Category: Mineral fertilizers Reading: 10 min Views: 4 787
Ammonium nitrate is used in 80% of large farms. This demand is due to the fact that the fertilizer has a beneficial effect on plants even in cold weather and with strong soil freezing. Ammonium nitrate is a universal fertilizer that is suitable for almost all plants in agriculture.
The price of the issue
Ammonium nitrate is an economically very profitable agrochemical. Its price is about 20-25 rubles per kg. Considering that the rate of application of this mineral dressing is, on average, about 10-20 g / m2, then for one hundred square meters (100 sq. m.), you need to spend only 1 kg of fertilizer.
Even considering that the use of ammonium nitrate is not very rational without other mineral fertilizers, it is very beneficial to fertilize with it.
You can buy ammonium nitrate both in bulk and in packaged form. Very often in stores selling goods for gardeners, you can find its varieties with various additives. They have a narrower application, but, at the same time, they solve specific problems better than the main fertilizer with a wide range of uses.
Action on different types of soils
The main advantage of the fertilizer is its versatility. It is used in all climatic conditions on lands of various types:
- On soils with an acidic environment (peat, red earth, sod-podzolic), an acidification effect is possible, which reduces the effectiveness of feeding. To eliminate it, parallel liming is carried out. You can do without neutralization using calcium ammonium nitrate.
- Chernozem, chestnut, gray earth soils have a slightly alkaline or close to neutral reaction. With the introduction of nitrogen fertilization, magnesium or calcium nitrate is formed in the soil, so there is no acidification.
- From the horizon of light sandy lands, ammonium nitrate is quickly washed out by groundwater or rainwater. Therefore, in such gardens, fractional multiple feeding is necessary.
- Heavy alumina and loam are characterized by high density and viscosity, for this reason, the entire norm of ammonium nitrate is applied once in the spring before sowing or in the fall for digging.
For areas with a large amount of precipitation and high humidity, a two-time main application is recommended - in the spring and autumn. For other regions, a single feeding is sufficient.
Types of ammonium nitrate
Almost always, this fertilizer is produced with the use of additives of various elements. The presence of such a large assortment is explained by the wide geography of the use of ammonium nitrate, and an attempt to adapt to the needs of agriculture in different climatic zones.
- Ammonia simple... This type was developed by the very first. The main idea behind it is to provide agricultural crops with powerful nitrogen nutrition. The use of ammonium nitrate in agro-industrial complexes of different countries has repeatedly confirmed its high efficiency as an optimal starting fertilizer for most plants cultivated in the middle lane. This type of nitrate can be used as an equilibrium substitute for another popular mineral supplement - carbamide (urea).
- Ammonia grade B... Divided into grades, first and second. Great for home use and storage. Sold in shops for gardeners, and has a convenient packaging, from 1 kg. Why might you need it at home? For flowers that are sick after a winter spent on the windowsill, for the primary feeding of seedlings, which, in the conditions of a short daylight hours, vitally needs nitrogen.
- Ammonia-potassium (K2NO3)... People call it "Indian saltpeter". This species is especially effective for early spring feeding of fruit trees. It is also ideal for pre-sowing application, and subsequent fertilizing for tomatoes, because potassium improves the taste of the fruit.
- Calcium ammonium (Norwegian nitrate). It can be simple and granular. Contains calcium. Its production is regulated by TU 2181-001-77381580-2006. The composition of this agrochemical, in addition to the main one, includes additional substances - potassium, calcium and magnesium. Lime-ammonium nitrate is characterized by high strength of granules, does not cake during storage. It is alarming that it is processed with fuel oil, and this fraction lives in the soil for a very long time, causing quite significant harm to it.
The Calcium Ammonia Grade is used to fertilize almost all crops. Does not increase soil acidity, is well absorbed. The main advantage is safety - calcium ammonium nitrate does not explode, and therefore it can be transported by any means of transport.
- Magnesium nitrate-water (magnesium nitrate). The formula of this substance looks like this: Mg (NO3) 2 - H2O. Used for vegetables and legumes as an additional source of magnesium.
- Calcium. Available in both dry and liquid form, which does not need to be diluted. It is called "Ammonized calcium nitrate solution".
- Porous ammonium nitrate (TU 2143-635-00209023-99). But this species has never been a fertilizer, and is a great danger. It was originally used only to create explosives.
Application against plant diseases
Why is ammonium nitrate so widespread in industrial agriculture? It not only nourishes the soil with essential macronutrients, but also protects plants from a host of diseasesstrengthening their immunity.
This property is especially relevant with increased exploitation of land or the cultivation of crops from the same class on one site annually (non-compliance with crop rotation). For example, many gardeners allot the same piece of land every year for potatoes in small summer cottages. And then they wonder why the tubers that are still in the soil begin to rot. Many people are familiar with this problem - you dig in a seemingly healthy bush, and the potatoes are half rotten and smell bad.
Long-term permanent cultivation of this crop in one place leads to the accumulation of huge quantities of pathogenic fungi in the upper layers of the soil. The harvest is declining. To improve the soil, it is treated with various disinfectants (the most accessible is a solution of potassium permanganate), and ammonium nitrate is added for spring plowingwhich helps to strengthen the plant's immunity from the very first leaves. Physiologically healthy cultures deprive fungi of their "home", the body rejects foreign microspores.
Precautions
In order to prevent negative consequences, you need to know the peculiarities of storage and transportation of fertilizers. A mineral supplement packaged in packages of 50 kg can be stored in stacks, but the number of layers should not exceed 12. The total weight of an agrochemical in one room should not exceed 300 tons. Almost any transport, except for aviation, is suitable for transporting the fertilizer.

When working with ammonium nitrate, it is advisable to use rubber gloves so as not to cause dermatitis, severe irritation on the skin.This mineral supplement poses no serious threat to human health if not taken internally. Even if you inhale nitrate dust, there will be no harm. But when introducing the composition into the soil, one should not neglect the elementary safety rules.
Ammonium nitrate has a beneficial effect on all plant organisms, the effect of its use is visible already in the shortest possible time. The foliage acquires a rich green color, the shoots become strong, the fruits form faster. The main thing is not to neglect the manufacturer's recommendations and apply fertilizer correctly.
Application rates


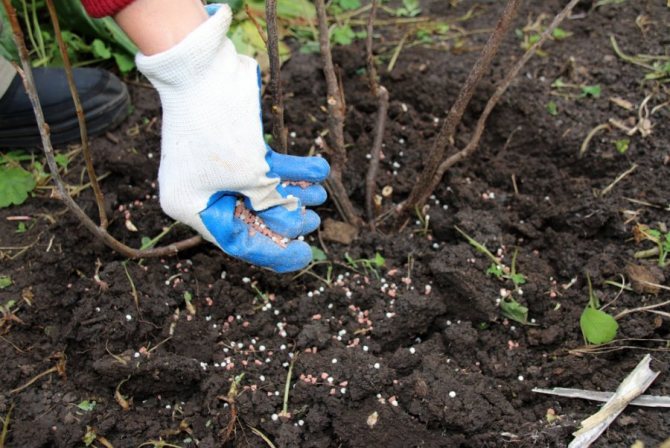
The amount of fertilizer used for pre-sowing application directly depends on the quality of the soil. If it is necessary to feed an already cultivated piece of land, then it is enough to use about 20-30 g / m2. sq. If we feed depleted and low-nutrient lands, then the consumption rate increases to 35-50 g / m. sq.
Ammonium nitrate can be used as a top dressing when planting seedlings. It strengthens young plants, nourishes them with essential macronutrients, and protects against various diseases. This fat is used when transplanting peppers, cucumbers, melons, as well as for tomatoes, at the rate of 1 tbsp. spoon without a slide under 1 bush.
For the subsequent feeding of various cultivated plants, the following consumption rates are recommended:
- Vegetables - 5-10 g / m2. sq. It is applied twice during the growing season, in June, before flowering, and in July, after the fruit set.
- Root crops - 5–7 g / m2. It is recommended to make shallow grooves between the rows, and add granules of ammonium nitrate there, burying them in the ground by 2-3 cm. Feed once, 3 weeks after germination.
- Fruit trees - 15-20 g / sq. In dry form, ammonium nitrate is used for feeding once, at the beginning of the season, when leaves appear, and the solution is fed two or three times during the summer, at the root. This method helps to quickly bring nutrients to the roots of the plant, so it is preferable. The solution is prepared in this proportion - 25-30 gr. must be diluted in 10 liters of water.
Dissolving ammonium nitrate, unlike many mineral fertilizers, will not be difficult, and the diffusion process begins already at 0 ° C.
What is this fertilizer?
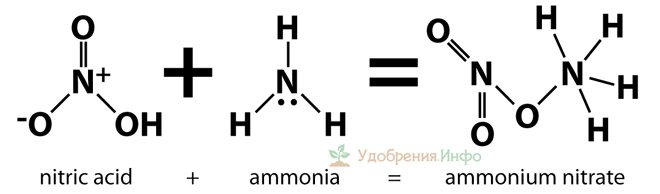
Ammonium nitrate is a product of the interaction of nitric acid with ammonia. Since the formula of the resulting compound looks like NH4NO3, it is sometimes called ammonium nitrate, ammonium nitrate or its nitrate.
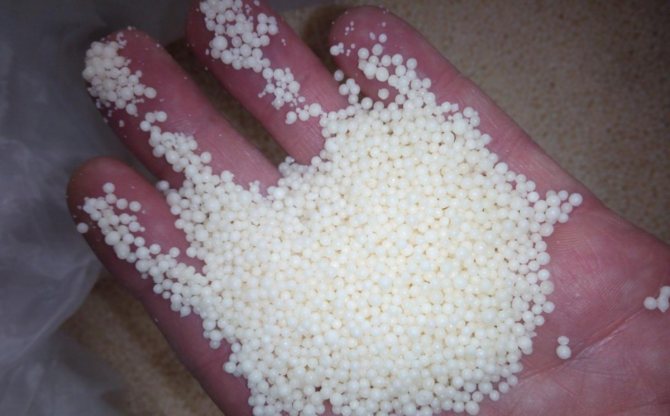
Pure crystalline substance is easily saturated with moisture and cakes. To eliminate this disadvantage, agrarian nitrate is produced in granular form with conditioning additives.
Main characteristics
- appearance - granules of white, light yellow or reddish hue (does not affect the quality);
- solubility - 212 g / 100 g of water at 25º C;
- granules - 1-4 mm in diameter;
- the acidity of the solution is 10% - 4-5%;
- friability - 100%;
- moisture content - no more than 0.3%.
Despite the acidic reaction of the solution, ammonium nitrate does not acidify soils with a normal pH reaction. When applied on soils of high acidity, pH 6.5 and below, parallel application of calcium carbonate is necessary.
Attention! Ammonium nitrate, when heated, releases ammonia and becomes flammable. When heated above 210º C, the acceleration of decomposition is accompanied by an explosion.


Composition and benefits
The main active agents of classical nitrate are nitrogenous compounds. They easily migrate along the soil profile, decompose with the release of nitrogen in a form available to plants. Its content ranges from 26% to 34% and depends on the varietal variety of fertilizer.
Based on the constituent components, ammonium nitrate is spoken of as a nitrate additive, the main function of which is to saturate vegetable and fruit crops with nitrogen. This element performs important functions in biological processes:
- is a part of nucleic acids responsible for the transmission of hereditary traits;
- is a component of chlorophyll - a direct participant in respiration and photosynthesis;
- increases the growth of green mass, especially at the beginning of the growing season;
- during fruit setting, it passes into amino acids, forms proteins;
- helps to heal parts of plants after infections;
- contributes to an increase in yield.
Please note: overfeeding shrubs and fruitstrees with nitrogen leads to a slowdown in development in autumn and a decrease in winter hardiness.
Operating principle
Nitrogen in all types of ammonium nitrate is in the form of ammonium and nitrate salts. Ammonium compounds act slowly to provide sustained nitrogen release, which is good for plants with long growing seasons. They work on unheated soil, so fertilization is effective with early spring main dressing.
The nitrate form - acts quickly, is easily absorbed by plant cells, has a quick effect on signs of nitrogen starvation, is useful for the restoration of cultures after diseases.
Are there nitrates in ammonium nitrate?
Yes, this is a nitrate fertilizer. Among a wide range of ordinary people, there is an opinion that nitrates are very harmful, and they appear in agricultural products when mineral fertilizers are used for its cultivation.
And this is true. But, not 100%. As always, lack of awareness breeds massive confusion. The fact is that organic fertilizers, for example, manure and compost, familiar to everyone, can oversaturate vegetables and fruits with nitrates even in the garden. They also contain nitrogen, and if they are used excessively, the harm will be felt, plant products will receive a powerful filling of nitrates.
Therefore, when using all types of dressings, both natural and mineral, the recommended application rates must be observed. And so that nitrates do not accumulate in fruits, roots and berries, it is necessary to stop using any top dressing two weeks before harvest.
Production, formula
To make ammonium nitrate, ammonia and concentrated nitric acid are used. The formula looks like this:
NH3 + HNO3 → NH4NO3 + Q
An isothermal reaction occurs with a large amount of heat generated. Excess water is evaporated, and the process of obtaining the substance is completed by drying it.

At the production stage, ammonium nitrate is enriched with various elements - calcium, potassium, magnesium, to obtain different varieties.
In principle, the process of obtaining this substance is quite simple, so much so that you can even make this fertilizer at home. But this is completely impractical, since it is much cheaper to buy it, the price is low.
Video: "explosive" properties of the AC - making a smoke bomb


Everyone knows that ammonium nitrate in spring is one of the best types of mineral dressings. The nitrogen-containing substance is selected at the preparatory stage for planting, as well as at the time of germination and accumulation of green mass. It is only important to apply top dressing correctly so that green spaces receive it on time and in a sufficient dose.
Storage


Since the main element of ammonium nitrate is nitrogen, if stored improperly, it can evaporate, significantly weakening the nutritional properties of this agrochemical.
When the temperature changes, the fertilizer recrystallizes, forming hardly soluble granules. Therefore, during storage, it is necessary to protect it from sudden temperature jumps.
The ammonium salt of nitric acid is dangerous. It can cause great harm if the storage conditions recommended in the instructions for use are not followed. The fact is that this fertilizer is explosive. It may explode if heated above 32.3 ° C.Therefore, in the summer, it must be stored under sheds, or in cool, well-ventilated rooms, and the temperature of the fraction must be monitored.
Characteristic properties of ammonium nitrate
Features of ammonium nitrate (positive and negative in terms of use):
- High hygroscopicity... By itself, ammonium nitrate is extremely hygroscopic, dissolves very quickly in water, damp, literally sucking in moisture from the air. This effect can be somewhat reduced due to the fact that the fertilizer is produced in the form of granules. A plus should be considered the convenience of using nitrate during watering. To carry out processing, it is not necessary to dig or loosen the ground.
- Traceability... Natural consequence of hygroscopicity. To prevent this phenomenon, lime and chalk are added to fertilizers. This property in itself does not impair the quality of the product. But before use, the caked substance must be crushed.
- Explosion and fire hazard... The 32.3 ° C mark on the thermometer is critical. When reached, ammonium nitrate may explode. It is because of this property in a number of countries (China, Ireland, Afghanistan, etc.) that a ban on trade in this agrochemical has been introduced.
- High diffusion capacity... It is also a consequence of the hygroscopicity of ammonium nitrate. A solution of ammonium nitrate is capable of going deep into the soil when irrigated.
- Ability to function in cold ground and at low temperatures... This is a fundamental difference from organic fertilizers. The first application of saltpeter is carried out at the beginning of March, without even waiting for the snow to melt. The substance "burns through" the snow and ice cover and, once on the ground, begins to saturate it with nitrogen.
- High natural acidity... This property does not at all interfere with the achievement of the desired effect when it comes to soils saturated with alkalis (serozem and chernozems). Otherwise, the procedure is carried out in a complex paired with lime or dolomite to prevent soil acidification and further decrease in yield.
































