Many experienced gardeners know that without proper care and additional components, the desired result cannot be achieved when growing plants. A variety of additives, fertilizers are used and, of course, the matter is not complete without the use of vermiculite. The use of this component in horticulture has gained popularity due to the large number of positive properties. It is simply impossible to refuse it in the future. Due to its qualities, vermiculite is used in many other areas, except for crop production.
- 2 The use of vermiculite in horticulture
- 3 The use of vermiculite in hydroponics
- 4 Rules for the use of vermiculite
- 5 Positive qualities of vermiculite
- 6 Conclusion
General information about the mineral
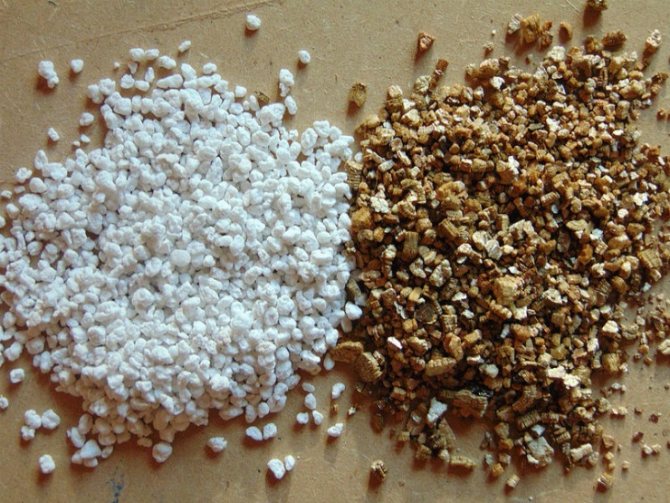
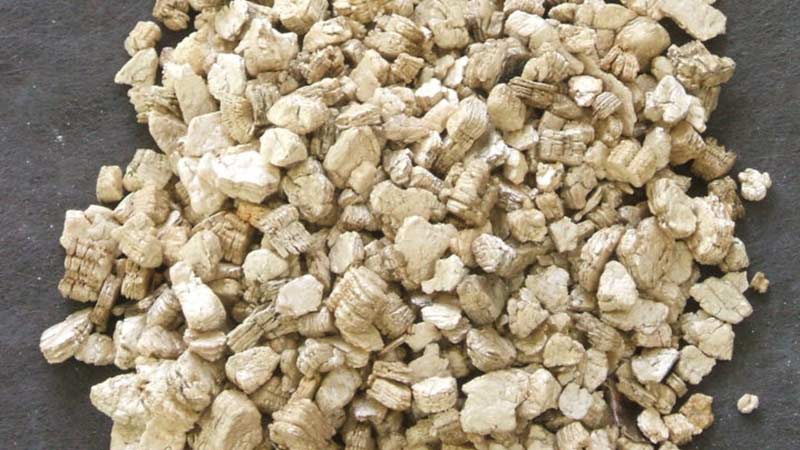
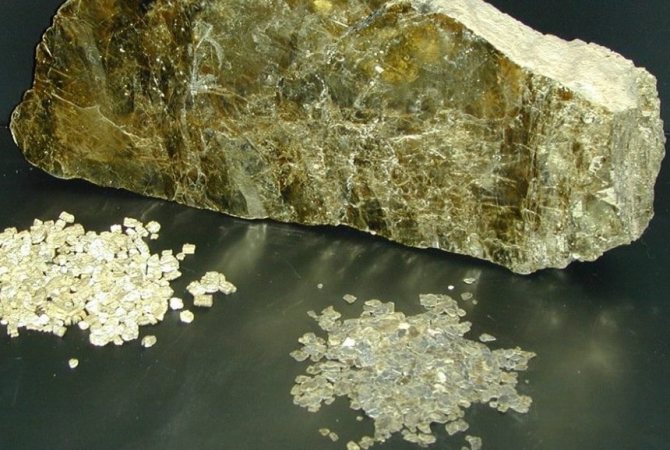
Vermiculite is a free-flowing material in the form of plates of a golden brown or silver hue, which is as similar as possible to hydromica, and in fact, it is. The term itself comes from the Latin vermiculus, which means "worm" in Russian.
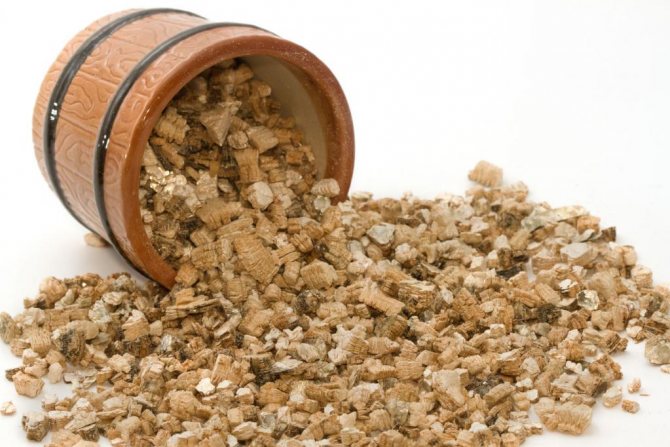

If vermiculite is exposed to high temperatures, its plates will take the form of thread-like granules, which outwardly resembles small worms. Due to the porous structure, the material is able to absorb and retain moisture, the volume of which can be 4 times its own weight. In other words, it acts like a good sponge.
This quality makes vermiculite an irreplaceable addition to earth mixes. At the same time, soil moisture remains for quite a long time, as well as nutrients.
Description and properties of vermiculite
Mineral vermiculite is a flaky clayey mica. The color of this mineral is not the same and can vary depending on the amount of impurities in the composition and the deposit of this rock.
Most often, the color of this mineral is golden yellow, but you can also find bronze-yellow vermiculite, and even golden brown or brown-green. On the photo vermiculite looks like a completely ordinary and unsightly pebble, but its properties make it in demand.


The formula that describes the chemical composition of this mineral looks like this: (Mg + 2, Fe + 2, Fe + 3) 3 [(Al, Si) 4O10] · (OH) 2 · 4H2O.
But it should be noted that vermiculite rarely meets this formula, often it contains impurities that must also be taken into account.
An interesting fact is that vermiculite can change its structure when heated and turn into expanded vermiculite... This happens at 900 degrees Celsius, at which time the vermiculite plates become like columns, which are vaguely similar to the very worms that served as the basis for the name of this mineral.
When heated, vermiculite swells strongly, it is enough to put this mineral in a fire, and then these pieces of vermiculite will turn into golden, almost weightless balls. However, in this form, vermiculite is unstable, with any, even very light, touch or from a gust of wind, the balls crumble into separate tiny flakes that look like dust.


Expanded vermiculite becomes when exposed to temperature
During the process of converting from one state of vermiculite to another, a characteristic crackling sound is heard. Many shamans and magicians use these quality of vermiculite.
If you look at other characteristics of this mineral, you get the following picture: on a mineralogical scale, the density of vermiculite is estimated at 1-1.5 units; density of vermiculite is 2.4-2.7 g / cm3, however, in expanded vermiculite this figure is much lower and amounts to 0.065-0.130 g / cm3.
When heated and transformed into an expanded state, vermiculite can increase in volume up to 25 times. It should be noted that vermiculite belongs to the class of natural minerals that are biologically stable. This means that vermiculite does not decompose and does not rot under the influence of various microorganisms.
In addition, vermiculite is not a favorable habitat for insects and rodents. Alkalis and acids do not have any effect on vermiculite, therefore this mineral is called chemically inert.


Vermiculite: is it an urgent need or a waste of time and energy?
Every gardener knows very well that the full development of plants depends on the quality of the soil. In the course of the growth of a horticultural culture, the soil undergoes certain changes, and not for the better. The soil cakes over time, becoming solid, water and air permeability decrease, as well as the amount of micronutrients.
An increase in irrigation ends with waterlogging and oversaturation of the soil, and the introduction of additional mineral fertilizers often turns into an overabundance of a number of components. Ultimately, this leads not only to a deterioration in plant development, but also to the appearance of unwanted diseases. The introduction of vermiculite into the soil avoids such problems.
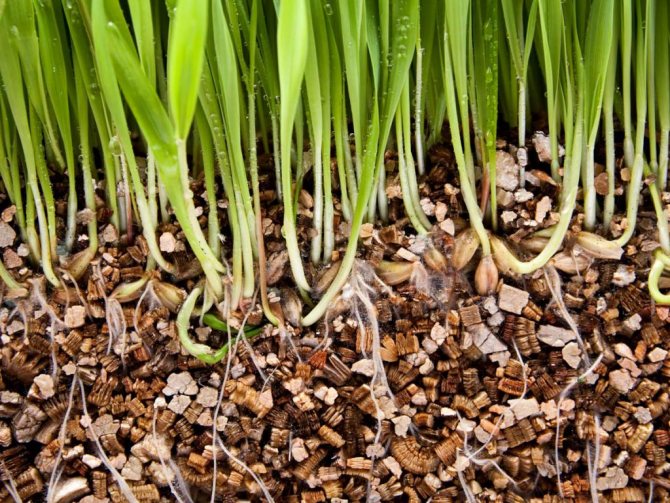


We got acquainted with the benefits of this mineral, but how to use vermiculite for plants? After all, every gardener wants to grow only healthy and strong seedlings. This will be discussed further.
How vermiculite is used in crop production
We will learn how to use vermiculite in plant growing:
- The stalk takes root better after applying vermiculite to germinate young seedlings and seeds.
For the reason that the described mineral does not provide soil for the development of mold, fungi and other microorganisms, rooting and reproduction is as simple and fast as possible.
- To enrich the composition of store-bought soil mixtures.
The proportions in which the mineral is added can be up to half of the composition. This improves most of the characteristics of the soil, making it porous, looser, and also better saturating it with moisture. It is worth noting that, subject to the presence of vermiculite in the ground, the plant or flowers receive more oxygen, and the roots have the ability to develop and grow, being evenly distributed over the entire area of the pot.
- Protecting the plant's root system after planting and during cultivation
In addition to the fact that the presence of vermiculite does not allow the earth to compact tightly, a dense crust does not form on the surface, which usually prevents the penetration of liquid, vermiculite serves as an excellent obstacle to the effects of temperature. Thus, no matter what the weather is outside, the root system will maintain the same temperature. And due to the fact that the acidity of vermiculite tends to neutral, soil salinity will be minimal.
- For growing plants using the hydroponic method
Vermiculite can be used when seedlings are grown without the use of land, only on one nutrient mixture.
- The most common method of application is drainage combined with sand in which to plant the plant.
This method of application is most often used in plant growing, in which case vermiculite is placed on the bottom of an earthen pot, laying in layers with sand for cultivation.
- For wintering and storing plants with bulbs
Due to the fact that the mineral does not depend on the external environment, a neutral temperature remains, therefore the bulbs hidden in vermiculite do not lend themselves to natural rotting, fungal growths do not develop there.
The composition of a useful mineral
The chemical composition of the mineral includes oxides of a number of elements from the periodic table:
- silicon;
- calcium;
- potassium;
- magnesium;
- gland;
- manganese;
- aluminum.
In addition, it contains various impurities - chlorine, sulfur. By its properties, vermiculite is chemically inert. For this reason, the mineral is not able to interact with solvents, alkalis and acids of organic origin.
Thanks to this, the material has a beneficial effect on the development of plants, because it is not able to change the reaction of the environment.
For soil
The properties of vermiculite can significantly improve the quality of the soil, reduce acidity, and retain moisture. For summer residents who have no time to water the flower garden - this is just a godsend. The mineral is applied independently or in combination with organic matter, in a ratio of 1:25.
Vermiculite for indoor plants plays the role of a baking powder. Most indoor flowers have a voluminous root system that quickly draws out all the nutrients from the soil, leaving it depleted. The mineral retains moisture without increasing the density of the soil, but on the contrary maintaining the distance between the fractions, accumulating oxygen there. Vermiculite, used at the dacha in greenhouse, unheated premises, is an excellent insulation material, especially in combination with horse manure.
Other features of vermiculite
What is vermiculite? A similar question may arise for many newcomers to the field of crop production who first hear such a definition. Experienced people are aware of the benefits of this mineral and know some of its features, which can be considered as advantages:
- The material does not rot - it is indifferent to the effects of various pests, including fungi and microbes.
- These durable stones can be used for several years.
- Thanks to vermiculite, the soil becomes softer and more airy.
- This material contains chemical elements necessary for many plants.
- Vermiculite can be used for composting.
- It is worth adding vermiculite to the potting soil, and the flowers can already be watered less often than usual.
As for the term of use of vermiculite, this is a rather impressive figure - up to 10 years.


However, the old material should not be thrown away - it is enough to rinse it well, dry it, and then ignite it in the oven or in a frying pan. It can now be reused.
Rules for the use of vermiculite
Vermiculite is distinguished by its fragility, lightness and scaly structureTherefore, it is not surprising that a large amount of dust is generated during the transport of the substrate. Inhalation of this dust can cause discomfort, therefore it is best to pre-wash the material and remove the dust. Even if, at first glance, the dust has completely disappeared, it is recommended to use a gauze bandage and glasses during the preparation of the soil.
In addition, although vermiculite is famous for creating a neutral environment, its pH can eventually rise. This happens when using hard water while watering plants. The accumulation of harmful substances begins, the level of acidity rises, and the neutral medium becomes alkaline, which as a result can destroy even a mature and strong plant.
To reduce the hardness of the water, you can use cleaning agents or, at best, boil the liquid and let it settle until all impurities settle to the bottom. Watering plants should be much less frequent when using vermiculite, since it retains enough moisture for plant life for a long time.Frequent watering can cause the plants to overflow.
Vermiculite can remain in the soil for almost 10 years, but even after this period it can be reused. For reuse, the material is dug out of the soil, washed and dried by calcining in a pan.
A number of disadvantages
It is important not only to know how to apply vermiculite to plants, but also to understand that everything has both pros and cons. And despite the obvious advantages, the material also has a number of disadvantages. On the one hand, the presence of a large number of chemical elements that are so necessary for plants is, of course, a plus. However, the fact that they are in an indigestible form is, without a doubt, already a minus. For this reason, vermiculite should not be considered a complete fertilizer.
Failure to comply with the dosage of vermiculite leads to a change in the acidity of the soil to the alkaline side. In addition, this can happen due to watering the plants with tap water, which is quite harsh.
How does the soil change after adding vermiculite
Let's summarize and bring together in one list exactly how vermiculite affects the quality of the soil:
- The soil changes for the better, regardless of what kind of soil - clay or sandy, indoor plant or garden plant growing in the beds
- The most favorable conditions for air enrichment are created
- The root system is maximally protected
- The acidity of the soil is normalized, and the salt content is also reduced
- Fertilizers are better accepted by the plant, both in horticulture and in plant growing
Application area
It is worth noting that there are materials that are unknown to the mass consumer, but at the same time have a lot of advantages and have a wide range of applications. And vermiculite is just one of those. This material is of natural origin - it is a product of volcanic activity. Humanity has adapted it to its needs for a long time.
Vermiculite is known to professional builders as a quality material. Experienced gardeners and gardeners also know about it. But how is vermiculite used?
Vermiculite price
Vermiculite is not expensive. It is a readily available mineral. Of course, it all depends on the purpose and scope of vermiculite. If you purchase it for use in plant growing or floriculture, then a small bag, about 3 liters, will cost 150 rubles.
Of course, this price can vary and depend on many factors. If you decide to use vermiculite as insulation, then you will need much more of this substance, respectively, and the amount will be higher.


However, compared to other heat and sound insulating materials, vermiculite will cost you significantly less.
Hydroponics
This term refers to the cultivation of plants and garden crops without the use of soil. On the one hand, this allows you to get rid of many problems. There is no stagnation of moisture, moreover, contact with harmful microorganisms and insects is completely excluded. But at the same time, this technology is complex. In addition, not every plant will be able to take root in such conditions.


The use of vermiculite in this case will be the best choice. The material will serve as a good alternative to soil. Small stones will strengthen the root system of plants. In addition, all the benefits that have already been discussed will be useful.
What is agrovermiculitis
Agrovermiculite is a material obtained as a result of secondary firing of ordinary vermiculite with a size from one to ten mm in diameter in a fraction. It is worth saying that minerals ranging in size from 3 to 5 mm are used for breeding plants at home, that is, it is agrovermiculite. If the porous material was needed in the country or for landscape work, it is recommended to use a larger diameter of vermiculite.
The described mineral contains useful trace elements and materials:
- Aluminum
- Calcium
- Potassium
- Silicon and others
Many growers mistakenly believe that due to its rich mineral composition, vermiculite can be a source of nutrition for the plant, but this is not the case. The fact is that all of the above elements cannot be obtained in the environment in which they are located, that is, in moist earth or other soil. And even if this happens, it will not be in the amount that is needed.
Agrovermiculite, which is used for plants or flowers in pots, which stand on the windowsill in every house, is also able to retain liquid, gradually giving it to the root system of the plant. However, this ability does not make the soil excessively heavy; on the contrary, it is better enriched with oxygen due to the porosity of the mineral.
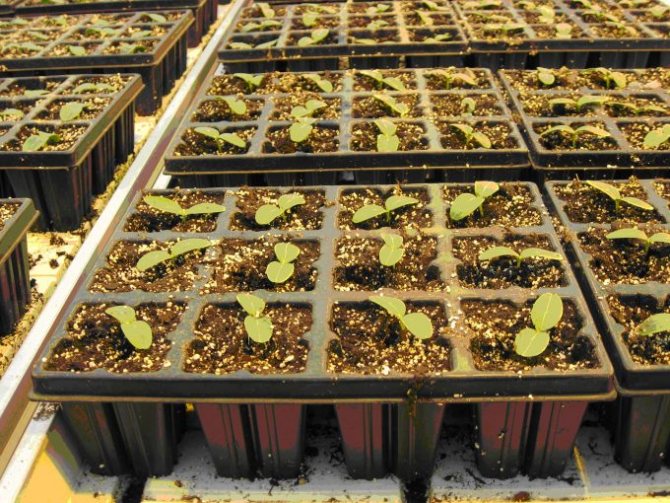
Dive seedlings
We already know about vermiculite (what kind of mineral it is), now it's worth getting to know one more option for its use. In this case, it is worth using a soil mixture of the following composition: 1 part of vermiculite with a fraction of 1-2 mm for 2-3 parts of soil. All must be mixed thoroughly, and then distributed in cups.
When the time comes for planting grown plants in open ground, it is worth adding vermiculite in the amount of 2-3 tablespoons to each open hole (fraction 2-4 mm). This will maintain the required moisture level near the roots, which, in turn, greatly facilitates the care of the planted crop.
Characteristics of Vermiculite
- ease;
- low density;
- thermal conductivity;
- rich mineral composition.
Properties
The stone has the following properties:
- lightweight porous mineral from which the substrate is obtained;
- holds a liquid that is 5 times its own weight in volume;
- perfectly conducts heat;
- isolates from noise;
- does not decompose when in soil with a biologically active environment.
Under the influence of high temperature, it exfoliates, acquires a porous structure. The mineral is mined in Kazakhstan, Ukraine, USA, Australia, in the Urals. Growing plants in vermiculite is considered completely safe. Due to its neutral level of acidity, naturalness, the use of vermiculite in the garden is completely safe.
Description of Agrovermiculite
There are 5 types of mineral, each of which is used in different fields, but only agrovermiculite is used in horticulture. The mineral has a rich chemical composition, which makes it possible to supply the soil with all the minerals necessary for the plant for adaptation after a pick and stable growth.
An agrotechnical variety of the mineral obtained by secondary firing of standard vermiculite, interspersed with stripes of mica. Each fraction of it has a size of 1-10 mm. Construction vermiculite has good thermal conductivity. For the production of plaster with vermiculite, a larger fraction No. 5 is suitable. A loose mineral can be used in a wide variety of areas of human activity.
Germinating seeds
Due to the ability to accumulate moisture, and in a fairly large amount, the mineral allows you to create an optimal moisture level, which contributes to the formation of strong and healthy seedlings. What is vermiculite? This is a humid environment that will remain unchanged for a long time, which is beneficial for the seedlings that have not yet matured.
For these purposes, it is better to use expanded vermiculite with a fraction of 1 mm. Everything should be packaged in plastic bags and placed in a warm place for seeds to germinate. And when the sprouts are already visible, they are sown in a container where the soil mixture is previously placed (1 part of vermiculite with a fraction of 2 mm per 2 parts of soil).


If you prepare the mixture correctly, the seedlings will sprout faster and the root system will be reliably protected from rot (black leg).
Vermiculite for seedlings
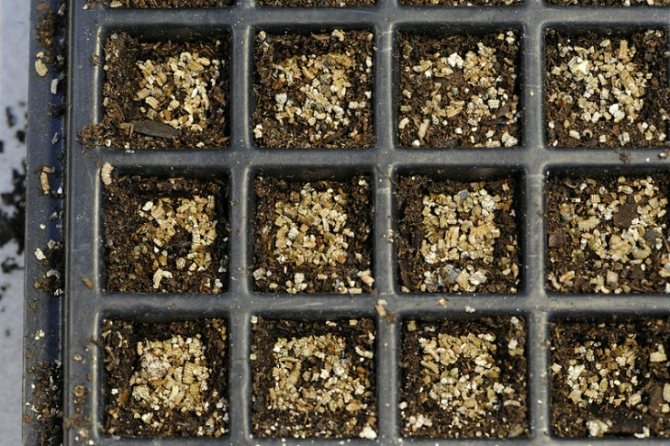


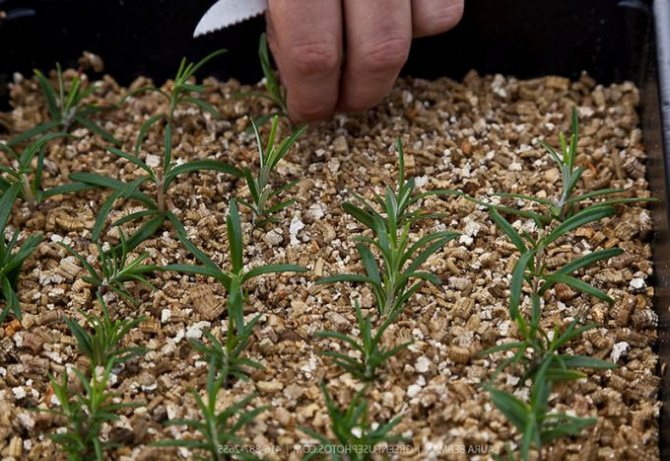
Vermiculite is useful for growing seedlings. A soil mixture with the addition of vermiculite retains moisture better. Thus, seedlings are less likely to get sick with root rot.
Seedling substrate is prepared from humus, peat, sand and vermiculite, taken in a ratio of 5: 3: 1: 1. This natural mineral is often used in the production of peat pots. To do this, it is mixed in equal proportions with peat.
Expanded vermiculite will help you in the pre-sowing preparation of seeds.
The seeds are placed in tight plastic bags filled with moistened vermiculite, which are kept in a warm place until they germinate.
It turns out that vermiculite can not only be added to seedling soil, but even seedlings can be grown in it from scratch! I suggest watching the video.
Benefits for indoor plants
Now there should be no doubts about vermiculite. We already know what kind of mineral it is, and its benefits for plants are also known. At the same time, the scope of this material is not limited to agricultural crops.
In home floriculture, there is also a use for it:
- The use of vermiculite helps to loosen the soil mixture. At the same time, the content of agrovermiculite can be up to 30%, which will significantly affect the characteristics of the soil, and for the better. It will become porous, loose, without lumps and seals.
- Vermiculite is also good as a drainage system. To do this, lay out the bottom of the pot with coarse material.
- Mulching. The use of vermiculite in pots avoids colonization of the soil with sciarides, mealybugs and other soil pests.
- Scenery. Vermiculite is able to attract attention due to its shade and crumbly structure. In this regard, the material is perfect for decorative dusting around plant stems, as well as in pots and pots.
And it should be noted that the use of vermiculite in indoor floriculture is gaining more and more popularity for obvious reasons.
How to use the mineral vermiculite for plants
Application of agrovermiculite:
- Additive (as well as hydrogel) to seedling and flower (for perilla, petunia, ...) soils (from 15% to 30% of the total volume, sometimes even up to 50%).
- Drainage (large fractions, 8 millimeters).
- Sterile substrate for hydroponics, forcing, rooting cuttings, germinating seeds before sowing, the initial stage of growing cucumbers and other pumpkin seeds.
- Adding to garden planting holes, especially on dry lands and heavy loams in summer cottages (for melons, cucumbers, flowers, etc. - half a glass per root; for potatoes - two handfuls to a tuber, from 50 liters per a hundred square meters; for bushes and fruit trees - 1 - 3 liters per planting pit).
- Mulch.
- Backfill for winter storage of bulbs and vegetables.
- Insulating protection of wooden surfaces against rapid decay.
Not a stimulant or growth regulator, contrary to some advertising claims.
Effects from application to soil
- The soil crust disappears.
- The substrate is loosened.
- Reduces the risk of drying out and excessive moisture.
- You can water less often.
- The balance of plant nutrition is being established.
- There is a smoothing of temperature differences in the root zone of potted crops and seedlings.
- Respiration, nutrition, development of the root system improve, which makes the plant as a whole gains.
Rules for the use of vermiculite
Before using vermiculite for indoor plants, rinse it well. This material is soft and quite fragile. Otherwise, large amounts of dust cannot be avoided, which will enter the lungs, eyes and nose.


In extreme cases, you can use appropriate protective equipment, but suitable goggles and a respirator are not always at hand. But in fact, why come up with unnecessary troubles, because it is much easier and faster to just rinse the material, and it will become absolutely safe. In addition, you can wash off all the dirt from it.
Since vermiculite is able to maintain soil moisture (especially when there is a lot of it), this fact should not be forgotten when watering. They should be regular, but rare at the same time. We already know what frequent watering can threaten.
Water quality should not be ignored. Pure vermiculite for plants has neutral acidity (pH). Using hard water for irrigation leads to alkalization of the material. And this is no less dangerous than acidification. Neither alkaline nor acidic environment is good for plants.
For this reason, hard water must be softened beforehand. In an extreme case, boiled, settled water is suitable.
Perlite, vermiculite and coconut fiber
Question: On flower sites, I often find recommendations to use perlite, vermiculite and coconut fiber for planting indoor plants. What are these additives and are they really necessary when making an earthen mixture?
Perlite
Answer: Until recently, our growers had little idea of the meaning of these terms, but this did not prevent them from growing any orchids and exotic plants. Nevertheless, with the advent of new materials, it has become much easier to grow rare and especially capricious species. What are these materials and how can they be replaced?
Perlite
Perlite - a product of heat treatment of volcanic glass. Outwardly, ready-to-use perlite looks like lumps of white washing powder. It can be of different fractions, light and inert, which determined its purpose when used in floriculture. Perlite is added to substrates to make them more loose and breathable. Also, perlite is used in its pure form for rooting cuttings that cannot tolerate excess moisture in the root formation zone.
You can replace perlite with regular sand., small expanded clay or polystyrene, pieces of charcoal. True, each of these components has its own drawbacks, but when properly combined, they can completely replace perlite soil.
Vermiculite
Vermiculite
Vermiculite belongs to the group of natural minerals. It is also heat treated for use in horticulture. Vermiculite is easily recognizable by its small, layered lumps of gray, golden or brownish color. When rubbed in the fingers, the lumps are separated into separate plates.
In the soil vermiculite has a dual function - loosening and retaining moisture. Loosening properties, like perlite, are provided by its bulk structure, and the lamination helps to retain a fairly large amount of moisture. Due to its qualities, vermiculite is also used as a component of soil mixtures and a substrate for rooting cuttings.
The best substitute for vermiculite can be considered finely chopped sphagnum moss, especially fresh. It is much superior to vermiculite in efficiency, but, unfortunately, it quickly decomposes and cakes in the soil, which is also important to consider when using it. An interesting new material capable of retaining and retaining moisture in the soil for a long time is hydrogel, but it can hardly be called affordable and inexpensive substitute for vermiculite.
Coconut fiber
Coconut fiber, coconut chips and coconut substrate
Coconut fiber, coconut chips and coconut substrate - products of plant origin, they are obtained from the outer porous layer of the shell of coconuts. In fact, this is waste that has been successfully used. By structure and its physical properties coconut fiber and coconut substrate closest to the usual high peat available in most regions of our country. They practically do not contain nutritional components and have an acidic environment. In this regard, the main field of application is a filler in the composition of earth mixtures and substrate for rooting cuttings.
Coconut chips are significantly different from coconut substrates - it is a loose fibrous shell of a coconut, chopped into pieces and cubes. Due to its fibrous structure, moisture content and lightness, it used as a component of landless mixtures for orchids and other epiphytic plants.
As a substitute, you can use the bark of coniferous trees.but it doesn't have the same moisture capacity as coconut chips.
The above descriptions once again confirm: there is no need to chase newfangled means, almost everywhere you can find the necessary components literally under your feet.
Note: Variegated violet leaves turn green. Why? Read on ...
Vermiculite realization
Vermiculite comes to retail in small packages from 250 ml to 3 liters. The following brands represent the Russian market:
- Fasco.
- Hera.
- Eco Garden.
- "Gardens of Aurica".
- Peter Peat.
- Florizel.
The average cost of 1 liter varies from 30 to 40 rubles.
At the same time, vermiculite can be purchased in large volumes: 10-50 liters. To do this, it is worth contacting one of the large garden or construction centers (yes, this is also a good building material). In this case, the cost of 1 liter will also reach 30 rubles.


As for the producers of vermiculite, the bulk of this concentrate is made in the USA and South Africa, and recently the volumes have only increased. Tellingly, the raw material base of vermiculite abroad is significantly limited on a territorial basis. Despite this, the use of the mineral is still cost-effective.
Various online stores are engaged in the implementation of wholesale supplies, to which one can include, "SibEcoVer", "Lotos". The cost of 1 kg will be 25-35 rubles.
Deposits and mining of vermiculite
Mineral vermiculite was discovered by accident, and it happened quite recently, in the 19th century. However, since then, the exploration of new deposits and the extraction of this mineral in already known places has been quite active.
It is known that there are deposits of this mineral in Russia, Ukraine, Kazakhstan, Uzbekistan. The Russian Federation actively uses vermiculite deposits in the Krasnoyarsk Territory, in the Irkutsk and Chelyabinsk regions.
In addition, this mineral can be found in the USA, Uganda, South Africa and India. These countries are also mining this useful mineral, which plays an important role in various fields of application.


Testimonials
As for the opinions about such a useful and necessary mineral as vermiculite, they are mostly positive. Someone came across it for the first time many years ago and was satisfied with the result. Many gardeners note that before using this fertilizer, they had never had such beautiful and blooming seedlings. The moisture in the soil really persisted for quite a long time.
As the reviews on vermiculite show, many were convinced from personal experience how much vermiculite is dusty. Therefore, it is better to rinse it before using it to minimize all risks.
What can replace perlite and vermiculite?
Found a bug? Report it: 1) Select the error with the mouse 2) Press CTRL + Enter. More details.
I cannot find any perlite or vermiculite in our stores (and I generally keep quiet about moss and cocoa). And I really want to please the violets. What can replace perlite and vermiculite? As I understand it, they are used to loosen and lighten the soil. Maybe you can loosen the soil with something else?
- Login or register to post comments
- print version
Fertilizing pros and cons
Let's consider the undeniable advantages:
- the ability to improve the quality characteristics of soil mixtures;
- decrease in acidity on acidified soils;
- high moisture absorption capacity;
- the content of trace elements in its composition;
- prevention of the multiplication of pathological microorganisms;
- increased aeration of the soil layers;
- preventing the formation of a crust film on the surface;
- protection of the root system from hypothermia, overheating;
- the possibility of using in hydroponics;
- the ability to prolong the shelf life of the harvested crop;
- predisposition to long-term use.
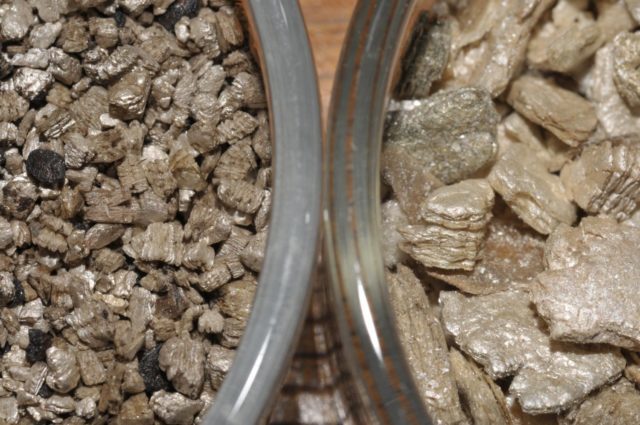


Vermiculite reduces acidity in acidified soils
Among the minor disadvantages are:
- slow release of moisture, the need for joint use with perlite;
- the ability to hide the beginning of the development of the larvae of some parasitic insects;
- the ability to alkalize soils;
- rarely fine fractions create a dust cloud that is hazardous if inhaled.
Place of Birth
In Russia, vermiculite is found in the Kovdor deposit, where it is found in carbonatites with forsterite, diopside, monticellite CaMg [SiO4] and magnetite.
From foreign deposits, we note the large industrial Libby deposits in Montana (USA) and in Western Australia.
Ural and other regions (Russia); Libby in pcs. Montana (USA); serpentinites of the Saxon Ore Mountains and Granulite Mountains (Seblitz, Anshsprung, ushnappel, Hohenstein-Ernsttal, Boerigen, Waldheim, etc.) (Germany).
Kovdor deposit of phlogopite and vermiculite
Located in the southwestern part of the Kola Peninsula, the Kovdor massif of alkaline-ultrabasic rocks is extremely complex in its geological structure.
Morphologically, it is a vertical pipe-like concentric-zonal body, breaking through intensively deployed Archean crystalline gneisses and schists of the Belomorian Group, with an outcropping area of about 40 km2. According to the data of absolute geochronology, the age of the massif is determined at 338–426 Ma (Late Silurian - Early Carboniferous). The formation of the massif was multiphase, and the intrusion and crystallization of subsequent portions of magma were accompanied by the formation of contact-reaction metasomatites. In the first phase, the introduction of olivinites occurred, preserved in the form of a central core with an area of 10–12 km2 and relics in the eastern and southern parts of the massif. The second phase - circular intrusion of ijolite-melteigites and ijolite-urtites - was accompanied by the formation of a zone of magmatic metasomatites over olivinites with a thickness of 1.5-2 km and a fenitization halo in the host gneisses and migmatites. The zone of magmatic metasomatites is represented by successively replacing formations (in the direction of olivinites): alkaline pyroxenites - mica-pyroxene rocks and brown phlogopite mica - pyroxenized olivinites; if the alkaline intrusion had an ijolite-urtite composition, then the specified series of metasomatites takes on a different form: melilite rocks - monticellites - olivinites, partially replaced by melilite and monticellite. All these metasomatic rocks contain a large amount of fine-flaked phlogopite. The listed igneous intrusive and metasomatic rocks were exposed to postmagmatic fluids with the formation of postmagmatic metasomatites, represented by garnet-amphibole-vesuvian-diopside-calcite skarns, developing after olivinites and magmatic metasomatites, as well as even later phlogopite-olivine-diopsomatite complex apatite-magnetite ores. The phlogopite complex contains large mica crystals and is an ore.It forms a semicircular zone in the northern part of the massif, developing along olivinites, magmatic and all preceding postmagma ethical metasomatites.
The rocks of the phlogopite complex are cut by dikes of feldspar ijolites of the third intrusion phase. Even younger formations are carbonatites composing veins and irregular bodies found in all rocks of the massif and in the adjacent Archean metamorphic strata. In the upper part of the massif, mainly along olivinites and phlogopite rocks, a preglacial weathering crust with a thickness of up to 100-150 m is developed. The industrial zone of phlogopite-diopside-olivine rocks with coarse-crystalline mica bends around the olivinite core in the form of a horseshoe 8-10 km long and up to 1 km. In the composition of the rocks of this zone, phlogopite, olivine, and diopside, which account for up to 95%, are in different proportions. Minor minerals: magnetite, apatite, calcite, in addition, tremolite, monticellite, amphibole; accessory: baddeleyite and others. Phlogopite ore bodies in this zone have lenticular and vein-like forms; the largest of them is the Main Deposit - a blind lens 10-100 m thick dipping gently to the north-west and traced for several hundred meters. The central part of the Main deposit, up to 20 m thick, is composed of pegmatoid and giant-grained phlogopite-olivine rocks, and its marginal (peripheral) parts, 5–20 m thick, are composed of pegmatoid phlogopite-diopside or monomineral phlogopite and diopside formations. Phlogopite is unevenly distributed in ores: it forms almost monomineral nests, large crystals, pockets up to 10-20 m in size. Industrial phlogopite is dark green, ferruginous in the form of thick-plate crystals, often of a mosaic structure, with an abundance of spots, closed areas of delamination, fibrous and fracturing, small inclusions of apatite, calcite, diopside and magnetite. The largest crystals can be up to several meters in size. The average yield of industrial raw material for the deposit is 46.6%. According to V.I.Ternovy and others, the formation of coarse-crystalline phlogopite at the deposit occurred metasomatically, mainly due to mica-pyroxene rocks and melilitized olivinites
The commercial vermiculite deposit of the deposit is associated with the linear-areal weathering crust of phlogopite-diopside-olivine rocks (phlogopite complex) and, to a lesser extent, phlogopite-bearing olivinites. The maximum crustal thickness (over 100 m) is established in the central part of the massif, along the fault that crosses it. In the section of the crust, three zones are distinguished (from top to bottom): sungulite-hydrochlorite (50-100 m thick), vermiculite (1-60 m), and hydrophlogopite (5-35 m); below is the disintegration zone (1-150 m) of phlogopite-diopside-olivine rocks. All three upper crustal zones contain commercial ores of sungulite-vermiculite, vermiculite, and hydrophlogopite composition. The vermiculite content varies from 5 to 30%. Ores with a vermiculite content of more than 20% are considered rich, provided that more than 70% of vermiculite flakes are more than 0.5 mm in size. Vermiculite and hydrophlogopite ores are well beneficiated with a vermiculite concentrate of 90–98%. Sungulite-vermiculite ores are difficult to beneficiate due to the abundance of clay minerals; the concentrate obtained from them contains up to 50% vermiculite.
According to MN Chueva and VI Ternovy, the transformation of phlogopite into vermiculite consisted of its continuous hydration, removal of potassium and oxidation of ferrous iron. The transition of vermiculite to sungulite consisted in the destruction of the three-layer vermiculite lattice, removal of iron and aluminum, and the formation of a mineral such as lizardite. Further development of the weathering process led to the replacement of lizardite by sepiolite.Thus, the sungulite rock is a mixture of lizardite, sepiolite and vermiculite and is formed due to vermiculite, which in turn is a product of phlogopite alteration.For flowers


Drainage material
The chemically active composition of vermiculite allows it to be used as drainage and mulch. The low density of multilayer vermiculite makes it easy for a flower to take root after picking, to grow a plant from a leaf (violet). Mulching the soil in a pot will allow you to leave the flowers for a week without watering and go on vacation.
The characteristics of vermiculite allow it to be reused several times in a row. In home floriculture, vermiculite can also be used in combination with organic matter. Use fractions 4 and 2 mm. It will be enough to fill the pot by 20%
Required amount
For plants with a small crown that has just begun to form, it is recommended to introduce KVV-2 insulation. 30% of all the soil in the pot will be enough. A larger material should be used for drainage. For tree-like plants, the largest material with fractions of 8 mm is used.
How much vermiculite to add will depend on the type of plant:
- desert cactus, palm-shaped - 30%;
- forest cactus - 20%;
- lithopus - 50%;
- violets, arrowroot, fern, cyclamen - 40%;
- monstera, gasteria, dracaena, cordilin, aspidistr - 30%.
Storing flower bulbs and vegetables
Vermiculite is used in the production of vegetables on an industrial scale as a soil for storing planting material. Thanks to its moisture-wicking properties, it reduces the risk of rot. Vegetables for planting are stored in boxes, layer by layer sprinkled with dry matter.
The flower bulbs are placed in sealed bags with vermiculite. The material helps to maintain all the quality indicators of the harvested crop in winter, with the slightest loss of weight. the mineral provides an optimal level of moisture, which does not allow the fruit to dry. Vermiculite plate is used as a heater for covering industrial buildings, which are located in areas with high humidity.
Tips from experienced florists
The use of vermiculite in floriculture has many nuances. Whether it is possible to plant flowers in such a substrate and how to do it correctly depends on the characteristics of growing each group of plants. So, for violets and geraniums, it is best to take a substrate made up of mica of medium fractions and ordinary soil in a 50/50 ratio.
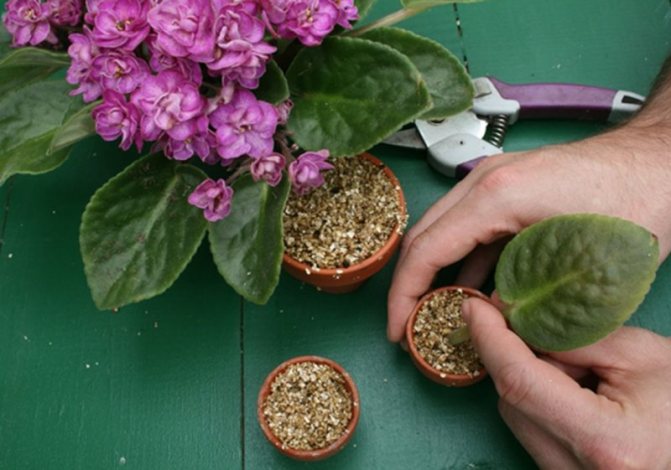


Rooting a violet leaf in vermiculite
Orchids need loose, air-permeable soil. In this case, vermiculite is ideal as a natural baking powder. An exception is made for Pafiopedilum or, as it is also called, "Lady's shoe". This is one of the few orchids popular in indoor floriculture that prefer an acidic environment. Soil-alkalizing additives for Paphylopedilum are only suitable in small quantities and in combination with dolomite.
Rooting a violet leaf in agrovermiculite is one of the most popular breeding methods for this domestic flower. The leaves are planted in a small container with damp mica of medium or fine fraction and covered with foil. After a few days, they put out roots. It is better to root violet leaves in the ground when the roots grow.
To store dahlias in an apartment, you can use ordinary plastic bags by making small holes for air in them. Packages are filled with tubers, covered with dry vermiculite and kept in a cool, always dry place. At high humidity, tubers can germinate.
For hoya, who loves loose, breathable soils, as well as constant moisture, this fertilizer can be used both as drainage and as an additive to the main substrate. The property of mica to absorb moisture will maintain the moisture level necessary for hoya.
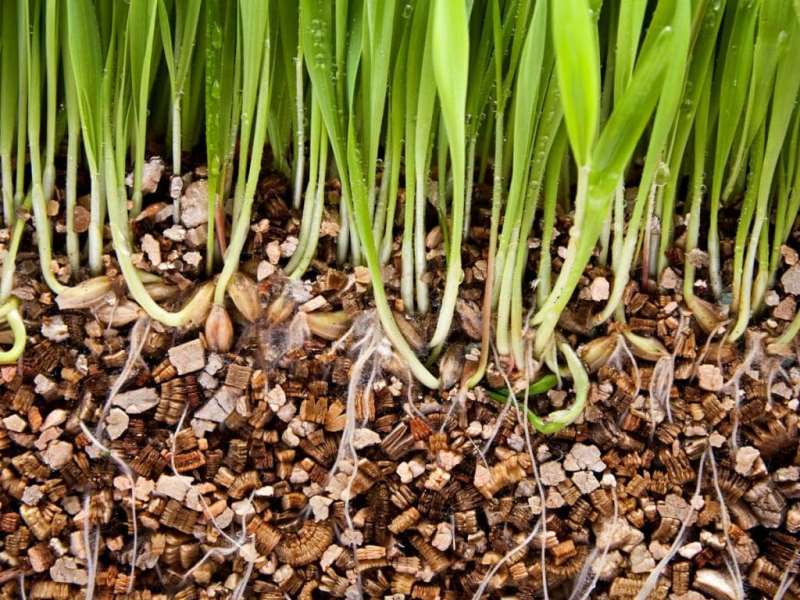


Vermiculite hydroponics
To germinate and root the cuttings of pelargonium in vermiculite, you need to soak it and then drain the excess water. It is not necessary to place cuttings in greenhouse conditions. After the roots appear, the cuttings, together with a small piece of vermiculite substrate, are transplanted into a pot.
For forcing tulips, vermiculite can be used as substrate instead of sand. The same soil is suitable for microgreening.
In such a substrate, it is very good to germinate citrus fruits, especially mandarin seeds (they have the fastest germination, about 3-5 days). It does not contain organic particles and retains moisture well. These properties of the mineral will not allow mold damage to germinated seeds.
When rooting roses in vermiculite, an almost 100% result is achieved. To do this, you need to make drainage holes in the container, fill in mica and moisten. Then stick the cuttings of roses into it about 2 cm. After two weeks, they can be transplanted.
Agrovermiculite is ideal for rooting grape cuttings, grape shanks and herbaceous shoots of this culture. Its use allows not to carry out such preparatory measures as furrowing and stimulation of root growth.


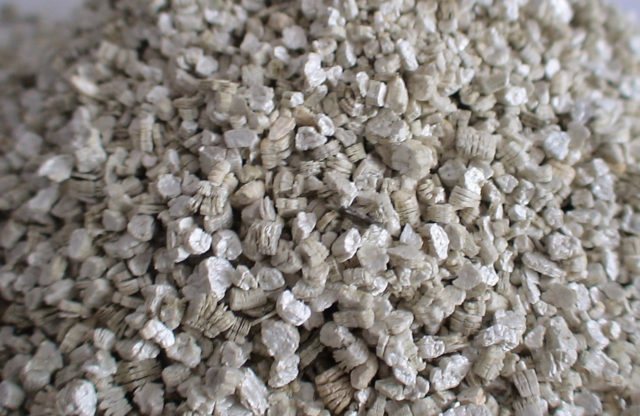
Ural vermiculite
The best vermiculite for agricultural machinery is Ural, light golden yellow in color. It gives a slight alkalization, easily compensated by the addition of peat infusion. The results of growing crops on dry hydroponics with Ural vermiculite are comparable to those achieved using expensive growth stimulants.
Vermiculite for greenhouses and plots
- For sowing by spreading, seed is mixed with soaked fine-grained vermiculite as 1: 2 or 1: 4.
- If the average evaporation rate during the summer is equal to the amount of moisture during the growing season, or exceeds it within 20%, then up to one tablespoon of moistened light vermiculite, with an average size of scales, can be poured into the planting holes.
- For planting fruit trees and berry bushes, plant roots are dipped in a solution of matured and fermented cow dung, and then vermiculite is added to this solution. The ratio will be as follows: for 3-4 liters of mullein, add any kind of wet vermiculite, even the cheapest and most uncommon, in an amount of 1 to 5 cm per bucket of fertilizer volume. The mixture prepared in this way is poured into a hole for planting at the rate of a quarter of a bucket for a bush or half a bucket for a tree sapling. Up to 20 cm of earth is added from above, a plant is planted, covered with earth, watered, tamped. With such a "safety cushion", the susceptibility of crops to fungal diseases sharply decreases.
- The addition of variegated, brown or ginger vermiculite to the mulch / mullein mixture will disinfect and loosen it. Vermiculite fractions can be from 0.5 to 3.0 cm. It is added to the trunk circle at the rate of 5-6 liters of filler per circle with a radius of 50 cm from the trunk.
- In heavy soils, the use of vermiculite gives excellent results if used as a soil loosening agent and sorbent for lawns.
It is highly undesirable to use vermiculite for strawberries or similar crops. They do not tolerate alkaline soils, which are necessarily formed in the presence of vermiculite!


What is vermiculite
The group of hydromicas contains a mineral of volcanic nature with the inclusion of small particles of water. After heat treatment, they turn into steam, which explodes the pores and the material breaks down into flaky particles. Its origin makes it possible to classify this mineral as environmentally friendly, natural minerals. The literal translation is consonant with the word "worm", which is justified by the appearance of the mineral after heat treatment.


Vermiculite is a mineral of volcanic nature
Vermiculite is a fertilizer with the ability to retain life-giving moisture and introduced minerals, with their gradual release to the roots of plant organisms.The amount of liquid it absorbs is four times its own mass. The porous structure retains air, which is required for the development of crops, improving the aerating properties of the planting soil
Expanded vermiculite after firing acquires a porous, free-flowing structure. When added to the soil, the hygroscopicity and aeration properties of the soil mixture are improved.
The use of this substance helps:
- reduce the amount of watering;
- prevent the formation of a crust covering on the surface of the earth clod;
- accumulate useful substances that are later received by the roots of plants.
Application in horticulture


Widely used in horticulture
Vermiculite is widely used in horticulture. The mineral is found in many agro-mixtures sold through stores in 50 kg bags, and is also sold separately, and is quite inexpensive. On the basis of vermiculite, you can make a mixture with your own hands, adding it in the required proportion. The fossil can perfectly replace expanded clay used as drainage.
Although the free-flowing mixture contains many useful substances, they are in a state difficult to access for the root system, so fertilizer will have to be applied. The main advantage of the mineral is the ability to accumulate active ions from dressings in the interfractional space. The shelf life of the mineral is practically unlimited, everything will depend on the safety of the fractions.
If you will be using a lot of vermiculite in your garden, wear a gauze bandage. The mineral is lightweight and quite fragile, therefore, during work with it, a large amount of dust is formed. If vermiculite is used for home flowers for the first time, it is better to rinse it first. When reused, the product must undergo a decontamination procedure by calcining. It is sent to the oven for 20 minutes, kept at 100 ℃.
Vermiculite. What is it and what is it for.
If you do not go into the intricacies of mineralogy, then vermiculite is actually the same mica and it belongs to the group of hydromicas. It would be naive to assume that such an intricate mineral is mined and subjected to special processing, specifically in order to meet the needs of flower growers. First of all, vermiculite is used as a sound and heat insulating material. But in this capacity it is of interest only to builders. Vermiculite, familiar to flower growers, is obtained by firing the source material at a high temperature. As a result, all moisture is removed from it, the structure becomes layered, while its volume increases almost 50 times. As a result, it takes on the form we are accustomed to, of light lamellar scales. By the way, translated from Latin, vermiculus is a worm.


These scales, not possessing the property of absorbing moisture from the air (hygroscopicity), perfectly absorb water. It was this ability of his that made vermiculite a valuable component of the earth for flowers.
Additionally enriched with various trace elements useful for flowers, it can even be considered, in some way, a fertilizer.
Possessing all these qualities, undoubtedly useful for floriculture, it is absolutely not subject to rotting, decomposition, exposure to aggressive environments and is considered an environmentally friendly material.
Description of vermiculite
Vermiculite is a mineral component that belongs to the hydromica group. It is formed in the earth's crust and therefore it can be safely attributed to an organic and environmentally friendly substance. Vermiculite, which has found itself in the field of crop production, after its extraction is pre-processed under the influence of high temperatures. Such processing allows it to dry and make it free-flowing with a scaly structure. This component is suitable for growing plants due to the large number of natural growth elements. These include:
- magnesium;
- calcium oxide;
- potassium;
- iron;
- silicon;
- aluminum.
The surface of vermiculite has a scaly structure, which allows it to retain a large amount of air necessary for plant life. The substrate helps to improve aeration performance in the soil. More precisely, the soil ceases to crumble and become covered with a hard crust that needs to be dug, which significantly increases the permeability of moisture. In the field of plant growing, foamed vermiculite can also be used, which has a positive effect on the root system.
The main properties of the substrate are the properties to absorb and release moisture when the root system needs it. Favorable conditions, constant supply of moisture and air contribute to the rapid growth of plants and their survival in a new place. The moisture absorption coefficient of vermiculite reaches almost 400 ml of water per 100 g of material. These properties make it possible to grow plants using hydroponics.
Fertilizer analogs
If the seedlings have not grown, it's time to start fertilizing. The most harmless will be vermiculite. But it is precisely it that is most often purchased in large quantities before planting. The search for an analogue, which is permissible to replace mineral feeding, may not be crowned with success. Reason: the lack of an exact analogous substance.
Do not despair. Just take the substitute more seriously. Each of the options has its positive aspects:
- Sawdust. Only rotten, but not rotten, are used. Otherwise, the soil will not receive the required dose of nitrogen. But the acidity will be more than necessary.
- Sand is suitable as a baking powder. Make sure there is no cement dust in it.
- To maintain moisture and for germination, sphagnum moss is suitable. Serves as a means for disinfection and for the preservation of moisture.
- You can use hydrogel or coconut fiber.
- From inorganic leavening agents, perlite is suitable. True, the soil will dry out faster.
Finding a product that can retain moisture and promote growth is difficult. But you can always consider mixtures and complex remedies.
How to improve soil quality
To make the soil on the site more moisture-absorbing and loose, vermiculite is applied along with organic fertilizers. This can be chicken manure, compost, or regular manure. Proportions - a bucket of vermiculite is required for 25 kg of organic fertilizer.
You can apply the mineral directly when sowing seeds. Pour the fraction along the entire length of the bed. About 10 tablespoons of the substance will be required per square meter of planting. When planting seedlings on a bed, it is recommended to add 3-4 tablespoons of vermiculite to each hole.
What is the effect of vermiculite on the soil? It cleans the soil by absorbing all gas exchange products, heavy metal salts. If the soil is heavily contaminated, the plants in it begin to ache first, then die.
Vermiculite makes clay soil more airy and looser. If this substance is not added, a dense, heavy crust forms on the surface of the soil after each rain. The soil does not allow air or moisture to pass through. Enough 2 liters of vermiculite per cubic meter of soil to improve its condition.
If the soil is too acidic, it is not suitable for many crops. The mineral neutralizes the acidity of the soil. It is advisable to use it together with perlite. Half a bucket of such a mixture, scattered over the surface of a square meter of land, will make the soil ideal in acidity for growing any plants.
Chemical composition
The chemical composition is not constant depending on the content of molecular water.
Magnesium oxide (MgO) 14-23%, iron oxide (FeO) 1-3%, iron oxide (Fe2Os) 5-17%, aluminum oxide (А12O3) 10-13%, silicon dioxide (SiO2) 37-42%, water (H2O) 8-18%. In addition, K2O is present - up to 5%, in some varieties of NiO - up to 11%.
Crystallographic characteristic
Syngonia Monoclinic.
Symmetry class... Vermiculite is probably of the prismatic type - 2 / t. in. from. Cc, a0 = 5.33 A, b0 = 9.18 A, c0 = 28.90 A, p = 97 °.Axis ratio. - 0.6: 1: ~ 3.2; {3 = 97 °.
Crystal structure layered.
How is it mined
The places where ore is mined for the production of a product suitable for use in agriculture include:
- Kazakhstan;
- Siberian field;
- Kola Peninsula;
- Far East mine;
- Ural quarries.
After mining, the ore is processed by high temperatures and packaged.
Expert opinion on Vermiculite
The addition of vermiculite to the planting soil helps to solve several problems at once. Scientifically proven the effectiveness of using vermiculite to improve aeration, reduce the need for plants in water. The substance eliminates the need for additional introduction of calcium and potassium preparations. With the help of vermiculite it is possible to solve the problem of the development of fungal diseases.
Properties
Basic properties of expanded vermiculite:
- high moisture absorption capacity;
- low hygroscopicity;
- does not decompose, has a low level of abrasion;
- prevents the development of decay processes;
- increased thermal insulation properties;
- chemical inertness;
- the ability to act as a loosening agent of the soil;
- breathability.


Vermiculite is used to impart looseness to the soil.
Material quality criteria
Usually, when vermiculite is packaged, the manufacturer indicates on the packaging the quality indicators of the substance, its compliance with the accepted quality standards.
Gost vermiculite contains the main criteria for product quality:
- moisture absorption percentage;
- maximum permissible temperature regime;
- thermal conductivity characteristics;
- resistance to low temperatures;
- swelling percentage;
- organic mineral content;
- toxicity indicator;
- volume, mass;
- warranty obligations.
Comments (1)
Coarse sand is added as a baking powder.
- Login or register to post comments
you can also take ready-made soils, where there is already perlite and vermiculite
- Login or register to post comments
I add styrofoam, because we also have neither perlite nor everything else.
- Login or register to post comments
You can try adding grated bark. Pine is recommended everywhere. I tried to add oak (I just bought it at the pharmacy). I'm not sure if it was good. So, according to the recommendations, pine is better.
- Login or register to post comments
I think crushed polystyrene is the best option in the absence of perlite and vermiculite. I can't say anything about the bark, since neither I have ever used it, nor the collectors I know. But the sand compacts the soil, eventually settling to the bottom of the pot during watering. I don't use sand anymore.
- Login or register to post comments
Coarse sand loosens the soil, while fine sand compacts it.
Imagine a sieve, if the sand is fine, it will clog the holes, and if the sand is coarse, it will remain in the sieve. So is the earth, it is porous, fine sand will clog the pores, and coarse sand will loosen.
Coarse sand can be found in pet stores or pet markets. Or if there are large mounds of sand, then the sandy streams from the top of the heap consist of large grains of sand.
- Login or register to post comments
Mineral safety
This mineral is considered safe to use. Formation of dust is possible, in cases with fine fractions. In order to prevent the dispersion of the dust cloud, it is recommended to work with the substance outside closed rooms, to protect the organs of vision and respiration, to use work clothes, and to slightly moisten the substance before use.


This mineral is considered safe to use.
Vermiculite for potted flowers
For pot plants, take a substrate up to 1 cm in size, pinkish, yellowish or pink varieties. You should not take very light ones - they will feel a lack of Fe + 2 and an excess of magnesium and potassium.You can make high vermiculite, up to 1/3 of the volume of the pot, drainage - this method of use is suitable for succulents (money tree, aloe, cacti), they are for soil salinity and their increased alkalinity. Fraction sizes for this should be in the range of 1.5-2.0 cm, that is, large.
But for azaleas, hydrangeas, gloxinia, this method is not suitable - even if all the water that has passed through the vermiculite layer passes through and seeps into the pan, then, due to the capillary effect, it will rise to the roots again and the plant will still use this lethal alkaline solution.
Another thing is the cultivation of these flowers in dry hydroponics, where the acidic reaction of nutrient solutions is used.
Why are there problems?
Some plant breeders consider vermiculite to be almost a poison for plants. Like, 2-3 months, and plants on a vermiculite substrate die, see eg. roller:
Video: an example of plant death due to the thoughtless use of vermiculite
Plots like these are controversial, and the evidence is quite convincing on both sides. What's the matter? If you look at the viewers' comments, it turns out: a) the supporters of the “pro” use vermiculite preim. for young plants (seedlings, seedlings) and cuttings, or outdoors; b) opponents of vermiculite most of all use it indiscriminately (see below) in the pot culture of certain types of plants. Hence, it is clear that the use of vermiculite must be made taking into account both the properties of the substance itself and the conditions of its use.
Chemical composition
In mineralogy, micas are classified as complex aluminosilicates of unstable composition. Technical characteristics of expanded vermiculite and perlite are given in table. in fig. below. The content of the components indicated in it is normalized by the technical specifications for the finished product, but besides them, vermiculite contains trace amounts of nickel, titanium, manganese, etc. compounds. The microelement of plant nutrition is only manganese; occasionally in vermiculite traces of molybdenum and boron also necessary for plants are found. The rest of the trace impurities - ballast, not always useful.
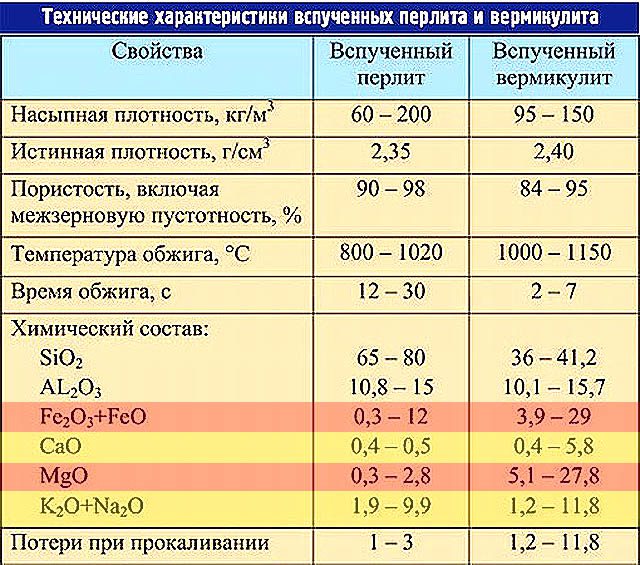

Chemical composition of expanded vermiculite and perlite
But it's not only and not so much about ballast. Let's pay attention to the lines highlighted in red. Iron is also a trace element necessary for plants, but only in the bivalent form of Fe (II); 3-valent iron Fe (III) is useless, and its excess is harmful. Fe (II) is present in vermiculite in the form of FeO; Fe (III) as Fe2O3 oxide. The proportions of both vary greatly even in samples from the same deposit, and therefore their ratio is not standardized.
Magnesium is a vital mesoelement (part of chlorophyll), but it can be in large excess in vermiculite. On the open ground, this is not scary: magnesium salts are easily leached out and in direct light, plants often do not have enough of it. But in a pot, magnesium will alkalize the soil, and with a lack of light, plants can deplete themselves by synthesizing excess chlorophyll.
Calcium is also a meso-element; potassium is the main nutrient. But their oxides, like sodium oxide, form alkalis in the presence of moisture. On the open ground, this is again not scary: vermiculite is a stable mineral, leaches very slowly, and alkalis are mobile. But in general, they have nowhere to go out of the pot, and 2-3 months. the period is just enough for plants that love acidic soil to wither in alkaline soil: uzambara violets of Saintpaulia, azalea, dieffenbachia.
Fractions of granules
Vermiculite is moisture-proof, insoluble in water, and its leaching occurs from the surface. The rate of release of alkalis from vermiculite into the substrate depends on the size of the granules according to a quadratic law: when the particle size decreases, say, by a factor of 10, the alkalization of the soil is accelerated by a factor of 100.


Fractions of vermiculite granules
Vermiculite for agricultural machinery is produced mainly in 2 fractions: granules about 1 cm in size (with a fingernail) and finely ground, see fig.Coarse-grained vermiculite is used in all cases, except for one - germination of seeds, cuttings and growing seedlings on a mixed neutral substrate, see below. If finely ground vermiculite is used in a potting culture of mature plants, the result is likely to be a failure due to alkalization of the soil.
Alkalis are not always bad
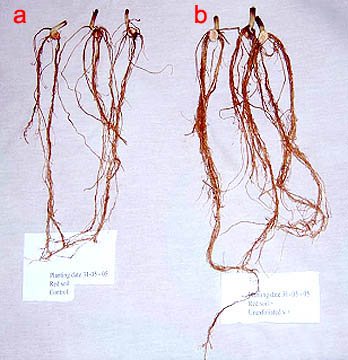

Results of rooting cuttings in a substrate with vermiculite (b) compared with control (a)
As we can see, there can be more potassium in vermiculite than in perlite. Potassium is known to promote root growth. Seeds, seedlings and young parts of adult plants (cuttings) that are on the brink of survival are much less sensitive to the composition and chemical reaction of the soil, but they need to take root as soon as possible. The main obstacles in this case are the lack of air for the forming roots and the spores of pathogenic fungi, but they need an acidic environment for their development. The use of nutritious but acidifying peat as a substrate for germination and rooting with finely crushed vermiculite alkalizing it (see below) gives impressive results: in Fig. on the right, the roots of the control group of cuttings a, treated with heteroauxin and rooted in the usual way, and group b rooted in a mixture of vermiculite with peat with and without a growth stimulator.
Note: when it is better to use vermiculite for seedlings, seedlings and cuttings, and when perlite, see the video:
Video: vermiculite and perlite, pros and cons
How to choose vermiculite for plants
The composition of vermiculite within the limits indicated above, and the content of ballast trace impurities in it vary greatly depending on the origin of the raw material. The deposit where the original mineral was mined, its quality and suitability for various agricultural purposes, in some cases, can be determined by the type of product on sale.
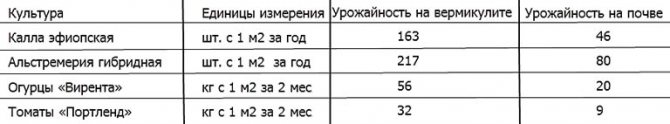

Results of growing flower and vegetable crops on vermiculite
The best vermiculite for agricultural technology is light, slightly yellow Ural (pos. 1 in the figure below). The Ural Mountains are ancient reviving. Together with the temperate continental climate, the conditions of erosion of vermiculite there are such that iron is contained in it predominantly. in the form of Fe (II), and magnesium is just enough for plants. Growing flower and vegetable crops on dry hydroponics with Ural vermiculite gives results comparable to those when using expensive and requiring regular use of growth stimulants, see table. on right. Alkalization of the Ural vermiculite gives insignificant and easily compensated by the addition of peat infusion to the nutrient solution.


Types of vermiculite for agricultural machinery
Kazakh vermiculite from deposits in young mountains of the alpine uplift is very similar to the Ural, but slightly paler, pos. 2, because Fe (II) is less in it. But there is also less Fe (III), so this variety is well suited for dwarf and potted plants. It practically did not go through natural leaching, and therefore, in dry hydroponics and pot culture, it is suitable for plants that love or tolerate slightly alkaline soil. Application outdoors and for seeds, seedlings, seedlings - no restrictions.
Pinkish vermiculite from Altai and old mountains of Europe (pos. 3) contains a lot of Fe (II), potassium and magnesium. It is the best substrate for seed germination and rooting of cuttings. On vermiculite of a similar composition, seedlings of nightshades grow best: tomatoes, vegetable (sweet) peppers.
Variegated vermiculite from the Kola Peninsula and Scandinavia (pos. 4) is similar in composition to the Ural and Kazakh vermiculite, but contains a lot of potassium, sodium, calcium, magnesium and trace impurities. Good finely crushed for germination and rooting in a mixture with peat. Brown of subtropical origin (pos. 5) and red ("red", pos. 6) tropical vermiculite is a less expensive alternative in substrates for the same purpose.They are not very suitable for open ground due to low moisture absorption, and for a pot culture they are not very suitable because of the high content of Fe (III) and components that give alkalis.
Expanded vermiculite
From this material you will learn:
What is vermiculite?
The benefits of vermiculite
Use of vermiculite: growing vegetables, germinating seeds, cuttings, growing seedlings, storing wax and fruits, floriculture on vermiculite


Vermiculite Is an environmentally friendly mineral from the hydromica group, which is formed in the earth's crust. After processing at a temperature of 800 C, it turns into a free-flowing flaky material. Its name is translated from Latin as "worm". If the vermiculite is heated, the plates begin to turn into columns, similar to worms (hence its name).
Due to the content of oxides of such microelements as calcium, magnesium, potassium, aluminum, iron, silicon - vermiculite is an effective biostimulator of plant growth!
Vermiculite is a highly porous mineral with air between the flakes. Its structure makes it possible to achieve the necessary aeration properties from the substrate, in which the earth does not cake, does not form a crust on its surface, it remains loose.
Expanded vermiculite has a positive effect on the development of the root system.
Vermiculite easily absorbs moisture and also easily gives it to the plant, creating an optimally moist environment for root nutrition.
The water absorption coefficient of vermiculite is 400% (100 grams of vermiculite absorbs 400 ml of water).
Vermiculite is widely used today in hydroponic growing plants. It gained such popularity due to its exceptional properties. Read more about the benefits of using it in the article vermiculite for hydroponics. You can purchase vermiculite in our online store at the link
The advantages of vermiculite (research by specialists from the Timiryazev Agricultural Academy)
- improve the structure of light (sandy) and heavy (clay and loam) open ground;
- optimally regulate the air-humidity regime;
- actively stimulate the growth of the root system and the plant as a whole;
- reduce acidity and salinization of non-replaceable soils by 8-14%;
- increase the efficiency of fertilizers;
- reduce root rot disease;
- increase the safety of vegetables and fruits by 10-16%;
- increase the yield by 12-17%.
Expanded vermiculite has a positive effect on the development of the root system
Root development without vermiculite and with the addition of vermiculite:
Application of vermiculite:
Growing vegetables on vermiculite
The introduction of expanded vermiculite together with potatoes during planting (0.5 cups -1 handful of expanded vermiculite of 2-4 mm fraction or 1-2 mm fraction) per well allows you to achieve the optimal size of tubers in the dry season. The most effective use of vermiculite in combination with a complex of mineral fertilizers (nitrogen-phosphorus and potassium, in a ratio of 1: 1: 1).
Germinating seeds on vermiculite
At the initial stage, the seeds of the germinated culture are mixed with moist expanded vermiculite of 1 mm fraction, packed in plastic bags, placed in a warm place until they germinate. Germinated seeds are sown in a container with a soil mixture, which consists of 1 volumetric part of vermiculite with a fraction of 2 mm and 2 parts of soil. A properly prepared soil mixture will help seedlings grow faster, protect them from root and stem rot (black leg). Before sowing seeds in open ground, vermiculite of a fraction of 2 mm or 1 mm and vermiculite of a fraction of 4 mm (50:50) are introduced into the bed along the entire length, at the rate of 1 tablespoon per 10 cm.
Many greenhouses work with Dutch technology. In their technology, they use expanded vermiculite with a fraction of 1 mm or 2 mm as a powder, after the seeds have been introduced into the soil.
Plant transplant at a young age (dive)
A soil mixture is used, which includes 1 volumetric part of vermiculite with a fraction of 1-2 mm and 2-3 parts of soil, everything is thoroughly mixed and distributed in cups.
When planting seedlings in open ground, for better rooting, add 2-3 tablespoons of vermiculite of expanded fraction 1–2 mm, preferably fraction 2–4 mm, to each hole. This application of vermiculite will help maintain constant moisture near the root system and facilitate plant care.
Composting
The introduction of vermiculite for composting is effective. For this, litter manure, bird droppings, peat, chopped straw and stems of various crops are used, with the exception of potato tops, tomatoes and cucumbers. For each centner of organic mixture add 3-4 buckets of expanded vermiculite fraction 2 - 4 mm.
Cuttings using vermiculite
When grafting various crops, a substrate of expanded vermiculite fraction of 1-2 mm and peat in a volume ratio of 1: 1 is used. The reaction of the peat medium is weakly acidic (pH-5.6), and in vermiculite it is neutral or slightly alkaline (pH-6.8-7), which, in accordance with the results of rooting, is favorable for cuttings of most crops. The root system of the cuttings is more developed under such conditions. The most effective becomes a substrate impregnated with the so-called "Californian" mixture, or any other mineral fertilizers. The influence of such a mixture, first of all, affects the number of first-order roots, their length and volume, as well as the timing of bud awakening. It is characteristic that the positive effect of mineral mixtures in the substrate continues to affect the place of planting and rooting even in the second year.
Growing seedlings on vermiculite.
For better rooting of seedlings of fruit, berry and ornamental crops, it is recommended to use vermiculite up to 30% of the hole volume of a fraction of 2-4 mm or fractions of 2-4 and 4-8 mm in a ratio of 1: 1. Due to their structure, porous vermiculite granules instantly absorb moisture and fertilizers, give them away gradually, creating favorable conditions for nourishing the root system.
Soil mulching
Expanded vermiculite fractions of 4-8 mm, 2-4 mm (1: 1) are used for mulching the trunks of fruit trees, while the consumption is 6-8 liters per 1 sq.m .; for berry bushes - 3-5 liters per 1 sq. m .; for flower bushes - 2-3 liters per 1 sq.m. For mulching, you need to dig up the soil around the root system of a tree or bush, sprinkle with vermiculite and embed it in the ground.
• When growing ornamental lawns and lawns, before sowing, 4-5 liters are applied per 1 sq. M. vermiculite brand KVV-2. This additive will help germinate the seeds much faster and facilitate your work on caring for the cover.
Storing vegetables and fruits in vermiculite
Expanded vermiculite is slightly hygroscopic, at a humidity of 40-60% its humidity is 6-8%, at 100% - no more than 10-11%. In addition, it has a high adsorption capacity in relation to various products of fruit gas exchange. These features make it possible to use expanded vermiculite for storing vegetables, fruits and flower bulbs. At the same time, the level of waste arising in the case of the development of rot decreases, the growth processes in the tubers slow down, the taste and nutritional value of vegetables and fruits are preserved. By pouring the fruits during container and bulk storage, you can save the harvest, providing yourself with tasty, healthy and wholesome products for a long time. Vegetables or fruits are laid in boxes in layers, shifting each row of fruits with a layer of expanded vermiculite, the thickness of which, depending on the size of the fruit, ranges from 2 to 5 cm.In the second year, the used vermiculite can be used after frying or simply put it into the ground in spring (without frying ).
Vermiculite for indoor plants
Anyone who tried to grow ornamental crops at home, outdoors or in greenhouses, faced the problem of caking and hardening of the soil. It entails limiting the access of air and moisture to the root system of plants. The plant develops slowly, often becomes decrepit and dies. Also, flower growers and gardeners are faced with the problem of decay of plant roots from overflow or leaching of nutrients from the soil when using various fertilizers and additives. To avoid these troubles and achieve greater efficiency of non-replaceable earthen mixtures, it is recommended to add a small amount of vermiculite - a mineral that, according to many years of observations, quite effectively creates a favorable microclimate for the development of the root system and the plant as a whole. Vermiculite of fine fine (up to 1 mm) fractions is used in pure form or as part of light mixtures (for example, with peat or sand in a 1: 1 ratio.
You can buy vermiculite in our online store following the link