The main purpose of agricultural activity is to collect a rich harvest. All agronomists know that vegetables have many enemies. Poor harvests are associated with unfavorable weather conditions and poor soil quality. But the reasons for crop failure are not always obvious. Often, the potato nematode causes severe damage to the fields. The scale of its negative impact on the quality of the crop is so great that the phytocontrol authorities classified this infection as a quarantine disease.
Golden potato nematode: what is it and is it dangerous

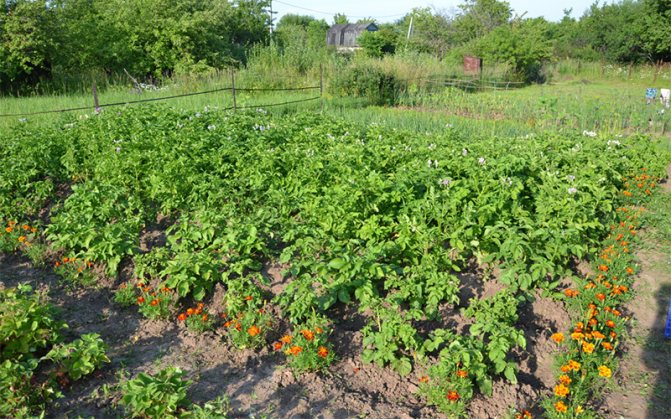
Healthy potato harvest
Potato nematode: a biological portrait


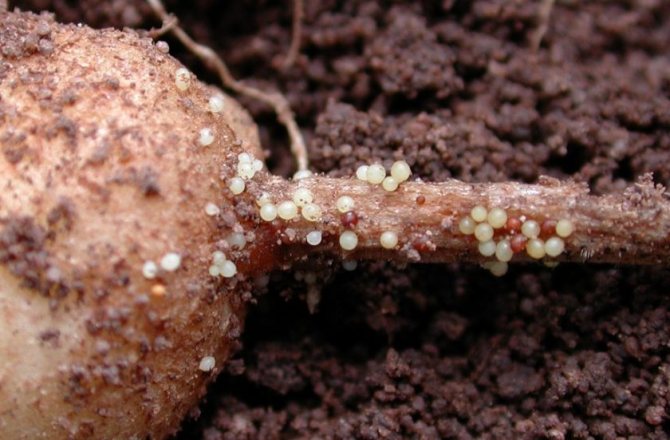
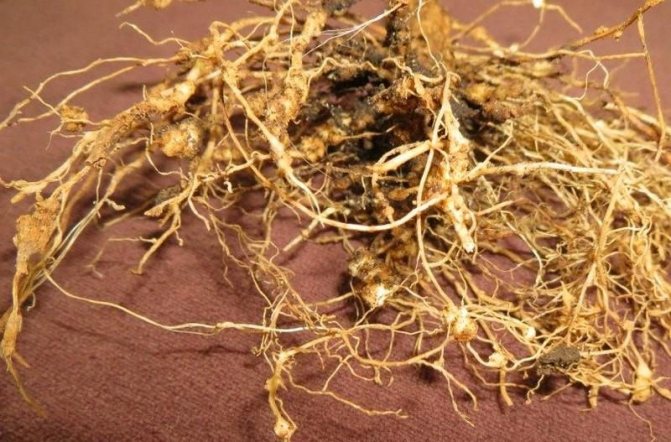
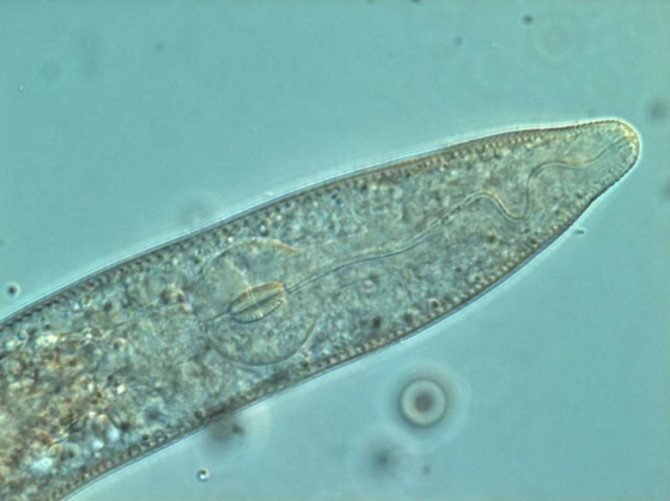
Golden potato nematode: photo of a mature female
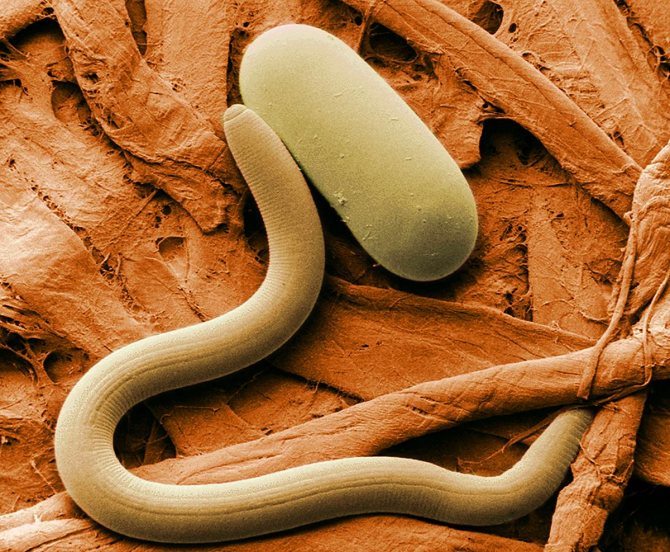
The potato nematode is a tiny worm, no more than 1 mm long. On very close examination with magnification, you can see that some worms are spherical with a small tail - these are females, while others are elongated, these are males. The female is white in spring, over time, by autumn, it darkens, acquiring brown. On the roots, the nematode is attached precisely with the help of an organ located in the oral cavity and has the name "spear". In addition, the pest cuts the cells of the fetus with it and, like a syringe, lets in saliva, moves along the tuber.
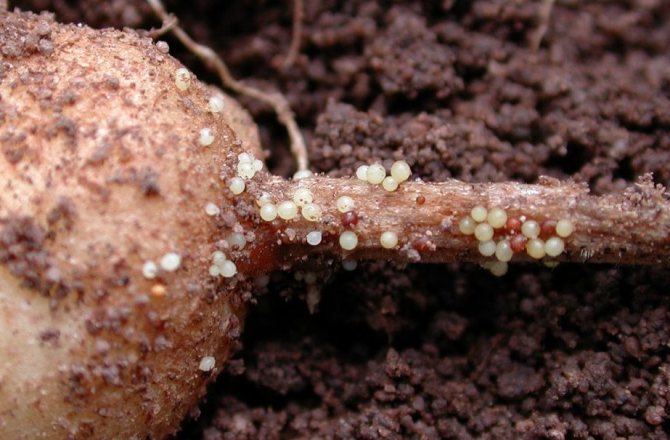
It is very difficult to examine a nematode on a potato with the naked eye, but it is possible. To do this, a supposedly infected bush must be dug out of the ground and carefully shaken off the remains of the soil from the roots. If round "grains" are visible on it, then the plant is infected. Reproduction takes place through egg-laying. In addition to changing color, by autumn, females turn into shells (cysts) the size of a grain of sand. containing more than 1000 eggs.
Important! A potato cyst nematode at the level of cyst development survives in the most unfavorable conditions for 10 years or more!
Description of the pest
Nematodes are a vast group of worms, the varieties of which number in the hundreds of thousands of species. In terms of species diversity, they are second only to insects. Herbivorous parasites leave a large proportion. The most harmful and dangerous potato nematode is golden. It is followed by stem and gallic. Each of the pests is distinguished by its characteristic features, localization and harm caused.
Golden potato nematode
The parasite specializes exclusively in nightshade crops: tomatoes, potatoes, peppers. It lives in the ground, as a result of which the popular name "soil nematode" has taken root. It affects the root system of plants, which negatively affects their growth. In Europe, it spread about 100 years ago as a result of the import of potatoes to Germany.
Potato nematodes (diseases caused by parasites) have been recorded in 42 countries of the world. In Russia, the potato nematode was found in 56 regions.
Due to its miniature size, it is impossible to see the worm with the naked eye. It clearly demonstrates the appearance of a potato nematode photo. The larvae are white. Growing up, they acquire a characteristic golden color, for which they got their name. The oral cavity is represented by a piercing-sucking apparatus, which bears some resemblance to a spear. With its help, the worm is fixed on the roots of plants, pierces tissue and absorbs nutrient juices.
Important! The golden potato nematode parasitizes the roots of the plant, not its tubers.
They overwinter in the cyst stage. This is the name of the female shell, in which the eggs and larvae are enclosed. Each cyst can contain up to 200 embryos. During the growing season of potatoes, the larvae leave the capsule, attach to the root system and begin to actively feed.
In the summer, if you carefully dig up a potato bush and shake off the soil from it, you can see the milky-white larvae, tightly stuck to the roots.
Like insects, they undergo several molts, after which a division into females and males occurs. The sex ratio directly depends on weather conditions and the availability of food resources. Females need more nutrition than males. Males die off after mating. By autumn, the fertilized female acquires a spherical shape, a caramel shade and turns into a cyst 0.5-0.6 mm in size. In regions with a warm climate, 2 generations of generations are possible per year.
Important! All the insidiousness and danger of the golden potato nematode lies in the resistance of cysts to the effects of the external environment: severe frosts, drought, flooding, the use of pesticides. They are able to lie in the soil for up to 10 years and remain viable, and the hatching of larvae can occur in stages over several years.
Varieties of nematodes
There are several types of this pest that multiplies and develops in different parts of the plant.
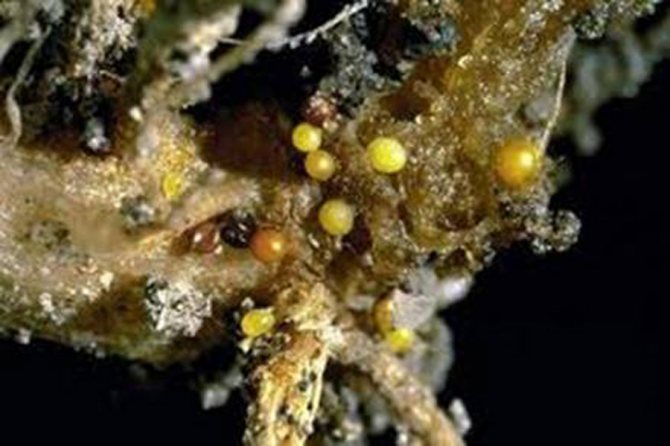


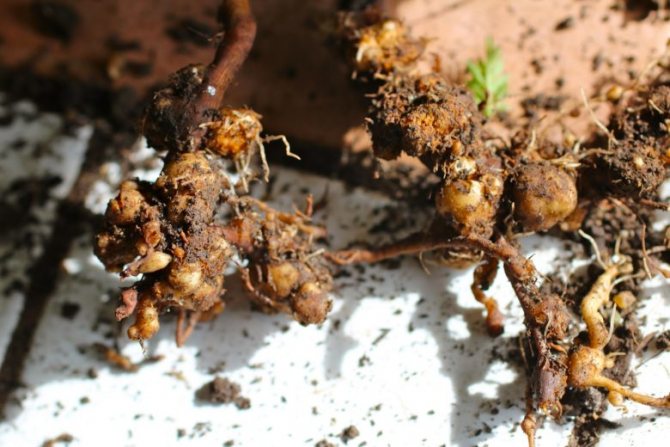
Examine the roots of the potato carefully - such balls indicate a problem
Soil
Golden potato nematode. The "saboteur" of this species is located mainly in the soil, on the roots of plants. Affecting the underground part, it does not allow the stem to develop properly. It grows (if it grows) weak, yellowing quickly, and the tubers, if they could form, are very small. The disease spreads quickly. Its signs can be seen after germination. They are small, underdeveloped, drooping bushes. The location is haphazard, in the form of islands throughout the landing site. During flowering, they either do not bloom at all, or they release small, few flowers. When the time comes for harvesting, there are only a couple of tubers or they are absent altogether, but the roots are quite branched and in many places are black.
Important! This type of nematode does not parasitize tubers. Damaging the base, consuming nutrients instead of the plant itself, it seems to block all the channels through which the necessary juices enter. The pest turns into an immobile sucking female or a mobile male, which goes in search of a female. Such development, at sufficiently high temperatures and normal soil moisture, occurs in 20-40 days. During harvest, tiny golden cysts can be seen on the roots.
Stem
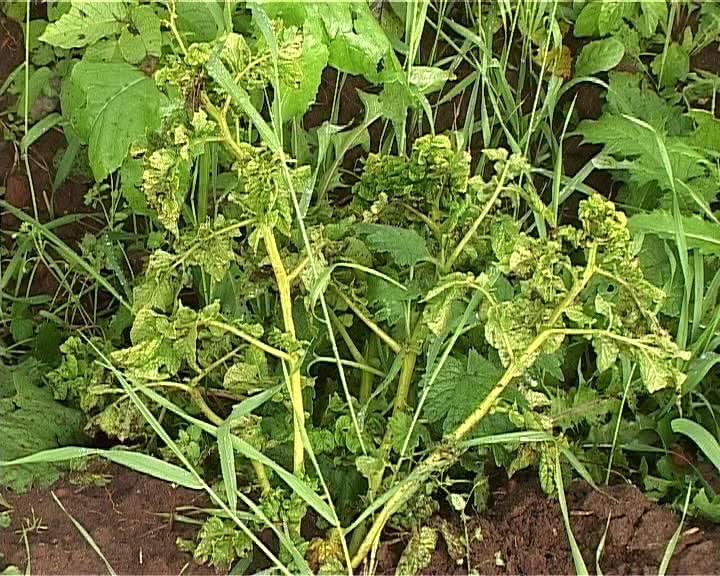


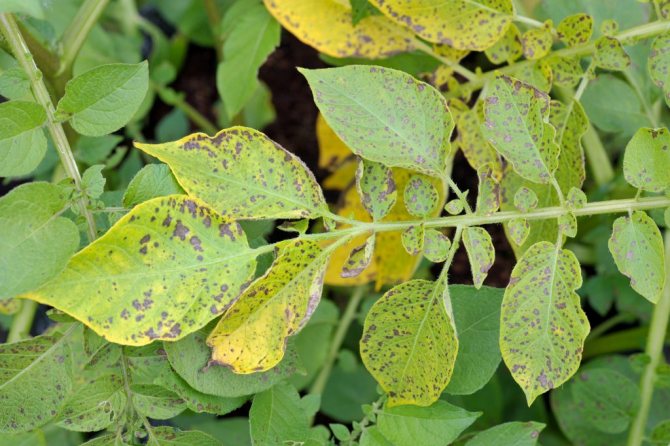
Signs of a nematode on stems
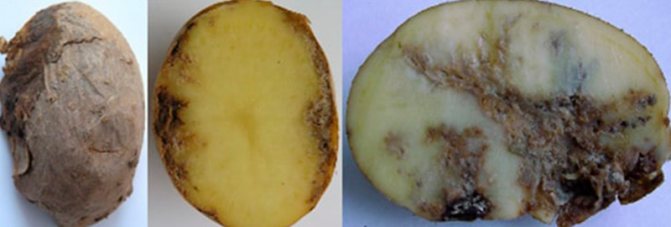
Potato stem nematode affects both the stem and tubers. Unlike golden, the stem affects the upper part of the plant. The stem thickens and bush quickly and violently. In addition, its presence is not detected at the stage of plant development, but during storage. At the beginning of infection, the tubers become covered with gray spots, then the peel cracks, under which a brownish rotten flesh is visible. Worms move through the cracks, onto healthy tubers. One infected fruit is able, by spring, to infect, and thereby destroy, more than 3/4 of the stored potatoes.
Soil contamination: how to avoid
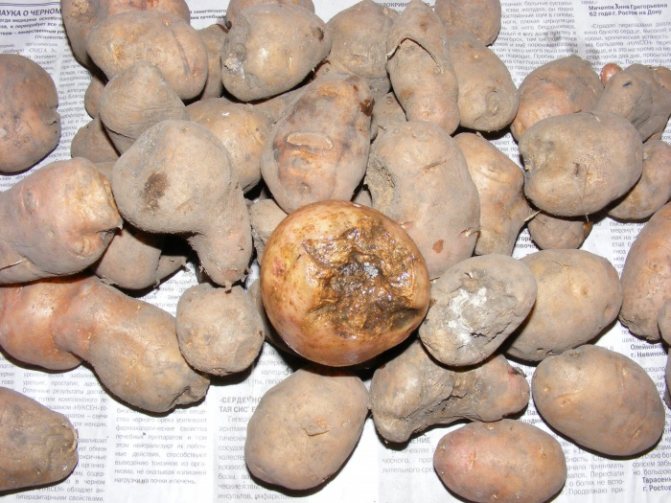


Infected seeds
One of the reasons for the spread of the disease is soil contamination, which leads to infection of the root system and stem. It happens trivially - as a result of mechanical transfer:
- planting infected tubers;
- joint storage of healthy and diseased fruits;
- using untreated garden tools (or shoes) after "contact" with contaminated soil;
- during harvesting, the capsules, with the nematode larvae separated from the root, remain in the ground;
- incorrect crop rotation or lack thereof;
- others.
Signs of appearance
The signs of the onset of the disease are not specific.
Symptoms are similar to those that appear with a lack of water or nutrients:
- growth slows down;
- leaves turn yellow early;
- flowering is delayed;
- the root system becomes ramified.


How to deal with potato nematode: preventing the problem
The fight against this very serious pest must begin with preventive measures. Quarantine measures are very important, even if you think your site is free of nematodes. It may very well be that these are false conclusions and therefore, in order to avoid unpleasant consequences, take into account the recommendations of professional agronomists.


Chemicals affect both worms and soil cysts
- Mandatory observance of crop rotation. In the area where nightshade crops were planted, plant only vegetables and legumes for 3-4 years. Which will also be an effective prophylaxis against wireworms. In addition, it should be borne in mind that such where strawberries or vegetables grew, nematodes may also be present.
- Never take land from greenhouses for your plot.
- Deep digging in the fall is a must!
- Before planting, it is imperative to inspect the seed material - it should only be of high quality. If it was purchased on the market, then thoroughly wash it with warm water before planting.
- Plant potato varieties resistant to nematodes such as Diamant, Picasso, Scarlett, Fresca, Sante, Aspia and others.
- You can strengthen the immunity of plants by introducing a complex of trace elements: superphosphate, ash, granular fertilizer with potassium.
- A positive protective effect is borne by the treatment of seed with the drugs "Bulba", "Gumi", "Albit".
- As a preventive measure, before planting potatoes, the site should be treated with urea, in the calculation - 1 kg per area of 10x10 m.
- Helps premature hatching of larvae and their early death, at low temperatures - a solution of potato sprouts. It is prepared at home: 1 kg of sprouts, twisted in a meat grinder, pour 10 liters of water and water the area, after adding urea.
- Pour into each hole, during planting, a little manure, dry bird droppings, a handful of ash, sprinkle with earth. Further, upward by shoots, plant a tuber.
- The answer to the question of which flowers kill the potato nematode is very simple - marigolds! These unpretentious undersized "suns" effectively act for soil disinfection. In the summer they are pleasing to the eye, and in the fall, before frosts, their tops must be crushed and dug up from the ground. Also, the nematode is afraid of sweet clover and calendula.
Prevention measures
Nematoda is a malicious parasite, the appearance of which on the site is easier to prevent. As a preventive measure, you must follow some rules:
- tubers for planting must be disinfected;
- comply with the rules of crop rotation, i.e. do not plant the same vegetables in the same place all the time;
- process holes and tubers before planting;
- timely apply fertilizers and biological preparations against pests;
- remove plant residues after harvest.
The best way out of the situation is to choose a potato variety for planting that is resistant to nematode attack. These are early ripening - Liga, Krepysh, Gloria, mid-ripening - Aurora, Yanka, Cascade and late-ripening - Volare, Vektar, Zhuravinka.
If the parasites decide to eat one of these types of potatoes, they will remain walled up in it.At the first attempts to penetrate into someone else's tuber, the tissues of the potato harden. Thus, the larvae remain inside the fetus, they lack nutrition and they die, unable to develop further.
Potato nematode is a quarantine disease. It is the duty of the owner of the garden where the pests were found to report this to the appropriate authorities. After that, the entire site is taken under the supervision of phytocontrol until the complete extermination of worms and their larvae.
Aggressive control measures
If nematode infection has already occurred, then the soil must be treated with modern chemicals. For instance:
- "Nematicide". Two weeks before planting the seed, spread evenly and mix with the soil. Complete destruction will not occur, but the development of cysts will be disrupted.
- "Nemabakt". It is a symbiosis of a nematode. Acts directly on the cyst, destroying it from the inside.
- BI-58 or 0.02% mercaptophos solution. Spray diseased plants up to 4 times with an interval of 5 days.
Attention! Nematodes are quarantine pests that pose harm and danger to humans, therefore, in case of large foci of potato damage, it is necessary to report to the phytosanitary service.
Check out articles on similar topics
- Caterpillars on potatoes: what they look like and how to get rid of
- Protection of potatoes against late blight (potato rot)
- Appearance and features of the Colorado potato beetle
- Potato scoop control measures
Comments (1)
leave a comment
Agrotechnical measures
The disease is easier to prevent than to cure after it. The results in preventing the spread of nematodes are clearly visible in the technology of crop rotation on the site. The greatest effect is obtained after sowing legumes in a potato field.
After harvesting the potatoes, the land must be dug to a considerable depth. All suspicious soil fragments are treated with hot water. At temperatures above 40 degrees, most of the larvae and eggs of the nematode die. This is the minimum that can be done, it is safer to completely destroy a piece of soil if it is small.
Note! Seed material is bought only in specialized stores, where all seeds have a safety certificate. Preference is given to special varieties with increased resistance to pests such as nematodes. Before planting potatoes, all tubers are carefully inspected for surface signs of infection.
Planting only nematode-resistant potato varieties is effective, but after a few years the parasites adapt to new conditions. Preventive measures alternate.
Use general pest control measures. This is the treatment of seed with protective agents such as "Bulba" or "Albit".
You can restore the soil after a site is infected with a nematode in a proven folk way. After the potatoes, the field is sown with unpretentious flowers - marigolds. Sowing these flowers completely destroys the nematode larvae. In the fall, marigolds are not removed, but dug up together with the ground. A similar, but slightly weakened effect is obtained after planting sweet clover or calendula.