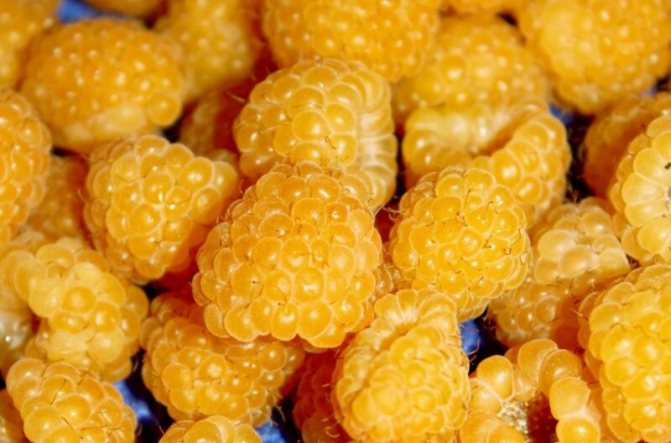
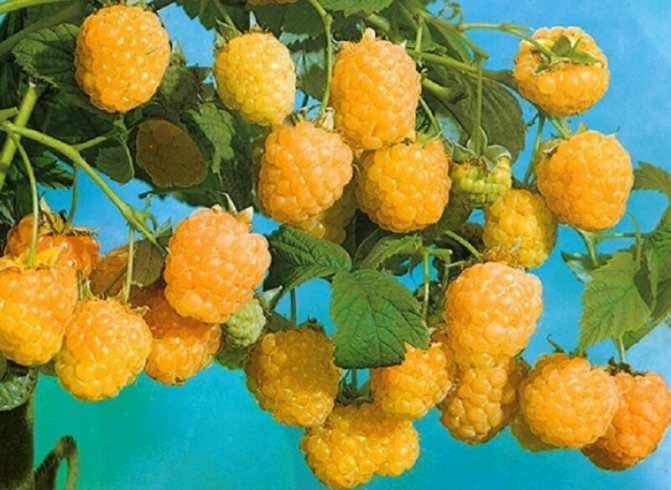
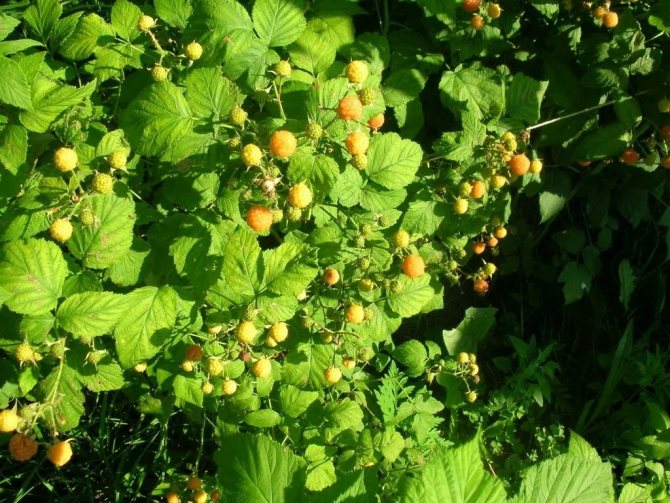
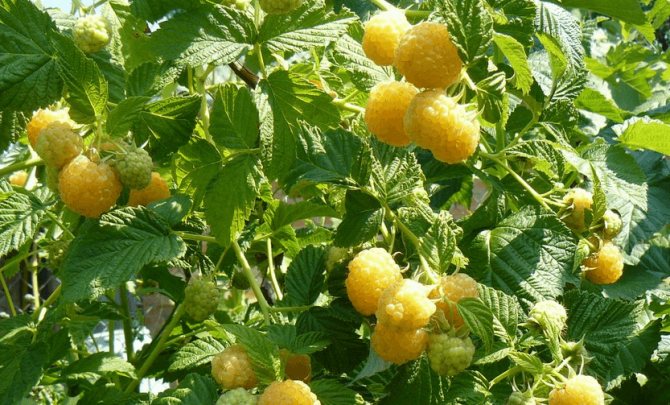
We are all used to red raspberries. They delight us from year to year with their delicious berries. But, as practice shows, the lion's share of gardeners and ordinary people are not even aware of the existence of varieties with a different color of the fruit. So, having met the Yellow Giant, whose shell has a yellow color, a person will most likely think that this is a GMO product and will not take it. But in vain. Yellow raspberries contain more sugar and organic acids, making them much sweeter than their red cousins. In addition, unlike the black and red varieties, yellow does not cause allergic reactions and is quite suitable for allergy sufferers.
And in this article we would like to give a detailed description of the variety, show photos and reviews of those who were lucky enough to taste the taste of the "yellow miracle".
Description of the variety
The variety has signs of remontantity, gives a small harvest in autumn on the tops of annual shoots.
The yellow giant was bred in 1979 by crossing the varieties Maroseyka and Ivanovskaya.
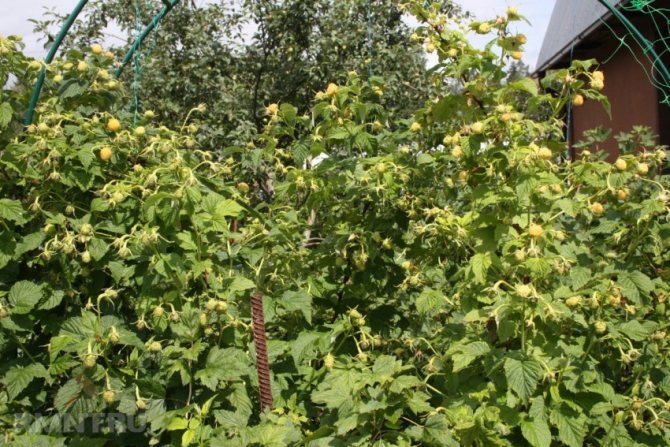
The bushes are medium-sized (up to 2 m in height), slightly spreading. Shoots of gray color, quite powerful and strong, pubescent. Form 8-10 shoots of replacement and 5-7 root suckers. Small thorns, unpainted. Leaves are dark green, large. Fruit branches are of medium length, thickened, strong. They have 2-4 orders of branching, form 15 or more berries.

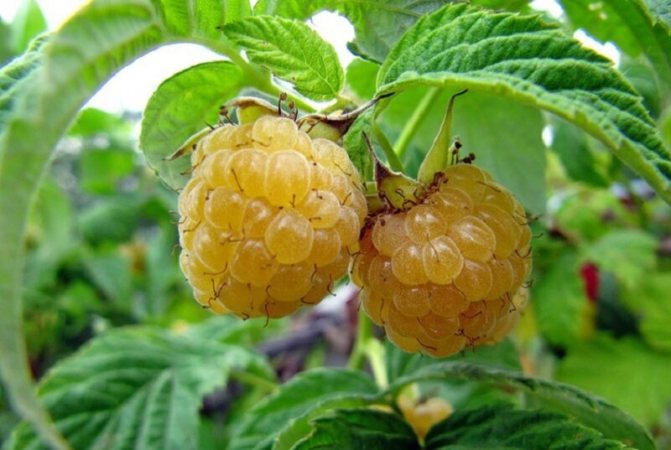
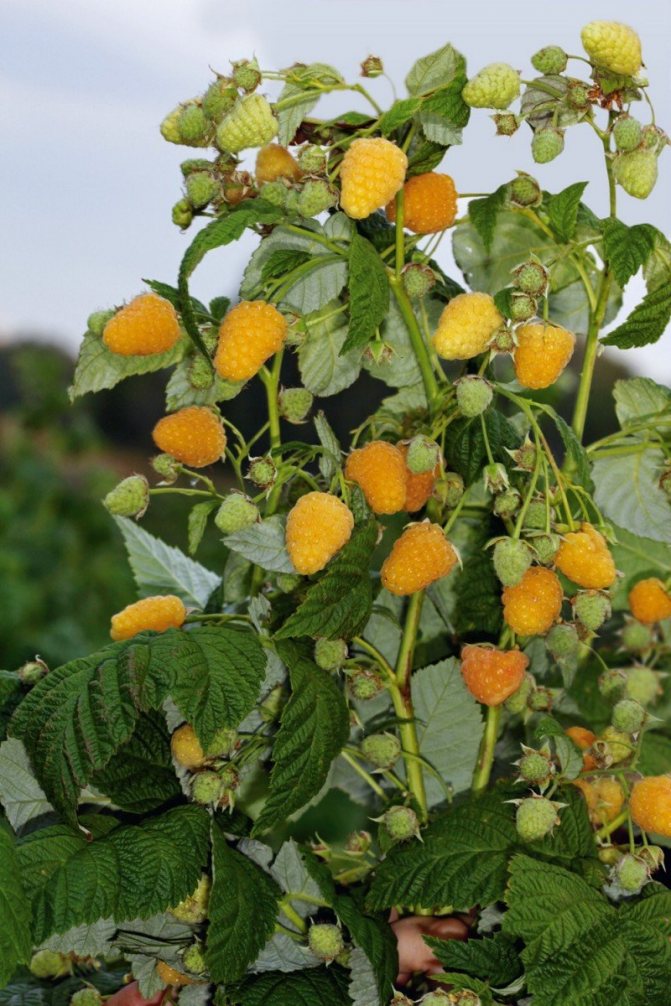
Raspberry bush of the Yellow Giant variety reaches a height of 2 m
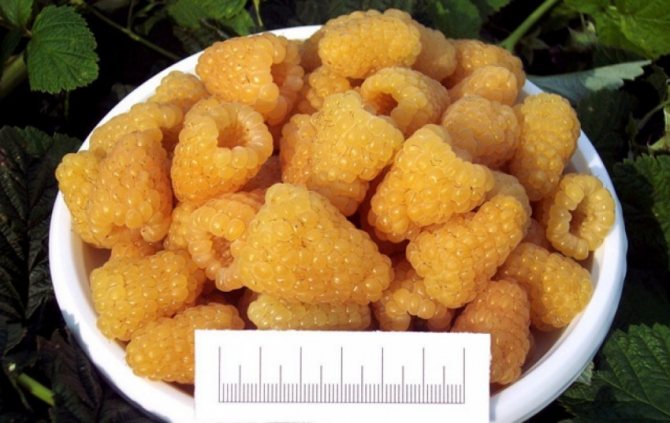
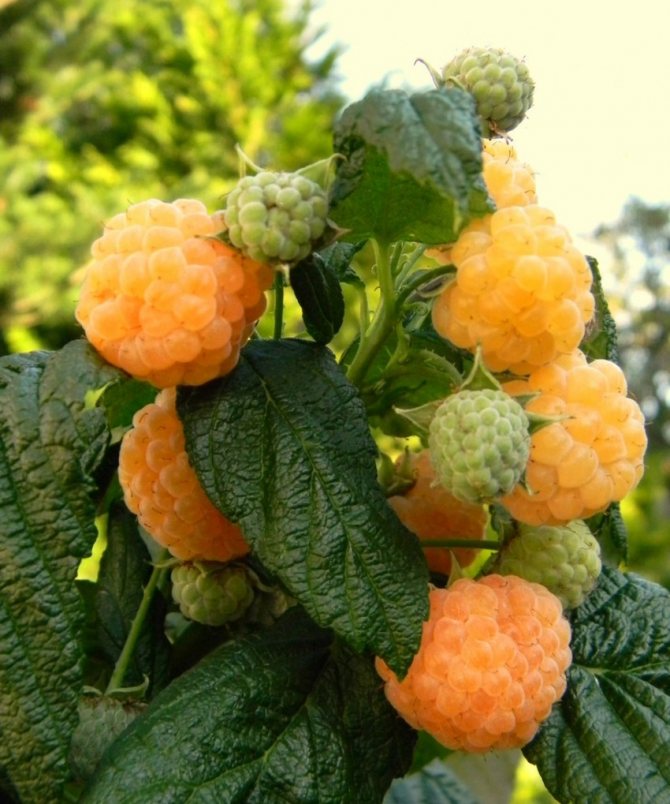
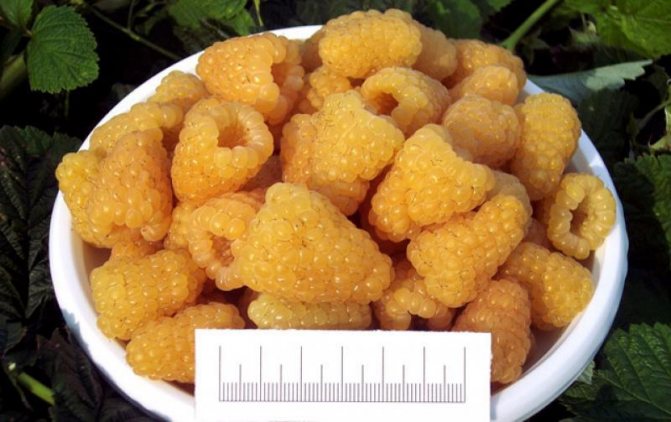
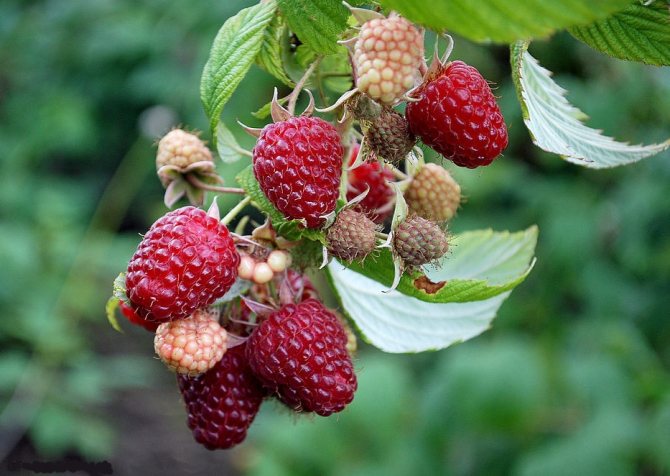
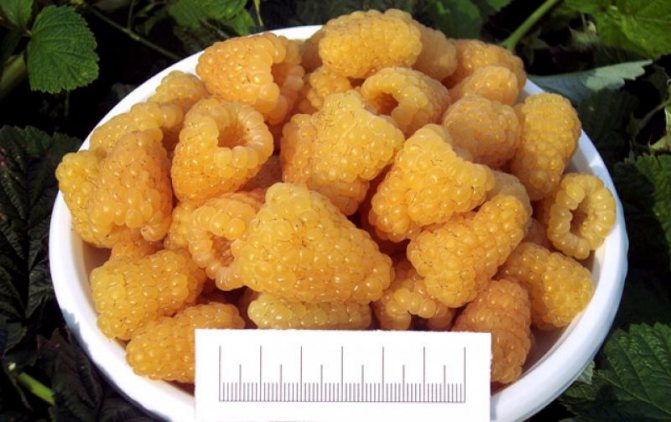
The fruits are large in size, their weight reaches 8 g. The berries are elongated-conical, light yellow in color with a barely noticeable bloom. They have a sweet taste and pleasant aroma. The seeds are small.
Tasting assessment of taste - 5 points on a five-point scale.
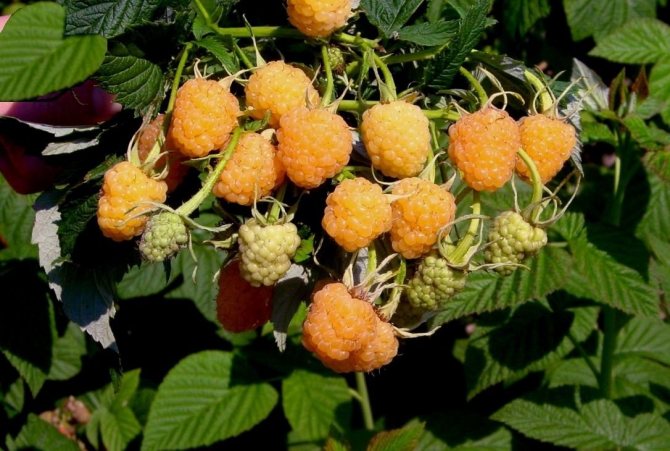


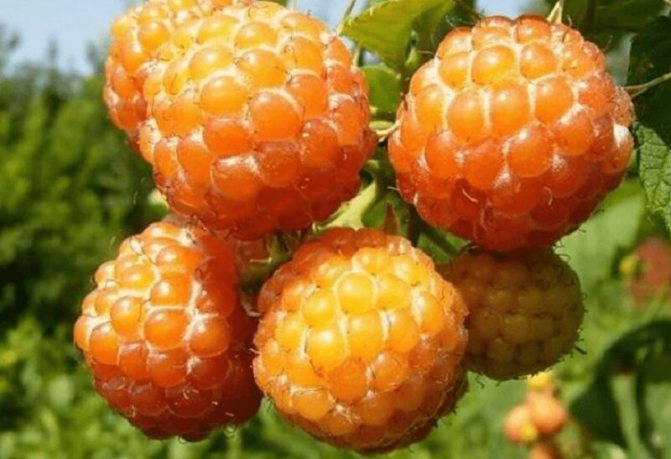
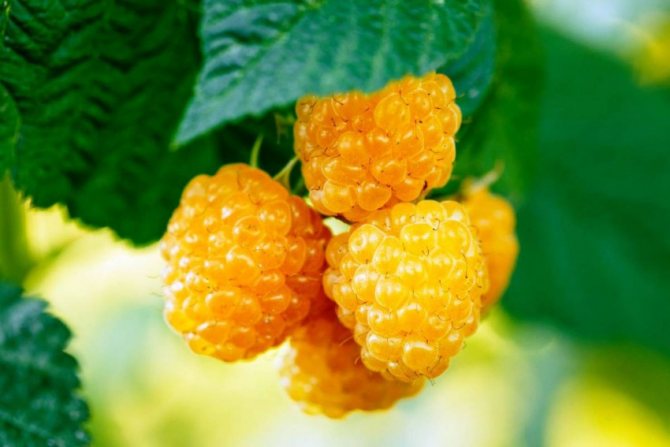
Fruit branches of the Yellow Giant variety are strong, the berries are collected in clusters
Distinctive features
The main features that distinguish the Yellow Giant from red raspberry varieties:
- Signs of remontability allow you to harvest on one-year and two-year shoots.
- Dietary value of fruits. Berries are suitable for use in case of allergy to red raspberries.
- The ability to use bushes in the form of natural hedges.
Advantages and disadvantages
| Benefits | disadvantages |
| winter hardiness | short shelf life of berries |
| disease and pest resistance | poor transportability and rapid loss of the presentation of the fruit |
| early maturity | shedding of berries when ripe |
| large fruits of high taste | rapid development of root growth |
| high yield | |
| long-term fruiting | |
| decorativeness of bushes |
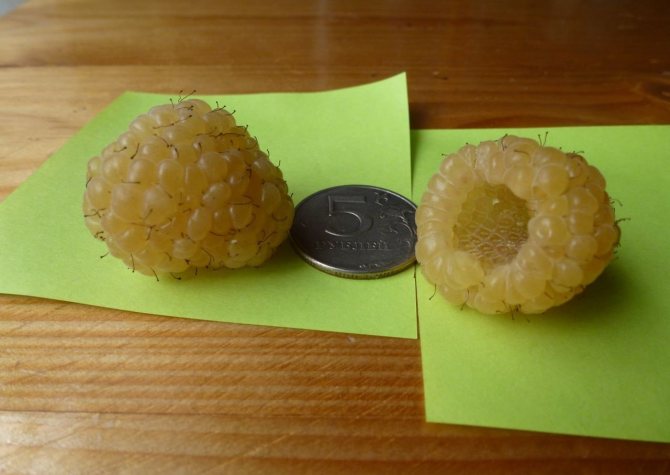


Berries of the Yellow Giant variety are large, blunt-conical
Raspberry variety Yellow giant (video)
Advantages and disadvantages of the variety
Amazing yellow raspberries have been on the tables of gardeners for quite some time. Thanks to this, they managed to highlight all its main pros and cons. First of all, let's appreciate the good sides of this amazing raspberry. The pluses of the Yellow Giant include:
- Excellent yield indicators. As noted earlier in our article, if you properly care for raspberries, then they will delight the gardener with at least 10 tons of quality products from 1 hectare of plantings.
- The berries keep their shape perfectly on the bush, even after ripening.
- The variety has excellent immunity, thanks to which even an inexperienced beginner gardener can cope with its cultivation.
- The bushes survive the winter quite well, so that they can be grown both in the warm regions of our country and in regions with a harsh Russian climate.
- The berries have good taste. Combined with an attractive yellow color, this raspberry can be a favorite treat for children.
- The bushes have an attractive, decorative look, so they can be used as decoration for a garden or a backyard.
However, despite such good qualities, on the market, you are unlikely to find the Yellow Giant variety. This is due to a number of disadvantages that negate the commercial value of this raspberry. The main disadvantages of the Yellow Giant include:
- Awful safety of the harvested crop. The berries are not stored at all and are only suitable for quick consumption or instant processing.
- Berries are generally not suitable for transportation. They instantly wrinkle, flow and lose their attractive presentation.
- The bush grows quickly enough, which makes it difficult to care for.
Landing features
It is recommended to plant raspberries in the fall in previously prepared trenches. When choosing a landing site, it should be borne in mind that the Yellow Giant loves elevated and well-lit places.
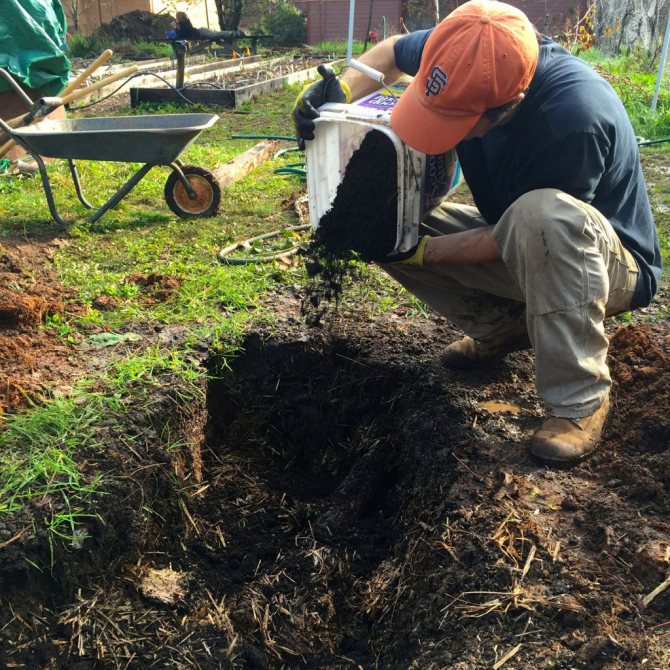


Prepare trenches for planting raspberries in advance
Landing technology
- Dig trenches 50 cm deep and 50 cm wide one month before planting. The length depends on the number of seedlings.
- Dig in a slate or linoleum fence along the edge to a depth of 10 cm. This will prevent overgrowth of root growth.
- Fill the third part of the trench with organic fertilizers:
- 10 kg of rotted manure;
- 200 g superphosphate;
- 80 g of potassium sulfate (per 1 sq. M).
- Form and install a trellis with a height of 1.5–2 m along the length of the trench.
- The distance between seedlings should be from 60 cm to 1 m and 1–1.5 m between rows.
- Pour the planting mixture in the form of a mound, on which to place the roots previously soaked in the mullein solution.
- The root collar of the seedling should be 4–6 cm above the soil surface.
- Cover with earth, pour 3 buckets of water on each plant and mulch with peat or humus with a layer of about 7–8 cm.
- When the buds are formed, the shoots are cut off, leaving 30 cm in length.
Reproduction
It is recommended to propagate the yellow giant raspberry variety by cuttings, or rather by root suckers, of which 5–7 pieces are formed for each plant.
- Cuttings are taken with an upper green part and a bleached bottom, which are harvested at the beginning of summer (during the period of regrowth of young shoots). They are cut off after they have risen above the ground by a distance of at least 3 cm. The leaves on the handle should not be fully developed.
- The stalk is cut and removed from the soil, and then transplanted into a greenhouse, the soil in which should consist of a mixture of peat and river sand in equal proportions. Landing takes place at a depth of 5-10 cm.
- The greenhouse is covered with a special material or plastic wrap, which is periodically removed to avoid overheating of the cuttings.
- At a temperature of 20-25 degrees and high humidity, the rooting of cuttings occurs in 20-25 days, after which they are gradually accustomed to the direct rays of the sun and air humidity. After a month, the cuttings are planted in open ground.
Chelyabinsk yellow
The variety is medium early and hardy. The bush is distinguished by a semi-spreading shape and a shoot height of 1.8-2 m. The shoots are distinguished by a drooping top and strong branching. The color of the shoots in autumn is purple-red. On the surface of the lignified shoots there is a dense waxy coating and a large number of thorns. The spines are rather long, thin and very stiff in structure. A large number of young shoots grow during the season.
Ripe fruits weigh up to 4-5 g. The shape of ripe fruits is oval or round.Ripe berries are dull yellow and have a pleasant honey aroma. The harvested crop can be transported over long distances.
Up to 3-4 kg can be harvested from a bush. ripe fruits.
Plant care
The Yellow Giant variety is unpretentious in care, and is also resistant to common pests and diseases that affect bushes and raspberries.
Pruning
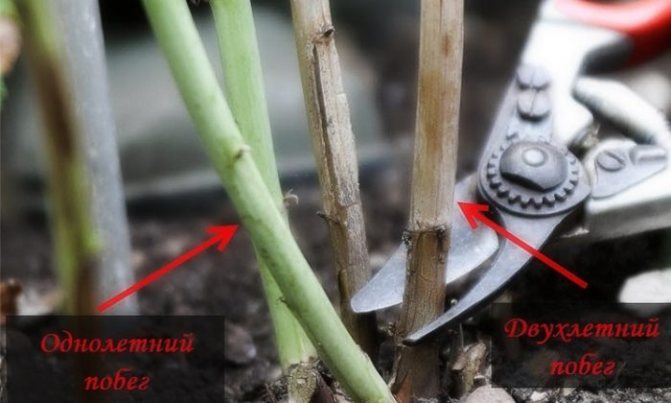
For the winter, the shoots are tied up and not pruned. This leads to an earlier harvest, but the rates will be lower and the fruit will be smaller.
Variety Yellow Giant has signs of remontance, however, the main crop is formed on last year's stems.
- With spring pruning, all dried, damaged and not survived winter branches are removed annually at the root. The remaining branches are pruned to the first healthy bud.
- In the fall, 3 weeks before the onset of frost, all weak shoots are removed under the root.
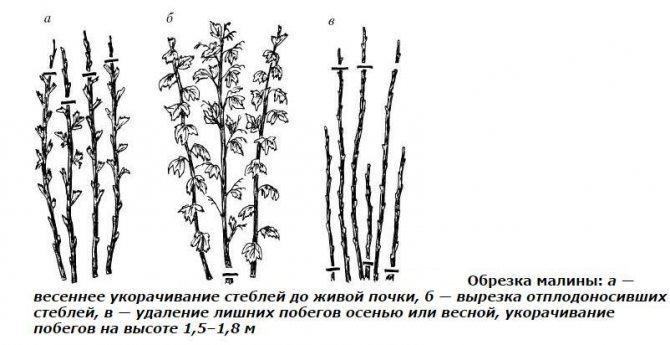

Pruning is the most important raspberry care activity
Raspberry pruning (video)
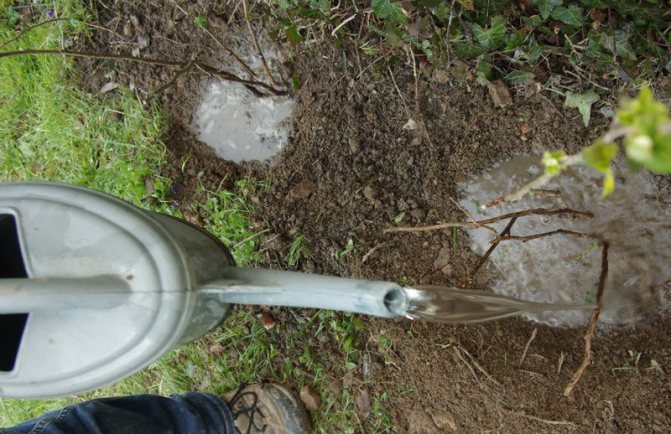
Watering
In the southern regions, raspberries are watered at least 5 times:
- during the growing season;
- in the phase of intensive growth;
- during the flowering period;
- with the formation of ovaries;
- after harvest.
In the middle lane, 3-4 times are enough: during the growing season and shoot growth, after harvesting.
The abundance and large-fruitedness of the subsequent harvest depends on watering the plant.
One bush requires about 3-5 buckets of water. Watering is carried out by sprinkling or in specially formed grooves.
Shelter for the winter
The yellow giant raspberry variety is frost-resistant, but at temperatures below 30 degrees, it requires shelter for the winter. The bushes are removed from the trellis, tied and bent to the ground, reinforcing with specially prepared metal hooks. The distance from the ground in a bent state should be no more than 40 cm. Then the bushes are covered with straw, and a little later with snow.
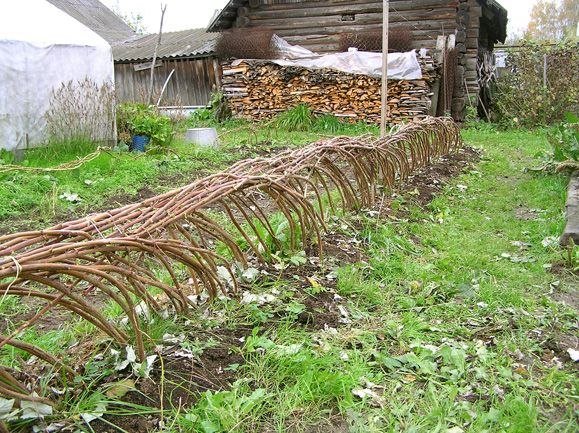


Be sure to bend the raspberries down for the winter - this will protect the plant from frost
Top dressing
If fertilizers were applied when planting raspberries, then the first 3 years of additional fertilizing to the plant is not required. In subsequent years, during the spring digging, nitrogen fertilizers are applied, as well as 200 g of ash and 80-100 g of potassium sulfate per 1 sq. m during fruiting.
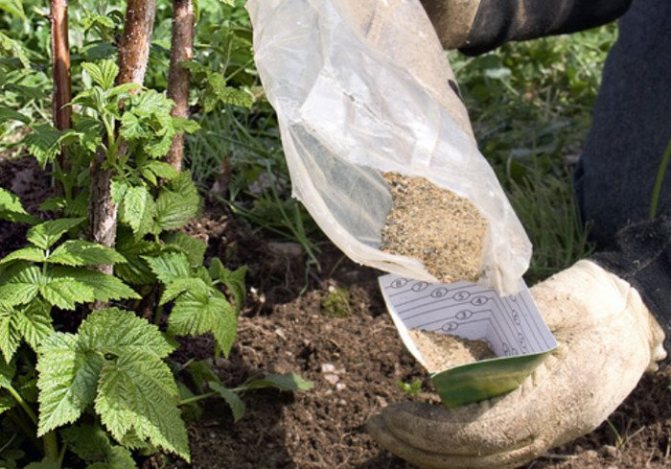


Top dressing of raspberries must be carried out in early spring, when the first loosening of the soil around the bush is carried out
Immunity
The Yellow Giant has good immunity, but it covers certain types of diseases. It has no protection against some sores and insects.


The main types of insect pests are:
- Raspberry beetle. He harms the plant by eating inflorescences, and his offspring damages berries and leaves. The fight against such a parasite comes down to two ways: spraying with chemicals or manual cleaning. The second option is pretty simple. You need to get up early in the morning, lay a film or blanket under the bush and shake it. Fallen parasites are drowned in water or burned.
- Raspberry fly. Harms the plant by laying eggs in leaf buds. Thus, their growth is inhibited. The fight against this infection is reduced to cutting off the tops every two weeks.
- Raspberry moth larvae. These are small butterflies of brown color. They, like the raspberry fly, harm the kidneys. Pupation in the middle of the stem, they inhibit its growth. In winter they feed on fruit stalks of berries. To destroy this parasite, special preparations such as "Iskra", "Fufanona", etc. are used.


The main plant diseases are:
- Bushy dwarfism. Initially, the sheets begin to thin out, and then completely die. Then, the peas of the fruit are observed and the subsequent complete wilting of the bush. To combat this scourge, the affected areas are cut off. If the whole plant is damaged, then it is completely uprooted and burned. Unfortunately, there is no other cure for this disease yet.
- Raspberry aphid. It leads to twisting of the branches, which subsequently dry out. For the treatment of "misfortune" use Karbofos.
Diseases and pests
Despite the resistance of the Yellow Giant variety to the main diseases and pests of raspberries, preventive measures should be taken annually. This will avoid major problems with the quality of the crop and possible damage to shoots, leaves and fruits.
Protection of raspberries from pests (table)
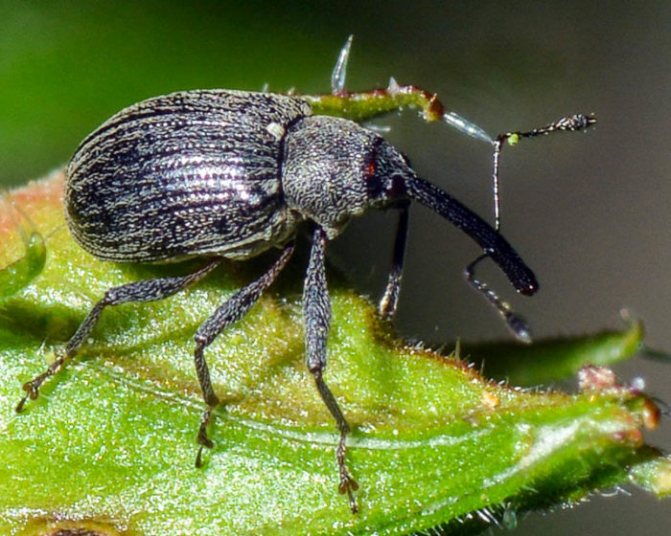
| Pest | Description, nature of the defeat | Processing period | Means of struggle | Prophylaxis |
| Strawberry-raspberry weevil | Black beetle up to 3 mm long with a long proboscis eats flower buds from the inside, which leads to loss of yield. |
|
|
|
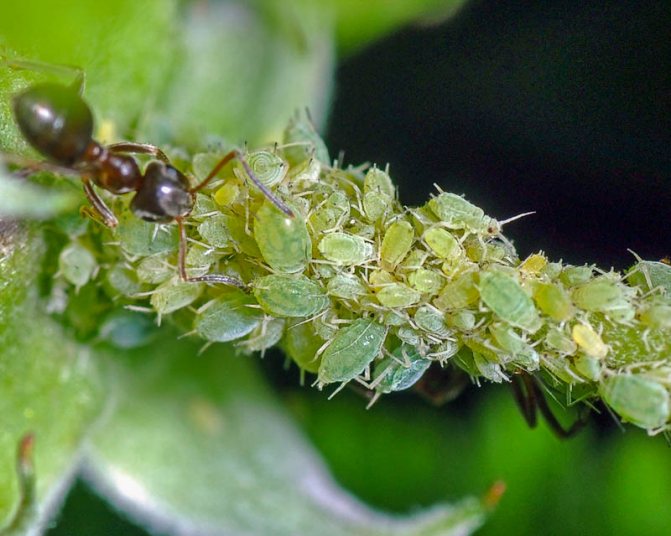
| Raspberry aphid | A small insect of light green color 2.5–3 mm in size affects shoots and leaves. |
| Treatment with Nitrafen (30 g per 10 L of water). |
|
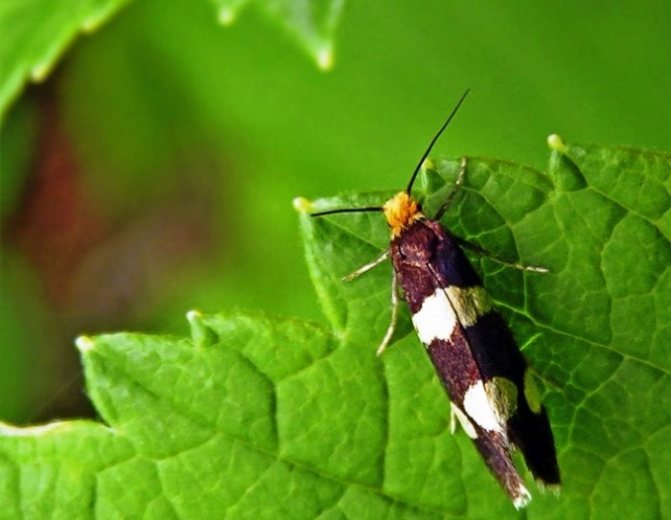
| Raspberry kidney moth | Caterpillars up to 9 mm long with a black head eat up the contents of the kidneys. Damaged buds die, the stem remains sterile. |
| Fufanon treatment (10 ml per 10 l of water). |
|
Common raspberry pests


Settling at the ends of shoots and leaf stalks, raspberry aphids form large colonies


Raspberry kidney moth damages raspberry buds


The raspberry-strawberry dognose does the maximum harm by destroying flower buds
Disease prevention and control (table)
| Disease | The nature of the defeat | Processing period | Means of struggle | Prophylaxis |
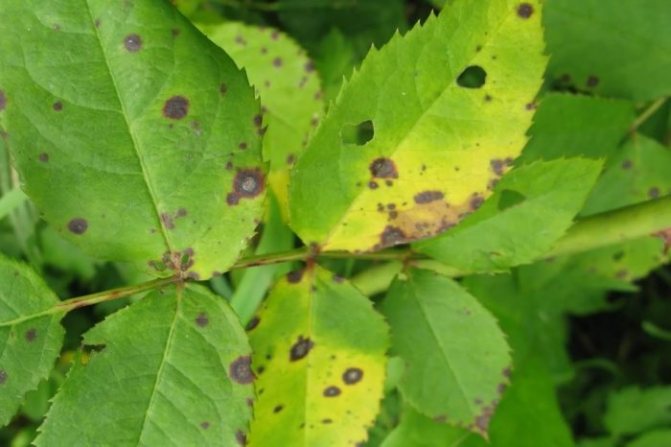
| Anthracnose | It manifests itself in spring on young shoots, as a result of which they lag behind in growth, and small purple spots appear on their surface. Gradually, the spots increase and acquire an ash-gray color. | before bud break | spraying with 3% Bordeaux liquid |
|
| spraying with 1% Bordeaux liquid | |||
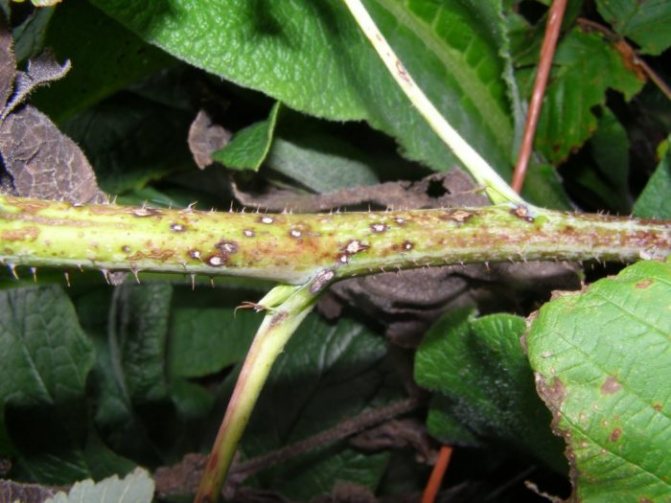
| Purple spot | Purple spots form on young shoots. Affected shoots do not tolerate winter, lose productivity and soon dry up. | before flowering | treatment with Topaz (10 ml per 10 l of water) |
|
| after harvest | fungicide treatment Colloidal sulfur (40 grams of the drug per 5 liters of water) | |||
| Root rot | The roots and root collar of the bush turn brown and collapse. The lower leaves turn yellow and wither. | of necessity | Removal of the affected bush along with the roots. The soil must be treated with ammonium nitrate at the rate of 100 g / sq. m. In the place of defeat, it is not recommended to plant raspberry bushes again. |
|
Important! Timely maintenance of trenches, removal of overgrowth and weeds, as well as mulching and loosening of the soil are excellent prevention of diseases and pests.
Common raspberry diseases


Purple spotting leads to a decrease in yield, and sometimes to the death of raspberry plantations


Most often, root rot develops if the soil is too dense and does not drain.


Anthracnose is a common fungal disease
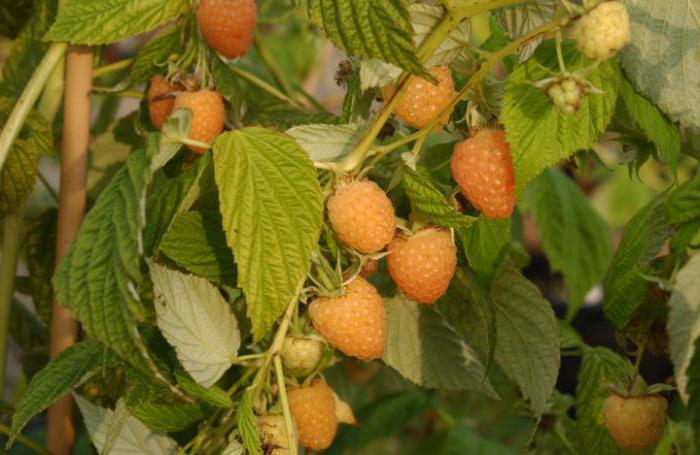
Raspberry morning dew
A repairing variety of yellow raspberries, resistant to viral and fungal diseases. The average height of the bush does not exceed 1.5-1.8 m. Shoots of the second year are brown in color, covered with small thorns. The leaves are oval, wrinkled and bright green in color.
The first berries ripen at the end of June, and the harvest continues until late autumn. The berries are distinguished by their oval shape, golden yellow in color. The pulp is quite dense with a sweet and sour taste. On average, a berry weighs 7-8 g. Under optimal growing conditions, berries weighing up to 10 g can be harvested. The variety is capable of forming a large number of shoots, so we recommend reading how to properly prune remontant raspberries.
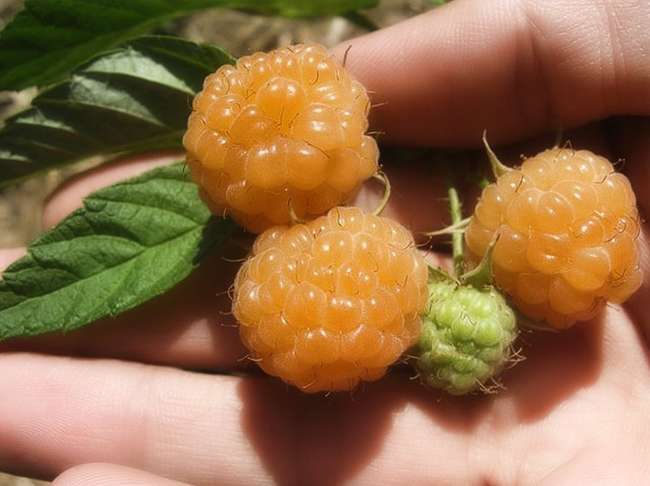


Shoots are able to withstand frosts down to -27 degrees in winter. The variety is very fond of timely watering and loosening the soil. On average, it is possible to collect up to 5 kg from each bush. ripe berries.
Harvesting
The yellow giant is a medium-early ripening variety with long-term fruiting (from mid-July to September). The yield per adult bush is 6–8 kg. When ripe, the berries are crumbly.
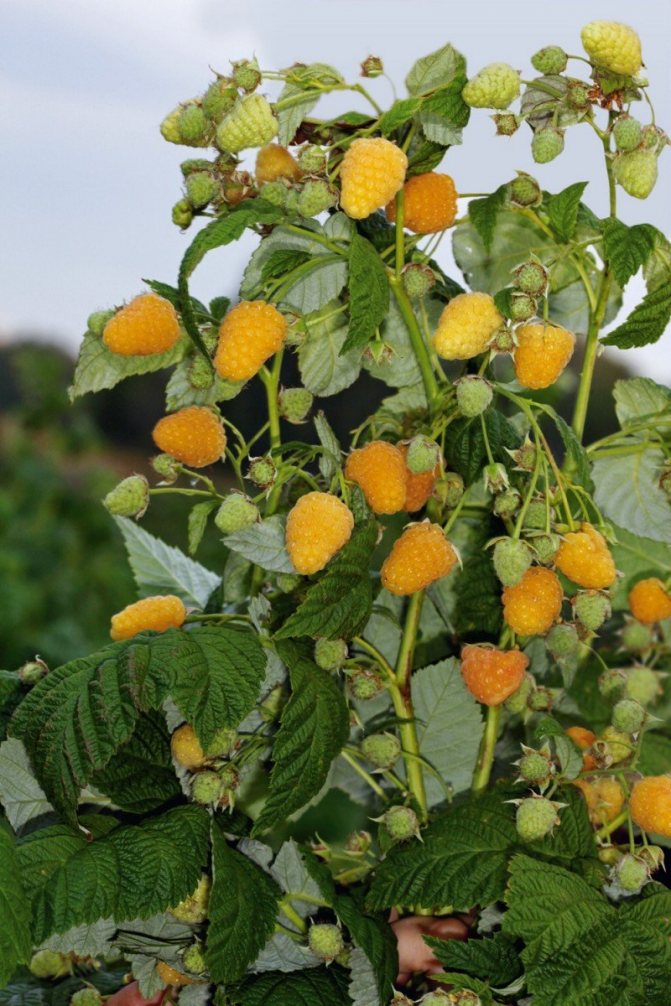


Sometimes in the fall the raspberry variety Yellow Giant gives a second crop at the tops of the shoots
Berries are most often consumed fresh, as they lose their presentation a day after harvest. Poor transportability.
When using raspberries for making jam or jam, it should be borne in mind that the berries are of a loose structure, therefore, they usually disintegrate.
Yellow raspberries - useful properties of berries
This plant is not very common in garden plots. However, it always attracts a lot of interest. Apparently, because it is somehow strange to imagine yellow raspberries.


The yellow-fruited plant has berries that are much sweeter than other types of raspberries. The biochemical composition of the fruit has its own characteristics:
- in comparison with red and black raspberries, yellow fruits contain more sugar and less organic acids
- the amount of anthocyanins, that is, coloring substances in plant cells, is very low in it
It is the low content of anthocyanins that makes it especially useful for people suffering from allergic diseases.
In addition, yellow raspberries are very beneficial for pregnant women and children.
And the berries of this plant are also rich in folic acid, vitamin B9, which is actively involved in hematopoiesis. As a result, the synthesis of important compounds and metabolism are activated.
Soil preparation
Raspberry The yellow giant thrives on sandy loam or loamy soil. On sandy or heavy soil, caring for raspberries is very difficult.
When planting raspberries in the autumn, before digging, you need to add at least 25 kg of manure, 60 grams of superphosphate per square.
The soil containing a large amount of peat is diluted with sand, for each square meter at least four buckets. Acidic soils are not suitable for the Yellow Giant; they can be deoxidized with lime.
Potash fertilizers are applied during the spring preparation of the soil.
Site selection
Yellow raspberries love sunlight, so a place for planting them should be allocated in a sunny part of the garden. Raspberry is a moisture-loving plant, but does not tolerate stagnant water.
More on the topic: Black (chokeberry) raspberry
The optimal direction of the ranks of the Yellow Giant is from north to south. In this case, each shoot will receive the share of heat and light necessary for development. The site should not be located in a low or high elevation.
In no case should the Yellow Giant be planted on old raspberry beds.Not only is the soil there is severely depleted, and pests can also be inherited.
Modern varieties of raspberries for growing in the country
Raspberries are one of the most delicious and beneficial fruit berries that both adults and children like so much. The queen among berries, red and yellow raspberries have many varieties that differ in yield, duration and ripening conditions.


New types of fruiting raspberries are an ideal solution for summer residents in Moscow and the Moscow region, since they do not require careful plant care.
Modern plant species are not susceptible to diseases such as mycoplasmosis and curliness, they are not afraid of aphids and spider mites.
Yielding varieties of garden fruit-bearing raspberries:
- Kalashnik - this species is used for the autumn harvest. Large juicy berries do not rot on the bushes for a long time.
- Indian Summer is the first breeding species bred in Russia. Ideal for cultivation in the south and central part of the country.
- Bryansk Jubilee - bears the harvest at the end of July, then again in the fall. Fruits are medium in size, firm, and keep their shape well.
- Tatiana - bears fruit from the beginning of July until the first frost. During the first harvest, 10 gram fruits can be harvested.
- Polka is a European species, leading in yield among other varieties. They do not tolerate heat and drought, as well as severe frost.
- Autumn beauty - has medium fruits that ripen at the end of summer and ripen until the beginning of October. The yield of one shrub is 7 kg of berries.


Choosing the best raspberry variety for your garden is easy. Based on the area of residence, you can select several species of different ripening periods and plant them on your site. It should also be noted that the taste of the berries is different - tart-sweet, with sourness.
Every year, remontant raspberries are becoming more and more popular due to their high performance, resistance to many negative factors. Today's summer residents prefer to grow modern varieties of red or yellow raspberries in order to get a decent harvest of delicious and beautiful berries.
How to harvest and where to store the crop?
The yellow giant, like any large-fruited raspberry, when ripe, suffers greatly from the vagaries of the weather. In extreme heat, ripe berries are baked in 3-4 days, if it rains frequently, gray rot develops. Therefore, the crop should ideally be removed daily or at least 2-3 times a week.


If you create optimal conditions for the Yellow Giant, a bucket of raspberries is quite real
This raspberry is separated from the receptacle very carefully. The slightest pressure shortens the already short shelf life of the fruit. Try to touch the berries to a minimum, holding them by the stalk. It is advisable to use a flat, shallow container, covered with a soft cloth or napkins, and lay out the raspberries in one layer so that the berries do not come into contact with each other. Both raspberries and containers must be absolutely dry. Therefore, early morning for harvesting is unacceptable.
Fresh Yellow Giant can be kept only for 1–2 days, and even then, if you put the berries in paper or open plastic bags and put them in a special compartment of the refrigerator as far away from pungent-smelling foods as possible. Part of the harvest is inevitably remembered.
More acceptable ways to store raspberries for a long time:
- Home canning and winemaking. The Yellow Giant variety is universal, it is equally well suited for jam, jam, compotes, liqueurs, and wines. The finished product, due to the color of the berries, looks somewhat unusual, but the taste is definitely on top.
- Drying. Best of all - in a special electric dryer, but a regular oven and a Russian stove will do. Dried raspberries become even sweeter, do not lose nutrients, their shelf life is practically unlimited.
- Freezing. It is advisable to use the "shock" freeze mode, so that when defrosting, the Yellow Giant does not lose its shape, turning into an unappetizing porridge.Shelf life is up to 12 months, then all the benefits and most of the taste are lost.
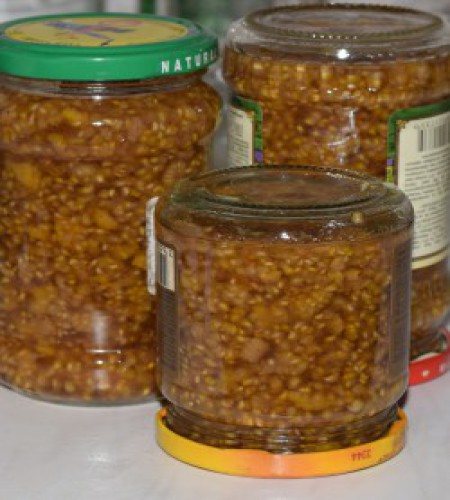


Yellow raspberry jam looks unusual, but tastes as good as a red berry product
How to care for a variety?
We recommend reading our other articles
- Peach variety Golden Jubilee
- Pear variety Just Maria
- Downy goat breeds
- Apple variety Bogatyr
High-quality care will allow you to harvest as early as possible, and the taste of the berries will pleasantly delight the gardener.
- Raspberry Yellow Giant loves moisture, but not its abundance. Watering is needed regularly, in small quantities, so that the land does not swamp. You can equip a drip system if the planting scale is large and this procedure takes a long time.


Weeds should not grow in plantings
- Weed plants should not grow in plantings, they must be uprooted all the time and burned outside the site, otherwise they will put seeds into the ground and germinate again. To simplify this procedure, you can pour a layer of mulch under the raspberry bushes in the rows. This is additional nutrition for the earth and plants, the ability to keep moisture in the soil longer, blocking the access of the sun to the weeds (they will have nowhere to grow).
- The first harvest of the year always ripens on last year's pagons. Young twigs usually bear fruit in early or mid-autumn. Proceeding from this, and it is necessary to carry out pruning. If you cut all the root pagons, the harvest in the new year will be late. Since the young growth needs to ripen so that berries begin to appear on it.
- Pagons of this variety are strong and thick, therefore they can withstand the load of the crop without any problems, do not break or bend much. However, the berries may not be very convenient to pick, especially if the bushes are overgrown. Therefore, they are usually grown on a trellis or simply formed in even rows and tied up. This makes harvesting and moving between rows easier.


Fertilizers are always applied before winter in the aisles
- Fertilizers are always applied in the aisles before winter. Organics or minerals are introduced for digging, you can alternate them over the years. From organic matter, humus, compost, ash are suitable. From minerals, you can choose superphosphate.
- Treatment from pests is rarely necessary, usually it is not carried out, except for prophylaxis by any folk remedies. Raspberry Yellow Giant copes well with these problems without the help of a gardener. Intervention is necessary only if the disease is incurable or if the disease (pest) quickly affects neighboring crops.
Raspberry remontant: the best varieties for growing
Selection does not stand still, every year the best agronomists of the country work on breeding the best varieties of fruits and vegetables. Crossing different types of raspberries, breeders were able to develop new remontant varieties that do not have similar ones in the whole world.
Repaired varieties can bear fruit for more than one month, as usual - the crop from the bushes can be harvested within three months from August to the first frost.
The main property is the ability to yield crops on biennial and annual shoots. However, modern breeders have identified such a feature: fruiting on two-year-old shoots can weaken the plant, reduce productivity and delay the fruiting of the second period. The fruit growers agreed that it is more profitable to grow annual raspberries, which bear fruit in late summer and early autumn.


The cultivated varieties of fruiting raspberries are devoid of the disadvantages inherent in ordinary berry bushes. The problem of winter hardiness disappears: when frost sets in, its branches are cut to ground level. Unlike ordinary raspberry bushes, which require some care (cutting off the fruiting stems, bending the bushes to the ground and wrapping them for the frost period), caring for the bushes of remontant varieties does not require special care.
Since with the onset of cold weather all the stems are removed from the garden, pests are destroyed along with them.This is one of the positive aspects, since infections and insects do not remain on the shoots, respectively, new branches are relieved of this scourge. For the cultivation of remontant raspberries, chemical preparations are practically not used, the berry is environmentally friendly.



































