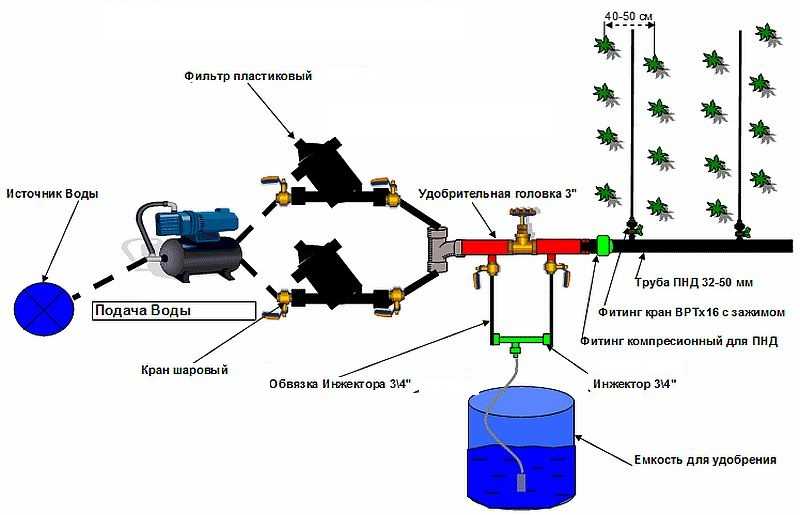
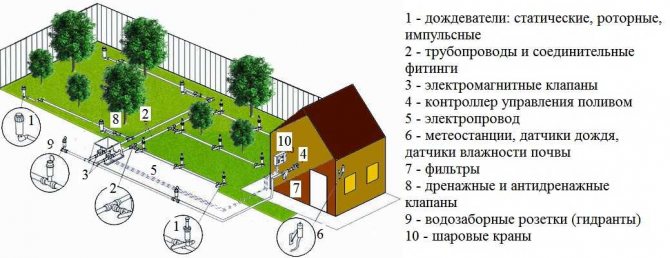
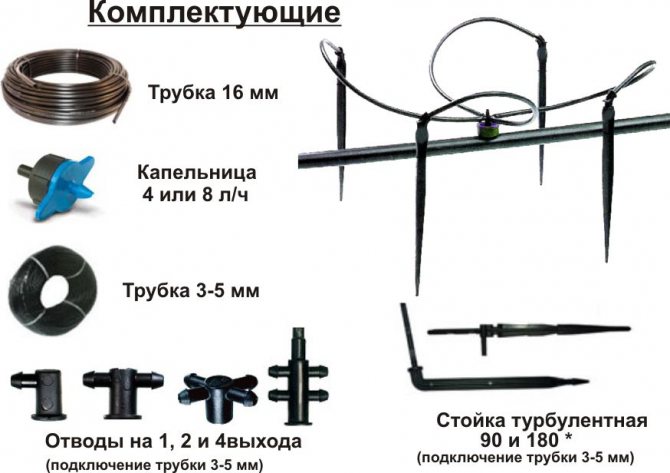
For the gardener, a garden and a vegetable garden should be economically viable. It is profitable to plant, grow vegetables, fruits when the harvest is of high quality in a short time. All this will be ensured if watering the garden is properly organized. The high quality of vegetables and fruits is their juiciness, freshness, and pleasant taste. With a lack of water in the soil, it is impossible to obtain high quality vegetable products. Vegetable crops have root systems of varying strength. The irrigation rate for each plant, the methods of watering, the number of waterings per season and when, during what period of the growing season of the vegetable plant, watering will be most useful depends on this.
Among vegetable crops there are biologically drought-resistant species - watermelon, melon, beans, as well as species that adapt to insufficiently moist soil - tomatoes, carrots, parsley, beetroot. However, with a shortage of water, their harvest is small, and the taste of the products is unsatisfactory.
With a lack of water in the soil, low air humidity, the growth of seedlings and seedlings is delayed, changes in the growth and development of vegetable crops unfavorable for the gardener occur. So, in cucumbers, tomatoes, peppers, eggplants, flowers and ovaries fall off. Lettuce, cauliflower, radish, radish are thrown out ahead of time, these crops, as well as celery, potatoes, kohlrabi, become a rough food part. Onions, garlic in the phase of 3-4 leaves weaken the growth - the bulbs are chopped.
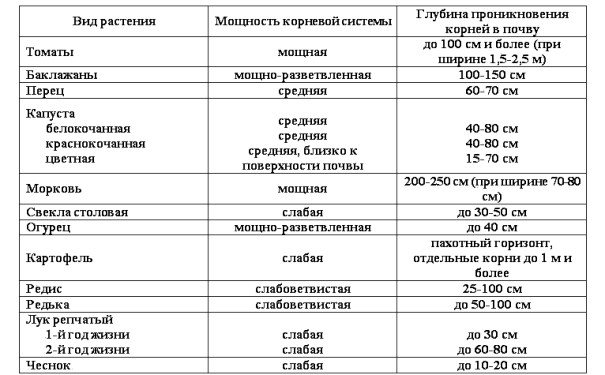
The power of the root system of vegetable crops is the basis for calculating the irrigation rate
The need of vegetable crops for moisture, like other plants, depends on the conditions of the external environment - air temperature, soil, their humidity, illumination, wind strength. With an increase in the intensity of these factors, the transpiration (evaporation of water) of plants increases, respectively, the absorption of water from the soil increases.
In addition to the reaction to the intensity of meteorological conditions, the need of plants for moisture is determined by their biological characteristics (see Table 1).
Table 1. Development of roots in different types of vegetable crops
The following groups of cultures are conventionally distinguished:
1st group. Includes heat-resistant, air-drought tolerant species: watermelon, melon, pumpkin, vegetable corn, beans.
2- group. Species with a well-developed root system, which allows them to use a large volume of soil to absorb water: cucumbers, tomatoes, eggplants, peppers, carrots, beets, parsley, potatoes, beans, peas. At the same time, rapid, powerful development of the root system, in a relatively shallow soil layer, abundantly moistened with regular watering, contributes to active growth, the formation of a yield in these species. This should be taken into account when opportunities are limited.
3rd group. Species that are unable to extract water from the soil in large quantities due to insufficiently powerful development of the root system: cabbage, lettuce, radish, radish, onion, garlic. Moreover, the first four species consume a large amount of water for transpiration (evaporation of water by plants).
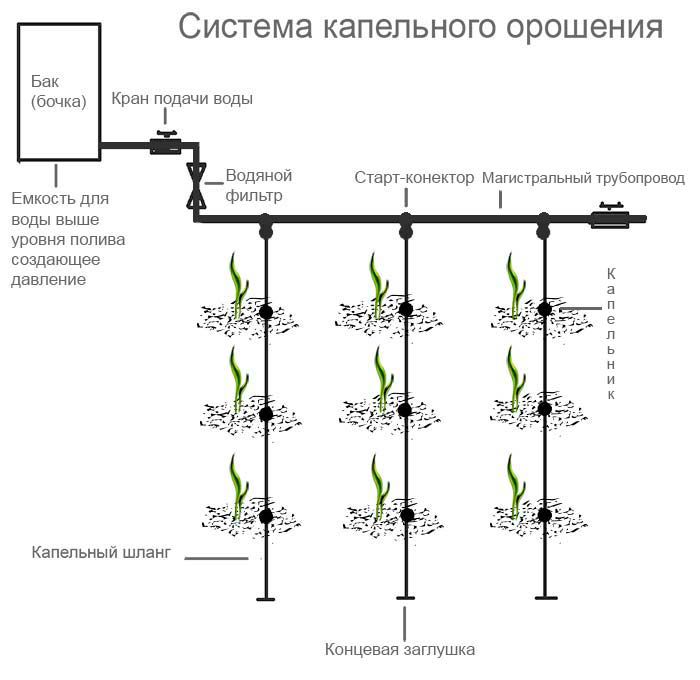
Moistening the soil with plastic bottles


Gardeners and gardeners use the following options for irrigating crops: using hoses directly between rows of vegetables and other plants, imitation of sprinkling with special spray nozzles.With all the advantages of these methods, they have a huge disadvantage - a large liquid consumption, which, when a water meter is installed, results in additional financial costs.
To prevent such a sad development of events, gardeners and gardeners use plastic bottles, flasks and other plastic vessels. Economical watering with the help of handy plastic containers can significantly reduce water consumption and material costs. The most effective bottle volume ranges from 2 to 5 liters. With the drip method of irrigation of the garden and vegetable garden, there is no need to often visit the summer cottage.
Optimum humidity, irrigation rates, quantity and time of watering vegetable crops
For vegetable crops, soil moisture, with some exceptions, is maintained at a level not lower than 70% of the maximum field moisture capacity (FEL), the optimal level as a percentage of FF for vegetable crops is as follows:
Tomatoes:
- early - 80%,
- medium - 70-80%,
- late - 60-80%,
Pepper
- early - 80%,
- late - 80%,
Potatoes
- before tuber formation - 70%,
- during tuber formation - 80%,
White cabbage - 80-90%,
Cucumbers - 85-90%,
Onions - 80%,
Watermelon, melon, pumpkin - 70%.
The specified soil moisture is maintained by periodic watering, the rate of which is determined depending on specific conditions:
- Water-charging irrigation is given at a rate of 100-300 liters per m2.
- Presowing or preplanting - give at a rate of 50-80 liters per m2.
- Pre-planting - when planting seedlings, it is 0.5-1.0 liters of water per hole. Depending on weather conditions, pre-planting watering is done at small rates - 10-20 liters per m2.
Vegetative watering of the garden is carried out during the entire period of growing plants before harvesting. In different soil and climatic zones, 1-2 to 15-20 waterings are carried out with a rate of 10 to 80 l / m2. In the daytime (hottest) time of the day or in the evening in the southern regions, refreshing watering is done in small portions of 2-4 l / m2.
Approximate norms and the number of vegetative irrigation of vegetable crops for the southern zone of the European part of Russia are given in table. 2.
Table 2. Irrigation rates, number and time of watering vegetable plants and potatoes
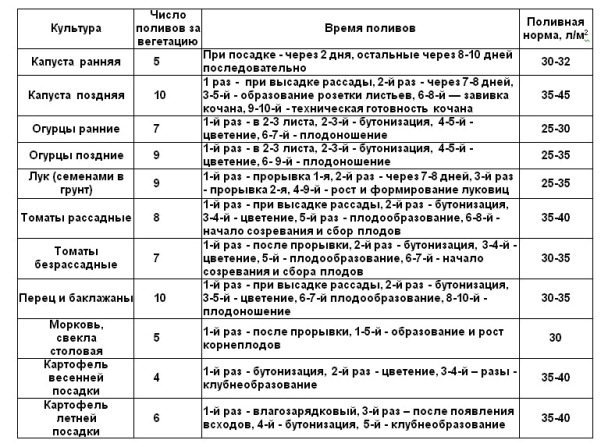

In years with insufficient moisture, the number of irrigations correspondingly increases by two or three. In addition, in the hottest time, it is recommended to carry out refreshing watering with a rate of 5-7 liters per 1 sq. m.
We draw the attention of readers: the period of watering must be determined before the plants show signs of insufficient water supply: wilting of leaves, residual water deficiency, shedding of fruits, ovaries. In this case, the loss of the crop cannot be replenished.
Table 2, the watering time is focused on the periods of the plant's greatest sensitivity to lack of water. Additional watering or its cancellation should be placed between these times.
Watering the garden is carried out depending on the specific conditions. Plants should be watered in the evening (in hot weather) or in the morning (if the nights are cold). It is better to finish the evening watering by 19 o'clock in the evening, so that the moisture that has got on the leaves evaporates by night.
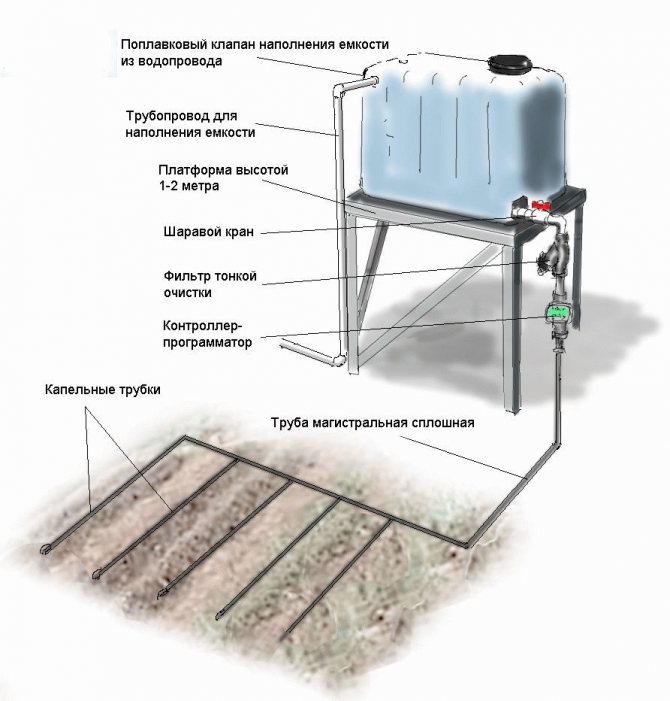
Lightweight construction for metered irrigation


In such products, no auxiliary means are used to provide moisture to the root system of plants, but only containers made of polyethylene and an unnecessary ball refill from under a fountain pen. The technology for preparing a miniature system for drip irrigation is as follows: - take the used ball rods from the fountain pens and take out the drawing element itself - the ball; - clean the cavity of the rod from the remnants of the writing composition with a solvent; - plug one end of the rod. Any thin wooden stick will play the role of a cork. - at a distance of 4 millimeters from the plug in the rod, make a hole up to 0.5 millimeters.
This diameter is not a fixed size once and for all and, if necessary, it can be increased. However, the owner himself empirically sets the desired hole size. For vessels with a capacity of 1.5 to 2 liters, this diameter is usually less than the diameter of the ball bar. An airtight paste can be used to satisfactorily seal the hole.
Ways to water the garden, how to water the beds
Furrow and check irrigation
Watering vegetable plants in a small area of the garden is carried out mainly superficially, with running water. Water is distributed over the entire surface or over part of the soil surface. Surface irrigation can be done by furrows or by checks. In the conditions of an amateur garden, where there is almost no possibility of a good leveling of the area, irrigation along furrows or checks is very suitable from the point of view of correct irrigation, uniform distribution of irrigation water, especially on light soils.
Ridge decoration
The combs are designed as follows: with a hoe, a hoe, manually or with a plow, they cut the furrows, the distance between which depends on the vegetable crop that will be planted in this area. Most often it is 60-70 cm. In this case, small earthen ramparts are formed between the furrows - they are called ridges. After that, transverse grooves are also cut with a plow or hoe with a distance of 5-6 m from each other. These transverse furrows will be used for irrigation, ridging. Every second or every second or third ridge is cut from the inside (at both ends) so that water can circulate during irrigation (Fig. 1. A). The ridges are leveled, the furrows are first compacted, then leveled. Thus, they make out the area for better water movement.
The combs are suitable for growing many vegetable crops - tomatoes, peppers, eggplants, cabbage, carrots, parsley, others - on heavy soils, especially in rainy spring.

Fig. 1. Organization of combs and checks
Registration of checks
Checks are flat rectangular or square areas, fenced with ridges (earthen ridges). The plot is divided into beds 5-6 m wide, limited by irrigation furrows. Rectangular checks are placed from one irrigation furrow to another with a width of 1.2 to 1.5 m. Square checks are drawn up by dividing each bed into 2 parts with a comb, notching with transverse ridges every 2 m.This gives almost square checks with dimensions of 2.5 x 2 m. Checks are used for growing many vegetable crops - pepper, Kaba onions, leeks, cucumbers, etc., also on light sandy soils (Fig. 1. B).
Watering the garden from a watering can
It is usually recommended to use a watering can when growing seedlings in greenhouses or in open beds. The irrigation rate depends on the weather, the characteristics of the cultivated vegetable crops, soil properties, the state of seedlings, etc. Practically, to moisten the soil layer in a greenhouse 15 cm thick, on the soil, per 1 sq. m you need to pour out 40-50 liters (4-5 lei) of water. On open ridges, water consumption increases, since the soil layer dries out to a greater depth, the roots of plants are located deeper, which can be determined empirically. If the soil is very dry, you first need to water it lightly from a watering can, after a while give the required remaining amount of water. Watering rates sometimes require watering multiple times at intervals to allow the soil to absorb moisture. With a one-time application of the irrigation rate, moisture will not have time to be absorbed by the soil, which will lead to stagnation of water on its surface or to loss of moisture as a result of surface runoff. You can water not the entire garden bed, but the root zone of the plants.
Regulation of relative humidity (sprinkling)


Vegetable plants have different requirements for the relative humidity of the air.Some of them, for example, cucumbers, cauliflower, lettuce, spinach, require a high relative humidity of 80-95%, while others, such as tomatoes, watermelons, melons - a lower 50-60%. However, some combinations of air humidity and temperature create conditions for the appearance of diseases and pests, which requires the regulation of these factors. By increasing or decreasing the number of watering the garden with running water, you can regulate the relative humidity. Refreshing sprinkling irrigation of the garden also has a beneficial effect on plants due to the increase in air humidity.
In private gardens, it is impossible to carry out sprinkling as it is done in the fields, but here, using a hose with different tips or by means of an electric pump, irrigation pipes of the appropriate length, with nozzles at the ends, you can achieve the effect of sprinkling. By sprinkling irrigation, it is easier to provide an optimal irrigation rate, as it helps to reduce fluctuations in the water content of the soil or plants. This is of great importance for vegetable crops such as peppers, eggplants, cucumbers, beans, potatoes, root crops, etc., which do not tolerate waterlogged soil. Sprinkling has a particularly good effect for all varieties of cabbage (white cabbage, cauliflower, Brussels sprouts, Savoy cabbage), spinach, lettuce, head lettuce, etc. Sprinkling of vegetable plants should be carried out in calm weather, as the wind falls in large drops on the plants. If it is necessary to conduct sprinkling in the wind, then the stream of water must be oriented in the direction of the wind. The most suitable time for sprinkling is in the afternoon, in the evening, at night. This is especially important when sprinkling peppers or cucumbers, as it prevents burns or disease. After fruit formation, tomatoes can only be sprinkled at night or early in the morning to prevent the fruit from cracking.
The most primitive artisanal irrigation options
Instead of the two proposed methods, it is possible to use an absolutely simple and reliable method - to pierce a hole in the container itself. In this case, it is necessary to take into account that the minimum hole diameter is desirable, and it must be made at the bottom of the bottle. The installation of the bottle also involves two solutions: the first - near the root system of the plant in the ground, the second - in a suspended state on a wire or twine above the plant. For irrigation without your own effort, use plastic flasks with absolutely no action.
Fill the containers with water, unscrew the cap and place the bottle near the stem of the plant. A certain period of time will pass and the water runs out, then refill the bottle. This process is quite simple and effective. Such methods of watering garden vegetables are also used using various polyethylene containers. Make a hole at the bottom of the bottle up to 0.4-0.5 millimeters in size to allow air to pass through, and pour liquid into the container. Then turn the flask upside down, fix it securely in the ground near the stem.
Try not to touch the roots of the vegetables. Containers are used in a completely unexpected and original way. For example, take a plastic bag and bake a small hole in it. Next, pour in the liquid, tie a bag and place it on the ground, near the roots of the plant. The principle of operation is similar to bottle irrigation - the liquid evenly and gradually comes out of the bag and saturates the soil around the root structure. If there is no need to perform metered irrigation, and the only task is to maintain sufficient air humidity, then everything is much simpler.
But this remark applies only to closed greenhouses and greenhouses. Place open containers filled with water between rows and around the perimeter of the premises.This method is used in the absence of a gardener in the country for a long time. High humidity guarantees the plants nutrition for a certain period of time and protects them from accelerated drying.
Watering young seedlings of fruit trees in the garden
Fruit trees for the garden
Saplings immediately after planting in a permanent place need watering every 2-3 days for the first two weeks. Then the frequency of moisture supply is reduced to 1 time per week. At the end of summer, they give a break so that the young wood gets stronger and the tree can survive the frosts. The soil around the stems is kept under a layer of mulch.


The soil around the stems is kept under a layer of mulch.
During the period of active growth of young shoots on the plantings of the first year, the bole is formed. All leaves and shoots below the 60 cm mark are removed. Without waiting for next spring, future skeletal branches can be formed.
Grape seedlings are watered frequently, every 3-4 days. It is better to plant them on a dark film. Under such mulch, moisture is well retained, despite the strong heating of the coating. Seedlings of pomegranate, lemon are watered every 5-6 days, a young coffee tree - every 3-5 days.
Sprayers from polyethylene containers
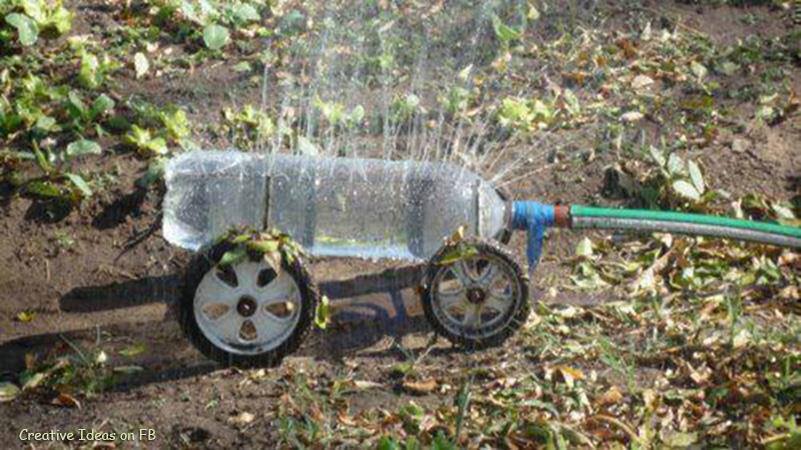


In order to make a homemade sprinkler, you need to find a plastic bottle with a lid on the farm. Then measure the diameter of the thinnest element of the handle, make a hole in the vessel with a slightly smaller diameter and, shortening the polyethylene handles to 7 centimeters in length, insert into each individual hole. Take the garden hose adapter and insert it into the hole in the container lid. It must be fixed with silicone glue. Apply glue also to the threads of the neck and tighten the cap.
After connecting the system through a hose to the water supply, turn on the water supply. Existing drip irrigation methods organize the supply of liquid with minimal consumption and directly to the root structure, supplying garden crops with constant moisture. This method of dosed irrigation, when used in greenhouses, does not allow active growth of weeds, does not allow the soil to dry out, reduces air humidity, preventing the formation of mold and other putrefactive processes.
Hoses and reels
The ideal choice for the garden is a hose. It will save time spent on watering and will make it easy to change the watering point. For trees over 3 years old and shrubs at any age, it is perfect. The hose does not wash out the roots and promotes abundant watering. The choice of watering point and all of the above makes the hose the best assistant for the gardener. For more mobility, it is worth purchasing a reel on wheels. Firstly, this will simplify the transfer of the hose from place to place, and secondly, during storage, the hose will take up less space.
The Foresta brand offers hoses made from the finest materials that will last you for years. There are also reels on wheels, they are made of durable plastic combined with metal.


Spray guns and nozzles
The main purpose of the spray guns and nozzles is to make it easier to moisten the soil. There are many different guns and attachments, they differ in several ways:
- Manufacturing material;
- Range of action;
The simplest nozzle is a watering gun. There are two main types of guns: with a multifunctional tip and a tip in which it is possible to regulate only the water pressure. The gun can water both ordinary flower beds and shrubs and trees.