diseases.


The most commonly used fertilizer is a 25% ammonia solution.
What plants is ammonia good for?
Ammonia alcohol is preferred by:
- Garden trees: cherry, plum.
- Berries: raspberries, blackberries.
- Flowers: dahlias, peonies, nasturtiums, roses, zinnias, lilies, violets. They need a lot of fertilization.
- Vegetables: cucumbers, tomatoes, beets, carrots, corn, onions, radishes. They need a moderate nitrogen fertilizer.
Solution preparation and dosage calculation for flowers
In order to help indoor flowers, it is important to correctly calculate the right amount of any fertilizer so as not to spoil the flowers. The same applies to the ammonium solution. It can be used for three main purposes:
- processing and disinfection of pots in which it is planned to plant indoor flowers;
- direct feeding of greens;
- pest control and insect control.
Options for the required concentrate, depending on the expected result:
- To prepare a disinfectant, rub 100 g of laundry soap into shavings, it is best to take the usual brown 72% without additives and fragrances. Prepare 5 liters of hot water and dilute the soap in it, then add 60 ml of ammonia (10%). Thoroughly wash the pots with the resulting liquid and rinse them under running water, after which you can plant flowers without a doubt.


Ammonia solution
- It is recommended to use different mixtures for decorative deciduous and flowering plants at home. For deciduous, an option of 2 tbsp is suitable. tablespoons of ammonia solution mixed with 1 liter of cold water. It is enough to use such fertilizer once a week. To improve the living conditions of flowering specimens, they should be watered with a weaker version of the mixture: 1 tbsp. a spoonful of ammonia per 1 liter of water. Such feeding should be started a few days after the buds appear.
- The most common pests that enter the home are aphids, weevils and midges. To eliminate them, the following options for drugs from ammonium are suitable:
- aphids: dilute 50 ml of an alcohol solution in 7 liters of water, you can spray and water with this product;
- weevil: 25 ml of ammonia per 5 liters of cold water for watering the soil;
- midge: mix 25 ml of liquid with 2 liters of settled water, suitable for watering.
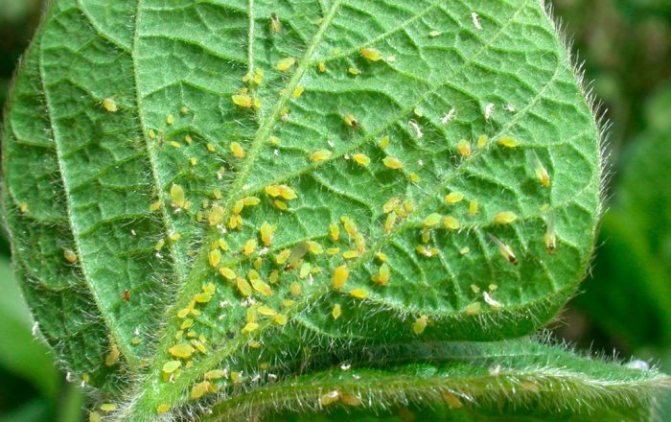


Aphids on indoor plants
The proposed options for the preparation of nitrogenous means for plants are universal. In this case, it is important to take into account the size of the pot and the flower itself when watering or spraying with a solution.
Pest control: ammonia solution application technique
Ammonium alcohol reliably saves from pests... The method for using diluted ammonia is presented below.
Aphid
Purchase a bottle of ammonia solution from the pharmacy. Pour half of the bottle into 10 liters of water. Grind a piece of laundry soap (100 g) on a grater, add to the general mixture. Mix well and let it brew to completely dissolve the soap.
Spray flowers and plants in the morning.


Ants
Unlike aphids, ants spoil not only the crop, but also create anthills on the site, which can lead to the death of plants. You can destroy an anthill in a short time if you fill it with a bottle of ammonia diluted in a liter of water. Such a burning composition will eliminate not only adult ants, but also their eggs.
You can also spray the crop for protection. from ants a weak solution of alcohol. To do this, stir a small amount of ammonia solution in a liter of water.
Carrot flies, onion flies
Add 5 drops of alcohol to a ten-liter bucket, mix.Sprinkle and water the roots of both plants already affected by pests and healthy ones (as a prophylaxis).
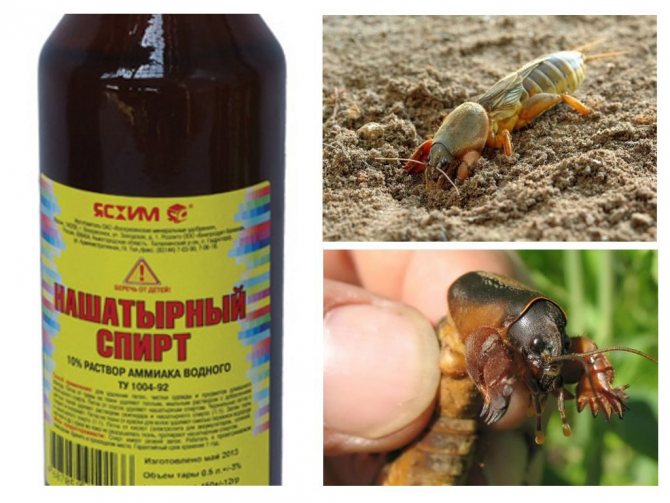
Medvedka
Medvedka is considered one of the most insidious pests for the garden and garden, it is very difficult to remove. It is possible to prevent damage to plants by a bear if you worry about their protection in advance. Before planting in the hole, pour half a liter of solution (10 drops of ammonia per 10 liters of water).
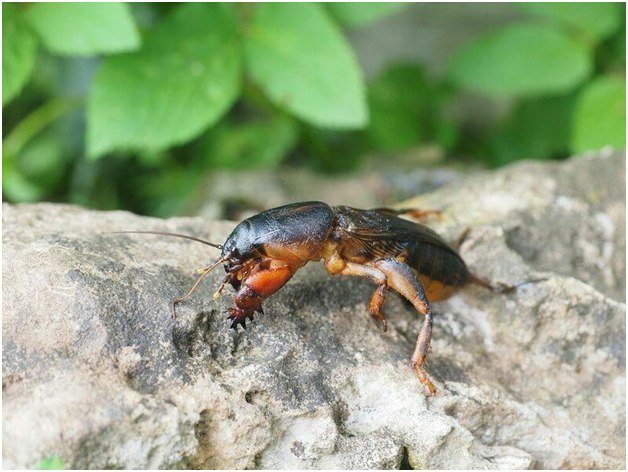


Lurker
This pest is especially partial to onions and garlic. To protect crops, stir 25 drops of ammonia solution in a large watering can. Beginning in summer, water the beds abundantly every week.
Weevil
Often found in strawberry beds. To remove the pest, you need to prepare an effective defense - dissolve 25 drops of ammonia in 5 liters of water. Water once a week.
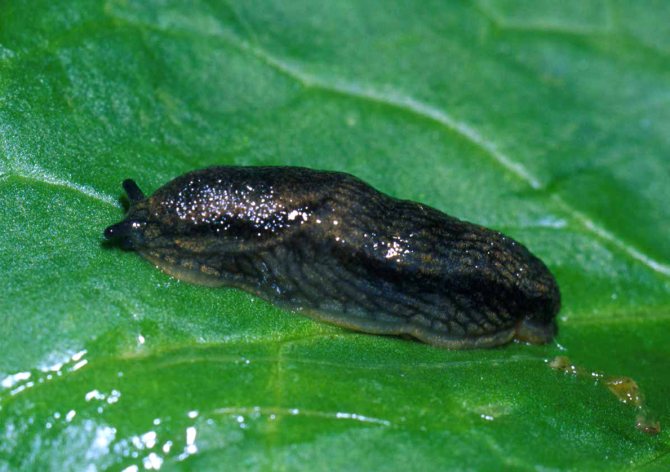
Caterpillars, slugs
These pests are common both in the garden and in the vegetable garden. They like to settle in hard-to-reach places, hide in the bark of trees and between leaves. You can remove pests with the most aggressive solution - 100 drops of alcohol, stirred in 10 liters of water. Water daily. In the presence of a large number of slugs and caterpillars, processing can be carried out several times a day.
Moles
Another common problem for gardeners and gardeners is the appearance of moles on the site. In order for this fluffy pest to leave the property forever, you need to use ammonia. To begin with, you should dig out the mole's hole a little, then put a cotton sponge soaked in ammonia solution in it. To increase the effect of this method, it is recommended to cover the entrance to the hole with slate, board or cling film.
In most cases, several mole burrows can be found on the site. It is necessary to prepare traps in each of them. Most often, it is possible to rid your site of the pest within a day.
And a few more useful tips for protecting the harvest of the garden and vegetable garden:
- Berries and fruits of fruit trees are often spoiled by birds. To protect the crop, you need to spray trees and shrubs with a solution prepared according to the recipe: add a tablespoon of shampoo (preferably baby) and ammonia to 4 liters of water.
- If frosts are expected, and the harvest is not yet fully ripe, the process can be accelerated. To prepare the solution, you will need the following ingredients:
- apple cider vinegar - 250 ml;
- shampoo (it is recommended to choose a baby shampoo) - 100 ml;
- concentrated pharmacy ammonia - a vial;
- water - 90 liters.
Combine all ingredients and mix well. Spray the unripe fruits abundantly with the resulting solution.
It is imperative to respect the indicated proportions. Too aggressive solution can harm plants.
Rules for using the drug for indoor plants
It is best to use ammonia to replenish nitrogen losses, "invigorate" deciduous trees during their active growth and improve flowering when buds appear, but this type of organic fertilizer should not be used for constant feeding of plants.
Foliage spraying
When using an ammonia mixture, do not allow it to get on the leaves of indoor flowers, as it can cause burns in flowers. If, nevertheless, this happens, then you should rinse the plants from the sprayer with running water to remove the remaining ammonia.
Pest control
To prevent the appearance of pests, you can water the plant at the foot with a universal solution of ammonia and water immediately after planting, this procedure will create additional disinfection of the soil.
Safety when using ammonia
An ammonia solution is poisonous even at a low concentration of 10%, therefore it is very important to observe safety rules when working with the substance in order to protect yourself and the plants from damage that it can cause.
For a plant
When working with flowers, it is very important not to use excessive doses of ammonia, which harm the flowers by deteriorating the quality of the soil. The correct amount of concentrate for irrigation should be calculated, avoiding its contact with the foliage.


It is also not recommended to prepare such a mixture for several weeks, it should be used immediately in order to preserve the minerals.
It is important to adhere to the recommended feeding regime, since shortening the interval between waterings will not benefit the flowers, but rather, on the contrary, will lead to rotting of the root system. In this case, you cannot use the ammonium solution at the same time as other nitrogen fertilizers.
For man
Ammonia vapors can seriously harm human health and cause poisoning or an allergic reaction, therefore it is important to adhere to these rules when working with the substance:
Do not ignore these rules even if you need to prepare a small amount of liquid for irrigation, which, if it comes into contact with the skin, causes burns, as well as disruption of the mucous membranes and respiratory tract.
Common questions
- fragile flower stalks;
- too light and yellowish leaves;
- lack of ovary;
- short-term flowering or lack thereof.
Having noticed such conditions, you should pay attention to nitrogen fertilizers and apply them.
A solution of ammonia is a universal remedy that helps to fill the nitrogen deficiency in indoor plants, as well as allows for the prevention of their diseases. You should not get carried away with this tool as the only option for improving the condition of flowers, because in some cases it can harm plants and the human body if the rules for working with it are not followed.


Indoor flowers are especially in need of nitrogen fertilization during the period of intensive growth and flowering. Over time, potted soil loses its supply of essential substances, which are absorbed by plant roots and washed out by irrigation water through drainage holes.
Using ammonia for indoor plants as nitrogen fertilizer is a simple and effective way to provide plants with this nutrient.
Ammonia for watering orchids. Iodine and hydrogen peroxide for orchids. Unique feeding


Orchids are very beautiful indoor plants that adorn any interior. To keep the plants healthy, it is necessary to regularly feed the flowers with a unique fertilizer prepared on the basis of iodine and peroxide. Consider how to properly prepare the solution and feed the orchids.
Iodine is an excellent antiseptic, and it also contains a trace element necessary for plant growth, including for orchids.
Hydrogen peroxide is an excellent disinfectant and acts like rainwater for plants. Everyone knows that rainwater is the best water for irrigating plants and is different in structure from tap water.


Why is feeding a solution based on iodine and peroxide useful for an orchid:
- strengthens the immune system,
- stimulates growth,
- protects the plant from pests and root rot.
How to properly prepare an orchid feed.
Making an orchid feed at home is quite simple. This will require iodine, hydrogen peroxide 3% and plain water. If from the tap, then you need to defend from the bleach.


In 1 liter of water, add 2 drops of iodine and 1 tbsp. l. hydrogen peroxide. Stir everything well so that the preparations dissolve.After that, water the orchid. You can make this top dressing once every two weeks.
How to prepare a solution to protect plants from pests and diseases.
Since midges, spider mites appear in pots of indoor flowers, including orchids, and root rot can also develop. To avoid this, prevention can be carried out by spraying orchid leaves with a special solution.


To prepare a solution in 1 liter of water, we dilute 2 tbsp. l. hydrogen peroxide, 3 drops of iodine and 2 tbsp. l. ammonia. Mix everything well and then pour the solution into a spray bottle. Then we spray the orchid. The treatment is best done in the morning or evening.
And you can find out how to use the resulting harvest on my channel "The Joy of Being", where I publish for you many exclusive recipes for homemade preparations.
Characteristics of the drug
Ammonium alcohol is ammonium hydroxide dissolved in water with an ammonia concentration of 10%. An aqueous solution of ammonia is a colorless liquid with an unpleasant and pungent odor.

Found in every first aid kit:
- with fainting - the evaporation of ammonia (a few drops on a cotton swab) stimulates breathing and cardiac activity;
- in case of alcohol poisoning - a weak solution (10-15 drops per glass of water) causes vomiting;
- as an antiseptic - 0.5% solution is used for washing hands and treating wounds.
At home, with an aqueous solution of ammonia, some gardeners recommend feeding indoor flowers, eliminating nitrogen deficiency, and destroying insect pests.
Often, ammonia is mistaken for ammonia. These two different substances are designated by different chemical formulas: ammonia, or aqueous ammonia, - NH₄OH, ammonia, or ammonium chloride, - NH₄Cl.
Prerequisites for use
In the flower substrate, the supply of nutrients after transplantation to plants is enough for 2 months. Ornamental and flowering plants, if they do not enter a dormant period, require regular feeding during growth and flowering.
Nitrogen, which is especially needed by the leaves, is an important element of the root nutrition of indoor flowers. With its lack, growth slows down and the color of the leaves changes, and low resistance to diseases and pests is manifested.
Signs of nitrogen starvation:
- old leaves lose their rich green color;
- on young, orange and red dots first appear, then the leaves die off;
- budding stops in flowering plants;
- tillering weakens.
Most of all, green pets suffer from a lack of nitrogen in early spring, when they begin active growth and prepare for flowering. Winter flowering plants need to be fed with nitrogen before flowering - in November-December.


Ammonia is used not only for dressing, but also for the destruction of pests. For example, small midges that appear in pots with indoor flowers as a result of waterlogging and a large amount of unrecoverable organic residues in the soil.
For the prevention of fungal diseases, containers for flowers are washed in a solution of ammonia.
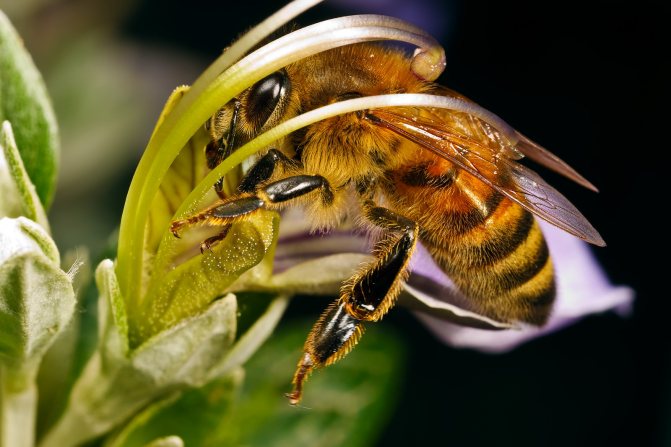
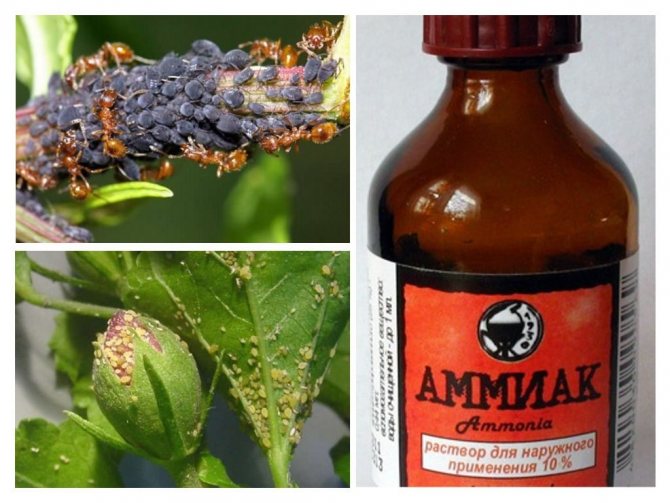
Aphid harm
The vegetable louse causes colossal damage to plants. At the very beginning of the spring season, it appears in vegetable gardens and garden plots. All berry and fruit bushes, as well as flowers, suffer from the aphid infestation.
Having found shelter on the leaves, it sucks the sap from the plants, the leaves and branches become lethargic, curl, and can crumble. Not only leaves, but fruits suffer from the invasion of pests. Young seedlings most often suffer from parasites.
Sucking out the sap, the aphid secretes honeydew, which covers the leaves, allowing a sooty fungus to develop, which interferes with photosynthesis.If you do not get rid of pests in a timely manner, all vegetation may die.
Safety engineering
When working with ammonia, it is necessary to protect the eyes and respiratory tract - volatile ammonia vapors irritate the mucous membranes. Large amounts of vapors can cause reflex respiratory arrest.
The solutions are prepared on the balcony with the windows open. If this is not possible, you should open the window and turn on the hood.
If the ammonia solution gets on flowers and leaves, it can cause burns in indoor plants. Indoor flowers are watered with a weak stream from a watering can from a low height, trying to prevent splashing of the solution. After treatment with ammonia, the leaves are washed from a spray bottle with clean, settled water.


Fertilizing a plant with dry soil leads to a burn of root hairs, therefore, the soil should be moistened beforehand.
During the dormant period, feeding indoor flowers is reduced or stopped altogether.
Many amateur flower growers use folk remedies when caring for plants. A proven and cheap remedy is liquid ammonia for indoor flowers. The use of an affordable pharmacy product has a positive effect on plants of many species.
It is useful to learn the rules for feeding with ammonia and methods of pest control of indoor flowers. All the nuances of using a solution with the smell of ammonia are reflected in the article.
Features of the fight against aphids
Having chosen a certain method of struggle, one should not forget that a one-time treatment will not bring the desired effect. The fact is that a single spraying will not completely destroy all representatives, those that remain will quickly restore the population, and the work done will be reduced to zero.
After the initial treatment, after a few days, it should be repeated. If necessary, process a few more times, in which case the pests will be completely destroyed.
Useful properties of the substance for indoor plants
Ammonia is a colorless liquid with a specific, unpleasant odor of ammonia. The concentration of the composition is 10%. The drug is actively used not only by doctors (to bring a person unconscious to life), but also by flower growers to care for plants at home, in the garden and in the vegetable garden.
A pharmacy product is a combination of ammonia gas and water. Ammonia contains 82% nitrogen. The pharmaceutical agent is often used in floriculture, for the processing and feeding of garden, fruit and vegetable crops.
The component has a positive effect on indoor flowers:
- activates a set of green mass;
- the plant is stronger and healthier;
- nitrates do not accumulate, as when using carbamide and ammonium nitrate;
- less harm to humans and flowers in the fight against pests: there are no toxic components in ammonia, as in the chemicals Aktara, Antiklesch, Mospilan, Aktellik, Confidor;
- a wide range of applications: as fertilizer for spraying and irrigation, to scare away and destroy parasitic ticks and insects;
- fruit and vegetable crops increase their yield.
An important advantage is that, while maintaining the optimal concentration and frequency of application of a solution based on ammonia, it is almost impossible to "overfeed" the plants.
Ammonium does not replace nitrogen fertilizers. You should not rely on a drugstore as a panacea in the fight against pests, chlorosis and other problems. A product with a bright smell of ammonia is allowed to be used in optimal concentration, taking into account the type and age of indoor plants. Moderate dosage and suitable frequency of various types of treatment: spraying, watering, fertilizing the soil are useful for the growth and development of decorative deciduous and decorative flowering species.
What is ammonia and how is it useful for plants
Ammonia is a volatile liquid with a characteristic pungent odor. It contains an aqueous solution of ammonia of various concentrations (10, 25, 50%). It has an alkaline reaction and is capable of being a "quencher" of acidity.


Ammonia is a rapidly evaporating liquid with a pungent odor.
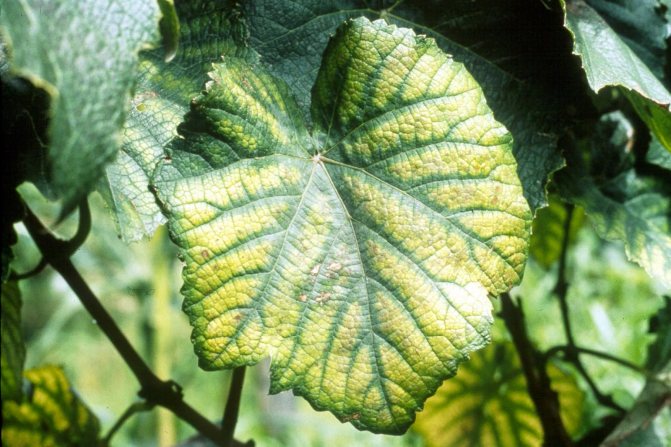
There is a large amount of nitrogen in ammonia - about 80%. This is an important element for plants, without it stems will not grow, leaves, plantings will be small and frail. The yellowing of the leaves also indicates a low nitrogen content in the soil. And garden crops that receive this substance in sufficient quantities boast bright green dense foliage and a powerful stem.


The leaves of plants that receive enough nitrogen from the soil are bright green
Of course, nitrogen is also present in many other substances, especially in organic fertilizers (compost, manure, herbal infusion). But in order for the plants to receive the microelement they need so much, mineral and organic fertilizers must be processed by soil microorganisms. But ammonia is absorbed by garden crops without any "helpers", therefore it is more effective.
Fertilizing with ammonia is an ambulance for the garden and garden, if, as a result of ineffective farming, the land is depleted, there are few useful microorganisms in it and standard fertilizers are poorly absorbed.
In addition, excessive fertilizing with nitrogen fertilizers (urea, nitrate, ammonium sulfate) can cause the accumulation of nitrates in plants. And ammonia does not have such an effect, that is, it is impossible to overfeed them.


You can't overfeed plants with ammonia
For humans, nitrates themselves are not harmful, but nitrites, into which nitrates are converted in our body, can worsen the functioning of the stomach and intestines and even lead to cancer.
For what and in what cases they are used
Signs of nitrogen deficiency:
- the leaves wrinkle, turn yellow;
- the growing season runs with deviations, the bush grows weakly;
- pale shade of leaf plates;
- the stem is fragile;
- weak flowering.
Formulations based on ammonia are used for several purposes:
- soil fertilization;
- spraying to destroy and repel pests of indoor flowers;
- improving the quality of vegetation;
- strengthening of the stem and leaves against the background of insufficient supply of nitrogen from the soil.
In pharmacies, a product with an ammonia smell of 10% concentration is sold. In some recipes for flower growers, a different indicator of the strength of the product is indicated - 25%. The drug is sold in stores as a technical variety.
It is necessary to strictly monitor the concentration of the working solution, so as not to prepare too "strong" product. The recipes indicate the concentration of the original product, the rules for the preparation of liquid for feeding and the fight against parasitic insects.
Ammonium is a cheap, affordable means for feeding plants in a green area, greenhouse, greenhouse, open field crops, shrubs and fruit trees. The composition is always on sale, the consumption is minimal, which significantly reduces the cost of growing plants of various types.
The effect of ammonia on plants and soil
Opinions about the advisability of using and the benefits of the pharmaceutical product are mostly positive. Many amateur flower growers, vegetable growers and gardeners use ammonia when caring for plants of various types and genera.
The main benefit of the pharmaceutical product is associated with the high nitrogen content, which plants absorb only from the substrate. A deficiency of a useful substance leads to a decrease in the rate of the photosynthesis process, insufficient production of chlorophyll.
Important nuances:
- The addition of a valuable component from a solution based on ammonia compensates for the lack of nitrogen, which has a positive effect on the state of the green mass and the growing season. An excellent result of feeding with a pharmacy agent is shown by seedlings.
- The second type of exposure - the smell of ammonia scares away pests. Ammonium is a biocide that provides a plant with protection from many insects and other types of parasitic creatures.Pests sense an unpleasant smell of ammonia even with a weak concentration of the working solution for soil treatment, which allows them to scare away insects without harm to indoor flowers, fruit and vegetable crops.
Preparation of the solution
Before using a nitrogen-containing product for the first time, it is important to study the methods of use, find suitable recipes, and clarify the concentration of the drug for a specific purpose.
rules
Ten important nuances:
- Always add water (little by little) to the ammonia in the container, and not vice versa.
- Wear rubber gloves.
- Do not lean low over the container, do not inhale vapors. Be sure to wear a medical mask.
- Do not use a stronger product than the prescription.
- Stick to watering and spraying frequency.
- Use a working solution based on ammonia immediately after preparation.
- You can not combine ammonia with other substances and preparations, except for iodine.
- It is strictly forbidden to use ammonia to treat plants for people who have been diagnosed with vegetative dystonia.
- The solution with ammonia should not be used in a poorly ventilated area. Optimal - take out the flowerpots to the balcony or yard.
- In hot weather, processing is not worth it.
Hand contact with undiluted ammonia may result in chemical burns and skin irritation. Be sure to rinse the problem area with running water, blot gently, contact a dermatologist.
Proportions
For indoor plants, a weak ammonia solution is used: 1 tbsp is taken for 3 liters of lukewarm water. l. ammonia. It is helpful to water and spray many types of home flowers from the beginning of the growing season to fall. Before using the working solution, it is important to clarify whether the water procedures are suitable for a particular type. Some exotic plants such as lithops or "living stones" cannot be sprayed or the fleshy leaves will rot.
Nuances
It's important to know:
- the frequency of application of the working solution for irrigation and irrigation of leaves - 1 time per week;
- it is impossible to combine mineral fertilizers containing nitrogen (ammonium nitrate, karbofos) with ammonia dressing, regardless of the strength of the finished product;
- it is allowed to increase the concentration of the home remedy gradually, when clarifying the reaction of a particular species to the pharmaceutical composition.
Nitrogen fertilizing
NH3H2O or, in the more familiar form of ammonium, NH4OH. That is, this substance is literally stuffed with nitrogen. Nitrogen in plant growing is both a green mass, a healthy and strong type of leaves and stems, and a developed root system.
But there are nuances in using ammonia as a top dressing that must be taken into account.
- Ammonium diluted in water in the dosages indicated below is used to a greater extent as a means of awakening flower potted plants after hibernation. Plants that do not bloom can be content with such feeding no more than 2 times a month.
- The remedy is strong, so the 10% solution sold in pharmacies is not suitable in any case! Its use in its pure form will simply kill any plant. Therefore, the "shock" dose that makes plants wake up after winter is 1.5-2 tablespoons of 10% ammonia per 5 liters of water.
- You need to feed the plants with this tool no more than 1 time in 2 weeks, starting from about mid-February, when the duration of daylight hours compared to the end of December will already become noticeable. Top dressing is done regardless of the frequency of irrigation with ordinary water or the need for certain plants in nitrogen: this need must be satisfied in the composition of complex nitrogen-containing fertilizers.
- Diluting this liquid in water is also not so easy: the ammonia will stay in it in layers for a long time, not wanting to mix. For full dissolution, water must be used warm, at 30-35 degrees. After dissolving the ammonia in it, wait for it to cool to room temperature.
- Top dressing is carried out on wet ground, that is, the solution should be poured into flower pots in 20-30 minutes after the usual watering.
- Feeding plants with a solution is done strictly at the root! To do this, you need to have a special watering can with a thin spout, without a sprinkler at the end, which will allow the solution to be poured exactly under the root of the plant, preventing drops from falling on the leaves, which can cause their chemical burns. Despite the precautions taken, it is still possible for drops to accidentally get on the green parts of the plant. To neutralize their effect, it is useful to spray the plants with ordinary water in the form of an aerosol immediately after watering.
- After the massive appearance of buds and the beginning of blooming, the dosage can be reduced by half - a tablespoon and a quarter of ammonia per 5 liters of water.
- In winter, such top dressing can be omitted at all or limited to carrying it out once a month.


How is nitrogen deficiency manifested?
The following signs observed in flowers can serve as a signal for the introduction of nitrogen-containing fertilizers:
- The leaves have acquired a yellowish tint, the green color has lost its saturation.
- The plant stems have become brittle, the bush does not hold on to a bunch, if it was previously inherent in it, but spreads out, disperses in different directions.
- New buds do not appear, but the existing ones die off, dry up.
- Flowering, if it occurs at all, lasts a short time.
Features of the
A big "plus" of ammonia is "superfluidity". It gives water with it the ability to penetrate into the most distant parts of the soil in a flower pot and is guaranteed to nourish the roots. Under natural conditions, this opportunity gives plants additional sources of nutrients, because the roots can easily reach areas and depths of the soil where mineral or organic fertilizers are still present.
How to use
Be sure to take into account the rules and recommendations specified in the previous section, to determine the optimal concentration. You will have to prepare a bowl or bucket, medical gloves, a spoon for stirring liquid, a measuring cup.
As nitrogen fertilizer
Important nuances:
- Watering indoor flowers with a solution based on ammonia is an easy way to improve the condition of the green mass, to support the production of chlorophyll. A solution of weak concentration: take 1 tsp for 1 liter of cool water. pharmacy product.
- After a few weeks, with a good reaction of the specimens from the green corner, you can slightly increase the concentration: take not a teaspoon, but a tablespoon of ammonia 10%. A stronger solution is harmful to indoor plants.
- Watering is carried out 1 time in 14 days according to the rate of liquid for a certain type. Too wet soil is a medium for the development of fungal infections.
Top dressing with ammonia, or rather, a solution based on a pharmacy composition, benefits indoor flowers. A good effect is given by the remedy when watering geranium, room rose, zinnia, lily, dahlias, violets, nasturtium. It is important not to overfeed the flowers, otherwise fungal lesions develop, an excess of nitrates accumulates in the underground part.
Spraying
The procedure is less popular than watering with diluted ammonia as a fertilizer. Not all plants respond well to a solution with a pharmacy product.
For this reason, diluted ammonia for spraying is used as a means to repel pests and, more often, on open ground plants. The next section describes the concentration of the composition and the nuances of use.
Fight against parasites
Many pests are sensitive to the action of ammonia:
To scare away small insects, it is enough to prepare a standard product (3 liters of water + a tablespoon of ammonia), spray the leaves and the ground. The frequency of processing is once every 7 days.
Such a remedy works badly on large pests: the particles of the solution evaporate quickly, the smell is weak, and the parasites further attack the indoor flowers.How to fix the situation? It is useful to prepare a warm soapy solution based on household or liquid soap (10 l), add ammonia 10% (100 ml), apply to the leaves.
What can be watered with ammonia in the garden and vegetable garden
Strawberry
Strawberries almost do not perceive nitrogenous compounds from ammonia. Therefore, it is impractical to use it as a fertilizer.
However, watering strawberry bushes in spring with an ammonia composition (40 ml per 10 liters of water) will help get rid of parasites in the soil. The same means and for the same purposes, you can process strawberries in late autumn.
Use for cucumbers
Cucumbers need to be fed with ammonia solution from the moment the first true leaves appear and until the formation of ovaries.
The solution is prepared from 1 teaspoon of alcohol and 1.5 liters of pure water.
Uses for raspberries
Raspberries are fed with ammonia solution three times per season.
- Early spring processing. 2 tablespoons are mixed with 10 liters of water and applied to the root at the rate of 5 liters of the drug per bush. After feeding, the raspberries are immediately watered with clean water. This is to prevent root burns.
- Processing before flowering. The product is prepared from 3 tablespoons of alcohol and 1 bucket of water. To enhance the effect, you can add 1 cup of ash, which is a source of potassium.
- Autumn processing before winter. 3 tablespoons of alcohol are mixed in 1 bucket of water. The solution is applied under each bush. Top dressing should be done in early autumn. If you harvested raspberries late, then it is better not to apply fertilizer.
Application for onions and garlic
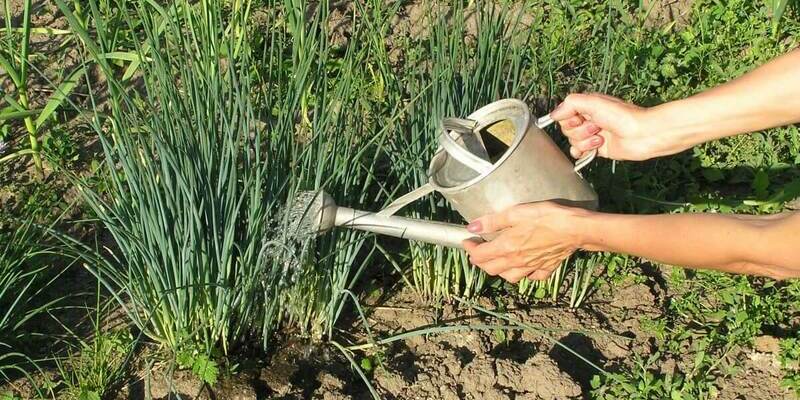


Watering onion and garlic with ammonia solution
Among all garden crops, ammonia is the most effective for onions and garlic. First, by watering the beds with these plants from a watering can, you simultaneously carry out root and foliar feeding. Second, you immediately treat the onions and garlic from insect pests.
The agent for garlic and onion is mixed as follows: 3 tablespoons of ammonia per 10 liters of water.
How to apply for tomato
Tomatoes are processed with ammonia in 2 cases:
- With growth retardation and obvious signs of nitrogen deficiency (1 tablespoon of ammonia solution per 2 liters of water). As soon as the tomatoes come to their senses, feeding with ammonia should be stopped.
- During the ripening of late varieties in autumn (10 ml per 10 liters of water).
Probable harm and precautions
The main rule when using a pharmacy product is to do no harm. Improper use of ammonia, excess concentration, refusal of nitrogen fertilizers can harm plants.
It is important to adhere to safety measures, to protect hands and respiratory organs. Vapors of ammonia can lead to poisoning, and a strong solution can provoke damage to the epidermis. Before starting the procedures for watering and spraying plants, be sure to wear gloves, a medical mask, and treat indoor flowers in the fresh air.
Video about the features of the use of ammonia as a top dressing of indoor plants:
>
























