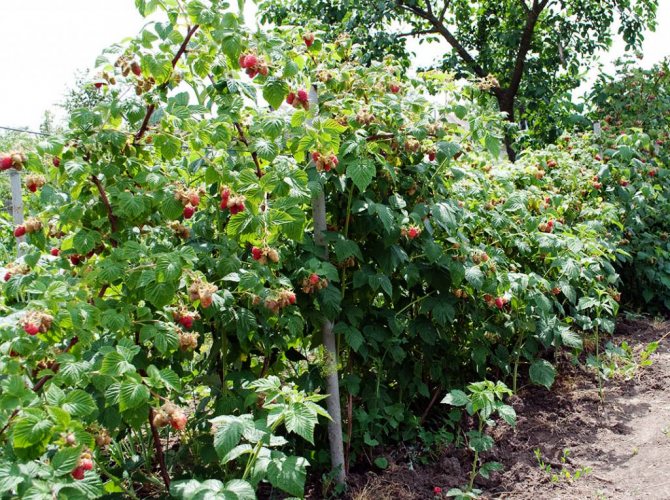
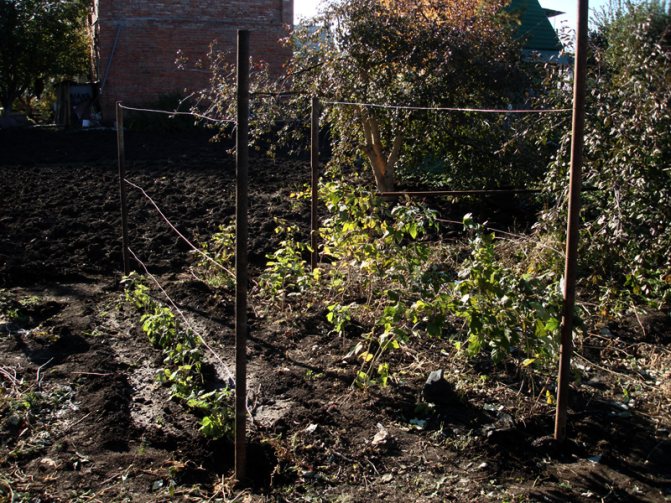
In the garden, I have quite a few varieties of this berry. They all differ in their characteristics: the height of the bush, maturity and taste. The latest acquisition is the raspberry Pride of Russia.
Although the variety is not remontant, but I pick the berries several times a season, the bush gives a good harvest. I want to share information about the main distinguishing features of this shrub, and how to plant it correctly. For an illustrative example, I offer photos and videos.

Description of the variety Pride of Russia
The pride of Russia is a non-repaired variety with annual fruiting. The bush is medium in size, compressed type, compact and powerful. The height of the stems is 1.6–1.8 m. Forms 7–12 replacement shoots and 5–7 root suckers. Annual shoots are strong, pubescent, with a rosette of leaves at the tops, thorns and wax coating are absent. In winter they acquire a gray-brown color. Fruit branches are medium in size, with 20-30 berries on them. The leaves are large, deep dark green, crenate. A mature leaf blade acquires shine. Raspberry blooms with white flowers, which are collected in racemose inflorescences.
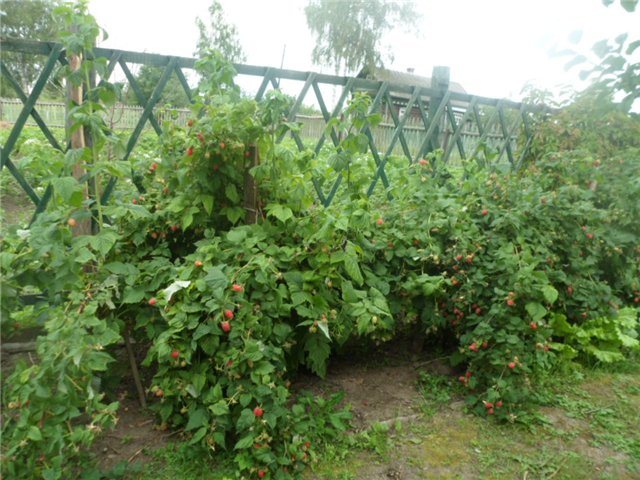


A medium-sized raspberry bush of the Pride of Russia variety develops quite quickly
The fruits of this variety are large, dark red, elongated cone-shaped. They have a velvety surface. The average berry weight is 6-10 g. The pulp is juicy, soft, sweet with sourness. Homogeneous small drupes are tightly linked, the separation is dry. The seeds are small, almost imperceptible to the taste. The aroma is weak.
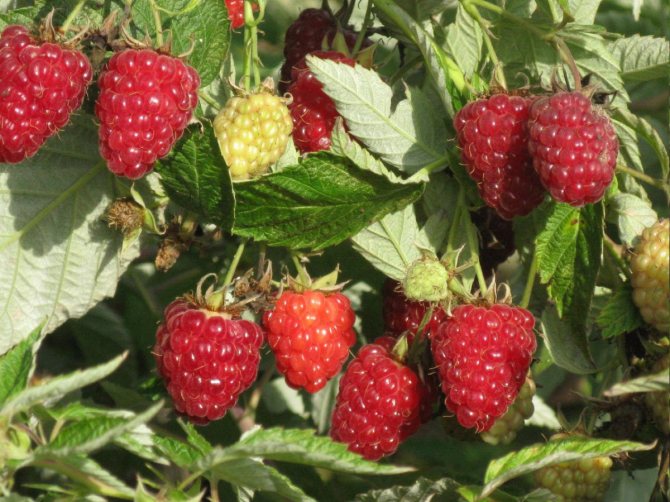


The fruits of the Pride of Russia variety are distinguished by a sweet and sour taste and a light raspberry aroma.
Advantages and disadvantages
The Pride of Russia variety has many advantages, among which the following can be distinguished:
- tasty, large fruits;
- high winter hardiness (tolerates low temperatures within –30 ° C);
- resistance to fungal diseases (anthracosis, botrytis, chlorosis);
- berries do not crumble when ripe;
- high annual yield.
The few disadvantages of the variety include:
- low sugar content of berries;
- exactingness to growing conditions;
- dependence of the quality of the crop on additional fertilizing;
- hypersensitivity to lack of moisture.
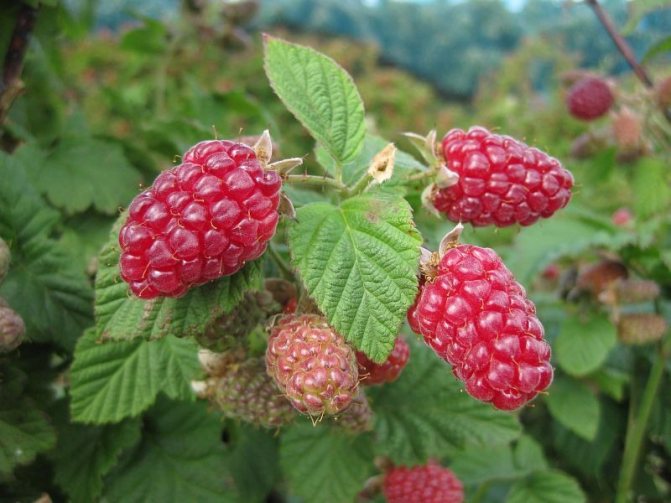


Berries of the Pride of Russia variety are not prone to shedding after ripening
a brief description of
Benefits of the variety
- large, tasty fruits;
- high productivity;
- lack of thorns;
- self-fertility;
- the ability to give a good harvest in different climatic zones;
- resistance to most diseases and pests.
Disadvantages of the variety
- average transportability of berries;
- vulnerability to sudden changes in air temperature;
- in case of insufficient illumination, the sugar content and aroma of berries are reduced.
Landing features
Raspberries are planted in spring (late March) or autumn (late September - early October). The autumn period is more preferable, since by the new season the soil will have time to settle and the plant will be able to root well.
The most suitable location is loamy and chernozem areas with good access to natural sunlight. Raspberries thrive on soils with neutral acidity. The groundwater level should not exceed 1.5 m.Too elevated places are not suitable, since the Pride of Russia variety does not like cold winds and droughts.
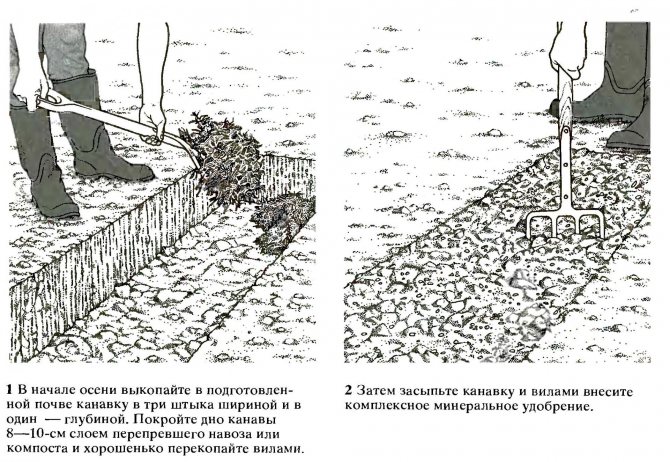
4 months before planting the seedlings, the site is cleared of root weeds and additionally fertilized. To do this, when digging for 1 sq. m, 5 kg of manure, 60 g of superphosphate, 25 g of potassium are introduced. If necessary, liming the soil is carried out.
When planting raspberries in a private area, you should choose a sunny place near a hedge or building. In industrial gardening, the following planting scheme is observed: the distance between the bushes is 0.5 m, between the rows - 2.5 m.
Step by step process
- Before planting along the row, rotted compost is introduced into the top layer of soil at the rate of 6-7 kg per 1 sq. m.
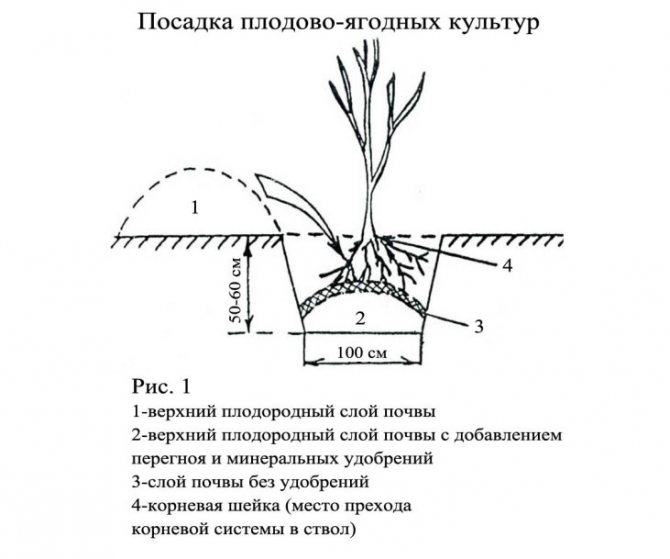
- Dig holes 40-50 cm wide and deep, cover 2/3 with fertile soil, forming a mound.
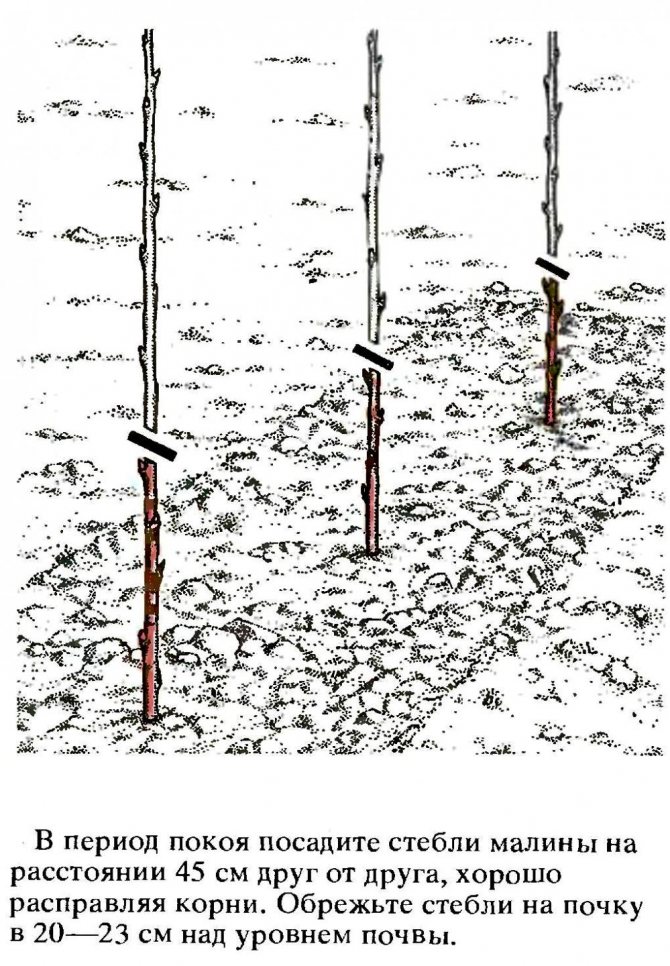
- A seedling is lowered into the hole, the roots are carefully straightened, and covered with earth. The root collar should be at ground level. With deeper embedding, fruiting may be delayed by a year.
- Each seedling is watered with 3-4 liters of water.
- Plants are mulched with humus or sawdust for better retention of irrigation and rainwater.

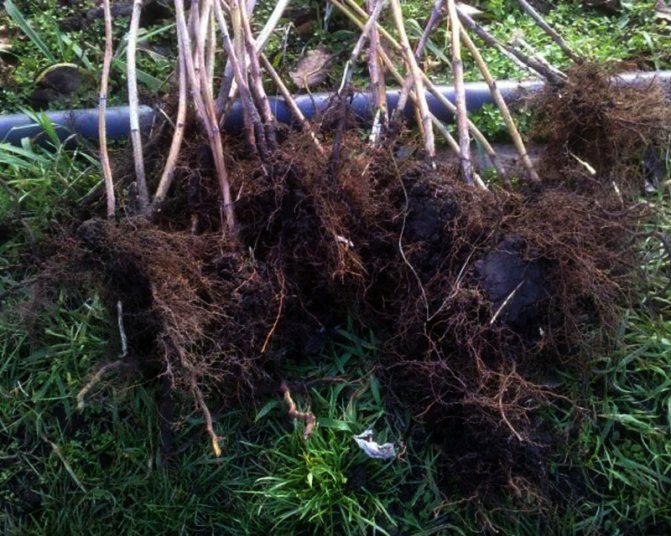
When planting, the roots need to be spread in different directions, shaking the seedling so that the soil fills all the void between them
Raspberries are propagated by cuttings, apical cuttings and root suckers. The variety takes root well and gives many shoots that can be used as planting material.
Plant care
Caring for raspberries is easy. It consists in following general recommendations: mulching, loosening, pruning, watering, fertilizing.
The area under the bush must be kept clean. Weeds are removed manually. In order not to damage the roots, the earth is dug at a distance of at least 30 cm from the bush.
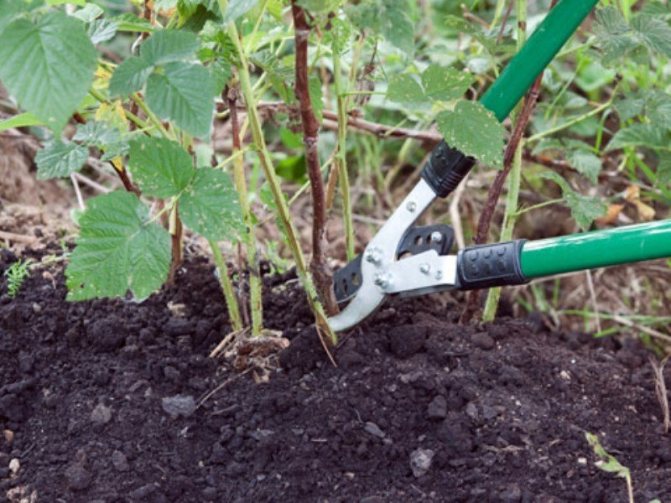
Pruning
- Spring pruning occurs in late March or early April. The time is selected depending on the climatic conditions of the growing region. All damaged, weak and underdeveloped branches, frozen stems are removed. All remaining shoots are shortened to the first healthy bud.
Pruning is done with a pruning shears or sharp garden shears.
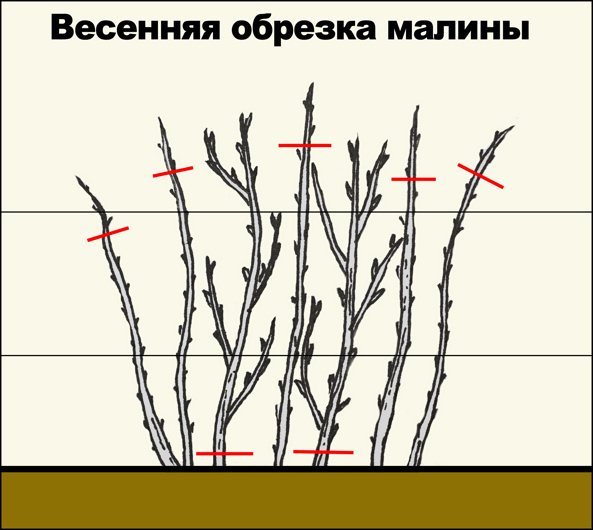

Pruning raspberries is a very important activity in the care of plantings.
- The second time the event is carried out after bud break. The previously cut stems are shortened by 15 cm. This will increase the yield.
- Autumn pruning is carried out 15–20 days before the onset of cold weather. At this time, remove:
- old and diseased stems;
- young shoots that are not able to withstand frost;
- shoots bearing fruit for two years;
- stems thickening the bush.
Shoots are cut to the ground. Maintain the recommended distance between bushes. If the raspberry has grown a lot, dig up the soil around the bush. To do this, a bayonet shovel is stuck several times around the bush at a distance of 30 cm, after which the entire area outside the circle is dug to the depth of the shovel.
Raspberry pruning (video)
Watering
Raspberry varieties Pride of Russia is a moisture-loving plant. During the season, four main waterings are carried out at the rate of 4 buckets of water for each bush.
Watering periods:
- before flowering;
- when fruit ripens;
- after harvest;
- before winter frosts.
The most suitable irrigation system is drip irrigation. After absorbing moisture, the soil is mulched with sawdust, peat, straw or fresh soil.
Shelter for the winter
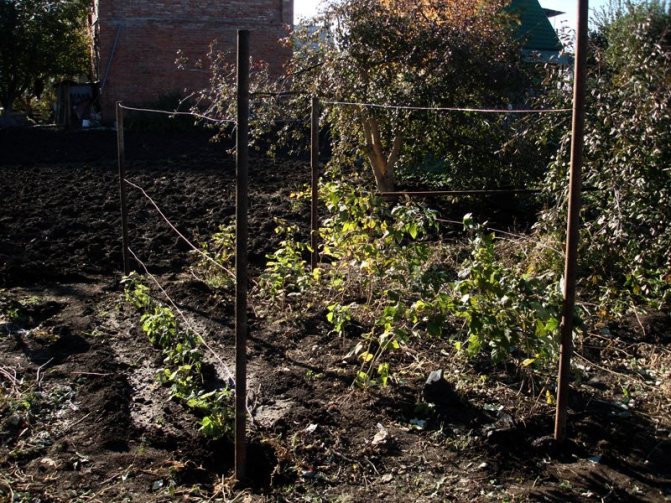
They start preparing raspberries for winter in November. For this, the shoots bending procedure is carried out.
- Metal or wooden pegs are dug in along the row.
- A wire is pulled on them at a level of 20-30 cm from the ground.
- Raspberry stalks are gently tilted and tied to the wire with nylon or nylon thread. In this case, the shoots should acquire the shape of an arc.
- Top raspberries are covered with lutrasil or agrofibre. You can also use polycarbonate sheets.A small arc-shaped greenhouse is formed from them.
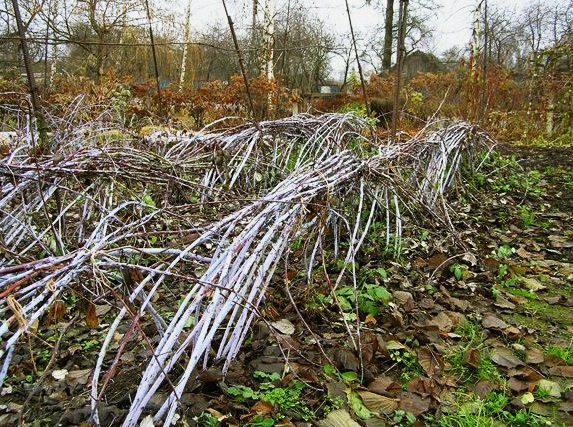


In the fall, bending of the shoots is carried out. To do this, two adjacent bushes are tilted to one another and the stems are tied
Top dressing
The taste of the berry and the yield depend on the timely and regular feeding of raspberries.
Important! Plant feeding is carried out every year.
- With autumn or spring top dressing, semi-rotted manure and superphosphates with potassium salt are introduced into the soil. Complex phosphorus-potassium preparations and wood ash are applied after harvesting.
- Nitrogen fertilizers such as ammonium nitrate are used as needed. A sign of a lack of nitrogen is poor development of shoots, pale color of leaves. The tool is applied in early spring when digging the soil.
- In the first year after planting, raspberries are fertilized with a slurry solution. Concentration: 2 parts slurry to 3 parts water. They are introduced into the grooves near the bush on both sides at the rate of 10 liters per four bushes.
- Mineral fertilizer is prepared from 30 g of ammonium nitrate, 60 g of superphosphate, 40 g of potassium salt. Everything is stirred in one bucket of water. The amount of solution is calculated for four bushes.
- For sandy soils, the addition of magnesium fertilizers is mandatory.


In the first years after planting, the raspberry yield gradually increases as the number of shoots and their capacity increase, and at the same time, the crop's need for nutrients increases.
Diseases and pests
The variety is highly resistant to various diseases and pests. Preventive treatment is quite enough to prevent their occurrence.
Raspberry The pride of Russia is practically not affected by aphids.
Prevention and means of pest control (table)
| Pests | Protective measures | Prophylaxis | ||
| before flowering | after flowering | growing season | ||
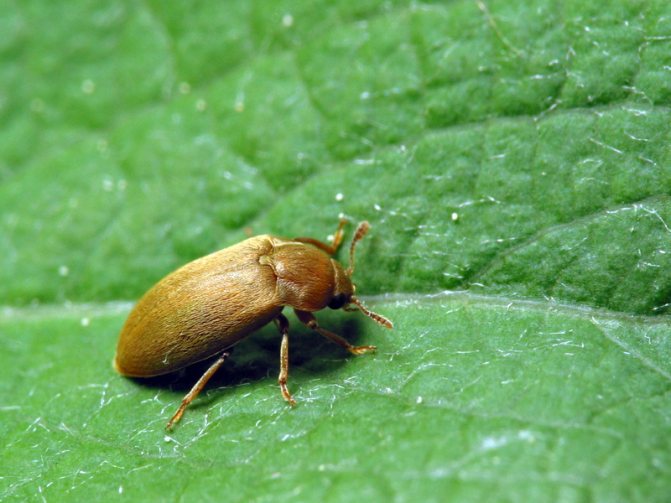
| Crimson beetle |
| Actellik - once. Repeat if necessary after 14 days | Fosbecid - once |
|
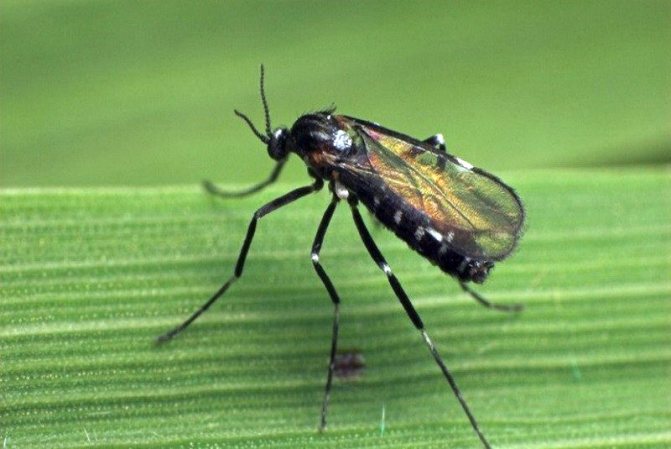
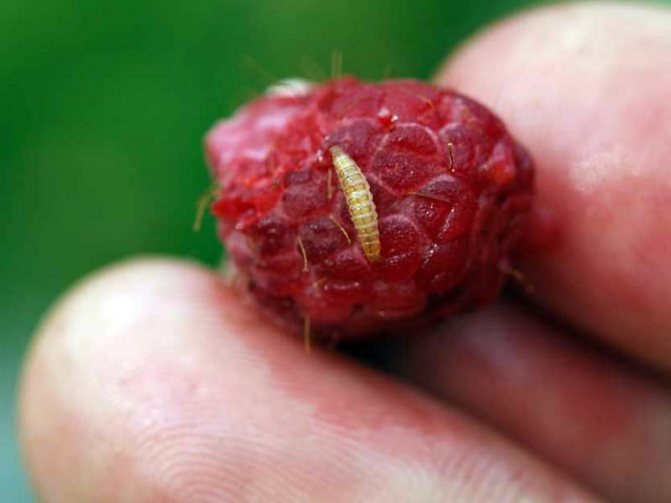
| Raspberry fly | treatment of bushes with Etaphos - once | Planriz, Reakom, Skor - once. Re-treatment after 14 days in the presence of a pest | Confidor - once. Repeated treatment in 10-12 days, if the pest is not destroyed | |
| Spider mite | Vofatox - once. Repeat if necessary after 10 days | Antio, Akartan - once | Cydial, metaphos - once. Reapply if necessary | |
Raspberry pests
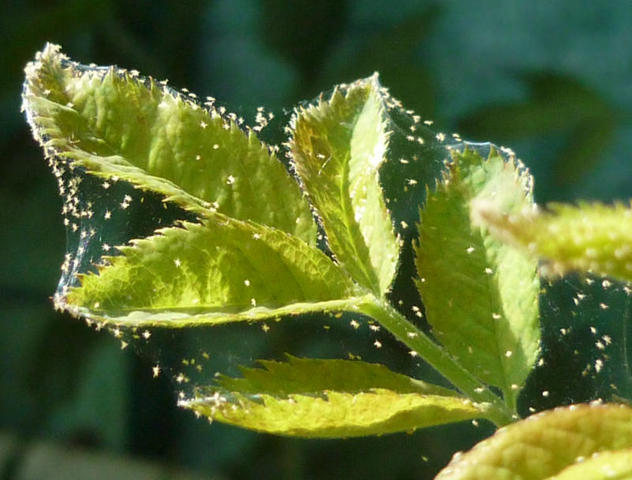


In dry years, spider mites can lead to a loss of 30-70% of the crop
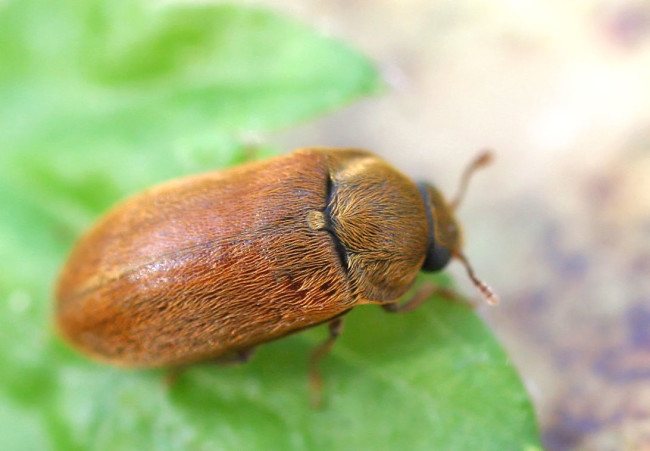


The raspberry beetle can destroy up to 100% of the crop or make it unsuitable for sale and processing
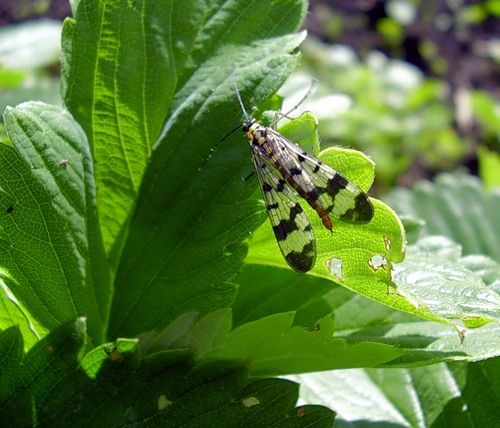


Raspberry fly is a dangerous pest that can deprive most of the crop
Prevention and control of diseases (table)
| Diseases | Means of protection | Prophylaxis | ||
| before flowering | after harvest | growing season | ||
| Anthracosis | Bordeaux liquid 1% - one-time treatment | Hom preparation, copper oxychloride - once | Oxyhom - 40 g per 10 liters of water. Processed twice with an interval of 10 days |
|
| White spot | bordeaux liquid 1% | copper oxychloride - 30 g per 10 l of water | colloidal sulfur solution: 50 g per 10 liters of water. Consumption rate - 2 liters per 10 sq. m | |
| Rust | Nitrafen 2%, cultivate the plant and soil in the aisle | oxychoma solution - 3 tablets per 10 l of water | Topaz - once | |
| Chlorosis |
| Nitrafen 3% | 0.1% emulsion 30% methyl mercaptophos. Processed 45 days before harvest | |
Raspberry diseases
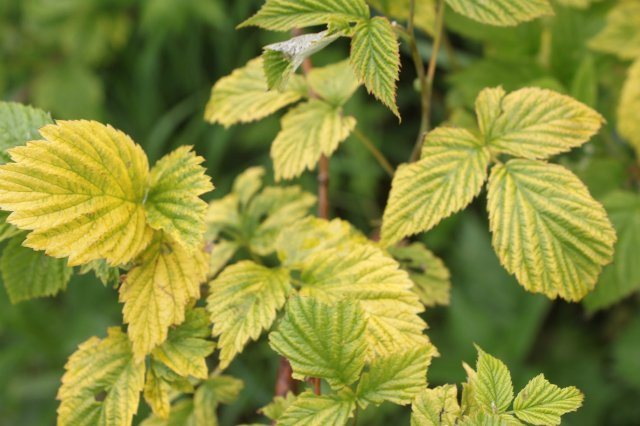


Chlorosis - a viral disease of raspberries
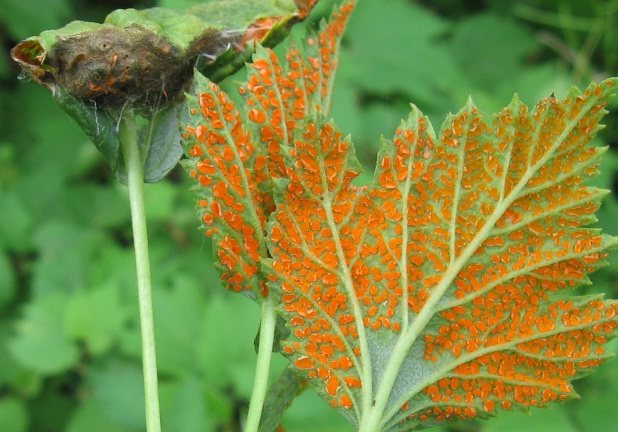


Rust causes great damage to crops, destroying up to 30% of the crop
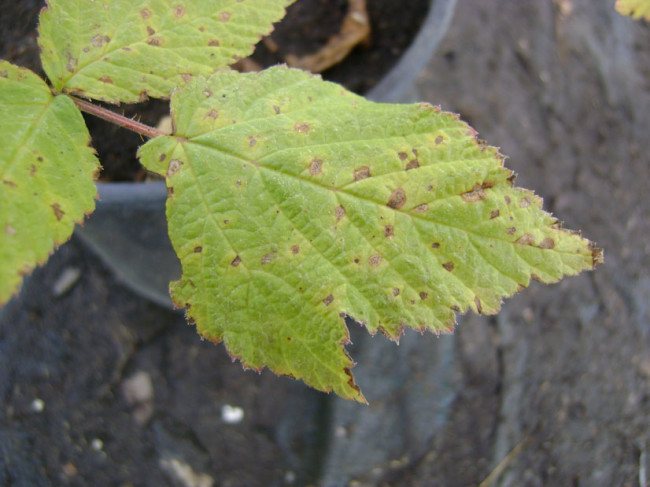


White spot affects the leaves and stems of the plant
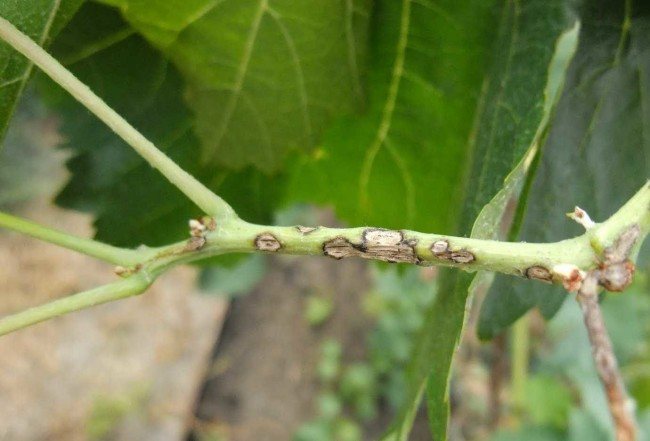


Anthracnose is spread by fungal spores
Harvesting
The pride of Russia is a medium-early ripening variety of raspberries. Ripe berries appear in early July. Fruiting lasts until early August. Harvesting is carried out in 5-6 stages.
The average yield of one adult bush is 4–5 kg or 30–40 centners per hectare. With intensive farming, the yield is 15–18 tons per hectare.
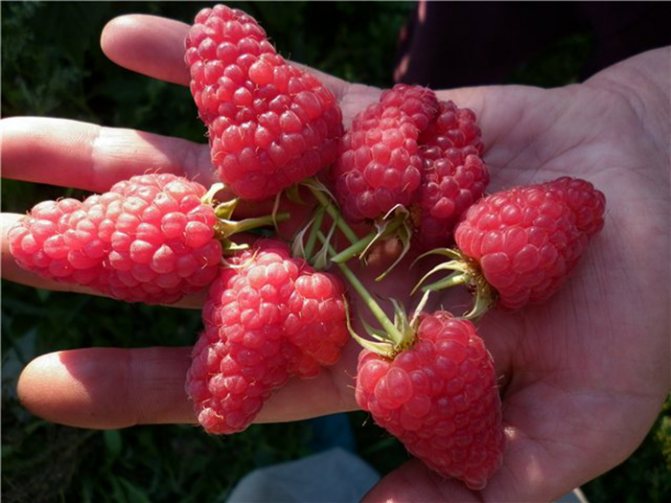


The Pride of Russia variety is distinguished by annual fruiting, which lasts from the first half of July to the beginning of August.
There are three main methods for storing berries:
- Cooling. At the same time, the berries remain fresh for three days. Optimal conditions: from 0 to +5 degrees with a relative humidity of 90%. Transportability is good.
- Freezing. For longer storage, raspberries are flash frozen. At temperatures from –19 to –35 degrees, the shelf life is increased to 7 months.
- Drying. Store dried berries in cotton bags or plastic containers at room temperature in a well-ventilated place. Drying is carried out in two ways:
- natural;
- using drying cabinets.
Raspberries are eaten fresh, and also used to prepare various preparations and desserts. Dried berries and leaves are often added to herbal teas.


Frozen raspberries make delicious cocktails
The specifics of purchasing planting material
Obviously, this raspberry is far from being as convenient plant as the advertisers claim. But that's not all: buyers of seedlings often choose a variety, tempted by those of its promised "features", which either have nothing to do with reality, or testify to the complete incompetence of the sellers.
Of the characteristics of this type, it is worth noting:
- positioning raspberries as remontants. It is not true. The Pride of Russia is a common variety that bears fruit exclusively on last year's shoots. Autumn radical pruning in this case is unacceptable. It leads to the loss of the next season's harvest;
- claims that one of the main advantages of the variety is its self-fertility. This cannot be taken seriously at all, since garden varieties of culture are overwhelmingly self-fertile.
“The Pride of Russia” is an interesting plant, but its cultivation requires a thorough knowledge of agricultural technology, solid experience and rather serious efforts. For summer residents who want to grow raspberries without any problems, this variety is not suitable.
Gardeners reviews
The variety is good for everyone: the berry is bristleless, the berry is large, it comes off beautifully, lies, “does not flow”, looks beautiful. But sweet and sour, with a large drupe. Conclusion: for the market - super, for the house - "nin", my wife said - for jam, limit the place, do not breed.
Varava
In my second year, Pride gave so many berries that they were tortured to pick. 170 kg were harvested from sixty bushes, and this is one shoot per bush. The berry is large and really sweet, you can't drag your wife out of raspberries by the ears.
Vvovva
If there is anything to compare, then it is better to get rid of the Pride of Russia. Neither special taste, nor density, the lustrous beetle also loves the aphid.
Spring
I have this variety growing. Unripe crumbles. And overripe does not crumble (sometimes, only single berries). When it is completely overripe, due to the fact that it hid somewhere and was not noticed when ripe, then it turns into porridge. Then there is no taste. But ripe in my conditions is delicious. And very large. Some berries grow together in 2 and a heart is obtained. In the first year of planting, I did not like the taste, even its size was not needed, since it was tasteless. And the next year (and subsequent) the taste is good.The berry begins to deteriorate a few hours after harvesting, therefore, immediately into processing. Fruiting is extended.
Turtle
GR begins to ripen. Sweet taste with sourness, with aroma. Like!
Viktor K
I have the pride of Russia, large and abundant raspberries, but the taste doesn’t roll at all, only for processing.
Gingerbread man
Either I don't like this Pride of Russia, or the variety is so unfortunate, but she did not impress me. Yes, the berries are very large and beautiful, but at the same time there are relatively few of them and they strive to sour from gray rot. And the taste is the most common. The bush itself is powerful, tall, but it gives few replacement shoots, because of the raspberry fly this is a disadvantage for me. In general, I put up with it for a couple of years and threw it away last fall.
aprel
Easy reproduction, high yield, large berry size, disease resistance are the hallmarks of the raspberry Pride of Russia. The variety is grown not only in private gardens, but also on an industrial scale.
Rate the article:
- 5
- 4
- 3
- 2
- 1
(0 votes, average: 0 out of 5)
Share with your friends!
Weak sides
- Frequent deformation of the berry, especially when it reaches a very large size. The fruits of the variety are heterogeneous, curved and doubled. The halves of a forked berry may ripen at different times.
- In unripe berries, drupes may crumble during picking.
- Normal, bland taste. The fruits contain little sugar, sometimes sourness can prevail.
- Weak unsaturated aroma.
- Poor transportability and keeping quality. Moreover, keeping quality is poor even when the fruit is stored in the refrigerator.
- Poor frost resistance. There are known cases of complete freezing of plants along with the root system, shoots freeze even in the south.
- The suitability of raspberries is mainly for personal consumption and processing.
- The pride of Russia forms a large number of shoots, regular cutting is required. Otherwise, the bush will thicken, the berry will become smaller, and the yield will fall.
Draw your own conclusions. But personally, I get the feeling that the variety is a little unfinished. With such outstanding indicators of the size of berries and high yields, the quality of the fruits itself leaves much to be desired. And the variety has enough other "roughness". But if not for them, it would really be the crimson Pride of Russia. And so ... In general, the grade is normal, no more. Sit down and test it yourself in practice. And about one more Kichinovskie studless varieties - Beauty of Russia and Maroseyka - read in our new articles.