Any garden plot will look beautiful and romantic with climbing roses on gazebos, fences and in a rose garden on supports. Thanks to vertical landscaping, you can admire the bright pyramids, flower columns, rose trellises. Any old building and structure near a house or summer cottage can be decorated with a luxurious climbing rose, if properly planted, cut, protected from drought and pests.
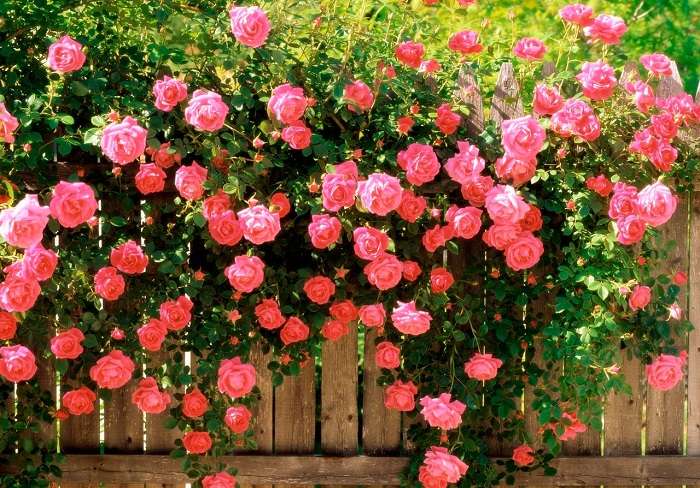

The buds can reach 2.5-12 cm in diameter, you can admire their flowering from June to the end of the warm season - 30-170 days. Shoot growth is continuous, but formation, bud development and flowering occur in different phases, depending on the type or variety of the plant. There are varieties that bloom once, others can bloom again. How a climbing rose develops, methods of planting and care in the open field - everything will be covered in this article.
Growing miniature roses.
If you grow miniature roses indoors, then you can easily cope with this task by reading the helpful tips below.
Mini rose plants can be found in stores. Although these beauties are small in size, their true home is a street flower bed, where they will thrive in the light and fresh air. Almost every garden has space for growing miniature roses, but if you don't have room for roses in your garden, you can store your potted plants in your sunny porch or patio patio.
Their miniature flowers (2.5-5 cm) are available in a wide range of colors, including red, pink, peach, orange, white, yellow and many other shades and combinations. Some varieties of roses grow in bushes, and some are curly, miniature roses on a small trellis.
Caring for miniature roses.
Give them sunshine. These mini and micro hybrids won't bloom if they don't get enough light. When growing miniature roses indoors, you need to find a place where they get several hours of direct sun every day. If you do not have space on a sunny window, you can move your flower outdoors for a while, as long as there is no danger of frost.
Water regularly. Blooming roses are thirsty and dry quickly in pots. Touch the soil with your finger to test for dryness every day or two, especially if you are growing miniature roses outdoors.
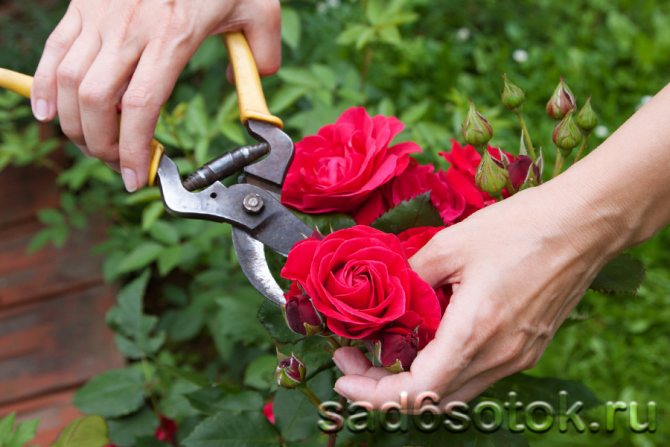
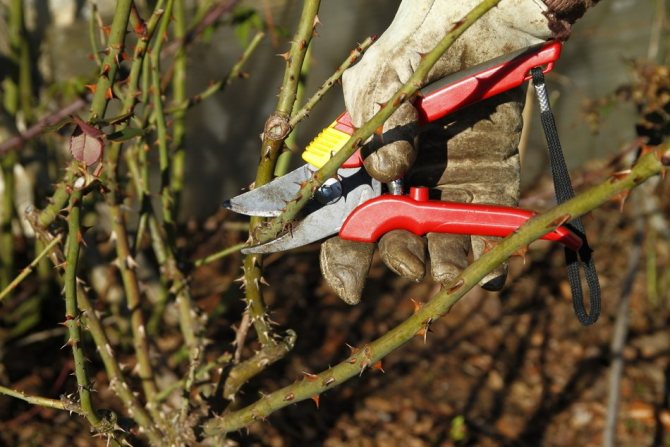
Remove old flowers. Remove the flowers as soon as they start to wilt to better preserve the plants and prolong their flowering. Do not pinch them with your hands, as this may damage the barrel. Use a sharp pruning shear to avoid damaging the twigs that can cause disease. Cut at a 45 degree angle.
Pruning miniature roses. New plants do not need pruning. As they get older, you need to remove dead branches or any cross branches that intersect with each other. Do not be afraid to cut the bush, it will reward you for taking care of the flowering. Pruning each year will promote vigorous new growth as well as an overall improvement in rose health. In addition, pruning will also give the miniature rose bush an attractive shape.Use clean, sharp pruning shears and cut at a 45-degree angle, five millimeters above the leaf axil.
Transplant a rose from the store. Roses in gift pots or store containers are not designed for long-term cultivation, so they need to be transplanted into a different, larger pot. Supporting the main trunk with your fingers, remove the rose bush, remove as much old soil as possible, and plant it separately in small pots with drainage holes. Repot after the rose is finished blooming.
Protect roses from frost. Roses should rest in winter and shed their leaves. By giving the rose a rest period in winter, you will prolong the life and health of the plants. Keep them cold during this time. They are cold-hardy, but if you are growing miniature roses outdoors, protect them from freezing temperatures by covering them with a layer of mulch. Place container-grown roses in your basement or garage for the winter so that the main branches don't freeze.
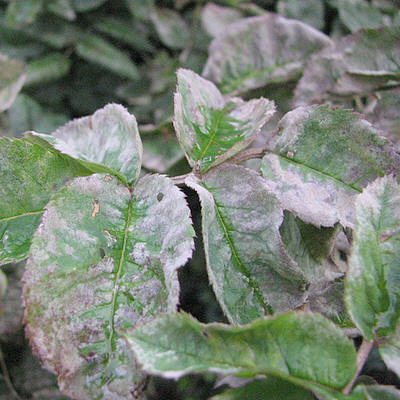
Miniature roses are susceptible to the same diseases that plague any other rose. Wet conditions can cause black spot on the leaves. Black spot is a fungus that must be treated immediately. Cut off diseased leaves and spray the foliage with a fungicide specifically formulated for spotting. Good air ventilation will help prevent disease. Fortunately, newer varieties and hybrids are more disease resistant. Yellow leaves on roses can be signs of several diseases or a signal for improper maintenance. Lack of sunlight, dry soil, dry air will cause roses to lose their leaves. Taking good care of your miniature roses again will help them recover.
Quick tips for growing miniature roses:
Light: Bright light, with as much direct sunlight as possible while the plant is growing.
Water: Keep the soil barely moist during the winter.
Humidity: Use a water tray or room humidifier.
Temperature: Average room temperatures of 16-24 degrees suit almost all growing miniature roses. Roses are cold-hardy, but need additional protection from frost.
Soil: Any good mixture that is neutral (pH 7).
Fertilizer: Every 2 weeks in spring and summer, fertilize rose bushes with a fertilizer with a high phosphorus content (6-12-6), which also contains micronutrients.
Reproduction: Take a rose stalk (10 cm) in early summer. Dip the end of the cutting into a rooting agent and plant the cutting in a moist soil mixture. Maintain high humidity.
Care and cultivation
When planting in spring, after 20 days, you need to carefully rake off the ground from the bush, and in autumn planting - in the first weeks of April, while choosing a cloudy day so that the plant does not experience stress when the temperature drops at night. The grafting sites should remain in the soil at a depth of 10 cm.
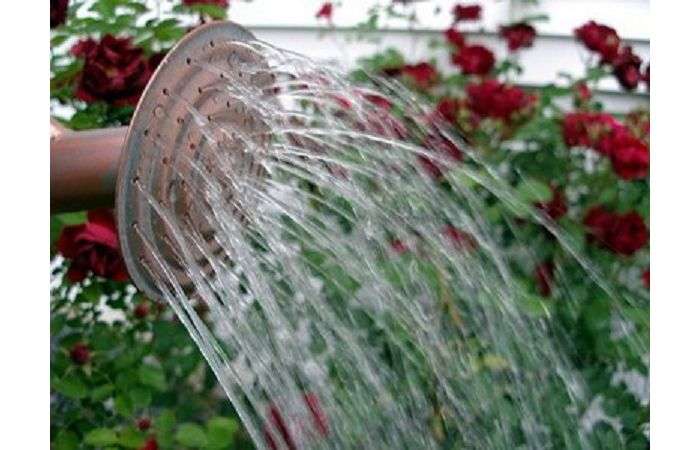


During the growing season, especially in hot and dry weather, it is required to water the plant generously every 5 days. When a bush forms and buds appear, water it after 10 days. 10-12 liters of water are poured under each bush so that it penetrates deeper than the root system. To keep water in the hole, a low soil shaft is erected around the trunk circle. After 2 days, the ground around the rose is loosened and mulched. It must be remembered that waterlogging, like a lack of water, is equally harmful to a rose.
After planting, the "skeleton" of the bush will form during the year. When many lashes are formed at the base of the bush, only the first 5-7 are left. For their normal maturation, the remaining lashes are removed. In the second year, when flowering begins, in June-July, the faded ends of the shoots are cut off. All growing shoots are pinched after August 20 to September 10.The stems need to be shortened in September to mature wood. By winter, up to 2-3 of the strongest lashes are left with lateral shoots, on which there should be 2-3 living buds and young shoots. In the spring, old shoots are cut out if the young are not frozen in winter and their growing season has begun.
Caring for a pet after flowering depends on its multiplicity. With a single flowering, wilting flowers are cut in the first half of summer. If flowers appear again in the second half of summer, then the buds are not cut off, since buds will grow and young shoots will germinate. By the end of August - the beginning of September, there is no need for growth, since it will not get stronger until frost, and may die along with the lignified shoot on which it grew. If fruits appear, then a large amount of nutrients is needed for the formation of seeds. If the fruits are not needed, seed propagation will not be carried out, then they are removed after flowering in order to direct sap flow (nutrition) to the stems and root system.
To prepare the plant for suspended animation (hibernation) and allow the roots to grow stronger before the cold period, the growth of green mass is suspended: the petals are removed. After the second flowering, seed pods will overwinter on the plant, if necessary: 2-3 per bush.
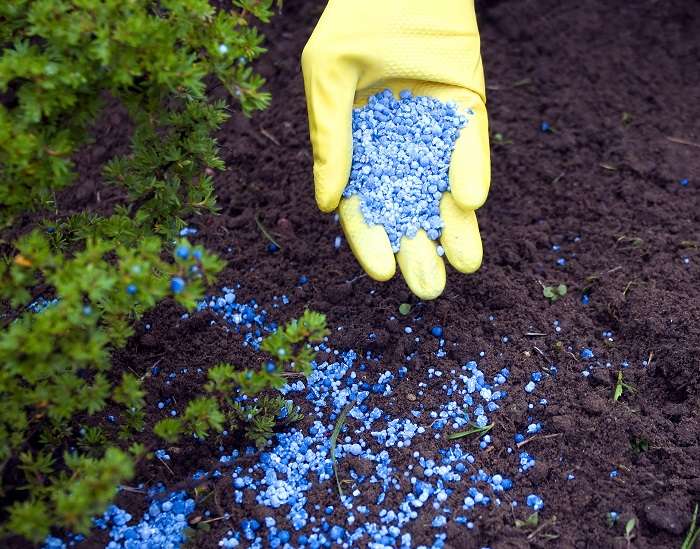


The bushes are fertilized in the summer with nitrogen supplements, alternating with complex fertilizers, which are applied every 15-20 days. In spring, complex mineral fertilizers are used, such as Agricola-Rosa, 15-20 days later, organic fertilizers:Flower "or" Ideal ". You can prepare the mixture for the additive yourself at the very root of the plant:
- water - 50 l;
- mullein - 10 kg;
- wood ash - 3 kg.
After June 15, potash and phosphorus supplements are added in small portions according to the instructions to prepare the plant for wintering.
It's important to know. During the flowering period, fertilizer is not applied to the soil, and with intensive growth, the plant is fed 5 times.
Weed control
Weeds aggravate the development of shoots and take food and moisture in the near-trunk circles. It is especially necessary to deal with vegetation that has a deep root system:
- creeping depressions;
- creeping wheatgrass;
- sow thistle;
- amaranth (shiritsa);
- field bindweed.
To prevent the growth of unwanted plants around the root system, many gardeners install black nonwoven spunbond, which is breathable and breathable. But black helps to increase evaporation by attracting the sun's rays. Therefore, mulch is laid on top of this material:
- dry cut grass;
- bark, wood chips or straw;
- crushed dry humus.
Mulch is a slow-acting fertilizer when exposed to water. When mulching with grass, it is necessary to exclude the ingress of pests and diseased vegetation residues so that the infection does not spread to the roses.


If chips or coniferous bark are used, the pH must be controlled as these materials acidify the soil. To remove acidity, mulch is mixed with fluff (slaked lime), chalk, dolomite flour, ash, ground egg shells. In this case, the rose also receives calcium-containing substances. With ash, it receives trace elements, including phosphorus and potassium.
Supports for roses
Before fixing the climbing rose, you need to prepare the support. It can be from old dried up wood, arched metal rods. A wooden, metal or polymer arch is great. If you need to decorate the corner of the building, then a lattice or guides are fixed in the wall, which will catch the shoots of the rose.
It's important to know. The plant is planted at a distance of at least 50 cm from the building wall on the south side. When the stems are arranged horizontally on a support, flowers will grow along their entire length. With the vertical growth of the stems, the flowers will bloom only at their tops. Any support is placed at a distance of 30-50 cm from the bush.


Since you need to tie up a climbing rose securely, plastic twine is more often used. Wire cannot be fixed, even after wrapping heavy stems with cloth or paper, as such fastening material may damage them. To exclude a break in the twine or electrical tape and damage to the branches of the rose, you need to periodically inspect the integrity of the fastening material.
Preparing for winter
The bushes in the fall are spud with a mixture of earth and sand (1: 1) to a height of 30 cm, then they are completely covered until the first frost in the second half of September as follows:
- the branches and the trunk are untied from the supports for independent adoption of an inclined position to the ground;
- after 8-14 days, the branches are gradually bent, each time increasing the slope for 10-12 days, so as not to break the stem;
- if the stem of an adult plant resists, then carefully dig in the stem and pull it to the ground, as far as the crown allows;
- foliage is cut off after the second half of October and the crown is tied with a rope;
- the bush is treated with 3% iron sulfate and allowed to dry;
- so that the snow does not flatten the crown in winter, you need to put foam or a plastic bottle under the bush;
- the grafting site is covered with peat, combining with hilling;
- the crown is covered with dried oak or birch leaves;
- rodent poison is laid out under the crown, deterrent substances, for example, sawdust soaked in cat urine;
- cover the plant with one layer of spunbond, which is fixed around the trunk with a wire or rope, from the side of the crown it is pressed with hairpins or stones;
- for air access in the spunbond, 2-3 holes are left at the base of the trunk;
- in November, they cover the crown and trunk with another layer of spunbond, covering all the vents.


Miniature roses: home and garden care
This is a group of the smallest, undersized roses that were brought to Europe from China in 1810. Miniature roses are characterized by low growth, long, abundant flowering and have more than 2000 varieties and hybrids in their genus. On their own roots, plants reach 15-25 cm in height, and individuals grafted on a rosehip grow up to 30-50 cm, the bush turns out to be well leafy and compact.
- Family: rosaceae (Rosaceae).
- Genus: miniature (Rose chinensis minima).
- Homeland: China.
- Shoots: lignified, straight-growing, up to 80 flowers are formed on each.
- Bloom: in most varieties it is long lasting (from June to frost).
- Content temperature: from +28 to -10 ° С, requires shelter for the winter.
- Illumination: bright light.
- Watering: spring-autumn plentiful, regular, does not require watering in winter.
Leaves are compound, consisting of 5-7 small, leathery, shiny leaves, ovoid, finely serrate along the edge. Most varieties are dark green, some varieties are bronze brown or light green with dark veins.


Miniature roses in the photo
Flowers with a large number of petals, small from 2 to 5 cm in diameter, retaining their color throughout the entire flowering period. At the same time, on one bush there are crimson-crimson, lemon-yellow, coral-pink flowers, which makes the plant exceptionally elegant. Cut flowers, standing in water, do not lose their decorative effect and exude aroma for 7-10 days.
Planting a rose according to the lunar calendar
For flower growers who are used to navigating any plantings according to the lunar calendar, we give the dates of favorable days in the current 2019. March: 12-17, 19, 20, 27-30; in April: 6-8, 11-13, 15-17, 24-26 ,, 29, 30; in May: 6-8, 10-17, 21-23, 26-28, 31; in June: 1, 2, 5, 6, 9-13, 16-20, 27-30.


Unfavorable days for planting roses in the spring-summer period according to the lunar version for 2019 are as follows: in March: 6, 7, 21; in April: 5, 19; in June: 3, 4, 17. Information from the magazine "1000 tips for summer residents."
Miniature roses in the garden
A worthy place is occupied by miniature roses in the garden due to their longer and more intense flowering than their tall counterparts.They are ideal for planting along paths, in groups on lawns, in compositions with perennials and ornamental shrubs, or separately in flowerpots.
In addition to species of roses with a compact bush, there are ground cover, climbing and trellis forms, which significantly expand the range of using miniature plants in landscaping. Such forms are ideal for creating borders, look great on flower beds and ridges, are used to create living arches and decorate walls, used for landscaping slopes, hills and places with rocky soil unsuitable for growing other types of plants.
Miniature roses grow well in the open field, and over time they adapt to indoor maintenance. In regions with air temperatures below -5 ° C in winter, they require mandatory shelter.


Content
- Listen to the article
- Description
- Growing features
- Planting roses When to plant
- How to plant
- Planting in autumn
- Planting in spring
- How to grow
- When to trim
- How to propagate
- Roses have faded - what to do
Miniature roses at home in a pot
There are types of roses for growing at home, they are divided into 2 groups:
- decorative flowering potted plants;
- decorative flowering indoor plants.
Potted flowers are used for temporary arrangements and wither after flowering.
Indoor miniature roses growing at home in a pot are evergreen rooted species that bloom profusely throughout the year. It is best to keep flowers grown from cuttings.


Shelter roses for the winter
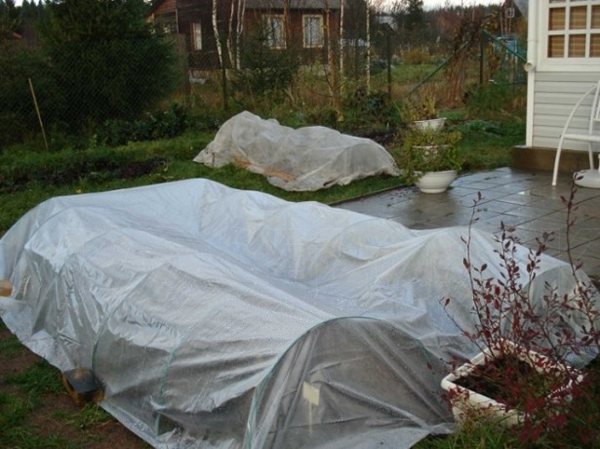


In mid-October, the preparation of roses for winter begins. Climbing rose bushes are gradually bent to the ground, and are treated with Bordeaux liquid or other fungicides.
Depending on the variety, the shelter of the bushes for the winter can be air-dry, using dry shearing, sawdust and obligatory hilling.
The bushes are covered with dry earth to a height of 30 centimeters.
Pruned Floribunda and hybrid tea roses are almost completely covered with soil.
In shrub roses, after bending to the ground, the base of the bush is spud. You can sprinkle with soil and shoots.
Hilling keeps a large number of buds in the plant, allowing any pruning method to be used in spring.
One of the simple materials used to cover roses is a layer of spruce branches or dry oak leaves 10 centimeters thick. A shelter above the plant forms a protective frame, which is insulated with a snow crust when snow falls.
A more reliable way of sheltering roses is to air dry. At the same time, wooden frames are installed above the bushes, boards with a height of 50-60 centimeters, any insulation material (cardboard, wrapping paper and others) is placed on top and on the sides. From above, everything is covered with a film. The ends of the shelter are closed when the temperature drops to -10 degrees.
The shelter is removed in spring, it is removed gradually so that the plants adapt more easily and do not freeze from possible frost.
Growing miniature roses
Plants in culture are very simple and unpretentious, but for good growth, long and abundant flowering, miniature roses prefer growing in a protected from northern winds and well-lit sunny area (especially in the morning). The morning sun's rays help the plant evaporate quickly, preventing powdery mildew and rust. The culture takes root well and grows on almost all types of soils, but prefers loams with weak acidity and good water-holding capacity.Dry sandy soil can be made favorable by laying in each hole during planting 1.5-2 buckets of a mixture of clay and humus in equal proportions. On wet and clayey areas, 2-2.5 buckets of humus and river sand 1: 1 are introduced into the pit.
To grow potted plants, it is necessary to use a nutrient substrate consisting of humus, river sand, peat and leafy soil in a ratio of 2: 0.5: 2: 1. A layer of polystyrene should be laid on the bottom of the pot as drainage, and on top of a 5-10 mm layer of sphagnum moss or charcoal. The transplant is carried out as needed by transferring the individual to another pot, without violating the integrity of the earthen coma of the root system.
The best breeding method is green cuttings. Indoors, a suitable time for breeding is from March to September, in the open field from May to August. For this, cuttings are used only from healthy individuals, cutting from the middle part of annual shoots in the bud staining phase. Each stalk should be 10-12 cm long and have at least 3 buds. Rooting occurs in river sand when the cutting is deepened by 3-5 cm. To speed up the process and prevent moisture evaporation, the cutting is covered with a glass jar on top. After 1.5-2 weeks, rooting will occur and the individual can be planted in a permanent place.
Preparing the soil for roses
For rose bushes, it is preferable to be in an area with sufficiently fertile soil with good moisture and air permeability. Preparatory measures are recommended not before planting, but at least 2-3 weeks before it.
Digging the soil should be done to a depth of 40 centimeters, if the acidity level is high, then lime or dolomite flour is used to normalize the environment. If the soil is heavy at the site of planting seedlings, then it is effective to add peat, compost and sand for digging.


Miniature roses: care
During the summer, miniature roses require care with regular abundant watering and dressing. Caring for roses in the garden includes at least 3-4 feeding. In the first half of the growing season, it is necessary to apply nitrogen fertilizers, in the second - phosphorus-potassium fertilizers. After removing the shelter and pruning in early spring, you need to fertilize with urea or ammonium nitrate and repeat the procedure as the shoots with leaves grow. After the buds appear, they are fed with a full mineral fertilizer.
Potassium nitrate and superphosphate should be added in August. The soil around the bushes must be constantly kept loose, preventing the formation of a crust that prevents air and moisture from reaching the root system.
Avoid the appearance of weeds under the bush. Morning spraying works well on garden plants, which cleans them of dust and prevents the appearance of pests. But when watering, waterlogging should not be allowed, and in cloudy weather, spraying harms the garden culture.
Miniature indoor roses require maintenance in a well-lit place all year round for at least 8-10 hours a day. To maintain the required humidity level, you need to spray the leaves from the underside 1-2 times a day. The leaves should be washed twice a month to prevent parasitic infestation. In the warm season, you need to provide the plant with access to fresh air.
Water the plant abundantly once every 4-6 days with non-chlorinated settled water. In winter, from October to April, the water temperature should be within + 16-18 ° С, in summer, from May to September + 20-24 ° С.
You can start feeding the indoor culture 1.5-2 months after rooting or transplanting with mineral fertilizers containing potassium, phosphorus and nitrogen. As a fertilizer, you can use wood ash - potassium in its composition contains almost no chlorine harmful to roses.
Even good care will not be able to protect plants from diseases and pests. It is necessary to constantly monitor the plantings and take action at the first sign.Most often, the culture is affected by spider mites and aphids, which suck the juices from the tissues of leaves and buds, which leads to their drying out and falling off. With a weak lesion, treatment with colloidal sulfur powder will help. With a strong one - spraying the bushes with a solution consisting of 200 g of laundry soap and 20 g. copper sulfate dissolved in 10 liters of water.
Rust infects stems and leaves. If rusty-brown spots are found, the bush must be treated with a Bordeaux mixture, and the affected parts must be removed and burned.
Possible landing errors
Given the exactingness of roses to the planting site, the composition of the soil and care, it is extremely problematic for novice florists to grow them in their garden. Due to the lack of experience during planting, numerous mistakes are made that do not allow getting beautifully flowering shrubs.


To do everything right, you must adhere to the following recommendations:
- Do not plant rose seedlings in peat. It is believed that such a planting allows plants to actively grow and develop, but, as practice shows, this is a delusion. In most cases, the bushes rot, begin to hurt and soon wither away. It is best to plant roses for effective rooting in loamy soil with sufficient mineral content.
- For plants, bending the roots up is not a useful technique, but, on the contrary, is quite traumatic and painful. The roots in the hole should be straightened on different sides without fail, only in this way the seedling will be able to take root faster and adapt to the new environment.
- Another misconception is that it is necessary to deeply deepen the vaccination site. The best option is a depth of 5 centimeters. When planted too deeply, garden plantings take on a painful appearance, begin to fade and lose their turgor.
Roses on a personal plot are a real decoration for any flower arrangement. Climbing varieties, which are used to decorate arched and other structures, look especially impressive.
Planting seedlings in the fall is an occupation that requires both certain knowledge and patience, but with the right approach, the result will exceed all expectations. The main thing is to purchase high-quality planting material and follow the recommendations of experienced gardeners.
Pruning miniature roses
Formative and sanitary pruning is a mandatory procedure that miniature roses are subjected to 3 times a year. Pruning is in summer, spring and autumn.
Summer pruning - minimal, with it wilted flowers are removed, and the shape of the bush is maintained by cutting off long young shoots. It is necessary to regularly remove drying and yellowed leaves, preventing the appearance of diseases and pests. Withered flowers are removed along with 3-5 cm of the stem - then new buds will form faster from the buds that are at rest, and the break in flowering will be minimal. In climbing types of roses, dried and excess branches are pruned.
Spring pruning - held no later than mid-March. Weak branches are cut, shoots are shortened to 10-15 cm in height. Each shoot should have 3-5 buds.
In individuals older than one year, small, weak and intertwining branches are cut off. On the bush, 4-5 strong shoots remain, each with 3-5 eyes. Dangling along the edges and thin branches with close leaves are removed, cut off, the shoots are blind and growing inside the bush.


After pruning, young shoots will be stronger, more flavorful and more abundant flowering.
Autumn pruning - held in late autumn or early winter. Roses are cut shortly, leaving 3-4 dormant buds on each shoot. Weak and dry shoots are removed to the base.
Climbing rose propagation
If the rose bush is already old, then you need to propagate it by cuttings, layering and grafting. You can sow seeds, but it is better to purchase them in a specialized store, since it is difficult to rejuvenate a climbing rose with your own seeds due to non-preservation of the varietal characteristics of the mother plant. It may not grow at all what gardeners hope for.
Propagation by cuttings
For grafting, stems that have already faded are more often used than flowering ones. Cutting time - late June - early August. An oblique lower cut is made under the kidney, i.e. at an angle of 45 °. Above the kidney, an upper straight cut is made, 2-3 internodes are left between the slices. The lower leaves are cut off, and the upper ones are shortened by half. A nutrient mixture is made by mixing the earth with sand, placed in a pot or box, and the cutting is planted, deepening it into the ground by 1 cm. From above it is covered with a jar or bottle made of plastic, cut in half. They put the plant in a lighted place, but protected from the scorching sun. Water around the cutting without removing the jar. If the planting material was prepared from a rose variety that takes root for a long time, then a growth-accelerating agent is introduced into the soil, according to the instructions.
Layers for reproduction
In the spring, the shoot above the bud is cut and placed in a groove 10-15 cm deep, prepared in advance. First, sprinkle with humus in a thin layer and sprinkle with earth. The shoot is fixed in several places and fall asleep, leaving the upper part above the ground. The cuttings are systematically watered, covered for the winter, and the next spring they are cut off from the mother plant and planted in a new place.
How to plant a rose
With the eye of the mother plant, budding is performed on the rosehip root (at the end of July to the last days of August). Before the procedure, the rosehip is watered abundantly, then an incision is made on the neck of the stock, in the form of the letter T. At the same time, the bark is pryed off and slightly torn from the wood. Together with the eye, part of the bark and wood of the rose is cut off. The shield is placed into the incision very tightly, until it stops: with one hand they hold the leaf handle, with the other, with the help of a knife, push the bark apart.
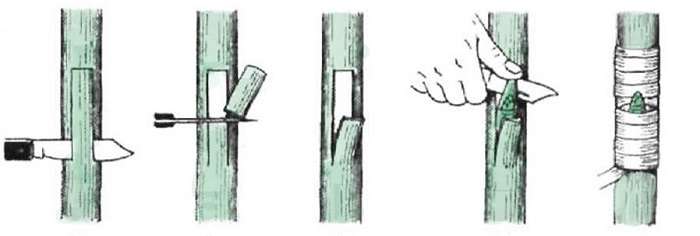

If the flap will not fit into the incision, then from above it is cut off along the intersecting section of the bark. Then the shield is fixed with an budding twine or film, and the rose hips are spud. After 14-15 days, when the eye grows with the stock, the bud should be green. The harness is loosened or replaced, and removed the next spring.
Seed for propagation
Purchased seeds are placed in a strainer and immersed in hydrogen peroxide to disinfect and prevent mold from forming on them during further stratification. They also moisten cotton pads with peroxide and spread on them. Then each disc is placed in a plastic bag, and the grade and date are indicated on it. They are placed in the lower container of the refrigerator and the contents are checked periodically. If mold is found on the seeds, they are washed, re-treated in peroxide and laid out on new discs. After 1.5-2 months, the seeds will sprout.
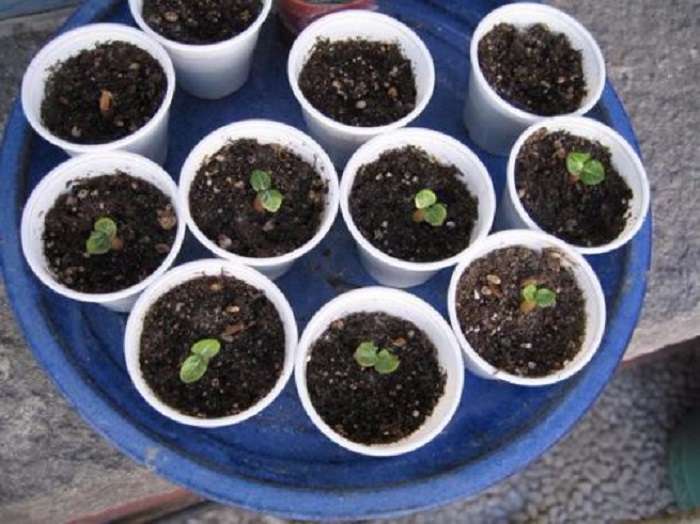


Consider how to plant climbing rose seeds. Usually they take peat tablets or small pots of soil and plant the sprouts. In pots, they are sprinkled with perlite mulch to exclude such a disease as "black leg". Small plants are provided with daylight hours lasting 10 hours or more, watered in a timely manner, not allowing the substrate to dry out too much. With normal development, after 2 months, buds may appear on the plant, and after another 1.5 months they will bloom. They are fed with a complex fertilizer, making a weak solution. In the spring, planting material is planted in open ground and looked after as an adult plant.
Miniature roses in spring
Spring is the most crucial period for roses. Miniature roses in spring require special attention:
- regular ventilation during daylight hours in frosty weather at night;
- timely removal of the winter shelter, which is removed gradually, and completely only after the soil has thawed;
- timely spring pruning;
- loosening and mulching the soil;
- feeding a plant weakened in winter;
- preventive treatment to prevent diseases and the appearance of parasites.
Caring for roses after planting
Agrotechnically correct care of the planted rose bushes is the basis for their future successful development and abundant flowering. It provides for the following regular activities:
- periodic weed control and shallow at first loosening;
- timely feeding with suitable types of fertilizers;
- the formation of the crown of a developing bush;
- regular abundant watering with settled warm water until the apparent rooting and development of the seedling daily, and then - you can limit yourself to once a week, followed by loosening and mulching of the trunks. The best time to water is in the morning or evening;
- special requirements are imposed on mulching, which will help protect the root system of seedlings from erosion with frequent watering and from drying out the soil, which can lead to dehydration of plants;
- taking into account the fact that when planting seedlings, all fertilizers in a full complex are introduced into the pit and the trunk circle with mulching, it is advisable to fertilize rose bushes only after 2 years of their development;
- The near-stem loosening of rose bushes is a necessary measure to enrich the roots of this plant with air, which should be carried out regularly until autumn. With the onset of autumn, it is not only not useful to loosen it, but it is even important to tamp the trunk circles loosely, preventing the weathering of the soil and excessive cooling of the rhizome;
- in addition to weed control, you should collect and burn rose leaves affected by black spot.
The rose is as beautiful as it is capricious - unfortunately, it is susceptible to aphids and certain infections. Therefore, it is not enough to admire a rose - it must be examined in a fatherly way and immediately provide appropriate qualified assistance, both with chemical preparations and folk remedies.


For example, with the help of useful bio-neighbors, plants with a pungent odor that has a deterrent effect: marigolds, sage, ornamental onions. In addition, infusions of calendula, onion, yarrow and garlic have shown themselves well for spraying. Practitioners use to control rose pests by dusting its bushes with wood ash until about mid-summer.
For your information! For the gradual formation of the desired crown of the rose bush, pinch all the lateral shoots after 4-5 leaves.
A useful preventive measure against fungal diseases of the rose is the thinning of the crown of its adult bushes. Do not consider the method of cutting almost all the buds on a young bush for cruelty, in which you can leave the most developed of them in order to admire the beauty of the flowering of this bush and so that in the next season the flowering is as abundant as possible. And do not forget about the correct preparation of the rose for winter - including pruning and shelter.
So, we reasonably come to the conclusion that planting rose seedlings is quite a feasible business, but, of course, meticulous - there are no trifles in it. For the triumph of the future beautiful rose bush, you need to work not only competently, but also with love, sparing no time and effort. There are plenty of sources of information on how to do everything right nowadays: articles in newspapers, on Internet sites, videos on YouTube, live experience of familiar practitioners who have achieved outstanding success in growing such beauty as lush and fragrant roses of various colors and shades.
Miniature roses in winter
The vast majority of garden rose varieties are damaged during frost. Overwintering depends on the winter hardiness of the variety, the condition of the plant, its readiness for winter, weather conditions and the method of shelter. Miniature roses need shelter in winter and must be prepared for winter. To do this, it is necessary to carry out a number of agrotechnical measures that will significantly increase the winter hardiness of plants:
- from the 2nd half of summer, it is necessary to completely exclude fertilizing with fertilizers containing nitrogen, which contributes to the formation of a green vegetative mass and delays the growing season;
- in August-September, feed with potassium-phosphorus fertilizers, which stop the growth of shoots, contribute to the ripening of wood and increase resistance to cold;
- at the beginning of autumn, pinch the ends of the growing shoots;
- loosening and watering the soil to a minimum;
- after the first frosts, you need to gradually cut off the leaves (first on the lower ones, then on the other branches) and remove the unripe shoots.
Before sheltering, you need to dig up the ground under the bushes and huddle (preferably dry earth) with a mound up to 15 cm high. When the soil is slightly frozen, the plant must be covered with a layer of spruce branches or dry foliage at least 10 cm thick. During thaws, it is recommended to ventilate the plants, partially removing the shelter for several hours.
Pest control


Spider mite on a rose
Garden roses are susceptible to attacks by specialized "rose" insects:
- Aphids. They settle on young shoots, occupy the lower parts of the leaves. You can try to get rid of this small fry with the help of wormwood infusion or a solution of fermented nettle. Large colonies will only be destroyed by an appropriate insecticide.
- Cicadocs. The lower surfaces of the leaves are also populated. Small whitish specks appear on the outside of the leaf plate. You can eliminate leafhoppers with a solution of laundry soap.
- Spider mites. They readily reproduce in heat and dryness, braiding the lower surfaces of the leaves with the thinnest cobweb. Severely affected foliage is removed, the plant is sprayed with garlic or tobacco infusion. Yarrow and horsetail also help.
- Leaf roll. These insects lay their eggs on the leaves so that the developing larvae wrap the leaf plate in a tight tube. Such formations must be removed and the rose must be sprayed with an insecticidal preparation.
- Sawflies. The larvae are settled inside the shoots. As a result, holes are formed in the stems. The affected areas are subject to immediate removal and destruction. As a preventive measure, rose bushes are sprayed with wormwood infusion.
Miniature roses for summer cottages
This type of plant is able to decorate any suburban area. Miniature roses are suitable for summer cottages most of all from the beginning of summer to the end of autumn, they are simply strewn with colorful flowers. Planted bushes look best separately from other flowers, next to conifers or as a padding to tall hybrid tea varieties of roses. The climbing forms will adequately decorate the fence, gazebos and walls, complementing the landscape design.


Rose: combination with other plants
As neighbors for roses, you can select plants that will not only look good next to them, but also bring a lot of benefits. For example, they will protect the rose from harmful insects.
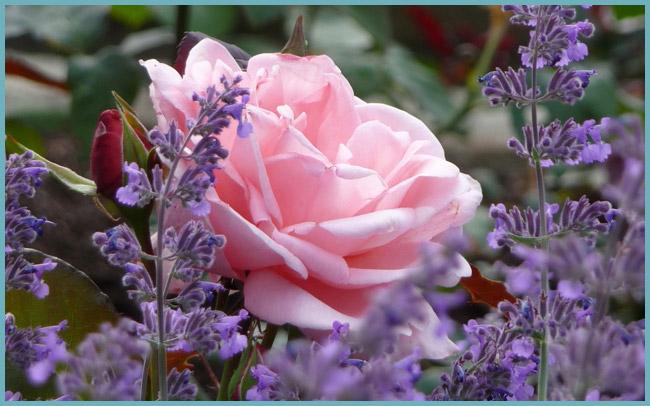


Rose combined with lavender
If you plant nasturtium or lavender together with roses, then this is guaranteed to protect the roses from the appearance of aphids. But marigolds and calendula will get rid of beetles. Onions and garlic have a beneficial effect on the health of roses and even add aroma to them.
Miniature roses of Cordana (Kordana rood)
It is a miniature semblance of a classic rose bush. Miniature Cordana roses are distinguished by their bright numerous flowers with various colors and shapes, and lush dense greenery. Bush up to 25 cm high with erect stems. Leaves are dark green up to 2 cm wide. Flowers are single, up to 3 cm in diameter.


The species does not require special care and is often used to decorate ornamental gardens, lawns in the form of a trunk or as a pot culture.
How to choose the right seedlings


Saplings of rose bushes are best purchased from nurseries.
To begin with, when choosing, it is determined which rose is needed and what size (low, high, miniature) and from which group it should come.The goal is determined, for example, landing on a front flower bed, creating a low curb, decorating a gazebo or fence.
The exactingness of the plant to care is also taken into account. For example, does the florist have the opportunity to shelter for the winter and other argotechnical subtleties.
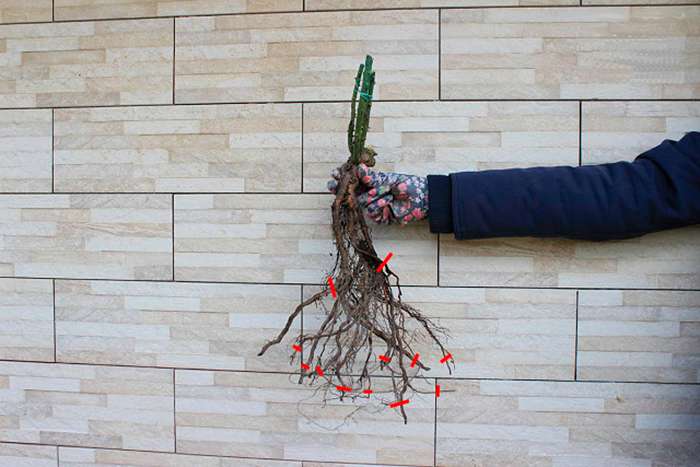
The seedling is taken one or two years old. It should consist of 2 or 3 lignified dark green stems (no visible blotches), with dormant buds and developed roots. The diameter of the root collar should be 8-10 millimeters. Flowers, fruits, foliage on the bush are cut off.
It is best to take a seedling planted in a container with closed roots.
Miniature roses of Cordes (R. kordesii Wulff.)
They are compact branched bushes from 15 to 25 cm tall, with small, glossy leaves of dark green color up to 12 mm wide. Shoots up to 5 cm long, each with 5-7 leaves. Small buds bloom in single or collected in an inflorescence flowers up to 3.5 cm in diameter.


Miniature roses of Cordes are obtained by crossing the Rugosa and Vihura roses with varieties of other garden groups. The variety is drought and disease resistant.
Features and planting schemes for various types of roses
Experienced flower growers know, but for beginners we suggest approaching the above rules as basic ones. The individual varieties of roses you have chosen should be treated differentially, according to the accompanying recommendations for breeding and caring for this particular type of garden beauty.
Climbing rose (curly)
Climbing rose seedlings are rooted in the planting hole according to the general rules, but the grafting site should be buried 8-10 centimeters into the ground. Instead of pruning for such a seedling, only the renewal of previous sections is used.


The interval between the bushes of such roses is preferable up to 1-1.5 meters. From the support (wall, fence, special lattice, column, arch or other type of support structure), the distance during planting should be 0.3 meters, which simplifies the process of tying its rapidly growing shoots to decorate the support.
Floribunda
When planting seedlings of this rose variety, it is necessary to deepen the grafting site in relation to the soil level to 3-8 centimeters. Planting intervals between bushes are 0.3-0.4 meters with an indentation in row spacings of 0.6-0.9 meters.
English roses
To the general rules for planting a rose, the recommendation is added to deepen the seedling 5 centimeters above the grafting, and when pruning the shoots, leave at least 5-7 buds on each of them. Allowable intervals between bushes are 1.2-2.0 meters.
Park roses
The requirements for their planting closely coincide with the rooting feature of the English rose: deepening the grafting site by 5 centimeters, buds on each shoot should remain 5-7 after pruning. There is a difference in the size of the intervals between the bushes, which should match half the height of an adult bush - 0.5 meters.
Ground cover roses
Roses of this variety are planted as usual, with a grafting depth of up to 5 centimeters. After deleting damaged branches, there is no need to prune them - just update the slices. The intervals between seedlings should be equal to half of the formed bush - 0.5-1.5 meters.
Hybrid tea roses
When deepening seedlings of a hybrid tea rose, it is allowed to immerse the grafting point up to 3-5 centimeters. After pruning, developed shoots should retain 2-3 full-fledged buds. Planting intervals between bushes in a row are appropriate within 0.3-0.5 meters, and in row spacings - 0.6-0.9 meters.
Features of border roses
Border roses are medium and low-growing bush varieties, differing from the usual roses in height, petals, and multiple abundant flowering. Its bushes do not exceed 60 cm. They are compact, do not take up much space, and their plantings beautifully frame the plot with a picturesque border. Growing roses in the garden gives it a unique and sophisticated look.
Rose petals have a double base. The variety of colors is striking.These can be buds of one color, or combining two. There are varieties that change color during the season. So, in the "masquerade" variety, the color from bright yellow gradually turns into pink, and in the fall it becomes dark crimson.
Border roses are considered an unpretentious crop to grow, easily tolerate a transplant, quickly take root, withstand frosts.
Miniature roses are prized by designers and landscape architects. They use them to decorate streets, parks, city sites, recreation areas, "dry streams". Flowers go well with many garden plants. One of their features is that they grow beautifully both in the garden and on the windowsill in a pot.


Plant propagation: methods
Summer rooting of cuttings. For grafting, the stems are not chosen the youngest, but not the old ones either. A sign that the stem is suitable for grafting is the ease with which the thorns break off. The stems are cut early in the morning and cut into 12-15 cm cuttings with a treated sterile knife. Each piece should contain two or three leaves and the same number of buds, but it should not have flowers. Leaves must be removed or cut by a third. This will prevent excessive moisture evaporation.
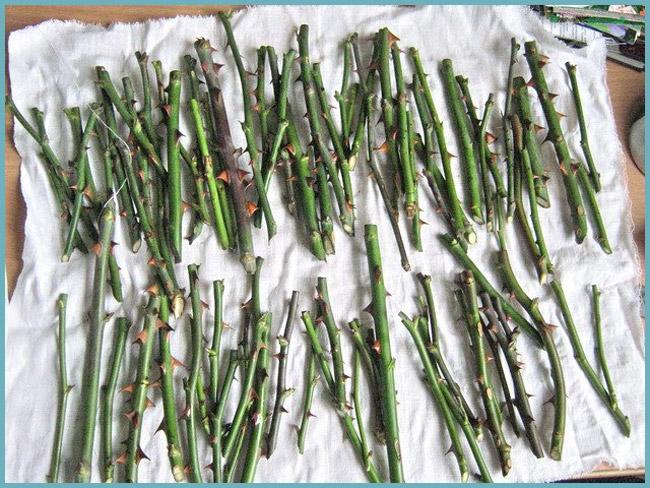


Rose cuttings
The wells must be pre-treated with a solution of potassium permanganate, and the future sprouts must be soaked in a honey solution (0.5 tsp honey in a glass of water), into which you can add chopped rose leaves. Cuttings are tilted into the holes at an angle and mini-greenhouses are made using glass jars. After a couple of weeks, you need to remove the cans for a short time to harden the processes. And after a week from the beginning of hardening, the cans can be completely removed. By autumn, when the shoots reach 30 cm, buds may appear on them, they are pinched so that the rose spends all its energy on the formation of the root system, and not on flowers.
Planting cuttings in the fall. It happens that you got a unique rose in the fall, and it will not be possible to force it to take root by winter, and it is not always convenient to store cuttings in the house in winter. In such cases, divide the stem into cuttings and dig them into the garden. Cover the top with a dry layer of leaves or covering material so that the plant does not freeze in winter, and in the spring, transfer it to a permanent place in the usual way.


Winter shelter for rose bushes
Rooting in potatoes - This is the most common method of breeding roses, because roses are fed from potatoes in addition to carbohydrates and starch. In a lighted place, it is necessary to dig a groove up to 15 cm deep and fill it with sand by about a third. We stick the cuttings up to 20 cm long into the potato and deepen it by 10 cm. Then everything is done as in the usual way: cover with jars and after a while harden the plants. Every five days, you can pour a sugar solution (2 teaspoons of sugar in a glass of water).
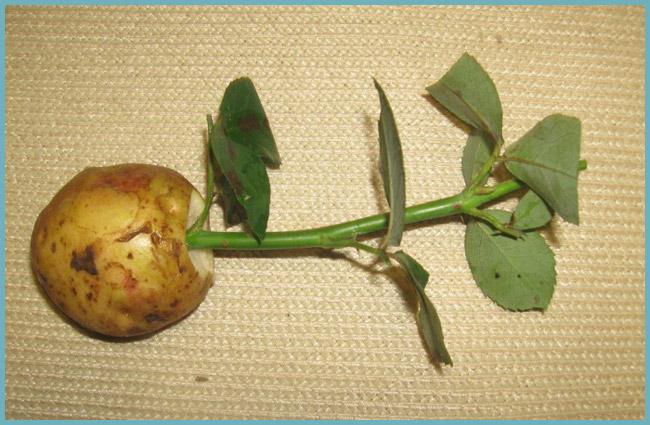


Rooting a rose in a potato
Reproduction in a package. The lower part of the cuttings is moistened with aloe juice in a 1: 9 ratio of aloe juice to water and stuck into sterile soil, packed in a bag. I fill the bag with air, tie it securely so that the air does not come out and hang it on the window. A month later, when the roots appear on the cuttings, they are planted in the above way.
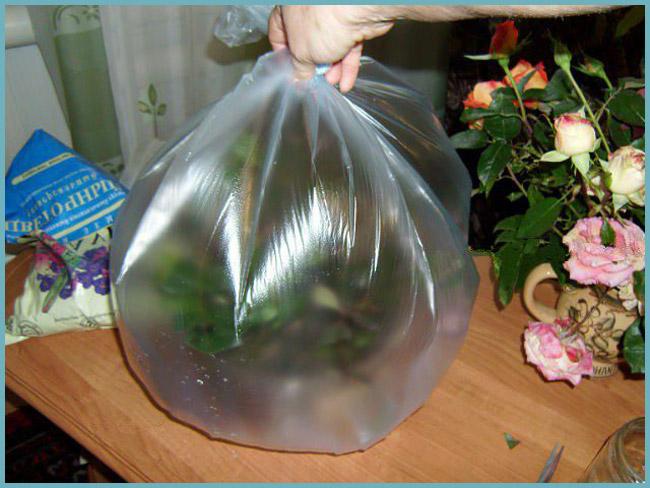


Reproduction of a rose in a package
Rooting in water. Freshly cut roses are rooted in this way. Plant stems cut into cuttings must be placed in distilled water. Remember to remove all thorns and flowers. Leaves can also be trimmed or shortened. Change the water periodically until the stems take root.
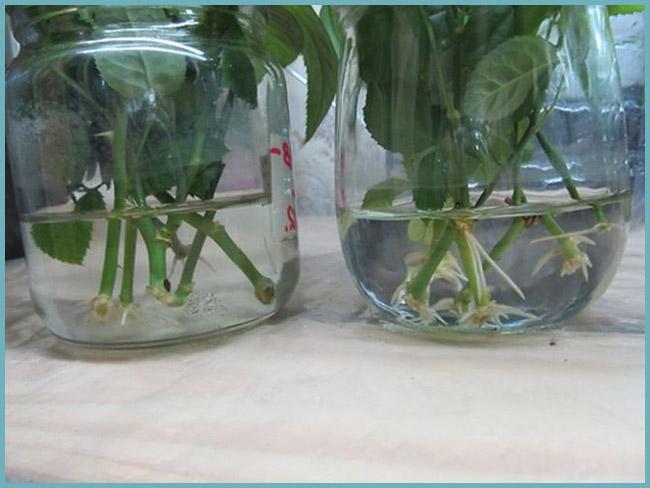


Rooting rose cuttings in water
Advice. With any rooting method, always remove the thorns and inflorescences from the stem, and shorten the leaves by a third.
How to plant?
Planting a curb rose is a simple process, but the gardener needs to know a few important points.
Landing should take place in an area protected from gusts of wind. In this case, there should be enough sunlight.A strong wind will take moisture from the crop, and its lack will affect growth and flowering. This condition is also important for roses growing in pots. The effect of the wind is enhanced, since the roots have a limited area of soil from which they could make up for the lack of moisture.
You can not plant it on a site where other representatives of the Rosaceae family grew for a long time. The effect of "soil fatigue from roses" arises when it is severely depleted by these plants and spores of fungal diseases, viruses and pests can be found in it.
Miniature beauties are undemanding to the composition of the soil. They grow on any soil, as long as it is not too dry, dense and waterlogged. Before planting, it is recommended to improve the soil by mixing it with drainage or organic fertilizers.
The best time is the beginning of spring, when the soil warms up a little. Such an early planting period makes it possible for the season to develop well, take root roots and then easily endure the winter.
While the plant takes root in a new place, it is better to cover its young bushes at night. This will protect fragile and weakened bushes from night frosts.
Planting is carried out in a hole, the size of which should slightly exceed the diameter of the planted root system. When planting, the roots are gently straightened, their neck is buried into the soil by only 3-5 cm.
The optimum distance between seedlings is 25-30 cm. After planting, the soil around the bush is carefully compacted and watered abundantly.


Landing features
Although the climbing type of plant is capricious in nature, many varieties compensate for this fact with a pronounced subtle and delicate aroma, which can be felt at a great distance during flowering. Do you want to see hanging roses on your site and in the rose garden? Experienced gardeners will tell you where to plant, how to take care of, the best recommendations of which we have combined on this page.
Sunny, but ventilated places will be favorable for the plant. In this case, drafts are excluded. Swampy, heavy clay and sandy soil is contraindicated. It can be diluted with a suitable soil: add sand to the clay to a depth of 30 cm, or, conversely, dilute with humus, humus and add phosphorus in the form of bone meal. The rose thrives on loose loam or fertile and permeable soil.
On the site, illuminated by the sun's rays before lunch, the dew will dry faster on the plant, which will exclude fungal diseases. After lunch, the site should be shaded from the scorching sun so that burns do not appear on foliage and petals. From the north and northeast, the bushes should be protected from the cold wind. Drafts always "walk" on the corner parts of buildings, so they are not planted in such places: drafts will simply destroy the delicate plant. How to plant a climbing rose to decorate part of a building? It is necessary to land it on the southern side of the building on a half-meter strip of soil that allows water to pass through well, retreating 50-100 cm from the wall.


In the case of a close location of groundwater, you need to make a special elevation, since the roots can go deep up to 200 cm. You also need to make a slight slope for the root system so that the liquid does not stagnate. Usually the soil is prepared six months before planting a rose, but it happens in two or even one month. Gardeners recommend planting climbing species of the "queen of flowers" in new, previously undeveloped areas. In the absence of such, it is required to replace the top layer of soil, where other roses grew, to a depth of 50-70 cm.
For planting, the plants are chosen at the end of September or the beginning of October, since it is necessary to transplant a climbing rose from one place to another before the cold weather, so that the roots have time to take root in the ground in a new area. Then in the spring the rose will actively grow and develop, and in the summer it will bloom. If spring time is chosen for planting (the end of April - the first week of May), then - only in the warmed-up ground up to + 10 ° С.At the same time, the buds on the plant should not be loose.
How to plant a rose in autumn
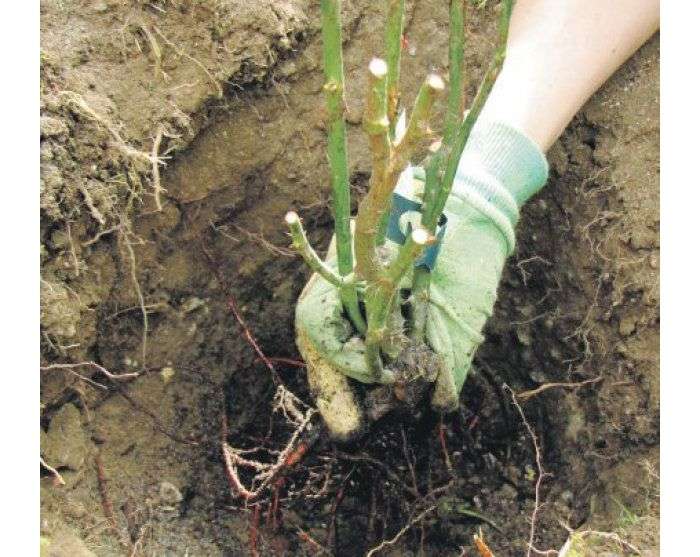
Cultivation of climbing roses in the open field is carried out from the end of September to October 15-18 with the most high-quality planting material: self-rooted or grafted onto a rosehip. Planting and caring for such seedlings has its own differences. A seedling, grafted onto a rosehip with a root system, is placed in the soil so that the graft is in the ground at a depth of 10-15 cm, in order to form its own root system. After that, the roots of the rose hips will gradually die off. If the scion is not buried in the ground, but left above the surface, the plant will die. Rosehip is a deciduous plant and rose is evergreen. In grafted seedlings, the buds that are located below the scion are carefully removed, since wild rose hips can grow from them. The planting material is disinfected: dipped in copper sulfate (3% solution).


You need to know how many leaves a climbing rose has in order to distinguish a cultivated shoot from a wild growth. There may be 9 or 7 of them, like a rose hip, hybrid tea may have 5 leaves. You can distinguish it from the wild by the color, size and density of the leaves. The rosehip leaf has a dull and dull color; it is thin in density and small in size. The rose leaf is distinguished by its glossy and shiny appearance, rich color and large size.


In seedlings with an open root system, all the leaves are cut off and damaged and unwanted stems are cut off with a pruner and the roots are shortened, leaving up to 30 cm in length, and the stems up to 20 cm. Places of cuts are treated with charcoal powder. But before this procedure, they are placed in water for a day, and then planted in a prepared pit 50x50cm in size. If there are several seedlings, then the distance between them should be 100 cm or more.
1-2 days before landing, the following works are carried out:
- mix half a bucket of manure with the top layer of soil from the pit;
- Pour part of the resulting mixture into a pit and pour plenty of water;
- on the day of planting, treat the roots of seedlings with a special solution: dissolve heteroauxin (1 tab.) + phosphorobacterin (3 tab.) in 500 ml of water and mix with a clay mash (9.5 l);
- add part of the remaining mixture of manure with soil to the pit, forming a mound out of it;
- place a seedling on the top of a mound from the mixture and gently straighten its roots;
- pour the rest of the manure mixture into the pit and compact it a little around the root system. Make sure that the graft site is submerged in the ground by 10 cm, and for a seedling with its own root system - by 5 cm;
- water the planted rose and, after absorbing water, add more fertile land with manure;
- spud the seedling to a height of 20 cm or even more and cover the tree trunk circle with mulch.
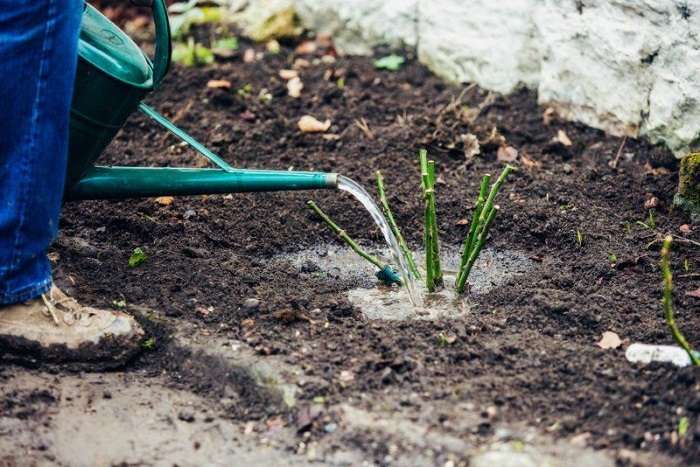




It's important to know. In order for the rose to take root faster, a mini-greenhouse is built from a transparent film on top of the seedling and it is ventilated daily, raising the shelter. To harden the plant, the airing time is gradually increased.
How to plant a rose in spring
Spring planting is carried out in stages according to the same rules as autumn planting. If the bush was covered with a film, then do not forget to raise it to air the plant. After the establishment of stable warm weather, it is removed and the trunk circle is mulched using leaf humus, crushed tree bark or straw.
Flower shops now sell climbing rose planting material, which can have an open or closed root system. When buying seedlings with an open root system, you need to pay attention to the fact that they must have 2 or more lignified shoots. A ripe shoot develops a crunch when bent. The roots must be well developed and strong, without dry fragments. Shoot length - 60-70 cm, not less. They are planted in the ground immediately after purchase.
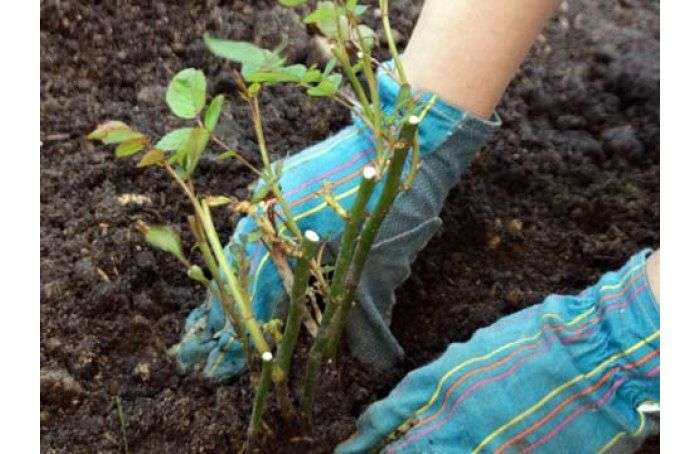


It is difficult to evaluate a plant with a closed root system as they grow in pots. It should not be very elongated and light green in color. The shoot is pulled out due to improper storage in a too warm room with poor lighting. Such planting material is unlikely to make a healthy plant. A weak and sickly rose may not survive the winter.
An important point. If the stalk is grafted correctly, then you can see the callus tissue at the junction: it promotes fusion. With a noticeable peeling of the graft site and an unhealthy appearance, such a rose should not be purchased.
If you need to plant a rose purchased in a store, then you should adhere to the following step-by-step instructions:
- With a closed root system, the seedling must be carefully removed from the pot with a lump of earth and planted in a pre-prepared place, too long - pinch.
- Wild growth, shoots or buds are removed below the grafting site, and the cut sites are powdered with charcoal or activated carbon powder.
- If the root system is open, then after removing the film from the roots, they are placed in a container with water and the Kornevin stimulator and kept for 3-4 hours to saturate with moisture.
- The roots are straightened and the rose is planted according to the rules that are indicated above in the article, and then the standard care of the climbing rose is carried out: they spud, water, apply top dressing, remove weeds and form a bush.


How should you care for a flower garden?
Caring for a curb rose will not cause difficulties even for those who are engaged in its cultivation for the first time. If the basic requirements for pruning, watering, feeding are met, the plant will thank you with good growth and lush flowering.
Miniature roses need regular, but not abundant irrigation. Drying and waterlogging of the earth must not be allowed. Watering is best done in the evening using sun-warmed and settled water.
Do not allow water to enter the aerial part of the plant. It should be watered at the root!
Growing roses is not complete without feeding. It is necessary to feed miniature plants several times. To do this, you must use fertilizers designed specifically for Rosaceae or other ornamental flowering plants. You can use organic matter: horse manure. It mixes with the soil and fits under the bushes. It is not necessary to use other manure, as the roots may burn.
Spring and autumn composting works well on miniature roses. It is laid out under the bushes at the rate of 5-6 kg per m2.
When the first buds form, the plant can be fed with calcium nitrate (1 tablespoon per bucket of water). This fertilizer has its own peculiarities of use:
- before feeding, the roses should be well watered so as not to burn them;
- after feeding - water again;
- the time of the procedure is in the morning or in the evening (when the heat subsides).
Additionally, every 15-20 days, you can feed it with mullein, mineral fertilizers or herbal infusions. Liming is necessary in September.
In hot, dry summers, top dressing is rare, in rainy summers - frequent and abundant. Young plants in the 1st year after planting are fed only in spring and autumn.


Leaving on hot days
Miniature roses do not tolerate rainy and very hot weather. It causes stress in them. During this period, reanimation agents will help to "cheer up" the plants: "Zircon", "Epin", "Ecosil", potassium humate.
It is important to protect the culture from overheating. A rise in temperature above 25 ºC leads to overheating of the roots and deterioration of the condition of the roses. Peat and hay laid under the bushes will help to cool them a little.
Leaving includes another important point - competent pruning. It consists in removing damaged and dry shoots, in the formation of a beautiful and correct aerial part.
To prevent decay and rapid damage to cut diseases, a clean and sharp pruner should be used when cutting.
Pruning is done 5-8 mm higher from the healthy kidney. This procedure can be carried out all season. In the last pruning, extended new shoots and buds are shortened.
If the shoot is damaged, it is cut from above between 2-3 leaves. It is important to cut wild growth from grafted roses. Eliminating the "wild" above ground level will not give any result - it will grow again. Correct pruning is the removal of wild shoots from the very base (from the root collar).
In order for the bushes to grow proportionally, in the 1st year of their life, it is necessary to pinch all the shoots that appear after 4 and 5 leaves, remove the buds. In "old" bushes, the central shoots growing vertically are not trimmed, only the lateral ones are trimmed a little.
Preparing for winter
Despite the fact that many varieties of border roses can withstand frost, they must be insulated for the winter. But first, all shoots and fallen leaves are removed. The first night frosts are a signal for the start of insulation. The sequence is as follows:
- to spud the plant, and the height of the embankment should not be less than 20 cm;
- put spruce or pine branches around;
- on them, gently pressing against the soil, lay the shoots;
- cover with dry leaves or spruce branches on top.
Many gardeners make a frame for insulating roses and cover it with a moisture-repellent material (roofing felt, insulating paper) folded in several layers. A plastic wrap is additionally laid on top. As soon as the thaw begins in spring, flowers can be opened slightly.


Planting process
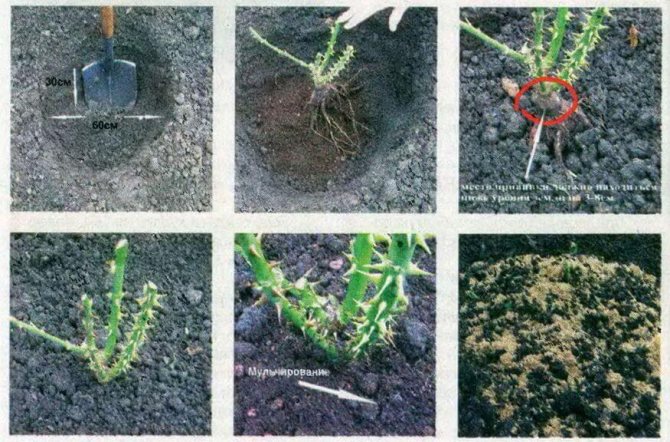
The technology of planting prepared seedlings in the ground provides for the following actions:
- Digging a hole 50-70 centimeters deep and 40 centimeters in diameter.
- Laying a drainage pad on the bottom (layer thickness 7-10 centimeters). For these purposes, brick fight, expanded clay, pebbles are suitable.
- A plant is placed in the center of the pit with a slope and the roots are spread on different sides.
- Sprinkle the roots of the seedling with a nutritious soil mixture, adding wood ash to it (1-2 glasses).
- To avoid voids, the soil is carefully compacted.
- Watering the bush in several stages at the rate of 1-2 buckets of water per planting.
See also
Description and characteristics of varieties of varieties of roses Lydia, planting and careRead


In order to prevent freezing of the underground part of the bush, it is necessary to lay mulch from dry peat, the layer thickness should be 15-20 centimeters. This simple agricultural practice still makes it possible to retain moisture in the soil and get rid of weeds. After 2 weeks, it is recommended to level the mulch.
Diseases and pests
Any plants, including the curb rose, can be attacked by insects and get sick.
Neighborhood with many species of plants can prevent the appearance of insect pests. If roses are planted next to marigolds, sage or onions, they will never have caterpillars, aphids, sawflies, spider mites.
In order to prevent and with a single lesion, rose bushes can be sprayed with infusions of onions, yarrow, garlic, calendula, and sprinkle the ground around them with ash. If pests nevertheless appeared en masse, you should not immediately run for chemicals. Try natural, less harsh remedies first.
Dissolve laundry soap in 10 liters of hot water and add a few branches of wormwood, mix, boil for 15 minutes. After the solution has cooled, mix everything again, strain and spray the bushes.
If after treatment the pests have not died, re-spraying can be repeated after 5-7 days.
When natural remedies fail and insects are spreading, insecticides can be used:
- against spider mites - "Sunmight";
- against aphids, caterpillars and sawfly - "Mospilan", BI-58, "Aktofit", "Aktara".
Miniature roses are highly susceptible to diseases:
- powdery mildew;
- black spot;
- rust;
- alteriosis.
It is easy to prevent their appearance. It is enough to spray the culture with solutions of copper sulfate (3%), DNOC (1-3%) or nitrophenol (2%) before sheltering the culture for the winter and after opening.
If an infection has occurred, then the following means are used in the treatment.
- Water-soluble sulfur (1%), Bordeaux mixture (1%) are effective against powdery mildew.
- Copper oxychloride (0.2%), Bordeaux (1%) mixture will help get rid of black spot.
- Rust can be cured with water-soluble sulfur (1%) and copper oxychloride (0.2%).
- Spraying with foundation (0.2%) or copper oxychloride (0.4%) will help to cure an infectious leaf burn.
Some fungal diseases (for example, powdery mildew) appear if the care and planting conditions have been violated: bushes are planted close to each other, abundant watering.
When caring for a plant, it is important to regularly examine each one, pick off “suspicious” leaves and burn them, cut off dry branches in a timely manner so that diseases or pests from one infected plant do not pass to neighboring ones.
Treatment brings a quick and effective result if it was started at an early stage of the disease, when the lesion was single.


Disease protection
Under adverse weather conditions, inappropriate growing place, thickened planting, roses are affected by a variety of infections.
| Disease | Description of the affected plant | Picture | Prevention and treatment |
| Black spot | On the leaves there are dark, purple-tinged spots with a clear border. Affected foliage quickly turns yellow and dies. |
| Spraying with Bordeaux liquid, infusions of nettle and / or horsetail. |
| Powdery mildew | The leaves are covered with whitish small grains of easily washable plaque. |
| Pruning thickening shoots, spraying with a 1% solution of Bordeaux liquid. |
| Rust | Brown, brown, yellow spots on foliage. |
| Spraying with a solution of copper sulfate with soap, Bordeaux liquid. |
| Downy mildew | The outer side of the leaves is covered with red-brown spots, and a grayish bloom forms on the inner side, which cannot be erased. |
| Exclude the ingress of irrigation water on the leaves. Spray with infusions of horsetail, nettle, sow thistle, ash solution. Strengthen the potassium component in root dressing. |
| Gray rot | Areas of intensive growth - the ends of shoots and buds - are covered with gray mold. The affected areas quickly dry out and fall off. |
| Top dressing with manganese, spraying with one percent Bordeaux liquid. |
How curb roses reproduce
Miniature beauties reproduce in 3 ways:
- cuttings;
- dividing the bush (seedlings);
- seeds.
Propagation by cuttings
It is considered the easiest way. From May to July, semi-lignified shoots can be cut off, divided into parts so that 2-3 buds remain on each of them. All the leaves on them are shortened by half.
Each shoot is planted only after 3-4 hours of keeping them in a root-forming solution. The distance between them when planting is 30-35 cm. Then each shoot is watered abundantly and covered with a container (glass jar, large plastic bottle). They stay in such a "greenhouse" for about a month and a half. All this time it is necessary to water them regularly. Once the shoots have developed roots, they can be dug up and transplanted to a new location in the garden.
Propagation by seedlings
This method is applicable in the fall or spring before bud break. It is very easy to divide an adult bush. It is dug up and neatly cut into pieces. The main thing to consider is that each part must have a shoot and roots. Then all the shoots obtained by dividing are planted in the garden.
How to transplant and prune a rose
Transfer. If the bush is planted in the wrong place, it is transplanted in late September - early November, but not later, so that the bush has time to take root in a new place. In the spring, this work is done before the kidneys awaken. The plant is removed from the support. The tops of young shoots are pinched at the end of August for early lignification. The old stems are cut off, and the long young ones are shortened by half the length of the claimings and climmers. Around the column, the bush is carefully dug in, retreating from the center to the length of 2 bayonet shovels.Then the groove around the base must be deepened, the roots must be tied with a lump of earth with a cloth and the bush must be dug under the very base. Too long roots are carefully pruned, a lever from an iron pipe or a crowbar is placed under the earthen ball, and the bush is carefully pulled out. Then it is transferred onto a bag and dragged to the desired location. If it needs to be transported over a long distance, then the fabric with which the lump was tied must be constantly moistened.
The root system of the plant reaches a great depth, so it must be dug out completely without any special damage. Shake off the soil from the roots and examine. The "shaggy" and damaged ends of the roots are cut off with a secateurs. After lowering into the prepared hole, the roots are straightened and covered with it, compacting the surface in the near-trunk circle. The plant is watered abundantly, and 2-3 days after transplanting, add soil with humus and spud.
Transplanting a climbing rose in summer is carried out only in cloudy weather. But then the bush is cut off strongly: young long shoots are shortened to 40-50 cm, and the old ones are completely removed. On a small bush, unripe young shoots are pruned.
Pruning. To form a beautiful crown, abundant flowering along the entire height of the bush and improve decorative qualities, the bush is pruned in spring or autumn. Remove stems that are dead and parts of frostbitten twigs. And also cut off the ends of the stems, focusing on the strongest outer bud.
With a single flowering, basal shoots (faded) are cut out at the root, leaving recovery shoots, which will be covered with buds and bloom the next year. This procedure is performed in the fall before preparing the plant for winter.
Repeatedly blooming roses grow in 3 years on the main stems of 2-5 flowering branches. With poor flowering, after a few years in the spring, the main shoots are removed at the 4th year of life. The bushes should have 3 annual recovery stems and 3-7 flowering (main) ones. It is necessary to take into account such a nuance: the flowers are formed on stems that have wintered well, therefore, in the spring, the upper part with immature buds is cut off from them.
In young plants grafted and planted this or last year, the rose hips are removed to form their own root system. After the root system of the rootstock (rosehip) dies off, a growth of a cultivated rose will appear.
Garden roses
The bush can be either pyramidal or spreading. Height is from 25 to 90 cm, the stems of a group of climbing roses reach 8 m.
The bush is formed by 2 types of shoots: perennial woody main stems. In annuals, they are softer, covered with leaves on petioles. Both species have sharp thorns, the size and number of which depends on the variety of the rose.
The bud is either located at the very top of the shoot, or along the entire length. The size of the flower is from 2 to 18 cm, according to the number of petals, 3 types are determined:
- non-double 5-8;
- semi-double 20;
- terry 70-128 cm.
Some varieties of floribunda or hybrid tea roses have curved petals, while many others have a straight shape. Sometimes they are wavy or with denticles along the edge.
The rose is loved due to the richness of monochromatic colors: white, cream, yellow, red. Also multicolored: the edge or back of the petal is painted in a different shade, there are even stripes and stains. Through selection, it has not yet been possible to obtain only one color - blue.
Many varieties have a strong and pleasant aroma, citrus, fruit and spice aromas are found.
Leaves with teeth along the edge of an elongated or rounded shape. The surface is matte and glossy, and the color is not only shades of green, but also interspersed with bronze.
Skeletal roots covered with bark with a diameter of 2-3 cm go into the ground. There are also thinner, the smallest branches of which are called lobes.
The connecting link between the underground part of the plant and the stems with leaves is the root collar, its size in centimeters depends on the degree of depth into the ground:
- long 10-15;
- average 5-9;
- short 3-4.
Selection of seedlings
The choice of planting material should be approached with all responsibility if you want beautiful and bright roses to grow in your garden. First of all, you need to carefully examine the seedlings. Appearance is very important. Shoots and stems should be elastic, strong, have a rich green tint, the bark should not have the slightest damage and defects. Live and healthy kidneys are a must. The root system should be examined equally carefully: the roots should be intact, unharmed, without fractures, fractures or rot. Try to touch the soil in which the seedling is located: it is not allowed to find the planting material in dry soil, the soil should be slightly damp. Live green leaves without spots are a sign of a high-quality and healthy seedling.
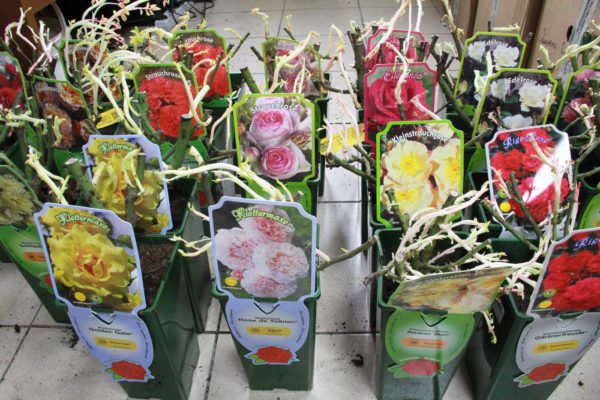


When choosing a planting material, you need to pay attention to several very important points:
- Label. In specialized stores and nurseries with high-quality products, the seedlings have a tag with all the necessary information: species, variety, selection.
- ADR marking. The indicated sign is not present on all varieties. Marking is available only on those varieties that have increased resistance to cold, diseases and good immunity to pests. The best decorative qualities are also found in species marked with ADR.
- Number of shoots. On the highest quality material, there are three shoots, two of which grow from vaccination. The price for such seedlings is higher. Cheap and, accordingly, lower quality seedlings have only two shoots, and both grow from grafting.
You can purchase closed-rooted roses, open-rooted roses or container seedlings. In any case, after the purchase, it is better to start planting as soon as possible. If after purchase it is not possible to plant flowers, it is necessary to store the seedlings correctly. To do this, hold them in a container with water for 2-3 days, and then wrap them with foil and leave them in a cool room, such as a basement or cellar. But it is not recommended to delay the landing.
Experienced gardeners advise planting roses in the fall, closer to winter. However, in the Moscow region and other regions of central Russia, it is necessary to plant roses in the spring. Otherwise, young roots will not be able to take root in a new area until frost. The probability of their death with the onset of frost is very high. Summer planting of roses is allowed, the result will be good. But it is worth noting that this option will cost several times more.
Spring planting dates
In order to plant roses in spring, you need to wait until the ground is completely thawed and warmed up. It is believed that the best time for disembarkation is the period from the last decade of April to the second decade of May.
Too delay the landing is not good, even a very early landing is better than a late one. In this case, young plants will not begin to develop, but will not die, but will wait for the onset of favorable weather. But at a later time, the earth will dry out, the sun will already begin to warm up strongly, and under such conditions it will be extremely difficult for a young plant to take root, it may simply die.
Fertilizing and feeding roses
In the year of planting on a soil well filled with nutrients, fertilization is not required for young plants. In the future, it is recommended to feed the perennial three times a year:
- before bud break;
- during the flowering period;
- after flowering before the arrival of cold weather.
Natural organic fertilizer will be the optimal feeding for rose bushes. Horse manure has the most beneficial effect on flowers. You can also use cow or chicken droppings.
Important. Do not add fresh organic matter under the roses. The manure should turn into a well-decomposed humus, or at least overheat. When fresh, it can cause burns to the plant.
It is much more effective to use liquid top dressing.When dry fertilizers are applied under the bushes, they must be combined with watering - this way the nutrients will sooner saturate the soil, and therefore the roots of the bush.
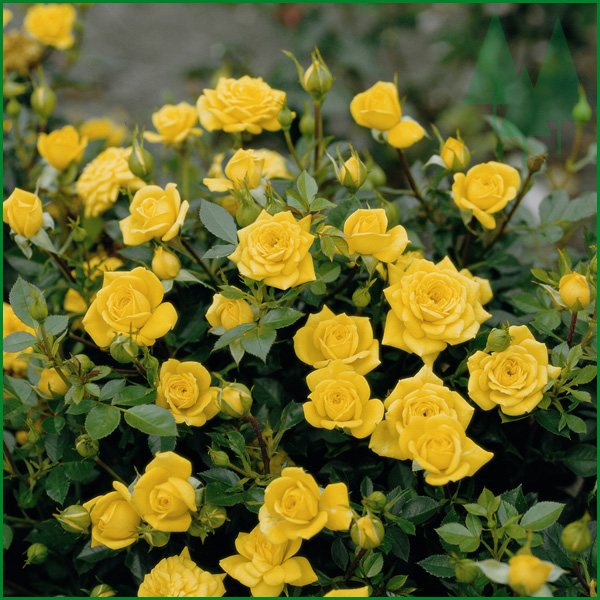


Miniature roses
The frequency of top dressing also depends on the quality of the soil. On heavy clay soil, they are carried out less often. On sandy soils, depleted areas, plants need more feeding.
Hello dear readers!


We continue talking about the rose - about this magical creation of nature.
From previous articles, we have learned what to be guided by when choosing a rose variety for your garden and how to choose high-quality seedlings.
Now another concern came to the fore - the right one. planting roses.
It's time for our beauty to grow up and start living in the garden, delighting its owner with a gentle fragrance.
But this will be on condition that the owner knows how to plant roses correctly and skillfully approaches this responsible mission.
After all planting roses - one of the most important events on which the fate of the rose bush depends.
When is the best time to plant


Roses can be planted in two periods: spring and autumn. In the conditions of the middle Russian strip, it is more reliable (according to experts) to plant in the spring.
But provided that the soil warms up to + 10-12 ° C and before bud break.
As a rule, this is mid-April to the second decade of May.
- Root seedlings are ideally best taken in containers. Plant them only in the spring by transshipment of an earthen coma. For many varieties of roses, only spring planting is acceptable (ask about this nuance when buying shoots).
But planting roses in spring has its drawbacks. These roses may be stunted (compared to fall seedlings). This lag is about two weeks.
Also, such queens are more capricious and require more supervision and care.
It is better to plan the autumn planting of roses in mid-September-mid-October.
If the timing of the event is shifted, the roses will not have time to get stronger before the first frost. In this case, it is very important that the buds of the plants have not yet begun to develop.
- After 10-12 days after the autumn planting, the roses form small young roots in themselves, which have time to gain strength before frost and feel great in a dry shelter until spring. In spring, young plants very quickly begin to form a strong, healthy bush.
If you do not have time with planting in the fall and do not want the seedlings to disappear, you can try to save them until spring by digging in.
To do this, shorten the stems and cut the roots to 30 cm. In this case, callus forms on the roots (callus that occurs at the site of the wound). Callus will develop healthy roots in the spring.
Video on how to properly plant roses in spring in open ground
Of course, everyone understands that proper planting is almost the main action in any cultivation. And so this moment is worth taking some extra time.
In this video, you can see how to plant the bushes correctly. Therefore, if there are some incomprehensible questions in the previous chapter, you can look here and get an answer to the question. The author of the video kindly shares his experience in this matter. And it's great that she not only talks about the nuances, but also shows you how to do what.
Here is a very small video, and how much useful information it contains. You can say, "take it and use it." I remember when I first bought my first bushes and how many questions I had about planting them.
And now everything has become simple, I opened the Internet, and received answers to all my questions.
When and how to plant?


Plants can be planted in spring or warm autumn. It is best to determine the seedlings to their "native" place in September-October. With a later planting, they may not have time to take root and freeze out in the first cold weather. Earlier - will wake up dormant kidneys, which will also die in winter.
Timely planting will ensure the formation of new roots in 10-12 days.They will grow up, become hardened and will not be afraid of frost. In spring, roses will quickly grow fresh shoots and delight caring owners with the first flowers!
So, let's start landing! We carefully examine the roots of the seedlings and, like a good sculptor, boldly remove all unnecessary things. We remove rotten, lethargic, broken ones, leaving only healthy, strong roots with a maximum length of 20 cm. If necessary, we shorten the shoots: there should not be more than 3-5 buds on them.
Then we arrange a comfortable home for our beauty. We dig a hole 50-60 cm wide, 80 cm deep. Add any organic matter to it: compost, humus, vermicompost. Mineral feeding (a mixture of 20 g of nitrogen, 10 g of phosphorus and 10 g of potassium) will not be superfluous.
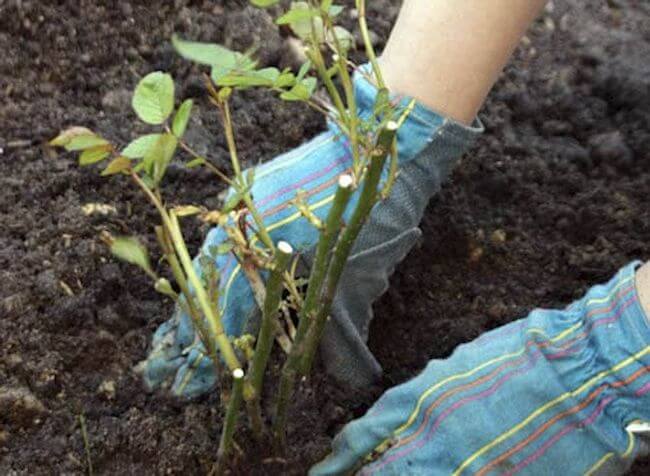


There are two options for planting - dry and wet.
With a dry method of planting, we lower the plant into a hole, straighten the roots and carefully cover it with earth. Then we water. When planting in a wet way, we first pour a bucket of water into the hole. You can add sodium humate to the water or dissolve one tablet of heteroauxin (the solution should be the color of weak tea). We hold the plant with one hand, cover it with earth with the other. In this case, watering is not needed.
When planting, we make sure that the root collar goes 2-3 cm into the ground - this will save the plant from drying out in the heat. After work, be sure to spud the bushes.
Preparation of seedlings and soil
Previously, rose seedlings are soaked in water for a day. When starting planting, choose a sunny area that is sufficiently protected from drafts. Next, dig a hole 50x50x50 cm in size and fill it with water.
It may seem that the fossa is too large, but it is not. Gardeners often make the mistake of digging a hole as large as the root of the plant. And then, after planting, the rose will feel cramped in space, the roots will have nowhere to grow.


And if you follow these recommendations, the roots will begin to form a mass of thin roots that absorb moisture, which will serve the development of a powerful bush. Having bothered once to prepare a place for her pet, she will repay a hundredfold with her abundant flowering in the future. So, after the water has been absorbed, 2-3 shovels of humus are placed in the hole and mixed with the ground. It is also recommended to add a handful of wood ash.
Home Floriculture What is the distance between roses when planting
How to preserve seedlings before planting?
If you bought seedlings in the cold season, do not rush to install them in a permanent place. In warm weather, it will be much easier for them to get used to the new conditions. Until then, let them live in the fridge on the bottom shelf. The temperature there is quite comfortable for them from 0 to +5 ° С. Notice drying out - slightly moisten the earthen lump. Seedlings with bare roots can be overexposed until spring and in the garden, in the greenhouse.
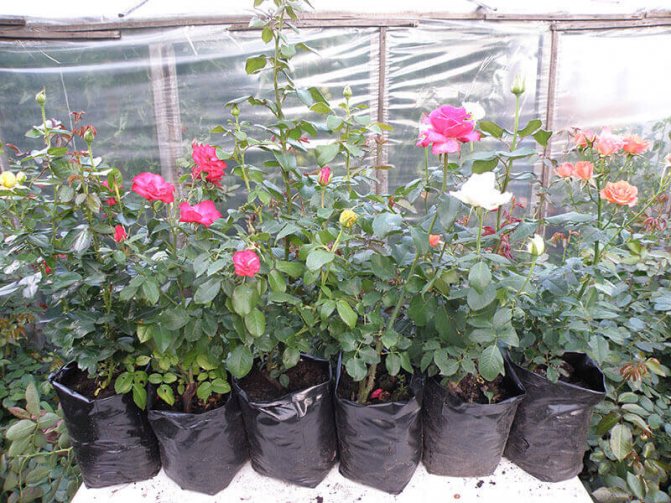


In the greenhouse, we dig a shallow, up to 40 cm, trench and place the plants at an angle. Then we fill the ditch with earth, and on top we insulate the seedlings with peat, spruce branches, and then with snow.
Rose planting material is also perfectly preserved in cold basements and cellars. We act in the same way - lightly add the seedling to a large pot. At zero temperature, our beauties will calmly sleep until the warm spring sun!
Park roses and care conditions for them
These amazing, luxurious shrubs are found not only in city parks and alleys. Often two-meter beauties can be seen in summer cottages. They give them a variety of colors and a rich look.


The flowering period for this species ranges from 30 to 60 days. The flowers are double, have hundreds of petals, the color range is predominant from white to pale purple. Representatives with a yellowish-orange color are less common. In the southern territory of Russia, this bush does not need shelter for the winter, but in the middle lane, one cannot do without the help of a gardener.
They come with single and repeated flowering. For the first type, it is required to preserve last year's shoots, otherwise the bush will not give inflorescences.They are more frost-resistant, and are more common in garden areas.
Separately, it is worth noting the good resistance to viral and fungal diseases. Which is very important at the present time. For prevention, periodically water the culture with infusion of green nettle or horsetail. And the flowers, in order to protect them from the attack of harmful insects, irrigate with a decoction of chamomile flowers.


The shrub takes up large volumes; when planting, keep a distance so that it is convenient for you to care for the plant. The roots continue to form for 3 years. Due to the increased branching, branches should be formed, dry and protruding ones should be cut off so that the rose looks well-groomed. The first pruning is done when the plant is 2 years old. Before the onset of autumn, all manipulations with the branches should be carried out no later than August, so that before the onset of cold weather, the plant is in a calm state.
This crop has very sharp thorns on the stems, so use heavy gloves when leaving to avoid injuring your hands.
Today there are a great many proposals on the choice of varieties. Check out some of them:
- Commander Baroper. The height and width of this culture is 120 - 150 cm. It has spherical flowers that have purple, violet stripes with light spotting. Demanding on the composition of the soil, good winter hardiness.


- Artemis. Repeated flowering bush, reaches a height of 120 cm, width - 50 cm. The dimensions of the blossoming buds are 5-6 cm, they are creamy white. Stand well when cut. The aroma is weak, but it perfectly tolerates frost.
- Ruban Rouge. Park beauty with bright, large, red - pink flowers. The structure is powerful, looks beautiful along the curb or facade of the house. Tall, can reach 170 cm.
It can be propagated using the layering method. To do this, in the spring, when the stems are in a lowered state, separate them and dig in with soil on top. After a year, they can already be separated from the parent bush and transplanted to a separate, sunny place.


Every 5 years, it is necessary to divide the bush. So that the rose is strong and healthy, it continues to delight you with its flowering. And also it will be a good reason to increase the number of your beloved beauty.
Golden rules for growing roses. Part 2
- Tall or slightly drooping: the distance between plants should be about half their height.
Curly roses for wall decoration, planting spacing - Low-growing varieties are planted at a distance of 2m. - Strong growing varieties - at a distance of 3-5 m. To decorate the gazebo, create an arch of roses, one plant is planted.
Shrub roses, planting distance. To create a hedge, plants are planted at a distance of half the height of the bush. When planting single bushes, the distance between them should be up to 3m.
Standard, cascading roses, planting distance. When planting in rows: standard roses are planted at a distance of 3m. from each other, cascading at a distance of 3-5 m. Standard, cascading roses look best in single plantings.
N. Ya. Ippolitova, candidate of agricultural sciences
Return - to the top of the page
Back to contents - "Once again about roses"
Back to section - Floriculture
Several roses can be found in almost every garden plot.
Roses: planting, care and pruning in fall and spring
Therefore, we recommend that you cut the cuttings for planting so that they have three buds. Remove all leaves, except for the top one.
At the bottom we make a cut obliquely. It is desirable that it is located just below the kidney itself, using a razor blade or pruner. Please note that scissors are not suitable as they can severely damage the stem.
Next, we place the cutting in a jar of water for a day.
Can I also add? heteroauxin tablets per liter. It helps to speed up rooting.After the expiration of the time, we plant the stalk of the flower in a previously prepared pot. Do you want to extend the life of the flowers presented in the bouquet?
Few know how to plant roses from a presented bouquet. It turns out to be simple enough. Only if we are not talking about Dutch roses, it will not work to root them.
Therefore, do not waste your time. For the plant to take root well, choose a cutting that has at least two buds.
Cut the thorns with pruning shears, split the lower part of the stem with a sharp knife, then dip it for a while in a special solution that stimulates the growth of roots, and plant it in the ground. Remember that the ground should be rich in humus.
Cover the planted stalk with a plastic bottle. The splendor of the bush will depend on the distance from each other you plant roses. The distance should not be less than 20-25 cm.
The first few years, the buds must be torn off. This will give you a luxurious rose bush.
How to care for rose seedlings
This begs the question: when is the best time to plant roses? The most optimal planting times are spring and autumn. But where you can plant roses depends on the condition of the soil. Loamy soils are best suited for successful development.
Be sure to enrich it with humus. The soil for planting roses should be easily permeable to moisture and air. Chernozems rich in trace elements are also great; remember to water the plants periodically.
In dry weather, it is best to do this twice a day: in the morning and in the evening. Fertilizing is also desirable twice a season. Buds that have withered should be cut off with a pruner or a sharp knife. If spots appear on the leaves, then a fungal infection may be the cause.
In this case, be sure to cut them off and burn them. Quite often, grafted seedlings develop wild shoots. If you leave them, the plant will eventually cease to resemble a gorgeous bush. Therefore, it is recommended to delete them.
Make sure that the soil is not clogged. Since weeds are quite a serious danger to roses.
Therefore, there is nothing difficult in caring for seedlings, the main thing is desire. Propagation by seeds is used exclusively when growing polyanthus flowers. To do this, you will need: for soil - sand, peat, turf and humus; "Epin-extrat" and, of course, rose seeds. It is recommended to start preparing seeds at the end of winter.
Video: how to plant roses
The only thing with which some difficulties may arise is how to plant roses with seeds. After all, we often plant a ready-made bush purchased at a flower shop. For reference, we recommend watching a video on how to plant roses.
Flowers in landscape design
The beauty of any variety is most vividly revealed with a successful choice of companions for it. The classic landscape design is a combination of undersized conifers with various varieties of roses. Both groups of plants coexist perfectly and do not oppress each other.
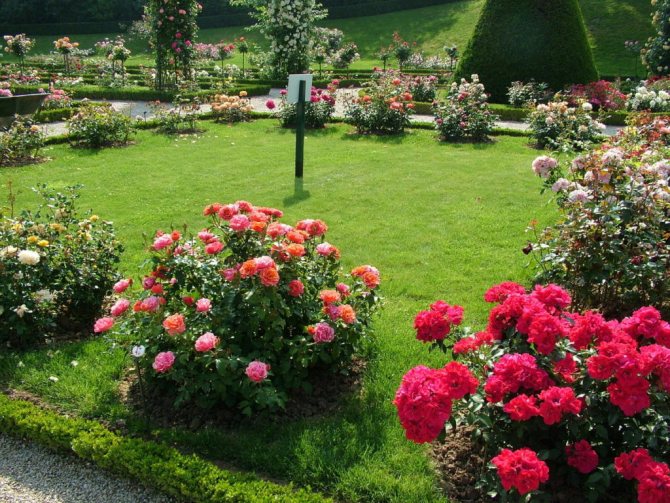


Rose bushes in landscape design
Single bushes look exquisite against the background of an even green lawn. If there is a goal to get a real rose garden, then it is worth planting only low-growing ground covers that serve as a background.
Important! When choosing a place for each rose bush, it is necessary to take into account its exactingness to watering, lighting, soil, as well as resistance to wind and rain.
Preservation of seedlings and cuttings of roses in the autumn prikop
If the rose seedlings were purchased late in the fall, and the weather does not allow the roses to be properly planted in a permanent place in the open ground, then it is better to abandon the autumn planting and postpone the planting to spring.
It is much safer to cover the roses obtained in late autumn in a garden "trench" - in a hole or trench 60-80 cm deep. A pile-up for winter storage of roses is made in a suitable place in the garden, where thawed and ground waters do not accumulate.Prepared rose seedlings must be laid in a trench at an angle of 45 degrees. Then evenly cover the roots of the roses with earth, and the stems with sand (do not allow voids, especially in the area of \ u200b \ u200bthe roots). A mound of earth formed at the site of a burrow of seedlings to protect stored roses from melt water can be covered with roofing material or a whole film (about 2x2 m). With the onset of stable frosts, additionally cover with spruce branches and snow. In this way, it is possible to successfully preserve in a garden pit and seedlings of roses, and cuttings of roses harvested in the fall.
Please note that the storage conditions for rose seedlings in the cellar differ significantly from the garden prikop. Excessive heat in the cellar can lead to the beginning of the growth of roses in February. In addition to excessive heat, the cellar is a powerful source of fungal diseases and mold. Storage of rose seedlings in cellars is carried out at a temperature of 0 .. + 2 degrees and a relative humidity of 80 percent.
Garden queen breeding
There are not so many ways to breed roses. But the desire to have as many of these undeniably beautiful and diverse plants as possible on the site is so great that gardeners strive to master them all and to the maximum extent. Here is a list of ways to propagate a rose:
- Budding. On the bark of the plant trunk, close to the ground level, a T-shaped incision is made, into which the bud of the cultivar is inserted, and then fixed with a film. The graft can use the developed root system of the rootstock. This operation is not difficult, but requires some experience.
- Seeds. This method is used extremely rarely due to the fact that the result has to wait a long time, and there is no certainty that it will turn out to be positive. And the germination of rose seeds leaves much to be desired.
- Layers. Shrub and climbing roses are propagated this way because they have long and strong stems. The shoot of the plant in the lower part is cut for 8 cm, a chip or a match is inserted into the cut. The cut part of the shoot is placed in the ground and fixed, and its free tip is tied to a peg. The rooted shoot is cut off from the parent bush.
- Cuttings. The method is good in that roses rooted in this way will not give wild shoots. The stalk is part of a strong shoot. It is cut next to the leaf bud and germinated using rooting stimulants. After the root appears, the rose can be planted in the ground.
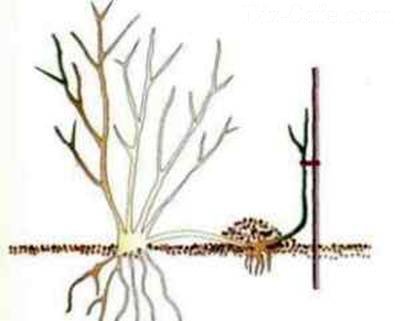

The layering method is good to use only for propagation of plants with long stems, which are used to create a new rose bush.
Watering, feeding, mulching
In spring, roses are rarely watered, but abundantly. Since the heat has not yet come, there is no need for frequent moistening of the soil. If waterlogging is allowed, root rot may occur. It is best to water the bushes in the evening, after sunset. As the soil becomes drier, you should water more often. In dry climates, it is recommended to install a spray irrigation system. In summer, plants are watered 1-2 times a week, depending on the weather.
Organic fertilizers are optimal for feeding young bushes that were planted in the fall: bird droppings, mullein.
Top dressing is applied in liquid form immediately after watering. If you fertilize the bushes dry, you can burn the roots. In the future, you can use mineral dressings, which include: magnesium, potassium, phosphorus, nitrogen and iron. The manufacturer produces these fertilizers both in liquid and granular form. It is enough to fertilize adult plants twice a year - immediately after spring pruning and after the first wave of flowering.
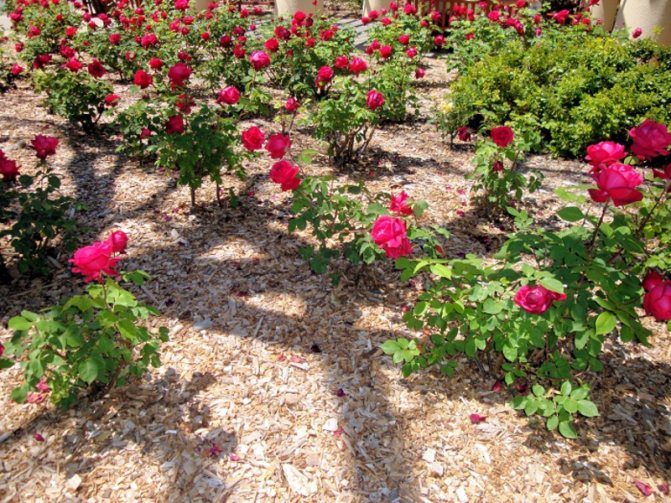


Mulching simplifies plant care and helps in solving many problems... Mulch is poured under the bushes after the first spring feeding. With its help, the required level of moisture in the soil is maintained, the growth of weeds and the leaching of fertilizers are prevented.Mulching preserves the loose structure of the soil, preventing the formation of a hard crust, protects the roots from overheating in the heat. Mulch can be of both organic and inorganic origin. For these purposes are used: bark, sawdust, hay, gravel, pebbles. Re-mulching is carried out at the end of summer.
Landing
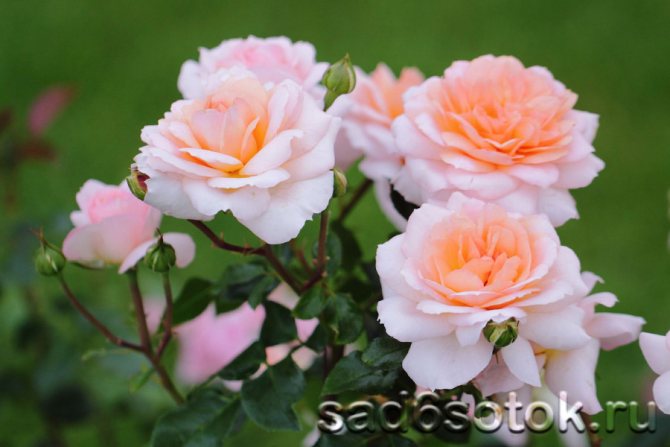


Planting roses. Park rose variety Schloss Eutin (Schloss Oytin).
Roses can be planted in spring and autumn, but for residents of the middle lane, experts still advise planting in spring. Roses prefer warm, sunny areas, while it is desirable that they are not in the sun. The ideal option is to plant closer to home, which will also protect the plant from cold winds. As for the soil - it is good if it is neutral, roses do not like acidic and alkaline earths. If there is no choice, you will have to lime the too oxidized soil, and mix the alkaline one with peat.
First you need to prepare holes of suitable size, so that the roots of the seedlings fit freely. If planting is carried out in spring, the dug soil should be mixed with compost; organic fertilizers are not required for autumn planting.
Lay a drainage layer of broken brick, pebbles or gravel at the bottom of the hole. Fill over the drainage with a half-meter layer of soil and fertilizers. Slightly trim the roots of the seedlings with pruning shears and straighten them along the dug hole. Sprinkle with fertile soil on top, water and tamp well. Do not forget that the grafting site or the root collar must be deepened. When planting in autumn, mulching the seedling with cut grass will be useful.
Helpful advice from professionals: planting and grooming:
- When choosing the location of roses in a summer cottage, be sure to take into account their variety and the height of an adult plant. Depending on this, make gaps between the seedlings when planting;
- If you want to create a composition of rose bushes of different colors, choose related varieties that reach the same height and bloom at the same time;
- To decorate gazebos, fences and other garden buildings, use climbing varieties of roses - they are quite easy to care for and plant.
Rose varieties
There is a huge variety of these plants. Let's consider the most popular varieties.
Large-flowered roses
They have the highest decorative qualities. These are single magnificent flowers blooming on a straight stem. Large-flowered rose varieties often have a wonderful scent.
Recommended varietal variety:
- Casanova - tea color, flowers are large, very fragrant, has shiny leaves. Vigorous variety, disease resistance - medium.


- Dame de Coeur - ideal for a gift to a loved one, has beautiful fragrant red flowers. Height - 80-120cm. Bloom - from June to October.


The following large-flowered varieties are also known:
- white and cream - Pascal, Mounte Shasta, Papt John XXIII;
- red - "Mr. Lincoln", "Dame de Coeur" (Lady of the Heart), "Papa Mayland";
- two-color - "Cronenburg", "Neue Revue", "Die Welt";
- purple - "Blue Moon", "Charles de Gaulle";
- orange - "Flora Danica", "Ave Maria", "Lady";
- yellow - "Peace", "Casanova", "Landora".
Multicolor roses
Often used in home gardens and increasingly in urban greenery. Flowers are smaller than large-flowered species in size, but they are more numerous, forming massive clusters on the shoots. Flowers often have a pronounced aroma, bloom very profusely and repeat flowering.
Popular varieties:
- Bonica 82 is a very lush blooming cultivar. Flowers of pale pink color are numerous, collected in bunches. They grow quickly, take root easily. Disease and pest resistance is average.


- Queen Elizabeth "Queen Elisabeth" - has flowers of intense pink color. Full, long-stemmed roses are ideal for cutting. The variety is very popular as it is disease resistant and has strong growth.


The following multi-flowered varieties are also known:
- white and creamy - "Swany", "Schneewittchen";
- red - "Pashta", "Lily Marlene", "Nina Weibull";
- orange - Samba, Rumba;
- pink - "Queen Elizabeth", "Kalinka", Bonica 80;
- yellow - "Frisia", "All Gold", "Marselisborg".
Ground cover roses
As the name suggests, they quickly cover the soil with shoots. It is a low, very stable group, does not freeze, does not get sick, does not require maintenance. Roses are decorative thanks to the abundant, slightly more subtle flowers that look very natural and charming.
Popular varieties are:
- Max Graf is a profusely flowering cultivar that has solid, deep pink flowers with a clearly visible core. The variety is valued for its high resistance to frost, air pollution, and disease.


- Fairy Dance is red flowers with different shades. The variety blooms so profusely that the shoots bend under the weight of the flowers. Plants are frost resistant. Grow well in urban areas.


The following ground cover varieties are also known:
- white - "Snow Ballet";
- red - "Mercury 2000";
- pink - "Sommerwind", "Weneda";
- yellow - "Sommermond".
Groundcover roses are easier to care for, grow easily and require less attention than other varieties. Plants are frost-resistant, so unlike other garden roses, they don't need to be protected from it.
The bushes do not require heavy pruning - every spring only diseased and damaged shoots should be removed - or wilted flowers should be removed (in the fall, the bush is decorated with numerous coral fruits). In addition, they are usually more resistant to disease than other varieties.
Landing... Seedlings are planted in spring or autumn in dug up soil, to which manure or compost (4-8 kg / m²) is added. You can also add fertilizer for roses (recommended by the manufacturer). Most varieties in the garden are planted in the amount of 4 pieces / m², but there are also vigorous varieties that need 2 pieces / m² (for example, "Max Graf", "Weisse Immensee") and weaker varieties, which should be planted in the amount of 5 -6 pieces / m² (for example, "Beautiful Fairy", "Fairy").
Climbing roses
This group is growing faster and stronger. Climbing varieties require reliable support in the form of supports to which the shoots are attached. These varieties often repeat flowering and are very aromatic.
Cultivars worth noting:
- Flammentanz is a highly aromatic cultivar with scarlet red flowers. Strong, fast-growing shoots require support, reaching a height of 5m.


- New Down is a very valuable variety, one of the oldest climbing roses, has flowers in pale pink color, which have a very pleasant aroma. Requires reliable support. The variety is very resistant to disease.


- Rosarium Uetersen is a full-bloom variety with an intense pink color and a pleasant aroma. The bush reaches a height of about 3 meters, it is recommended for individual plantings. The variety is resistant to disease and frost.


The following popular climbing varieties are also known:
- white - "Snow White", "Elf";
- red - "Flammentanz", "Baikal", "Amadeus", "Dortmund";
- pink - "New Dawn", "American Pillar";
- yellow - "Golden Rain", "Goldstern".
These varieties belong to the group that requires more time and patience. Sometimes you have to wait 3-4 years or even longer to get the effect of a blooming wall. Plants can climb a pergola or tree by clinging to thorns, however, sometimes they need help in the form of a garter to a support.
Climbing varieties tend to have smaller flowers than large-flowered varieties, but the newer varieties are also characterized by fairly large flowers. The assortment has recently expanded significantly, so it is easy to find an option in almost any color.


Climbing varieties are less demanding on the soil and relatively resistant to frost, but more vulnerable to damage by pests on leaves and shoots. Climbing varieties are best planted with an existing support such as a trellis or pergola. They can also be planted in a wooden pot with a trellis, in which they will be presented very exquisitely.


It is very important to carry out correct and timely pruning. For varieties that bloom once a season, pruning should only be done after the shoots have faded.
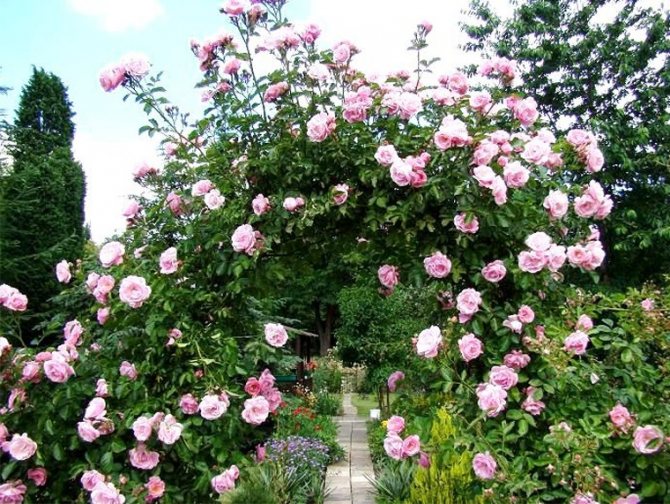


Ramblers with tough shoots, characterized by smaller flowers, are pruned every year, removing the whitened shoots and the entire mass of thin long branches growing at the base of the bush. To speed up the growth of the bush, we can only cut off half of the two-year-old shoots that will fill in the gaps. Heavy pruning in the lower parts of the bush is especially necessary for some varieties (such as Dorothy Perkins) because the plants are easily attacked by powdery mildew, a rose disease that develops when leaves remain wet for a long time.
Climbing rose varieties that repeat flowering do not require as much pruning. It is enough to remove the oldest or very thin shoots thickening the crown every 2 or 3 years. Frozen stems or those damaged by disease should be removed every spring.
What beginners need to know to grow bush roses
One of the most popular species with over 200 varieties. It is found even in the wild.
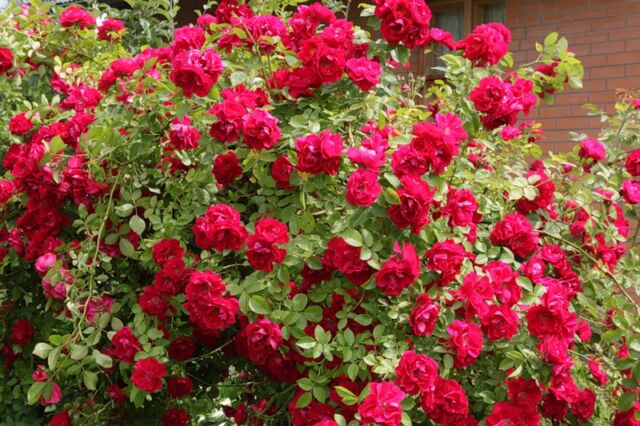


They are fairly easy to grow and care for. Their beauty is amazing, because the fluffy bushes are covered with numerous bright buds that exude a light, incredible aroma.
Depending on the selected variety, the shape of the bush can be different. There are pyramidal, straight, spreading shrubs. They are low, up to 80 cm, flowers can be small and large.
They need to be grown in a well-lit place. At the same time, the seedlings must be kept in partial shade for the first 14 days. After planting, water it after 2 days. In this case, make the distance between the bushes at least two meters. After all, they are spreading and should not interfere with each other. In addition, this will protect the bushes from the spread of diseases.
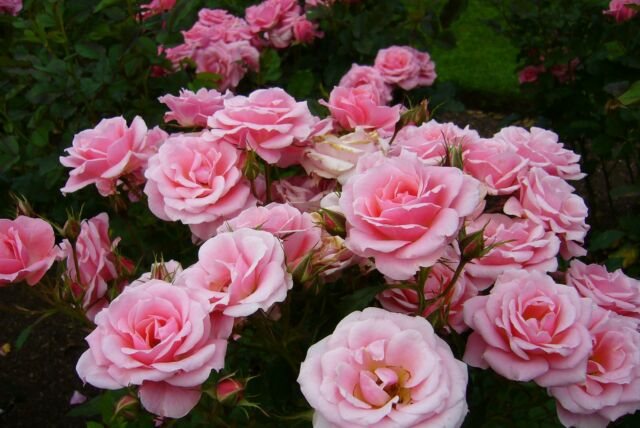


Common varieties include:
- Red Lex. Sprawling bush, high enough, up to one meter. It blooms with scarlet flowers of small size, peony-shaped, and velvet petals. Differs in abundant, continuous flowering, which lasts the entire period of vegetative growth.
- English. A classic variety, the bush reaches a length of 150 cm. Beginning in June, flowering lasts for 30-40 days. The color is varied, mostly calm, neutral tones, but there are also bright yellow buds. The plus is frost resistance, because this variety can not be wrapped up for the winter.
- Freesia. Beautiful, bright flowers that are yellow in color. They have a short, spreading bush shape. They are distinguished by increased resistance to diseases and fungi.
- Iguana. Medium-sized plant, reaches 60 - 65 cm in height. The foliage is medium. Red buds with copper edging, velvety, rounded petals.
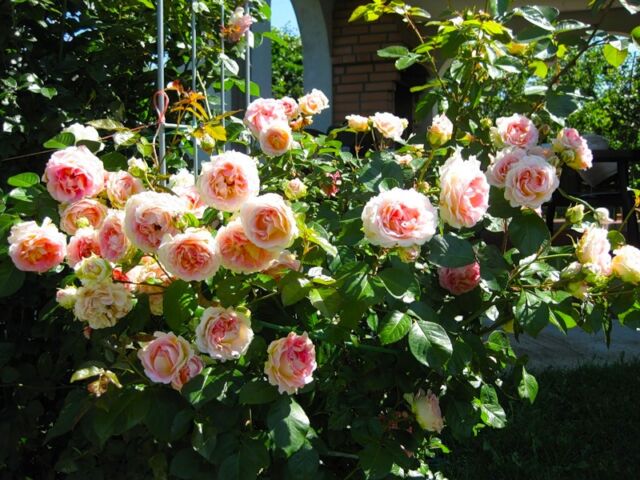


Watering must be done carefully so that water does not fall on the leaves, right under the root. After all, this can lead to the development of fungal diseases. 10 liters are enough for each bush, the frequency is 1 - 2 times a week, depending on weather conditions. With proper watering, new shoots will grow and bloom in a timely and abundant manner. But closer to autumn, the frequency of watering must be reduced so that new shoots do not appear, because there is a risk that they will not get stronger before the onset of frost.
Top dressing should be done 3-4 times during the summer. The first is at the beginning of vegetative growth, the next is during the formation of buds, the third is after the end of flowering, and the last is in the fall, before the onset of cold weather.
Also, bush roses need support, because they have a branched structure. It is recommended to tie the bush to the installed support. Especially the risk of branch breakage increases at the time of rains and strong gusts of wind.



























