Category: Houseplants
Flower miltonia (lat.Miltonia) belongs to the genus of herbaceous perennials of the Orchid family, which was first described in the middle of the 19th century. The plant got its name in honor of the prominent patron of arts and orchid collector Viscount Adligen Milton. In the wild, the miltonia orchid grows in the southern and central regions of Brazil, in eastern Paraguay and in northeastern Argentina, preferring shady moist forests at an altitude of 200 to 1500 m above sea level, with many types of miltonia are more common at an altitude of 600 to 900 m. Species growing high in the mountains are considered a species called miltoniopsis.
Miltonia: tropical orchids native to South America
Miltonia is a genus of orchids named after the famous patron and collector of these plants, Adligen Milton. Like all its relatives, it is a monocotyledonous herbaceous perennial.

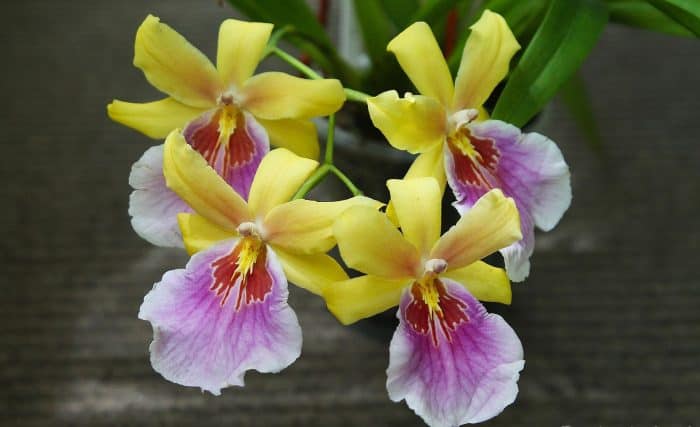
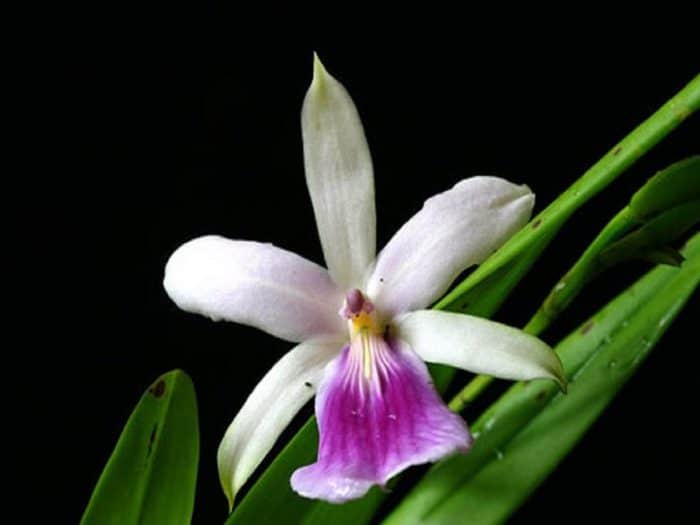
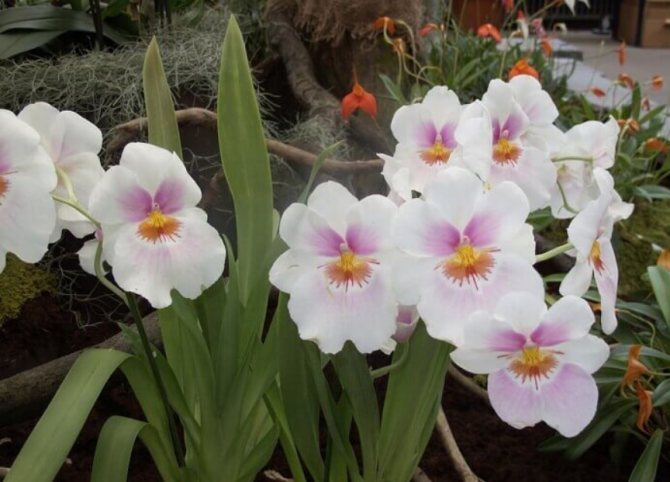
Blooming miltonia, like all orchids, looks very impressive.
This orchid was first described in 1837, but classification inaccuracies still exist. Since the middle of the last century, the genus has been divided into two - Miltonia proper and Miltoniopsis (literally - Miltoni-like). The latter are more cold-loving, so it is more difficult to grow them at home.
Under natural conditions, miltonia grow in the tropical forests of Brazil (where, it turns out, there are many not only wild monkeys). Most of them are sympodial ("growing sideways") epiphytes ("air plants"), which settle on the trunks and branches of trees. Orchids are not parasites, as the environment serves as a source of nutrients and moisture for them. The tree for them is only a support.


Miltonia feel great on trees, the aerial roots absorb the necessary moisture and nutrients from the atmosphere
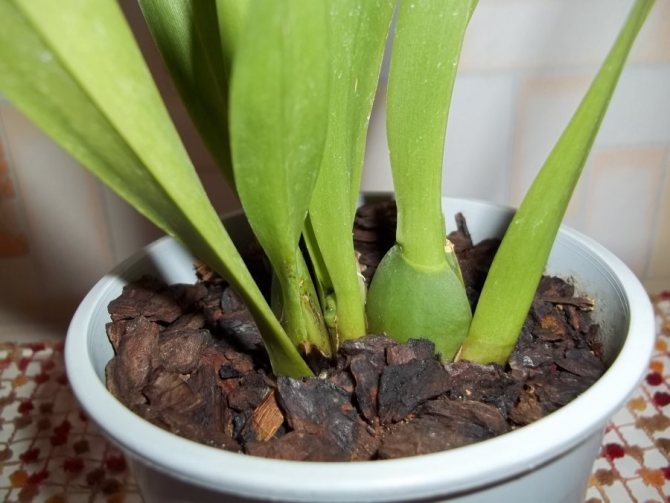
Miltonia have a rhizome - a growing horizontally modified stem, on which tuberidia are formed, better known as pseudobulbs - thickenings with a supply of nutrients and moisture. It is because of these formations, similar to testicles, that orchids got their name.


»Class =
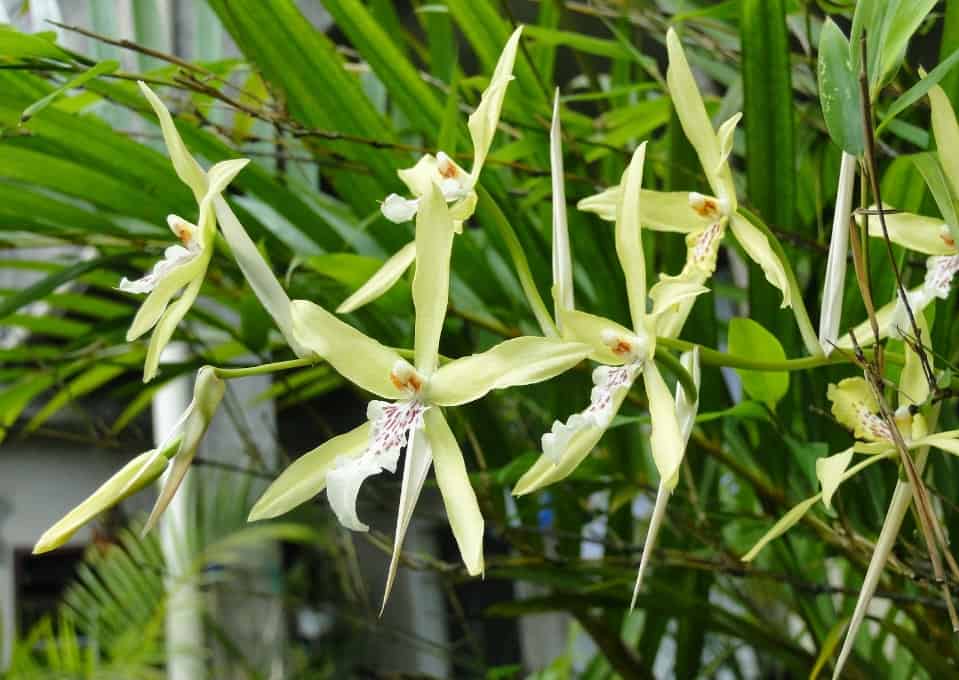
Thin, soft and light linear-lanceolate elongated leaves, growing together with roots from the similarity of internodes on the rhizome, cover pseudobulbs with sheaths, at the base of which peduncles appear. The flowers are fragrant, varied in shape, 4–10 cm in size. The petals of miltonia, in comparison with other orchids, are rather wide, and the lip is less pronounced.


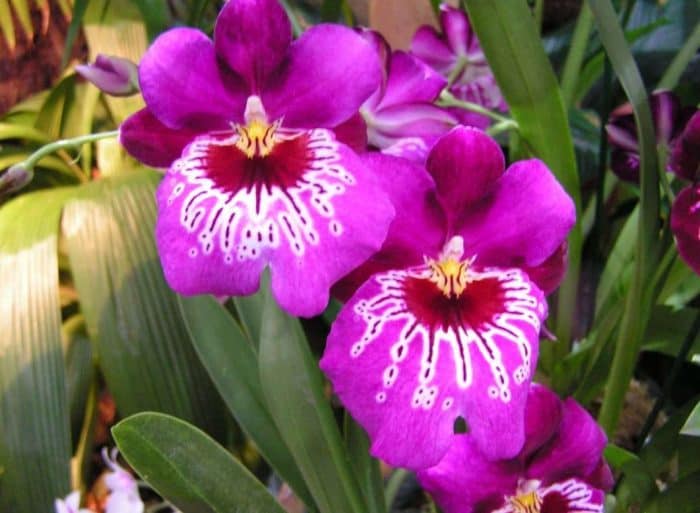
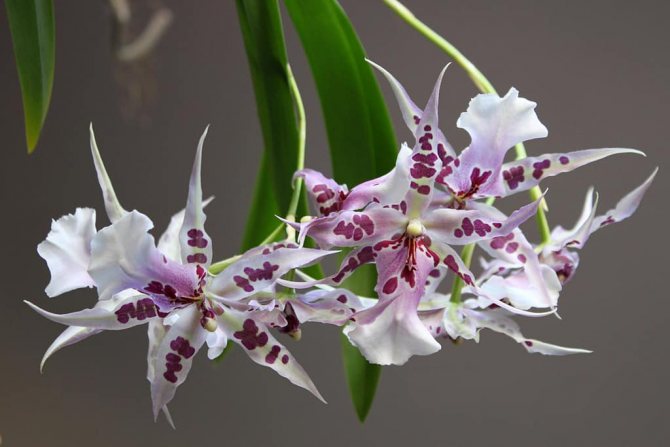
Miltonia flowers are similar to viola ("pansies"), but much larger; and to some they resemble bright tropical butterflies
Types and varieties of miltonia
There are 11 species and 6 natural hybrids in the Miltonia genus, many of which not only have earned popularity among amateur flower growers, but are also used by breeders to develop new varieties and hybrids. There are also known about 40 intergeneric artificial hybrids from crossing miltonia with orchids brassia, oncidium, cochliod, aspasia, odontoglossum, komparettia and others. Of the most popular species and varieties of miltonia in culture, one can name the following:
Miltonia white (Miltonia candida)
Orchid, which got its name from the boiling white lip on brown star-shaped flowers up to 9 cm in diameter, which in the fall open on the plant from three to five;
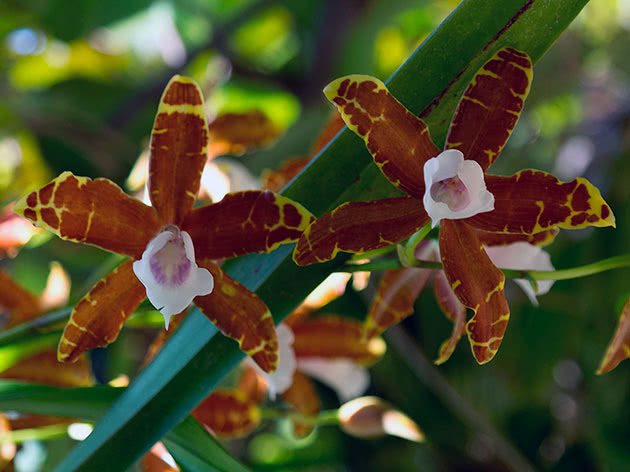


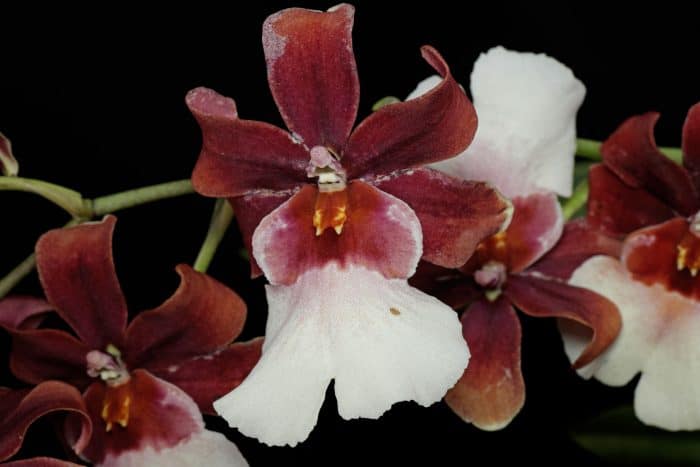
Miltonia clowesii
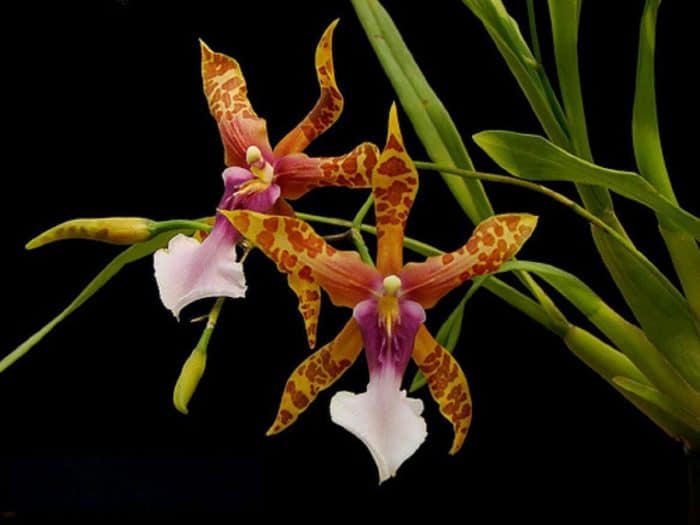
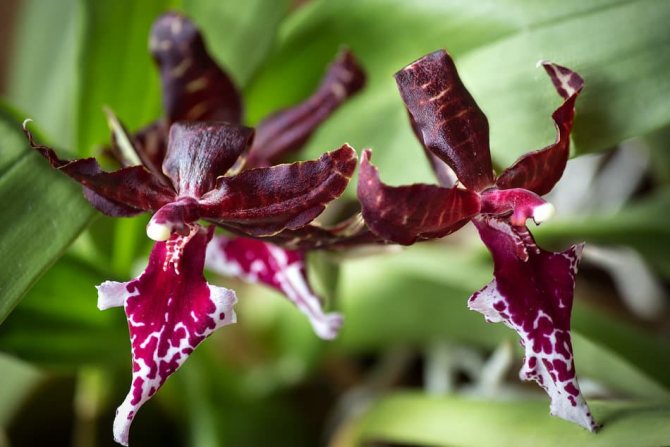
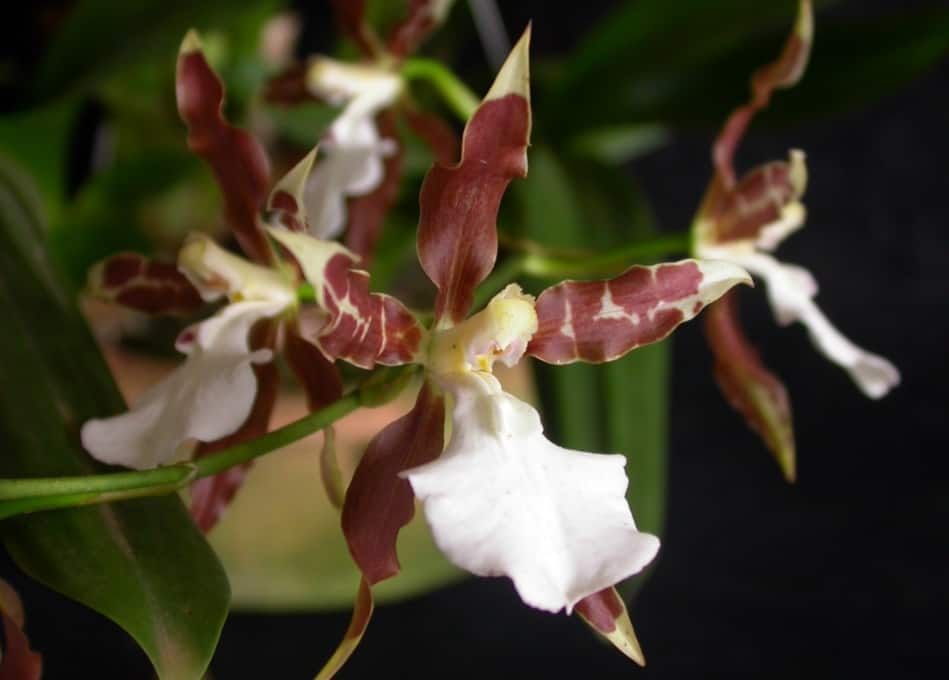
Tiger orchid with brown stripes on a yellow background and a white lip that becomes purple-purple at the base. Flowers, shaped like cambria, form an inflorescence of 8-10 pieces;
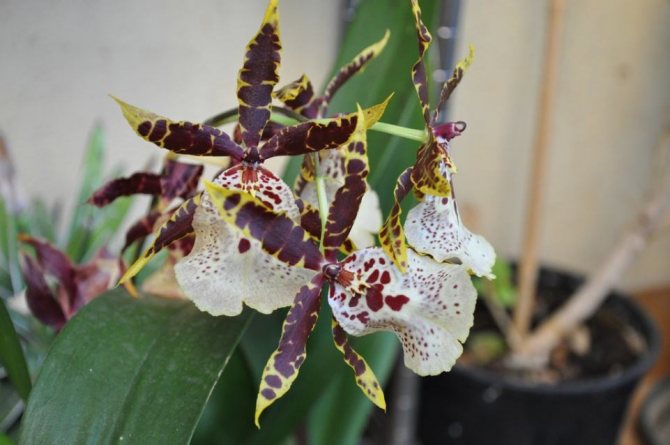
Miltassia
A hybrid between miltonia and brassia with large star-shaped flowers of various colors;
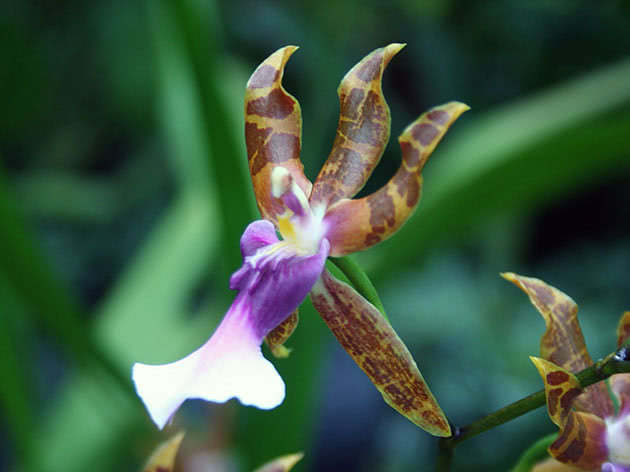


Miltoniopsis moth (Miltoniopsis phalaenopsis)
It has flowers that at the same time resemble the phalaenopsis orchid and pansies. They are small - no more than 5 cm in diameter, white with yellow and red spots;
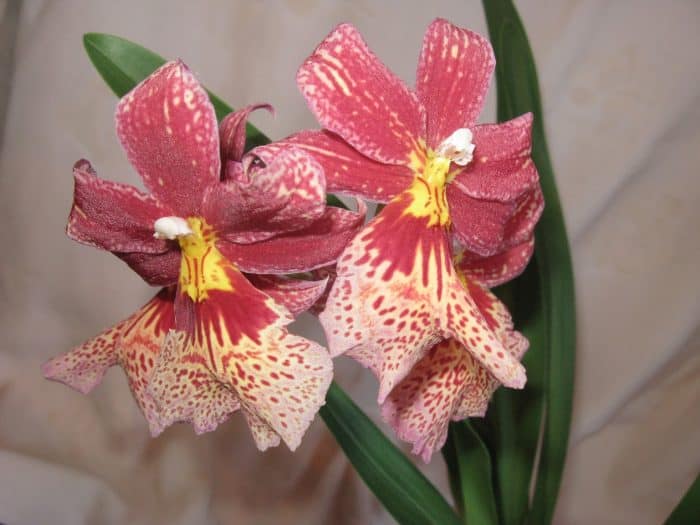
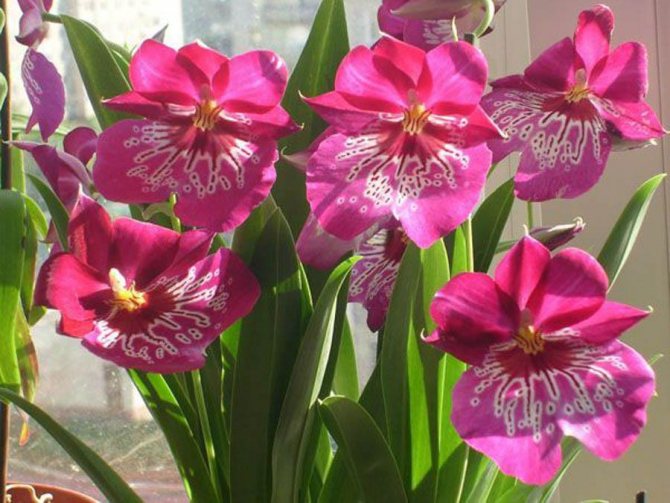
Miltonia, popular with amateur flower growers
How many species of miltonia and miltoniopsis exist in nature, it is difficult to find out exactly. This is due to ongoing disputes regarding the classification and ease of formation of natural hybrids, including interspecific. Most often it is believed that there are about 20 "real" miltonias. At home, the most common are:
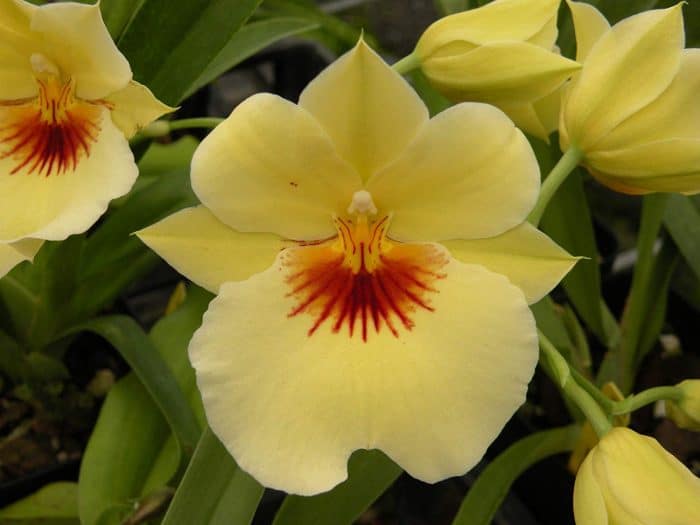
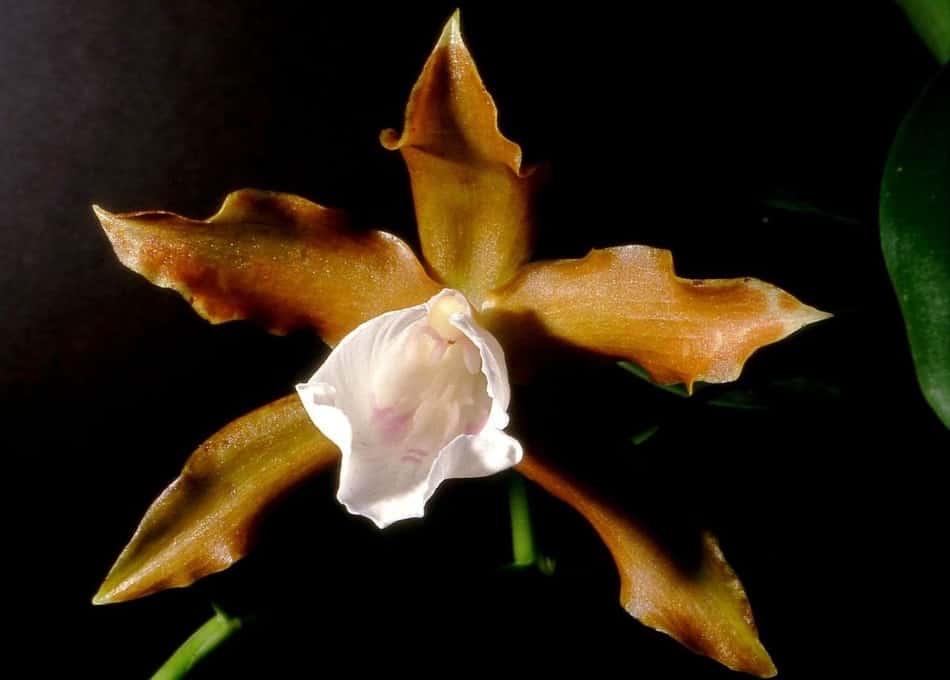
- Miltonia is snow-white. The height of the peduncles is up to 40 cm. Each has 3-5 flowers up to 10 cm in diameter. The petals are pastel yellow or brownish, with brick-colored spots. The plant owes its name to a snow-white lip.
- Miltonia is brilliant. Pseudobulbs are small (7–10 cm), flattened. Each has two sheets. The height of the peduncle is up to 30 cm. The petals are bright purple, the lip is pale purple with darker stains. Flowering lasts up to one and a half months.
- Miltonia Varshevich. Differs in large inflorescences. Rippled petals. If you do not cut the flower stalks, limiting yourself to removing wilted buds, you can achieve almost continuous flowering.
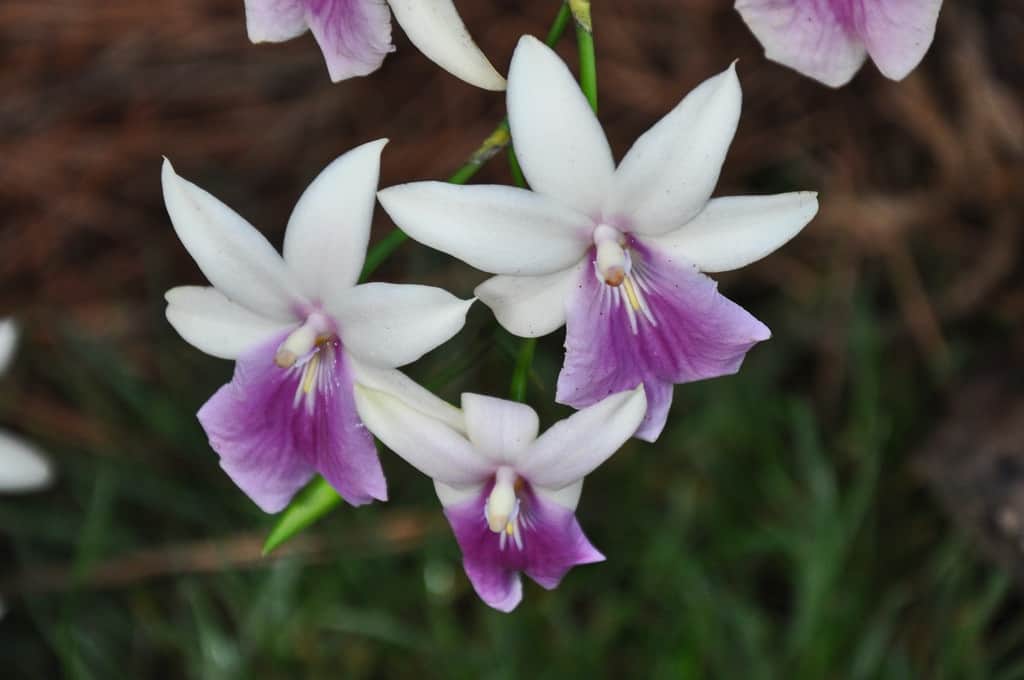
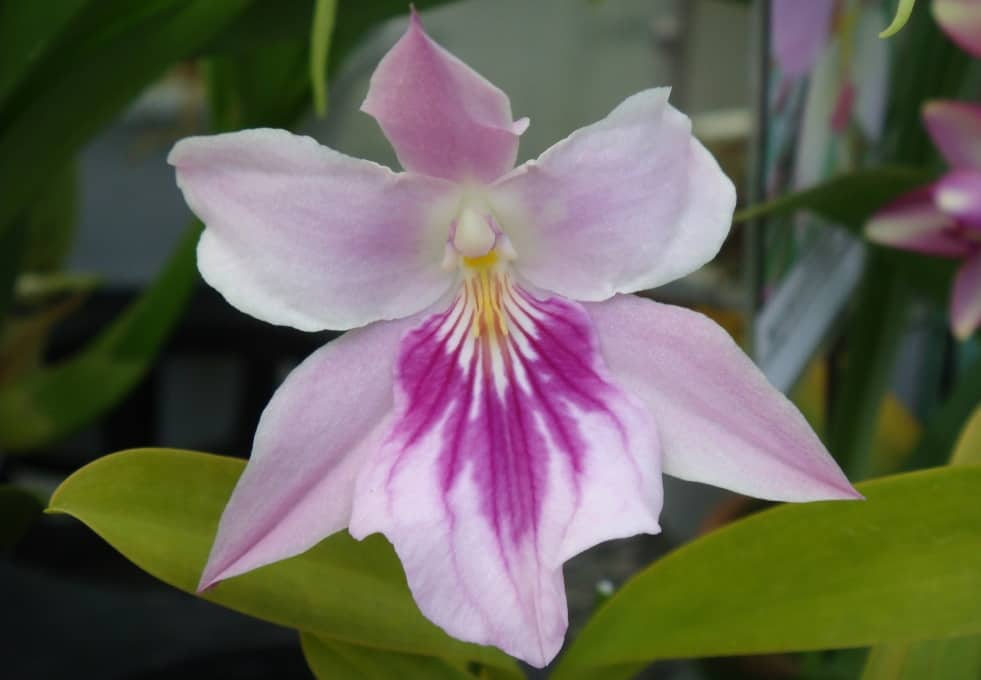
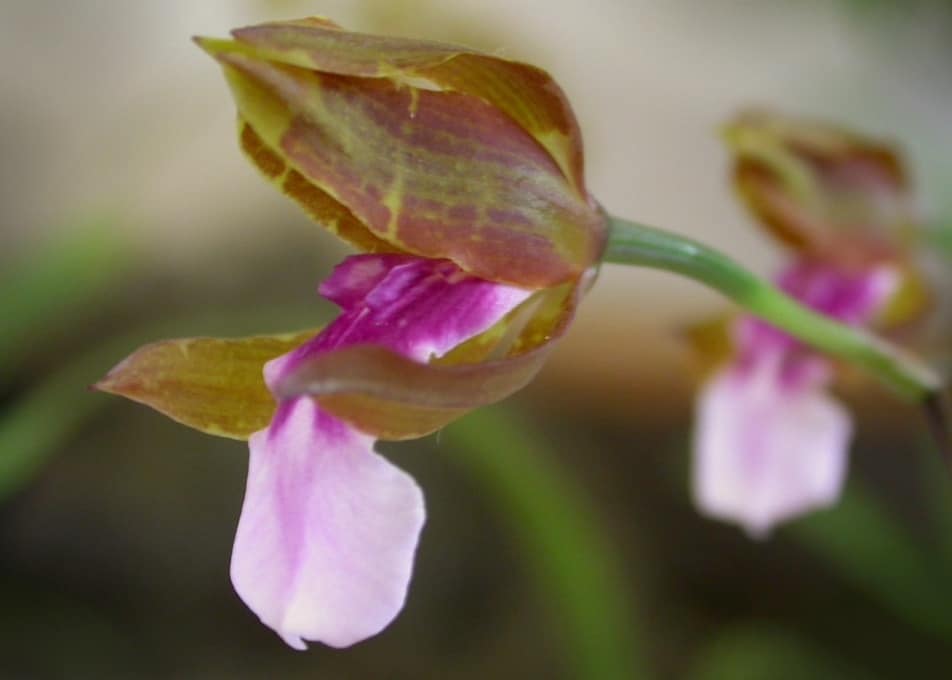
- Miltonia Renelli (sometimes not quite correctly called Miltonia Regnelli). Shiny leaves. Each peduncle has 3–7 flowers with a pronounced pleasant aroma. The petals are snow-white, the lip shimmers in different shades of pink and lilac.
- Miltonia Close. Peduncle up to 45 cm high. Flowers in the inflorescence 7-10. The yellow petals are streaked with brownish strokes and irregular spots. The dark purple tone of the lip turns sharply into snow-white.
- Miltonia Lawless Falls. Breeding hybrid, characterized by long and abundant flowering, as well as comparative unpretentiousness. On the initially white petals, streams of pink and scarlet paint seem to flow down. It blooms 2-3 times a year under optimal conditions.
Photo gallery: home-grown species
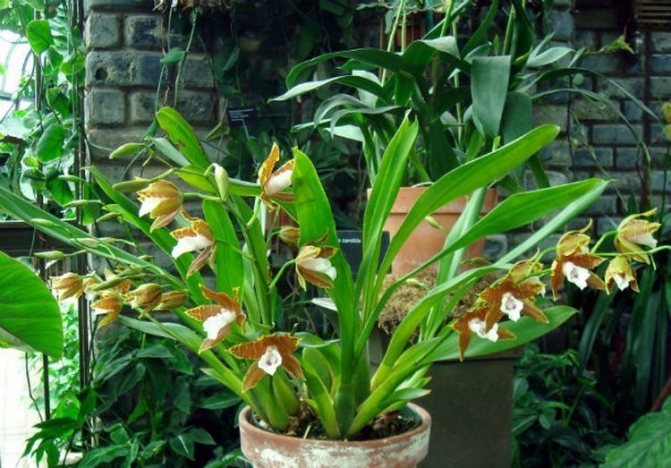


The name Miltonia snow-white owes to the lip of the corresponding shade, which stands out sharply against the background of dark brown petals
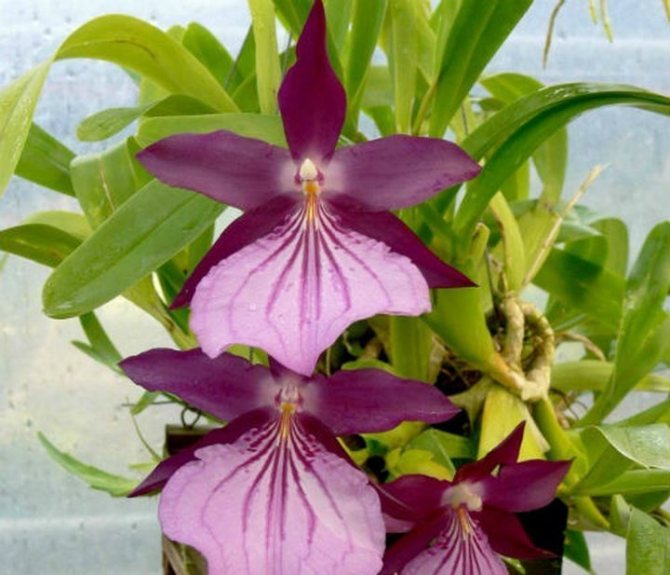


The heat-loving miltonia brilliant is capable of almost continuous flowering when properly cared for.
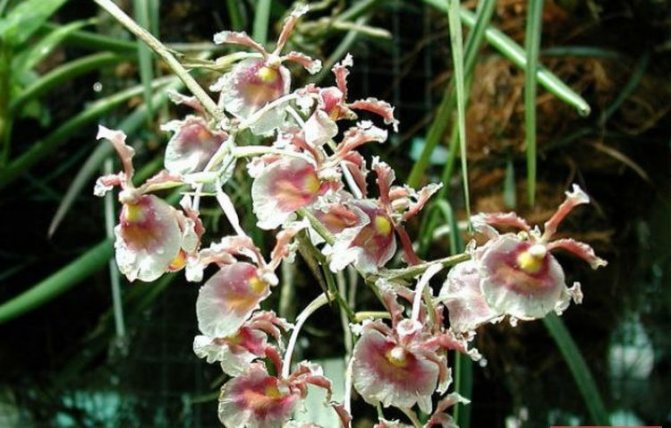


Miltonia Varshevich forms lateral peduncles, therefore it can bloom continuously for a year and a half.
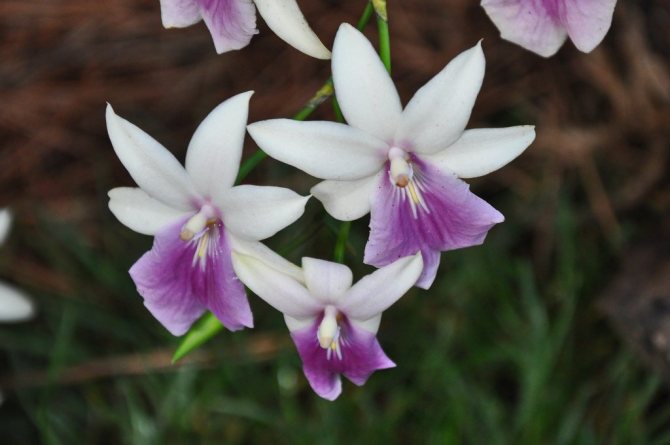


Peduncle of Miltonia Renelli holds up to 7 fragrant flowers for 1.5-2 months


Miltonia Close looks like an exotic insect
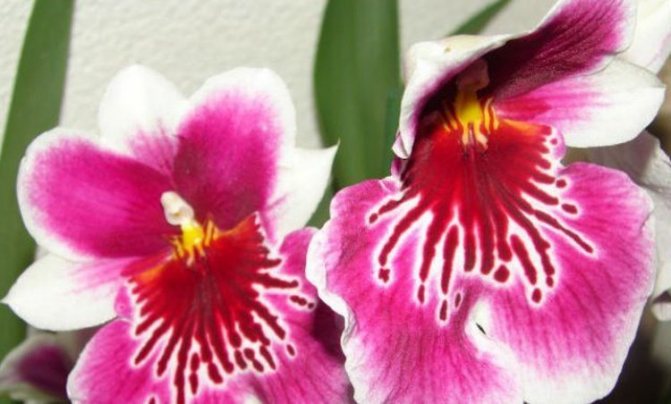


Hybrid Lawless Falls,
Description of miltonia
Miltonia orchid is ideal for growing at home. This genus is characterized by large flowers with a diameter of 10-12 cm, gray-green pointed leaves 40 cm in length. The color is varied: there are pink, burgundy, snow-white petals, some hybrids also have a pattern on the throat. Miltonia reaches no more than 40 cm in height, but some species can grow up to a meter. Blooms for 5-6 weeks. The roots are airy, at their base there are pseudobulbs. This genus has false bulbs. In the future, panicle-shaped stems, differing in color, appear from them.
How to create optimal conditions for miltonia?
Although the orchids that flower growers have to deal with, as a rule, are more or less adapted to the conditions of modern dwellings, you need to try to create for them a microclimate to which they are accustomed to in their historical homeland.
In order to avoid damage by fungi and other diseases, the room in which miltonia is located should be well ventilated, while remembering that this plant does not tolerate drafts.
Table: recommendations for creating the right microclimate
| Criterion | Recommendations |
| Lighting | Diffuse light for 10-12 hours or partial shade. East or west windows are best suited for placing miltonia. On the south, shading is necessary. Direct sunlight causes burns in the form of gray spots. It is possible to place miltonia on the north window only with additional artificial lighting. Additional lighting is required in winter. Normally, the leaves are light, with a pinkish tinge. If they are darkened, then there is not enough light. |
| Air humidity | In nature, the figure reaches 80%. Therefore, the humidity in the room should be at least 50% (this is the "survival threshold"). You can provide a comfortable environment using special humidifiers or by placing a container of water next to the flower. Wet moss, wet pebbles or expanded clay are placed in the pan of the pot. It is not the orchids themselves that are sprayed, but the air around the flower. The ingress of moisture on the plant can cause rotting, the appearance of spots on the petals. It is believed that spraying in the morning is desirable, but with the condition of the subsequent removal of wet drops. |
| Temperature | Miltonia is a moderately thermophilic plant. The most comfortable temperature for her is on average 20-23 ° C in summer and 15-18 ° C in winter, with a mandatory daily difference of about 3-6 ° C. In this case, sharp temperature fluctuations should not be allowed. In extreme heat, additional moisture is required. But there are miltonia, "knocking out" of this regime, for example, the brilliant one who "likes it hot." |
Conditions of detention
For the harmonious development of Miltoniopsis, it is necessary to create an appropriate microclimate.
- Space. Miltoniopsis cannot grow in the shadow of its neighbors, preferring a solitary arrangement.
- Sufficient degree of illumination... Light partial shade is suitable. In winter and in cloudy weather, it is better to place the plant on the windowsill, and in the hot season - in the back of the room.
- Ventilation... Forced ventilation (draft-free) acts as a preventive measure against fungal and bacterial diseases.
- Optimum humidity... The average is 60-75% with a tolerance of 10-15% in both directions. The warmer, the higher the room humidity should be.
- Moderately warm temperature... This plant can easily put up with a drop in temperature to + 10 ° C, provided that the soil is dry enough, but the roots are not overdried. Do not allow the temperature to rise above + 26-29 ° C.
Optimum temperature range depending on the season:
| Period of the year | Recommended temperature range, ° C | |
| In the afternoon | At night | |
| Spring-summer | +20-22 | +16-18 |
| Autumn-winter | +16-18 | +13-15 |
Tip # 1... To maintain optimal air humidity, the plant is placed in the immediate vicinity of an indoor aquarium, a decorative fountain, a container with wet moss, or placed in a tray with wet expanded clay.
Important nuances of plant care
Orchids are rightfully considered almost the most capricious and demanding among all indoor plants. But the time spent caring for them is more than offset by the abundance of bright colors.
Watering
It is best to water miltonia in the morning, with soft (settled, boiled or filtered) water with a temperature slightly higher than room temperature. In summer - once every three to four days with the obligatory removal of water collected on the pallet. In no case should the soil become overmoistened or completely dry out between waterings. The interval between them depends on several factors: the composition of the substrate, the general humidity, the temperature outside and indoors, the type of orchid.
It is advisable to immerse a pot with a flower for 10 minutes to half in water heated to 35–37 ° C once a week. After the procedure, it is imperative to let the excess drain off and dry the substrate well (at least 10-12 hours).
Some growers recommend watering in the form of a hot shower in the morning. If you choose this method, then be sure to remove moisture from the plant that has not dried out until the middle of the day, wiping off the drops with a cotton pad or soft cloth.


Miltonia, like other orchids, are watered from a watering can with a long narrow spout so that water does not fall on pseudobulbs and flowers
During the dormant period, the need for water in these plants decreases, so the breaks between watering are increased to once a week.
Fertilization
During active growth, you need to dissolve special fertilizers for orchids in water for irrigation twice a month. Some richly flowering plants, such as the brilliant miltonia, are fed weekly. During the dormant period, the plant does not need additional nutrition.
Flowering and dormant period
When determining the duration of the dormant phase, it is best to be guided by the appearance of the plant. "Rest" begins when young pseudobulbs reach adult size (usually at the beginning of autumn), and ends with the appearance of the first peduncles. Some species, for example, brilliant miltonia, do not need a rest period if they are in optimal conditions.
Miltonia bloom on average 2-4 months. In all plants, dying peduncles must be carefully removed without damaging the plant with a sharp, clean knife. The cut is made at a slight angle. An exception is Varshevich's miltonia, from which only wilted flowers are removed, because the remaining peduncle forms lateral shoots.
Video: how to properly care for miltonia
Features of flowering and dormancy
By observing the rules of care, they achieve flowering twice a year. During flowering, an adult plant produces 2-3 peduncles with several flowers on each. The colors are different. There are very interesting hybrids with blue, red and yellow flowers. Each hybrid is distinguished by its individual, unique color.
Full care leads to long-term flowering - up to 2 months. After a short rest, literally 2 months later, miltonia forms buds again. Resting immediately after flowering and in winter. At this time, special conditions are created for her. A withered peduncle is cut at the root, trying not to injure the pseudobulbs. For 2 months, the flower pot is removed to a cool place of 15-18 ° C, the intensity of watering is reduced, and artificially illuminated if necessary. With the advent of new peduncles, they are transferred to the heat, they return to the usual care schedule.
Problems that a novice florist may face
The problems of a plant can be judged by a change in its appearance. If nothing is done, the orchid can quickly die. Therefore, you need to be able to interpret the "signals" given by the flower and know how to react to them.
Table: how errors appear in the care of miltonia (leaves dry or turn yellow, buds fall) and how to save a plant
| Problem | Cause | What should I do? |
| Leaves darken. | Lack of light. | Use special phytolamps for additional lighting, if it is not possible to move the pot. |
| The leaves turn reddish. | The lighting is too bright. | Shade the orchid with a tulle curtain, gauze, thick paper. |
| Gray spots appeared on the leaves | Burn from direct sunlight. | |
| The leaves dry out in the form of an accordion, the shoots become "rickety", their number decreases. | Too low temperature of the content. | Move the flower to a warmer place. |
| The leaves turn yellow and dry. | Heat and stuffiness in the room. | Place the plant in a dark, cool place for several days. |
| The leaves at the base become corrugated, the growth of the orchid is greatly slowed down. | Irregular watering and fertilization or insufficient nutritional value of the substrate (a lot of time has passed since the last transplant). | Transplant the orchid immediately, completely changing the substrate. |
| The tips of the leaves dry out. | Watering with hard water (as a result, soil salinity). | Use only soft water for irrigation - rain or melt. The water supply must be passed through a filter, defended, boiled. |
| Roots rot. | Frequent and / or excessive watering. | Transplant miltonia into a disinfected substrate. Water very carefully for the next 1.5–2 months. |
| The orchid stops growing, flowers and buds fall off. | Low humidity in the room (as a result - drying out of the soil). | Increase humidity in all available ways, increase the frequency of watering. |
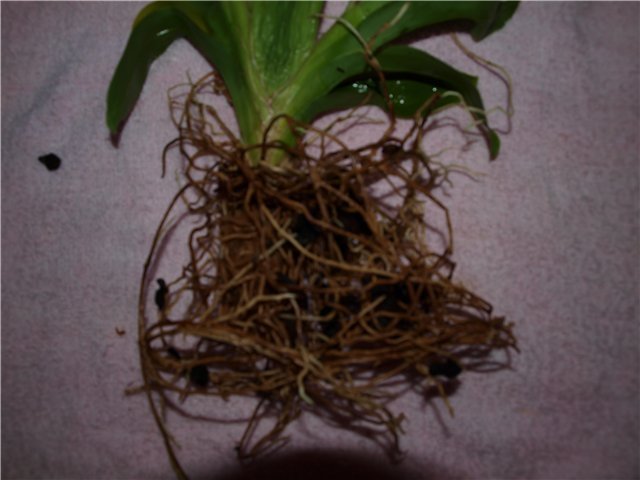


Decaying roots and shriveled leaves of miltonia are symptoms that, upon seeing which the grower must immediately begin to take action, otherwise he will soon lose the plant
Watering miltassia
Miltassia needs abundant watering, especially at high temperatures, but not to such an extent that the water ceases to be absorbed by it. Excess moisture contributes to decay of roots and pseudobulbs.
As soon as new bulbs have formed and the orchid is going to bloom, watering is stopped and they begin to spray the substrate from a spray bottle only once a week. After three weeks, watering is resumed again. The plant itself needs spraying occasionally.


Often diseases and pests affecting the plant
Miltonia can get sick not only due to content errors, but also as a result of pest damage.
To combat any pests, plants can be treated with broad-spectrum insecticides, for example, Aktara, Borey, Mospilan, Tanrek. Garlic solution, Apollo, Neoron, Fitoverm preparations work well against all types of mites.
The general rule when dealing with any pests is repeated treatments to destroy the fry emerging from the eggs. As a rule, you need at least 3-4 procedures with a frequency of 7-10 days. At the same time, it is advisable to change the drugs - pests very quickly develop immunity.
Neem oil can be used to prevent infection. This natural biopesticide is effective against most insects and is safe for humans. Plants are sprayed with a solution, diluting 1 ml of the product in a glass of warm water. For better adhesion to the leaves, small shavings of laundry or green potassium soap can be added to it.
It happens that due to treatment with chemicals, the plant loses its leaves. Over time, they grow back.
Table: the most common pests affecting the plant
| Pest | What does a plant look like | Control measures |
| Mealybug | Drying of leaves and stems, sticky drops, white bloom at the base of the shoots, leaf axils. | Mechanical removal of the pest, spraying with insecticidal preparations. |
| Thrips | The plant has black dots with round holes inside. The leaves wither, turn yellow and gradually die off. | Mechanical removal of the pest, treatment of the plant with soapy water. Using homemade thrips traps and sticky tape to catch flies. |
| Whitefly | Yellow and whitish spots on the inside of the leaf. | Collect visible pests in the early morning, when they are least active, with a vacuum cleaner. Treatment of the plant with a soap-alcohol solution. |
| Shield | The leaves and stems are dotted with sticky brown plaques. | Lubrication of the shells of the pest with turpentine, kerosene, alcohol, vinegar, after 2-3 hours - removal of the scabbards. Treatment of a flower with ethyl alcohol, after 15–20 minutes - a hot (40–45 ° C) shower. |
| Spider mite | The plant is covered with white dots and cobwebs. | Mechanical removal, processing with garlic or onion solution. |
Photo gallery: pests infecting miltonia
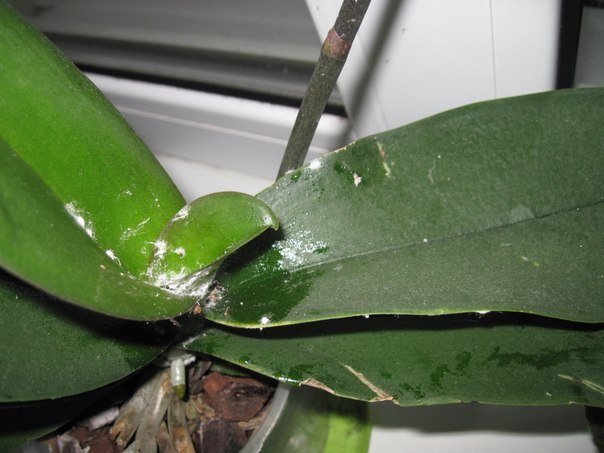


Mealybug, despite its seeming harmlessness, can lead to the death of an orchid
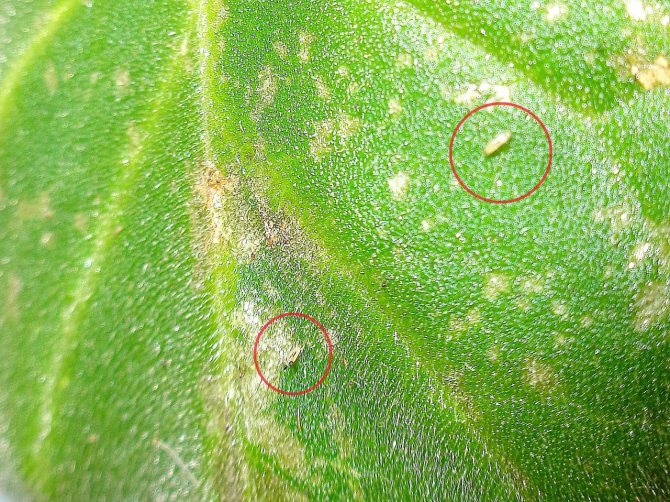

Good prevention of the appearance of thrips - regular spraying of miltonia with infusions of any pungent-smelling herbs, citrus peel, tobacco crumbs
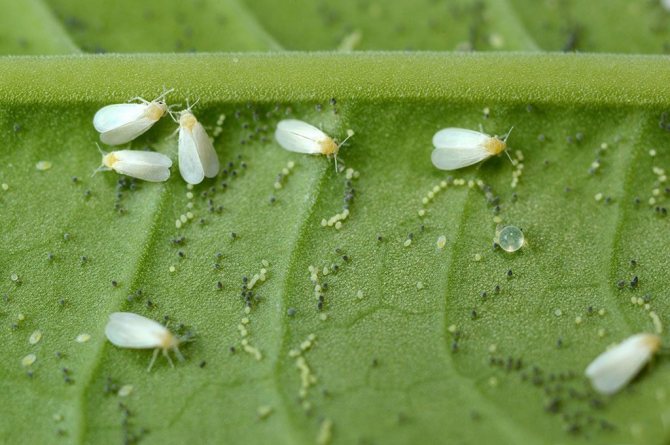


Whitefly is easy to spot -


To remove scale insects from miltonia, alcohol, turpentine, kerosene are applied to the shells of pests for 2-3 hours with a cotton swab


To combat spider mites, acaricides are used - Fitoverm, Apollo, Neoron
Table: Common Orchid Diseases
| Disease | Symptoms | How to fight? | Prophylaxis |
| Bacterial spot | Brown or black depressed spots with a yellow rim. | All spots are cut out, wounds are treated with activated charcoal or cinnamon, any powder antibiotics. | To prevent infectious diseases, thorough disinfection of equipment and pots is necessary. The diseased plant is immediately isolated. New specimens are kept in quarantine for at least 2-3 weeks. |
| Bacterial rot | Wet, transparent or yellow-brown spots. | The affected areas are cut off, the tissues are treated with bactericidal preparations, after the wound dries up, they are sprayed again with Bordeaux liquid (2% solution). | |
| Root rot | Stormy leaves, brownish and softening roots. | The affected roots are removed, the sections are treated with charcoal or colloidal sulfur. The plant is transplanted into new soil and a disinfected pot. The substrate is treated with a 0.2% solution of Fundazol or Topsin (three times, with a break of 10-14 days). | |
| Anthracnose | Rapidly growing spots similar to a burn and the appearance of annular deposits of spores on damaged tissues. | Damaged tissues are cut out, the sections are treated with coal powder, after drying - with fungicides (Trichodermin, copper sulfate, HOM). |
Photo gallery: common diseases of miltonia


Orchid bacterial spot is a dangerous disease, for which there are currently no effective remedies.
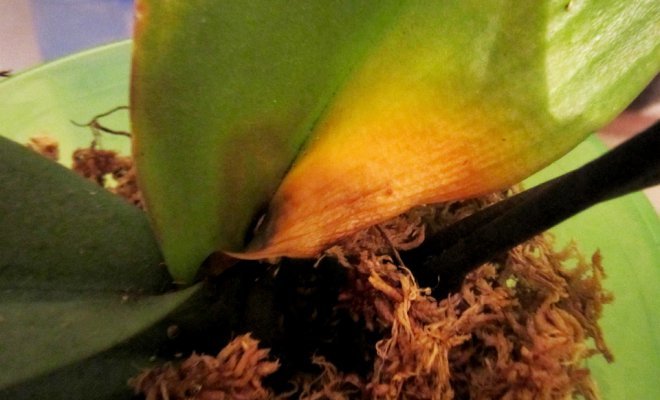


In the early stages, fungicides are used to combat bacterial rot - HOM, Kuprozan, Abiga-Peak
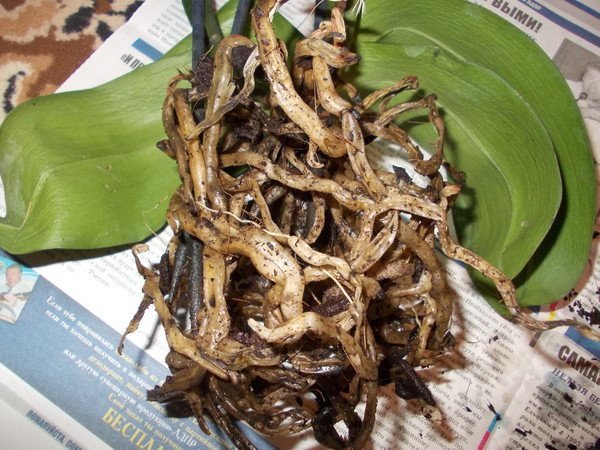


Miltonia, which has suffered from root rot, must be transplanted by completely changing the soil and sterilizing the pot


Miltonia, severely affected by anthracnose, can only be thrown away
Plant transplant procedure
Orchids do not like transplants, therefore, unnecessarily (too tight pot, rotten roots, substrate that has lost its properties) should not repeat this operation more often than once every 2-3 years. But there are exceptions, for example, brilliant miltonia, which must be replanted annually.
It is best to tackle this spring when the pseudobulbs begin to grow. The new container should not be too spacious; choose one that is only 2-3 cm larger than the old one. It is advisable to plant an orchid in a transparent pot - this allows you to control the state of the substrate, roots, and contributes to plant nutrition, since the roots of miltonia are involved in the process of photosynthesis.
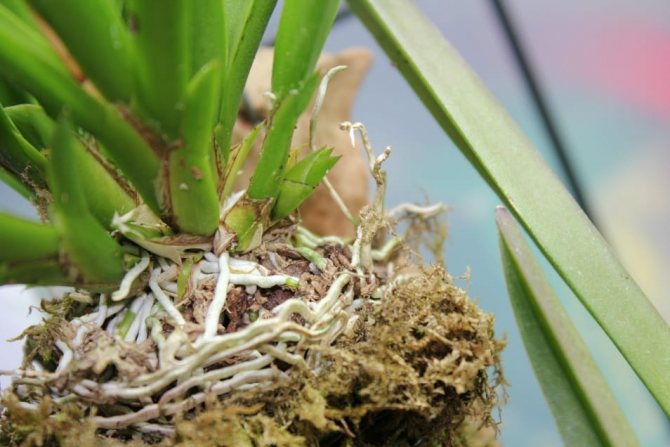
To be afraid that the roots are sticking out of the pot, and because of this, you should not rush to transplant. Aerial roots are the norm for these orchids.
The bottom of the container in which your orchid will live must necessarily have holes over which a drainage layer (pebbles, expanded clay) is laid to facilitate water flow. Disinfection is desirable - for this it is enough to treat the vessel with boiling water.
If everything is prepared, you can start the transplant:
- Remove miltonia from the old pot, being careful not to damage the roots. To facilitate the process, water the plant abundantly half an hour before.
- To clean the roots from the remnants of the old substrate, place them in water at a temperature of 35–37 ° C.
- Remove rotten parts, from which liquid escapes when pressed lightly, with a sharp knife. Sprinkle the slices with activated carbon powder. You can use antibiotics and fungicides, but not green stuff or alcohol solutions: they cause burns with subsequent tissue death.
- Leave the plant in a warm room for several hours to dry the roots.
- Place miltonia in the center of the pot and cover with substrate so that the soil covers only the roots, without interfering with the growth of leaves and pseudobulbs.
- Watering time depends on the condition of the roots. If they have dried well, then you can moisten the substrate almost immediately after transplanting. If not, then after 2-3 days.
When the condition of the purchased flower causes you anxiety, after removing it from the pot, it is necessary to remove all diseased, decaying and dying parts of the plant to healthy tissue, treat the sections with antiseptics and fungicides.
The color of healthy orchid roots is from white to light brown, aerial roots are green, dense and firm.
After drying, you can transplant the orchid into the old soil and pot, if their quality is satisfactory, but be sure to disinfect them by boiling or steaming. In any case, the purchased plant is transplanted into a fresh substrate within six months after purchase, even if the size of the container corresponds to it.
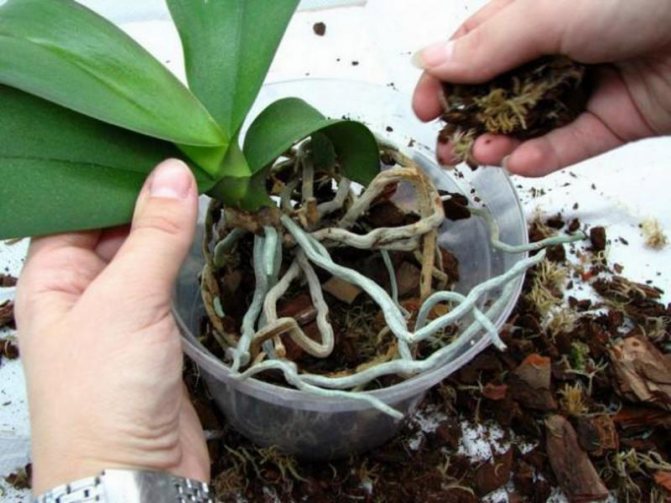


In a pot that is too tight, miltonia will not bloom, so transplanting is an important part of caring for the plant.
Video: correct Miltonia transplant
Soils
A good orchid soil should be breathable, loose, water-absorbing, stable, and pest-suppressing. The optimum pH is 5.5–6.5, that is, slightly acidic, almost neutral.
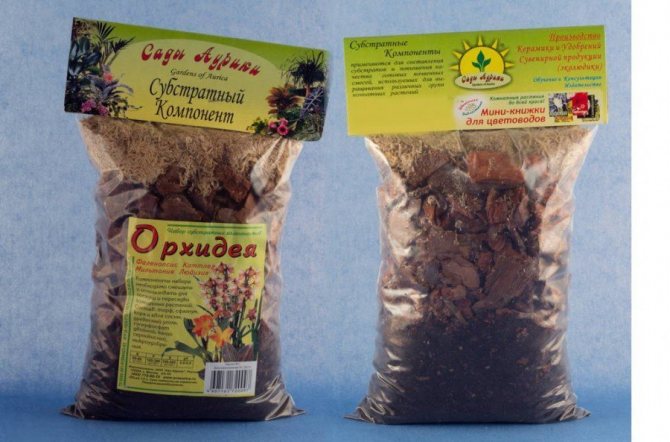


Orchids need a specific substrate, not very similar to soil in the usual sense of the word.
The composition of the substrate may include:
- sphagnum moss;
- peat,;
- bark of trees;
- fern rhizomes;
- perlite;
- charcoal;
- clay;
- coconut fiber;
- dolomite;
- Styrofoam;
- mineral wool.
Some of these components make up the base (bark, peat, moss), and some are added in small amounts to correct the stable state of the soil (foam, mineral wool) or as antiseptics (coal, sphagnum).
The composition may vary depending on the condition of your plant. For example, in conditions of insufficient light for a dormant plant, a soil with a reduced nutrient content is suitable so as not to provoke growth. A flower with diseased roots is a substrate with the addition of coal or sphagnum.
If you decide to buy soil from the store, choose a special soil for orchids, because their "needs" are different from those of other plants.
Miltonia transplant after purchase
The optimal time for the first plant transplant after purchase is after 1-2 weeks. It is undesirable to transplant an orchid immediately after a change in conditions due to the need for adaptation, it is also impossible to delay with this, since for sale the plants are most often planted in a temporary substrate that is not suitable for permanent maintenance at home. However, each case must be considered subjectively. If the purchased specimen grows in a full-sized pot and in a soil suitable for its composition, it is better to postpone the transplant until the roots begin to grow on top of the pot. This means that the plant has become cramped.


Resuscitation of an orchid without roots
Before proceeding with the rescue, be sure to first eliminate the reasons for the need for resuscitation. The chance of success is greater if the young plant is damaged.
Resuscitation begins with the removal of all damaged and dead plant parts. Then - the processing of sections with crushed activated carbon, colloidal sulfur, any powdered antibiotics and fungicides.
Mini-greenhouses cannot be used to save miltonia, since these orchids cannot stand air stagnation. But you can try to do it in a regular plastic cup. To do this, a small layer of pebbles or expanded clay is poured on the bottom of the container, wet sphagnum moss is placed on top. The plant can be lightly powdered with Kornevin in the place where the roots should be.
The orchid is placed on the sphagnum with the sprout up. Moss needs to be sprayed regularly to keep it moist. Once every 10–20 days, the plant can be soaked in a weak solution of complex fertilizer (with a nitrogen content of no more than 14%). It is also possible to use growth stimulants, for example, Epin, Zircon (1 drop per liter of water), but not more often than once a month.
An orchid that has lost its roots can be soaked daily in a container of water for 3-4 hours, once a week adding a weak solution of a growth stimulator (succinic acid). When the first roots appear, feeding is stopped, and the stay in the water is increased to 6 hours. It remains to wait until they grow up to about 5 cm and plant the plant in a pot. If, due to insufficient development of roots, the orchid "dangles", then it is necessary to fix it with a support. The plant is provided with a temperature of 18-24 ° C and good lighting.
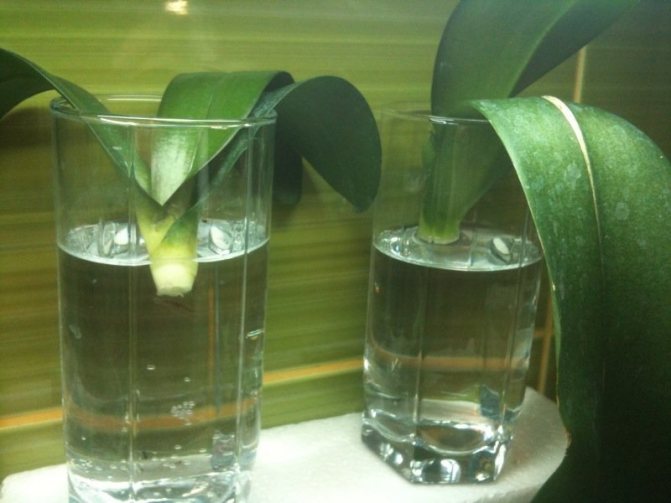


Rescued miltonia are soaked in water with the addition of succinic acid - this is a powerful growth stimulator
The main features of a correct fit
Usually they use store substrates for orchids based on pine or pine. Also perfect is a "home" substrate made of prepared pine bark, expanded clay and coal in a ratio of 3: 1: 1.
Orchid planting containers are absolutely indifferent. Perfect fit ordinary plastic pots or special baskets. Orchids attached to a block look very impressive. It is important that there are drainage holes in the pot.
The technology of planting orchids is fundamentally no different from planting other indoor plants. Neatness is key work with a fragile root system most orchids, especially epiphytes.
Reproduction of a flower at home
At home, miltonia reproduces only vegetatively: either by rooting pseudobulbs, or by dividing the bush. For this, only a well-developed plant with healthy roots is suitable and preferably before the appearance of peduncles.
Rooting pseudobulbs
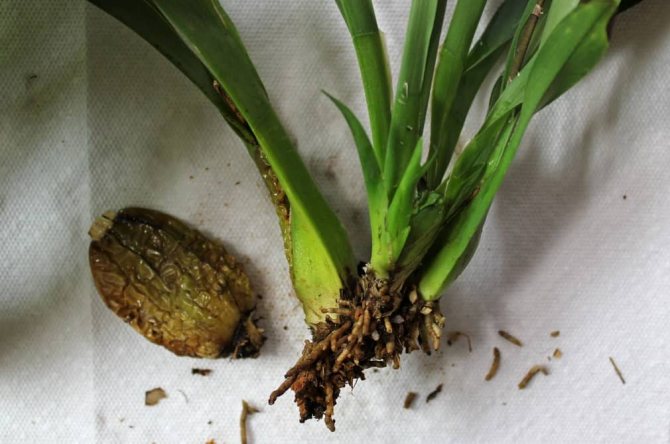
This method is questionable, but if there are extra plants, why not try it? The method is not popular among amateur flower growers, because pseudobulbs often rot instead of giving roots.
- When transplanting, the pseudobulb is separated from the plant with a sharply sharpened disinfected knife.
- The place of separation is treated with activated carbon powder, crushed chalk, cinnamon.
- The pseudobulba is rooted, as during resuscitation in a container with moss.
Reproduction by division
Dividing the rhizomes is the easiest way to get a new orchid. The procedure is carried out simultaneously with the transplant. The plant should not be too young - at least 2-3 years.
- The orchid is removed from the pot and the roots are cleaned of the substrate.
- The rhizome is divided into parts with a sharp knife, leaving 3-4 pseudobulbs on each.
- Sections are processed to prevent decay.
- Each piece is planted in a new pot. New plants are provided with light partial shade and a temperature of about 25 ° C.
- A few days later, miltonia are watered.
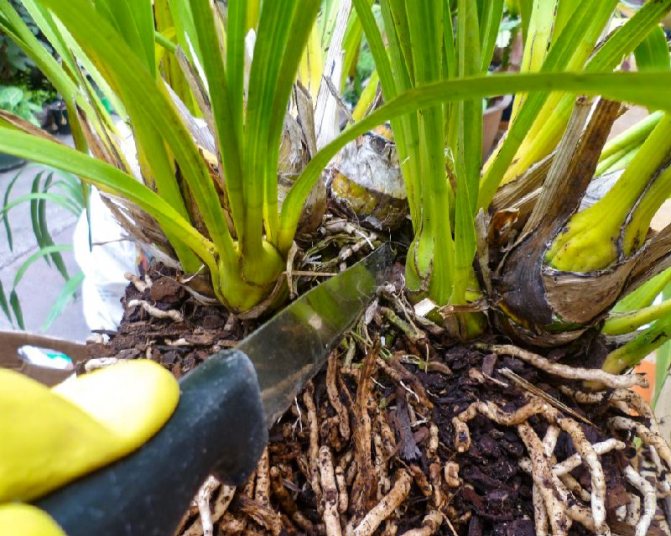


The rhizome is divided into parts only with a sharply sharpened disinfected knife so as not to introduce infection and minimize damage
In order for the green "pet" to please you with abundant flowering and excellent health, it is necessary to create a microclimate for it that is as close as possible to the growing conditions in its natural habitat. This also applies to miltonia.A flower grower who has spared no time and effort to clarify "wishes" and regularly pay attention to caring for the orchid, she will regularly delight with long, abundant flowering - that is why these plants are appreciated in the first place.
Reproduction methods
Miltonia reproduces both by dividing the rhizome and using pseudobulbs. It is recommended to reproduce Miltonia during transplantation.
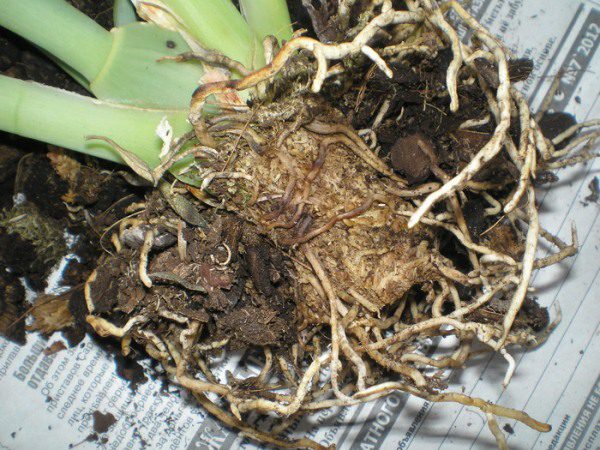


Reproduction of Miltonia orchid by dividing rhizomes
If you have chosen method of breeding Miltonia by dividing the rhizome, then you need to know that this procedure should be done in early spring. In this case, a part of the tuber should be jewelry separated from the orchid, capturing the shoot. Plant a cropped flower in a pot with a mixture of peat, perlite and humus.
After transplanting, the orchid cannot be watered for a week!
Reproduction of Miltonia by pseudobulbs Is the more common way. Pseudobulbs are the parts of tubers that, after flowering, must be separated and placed in a narrow pot of sand and peat.
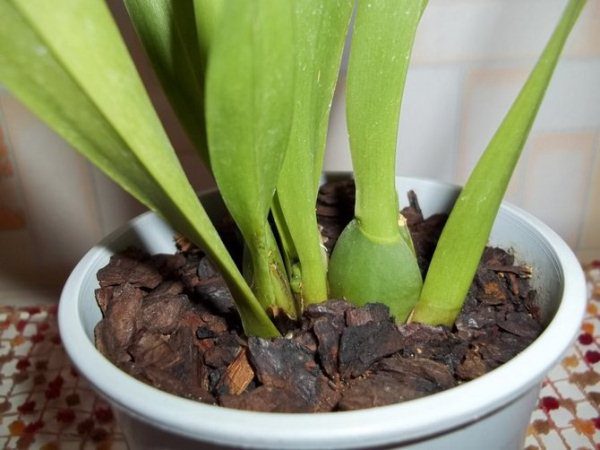


Propagation of Miltonia orchids by pseudobulbs
After that, it is necessary to create a greenhouse effect by putting a film or a plastic bag on the pot (it must be opened daily for 5-10 minutes), you need to water the flowerpot once every 3-5 days, after a week the pseudobulb will sprout, and then free the flowerpot from polyethylene.

































