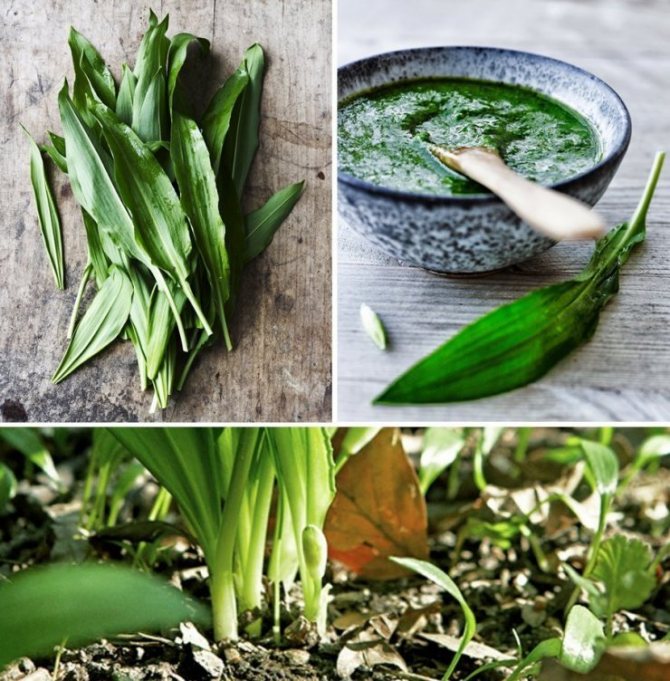
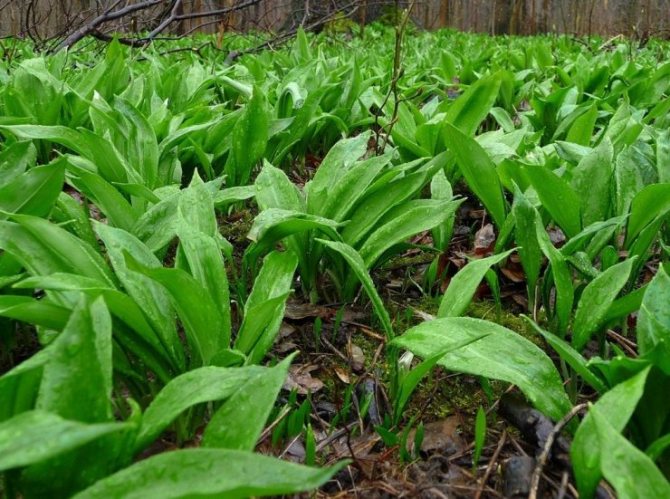
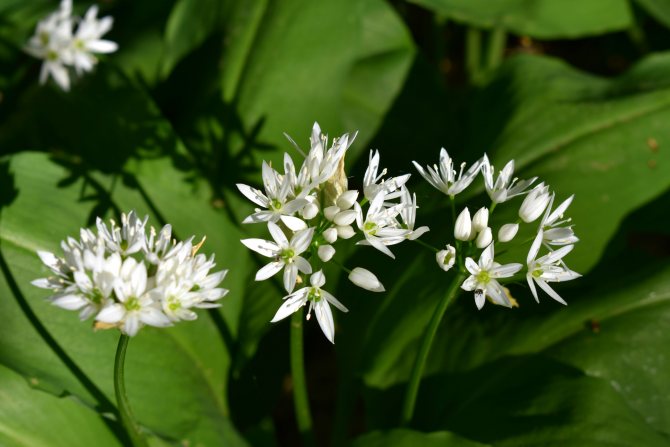
Ramson, or Bear onion (Allium ursinum) in our country, a little-known, although very valuable plant. This species belongs to the Amaryllis family and grows throughout the forests in Turkey, the Caucasus and Europe. In our country, it is found mainly in Siberia, the Urals, the Far East, and also settles in forests and in other parts of Russia. Ramson leaves in very early spring (March) and is one of the first plants to appear after winter. Because of this, many animals, including bears, enjoy the aromatic plant with pleasure, especially since wild garlic is very nutritious and has the properties of a natural antibiotic that strengthens the body weakened in winter. However, it is worth knowing that in natural conditions wild garlic is protected, because because of its valuable medicinal properties, it is under the threat of extinction. Therefore, you should not dig it out of the forest in order to plant it in the garden, but rather purchase seedlings or seeds from a reputable seller or in a plant breeding nursery.
What is wild garlic: types of plants with photos and descriptions
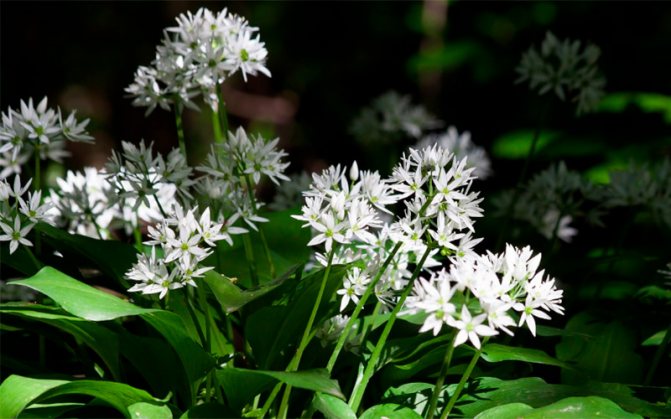
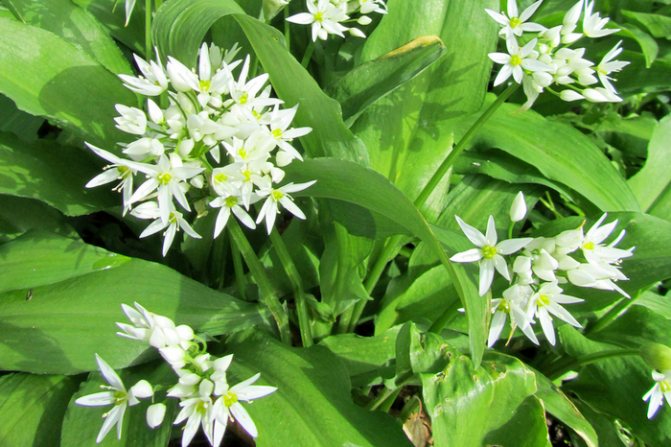
Wild garlic, chenzels, bear bow, levurda, flask, wild garlic - a discreet perennial herb that reveals its full beauty in late spring - early summer. Its light green leaves, similar to lily of the valley, are prized for their pleasant garlic taste and useful properties that not only strengthen, but also heal the body.
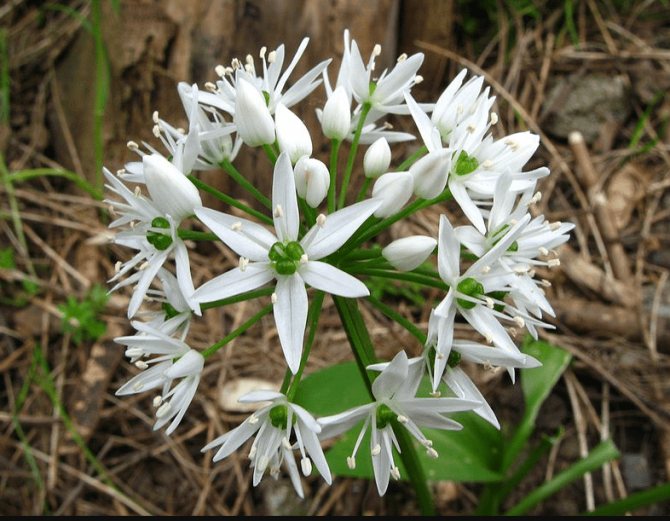

Bear onion (Allium ursinum) grows throughout Europe and the Caucasus.
Wild garlic can be found most often in shady deciduous and deciduous-spruce forests, in beams, lowlands - where it is humid enough. The area of its growth is incredibly wide. Austria, Great Britain, Georgia, Spain, Netherlands, Slovakia, France ... Wherever it does not grow!
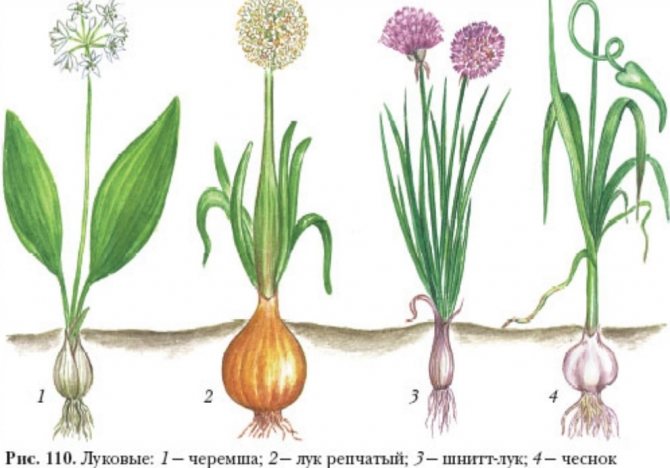
To call everything a wild garlic is, to put it mildly, wrong. It can be of two main types, which are quite different from each other.
- Allium ursinum - Bear onion (in our country it is found in the Caucasus).
- Allium victorialis - Victory bow (distributed mainly in the Far East and Siberia).
On a note! In many countries, wild garlic is protected and included in the Red Book, for this reason it is increasingly grown as a cultivated plant.
In stores, the "European" wild garlic is more common, or, more simply, bear onion.
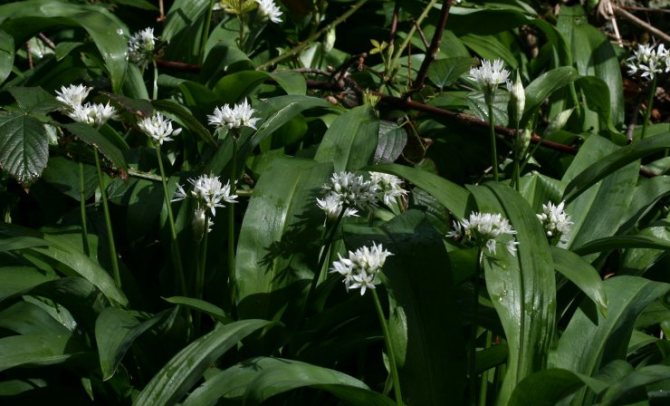
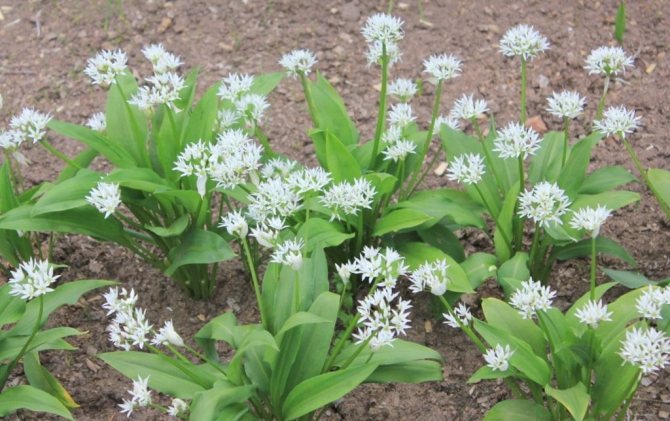
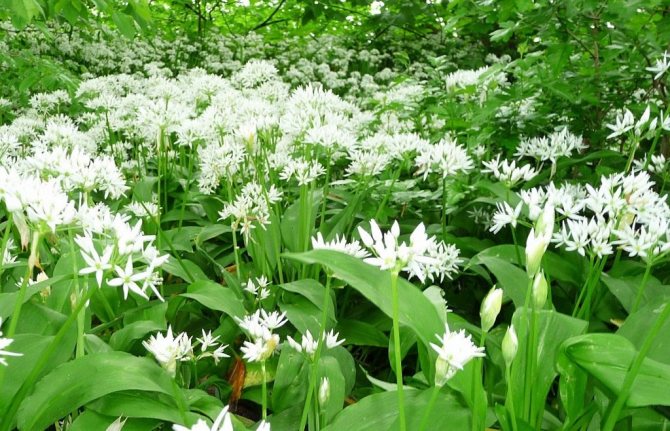
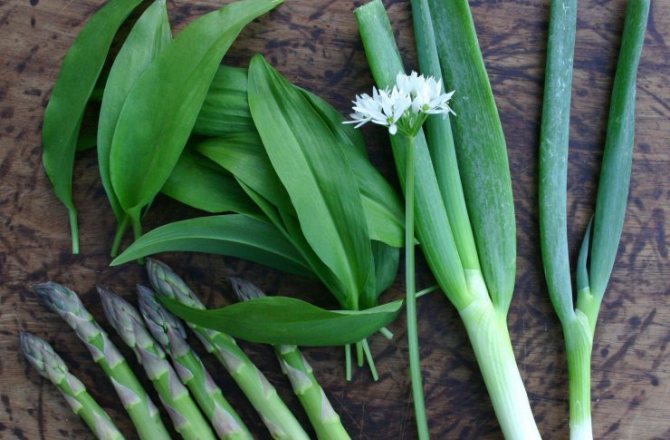
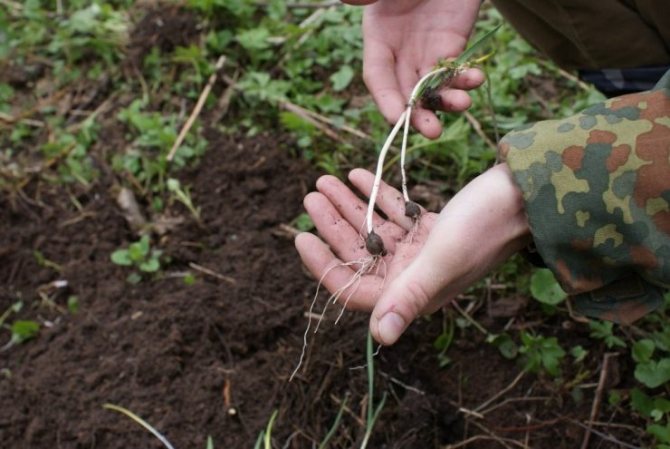
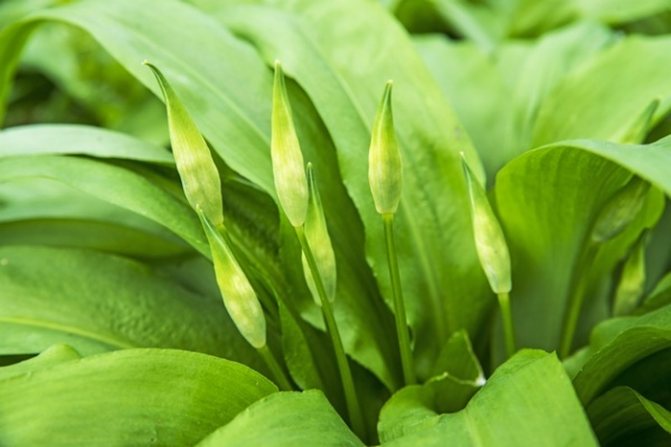
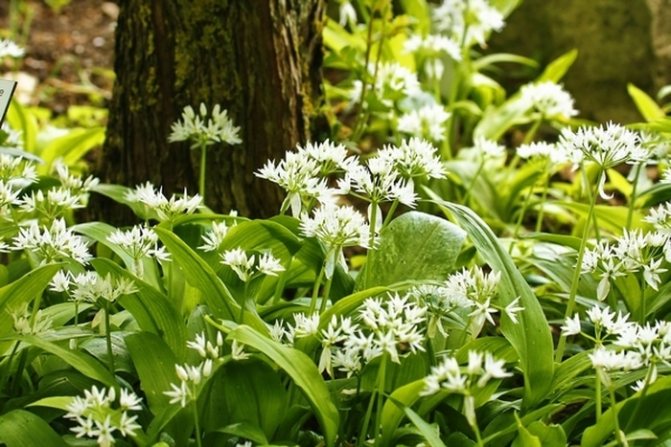
The plant has bulbs, oblong in shape, about a centimeter long, a triangular high stem and a pair of leaves, tightly covering the stem at the base. The blade of the leaf is also peculiar, it is lanceolate, gradually turning into a petiole. The bear onion forms a hemispherical, bearing some snow-white flowers, the inflorescence and the fruit - a spherical box, in which there is a handful of black seeds.


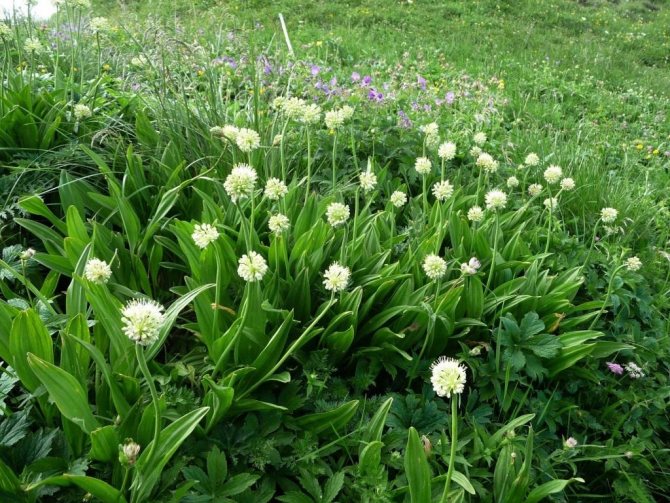
The second type is the so-called victorious wild garlic, or victorious bow. It is such a plant that can often be found in the beds in Siberia. It is usually larger than the previous species. It is based on a cylindrical-conical bulb. Often there are two or three small diameters. Each onion, separately from its neighbor, is attached to the oblique rhizome.
On a note! It is believed that the victorious wild garlic originated in Asia. The plant is also found in the wild in the Far East, Siberia and the Urals.And in Europe, archaeologists have found ancient wild garlic seeds during excavations of settlements that existed in the Stone Age.
The stem of Siberian wild garlic is taller, its average "height" is about a meter. Individual specimens may even exceed this bar. The stem is not bare, it is covered with leaves up to half. The plant bears a spherical graceful inflorescence with numerous whitish flowers.
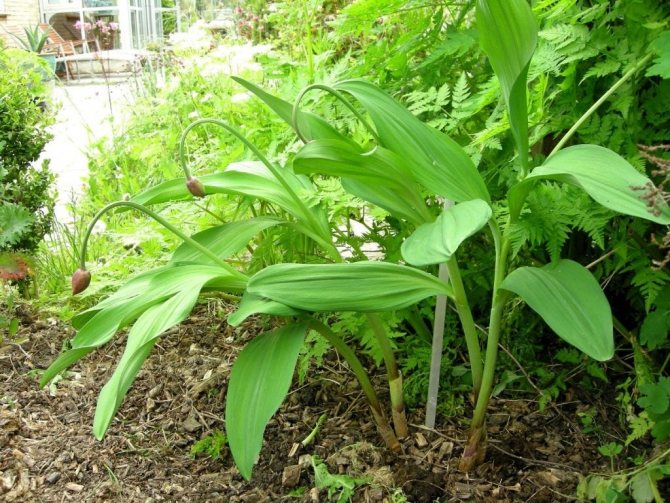


The victorious onion grows in Europe, the Caucasus and Siberia.
This type of wild garlic is suitable for cultivation both as a vegetable crop and as a decorative one, since it can form a very effective dense bush. Its globular inflorescences are formed at a time when other cultures, such as onions, are just beginning to develop. Sometimes wild garlic is planted literally along the borders of a garden plot, not far from large trees, a fence or a wall of a residential building. Comparative characteristics of bear onion varieties:
| Variety name | Bush height, cm | Leaf sizes, cm | Days from the beginning of regrowth to the first collection of leaves | Productivity, kg / sq.m | Originator company |
| Bear delicacy | 55 | 20–25 | 15 | up to 2.0 | "Sortsemovosch", St. Petersburg |
| Teddy bear | up to 60 | 20–30 | 1,6 | "Russian seeds", Moscow | |
| Bear ear | 55–60 | 20 | 1,9–2,5 | IP Kudryavtseva, Moscow |
Siberian wild garlic (victorious onion) has not yet been developed culturally zoned varieties. Hobby gardeners successfully grow plants taken from the wild or purchased from other gardeners. In Siberia and the Far East, there is still a lot of wild garlic, so you can carefully dig a few bushes in the forest or collect seeds from wild thickets.
Natural habitat
It is necessary to remember what wild garlic is, what kind of plant it is and where it grows. Most often it can be found in the forest and in valleys near rivers, in meadows and fields, but many people grow this plant in their country houses. Ramson grows rapidly, therefore its natural habitat in a temperate and subtropical climate is very wide.
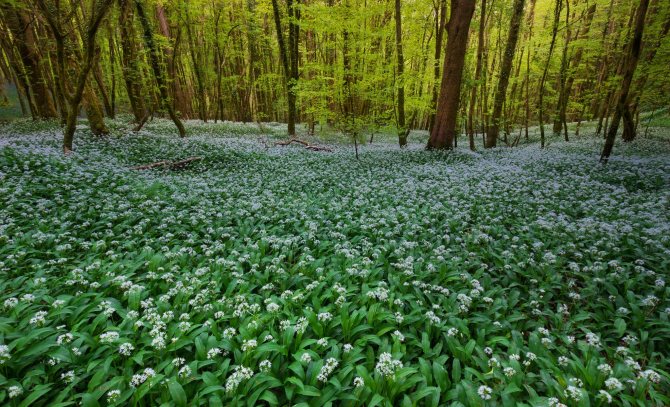


Forest thickets
Where does wild garlic grow:
- Central Europe.
- Scandinavia, Great Britain, Ireland.
- Southern Europe, Corsica, Sicily.
- Ukraine, Belarus.
- Russia (all territories, except for the Far North and the tundra).
- Caucasus and Transcaucasia.
- Turkey.
Wild garlic feels most comfortable at a temperature of +12 .. + 17 ° C. Too warm, dry weather (above +20 ° C) and even more so the heat is destructive for it. Due to unfavorable weather conditions, this plant loses its beneficial properties and taste.
Attention! In many regions of Russia and in some other countries, wild garlic is listed in the Red Book.
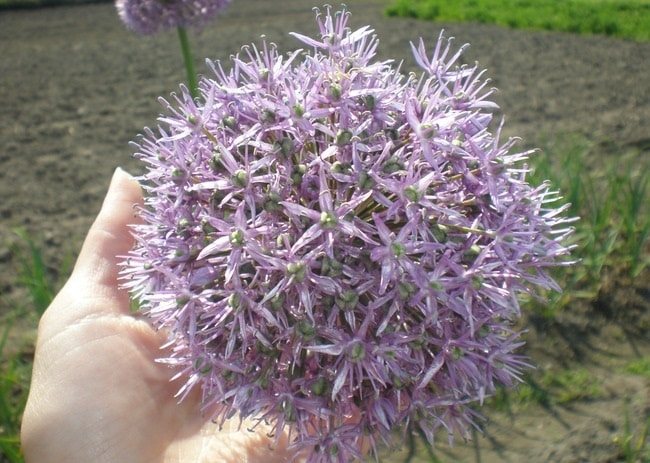


The petals can be purple or lilac.
Cultural varieties of wild garlic in Russia
The introduction of the bear onion into culture began not so long ago. In our country, scientists have bred three varieties with very romantic names - Bear delicacy, Teddy bear, Bear ear.
Such close names, obviously, were chosen for it due to the fact that in nature a bear likes to feast on a plant.
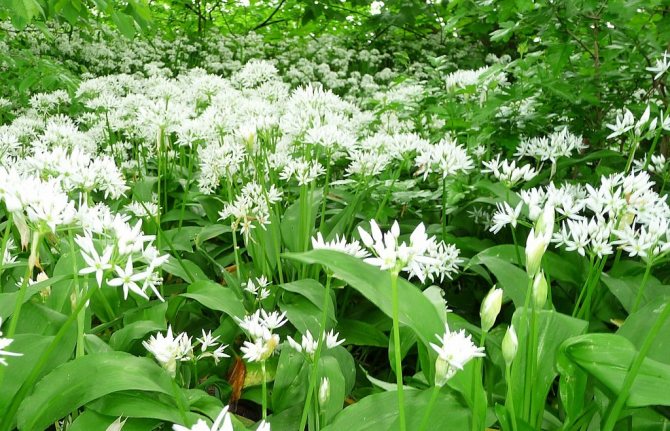


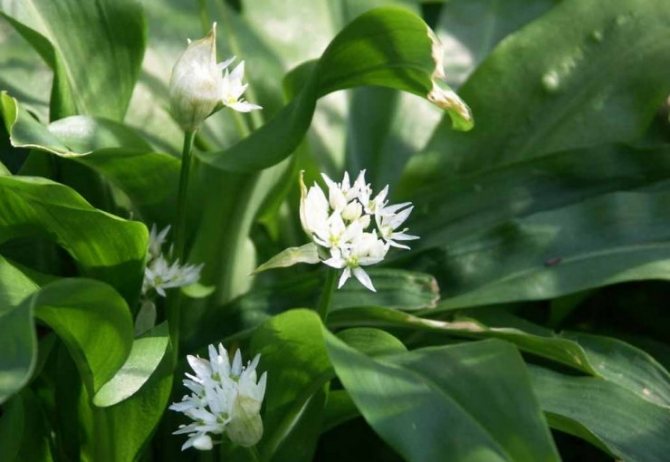
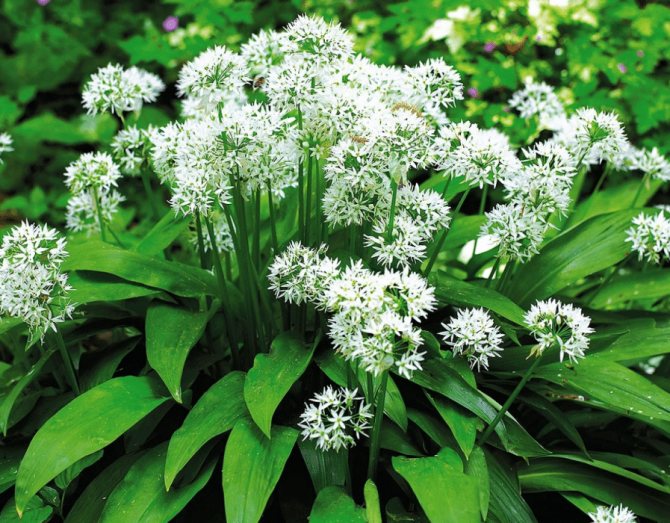
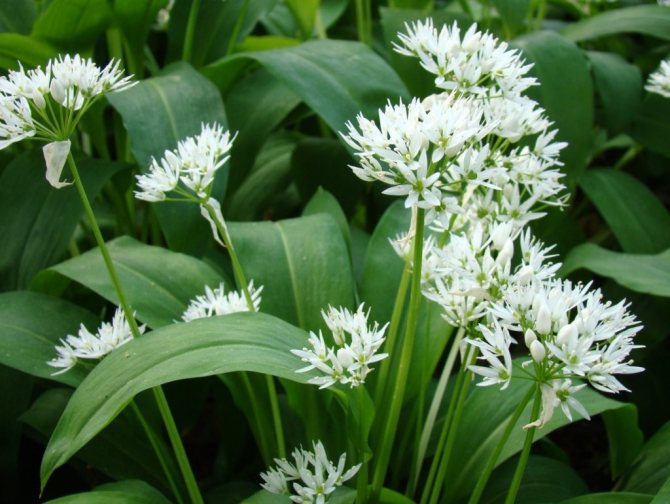
Blooming bear onion.
All three contain a large amount of biologically active substances and can be grown on an industrial scale. Their taste and appearance in general coincide with the description of the natural wild-growing species, there are only minor differences in the size of the leaves and the speed of their regrowth. All varieties are intended for garden plots and personal subsidiary plots, can be grown throughout the territory of the Russian Federation and in neighboring regions.
In turn, the victory bow is widespread in Siberia and the Far East. However, it is almost impossible to find this plant in the center of the country. For its full adaptability to the harsh climatic conditions, the locals called it - Siberian wild garlic.
Application
Bird cherry is bred in gardens and parks as an ornamental plant; especially elegant are its modern forms with pink or double flowers, purple or variegated leaves.
But it is not only decorative, but also known as a fruit crop, which has recently received state recognition: some varieties of bird cherry are included in the State Register of Breeding Achievements of the Russian Federation. The fruits are used for food, for tinting drinks; decoctions or infusions of them are used as astringent and anti-inflammatory agents. The fruits contain sugar, pectin substances, organic acids (citric, malic, caffeic, etc.), amino acids, ascorbic acid (vitamin C), P-active substances (rutin, catechins, anthocyanins, leukoanthocyanins, flavonols, tannins), tocopherols (vitamin E), carotenes (provitamin A), glycosides, fatty and essential oils, macro- and microelements.
A dye is extracted from the bark of the bird cherry; fine-grained wood is used for crafts.
In culture, the common bird cherry (Padus racemosa) with black, astringent, lacquered fruits, and the American species - the Virginia bird cherry ( Padus virginiana
) with red fruits and bird cherry late (
Padus serotina
). In the USA and Canada, more than 15 varieties of Virginia bird cherry for food purposes have been obtained. In new varieties of bird cherry, the fruits are larger and less tart, with a peculiar piquant taste.
The genus Bird cherry is close to the genus Cherry, related to the genera Lavrovishnya, Plum and Almond; often all these 5 genera are combined into a single genus (Prunus).
The hybrid of bird cherry and cherry Cerapadus 1, bred by IV Michurin, has bitter fruits and is used in breeding work. With the participation of this plant and the Maak bird cherry, such cherry varieties as Renaissance, Novella, Olympus, Pamyat Shcherbakov, Rusinka, Feya, Kharitonovskaya, etc. were obtained.
In folk medicine, bird cherry is used for many diseases.
Features and morphology of the wild garlic plant
Ramson is an ephemeroid. In other words, a perennial, the aerial part of which develops in spring, and dies off by the end of summer. Its tender leaves sprouted in March are the first vitamin greens. But, the older the plant becomes, the coarser its tissue, therefore, the collection of wild garlic continues only until flowering, which begins in May.
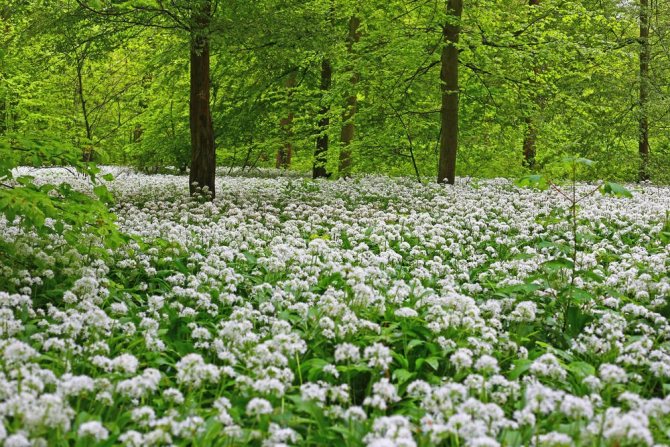


Ramson (bear onion, victory onion, wild garlic, flask) is a perennial herb from the Onion family.
After flowering, seeds fall off the wild garlic. They will germinate only next year. If they are kept and sown in the spring, they will not sprout until the next spring season. But wild garlic reproduces in another way - vegetatively. Well-formed plants form two replacement bulbs, which can be detached and planted in the garden.
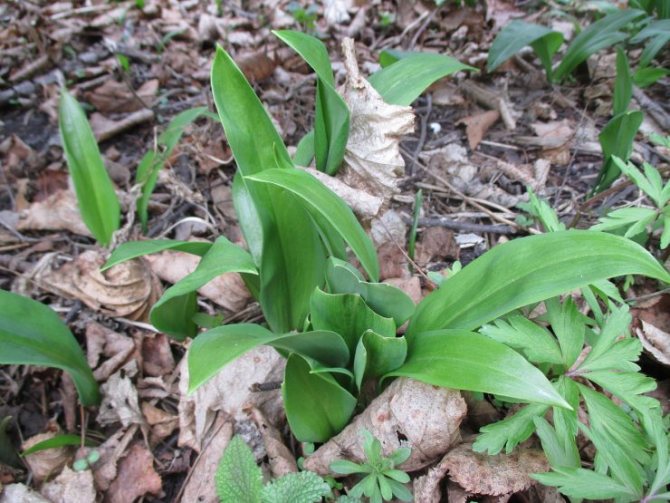
It is not by chance that the Amaryllis wild garlic belongs to the genus Onions, subfamily Onions. It really has a small elongated bulb, about 1 cm in diameter. During flowering, it throws out an umbrella inflorescence, on a rather long, from 15 to 50 cm triangular stem. Has linear-lanceolate, white tepals. The fruit forms a box with almost round seeds. But wild garlic has only two true leaves. Rather narrow, 3 - 5 cm wide, sharp, lanceolate, they are somewhat inferior in height to the stem. Their petiole is narrower than the base plate and is almost twice as long as it.
Description of culture
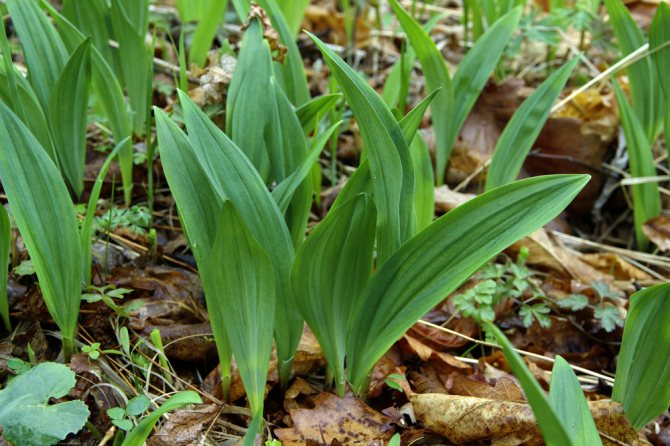
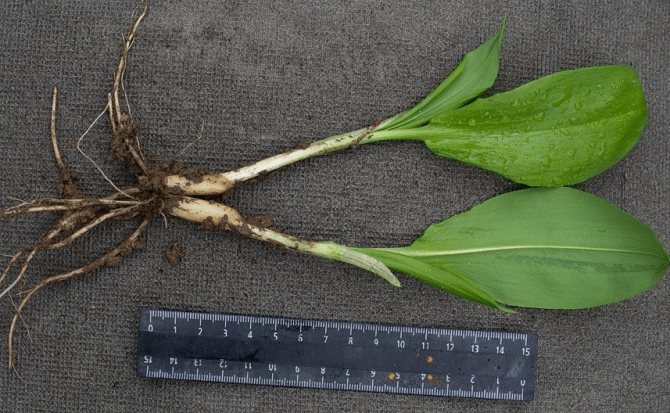
What is ramson? What does wild garlic look like? Ramson is a perennial aromatic herb. In smell and taste, it resembles onion, garlic. However, according to reviews, its taste is similar to other onion plants, but much softer, richer. The plant has a height of 20 to 60 cm. The stem and leaves of wild garlic develop from a bulb in the ground. The onion is elongated, narrow. The stem is emerald erect, has three sides. Its base is framed by leaf stalks. The shape of the leaves is oblong, the apex is sharp.The color is bright light green. The stem has two leaves. Each of the petioles extends slightly longer than the leaf plate.
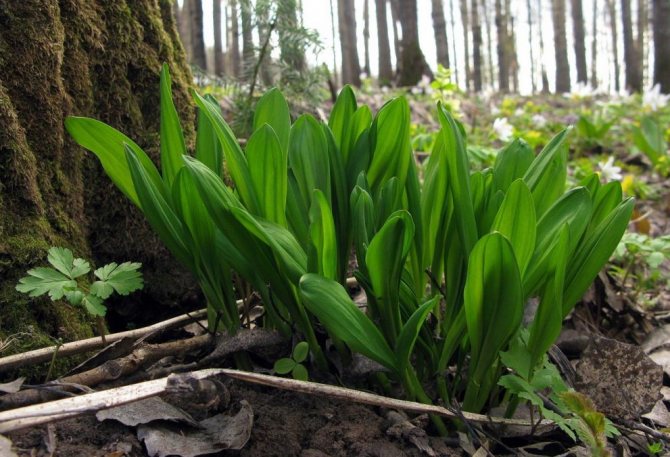


Ramson in deciduous-coniferous forest
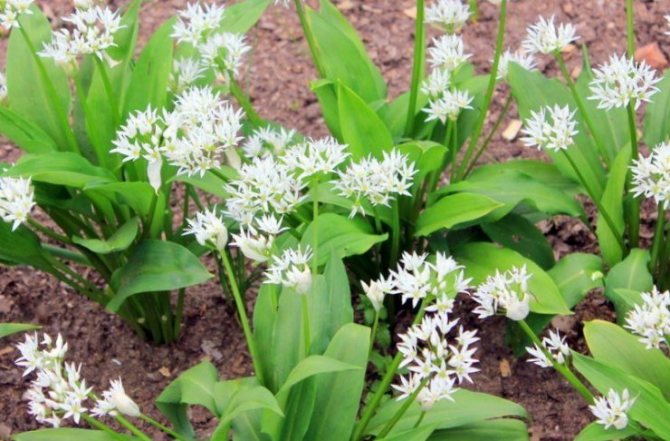
Leaves of wild garlic can be seen as soon as the snow begins to melt. The collection of wild-growing wild garlic takes place from March to May. Then its greens can have a juicy taste. In May-June, wild garlic begins to bloom. At this time, a very beautiful blooming umbrella in the form of a ball appears from an elongated stem. The flowers are star-shaped. The color is whitish, white. After a few weeks, the umbrella changes color to yellow-black. In place of the flowers, oil-colored peas appear. In August-September, the bulbs of the plant are collected.
The plant outwardly does not look like an ordinary onion that grows in the garden. In shape and color of the leaf plate, it resembles a lily of the valley.
How to grow wild garlic outdoors
The culture is just perfect for growing both in the open field and in a protected one, or it can settle on your balcony or loggia.
On a note! When determining a place for planting wild garlic, it is worth remembering that this culture loves sufficiently fertile soils, shading from direct sunlight and moisture. For this reason, it is better to place it under trees or a fence - where there is no scorching sun, there is no stagnation of water and the soil is not highly acidic.
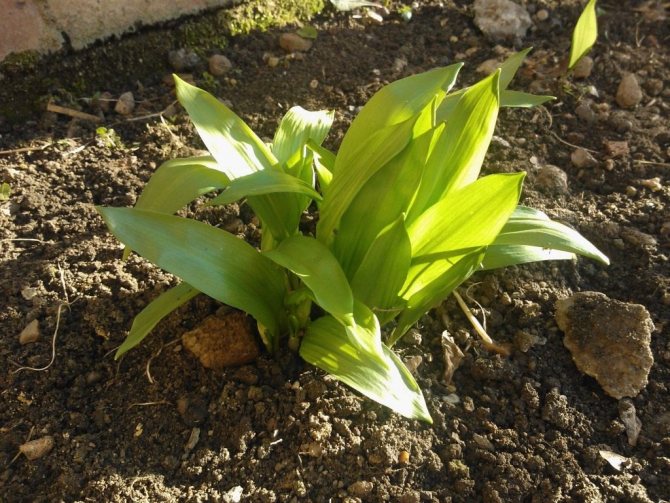


Ramson, or Bear Onion, or Wild Garlic.
Cheremshina what kind of plant is it?
Leaves are simple, alternate, oblong-elliptical, pointed, sharply serrate along the edge; drooping stipules; on the top of the petiole, at the base of the leaf blade, there are two glands.
The flowers are white (less often pinkish), collected in long drooping racemes, with a strong odor; honey plant. There are 5 sepals and petals, many stamens, one pistil. Blooms in late April - early May. Bird cherry flowers, as well as leaves and even bark, emit a large amount of phytoncides that disinfect the air.
Planting and caring for wild garlic outdoors
For the first two years, the plants are only looked after: watered, loosened, fed (with any complex fertilizer once or twice a season). Since the wild garlic bulbs tend to rise from the ground by about 0.5 cm every year, starting from the second year, the garden bed is mulched with a thin layer of fallen leaves.
The victorious onion loves sunny areas, which usually goes against the wishes of the average owner of six acres, because, as a rule, such crops are tried to be placed on more shaded lands. However, even in such unfavorable conditions, wild garlic can grow well.


Ramson comes out of the soil very early.
She is picky only about the acidity of the soil. In a too acidified area, wild garlic will not grow at all. She also loves an abundance of moisture, but not an excess of it. The main thing is not to allow the soil to dry out, the leaves in this case can become rough.
After a one-time planting, wild garlic can grow in one place for many years. But for this it requires simple maintenance. You need to fight weeds only at the initial stage, while the plants have not yet gained strength. They will then deal with this threat on their own.
How to feed wild garlic
If the soil is fertile enough, then the first few years can not be fertilized. Over time, the earth will begin to deplete, and then the time will come for artificial recharge. You can use nitrogen fertilizers, for example, in the form of ammonium nitrate in a ratio of 20-30 grams per square meter.
On a note! Ramson also adores organic matter introduced for digging the soil. The plant will respond to such feeding with active growth and rapid formation of vegetative mass.
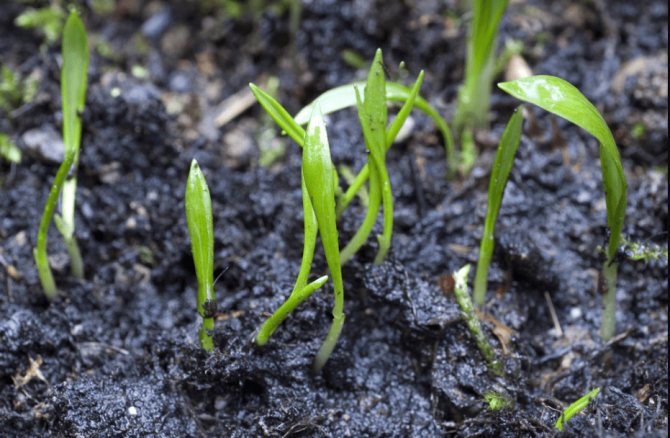


Wild garlic (wild garlic) grows almost everywhere.
The best fertilizer for wild garlic is leaf humus, which is scattered in a thin layer over the surface of the earth with the onset of autumn. As a last resort, you can replace it with completely decomposed compost.
Transplanting wild garlic: bulb conservation technology
Seedlings planted in the garden usually grow for another year. When they are strong enough, they can be transplanted to a permanent place. This is best done in the spring, as the soil is very soft at this time. Under these conditions, it is easy to dig up the plants without damaging the bulbs.
When planting, they can be slightly deepened. This technology is often used in suburban areas where the gardener is not able to work daily. Deepening allows you to save bulbs and plants in general from possible short-term drought.
After planting wild garlic, it is necessary to water it with warm water, in which small doses of nitrogen fertilizers can be dissolved. When transplanting, you should pay attention to the possible presence of peduncles on the plants. If they are present, then they must be trimmed. This is done in order to allow the bulbs to take root normally in a new place, while saving nutrients.
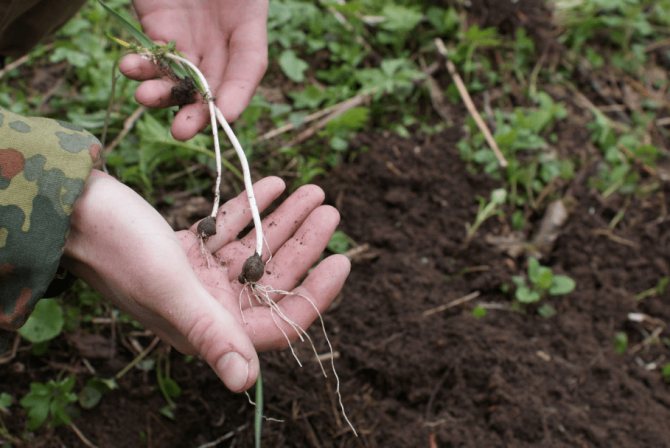


The safest and fastest way to get vitamin greens in your garden is to plant bear onion bulbs.
Sometimes wild garlic is transplanted not in spring, but closer to autumn. At this time, the entire aerial part of the plants dies off and the bulbs are dormant. They are planted in such a way that they are buried a couple of centimeters into the soil. Otherwise, the bulbs may not take root.
On a note! If you decide to set aside a large area for wild garlic, then plan the planting in advance. It should be borne in mind that no more than 75 bulbs should fall on one square meter of land. From them it will be possible to collect up to 1.5 kg of fresh herbs. By the way, it is necessary to cut it off selectively so that the onions are not very depleted.
Folk recipes using wild onions
All kinds of decoctions, infusions and ointments are prepared on the basis of the leaves and stem of the plant. All useful qualities of wild garlic are in its juice, it is used both inside and outside. We present you with several recipes:
- tincture against joint diseases - finely chop fresh wild garlic and fill with vodka in a ratio of 1 to 4. Soak for 10 days, then strain and use to rub the joints twice a day for arthritis, arthrosis and rheumatism until symptoms disappear. Also, the tincture can be taken orally for a month, twice a day, 30 drops for atherosclerosis;
- ramson juice against herpes, purulent wounds and bedsores - for infected wounds, as well as ulcers, bedsores, etc. wipe the affected areas with plant juice up to 4 times a day. And for lichen and warts, juice-based lotions are applied to the affected areas for 15 minutes. The same juice can be dripped into the ears with purulent otitis media twice a day, then after 15 minutes the ears are washed;
- remedy for periodontal disease - in a one-to-one ratio, combine wild garlic juice and vodka, then dilute a spoonful of the resulting product in 100 ml of water and rinse your mouth twice a day with the resulting liquid. Treatment lasts 2 weeks;
- infusion against gastritis, colds and kidney diseases - leaves and onions from two plants of bear onion are poured with 300 ml of water and heated over a fire for 10 minutes, then leave for two hours. Strain the infusion and drink for digestive diseases, inflammation of the bladder, kidney stones or pyelonephritis, a quarter cup three times a day for two weeks;
- for pain in the spine and eye inflammation - fresh wild garlic is crushed and pounded into gruel, put in gauze and attach to the sore spot. In the presence of conjunctivitis, the gruel is placed on the eyelids twice a day for 5 minutes, and the product can be kept on the back for up to an hour. The treatment lasts about 10 days;
- infusion for vitamin deficiency or bronchitis - boil 10 leaves of the plant in a glass of white wine for 5 minutes and then strain. Add a small spoonful of honey and drink in small portions throughout the day. With pulmonary diseases, the course of treatment is 10 days, with avitaminosis - 2 weeks;
- remedy for hypertension - take 0.5 kg of wild garlic, horseradish, onion and lemons. We clean all of the above, except for lemons, then grind everything through a meat grinder. Fill with two liters of water and leave for a month. Drink one spoonful on an empty stomach three times a day to stabilize blood pressure.
Remember that all the recipes listed above cannot fully replace the help of a qualified doctor. Any use of such funds must be agreed with a doctor.
Joint planting: companion plants of wild garlic
Due to the complete death of leaves in the middle of summer, there is always a danger of losing, drying out or accidentally trampling the wild garlic plantation. The easiest way to solve this problem is by planting suitable plant neighbors. For this, large, slowly growing perennials are suitable, which feel good in damp shade and retain their beautiful foliage until late autumn. For areas with severe winters, these are, first of all, local species of large rosette ferns (ostrich, shititnik, kochedyzhnik), volzhanka (aruncus), winter-hardy species and varieties of meadowsweet (meadowsweet). In the middle lane and to the south, rogers and large-leaved hosta varieties are added to them.
The benefits of such joint plantings are obvious:
- The plot looks decorative throughout the season.
- The ramson will not be lost or trampled; if necessary, it is easy to find and dig it out even in a leafless state.
- Watering ornamental perennials provides sufficient moisture for wild garlic.
- Weeds grow less in this area than on bare ground with dormant bulbs.
Companion plants are planted about a meter apart, and wild garlic curtains are placed between them. Such a composition withstands well 5-7 years without transplanting and dividing.
If there is very little space or there are problems with water for irrigation, you can do without accompanying plants. In this case, wild garlic bulbs are placed 15-25 centimeters apart. To protect against weeds, you can cover the plantings with black mulching agrofibre in the second half of summer. At the beginning of autumn, this protective coating must be removed.
Breeding methods for wild garlic
As for reproduction, the best option here is vegetative, bulbs. To do this, in early spring or on a cloudy summer day, it is necessary to separate part of the bulbs (necessarily with roots) from the curtain and plant them in rows at a distance of 20 - 35 cm from each other with row spacing of 30 - 45 cm.
However, getting them even in our time is very problematic. Instead, you can master the seed propagation method. If you decide not to acquire them, but to assemble them yourself, then it is worth remembering a number of nuances so that there are no unpleasant surprises in the future.


When transplanting wild garlic, it is important to protect the roots from drying out and mechanical damage.
It should be borne in mind that the seeds ripen quite early, already in the middle of summer. You should not wait for them to fall out of the boxes, because collecting from the ground will become problematic. In addition, they will take a very long time to germinate. The ideal option is to extract the seeds that have not yet formed a hard shell directly from the capsules. Such planting material will germinate much faster, and the germination percentage will be significantly higher.
Note! When sowing, the seeds are not buried in the soil, but mulched with a small layer of earth.
Seeds can be sown right in the summer, when the workload in the garden is not so great. It is better to place them immediately in the peat pots, which are now in vogue. Thus, you completely eliminate the need for a transplant. After a while, the pots can simply be dug into the ground, their shell will dissolve and will also become additional food for plant beginners.
How to collect and prepare wild garlic seeds for sowing
After flowering, seed pods are formed from flower umbrellas, which must be closely monitored, because they ripen very unevenly. Once the seeds are ripe, the pods dry out and open so that the seeds can spill out onto the ground.At this point, they must be collected and immediately sown in a permanent place. They are scattered over the surface of a loosened and leveled area, without falling asleep with soil, and watered carefully. Such sowing with freshly harvested seeds gives good shoots in the coming spring.
On a note! waiting until all the boxes burst is not worth it. You need to take a bowl and periodically shake off what has already ripened into it. Or put paper bags on the inflorescences and wait until the seeds fall into them themselves.
If the ripe seeds do not immediately fall into the moist soil and remain dry for more than a month, they begin a period of deep dormancy. Such seeds usually sprout after 2 winters. Older seeds completely lose their germination.
The easiest way to sow seeds before winter is immediately to a permanent place. But sometimes, for some reason, this is impossible (for example, if the seeds were purchased in late autumn or early winter, when deep snow has already fallen). In this case, the seeds need special preparation - stratification, without which they will never sprout.
At home, it is convenient to stratify the seeds in an ordinary household refrigerator. There are 2 main options:
- wrap the seeds in a damp cloth and wrap them in plastic;
- place the seeds in a small container with wet sand.
The napkin option is convenient in that you can periodically check the condition of the seeds. The package with wet seeds is placed in a refrigerator and kept at near-zero temperature for at least three months. In the spring, stratified seeds are sown in a permanent place. If suddenly the seeds began to actively germinate right in the refrigerator, and the snow is still far away, you can sow the germinated seeds in pots or boxes with soil, and then carefully plant them in the garden.
Features of growing wild garlic in the regions
Ramson feels great in all regions of the forest zone of the former USSR and even in the tundra. It is easy to grow it in the forest-steppe zone.
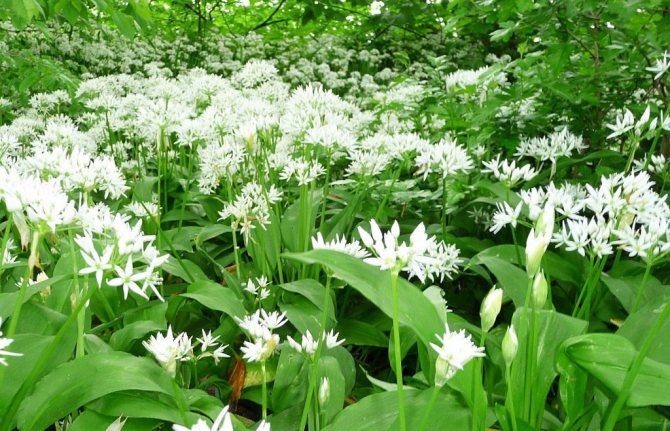


During flowering, wild garlic is very decorative.
Cultivation of wild garlic in the Urals, Siberia and the Far East... This is a favorable region for wild garlic, in the local forests its Siberian variety (flask, victory onion) grows in huge quantities. In areas with deep snow cover, you can also grow bear onion varieties. But for areas with little snow, with especially severe frosts, bear onions are not winter-hardy enough; in such conditions, only a local flask from the nearest forest survives.
Cultivation of wild garlic in the North-West, including the Leningrad region. The region is very favorable for both types of wild garlic. Cool, cloudy, rainy summers make it possible to grow wild garlic even in open areas. Watering is rarely required, only in the absence of rain for a long time.
Cultivation of wild garlic in Belarus, northern Ukraine and central Russia, including the Moscow region. When planted in a semi-shady or shady place, both types of wild garlic grow well here. In hot dry weather, watering is required at least 1 time per week. If wild garlic is planted under trees, watering is especially important: the roots of the trees dry out the soil a lot.
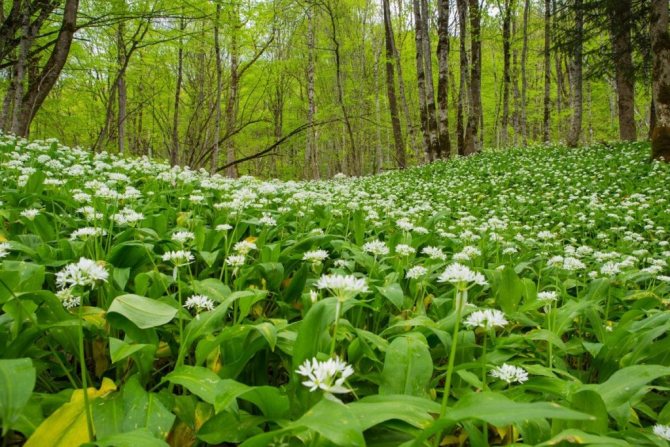


Ramson is a "leisurely" plant, grows slowly, yields only 1-2 replacement bulbs per year.
Cultivation of wild garlic in the steppe zone of Ukraine and in the south of Russia. It is uncomfortable for wild garlic here: it is too hot and too dry. The problem can be solved by landing in dense shade on the north side of the buildings. Watering is required 1-2 times a week. Here wild garlic grows best on the northern slopes, in deep ravines. The neighborhood with a stream humidifying the air will be favorable.
Diseases and pests of wild garlic
Pests and diseases of wild garlic are practically not scary. In rare cases, with strong waterlogging and on acidic soils, rust appears on it, and then gray rot.
On a note! The yellowing and death of leaves soon after flowering is a normal physiological process.


After flowering, wild garlic leaves gradually turn yellow and die off, this is a normal natural process.
Of the pests, the onion leaf beetle (onion cracker) is sometimes found. Beetles and their larvae feed on the leaves of wild garlic, other types of onions and garlic, as well as lilies, hazel grouses and other bulbous plants. The brightly colored red beetles are highly visible on plants and can be easily picked by hand and destroyed.
How to collect and procure


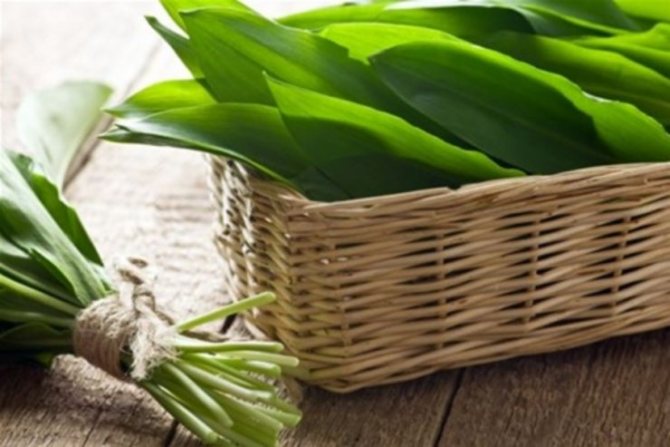
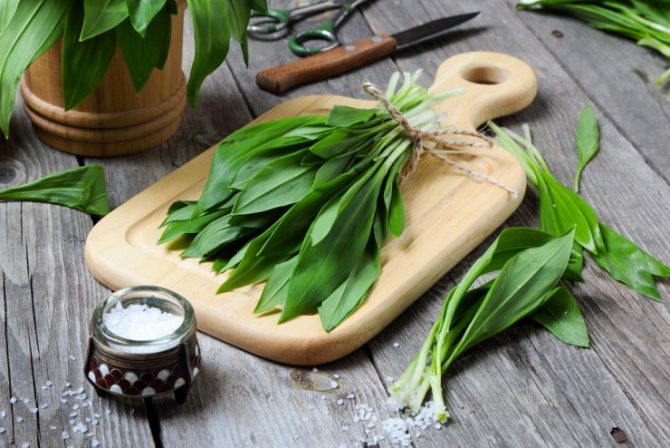
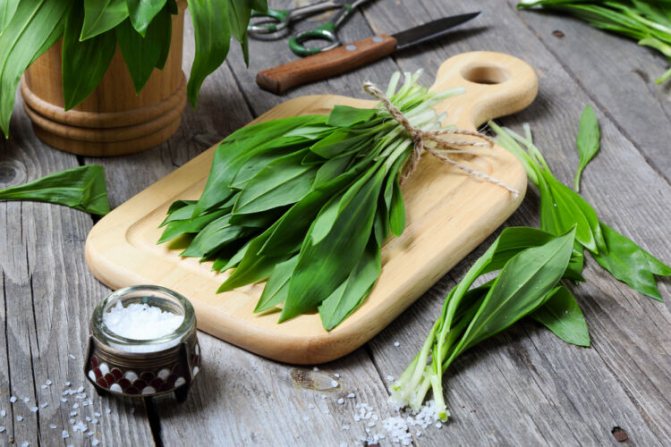
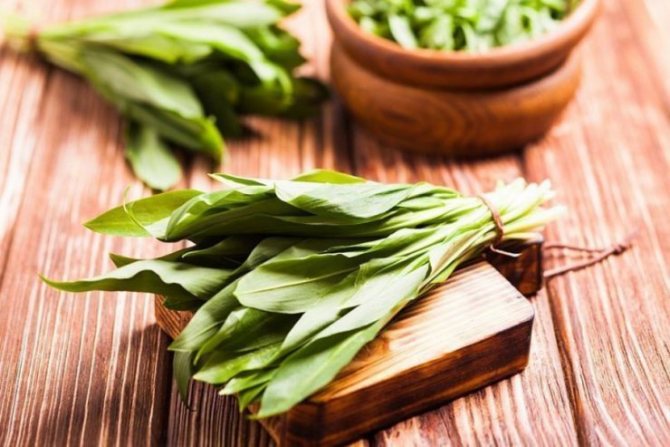
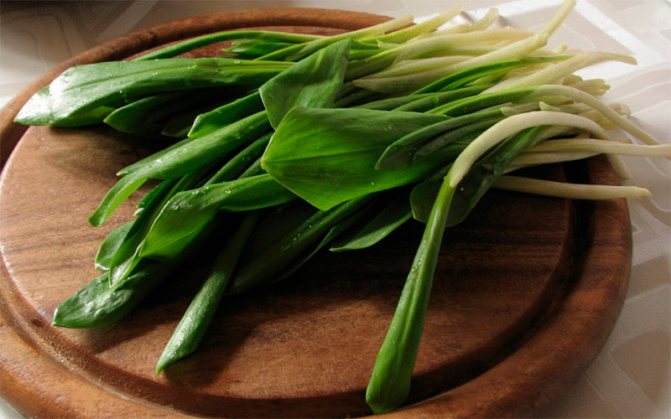
Green shoots of wild garlic are harvested exclusively before flowering begins, so they will be softer and less sharp. The bulbs are harvested in late August - early September.
Greens of wild garlic should be chosen young, there should be no spots, dry ends on it. It is not necessary to pull out the plant, the fragrant plates should be carefully cut off. The bulbs are dug out with a garden shovel like regular garlic.


The maximum useful properties are contained in a fresh plant, but you can prepare it for future use:
- greens are well stored in a polyethylene bag in the refrigerator. You can keep in a glass of water no more than 5 days;
- wild garlic can be frozen. To do this, it is washed and packaged in bags, placed in the freezer. It is better to set the freezing date, so it will be seen which workpiece is fresher;
- there are recipes that allow you to salt, pickle and ferment wild garlic. This will extend the shelf life up to 2 weeks;
- when dried, wild garlic loses almost all properties and aroma, but this method is also used. Greens are dried in the shade and then stored in an airtight container;
- chopped fresh wild garlic can be folded into a jar and filled with refined sunflower oil. In this form, wild onions can be stored for up to 4 months.
Collection of wild garlic leaves
The yield of wild garlic reaches 3 kg per square meter. However, you can cut off leaves from plants only in the third year of development. At the same time, you need to know that the remote vegetative part of the current year will no longer be renewed, and therefore, it will be possible to harvest greens again in the same place only after two or three years.


Bulbs, leaves and young shoots with a spicy taste are used for food.
Based on this, it makes sense to grow wild garlic in three beds at once, with a planting step of one year, or to collect leaves selectively.
Wild garlic appetizer salad
Ramson is practically a delicacy. And cooking it in such a delicious and original form will be a great idea not only for a family meal, but also for a wide feast. Try it. It is very tasty and simple.


Ingredients:
- 40 milliliters of balsamic vinegar (6%);
- A tablespoon of sweet paprika;
- 40 milliliters of vegetable oil;
- Salt tastes;
- A little fresh cilantro to taste (optional);
- 2 kilograms of wild garlic (shoots).
Preparation:


1. Thoroughly rinse and clean ramsons. Transfer the shoots to boiling water, boil after boiling for 2-3 minutes. In this case, you can immediately salt (half a teaspoon per 2 liters of water). Then put it in a colander and dry slightly.
2. For the sauce, mix the bell pepper, oil and vinegar. You can use finely chopped dried or chapped.


3. Transfer the rams to a salad bowl, pour over the sauce, add finely chopped greens. You can use any flavor or not add it at all.
4. Stir well and put in the refrigerator until the next morning.
Useful properties and use of wild garlic
Wild garlic is valued primarily for its high content of nutrients. Vitamin A, B1, B2, C, PP, folic acid, niacin, iodine, fluorine, calcium, selenium, zinc - which is just not there! Due to this, it stimulates the work of the gastrointestinal tract, has a positive effect on blood composition, cleanses the skin, helps with colds, strengthens the immune system, heals the cardiovascular system, speeds up metabolism, and is characterized by pronounced bactericidal properties.
On a note! It is recommended to eat no more than 15–20 leaves of asthenia per day. At the same time, raw wild garlic is best eaten in combination with butter or sour cream.So you can avoid damage to the walls of the stomach by the active substances contained in the plant. However, excessive consumption of wild garlic can still cause unpleasant consequences - headaches and insomnia.
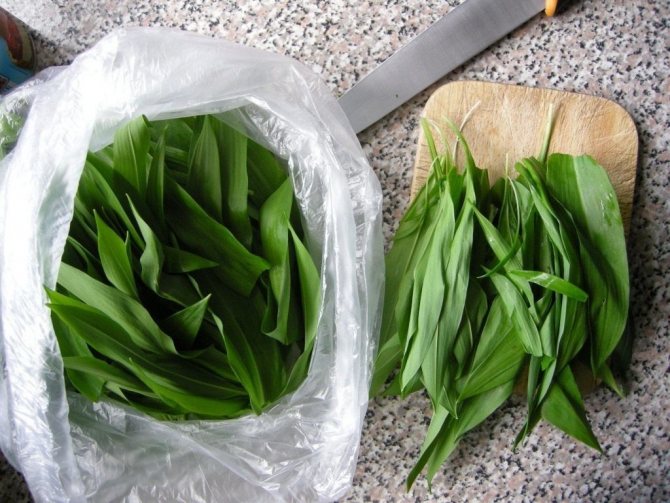


Leaves and stems of wild garlic are harvested and used as food before flowering.
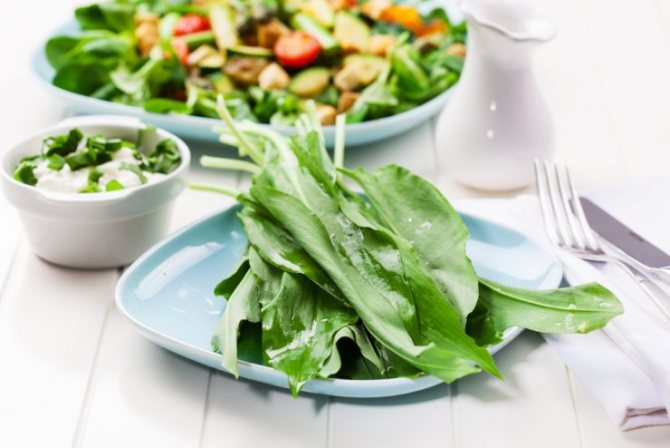
Leaves, stem and bulb are edible in wild garlic. It is used raw, in salads, as a side dish, in cooking, pickled, dried, insisted.
Properties
Growing a bear onion is not difficult, but its requirements, however, are quite specific. Despite this, it is worth making an effort to satisfy them, as it is a very valuable and medicinal plant, the properties of which are definitely worth taking advantage of, especially since it supplies nutrients during a period when natural vitamins and fresh vegetables are lacking. The most valuable are young, green leaves (harvested before flowering), which are tender and fragrant in early spring (later they become tough and fibrous). It contains, in particular: a lot of vitamin C and other vitamins (A, E), essential oils (vinyl sulfide, thiol), flavonoids, alliin, amino acids, micro and macroelements (sulfur, selenium, manganese, iron), as well as a lot other useful substances. Thanks to them, wild garlic has a bactericidal and antifungal effect. It also lowers blood pressure and "bad cholesterol" levels. Because it has similar properties to common onion, its use is recommended for people weakened by a long illness, suffering from diseases of the upper respiratory tract, as well as having digestive problems. Ramson also works as an antipyretic and is recommended for colds. From its bulbs, you can prepare a drug that allows you to fight some plant diseases (powdery mildew, late blight).


Reviews of wild garlic
Helen 2561:
And for several years I tried to germinate wild garlic from seeds, and the result was 0. I sowed before winter and tried to seedlings - all to no avail. Seeds from different producers, but the result is the same. Apparently, until the seeds reach us, they already lose their germination. It is safer to find bulbs from someone, but so far it has not been possible.
Sveta2609:
It grows with me, it requires a minimum of care. But in the spring it is a storehouse of vitamins. We use it mostly fresh. The plant is shade-loving, grows under trees and shrubs, but requires a sufficient amount of moisture. Prefers neutral soils, very poorly tolerates alkaline and highly acidic. Propagated mainly vegetatively, replacing bulbs, propagated by seeds only by winter sowing. If you sow with seeds, then the greenery is cut off no earlier than in the third year, in order to enable it to grow well in the allotted place.
SAD:
And we did it with wild garlic in a pretty funny way. Sowed seeds, they did not sprout They sowed for the sake of experiment, not really hoping for seedlings, under an apple tree, in the shade. A year later, tearing up the weeds, my wife discovered wild garlic, which “deigned” to come out into the light of day only in the second year. There were few ramsons, there were three or four bushes, and they were "clogged" with weeds.
Olga5432:
Ramson, popularly called wild garlic, it has a strong garlic smell, grows up to 40 cm, the stem is erect, the leaves are pointed and resembles the leaves of a lily of the valley. Wild garlic is harvested from mid-May to early summer, I use the fresh plant as a spice, I make salads with wild garlic and egg, I use mayonnaise or sour cream as a dressing, if you wish, you can chop a radish or a cucumber. Ramson can be harvested for use in the winter, it is useful both fresh and salted, I use it every year in moderation.
Iliad:
I bought wild garlic plants for planting in the garden in early spring at the market. Weak plants with a not too good root system were planted near cherry trees, in partial shade. I watered for several days. The ramson took root and even bloomed in the same year.Leaves of wild garlic in the first year do not need to be cut off for food - let them take root better. Delicate greens appear already in April and from the second year they can already be torn off (several leaves from a plant) and eaten. Very useful greens with many vitamins, smelling of garlic, which is very useful in spring salads, however, they are eaten both boiled and pickled.
Growing wild garlic in the garden is not at all difficult. If you follow the simple rules of care, this beautiful, unpretentious plant will decorate the garden for many years and delight with the spring harvest of delicious vitamin greens. Breeding wild garlic in garden plots will help keep its thickets intact in the wild, which is especially important for those regions where wild garlic has already become a rarity.
Note! In nature, wild garlic grows in large clumps, filling vast areas. If allowed to shed seeds in the garden, over time the plant will turn into a vicious weed.
Immunity will be fine
Since the plant contains a large amount of vitamin C, if you regularly use it, then the benefits of wild garlic for women will be quite difficult to overestimate. It can perfectly help in recovery from winter and awaken all the defenses of your body.


Very often, against the background of a lack of the required amount in the body of ascorbic acid, scurvy disease can develop. Wild garlic will also help to cope with it in a short time.


In addition, if a high temperature suddenly rises, then it is the wild garlic that can be used in order to try to bring it down.
We recommend reading:


The benefits of okra - properties, indications for use, composition and options for use in cooking (85 photos)

What is horseradish useful for the body? 120 photos of herbs and video description of useful properties
- The benefits and harms of leeks are the effect on the human body. Review of the composition and rules for the use of leeks (110 photos and videos)