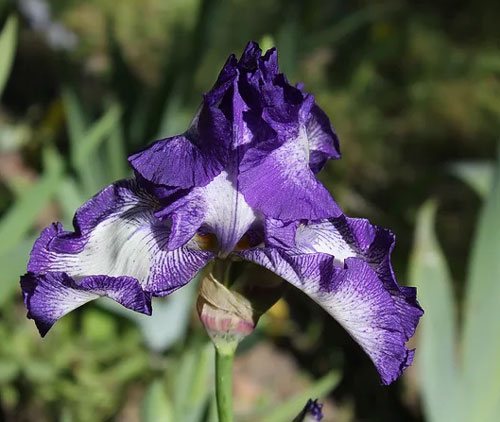
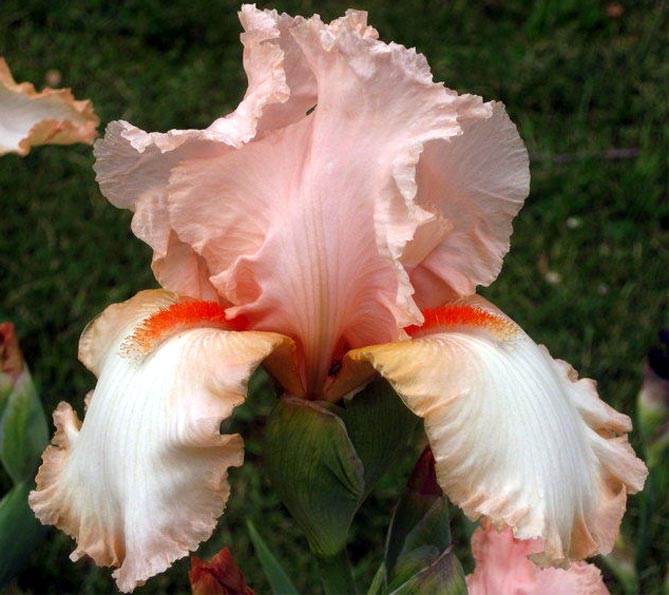
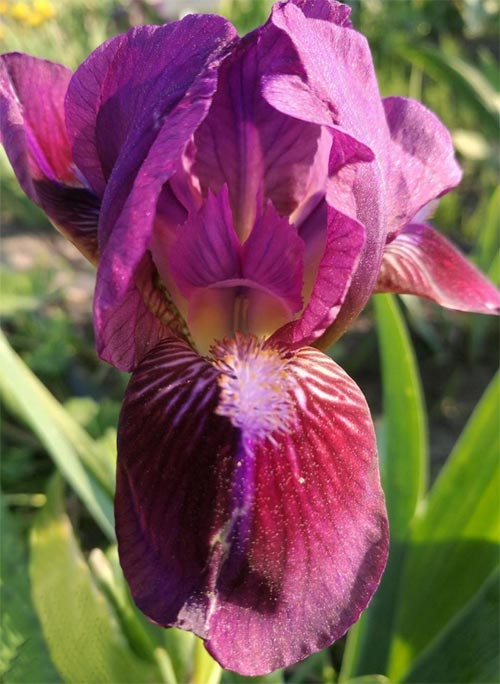
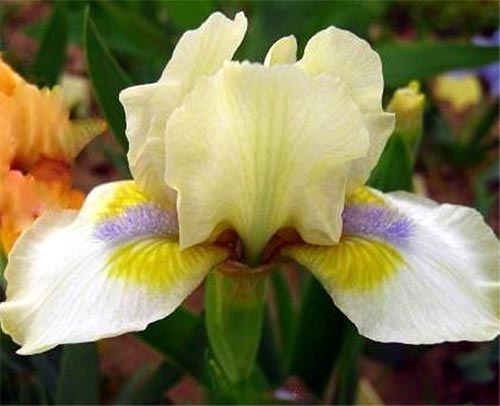
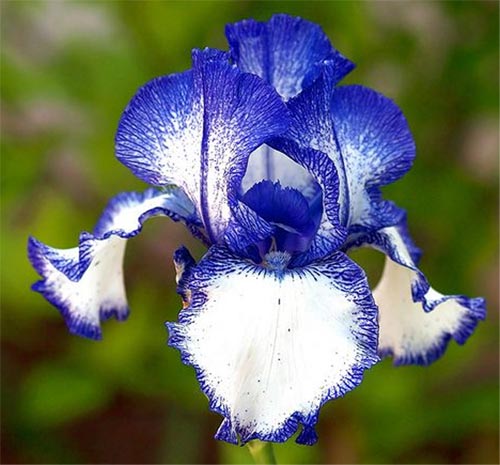
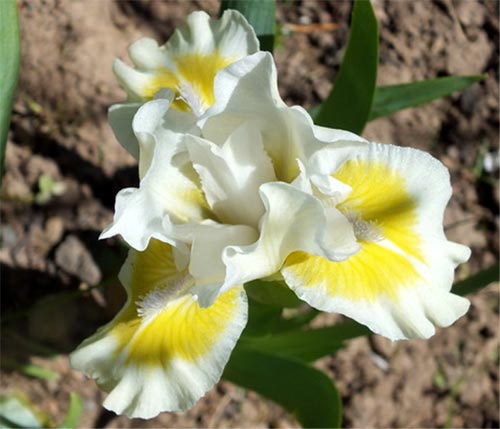
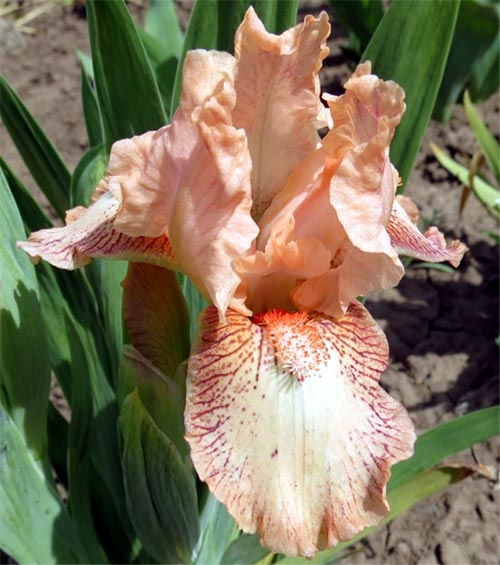
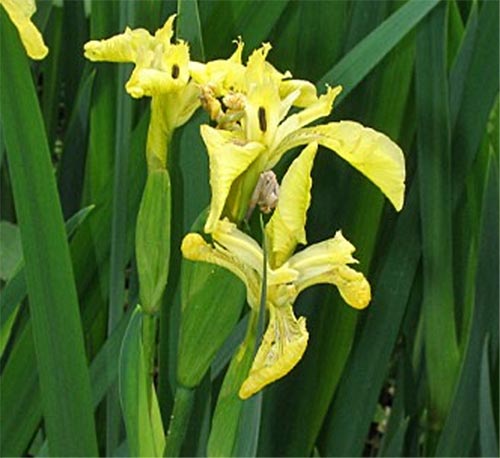
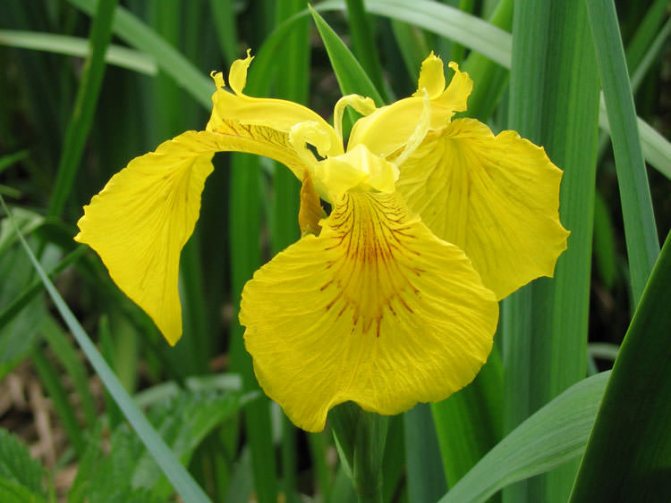
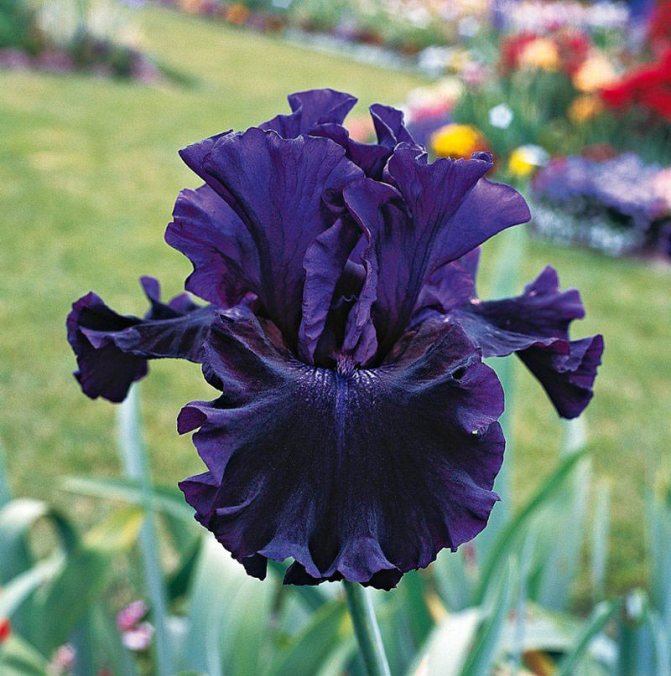
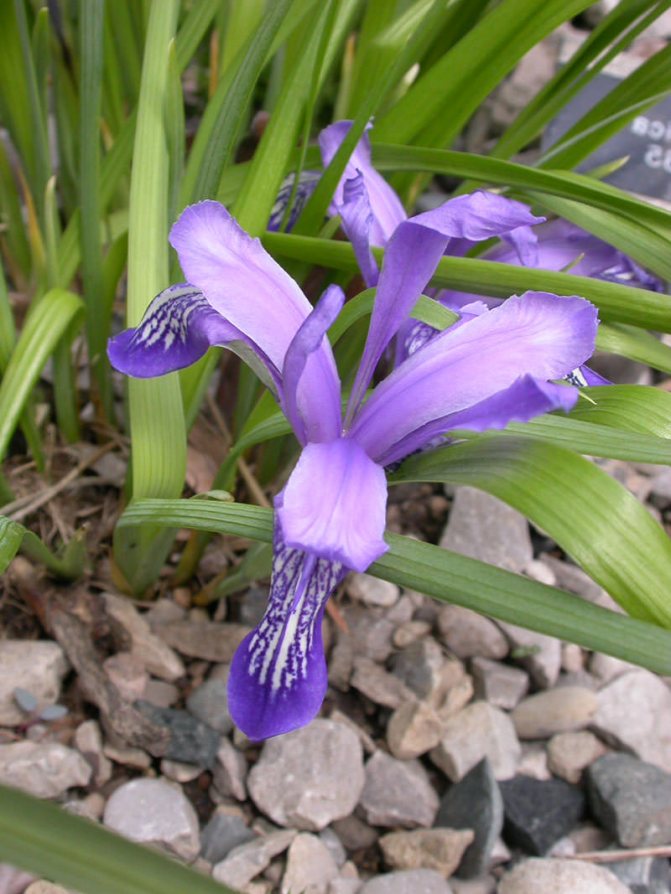
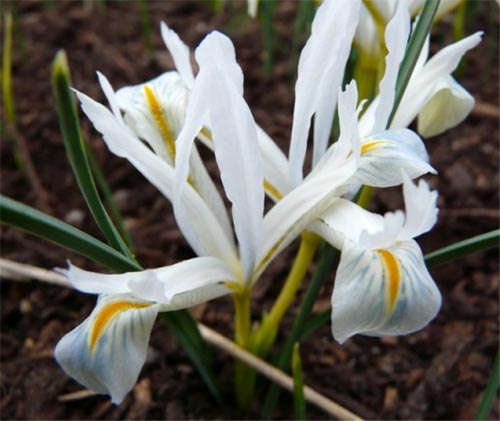
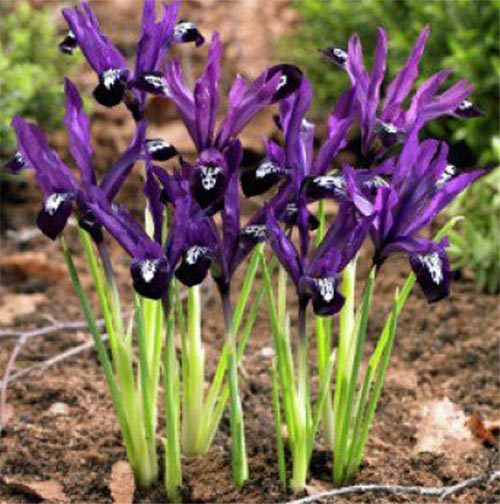
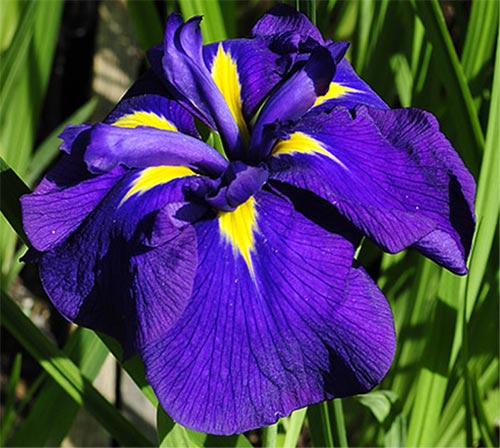
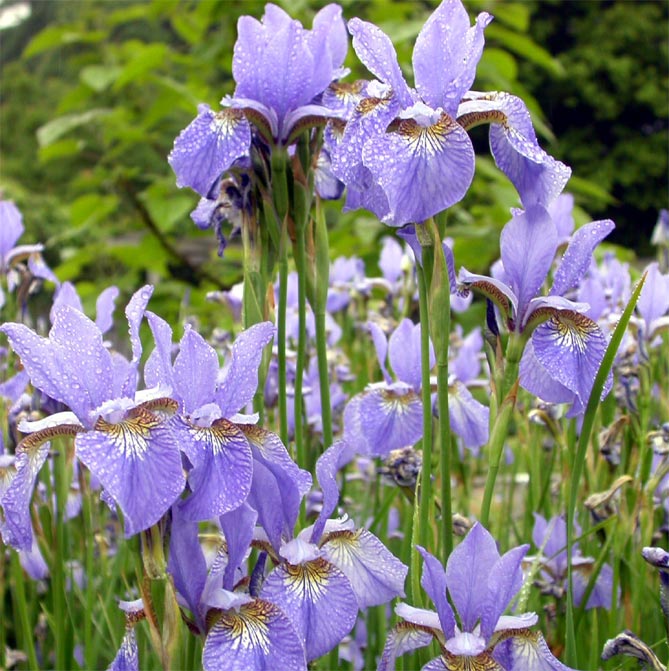
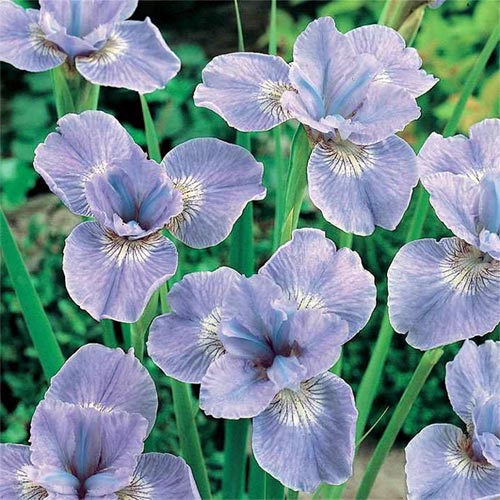
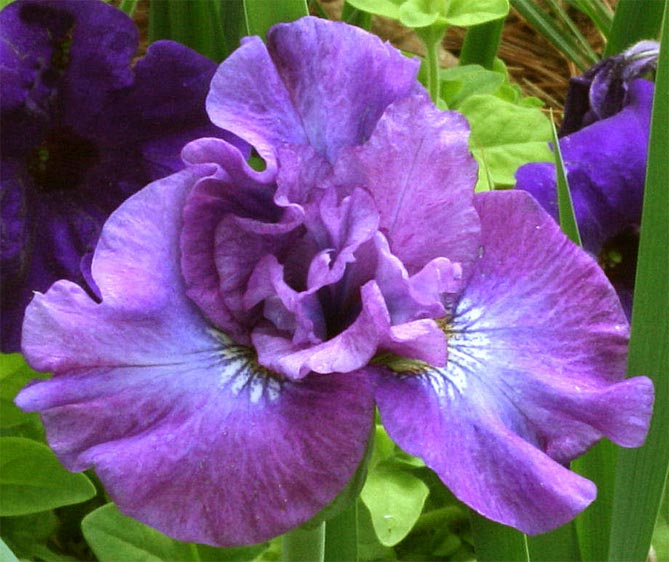
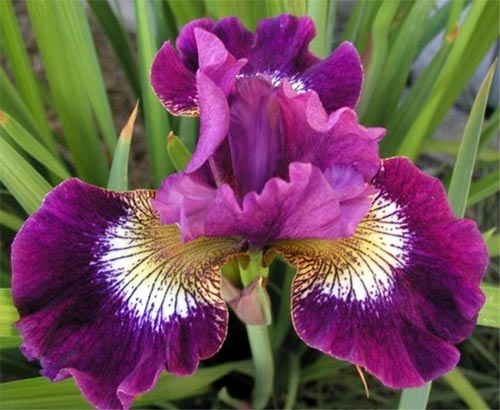
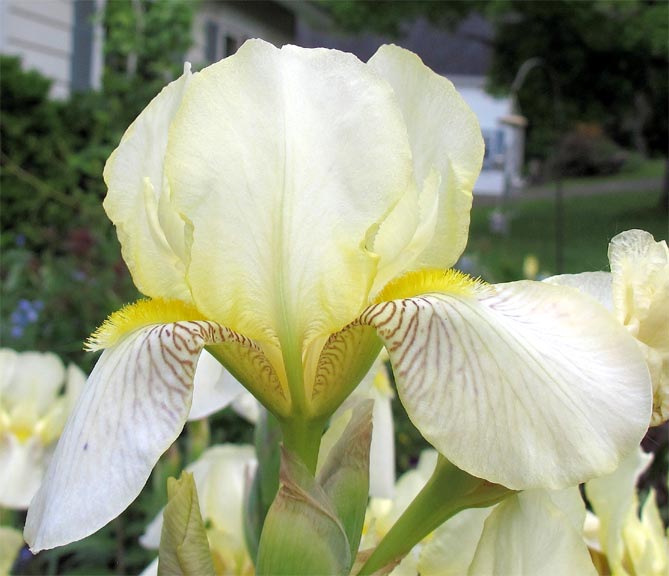
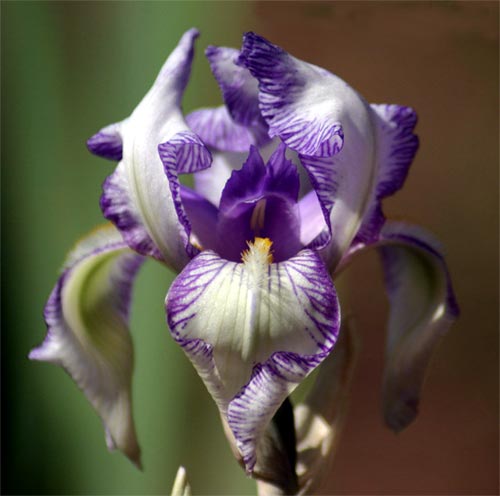
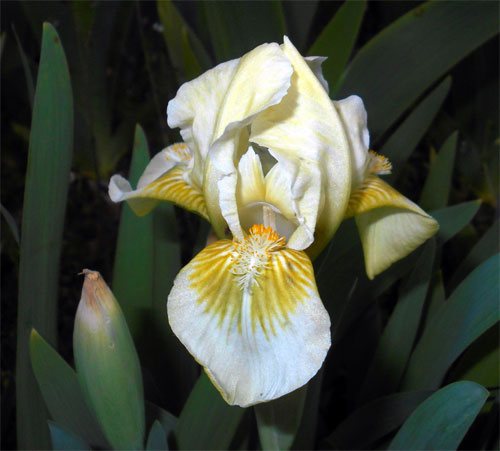
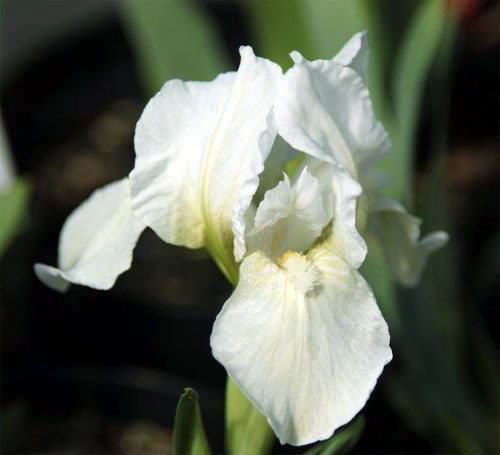
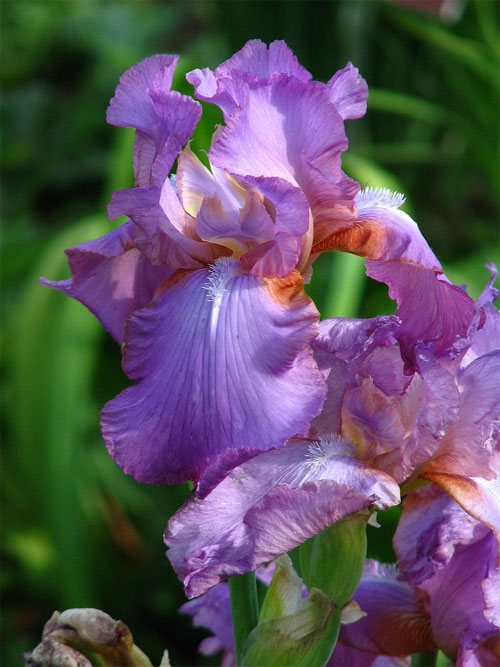
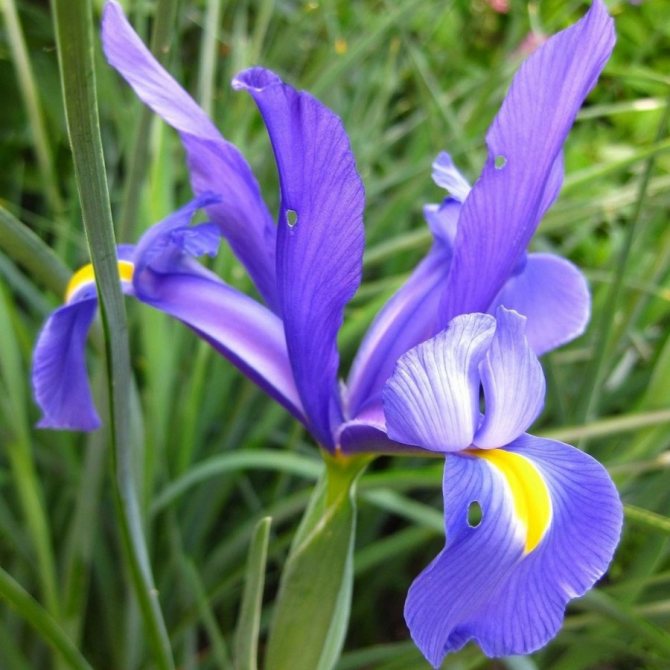
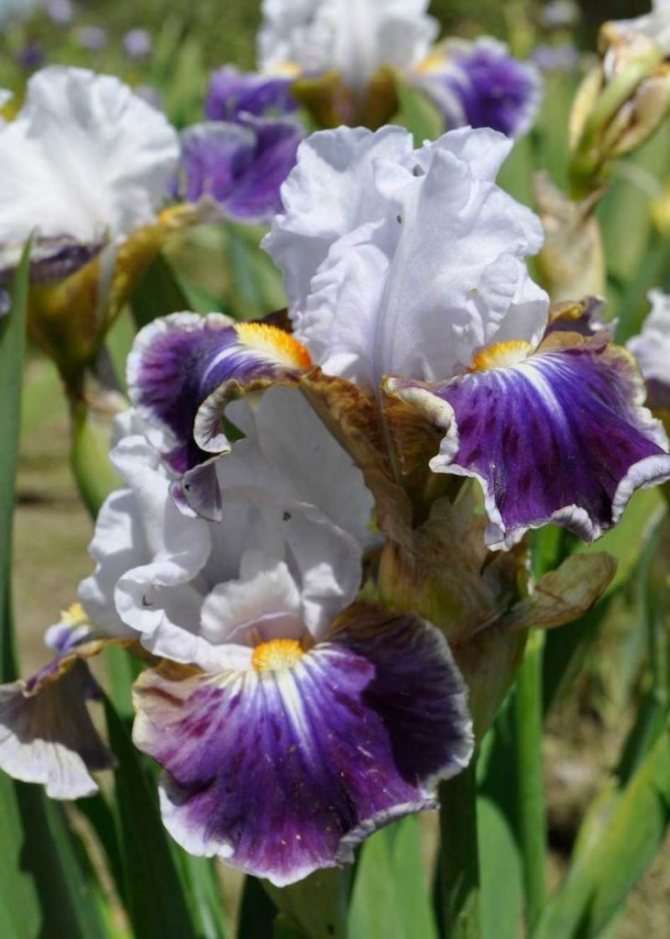
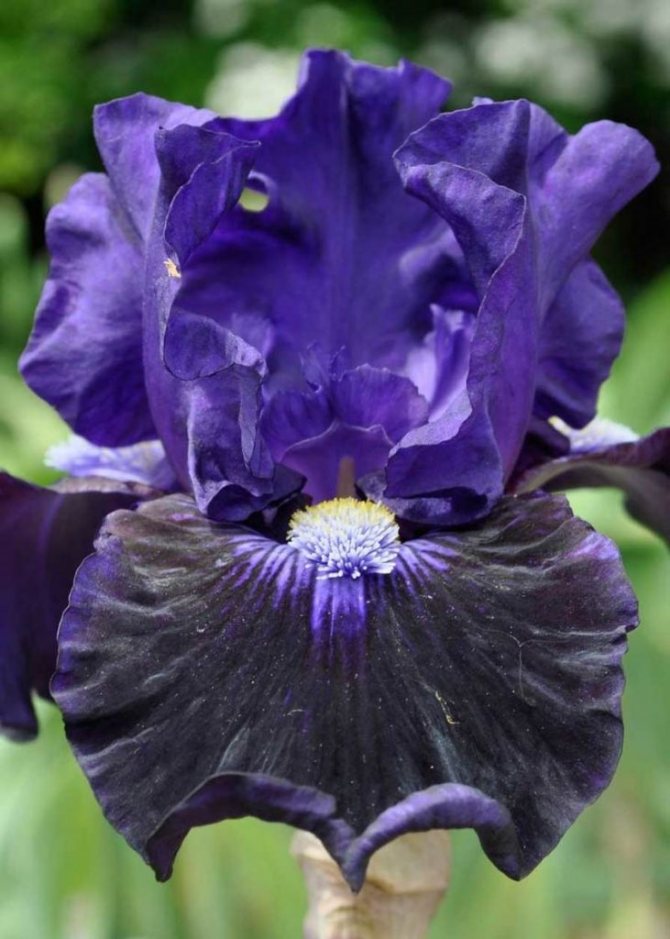
Irises or cockerels are some of the most beautiful and popular flowering perennials found in gardens. Among them, more than 200 species and many varieties are known. Breeders compete to create more complex shapes and color combinations of these flowers, even created their own associations (Russian Iris Society, American Iris Association).
The American Association awards grants and prizes annually for the best varieties. Therefore, the scheme and division into species and varieties are rather complicated. Consider the most popular irises - varieties with photos and names of especially valuable specimens, most often grown in our country - bearded and beardless.
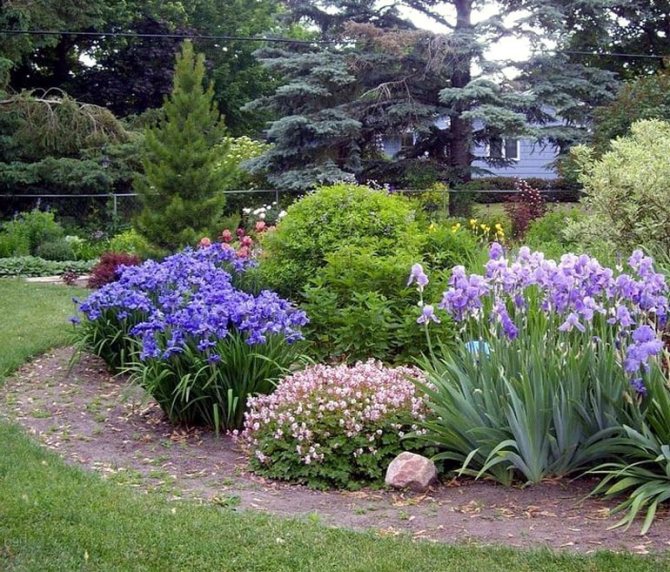

Types and varieties of irises
Attempts to understand the varieties of irises very quickly turn any grower into a collector of these flowers. There are a lot of varieties and you want to have all of them in your garden. Rhizome irises are divided into two large groups according to the flower shape - bearded and non-bearded.
There are also bulbous flowers, they are similar to rhizomes in appearance, needs, and have common enemies. Care for all varieties differs only in nuances.
Bearded irises
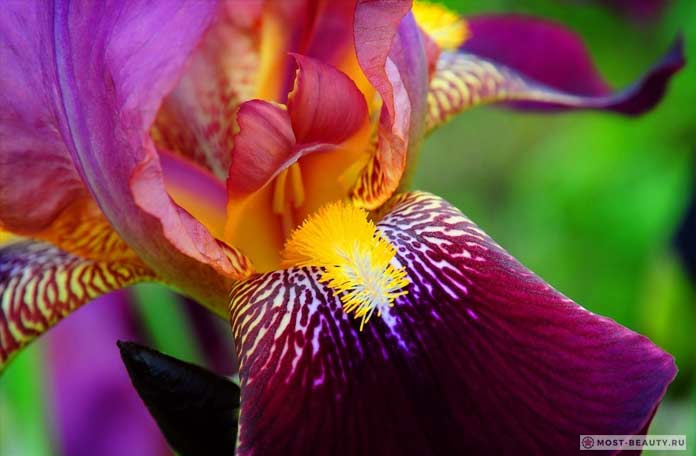
Named so because of the shaggy "beard" paths on the petals. The flowers have an exquisite shape. Three vertical petals are standards, and three drooping fouls are the outer perianth lobes.
The origin of cultivated bearded irises is rather complicated, and the variety of forms and species is inexhaustible, so they are difficult to classify. The most common methods of dividing irises are according to the height of growth (from 20 centimeters to one meter), the timing of flowering and the color of flowers.
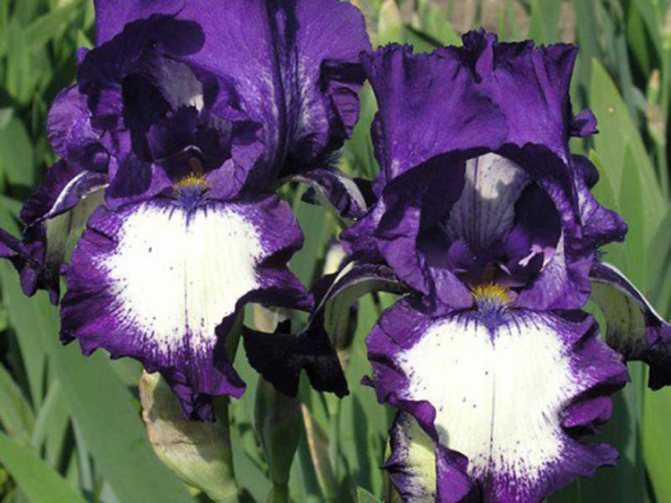


Only a person with special knowledge in the field of botany can thoroughly understand the intricacies of classification. In this article, we will limit ourselves only to a description of the most popular varieties, despite the fact that the basic rules for growing and care are practically the same.
Most of the tall bearded ones are hybrid forms from the German iris, the brightest varietal representatives:
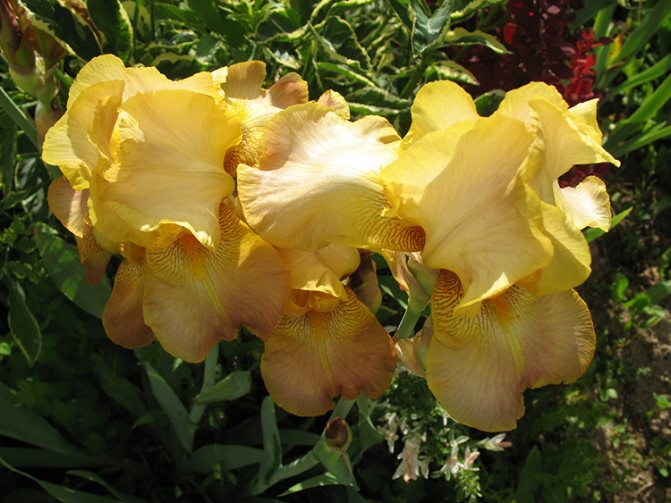
Starfall - variety of medium-early flowering period from 70 centimeters high, flowers from pale yellow to rich yellow with an orange beard.
Abkhazia - late-flowering irises with a beautiful brown-yellow-orange color, no more than 75 centimeters high.


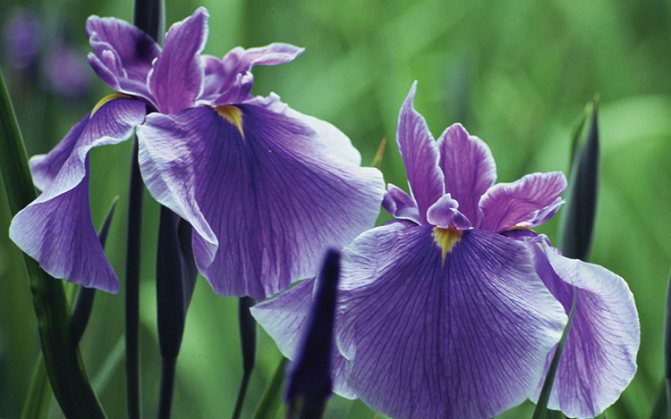
Baltic Sea - tall irises with deep blue flowers and blue villi, corrugated petals.
Arils and Arilbreds
With an outward resemblance, this is a more thermophilic group, which is why it is not so popular for garden cultivation. Arylbreds - hybrids of the bearded and Aryl proper - are more adapted to growing in the open field.
They differ in that after flowering, these plants fall into a dormant period - the foliage dies off and grows back only closer to autumn.


Non-bearded irises
The generalized name for a number of plants, whose outer lobes are devoid of hairs. The flower shapes of non-bearded irises are more varied: there are varieties with miniature or drooping standards like fouls. On Siberian terry specimens, it is often impossible to find differences between the two types of petals.
Siberian
As the name implies, these irises are hardy. Almost odorless. Natural colors range from light blue to purple. The color of new hybrid varieties based on Siberian is much wider:
The Snow Queen - white petals with yellow blotches on the bends reach 10 centimeters in diameter, 70-90 centimeters high, mid-late flowering, frost-hardy.
Bundle of Joy - a terry variety with a very interesting atypical flower structure, mauve color, flowers up to 10 centimeters in diameter, peduncle height reaches a meter.
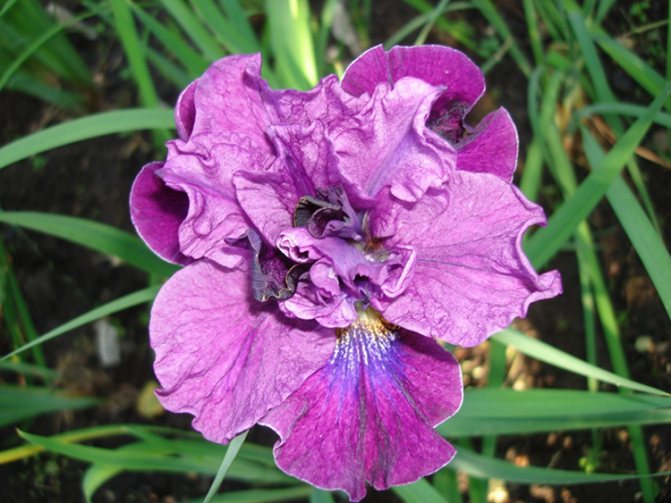


Flying Fidless - undersized specimen of average flowering time, flowers are creamy yellow: monochromatic standards, fouls are penetrated with contrasting burgundy veins.
Chrysographes
For Russian gardens, this Chinese variety of irises is a real rarity. They have much in common with Siberian irises, their second name is "Sino-Siberian". They are distinguished by a lighter color of foliage, patterned veins on the petals.
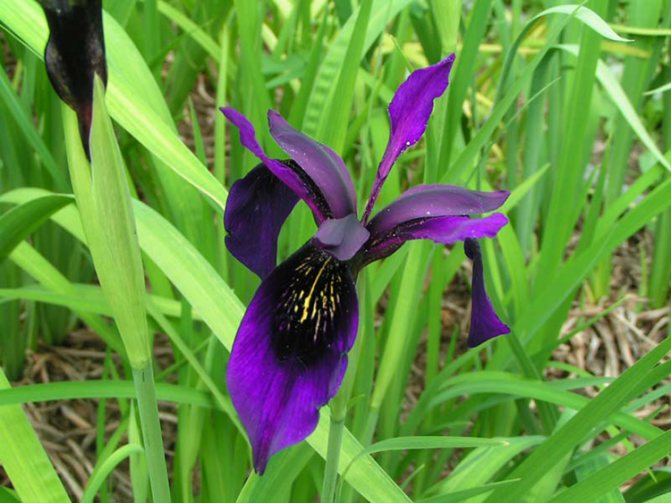


Japanese or xiphoid irises (Japanese)
Low, but hardy plants. They love a humid environment, great for coastal cultivation:
Cry of rejoyce - a variety of early flowering, up to 80 centimeters high, large burgundy-purple flowers with unexpressed standards.
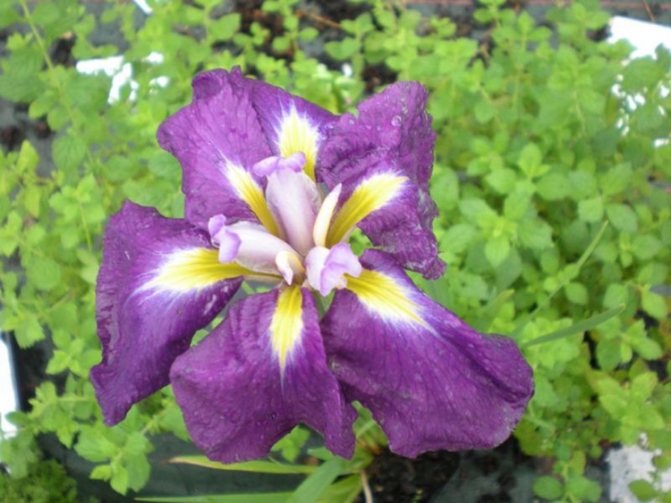


Eden charm - late flowering, bright purple flowers are flat with a yellow heart and miniature standards.
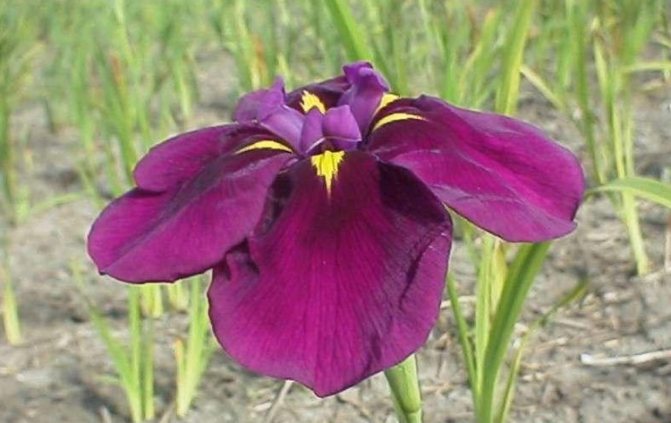


Paintbrush - up to 85 centimeters high, average flowering period, mauve flowers with white veins.


Spuria
The peculiarity of this species is thin elongated petals of an exquisite shape. At first glance, they look poorer than other non-bearded ones, but no other variety looks like that in a flower bed. Hybrid varieties are suitable for growing in Russia:
Imperial bronze - late flowering variety with yellow-brown flowers.
Blueberry sunday - petals with a dark blue border and a golden core.


Zamboanga - with reddish brown standards and gold fouls.
Swamp irises
These unpretentious, moisture-loving flowers are found everywhere, they grow in floodplains of rivers and in wetlands. Hybrids based on them are viable and original. But breeders began to work with this subspecies relatively recently.


Louisiana and Californian irises
In Russia, they are not widespread due to their thermophilicity. They are available for cultivation only in the subtropics and greenhouses and are not able to compete with many frost-resistant varieties.
Bulbous irises
They have a lot in common with the usual irises, but not the root system. According to the characteristics of cultivation, preferences and flower shape, they are closer to non-bearded ones.
Bulbous, in turn, are divided into three genera:
- Iridodictium or reticulated iris. Low-growing early flower up to 15 centimeters high; The most characteristic variety is Katharina Hodgkin. It blooms from April to May, then the peduncle and leaves die off.
- Juno is not as resistant to low temperatures as iridodictium, but stronger than xyphium; blooms at the end of June, after which the aerial part dies off. The most popular are Juno Bukhara, Worley, blue, substitute.
- The most capricious and at the same time the most popular among bulbous irises are xyphyums.
The most frost-resistant among them are English hybrids, they are also, ironically, the rarest, most gardeners prefer two-color Dutch varieties. Spanish varietal xyphyums are the most vulnerable to our climate. Bulbs of these varieties must be removed from the soil for the winter.
When working with irises, all manipulations are best done with gloves, since the caustic sap of these plants can cause irritation and even poisoning.
Bearded
This is the most diverse and most beautiful group of irises. Their flowers are very large, petals can appear in almost the entire color palette and in different color combinations. In many varieties, the edges of the petals have contrasting colored frames, beautiful frills or decorative curls."Beards" may have a different color from the rest of the flower.
Hybrid bearded irises, arose as a result of selection work. Their height reaches 25-70 cm. The name comes from one characteristic feature. Namely, there is a strip of hairs on the outer petals of the perianth, which is called a beard. The species has a rigid, branched stem on which a flower grows, the leaves are narrow, lanceolate.
Bearded iris makes little demands on pot and garden cultivation. It is important that the soil is permeable, not too wet. Better to choose a sunny position, especially for young seedlings. You can grow them in partial shade. Reproduction is done by dividing the rhizomes in August. The seedlings must be free from disease. Depending on the variety, the distance between them should be 20 × 25, 30 × 40, 45 × 60 cm.
Bearded varieties can be grown in pots. These garden flowers are great at home.
There are many varieties, they are divided into several groups. In Russian society, bearded species are divided into:
- actually bearded (tall, medium-sized, dwarf);
- aryls.
Varieties are also classified according to the color of the flowers.
With two-tone flowers
| Variety name | Photo |
| Pinacle | |
| Toll Gate |
|
| Helen Collingwood | |
| Broadway Star or Broadway Star | |
| Symphony |
Monochrome varieties
| Name | Photo |
| Great Lakes |
|
| Violet Harmony | |
| Swahili |
|
| Orelio |
|
German
This is a typical species of Iris. Differs in a powerful rhizome. A type of perennial plant from which many garden hybrids with large, beautiful flowers originate. Originally from southern Europe, it is the representative of the largest group of tall bearded irises (TB).
The plant forms a creeping rhizome with numerous roots. Iris leaves are xiphoid or saber-shaped, round, hard, with characteristic fan-shaped lobes, 4 cm wide.The flowers are collected in 4-5 inflorescences, from bluish-violet to purple with a yellowish beard, 10-12 cm in diameter.It blooms in May-June, grows up to a height of 60-120 cm. It is used in perennial flower beds in combination with peonies, chrysanthemums, on the banks of reservoirs and as cut flowers. Full frost resistance.


The soil should be fertile, sandy loam, with a high humus content. The position is sunny, then the plant will give many bright colors. Flowers do not tolerate stagnant water, it is worth growing them on elevated beds, small slopes.
Reproduction: by cutting out lateral fragments of rhizomes, each with 1-2 rosettes of leaves, once every 3 years and planting them after flowering, no later than early autumn.
The varieties of German iris planted in the wrong position are susceptible to numerous fungal and viral diseases. The most common disease is wet rhizome rot. Most rhizomes are susceptible to snail attacks. Aphids carry viral diseases. Sometimes the flowers are threatened with rust. Brown blisters on the leaves are a sign of a disease called bacterial leaf wilting.
Germanic iris varieties are divided by height.
| Name | Photo |
| Low - up to 25 cm | |
| Baria | |
| Lilli Var | |
| Lenna M. | |
| Average height - about 60 cm | |
| Red Orchid | |
| High - more than 70 cm | |
| Winter Carnival | |
| Dotted Swiss | |
| Rococo |
|
| Cayenne Capers | |
A plant whose requirements are low can beautify many gardens and home spaces. A big plus is the variety of colors, from white to cream, yellow, orange, red, pink, purple and blue.
There are a huge number of varieties of bearded irises, and breeders present new proposals every year. The most beautiful plants are found among the varieties of high and medium growth.
| Name | Photo |
| Decadence - two-ton | |
| Peach Frost is a charming variety |
|
| Ming Dynasty - yellow | |
| Superstition - almost black iris | |
| Spiced Lemon - brownish yellow |
|
| Change of Pace |
The dwarf iris also boasts many beautiful flowers, for example.
| Iris name | Photo |
| Yo-yo |
|
| Dixie Pixie |
|
| Blue Line |
|
| Captive Sun |
|
| Firestorm | |
| Music |
|
| Pele |
Depending on the variety, bearded irises bloom from April to June-July.
What type of iris to choose for the site
It is possible to recommend specific species for cultivation based on climatic conditions and characteristics of the land.
If the garden is located in a lowland, and the groundwater lies close to the surface, then marsh irises, spuria or Japanese will feel great on such a site.
For areas with harsh weather conditions, Siberian and Sino-Siberian varieties, frost-resistant bearded hybrids are suitable.
Spuria are afraid not so much of Russian winters as of a long, hot summer - they will be more comfortable in the middle lane.
Bulbous irises, provided that they are dug up for winter storage, will take root in any conditions. In the northern regions, they can not even be planted in the ground, but taken out for the season directly in pots, they do not branch under the ground as actively as rhizomes.
Yellow (marsh)
The marsh iris (Iris pseudacorus) is a vigorous perennial with narrow green decorative leaves and gorgeous, bright yellow flowers. Blooms from May to July. Grows well in the sun and in partial shade at the edge of the pond and in water up to 40 cm deep. The plant is completely hardy. Recommended for ponds.
Although yellow irises are associated with one type of flower, many varieties have been created in controlled breeding. These include.
| Name | Iris airovidny (marsh) - photo |
| Bastard (Iris pseudacorus Bastard) is an aquatic iris characterized by small, light yellow flowers. |
|
| Berlin Tiger (Berlin Tiger) - the variety has a yellow tint, the petals are decorated with brown veins. | |
| Creme de la Creme (Creme de la Creme) - a variety with an extremely light yellow tint, turning into a delicate cream color, a characteristic feature - delicate purple veins. | |
| Holden Clough - exotic pseudo-aire iris, yellow petals are covered with thick and characteristic veins of a purple-brown hue. The variety appeared in breeding in the 70s of the last century in the Holden Clough nursery in the British Isles. |
|
The choice of planting material
Buying iris seedlings requires a picky attitude:
- the link of the rhizome should be complete, dense and elastic;
- it is good if there are several links on one share;
- the root cut should be uniform in color, without blackness and rot inside;
- it is better not to take too fat thick rhizomes;
- hairy roots on the share are undesirable, they are too fragile and will break off when planted;
- it is necessary to choose links with rudimentary tubercles of small roots;
- the fan of leaves is green, fresh, cut off by at least 15-20 centimeters;
- the presence of additional axillary leaves is good.
Irises are often sold during flowering, keeping the peduncle on the share is considered good form among gardeners. This allows the buyer to judge the variety and health of the plant.
Onion specimens are subject to standard requirements for this species - the onion must be complete, elastic, without affected areas.
Irises photo gallery
Site selection and soil preparation
For planting irises, sunny open spaces are suitable. You can protect them from the winds using a blind fence or hedge. However, the wind is not welcomed by any plants, and protection from it needs to be thought out already at the planning stage of the site. Direct sunlight at noon hours is undesirable, at this time it is necessary to organize partial shade.
On acidic soils, irises actively form new leaves and bloom reluctantly. The best option for them is alkaline or neutral earths. Liming the soil with wood ash, chalk, river sand and even medium-sized blocks of limestone or sandstone is the right solution.
Weeds must be removed especially carefully, since weeding them over the growing irises is problematic - you can damage the roots of flowers.
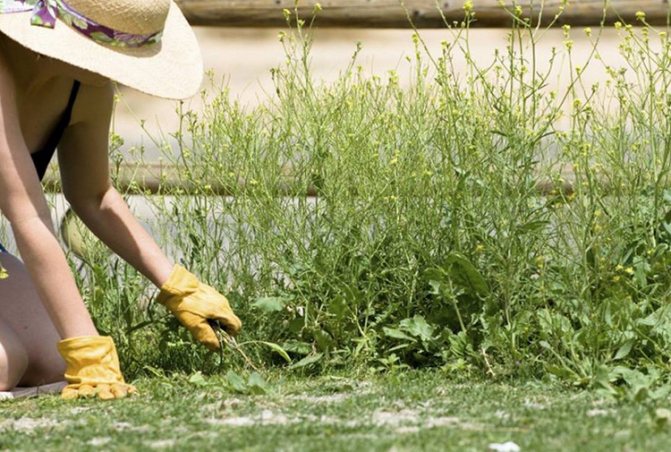


For bearded and bulbous irises, you can organize a dwelling on rocky slopes, natural rockeries or at the base of alpine hills.
Swamp or similar moisture-loving specimens from among the beardless are good to settle near a small reservoir or well. Bulbous and bearded subspecies will not survive such content.
Fresh organic matter is harmful for irises, compost and fecal fertilizers should be applied already well rotted and to a depth below the occurrence of rhizomes.
In order to avoid stagnation of moisture, the beds can be raised above the ground or a drainage layer in the form of river sand or expanded clay can be provided. Lay the drainage to a depth of 20 centimeters, since the root system of irises is horizontal and shallow.
During spring digging, a liquid phosphorus-potassium supplement is applied at the rate of 15 g of superphosphate and 10 g of potassium sulfate per 10 liters of water. Dry fertilizers are not applied before planting, and even more so on the roots of irises.
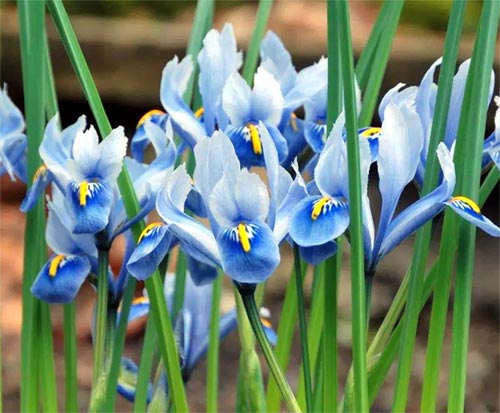
Reticulate
Iris reticulata is the main representative of the bulbous iris species. Usually it reaches a small size (about 15-20 cm), one of the first blooms in spring (III-IV). After flowering in early summer (VII), it dries up, and you can start propagating the plant. Flowers usually have various shades of purple, contrasting yellow spots on the petals, although some are also quite yellow. Blue irises are common.
The netted iris should grow in a sunny location, sheltered from the wind. The best earth for him is permeable and warm. The view is ideal for rock gardens, rabatki, creating an early spring garden in a container. The soil should warm up quickly. The bulbs are planted to a depth of 5 to 6 cm.
Most popular varieties
| Name | Photos |
| Ash Gem (Purple Gem) | |
| Cantab - light blue |
|
| Harmony - deep blue sky colors | |
| Ida - blue with dark blue and yellow spots | |
| Joyce - sky blue | |
| Katharine Hodgkin - pale blue and yellow | |
| Natasha (Natascha) - light blue with white and golden yellow spots |
|
| Pauline - purple with white spots |
|
| Ash Gem or Violet Gem - purple and plum purple |
Landing
Planting in spring is the wrong decision for rhizomes. During the period of active growth of fragile hairy roots, these plants are very vulnerable. Iris is difficult to plant without damaging it. And the injured root will hurt for a long time and will not bloom soon.
Therefore, rhizome irises are planted on time or immediately after flowering. At this time, the plant is already preparing for the resting phase; the rudiments of future hair roots only swell on the sectional root. Depending on the type of plant, the planting period is from the end of May to September.
The prepared soil is loosened, watered with water, and a shallow hole is formed in it with an elevation in the center. The root is placed on this elevation, distributing thin hairy roots around. Then the seedling is covered with earth and slightly compacted. You don't need to water it again.
Tall irises need to be tied up, it is better to install the pegs immediately at the planting stage so as not to get into the root later with the tip.
Bearded irises are planted at a shallow depth of 3-5 centimeters. Some gardeners recommend stripping the roots during flowering so that they receive more oxygen and sunlight.
Non-bearded ones deepen more, from above they must be covered with moisture-retaining mulch (peat) and watered.
A too deep plant will rise to the surface, but this will not happen in one season.
The landing distance is relevant for most varieties:
- between tall specimens maintain an interval of 50-60 centimeters;
- the average height of the plant is seated at 30-40 centimeters;
- for dwarf varieties, 10-20 centimeters are enough;
- the landing strategy is chosen in one line or in a checkerboard pattern.
Properly planted, healthy plants will continue to bloom that same year. They reach the greatest abundance of flowering in the second or third year after planting.
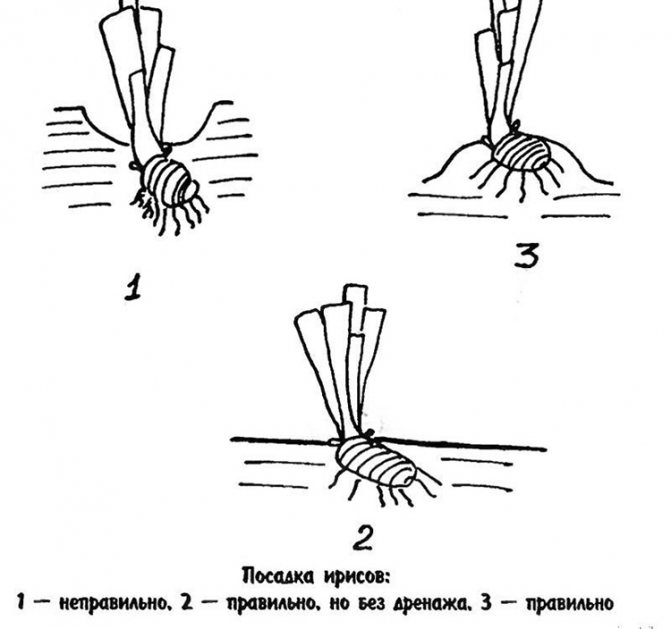
When planting iris, the rhizome must be oriented to the south so that it is well warmed up by the sun - this will be the key to the formation of new buds. It is better to place a fan of leaves along the row, so the planting will look neater, even when the irises in growth budge.

In autumn
Another option for planting rhizomes is immediately after the termination of the growing season. This is the best time for dividing bushes.
It is recommended to plant rhizome irises once every three to four years. In a good location and with proper care, they can happily exist for up to five to seven years.
The biggest "couch potatoes" are spuria, they do not like transplants, they get sick for a long time and take root. But in one place they can grow safely for more than fifteen years.
But even if there is no need to move these plants to another place, their expansion on the site must be controlled. Rhizomes grow, disrupting the layout of the flower beds, young shoots oppress the mother plant and surrounding flowers.
To carry out the division procedure, you must wait until the plants enter the dormant period, after which:
- the plant in the flowerbed is well filled with water;
- the scallop of leaves is cut obliquely by about a third;
- gently dig in and remove from the ground;
- the root is divided into sections with a sharp clean knife, making an incision on the thinned part;
- the slices are sprinkled with charcoal, you can treat with phytosporin according to the instructions;
- young divisions are planted in a new place.
If there is a need to store planting material for some time, they do it in a cool dry place, laying the rhizomes in one layer on newspapers or sprinkling them with onion peels. Storage in a damp environment is not acceptable.
Planting bulbous irises
Planting in spring after the end of frost is most suitable for xyphyums. Iridodictium and Junon bulbs planted in spring will most likely be able to bloom only after a year.
Early autumn is best suited for planting them. You need to have time with this procedure two weeks before the first frost. Later, the bulbs will not have time to take root and will die.
Bulb irises are planted with the bottom down to a depth of no more than 8 centimeters, with an interval of 10 - 15 centimeters, so that the bulb does not rest against the ground with its bottom. Some gardeners take the size of the bulb as a basis, deepening it two lengths. The planting site is not watered.
When planting bulbous irises in autumn, it is recommended to deepen the bulb as much as possible - by 10-15 centimeters. In the south of Russia, experienced flower growers achieve long-term cultivation of xyphyums by burying the bulbs up to 20 centimeters.
Japanese
These species are slightly less popular than the bearded ones, rarely found in home gardens, but deserve interest. Despite their exotic origins, Japanese irises are not difficult to grow. They prefer sunny positions (although they tolerate a little shading). The soil should be moderately moist and neutral. Plants on the banks of ponds look great. A flower is planted from March to May.
Japanese irises are beardless plants. They usually reach a height of 1 meter, bloom quite late (July-August). The inflorescence of Japanese irises has a slightly different shape than that of other species, it is flattened, has smaller central petals.
White or burgundy flowers usually appear on the shoots. The flower has high frost resistance - it can winter outdoors, but should not stand in water.
There are many varieties in this group that differ from each other mainly in the color of the flowers.
| Name | Photo |
| Edmonton | |
| Marmoura (Marmouroa) | |
| Azure |
|
| White Lady | |
| Oriental Eyes |
Reproduction of bulbous
In the second year of life, the iris is overgrown with children. After flowering, when the aboveground part of the plant dies off, the bulb is taken out of the ground, the children are separated from it and sent to grow in fertile soil, placing them at intervals of 10-15 centimeters. In autumn, larger bulbs can be planted in a flower bed or stored. They will bloom in two to three years. It is clear that the easiest way to achieve division by children is from juno and iridodictiums, since in most regions xyphyums are grown as annuals.
To work with irises and any bulbs, you should pay attention to special baskets for growing these types of plants. They will allow even the smallest children to be removed from the ground without loss.


Dutch
Siberian iris is not the last suggestion for a garden. It is also worth paying attention to other species, one of which is the Dutch bulbous iris (Xiphium hollandicum). The plant can grow up to 60 cm in height and blooms in June. It is a bulbous hybrid that produces tall shoots on which single flowers appear. Some petals have yellow spots. The flowers are yellow, white, purple and blue. Dutch irises are used for cut flower beds.


They are some of the easiest irises to grow, although they can freeze in winter. The Dutch iris needs a sunny position, protection from the wind. The optimal soil is fertile, rich in humus, and permeable. The bulbs are planted from April to May to a depth of 10-12 cm. The soil should warm up.
Important! The Dutch iris is not as frost-resistant as the Siberian iris. It can winter outdoors, but requires good shelter.
Reproduction is carried out by separating the baby bulbs. This is done during the resting period of the plant.
Dutch iris varieties
| Name | Photos |
| Barboletta (Barboletta) - variety gives large blue flowers, flowering period - May-June |
|
| Pink Parafit - lavender-colored petals, arranged in a slightly different way, reminiscent of terry begonia. Flowers reach 16 cm. |
|
Root iris care
Watering is carried out in the morning as needed. The determining factor is, first of all, the type of irises: non-bearded ones are more in need of dampness.
During the growing season, several dressings are made taking into account the state of the plants. It is necessary to fertilize with organic matter with caution, it is better to limit it to its introduction into the soil. Mineral fertilization is carried out in several stages:
- the first nitrogen fertilization (10 g of ammonium nitrate in 10 liters of water per 1 square meter) is carried out when the leaves begin to grow intensively;
- the second feeding (10 g of nitrogen, 15 g of phosphorus and 20 g of potash fertilizers per 10 liters) after two weeks;
- during the flowering period, 10 g of phosphorus and 10 g of potash fertilizers are applied per 10 liters of water;
- at the end of flowering, the procedure is repeated;
- the last time in the season irises are fed shortly before the end of the growing season - 10 g of phosphorus and 10 g of potash fertilizers per 10 liters of water.
All top dressing is applied early in the morning or in the evening on damp soil, avoiding contact with the leaves.
If irises do not bloom well with massive healthy foliage, before the formation of peduncles they are stressed out - they limit watering and stop fertilizing. The soil is additionally limed with a solution of wood ash during rare watering.
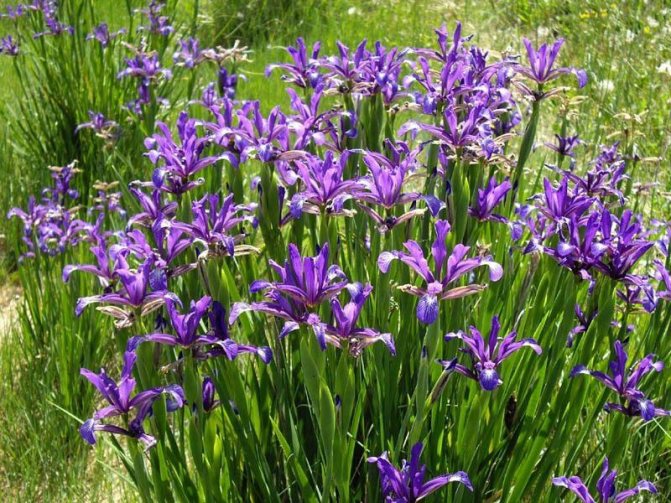
Siberian
It is rare to find Siberian iris in the garden, more often it is found in natural meadows. The Siberian species prefers sunny positions. It forms large bales, not particularly picky about the ground. Siberian iris can grow up to 70 cm in height. Leaves stand out in appearance, they are rather long, thin, acquire a slightly blue tint.
The plant forms small white or purple flowers, developing 2-3 pieces at the end of a long, thin shoot. These are not the only colors, there are also blue irises. Flowering period: May - July.


The Siberian species is frost-resistant, therefore it grows well in our climate. However, this requires fertile soil with a slightly acidic reaction. Its cultivation is not difficult, there are no big requirements. Since the Siberian species loves moisture, regular watering is most important, especially during a drought. Fertilization is carried out only before planting if the soil in the garden is not fertile enough. The plant can overwinter in the ground and not freeze. Regardless, it is worth covering it with leaves or straw.
The most popular varieties are purple-blue flowers. However, in addition to this, other colors are also available. White Siberian iris is a distinctive feature - beautiful white flowers. Siberian white irises are considered a variety originating from Germany, although this is not an official figure. Grows well in sunny places, on fertile soil. The variety is considered the most noble.
| Iris name | Photo |
| Snow Queen | |
| Barbata Media is a 40 cm tall plant. | |
| Barbata Elatior - flowers 70 cm high. | |
| Siberian varieties of blue-blue color - flowers bloom from July to August. Flower petals are smaller, but with more inflorescences. One of the more interesting varieties is Perrys Blue. This variety blooms very profusely with blue spring flowers (flowering: May-June). The plant is completely frost-resistant. It can be planted on flower beds. Looks great next to the pond. |
|
Cultivars are usually intensely colored, may have white or yellow patterns, and have larger inflorescences.
Some varieties of the Siberian species - photos and descriptions
| Variety name | Siberian iris - photo |
| Concord Crush - flower petals turn blue, turning into a purple hue. The variety is called multi-petal. Flowering begins in May. |
|
| Dear Delight is a flower with blue petals with white spots, a visible vein structure. |
|
| Hubbard (Hubbard) - varieties that are distinguished by an intense purple-pink color. The flowers are very large, with white bloom along the edges of the petals. | |
| Jamaican Velvet is an intense purple variety. The petals are distinguished by the lighter spots that are characteristic of this flower. | |
| Pink Parfait Pink Parfait is a multi-petal variety, the flowers of which reach a diameter of 16 cm. The color of the flowers is pink. | |
| Miss Aplle is a hardy flowering plant with a relatively young age compared to other varieties. The color of pink petals turns into lavender, purple. |
|
| Rosy Bows is a double petal variety. The pink color turns into light purple, blue. |
|
| Jewelled Crown |
|
| Fortel | |
| Contrast in Styles |
Bulb iris care
After the bulbous have faded and the foliage has dried, they are removed from the ground. They are kept for a couple of hours in a weak solution of potassium permanganate (other disinfectants can be used), dried and stored in a dry ventilated room. Climatically adapted varieties are recommended to be returned to the ground before the onset of frost.
Heat-loving bulbs are left to wait for spring in pantries and sheds. It is important that in winter the storage temperature does not drop below 2 C.
How do irises propagate?
Iris flower propagates by dividing rhizomes. Once every 4-5 years, after the end of flowering (July - early August), a piece of 1-2 years old with a bud of renewal and a bunch of leaves is separated from the maternal root. But before separating the kidney, you need to warm the mother's root in the sun for 5-6 days.
After dividing, the delenki must be disinfected in Homa solution for 30 minutes in order to kill all pathogenic bacteria.After that, the young roots are dried for 2-3 days in the sun, sprinkled with crushed coal on all sections, and only then used for planting.
Growing from seeds
After flowering, bolls are formed. Peduncles are not removed, the seeds are allowed to ripen. They are sown on fertile soil in boxes and put away for the winter in a room with a positive temperature.
In the spring, a greenhouse is pulled over the sowing and watering begins moderately. The plants obtained in this way are planted in the fall. However, it takes more than one year to wait for them to bloom.
During seed propagation, most irises do not retain varietal characteristics. It is highly likely that you will end up with a wild specimen, on the basis of which the hybrid you like was bred.


Varieties with a rich history
The most numerous are high varieties bred in different periods of the last century. In addition, several of the oldest varieties, developed in the 19th century, stand out.
| Name | Photos |
| Flavescens (De Candolle, 1813) |
|
| Honorabile (Lémon, 1840) | |
| "M-me Chereau" (Lémon, 1844) |
|
| Mrs Horace Darwin (Foster, 1888) |
The group of low (miniature, dwarf) and early flowering represents about 20 varieties, including:
| Name | Photo |
| Buddha Song | |
| Derring-Do | |
| Forest Light |
|
| Lilli-White |
|
| Scribe |
It is difficult to name the most beautiful varieties of irises. However, it is worth mentioning a few of them that have received many awards, including the highest award, the British Dykes Medal from the British Iris Society.
| Name | Photo |
| Amethyst Flame with amethyst pink flowers |
|
| Eleanor's Pride with blue | |
| Stepping Out background with white and purple | |
| Sable Night with black veins |
Irises after flowering
Most rhizome irises, having stopped flowering, retain their spiky glossy leaves. By themselves, they are very decorative. It is not recommended to trim them. It is only necessary to remove dried and diseased parts in time.
Immediately after wilting, the peduncles of rhizomes must be cut off without waiting for the seeds to ripen. They become the most vulnerable part of the plant to diseases and pests.
The aerial parts of aryl and bulbous specimens dry up after the death of the peduncles. This is a natural process when the daylight hours will decrease, the foliage will grow back. During the summer dormancy, they need mulching shelter and protection from excess moisture. Otherwise, the rhizomes can rot. When new leaves appear from the ground at the end of summer, the mulch should be raked out and watering resumed.
Tips for growing irises from experienced gardeners
- When choosing a planting site for an iris (iris), try it on seven times so as not to disturb it for 3-5 years, taking into account other plants growing next to it, which may subsequently become a shadow hindrance to the light-loving iris.
- Neighbors should also choose iris (iris) according to the irrigation regime - it is not recommended to plant next to those plants that need increased moisture - iris can get sick with rhizome rot.
- Irises (irises) bloom brightly and fantastically, but faded flowers spoil the look of the entire curtain or iris garden. For this reason, you should regularly cut off or simply break off the faded flowers, which not only spoil the aesthetic appearance, but also take the juices of the plant for the formation of unnecessary seed bolls. But if there is still a need for them, then make a reasonable exception.
Irises are flawless in the bouquet cut, especially with tall stalks. They look good in a tall vase, but picking off faded flowers in this case is especially necessary in order to allow the next buds to open. As a rule, all the buds manage to become a flower and such a bouquet pleases for a long time with its beautiful appearance.
Preparing for winter
It is not recommended to dig up zoned varieties for wintering. However, it would be wrong to leave them without shelter for the winter. The rhizomes are covered with earth.The garden bed is covered from above with fallen leaves, needles or straw.
An interesting way: to plant green manures or winter cereals right in the fall. Plants will fall in winter, forming a natural fur coat over the flower bed, and at the same time enrich the soil with nitrogen.
If it snows all winter, these measures will be sufficient. During periods of thaw, care must be taken to ensure that the covering layer is not saturated with moisture - with subsequent glaciation, the irises may die.
How to plant irises correctly?
How to plant irises outdoors? Before proceeding directly to planting, you need to make sure that the place suits them. This is a very light-loving culture. She needs a lot of light, so the landing site should be in an open area, without constant natural or artificial shade.
As for soil moisture, it all depends on the variety. "Kempfera", "Bristly" and "Yellow" iris flowers are grown in swampy areas, and "Siberian" needs moderate humidity. Most bearded irises prefer drained soil. So this point needs to be clarified in each individual case.
Important!
Irises cannot be called finicky flowers, otherwise they would not be so common around the world. But it is also not worth equating them all under one. Different varieties may have their own special preferences for the amount of moisture, type of soil and other points for care and planting.
Planting is carried out in autumn or spring. Before the procedure, you need to fertilize the soil (with humus, phosphorus, potassium and nitrogen, or compost), remove all weeds and their roots, or treat the land with herbicides so that weeds do not grow on the site. If the soil is too heavy or light, it needs to be balanced - peat and sand are added to the clay, and clay soil is added to the sand. You also need to adjust the acidity - the iris flower prefers a medium acidity soil.
Interesting!
Herbicides, against which gardeners are actively "fighting", are very popular when growing flowers. After all, flowers are not used for food and therefore such chemistry will not bring harm on a flower bed.
To plant irises, you need to make holes or a trench, to double the height of the root. Then moisten the soil and plant the roots. After that, they are sprinkled with earth, the soil is mutely compacted and left to germinate. If the ground section is very high, it should be cut in half immediately after planting.
Separated roots are always planted superficially. Only a thin layer of soil should cover them from above. If the planting was carried out in the fall, the planting should be covered with spruce branches for the winter and mulched with sawdust or some similar raw material.
Bouquets of irises


Iris are considered a symbol of friendship, so a bouquet of them is a great opportunity to express your gratitude to a close friend. Floral arrangements of these flowers will be appropriate only as a gift for romantic girls. Also, as a symbol of good news, it is appropriate to give a bouquet of irises when you leave the hospital. But don't give these flowers to business partners.
Beautiful bouquets of irises are obtained in combination with tea and any yellow roses, pink and snow-white carnations, lilies and daisies. Colorful spring compositions are obtained with yellow tulips and crocuses, and autumn compositions with sprigs of white chrysanthemums. It is not customary to combine them with gladioli.
Irises in a wedding bouquet are a vivid evidence that the bride is ready to throw a daring challenge to all established stereotypes. Flowers of the traditional violet-lilac scale will look most advantageous against the background of a white dress. For such a solemn occasion, compositions of irises with tulips, white roses and bells, which will emphasize the delicate image of the bride, are also perfect. Bouquets of lilac and yellow flowers will be appropriate for a wedding where boho style reigns.
And you can read about other equally beautiful bouquets in an interesting article on our website.
Content
- Listen to the article
- Description
- Growing features
- Planting irises When and where to plant
- Planting in spring
- Planting in autumn
- How to care
- Bearded irises
Popular types of Siberian irises
The varieties of this group are odorless, slightly smaller than the bearded ones, without a beard and with longer narrow petals. They grow in large bushes and are the most cold-resistant, unpretentious centenarians. These flowers look beautiful as a flower decoration of a garden pond and grow better in moist soil.
The Snow Queen
This is the most effective variety in terms of the minimalism of its color range. An incredibly snow-white flower with golden splashes really seems to be the queen of the winter kingdom, whose head is crowned with a gilded crown.
Dance ballerina dance
This is another popular variety of Siberian irises. The elegant flower of airy pink color resembles a gracefully dancing ballerina. Among the beautiful irises, it is considered one of the most popular, which is not surprising given such beauty.
Lady Vanessa
These flowers fascinate with an amazing range of purple shades, close to the color of lavender inflorescences, slightly corrugated edges of the lower petals and a white patterned speck that stands out in contrast at the base.
Groups of bearded irises by color
Bearded irises are the largest and most beloved group of garden flowers. By color, they are divided into several main groups:
- monochromatic - all colors of the rainbow and even more;
- two-tone - one color, with shade options;
- two-color - bottom and top of different colors.


The color of the neglect also stands out - a complex combination of blue-violet shades.
White
White irises are a rarity in our flower beds. Snow-white petals sometimes have small blotches at the core of a bright tone, which enliven the flowers. Famous varieties - White Nights, Bianca, Immortality, Snowflake Lacey, Lady Snowflake.
Blue
Irises of the color of the sky are frequent guests of flower beds. Breeders spend a lot of effort to get blue roses or gladioli, and there are many varieties of blue irises.
Blue irises are distinguished by tenderness and sophistication, they are planted next to blue or purple flowers, creating wonderful combinations. The best varieties are Divine Duchess, Lake Placid, Superman.
See also
Growing and caring for a diploma at home, methods of reproductionRead
Blue
Bright and cold blue flowers are noticeable in any flower garden, they look spectacular in a bouquet. Blue irises are not uncommon; the most favorite varieties are Honky Tonk Blues, Dusky Challenger, Victoria Falls, Sapphire Zarya.
Purple
Irises of violet hues are usually combined with delicate flowers of white and pink tones to dilute the intensity of their color. The best purple hybrids are Explosive, Lady Vanessa, Smile, Cupid-Father.
Lilac
The delicate color of lilac is loved by most summer residents. These irises go well with light and purple flowers. Good choice - Attention, Mriya, Super Model.
Red
Red flowers are always particularly eye-catching, standing out against the greenery. Popular among red irises are New Centurion, Play with Fire, Rhett.
Pink
Delicate flowers of pink-apricot shades do not stand out so brightly in flower beds, but they look great in bouquets and apartments. They are best viewed at close range to enjoy all the nuances of colors. Representatives are Windsor Rose, Adorable Pink, Lace and Ruffles.
Yellow
Yellow irises look harmonious against the background of greenery, cheerful and bright. They cheer up with their sunny colors - Martile Rowland, Muffin, Autumn Fiesta.
Orange and brown
Warm colors are loved by all growers.In combination with cold ones, they create multicolor in flower beds and delight with exquisite combinations. The best hybrids with shades of orange and brown are Brown Lasso, Sunset in Avalon, Silkyrim, Gambler.
Black
Many people love the gloominess of the dark shades of irises among the bright greenery of the garden. For lovers of Gothic, pay attention to the varieties - Before the Storm, Night Game, Black Dragon.


Features of irises
Irises have rhizomes on which roots grow, which have a cord-like or thread-like shape. There are one or several annual peduncles. Flat thin two-row leaf plates have a xiphoid shape, linear ones are rarely found. There is a thin layer of wax on their surface. They are collected at the base of the peduncle in a fan-shaped bundle, while the stem leaves are practically absent. As a rule, the flowers are single, but not very large inflorescences are found on such plants. They are usually fragrant and large in size, distinguished by a very unusual shape, as well as a bizarre color. So, the color can be of different color shades, as well as their very bizarre combinations. The flower has 6 petals, which are the perianth lobes. The outer lobes in the amount of 3 pieces are slightly turned downwards and have a color different from the upper lobes. The fused upper lobes resemble a tube in shape. Long bloom from May to July. 2 or 3 flowers bloom at the same time, and they do not fade within 1–5 days. The fruit is a three-nested capsule.
Cultivation of rhizome irises - bearded and beardless
Bearded irises come in a very wide range of colors - brown, black, blue, apricot, purple and various interesting two-tone combinations. Among the beardless varieties, the most popular are Siberian and Japanese. There are hundreds of flowers and thousands of iris varieties to suit everyone. These amazing plants are loved by many summer residents, flower growers, collectors, so you need to know the secrets of growing them. How to care for irises so that they bloom profusely is the most popular question that arises among gardeners.
The classification of bearded irises is due to the height of the plants and the size of the flowers:
- miniature low (10-20 cm);
- low (20-30 cm);
- medium (30-40 cm);
- miniature high (30-50 cm);
- high (70-90 cm).
Planting time, soil selection
For best results, it is important to know when to plant irises outdoors. Usually males should be planted in late summer, from late July to September. If the summer is hot, it is better to plant irises in the fall - in September. It is important that they take root long before the end of the growing season.
On light soils, the rhizome is sprinkled on a centimeter; on a heavy site, it is impossible to plant cockerels.
Siberian species tolerate partial shade, although they bloom worse in the shade.
An important difference between bearded irises and Siberian ones is that bearded irises cannot stand shade, they love the sun very much!
Bearded species require at least half a day of sunlight. They like completely sunny places. Good drainage is needed, which is obtained by planting plants in elevated flower beds, ridges or on slopes. About 60% of cockerels bloom in the first year, some bloom in the next season.
Attention! In the sun rhizome irises grow and bloom better, rhizomes are healthier. In sunny positions, the flowering period is slightly shorter, and in light shade, flowering can be enjoyed much longer.
Features of Siberian varieties:
- Requires a sunny position for good growth.
- The flower loves warmth, especially during the flowering period, but it is quite frost-resistant, copes well with the winters of the middle lane.
- The Siberian species comes from cold regions, tolerates low temperatures well.
- Loves water - in its natural environment it grows on moist soils, therefore insufficient moisture, rapid drying of the soil is not recommended. No need to worry about drainage.
- He likes a little acidification of the soil, it is worth remembering this when using fertilizers before planting.
Some rhizome irises, such as Siberian (Iris sibirica) or yellow (Iris pseudacorus), require more fertile and moist soils, and can grow at the edge of the pond.
Soil preparation
Irises grow in many soils. If the soil is too heavy, coarse sand, compost can be added to improve the permeability of the soil.
For bearded varieties
The ideal pH is 6.8, but males are tolerant of soil acidity, small deviations will not harm. To reduce the acidity to their requirements, the soil is mixed with lime or sulfur is added.
If this is not possible, it is worth digging up the entire flower bed where the cockerels should grow, mixing earth with organic matter, sand and making a small elevation. Then the rhizomes will definitely not get wet. The prepared rhizome with shortened leaves and roots is laid so that the leaves are located from the north, and the rhizome from the south.
It is important that the roots are on a small mound. During planting, you should think about a drainage layer so that the plants do not stand in the water, in which case they may have problems with fungal diseases.
For Siberian
These varieties have no special soil requirements. The acidity needs medium. Wet locations are preferred.
An important difference between bearded irises and moisture-loving Siberian ones is that they do not like too wet soil! They get sick in wet places.
Planting depth
Rhizomes are planted in a special way. A prepared plant with shortened leaves and roots is planted so that the leaves are located from the north, and the rhizome from the south. Thanks to this, the leaves do not shade the rhizome, and the rhizome is warmed up by the sun.
This is important: the roots should point downwards, not twisted.
The rhizomes are not buried deep in the ground, they are laid on an elevation (mound), and lightly sprinkled with earth on the side, squeezing the roots. The top should protrude.
Attention! The most important mistake when growing bearded irises is planting too deep, due to which the rhizomes rot, the plants do not bloom or bloom poorly.
The top of the rhizome should protrude.
Landing scheme
Usually, the distance between the bushes is 30-60 cm. The planting pattern depends on the height of the iris and the strength of growth. Some plants are too expansive, others are not. If we plant too many bushes, the males will quickly grow, come into contact with each other, and soon rejuvenation and transplantation will be needed. On average, you need to plant irises every 3-5 years.
Planting irises - scheme
Watering
Newly planted plants need moisture in order for their root system to develop quickly. The amount of water depends on the type of soil. Flowers planted in heavy soils are not watered often because the soil retains moisture. When the irises grow in the next season, they no longer need watering except in hot and dry weather. Watering plants too often is another common mistake when growing irises.
Fertilizer
For feeding irises, bone meal and superphosphate are used. Fertilizers with a large amount of nitrogen adversely affect the plant and cause many problems. Fertilizing irises should be careful and thoughtful. A month before flowering, during the flowering of irises, phosphorus fertilizers are applied - superphosphate, scattering it far from the roots, in no case directly on the rhizome. In September, the plants are fed with bone meal.
Iris transplant
Reproduction of irises is carried out by dividing the rhizome. It is better to replant irises when the bushes inside are "bald", preferably every 3-4 years. Overcrowded rhizomes suffer from lack of nutrients, crowded conditions, and diseases. The division of the rhizome is very simple, the roosters are transplanted in spring or autumn - in September. You can do the separation in 2 ways:
- Dig up whole bushes, remove old rhizomes from the inside and plant large outer and young ones, which is clearly visible in the figure.
- Cut out the best iris rhizomes from the outside and discard the remainder.
This creates a great opportunity to trade cockerels with friends. Rhizomes are easy to dig up, unlike some other plants. The roots do not grow deeply, and the rhizomes "sit" close to the surface of the earth. Thanks to this, new, interesting varieties can be obtained.
How to send irises? The rhizome can be shipped in a plastic box or bubble envelope, the plants do not dry out in transit.
How to grow irises from seeds?
Some growers grow irises from seeds. This is an unpopular and long-term breeding method. Iris seeds are planted in October of the same year when the plants bloom so they don't germinate until winter and stay fresh.
Sowing depth - 3-5 cm, crops can be covered. They should sprout in the spring.
Photo. This is how sprouts planted from seeds in October look like at the end of May.
Photo. Seedlings at the end of June


Irises from seeds begin to bloom in 2-4 years, sometimes later.
Care in the growing season
- In summer. It is important that there are no weeds on the beds, so that the tips of the rhizomes are warmed up in the sun. Weeds are removed carefully so as not to damage the roots. There is no need to mulch the soil by covering the ground with bark or other mulch.
- Caring for irises after flowering includes the obligatory pruning of each faded flower one by one. When all the flowers have faded, all the stems are cut out from the ground. Healthy green leaves are left, diseased leaves and brown ones are removed.
- In late autumn, caring for irises is to prepare for winter - we cut the leaves by about 15 cm.
- In winter, newly planted males need shelter, especially in regions with cold winters. Good materials are straw, needles, dry leaves. They remove the shelter in early spring. If you don't know how to properly prepare irises for winter, late frosts can harm flowering.
Japanese iris is highly frost-resistant. He can stay in the ground, but during these unfavorable months he should not stand in the water.
Irises in landscape design - photo


Diseases and pests
Irises are often victims of fungal diseases such as leaf spot. If the first symptoms are noticed, the infected flowers and leaves should be quickly removed and the plant should be sprayed with a suitable fungicide (eg Topsin M 500 S.C, Gwarant 500 SC).
Rhizomes attack bacteria, causing rhizome rot. The disease is facilitated by:
- excessive moisture in the substrate;
- nitrogen fertilization of plants;
- mechanical damage to rhizomes.
To stop the development of bacterial rot, all infected and damaged rhizomes are removed, the rest are sprayed with copper preparations.
Iris is threatened by pests such as aphids, other insects that crawl in the leaves, making corridors and small holes. Insects are fought by spraying with a suitable insecticide (Karate Zeon 050 CS, ABC, for aphids Decis, Mospilan 20 SP).
Growing in pots
A very interesting way to arrange a garden is to grow irises in decorative pots.
The pots should have a drainage hole at the bottom. A layered drainage layer in the form of broken pots, expanded clay is laid at the bottom of the pot. A light, permeable soil with a slightly acidic pH is poured on top. You can add pine bark compost to the ground.
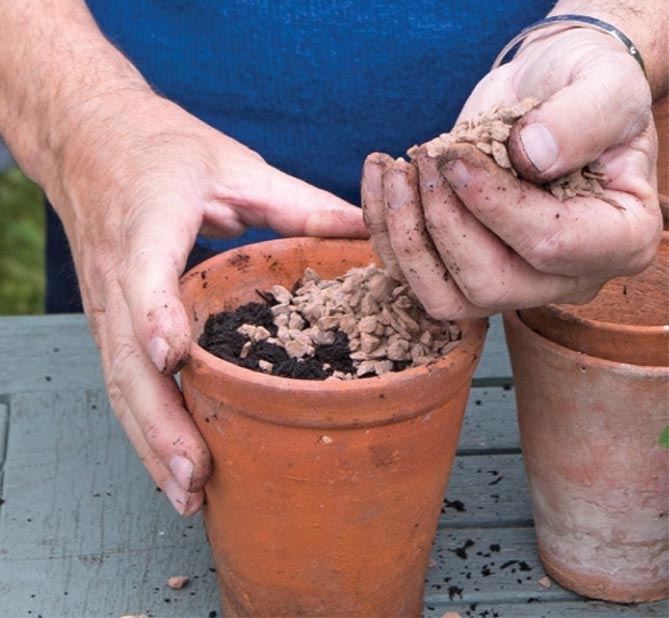


Over-watering the rhizomes will rot in too moist soil. After flowering, the iris pot is kept outside (preferably in holes) until next year, or the plant is planted in the ground. Plants are transplanted every 2 years, otherwise the flowering will disappear.
Bearded irises in pots - photo


Planting and care in the open field
If you adhere to the planting rules, then on your site you can grow flowers of extraordinary beauty.
Landing dates
You can plant a plant at any time of the year. But most gardeners recommend choosing a period immediately after flowering, so that the flowers have time to gain strength before the winter cold.
Important! Irises require regular replanting every 3-4 years.Then they will bloom annually and serve you for a very long time.
Material preparation
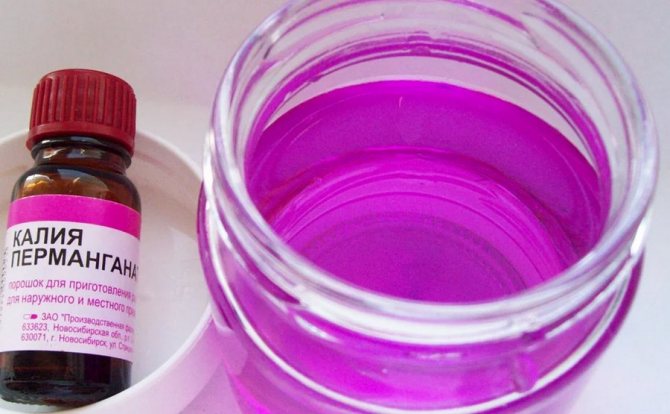
If the seedlings are purchased from a store or market, they can be treated with a growth stimulant before planting. Be sure to remove long roots. If there are places with rot, then they also need to be cut off. Before planting, the seedlings should be placed in a light solution of potassium permanganate. They should be in it no more than 20 minutes.


In cases where the prepared or purchased material needs to be held for several days, it is important not to make such mistakes:
- store seedlings in packages;
- leave them in a damp place or material for more than a day.
Planting
In autumn and spring, planting is the same.
A few words about irises
The iris genus includes up to 200 species! In our climatic conditions, only a few are grown - many species and varieties are not frost-resistant enough. All irises are divided into:
- bulbous,
- rhizome (bearded, beardless).
Although there are significant differences between species, garden irises are easy to recognize. Irises have a distinctive feature - the plants produce numerous dark green xiphoid leaves that grow out of the ground. Fleshy stems grow in the accumulation of leaves, at the top of which a huge, eye-catching, colorful inflorescence appears. Irises bloom for about a month, with the highest flowering intensity in May. To maximize the flowering period, varieties with different flowering periods are chosen: early, middle and late.
It is interesting! All about iris varieties - an article with photographs on the classification of irises, varieties.
The flower consists of several colored petals pointing upward and several gently hanging downward. The inner portions of the calyx usually rise upward and touch each other to form a dome. An inflorescence with a very complex structure that makes the flower exotic.
The most common are bearded garden irises (rhizome). Their peculiarity is that on the surface of the outer parts of the calyx, along the vein, the petals are covered with tiny hairs resembling a "beard". The flower blooms in May - June, gives beautiful, large flowers of different colors. This perennial plant produces multiple stems, so even one rhizome planted in the garden can create a true flower bush. The flower is usually decorated with a yellow or brown beard.
Siberian (iris sibirica) deserves attention. As the name suggests, Siberian irises are native to Siberia. This amazing plant will bring any garden to life. The view is tall, bearded, but due to the smaller leaves and flowers, it looks different. The flower produces numerous xiphoid leaves. The plant gives many flowers - usually blue, blue, flowers are slightly less bearded.
Consider the features of growing bulbous and rhizome irises. Particular attention should be paid to species differences, since the conditions of planting, cultivation of some species are fundamentally different.
Legends and symbols
According to one of the legends, a rainbow was formed from the drops of fire stolen by Prometheus, in the place of which, after disappearing, these colorful flowers grew. According to another legend, they appeared from the tears of the sailor's wife, who was waiting for the return of her husband on the coast. That is why they are also called beacon flowers. Their bright colors from a distance pointed to the sailors on the approaching coast.
"Beauty with Irises", Tsukioka Yoshitoshi
The Japanese see iris as the personification of strength and courage and consider it the flower of warriors. The warrior spirit and the name of the plant are indicated by one hieroglyph.
In Europe, these flowers have long been considered an exclusively royal decoration. Blue irises are associated with the sky and are a symbol of serenity, while white irises symbolize perfection and purity of thoughts and are considered the best choice for special occasions. In general, the iris are a symbol of hope.
The variegated colors and bizarre shapes of petals and buds make irises look like wondrous butterflies fluttering in gardens, especially when the flowers sway in the wind. They always remain at the top of the flower Olympus, like the ancient Greek goddess, after whom they are named, serving as messengers of joy, creating a positive mood. Even looking at a photo of irises, it is impossible not to fall in love with their enchanting beauty.
Varieties of Japanese irises
Japanese iris varieties have large flowers and expressive greenery. In the inflorescence - 3-5 flowers, the total flowering time is about 3 weeks.
Kogesho
The most beautiful representative of Japanese varieties. A flower of exquisite shape - with a strongly open rosette. The petals are snow-white with lilac-purple streaks and delicate yellow strokes in the center. A dense, stable stem grows above a meter.
Vasily Alferov
The peduncle of this variety rises to 110 centimeters, bears flowers of a purple hue with small bright spots of yellow. The lower petals are large, slightly pulled down.
The lion king
A flower of an unusual shape with narrow, bizarre petals. The color of the petals combines several warm shades - yellow, bronze, lilac brown. The lower petals are densely shaded. Iris grows up to 75 centimeters.
Repeating flowering varieties
Some iris varieties grown in warm regions with long summers are capable of blooming twice a season. They are called reblooms or remontants. In August-September, they throw out the peduncle again during the season and delight with another flowering.
Immortality
The Immortality variety is classified as remontant. The first time the iris blooms in May, re-flowering with timely feeding - August-September. The flowers are white, large, the beard is yellow.


Jennifer Rebecca
Exquisite large pink flowers with fringed petals. The beard is orange. The stem rises up to 80 centimeters, firm and strong.
Mother Earth
The petals are lilac-pink, the lower ones are brighter. Small blotches of yellow - in the center of the petals and on the beard. The peduncle bears up to 9 buds. Blooms in June, the stem is high - 90 centimeters.


Harvest memories
Monochromatic flower of muted yellow color. Grows on a tall stem. Blooms again in August. The foliage is waxy, the rosette is dense, the leaf is narrow, xiphoid.
Autumn date
White flower petals are densely covered with dusting and strokes of a blue-lilac shade. The overall impression is a bluish purple iris. It almost always blooms again.
Irises are the favorites of landscape designers and florists. Having correctly selected the varieties for the flower bed, they achieve a long flowering of the group. Greens of many varieties remain decorative for most of the summer. Alpine slides are decorated with flowers, grown in flowerpots and on window sills. From irises they create bouquets that delight for a long time with exquisite beauty.
Division of flowers into varieties
In botany, root irises are divided according to the shape of the flower by the presence of shaggy hairs on the flower petal. There are not beards without hairs and beards with shaggy hairs.
The most famous bearded flower variety is the German iris. It can be of different colors - from a rich blue hue to creamy burgundy, reds.
Non-bearded varieties include: spuria iris, marsh iris, Californian, Louisiana, Japanese.
You can classify iris varieties by their color:
- one-color (when the color is the same for the whole flower);
- two-tone (the top and bottom of the flower have different shades);
- variegata (top - yellow, bottom - red-brown);
- amena (the top of the flower must be white).
Pests, diseases
Amazing flowers are susceptible to disease and pest infestations. To maintain plantings, you need to know how to deal with harmful insects.
Thrips.
In the dry season, thrips appear on the plants. They spoil the appearance of flowers, the beauty and attractiveness of the buds are lost, photosynthesis is disrupted in the leaves.The leaf plates turn brown and dry out.
Control measures... Experienced gardeners use folk methods. The infusion of laundry soap with makhorka has proven itself well. To prepare the solution, you will need to take 40 g of laundry soap, grate it on a coarse grater and add 40 g of shag. Pour all this mixture with water and leave to infuse. After 10 days, the infusion must be filtered. The irises are processed in dry, calm weather, preferably in the evening.
Thrips on iris
Of the chemicals, Karbofos is recommended. The solution is prepared in accordance with the instructions.
Scoops.
The bases of the peduncles suffer from the insidious pest. The plants themselves turn yellow and die.
Control measures. In the fight against scoops use "Karbofos". During the growing season, double treatment is carried out with an interval between spraying of 7 days.
Caterpillars and grinder.
The appearance of pests is indicated by perforated leaves, which turn yellow and dry out. The plant develops poorly and dies.
Healthy plant
Control measures... For spraying it is recommended "Confidor". Solution preparation: dilute 2 ml of the product in 10 liters of water. Stir until complete dissolution and process the plants.
Attention! Treatment is considered most effective when done 6 weeks before flowering. But pests are not the main enemy of irises, the flower often suffers from diseases.
Root rot.
An insidious disease that can lead to the death of a plant. It is necessary to dig out the rhizomes, clean them to healthy tissue and treat the cleaning site with a special compound. Then the rhizomes are dried and planted in a new place.
Ascochitis and cercosporia.
When irises are actively growing, you can notice unusual curling of the leaves, which subsequently die off. Over time, the foliage appears again, but the irises spend a lot of energy on renewal and this has a bad effect on the development of buds and flowering.
Control measures... Copper oxychloride will help. To prepare the solution, you will need to dilute 30 g of the product in 10 liters of water and spray the plants.
Copper oxychloride
Species diversity
In total, there are almost 800 species of these representatives of plants of the family of iris, growing in various parts of the world.


Since their color range is incredibly wide, the following categories are distinguished according to the color of the petals:
- one-color (snow-white and dark purple, almost black flowers);
- with standard (white with blue or yellow with terracotta) or contrasting (pale pink with bright lilac) color combinations;
- variegated (with multi-colored blotches and edging)
According to another classification, the most common in garden design are bearded (more than 500 varieties and hybrids), Japanese and Siberian irises. Before you buy this or that variety, it is worth finding out in what climatic conditions cultivation is possible. Japanese varieties are thermophilic, and Siberian varieties are the most frost-resistant.
general information
It is very important to find out how resistant the plant is to coolness, dampness, and other negative features of the climate before buying your favorite iris. Especially when it comes to a variety obtained in Japan, Australia, USA, and you are going to grow a flower somewhere in Siberia. Such varieties are often thermophilic and not very suitable for our climate.
The following types of flowers are best suited for growing in Russian gardens:
- bearded - the most popular, showy, numerous;
- Siberian - well adapted to cold climates;
- Japanese - with the highest decorative qualities.
Next, I will consider the varieties of irises according to the above classification.
The benefits of irises
In modern medicine, the benefits of the iris plant are known. True, it is allowed to use only a few varieties, which include the Germanic and Florentine varieties.The raw material for the production of medicines is the rhizome of the plant, from which the essential oil is extracted.
Rhizomes are harvested three years after planting. In order to use the rhizome, it must be thoroughly rinsed with water and removed from the roots. After drying, they are stored in a closed jar.
Unusual varieties of irises
Irises obtained by interspecific crosses are sometimes difficult to classify into specific groups. They stand apart, differ in an unusual appearance, often resemble orchids or other flowers, and bear little resemblance to the familiar irises.


Chrysographers
A little-known variety of irises, cultivated in China. Chrysographs are not distinguished by dense abundant foliage, the bushes are decaying, loose and loose. Flowers - with graceful narrow petals, having strokes and spotting in the lower part. These varieties rarely enter the market, so you rarely find them in flower beds.
Spuria
A little-known species of spuria is rarely found in our flower beds. Flowers are similar in shape to orchids, the lower petals are narrower than most irises. Each flower lives up to a week, the whole plant blooms for several weeks. The varieties Golden Lady, Sultan's Sash, Imperial Bronze are popular in Russia.


Louisiana
Breeders of the United States are working on the rare species of Louisiana irises in the Eastern Hemisphere. They are found only in botanical gardens, as they require special conditions of detention. In the United States, these varieties are used for planting near bodies of water.
The well-known varieties include Longue Vue (white-cream), Classiсal Nоte (yellow-orange), Ice Angel (blue).
California irises
Natural species of irises are native to the Pacific Ocean. Grow well in acidic soils. The flowers are not large, they are not particularly decorative. They multiply hard, so they did not receive wide distribution. The bush is evergreen with narrow glossy foliage. Siberian-Californian hybrids are more common, free from most of the problems of purely Californian irises.
Irises: the best varieties, description and photo.
Here is a list of the winners - the best of the best bearded irises. They have already won the hearts of many gardeners, perhaps they will conquer yours too!
Crowned Heads
Medium-sized flower up to 90 cm in height. Ruffled curved vertical petals stand out against the background of snow-white fouls with a bright purple color. The buds are pale blue, open from June to July.
Bred in 1997 and won the Dykes Award for Best Iris in 2004.


Crowned heads
Nine Lives
"Nine Lives" is a dwarf bearded iris up to 35 cm high. The domed standards have a pale creamy white hue. The fouls are claret-lilac, with a well-defined pale pink border. At the very bottom of the fouls, at the point of contact with the standards, you can see yellow-purple streaks.
Very aromatic, introduced in 2007


Nine Lives
Florentine Silk
Tall plant, up to 1 meter in height. The flowers are large, up to 20 cm wide, very beautiful. The standards are pale pink with a peach tint, bordered by a purple rim, and rise above three dangling dark lilac fouls. The beards are violet coral. The petals are covered with veins, curly, corrugated along the edges.
Known all over the world as one of the best, awarded with many medals and awards.
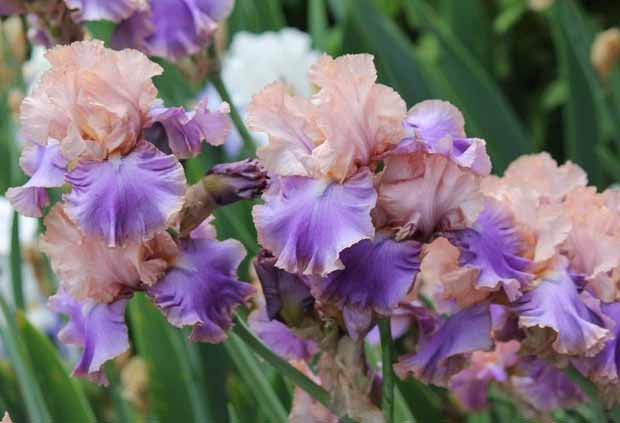


Florentine silk
Arctic Age
A medium-sized variety "Arctic Age" - a snow-white bearded irisos. The petals are dense, with a curly corrugated edge, reminiscent of porcelain. The beard is pale yellow, fouls with golden streaks in the center. Peduncles reach 85-90 cm in height.
The flowers are perfectly white, rising majestically in the shape of a crown above the lower petals.
Arctic Age
Obsidian
The "Obsidian" variety represents the most beautiful irises. Its petals seem to be made of velvet - just as shiny, terry and gorgeous. The color of fouls and standards is black with a purple tint.Dark blue beards, and the same color edging of the petals, give the flower additional sophistication. Stem height up to 85 cm in height, medium flowering period.
He repeatedly won various flower exhibitions and competitions, was nominated for the Dykes medal.
Obsidian
Caribbean Dream
Bearded iris "Caribbean Dream" is an early flowering medium-sized variety. Its flowers are pale blue, azure, monochromatic with blue veins. The beards are light yellow. The bush is tall, up to 80 cm in height.
The bloom exudes an incredibly pleasant vanilla aroma.
Caribbean dream
Varieties of water-loving irises
The group of water-loving irises includes not only marsh, but also multi-colored, bristly, smooth hybrids. All of them are united by a love for water. Plants do well near water bodies, they can be planted in shallow water. Irises are attractive for long, early flowering, resistance to adverse environmental conditions.
Compared to other species, water-loving plants have elongated, narrow leaves of the xiphoid type. The color of the flowers is modest. In most cases, these are variations of blue and yellow shades. Swamp iris reproduces by seeds and vegetatively. Grows quickly in moist, acidic soils.
Berlin Tiger
The flower got its name due to the similarity with the color of the tiger's skin. Key Features:
- stem height up to 70 cm;
- the diameter of the flowers is about 10 cm;
- fouls and standards are lowered, yellow, with densely located brown veins;
- styles are light yellow, interspersed with brown streaks at the tips.
The variety thrives on the territory of Russia. Needs regular hydration. The splendor of its flowering depends on this.
Variegata
The original iris, loved by flower growers not with flowers, but with leaves. The main characteristics of the variety:
- flowers are small, yellow;
- leaves are long, light green, with a longitudinal white stripe.
Due to the unusual color of the foliage, the iris remains decorative until the very frost. It is combined with other perennials, planted in groups near water bodies.
Flore Plena
Luxurious, tall irises. The best varietal qualities are shown when planted on moist, acidic soils. Main characteristics:
- peduncle height up to 1.8 m;
- the petals are bright yellow, at the base a tone darker, due to the brown pattern they form a small spot;
- styles are pure yellow.
Irises can be used for cutting. They are also planted in the background of flower beds in combination with other perennials.
Why don't irises bloom?
Irises are beautiful flowers, but sometimes they don't bloom or they stop blooming. Due to their popularity, irises have received a huge number of varieties that differ not only in size and color of flowers, but in height and shape. Unfortunately, although iris flowers are extremely beautiful and decorative, sometimes they may not appear at all, which is a huge disappointment to us. Below are the main reasons why irises do not have flowers.
Planting depth
One of the reasons for this situation is incorrect planting of rhizomes. Plants have very specific requirements in this regard, if you do not take them into account, irises will not bloom. To wait for beautiful flowers, you need to plant the rhizomes shallow, almost without covering them with soil (if planting too deep, the flowers will not bloom).
Instead of a hole, you need to prepare a small tubercle of soil, on which the rhizome and roots are laid (the roots cannot be folded), and then lightly sprinkle them with soil, covering only the roots and sides of the rhizomes.
Features of planting and root division
- The old school of iris growers focuses on how to properly plant irises. The rhizome should be placed in the ground to the south so that it is not shaded by wide leaves and can heat up.
- Before planting rhizomes, the leaves growing from them must be shortened, due to which the evaporation of water and drying of the roots will decrease.
- Plants should not be planted and divided immediately after flowering - during this time the irises will form flower buds for the next season.
- When digging up rhizomes, it is easy to damage the buds, having lost the flowers of the next year, therefore, when rejuvenating irises, it is better to wait until the end of summer (the second half of August - September). Flower buds are also damaged by gardening tools when carelessly weeding the plants.
Moisture and soil quality
When planting irises, remember that flowers are sensitive to stagnant water, excessive moisture, flooding. When planted in moist, cold soil, the plants will rot rather than bloom. This does not mean that plants should grow on barren sands, they like fertile, permeable, slightly moist soils with humus, sunny places.
If the irises stop blooming
A noticeable weakening or complete absence of flowering may be associated with the age of the bushes. Irises are perennial plants, but short-lived, so after a few years (4-5) they stop producing flower shoots and lose their decorative value. Bushes “go bald” in the middle, plants become susceptible to diseases, drying out, decay.
To continue enjoying wonderful flowers, you need to rejuvenate them by choosing strong, young, healthy, strong rhizomes with several distinct buds for further cultivation.
How to keep iris until spring?
Proper storage of dug irises in winter is the key to beautiful flowers in your garden.
Find out what to do if the irises aren't blooming.
To do this, you must observe the following rules:
- For bearded irises... Place the rhizome in a dry container with a lid in a cool place. Before that, it is recommended to dry them well and wrap them in cloth or paper.
- For other species... Place in flowerpots with soil. But first you need to hold the rhizome in a light solution of potassium permanganate for no more than 20 minutes. Next, they need to be dried and only after that they should be planted shallowly in a prepared flowerpot.
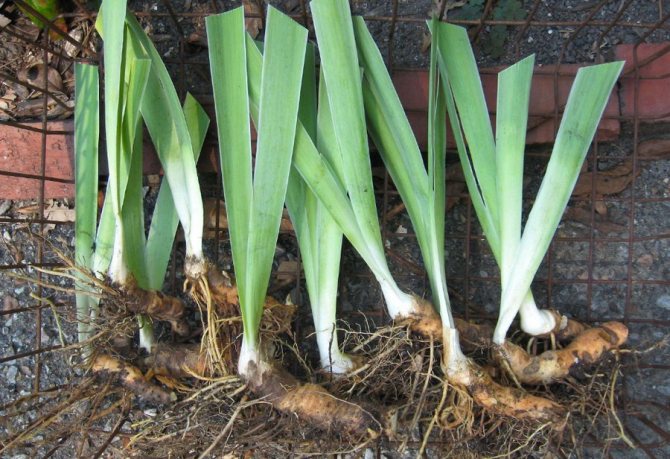


It is difficult not to love irises, because they are beautiful and diverse, and their cultivation will not bring much trouble. Proper care of them can provide a bright and effective flower bed. With the help of a huge number of species (monochrome, spotted, velvety, etc.), you can transform the design of your site.
Iris storage
If you bought or dug up rhizomes of bearded irises in the fall and want to keep them until spring, the best place to store them is in a cold, dry room. Fold the well-dried roots in a box and take them out to the balcony or loggia. You just need to first wrap each root in paper, cloth or sprinkle them in a box with dry sawdust or dry peat.
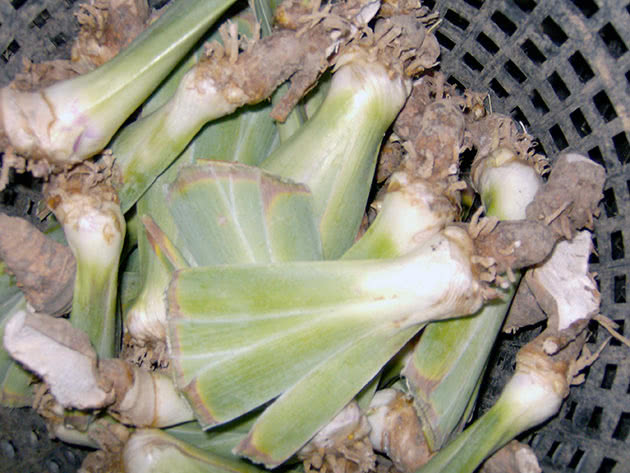


Photo: Preparing irises for storage
All other types of irises are moisture-loving, so the best way to keep the root of the iris until spring is to plant it in a flowerpot, after cutting off the long roots, disinfecting it in a weak solution of potassium permanganate and drying it after that. The root is not immersed deeply in the ground, lightly sprinkled with earth on top. In the spring, the sprouted root, together with an earthy clod, is planted in the ground.
How much does it cost in a vase of water?
You won't have to enjoy the beauty of irises in a vase of water for a long time. In this form, they usually last no more than 2 days. These are delicate flowers and they lose their beauty very quickly.
Did you know? The ancestors of the Western Slavs believed that iris is a special flower, since it grew in places where Perun's lightning fell.
If you want to extend the storage period of the bouquet, you need:
- wait a few minutes before placing them in a vase of water for the flowers to adapt to the room temperature;
- for better contact with water, it is necessary to cut the stems;
- collect settled water in a container;
- change the water every day and add sugar or aspirin to it.
Part 3.Difficulties
Iris, like any other crop, can bring a lot of trouble to its owners. Usually the reason for this is inadequate care of them.
Diseases
The most common diseases in beards and other iris species are viral and fungal infections. What should be the treatment and control of iris diseases?
Mosaic Is a viral disease. It manifests itself in the form of stripes and spots on the leaves. The virus is carried by aphids.
To date, effective methods of treating the viral mosaic have not been found, therefore, preventive measures must be followed:
- Remove infected seedlings immediately;
- Observe the watering regime, apply fertilizers, and also treat the plant from insect pests and diseases. Suitable drugs such as "Actellik", "Confidorm" and others).
Bacterial rot found on brown spots on the leaves of the plant. The disease can be detected in the spring after wintering. It will be necessary to remove the affected areas, then treating the areas with a solution of potassium permanganate. If the disease has gone too far, then it is better to destroy the affected plants and treat the soil with antibacterial agents.
The causes of bacterial rot are:
- Freezing of the root system;
- Excessive soil moisture;
- Dense plantings;
- Lack of calcium and phosphorus in the soil.
The material in the video below is about bacterial rot and how to deal with it.
Gray rot can affect either stems and leaves or the root system. The main reason is stagnation of water in the ground. Therefore, iris should be planted exclusively in well-drained soil. An exception is marsh iris. Also, the reason may be a lack of phosphorus and potassium in the soil. It is required to treat the disease with the help of fungicides, and if the plants are very badly affected, then it is better to destroy them.
Pests
The most common pests include:
- Scoops;
- Iris fly;
- Thrips;
- Medvedka;
- Slugs.
Scoops - this is an extremely dangerous pest for a flower. Firstly, they eat up the base of the peduncle, as a result of which the plant turns yellow and may even die, and, secondly, the activity of scoops leads to the development of bacteriosis. As a preventive measure, it is necessary to treat the plant with karbofos.
Iris fly (iris flower girl) visually similar to an ordinary fly. Because of this pest, bud diseases develop. She feeds on the buds of culture that have not yet opened. As a result, the bud begins to rot. As a preventive measure, it is necessary to treat iris with insecticidal preparations (Aktellik, Aktara) even at the stage of bud formation.
Iris buds infested with iris fly larvae.
About the iris fly and the fight against it - on video
Thrips - very dangerous pests despite their miniature size. Initially, these pests settle on the leaves, which leads to their gradual drying and yellowing. Then they move to the buds. Subsequently, the buds are damaged and do not open. You can treat it with karbofos with the addition of laundry soap. You can also use insecticidal preparations (Aktellik, Aktara).
Medvedka - a very common pest, especially in the southern regions of Russia. It can cause irreparable damage to irises. The pest damages the root system and bulbs. You can fight the bear by adding crushed eggshells dipped in vegetable oil to the soil. It will also be effective to fill the pest moves with soapy water or a solution of washing powder. In the fight against the bear, the marigolds planted nearby help.
Slugs infect iris leaves, and are also a distributor of bacterial rot. They are collected by hand, and the soil is also treated with superphosphate. For prevention, it is recommended to remove weeds around the plants in time.
Problems
Often, iris owners are faced with the following problems:
- The appearance of spots on the leaves of brown or yellow color... The reason is waterlogging of the soil or frequent precipitation. Damaged leaves must be trimmed. As a preventive measure, it is necessary in the spring, a month or two before flowering, to treat the culture with fungicides;
- If a the flower blooms poorly and sluggishly, then it does not have enough sunlight. Also, a possible reason is the excessive acidity of the soil;
- Wrinkles on the leaves Is a temporary phenomenon caused by bad weather conditions. Does not harm the plant;
- Suspension of flowering can be caused by: strong growth of the root system, depletion of the soil, freezing of flower buds, damage to the crop by pests and diseases, lack of watering in drought.
These are not all the difficulties in growing irises, we will be glad to see your other questions and comments.































































