Shrub propagation is an effective way to propagate a garden or home rose, rejuvenate it, and get some new plants. In this article, we will look at how to successfully propagate a rose from a bush. Follow the rules and adhere to the recommendations, and you will certainly get an excellent result!
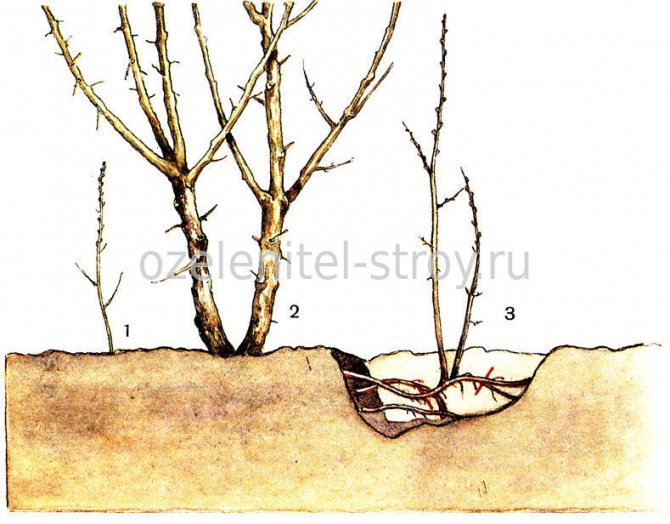
It should be noted that this method is not suitable for grafted roses, but only for growing on their own roots (otherwise, if you divide the grafted bush, you will essentially get two different plants). It is best suited for park bush roses such as French, centifol, rugosa, etc.
What is the essence of the burrito cuttings method?
In general, burrito (burrito, diminutive of the Spanish burro - donkey; "donkey") is a Mexican dish consisting of a soft wheat cake, which is wrapped in various fillings (minced meat, fried beans, rice, tomatoes, avocado and cheese). This is a kind of Mexican analogue of shawarma. And this word accurately reflects the essence of the method of propagation of roses, when the cuttings are wrapped in a dampened newspaper (a kind of pancake), which provides specific optimal conditions under which they germinate, forming the so-called callus, and then the roots.

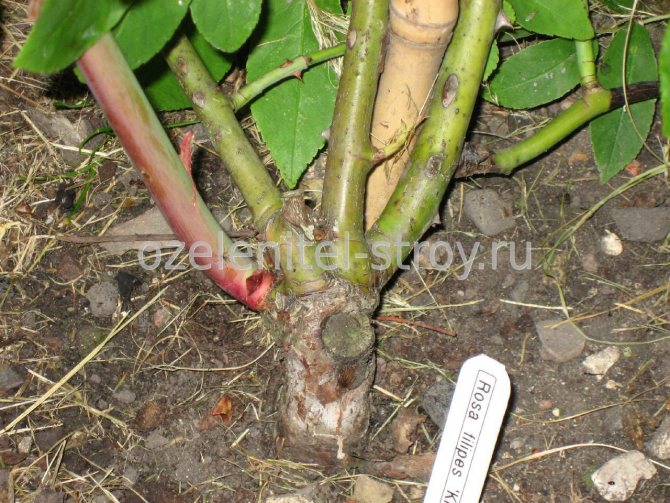
Propagation of roses by cuttings (burrito method). <>


Propagation of roses by cuttings (burrito method). <>


Propagation of roses by cuttings (burrito method). <>
Callus or callus (from the Latin callus - corn), plant tissue (growth), formed on the surface of wounds as a result of the division of nearby living cells. It is she who promotes the formation of roots during vegetative propagation of plants.
In a few weeks, such a "shawarma" stuffed with rose cuttings gives quite viable shoots. This is the whole method, the phrase “all ingenious is simple” is the best fit for this method, although there are many nuances here too. Let's analyze the application of the method step by step.
Required tools
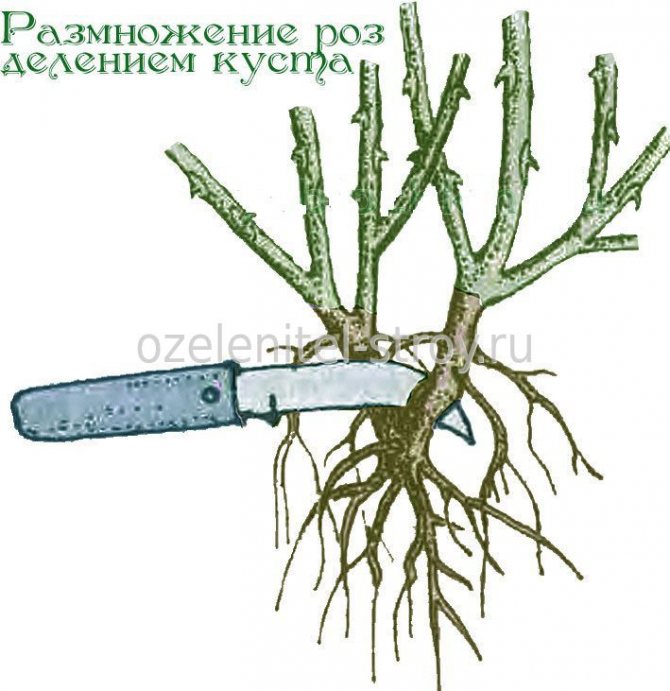
To plant roses by dividing a bush, you do not need many tools - a shovel and a knife (or pruner). The knife must be very sharp and leave an even cut, otherwise pathogenic microbes and bacteria can enter the plant through the "soaked" cut points, which will lead to its death. Also, the instrument itself must be disinfected before work. To do this, you can use pure alcohol or liquids containing it (cologne, vodka, etc.). If the bush is too large and old, a saw or ax may be required to separate the roots (these should meet the same requirements).
Cutting cuttings of a rose.
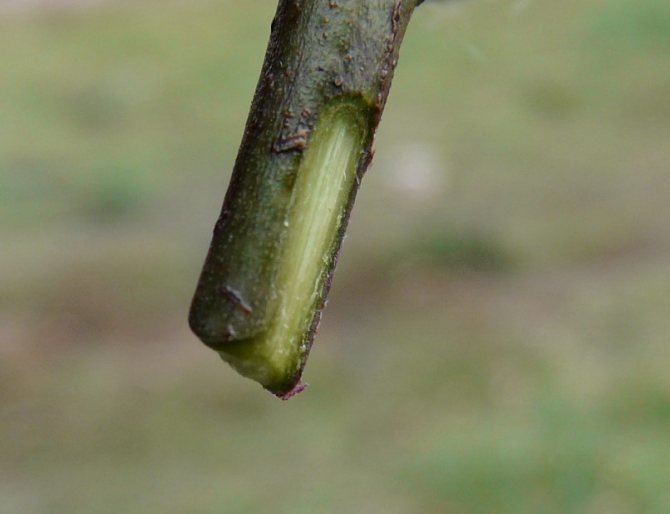
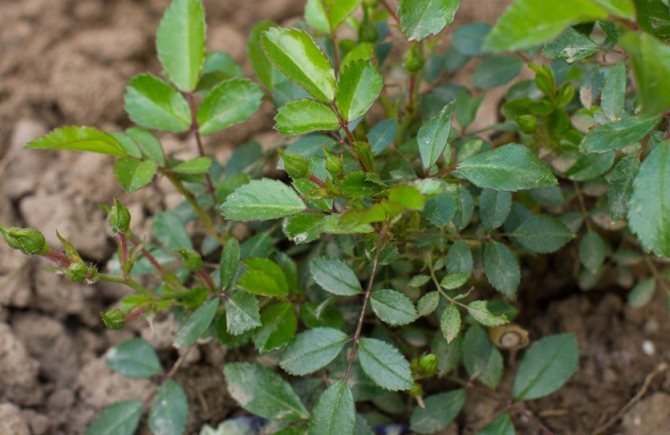
Cutting cuttings can be carried out in the fall, but it is especially convenient in the spring, when pruning of rose bushes is usually carried out. Cuttings are usually up to 20 cm long with 3-4 buds. The thickness is very important, at least 0.5 cm, then the nutrients contained in the stem are enough for the formation of callus and roots. Sometimes thin ones sprout, but this is rather an exception.
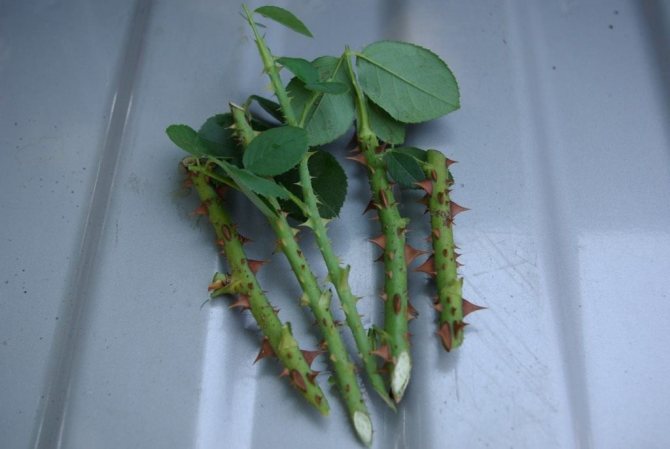


Cuttings of roses.
What material can be taken for planting
Breeding roses using the burrito method is just as justified in winter as it is at other times of the year. The biggest challenge is getting the right planting material. Most often, in the cold season, in stores you can only find rooted plants in pots, intended for spring planting.In addition, in every flower shop you can find luxurious roses on a long stem, which you want to immediately cut into cuttings and try to grow a new plant. We hasten to disappoint you. Cuttings obtained from such peduncles almost never take root. Therefore, do not rush to cut the donated flowers, let them better please you with their magnificent view. In addition, Dutch varieties hardly survive outdoors, especially in Russian climatic conditions.


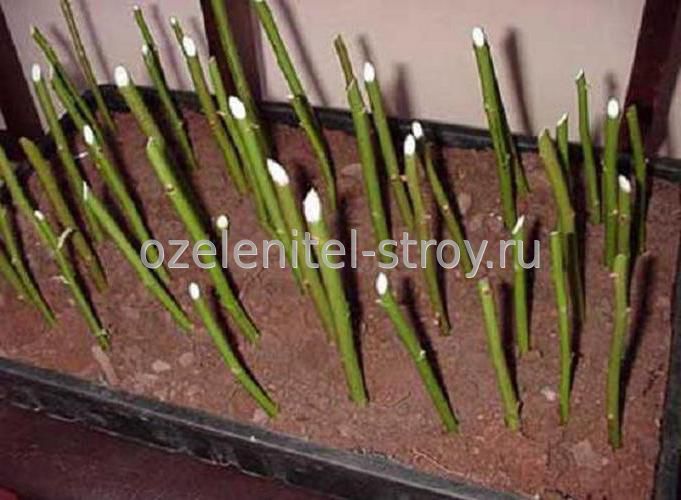
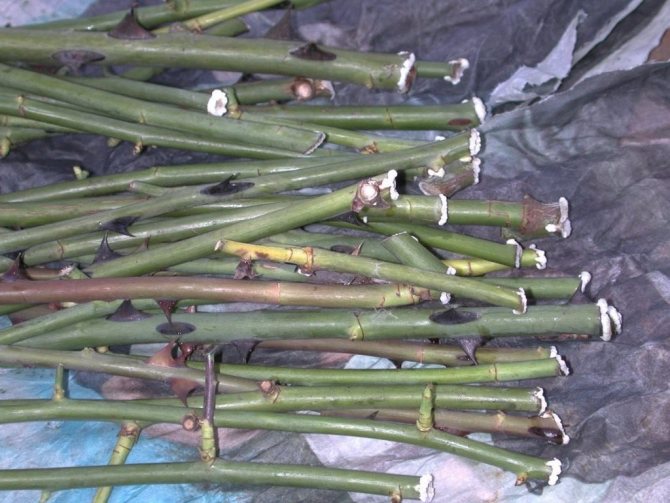
Rose cuttings packaging.
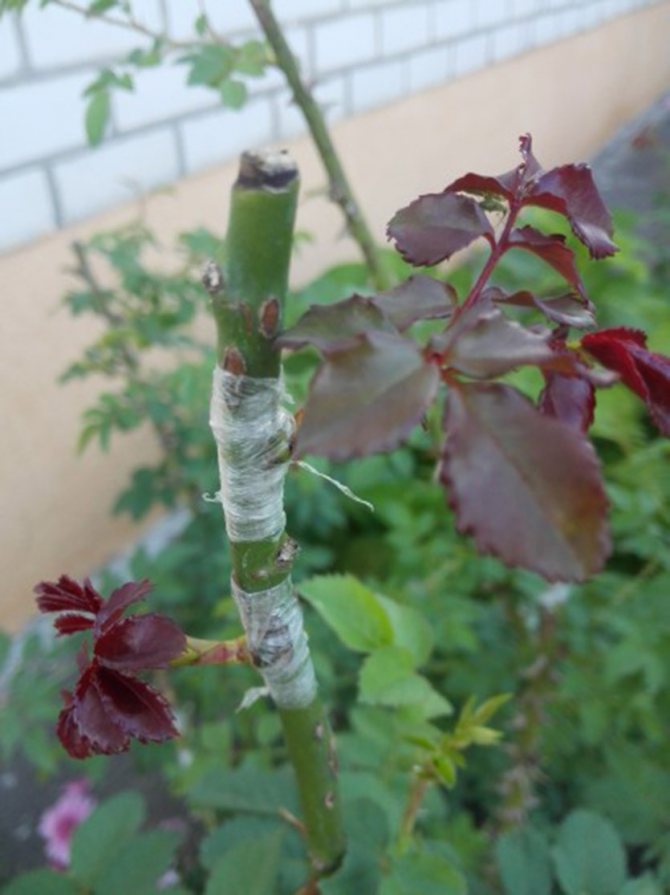
Cuttings of 4-7 pieces are wrapped in newspaper (in 2-3 layers) or paper towels and moistened with water, then wrapped in polyethylene and placed in a dark place at a temperature of 14-18 degrees. This is a very important point. If packages with cuttings are stored at a lower temperature, then the process of plant development is greatly inhibited, the plant is, as it were, in a dormant period, and at a high temperature, the roots quickly dry out and die off (and even if they are constantly wetted, then there is a high probability of mold growth ). It is this temperature regime (14-18 degrees) that is most favorable for the gradual development of the plant, when, first of all, roots and callus are formed. Therefore, usually, an apartment is not quite suitable for these purposes.


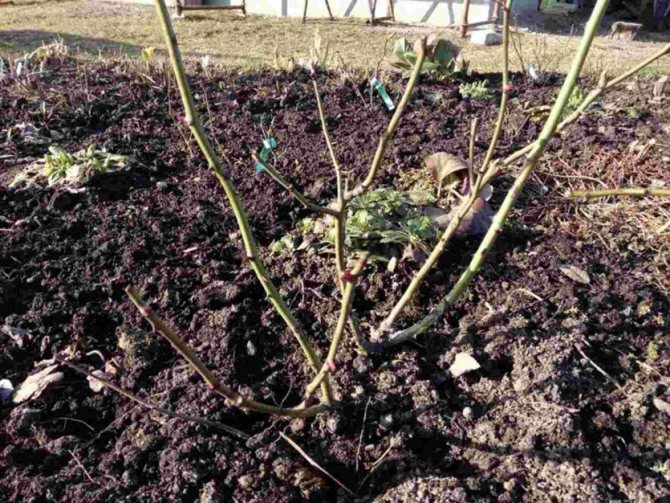
Callus and root formation on cuttings.
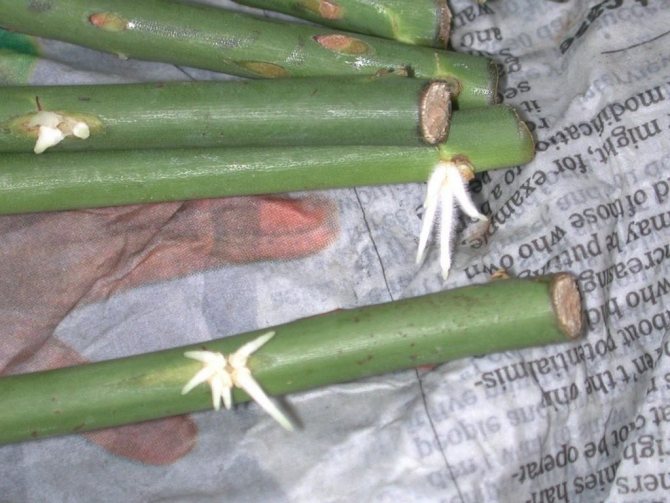


Callus and root formation on cuttings.
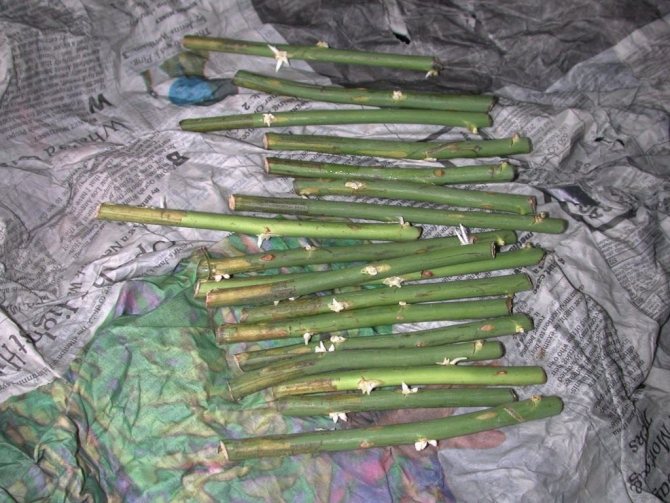


Callus and root formation on cuttings.
How to budding roses on rose hips (with video)
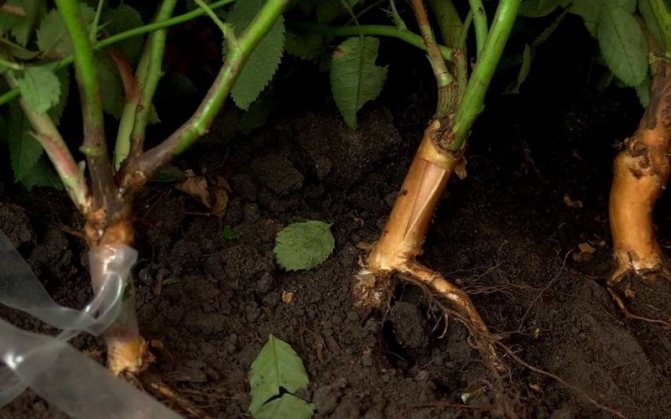


Budding roses on rose hips in the photo
Budding roses on rose hips (grafting with an eye) is the main method of reproduction. If you have already mastered this simple matter, then now you need to know how to form a bush from an oculant, because there was a rosehip, and now there will be a rose!
The best time to propagate roses by grafting is from mid-July to the end of August. The occulted peephole hibernates on a rose hip in a huddled form. In early spring, the eyepieces are unlocked, the bandage is removed, and the wild is cut off 0.7-1 cm above the grafted kidney. It is desirable to cover the cut with a garden pitch.
Before budding roses, you need to prepare the tools. The work must be done with a well-honed garden knife or pruner. From a poor tool, the fabrics crumple, the bark bulges and falls behind the wood. It is necessary to ensure that the cutting blade of the secateurs passes over the lagging part of the plant. The cut should be smooth, slightly oblique (from the kidney), with intact and non-flaking bark.
After pruning the rose hips, the grafted buds begin to grow rapidly. Oculants with a dead eye, but with a green bark of the scutellum should not be removed, since cultivated shoots may develop later from dormant Buds on the scutellum. As a rule, small sleepers are located on both sides of the main kidney. Sometimes all three eyes start growing at the same time, but usually one shoot begins to grow back.
When forming a bush, one should strive to ensure that branching begins as low as possible. Plants in which the main skeletal branches (2-3) are formed from buds on the shield, that is, in the zone of the root collar, are of the greatest value. Therefore, it is necessary to try to induce the formation of the main shoots from all three eyes.
If the eyepieces grow freely, without pinching, then most develop one main shoot, which blooms quite quickly, after the 7-8th leaf. The plant turns out to be weak, lateral shoots are formed most often in the axils of the upper leaves, that is, they do not participate in the formation of the skeleton of the bush. Additional shoots from the grafting site on the rosehip do not develop at all during the reproduction of the rose or begin to grow at the end of summer. Usually they turn out to be fatty, do not have time to ripen well by autumn, and freeze over in winter.
In order to quickly awaken the dormant buds, it is necessary to pinch the cultivated shoot growing from the central eye as soon as possible.In this case, the main thing is not its length, but the number of developing leaves. Roses are pinched over the 3-4th leaf. Simultaneously with the first pinch, wild growth is removed, if it has appeared.
Soon after the pinching, shoots of the second order begin to grow from the axils of the upper leaves. Below, from the dormant buds of the grafted scutellum, 1-2 strong additional stems appear. In addition, buds located in the axils of the lower (scale-like) leaves of the main shoot start to grow. If the first pinching did not cause the awakening of the lower buds, then the leader shoot is pinched again over the 2-3rd leaf.
It should be borne in mind that even in plants of the same variety, the growth of the scion does not occur simultaneously, therefore pinching must be carried out selectively.
With a later pinching (above the 5-6th leaf), branching occurs mainly from the axils of the lower true leaves of the main shoot. The bushes are obtained on a low bole, such a plant is more in danger of freezing.
Roses grafted on rose hips need rest in winter, while self-rooted roses can be successfully used for forcing in greenhouses throughout the year. In greenhouses, they are not inferior in yield and even surpass grafted ones in greenhouses.
The good development of young rose bushes depends largely on proper plant and soil care. Weeds must be removed regularly. They not only impoverish the soil, but also strongly shade the roses. Loosening is carried out at least 5 - 6 times during the growing season. If the soil was well filled when planting rootstocks, and the weeds were removed in time, then there is no need to feed the plants in the first year.
The video "Budding roses on rose hips" clearly demonstrates how to propagate plants in this way:
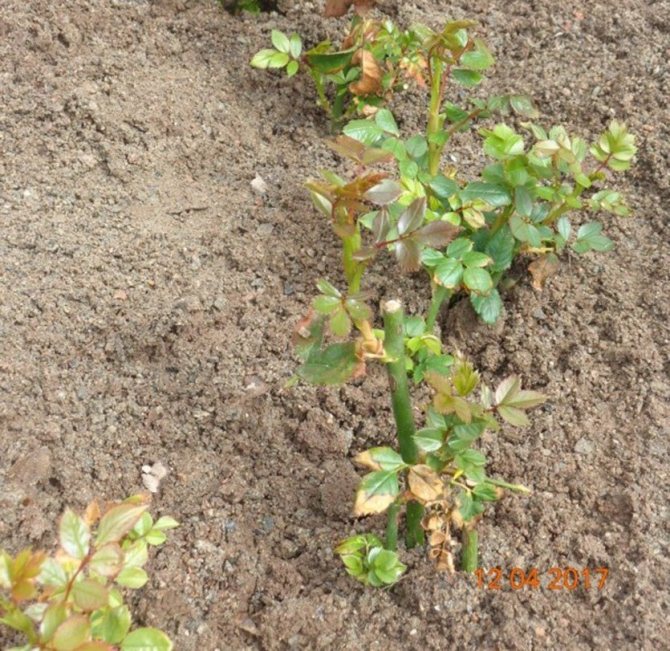
Planting sprouted rose cuttings.
When a full-fledged callus is formed and roots appear, the cuttings of the rose are planted in jars or pots (one at a time) in the soil, so that the upper bud rises above the surface. Cover the pot or jar with plastic wrap to create a water bath. The temperature should now be above 23-25 degrees. Often sprayed, gradually opening the film as the cuttings grow.
That's the whole technology. It does not require large expenses and gives very good results, the percentage of survival rate of cuttings of roses is high and allows reproduction of even the most capricious varieties of roses. However, not only roses ...
What it is
In fact, you all know very well what it is, even if you hear such a term for the first time. The burrito method is the vegetative propagation of the bush, that is, cuttings. True, this does not make it much easier for a novice gardener, especially if you managed to get a rare variety or hybrid. At the same time, the amount of starting material is very limited, and the samples themselves are extremely sensitive to environmental conditions and growing technology.
It is very good if at this moment an experienced florist comes to the rescue, who has already performed a similar procedure more than once and knows how to reproduce roses. The burrito method originated in the United States and has proven to be extremely effective, quickly spreading throughout the world. Russia and the CIS also did not stand aside, however, we still have very little professional literature devoted to this problem. Therefore, the sacrament of cuttings is passed from gardener to gardener, and even not everyone wants to share the secret they have received. Let us today lift the veil of secrecy and penetrate into its essence.
Regular inspection
Breeding roses using the burrito method in winter is very suitable for busy people. It does not take much time from you to take care of your blanks, but at the same time, you can immediately lay dozens of future bushes for germination. After about 2.5 weeks, the packages can be taken out and carefully unwrapped.Evaluate how the process of root formation is going, if necessary, you can give a few more weeks for its completion. Check moisture, you may need to moisten extra.
Problems, difficulties and solutions
- The defeat of young seedlings with infections (for example, aphids or spider mites).
The reason for this may be the soil that is used to plant an already rooted cuttings. Therefore, it is necessary to use a commercially available substrate or treat the mixture prepared by yourself with fungicides or thermally. Also, improper care of a room rose can also be the reason. To prevent such a phenomenon, it is enough to provide all the necessary conditions of detention, which were discussed above. The stalk withers in the water.
It is possible that the cut has dried up. It is enough to get the petiole out of the water and update the cut. And also make sure that direct sunlight does not fall on the escape. The plant does not bloom.
If the rose did not release the buds in due time, then, most likely, the problem, oddly enough, is in the pot. An overly large pot will encourage the plant to actively develop the root system, to grow deciduous mass, and not buds. Therefore, it is necessary to transplant the flower into a smaller pot. And this fact must be taken into account when choosing a pot for planting a young plant.
Indoor rose is a capricious plant. Its reproduction is a troublesome process. But all the efforts of the grower will be rewarded with the lush bloom of the self-grown flower queen.
Suitable varieties
Before talking about the methods of cutting roses, it is necessary to find out which varieties of garden beauties easily and quickly form their own rooted plants. Not all representatives of this class are cut equally successfully, therefore, when propagating plants, it is important to take into account the following recommendations:
- Any varieties of ground cover, miniature, polyanthus and climbing roses with small flowers are ideal for propagation by cuttings. Cuttings of these varieties quickly root, forming strong bushes. Miniature roses can easily root in water.
- When grafting floribunda varieties, you need to be prepared for failure - only about 50% of the planted cuttings take root.
- Of great difficulty is the propagation of climbing roses with large flowers, as well as park and hybrid tea varieties, in this case the yield of new plants is extremely small.
- You should not propagate a yellow rose by cuttings; for plants with such a color of petals, it is best to use other breeding methods (for example, grafting).


Miniature varieties can be rooted even in water.
Description of methods
There are several ways to propagate roses:
- Seeds. They can be used purchased or assembled by yourself. Rose seeds are harvested after the fruit starts to turn red. They must be carefully cut, remove the seeds, put in a solution (one glass of water and 2 teaspoons of bleach), rinse and soak in a solution of 3% hydrogen peroxide for a day. It is necessary to constantly check the seeds, throw away those that have surfaced.
- Vegetation. This method involves propagating a plant from a leaf, root or stem. Such roses develop more slowly and do not tolerate cold well. But their cultivation and production takes less time and effort.
- Layers. For this, branches located above the surface are used. As a rule, such reproduction is carried out in early spring.
- Root offspring. These are straight shoots that are located along the borders of plants. If you separate them from the main flower, you can get a new rose. The method is easy, but less effective. Used for propagation of park roses. This is best done in early spring. 1/3 of the stem is used for transplanting.
- By cuttings. It is better to choose summer for breeding. Cuttings without leaves and thorns are used.
- By dividing the bush. Bushes with a lot of shoots are used.The procedure is carried out in the spring in the evening. Each bush should have a part of the root system and one shoot with two or three buds.
- Vaccination. This method is an artificial option for growing the cutting. For this, plants that are close in appearance are used. Such reproduction takes place in winter or from April to August.
Roses are propagated most often in two ways - by seeds or by a vegetative method. Let's consider the second option in more detail.
How to propagate roses by cuttings
All types of this flower can be used as a donor for rose propagation, but only from a domestic manufacturer. Don't use Dutch roses. What is needed for plant propagation at home:
- Prepared soil. To do this, you need to take: sod land - 2 parts, leaf - 1 part, sand - 1 part. On top of these layers, it is necessary to pour washed river sand in a layer of 3–3.5 cm. It will promote the penetration of air and moisture to the base of the shoot.
- Prepared stalk. For reproduction, you need to take ripe shoots that are ready to open their buds. Cuttings with two or three buds need to be cut from the shoot. The upper cut must be made 2 cm higher than the kidney, and the lower one - under the kidney. At the bottom, all the leaves are removed, and at the top, they are halved.
- Preparing for planting. The lower part of the cut is best treated with growth substances. It could be heteroauxin. It is necessary to plant cuttings to a depth of 1.5–2 cm. The distance in a row should not exceed 8 cm, between rows - 10 cm.
After planting, the plants must be kept in the greenhouse for at least 15 days. Under these conditions, the cuttings will receive enough heat, moisture and light. It is not necessary to water the ground often, but it is necessary to keep high humidity in the greenhouse, about 80–90%. To do this, you need to spray the plants with water. The greenhouse must always be closed. The exception is overheating inside. In this case, it is necessary to ventilate the space in the morning and evening hours so that there are no burns on the leaves of the rose.
After that, it is necessary to transplant the cuttings into pots with a diameter of 9–11 cm. The pots are dug into the greenhouse.
Cutting a room rose
The easiest way to propagate a room rose is by cuttings. First you need to prepare the stalk:
- It should not be more than 10 cm in length.
- The cut is made obliquely under the kidney. In this case, it will take root faster.
- The upper cut is made 5 mm above the kidney.
- Leaves are removed from the bottom.
There are two ways to propagate a flower:
- Soil. Before planting, the cuttings are placed in water, to which it is necessary to add heteroauxin (14 tablets per one glass of water). In such a solution, the cuttings should lie for 10 hours. After that, they can be planted in the ground - a mixture of sand, peat, you can just use sand. It is imperative to make greenhouse conditions - cover with a film or a bottle. Often watering the cuttings is not worth it. The temperature in the greenhouse should not drop below +18 degrees. It is necessary to root the cuttings in a month. Then they need to be opened and transplanted into another container.
- Water. In this case, it is necessary to prepare 15 cm slices. After that, they must be placed in a container with water and covered with a lid with a hole. It is in the hole that you need to insert the cuttings. They must be transplanted after they grow 1–1.5 cm.
Reproduction of a rose at home adapts the new plant to the exact temperature at which it was grown. That is why the problem with adaptation disappears.
How to propagate a climbing rose
It is necessary to harvest cuttings for propagation of a climbing rose in the fall. You can root them in soil or water. If water is used, it must first be boiled to kill germs. Otherwise, the cuttings of the climbing rose will rot. They should be 20 cm long and have 4 buds.
As a rule, the root system develops in a month. After that, you need to transplant the cutting into a flowerpot.You need to take care of him like an ordinary houseplant. The soil is poured into the pot and a hole is made, filled with sand. Then you need to stick in the handle. Cover the cut with a jar on top. Be sure to keep an eye on the humidity.
Further care
Rose is a light-loving plant, it needs a lot of sunlight, but without direct sunlight. The best location is south and southwest windows.
Watering should be moderate as the soil in the pot dries out. Watering is done from above with settled warm water. Avoid stagnant moisture, as the roots can rot: be sure to drain the water from the pallet. On hot days, the air around the rose must be sprayed.
Important! Moisture on rose leaves can cause fungal diseases.
2 weeks after planting a young seedling in a permanent pot, you can start feeding it with complex fertilizers 1 time in 10-14 days.
The optimum temperature for rose growth is + 20C - + 22C. If the thermometer reads above + 25C, then the plant can drop leaves and buds. Drafts are harmful to a young seedling, but a small difference in daily temperatures is beneficial.
Treatment
Since planting a rose with a handle in the fall is not difficult, many summer residents take edged material from each other. Unfortunately, most of the landings are lost. Cuttings rot due to excess moisture, dry out without proper moisture. In addition, the future rosette sometimes lacks additional incentive in order to give roots. Today in specialized departments and stores there is a large selection of growth regulators. By dipping the bottom of the planting cuttings into this powder, you increase its chances of germination.
If such drugs are not available today, then a similar growth stimulant can be prepared by yourself. To do this, you need to take annual willow shoots (yellow or green). They can be prepared in advance. As necessary, the raw materials are taken out and finely chopped and poured with boiling water. In just a few hours, the solution that activates the development and growth of cuttings will be ready.


For the busiest
If you do not have time to complete this procedure, but there are several cuttings that need to be saved until spring, then you can leave them for the winter right on the site. Reproduction of roses in the fall in the ground allows you to completely save yourself from worrying about future plants until spring. For this, a hole is dug, a cotton fabric is lined at the bottom. Cuttings are laid out on it at a distance from each other. After that, the fabric is laid on top and the earth is filled up. When the soil thaws in the spring, you will need to remove the cuttings. Each of them will have a thick white growth with which they can be planted. While - in pots, and closer to autumn it will be possible to transfer to open ground.
Photo
Here you can see a photo of the rose:
How to propagate by seeds?
One of the most difficult ways to propagate roses is by sowing seeds. This method is rarely used, because the probability of growing a strong plant is rather small. In order to grow a rose from seeds, it is necessary to prepare good material for planting, these should be seeds harvested in late July and early August. For sowing, not fully ripe fruits are used, they are cut with a knife and the seeds are separated from the pulp, the seeds should be brown.
Purchased material is fraught with many mysteries; the rose that is shown in the picture does not always grow.
Preliminary inspection
Look carefully at the material to be germinated. All stems should be green, smooth and shiny. The bark should be free of black spots, damage and rot. In this case, everyone else who is in the immediate vicinity will also suffer.After you have rejected all unsuitable cuttings, you can proceed directly to preparation. For this:
- Directly under the bud, stepping back 1.5 mm from it, make a cut of the future cutting. It is performed slightly obliquely.
- Remove all the lower leaves and shorten the upper ones by a third. This is important to prevent rotting and drying out of the cuttings.
- All thorns need to be cut, they often cause decay.
- Cut and bundled cuttings must be placed in a pre-prepared newspaper and carefully packaged. All that remains is to put the bag on top and moisturize them regularly.